Get science-backed answers as you write with Paperpal's Research feature

How to Write a Research Paper Introduction (with Examples)

The research paper introduction section, along with the Title and Abstract, can be considered the face of any research paper. The following article is intended to guide you in organizing and writing the research paper introduction for a quality academic article or dissertation.
The research paper introduction aims to present the topic to the reader. A study will only be accepted for publishing if you can ascertain that the available literature cannot answer your research question. So it is important to ensure that you have read important studies on that particular topic, especially those within the last five to ten years, and that they are properly referenced in this section. 1 What should be included in the research paper introduction is decided by what you want to tell readers about the reason behind the research and how you plan to fill the knowledge gap. The best research paper introduction provides a systemic review of existing work and demonstrates additional work that needs to be done. It needs to be brief, captivating, and well-referenced; a well-drafted research paper introduction will help the researcher win half the battle.
The introduction for a research paper is where you set up your topic and approach for the reader. It has several key goals:
- Present your research topic
- Capture reader interest
- Summarize existing research
- Position your own approach
- Define your specific research problem and problem statement
- Highlight the novelty and contributions of the study
- Give an overview of the paper’s structure
The research paper introduction can vary in size and structure depending on whether your paper presents the results of original empirical research or is a review paper. Some research paper introduction examples are only half a page while others are a few pages long. In many cases, the introduction will be shorter than all of the other sections of your paper; its length depends on the size of your paper as a whole.
- Break through writer’s block. Write your research paper introduction with Paperpal Copilot
Table of Contents
What is the introduction for a research paper, why is the introduction important in a research paper, craft a compelling introduction section with paperpal. try now, 1. introduce the research topic:, 2. determine a research niche:, 3. place your research within the research niche:, craft accurate research paper introductions with paperpal. start writing now, frequently asked questions on research paper introduction, key points to remember.
The introduction in a research paper is placed at the beginning to guide the reader from a broad subject area to the specific topic that your research addresses. They present the following information to the reader
- Scope: The topic covered in the research paper
- Context: Background of your topic
- Importance: Why your research matters in that particular area of research and the industry problem that can be targeted
The research paper introduction conveys a lot of information and can be considered an essential roadmap for the rest of your paper. A good introduction for a research paper is important for the following reasons:
- It stimulates your reader’s interest: A good introduction section can make your readers want to read your paper by capturing their interest. It informs the reader what they are going to learn and helps determine if the topic is of interest to them.
- It helps the reader understand the research background: Without a clear introduction, your readers may feel confused and even struggle when reading your paper. A good research paper introduction will prepare them for the in-depth research to come. It provides you the opportunity to engage with the readers and demonstrate your knowledge and authority on the specific topic.
- It explains why your research paper is worth reading: Your introduction can convey a lot of information to your readers. It introduces the topic, why the topic is important, and how you plan to proceed with your research.
- It helps guide the reader through the rest of the paper: The research paper introduction gives the reader a sense of the nature of the information that will support your arguments and the general organization of the paragraphs that will follow. It offers an overview of what to expect when reading the main body of your paper.
What are the parts of introduction in the research?
A good research paper introduction section should comprise three main elements: 2
- What is known: This sets the stage for your research. It informs the readers of what is known on the subject.
- What is lacking: This is aimed at justifying the reason for carrying out your research. This could involve investigating a new concept or method or building upon previous research.
- What you aim to do: This part briefly states the objectives of your research and its major contributions. Your detailed hypothesis will also form a part of this section.
How to write a research paper introduction?
The first step in writing the research paper introduction is to inform the reader what your topic is and why it’s interesting or important. This is generally accomplished with a strong opening statement. The second step involves establishing the kinds of research that have been done and ending with limitations or gaps in the research that you intend to address. Finally, the research paper introduction clarifies how your own research fits in and what problem it addresses. If your research involved testing hypotheses, these should be stated along with your research question. The hypothesis should be presented in the past tense since it will have been tested by the time you are writing the research paper introduction.
The following key points, with examples, can guide you when writing the research paper introduction section:
- Highlight the importance of the research field or topic
- Describe the background of the topic
- Present an overview of current research on the topic
Example: The inclusion of experiential and competency-based learning has benefitted electronics engineering education. Industry partnerships provide an excellent alternative for students wanting to engage in solving real-world challenges. Industry-academia participation has grown in recent years due to the need for skilled engineers with practical training and specialized expertise. However, from the educational perspective, many activities are needed to incorporate sustainable development goals into the university curricula and consolidate learning innovation in universities.
- Reveal a gap in existing research or oppose an existing assumption
- Formulate the research question
Example: There have been plausible efforts to integrate educational activities in higher education electronics engineering programs. However, very few studies have considered using educational research methods for performance evaluation of competency-based higher engineering education, with a focus on technical and or transversal skills. To remedy the current need for evaluating competencies in STEM fields and providing sustainable development goals in engineering education, in this study, a comparison was drawn between study groups without and with industry partners.
- State the purpose of your study
- Highlight the key characteristics of your study
- Describe important results
- Highlight the novelty of the study.
- Offer a brief overview of the structure of the paper.
Example: The study evaluates the main competency needed in the applied electronics course, which is a fundamental core subject for many electronics engineering undergraduate programs. We compared two groups, without and with an industrial partner, that offered real-world projects to solve during the semester. This comparison can help determine significant differences in both groups in terms of developing subject competency and achieving sustainable development goals.
Write a Research Paper Introduction in Minutes with Paperpal
Paperpal Copilot is a generative AI-powered academic writing assistant. It’s trained on millions of published scholarly articles and over 20 years of STM experience. Paperpal Copilot helps authors write better and faster with:
- Real-time writing suggestions
- In-depth checks for language and grammar correction
- Paraphrasing to add variety, ensure academic tone, and trim text to meet journal limits
With Paperpal Copilot, create a research paper introduction effortlessly. In this step-by-step guide, we’ll walk you through how Paperpal transforms your initial ideas into a polished and publication-ready introduction.

How to use Paperpal to write the Introduction section
Step 1: Sign up on Paperpal and click on the Copilot feature, under this choose Outlines > Research Article > Introduction
Step 2: Add your unstructured notes or initial draft, whether in English or another language, to Paperpal, which is to be used as the base for your content.
Step 3: Fill in the specifics, such as your field of study, brief description or details you want to include, which will help the AI generate the outline for your Introduction.
Step 4: Use this outline and sentence suggestions to develop your content, adding citations where needed and modifying it to align with your specific research focus.
Step 5: Turn to Paperpal’s granular language checks to refine your content, tailor it to reflect your personal writing style, and ensure it effectively conveys your message.
You can use the same process to develop each section of your article, and finally your research paper in half the time and without any of the stress.
The purpose of the research paper introduction is to introduce the reader to the problem definition, justify the need for the study, and describe the main theme of the study. The aim is to gain the reader’s attention by providing them with necessary background information and establishing the main purpose and direction of the research.
The length of the research paper introduction can vary across journals and disciplines. While there are no strict word limits for writing the research paper introduction, an ideal length would be one page, with a maximum of 400 words over 1-4 paragraphs. Generally, it is one of the shorter sections of the paper as the reader is assumed to have at least a reasonable knowledge about the topic. 2 For example, for a study evaluating the role of building design in ensuring fire safety, there is no need to discuss definitions and nature of fire in the introduction; you could start by commenting upon the existing practices for fire safety and how your study will add to the existing knowledge and practice.
When deciding what to include in the research paper introduction, the rest of the paper should also be considered. The aim is to introduce the reader smoothly to the topic and facilitate an easy read without much dependency on external sources. 3 Below is a list of elements you can include to prepare a research paper introduction outline and follow it when you are writing the research paper introduction. Topic introduction: This can include key definitions and a brief history of the topic. Research context and background: Offer the readers some general information and then narrow it down to specific aspects. Details of the research you conducted: A brief literature review can be included to support your arguments or line of thought. Rationale for the study: This establishes the relevance of your study and establishes its importance. Importance of your research: The main contributions are highlighted to help establish the novelty of your study Research hypothesis: Introduce your research question and propose an expected outcome. Organization of the paper: Include a short paragraph of 3-4 sentences that highlights your plan for the entire paper
Cite only works that are most relevant to your topic; as a general rule, you can include one to three. Note that readers want to see evidence of original thinking. So it is better to avoid using too many references as it does not leave much room for your personal standpoint to shine through. Citations in your research paper introduction support the key points, and the number of citations depend on the subject matter and the point discussed. If the research paper introduction is too long or overflowing with citations, it is better to cite a few review articles rather than the individual articles summarized in the review. A good point to remember when citing research papers in the introduction section is to include at least one-third of the references in the introduction.
The literature review plays a significant role in the research paper introduction section. A good literature review accomplishes the following: Introduces the topic – Establishes the study’s significance – Provides an overview of the relevant literature – Provides context for the study using literature – Identifies knowledge gaps However, remember to avoid making the following mistakes when writing a research paper introduction: Do not use studies from the literature review to aggressively support your research Avoid direct quoting Do not allow literature review to be the focus of this section. Instead, the literature review should only aid in setting a foundation for the manuscript.
Remember the following key points for writing a good research paper introduction: 4
- Avoid stuffing too much general information: Avoid including what an average reader would know and include only that information related to the problem being addressed in the research paper introduction. For example, when describing a comparative study of non-traditional methods for mechanical design optimization, information related to the traditional methods and differences between traditional and non-traditional methods would not be relevant. In this case, the introduction for the research paper should begin with the state-of-the-art non-traditional methods and methods to evaluate the efficiency of newly developed algorithms.
- Avoid packing too many references: Cite only the required works in your research paper introduction. The other works can be included in the discussion section to strengthen your findings.
- Avoid extensive criticism of previous studies: Avoid being overly critical of earlier studies while setting the rationale for your study. A better place for this would be the Discussion section, where you can highlight the advantages of your method.
- Avoid describing conclusions of the study: When writing a research paper introduction remember not to include the findings of your study. The aim is to let the readers know what question is being answered. The actual answer should only be given in the Results and Discussion section.
To summarize, the research paper introduction section should be brief yet informative. It should convince the reader the need to conduct the study and motivate him to read further. If you’re feeling stuck or unsure, choose trusted AI academic writing assistants like Paperpal to effortlessly craft your research paper introduction and other sections of your research article.
1. Jawaid, S. A., & Jawaid, M. (2019). How to write introduction and discussion. Saudi Journal of Anaesthesia, 13(Suppl 1), S18.
2. Dewan, P., & Gupta, P. (2016). Writing the title, abstract and introduction: Looks matter!. Indian pediatrics, 53, 235-241.
3. Cetin, S., & Hackam, D. J. (2005). An approach to the writing of a scientific Manuscript1. Journal of Surgical Research, 128(2), 165-167.
4. Bavdekar, S. B. (2015). Writing introduction: Laying the foundations of a research paper. Journal of the Association of Physicians of India, 63(7), 44-6.
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
- Scientific Writing Style Guides Explained
- 5 Reasons for Rejection After Peer Review
- Ethical Research Practices For Research with Human Subjects
- 8 Most Effective Ways to Increase Motivation for Thesis Writing
Practice vs. Practise: Learn the Difference
Academic paraphrasing: why paperpal’s rewrite should be your first choice , you may also like, academic editing: how to self-edit academic text with..., measuring academic success: definition & strategies for excellence, phd qualifying exam: tips for success , ai in education: it’s time to change the..., is it ethical to use ai-generated abstracts without..., what are journal guidelines on using generative ai..., quillbot review: features, pricing, and free alternatives, what is an academic paper types and elements , should you use ai tools like chatgpt for..., 9 steps to publish a research paper.
- Privacy Policy

Home » Research Paper Introduction – Writing Guide and Examples
Research Paper Introduction – Writing Guide and Examples
Table of Contents

Research Paper Introduction
Research paper introduction is the first section of a research paper that provides an overview of the study, its purpose, and the research question (s) or hypothesis (es) being investigated. It typically includes background information about the topic, a review of previous research in the field, and a statement of the research objectives. The introduction is intended to provide the reader with a clear understanding of the research problem, why it is important, and how the study will contribute to existing knowledge in the field. It also sets the tone for the rest of the paper and helps to establish the author’s credibility and expertise on the subject.
How to Write Research Paper Introduction
Writing an introduction for a research paper can be challenging because it sets the tone for the entire paper. Here are some steps to follow to help you write an effective research paper introduction:
- Start with a hook : Begin your introduction with an attention-grabbing statement, a question, or a surprising fact that will make the reader interested in reading further.
- Provide background information: After the hook, provide background information on the topic. This information should give the reader a general idea of what the topic is about and why it is important.
- State the research problem: Clearly state the research problem or question that the paper addresses. This should be done in a concise and straightforward manner.
- State the research objectives: After stating the research problem, clearly state the research objectives. This will give the reader an idea of what the paper aims to achieve.
- Provide a brief overview of the paper: At the end of the introduction, provide a brief overview of the paper. This should include a summary of the main points that will be discussed in the paper.
- Revise and refine: Finally, revise and refine your introduction to ensure that it is clear, concise, and engaging.
Structure of Research Paper Introduction
The following is a typical structure for a research paper introduction:
- Background Information: This section provides an overview of the topic of the research paper, including relevant background information and any previous research that has been done on the topic. It helps to give the reader a sense of the context for the study.
- Problem Statement: This section identifies the specific problem or issue that the research paper is addressing. It should be clear and concise, and it should articulate the gap in knowledge that the study aims to fill.
- Research Question/Hypothesis : This section states the research question or hypothesis that the study aims to answer. It should be specific and focused, and it should clearly connect to the problem statement.
- Significance of the Study: This section explains why the research is important and what the potential implications of the study are. It should highlight the contribution that the research makes to the field.
- Methodology: This section describes the research methods that were used to conduct the study. It should be detailed enough to allow the reader to understand how the study was conducted and to evaluate the validity of the results.
- Organization of the Paper : This section provides a brief overview of the structure of the research paper. It should give the reader a sense of what to expect in each section of the paper.
Research Paper Introduction Examples
Research Paper Introduction Examples could be:
Example 1: In recent years, the use of artificial intelligence (AI) has become increasingly prevalent in various industries, including healthcare. AI algorithms are being developed to assist with medical diagnoses, treatment recommendations, and patient monitoring. However, as the use of AI in healthcare grows, ethical concerns regarding privacy, bias, and accountability have emerged. This paper aims to explore the ethical implications of AI in healthcare and propose recommendations for addressing these concerns.
Example 2: Climate change is one of the most pressing issues facing our planet today. The increasing concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere has resulted in rising temperatures, changing weather patterns, and other environmental impacts. In this paper, we will review the scientific evidence on climate change, discuss the potential consequences of inaction, and propose solutions for mitigating its effects.
Example 3: The rise of social media has transformed the way we communicate and interact with each other. While social media platforms offer many benefits, including increased connectivity and access to information, they also present numerous challenges. In this paper, we will examine the impact of social media on mental health, privacy, and democracy, and propose solutions for addressing these issues.
Example 4: The use of renewable energy sources has become increasingly important in the face of climate change and environmental degradation. While renewable energy technologies offer many benefits, including reduced greenhouse gas emissions and energy independence, they also present numerous challenges. In this paper, we will assess the current state of renewable energy technology, discuss the economic and political barriers to its adoption, and propose solutions for promoting the widespread use of renewable energy.
Purpose of Research Paper Introduction
The introduction section of a research paper serves several important purposes, including:
- Providing context: The introduction should give readers a general understanding of the topic, including its background, significance, and relevance to the field.
- Presenting the research question or problem: The introduction should clearly state the research question or problem that the paper aims to address. This helps readers understand the purpose of the study and what the author hopes to accomplish.
- Reviewing the literature: The introduction should summarize the current state of knowledge on the topic, highlighting the gaps and limitations in existing research. This shows readers why the study is important and necessary.
- Outlining the scope and objectives of the study: The introduction should describe the scope and objectives of the study, including what aspects of the topic will be covered, what data will be collected, and what methods will be used.
- Previewing the main findings and conclusions : The introduction should provide a brief overview of the main findings and conclusions that the study will present. This helps readers anticipate what they can expect to learn from the paper.
When to Write Research Paper Introduction
The introduction of a research paper is typically written after the research has been conducted and the data has been analyzed. This is because the introduction should provide an overview of the research problem, the purpose of the study, and the research questions or hypotheses that will be investigated.
Once you have a clear understanding of the research problem and the questions that you want to explore, you can begin to write the introduction. It’s important to keep in mind that the introduction should be written in a way that engages the reader and provides a clear rationale for the study. It should also provide context for the research by reviewing relevant literature and explaining how the study fits into the larger field of research.
Advantages of Research Paper Introduction
The introduction of a research paper has several advantages, including:
- Establishing the purpose of the research: The introduction provides an overview of the research problem, question, or hypothesis, and the objectives of the study. This helps to clarify the purpose of the research and provide a roadmap for the reader to follow.
- Providing background information: The introduction also provides background information on the topic, including a review of relevant literature and research. This helps the reader understand the context of the study and how it fits into the broader field of research.
- Demonstrating the significance of the research: The introduction also explains why the research is important and relevant. This helps the reader understand the value of the study and why it is worth reading.
- Setting expectations: The introduction sets the tone for the rest of the paper and prepares the reader for what is to come. This helps the reader understand what to expect and how to approach the paper.
- Grabbing the reader’s attention: A well-written introduction can grab the reader’s attention and make them interested in reading further. This is important because it can help to keep the reader engaged and motivated to read the rest of the paper.
- Creating a strong first impression: The introduction is the first part of the research paper that the reader will see, and it can create a strong first impression. A well-written introduction can make the reader more likely to take the research seriously and view it as credible.
- Establishing the author’s credibility: The introduction can also establish the author’s credibility as a researcher. By providing a clear and thorough overview of the research problem and relevant literature, the author can demonstrate their expertise and knowledge in the field.
- Providing a structure for the paper: The introduction can also provide a structure for the rest of the paper. By outlining the main sections and sub-sections of the paper, the introduction can help the reader navigate the paper and find the information they are looking for.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

How to Cite Research Paper – All Formats and...

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Paper Format – Types, Examples and...

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples

Research Paper Title – Writing Guide and Example

Research Paper Conclusion – Writing Guide and...
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
- Research Papers
How to Write a Research Introduction
Last Updated: December 6, 2023 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Megan Morgan, PhD . Megan Morgan is a Graduate Program Academic Advisor in the School of Public & International Affairs at the University of Georgia. She earned her PhD in English from the University of Georgia in 2015. There are 7 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 2,653,049 times.
The introduction to a research paper can be the most challenging part of the paper to write. The length of the introduction will vary depending on the type of research paper you are writing. An introduction should announce your topic, provide context and a rationale for your work, before stating your research questions and hypothesis. Well-written introductions set the tone for the paper, catch the reader's interest, and communicate the hypothesis or thesis statement.
Introducing the Topic of the Paper

- In scientific papers this is sometimes known as an "inverted triangle", where you start with the broadest material at the start, before zooming in on the specifics. [2] X Research source
- The sentence "Throughout the 20th century, our views of life on other planets have drastically changed" introduces a topic, but does so in broad terms.
- It provides the reader with an indication of the content of the essay and encourages them to read on.

- For example, if you were writing a paper about the behaviour of mice when exposed to a particular substance, you would include the word "mice", and the scientific name of the relevant compound in the first sentences.
- If you were writing a history paper about the impact of the First World War on gender relations in Britain, you should mention those key words in your first few lines.

- This is especially important if you are attempting to develop a new conceptualization that uses language and terminology your readers may be unfamiliar with.

- If you use an anecdote ensure that is short and highly relevant for your research. It has to function in the same way as an alternative opening, namely to announce the topic of your research paper to your reader.
- For example, if you were writing a sociology paper about re-offending rates among young offenders, you could include a brief story of one person whose story reflects and introduces your topic.
- This kind of approach is generally not appropriate for the introduction to a natural or physical sciences research paper where the writing conventions are different.
Establishing the Context for Your Paper

- It is important to be concise in the introduction, so provide an overview on recent developments in the primary research rather than a lengthy discussion.
- You can follow the "inverted triangle" principle to focus in from the broader themes to those to which you are making a direct contribution with your paper.
- A strong literature review presents important background information to your own research and indicates the importance of the field.

- By making clear reference to existing work you can demonstrate explicitly the specific contribution you are making to move the field forward.
- You can identify a gap in the existing scholarship and explain how you are addressing it and moving understanding forward.

- For example, if you are writing a scientific paper you could stress the merits of the experimental approach or models you have used.
- Stress what is novel in your research and the significance of your new approach, but don't give too much detail in the introduction.
- A stated rationale could be something like: "the study evaluates the previously unknown anti-inflammatory effects of a topical compound in order to evaluate its potential clinical uses".
Specifying Your Research Questions and Hypothesis

- The research question or questions generally come towards the end of the introduction, and should be concise and closely focused.
- The research question might recall some of the key words established in the first few sentences and the title of your paper.
- An example of a research question could be "what were the consequences of the North American Free Trade Agreement on the Mexican export economy?"
- This could be honed further to be specific by referring to a particular element of the Free Trade Agreement and the impact on a particular industry in Mexico, such as clothing manufacture.
- A good research question should shape a problem into a testable hypothesis.

- If possible try to avoid using the word "hypothesis" and rather make this implicit in your writing. This can make your writing appear less formulaic.
- In a scientific paper, giving a clear one-sentence overview of your results and their relation to your hypothesis makes the information clear and accessible. [10] X Trustworthy Source PubMed Central Journal archive from the U.S. National Institutes of Health Go to source
- An example of a hypothesis could be "mice deprived of food for the duration of the study were expected to become more lethargic than those fed normally".

- This is not always necessary and you should pay attention to the writing conventions in your discipline.
- In a natural sciences paper, for example, there is a fairly rigid structure which you will be following.
- A humanities or social science paper will most likely present more opportunities to deviate in how you structure your paper.
Research Introduction Help

Community Q&A
- Use your research papers' outline to help you decide what information to include when writing an introduction. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 1
- Consider drafting your introduction after you have already completed the rest of your research paper. Writing introductions last can help ensure that you don't leave out any major points. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0

- Avoid emotional or sensational introductions; these can create distrust in the reader. Thanks Helpful 50 Not Helpful 12
- Generally avoid using personal pronouns in your introduction, such as "I," "me," "we," "us," "my," "mine," or "our." Thanks Helpful 31 Not Helpful 7
- Don't overwhelm the reader with an over-abundance of information. Keep the introduction as concise as possible by saving specific details for the body of your paper. Thanks Helpful 24 Not Helpful 14
You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://library.sacredheart.edu/c.php?g=29803&p=185916
- ↑ https://www.aresearchguide.com/inverted-pyramid-structure-in-writing.html
- ↑ https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide/introduction
- ↑ https://writing.wisc.edu/Handbook/PlanResearchPaper.html
- ↑ https://dept.writing.wisc.edu/wac/writing-an-introduction-for-a-scientific-paper/
- ↑ https://writing.wisc.edu/handbook/assignments/planresearchpaper/
- ↑ http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3178846/
About This Article

To introduce your research paper, use the first 1-2 sentences to describe your general topic, such as “women in World War I.” Include and define keywords, such as “gender relations,” to show your reader where you’re going. Mention previous research into the topic with a phrase like, “Others have studied…”, then transition into what your contribution will be and why it’s necessary. Finally, state the questions that your paper will address and propose your “answer” to them as your thesis statement. For more information from our English Ph.D. co-author about how to craft a strong hypothesis and thesis, keep reading! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Abdulrahman Omar
Oct 5, 2018
Did this article help you?
May 9, 2021
Lavanya Gopakumar
Oct 1, 2016
Dengkai Zhang
May 14, 2018
Leslie Mae Cansana
Sep 22, 2016

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Don’t miss out! Sign up for
wikiHow’s newsletter
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- 4. The Introduction
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Applying Critical Thinking
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
The introduction leads the reader from a general subject area to a particular topic of inquiry. It establishes the scope, context, and significance of the research being conducted by summarizing current understanding and background information about the topic, stating the purpose of the work in the form of the research problem supported by a hypothesis or a set of questions, explaining briefly the methodological approach used to examine the research problem, highlighting the potential outcomes your study can reveal, and outlining the remaining structure and organization of the paper.
Key Elements of the Research Proposal. Prepared under the direction of the Superintendent and by the 2010 Curriculum Design and Writing Team. Baltimore County Public Schools.
Importance of a Good Introduction
Think of the introduction as a mental road map that must answer for the reader these four questions:
- What was I studying?
- Why was this topic important to investigate?
- What did we know about this topic before I did this study?
- How will this study advance new knowledge or new ways of understanding?
According to Reyes, there are three overarching goals of a good introduction: 1) ensure that you summarize prior studies about the topic in a manner that lays a foundation for understanding the research problem; 2) explain how your study specifically addresses gaps in the literature, insufficient consideration of the topic, or other deficiency in the literature; and, 3) note the broader theoretical, empirical, and/or policy contributions and implications of your research.
A well-written introduction is important because, quite simply, you never get a second chance to make a good first impression. The opening paragraphs of your paper will provide your readers with their initial impressions about the logic of your argument, your writing style, the overall quality of your research, and, ultimately, the validity of your findings and conclusions. A vague, disorganized, or error-filled introduction will create a negative impression, whereas, a concise, engaging, and well-written introduction will lead your readers to think highly of your analytical skills, your writing style, and your research approach. All introductions should conclude with a brief paragraph that describes the organization of the rest of the paper.
Hirano, Eliana. “Research Article Introductions in English for Specific Purposes: A Comparison between Brazilian, Portuguese, and English.” English for Specific Purposes 28 (October 2009): 240-250; Samraj, B. “Introductions in Research Articles: Variations Across Disciplines.” English for Specific Purposes 21 (2002): 1–17; Introductions. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; “Writing Introductions.” In Good Essay Writing: A Social Sciences Guide. Peter Redman. 4th edition. (London: Sage, 2011), pp. 63-70; Reyes, Victoria. Demystifying the Journal Article. Inside Higher Education.
Structure and Writing Style
I. Structure and Approach
The introduction is the broad beginning of the paper that answers three important questions for the reader:
- What is this?
- Why should I read it?
- What do you want me to think about / consider doing / react to?
Think of the structure of the introduction as an inverted triangle of information that lays a foundation for understanding the research problem. Organize the information so as to present the more general aspects of the topic early in the introduction, then narrow your analysis to more specific topical information that provides context, finally arriving at your research problem and the rationale for studying it [often written as a series of key questions to be addressed or framed as a hypothesis or set of assumptions to be tested] and, whenever possible, a description of the potential outcomes your study can reveal.
These are general phases associated with writing an introduction: 1. Establish an area to research by:
- Highlighting the importance of the topic, and/or
- Making general statements about the topic, and/or
- Presenting an overview on current research on the subject.
2. Identify a research niche by:
- Opposing an existing assumption, and/or
- Revealing a gap in existing research, and/or
- Formulating a research question or problem, and/or
- Continuing a disciplinary tradition.
3. Place your research within the research niche by:
- Stating the intent of your study,
- Outlining the key characteristics of your study,
- Describing important results, and
- Giving a brief overview of the structure of the paper.
NOTE: It is often useful to review the introduction late in the writing process. This is appropriate because outcomes are unknown until you've completed the study. After you complete writing the body of the paper, go back and review introductory descriptions of the structure of the paper, the method of data gathering, the reporting and analysis of results, and the conclusion. Reviewing and, if necessary, rewriting the introduction ensures that it correctly matches the overall structure of your final paper.
II. Delimitations of the Study
Delimitations refer to those characteristics that limit the scope and define the conceptual boundaries of your research . This is determined by the conscious exclusionary and inclusionary decisions you make about how to investigate the research problem. In other words, not only should you tell the reader what it is you are studying and why, but you must also acknowledge why you rejected alternative approaches that could have been used to examine the topic.
Obviously, the first limiting step was the choice of research problem itself. However, implicit are other, related problems that could have been chosen but were rejected. These should be noted in the conclusion of your introduction. For example, a delimitating statement could read, "Although many factors can be understood to impact the likelihood young people will vote, this study will focus on socioeconomic factors related to the need to work full-time while in school." The point is not to document every possible delimiting factor, but to highlight why previously researched issues related to the topic were not addressed.
Examples of delimitating choices would be:
- The key aims and objectives of your study,
- The research questions that you address,
- The variables of interest [i.e., the various factors and features of the phenomenon being studied],
- The method(s) of investigation,
- The time period your study covers, and
- Any relevant alternative theoretical frameworks that could have been adopted.
Review each of these decisions. Not only do you clearly establish what you intend to accomplish in your research, but you should also include a declaration of what the study does not intend to cover. In the latter case, your exclusionary decisions should be based upon criteria understood as, "not interesting"; "not directly relevant"; “too problematic because..."; "not feasible," and the like. Make this reasoning explicit!
NOTE: Delimitations refer to the initial choices made about the broader, overall design of your study and should not be confused with documenting the limitations of your study discovered after the research has been completed.
ANOTHER NOTE : Do not view delimitating statements as admitting to an inherent failing or shortcoming in your research. They are an accepted element of academic writing intended to keep the reader focused on the research problem by explicitly defining the conceptual boundaries and scope of your study. It addresses any critical questions in the reader's mind of, "Why the hell didn't the author examine this?"
III. The Narrative Flow
Issues to keep in mind that will help the narrative flow in your introduction :
- Your introduction should clearly identify the subject area of interest . A simple strategy to follow is to use key words from your title in the first few sentences of the introduction. This will help focus the introduction on the topic at the appropriate level and ensures that you get to the subject matter quickly without losing focus, or discussing information that is too general.
- Establish context by providing a brief and balanced review of the pertinent published literature that is available on the subject. The key is to summarize for the reader what is known about the specific research problem before you did your analysis. This part of your introduction should not represent a comprehensive literature review--that comes next. It consists of a general review of the important, foundational research literature [with citations] that establishes a foundation for understanding key elements of the research problem. See the drop-down menu under this tab for " Background Information " regarding types of contexts.
- Clearly state the hypothesis that you investigated . When you are first learning to write in this format it is okay, and actually preferable, to use a past statement like, "The purpose of this study was to...." or "We investigated three possible mechanisms to explain the...."
- Why did you choose this kind of research study or design? Provide a clear statement of the rationale for your approach to the problem studied. This will usually follow your statement of purpose in the last paragraph of the introduction.
IV. Engaging the Reader
A research problem in the social sciences can come across as dry and uninteresting to anyone unfamiliar with the topic . Therefore, one of the goals of your introduction is to make readers want to read your paper. Here are several strategies you can use to grab the reader's attention:
- Open with a compelling story . Almost all research problems in the social sciences, no matter how obscure or esoteric , are really about the lives of people. Telling a story that humanizes an issue can help illuminate the significance of the problem and help the reader empathize with those affected by the condition being studied.
- Include a strong quotation or a vivid, perhaps unexpected, anecdote . During your review of the literature, make note of any quotes or anecdotes that grab your attention because they can used in your introduction to highlight the research problem in a captivating way.
- Pose a provocative or thought-provoking question . Your research problem should be framed by a set of questions to be addressed or hypotheses to be tested. However, a provocative question can be presented in the beginning of your introduction that challenges an existing assumption or compels the reader to consider an alternative viewpoint that helps establish the significance of your study.
- Describe a puzzling scenario or incongruity . This involves highlighting an interesting quandary concerning the research problem or describing contradictory findings from prior studies about a topic. Posing what is essentially an unresolved intellectual riddle about the problem can engage the reader's interest in the study.
- Cite a stirring example or case study that illustrates why the research problem is important . Draw upon the findings of others to demonstrate the significance of the problem and to describe how your study builds upon or offers alternatives ways of investigating this prior research.
NOTE: It is important that you choose only one of the suggested strategies for engaging your readers. This avoids giving an impression that your paper is more flash than substance and does not distract from the substance of your study.
Freedman, Leora and Jerry Plotnick. Introductions and Conclusions. University College Writing Centre. University of Toronto; Introduction. The Structure, Format, Content, and Style of a Journal-Style Scientific Paper. Department of Biology. Bates College; Introductions. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Introductions. The Writer’s Handbook. Writing Center. University of Wisconsin, Madison; Introductions, Body Paragraphs, and Conclusions for an Argument Paper. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; “Writing Introductions.” In Good Essay Writing: A Social Sciences Guide . Peter Redman. 4th edition. (London: Sage, 2011), pp. 63-70; Resources for Writers: Introduction Strategies. Program in Writing and Humanistic Studies. Massachusetts Institute of Technology; Sharpling, Gerald. Writing an Introduction. Centre for Applied Linguistics, University of Warwick; Samraj, B. “Introductions in Research Articles: Variations Across Disciplines.” English for Specific Purposes 21 (2002): 1–17; Swales, John and Christine B. Feak. Academic Writing for Graduate Students: Essential Skills and Tasks . 2nd edition. Ann Arbor, MI: University of Michigan Press, 2004 ; Writing Your Introduction. Department of English Writing Guide. George Mason University.
Writing Tip
Avoid the "Dictionary" Introduction
Giving the dictionary definition of words related to the research problem may appear appropriate because it is important to define specific terminology that readers may be unfamiliar with. However, anyone can look a word up in the dictionary and a general dictionary is not a particularly authoritative source because it doesn't take into account the context of your topic and doesn't offer particularly detailed information. Also, placed in the context of a particular discipline, a term or concept may have a different meaning than what is found in a general dictionary. If you feel that you must seek out an authoritative definition, use a subject specific dictionary or encyclopedia [e.g., if you are a sociology student, search for dictionaries of sociology]. A good database for obtaining definitive definitions of concepts or terms is Credo Reference .
Saba, Robert. The College Research Paper. Florida International University; Introductions. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina.
Another Writing Tip
When Do I Begin?
A common question asked at the start of any paper is, "Where should I begin?" An equally important question to ask yourself is, "When do I begin?" Research problems in the social sciences rarely rest in isolation from history. Therefore, it is important to lay a foundation for understanding the historical context underpinning the research problem. However, this information should be brief and succinct and begin at a point in time that illustrates the study's overall importance. For example, a study that investigates coffee cultivation and export in West Africa as a key stimulus for local economic growth needs to describe the beginning of exporting coffee in the region and establishing why economic growth is important. You do not need to give a long historical explanation about coffee exports in Africa. If a research problem requires a substantial exploration of the historical context, do this in the literature review section. In your introduction, make note of this as part of the "roadmap" [see below] that you use to describe the organization of your paper.
Introductions. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; “Writing Introductions.” In Good Essay Writing: A Social Sciences Guide . Peter Redman. 4th edition. (London: Sage, 2011), pp. 63-70.
Yet Another Writing Tip
Always End with a Roadmap
The final paragraph or sentences of your introduction should forecast your main arguments and conclusions and provide a brief description of the rest of the paper [the "roadmap"] that let's the reader know where you are going and what to expect. A roadmap is important because it helps the reader place the research problem within the context of their own perspectives about the topic. In addition, concluding your introduction with an explicit roadmap tells the reader that you have a clear understanding of the structural purpose of your paper. In this way, the roadmap acts as a type of promise to yourself and to your readers that you will follow a consistent and coherent approach to addressing the topic of inquiry. Refer to it often to help keep your writing focused and organized.
Cassuto, Leonard. “On the Dissertation: How to Write the Introduction.” The Chronicle of Higher Education , May 28, 2018; Radich, Michael. A Student's Guide to Writing in East Asian Studies . (Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Writing n. d.), pp. 35-37.
- << Previous: Executive Summary
- Next: The C.A.R.S. Model >>
- Last Updated: May 9, 2024 11:05 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide
- How it works

How to Write the Research Questions – Tips & Examples
Published by Owen Ingram at August 13th, 2021 , Revised On October 3, 2023
Conducting research and writing an academic paper requires a clear direction and focus.
A good research question provides purpose to your research and clarifies the direction. It further helps your readers to understand what issue your research aims to explore and address.
If you are unsure about how to write research questions, here is a list of the attributes of a good research question;
- The research question should contain only a single problem
- You should be able to find the answer to it using primary and secondary data sources
- You should be able to address it within the time limit and other constraints
- Can attain in-depth and detailed results
- Relevant and applicable
- Should relate to your chosen field of research
Whenever you want to discover something new about a topic , you will ask a question about it. Therefore, the research question is important in the overall research process and provides the author with the reading and writing guidelines.
In a research paper or an essay, you will need to create a single research question that highlights just one problem or issue. The thesis statement should include the specific problem you aim to investigate to establish your argument’s central position or claim.
A larger project such as a dissertation or thesis , on the other hand, can have multiple research questions, but every question should focus on your main research problem . Different types of research will help you answer different research questions, but they should all be relevant to the research scope.
How to Write a Research Question
Steps to develop your research question.
- Choose a topic with a wide range of published literature
- Read and skim relevant articles to find out different problems and issues
- Specify a theoretical or practical research problem that your research question will address
- Narrow down the focus of your selected core niche

Example Research Question (s)
Here are examples of research problems and research questions to help you understand how to create a research question for a given research problem.
Types of Research Questions
There are two main types of research; quantitative and qualitative research . Both types of research require research questions. What research question you will answer is dependent on the type of research you wish to employ.
The first part of designing research is to find a gap and create a fully focused research question.
The following table shows common research questions for a dissertation project. However, it is important to note that these examples of dissertation research questions are straightforward, and the actual research questions may be more complicated than these examples.
What data collection method best suits your research?
- Find out by hiring an expert from ResearchProspect today!
- Despite how challenging the subject may be, we are here to help you.
Steps to Write Research Questions
The research question provides you with a path and focuses on the real problem and the research gap you aim to fill. These are steps you need to take if you are unsure about how to write a research question:
Choose an Interesting Topic
Choose a topic of research according to your interest. The selected topic should be neither too broad nor too narrow.
Do Preliminary Research on the Topic
Find articles, books, journals, and theses relevant to your chosen topic. Understand what research problem each scholar addressed as part of their research project.
Consider your Audience
It is necessary to know your audience to develop focused research questions for your essay or dissertation. You can find aspects of your topic that could be interesting to your audience when narrowing your topic.
Start Asking Questions
What, why, when, how, and other open-ended questions will provide in-depth knowledge about the topic.
Evaluate your Question
After formulating a research question, evaluate to check its effectiveness and how it can serve the purpose. Revise and refine the dissertation research question.
- Do you have a clear research question?
It would help if you formed the research question after finding a research gap. This approach will enable the research to solve part of the problem.
- Do you have a focused research question?
It is necessary that the research question is specific and relating to the central aim of your research.
- Do you have a complex research question?
The research question cannot be answered by yes or no but requires in-depth analysis. It often begins with “How” or “Why.”
Begin your Research
After you have prepared dissertation research questions, you should research the existing literature on similar topics to find various perspectives.
Also See: Formulation of Research Question
If you have been struggling to devise research questions for your dissertation or are unsure about which topic would be suitable for your needs, then you might be interested in taking advantage of our dissertation topic and outline service, which includes several topic ideas in your preferred area of study and a 500/1000 words plan on your chosen topic. Our topic and outline service will help you jump-start your dissertation project.
Find out How Our Topics & Outline Service Can Help You!
Tips on How to Write a Strong Research Question
A research question is the foundation of the entire research. Therefore, you should spend as much time as required to refine the research question.
If you have good research questions for the dissertation, research paper , or essay, you can perform the research and analyse your results more effectively. You can evaluate the strength of the research question with the help of the following criteria. Your research question should be;
Intensive and Researchable
- It should cover a single issue
- The question shouldn’t include a subjective judgment
- It can be answerable with the data analysis or research=
Practical and Specific
- It should not include a course of action, policy, or solution
- It should be well-defined
- Answerable within research limits
Complicated and Arguable
- It should not be simple to answer
- Need in-depth knowledge to find facts
- Provides scope for debate and deliberation
Unique and Relevant
- It should lie in your field of study
- Its results should be contributable
- It should be unique
Conclusion – How to Write Research Questions
A research question provides a clear direction for research work. A bigger project, such as a dissertation, may have more than one research question, but every question should focus on one issue only.
Your research questions should be researchable, feasible to answer, specific to find results, complex (for Masters and PhD projects), and relevant to your field of study. Dissertation research questions depend upon the research type you are basing your paper on.
Start creating a research question by choosing an interesting topic, do some preliminary research, consider your audience, start asking questions, evaluating your question, and begin your research.
At ResearchProspect, we have dissertation experts for all academic subjects. Whether you need help with the individual chapters or the whole dissertation paper, you can be confident that your paper competed to the highest academic standard. There is a reason why our clients keep returning to us over and over. You can also look at our essay services if you are struggling to draft a first-class academic paper.
At ResearchProspect, we have dissertation experts for all academic subjects. Whether you need help with the individual chapters or the whole dissertation paper, you can be confident that your paper competed to the highest academic standard. There is a reason why our clients keep returning to us over and over.
You can also look at our essay services if you are struggling to draft a first-class academic paper.
Place Order
Frequently Asked Questions
How are research questions written.
Research questions are written by:
- Identifying your topic.
- Considering what you want to explore.
- Making questions clear and concise.
- Ensuring they’re researchable.
- Avoiding bias or leading language.
- Focusing on one main idea per question.
What are examples of research questions?
- Does regular exercise improve mental well-being in adults over 50?
- How do online courses impact student engagement compared to traditional classes?
- What are the economic effects of prolonged pandemic lockdowns?
- How does early childhood nutrition influence academic performance in later life?
- Does urban green space reduce stress levels?
How to write a research question?
- Identify a specific topic or issue of interest.
- Conduct preliminary research to understand existing knowledge.
- Narrow the focus to address gaps or unresolved issues.
- Phrase the question to be clear, concise, and researchable.
- Ensure it is specific enough for systematic investigation.
How to formulate my research questions for my geography dissertation?
- Identify a geographical topic or phenomenon of interest.
- Review existing literature to find gaps.
- Consider spatial, temporal, environmental, or societal aspects.
- Ensure questions are specific, feasible, and significant.
- Frame questions to guide methodology: quantitative, qualitative, or mixed.
- Seek feedback from peers/advisors.
You May Also Like
Make sure that your selected topic is intriguing, manageable, and relevant. Here are some guidelines to help understand how to find a good dissertation topic.
To help students organise their dissertation proposal paper correctly, we have put together detailed guidelines on how to structure a dissertation proposal.
Struggling to find relevant and up-to-date topics for your dissertation? Here is all you need to know if unsure about how to choose dissertation topic.
USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

- How It Works
Research Aims, Objectives & Questions
The “Golden Thread” Explained Simply (+ Examples)
By: David Phair (PhD) and Alexandra Shaeffer (PhD) | June 2022
The research aims , objectives and research questions (collectively called the “golden thread”) are arguably the most important thing you need to get right when you’re crafting a research proposal , dissertation or thesis . We receive questions almost every day about this “holy trinity” of research and there’s certainly a lot of confusion out there, so we’ve crafted this post to help you navigate your way through the fog.
Overview: The Golden Thread
- What is the golden thread
- What are research aims ( examples )
- What are research objectives ( examples )
- What are research questions ( examples )
- The importance of alignment in the golden thread
What is the “golden thread”?
The golden thread simply refers to the collective research aims , research objectives , and research questions for any given project (i.e., a dissertation, thesis, or research paper ). These three elements are bundled together because it’s extremely important that they align with each other, and that the entire research project aligns with them.
Importantly, the golden thread needs to weave its way through the entirety of any research project , from start to end. In other words, it needs to be very clearly defined right at the beginning of the project (the topic ideation and proposal stage) and it needs to inform almost every decision throughout the rest of the project. For example, your research design and methodology will be heavily influenced by the golden thread (we’ll explain this in more detail later), as well as your literature review.
The research aims, objectives and research questions (the golden thread) define the focus and scope ( the delimitations ) of your research project. In other words, they help ringfence your dissertation or thesis to a relatively narrow domain, so that you can “go deep” and really dig into a specific problem or opportunity. They also help keep you on track , as they act as a litmus test for relevance. In other words, if you’re ever unsure whether to include something in your document, simply ask yourself the question, “does this contribute toward my research aims, objectives or questions?”. If it doesn’t, chances are you can drop it.
Alright, enough of the fluffy, conceptual stuff. Let’s get down to business and look at what exactly the research aims, objectives and questions are and outline a few examples to bring these concepts to life.

Research Aims: What are they?
Simply put, the research aim(s) is a statement that reflects the broad overarching goal (s) of the research project. Research aims are fairly high-level (low resolution) as they outline the general direction of the research and what it’s trying to achieve .
Research Aims: Examples
True to the name, research aims usually start with the wording “this research aims to…”, “this research seeks to…”, and so on. For example:
“This research aims to explore employee experiences of digital transformation in retail HR.” “This study sets out to assess the interaction between student support and self-care on well-being in engineering graduate students”
As you can see, these research aims provide a high-level description of what the study is about and what it seeks to achieve. They’re not hyper-specific or action-oriented, but they’re clear about what the study’s focus is and what is being investigated.
Need a helping hand?
Research Objectives: What are they?
The research objectives take the research aims and make them more practical and actionable . In other words, the research objectives showcase the steps that the researcher will take to achieve the research aims.
The research objectives need to be far more specific (higher resolution) and actionable than the research aims. In fact, it’s always a good idea to craft your research objectives using the “SMART” criteria. In other words, they should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant and time-bound”.
Research Objectives: Examples
Let’s look at two examples of research objectives. We’ll stick with the topic and research aims we mentioned previously.
For the digital transformation topic:
To observe the retail HR employees throughout the digital transformation. To assess employee perceptions of digital transformation in retail HR. To identify the barriers and facilitators of digital transformation in retail HR.
And for the student wellness topic:
To determine whether student self-care predicts the well-being score of engineering graduate students. To determine whether student support predicts the well-being score of engineering students. To assess the interaction between student self-care and student support when predicting well-being in engineering graduate students.
As you can see, these research objectives clearly align with the previously mentioned research aims and effectively translate the low-resolution aims into (comparatively) higher-resolution objectives and action points . They give the research project a clear focus and present something that resembles a research-based “to-do” list.


Research Questions: What are they?
Finally, we arrive at the all-important research questions. The research questions are, as the name suggests, the key questions that your study will seek to answer . Simply put, they are the core purpose of your dissertation, thesis, or research project. You’ll present them at the beginning of your document (either in the introduction chapter or literature review chapter) and you’ll answer them at the end of your document (typically in the discussion and conclusion chapters).
The research questions will be the driving force throughout the research process. For example, in the literature review chapter, you’ll assess the relevance of any given resource based on whether it helps you move towards answering your research questions. Similarly, your methodology and research design will be heavily influenced by the nature of your research questions. For instance, research questions that are exploratory in nature will usually make use of a qualitative approach, whereas questions that relate to measurement or relationship testing will make use of a quantitative approach.
Let’s look at some examples of research questions to make this more tangible.
Research Questions: Examples
Again, we’ll stick with the research aims and research objectives we mentioned previously.
For the digital transformation topic (which would be qualitative in nature):
How do employees perceive digital transformation in retail HR? What are the barriers and facilitators of digital transformation in retail HR?
And for the student wellness topic (which would be quantitative in nature):
Does student self-care predict the well-being scores of engineering graduate students? Does student support predict the well-being scores of engineering students? Do student self-care and student support interact when predicting well-being in engineering graduate students?
You’ll probably notice that there’s quite a formulaic approach to this. In other words, the research questions are basically the research objectives “converted” into question format. While that is true most of the time, it’s not always the case. For example, the first research objective for the digital transformation topic was more or less a step on the path toward the other objectives, and as such, it didn’t warrant its own research question.
So, don’t rush your research questions and sloppily reword your objectives as questions. Carefully think about what exactly you’re trying to achieve (i.e. your research aim) and the objectives you’ve set out, then craft a set of well-aligned research questions . Also, keep in mind that this can be a somewhat iterative process , where you go back and tweak research objectives and aims to ensure tight alignment throughout the golden thread.
The importance of strong alignment
Alignment is the keyword here and we have to stress its importance . Simply put, you need to make sure that there is a very tight alignment between all three pieces of the golden thread. If your research aims and research questions don’t align, for example, your project will be pulling in different directions and will lack focus . This is a common problem students face and can cause many headaches (and tears), so be warned.
Take the time to carefully craft your research aims, objectives and research questions before you run off down the research path. Ideally, get your research supervisor/advisor to review and comment on your golden thread before you invest significant time into your project, and certainly before you start collecting data .
Recap: The golden thread
In this post, we unpacked the golden thread of research, consisting of the research aims , research objectives and research questions . You can jump back to any section using the links below.
As always, feel free to leave a comment below – we always love to hear from you. Also, if you’re interested in 1-on-1 support, take a look at our private coaching service here.

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
You Might Also Like:

39 Comments
Thank you very much for your great effort put. As an Undergraduate taking Demographic Research & Methodology, I’ve been trying so hard to understand clearly what is a Research Question, Research Aim and the Objectives in a research and the relationship between them etc. But as for now I’m thankful that you’ve solved my problem.
Well appreciated. This has helped me greatly in doing my dissertation.
An so delighted with this wonderful information thank you a lot.
so impressive i have benefited a lot looking forward to learn more on research.
I am very happy to have carefully gone through this well researched article.
Infact,I used to be phobia about anything research, because of my poor understanding of the concepts.
Now,I get to know that my research question is the same as my research objective(s) rephrased in question format.
I please I would need a follow up on the subject,as I intends to join the team of researchers. Thanks once again.
Thanks so much. This was really helpful.
I know you pepole have tried to break things into more understandable and easy format. And God bless you. Keep it up
i found this document so useful towards my study in research methods. thanks so much.
This is my 2nd read topic in your course and I should commend the simplified explanations of each part. I’m beginning to understand and absorb the use of each part of a dissertation/thesis. I’ll keep on reading your free course and might be able to avail the training course! Kudos!
Thank you! Better put that my lecture and helped to easily understand the basics which I feel often get brushed over when beginning dissertation work.
This is quite helpful. I like how the Golden thread has been explained and the needed alignment.
This is quite helpful. I really appreciate!
The article made it simple for researcher students to differentiate between three concepts.
Very innovative and educational in approach to conducting research.
I am very impressed with all these terminology, as I am a fresh student for post graduate, I am highly guided and I promised to continue making consultation when the need arise. Thanks a lot.
A very helpful piece. thanks, I really appreciate it .
Very well explained, and it might be helpful to many people like me.
Wish i had found this (and other) resource(s) at the beginning of my PhD journey… not in my writing up year… 😩 Anyways… just a quick question as i’m having some issues ordering my “golden thread”…. does it matter in what order you mention them? i.e., is it always first aims, then objectives, and finally the questions? or can you first mention the research questions and then the aims and objectives?
Thank you for a very simple explanation that builds upon the concepts in a very logical manner. Just prior to this, I read the research hypothesis article, which was equally very good. This met my primary objective.
My secondary objective was to understand the difference between research questions and research hypothesis, and in which context to use which one. However, I am still not clear on this. Can you kindly please guide?
In research, a research question is a clear and specific inquiry that the researcher wants to answer, while a research hypothesis is a tentative statement or prediction about the relationship between variables or the expected outcome of the study. Research questions are broader and guide the overall study, while hypotheses are specific and testable statements used in quantitative research. Research questions identify the problem, while hypotheses provide a focus for testing in the study.
Exactly what I need in this research journey, I look forward to more of your coaching videos.
This helped a lot. Thanks so much for the effort put into explaining it.
What data source in writing dissertation/Thesis requires?
What is data source covers when writing dessertation/thesis
This is quite useful thanks
I’m excited and thankful. I got so much value which will help me progress in my thesis.
where are the locations of the reserch statement, research objective and research question in a reserach paper? Can you write an ouline that defines their places in the researh paper?
Very helpful and important tips on Aims, Objectives and Questions.
Thank you so much for making research aim, research objectives and research question so clear. This will be helpful to me as i continue with my thesis.
Thanks much for this content. I learned a lot. And I am inspired to learn more. I am still struggling with my preparation for dissertation outline/proposal. But I consistently follow contents and tutorials and the new FB of GRAD Coach. Hope to really become confident in writing my dissertation and successfully defend it.
As a researcher and lecturer, I find splitting research goals into research aims, objectives, and questions is unnecessarily bureaucratic and confusing for students. For most biomedical research projects, including ‘real research’, 1-3 research questions will suffice (numbers may differ by discipline).
Awesome! Very important resources and presented in an informative way to easily understand the golden thread. Indeed, thank you so much.
Well explained
The blog article on research aims, objectives, and questions by Grad Coach is a clear and insightful guide that aligns with my experiences in academic research. The article effectively breaks down the often complex concepts of research aims and objectives, providing a straightforward and accessible explanation. Drawing from my own research endeavors, I appreciate the practical tips offered, such as the need for specificity and clarity when formulating research questions. The article serves as a valuable resource for students and researchers, offering a concise roadmap for crafting well-defined research goals and objectives. Whether you’re a novice or an experienced researcher, this article provides practical insights that contribute to the foundational aspects of a successful research endeavor.
A great thanks for you. it is really amazing explanation. I grasp a lot and one step up to research knowledge.
I really found these tips helpful. Thank you very much Grad Coach.
I found this article helpful. Thanks for sharing this.
thank you so much, the explanation and examples are really helpful
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
- Affiliate Program

- UNITED STATES
- 台灣 (TAIWAN)
- TÜRKIYE (TURKEY)
- Academic Editing Services
- - Research Paper
- - Journal Manuscript
- - Dissertation
- - College & University Assignments
- Admissions Editing Services
- - Application Essay
- - Personal Statement
- - Recommendation Letter
- - Cover Letter
- - CV/Resume
- Business Editing Services
- - Business Documents
- - Report & Brochure
- - Website & Blog
- Writer Editing Services
- - Script & Screenplay
- Our Editors
- Client Reviews
- Editing & Proofreading Prices
- Wordvice Points
- Partner Discount
- Plagiarism Checker
- APA Citation Generator
- MLA Citation Generator
- Chicago Citation Generator
- Vancouver Citation Generator
- - APA Style
- - MLA Style
- - Chicago Style
- - Vancouver Style
- Writing & Editing Guide
- Academic Resources
- Admissions Resources
Where to Put the Research Question in a Paper
Silke Haidekker has a PhD in Pharmacology from the University of Hannover. She is a Clinical Research Associate in multiple pharmaceutical companies in Germany and the USA. She now works as a full-time medical translator and writer in a small town in Georgia.
Of Rats and Panic Attacks: A Doctoral Student’s Tale
You would probably agree that the time spent writing your PhD dissertation or thesis is not only a time of taking pride or even joy in what you do, but also a time riddled with panic attacks of different varieties and lengths. When I worked on my PhD thesis in pharmacology in Germany many years back, I had my first panic attack as I first learned how to kill rats for my experiments with a very ugly tool called a guillotine! After that part of the procedure, I was to remove and mash their livers, spike them with Ciclosporin A (an immunosuppressive agent), and then present the metabolites by high-pressure liquid chromatography.
Many rats later, I had another serious panic attack. It occurred at the moment my doctoral adviser told me to write my first research paper on the Ciclosporin A metabolites I had detected in hundreds of slimy mashes of rat liver. Sadly, this second panic attack led to a third one that was caused by living in the pre-internet era, when it was not as easy to access information about how to write research papers .
How I got over writing my first research paper is now ancient history. But it was only years later, living in the USA and finally being immersed in the language of most scientific research papers, that my interest in the art of writing “good” research papers was sparked during conferences held by the American Medical Writers Association , as well as by getting involved in different writing programs and academic self-study courses.
How to State the Research Question in the Introduction Section
Good writing begins with clearly stating your research question (or hypothesis) in the Introduction section —the focal point on which your entire paper builds and unfolds in the subsequent Methods, Results, and Discussion sections . This research question or hypothesis that goes into the first section of your research manuscript, the Introduction, explains at least three major elements:
a) What is known or believed about the research topic?
B) what is still unknown (or problematic), c) what is the question or hypothesis of your investigation.
Some medical writers refer to this organizational structure of the Introduction as a “funnel shape” because it starts broadly, with the bigger picture, and then follows one scientifically logical step after the other until finally narrowing down the story to the focal point of your research at the end of the funnel.
Let’s now look in greater detail at a research question example and how you can logically embed it into the Introduction to make it a powerful focal point and ignite the reader’s interest about the importance of your research:
a) The Known
You should start by giving your reader a brief overview of knowledge or previous studies already performed in the context of your research topic.
The topic of one of my research papers was “investigating the value of diabetes as an independent predictor of death in people with end-stage renal disease (ESRD).” So in the Introduction, I first presented the basic knowledge that diabetes is the leading cause of end-stage renal disease (ESRD) and thus made the reader better understand our interest in this specific study population. I then presented previous studies already showing that diabetes indeed seems to represent an independent risk factor for death in the general population. However, very few studies had been performed in the ESRD population and those only yielded controversial results.
Example : “It seems well established that there is a link between diabetic nephropathy and hypertensive nephropathy and end-stage renal disease (ESRD) in Western countries. In 2014, 73% of patients in US hospitals had comorbid ESRD and type 2 diabetes (1, 2, 3)…”
b) The Unknown
In our example, this “controversy” flags the “unknown” or “problematic” and therefore provides strong reasons for why further research is justified. The unknown should be clearly stated or implied by using phrases such as “were controversial” (as in our example), “…has not been determined,” or “…is unclear.” By clearly stating what is “unknown,” you indicate that your research is new. This creates a smooth transition into your research question.
Example : “However, previous studies have failed to isolate diabetes as an independent factor, and thus much remains unknown about specific risk factors associated with both diabetes and ESRD .”
c) The Research Question (Hypothesis)
Your research question is the question that inevitably evolves from the deficits or problems revealed in the “Unknown” and clearly states the goal of your research. It is important to describe your research question in just one or two short sentences, but very precisely and including all variables studied, if applicable. A transition should be used to mark the transition from the unknown to the research question using one word such as “therefore” or “accordingly,” or short phrases like “for this reason” or “considering this lack of crucial information.”
In our example, we stated the research question as follows:
Example : “Therefore, the primary goal of our study was to perform a Kaplan-Meier survival study and to investigate, by means of the Cox proportional hazard model, the value of diabetes as an independent predictor of death in diabetic patients with ESRD.”
Note that the research question may include the experimental approach of the study used to answer the research question.
Another powerful way to introduce the research question is to state the research question as a hypothesis so that the reader can more easily anticipate the answer. In our case, the question could be put as follows:
Example : “To test the hypothesis that diabetes is an independent predictor of death in people with ESRD, we performed a Kaplan-Survival study and investigated the value of diabetes by means of the Cox proportional hazard model.”
Note that this sentence leads with an introductory clause that indicates the hypothesis itself, transitioning well into a synopsis of the approach in the second half of the sentence.
The generic framework of the Introduction can be modified to include, for example, two research questions instead of just one. In such a case, both questions must follow inevitably from the previous statements, meaning that the background information leading to the second question cannot be omitted. Otherwise, the Introduction will get confusing, with the reader not knowing where that question comes from.
Begin with your research purpose in mind
To conclude, here is my simple but most important advice for you as a researcher preparing to write a scientific paper (or just the Introduction of a research paper) for the first time: Think your research question through precisely before trying to write it down; have in mind the reasons for exactly why you wanted to do this specific research, what exactly you wanted to find out, and how (by which methods) you did your investigation. If you have the answers to these questions in mind (or even better, create a comprehensive outline ) before starting the paper, the actual writing process will be a piece of cake and you will finish it “like a rat up a drainpipe”! And hopefully with no panic attacks.
Wordvice Resources
Before submitting your master’s thesis or PhD dissertation to academic journals for publication, be sure to receive proofreading services (including research paper editing , manuscript editing , thesis editing , and dissertation editing ) to ensure that your research writing is error-free. Impress your journal editor and get into the academic journal of your choice.

The Plagiarism Checker Online For Your Academic Work
Start Plagiarism Check
Editing & Proofreading for Your Research Paper
Get it proofread now
Online Printing & Binding with Free Express Delivery
Configure binding now
- Academic essay overview
- The writing process
- Structuring academic essays
- Types of academic essays
- Academic writing overview
- Sentence structure
- Academic writing process
- Improving your academic writing
- Titles and headings
- APA style overview
- APA citation & referencing
- APA structure & sections
- Citation & referencing
- Structure and sections
- APA examples overview
- Commonly used citations
- Other examples
- British English vs. American English
- Chicago style overview
- Chicago citation & referencing
- Chicago structure & sections
- Chicago style examples
- Citing sources overview
- Citation format
- Citation examples
- College essay overview
- Application
- How to write a college essay
- Types of college essays
- Commonly confused words
- Definitions
- Dissertation overview
- Dissertation structure & sections
- Dissertation writing process
- Graduate school overview
- Application & admission
- Study abroad
- Master degree
- Harvard referencing overview
- Language rules overview
- Grammatical rules & structures
- Parts of speech
- Punctuation
- Methodology overview
- Analyzing data
- Experiments
- Observations
- Inductive vs. Deductive
- Qualitative vs. Quantitative
- Types of validity
- Types of reliability
- Sampling methods
- Theories & Concepts
- Types of research studies
- Types of variables
- MLA style overview
- MLA examples
- MLA citation & referencing
- MLA structure & sections
- Plagiarism overview
- Plagiarism checker
- Types of plagiarism
- Printing production overview
- Research bias overview
- Types of research bias
- Example sections
- Types of research papers
- Research process overview
- Problem statement
- Research proposal
- Research topic
- Statistics overview
- Levels of measurment
- Frequency distribution
- Measures of central tendency
- Measures of variability
- Hypothesis testing
- Parameters & test statistics
- Types of distributions
- Correlation
- Effect size
- Hypothesis testing assumptions
- Types of ANOVAs
- Types of chi-square
- Statistical data
- Statistical models
- Spelling mistakes
- Tips overview
- Academic writing tips
- Dissertation tips
- Sources tips
- Working with sources overview
- Evaluating sources
- Finding sources
- Including sources
- Types of sources
Your Step to Success
Plagiarism Check within 10min
Printing & Binding with 3D Live Preview
Research Questions – Definition, Examples & Tips
How do you like this article cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

At the heart of every research endeavor lies a fundamental driving force: the research question. It not only defines the scope and direction of inquiry, it also inspires people to seek knowledge. In the complex journey of the research process , key questions act as guiding stars. In this article, we’ll cover everything you need to know about research questions and provide various examples.
Inhaltsverzeichnis
- 1 Research Questions in a nutshell
- 2 Definition: Research Question
- 3 Characteristics of a Research Question
- 4 How to Create a Research Question
- 5 Types of Research Questions
- 6 Example Questions
- 7 Research Frameworks
- 8 Dos & Donts
- 9 Sub-Questions
- 10 Tips for a Good Research Question
Research Questions in a nutshell
A research question is a clear and concise inquiry around which you center a research study. It helps to define the scope of the study and provides a basis for gathering and analyzing a variety of data.
Definition: Research Question
A research question is a concise inquiry that guides the direction of a research study or investigation. It articulates the specific type of subject that the researcher aims to explore, often framed in a way that suggests investigation or analysis . It serves as a fundamental element in the research process, guiding the selection of appropriate methodologies, the collection of evidence, and the interpretation of results. In essence, a research question serves as the starting point for scholarly inquiry, driving the pursuit of knowledge and understanding within a particular field.
Characteristics of a Research Question
The characteristics of a research question play a pivotal role in shaping the direction and success of a research study. The inquiry not only guides the research process, but also ensures its effectiveness in addressing key issues within the field of study.
It should serve three key purposes:
- Interesting : It should stimulate curiosity and appeal from both the researcher and the audience, motivating researchers to explore the topic further. It also increases the likelihood of commitment from both sides, fostering a deeper understanding and appreciation of the research topic.
- Well-defined : A well-defined research question provides clarity and focus, ensuring that the research study addresses a specific aspect of the topic. This helps avoid ambiguity and ensures that the research process is coherent and purposeful.
- Tractable : By ensuring tractability, researchers can conduct the study effectively, maximizing the likelihood of achieving meaningful results. Tractable research questions are also more likely to lead to successful completion of the study, avoiding setbacks due to unattainable goals.
Furthermore, a good research topic should answer three questions:
- Why is this question significant within the context of the field?
- How does your research build upon and enhance the current body of literature?
- What tangible outcomes can be expected if the question is thoroughly investigated and answered?
By answering these questions and ensuring that your research question is interesting, well-defined, and tractable, you can establish the relevance and significance of your research within the field.
How to Create a Research Question
Formulating an impactful research inquiry can be quite difficult. Nevertheless, by employing a comprehensive multistep approach, this task may turn out to be more manageable for you.
1. Identify a broad topic
Begin by identifying a broad area of interest within your field of study and generate questions based on curiosity and knowledge gaps. This could be based on current trends in the field or gaps in existing literature.
2. Conduct background research
Explore existing literature related to your topic to understand what has already been studied and what questions remain unanswered. This will help you identify potential gaps or areas for further exploration, and narrow your focus . Consider the characteristics mentioned earlier.
3. Consider your audience
Reflect on who your specific target audience is — whether it’s academic researchers or the general public. Tailor your research question to be relevant and accessible for your primary audience, considering their interests and level of expertise.
4. Narrow down the focus
Gradually narrow down your topic to a specific research question or a couple of questions based on the gaps found in existing research.
5. Define your questions
Now that you have found your niche, consider all the steps above and start asking open-ended “how” and “why” questions about your topic. A framework such as SMART Goals , PICOT , or FINER , which we will elaborate on in a later section more thoroughly, might be helpful when generating your key questions.
6. Evaluate your question
Now that you have written down your questions, evaluate them to establish if they are effective or if they need further refinement . For this step, look at the characteristics above again, and determine if they answer all the questions and check all the boxes. Is the research question well-defined and interesting to you and your audience? Think about the possible paths your research could take, which is the question, that effectively captures the essence of your research and aligns with your overarching objectives? It shouldn’t be too broad and also not easily answerable with quick searches.
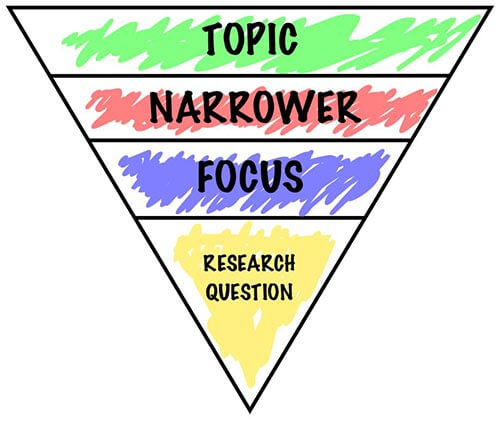
Types of Research Questions
Research questions can be classified into various types, depending on the types of studies to be undertaken. Below, we will discuss each one of them, and their specifics.
Qualitative
Quantitative, mixed-methods.
A qualitative question is concerned with comprehending a phenomenon , and focuses on finding , explaining , and exploring . Qualitative research is primarily used in social sciences and uses open-ended research questions, and seeks to uncover rich and descriptive data .
The most common types of qualitative questions include:
- Exploratory questions , which seek to understand without influencing the results. The objective is to investigate an issue that has limited existing knowledge, and is typically conducted at the preliminary stages of a research process without research bias .
- Predictive questions , which seek to understand the intent or future outcome around a topic. The objective here it to use past information to predict reactions to hypothetical events.
- Interpretive questions , which aim to understand people’s behavior in a natural setting. The objective is to gather feedback on a group’s behavior without affecting the outcome.
A quantitative question is used to prove or disprove a researcher’s hypothesis through descriptions , comparisons , and relationships . It typically involves the population to be studied, identifying independent vs. dependent variables , and the research design. Quantitative questions are created to express the causality between variables and whether this relationship is relevant.
The most common types of quantitative questions include:
- Descriptive questions , which aim to explain when, where, why, or how something occurred, are the most basic type of quantitative research. They use numerical data and statistical analysis to describe a phenomenon, and their objective is to provide a clear and detailed description of a particular phenomenon.
- Comparative questions are used to compare groups or dependent variables to identify similarities, differences, or relationships between them. Their objective is to uncover the “how” or “why” of a topic by examining variations or relationships.
- Relationship-based questions , such as causal and correlational questions, try to answer whether one variable influences another. These types of questions are used in experimental or in quasi-experimental design studies, to focus on understanding how they are connected or influence each other.
Mixed methods research involves the integration of both qualitative and quantitative approaches within a single study, and for this reason, it’s a popular research method for researching nowadays. Mixed methods research combines both quantitative and qualitative data to explore a research question more thoroughly, and is often used in the behavioral, health, and social sciences.
Mixed methods research questions can help you achieve a more comprehensive picture than a standalone quantitative or qualitative question. However, they can be difficult to implement and come with the same risk of research bias as standalone studies.
Example Questions
In this section, we will provide you with numerous research question examples for each type of quantitative, qualitative, and mixed-method question.
Exploratory Question
- What are the factors influencing employee satisfaction in a new startup company?
Predictive Question
- How much can high schoolers’ GPA and grades predict their academic college performance?
Interpretive Question
- How do cultural beliefs shape peoples view of mental health and help-seeking behaviors?
Descriptive Question
- What are the demographics of students enrolled in online courses at a university?
Comparative Question
- How does lecture-style teaching compare to interactive learning in math comprehension?
Relationship-based Question
- What’s the correlation between social media use and young adults’ feelings of loneliness?
Mixed-Methods Questions
- How does the implementation of a new online learning platform (quantitative) impact student engagement and satisfaction (qualitative) in undergraduate courses?
- How do the perceptions of teachers (qualitative) and the academic performance of students (quantitative) vary across different teaching methodologies?
- How do cultural beliefs and values (qualitative) influence consumer purchasing behavior (quantitative) in the cosmetics industry?
Sample Format
Crafting effective research inquiries is most important for guiding your study and achieving your research goals. Below, you’ll find various question formats, designed to inspire and guide your inquiry. Refer to the accompanying picture for a comprehensive range of question formats suitable for a variety of research purposes and contexts.

Research Frameworks
There are three types of frameworks you can use as foundational elements to ensure that your research question is succinct.
- The PICO framework, which stands for P opulation, I ntervention, C omparison, and O utcome, is commonly used in healthcare research to structure clinical questions. It helps researchers define the key elements of a research question, including the population of interest, the intervention, or exposure being studied, the comparison group, and the outcome of interest.
- The SMART framework, which stands for S pecific, M easurable, A chievable, R elevant, and T ime-bound, is widely used and helps ensure that the question is clear, quantifiable, feasible, aligned with the research objectives, and has a defined time frame for completion.
- The FINER framework, which stands for F easible, I nteresting, N ovel, E thical, and R elevant, provides criteria for evaluating the quality and appropriateness of research questions. It ensures that the question is feasible to address, interesting and relevant to the field, innovative, ethically sound, and directly related tot the research objectives.
Below, we have illustrated each framework with appropriate questions you can ask yourself in order to find out if your research question can be improved.
Dos & Donts
Below you’ll find an illustration depicting what you should do and what you should not do when it comes to research questions.
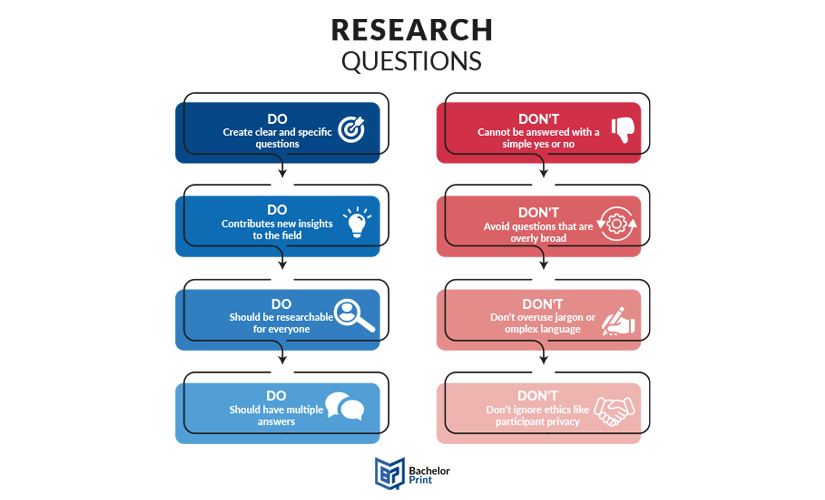
Below you’ll find a table with numerous good and bad examples of research questions together with explanations for each of them.
Sub-Questions
Sub-questions can be essential in research for clarifying complex topics and providing depth to the analysis when your main research question can’t be answered all at once. They are optional and should be used only if necessary to address the main question. If the main question is straightforward, sub-questions can be omitted. Let’s say that the main research question is “How has the transition to online schooling during COVID-19 pandemic affected sophomore and junior students’ academic performance and engagement?”. Some potential sub-questions could be:
- What impact has online schooling had on grades and test scores during the pandemic?
- How has student participation in classes changed with online schooling?
- How effectively have teachers adapted their instruction methods for online teaching?
Tips for a Good Research Question
Crafting a good research inquiry is a critical step in conducting a successful research project, as we have learned. The selection of successful research topics is crucial for guiding the direction of a study and ensuring that the research addresses relevant issues within the field. Here are some general tips to help you develop a strong research question.
- Be specific and clear : A good question should allow for focused study and straightforward answers. Avoid being broad or vague since this could lead to a sprawling investigation.
- Make it measurable : Your research question should be framed in a way that allows for gathering and analyzing data. It should be possible to measure the aspects of the question through available methods.
- Ensure relevance : The question should be relevant to current issues or contribute to a field of study that interests you. It should address a gap in knowledge or add a new perspective to existing studies.
- Test your question : Before finalizing your research question, test it. Discuss it with peers, mentors, or through preliminary literature reviews to ensure it is focused and engaging.
The most important thing is that whatever subject you focus on, it should be interesting to you and your field. Because that way, the writing and analyzing process will be much more enjoyable and rewarding.
Note: Do not figure out your research question after you have finished your research paper.

What are 5 good research questions?
- What impact does incorporating technology into classroom instruction have on student engagement and academic performance in elementary schools?
- How does mindfulness-based stress reduction therapy compare to cognitive-behavioral therapy in reducing symptoms of anxiety and depression among young adults?
- What are the long-term effects of microplastic pollution on marine biodiversity in coastal ecosystems, and how can we mitigate these effects?
- To what extent do socioeconomic factors influence access to healthcare services among marginalized communities, and what policy interventions could address these disparities?
- How do leadership styles and organizational culture impact employee job satisfaction rates in remote work settings?
What is a research question?
A well-developed research question identifies the main issue that the researchers want to investigate and provides a framework for gathering data to address that issue and also proposes a conclusive solution depending on the research type. It serves as a foundation for the writing process and guides the research project.
What types of research questions are there?
Research questions can be classified into three types:
- Descriptive research questions
- Quantitative research questions
- Mixed-methods research questions
What are 6 research questions?
- Descriptive questions
- Comparative questions
- Relationship-based questions
- Exploratory questions
- Predictive questions
- Interpretive questions
We use cookies on our website. Some of them are essential, while others help us to improve this website and your experience.
- External Media
Individual Privacy Preferences
Cookie Details Privacy Policy Imprint
Here you will find an overview of all cookies used. You can give your consent to whole categories or display further information and select certain cookies.
Accept all Save
Essential cookies enable basic functions and are necessary for the proper function of the website.
Show Cookie Information Hide Cookie Information
Statistics cookies collect information anonymously. This information helps us to understand how our visitors use our website.
Content from video platforms and social media platforms is blocked by default. If External Media cookies are accepted, access to those contents no longer requires manual consent.
Privacy Policy Imprint
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Welcome to the Purdue Online Writing Lab

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
The Online Writing Lab at Purdue University houses writing resources and instructional material, and we provide these as a free service of the Writing Lab at Purdue. Students, members of the community, and users worldwide will find information to assist with many writing projects. Teachers and trainers may use this material for in-class and out-of-class instruction.
The Purdue On-Campus Writing Lab and Purdue Online Writing Lab assist clients in their development as writers—no matter what their skill level—with on-campus consultations, online participation, and community engagement. The Purdue Writing Lab serves the Purdue, West Lafayette, campus and coordinates with local literacy initiatives. The Purdue OWL offers global support through online reference materials and services.
A Message From the Assistant Director of Content Development
The Purdue OWL® is committed to supporting students, instructors, and writers by offering a wide range of resources that are developed and revised with them in mind. To do this, the OWL team is always exploring possibilties for a better design, allowing accessibility and user experience to guide our process. As the OWL undergoes some changes, we welcome your feedback and suggestions by email at any time.
Please don't hesitate to contact us via our contact page if you have any questions or comments.
All the best,
Social Media
Facebook twitter.
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
34 Research Questions
Identifying what you know & don’t know.
Once you have narrowed down your research topic and done some preliminary background reading on your topic, it’s time to start thinking about—and writing down—what you already know about your topic and what you are interested in finding out. Identifying the gaps in your knowledge will help you to create research questions that will guide your research. For instance, if you have decided to research the effects of divorce on children, you’d want to first think about what knowledge you already have on that topic. Next, write down what you do not know but are curious to find out.
What I know:
- Divorce is common in the United States
- Sometimes children are negatively affected by their parents getting divorced
What I don’t know:
- Is there a certain age that children are more prone to the negative effects of divorce?
- Can children carry negative effects of divorce with them into adulthood?
- How can divorce impact academic performance?
- How can the effects of divorce be mitigated?
Though you may not be aware of it, you are mentally engaging in this process many times throughout the day. The process of seeking information for everyday questions is a bit different than for research questions, however. Take a look at the examples of regular questions and research questions below. While regular questions are easily answered by a quick online search (e.g., Google), research questions will take more exploration.
Examples: Regular vs. Research Questions
Regular Question : What time is my movie showing at Lennox on Friday?
Research Question : How do “sleeper” films end up having outstanding attendance figures?
Regular Question : What can I do about my insomnia?
Research Question : How do flights more than 16 hours long affect the reflexes of commercial jet pilots?
Regular Question : How many children in the U.S. have allergies?
Research Question : How does his or her country of birth affect a child’s chances of developing asthma?
Regular Question : What year was metformin approved by the U.S. Food and Drug administration?
Research Question : Why are nanomedicines, such as doxorubicin, worth developing?
Regular Question : Could citizens register to vote at branches of the Columbus Public Library in 2016?
Research Question : How do public libraries in the United States support democracy?
Choosing the Right Question
Once you have a list of several aspects of your topic that you are curious about, choose one that interests you most and create a research question from it. Be sure to choose something that aligns with the parameters of your assignment and that you believe is feasible to research given the amount of time and resources you have access to. Research questions that are too vague will leave you swimming in a sea of irrelevant information, while a research question that is too specific will make it very difficult to find enough information sources to support your research.
Too broad: What is the impact of divorce on academic performance?
Too narrow: What is the impact of divorce on female student’s grades during fifth grade in the United States?
Just right: How can divorce affect a student’s GPA in high school?
Examples adapted from “ Regular vs. Research Questions ” by Teaching & Learning, Ohio State University Libraries, licensed under CC BY 4.0
A question that research sets out to answer. Research questions should be not be able to be answered with a simple "yes" or "no" and should be clear, concise, and focused.
Introduction to College Research Copyright © by Walter D. Butler; Aloha Sargent; and Kelsey Smith is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Differences in quality of anticoagulation care delivery according to ethnoracial group in the United States: A scoping review
- Open access
- Published: 11 May 2024
Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article

- Sara R. Vazquez ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-9267-8980 1 ,
- Naomi Y. Yates 2 ,
- Craig J. Beavers 3 , 4 ,
- Darren M. Triller 3 &
- Mary M. McFarland 5
64 Accesses
2 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
Anticoagulation therapy is standard for conditions like atrial fibrillation, venous thromboembolism, and valvular heart disease, yet it is unclear if there are ethnoracial disparities in its quality and delivery in the United States. For this scoping review, electronic databases were searched for publications between January 1, 2011 – March 30, 2022. Eligible studies included all study designs, any setting within the United States, patients prescribed anticoagulation for any indication, outcomes reported for ≥ 2 distinct ethnoracial groups. The following four research questions were explored: Do ethnoracial differences exist in 1) access to guideline-based anticoagulation therapy, 2) quality of anticoagulation therapy management, 3) clinical outcomes related to anticoagulation care, 4) humanistic/educational outcomes related to anticoagulation therapy. A total of 5374 studies were screened, 570 studies received full-text review, and 96 studies were analyzed. The largest mapped focus was patients’ access to guideline-based anticoagulation therapy (88/96 articles, 91.7%). Seventy-eight articles made statistical outcomes comparisons among ethnoracial groups. Across all four research questions, 79 articles demonstrated favorable outcomes for White patients compared to non-White patients, 38 articles showed no difference between White and non-White groups, and 8 favored non-White groups (the total exceeds the 78 articles with statistical outcomes as many articles reported multiple outcomes). Disparities disadvantaging non-White patients were most pronounced in access to guideline-based anticoagulation therapy (43/66 articles analyzed) and quality of anticoagulation management (19/21 articles analyzed). Although treatment guidelines do not differentiate anticoagulant therapy by ethnoracial group, this scoping review found consistently favorable outcomes for White patients over non-White patients in the domains of access to anticoagulation therapy for guideline-based indications and quality of anticoagulation therapy management. No differences among groups were noted in clinical outcomes, and very few studies assessed humanistic or educational outcomes.
Graphical Abstract
Scoping Review: Differences in quality of United States anticoagulation care delivery by ethnoracial group. AF = atrial fibrillation; AMS = anticoagulation management service; DOACs = direct oral anticoagulants; INR = international normalized ratio; PSM = patient self-management; PST = patient self-testing
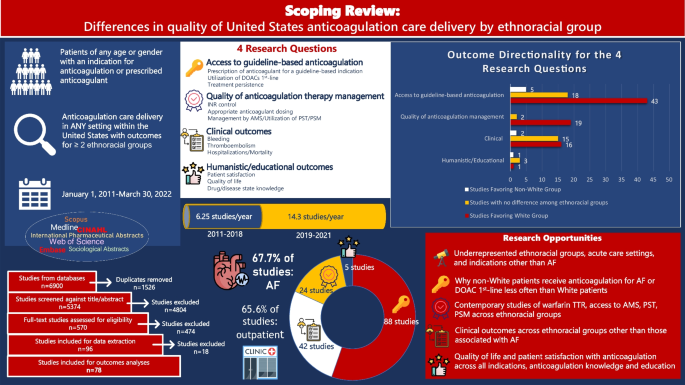
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
It is well-established that in the United States (US) ethnoracial disparities exist in various aspects of health care. Specifically, persons identifying with an ethnoracial minority group may have more challenging access to health care, worse clinical outcomes, and higher dissatisfaction with care compared to White persons [ 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 ]. There are differences by ethnoracial group in the prevalence of the three most common indications for which anticoagulants are prescribed, stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation (AF), treatment of venous thromboembolism (VTE), and valvular heart disease [ 6 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 , 11 , 12 , 13 , 14 , 15 , 16 , 17 ]. Specifically, VTE is most prevalent in Black patients compared to White and Asian patients, whereas AF is most prevalent in White patients compared to Black, Asian, and Hispanic patients [ 9 , 10 , 15 ]. Calcific heart valve disease has the most relevance to the US population, and epidemiologic data has shown that aortic stenosis is more prevalent in White patients compared to Black, Asian, and Hispanic patients [ 17 ]. Despite these epidemiologic differences, there is no evidence to suggest there should be any difference in treatment strategies across ethnoracial patient groups.
While studies have demonstrated genotypic differences that may result in different warfarin dose requirements[ 18 ], and early studies may indicate genotypic differences in direct oral anticoagulant (DOAC) response [ 19 ], no US-based labeling or guidelines recommend a difference in prescription or delivery of anticoagulation care based on race or ethnicity. However, it is unclear if there are in fact differences in the type and quality of anticoagulation therapy, which is standard of care for each of these conditions [ 20 , 21 , 22 , 23 , 24 ]. Anticoagulants remain in the top three classes of drugs causing adverse drug events (primarily bleeding) in the United States, according to the 2014 National Action Plan for Adverse Drug Event Prevention. One of the goals of the National Action Plan was to identify patient populations at higher risk for these adverse drug events to inform the development of targeted harm reduction strategies [ 25 ]. If ethnoracial minority patients are receiving sub-optimal anticoagulation therapy in certain measurable areas of anticoagulation quality, it is vital to highlight the areas of disparity so that these can be explored and care optimized. Anticoagulation providers often have high frequency contact with their patients and can be a reliable connection between disproportionately affected patients and a system in need of change. Systematic reviews of ethnoracial disparities in AF and VTE have been conducted. The AF review assessed AF prevalence among racial groups as well as differences in symptoms and management, including stroke prevention with warfarin or DOACs [ 9 ]. The VTE review specifically assessed VTE prevalence and racial differences in COVID-19 and did report the use of any prophylactic anticoagulation, but this was not part of the analysis [ 26 ]. No review of racial disparities in quality of anticoagulation therapy was found in search results conducted prior to protocol.
In this study we aimed to identify any potential ethnoracial disparities in anticoagulation care quality in the US. The decision to limit the study to a US population was based on our observation that the US has a unique history of interactions between racial and ethnic groups that may not necessarily be reflected by studies conducted in other countries. Additionally, health care delivery systems vary widely across the world, and we wanted to include the data most relevant to the potential racial disparities existing in the US health care system. The term “race” was used to identify a group of people with shared physical characteristics believed to be of common ancestry whereas the term “ethnicity” refers to a group of people with shared cultural traditions [ 27 ]. We recognize these terms may be far more complex. In order to encompass both the physical and cultural aspects of a patient’s identity we have chosen to use the term “ethnoracial” for this study [ 27 ]. Highlighting existing differences will serve as a stimulus for institutions and clinicians to assess current services, implement quality improvement measures, and inform future research efforts to deliver optimal anticoagulation care for all patients. The scoping review protocol was registered December 22, 2021 to Open Science Framework, https://doi.org/10.17605/OSF.IO/9SE7H [ 28 ].
We conducted this scoping review with guidance from the 2020 version of the JBI Manual for Evidence Synthesis and organized to Arksey's five stages: 1) identifying the research question, 2) identifying relevant studies, 3) study selection, 4) charting the data and 5) collating, summarizing and reporting the results [ 29 , 30 ]. For transparency and reproducibility, we followed the PRISMA-ScR and PRISMA-S reporting guidelines in reporting our results [ 31 ]. We used Covidence (Veritas Health Innovation,) an online systematic reviewing platform to screen and select studies. Citation management and duplicate detection and removal was accomplished with EndNote, version 19 (Clarivate Analytics.) Data was charted from our selected studies using REDCap, an electronic data capture tool hosted at the University of Utah [ 32 ].
Literature searching
An information specialist developed and translated search strategies for the online databases using a combination of keywords and controlled subject headings unique to each database along with team feedback. Peer review of the strategies was conducted by library colleagues using the PRESS guidelines. [ 33 ] Electronic databases searched included Medline (Ovid) 2011–2022, Embase (embase.com) 2011–2022, CINAHL Complete (Ebscohost) 2011–2022, Sociological Abstracts (ProQuest) 2011–2022, International Pharmaceutical Abstracts (Ovid) 2011–2022, Scopus (scopus.org) 2011–2022 and Web of Science Core Collection (Clarivate Analytics) 2011–2022. Limits included a date range from January 1, 2011 to March 30—April 19, 2022, as not all database results were exported on the same day. See Supplemental File 1 for detailed search strategies. A search of grey literature was not conducted due to time and resource constraints.
Study Selection
For inclusion, each study required two votes by independent reviewers for screening of titles and abstracts followed by full-text review. A third reviewer provided the deciding vote. Data extraction was performed by two independent reviewers, and consensus on any discrepancies was reached via discussion between the reviewers. The data form was piloted by two team members using sentinel articles prior to data extraction.
Eligible studies included all types of study designs in any setting with a population of patients of any age or gender located within the US who were prescribed anticoagulant therapy for any indication, published between January 1, 2011 – March 30, 2022 in order to capture contemporary and clinically relevant practices.
We defined the following research questions for this scoping review as described in Table 1 .
Studies must have reported any of these anticoagulation care delivery outcomes for at least 2 distinct racial or ethnic groups. We excluded genotyping studies and non-English language articles at full text review, as we had no funding for translation services. In checking references of included studies, no additional studies met inclusion criteria. In accordance with scoping review methodology, no quality assessment of included studies was conducted as our goal was to rapidly map the literature. As this is a scoping review of the literature, no aggregate or pooled analysis was performed; however, for ease of interpretation, when assessing for the directionality of the outcomes in the various studies, we categorized studies into Favoring White Group, Favoring Non-White Group, and No Differences Among Ethnoracial Groups. If studies had mixed outcomes of favoring one group for one outcome and no difference for another, then the study was categorized with the favoring group.
A PRISMA flow diagram in Fig. 1 depicts search results, exclusions, and inclusions. The search strategies retrieved 6900 results with 1526 duplicates removed. Following title and abstract screening of 5374 references, 570 articles received full-text review. The most common reason for the exclusion of 474 studies was that outcomes were not reported for two distinct ethnoracial groups (171 studies). Ninety-six studies underwent data extraction.
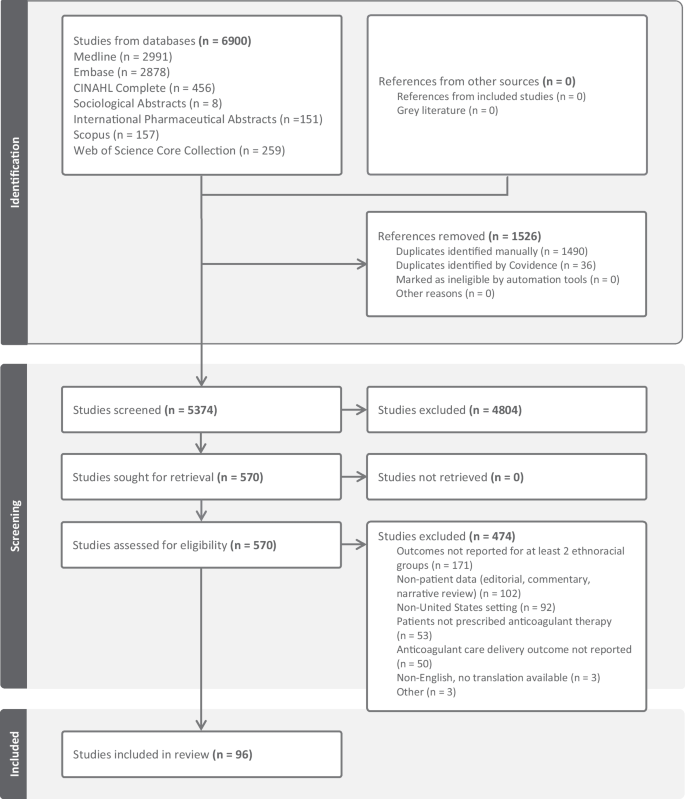
PRISMA Flow Diagram
Study characteristics-overall
Fifty of the 96 studies were published between 2011 and 2018 (an average of 6.25 articles per year that compared outcomes between two ethnoracial groups) and 43 of 96 studies were published in the years 2019–2021 (average 14.3 articles per year; 2022 excluded here because only 4 months of data was captured) (Fig. 2 ). Most studies analyzed an outpatient population (65.6%) for an indication of stroke prevention in AF (67.7%) in patients taking warfarin (71.9%) or DOACs (49.0%). Study population size was heterogenous, ranging from a study size of 24 patients to over 1.3 million patients (median 5,238 patients) in the 69 studies that reported population size by racial group. When stratified by size, 60.9% of the articles in the scoping review (42 articles) represented < 10,000 patients (Table 2 ).
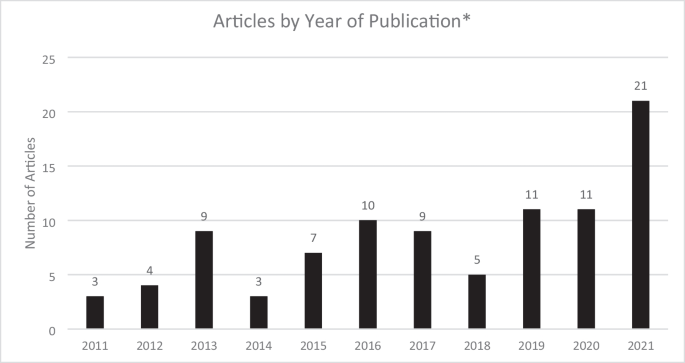
Number of Articles by Publication Year. *2022 excluded from this figure since the search period did not capture the entire year
Study characteristics-by ethnoracial group
There were 50 studies (52.1%) where race or ethnicity was either mentioned in the title or objective of the article, with 24 of these published over the 7-year period 2011–2018 and 26 published over the 3-year period 2019 to first quarter 2022. The method for reporting race or ethnicity was unclear or unspecified in most studies (77.1%) and 16 articles (16.7%) utilized self-reporting of race or ethnicity. Most studies analyzed White or Caucasian racial groups (94.8%), followed by Black or African-American (80.2%), and many studies grouped all other racial groups into an “Other” category (41.7%) (Fig. 3 ).
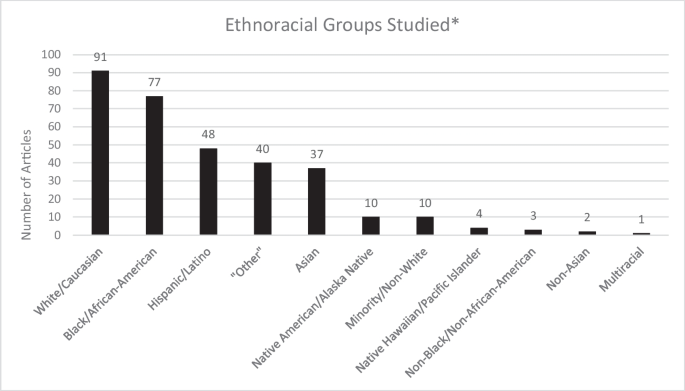
Number of Articles by Ethnoracial Groups. *For study inclusion, a study had to compare outcomes for least two distinct ethnoracial groups
White patients accounted for a median 77% of study populations, Black patients 9.5%, Hispanic/Latino patients 6.2%, “Other” racial groups 5.3%, and Asian patients 2.5%.
Study outcomes-overall
Of the 4 research questions, most studies included in this review analyzed patients’ access to guideline-based anticoagulation therapy (88/96 articles, 91.7%), clinical outcomes (42/96 articles, 43.8%), or quality of anticoagulation management (24/96 articles, 25.0%), while very few addressed humanistic or educational outcomes (5/96 articles, 5.2%) (Fig. 4 ). Many studies addressed multiple outcomes within the single study.
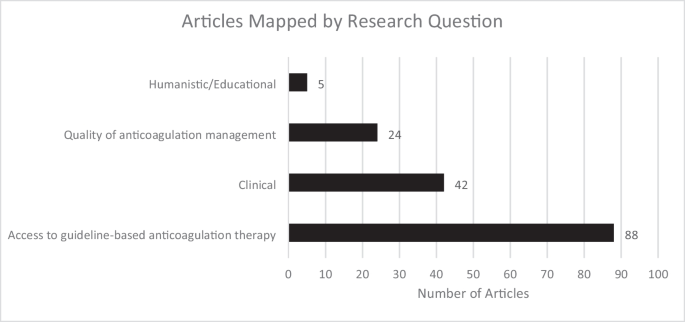
Number of Articles Mapped by Research Question
Seventy-eight of the 96 included studies provided statistical comparisons between ethnoracial groups, and these data are presented below.
Outcomes for research question 1: Do ethnoracial differences exist in access to guideline-based anticoagulation therapy?
Anticoagulation for a guideline-based indication.
This question focused on patients who had an indication for anticoagulation actually receiving an anticoagulant, specifically AF and VTE prophylaxis (based on risk stratification) and acute VTE. The majority of the AF studies (25/34 studies) demonstrated White patients receiving anticoagulation at significantly higher rates compared to non-White patients [ 36 , 37 , 38 , 39 , 40 , 41 , 42 , 43 , 44 , 45 , 46 , 47 , 48 , 49 , 50 , 51 , 52 , 53 , 54 , 55 , 56 , 57 , 58 , 59 , 60 ], while the six VTE studies largely demonstrated no difference among ethnoracial groups [ 61 , 62 , 63 , 64 , 65 , 66 ].
DOACs as first-line therapy for AF or VTE
Eighteen individual studies statistically assessed the outcome of DOAC as first-line therapy (compared to warfarin) for AF (15 studies), VTE treatment (2 studies), or both indications (1 study). Twelve of the 15 AF studies showed a significantly higher proportion of White patients received DOACs as first-line therapy compared to non-White patients [ 36 , 40 , 41 , 42 , 43 , 44 , 45 , 46 , 54 , 55 , 67 , 68 ]. Of those 12, 9 specifically compared White patients to Black patients. Both VTE treatment studies and the study that assessed both AF and VTE indications showed significantly higher DOAC prescribing rates for White patients compared to Black patients [ 69 , 70 , 71 ].
Anticoagulant therapy adherence/persistence
The eight studies that addressed anticoagulation therapy adherence/persistence showed variability in outcome directionality by ethnoracial group: 5 no difference [ 41 , 72 , 73 , 74 , 75 ], 2 showed better treatment adherence/persistence for White patients compared to Black patients[ 76 ] or non-White patients [ 77 ], and one showed better treatment adherence/persistence for White patients compared to Hispanic patients, but no difference in White versus Black patients [ 78 ].
Figure 5 summarizes the outcome directionality for Research Question 1 regarding access to guideline-based anticoagulation therapy. Overall, the areas of disparity identified included anticoagulation for atrial fibrillation and preferential use of DOAC therapy for AF and VTE treatment.
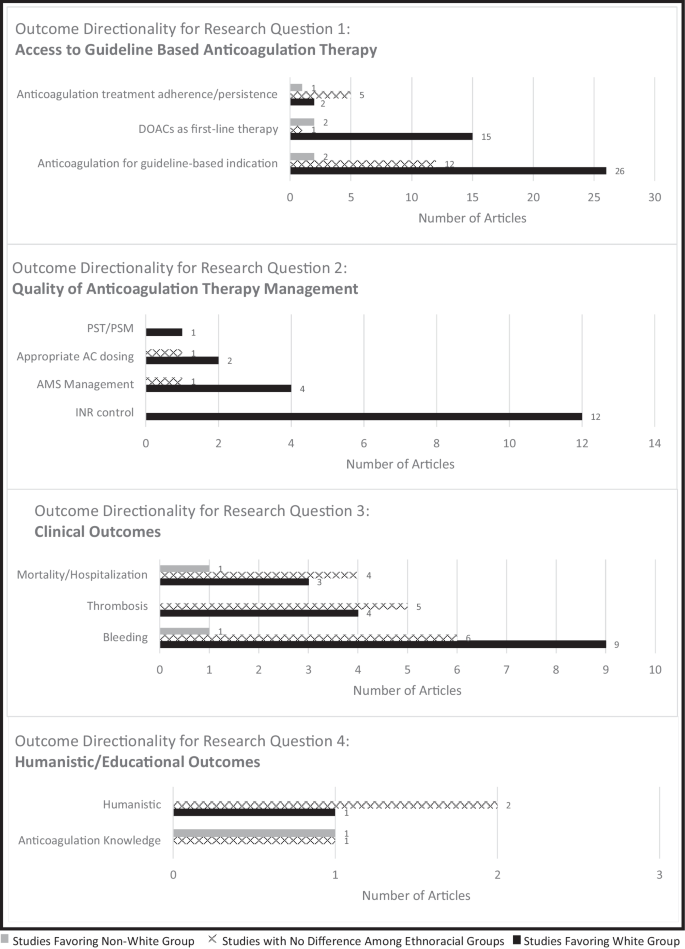
Outcome Directionality for the 4 Research Questions and their Subcategories. AC = anticoagulant; AMS = anticoagulation management service; INR = international normalized ratio; PST = patient self-testing; PSM = patient self-management
Research question 2: Do ethnoracial differences exist in the quality of anticoagulation therapy management?
A total of 21 studies assessed quality of anticoagulation therapy management: Warfarin time in therapeutic range (TTR)/INR (International Normalized Ratio) control 12 studies, appropriate anticoagulant dosing 3 studies, enrollment in an anticoagulation management service 5 studies, and PST/PSM one study.
In statistical comparisons of INR control in warfarin patients, all 12 studies (7 assessed mean or median TTR, 5 assessed other measures of INR control such as days spent above/below range, gaps in INR monitoring) showed White patients had favorable INR control compared to non-White patients (most comparisons included Black patients) [ 41 , 75 , 79 , 80 , 81 , 82 , 83 , 84 , 85 , 86 , 87 ]. Enrollment in an anticoagulation management service was statistically compared among ethnoracial groups in 5 studies, and this opportunity favored White patients compared to other racial groups in four of the five [ 41 , 82 , 86 , 88 ]. Two of the three studies that statistically analyzed appropriate anticoagulant dosing showed a higher rate of appropriate DOAC dosing in White patients compared to non-White patients [ 41 , 89 ], and the third showed no difference among ethnoracial groups for enoxaparin dosing in the emergency department [ 90 ]. The one study assessing access to PST/PSM showed that more White patients used PST compared to Black or Hispanic patients[ 91 ] (Fig. 5 ).
Research question 3: Do ethnoracial differences exist in the clinical outcomes related to anticoagulation care?
Articles assessing clinical outcomes among ethnoracial groups primarily assessed bleeding (15 articles) or thrombosis (9 articles) outcomes, and 8 articles assessing anticoagulation related hospitalization or mortality. One article addressed a net clinical outcome including major bleeding, stroke or systemic embolism, and death from any cause. This was included in the bleeding outcomes category so that it was not double-counted in the other two outcome categories. Additional details about the 24 unique studies that statistically assessed clinical outcomes including the study design, population size, ethnoracial groups studied, anticoagulants used, and statistical outcomes measured can be found in Supplementary Tables 1 and 2 .
Sixteen studies statistically assessed bleeding outcomes of varying definitions (major bleeding 13 studies, clinically relevant non-major bleeding 3 studies, any bleeding 3 studies, bleeding otherwise defined 3 studies). Six studies demonstrated no difference in bleeding outcomes by ethnoracial group [ 55 , 92 , 93 , 94 , 95 , 96 ]9 reported that White patients had lower rates of bleeding compared to Black or Asian patients,[ 53 , 80 , 83 , 85 , 97 , 98 , 99 , 100 , 101 ]. In the remaining study, Asian patients had a more favorable net clinical outcome compared to non-Asian patients [ 102 ].
Nine studies statistically assessed thrombosis outcomes among ethnoracial groups, including stroke/systemic embolism (5 studies), recurrent VTE (3 studies), or any thrombosis (1 study). The stroke outcomes by racial group were heterogeneous, with 3 studies showing better outcomes for White patients compared to Black patients[ 103 , 104 , 105 ] and two studies showing no difference in outcomes when White patients were compared to Non-White patients [ 55 , 95 ]. In three of the four VTE studies there were no differences in outcomes by ethnoracial group [ 61 , 93 , 96 ], and in one study White patients had more favorable outcomes compared to Black patients [ 106 ].
Nine studies assessed anticoagulation-related hospitalizations or mortality by ethnoracial group. Outcomes were mixed, as four studies showed no difference in hospitalizations or mortality among ethnoracial groups,[ 89 , 95 , 96 , 107 ], three studies showed White patients had a lower rate of hospitalizations[ 85 , 105 ] or mortality[ 104 , 105 ] Another study showed lower rate of mortality or hospice after intracranial hemorrhage in Black and Other race patients [ 108 ].(Fig. 5 ).
Research question 4: Do ethnoracial differences exist in the humanistic/educational outcomes related to anticoagulation therapy?
The five studies reporting this category of outcomes were heterogeneous. Of the two studies assessing anticoagulation knowledge, one showed no difference by ethnoracial group [ 109 ], and the other favored the non-White group in appropriately estimating bleeding risk [ 110 ]. One study assessed an atrial fibrillation quality of life score at 2-year follow-up after AF diagnosis and found the outcomes favored White patients [ 79 ]. Another study assessed satisfaction with VTE care and found no difference among ethnoracial groups [ 111 ]. A third study found no difference in the percentage of racial groups having a cost conversation when initiating DOAC therapy (78% Whites, 72.2% non-Whites)[ 112 ] (Fig. 5 ).
Overall outcome directionality for all four research questions is shown in Fig. 6 . A total of 79 articles demonstrated favorable outcomes for White patients compared to non-White patients, 38 articles showed no difference between White and non-White groups, and 8 articles had outcomes favoring non-White groups (the total exceeds the 78 articles with statistical outcomes as many articles reported multiple outcomes). The biggest areas of disparity between White and non-White groups are access to guideline-based anticoagulation therapy and quality of anticoagulation therapy management. Clinical outcomes relating to anticoagulation care had the least difference among ethnoracial groups. Relatively few studies assessed potential ethnoracial disparities in humanistic and educational outcomes.
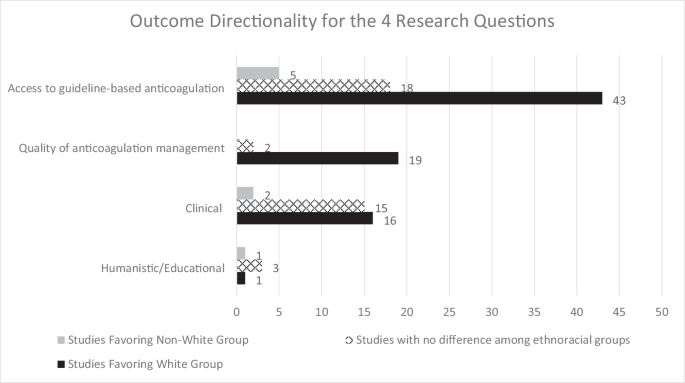
Outcome Directionality for All 4 Research Questions
This scoping review assessing ethnoracial differences in the quality of anticoagulation care and its delivery to patients in the United States encompassed eleven full years of literature and resulted in the inclusion of 96 studies, 78 of which contained statistical outcomes comparisons among ethnoracial groups. The most common reason for study exclusion was that outcomes were not reported for at least two distinct ethnoracial groups. We observed that beginning in 2019 and following the racial unrest of 2020, the density of articles addressing ethnoracial disparities in anticoagulation care more than doubled. During the entire study period, half of studies had race or ethnicity as the focus or objective of the paper, but this was largely driven by articles published after 2019.
Only 16% of included articles documented self-reporting of racial identity, with most of the remainder using an unspecified method for documenting racial identity. It is likely that many studies utilize demographic information extracted from an electronic medical record (EMR), but it is often unclear if that is truly self-reported race. A second element this scoping review identified was that many studies analyzed two or three ethnoracial groups and then categorized all others into a heterogenous “Other” category. For example, frequently studies would categorize patients as White, Black, and “Other.” It is unclear whether those in a racial category labeled as “Other” had an unknown or missing racial identity in the EMR, or intentionally chose not to disclose. It is also likely that study investigators decided to classify ethnoracial groups with lower population sizes into a miscellaneous category. There were few studies (15%) that specifically assessed patients identifying as Native American/Alaska Native, Native Hawaiian/Pacific Islander, and multiracial. While Hispanic/Latino is an ethnicity, most studies categorized it as a separate “race” category. Of the 37 studies that analyzed “Asian” patient populations, none specifically defined “Asian” beyond that. The US Census Bureau defines “Asian” race as a person having origins of the Far East, Southeast Asia, or the Indian subcontinent [ 113 ]. This broad definition encompasses many different ethnicities which could represent variability in health outcomes if better defined and more frequently analyzed. These may be opportunities for EMR systems to improve transparency for how race, ethnicity, and language preference are captured and for those designing research studies to be thoughtful and intentional about analyzing the ethnoracial identities of the study population, perhaps in alignment with the minimum 5 racial categories utilized by the US Census Bureau, the National Institutes of Health, and the Office of Management and Budget (White, Black, American Indian/Alaska Native, Asian, Native Hawaiian/Pacific Islander, with permission for a “some other race” category and the option to select multiple races) [ 113 ]. Since 2017 Clinicaltrials.gov has required the reporting of race/ethnicity if collected, and there is good compliance with this requirement, but less so in publication of the work [ 114 ].
We examined the proportion of ethnoracial groups represented for each of the disease states in the studies included in this scoping review, relative to disease state prevalence and found a discrepancy. For AF, prevalence in White patients was 11.3%, in Black patients 6.6%, and in Hispanic patients 7.8% [ 15 ]. However, the representation in AF studies in this review were 74% White, 13% Black, and 8% Hispanic. Assessing VTE incidence by race is more difficult, as studies have shown regional and time variation, with Black patients typically having a higher incidence compared to other ethnoracial groups [ 16 ]. In this review, however, of the studies assessing VTE treatment or prophylaxis, only 16% of the patient population identified as Black, whereas 70% identified as White. There were only 3 studies that assessed a valvular heart disease population, making ethnoracial group representation difficult to assess.
The majority of studies captured in this review analyzed patients in the outpatient setting, for the anticoagulation indication of stroke prevention in AF, taking either warfarin or DOAC. Few studies involved the acute care setting or injectable anticoagulants, representing an area for future study of potential ethnoracial disparities.
Overall, the majority of studies in this scoping review addressed ethnoracial disparities in patients’ access to guideline-based anticoagulation therapy, clinical outcomes related to anticoagulation care, and quality of anticoagulation management. A research gap identified was more study is needed to assess gaps in educational outcomes such as anticoagulation and disease state knowledge, shared decision-making willingness and capability, and humanistic outcomes such as quality of life or satisfaction with anticoagulation therapy.
In analyzing the first research question regarding ethnoracial differences in access to guideline-based anticoagulation therapy, the majority of studies addressed use of any anticoagulation for stroke prevention in AF in patients above a threshold risk score and the preferential use of DOACs as first-line therapy instead of warfarin for AF. In both categories, patients in a non-White ethnoracial group (particularly Black patients) received recommended therapy less often than patients identified as White. It is unclear why this is the case. It could be on the patient, provider, and/or system level. It is possible that some studies more successfully adjusted for covariates than others. Sites or settings with systematic processes like order sets or clinical decision support systems in place for standard prescribing may be more successful in equitably prescribing indicated therapies. In one large study in the Veterans Affairs population of AF patients, even after adjusting for numerous variables that included clinical, demographic, socioeconomic, prescriber, and geographic site factors, DOAC prescribing remained lower in Asian and Black patients when compared with White patients. The authors in that study postulate that non-White populations may be less receptive to novel therapies due to historical mistrust of the health care system or have reduced access to education about the latest treatments, and they give the example of direct-to-consumer advertising [ 42 ]. It has also previously been demonstrated that prescribing of oral anticoagulation and particularly DOACs is lower in non-White patients [ 41 ]. These are difficult to capture as standard covariates, which is why further study is needed. We examined the publication dates for both access categories to see if perhaps there was a lack of contemporary data skewing the outcomes. However, for both anticoagulation for a guideline-based indication and DOACs as first-line therapy, the majority of articles came from the time period 2019–2021 (24 of 40 articles, and 15 of 18 articles, respectively), well after guideline updates preferentially recommended DOACs [ 34 , 35 ]. Also, there were relatively few studies addressing guideline-based therapy for VTE treatment and prophylaxis, making assessment of disparities difficult. Regarding access, it is well established that race and ethnicity often determine a patient’s socioeconomic status and that low socioeconomic status and its correlates (e.g., reduced education, income, and healthcare access) are associated with poorer health outcomes [ 115 ]. However, at each level of income or education, Black patients experience worse health outcomes than Whites [ 116 ]. So, low socioeconomic status does not fully explain poorer health outcomes for non-White individuals.
After examining access to appropriate and preferred anticoagulation therapy, the second research question of this scoping review examined potential ethnoracial disparities in the quality of anticoagulation therapy management. INR control measures such as time in therapeutic INR range are a surrogate measure of both thrombotic and bleeding outcomes and frequently used as a way to assess quality of warfarin therapy. The studies identified in this review showed clear disparity between White and non-White patient groups (especially Black patients), however all twelve studies comparing TTR among ethnoracial groups were published prior to 2019. This could be due to the decline in warfarin prescribing relative to increases in DOAC prescribing [ 117 , 118 , 119 ], but there remain patient populations that require or choose warfarin, so this marker of anticoagulation control remains relevant and requires continued reassessment. There were relatively few studies assessing other markers of anticoagulation management quality such as anticoagulation management service enrollment, appropriate DOAC dosing, and access to quality improvement strategies like PST or PSM. Few studies assessed educational outcomes, yet this may have relevance to the above anticoagulation care quality question. For those patients who remain on warfarin, dietary Vitamin K consistency is an example of a key educational point that links directly to INR control. It is unclear if there are disparities in this type of education among ethnoracial groups that may have more far-reaching effects.
Of note, clinical outcomes related to anticoagulant therapy seemed to have the fewest areas of disparity, although the number of articles was small. This suggests that if patients have access to high quality anticoagulation therapy, there is a promising sign that optimal clinical outcomes can be achieved for all ethnoracial groups.
There are some limitations of this scoping review that warrant consideration. First, we chose fairly broad inclusion criteria (all anticoagulants, all study types) because a review of this type had never been performed before. This resulted in a relatively large number of included articles for a scoping review. Second, there is likely a high degree of heterogeneity among patient populations and outcomes definitions. However, as this is a scoping review with the goal to present an overview of the literature and not report on composite outcomes, a risk of bias assessment was not performed. Third is our decision to group patients into White and non-White groups for assessment of outcome directionality. In doing so, we may have missed subtle differences in outcomes between various non-White ethnoracial groups. Fourth, in our main search we included all studies that reported outcomes, but due to scope, we only reported outcome directionality for studies that statistically compared outcomes between ethnoracial groups. Finally, due to the large number of studies that required review and analysis, this was a lengthy undertaking and we are certain that additional studies have been published since the closure of our search period.
In line with the 2014 National Action Plan for Adverse Drug Event Prevention’s goal of identifying patient populations at higher risk of adverse drug events, this scoping review highlights several areas where quality of anticoagulation care can be optimized for all patients. Future research opportunities in ethnoracial differences in the quality of anticoagulation care are summarized in Table 3 . While the scoping review focused exclusively on the evaluation of peer-reviewed manuscripts, the heterogeneity of terminology and methodologies identified in the published papers may have implications for national health policy relating to the quality and safety of care (e.g.the Medicare Quality Payment Program) [ 120 ]. To accurately and reliably quantify important disparities in AC-related care and support effective improvement initiatives, attention and effort will need to be invested across the full continuum of quality measure development [ 121 ], measure endorsement [ 122 ], measure selection, and status assignment within value-based payment programs (e.g., required/optional, measure weighting) [ 123 ]. The findings of the scoping review may be of utility to such efforts, and the development and implementation of suitable quality measures will likely be of value to future research efforts in this important therapeutic area.
Conclusions
Treatment guidelines do not recommend differentiating anticoagulant therapy by ethnoracial group, yet this scoping review of the literature demonstrates consistent directionality in favor of White patients over non-White patients in the domains of access to anticoagulation therapy for guideline-based indications, prescription of preferred anticoagulation therapies, and quality of anticoagulation therapy management. These data should serve as a stimulus for an assessment of current services, implementation of quality improvement measures, and inform future research to make anticoagulation care quality more equitable.
Data Availability
Data are available on request from the corresponding author.
Wheeler SM, Bryant AS (2017) Racial and Ethnic Disparities in Health and Health Care. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am 44(1):1–11
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Manuel JI (2018) Racial/Ethnic and Gender Disparities in Health Care Use and Access. Health Serv Res 53(3):1407–1429
Nadeem MF, Kaiser LR (2022) Disparities in Health Care Delivery Systems. Thorac Surg Clin 32(1):13–21
Wallace J et al (2021) Changes in Racial and Ethnic Disparities in Access to Care and Health Among US Adults at Age 65 Years. JAMA Intern Med 181(9):1207–1215
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Churchwell K et al (2020) Call to Action: Structural Racism as a Fundamental Driver of Health Disparities: A Presidential Advisory From the American Heart Association. Circulation 142(24):e454–e468
Gomez SE et al (2023) Racial, ethnic, and sex disparities in atrial fibrillation management: rate and rhythm control. J Interv Card Electrophysiol 66(5):1279–1290
Tamirisa KP et al (2021) Racial and Ethnic Differences in the Management of Atrial Fibrillation. CJC Open 3(12 Suppl):S137–S148
Eberly LA et al (2021) Racial/Ethnic and Socioeconomic Disparities in Management of Incident Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation. JAMA Netw Open 4(2):e210247
Ugowe FE, Jackson LR, Thomas KL (2018) Racial and ethnic differences in the prevalence, management, and outcomes in patients with atrial fibrillation: A systematic review. Heart Rhythm 15(9):1337–1345
Xu Y, Siegal DM, Anand SS (2021) Ethnoracial variations in venous thrombosis: Implications for management, and a call to action. J Thromb Haemost 19(1):30–40
Erinne I et al (2021) Racial disparities in the treatment of aortic stenosis: Has transcatheter aortic valve replacement bridged the gap? Catheter Cardiovasc Interv 98(1):148–156
Ali A et al (2022) Racial and Ethnic Disparities in the Use of Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement in the State of Connecticut. Cardiovasc Revasc Med 37:7–12
Pienta MJ et al (2023) Racial disparities in mitral valve surgery: A statewide analysis. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 165(5):1815-1823.e8
Alkhouli M et al (2019) Racial Disparities in the Utilization and Outcomes of Structural Heart Disease Interventions in the United States. J Am Heart Assoc 8(15):e012125
Heckbert SR et al (2020) Differences by Race/Ethnicity in the Prevalence of Clinically Detected and Monitor-Detected Atrial Fibrillation: MESA. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol 13(1):e007698
Zakai NA et al (2014) Racial and regional differences in venous thromboembolism in the United States in 3 cohorts. Circulation 129(14):1502–1509
Lamprea-Montealegre JA et al (2021) Valvular Heart Disease in Relation to Race and Ethnicity: JACC Focus Seminar 4/9. J Am Coll Cardiol 78(24):2493–2504
Tamargo J et al (2022) Racial and ethnic differences in pharmacotherapy to prevent coronary artery disease and thrombotic events. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Pharmacother 8(7):738–751
Kanuri SH, Kreutz RP (2019) Pharmacogenomics of Novel Direct Oral Anticoagulants: Newly Identified Genes and Genetic Variants. J Pers Med 9(1):7
Craig TJ, Wann LS, Calkins H, Chen LY, Cigarroa JE, Cleveland CJ Jr, Ellinor PT, Ezekowitz MD, Field ME, Furie LK, Heidenreich PA, Murray KT, Shea JB, Tracy CM, Yancy CW (2019) Circulation 140 (2):e125–e151. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIR.000000000000066
Ortel TL et al (2020) American Society of Hematology 2020 guidelines for management of venous thromboembolism: treatment of deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. Blood Adv 4(19):4693–4738
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Stevens SM et al (2021) Antithrombotic Therapy for VTE Disease: Second Update of the CHEST Guideline and Expert Panel Report. Chest 160(6):e545–e608
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Schünemann HJ et al (2018) American Society of Hematology 2018 guidelines for management of venous thromboembolism: prophylaxis for hospitalized and nonhospitalized medical patients. Blood Adv 2(22):3198–3225
Otto CM et al (2021) 2020 ACC/AHA Guideline for the Management of Patients With Valvular Heart Disease: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation 143(5):e72–e227
PubMed Google Scholar
National Action Plan for Adverse Drug Event Prevention (2014) Office of Disease Prevention and Health Promotion. US Department of Health and Human Services, Washington, DC
Google Scholar
Bhakta S et al (2022) A systematic review and meta-analysis of racial disparities in deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism events in patients hospitalized with coronavirus disease 2019. J Vasc Surg Venous Lymphat Disord 10(4):939-944.e3
Corbie-Smith G et al (2008) Conceptualizing race in research. J Natl Med Assoc 100(10):1235–1243
Vazquez SR, Yates NYY, McFarland MM (2022). Differences in anticoagulant care delivery according to ethnoracial group in the United States: a scoping review protocol. Open Sci Fram osf.io/eydsa. https://doi.org/10.17605/OSF.IO/9SE7H
Peters MDJ, Godfrey C, McInerney P, Munn Z, Tricco AC, Khalil H (2020) Joanna briggs institute reviewer's manual. Aromataris E, Munn Z (eds). Publisher: Joanna briggs institute. Chapter: chapter 11: scoping reviews
Arksey H, O’Malley L (2005) Scoping studies: towards a methodological framework. Int J Soc Res Methodol 8(1):19–32
Article Google Scholar
Rethlefsen ML et al (2021) PRISMA-S: an extension to the PRISMA Statement for Reporting Literature Searches in Systematic Reviews. Syst Rev 10(1):39
Harris PA et al (2009) Research electronic data capture (REDCap)–a metadata-driven methodology and workflow process for providing translational research informatics support. J Biomed Inform 42(2):377–381
McGowan J et al (2016) PRESS Peer Review of Electronic Search Strategies: 2015 Guideline Statement. J Clin Epidemiol 75:40–46
Kearon C et al (2016) Antithrombotic Therapy for VTE Disease: CHEST Guideline and Expert Panel Report. Chest 149(2):315–352
Lip GYH et al (2018) Antithrombotic Therapy for Atrial Fibrillation: CHEST Guideline and Expert Panel Report. Chest 154(5):1121–1201
al Taii, H. and S. Al-Kindi, Racial disparities in prescriptions of oral anticoagulants among patients with atrial fibrillation., in 24th International Atrial Fibrillation Symposium (2019) Boston. MA, USA
Bhave PD et al (2015) Race- and sex-related differences in care for patients newly diagnosed with atrial fibrillation. Heart Rhythm 12(7):1406–1412
Chapman SA et al (2017) Adherence to treatment guidelines: the association between stroke risk stratified comparing CHADS. BMC Health Serv Res 17(1):127
Chen Q et al (2021) Prevalence and the factors associated with oral anticoagulant use among nursing home residents. J Clin Pharm Ther 46(6):1714–1728
Deitelzweig S et al (2020) Utilization of anticoagulants and predictors of treatment among hospitalized patients with atrial fibrillation in the USA. J Med Econ 23(12):1389–1400
Essien UR et al (2018) Association of Race/Ethnicity With Oral Anticoagulant Use in Patients With Atrial Fibrillation: Findings From the Outcomes Registry for Better Informed Treatment of Atrial Fibrillation II. JAMA Cardiol 3(12):1174–1182
Essien UR et al (2021) Disparities in Anticoagulant Therapy Initiation for Incident Atrial Fibrillation by Race/Ethnicity Among Patients in the Veterans Health Administration System. JAMA Netw Open 4(7):e2114234
Essien UR, Kim N, Hausmann LR, Mor MK, Good C, Gellad WF, Fine MJ (2020) Abstract: racial and ethnic disparities in anticoagulant choice for atrial fibrillation in the veterans health administration: results from the reach-af study. J Gen Int Med J 35(1):S250–251
Essien UR et al (2022) Association of Race and Ethnicity and Anticoagulation in Patients With Atrial Fibrillation Dually Enrolled in Veterans Health Administration and Medicare: Effects of Medicare Part D on Prescribing Disparities. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes 15(2):e008389
Essien UR et al (2020) Race/Ethnicity and Sex-Related Differences in Direct Oral Anticoagulant Initiation in Newly Diagnosed Atrial Fibrillation: A Retrospective Study of Medicare Data. J Natl Med Assoc 112(1):103–108
Fohtung RB, Novak E, Rich MW (2017) Effect of New Oral Anticoagulants on Prescribing Practices for Atrial Fibrillation in Older Adults. J Am Geriatr Soc 65(11):2405–2412
Lewis WR et al (2011) Improvement in use of anticoagulation therapy in patients with ischemic stroke: results from Get With The Guidelines-Stroke. Am Heart J 162(4):692-699.e2
Martin Diaz C et al (2021) Anticoagulation After Ischemic Stroke or Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA) in the Time of Direct Oral Anticoagulation (DOAC) and Thrombectomy. Cureus 13(8):e17392
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Mentias A et al (2021) Racial and Sex Disparities in Anticoagulation After Electrical Cardioversion for Atrial Fibrillation and Flutter. J Am Heart Assoc 10(17):e021674
Obi CA et al (2022) Examination of anticoagulation prescription among elderly patients with atrial fibrillation after in-hospital fall. J Thromb Thrombolysis 53(3):683–689
Piccini JP et al (2019) Adherence to Guideline-Directed Stroke Prevention Therapy for Atrial Fibrillation Is Achievable. Circulation 139(12):1497–1506
Raji MA et al (2013) National utilization patterns of warfarin use in older patients with atrial fibrillation: a population-based study of Medicare Part D beneficiaries. Ann Pharmacother 47(1):35–42
Schwartz SM et al (2019) Discriminative Ability of CHA. Am J Cardiol 123(12):1949–1954
Shahid I et al (2021) Meta-Analysis of Racial Disparity in Utilization of Oral Anticoagulation for Stroke Prevention in Atrial Fibrillation. Am J Cardiol 153:147–149
Tedla YG et al (2020) Racial Disparity in the Prescription of Anticoagulants and Risk of Stroke and Bleeding in Atrial Fibrillation Patients. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 29(5):104718
Thomas KL et al (2013) Racial differences in the prevalence and outcomes of atrial fibrillation among patients hospitalized with heart failure. J Am Heart Assoc 2(5):e000200
Waddy SP et al (2020) Racial/Ethnic Disparities in Atrial Fibrillation Treatment and Outcomes among Dialysis Patients in the United States. J Am Soc Nephrol 31(3):637–649
Wetmore JB et al (2019) Relation of Race, Apparent Disability, and Stroke Risk With Warfarin Prescribing for Atrial Fibrillation in Patients Receiving Maintenance Hemodialysis. Am J Cardiol 123(4):598–604
Winkelmayer WC et al (2012) Prevalence of atrial fibrillation and warfarin use in older patients receiving hemodialysis. J Nephrol 25(3):341–353
Zahuranec DB et al (2017) Stroke Quality Measures in Mexican Americans and Non-Hispanic Whites. J Health Dispar Res Pract 10(1):111–123
Addo-Tabiri NO et al (2020) Black Patients Experience Highest Rates of Cancer-associated Venous Thromboembolism. Am J Clin Oncol 43(2):94–100
Freeman AH et al (2016) Venous thromboembolism following minimally invasive surgery among women with endometrial cancer. Gynecol Oncol 142(2):267–272
Friedman AM et al (2013) Underuse of postcesarean thromboembolism prophylaxis. Obstet Gynecol 122(6):1197–1204
Lau BD et al (2015) Eliminating Health Care Disparities With Mandatory Clinical Decision Support: The Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Example. Med Care 53(1):18–24
Owodunni OP et al (2020) Using electronic health record system triggers to target delivery of a patient-centered intervention to improve venous thromboembolism prevention for hospitalized patients: Is there a differential effect by race? PLoS ONE 15(1):e0227339
Shah S et al (2021) Implementation of an Anticoagulation Practice Guideline for COVID-19 via a Clinical Decision Support System in a Large Academic Health System and Its Evaluation: Observational Study. JMIR Med Inform 9(11):e30743
Steinberg BA et al (2013) Early adoption of dabigatran and its dosing in US patients with atrial fibrillation: results from the outcomes registry for better informed treatment of atrial fibrillation. J Am Heart Assoc 2(6):e000535
Vaughan Sarrazin MS et al (2014) Bleeding rates in Veterans Affairs patients with atrial fibrillation who switch from warfarin to dabigatran. Am J Med 127(12):1179–1185
Nathan AS et al (2019) Racial, Ethnic, and Socioeconomic Inequities in the Prescription of Direct Oral Anticoagulants in Patients With Venous Thromboembolism in the United States. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes 12(4):e005600
Singh BP, Sitlinger A, Saber I, Thames E, Beckman M, Reyes N, Schulteis RD, Ortel T (2016) Direct oral anticoagulant usage in the treatment of venous thromboembolism across racial groups in Durham County, NC. J Gen Int Med 31:S191–S192
Schaefer JK et al (2017) Sociodemographic factors in patients continuing warfarin vs those transitioning to direct oral anticoagulants. Blood Adv 1(26):2536–2540
Lank RJ et al (2019) Ethnic Differences in 90-Day Poststroke Medication Adherence. Stroke 50(6):1519–1524
O'Brien EC, Holmes ND, Thomas L, Fonarow GC, Kowey PR, Ansell JE, Mahaffey KW, Gersh BJ, Peterson ED, Piccini JP, Hylek EM (2018) J Am Heart Assoc 7(12):e006391
Singh RR et al (2016) Adherence to Anticoagulant Therapy in Pediatric Patients Hospitalized With Pulmonary Embolism or Deep Vein Thrombosis: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost 22(3):260–264
Yong C, Xu XY, Than C, Ullal A, Schmitt S, Azarbal F, Heidenreich P, Turakhia M (2013) Abstract 14134: racial disparities in warfarin time in INR therapeutic range in patients with atrial fibrillation: Findings from the TREAT-AF Study. Circul 128(22). https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/10.1161/circ.128.suppl_22.A14134
Chen N, Brooks MM, Hernandez I (2020) Latent Classes of Adherence to Oral Anticoagulation Therapy Among Patients With a New Diagnosis of Atrial Fibrillation. JAMA Netw Open 3(2):e1921357
Pham Nguyen TP et al (2003) Does hospitalization for thromboembolism improve oral anticoagulant adherence in patients with atrial fibrillation? J Am Pharm Assoc 60(6):986-992.e2
Patel AA et al (2013) Persistence of warfarin therapy for residents in long-term care who have atrial fibrillation. Clin Ther 35(11):1794–1804
Golwala H et al (2016) Racial/ethnic differences in atrial fibrillation symptoms, treatment patterns, and outcomes: Insights from Outcomes Registry for Better Informed Treatment for Atrial Fibrillation Registry. Am Heart J 174:29–36
Limdi NA et al (2017) Quality of anticoagulation control and hemorrhage risk among African American and European American warfarin users. Pharmacogenet Genomics 27(10):347–355
Lip GY et al (2016) Determinants of Time in Therapeutic Range in Patients Receiving Oral Anticoagulants (A Substudy of IMPACT). Am J Cardiol 118(11):1680–1684
Rao SR et al (2015) Explaining racial disparities in anticoagulation control: results from a study of patients at the Veterans Administration. Am J Med Qual 30(3):214–222
Thigpen JL, Yah Q, Beasley M, Limdi NA (2012) Abstract: racial differences in anticoagulation control and risk of hemorrhage among warfarin users. Pharmacoth 32(10):E189
Yong C et al (2016) Racial Differences in Quality of Anticoagulation Therapy for Atrial Fibrillation (from the TREAT-AF Study). Am J Cardiol 117(1):61–68
Moffett BS, Kim S, Bomgaars LR (2013) Readmissions for warfarin-related bleeding in pediatric patients after hospital discharge. Pediatr Blood Cancer 60(9):1503–1506
Rose AJ et al (2013) Gaps in monitoring during oral anticoagulation: insights into care transitions, monitoring barriers, and medication nonadherence. Chest 143(3):751–757
Mahle WT et al (2011) Management of warfarin in children with heart disease. Pediatr Cardiol 32(8):1115–1119
Meade M et al (2011) Impact of health disparities on staff workload in pharmacist-managed anticoagulation clinics. Am J Health Syst Pharm 68(15):1430–1435
Aguilar F et al (2021) Off-label direct oral anticoagulants dosing in atrial fibrillation and venous thromboembolism is associated with higher mortality. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther 19(12):1119–1126
Jellinek-Cohen SP, Li M, Husk G (2018) Enoxaparin dosing errors in the emergency department. World J Emerg Med 9(3):195–202
Triller DM et al (2015) Trends in Warfarin Monitoring Practices Among New York Medicare Beneficiaries, 2006–2011. J Community Health 40(5):845–854
Akhtar T et al (2020) Factors associated with bleeding events in patients on rivaroxaban for non-valvular atrial fibrillation: A real-world experience. Int J Cardiol 320:78–82
Cires-Drouet RS et al (2022) Prevalence and clinical outcomes of hospitalized patients with upper extremity deep vein thrombosis. J Vasc Surg Venous Lymphat Disord 10(1):102–110
Doucette K et al (2020) Efficacy and Safety of Direct-Acting Oral Anticoagulants (DOACs) in the Overweight and Obese. Adv Hematol 2020:3890706
Gu K et al (2021) Racial disparities among Asian Americans with atrial fibrillation: An analysis from the NCDR® PINNACLE Registry. Int J Cardiol 329:209–216
Yamashita Y et al (2018) Asian patients versus non-Asian patients in the efficacy and safety of direct oral anticoagulants relative to vitamin K antagonist for venous thromboembolism: A systemic review and meta-analysis. Thromb Res 166:37–42
Di Nisio M et al (2016) Risk of major bleeding in patients with venous thromboembolism treated with rivaroxaban or with heparin and vitamin K antagonists. Thromb Haemost 115(2):424–432
Hernandez I et al (2015) Risk of bleeding with dabigatran in atrial fibrillation. JAMA Intern Med 175(1):18–24
Majeed A et al (2016) Bleeding events with dabigatran or warfarin in patients with venous thromboembolism. Thromb Haemost 115(2):291–298
Hankey GJ et al (2014) Intracranial hemorrhage among patients with atrial fibrillation anticoagulated with warfarin or rivaroxaban: the rivaroxaban once daily, oral, direct factor Xa inhibition compared with vitamin K antagonism for prevention of stroke and embolism trial in atrial fibrillation. Stroke 45(5):1304–1312
Kobayashi L et al (2017) Novel oral anticoagulants and trauma: The results of a prospective American Association for the Surgery of Trauma Multi-Institutional Trial. J Trauma Acute Care Surg 82(5):827–835
Gencer B et al (2022) Edoxaban versus Warfarin in high-risk patients with atrial fibrillation: A comprehensive analysis of high-risk subgroups. Am Heart J 247:24–32
Chen N et al (2021) Joint Latent Class Analysis of Oral Anticoagulation Use and Risk of Stroke or Systemic Thromboembolism in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs 21(5):573–580
Kabra R et al (2015) Effect of race on outcomes (stroke and death) in patients >65 years with atrial fibrillation. Am J Cardiol 116(2):230–235
Kim MH, Xu L, Puckrein G (2018) Patient Diversity and Population Health-Related Cardiovascular Outcomes Associated with Warfarin Use in Atrial Fibrillation: An Analysis Using Administrative Claims Data. Adv Ther 35(11):2069–2080
Abu-Zeinah G, Oromendia C, DeSancho MT (2019) Thrombotic risk factors in patients with antiphospholipid syndrome: a single center experience. J Thromb Thrombolysis 48(2):233–239
Banala SR et al (2017) Discharge or admit? Emergency department management of incidental pulmonary embolism in patients with cancer: a retrospective study. Int J Emerg Med 10(1):19
LaDuke ZJ et al (2019) Association of mortality among trauma patients taking preinjury direct oral anticoagulants versus vitamin K antagonists. Surgery 166(4):564–571
Moreland CJ et al (2013) Anticoagulation education: do patients understand potential medication-related emergencies? Jt Comm J Qual Patient Saf 39(1):22–31
Bamgbade BA et al (2021) Differences in Perceived and Predicted Bleeding Risk in Older Adults With Atrial Fibrillation: The SAGE-AF Study. J Am Heart Assoc 10(17):e019979
Webb D et al (2019) Patient Satisfaction With Venous Thromboembolism Treatment. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost 25:1076029619864663
Kamath CC et al (2021) Cost Conversations About Anticoagulation Between Patients With Atrial Fibrillation and Their Clinicians: A Secondary Analysis of a Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Netw Open 4(7):e2116009
U.S. Census Bureau . [cited 2023 10/20/23]; Available from: https://www.census.gov/quickfacts/fact/note/US/RHI625222#:~:text=Asian.,Japan%2C%20Korea%2C%20or%20Vietnam .
Fain KM et al (2021) Race and ethnicity reporting for clinical trials in ClinicalTrials.gov and publications. Contemp Clin Trials 101:106237
American Psychological Association Ethnic and racial minorities & socioeconomic status. 3/22/24]; Available from: https://www.apa.org/pi/ses/resources/publications/minorities#:~:text=The%20relationship%20between%20SES%2C%20race,SES%2C%20race%2C%20and%20ethnicity . Accessed 22 Mar 2024
Braveman PA et al (2010) Socioeconomic disparities in health in the United States: what the patterns tell us. Am J Public Health 100 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):186–96
Wheelock KM et al (2021) Clinician Trends in Prescribing Direct Oral Anticoagulants for US Medicare Beneficiaries. JAMA Netw Open 4(12):e2137288
Barnes GD et al (2015) National Trends in Ambulatory Oral Anticoagulant Use. Am J Med 128(12):1300–5.e2
Iyer GS et al (2023) Trends in the Use of Oral Anticoagulants for Adults With Venous Thromboembolism in the US, 2010–2020. JAMA Netw Open 6(3):e234059
MACRA Medicare Access and CHIP Reauthorization Act of 2015 (MACRA). 03/19/24]; Available from: https://www.cms.gov/medicare/quality/value-based-programs/chip-reauthorization-act . Accessed 19 Mar 2024
Blueprint Measure Lifecycle Overview. 03/19/2024]; Available from: https://mmshub.cms.gov/blueprint-measure-lifecycle-overview . Accessed 19 Mar 2024
Endorsement and Maintenance (E&M) Guidebook. 3/19/24]; Available from: https://p4qm.org/sites/default/files/2023-12/Del-3-6-Endorsement-and-Maintenance-Guidebook-Final_0_0.pdf . Accessed 19 Mar 2024
Measure Implementation. 3/19/24]; Available from: https://mmshub.cms.gov/measure-lifecycle/measure-implementation/selection . Accessed 19 Mar 2024
Download references
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to acknowledge the following individuals for their work in screening articles for this scoping review: April Allen, PharmD, CACP; Allison Burnett, PharmD, PhC, CACP; Stacy Ellsworth, RN, MSN, CCRC; Danielle Jenkins, MBA, RN, BSN, CRNI; Amanda Katz, MBA; Lea Kistenmacher, Julia Mulheman, PharmD; Surhabi Palkimas, PharmD, MBA; Terri Schnurr, RN, CCRC; Deborah Siegal, MD, MSc, FRCPC; Kimberly Terry, PharmD, BCPS, BCCCP; and Terri Wiggins, MS.
The authors wish to acknowledge the support of the Anticoagulation Forum in the development of this manuscript. The Anticoagulation Forum is a non-profit organization dedicated to improving the quality of care for patients taking antithrombotic medications.
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
University of Utah Health Thrombosis Service, 6056 Fashion Square Drive, Suite 1200, Murray, UT, 84107, USA
Sara R. Vazquez
Kaiser Permanente Clinical Pharmacy Services, 200 Crescent Center Pkwy, Tucker, GA, 30084, USA
Naomi Y. Yates
Anticoagulation Forum, Inc, 17 Lincoln Street, Suite 2B, Newton, MA, 02461, USA
Craig J. Beavers & Darren M. Triller
University of Kentucky College of Pharmacy, 789 S Limestone, Lexington, KY, 40508, USA
Craig J. Beavers
University of Utah Spencer S. Eccles Health Sciences Library, 10 N 1900 E, Salt Lake City, UT, 84112, USA
Mary M. McFarland
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation was performed by Sara Vazquez, Naomi Yates, and Mary McFarland. Data collection and analysis were performed by Sara Vazquez, Naomi Yates, Craig Beavers, and Darren Triller. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Sara Vazquez and all authors edited subsequent drafts. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Sara R. Vazquez .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
Dr. Vazquez discloses that she is a member of the Anticoagulation Forum Advisory Council and an editorial consultant for UptoDate, Inc.
Dr. Yates has no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Dr. Beavers has no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Dr. Triller has no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Ms. McFarland has no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary file1 (DOCX 22 KB)
Supplementary file2 (docx 14 kb), rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Vazquez, S.R., Yates, N.Y., Beavers, C.J. et al. Differences in quality of anticoagulation care delivery according to ethnoracial group in the United States: A scoping review. J Thromb Thrombolysis (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11239-024-02991-2
Download citation
Accepted : 27 April 2024
Published : 11 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s11239-024-02991-2
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Ethnoracial
- Disparities
- Anticoagulation
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Step 1: Introduce your topic. Step 2: Describe the background. Step 3: Establish your research problem. Step 4: Specify your objective (s) Step 5: Map out your paper. Research paper introduction examples. Frequently asked questions about the research paper introduction.
Define your specific research problem and problem statement. Highlight the novelty and contributions of the study. Give an overview of the paper's structure. The research paper introduction can vary in size and structure depending on whether your paper presents the results of original empirical research or is a review paper.
The first question asks for a ready-made solution, and is not focused or researchable. The second question is a clearer comparative question, but note that it may not be practically feasible. For a smaller research project or thesis, it could be narrowed down further to focus on the effectiveness of drunk driving laws in just one or two countries.
Research Paper Introduction. Research paper introduction is the first section of a research paper that provides an overview of the study, its purpose, and the research question(s) or hypothesis(es) being investigated. It typically includes background information about the topic, a review of previous research in the field, and a statement of the research objectives.
As the name suggests, the research question is the core question (or set of questions) that your study will (attempt to) answer. In many ways, a research question is akin to a target in archery. Without a clear target, you won't know where to concentrate your efforts and focus. Essentially, your research question acts as the guiding light ...
Step 2: Building a solid foundation with background information. Including background information in your introduction serves two major purposes: It helps to clarify the topic for the reader. It establishes the depth of your research. The approach you take when conveying this information depends on the type of paper.
Download Article. 1. Announce your research topic. You can start your introduction with a few sentences which announce the topic of your paper and give an indication of the kind of research questions you will be asking. This is a good way to introduce your readers to your topic and pique their interest.
The introduction leads the reader from a general subject area to a particular topic of inquiry. It establishes the scope, context, and significance of the research being conducted by summarizing current understanding and background information about the topic, stating the purpose of the work in the form of the research problem supported by a hypothesis or a set of questions, explaining briefly ...
Most professional researchers focus on topics they are genuinely interested in studying. Writers should choose a broad topic about which they genuinely would like to know more. An example of a general topic might be "Slavery in the American South" or "Films of the 1930s.". Do some preliminary research on your general topic.
Provide a background of the problem you wish to study. Explain why you have undertaken the study. Describes your research problem. Summarizes the existing knowledge related to your topic. Highlights the contribution that your research will make to your field. States your research question clearly. You can look up these resources to have a clear ...
Example Research Question (s) Here are examples of research problems and research questions to help you understand how to create a research question for a given research problem. Example Research Problem. Example Research Question (s) A small-scale company, 'A' in the UK, cannot allocate a marketing budget for next year due to their poor ...
A research question is a question that a study or research project, through its thesis statement, aims to answer. This question often addresses an issue or a problem, which, through analysis and interpretation of data, is answered in the study's conclusion. ... Introduction. The importance of the problem; Review of relevant scholarship ...
1 Answer to this question. Answer: The research question is a concise expression of a suggested solution to a research problem. It is a crystallization of the topic you are studying and offers a specific direction for the research. It is written toward the end of the introduction section of the proposal, after you have provided the background ...
The research aims, objectives and research questions (collectively called the "golden thread") are arguably the most important thing you need to get right when you're crafting a research proposal, dissertation or thesis.We receive questions almost every day about this "holy trinity" of research and there's certainly a lot of confusion out there, so we've crafted this post to help ...
Good writing begins with clearly stating your research question (or hypothesis) in the Introduction section —the focal point on which your entire paper builds and unfolds in the subsequent Methods, Results, and Discussion sections. This research question or hypothesis that goes into the first section of your research manuscript, the ...
The process of seeking information for everyday questions is a bit different than for research questions, however. Take a look at the examples of regular questions and research questions below. While regular questions are easily answered by a quick online search (e.g., Google), research questions will take more exploration.
INTRODUCTION. Scientific research is usually initiated by posing evidenced-based research questions which are then explicitly restated as hypotheses.1,2 The hypotheses provide directions to guide the study, solutions, explanations, and expected results.3,4 Both research questions and hypotheses are essentially formulated based on conventional theories and real-world processes, which allow the ...
Case study: Research question development: Revised questions. What is the impact of. 1) the intervention on healthy item vending sales as determined by a comparison of item and overall sales at control and intervention sites and. 2) nutrition education training on park staff nutrition knowledge, attitude and behavior through comparison of pre ...
Abstract. Formulation of research question (RQ) is an essentiality before starting any research. It aims to explore an existing uncertainty in an area of concern and points to a need for deliberate investigation. It is, therefore, pertinent to formulate a good RQ. The present paper aims to discuss the process of formulation of RQ with stepwise ...
Research question. Interest in a particular topic usually begins the research process, but it is the familiarity with the subject that helps define an appropriate research question for a study. 1 Questions then arise out of a perceived knowledge deficit within a subject area or field of study. 2 Indeed, Haynes suggests that it is important to know "where the boundary between current ...
Definition: Research Question. A research question is a concise inquiry that guides the direction of a research study or investigation. It articulates the specific type of subject that the researcher aims to explore, often framed in a way that suggests investigation or analysis.It serves as a fundamental element in the research process, guiding the selection of appropriate methodologies, the ...
The Online Writing Lab at Purdue University houses writing resources and instructional material, and we provide these as a free service of the Writing Lab at Purdue.
The process of seeking information for everyday questions is a bit different than for research questions, however. Take a look at the examples of regular questions and research questions below. While regular questions are easily answered by a quick online search (e.g., Google), research questions will take more exploration.
Additionally, the topics covered in the marketing literature reviewed often present LGBTQ+ participants as 'other', that is, in contrast to heteronormative populations. This is predominately revealed in research that examines gay imagery in advertising on mainstream consumers.
We conducted this scoping review with guidance from the 2020 version of the JBI Manual for Evidence Synthesis and organized to Arksey's five stages: 1) identifying the research question, 2) identifying relevant studies, 3) study selection, 4) charting the data and 5) collating, summarizing and reporting the results [29, 30].For transparency and reproducibility, we followed the PRISMA-ScR and ...