- MyLawman Team
- Our Partners
- Testimonials
- Int Session Testimonials

- Submt your Post Through Email
- Our Journal
- Opportunities
- _Call for Papers
- _Legal Jobs
- _Internships
- _Certificate Courses
- _Fellowships
- _Scholarships
- _Conferences & Seminars
- _Publication Opportunities
- _Online Opportunities
- _Moot Court Comp's
- _Quiz Competitons
- _Legal Competitions
- _Summer Schools
- _Call for Blogs
- _Legal Article
- _Case Briefs
- _Legal Resources
- _Know Your Rights Series
- _Know Your Law Series
- _Expert Corner Series
- _Guest Posts
- _Company Law
- _Constitutional Law
- _Consumer Protection Law
- _Criminal Law
- _Criminology
- _Competition Law
- _Family Law
- _Indian Contract Act
- _Jurisprudence
- _Labour Law
- _Legal Research & Methodology
- _Muslim Law
- _International Trade Law
- _Legal Updates
- _Exam Updates
- _E- Library

MyLawman Events
- _Courses & Events
- _Interactive Sessions
- MyLawman Publications
- Submit Post
- _Advisory Board
- _Our Core Team
- _Our Partners
- _Our Supporters
- Career @ MyLawman
Follow us on Social Media!
[case brief] top 5 cases on the validity of contract.

I. BALFOUR v. BALFOUR
⮚ Citation: [1919] 2KB 571
⮚ Introduction: Landmark judgement on the intention to create a legal relationship as an essential element of contract.
⮚ Parties: Mr. Balfour & Mrs. Balfour
⮚ Brief facts: Mr. & Mrs. Balfour use to live in Ceylon (now Sri Lanka), a happily married couple. They went on a vacation to England and during their stay Mrs. Balfour was diagnosed with ‘Rheumatic Arthritis’. The doctor advised her proper rest. Her health could deteriorate, with the change in weather, therefore she stayed back in England whereas her husband returned back to Ceylon. As Mr. Balfour promised to send her £30 every month until she stayed back. He regularly made the due monthly allowance as promised but subsequently, stopped sending the amount. Mrs. Balfour sued him for the payment of monthly payments.
⮚ Issue(s): Was there a valid contract between Mr. Balfour & Mrs. Balfour?
Justice Sargent held that the said contract between the husband & wife was valid and binding as Mr. Balfour was under obligation to support his wife. The prior monthly transfers were enough to form the basis of the contract between Mr. & Mrs. Balfour and the consent of Mrs. Balfour to this arrangement constituted a valid consideration. Mr. Balfour went to the Court of Appeal against the judgment of the Division Bench.
⮚ Decision: The appellate court held that the arrangement between Mrs and Mr Balfour was merely a social agreement and no a contract. a domestic matter and Mr. Balfour had ‘no intention to create a legal obligation’. The court also pointed out that, Though Mr. Balfour made a promise to pay £30 per month and Mrs. Balfour agreed to it but there was no intention to bound by legal consequences on behalf of Mr. Balfour. The Court also held that such types of agreements can’t be a contract because usually in such agreements between the spouse, either of the parties do not intend to bound themselves by legal consequences. Court also made the argument that if the courts will they’ll start to enforce such intimate arrangements made between couples treating them as a legal contract then the courts shall be flooded by with matrimonial disputes.
II. LALMAN SHUKLA v. GAURI DUTT
⮚ Citation: 1913 40 ALJ 489
⮚ Introduction: Acceptance of the offer as an essential element of a valid contract.
⮚ Parties: Lalman Shukla & Gauri Dutt
⮚ Brief: Gauri Dutt’s nephew went missing. He therefore sent all his servants in search of the absconding child, different places. One of his servants, Lalman Shukla was sent to Haridwar from Cawnpore (Kanpur) to search him, his travelling allowances and other expenses were paid by the master Gauri Dutt. When he returned back to Kanpur after getting succeeded in finding his master’s nephew, he was given two sovereigns along with Rs. 20. During the period while everyone was searching master’s nephew and the plaintiff was also searching him, defendant circulated pamphlets stating that whosoever finds the boy gets a reward of Rs. 501. The plaintiff had no idea about the reward and did not asked for anything further and continued his service for six months. After that, he filed a suit for the recovery of reward from his master, he claimed for Rs. 499 out of the money that was offered in the handbill. Then, the lower court dismissed the plaintiff’s plea.
⮚ Issue(s):
1. Does the arrangement amounts to a valid contract?
2. Is Mr. Lalman entitled to the reward amount?
3. Decision of the subordinate court was appropriate?
⮚ Decision: Court held that, none of the essential ingredients required to for a for an agreement to be enforceable were not fulfilled in the situation. The primary need for an agreement to be enforceable is the ‘knowledge and assent of the particular offer. Here, he was not aware about the offer and had no assent about the act. Thus, it can be concluded that acceptance is the essence to contract and the plaintiff was just fulfilling his obligation by searching the missing boy.
Also, this is a leading case wherein the important principle of General Offer was laid down. In such case, a contract could be made only with the person who has the knowledge about the offer and accepts it by acting accordingly to fulfil the conditions mentioned in the offer.
III. HARVEY v. FACEY
⮚ Citation: 1893 A.C. 552
⮚ Introduction: invitation to an offer is not an offer
⮚ Parties: Facey & Harvey
⮚ Brief facts: Mr. Facey was a real estate owner who was interested to sell his property which was in Jamaica. Harvey who was interested in buying that property sent a telegraph asking he would sell his property to Harvey on lowest cash price to be paid. Replying to his telegraph Facey replied to his second question only. Facey’s telegraph read, lowest price for Bumper Hall Pen is £900. To which Harvey later replied, he agreed to buy Bumper Hall Pen which was asked for and he also asked Facey to send him property deed so that he could get early possession. Facey denied to sell his property to Harvey at that price. Later, Harvey filed a case in the court of appeal, Harvey won the case. Facey who was unhappy appealed against the decision and case went to Privy Council which upheld the trial court’s decision.
⮚ Issue(s): Was there any offer from Facey to sell the property for £900?
⮚ Decision: It was held by the Privy Council that; it would be a contract only if Facey had replied to Harvey’s third telegraph. Harvey took Facey’s response to his question as an offer to sell at the named price by him. There was no commitment to sell the property because the offer which was made by the Harvey by replying to the invitation of an offer was not accepted. Thus, there was no contract between the two.
IV. MOHORI BIBEE v. DHARMODAS GHOSE
⮚ Citation: 1903 30 Cal 539
⮚ Introduction: competency or Ccapacity of the parties to contract / Minor’s contract
⮚ Parties involved: Dharmodas Ghose & Mohori Bibee
⮚ Brief facts: Plaintiff, Dharmodas Ghose was in need of money therefore, he pledged his property and asked for loan of Rs. 20,000 from the moneylender Brahmo Dutt. The debt amount given was less than Rs. 20,000. Brahmo Dutt who was acting as attorney at that time on the behalf of the moneylender, knew that Dharmodas Ghose was a minor. Plaintiff filed a suit against Brahmo Dutt stating that the mortgage deed should be null and void because he was a minor at the time of contract and hence, it should be cancelled. Later, Brahmo Dutt passed away and the appeal was prosecuted by his executors. And it was contended by the defendant that plaintiff should not be excused as he misrepresented his age to him. Even if the deed is void, the debt that was advanced to him i.e., Rs. 10,500 should be repaid.
1. Was the mortgage deed void?
2. Deed signed by defendant was voidable or not?
3.Was the defendant entitled liable to receive the mortgage money?
⮚ Decision: The Privy Council held that the; person who mortgaged the property was infant at the time of execution. So, the contract or mortgage deed which was made between the plaintiff and the defendant was not merely voidable but it was void. It also held that any contract with a minor or an infant is ‘void ab-initio’. Since minors are incompetent to contract hence, such contracts are void and invalid in the eyes of law. The minor is not obliged to pay back the amount that was advanced to him as he was not bound by the promise that was executed in contract.
Minor is a person who has not attained or is below the age of 18 years.
And any contract entered into with a minor shall be be null and void (void ab initio) owing to his incapacity. Dealings done by the minors without the knowledge and consent of their custodians or parents shall not be liable to them.
V. RAFFELS v. WICHELHAUS
⮚ Citation: 2 H. & C. 906
⮚ Introduction: consensus ad idem- “meeting of minds”
⮚ Parties: Raffels & Wichelhaus
⮚ Brief facts: Mr. Raffels and Mr. Whichelhaus had a contract that Mr. Raffels would send him 125 bales of Surat cotton via a ship named peerless from Bombay. But there were two ships with the name peerless. The same name of two different ships mislead them and they agreed upon two different ships in their minds, which means there was no meeting of mind while binding the contract. When the ship containing cotton reached Liverpool in December, Wichelhaus refused to receive the shipment and to pay for it. In his understanding the consignment was late as he mis- understood that the ship earmarked with nomenclature as some other which was supposed to reach in the month of October. Both of them had mis-understanding in reference to ship names. Later, due to this delay according the defendant who did not received the order was sued for the breach of contract by the plaintiff (Raffels).
⮚ Issue(s): Was there an enforceable contract between the parties?
⮚ Decision: The court held that the contract was vague and hence, it was not an enforceable contract. For binding of a contract, there should be meeting of minds between the parties.In this case, there was no consensus ad-idem. At the time they had entered into this contract, there was ambiguity on the issue as to which ship shall carry the cotton to be delivered. Since, it was a well-documented deed and not a fraud and hence, it should not be interrupted by extrinsic evidence.
This case briefs has been prepared by Ms. Urvi Yadav, who was an intern at MyLawman & edited by Ms. Samreen Ahmed, Research Assistant, ARIL, MyLawman.
You may like these posts
Post a comment, get privacy enabled whatsapp updates.

To Stay Updated about the Posts of MyLawman: Legal Updates on the go, Join our Social Media Pages

Like us on FB
Follow us on Instagram
Follow us on linkedin.

UGC NET Crash Course, Coming Soon!!!

Join our New Follow cult. Get new posts by email:
Follow us on fb, social plugin, we are mylawman.

We love to hear, Write to us
Menu footer widget.
- Submission Guidelines
- Publication Policy
- Privacy Policy

Contract Law - Notes, Case Laws And Study Material
Explore comprehensive contract law notes, insightful case laws, and valuable study material on legal bites..

Contract Law is a form of civil law. The chief component of the contract law in India is the Indian Contract Act , which was enacted in 1872 and enforced on September 1, 1872 .
From arbitration enthusiasts to budding sports lawyers, the knowledge of contract law is indispensable to every law student. Legal Bites has created the most comprehensive course on Contract Law you'll find online. The fifteen modules of the study material not only cover the ins and outs of the Indian Contract Act but also provide an excellent analysis of key concepts like bailment, partnership, breach of contract, indemnity, etc.
Additionally, a 10-part series of important questions based on the syllabus of major university-level and competitive exams has been created to help students master the nuances of contract law.
Important articles and study material on Contract Law – Click on the links to Read:
- Historical evolution of contract law in India
- Introduction and Nature of Indian Contract Act, 1872
- 1000+ Detailed Questions MCQ Test Series for Competitions (Redirect to Law Aspirants)
- Meaning of contract and other definitions as per Indian Contract Act, 1872
- Types of Contract
- Essentials of a Valid Contract under The Indian Contract Act
- 8 Contract Law Doctrines: You Must Know
- Landmark Cases Related to Contract Law
Important Books and Practice Tests (Must Have)
- Avtar Singh's Law of Contract & Specific Relief
- Offer and Acceptance (Overview)
- Offer- Types and Invitation to Treat
- Revocation- Meaning and Modes
- Capacity to Contract
- Consideration Under the Indian Contract Act 1872
- Exception to the Rule of Consideration
- Lawfulness of Consideration
- The Lawfulness Of Object And Consideration
- Privity of Contract and Consideration
- Voidable agreements
- Void agreements
- Contingent Contracts: Concept and Scope
- Formation of contract by Click Wrap, Shrink Wrap and Via Exchange of E-Mails
- Jurisdictional Issues
- UNCITRAL Model of Law on Electronic Commerce 1996
Module VI: Performance Of Contract And Discharge
- Contracts which must be performed
- Time and Place of Performance
- Quasi Contracts And Claims for Compensation
- Obligation of Person Enjoying the Benefit of a Non-gratuitous Act
- Responsibility of the Finder of Goods
- Consequences Of Breach Of Contract
- Doctrine of Frustration | Explained
Module VIII
- Need for indemnity to facilitate commercial transactions
- Insurance Contract and Indemnity in India
- Rights of Indemnity-Holder
- Nature of Indemnity Clauses
- Guarantee: Concept, Definition and Basic Essentials for a valid guarantee contrac t
- Nature, Duration & Termination of Surety's Liability
- Various judicial interpretations to protect the surety
- Co-Surety and manner of sharing liabilities and rights
- Analysis of Co-extensive Liability of Surety with that of Principal Debtor
- Bailment: Concept And Definition
- Bailment contracts in day-to-day life
- Duties of a Bailee and a Bailor
- Concept/Definition of Pledge
- Pledge & Bailment : Difference & Comparison
- Rights of the Pawner & Pawnee
- Right of sale of the pledged goods
- Concept/Definition of Agency
- Difference Between Servant And Agent
- Various Methods of Creation of Agency
- Liability of the principal for acts of the agent including misconduct & tort
Module XIII: Specific Relief Act
- Introduction to the Specific Relief Act
- Recovery of Possession of Property
- Specific Performance of Contracts
- Cancellation of Instruments
- Declaratory Decrees
- Preventive Relief
Module XIV: Sale of Goods Act
- Formation of Contract of Sale: Everything you Need to Know
- Conditions and Warranties under the Sale of Goods Act
- Effects of the Contract of Sale: Explained with Relevant Provisions
- Rights of Unpaid Seller | Explained
Module XV: Partnership Act
- Partnership: Concept, Definition and Essentials
- Partnership & Private Limited Company: Advantages & Disadvantages
- Properties of Firm
- Formation of Partnership | Indian Partnership Act, 1932
- Test of Partnership: Explanation, Components & Case Laws
- Registration of Firms and the Effect of non-registration
- Rights and Duties of Partners
- Admission & Outgoing of Partners
- Registration & Dissolution of Partnership
Important Cases
- Balfour v. Balfour (1919)
- Kedarnath v. Gorie Mohammad (1887)
- Mohori Bibee v. Dharmodas Ghose (1903)
- Carlill v. Carbolic Smoke Ball Co. (1892)
- Chacko v. Mahadevan (2007)
Leslie Ltd. v. Sheill, (1914)
Other articles
Doctrine of Restitution
All you need to know about Contract of Indemnity
- Doctrine of Privity
- Fraud, Misrepresentation and Mistake under the Indian Contract Act
- Promissory Estoppel – Meaning and Explanation
- Surety's Liability: Judicial Interpretation
- A Brief Analysis Of Wagering Agreements
- Remedies For The Breach Of Contract
- Remedies available under the Specific Relief Act, 1963
Primer on E-Contracts
Law of Contract Mains Questions Series: Important Questions for Judiciary, APO & University Exams
- Law of Contract Mains Questions Series Part-I
- Law of Contract Mains Questions Series Part-II
- Law of Contract Mains Questions Series Part-III
- Law of Contract Mains Questions Series Part-IV
- Law of Contract Mains Questions Series Part-V
- Law of Contract Mains Questions Series Part-VI
- Law of Contract Mains Questions Series Part-VII
- Law of Contract Mains Questions Series Part-VIII
- Law of Contract Mains Questions Series Part-IX
- Law of Contract Mains Questions Series Part-X
Law of Contract MCQs for Law Aspirants: Solved High-Quality MCQs for Judiciary Prelims Your valuable feedback in the form of comments or any desired inputs are encouraged and always welcome. Every contribution toward a goal is valuable, regardless of how small it may be.
Admin Legal Bites
Legal Bites Study Materials correspond to what is taught in law schools and what is tested in competitive exams. It pledges to offer a competitive advantage, prepare for tests, and save a lot of money.
Related News

Presidential Power in 2017 , Live from Town Hall, Seattle LIVE STREAM 7:30–9 p.m. Pacific
Index to Lesson Topics
Introduction to law, juvenile justice, criminal law, consumer law/contracts, individual rights, employment/housing law, intellectual property, mock trial preparation, environmental law, street law at the uw school of law, model lesson plans.
The following lesson plans have been developed by University of Washington School of Law Students for the Street Law Course and are available for use at no charge. Most lesson plans are available in Microsoft Word , Adober PDF or Power Point document. Additional files are available as noted.
Users should note that the law changes, and varies from state to state. Please check for updates on the law, and variations in your state.
Get Microsoft Office Viewers Get Adobe Reader
Top of Page

Connect with us:
- Required Disclosures
© Copyright 2024, All Rights Reserved University of Washington School of Law
4293 Memorial Way Northeast, Seattle, WA 98195
Got any suggestions?
We want to hear from you! Send us a message and help improve Slidesgo
Top searches
Trending searches

teacher appreciation
11 templates

cybersecurity
6 templates

spring season
34 templates

archaeology
45 templates

46 templates

23 templates
Law Presentation templates
Edit professional themes and templates for google slides and powerpoint about law. you have the right to impress your audience with your presentations.

History Subject for High School in Spain: Constitution Day Infographics
Download the "History Subject for High School in Spain: Constitution Day Infographics" template for PowerPoint or Google Slides and discover the power of infographics. An infographic resource gives you the ability to showcase your content in a more visual way, which will make it easier for your audience to understand...

Premium template
Unlock this template and gain unlimited access
Present your Law Center and offer legal advice with this formal template! It includes flat illustrations related to justice and law, together with a set useful sections and icons. I rest my case, your honor!

Legal Consulting Toolkit
As everyone needs an ace up his sleeve for succeeding, we bring you here the tools that a consultant cannot miss, and in this particular case, for those specialized in legal consulting. These 50 slides lack nothing, as they include different very useful resources, such as Ansoff matrix, different tables...

Judges and Lawyers Legal Consulting
Download the "Judges and Lawyers Legal Consulting" presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. Your business demands smart solutions, and this consulting toolkit template is just that! This versatile and ingenious toolkit will provide you with the essential tools you need to shape your strategies and make informed decisions. Whether you...

Criminal Justice Degree for College
Do you want to explain in detail what the Criminal Justice degree is all about? With this Google Slides and PowerPoint template it will be a very easy task! We have designed this presentation thinking about all the sections you need to attract future lawyers and judges. However, don't worry...

Business Law Annual Meeting
Download the "Business Law Annual Meeting" presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. Gone are the days of dreary, unproductive meetings. Check out this sophisticated solution that offers you an innovative approach to planning and implementing meetings! Detailed yet simplified, this template ensures everyone is on the same page, contributing to...

Human Rights Lesson
There are a series of norms that are fundamental, universal and, most importantly, egalitarian. It’s none other than human rights, and it’s essential that all the people know about them. Prepare a lesson with this cool presentation template by Slidesgo!

Federal Law Enforcement Training Center
He who breaks the law... cannot download our templates! When talking about federal law enforcement, we instantly think of the FBI or the DEA, for example. Where do their agents train? In the best centers, of course! You can use this template to talk about training centers for police agents...

Pastel Law School Center Theme
To live happily in harmony, society has designed a set of rules to follow so no one harms others. This is the (very, very summarized) essence of the law! To make sure that laws are followed and updated, law experts like judges, lawyers or attorneys study very hard to ensure...

Family Lawyer Firm
Download the "Family Lawyer Firm" presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. Presenting a comprehensive company profile can be a game-changer for your business. A well-crafted profile connects with potential clients and vendors on another level, giving them a deep understanding of your organization. This company profile template can help you...

Legal Rights and Criminal Records
Download the "Legal Rights and Criminal Records" presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides and start impressing your audience with a creative and original design. Slidesgo templates like this one here offer the possibility to convey a concept, idea or topic in a clear, concise and visual way, by using different...

Social Justice and Activism - Spanish - 12th Grade
Download the "Social Justice and Activism - Spanish - 12th Grade" presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. High school students are approaching adulthood, and therefore, this template’s design reflects the mature nature of their education. Customize the well-defined sections, integrate multimedia and interactive elements and allow space for research or...

We believe in the uses of technology in education, so that’s why we thought of creating a free presentation template for law lessons. This could be useful for law schools or universities, and its design is as formal and professional as this topic requires.

Master of Jurisprudence
Waking the interest of new students for your Master of Jurisprudence is going to be very easy with this formal template. The design combines dark colors and serif fonts that make the slides very appealing. In addition, you can use the different resources we’ve included to support your case! They...

Labor Law: Workers' Duties
In labor law, generally speaking, an employee’s primary duty is to faithfully carry out the work for which they are employed and obey reasonable instructions from their employer. Duties may include, but are not limited to, keeping the workspace free from hazards, reporting any issues or safety violations to management...

Criminal Justice Degree for College Infographics
Download the "Criminal Justice Degree for College Infographics" template for PowerPoint or Google Slides and discover the power of infographics. An infographic resource gives you the ability to showcase your content in a more visual way, which will make it easier for your audience to understand your topic. Slidesgo infographics...

Gender Discrimination Lawyers Company Profile
Download the "Gender Discrimination Lawyers Company Profile" presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. Presenting a comprehensive company profile can be a game-changer for your business. A well-crafted profile connects with potential clients and vendors on another level, giving them a deep understanding of your organization. This company profile template can...


Labor Law Thesis Defense
Labor laws are designed to ensure the safety and rights of employed individuals. They stipulate regulations that employers must follow, such as providing fair wages, protecting workers from harassment or discrimination in the workplace, establishing clear work hours and overtime pay, among other things. An interesting topic for a dissertation!...
- Page 1 of 12
New! Make quick presentations with AI
Slidesgo AI presentation maker puts the power of design and creativity in your hands, so you can effortlessly craft stunning slideshows in minutes.

Register for free and start editing online
Contract Law
Notes, cases, and materials on contract law, topic notes.
Past Papers
Back to Subjects | Back to Law
Introduction to contract law
Forming the agreement
Certainty and clarity
Intention to create legal relations
Consideration
The doctrine of promissory estoppel
Privity of contract
Terms of a contract
Exclusion clauses
Duress, undue influence & unconscionable bargains
Misrepresentation
Frustration
General cases
Past Papers & Questions
1. There is in my view a real danger that if a general principle of good faith were established it would be invoked as often to undermine as to support the terms in which the parties have reached agreement’, per LJ Moore-Bick in MSC Mediterranean Shipping Co v Cottonex Anstalt [2016] EWCA Civ 789, at [45]. Critically discuss
2. ‘The foundation of consideration is unconscionability and promissory/proprietary estoppel is the best example of this. It would be better to just call the beast by its name and allow the courts to assess whether the deal was unconscionable or not.’ Critically discuss.
3. “The English courts’ approach to the doctrine of consideration is artificial since it has very little to do with the parties’ agreement. A change in the law is imperative to ensure clarity in the law and to stop a slavish adherence to the neo-classical theory of contract law.” Critically discuss.
4. To what extent is “business common sense” the fundamental approach of the courts in resolving ambiguities and ascertaining the meaning of contractual terms and statements?
5. Critically discuss the impact of the Consumer Rights Act 2015 on the regulation of ‘unfair terms’ in contracts.
The University of Retexe owns a painting titled ‘the scales out of balance’ which was given to it by a grateful graduate in 1955. The University has decided that nobody really looks at the piece and therefore wants to sell it. They contact a former student, Stefan, by letter:
‘We are considering selling the painting you knew and loved when you were a student here, ‘the scales out of balance’, as long as you are willing to pay £2m for it. The sale must be within the next two months. As you will remember it was included in the BBC television series ‘the art of Hogarth’ and they considered it to be one of his best pieces. Would you be interested in purchasing this Hogarth?’
Stefan immediately replies that the gallery he owns would be happy to pay that price for the Hogarth.
The University does not reply but the accountant removes the Hogarth from the list of art pieces to be insured. Shortly after Stefan succeeds in selling the painting on to an American art gallery for £5m. He contacts the University and leaves a message:
‘I hope you don’t mind but I have managed to sell the painting to a fantastic gallery.’ A few days later the university representative, Tammy, calls Stefan back and comments that she is glad they have found a good home for the painting and asks when Stefan would like the painting to be delivered.
Stefan is about to call back when he finds out from another dealer that the Hogarth, due to the time when it was donated, must have been a forgery. The discovery was made by accident last week when a gallery moved other Hogarths to a new building.
Advise Stefan, who does not want the painting anymore.
Ugo, an architect, earns a little extra money as a self-employed author of fiction. He has previously used an accountant in his town who has recently retired.
For this year’s tax return, due in January 2018, Ugo decides to use Valentina’s online tax return service. The website offers ‘a complete preparation and filing service for your income tax’. The website offers ‘complete peace of mind’. The first page of the website asks for the income. The page states that the customer ‘must submit all statements by post’ and, provided that she pays the £200 fee, they will then send her the completed tax return back.
On the very first page of the website there is a button titled ‘what we promise’. If the customer clicks on this it takes the customer to another website with terms and conditions, which include the following:
- What we promise: We undertake to calculate the tax you must pay from the figures you give us when you tell us your income. We take no responsibility for checking that you have entered the amounts correctly
- Liability. We are not responsible for any penalty imposed on you because your income is incorrectly stated; or because your return is not submitted on time unless we are shown to have acted intentionally or with gross negligence.
This button only appears on the first page. Ugo does not see or read the terms and conditions before sending in the requested information. Ugo does not notice that he has entered the amount he has earned as £2,500 rather than £25,000. The correct amount is clearly visible from the statements but Valentina does not notice the mistake. She sends the tax return back to Ugo, who signs it without checking.
The tax authorities notice the mistake and fine Ugo a total of £500.
Advise Ugo of any rights he may have against Valentina.
Trista and Kevin have been business partners of a local garage since 2010 valued at about £200,000, with Trista owning a 25% share in the business (worth approximately £50,000). In March 2015, Trista approached Kevin about the possibility of buying her out of the business to enable Trista sort out her own personal problems. When Kevin refused, Trista threatened to do such shoddy work at the garage that the business would lose clients and eventually become financially unviable.
Initially, Kevin refused Trista’s proposal and told her that, while sympathetic with her plight, he just did not have access to the necessary funds. During the next several months, Trista did as she threatened and her work was so slow and sloppy that the business began to lose customers.
Fearing that he would lose the business completely, Kevin approached his new husband, Gamu, about the possibly of putting up their jointly-owned £100,000 home as security on a £50,000 bank loan, so that Kevin could buy Trista out of the business. Kevin told Gamu that he felt he had no choice but to get the loan if his business were to survive. Gamu agreed and signed the necessary documents at the bank in the presence of Kevin. Kevin, in turn, entered into contract with Trista in October 2015 to buy her out of the business for £50,000.
By February 2016, as a result of the damage to the business’ reputation after Trista’s behaviour, Kevin had lost customers and was struggling to pay his bills, including the payments on the bank loan. In May 2016, Kevin was informed that the bank now intended to take possession of his and Gamu’s house.
Advise Kevin and Gamu on whether they have any rights against Trista and the bank.
Phoebe, who won £1 million from a lottery, decided to take her parents, Monica and Chandler, and her best friends, Jahangir and Ramona, on “luxury cruising” to thank them for being there for her. Phoebe remembered seeing the following Facebook advertisement by Superb Ltd:
“Get the experience of a lifetime via our two weeks cruise; Our luxury ship will be stopping at exotic places; Enjoy five-star hotels; Fine dining all the time; Our crew and passengers are special and the nicest; £1000 per person; Discounts for groups of five or more.”
Phoebe phoned Superb’s office and asked whether “that Facebook deal is still on” and got a confirmation. She later went to Superb’s office and signed a contract after paying a discounted price of £4000 for five persons.
Phoebe, her parents and her friends left the ship after two days due to the following facts:
- The ship, Konkordium, was an ugly-looking converted fishing boat lacking some basic facilities normally seen in cruise ships. Konkordium was only going round the southeast coast of England.
- Fine dining was not available on Konkordium and passengers were often given sandwiches. The food made Phoebe’s parents quite ill and Phoebe, Jahangir and Ramona suffered varying levels of discomfort from the food.
- Konkordium’s crew were swearing and shouting at passengers at will. One pushed Jahangir for no reason.
- Other passengers on Konkordium were groups of students who were always drunk, swearing, shouting and playing loud music. Some students whistled whenever they saw Ramona. The students paid £100 per person and £80 for groups of five.
Advise Phoebe, Monica, Chandler, Jahangir and Ramona on whether they have any legal claims in contract law.
Tara wanted to extend her house. Accordingly she engaged an architect to draw up some plans. Subsequently she placed a notice in her local newspaper requesting tenders in respect of the work to be undertaken. The notice stated that the deadline for the submission of tenders was noon on 4 March and the contract would be awarded to the person submitting the lowest tender. The notice also stated that further details, including plans, could be obtained from Tara at an address provided but did not state the method for submitting tenders.
Eoin, Belinda, Siobhan and David all requested further information and subsequently submitted tenders. Eoin submitted a tender of £20,000 by e-mail. Belinda submitted a tender of £15,000 by post. Siobhan submitted a tender of “£100 lower than any other tender received” by post. David submitted a tender of £10,000 by e-mail. Tara decided not to accept David’s tender as she had heard worrying rumours about the standard of David’s work. Instead she decided to accept Siobhan’s tender. David and Belinda are very angry about this and are threatening legal action. Moreover it appears that Tara did not consider Eoin’s tender at all as there was a problem with her computer server.
Advise the parties.
Digestible Notes was created with a simple objective: to make learning simple and accessible. We believe that human potential is limitless if you're willing to put in the work.
© 2024 Digestible Notes All Rights Reserved.
Our Socials

Indian Contract Act 1872 Case Study PPT: Legal Analysis & Examples
The fascinating world of indian contract act 1872 case study ppt.
When it comes to the Indian Contract Act 1872, there are endless possibilities for case studies and examples that showcase the intricacies of contract law in India. One particularly interesting way to study and understand this topic is through the use of PowerPoint presentations (PPT). In this blog post, we will delve into the world of Indian Contract Act 1872 case study PPTs, and explore the significance of this approach in legal education and practice.
Why Indian Contract Act 1872 Case Study PPTs are Valuable
Before we dive into specific case studies, let`s first discuss why using PPTs for contract law case studies is so valuable. PPTs can present information in a visually appealing and organized manner, making it easier for both students and professionals to grasp complex legal concepts. Additionally, the use of visual aids such as charts, tables, and diagrams can enhance comprehension and retention of information.
Case Study: Breach of Contract in the Indian Context
Let`s consider a hypothetical case study of a breach of contract in the Indian context. Imagine a scenario where Party A enters into a contract with Party B to deliver a certain quantity of goods by a specified date. However, Party B fails fulfill obligations contract, resulting Financial losses for Party A.
Case Details
Legal analysis.
Under the Indian Contract Act 1872, the failure of Party B to deliver the goods as per the contract constitutes a breach of contract. Party A has the right to seek remedies for the breach, such as claiming compensation for the financial losses incurred. In this case, the principles of contract law, as outlined in the Indian Contract Act 1872, will be invoked to resolve the dispute between the parties.
Indian Contract Act 1872 case study PPTs offer a dynamic and engaging way to explore the nuances of contract law in India. Through visually compelling presentations, complex legal concepts can be presented in a manner that is accessible and understandable. By using real-life case studies, such as the breach of contract example discussed above, legal professionals and students can gain practical insights into the application of the Indian Contract Act 1872 in the business world.
Unraveling the Intricacies of the Indian Contract Act 1872: A Case Study
Professional legal contract.
This contract is entered into by and between the parties involved in the Indian Contract Act 1872 case study PPT.
Share this post
Contract Law Cases: 21 Leading Case on the Law of Contract
- Post author: Edeh Samuel Chukwuemeka ACMC
- Post published: November 11, 2019
- Post category: Law Reporting
In today’s post, I will be sharing a list of some of the leading cases on contract law. This is basically to help scholars, lawyers and law students all of the world, find contract law cases so as to enable them consolidate their legal arguments, articles and points in law examinations. If you have been searching for cases to fortify your points in any matter that concerns contract, then search no further. Trust me; this article contains almost all the leading cases on the law of contract.

Nonetheless, before I move to the crux of this article, I would like to share some of basic information about the law of contract with you. This is also very pertinent because it will help you to understand the cases that will be mentioned here wholesomely. So what is a contract?
MUST READ: 10 Differences between military and democratic government
Table of Contents
What is a contract?
Contract has been given different definitions by different people. According to Sir Fredrick Pollock , A contract is a promise or set of promises which the law will efforce. More so, the American Law Institute gave an elaborate definition in their paper titled “ Restatement of American Law: Contracts ” when they defined contract as “ a promise or set of promises, the breach of which the law gives a remedy, or performance of which the law in some way recognizes as a duty.”
In my view, “a contact is an agreement giving rise to obligations which are enforced or recognized by law”. Conversely, it should be noted that while every contract is ultimately an agreement, it is not every agreement that is a contract.
Characteristics of a contract
Below are some of the characteristics of a binding contract:
- There must be an offer and acceptance (the agreement)
- There must be an intention to create legal relations
- There is a requirement of written formalities in some cases
- There must be consideration (Except if the agreement is under seal)
- The parties must also have the capacity to contact
- There must be genuineness of consent by the parties to the terms of the contract
- The contract must not be contrary to public policy
Also read : Fundamental human rights in Nigerian Constitution and cases
Classification of Contract

Basically, contract is classified into Simple contract or Formal contract. The two classifications of contract will be explained explicitly below:
Simple contract:
A simple contract is also called an informal contract. It is a contract, whether writen or oral, which is not under seal. It can also be implied from the conduct of parties. Simple contract are not binding except there is consideration. In a simple or informal contract, only a party who has furnished consideration can bring an action to enforce the contract.
Formal contract:
On the other hand, a formal contract is a contract which is reduced to writing, singed by parties contracting and impressed with a seal. It is also called a specialty contact or a deed. The basic features of a formal contract is to that it must be signed, sealed and delivered. These actions constitute the execution of a deed.
Now that you known what a contract is, the various types of contract and the characteristics of a contract, we will now see some of the leading cases in contract law.
Contact law cases
Below are some of the cases in the law of contract:
Carlill v Carbolic Smoke Ball Co
Andrews v hopkinson, fisher v bell, spencer v harding, central london property trust ltd v high trees house ltd, brodgen v metropolitan railway co., lampleigh v braithwaite, roscolar v thomas, stevenson v mclean, eastwood v kenyon, white v bluet, combe v combe, dela bere v pearson, read v dean, bournemouth athletic football club ltd v manchester united football club, tinn v hoffman & co, couturier v hastie.
- Dunlop Pneumatic Tyre Co Ltd v Selfridge
Griffith v Brymer
Darkin v lee, startup v macdonald.
Yeah! Those are some of the leading cases in contract law. Nevertheless, as we continue, will be sharing with you the case summary of each of the cases mentioned in the list above with their citations. I enjoin you to read painstakingly so that you will achieve your purpose for reading this work. Now, below is the case summary of the leading cases in the law of contract.
MUST READ: Problems facing the legal profession in Nigeria: 5 cogent solutions
Citation : [1893] 1 QB 256
The case of Carlill v Carbolic Smoke Ball Co is a good illustration of a unilateral contract. In this case, the defendant were proprietors of a medical preparation called “ The Carbolic Smoke Ball” . They advertised in various newspapers and magazines offering to pay €100 to any person who contracted influenza after using the ball three times a day for two weeks.
They added that they had deposited €1,000 at the Alliance Bank, Regent Street, to show their sincerity in the matter. The plaintiff, a lady, used the ball as was advertised and was attacked by influenza. She sued for €100 and the company agured that there was no intention to create legal relations.
The court held in favor of the plaintiff and said that the fact that €1,000 was deposited at the Alliance Bank, shows that there was an intention to create legal relations.
Citation: [1956] 3 All ER 422
The case of Andrews v Hopkinson is one of the contract cases that explains where a collateral contract will fail with the main contract. Apparently, a collateral contract is a preliminary contract which is usually oral and forms the reason or the inducement for the making of another related contract.
In the case of Andrews v Hopkinson, the collateral contract failed with the main contract. Here, a dealer said to the plaintiff, “ It is a nice little bus, I would stake my life on it. You will have no trouble with it. ” The plaintiff entered into a written hire-purchase contract with a finance company. The car was not roadworthy. The court held that the dealer was liable.
Also read : Richest lawyers in Ghana: Top 5
Citation: [1960] 3 All ER 731
The case of Fisher v Bell is a contract case that is usually used to explain the difference between an invitation to treat and an offer. In this case, the respondent, shopkeeper, displayed a knife with a price tag. He was charged for offering to sale a knife contrary to section 1(1) of the Restriction of Offensive Weapons Act 1959 .
The question that arose for determination in court was whether the display of this knife constituted an offer for sale within the meaning in the Restriction of Offensive Weapons Act 1959. It was held by the Court of Appeal that the display was an invitation to offer and so the shopkeeper was not liable.
Citation: [1870] LR 5 CP 561
In Spencer v Harding, the defendant sent out circulars inviting tenders to buy stock. The Plaintiff claimed that the circular was an offer to sell the stock to the highest bidder and that they had sent the highest bid which the plaintiff had refused to accept.
The court held that the circular was an invitation to treat and not an offer. Wiles J said thus: “ It is a mere attempt to ascertain whether an offer can be obtained within such a margin as the seller are willing to accept.”
Citation : [1947] KB 130
The case of Central London Property Trust Ltd v High Trees House Ltd is also one of the leading cases in the law of contract. This case changed the former rule of law in pinnel’s case. The case is usually referred to as the High Trees case or principle of Equitable Estoppel.
In Central London Property Trust Ltd v High Trees House Ltd, the plaintiff least a block of flat to the defendant at a rent of €2,500 per annum in September 1939. In January 1940 the plaintiff agreed in writing to reduce the rent by half because of war condition which had caused many vacancies in the flats. No express limit was set for the operation of this reduction.
From 1940 to 1945 the defendant paid the reduced rent. In 1945, the flats became fully occupied again. The plaintiff’s company then claimed the full rent, suing for rent at the ordinary rate for the last two quarters of 1945.
It was held by Lord Denning that, as agreement for the reduction of rent had been acted upon by the defendants, the plaintiff were estopped in equity from claiming the full rent from 1941 until early 1945 when the flats were fully let.
Also read: Defences to strict liability in tort: 5 Defences A Defendant Can claim
Citation: [1877] 2 AC 666
This is one of the contract cases that is offen cited to backup the rule that a contract can be made by conduct. In this case, Brodgen had for many year supplied the defendant company with coal without a formal contract. Brodgen then suggested that the relationship be regularised through a formal contract. Metropolitan’s agent sent a draft agreement to Brodgen who inserted an Arbitrator’s name in the space provided for it, signed it and wrote it away in his drawer and nothing further was done to complete its execution.
Both parties acted on the strength of the terms contained in the draft, supplying and paying for the coal in accordance with its clauses until a dispute arose and Brodgen denied that any binding contract existed between them. The house of Lord’s held that a contract arisen by conduct.

Citation : [1615] Hob 105
In this case, the defendant, Braithwaite, had killed Patrick Mahume. He then requested the plaintiff to do all he could to obtain a royal pardon for him from the king. To this end, the plaintiff exerted himself and undertook a lot of journeys to and from London, incurring certain expenses.
He succeeded in obtaining the pardon and the defendant promised to pay him the sume of €100 for his trouble and expenses. It was held that the plaintiff was entitled to the sum as his services were procured at the defendant’s previous request an in circumstances in which it was responsible to expect that payment would be made for the services. Accordingly, there was consideration for the defendant’s promise.
Also read : Nigerian leading cases on frustration of contract
Citation: [1842] 2QB 234
To wholesomely discuss past consideration as a topic in the law of contract, the case of Roscolar v Thomas must be mentioned. In this case, the plaintiff bought a horse from the defendant. After sometime, the defendant promised the plaintiff that it was a sound horse, free from vice. The horse was in fact a vicious horse. The plaintiff sued the defendant for breach of promise.
It was held that the action will fail. If the promise had been given at the time of the sale, it would have been supported by consideration, but since it was given after the sales had taken place, the consideration which the plaintiff furnished was past and he had furnished no new consideration for the defendant’s promise.
Citation: [1880] 5 QBD 346
In Stevenson v McLean, the defendant offered on a Sunday to sell the plaintiff some quantity of iron. The offer was left open till close of business on Monday. On Monday, the plaintiff telegraphed ro ask for information. On that same Monday, at 10:00am, the defendant received a telegram but didn’t reply it. On that same day, the plaintiff accepted the original offer at 1.34pm. At 1.25pm the defendant revoked the offer by telegram. At 1.46pm the plaintiff received telegram of revocation.
On hearing the matter, the court held that the plaintiff first telegram was not a counter offer but a mere inquiry, so that the offer was still open when the plaintiff accepted it. The plaintiff had accepted the offer before the defendant’s revocation was communicated to him.
Citation: [1840] 11 Ad & El 438
Eastwood v Kenyon is the case in contract that is used to explain that moral obligation does not amount to consideration. In this case, the death of John Sutcliff left his infant daughter as his sole heiress. The plaintiff, as the girl’s guardian, spent money on her education and for the benefit of the estate, and the girl, when she came of age, promised ro reimburse him.
She then married the defendant, who also promised to pay. The plaintiff sued the plaintiff on this promise and the court dismissed the action, reiterating the rule that moral obligation does not amount to consideration. The court noted that if the notion is accepted it would destroy the requirement of consideration as the law requires an additional element to the defendant’s promise. That element is consideration and it cannot be a mere moral obligation.
Citation: [1853] 23 LJ Ex 36
The case of White v Bluet explains the position that consideration in contract need not to be adequate by sufficient. In this case, a sun owned his father a sum of money. Subsequently, the sun harassed his father with frequent complaints about the way his father distributed his wealth among his children which was unfavorable to him.
The son then alleged that his father promised him that if he would stop complaining, he (the father) would discharge him from the debt and he stopped. The question before the court was whether this action of the son constituted consideration for the father’s promise. The court held that it did not because:
The father had a right to distribute his property in any manner he liked and so the son had no right to complain in the first place.
The son had no right to complain; thus is abstaining from doing what he had no right to do constituted no consideration for the father’s promise.
Citation : [1951] 2 KB 213
This is a contract case where the court held that consideration is an essential element of a binding contract. Here, a wife started proceedings against the husband for divorce and she obtained a decree nisi against the husband. The husband then promised to pay her an annual allowance of €100 free of tax as a permanent maintenance for her.
After the decree nisi was made absolute, the husband never kept his promise. Thereupon the wife brought an action against him to make him pay the money. The court held that she didn’t offer consideration for the husband’s promise.
Citation : [1908] 1 KB 280
In this case, the defendant placed an advertisement in the newspaper to give financial advice to readers. The plaintiff wrote, asking for the name of a good stockbroker. The editor negligently recommended someone who was an undischarged bankrupt.
On the strength of the editor’s advice, the plaintiff sent some money to the broker, who misappropriated it. The plaintiff brought an action in court seeking to recover his money from the the newspaper. The issue in court was whether the plaintiff furnished any consideration.
The court considered that many people bought newspaper because of that publication. It further held that the plaintiff had furnished consideration for the contract. The defendant could and did benefit from the plaintiff buying the newspaper and the plaintiff had also consented to the publication of his question in the defendant’s newspaper if the defendants wished to do so.
Citation: [1949] 1 KB 188
In the case of Read v Dean, the plaintiff hired the defendant’s moto launch for a holiday with his family on the river Thames. Two hours after he had set sail, the launch caught fire.
The firefighting equipment provided in the launch was out of order and the plaintiff suffered serious injuries and lost all his belongings on board. It was held that there must be implied into the contract of hire an undertaking by the defendant to make the launch as fit for the purpose of the hiring as reasonable care could make it, and that the defendant was therefore liable.
Citation: Vol Xi (2) Student Law Report 22
The case of Bournemouth Athletic Football Club Ltd v Manchester United Football Club is another popular case in the law of contract. In this case, a transfer agreement was made between the two football clubs. Under it, a footballer was to be transferred from Bournemouth to Manchester united for €194,445 in addition, a further sum of €27,777 was to be paid to Bournmouth if the footballer scored 20 goals in the first-team competitive matches. From October to December 1972, the football scored 4 goals in 11 matches. In December, Manchester United appointed a new manager who re-organised the team.
As a result, the footballer was transferred in early 1973 to Westham United Football club for €170,000. The plaintiff argued that the contract of the defendant in transferring the footballer was in Breach of the contract because there was an implied term in the contract that the footballer was entitled to a reasonable opportunity to score the goals. The court of appeal held that such term must be implied in order to give business efficacy to a contract.
MUST READ : Ukeje v Ukeje | Inheritance Right of Women
Citation: [1873] 29 LT 271
The court in Tinn v Hoffman & Co held that a cross-offer does not constitute a contract.
The facts of the case are as follows: the defendant wrote to the plaintiff offering to sell him 800 tons of iron at 69s per ton. The plaintiff wrote to the defendant, on the same day offering to buy 800 tons of iron at 69s per ton. The letters crossed in the post and the court held that there was no contract.
Citation: [1856] 5 HLC 673
This is the leading contract law case that stipulates the position of the law where there is a mistake as to the existence of the subject matter of the contract. In Couturier v Hastie, a man bought a cargo of corn which he and the seller thought at the time of the contract, to be in transit from Salonica to England, but which, unknown to them had become fermented and had already been sold by the master of the ship to a Tunis. It was held that the contract was void and the buyer not liable for the price of the cargo.
In the words of Lord Cranworth , “ The contract plainly imports that there was something which was to be sold at the time of the contract and something to be purchased. No such thing existing; I think the Court of Exchequer Chamber has come to the only reasonable conclusion upon it . ..”
Dunlop Pneumatic Tyre Co Ltd v Selfridge Ltd
Citation: [1915] AC 847
This is one of the leading contract cases that is associated with the principle of privity of contract. The principle states that only a party to a contract can enjoy right or suffer burdens partaining to the contract.
In Dunlop Pneumatic Tyre Co Ltd v Selfridge Ltd, the plaintiff sold tyres to a certain dealer on the understanding that he would not re-sell below a certain price and that in the event of a sale to customers the dealer would extract the same promise from them.
The dealer sole the tyres to Selfridge who agreed to observe the restrictions and to pay Dunlop €5 for each Tyre they sold below the restricted price. Selfridge in fact sold the tyres below the restricted price to a customer and Dunlop brought an action against them to enforce the promise to pay €5 per tyre, for each breach.
It was held that while Selfridge had committed to breach the contract between him and the dealer, Dunlop was not a party to this contract and had furnished no consideration for the defendant’s promise.
Citation: [1903] 19 TLR 434
This is one of the cases under Mistake as a topic in contract law. In Griffith v Brymer, a contract was made for the hire of a room on 26 June 1902, the day fixed for the coronation of King Edward VII, for the purpose of viewing the coronation procession.
At the time the contract was made, it was unknown to the parties, the decision to postpone the coronation had already been taken. Since the contract was merely for the hire of the room on 26 June to view the coronation procession, performance was impossible. The contract was held to be void.
Must read : The case of Mojekwu v Mojekwu: Case Summary
Citation: [1916] 1 KB 566.
This contract case explains the principle that where a party who performed his obligation defectively but substantially can sue for the contract price, but he will be liable to have deducted from the price the cost of making good the deficiency.
In Darkin v Lee, the plaintiff contracted to carry out repairs on the defendant’s house. He carried out the repairs but the work was not done in accordance with the contact’s specification. It was held that the plaintiff was entitled to be paid the agreed sum subject to a deductive equal to the cost of putting the defect right.
Citation: [1843] 6 M & G 593.
The rule of law in Startup v Macdonald is that; where the obligation under a contract is to deliver goods or render services, tender of such goods and services which is refused, discharges the party making the tender from any further obligation and enables him to sue for a breach of contract.
In Startup v Macdonald, the plaintiff agreed to sell 10 tonnes of oil to the defendant within the last 14 days of March. Pursuant to this agreement, the plaintiff delivered the oil to the defendant at 8:30pm on 31 March, a Saturday, but the defendant refused to accept the delivery because of the lateness of the hour.
It was held that the plaintiff made a valid tender of the goods and therefore discharged his obligations under the contract and the defendant was therfore liable in damages for non-acceptance of the goods.
Also read: How to become a successful lawyer in your country Best law firms in Nigeria: Top 10 Cheapest universities in Nigeria to study law
Final words
Those are some of the leading contract law cases you should know. Hope this article was able to give you exactly what you wanted. If you have any case you were really expecting to be in this list but was not mentioned here, kindly let us know using the comment section. Accordingly, share you comments and questions in the comment section too. I will be very glad to give you a reply.

Edeh Samuel Chukwuemeka, ACMC, is a lawyer and a certified mediator/conciliator in Nigeria. He is also a developer with knowledge in various programming languages. Samuel is determined to leverage his skills in technology, SEO, and legal practice to revolutionize the legal profession worldwide by creating web and mobile applications that simplify legal research. Sam is also passionate about educating and providing valuable information to people.
- Preferences

Contract Law Case Study Assignment - PowerPoint PPT Presentation

Contract Law Case Study Assignment
If you are searching for contract law case study assignment, then you are in the correct place. no1assignmenthelp.com is a reliable source of this type of service. our teams members are expert in all areas and have experience in writing across all formats. avail the opportunity. for more visit - email - [email protected] – powerpoint ppt presentation.
- Contract law is a private agreement of law between two parties for the enforcement of promises.
- It is the most important law in the legal system.
- Every business transaction is only considered legal when it fulfills the rule and regulation of the prevailing Contract law.
- It is also referred as a legal bond that is used to protect two parties who are about to enter into an agreement.
- Bilateral Contract
- Unilateral Contract
- Express Contract
- Contract under seal
- Implied Contract
- Aleatory Contract
- Adhesion Contract
- Executive Contract
- Unconscionable Contract
- Void and Voidable Contracts
- Letter Contracts
- Introduction Clauses
- Defining the Parties and Key items
- Statements of Purpose
- Obligation of each Party
- Assurances and Warranties
- Attachments
- Signature Block
- Consideration
- Definitions
- Materials/ Information
- Liability/ Indemnity
- Consideration/ payment option
- Obligation of each party
- Terms of validity
- Governing law and arbitration
- It gives clear understanding of the condition when the parties are directly involved in an agreement.
- It refers to all the terms and conditions and the applications and the rights of each party, which may vary based on the nature of the contract agreement.
- It helps both parties to be mentally and logically sound and be competent when entering into contracts.
- Business contracts should always have legal purpose for validation.
- Breaching of a contract occurs when one of the parties in the contact violates any clauses mentioned in the agreement.
- It damages the reputation of the party, their business and also the person.
- If the damages are caused due to a breach of contract, the other party can lead the business into a lawsuit.
- If the court finds that the violation towards the contract is momentous then the court can hold the party contempt, fine and even imprison.
- An extensive summary
- Introduction/ Abstract
- Recommendations and implementations
- Australian writers
- Team of 5000 Ph.D., Management Graduates as writers
- Use of Proper Referencing Styles
- Unlimited Reworking
- 247 online assistance
- Service for all subjects
- Pocket-friendly Prices
PowerShow.com is a leading presentation sharing website. It has millions of presentations already uploaded and available with 1,000s more being uploaded by its users every day. Whatever your area of interest, here you’ll be able to find and view presentations you’ll love and possibly download. And, best of all, it is completely free and easy to use.
You might even have a presentation you’d like to share with others. If so, just upload it to PowerShow.com. We’ll convert it to an HTML5 slideshow that includes all the media types you’ve already added: audio, video, music, pictures, animations and transition effects. Then you can share it with your target audience as well as PowerShow.com’s millions of monthly visitors. And, again, it’s all free.
About the Developers
PowerShow.com is brought to you by CrystalGraphics , the award-winning developer and market-leading publisher of rich-media enhancement products for presentations. Our product offerings include millions of PowerPoint templates, diagrams, animated 3D characters and more.


An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
Take action
- Report an antitrust violation
- File adjudicative documents
- Find banned debt collectors
- View competition guidance
- Competition Matters Blog
New HSR thresholds and filing fees for 2024
View all Competition Matters Blog posts
We work to advance government policies that protect consumers and promote competition.
View Policy
Search or browse the Legal Library
Find legal resources and guidance to understand your business responsibilities and comply with the law.
Browse legal resources
- Find policy statements
- Submit a public comment

Vision and Priorities
Memo from Chair Lina M. Khan to commission staff and commissioners regarding the vision and priorities for the FTC.
Technology Blog
Consumer facing applications: a quote book from the tech summit on ai.
View all Technology Blog posts
Advice and Guidance
Learn more about your rights as a consumer and how to spot and avoid scams. Find the resources you need to understand how consumer protection law impacts your business.
- Report fraud
- Report identity theft
- Register for Do Not Call
- Sign up for consumer alerts
- Get Business Blog updates
- Get your free credit report
- Find refund cases
- Order bulk publications
- Consumer Advice
- Shopping and Donating
- Credit, Loans, and Debt
- Jobs and Making Money
- Unwanted Calls, Emails, and Texts
- Identity Theft and Online Security
- Business Guidance
- Advertising and Marketing
- Credit and Finance
- Privacy and Security
- By Industry
- For Small Businesses
- Browse Business Guidance Resources
- Business Blog
Servicemembers: Your tool for financial readiness
Visit militaryconsumer.gov
Get consumer protection basics, plain and simple
Visit consumer.gov
Learn how the FTC protects free enterprise and consumers
Visit Competition Counts
Looking for competition guidance?
- Competition Guidance
News and Events
Latest news, ftc announces rule banning noncompetes.
View News and Events
Upcoming Event
Informal hearing on proposed trade regulation rule on unfair or deceptive fees – april 24, 2024.
View more Events
Sign up for the latest news
Follow us on social media
--> --> --> --> -->

Playing it Safe: Explore the FTC's Top Video Game Cases
Learn about the FTC's notable video game cases and what our agency is doing to keep the public safe.
Latest Data Visualization
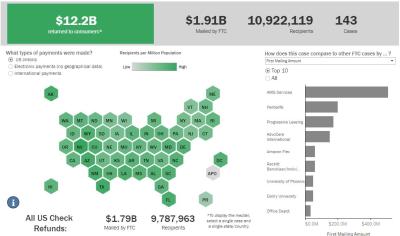
FTC Refunds to Consumers
Explore refund statistics including where refunds were sent and the dollar amounts refunded with this visualization.
About the FTC
Our mission is protecting the public from deceptive or unfair business practices and from unfair methods of competition through law enforcement, advocacy, research, and education.
Learn more about the FTC

Meet the Chair
Lina M. Khan was sworn in as Chair of the Federal Trade Commission on June 15, 2021.
Chair Lina M. Khan
Looking for legal documents or records? Search the Legal Library instead.
- Cases and Proceedings
- Premerger Notification Program
- Merger Review
- Anticompetitive Practices
- Competition and Consumer Protection Guidance Documents
- Warning Letters
- Consumer Sentinel Network
- Criminal Liaison Unit
- FTC Refund Programs
- Notices of Penalty Offenses
- Advocacy and Research
- Advisory Opinions
- Cooperation Agreements
- Federal Register Notices
- Public Comments
- Policy Statements
- International
- Office of Technology Blog
- Military Consumer
- Consumer.gov
- Bulk Publications
- Data and Visualizations
- Stay Connected
- Commissioners and Staff
- Bureaus and Offices
- Budget and Strategy
- Office of Inspector General
- Careers at the FTC
Fact Sheet on FTC’s Proposed Final Noncompete Rule
- Competition
- Office of Policy Planning
- Bureau of Competition
The following outline provides a high-level overview of the FTC’s proposed final rule :
- Specifically, the final rule provides that it is an unfair method of competition—and therefore a violation of Section 5 of the FTC Act—for employers to enter into noncompetes with workers after the effective date.
- Fewer than 1% of workers are estimated to be senior executives under the final rule.
- Specifically, the final rule defines the term “senior executive” to refer to workers earning more than $151,164 annually who are in a “policy-making position.”
- Reduced health care costs: $74-$194 billion in reduced spending on physician services over the next decade.
- New business formation: 2.7% increase in the rate of new firm formation, resulting in over 8,500 additional new businesses created each year.
- This reflects an estimated increase of about 3,000 to 5,000 new patents in the first year noncompetes are banned, rising to about 30,000-53,000 in the tenth year.
- This represents an estimated increase of 11-19% annually over a ten-year period.
- The average worker’s earnings will rise an estimated extra $524 per year.
The Federal Trade Commission develops policy initiatives on issues that affect competition, consumers, and the U.S. economy. The FTC will never demand money, make threats, tell you to transfer money, or promise you a prize. Follow the FTC on social media , read consumer alerts and the business blog , and sign up to get the latest FTC news and alerts .
Contact Information
Media contact.
Victoria Graham Office of Public Affairs 415-848-5121

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Indian contract act 1872 key cases. Aug 28, 2012 • Download as PPTX, PDF •. 37 likes • 55,675 views. AI-enhanced title and description. M. manjit29. This document summarizes key concepts from Indian contract law: 1) It discusses offer and acceptance through examples like offers to buy a car or house. It also examines the Carlil v.
Minor is a person who has not attained or is below the age of 18 years. And any contract entered into with a minor shall be be null and void (void ab initio) owing to his incapacity. Dealings done by the minors without the knowledge and consent of their custodians or parents shall not be liable to them. V. RAFFELS v.
H. This document discusses a case law involving Lalman Shukla, a servant, and Gauri Dutt, his nephew's uncle. Gauri Dutt's nephew went missing one day. Gauri Dutt announced an offer of a reward for anyone who found his nephew. Lalman Shukla searched for and found the nephew. However, Gauri Dutt refused to pay the reward.
Simply put, a contract can be described as a legally binding oral or written agreement which exchanges any combination of goods, services, money and property. It is a common misconception that a contract may only be in written form, as oral or conduct agreements can be just as credible in contract formation. A contract is unique in that unless ...
Contract Law Case Summary. Adams v Lindsell (1818) 1 B & Ald 681. The case of Adams v Lindsell is taught to university law students when studying offer and acceptance. It is often thought by students to have set a rather strange precedent. However, this is because modern students are viewing Adams v Lindsell in a modern context, rather than the ...
Contract Cases This page provides a list of cases cited in our Contract Law Lecture Notes, as well as other cases you might find useful. It also provides links to case-notes and summaries. (A) Abbey National Bank plc v Stringer Adams v Lindsell Addis v Gramophone AEG (UK) Ltd v Logic Resource Ltd African Export-Import Bank…
Contract law refers to that body of law, which enforces, interprets, and governs agreements associated with exchange of services, goods, money, or properties. This law basically comes under civil law. Law students have to become well-acquainted with each and every aspect of this law. They are even assigned to compose case studies on this area.
Contract case studies 2020 - Free download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online.
Explore comprehensive Contract Law notes, insightful Case Laws, and valuable Study Material on Legal Bites. Contract Law is a form of civil law. The chief component of the contract law in India is the Indian Contract Act, which was enacted in 1872 and enforced on September 1, 1872. From arbitration enthusiasts to budding sports lawyers, the ...
IMPORTANT LANDMARK CASES IN CONTRACT LAW. Contributed by: Adv. PIYALI MUKHERJEE. 1. Balfour vs. Balfour (King's Bench-1919) Rule of Law: Where parties to the contract do not intend to create a binding agreement, the agreement cannot be enforced.. Fact: The case of Balfour vs. Balfour is a well-known illustration of a domestic agreement. In this case, Mr Balfour was working in Ceylon.
Premium Google Slides theme and PowerPoint template. Case Law! This creatively illustrated template is designed for lawyers, law students, judges and any other professionals who want to present law cases in a clear and organized way. The slide deck provides different structures to achieve this. You know, trust the law, but trust Slidesgo too!
Power Point presentation Adobe PDF document: Contracts Law - lecture with worksheet, short case studies (2010) Lesson plan Power Point presentation Drafting document Contract sample Worksheet: Negotiation for NFL Player Contract (2010) Word document: Consumer Law - letters to Attorney General (2010)
Download the "Social Justice and Activism - Spanish - 12th Grade" presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. High school students are approaching adulthood, and therefore, this template's design reflects the mature nature of their education. Customize the well-defined sections, integrate multimedia and interactive elements and allow space ...
Introduction . According to Section 2(h) of the Indian Contract Act, 1872, an agreement enforceable by law is known as a contract.The contract law generally concerns rights in personam which means private rights that only affect two private individuals entering into a contract with each other. There are several important concepts in relation to contract law that can be better understood by ...
3. "The English courts' approach to the doctrine of consideration is artificial since it has very little to do with the parties' agreement. A change in the law is imperative to ensure clarity in the law and to stop a slavish adherence to the neo-classical theory of contract law.". Critically discuss. 4.
The Fascinating World of Indian Contract Act 1872 Case Study PPT. When it comes to the Indian Contract Act 1872, there are endless possibilities for case studies and examples that showcase the intricacies of contract law in India. One particularly interesting way to study and understand this topic is through the use of PowerPoint presentations ...
The case of Central London Property Trust Ltd v High Trees House Ltd is also one of the leading cases in the law of contract. This case changed the former rule of law in pinnel's case. The case is usually referred to as the High Trees case or principle of Equitable Estoppel. ... Top 10 Cheapest universities in Nigeria to study law. Final words.
Title: Contract Law Case Study Assignment 1 Contract Law Case Study Assignment Help 2 Define Contract Law. Contract law is a private agreement of law between two parties for the enforcement of promises. It is the most important law in the legal system. Every business transaction is only considered legal when it fulfills the rule and regulation of
It also discusses employment law, real estate law, and contract law considerations when buying an existing business. The presentation provides overviews of the Indian Contract Act of 1872 and defines key contract law terms like agreement, consent, and essential elements of a valid contract. Read more. Law. 1 of 16. The Contract Act "PART 1 ...
Download our professional Contract law powerpoint templates to prepare the coming presentation. Google Slides theme templates are also available for free download. 100% FREE! ... We are dedicated to making your work and study much easier than before with professional presentation templates, docs and other office templates. Slidesdocs provides a ...
Fewer than 1% of workers are estimated to be senior executives under the final rule. Specifically, the final rule defines the term "senior executive" to refer to workers earning more than $151,164 annually who are in a "policy-making position.". The FTC estimates that banning noncompetes will result in: Reduced health care costs: $74 ...
5. Invitation to offer: Invitation to offer is an advertisement inviting others to make an offer. It is not an offer, which capable of being turned into an agreement by acceptance. Thus, (1) Auction (2) A Catalogue of goods (3)Advertisement of job (4) Quotation of price (5)Time table. Case study analysis: Problem No: 1 Harish says in conversation to Suresh that he will give Rs.10,000 to a ...