Making quality assurance smart
For decades, outside forces have dictated how pharmaceutical and medtech companies approach quality assurance. The most influential force remains regulatory requirements. Both individual interpretations of regulations and feedback received during regulatory inspections have shaped quality assurance systems and processes. At the same time, mergers and acquisitions, along with the proliferation of different IT solutions and quality software, have resulted in a diverse and complicated quality management system (QMS) landscape. Historically, the cost of consolidating and upgrading legacy IT systems has been prohibitively expensive. Further challenged by a scarcity of IT support, many quality teams have learned to rely on the processes and workflows provided by off-the-shelf software without questioning whether they actually fit their company’s needs and evolving regulatory requirements.
In recent years, however, several developments have enabled a better way. New digital and analytics technologies make it easier for quality teams to access data from different sources and in various formats, without replacing existing systems. Companies can now build dynamic user experiences in web applications at a fraction of the cost of traditional, enterprise desktop software; this development raises the prospect of more customized, user-friendly solutions. Moreover, regulators, such as the FDA, are increasingly focused on quality systems and process maturity. 1 MDIC Case for Quality program. The FDA also identified the enablement of innovative technologies as a strategic priority, thereby opening the door for constructive dialogue about potential changes. 2 Technology Modernization Action Plan, FDA.

Smart quality at a glance
“Smart quality” is a framework that pharma and medtech companies can apply to redesign key quality assurance processes and create value for the organization.
Smart quality has explicit objectives:
- to perceive and deliver on multifaceted and ever-changing customer needs
- to deploy user-friendly processes built organically into business workflows, reimagined with leading-edge technologies
- to leapfrog existing quality management systems with breakthrough innovation, naturally fulfilling the spirit—not just the letter—of the regulations
The new ways in which smart quality achieves its objectives can be categorized in five building blocks (exhibit).
To learn more about smart quality and how leading companies are reimagining the quality function, please see “ Smart quality: Reimagining the way quality works .”
The time has arrived for pharmaceutical and medtech companies to act boldly and reimagine the quality function. Through our work on large-scale quality transformation projects and our conversations with executives, we have developed a new approach we call “smart quality” (see sidebar, “Smart quality at a glance”). With this approach, companies can redesign key quality processes and enable design-thinking methodology (to make processes more efficient and user-friendly), automation and digitization (to deliver speed and transparency), and advanced analytics (to provide deep insights into process capability and product performance).
The quality assurance function thereby becomes a driver of value in the organization and a source of competitive advantage—improving patient safety and health outcomes while operating efficiently, effectively, and fully aligned with regulatory expectations. In our experience, companies applying smart quality principles to quality assurance can quickly generate returns that outweigh investments in new systems, including line-of-sight impact on profit; a 30 percent improvement in time to market; and a significant increase in manufacturing and supply chain reliability. Equally significant are improvements in customer satisfaction and employee engagement, along with reductions in compliance risk.
Revolutionizing quality assurance processes
The following four use cases illustrate how pharmaceutical and medtech companies can apply smart quality to transform core quality assurance processes—including complaints management, quality management review, deviations investigations, and supplier risk management, among others.
1. Complaint management
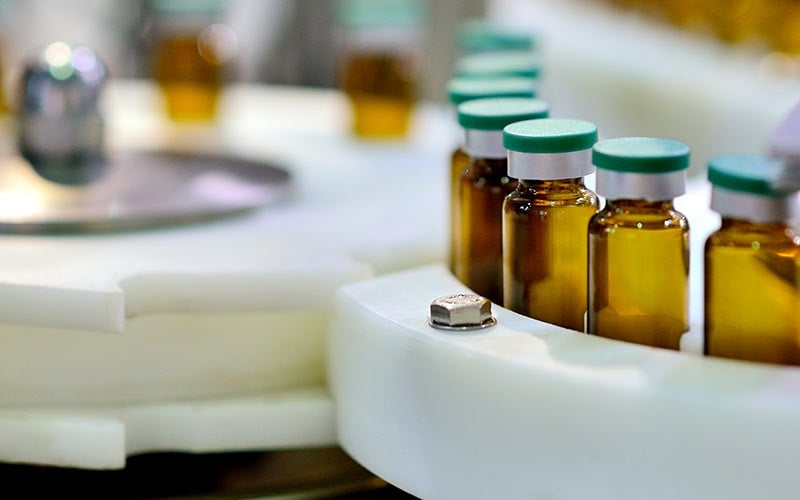
Responding swiftly and effectively to complaints is not only a compliance requirement but also a business necessity. Assessing and reacting to feedback from the market can have an immediate impact on patient safety and product performance. Today, a pharmaceutical or medtech company may believe it is handling complaints well if it has a single software deployed around the globe for complaint management, with some elements of automation (for example, flagging reportable malfunctions in medical devices) and several processing steps happening offshore (such as intake, triage, and regulatory reporting).
Yet, for most quality teams, the average investigation and closure cycle time hovers around 60 days—a few adverse events are reported late every month, and negative trends are addressed two or more months after the signals come in. It can take quality assurance teams even longer to identify complaints that collectively point to negative trends for a particular product or device. At the same time, less than 5 percent of incoming complaints are truly new events that have never been seen before. The remainder of complaints can usually be categorized into well-known issues, within expected limits; or previously investigated issues, in which root causes have been identified and are already being addressed.
The smart quality approach improves customer engagement and speed
By applying smart quality principles and the latest technologies, companies can reduce turnaround times and improve the customer experience. They can create an automated complaint management process that reduces costs yet applies the highest standards:
- For every complaint, the information required for a precise assessment is captured at intake, and the event is automatically categorized.
- High-risk issues are immediately escalated by the system, with autogenerated reports ready for submission.
- New types of complaints and out-of-trend problems are escalated and investigated quickly.
- Low-risk, known issues are automatically trended and closed if they are within expected limits or already being addressed.
- Customer responses and updates are automatically available.
- Trending reports are available in real time for any insights or analyses.
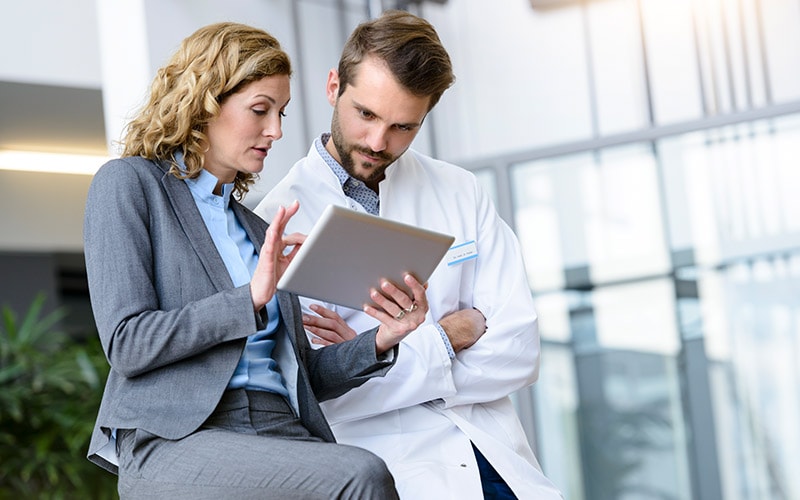
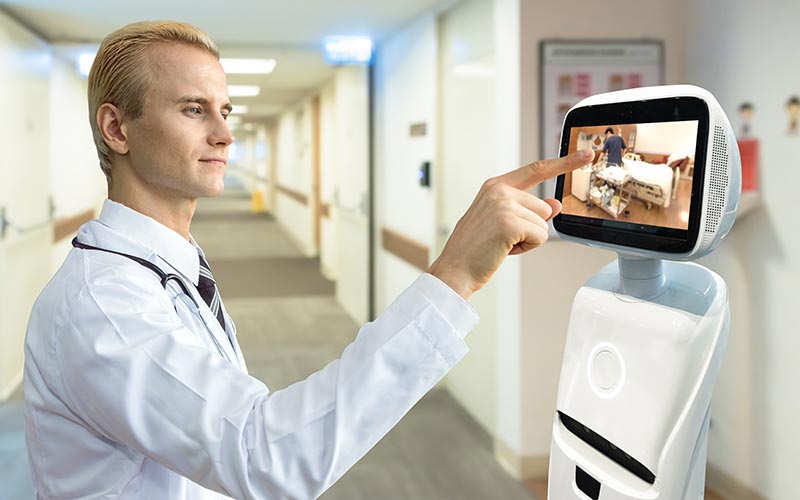
To transform the complaint management process, companies should start by defining a new process and ensuring it meets regulatory requirements. The foundation for the new process can lie in a structured event assessment that allows automated issue categorization based on the risk level defined in the company’s risk management documentation. A critical technological component is the automation of customer complaint intake; a dynamic front-end application can guide a customer through a series of questions (Exhibit 1). The application captures only information relevant to a specific complaint evaluation, investigation, and—if necessary—regulatory report. Real-time trending can quickly identify signals that indicate issues exceeding expected limits. In addition, companies can use machine learning to scan text and identify potential high-risk complaints. Finally, risk-tailored investigation pathways, automated reporting, and customer response solutions complete the smart quality process. Successful companies maintain robust procedures and documentation that clearly explain how the new process reliably meets specific regulatory requirements. Usually, a minimal viable product (MVP) for the new process can be built within two to four months for the first high-volume product family.
In our experience, companies that redesign the complaint management process can respond more swiftly—often within a few hours—to reduce patient risk and minimize the scale and impact of potential issues in the field. For example, one medtech company that adopted the new complaint management approach can now automatically assess all complaints and close more than 55 percent of them in 24 hours without human intervention. And few, if any, reportable events missed deadlines for submission. Now, subject matter experts are free to focus on investigating new or high-risk issues, understanding root causes, and developing the most effective corrective and preventive actions. The company also reports that its customers prefer digital interfaces to paper forms and are pleased to be updated promptly on their status and resolution of their complaints.
2. Quality management review
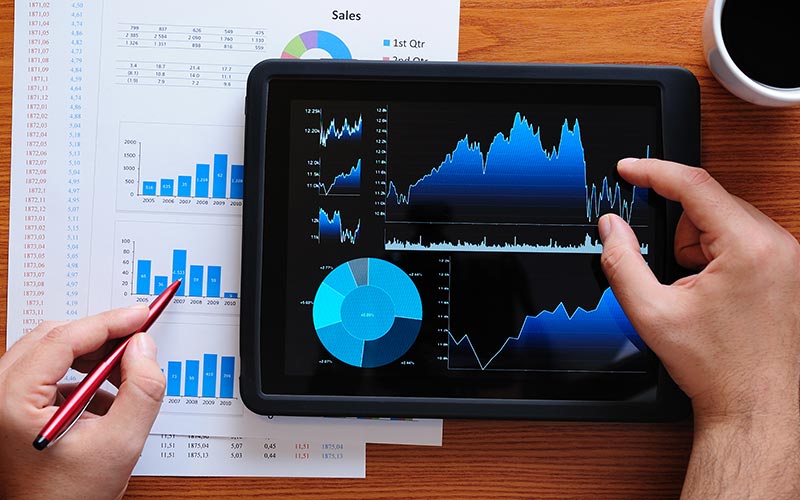
Real-time performance monitoring is crucial to executive decision making at pharmaceutical and medtech companies. During a 2019 McKinsey roundtable discussion, 62 percent of quality assurance executives rated it as a high priority for the company, exceeding all other options.
For many companies today, the quality review process involves significant manual data collection and chart creation. Often, performance metrics focus on quality compliance outcomes and quality systems—such as deviation cycle times—at the expense of leading indicators and connection to culture and cost. Managers and executives frequently find themselves engaged in lengthy discussions, trying to interpret individual metrics and often missing the big picture.
Although many existing QMS solutions offer automated data-pull and visualization features, the interpretation of complex metric systems and trends remains largely a manual process. A team may quickly address one performance metric or trend, only to learn several months later that the change negatively affected another metric.
The smart quality approach speeds up decision making and action
By applying smart quality principles and the latest digital technologies, companies can get a comprehensive view of quality management in real time. This approach to performance monitoring allows companies to do the following:
- automatically collect, analyze, and visualize relevant leading indicators and outcomes on a simple and intuitive dashboard
- quickly identify areas of potential risk and emerging trends, as well as review their underlying metrics and connections to different areas
- rapidly make decisions to address existing or emerging issues and monitor the results
- adjust metrics and targets to further improve performance as goals are achieved
- view the entire value chain and create transparency for all functions, not just quality
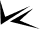
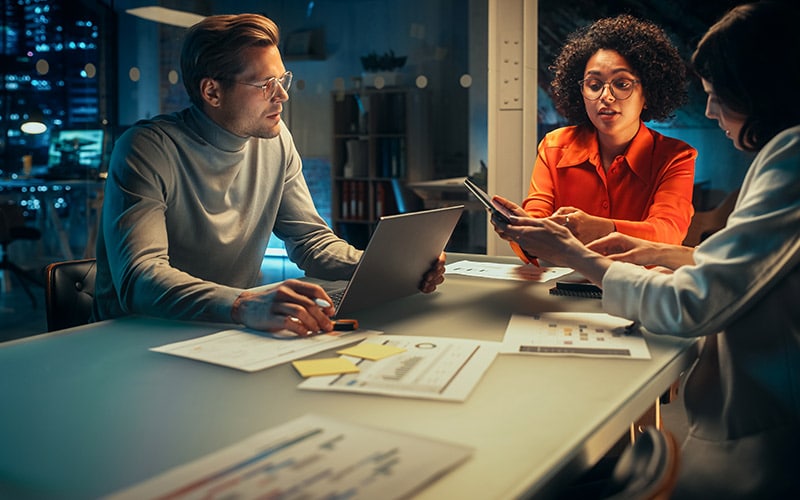
To transform the process, companies should start by reimagining the design of the process and settling on a set of metrics that balances leading and lagging indicators. A key technical enabler of the system is establishing an interconnected metrics structure that automates data pull and visualization and digitizes analysis and interpretation (Exhibit 2). Key business processes, such as regular quality management reviews, may require changes to include a wider range of functional stakeholders and to streamline the review cascade.
Healthcare companies can use smart quality to redesign the quality management review process and see results quickly. At one pharmaceutical and medtech company, smart visualization of connected, cross-functional metrics significantly improved the effectiveness and efficiency of quality management review at all levels. Functions throughout the organization reported feeling better positioned to ascertain the quality situation quickly, support decision making, and take necessary actions. Because of connected metrics, management can not only see alarming trends but also link them to other metrics and quickly align on targeted improvement actions. For example, during a quarterly quality management review, the executive team linked late regulatory reporting challenges to an increase in delayed complaint submissions in some geographic regions. Following the review, commercial leaders raised attention to this issue in their respective regions, and in less than three months, late regulatory reporting was reduced to zero. Although the company is still in the process of fully automating data collection, it has already noticed a significant shift in its work. The quality team no longer spends the majority of its time on data processing but has pivoted to understanding, interpreting, and addressing complex and interrelated trends to reduce risks associated with quality and compliance.
Healthcare companies can use smart quality to redesign the quality management review process and see results quickly.
3. Deviation or nonconformance investigations
Deviation or nonconformance management is a critical topic for companies today because unaddressed issues can lead to product recalls and reputational damage. More often, deviations or nonconformances can affect a company’s product-release process, capacity, and lead times. As many quality teams can attest, the most challenging and time-consuming part of a deviation or nonconformance investigation is often the root cause analysis. In the best of circumstances, investigators use a tracking and trending system to identify similar occurrences. However, more often than not, these systems lack good classification of root causes and similarities. The systems search can become another hurdle for quality teams, resulting in longer lead times and ineffective root cause assessment. Not meeting the standards defined by regulators regarding deviation or nonconformance categorization and root cause analysis is one of the main causes of warning letters or consent decrees.
The smart quality approach improves effectiveness and reduces lead times
Our research shows companies that use smart quality principles to revamp the investigation process may reap these benefits:
- all pertinent information related to processes and equipment is easily accessible in a continuously updated data lake
- self-learning algorithms predict the most likely root cause of new deviations, thereby automating the review of process data and statements
In our experience, advanced analytics is the linchpin of transforming the investigation process. The most successful companies start by building a real-time data model from local and global systems that continuously refreshes and improves the model over time. Natural language processing can generate additional classifications of deviations or nonconformances to improve the quality and accuracy of insights. Digitization ensures investigators can easily access graphical interfaces that are linked to all data sources. With these tools in place, companies can readily identify the most probable root cause for deviation or nonconformance and provide a fact base for the decision. Automation also frees quality assurance professionals to focus on corrective and preventive action (Exhibit 3).
Pharmaceutical and medtech companies that apply these innovative technologies and smart quality principles can see significant results. Our work with several companies shows that identifying, explaining, and eliminating the root causes of recurring deviations and nonconformances can reduce the overall volume of issues by 65 percent. Companies that use the data and models to determine which unexpected factors in processes and products influence the end quality are able to control for them, thereby achieving product and process mastery. What’s more, by predicting the most likely root causes and their underlying drivers, these companies can reduce the investigation cycle time for deviations and nonconformances by 90 percent.
4. Supplier quality risk management
Drug and medical device supply chains have become increasingly global, complex, and opaque as more pharmaceutical and medtech companies outsource major parts of production to suppliers and contract manufacturing organizations (CMOs). More recently, the introduction of new, complex modalities, such as cell therapy and gene editing, has further increased pressure to ensure the quality of supplier products. Against this backdrop, it is critical to have a robust supplier quality program that can proactively identify and mitigate supplier risks or vulnerabilities before they become material issues.
Today, many companies conduct supplier risk management manually and at one specific point in time, such as at the beginning of a contract or annually. Typically, risk assessments are done in silos across the organization; every function completes individual reports and rarely looks at supplier risk as a whole. Because the results are often rolled up and individual risk signals can become diluted, companies focus more on increasing controls than addressing underlying challenges.
The smart quality approach reduces quality issues and optimizes resources
Companies that break down silos and apply a more holistic risk lens across the organization have a better chance of proactively identifying supplier quality risks. With smart quality assurance, companies can do the following:
- identify vulnerabilities by utilizing advanced analytics on a holistic set of internal and external supplier and product data
- ensure real-time updates and reviews to signal improvements in supplier quality and any changes that may pose an additional risk
- optimize resource allocation and urgency of action, based on the importance and risk level of the supplier or CMO
Current technologies make it simpler than ever to automatically collect meaningful data. They also make it possible to analyze the data, identify risk signals, and present information in an actionable format. Internal and supplier data can include financials, productivity, and compliance metrics. Such information can be further enhanced by publicly available external sources—such as regulatory reporting, financial statements, and press releases—that provide additional insights into supplier quality risks. For example, using natural language processing to search the web for negative press releases is a simple yet powerful method to identify risks.
Would you like to learn more about our Life Sciences Practice ?
Once a company has identified quality risks, it must establish a robust process for managing these risks. Mitigation actions can include additional monitoring with digital tools, supporting the supplier to address the sources of issues, or deciding to switch to a different supplier. In our experience, companies that have a deep understanding of the level of quality risk, as well as the financial exposure, have an easier time identifying the appropriate mitigation action. Companies that identify risks and proactively mitigate them are less likely to experience potentially large supply disruptions or compliance findings.
Many pharmaceutical and medtech companies have taken steps to improve visibility into supplier quality risks by using smart quality principles. For example, a large pharmaceutical company that implemented this data-driven approach eliminated in less than two years major CMO and supplier findings that were identified during audits. In addition, during the COVID-19 pandemic, a global medtech company was able to proactively prevent supply chain disruptions by drawing on insights derived from smart quality supplier risk management.
Getting started
Pharmaceutical and medtech companies can approach quality assurance redesign in multiple ways. In our experience, starting with two or three processes, codifying the approach, and then rolling it out to more quality systems accelerates the overall transformation and time to value.
Smart quality assurance starts with clean-sheet design. By deploying modern design techniques, organizations can better understand user needs and overcome constraints. To define the solution space, we encourage companies to draw upon a range of potential process, IT, and analytics solutions from numerous industries. In cases where the new process is substantially different from the legacy process, we find it beneficial to engage regulators in an open dialogue and solicit their early feedback to support the future-state design.
Once we arrive at an MVP that includes digital and automation elements, companies can test and refine new solutions in targeted pilots. Throughout the process, we encourage companies to remain mindful of training and transition planning. Plans should include details on ensuring uninterrupted operations and maintaining compliance during the transition period.
The examples in this article are not exceptions. We believe that any quality assurance process can be significantly improved by applying a smart quality approach and the latest technologies. Pharmaceutical and medtech companies that are willing to make the organizational commitment to rethink quality assurance can significantly reduce quality risks, improve their speed and effectiveness in handling issues, and see long-term financial benefits.
Note: The insights and concepts presented here have not been validated or independently verified, and future results may differ materially from any statements of expectation, forecasts, or projections. Recipients are solely responsible for all of their decisions, use of these materials, and compliance with applicable laws, rules, and regulations. Consider seeking advice of legal and other relevant certified/licensed experts prior to taking any specific steps.
Explore a career with us
Related articles.

Smart quality: Reimagining the way quality works

Ready for launch: Reshaping pharma’s strategy in the next normal

Healthcare innovation: Building on gains made through the crisis
- Browse All Articles
- Newsletter Sign-Up

- 11 Apr 2023
- Cold Call Podcast
A Rose by Any Other Name: Supply Chains and Carbon Emissions in the Flower Industry
Headquartered in Kitengela, Kenya, Sian Flowers exports roses to Europe. Because cut flowers have a limited shelf life and consumers want them to retain their appearance for as long as possible, Sian and its distributors used international air cargo to transport them to Amsterdam, where they were sold at auction and trucked to markets across Europe. But when the Covid-19 pandemic caused huge increases in shipping costs, Sian launched experiments to ship roses by ocean using refrigerated containers. The company reduced its costs and cut its carbon emissions, but is a flower that travels halfway around the world truly a “low-carbon rose”? Harvard Business School professors Willy Shih and Mike Toffel debate these questions and more in their case, “Sian Flowers: Fresher by Sea?”

- 17 Sep 2019
How a New Leader Broke Through a Culture of Accuse, Blame, and Criticize
Children’s Hospital & Clinics COO Julie Morath sets out to change the culture by instituting a policy of blameless reporting, which encourages employees to report anything that goes wrong or seems substandard, without fear of reprisal. Professor Amy Edmondson discusses getting an organization into the “High Performance Zone.” Open for comment; 0 Comments.

- 27 Feb 2019
- Research & Ideas
The Hidden Cost of a Product Recall
Product failures create managerial challenges for companies but market opportunities for competitors, says Ariel Dora Stern. The stakes have only grown higher. Open for comment; 0 Comments.

- 31 Mar 2018
- Working Paper Summaries
Expected Stock Returns Worldwide: A Log-Linear Present-Value Approach
Over the last 20 years, shortcomings of classical asset-pricing models have motivated research in developing alternative methods for measuring ex ante expected stock returns. This study evaluates the main paradigms for deriving firm-level expected return proxies (ERPs) and proposes a new framework for estimating them.
- 26 Apr 2017
Assessing the Quality of Quality Assessment: The Role of Scheduling
Accurate inspections enable companies to assess the quality, safety, and environmental practices of their business partners, and enable regulators to protect consumers, workers, and the environment. This study finds that inspectors are less stringent later in their workday and after visiting workplaces with fewer problems. Managers and regulators can improve inspection accuracy by mitigating these biases and their consequences.
- 23 Sep 2013
Status: When and Why It Matters
Status plays a key role in everything from the things we buy to the partnerships we make. Professor Daniel Malter explores when status matters most. Closed for comment; 0 Comments.
- 16 May 2011
What Loyalty? High-End Customers are First to Flee
Companies offering top-drawer customer service might have a nasty surprise awaiting them when a new competitor comes to town. Their best customers might be the first to defect. Research by Harvard Business School's Ryan W. Buell, Dennis Campbell, and Frances X. Frei. Key concepts include: Companies that offer high levels of customer service can't expect too much loyalty if a new competitor offers even better service. High-end businesses must avoid complacency and continue to proactively increase relative service levels when they're faced with even the potential threat of increased service competition. Even though high-end customers can be fickle, a company that sustains a superior service position in its local market can attract and retain customers who are more valuable over time. Firms rated lower in service quality are more or less immune from the high-end challenger. Closed for comment; 0 Comments.
- 08 Dec 2008
Thinking Twice About Supply-Chain Layoffs
Cutting the wrong employees can be counterproductive for retailers, according to research from Zeynep Ton. One suggestion: Pay special attention to staff who handle mundane tasks such as stocking and labeling. Your customers do. Closed for comment; 0 Comments.
- 01 Dec 2006
- What Do You Think?
How Important Is Quality of Labor? And How Is It Achieved?
A new book by Gregory Clark identifies "labor quality" as the major enticement for capital flows that lead to economic prosperity. By defining labor quality in terms of discipline and attitudes toward work, this argument minimizes the long-term threat of outsourcing to developed economies. By understanding labor quality, can we better confront anxieties about outsourcing and immigration? Closed for comment; 0 Comments.
- 20 Sep 2004
How Consumers Value Global Brands
What do consumers expect of global brands? Does it hurt to be an American brand? This Harvard Business Review excerpt co-written by HBS professor John A. Quelch identifies the three characteristics consumers look for to make purchase decisions. Closed for comment; 0 Comments.
Case Study: Freshly Builds New Quality Assurance Programme

This case study investigates how Freshly, the ready-to-eat healthy meal delivery company, improved customer satisfaction with a new, robust quality assurance (QA) programme.
The Challenge
Freshly needed to improve customer outcomes. They had a unique product and a strong operations team, but they wanted to ensure world-class customer service with every interaction.
With a quality assurance process already in place, Freshly realized they needed a more comprehensive and feature-rich solution that provided a centralized agent dashboard so the team could track progress and performance in real time.
“We never had agent dashboards with the tool we’d been using, and it was leaving us with a major blind spot,” said Ben Segal, Freshly’s Associate Director of Infrastructural Efficiency.
“We had asked the vendor to help us replace Google Sheets, which was what our agents had been using to see their metrics and their QA score. But the vendor wasn’t able to deliver a solution.”
Playvox had the tools ready to meet the agents’ need for a QA dashboard ready to go right out of the box. Freshly was looking for centralized visualizations of agents’ metrics, evaluations, training progress, campaigns and achievements. Playvox was able to deliver on all fronts.
Susan Mihalick, Customer Experience, Quality Assurance Manager for Freshly, now has a great perspective on agent performance with the Playvox dashboards.
Not only can agents learn about how they are doing, but managers like Mihalick have clearer insight into the tasks at hand for agents. She can do her job better and be a more effective manager and coach to Freshly’s agents.
“Things are more out in the open and we love that transparency,” said Mihalick.
“One of the main pillars of our programme is empathy for customers. If we’re expecting agents to demonstrate empathy for their customers, how can we not be demonstrating empathy for the agents in terms of consistent QA and how we’re scoring everything? So we’ve been trying to keep that in mind, and the dashboards are essential to this task.”
Mihalick believes that it is crucial to invest in agent experience.
“We look at how we can be kinder, more reasonable and empathetic about how many things the agent juggles,” Mihalick said. “And we focus on what is most crucial to the interaction the agent has with the customer.”
“Are we going to fail the agent because they didn’t say the customer’s name twice? No.”
These are the critical elements of world-class customer service that Freshly couldn’t accomplish before Playvox.
The Solution
Playvox’s customizable scorecards afford Freshly the opportunity to use different evaluations across its five customer service teams.
In addition, Freshly can set up scorecards to align with the various communication channels agents rely on.
Freshly uses email, phone, chat and text messaging. Many of their customers are also active on social media sites, so the customer service team also engages on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, Tik Tok, and various food review websites.
With multiple teams and myriad communication channels, Mihalick is pleased with how easy it is to change or update a Playvox scorecard.
“The scorecards we had previously were definitely not as nimble or agile,” she said. “The Playvox scorecards are user-friendly.”
“We just decided on a scorecard change two hours ago. One of my team members is going to make the update, and it’s going to be live for the whole team right away. We can make a decision on Friday and implement it without a hitch on Monday or even that same day.”
Mihalick’s favourite part of the Agent Optimization Suite is the Workloads feature, which is tied directly to the Quality Product.
Workloads allows managers to create customized assignments for quality analysts, enabling managers to automatically track the analysts’ tasks and goals.
“Workloads is set it and forget it,” Mihalick said. “I can set it up for a team and Playvox just does the calculations without me needing to think about it. That makes things straightforward.”
Managers enjoy using Workloads to view the progress of their analyst team members. They can get the information they need without having to ask agents, letting them focus on what they do best – helping customers.
“I’m tracking my team’s progress through evaluations on a daily basis,” Mihalick said.
One of the key benefits of the Workloads feature is the random assignment of evaluations. Analysts don’t need to spend time choosing which evaluation to do, which provides the added advantage of eliminating bias or favouritism in the contact center.
The Results
When Freshly started using Playvox in November 2019, the team started with four scorecards. As the company and the teams grew, they had built 18 scorecards in less than a year. Mihalick said they are actually in version four of many of the scorecards.
“We have scorecards that are specific to the online engagement team,” Mihalick said. “So the people who are answering Facebook messages and Twitter are held to slightly different standards and asked slightly different questions. It’s a unique environment that requires its own considerations.”
Freshly has created training scorecards for new employees and new teams, or those who move from one team to another.
“Frankly, we’re learning as we go,” she said. “It’s essential that scorecards be fully flexible and changeable. Playvox makes all of that easy.”
Freshly conducts more than 1,800 evaluations a month. The company’s eight analysts are each aiming to do 70 evaluations per week. That would put the team at 2,240 evaluations a month, enriching team insights and maximizing opportunities to improve.
Agents’ average scores have been consistently high, reaching a peak of 92 one month. The team generally scores in the high 80s.
“Agents like Playvox because it enables clarity and transparency. It’s not like this big scary boogie man behind the curtain who’s grading you and you don’t know where they’re coming up with these numbers,” Segal said.
“It’s right there. You know how you did. And there’s actionable items to say, hey, if you do this, your score will go up.”
If for some reason the numbers don’t go up, Freshly takes advantage of Playvox’s Coaching add-on, averaging more than 220 Coaching sessions per month with a 100% signature rate.
And the coaching is effective. Freshly agents average 424 recognitions per month, helping keep agents motivated.
Agents and analysts alike get tremendous value from Playvox. The team gives Playvox an average score of 9.5 on the Net Promoter Score (NPS). A lot of that has to do with the agent dashboards.
And it’s all in one place.
“The QA team lives in Playvox,” Segal said. “That was our main reason for choosing the software. But now it’s also become the agents’ home for seeing their metrics, working towards their goals and getting their badges.”
“It’s so much more than QA – and more than we were ever able to achieve with our previous vendor.”
This case study has been re-published by kind permission of Playvox – View the original post
Published On: 5th Apr 2021 - Last modified: 6th Apr 2021 Read more about - Contact Centre News , Case Studies , Playvox
Recommended Articles


Article & Observations About Diverse Teams Working Better Together
Software Testing Client Project Case Study
Apr 21 • Case Studies
We are often asked what software testing is . The video below shares a solid definition of the term.
But we thought a software testing project case study might be helpful to better understand what software testers do on a typical day. This includes testing software, writing requirement documents for our clients, and creating user guides to ensure compliance for our clients to use for quality assurance and auditing purposes.
Iterators LLC was hired to complete accessibility testing for a few projects for the Library of Congress (LOC). Accessibility testing is required on all government websites, with Section 508 and WCAG 2.2 requirements used. To become a Trusted Tester an employee must complete the DHS Trusted Tester online training course requirements and pass the DHS Section 508 Trusted Tester Certification Exam of Homeland Security in Accessibility, and we are in a unique position to help on this project. We cross-train all our employees so that we can work on several projects at one time or several different aspects of a project to complete the work and reduce the cost to our clients.
Our first project assigned by LOC was testing their new braille feature on BARD Mobile for Android. We were tasked with testing the braille feature with several refreshable braille displays.
During our testing, we used the Orbit Reader 20 , and two different braille displays from Freedom Focus 14 and Freedom Focus 40 . There are plans to use other refreshable displays such as Humanware, but this testing has not occurred yet. We needed to test refreshable braille displays and their use in tandem with Google BrailleBack and Google TalkBack .
This work was to ensure that all hardware worked as expected with the apps we were testing. For this testing, we had to complete functional testing, smoke testing, exploratory testing and had a user panel to ensure we caught all issues that a visually impaired individual might experience while using the app.
Initially, our client was unsure if we would find any bugs and hesitant to have us enter bugs into Bugzilla as they stated the software was “complicated”. Bugzilla is a web-based general-purpose bug tracking system and not unlike other bug tracking systems we use every day such as Jira, TestRails, PractiTest, and Click-Up.
Testing was completed over several agile sprints with many significant software testing bugs found. Our testing had us test against the National Library Service requirements document. Next, we had to create an up-to-date user manual. While the manual had been updated several times, the testing had not been.
For example, when downloading a book or magazine from the Now Reading section of the mobile app, the download would end up at the bottom of the page. For years, the user guide had listed the download being at the top of the page once the document was downloaded.
Our testing team, on several occasions, said this was an error in the documentation and that the download ends up at the bottom of the page. This was corrected in the user document and sent to the development team to fix per the requirement document.
Over the next several months, we reported 30 high-priority bugs with about half fixed at this point. We have encouraged our client to test in an agile fashion because once the development team is finished, it’s harder to get these bugs fixed.
Our bugs were reported and based on the requirement document used to create the software. Lastly, the user guide had to be rewritten to reflect the app's behavior and general updates.
Once the app was tested and created, the user guide was sent to Communication Services to ensure the style used per other requirement documentation. This document had to be approved before being disseminated to the public. For example, how does the library determine what the Most Popular Books are, and over what period.
Once the document was returned from COS, this PDF document had to be remediated . The process of remediation is to make a PDF, create the heading for the document, alt text added to meaningful images, and decorative images either ignored or taken out of the digital document altogether.
Once the remediation process is complete and validated, the document becomes ADA-compliant. We then provide an accessible PDF that can be read with the use of a screen reader and create the HTML output so that the document can be added to the Library of Congress website.
You can find the current user guide we completed here: https://www.loc.gov/nls/braille-audio-reading-materials/bard-access/bard-mobile-android/#creatingfolders3.3
Case studies can be a great learning tool in software testing and project management. By looking at project case study examples, you can see how the project was planned and executed, as well as how certain tasks were managed. This can give a better understanding of what software testing involves on a daily basis. With the right software testing case studies example, software testers can hone their skills, improve project performance, and ultimately deliver better software testing results.
Related Resources:
- Crafting an Effective Test Plan: A Step-by-Step Guide
- Top Test Management Tools
- Mobile Application Functional and Performance Testing
About the Author
Jill Willcox has worked on accessibility issues for most of her professional career. Iterators is an inclusive women-owned small business (WOSB) certified by the Small Business Administration and WBENC. We provide software testing services for websites, mobile apps, enterprise software, and PDF remediation services, rendering PDFs ADA compliant.
Jill Willcox
Clutch names iterators llc as a top certified women-owned business for 2022.
Iterators LLC named Top Certified Women0owned Business Again 2022
Test Strategy vs Test Plan: What’s the Difference?
What is the difference between a test strategy and a test plan? Read this article to b...
May 05 • Reference
QA Case Study
- Industry Financial
- Solution E-mail platform build automation
- Company The customer needed an outsourced QA team to start manual testing of their products. As an established business Client required full-time QA engineers in-house so they needed a company that had experts in place that they could use.
- Tools & platforms Usually startups are less concerned
Software Quality Assurance Case Study
QA case study : Usually startups are less concerned about the quality and in many cases developers are doing QA part of work, we understand that it saves cost and gives chance to release product in a short period of time but on another hand clients will face poor quality this is exactly the situation we saw happened with our customer in Vancouver – financial technology company was looking for a way how to improve their quality and decided to find an outsourcing partner in order to set up QA team from scratch. After RFP process – GeeksForLess been chosen as a strategic partner in order to start manual testing and then move towards automation testing.
Solution we made
- SEPARATED TEST CASES PER APPLICATIONS AND PROJECTS
- COVERED 99% OF ALL REQUIREMENTS AND ALREADY EXISTING FUNCTIONALITY WITH TEST CASES
- ADDED BASIC TEST PLANS
- AUTOMATED ALL TEST CASES WHICH ARE STABLE AND COULD BE COVERED BY JS TOOL
- ESTABLISHED PROCESS – NO MORE RELEASES TO PRODUCTION WITHOUT QA CONFIRMATION
- SETUP DAILY CALLS WITH UPDATES ON THE PROGRESS
- MOVED TOWARDS CONTINUOUS INTEGRATION BY USING SPECIAL TOOLS, AUTOTESTS WERE RUNNING AUTOMATICALLY AFTER PRODUCTION RELEASES
- QA ENVIRONMENT HAS BEEN SET UP INTEGRATED QA TEAM INTO ALL PROJECT ASPECTS SO THEY BECAME A FULL PART OF CLIENT ECO-SYSTEM CUSTOMERS
or check our contact info
Case Studies
Home » Case Studies
Below are synopses of actual Beta Breakers automation engagements. In each synopsis however, customer and/or product identities have been scrubbed in order to protect Non-disclosure agreements. If you are interested in similar results for your QA needs, complete the form or call us to get started.
Case Study #1 – Android Application Acceptance Test Suite
The Android Acceptance Test Suite covers all essential regression features and provides timely feedback and reporting to Android Application developers and QA. This suite is easily run within the CI process or in QA by pulling the most recent HockeyApp build on which to test. By providing constant feedback to QA and reporting regression bugs, the suite saves hours of QA testing per run and allows manual testers to focus on tighter feedback cycles for brand new features. Test results are provided via Cucumber Reports with attached debug information such as custom exception messages, screenshots at the time of the error, and a snapshot of the page XML. Reporting features useful metrics in addition to results, such as percentage of features passed, features failed, skipped, and pending implementation. Utilizing Selenium /Appium, we leverage a single codebase against Google Android and Amazon Fire OS mobile operating systems. No third party vendors were involved. The Beta Breakers team consisted of one full-time QE resource with occasional augmented and collaborative support from other Beta Breakers QE staff. The completed automation suite was delivered on time and was very well accepted.
Case Study #2 – API Acceptance Test Suite
The API Acceptance Test Suite covers all of the exposed endpoints in the customer’s backend API. The test cases are written from the perspective of user stories as opposed to merely unit testing the endpoints. In addition to the backend API, the test suite leverages other dependent APIs. In order to easily facilitate the testing requirements of the Mosaic development team, an HTTP Client was designed and developed for testing REST and REST-like APIs. It currently resides in a Nexus repository and is used by other teams. The Test Suite is fully integrated into the API’s Continuous Integration pipeline on Jenkins. In addition to testing new builds at every deployment, the test suite runs twice a day on a timer. The test suite is configured to accept environmental variables as testing arguments allowing multiple Jenkins jobs to leverage the same test suite while testing multiple environments and features. The Jenkins jobs are configured to conditionally notify the development team of test failures based on the urgency around the features. Developers are notified via email and slack notifications. Test results are stored and displayed on the Jenkins job via the Jenkins Cucumber-JVM plugin. In addition to displaying feature coverage and test results, the reports contain step-by-step user flows with detailed drop downs. These step drop downs convert the HTTP requests made by the test suite into curl commands that the reader can copy and paste directly into their terminal. The reports also contain the REST responses (in this case JSON responses) that were returned via each API call. This approach allows for a high level look at Behavior Driven reports while still allowing readers of the reports to zoom to a lower level view of the flows and what may have gone wrong. This approach also allows many hours of manual QA to be replaced by automation, as well as supplemented by automation. The look and feel of the reports are perfect for giving management a high level look at the quality engineering product velocity while also maintaining low level use for developers and manual QA alike. Baked into the API test suite is a series of tests specifically for monitoring the status of various user-facing processes and service health checks. These test results are sent to an InfluxDB instance where they are read and displayed on another customer product, the “Quality Monitoring Dashboard”. Again, no third party vendors were involved. The Beta Breakers team consisted of two full-time QE resources with occasional augmented and collaborative support from other Beta Breakers QE staff. The completed automation suite was delivered on time and was very well accepted.
Case Study #3 – Web Acceptance Test Suite
The Web Acceptance Test Suite covers all user-facing web features available on the customer’s web application. In addition to covering user features, compatibility testing with various browsers is baked in. Currently, the Web Acceptance test suite measures compatibility with Firefox, Chrome, Safari, Edge, and Internet Explorer. Within this compatibility testing, it also tests video playback and video player functionality. The core engine that drives the Web Acceptance Test suite is Selenium Webdriver and Cucumber. Cucumber allows all test plans to be written and expressed via user stories compatible with Behavior Driven Development. Given the many stages of the development process, and numerous environments, the test suite is parameterized to build and test environments, browsers, and features within the specifications of the user running the test suite. The suite itself manifests in many Jenkins jobs that run the specific tasks required for each environment and browser. The core purpose of the test suite is for complete integration within the development CI pipeline. When developers push new builds to their respective environments, this action triggers a test suite run against those specifications. The results are displayed in HTML Cucumber Reports and the development teams are notified via email and slack. The manual QA team also has access to a number of Jenkins jobs in order to supplement their regression testing, saving hours of manual QA time in the process. The team’s Selenium Grid instance allows for multiple jobs to be running simultaneously against different environments and browsers. This architecture means the manual QA team can run their own regression tests without fear of interfering with the development CI process. Embedded in the test reports are screenshots of test failures as well as links to video playback of the tests in question.
Case Study #4 – iOS Acceptance Test Suite
The iOS Mobile Acceptance Test Suite, similar to the Android Acceptance Test Suite, utilizes our in-house Selenium/Appium framework and covers all essential regression features as well as all other automatable feature tests. The test suite built as a Maven project is integrated into the development CI pipeline. The test suite is configured to test against real devices or iOS simulators; however, due to limitations of the applications requirements, key functionality is not possible on simulators. The test suite thereby will trigger test runs on physical devices located on campus. Test results are provided in the form of Cucumber Reports, via the Jenkins Cucumber-JVM plugin. Embedded in the reports are screenshots of key steps during failure as well as other exception messages, stack traces and other key debug information for developers. The reports themselves provide a good high level view of the user stories which are tested. The test suite is also configured to test against environments throughout the entire development process, including development, staging, QA, and production.
Case Study #5 – Product Acceptance Test Suite
This product (herein referred to as Product A) is available on Web and iOS applications. Our team integrated into the development process, attending sprint planning meetings, daily standups and weekly scrums. Our team developed automated test suites using our in-house Selenium wrapper for both Web and iOS applications. Test suites cover all essential regression features as well as all other automatable feature tests. The Product A iOS Mobile Acceptance Test Suite is configured to test against real devices or iOS simulators; however, due to limitations of the application’s requirements, key functionality is not possible on simulators. The test suite thereby will trigger test runs on physical devices located on campus. Both Web and iOS test suites are integrated within the development CI/CD pipeline. Test results are provided in the form of Cucumber Reports, via the Jenkins Cucumber-JVM plugin. Embedded in the reports are screenshots of key steps during failure as well as other exception messages, stack traces and other key debug information for developers. The reports themselves provide a good high level view of the user stories for which are tested. The test suite is also configured to test against environments throughout the entire development process, including development, staging, QA, and production. In addition to the standard automation of the product, a detailed cost analysis and recommendation was performed and given with regards to the Google App Engine configuration of the product.
Case Study #6 – Product A Performance/Cost Test Suite
In order to properly cost test Product A on the Google App Engine, a parameterized performance test suite needed to be made first in order to simulate the proper user behaviors at expected traffic count. The performance test suite leverages JMeter, using the Maven Blazemeter plugin. The JMeter test plan was written to include the developers’ unit test suite, written in JUnit, in order to simulate user interaction with the site. The JMeter test plan also included manual http requests against features that were not tested in the developers’ unit test suite as user stories. The test suite allows thread count to be passed as an argument by the test runner. A custom sandbox GAE instance was created for the front and back end of the application. Front and back end instances were then tested using the performance test suite, and GAE metrics were measured as the tests were run multiple times against various configurations. For the backend instance, the Cron jobs also had to be taken into consideration. The Cron buckets were filled with user activity and in swoop emptied to allow isolated data analysis of the GAE configuration’s behavior. Once each test was run with each instance type, configurations were further narrowed in on by fine tuning other test parameters. Eventually, an expected cost for each configuration was attained, and a recommendation was made based on the best user experience at the lowest cost.
Case Study #7 – API Acceptance Test Suite
A full regression test was developed for Product A, a collection of REST API endpoints for financial services. The test cases were developed by the automation engineer and finalized collaboratively with the client. A list of bugs and flaws in the behavior of the APIs was delivered. The client did not utilize a CI/CD process, and wished to run the test suite with a manual trigger. Thus, a solution was provided to run the suite via the Maven command line, with an integrated Cucumber HTML report to provide a convenient log of the results for each test run. Technical assistance was provided to configure the Maven project to run securely on a VM. A JMeter load testing script was also developed and provided to the client, with a demonstration of how to use the script on their own, as well as recommendations of load limits from a round of in-house testing.
Case Study #8 – New Product Integration Into A Software Ecosystem
Our customer’s project was to replace a crucial but outdated in-house software application with a customized third-party SAAS solution. The whole of the project included a web front-end SAAS, legacy desktop software, REST APIs, Amazon Web Services and PostgreSQL. Test cases were developed from ‘User Stories’ which documented the end-to-end flows of typical product usage. Since the User Stories could branch into different types of usage or into error conditions, multiple test cases were derived from a single User Story. Generally, a test case would begin by creating assets via front-end Selenium automation through the third-party SAAS. Next, automated back-end validation of the downstream components was performed, testing the handling, storage and distribution of the information in the assets. Integration tests were also created to test individual components using mocked data. Our customer used an in-house Selenium solution for front-end automation, SmartBear ReadyAPI, and NodeJS with strict linting rules for AWS interactions. Test cases were tied together using Atlassian Bamboo and results were pushed to Practitest. Our automation engineer worked closely with the customer’s QA resources, and integrated into their AGILE workflow, participating in daily SCRUMS, Sprint planning and retrospectives. Our engineer was also responsible for providing live or recorded demonstrations of completed tasks, as well as extensive documentation of the testing behavior.
What Can We Test for You?
" * " indicates required fields
© 2024 Beta Breakers | Privacy Policy
Privacy Policy | Contact Us
Beta Breakers
Sign up for the newsletter
Digital editions.

Total quality management: three case studies from around the world
With organisations to run and big orders to fill, it’s easy to see how some ceos inadvertently sacrifice quality for quantity. by integrating a system of total quality management it’s possible to have both.

Top 5 ways to manage the board during turbulent times Top 5 ways to create a family-friendly work culture Top 5 tips for a successful joint venture Top 5 ways managers can support ethnic minority workers Top 5 ways to encourage gender diversity in the workplace Top 5 ways CEOs can create an ethical company culture Top 5 tips for going into business with your spouse Top 5 ways to promote a healthy workforce Top 5 ways to survive a recession Top 5 tips for avoiding the ‘conference vortex’ Top 5 ways to maximise new parents’ work-life balance with technology Top 5 ways to build psychological safety in the workplace Top 5 ways to prepare your workforce for the AI revolution Top 5 ways to tackle innovation stress in the workplace Top 5 tips for recruiting Millennials
There are few boardrooms in the world whose inhabitants don’t salivate at the thought of engaging in a little aggressive expansion. After all, there’s little room in a contemporary, fast-paced business environment for any firm whose leaders don’t subscribe to ambitions of bigger factories, healthier accounts and stronger turnarounds. Yet too often such tales of excess go hand-in-hand with complaints of a severe drop in quality.
Food and entertainment markets are riddled with cautionary tales, but service sectors such as health and education aren’t immune to the disappointing by-products of unsustainable growth either. As always, the first steps in avoiding a catastrophic forsaking of quality begins with good management.
There are plenty of methods and models geared at managing the quality of a particular company’s goods or services. Yet very few of those models take into consideration the widely held belief that any company is only as strong as its weakest link. With that in mind, management consultant William Deming developed an entirely new set of methods with which to address quality.
Deming, whose managerial work revolutionised the titanic Japanese manufacturing industry, perceived quality management to be more of a philosophy than anything else. Top-to-bottom improvement, he reckoned, required uninterrupted participation of all key employees and stakeholders. Thus, the total quality management (TQM) approach was born.
All in Similar to the Six Sigma improvement process, TQM ensures long-term success by enforcing all-encompassing internal guidelines and process standards to reduce errors. By way of serious, in-depth auditing – as well as some well-orchestrated soul-searching – TQM ensures firms meet stakeholder needs and expectations efficiently and effectively, without forsaking ethical values.
By opting to reframe the way employees think about the company’s goals and processes, TQM allows CEOs to make sure certain things are done right from day one. According to Teresa Whitacre, of international consulting firm ASQ , proper quality management also boosts a company’s profitability.
“Total quality management allows the company to look at their management system as a whole entity — not just an output of the quality department,” she says. “Total quality means the organisation looks at all inputs, human resources, engineering, production, service, distribution, sales, finance, all functions, and their impact on the quality of all products or services of the organisation. TQM can improve a company’s processes and bottom line.”
Embracing the entire process sees companies strive to improve in several core areas, including: customer focus, total employee involvement, process-centred thinking, systematic approaches, good communication and leadership and integrated systems. Yet Whitacre is quick to point out that companies stand to gain very little from TQM unless they’re willing to go all-in.
“Companies need to consider the inputs of each department and determine which inputs relate to its governance system. Then, the company needs to look at the same inputs and determine if those inputs are yielding the desired results,” she says. “For example, ISO 9001 requires management reviews occur at least annually. Aside from minimum standard requirements, the company is free to review what they feel is best for them. While implementing TQM, they can add to their management review the most critical metrics for their business, such as customer complaints, returns, cost of products, and more.”
The customer knows best: AtlantiCare TQM isn’t an easy management strategy to introduce into a business; in fact, many attempts tend to fall flat. More often than not, it’s because firms maintain natural barriers to full involvement. Middle managers, for example, tend to complain their authority is being challenged when boots on the ground are encouraged to speak up in the early stages of TQM. Yet in a culture of constant quality enhancement, the views of any given workforce are invaluable.
AtlantiCare in numbers
5,000 Employees
$280m Profits before quality improvement strategy was implemented
$650m Profits after quality improvement strategy
One firm that’s proven the merit of TQM is New Jersey-based healthcare provider AtlantiCare . Managing 5,000 employees at 25 locations, AtlantiCare is a serious business that’s boasted a respectable turnaround for nearly two decades. Yet in order to increase that margin further still, managers wanted to implement improvements across the board. Because patient satisfaction is the single-most important aspect of the healthcare industry, engaging in a renewed campaign of TQM proved a natural fit. The firm chose to adopt a ‘plan-do-check-act’ cycle, revealing gaps in staff communication – which subsequently meant longer patient waiting times and more complaints. To tackle this, managers explored a sideways method of internal communications. Instead of information trickling down from top-to-bottom, all of the company’s employees were given freedom to provide vital feedback at each and every level.
AtlantiCare decided to ensure all new employees understood this quality culture from the onset. At orientation, staff now receive a crash course in the company’s performance excellence framework – a management system that organises the firm’s processes into five key areas: quality, customer service, people and workplace, growth and financial performance. As employees rise through the ranks, this emphasis on improvement follows, so managers can operate within the company’s tight-loose-tight process management style.
After creating benchmark goals for employees to achieve at all levels – including better engagement at the point of delivery, increasing clinical communication and identifying and prioritising service opportunities – AtlantiCare was able to thrive. The number of repeat customers at the firm tripled, and its market share hit a six-year high. Profits unsurprisingly followed. The firm’s revenues shot up from $280m to $650m after implementing the quality improvement strategies, and the number of patients being serviced dwarfed state numbers.
Hitting the right notes: Santa Cruz Guitar Co For companies further removed from the long-term satisfaction of customers, it’s easier to let quality control slide. Yet there are plenty of ways in which growing manufacturers can pursue both quality and sales volumes simultaneously. Artisan instrument makers the Santa Cruz Guitar Co (SCGC) prove a salient example. Although the California-based company is still a small-scale manufacturing operation, SCGC has grown in recent years from a basement operation to a serious business.
SCGC in numbers
14 Craftsmen employed by SCGC
800 Custom guitars produced each year
Owner Dan Roberts now employs 14 expert craftsmen, who create over 800 custom guitars each year. In order to ensure the continued quality of his instruments, Roberts has created an environment that improves with each sale. To keep things efficient (as TQM must), the shop floor is divided into six workstations in which guitars are partially assembled and then moved to the next station. Each bench is manned by a senior craftsman, and no guitar leaves that builder’s station until he is 100 percent happy with its quality. This product quality is akin to a traditional assembly line; however, unlike a traditional, top-to-bottom factory, Roberts is intimately involved in all phases of instrument construction.
Utilising this doting method of quality management, it’s difficult to see how customers wouldn’t be satisfied with the artists’ work. Yet even if there were issues, Roberts and other senior management also spend much of their days personally answering web queries about the instruments. According to the managers, customers tend to be pleasantly surprised to find the company’s senior leaders are the ones answering their technical questions and concerns. While Roberts has no intentions of taking his manufacturing company to industrial heights, the quality of his instruments and high levels of customer satisfaction speak for themselves; the company currently boasts one lengthy backlog of orders.
A quality education: Ramaiah Institute of Management Studies Although it may appear easier to find success with TQM at a boutique-sized endeavour, the philosophy’s principles hold true in virtually every sector. Educational institutions, for example, have utilised quality management in much the same way – albeit to tackle decidedly different problems.
The global financial crisis hit higher education harder than many might have expected, and nowhere have the odds stacked higher than in India. The nation plays home to one of the world’s fastest-growing markets for business education. Yet over recent years, the relevance of business education in India has come into question. A report by one recruiter recently asserted just one in four Indian MBAs were adequately prepared for the business world.
RIMS in numbers
9% Increase in test scores post total quality management strategy
22% Increase in number of recruiters hiring from the school
20,000 Increase in the salary offered to graduates
50,000 Rise in placement revenue
At the Ramaiah Institute of Management Studies (RIMS) in Bangalore, recruiters and accreditation bodies specifically called into question the quality of students’ educations. Although the relatively small school has always struggled to compete with India’s renowned Xavier Labour Research Institute, the faculty finally began to notice clear hindrances in the success of graduates. The RIMS board decided it was time for a serious reassessment of quality management.
The school nominated Chief Academic Advisor Dr Krishnamurthy to head a volunteer team that would audit, analyse and implement process changes that would improve quality throughout (all in a particularly academic fashion). The team was tasked with looking at three key dimensions: assurance of learning, research and productivity, and quality of placements. Each member underwent extensive training to learn about action plans, quality auditing skills and continuous improvement tools – such as the ‘plan-do-study-act’ cycle.
Once faculty members were trained, the team’s first task was to identify the school’s key stakeholders, processes and their importance at the institute. Unsurprisingly, the most vital processes were identified as student intake, research, knowledge dissemination, outcomes evaluation and recruiter acceptance. From there, Krishnamurthy’s team used a fishbone diagram to help identify potential root causes of the issues plaguing these vital processes. To illustrate just how bad things were at the school, the team selected control groups and administered domain-based knowledge tests.
The deficits were disappointing. A RIMS students’ knowledge base was rated at just 36 percent, while students at Harvard rated 95 percent. Likewise, students’ critical thinking abilities rated nine percent, versus 93 percent at MIT. Worse yet, the mean salaries of graduating students averaged $36,000, versus $150,000 for students from Kellogg. Krishnamurthy’s team had their work cut out.
To tackle these issues, Krishnamurthy created an employability team, developed strategic architecture and designed pilot studies to improve the school’s curriculum and make it more competitive. In order to do so, he needed absolutely every employee and student on board – and there was some resistance at the onset. Yet the educator asserted it didn’t actually take long to convince the school’s stakeholders the changes were extremely beneficial.
“Once students started seeing the results, buy-in became complete and unconditional,” he says. Acceptance was also achieved by maintaining clearer levels of communication with stakeholders. The school actually started to provide shareholders with detailed plans and projections. Then, it proceeded with a variety of new methods, such as incorporating case studies into the curriculum, which increased general test scores by almost 10 percent. Administrators also introduced a mandate saying students must be certified in English by the British Council – increasing scores from 42 percent to 51 percent.
By improving those test scores, the perceived quality of RIMS skyrocketed. The number of top 100 businesses recruiting from the school shot up by 22 percent, while the average salary offers graduates were receiving increased by $20,000. Placement revenue rose by an impressive $50,000, and RIMS has since skyrocketed up domestic and international education tables.
No matter the business, total quality management can and will work. Yet this philosophical take on quality control will only impact firms that are in it for the long haul. Every employee must be in tune with the company’s ideologies and desires to improve, and customer satisfaction must reign supreme.
Contributors
- Industry Outlook

- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
Quality management
- Business management
- Process management
- Project management
Six Sigma Pricing
- Manmohan S. Sodhi
- Navdeep S. Sodhi
- From the May 2005 Issue
Creating a Culture of Quality
- Ashwin Srinivasan
- Bryan Kurey
- From the April 2014 Issue

The CEO of Canada Goose on Creating a Homegrown Luxury Brand
- From the September–October 2019 Issue
Design Your Product to Sell Itself
- Jessica Herrin
- May 31, 2012
Framing the Big Picture
- Scott D. Anthony
- March 31, 2011

A Better Way to Onboard AI
- Boris Babic
- Daniel L. Chen
- Theodoros Evgeniou
- Anne-Laure Fayard
- From the July–August 2020 Issue
The Contradictions That Drive Toyota's Success
- Hirotaka Takeuchi
- Norihiko Shimizu
- From the June 2008 Issue
Each Employee's Retirement Is Unique
- Charalambos Vlachoutsicos
- September 30, 2014

Teaching Smart People How to Learn
- Chris Argyris
- From the May–June 1991 Issue
Beyond Toyota: How to Root Out Waste and Pursue Perfection
- James P. Womack
- Daniel T. Jones
- From the September–October 1996 Issue
Reign of Zero Tolerance (HBR Case Study and Commentary)
- Janet Parker
- Eugene Volokh
- Jean Halloran
- Michael G. Cherkasky
- From the November 2006 Issue

Coming Commoditization of Processes
- Thomas H. Davenport
- From the June 2005 Issue

Learning to Lead at Toyota
- Steven J. Spear
- From the May 2004 Issue
Why (and How) to Take a Plant Tour
- David M. Upton
- Stephen E. MacAdam
- From the May–June 1997 Issue

The Case for Capitation
- Brent C. James
- Gregory P. Poulsen
- From the July–August 2016 Issue
Manage Your Human Sigma
- John H. Fleming
- Curt Coffman
- James K. Harter
- From the July–August 2005 Issue

Health Care Needs Real Competition
- Leemore S Dafny
- Thomas H. Lee M.D.
- From the December 2016 Issue
Benchmarking Your Staff
- Michael Goold
- David J. Collis
- From the September 2005 Issue
Will Disruptive Innovations Cure Health Care?
- Clayton M. Christensen
- Richard Bohmer
- John Kenagy
- September 01, 2000
Growth as a Process: The HBR Interview
- Jeffrey R. Immelt
- Thomas A. Stewart
- From the June 2006 Issue

Health-Tech Strategy at KG Hospital Part A: Identification and Prioritization of Key Focus Areas
- Vijaya Sunder M
- Meghna Raman
- January 09, 2022
Strategy Execution Module 12: Aligning Performance Goals and Incentives
- Robert Simons
- November 21, 2016
Account Opening in Blue Bank - Part A: Process Visualization
- March 31, 2023
Onnie Jewellers
- P. Fraser Johnson
- Larry Menor
- August 01, 2017
Kaizen in Translation: Suggestion Systems Across Cultures
- Elliott N. Weiss
- Donald Stevenson
- February 04, 2016
Swachh Rail, Swachh Bharat (Clean Railways, Clean India): Adoption of Bio-Toilets by the Indian Railways
- Milind Sohoni
- Sanjeev Kishore
- Alok Kumar Tewari
- Sudheer Kumar
- February 18, 2021
Organizational Transformation in a Taiwanese Company
- Anne Marie Francesco
- Chang-I Bonnie Chen
- March 27, 2000
Health-Tech Strategy at KG Hospital Part B: Tech Strategy Design and Implementation
Ritz-carlton hotel co..
- Sandra J. Sucher
- Stacy McManus
- March 20, 2001
- Ray A. Goldberg
- October 12, 2004

Understand Business Process Improvement
- Harvard Business Publishing
- September 14, 2014
Oberoi Hotels: Train Whistle in the Tiger Reserve
- Ryan W. Buell
- Ananth Raman
- Vidhya Muthuram
- January 09, 2015
Chantale and Clinton Call for Service
- Christopher A. Ross
- March 25, 2009
Impacore - A Disruptive Force in Consulting
- Dennis Campbell
- Emer Moloney
- June 15, 2016
- Elaine Landry
- January 01, 2000
LYFEN: Building a Supply Chain to Create Competitive Advantage
- May 17, 2019
Year Up: A Social Entrepreneur Builds High Performance
- Allen S. Grossman
- Naomi Greckol-Herlich
- June 11, 2008
A Profile of Toyota's Production System
- Scott A. Moore
- January 28, 2010
Koo Foundation Sun Yat-Sen Cancer Center: Breast Cancer Care in Taiwan
- Michael E. Porter
- Jennifer F. Baron
- C. Jason Wang
- December 08, 2009
Six Sigma at Cintas Corporation
- Adam Bortolussi
- August 29, 2010
Popular Topics
Partner center.
Success Stories
- Case Studies
- Client Testimonials

Attaining 99% claims processing accuracy for a health plan with a diverse application landscape
- a.prlst-para')[this.getAttribute('data-index')].href, encodeURIComponent(this.getAttribute('data-title')));" class="share">

Multi-state Blue reduces production defects by 30% through streamlined application testing

Ensuring Harmonized Onboarding; Provider Data Access for a Regional Medicaid Payer

Success Story
Infosys Quality Engineering eBook: A Collection of Transformational Success Stories

Infosys Helps a Leading 5G Mobile Network Operator Implement World’s First Greenfield Cloud-native Solution
Leading US-based Multinational Bank Achieves 70% Reduction in Manual Effort with Automated Data Validation Solution

Telenet delivers exceptional customer experience by leveraging automated business acceptance testing

Trade Finance Market Leader Achieves 50% Increase in E-penetration of Business After Digitalization

Implementing Automated SAP Regression Test Suite for an Australia-based Public Sector Shared Services Platform

Extreme automation and RPA bots reduce PDF validation effort by 87% for a leading global bank

Infosys helps National Australia Bank implement zero defect delivery with 80% savings in testing effort

DevOps Quality Engineering Approach Results in Significant Year-on-Year Savings

Extreme automation and continuous testing cut test cycle time by 99% for a Fintech company

DevOps driven platform raises production stability by 30% for a financial services company

Zero-touch automation and continuous testing framework help US bank soft save $14+ million

Major European Telecom company saves 70% in storage cost using data virtualization

Data validation using AWS Cloud Native Solution and Infosys Automation Framework

Cloud-based testing service ensures smooth post-M&A data integration

A US Healthcare company slashes new product line launch time by 50% with Infosys Test-driven approach leveraging analytics

Automated validation solution for digital Product Information Management (PIM) implementation

Invoice Processing and Statement Verification for a Middle Eastern Bank

A Global pharma major adheres to E2B R3 compliance leveraging design thinking driven automation solution

Microservices Testing and Service Virtualization for B2B Platform

A Water Utility Company Improves its Service Quality with an Automated Validation Solution for SAP Cloud Platform

Design thinking enabled extreme automation strategy for a bank
Life sciences company improves business outcomes with Infosys SFDC testing solution

Scalable, configurable and successful EDI X12 solution

Network provider improves quality of business models with Infosys package automation solutions

Validation of analytics models which detect the warranty claims for locomotive engines

End-to-End Testing of Smart Lighting Applications using Open Source-Based Automation Framework

Business information solutions provider ups service quality with agile testing automation

Putting our expertise in automation and validation to create an AML solution

Big Data Testing for a leading global brewer

Retailer improves cross-channel visibility with Infosys Big Data Testing solution

Optimal data testing coverage for a data lake implementation
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Case Study on Quality Assurance and Continuous Improvement

This case study focuses on important production processes within an aluminium extrusion plant and their focus to automate their production shop floor using PLC automation and optimizing the production process by eliminating scrap and re work. Various aspects such as logistics, pre and post production processes, supporting departments etc are studied and their impact have been studied in this report..
Related Papers
IFIP Advances in Information and Communication Technology
Helcio Raymundo
Management of Sustainable Development
Alina Bianca
In this paper, the most important aspects of the quality management of end milling processes on aluminum alloys, are presented. The first part of the paper includes the presentation of the machining activities such: design, planning, programming and control that transform the inputs (workpiece) into finished products. In the second part the research problem was defined by setting a fundamental objective and identifying the specific objectives which contribute to achieve the fundamental objective. In this context an experimental study, was performed, starting with the organization and conducting the end milling process, in which the cutting regime were established, then the characteristic measured parameters were determined, so that the research factors and parameters will result.
IJESRT Journal
In a productive process, the implementation of automation systems is not always justified, but there are certain indicators that justify and make necessary the implementation of these systems. As manufacturing systems, grow in complexity, certain processes become obsolete and difficult to manage manually, hindering compliance and expansion of production standards. Automation emerges as a solution to these problems, and when applied correctly, it can minimize time, increase quality and perform other tasks that are impossible for the worker, among other benefits. When a process is automated, it is because after performing various analyzes it is known that said automation would positively and significantly affect at least one of the company's indicators. This article describes the characterization of a company manufacturing cooling products, as well as the analysis to detect a process that can be improved through automation. This process turned out to be the cutting and punching of the metal sheets that make up the main structure of the chillers, which are the processes with which the entire production cycle begins. The present proposal will allow the company to generate an economic impact that encompasses the improvement of a process in time and quality, in addition to promoting the reduction of labor and energy expenditure, which leads to substantial economic savings.
Journal ijmr.net.in(UGC Approved)
Continuous quality improvement process assumes and requires that a team of experts together with the company leadership actively use six sigma and quality tools in their improvement activities and decision making process. Currently there are a significant number of quality assurance and quality management tools available, so the selection of the most appropriate is not always an easy task. Tools are essential ingredients of a process and basic instruments for the success of a quality program. Many companies have used tools without giving sufficient thought to their selection and have then experienced barriers to progress. Six sigma & Quality Tools cannot remedy every quality problem but they certainly are a means for solving problems. Consequently, it needs to be emphasized that while tools can be very effective in the right hands, they can be very dangerous in the wrong hands. It is, therefore, important to know how, when and which tools should be used in problem solving or improvement processes.
IRJET Journal
As we know that there are many researches is going on to the growth of manufacturing industry and how we can improve it and in today's world the growth of automobile industry or growth aluminum alloy wheel manufacturing industry is very high. If we talk about the use of aluminum alloy then the aluminum is very strong material for various applications, so we can use the aluminum alloy in the automobile industry/aluminum alloy wheel industry. The objective of this project is to study of the production line of an aluminum alloy wheel manufacturing industry and to improve the quality of production using quality control tools. The defects during the manufacturing process occurs which are responsible for reducing the quality of product are analyzed with the help of using technique like check sheet, pareto diagram, cause-effect diagrams or figures, design of experiments and root cause. The all data and information is collected for various inspection methods. Using check sheet facts has been collected and all of the defects are studied. The results find by this study shows that major defects or reason for rejection of product or component during manufacturing process were shrinkage non-metallic inclusions, micro cavity and gas holes. All defects that are occurring during the manufacturing process are studied and the possible causes for defects are shown in Fishbone diagram. The Fishbone diagram or figure may be called as cause defect. Shrinkage mainly occurs due to lack of accounting error, lack of feed and ineffective inventory. The basic phenomena for lack of feed are that while hydrogen bureaucracy gasoline holes and porosity in aluminum casting, due to the amount of the hydrogen present in molten metal. The hydrogen absorbing capacity of molten metal is due to temperature effect.
Engineering Journal
GVSS Sharma
Quality Production Improvement
Renata Stasiak-Betlejewska
2016 IEEE International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Engineering Management (IEEM)
Sérgio Sousa
Rio Pipeline Conference & Exhibition 2017
Carlos Eduardo R . B . Barateiro
The increase in industrial productivity is the basis of business success and often the reason for its own survival in increasingly globalized markets. Industrial automation has evolved at an increasing pace and particularly in the last decades and today it has the capacity to be much more than simply a tool for process control, having an impact on the execution of the projects and very strongly on the plant maintenance. The objective of this work is to make a punctual analysis of how automation solutions for process control can contribute to the improvement of the operational efficiency of industrial plants. The starting point was a comparative study conducted by Solomon Associates, a North American consulting firm, which has conducted extensive research with the management team of more than 8,000 processing plants installed to serve the chemical, petrochemical and refining operations markets, enabling the framing of companies In performance quadrants. Based on this preliminary report, a qualitative research was conducted using the brainwriting technique with directors, managers and process engineers (a total of 25 participants) responsible for the operation of five major petrochemical plants in operation in Brazil. This process allowed the selection of the most important automation technologies that should be implemented in function of their cost / benefit and that bring real gains to obtain the best operational performance, allowing the framing of the companies in the top quartile of efficiency. In addition, through an extensive bibliographical research among manufacturers of automation systems, this work presents a detail of the solutions raised in the brainstorming that can serve as an illustrative example of these best practices.
Dr. Sushil K U M A R Choudhary
In the last decades, industrial automation has become a driving force in all production systems. Technologies and architectures have emerged alongside the growing organizational structures of production plants. Industrial automation plays an important role in industrial and manufacturing environment. Industrial automation means automatically control of industrial appliances which save money, time also reduce human efforts. Automation devices such as controllers and data systems and/or services. Systems and methods are provided that receive statements or other unit of data interaction from an automation device, provide the statements to an appropriate system or service for processing, and optionally return a response such as a result set. In this paper brief study about the automation, level of automation, Industrial automation and types of industrial automation etc.
RELATED PAPERS
sub\urban. zeitschrift für kritische stadtforschung
Arquivos brasileiros de cirurgia digestiva : ABCD = Brazilian archives of digestive surgery
luciana bolfarini
Andrew Calver
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health
Piero Ruggeri
Heiner Goldbach
Canadian Journal of African Studies / Revue canadienne des études africaines
Kwabena Opoku-Agyemang
SMART MOVES JOURNAL IJOSCIENCE
Dr Shivnath Ghosh
RECIMA21 - Revista Científica Multidisciplinar - ISSN 2675-6218
Romildo De Holanda
Yasuharu Den
Anuario Filosófico
Josep-Ignasi Saranyana Closa
Polish Journal of Surgery
Roman Herman
Revista Ciência Agronômica
Marcio Busi Da Silva
Amrita Bhattacharyya
Rinto Agustino
Nature Immunology
Thomas Korn
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis
Pierre-yves Turpin
Advanced Materials
PROCEEDING AISELT (Annual International Seminar on English Language Teaching)
Eri Rahmawati
Optics letters
Philippe Velha
Paediatric Respiratory Reviews
Maciej G Kaczmarski
Conditio feminae. Imágenes de la realidad femenina en el mundo romano, Roma 2021
ROSALÍA RODRÍGUEZ LÓPEZ
International Journal of Biomaterials
aniek setiya budiatin
Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters
Alejandra Orrego
Open Access Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences
Ilham Muddin
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Using Exploratory Data Analysis to Improve the Fresh Foods Ordering Process in Retail Stores. This case study presents a real-world example of how the thought processes of data scientists can contribute to quality practice. See how explorative data analysis and basic statistics helped a grocery chain reduce inefficiencies in its retail ...
Case study. Healthcare companies can use smart quality to redesign the quality management review process and see results quickly. At one pharmaceutical and medtech company, smart visualization of connected, cross-functional metrics significantly improved the effectiveness and efficiency of quality management review at all levels.
In this research, we talk about case studies that show how businesses have effectively used QA testing to attain quality assurance. We also talk about the issues and difficulties these case ...
Quality Management Systems (QMS) & ISO 9001 - Case Studies. Implementing ISO 9001:2015 can help ensure that customers get consistent, high-quality products and services, which in turn can benefit your organization. The following ISO 9001:2015 case studies offer a look at the difference ISO 9001 can make for organizations in terms of process ...
The IQA system of academic programs continues to receive attention from Vietnamese higher education. To facilitate the IQA process, first, the Vietnamese HEIs built a technology system, designed to: support the export of the self-study report for programmatic accreditation (Cao, 2020; Nguyen, 2020); integrate data among offices in the institution (Huynh & Nguyen, 2020); facilitate the sharing ...
by by Jim Heskett. A new book by Gregory Clark identifies "labor quality" as the major enticement for capital flows that lead to economic prosperity. By defining labor quality in terms of discipline and attitudes toward work, this argument minimizes the long-term threat of outsourcing to developed economies.
In the realm of Quality Assurance (QA), the integration of Power BI has proven to be a game-changer, revolutionizing how organizations approach and enhance their QA processes. This case study ...
A Case Study in Integra ted Quality Ass urance for. Performance Management Systems. Liam Peyton, Bo Zhan, Ber nard Stepien. School o f Information Technology and Engineering, University of Ottaw a ...
Read more about - Contact Centre News, Case Studies, Playvox. This case study investigates how Freshly, the ready-to-eat healthy meal delivery company, improved customer satisfaction with a new, robust quality assurance (QA) programme. The Challenge Freshly needed to improve customer outcomes. They had a unique product and a strong.
This study utilized a case study research approach to investigate the implementation of a sustainable quality assurance system at Prince Sultan University (PSU). According to Yin [ 31 ], a case study research approach is appropriate for investigating a phenomenon within its real-life context and when the boundaries between the phenomenon and ...
Case 1. Customer wants. to have a solid quality of the product. 3 environments - dev, qa and production. 10 QAs, half of them is new to the project , and 4times more developers working on one ...
This case study (PDF, 1.2 MB) focuses on the successful quality improvement methods employed by a health plan to improve customer service for its members. Published by RAND, August 2007. Published by RAND, August 2007.
Software Testing Client Project Case Study. We are often asked what software testing is. The video below shares a solid definition of the term. But we thought a software testing project case study might be helpful to better understand what software testers do on a typical day. This includes testing software, writing requirement documents for ...
QA case study: Usually startups are less concerned about the quality and in many cases developers are doing QA part of work, we understand that it saves cost and gives chance to release product in a short period of time but on another hand clients will face poor quality this is exactly the situation we saw happened with our customer in Vancouver - financial technology company was looking for ...
CASE STUDY ON QUALITY ASSURANCE SYSTEM IN . CONSTRUCTION . Vikas Patel 1, Brijesh Singh* 2, P N Ojha 3, Amit Sagar 4. 1 Project Engineer, Construction Development & Rese arch, NCCBM, 34 KM Stone ...
Our engineer was also responsible for providing live or recorded demonstrations of completed tasks, as well as extensive documentation of the testing behavior. Test Cases Written (64) Implementation Time (3 weeks) Execution Time (30 minutes) Customer Satisfaction. The software quality assurance professionals at Beta Breakers test web and mobile ...
According to Teresa Whitacre, of international consulting firm ASQ, proper quality management also boosts a company's profitability. "Total quality management allows the company to look at their management system as a whole entity — not just an output of the quality department," she says. "Total quality means the organisation looks at ...
Organizational Development Case Study. Gail Berger Darlow; ... In most industries, quality has never mattered more--but with cycle times compressing and output gains outpacing employment growth ...
To ensure maximum productivity, all testers receive specialized education on their clients' industry and issues before starting projects. Learn more about how QA Consultants helps our customers with software testing and quality assurance by reading our case studies. QA Consultants is an award-winning provider of software testing and quality ...
efforts in the country. This study explores the impacts of internationalisation for quality assurance in higher education and it particularly accounts institutional best practices for quality assurance in a research university. The study used literature review, case study and document analysis as research methods.
Brennan, James, "Case Study: Implementing Tools for Software Quality Assurance" (2009). Regis University Student Publications (comprehensive collection). 794. This Thesis - Open Access is brought to you for free and open access by the Regis University Student Publications at ePublications at Regis University. It has been accepted for inclusion ...
Network provider improves quality of business models with Infosys package automation solutions. Case Study. Validation of analytics models which detect the warranty claims for locomotive engines. Case Study. End-to-End Testing of Smart Lighting Applications using Open Source-Based Automation Framework. Case Study.
Download Free PDF. View PDF. Case Study on Quality Assurance and Continuous Improvement INTERNSHIP REPORT Submitted by Abel Jacob Date: June 2012 - August 2012 1 f2 f3 f4 fHindalco Alupuram Hindalco Alupuram Works is situated in the Ernakulam district of Kerala, India's southern-most state.
Moreover, the quality assurance strategy of the curriculum system is discussed from three angles of enhancing professional emotion, enhancing professional practice and strengthening innovation ability, to reach the training objective of outstanding applied horticultural talents under the background of new agricultural science.