- Essay Guides
- Other Essays

How to Write a Theme Essay
- Speech Topics
- Basics of Essay Writing
- Essay Topics
- Main Academic Essays
- Research Paper Topics
- Basics of Research Paper Writing
- Miscellaneous
- Chicago/ Turabian
- Data & Statistics
- Methodology
- Admission Writing Tips
- Admission Advice
- Other Guides
- Student Life
- Studying Tips
- Understanding Plagiarism
- Academic Writing Tips
- Basics of Dissertation & Thesis Writing
- Research Paper Guides
- Formatting Guides
- Basics of Research Process
- Admission Guides
- Dissertation & Thesis Guides

Table of contents
Use our free Readability checker
A thematic essay is a type of writing assignment that focuses on a specific theme or topic. It requires you to identify a central theme, discuss it in detail, and make connections between various facts. Your main goal is to demonstrate understanding and interpretation of the given subject matter. This type of essay is commonly used in literature classes or history exams.
If you’ve got an assignment to write a theme essay, you might wonder where you should even start from. No worries, we’ve got you covered here! The first thing you must know about this specific type of paper is that it aims to analyze a certain well-known theme and make an interesting statement about it. Here, you must explain meaning and relevance or complexity of your topic. You should summarize details that support your conclusion. In this article, we will conduct a detailed review of theme essay concept. We will also provide you a step by step guide on how to write a proper one. Let's dive right into it!
Thematic Essay Definition
Let’s start with defining what is a thematic essay and its purpose. In this type, one should select a thesis and form unique statement related to its aspects. You should write about it, explaining or elaborating to your audience the following:
- How is your statement related to your topic?
- Which important or interesting aspects does it highlight?
- What approaches and literary devices are you using for analysis ? How do you explain your general theme? This can be comparison, metaphor, personification etc.
When composing such an essay, you must formulate and defend your statement. Here, you will demonstrate abilities of analysis and literary devices usage. At least several paragraphs would be needed to display such skills properly.
Thematic Essay Outline: What's Inside
The best way to begin is creating a theme essay outline for your topic. An outline should contain all key parts, concepts and ideas of your paper. You should put it in a sketchy but logical manner. This way you'll quickly prepare a shortened version of your assignment. It will also help you in reviewing it. Adding missing points and correcting significant mistakes would be easier at this early stage. Outline should include all main essay parts:
- Introduction
- Thesis statement
- Body section
- Conclusion.
Keeping it brief, you should not provide complete sentences to describe your statements, ideas and arguments. A few words would suffice for each important point. Purpose is to make it readable for yourself! You should review it quickly and spot any inconsistencies.
How to Write a Thematic Essay Step-By-Step
Now it is time to focus on how to write a theme analysis essay – the complete text from scratch. Is your goal to impress readers and achieve a good grade? Then it is important that you create a proper essay structure template and don't lose any of your key questions! Stay methodical and keep it logical! Make sure your audience is engaged and don’t disappoint them in the end. Below we’ll provide a general idea for each step of this process.
Step 1. Define the Topic for Your Thematic Essay
When it comes to choosing among thematic essay topics, it is important that you pick an interesting and maybe even a controversial one. At the same time, make sure you can actually provide some meaningful input about it. Your assignment should impress readers with detailed analysis and its author’s writing skills. That's why your chosen topic must provide enough material for that. There is a diverse choice of topics. Choose the one you are really interested in whether it is Bullying essay or Happiness essay . If you need some ideas for great essay topics, feel free to check out our other articles.
Step 2. Create a Thematic Essay Outline
We've already covered the main points of theme essay outline concept. When writing it, include all the main parts of your future work. Keep it as short as possible, one paragraph per each key point will be enough. It isn’t even necessary to describe everything with complete sentences! A few words would suffice. Once done, review it first and make necessary corrections. It is advised to review an outline several times. That's how any noticeable gaps or mistakes would be spotted early.
Step 3. Start a Thematic Essay with a Hook
A good thematic essay introduction ought to captivate readers right from the start. That’s why it is always advised to add some ‘hook’ into it. You can begin with an unexpected statement, use wordplay or a plot twist. Then you can explain this in the main body part. This way your audience would be interested to hear those explanations. As a result, your paper will have better chances of success. Apart from that, introduction should contain the main statement and some information about its content.
Step 4. Write Body Paragraphs for Your Theme Essay
Goal of thematic essay body is to answer all the questions stated in an introduction. You must elaborate the meaning of each key idea. Finally, display your usage of literary devices, as we’ve specified earlier. Common practice is to use at least one paragraph per a literary device disclosure. Besides, the main body is the right place to use all relevant sources that can support your analysis or provide you with helpful analogies. Keep the main body logical, so that every paragraph is somehow connected to the previous and the next ones.
Step 5. Create a Thematic Essay Conclusion
A strong thematic essay conclusion should highlight all important points from tyourhe essay while avoiding adding new facts or evidence. Just restate your thesis, answer all questions and summarize your arguments. It might be also useful to leave some final note for readers with some deeper analysis of your topic. You can also highlight the need for further exploration of the chosen theme and thus to prepare readers for your future works on this topic.
Step 6. Proofread Your Thematic Analysis Essay
After completing theme essay, it is highly recommended to review it thoroughly, even several times if possible. The goal is to find mistakes and to spot logical gaps or missing details. Even best essays typically have inconsistencies left at the early stage. Taking a fresh look at your text often reveals some issues. If possible, ask your friends or colleagues to review your text. They might notice something you could not.
How to Format a Thematic Essay
When it comes to thematic essay format, you need to find out what are the requirements in your assignment or which format is common in the institution you will be presenting your essay for. In case no special requirements were made for you, just choose one of the most popular formats for scholarly papers:
- APA paper format : typically used in natural sciences, education and psychology fields
- MLA: typically used for works in humanities
- Chicago: typically used in business, history, and fine arts fields.
Thematic Essay Example
Let’s illustrate the explanations above with a few theme essay examples. We’ll provide some real ones here so that your every question would be answered. Hopefully you’ll find some inspiration in these examples for your own winning paper! The examples can be found below. Please scroll down to find them.
Thematic Essay: Final Thoughts
In this article we have explored the theme essay concept in detail. Its central purpose and main definition were examined and a step by step guide for writing a strong one was suggested. We’ve also provided a few working examples for your convenience. Hopefully, all this information will be useful for your scholarly endeavors!
Feel free to check out our paper writing services ! We’ve got a team of skilled writers with expertise in different literary areas, ready to help you. They deliver high quality content, always on time.
Frequently Asked Questions About Theme Essay
1. what is the thematic statement.
A thematic statement typically takes the place of a thesis in a thematic essay. It consists of 1-2 complete sentences that express a theme which you have chosen for your work. This statement must convey the main message and also show what analysis will be done. It should be brief however as most of the details are to be provided in the main body.
2. What is the goal of thematic essay?
The thematic essay goal is to express an idea or some insights about the surrounding world and to change readers' minds about certain issues. As an author, you are expected to illustrate the team, provide all necessary explanations and conduct an analysis if needed. Besides, you typically should demonstrate familiarity with some literary interpretations and methods which are used to examine your theme.
3. How long should a theme essay be?
The minimum length of a theme essay is five paragraphs. One is for introduction, one for conclusion and remaining three for the main body. Of course, it can be more than that, depending on the depth of the theme that was chosen. The main rule is to keep your essay logical and concise, avoiding adding too many details. Otherwise your audience might get tired and the effect produced by your writing would be damaged.
4. What is a thematic essay history?
Thematic essay (history class) should be written to analyze some historical facts or significance of specific literary pieces. A typical case is examining different aspects of a controversial leader from the past or a political event that has produced a number of various important consequences. Or you might argue about a specific role of a certain book during a certain period or its influence on different nations or cultural groups.

Daniel Howard is an Essay Writing guru. He helps students create essays that will strike a chord with the readers.
You may also like

Essay Papers Writing Online
Tips and guidelines for crafting a strong thematic essay.

Writing a thematic essay can be a challenging task for many students, as it requires a deep understanding of the subject matter and the ability to connect different concepts in a coherent and meaningful way.
Whether you’re a high school student tackling your first thematic essay or a college student working on a more advanced assignment, mastering the art of writing a thematic essay is essential for academic success.
In this article, we will provide you with valuable tips and guidelines to help you navigate the process of writing a thematic essay with confidence and skill.
Mastering the Art of Writing a Thematic Essay
Writing a thematic essay requires a clear understanding of the topic and the ability to explore the central theme in depth. To master the art of writing a thematic essay, there are several key steps to follow:
- Choose a Relevant Theme: Select a theme that is significant and meaningful to the topic at hand. It should be broad enough to allow for in-depth analysis.
- Develop a Strong Thesis Statement: Your thesis statement should clearly state the main theme or argument of your essay. It will guide the direction of your essay and provide a focus for your analysis.
- Organize Your Ideas: Create an outline to organize your thoughts and ideas. This will help you structure your essay and ensure a logical flow of information.
- Provide Evidence and Examples: Support your thesis statement with evidence from the text or other sources. Use specific examples to illustrate your points and provide context for your analysis.
- Analyze the Theme: Analyze the theme in depth, exploring its significance and implications. Consider how the theme is developed throughout the text and its impact on the characters and plot.
- Draw Conclusions: Conclude your essay by summarizing your main points and reiterating the significance of the theme. Reflect on the broader implications of the theme and its relevance to the text as a whole.
By following these steps and practicing your writing skills, you can master the art of writing a thematic essay and provide a compelling analysis of the central theme in any given text.
Tips for Choosing a Strong Theme
1. Consider your interests and passions: Choose a theme that you are passionate about or have a strong interest in. This will make the writing process more enjoyable and engaging.
2. Look for universal themes: Consider themes that are relevant to a wide audience and have the potential to resonate with readers on a deeper level.
3. Explore different perspectives: Don’t be afraid to choose a theme that challenges your beliefs or offers a unique perspective. This can lead to a more thought-provoking essay.
4. Connect the theme to your thesis statement: Ensure that the theme you choose aligns with the main argument or message you want to convey in your essay.
5. Research potential themes: Take the time to explore different themes and gather information to help you make an informed decision. Consider the depth and complexity of each theme before making a final choice.
Researching and Gathering Relevant Information

Before you start writing a thematic essay, it is crucial to conduct thorough research and gather relevant information on the chosen topic. Here are some tips to help you with this process:
- Begin by understanding the theme or topic of the essay. What is the main idea that you want to explore and discuss?
- Utilize a variety of sources such as books, articles, journals, and reputable websites to gather information. Make sure to cross-reference information to ensure accuracy.
- Take detailed notes while researching to keep track of key points, quotes, and references that you may want to include in your essay.
- Consider different perspectives and viewpoints on the topic to provide a well-rounded analysis in your essay.
- Organize your research material in a logical and systematic way to make it easier to refer back to when writing your essay.
By dedicating time to researching and gathering relevant information, you will be better equipped to write a well-informed and insightful thematic essay.
Creating the Outline and Structuring Your Essay
Before diving into the writing process, it is essential to create an outline for your thematic essay. An outline serves as the roadmap for your essay, helping you organize your thoughts and ideas in a logical manner.
Step 1: Identify the Theme
Start by identifying the theme or central idea that you will explore in your essay. This theme will serve as the foundation for your entire piece.
Step 2: Brainstorm Ideas
Once you have identified the theme, brainstorm ideas and examples that relate to the theme. Consider different aspects, perspectives, and elements that you can include in your essay.
Step 3: Create a Thesis Statement
Develop a strong thesis statement that clearly states the main argument or interpretation of the theme. Your thesis should provide a roadmap for the reader and guide the direction of your essay.
Step 4: Outline Your Essay
Organize your ideas and examples into a clear and coherent outline. Begin with an introduction that introduces the theme and your thesis statement. Then, outline the main points and supporting evidence in the body paragraphs. Finally, conclude your essay by summarizing your main points and restating your thesis.
By following these steps and creating a well-structured outline, you will be on your way to mastering the art of writing a thematic essay.
Developing a Compelling Thesis Statement

A strong thesis statement is the backbone of a thematic essay, as it serves as the foundation upon which the rest of the essay is built. To develop a compelling thesis statement, you need to clearly identify the main theme or idea that you will be exploring in your essay. Your thesis statement should be concise and specific, providing a clear indication of the argument or perspective you will be presenting.
When crafting your thesis statement, it is essential to consider the key points that you plan to discuss in your essay and ensure that they align with your main argument. Additionally, your thesis statement should be engaging and thought-provoking, drawing your reader in and setting the tone for the rest of your essay.
Remember to revise and refine your thesis statement as you work on your essay, ensuring that it accurately reflects the content of your paper and guides your reader through your analysis. A well-developed thesis statement will help you stay focused and on track as you write your thematic essay, leading to a more coherent and compelling piece of writing.
Writing Clear and Coherent Body Paragraphs
When writing a thematic essay, your body paragraphs should be clear and coherent, providing a strong argument to support your thesis statement. Here are some tips to help you achieve this:
1. Topic Sentence: Start each body paragraph with a clear topic sentence that introduces the main idea of the paragraph. This sentence should relate directly to your thesis statement and guide the reader on what to expect.
2. Evidence and Examples: Support your topic sentence with relevant evidence and examples from the text or other sources. Make sure to provide specific details that help to strengthen your argument and make your point clear.
3. Analysis: After presenting your evidence, analyze and explain how it supports your thesis. Discuss the significance of the evidence in relation to your main argument and show how it helps to prove your point.
4. Transition: Use transitions to smoothly connect your ideas and move from one paragraph to the next. Transitions help to guide the reader through your essay and maintain the flow of your arguments.
5. Clarity and Conciseness: Be clear and concise in your writing. Avoid unnecessary words or information that does not directly contribute to your argument. Keep your paragraphs focused and to the point.
By following these guidelines, you can write clear and coherent body paragraphs that effectively support your thesis and engage your reader. Remember to stay focused on your main argument and provide strong evidence to back up your claims.
Concluding with a Strong Summary and Reflection
As you wrap up your thematic essay, it is important to provide a strong summary that ties together all the key points you have discussed in the body paragraphs. Your conclusion should reiterate your thesis statement, summarise your main arguments, and leave the reader with a clear understanding of your interpretation of the theme.
Additionally, you can include a reflection on the significance of the theme you have explored and its relevance to the broader context. Consider how the theme relates to society, history, literature, or any other relevant fields. This reflection can add depth to your essay and show your critical thinking skills.
Remember, your conclusion is your final opportunity to leave a lasting impression on the reader, so make sure it is strong and impactful. End with a thought-provoking statement or question that encourages further contemplation of the theme you have explored.
Related Post
How to master the art of writing expository essays and captivate your audience, step-by-step guide to crafting a powerful literary analysis essay, convenient and reliable source to purchase college essays online, tips and techniques for crafting compelling narrative essays.
How to Write a Thematic Essay

Every piece of writing ever written has its agenda. Whether it’s to teach a lesson or show the impact of a particular emotion or action, a central theme can be developed. The goal for us as readers is to uncover what the author was trying to tell us between the lines in their literature. When we do finally discover it, we’ve accomplished the first step of thematic essay writing! Let’s see below how to write a thematic essay with our papers writing service .
What Is a Thematic Essay?
Let’s look at the thematic essay definition; a thematic essay is a piece of writing in which an author develops the central theme in some literature using literary devices like foreshadowing, imagery, personification, etc.
A professional essay writer will uncover the primary subject, elaborate upon the literary devices employed, and express the overall significance of the theme. The primary challenge comes from the fact that although there are various subjects, finding the most meaningful and impactful one can be challenging.
Naturally, each person has their own varied interpretation, making it hard to agree on a central theme wholesomely. In short, a well written thematic essay comes from a healthy central idea that is conclusively proven via literary devices and logical arguments.
If you're thinking " i need help with my homework " - contact us!
How to Pick a Thematic Topic?
A crucial aspect of writing a good thematic essay is choosing a theme. Follow the hints listed below to help you create a thematic topic:

Brainstorm from your own experiences. Recall what you were talking about in class, with your mates or parents. Do some of these conversations remind you of some book, novel or another piece of literature?
Write down every idea that comes to mind. Sometimes, your most absurd ideas are the best way to go.
List your favourite literature pieces. Which literature piece was the most touching for you? Try to analyze its subject and problems the author built upon within the story; it might help you come up with your own ideas.
Look at the details of other literature pieces: You might find some interesting details within other literature that can help you come up with your theme.
Still have no idea what to write about? No worries, we have your back.
Thematic Essay Topics
- What is George Orwell’s deliberation in portraying a “Perfect Utopia” in his book 1984?
- What main idea is George Orwell painting about Communism in the book Animal Farm?
- What is Harper Lee saying about innocence in her novel To Kill A Mockingbird?
- What is John Steinbeck saying about loneliness and isolation in Of Mice and Men?
- What is F. Scott Fitzgerald saying about the American Dream in The Great Gatsby?
Still Not in the Mood to Write Your thematic essay?
Send us your write my essays request.
How to Find and Explore the Central Theme
As stated before, uncovering the main subject and central theme respectively is the first significant step in a thematic paper. However, with so many things going on within the literature, it may be difficult to interpret the central theme accurately. To make sure you choose it correctly, follow these steps:
1. Summarize the literature: What main idea is the author trying to purvey? Usually, there will be many hints along the way, so choosing the right direction may not be so challenging.
2. Pick the most prevalent subject: One thing to note is the significant difference between a subject and a theme. A subject is the general topic of conversation—whether it be love, bravery, deception, etc. A theme is a specific point the author is making about said subject. So, find the talking point that is most commonly being brought up. This will be the focal point of the essay.
3. Read between the lines: After finding the most suitable subject, decipher what main point the author is trying to make. This will become clearer as you get deeper into the literature since clues and examples will appear frequently. After fully deciphering the central theme, there is one more significant step.
4. Overall significance: What is the overall significance that comes from the author’s point? What can be taken from this and applied to our personal lives? In other words, what is the lesson from all of this? What have we learned?
Feeling difficult to write thematic essay? Leave us a notice and our persuasive essay writer we'll help.
Thematic Essay Outline
The thematic essay has several key components. First of all, it should be five paragraphs or more, depending on the depth of the theme. Next, it should have a concrete thesis statement, which, in other words, is the thematic statement that comes from the main subject. The introduction presents the reader with the subject and the thesis statement. The body paragraphs each discuss one literary element or more to defend the validity of your thesis, all the while providing many supporting details from the text itself. Lastly, the thematic essay conclusion summarizes the main points presented and finishes off with a statement of significance.
Follow the link to learn more about HOW TO CREATE A WINNING OUTLINE
The thematic essay introduction presents the main subject of discussion in a captivating way. The first sentence of the intro should be a hook statement that makes some intriguing claim about the subject of discussion. If done correctly, this will grab your reader's attention. Afterwards, provide any necessary background information from the literature that will help the audience understand your claims later on. Lastly, put together a well thought out thesis statement that reflects the central theme of the novel.
The body paragraphs follow a thematic essay format. Since each body paragraph’s purpose should be to present a literary device as evidence, the topic sentence should introduce the claim and gateway into the evidence. Every topic sentence must mention a literary device and its relationship to the literature.
Afterwards, to validate your claim, use examples from the book that strengthen the reasoning of your statement. These can be actions from the plot or quotations that are parallel with the central theme. It’s imperative to explain how the action/quote links back to your thesis statement, as it shows that you can support your logic.
Remember: each claim must use a literary device. It can not just be a random moment or inference. Thematic essays are all about proving thesis statements through the use of critical literary devices.
The thematic essay conclusion has three main objectives to complete before wrapping up the entire paper. It should not present any new information or facts, but should summarize the information already given. First of all, restate your thesis statement in a new way. Then, summarize the central claims you made within the body of your paper and their influence on the thesis statement. To finish off the entire work, present an overall concluding statement with a global analysis of the subject. Leave your reader with another hook, making him/her interested in digging deeper into the topic.
Try also read an article on poetry analysis essay , it could be useful and can give you new insights.
Thematic Essay Example
The best way to familiarise yourself with this type of writing is to learn from an example.
Even though the ancient Greek cities of Athens and Sparta were geographically close to each other, they had very distinct cultures, lifestyles, values, and political systems that defined them. The following paper compares and contrasts the cultural impacts of the two cities by examining some of the duties and responsibilities of the citizenry as well as the different values that were deemed important. The paper further evaluates the impact of accomplishments that would have been left by both city-states on the history of western civilization.
Wrap Things Up
Before submitting your thematic essay, make sure to check a couple of things to correct any possible errors.

- Double-check and confirm that the central theme you have decided is the one that the author likely meant to focus on. Unless you can provide a secondary issue and present it strongly enough as a primary, validate the primary subject.
- Go through and proofread your entire paper. Nothing makes reading more irritating than grammatical mistakes, clean that stuff up as much as possible.
- Get a second pair of eyes to read through your paper. It’s best to ask a classmate for help, as they most likely have or had a similar assignment. Another great way to polish things up is to ask one of our writers to give you some helpful advice.
We also recommend reading about Jem Finch character traits , our readers find it very interesting.
Having a Trouble with Your Thematic Essay?
Having a hard time thinking up a proper topic to write about? Or, do you have one but are having a hard time deciphering the theme? Let our custom essay writing service do all the work for you. Check out our price calculator to estimate the cost of your assignment.

is an expert in nursing and healthcare, with a strong background in history, law, and literature. Holding advanced degrees in nursing and public health, his analytical approach and comprehensive knowledge help students navigate complex topics. On EssayPro blog, Adam provides insightful articles on everything from historical analysis to the intricacies of healthcare policies. In his downtime, he enjoys historical documentaries and volunteering at local clinics.

Related Articles
.webp)
How to Write a Thematic Essay?
06 August, 2020
12 minutes read
Author: Kate Smith
The road to graduation from any educational institution is lined with essays and written assignments – and the majority of these happen to be thematic essays, as they are supposed to demonstrate that the students understand the topic or material well. A thematic essay is almost as old as writing is, for it focuses on investigating a topic to provide detailed analysis and evidence of why a certain claim can be made.

What is a Thematic Essay?
Although this type of essay is commonly used to analyze some historical facts or a specific literary piece and its significance, a thematic essay can be assigned on a variety of subjects. It is also a traditional classroom essay that may be a part of different exams, so students may be required to craft a thematic essay within limited time, sticking to the topic provided. This is the main reason why they consider thematic essays difficult, but whenever there’s a longer deadline and a choice of topics, the writing process is easier.
However, there’s an important thing that everyone who’s wondering ‘what is a thematic essay?’ needs to know. This type of essay mainly lets the teacher determine your knowledge of the material, and it should demonstrate your comprehension of the topic that you can back up with solid arguments and relevant examples. But proper structure is just as essential to your writing as the scope of the topic. All of the points you want to make, as well as the supporting evidence must be organized in a clear, consecutive way. If your essay lacks focus or is illogical in its organization, your readers will not be able to recognize neither the thoroughness of your research, nor the significance of your critical thinking. They might even have trouble following what evidence you found to help you arrive at a certain conclusion.
How to Find and Explore the Central Theme?
To tackle this type of essay, you often have to narrow down a topic that’s too broad before getting started on your writing. A theme is what an author portrays in a literary work, or the specific point the author is making. Often, it is the most frequently discussed one, or it is a lesson of the greatest overall significance that can be derived from the work and applied to our lives. Thus, to effectively plan out how you are going to write a thematic essay, identify the theme first. Focus on the main point the author is trying to make about a particular subject, the message he is trying to convey, why it is relevant or important at the moment, and the way the reader can benefit from it.
That’s why having a place to start and an outline to follow lays the groundwork for your thematic essay. It is the most important step in the entire essay writing process.
Thematic Essay Outline
By using an outline to shape your essay, you have a format to follow that ensures knowledge of the topic, addressing all the questions of the assignment, and keeping all of the points you want to make well-organized. A thematic essay outline lets you effectively draw parallels between different facts, formulate a coherent and detailed evaluation of the topic, and see whether something in the essay is lacking or needs to be rearranged and revised.
Some essay types may have less rigid layouts and writing requirements, allowing for more creativity and freedom when it comes to formatting. However, this is not the case with instructions on how to write a thematic essay. Just as with other traditional essays, there should be at least five paragraphs in a thematic essay, including an introduction with a thesis statement, three body paragraphs that will support your thesis with relevant arguments and examples, and a logical conclusion to wrap everything up at the end.
Introduction
Generally, to write a thematic essay you need to have an idea of what your thesis will be, how your body paragraphs will prove it, and how you are going to summarize all of the arguments detailed in the body of the essay in your conclusion. The introduction has to present the main subject of your essay as well as any necessary background information and your thesis statement. At the same time, it should be interesting enough to make the reader want to learn more about the topic. The opening sentence of the introduction is often referred to as a ‘hook’ because it is supposed to grab the reader’s attention. For this purpose, it can evoke anticipation, controversy, irony, or ask a question. The thesis statement is very important because it gives your topic a direction and a specific purpose.
The thesis statement lays the ground for further analysis, for answering a specific question, asserting an opinion or explaining how and why something works (or has worked/failed to produce an expected result). Think of your thesis statement as a compelling and concise headline that gives the reader a good idea of what the rest of the paper is about and what to expect next. It should be engaging, but not confusing to your audience. Have you ever been extremely disappointed by reading an article or watching a movie because it wasn’t what the headline, magazine cover or a movie trailer promised it to be? To make sure your reader doesn’t feel like that, you want your thesis to be integral to the essay and to all of the evidence that you provide in the following body paragraphs. Quite often, a thesis statement needs a few revisions to acquire more focus and clarity as you add the body paragraphs to your thematic essay.
Body paragraphs
While the 5-paragraph structure gives you a basic layout to work with, it should have three body paragraphs because the thesis must be supported by at least three significant arguments. However, unless the essay has a required length, you can include more supporting facts or examples. There may be more body paragraphs than just three, depending on the details of the assignment or the points you are required to address, but keep in mind that your essay should be concise and devoid of wordiness. Usually, the essay writer should focus on one point or sub-topic per paragraph, but depending on the complexity of the topic, the quantity of paragraphs for validating each claim or explaining your reasoning may vary.
You can think of body paragraphs as building blocks that include expert quotes or specific examples to add weight to them, as well as to your arguments. This is the ‘meat of your essay’ as long as you make sure that you explain the logic behind each quotation or evidence supporting your claim, and that it is in sync with your thesis statement. Such connections are essential as they tie not only the evidence and arguments, but an entire essay together.
The conclusion is not simply a reiterated thesis, but a reinforced one. However, it’s important to keep in mind that it should not introduce any new facts not discussed in the body of a thematic essay. The conclusion has to summarize the information presented in the essay, briefly going over the main ideas or claims and explaining how they influence your thesis. Finally, it should wrap up your essay in the most meaningful way, emphasizing the significance and relevance of your topic.

Thematic Essay Examples
Check the examples of thematic essays to use as writing models:
https://www.template.net/business/essay/five-paragraph-essay-template/
Thematic essay topics
To sum up, reading some properly structured thematic essay examples may be the most helpful tip for understanding what your essay should look like, and how to organize your thoughts into a logical sequence. Besides, a list of the most commonly used thematic essay topics is a frequent search query along with ‘thematic essay examples’, as it helps students to get an idea of what to expect at exams.
US History Thematic Essay
In this essay, there will be fewer words that address the reader. The purpose of this writing is to present a balanced analysis of a topic based on facts, explaining a topic in a logical and straightforward manner.
US History thematic essay example topics:
- Major movements in U.S. history
- Major advances in U.S. history
- Significant government reforms
- U.S. Presidents and their major decisions
- U.S. wars and conflicts
Global Regents Thematic Essay
These topics are likely to feature broad concepts, but they usually include tasks and suggestions that are more specific. In your essay, you are supposed to address this detailed task and the issues, concepts or questions it prompts you to explain or interpret. Using examples from your course of global history or geography is also required in your thematic essay.
Global Regents thematic essay example topics:
- Impact of colonizations on world history
- Migrations of people and their effects
- Major characteristics of world civilizations
- Cultures and their contributions
- Economic Systems
- Political Systems
- The turning points in history (revolutions, conflicts, wars)
- Revolutions and clashing of ideas
- Revolutions and new discoveries
- Scientific development
- Technological progress
- Human rights: impactful leaders and their ideas
- Human rights violations
Belief Systems Thematic Essay
A belief system is a way a group or an individual regards religious or philosophical principles. The beliefs that have formed major religions or a mainstay of a civilization may be similar or different, but each belief system has influenced the lives of its followers as well as the history, culture, politics, or economy of a specific nation or country.
Belief Systems thematic essay example topics:
- How belief systems influenced ancient civilizations?
- How did a belief form a religion?
- Cultures as systems of interconnections between humans
- The role of religion in Ancient Roman society
- The three major monotheistic religions: Judaism, Christianity and Islam
- Judaism: the first monotheistic religion
- The personal belief system and life values
- Compare Christianity to another religion. Are there more similarities or differences?
- Compare two struggles for religious freedom in different countries and time periods
- What makes all struggles for religious freedom similar?
The bottom line
While students often have difficulties writing thematic essays, these are not the most complicated tasks to complete within a certain course or subject. They just require making a detailed examination of the topic using relevant facts, examples or other evidence that you should be able to find in order to make your arguments more solid, and to show that you have gained a thorough understanding of the topic. However, you mustn’t just summarize the well-known facts or what you have learned from a course or book. In a thematic essay, you are supposed to identify and explain or compare issues, causes, patterns, outcomes, and connections between facts or events as well as their consequences or influences.

A life lesson in Romeo and Juliet taught by death
Due to human nature, we draw conclusions only when life gives us a lesson since the experience of others is not so effective and powerful. Therefore, when analyzing and sorting out common problems we face, we may trace a parallel with well-known book characters or real historical figures. Moreover, we often compare our situations with […]

Ethical Research Paper Topics
Writing a research paper on ethics is not an easy task, especially if you do not possess excellent writing skills and do not like to contemplate controversial questions. But an ethics course is obligatory in all higher education institutions, and students have to look for a way out and be creative. When you find an […]

Art Research Paper Topics
Students obtaining degrees in fine art and art & design programs most commonly need to write a paper on art topics. However, this subject is becoming more popular in educational institutions for expanding students’ horizons. Thus, both groups of receivers of education: those who are into arts and those who only get acquainted with art […]
How to Write a Thematic Essay With Explanations and Examples
- Icon Calendar 18 May 2024
- Icon Page 4290 words
- Icon Clock 20 min read
Thematic essays are common essay assignments in college across all disciplines. Basically, this guide begins with a definition of a thematic essay and provides sample topics for illustration. Next, the manual deconstructs the process of writing a thematic essay. Moreover, the guide covers three core stages of thematic essay writing: preliminary actions, establishing the paper’s foundation, and writing. Finally, the manual presents a sample outline and an example of a thematic essay to demonstrate a real writing situation where a student implements these guidelines of thematic paper writing correctly. Hence, students need to learn how to write a thematic essay.
Definition of a Thematic Essay
A thematic essay is a form of academic writing that requires an author to react to a particular question or theme. In this case, instructors expect students to develop a written reaction to a question or theme by connecting various pieces of information to reach a reasonable conclusion. Moreover, writing a thematic essay has a high demand for research and a critical examination of subtle relationships that exist between sources. Then, the research process yields a significant amount of information, which learners may use to generate numerous logical relationships that lead to rational inferences. Consequently, students may select any set of evidence with a clear, logical association provided that their central claim centers on a theme of interest.

Sample Topics for Writing Thematic Essays
- A pure democracy.
- Privacy rights in the big data age.
- Life in prison and the ex-convict experience.
2. Sociology
- Major parenting issues of the 21 st century.
- Thematic family bonds in immigrant families.
- Escaping the cycle of poverty.
3. Literature
- The thematic significance of a muse.
- Corruption in 18th-century short stories.
- Female authors who left a mark on classical literature.
- Memories of the holocaust.
- Landmines on the modern political landscape.
- The cause of the collapse of Middle East alliances in the 20 th century.
5. Psychology
- Teenage confidence after the thematic emergence of social media.
- The impact of abuse on the formation of relationships.
- The efficacy of proactive counseling.
How Do You Know if Your Paper Is Thematic?
A student can readily identify a thematic essay topic because it boldly pronounces a writing theme but does not hint at any specific point of view. In particular, the primary goal of a topic of a thematic essay is to inform readers of a theme rather than the particular approach of an author, which becomes more apparent in the introductory paragraph. Specifically, a thematic essay topic does not allow students to develop a particular supposition concerning a theme because authors realize there may be multiple points of view concerning the idea of a thematic essay.
3 Steps For Writing an Effective Thematic Essay
Step 1: preliminary actions, a. define a thematic topic.
The ability of students to define a topic is dependent on the extent to which they understand essay rubric and instructions. Basically, once learners receive thematic essay instructions, they should critically read their prompts to ensure they comprehend all demands of writing requirements. Then, writers should use keywords from their instructions to write one or more questions, which represent the expectations of instructors. Based on developed questions, students can create a topic that adequately captures the content of possible responses holistically. Also, authors must consider the information in the instructions, which establishes the leeway they have in the selection of a topic, for example, choose a theme not covered in-class readings.
B. Identify a Purpose for Writing a Thematic Essay
The procedure of identifying a purpose occurs in two distinct stages: the selection of a general goal and defining a specific purpose. Basically, authors may write a thematic essay to achieve two general purposes: explanation and persuasion. In this case, expectations of instructors influence the choice of the general purpose of a thematic essay to a large extent. After learners pick the general purpose for writing a paper, they should create a specific purpose that shows the particular effect their papers must have on readers. Mostly, writers generate a specific purpose from questions that represent thematic essay instructions. In turn, the early determination of the purpose is crucial because it affects the students’ approach to research and word choice during drafting.
C. Analyze an Audience
Before writing a thematic essay, students need to determine the characteristics and expectations of readers. Basically, knowledge concerning the characteristics and expectations of the audience is valuable because writing allows authors to understand the interaction between the characteristics and attitudes toward a topic, the readers’ level of expertise, and the significance of misconceptions, which aid in selecting the appropriate presentation approach. Specifically, learners can determine the most effective organization patterns, identify the best evidence, and employ an accepted documentation style. Moreover, students ensure a suitable level of explanation accompanies specialized writing terms that appear in a thematic essay.
D. Generate and Write Ideas
After learners define the purpose and comprehend the needs and traits of the audience, they begin to develop ideas for the content of a thematic essay. Mostly, thematic essay assignments for writing a particular subject focus on topics lecturers discuss in classrooms and other course readings. Consequently, students may generate ideas through brainstorming based on the relevant information from the unit and other related units they encounter during their schooling. During brainstorming, writers engage in idea mapping and clustering, which enables them to keep track of relationships between ideas.
Step 2: Establishing a Foundation for Writing a Thematic Essay
A. search for sources.
The author’s initial ideas regarding a topic act as the starting point for acquiring credible sources that support and refine those ideas. Basically, contemporary learners engage in electronic searches to find useful and reliable sources for thematic essays. In this case, students should begin their search on the library’s website, which provides them with material that is reliable for academic writing. Also, library search engines have complex filter functionalities, which make the process of searching for academic sources quite simple. Then, authors turn to open-web searches using Google Scholar or other public search engines that generate a significantly larger number of sources. However, some articles may not be accessible to students. Moreover, the burden of determining the reliability of sources falls on authors when they use open-web search engines. In turn, students rely entirely on keywords or keyword combinations to generate working bibliographies.
B. Evaluate Sources Before Writing
Working bibliographies undergo an intensive evaluation process to establish whether they meet the necessary quality standards for inclusion in writing a college-level thematic essay. In this case, the evaluation process involves two primary stages: relevance determination and reliability test. During relevance determination, authors should examine each source by using three criteria:
- The level of attention that the source gives to the topic.
- The suitability of the sources’ sophistication to the purpose and audience’s needs.
- Impact of publication date on the relevance of its information.
Next, the reliability test investigates five critical writing aspects:
- The origin of the thematic source.
- The level of expertise of authors.
- Biases of a source in the context of existing literature.
- Availability and quality of the evidence supporting the source’s claims.
- Objectivity in the presentation of the author’s claims and handling of evidence.
C. Write a Thematic Annotated Bibliography
At this point, the revised working bibliography now contains fewer sources that are relevant and reliable. In particular, students should engage in critical reading of all sources in the working bibliography to identify useful pieces of information they may incorporate into a thematic essay. After reading each source, learners write an annotation that contains a summary of a source, ideas for using this source, and an assessment of this source. Besides the three main elements of an annotated bibliography entry, writers may choose to mention specific pieces of evidence, which are the most significant contributions of a source to a thematic essay. Typically, writers develop an annotated bibliography from notes they make as they read through a text.
D. Develop an Outline
Based on an annotated bibliography, students create an essay outline. Basically, the content of an annotated bibliography entry allows learners to develop relationships between sources, which is essential because it begins to shape an essay structure. In this case, writers identify and group sources that support a general point, which splits a body of a thematic essay into discernible sections. Then, authors break down each general point into specific points that can exist as a body paragraph and assign appropriate sources to individual body paragraphs. Furthermore, scholars logically organize particular points and establish some form of flow within each section of a body paragraph. In turn, writers document the organization of general and specific ideas and the distribution of evidence in a list, like a format that allows for easy identification of hierarchy.
Step 3: Writing a Thematic Essay
A. design a working thesis.
A student develops a working thesis statement, which presents his or her central claim. Basically, questions that writers derive from assignment instructions and specific minor arguments listed in a thematic essay outline are the main pieces of information they use to generate a thesis statement. Initially, writing a working thesis statement may appear as a simple combination of individual responses to assignment questions in the context of the information that forms an outline. However, authors must unite individual answers under a specific inference that demonstrates the significance of writing a thematic essay. Also, a working thesis statement undergoes multiple revisions, which occur randomly during the writing process.
B. Review an Outline
Once an author writes a working thesis statement, a person subjects an informal outline to a revision that results in the creation of a formal outline for a thematic essay. Basically, body paragraphs of a thematic essay are building blocks for a central claim. Consequently, learners must review an informal outline to ensure there is an apparent logical build-up to the inference, which they announce in a written thesis statement. During this review, students focus on the organization of minor arguments to ensure that body paragraphs contain a single minor idea while maintaining a rational relationship with other body paragraphs. Moreover, writing a formal outline contains a systematic arrangement where information with the same level of significance or roles has identical indentation or numbering.
C. Select Sources for Writing
Based on writing a formal outline, students make a final assessment of sources for each body paragraph. In particular, a formal outline contains some changes in its organization and the framing of minor arguments of a thematic essay. Also, these changes may affect the relevance of sources to each body paragraph’s argument. Then, the subdivision or merging of minor arguments may cause some sources to become inadequate because they do not extensively cover new minor ideas. Therefore, writers should check the suitability of each source to arguments it supports to ensure each source provides strong, relevant, and accurate evidence before commencing the drafting process.
D. Draft a Thematic Paper
During the drafting stage, authors expand a thematic outline into a complete paper by changing statements and brief notes into coherent paragraphs. Basically, there is no fixed approach to the drafting of a thematic essay because students may start writing at any point in a thematic essay with the aid of a formal outline. Nonetheless, it is an excellent practice for learners to begin drafting from a paragraph they understand the best because it ensures writers waste very little time trying to overcome the fear of creating the first draft. In turn, scholars should allocate adequate time for drafting.
How to Perfect a Thematic Essay
1. revision, a. self-critic.
After completing the first draft, students undertake a self-conducted revision process, which involves rethinking and rewriting. Basically, the process of revision focuses on the evaluation of the evidence and organization of body paragraphs to ensure they support a working thesis statement entirely. Further, learners revisit a working thesis statement to refine its wording and the claim it presents. Before starting the revision process, writers should take a break, which allows a human brain to reset and attain a higher level of objectivity while revising. Moreover, scholars should use a checklist to reduce the risk of overlooking various crucial thematic essay dynamics during individual revision.
B. Peer Review
The individual revision process identifies the apparent flaws in content presentation, but numerous flaws may go unnoticed due to the authors’ subconscious biases concerning their writing styles. As a result, students should subject their thematic essays to a peer review by a classmate, tutor, parent, or writing center staff. In this case, learners should select a peer reviewer that best represents a member of the target audience. Moreover, authors may provide peer reviewers with a checklist to guide them through the revision process, especially if a person is not an expert editor. Then, students should assign adequate time to the peer review process to allow reviewers to carry out the revision task comfortably. In turn, once writers receive feedback from peer reviewers, they consider comments when making the final revision of a paper.
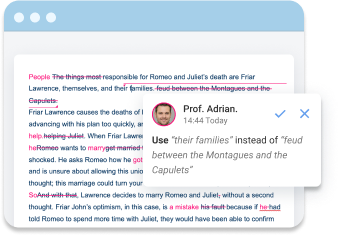
A. Clarity and Effectiveness
The first consideration in the editing process is the clarity and effectiveness of sentences in a thematic essay. Basically, authors should edit each sentence to ensure statements convey the intended meaning to readers. In this case, it is advisable to focus on six clarity issues, which are the most common in writing thematic papers: lack of parallelism, dangling modifiers, vague references to pronouns, incomplete sentences, and incorrect separation of sentences. Besides clarity, learners should evaluate the efficacy of each statement separately and as part of a paragraph. In turn, the effectiveness of writing statements revolves around the smoothness of transitions, conciseness, variability in sentence structure and length, the distinctiveness of the author’s voice, and emphasis on core ideas.
B. Surface Errors
The subsequent stage of the editing process involves editing for thematic surface and documentation errors. In particular, students should strive to eliminate all surface errors because they divert the readers’ attention to meaning, although some writing errors do not necessarily change the meaning of sentences. For example, learners can edit surface errors by using six-item criteria: spelling errors, comma splices, sentence fragments, verb errors, punctuation errors, and pronoun errors. Moreover, students should not attempt to conduct clarity and effectiveness editing simultaneously with surface error editing, which may result in poor writing because of the extensive nature of rules governing the English language. In turn, the final step in editing a thematic essay is the correction of any documentation errors while referring to the appropriate style manual.
Sample Outline for Writing a Thematic Essay
I. introduction.
A. Hook sentence. B. Background information. C. Thematic thesis statement.
A. First paragraph
1. The idea for writing the first thematic paragraph. 2. Evidence supporting this paragraph’s claim. 3. Interpretation and analysis of evidence.
- First specific deduction from evidence.
- Second specific deduction from evidence.
4. A concluding statement that demonstrates the link between the first paragraph’s claim and thesis statement.
B. Second body paragraph
1. The idea for writing the second thematic paragraph. 2. Evidence supporting this paragraph’s claim. 3. Interpretation and analysis of evidence.
4. A concluding statement that demonstrates the link between the second paragraph’s claim and thesis statement.
C. Third body paragraph
1. The idea for writing the third thematic paragraph. 2. Evidence supporting this paragraph’s claim. 3. Interpretation and analysis of evidence.
4. A concluding statement that demonstrates the link between the third paragraph’s claim and thesis statement.
III. Conclusion
A. Restatement of the thesis statement written in a thematic essay. B. Summary of the three minor arguments in the body paragraphs. C. Closing remarks emphasizing the significance of the central claim in the context of the three minor arguments.
Commentary on a Thematic Essay Outline
1. identify a central theme.
The audience can determine the central theme of a thematic essay from a thesis statement or an overview of topic statements. Basically, writing a well-composed thesis statement must explicitly mention the central theme or implicitly hint at the central theme. Alternatively, the audience can read through topic sentences and correctly speculate the central theme of a thematic essay because minor arguments in individual body paragraphs are building blocks of a thesis statement. However, the readers’ ability to identify the central theme from a formal outline is dependent on their pre-existing knowledge concerning a topic because an outline uses statements and annotations with writing little explanation.
2. Uniqueness
A thematic essay stands out from other types of essays because of the high level of freedom that writers enjoy during authorship. During the writing of a thematic essay, authors can choose any purpose or a combination of purposes to use in different sections of 5 parts of an essay, which is a luxury that argumentative essays and expository essays do not extend to writers. Also, essay instructions for writing a thematic essay tend to define a broad scope for research, which implies that authors may develop a wide variety of arguments. In turn, the expansive nature of the subject of a paper is not present for argumentative essays, which forces students to choose one of the two sides of a controversial issue.
Outlining a Thematic Essay
The introduction section is the first part of a thematic essay, which consists of three main elements: hook, background information, and thesis statement. Firstly, a hook is the first statement of any paper that plays the role of capturing the audience’s attention through creative wording, which gives them a reason to read the entire paper. Since students know how to write a hook, they provide the essential background information that readers require to understand a thesis statement. Moreover, the background information element does not have a fixed length. Instead, it is dependent on the complexity of a thesis statement and the overall length of a thematic essay. Also, writing a thesis statement is the final item of the introductory paragraph. In turn, the length of introductions is approximately 10% of the essay’s word count.
II. Body Paragraphs
A. topic sentence.
A topic sentence contains a minor claim that an author discusses within a paragraph. For example, its primary role is to establish content boundaries, which ensures students focus on a particular idea in each paragraph. Moreover, a topic statement should present a minor argument and mention a relation that it has to the central idea of writing a thematic essay or make a tacit suggestion of its link to a thesis statement. Therefore, writers should avoid the use of in-text citations in a topic statement because it implies that an idea is not original.
B. Evidence
After a topic sentence, students unveil the evidence that supports their claims. In college writing, an in-text citation should accompany any evidence that learners introduce into a thematic essay to direct readers to its origin. Also, learners should rely heavily on summary and paraphrasing in their writing, as opposed to direct quotations from sources. Nevertheless, some thematic essay instructions may specify a particular technique writers must use when integrating evidence into a paper.
C. Evaluation
This element of a paragraph structure allows authors to explain the significance of the evidence to the paragraph’s argument. In this section of a thematic essay, students provide an interpretation of the evidence, which informs the audience of the meaning of the evidence in the context of a source text. Then, writers explain the value of the evidence in developing a reasonable justification for the idea proposed in topic sentences. In turn, learners should avoid the inclusion of lengthy pieces of evidence because it creates a situation where the voice of sources is more dominant than the author’s voice.
D. Concluding Statement
A concluding statement emphasizes the logical relationship that exists between the topic sentence, evidence, evaluation, and thesis statement. In some cases, it may establish the relationship of a paragraph with the preceding paragraph. Also, students should ensure a concluding sentence of a paragraph does not contain a meaningless summary of the key pieces of evidence. Then, a concluding statement of a thematic essay must not contain any new evidence because there is no opportunity to explain the contribution of the evidence in supporting the paragraph’s argument.
A concluding paragraph has three critical features: a restatement of the main claim, a summary of minor arguments, and closing remarks. Basically, the opening statement of a thematic essay reminds students of the central argument by using new words and syntax. After the opening statement, learners summarize minor claims that appear in individual body paragraphs while maintaining a logical organization, which is identical to the arrangement of ideas in the body. Finally, authors write a strong closing statement that knits together the introduction, thesis statement, and minor claims to create a lasting impression on the audience. Moreover, students should ensure they do not introduce new evidence or arguments in a concluding paragraph. In turn, authors must not apologize for a lack of expertise on a topic or make absolute claims because it diminishes the efficacy of writing a good conclusion.
Example of Writing a Thematic Essay
Topic: Recruitment of Terrorists
I. Sample Introduction of a Thematic Essay
Terrorism is a global problem, which appears to be spreading despite an increment in the efforts to suppress its growth. Basically, the prevention of recruitment is a crucial counterterrorism strategy. Moreover, its efficacy is dependent on the understanding of the terrorists’ recruitment techniques. In turn, the terrorist groups’ recruitment methods focus on the target’s identity crisis, which puts a potential member at risk of falling for the ‘appeal’ of terrorism.
II. Examples of Body Paragraphs in a Thematic Essay
A. motivation.
An individual’s desire to be part of a movement that is effecting a radical change in society is a significant motivator for participation in terrorism. For example, recent studies show that terrorist groups begin conversations with most young recruits on social media platforms, which discuss topics concerning social, political, and economic oppression (Jacks, 2020). Basically, this finding suggests that young people in contemporary society have a desire to correct the ‘wrongs’ in society as a means of identity. Consequently, terrorists use the increased sensitivity to social injustices as a common ground to initiate and build a relationship with a prospective recruit. In turn, the youth’s strong desire to do something to stop social injustices that their respective governments ignore leaves them vulnerable to radicalization by terrorist groups.
B. Religious Beliefs
Fanatical religious belief may drive an individual to support or participate in terrorism for the sake of being part of a group. According to Mohammed (2020), the constant pressure from religious parents causes the blind indoctrination of adolescents and young adults, which enables recruiters from terrorist groups to present religious concepts as justifications for terrorism, for example, the holy war. In this case, Mohammed concedes that the mosque is an ideal site for the recruitment of terrorism because of the presence of youth with highly impressionable minds. Moreover, youths depend on teachings at places of worship for knowledge that defines their perspective of the world. As a result, terrorist recruiters disguised as spiritual leaders can easily nurture fanatical beliefs that endorse terrorist activities. Eventually, a feeling of separation from the conservative believers pushes them to pursue groups that share their fanatical religious beliefs.
C. Recruiting
The loss of a family member to counterterrorism activities may act as a motivation factor for grievers who are trying to re-establish their identities because they no longer fit into the traditional social structures. For instance, Tobias (2020) argues that recruiters prey on the pain of grieving family members by offering them retribution as a solution to the overwhelming feeling of incompleteness. After the death of a family member, the emotional turmoil increases the susceptibility of individuals to the idea that terrorist acts are an appropriate response to the ‘killers’ of their loved ones. Often, recruitment occurs during this unstable state and encourages the individual to relive the pain each day, which results in the permanent erosion of their former identity. Accordingly, grievers may find themselves as sympathizers of terrorism, which leads to active or passive participation.
III. Sample Conclusion of a Thematic Essay
Most members of terrorist organizations experience an identity crisis at the time of recruitment. Basically, the need to gain membership to a group that fights against social injustices tolerates fanatical religious beliefs or seeks revenge for the death of loved ones is a sign that identity crisis is a common characteristic in recruits. In turn, current counterterrorism initiatives should seek to break the cycle of recruitment, which will weaken terrorist groups.
Takeaway on How to Write a Good Thematic Essay
- Students should define a narrow writing topic to guide them in generating ideas in response to a thematic paper prompt.
- The characteristics and expectations of the audience are vital in determining an appropriate presentation approach.
- Before drafting a thematic essay, authors must write a formal outline and annotated bibliography, which are critical for organization and evidence selection.
- The maintenance of a high level of fluidity during drafting is critical during drafting because it allows writers to experiment with different styles of expression.
- Revision and editing are aspects of the writing process that a student should not take lightly.
- All body paragraphs must adhere to the four-element paragraph structure.
- The conclusion of a thematic essay should not contain any new evidence or arguments.
- Learners must write a thesis statement that captures a theme that instructors highlight in essay prompts.
To Learn More, Read Relevant Articles

How to Write a Profile Essay With Tips and Examples
- 18 September 2020

670 Personal Essay Topics & Free Ideas
- 16 September 2020
How to Write a Thematic Essay: Detailed Guidelines
Table of contents
- 1 What Is a Thematic Essay?
- 2.1 Introduction
- 2.2 Body Paragraphs
- 2.3 Conclusion
- 3.1 Prepare
- 3.2 Take Notes
- 3.3 Write a Perfect Thematic Essay Introduction
- 3.4 Generate the Main Section
- 3.5 Develop a Perfect Thematic Essay Conclusion and edit your work
- 4.1 How is the dog-human relationship portrayed in the Call of the Wild novel?
- 5.1 What is a good hook for a thematic essay?
- 5.2 How to Write a Thesis for a Thematic Essay?
- 5.3 What is a Perfect Topic Sentence for a Thematic Paper?
- 5.4 What is the difference between a Theme Essay and a Research Paper?
Writing a great thematic essay can be difficult, especially when you are unsure about the topic you want to write about. All you do is find a good thesis statement and ensure you start strong, so readers keep reading.
To get a clear thematic essay definition and what makes it good, we first need to know what makes a good thesis statement . It is the first sentence of your paper that states the main point. It should be clear, concise, and compelling. But are there are tricks on how to compose an excellent thematic paper? What should you do to get the perfect thematic paper? Read on to understand how to write a theme essay.
What Is a Thematic Essay?
A thematic essay is one of the types of academic writing that focuses on a single topic and analyzes it from various angles. It can be about anything from the environment to something as personal as a person’s life story.
A thematic essay is not just about what you have to say; it’s also about how you say it. This is a similarity this type of paper shares with discursive texts. You must create an authentic voice. If you are good at writing a perfect discursive essay , you are probably good with the thematic kind.
In a thematic essay, the author develops the main ideas of literature using literary devices and techniques like personification, imagery, foreshadowing, etc. Skilled writers tend to identify the main topic, comment on the paper’s literary strategy, and convey the theme’s relevance.
Thematic Essay Outline
This outline gives you a structure and table of contents to follow. The paper outline helps you answer all the assignment questions and organize your points.
Outlines enable you to effectively compare various data and create a thorough and cohesive subject analysis. Some styles could have less strict writing guidelines, like entrepreneurship essay writing, allowing for greater formatting styles innovation. When generating a thematic paper, you need at least five paragraphs. These paragraphs should entail an introduction, body and conclusion format.
Introduction
When developing a thematic paper, focus on your outline: Get a concept of the thesis and how the body will support it. Understand how to synthesize all the information before writing your theme essay.
For the paper’s intro, you must include the thesis statement and relevant background data. Your framework sets the stage for future investigation for responding to a particular query, expressing a specific opinion, or describing why and how something operates. It informs the audience about the main points of your work and what will come next.
This segment should also be captivating enough to reel the reader in and urge them to read more. It is the hook that raises interest, stirs debates, or even poses a simple query to the reader. It offers your thematic essay a focus and a clear goal.
Body Paragraphs
The five-paragraph thematic essay format stipulates a basic framework to follow. Ensure the body has three paragraphs. To make your paper more interesting, include extra illustrative details or instances if it does not have a length requirement. If this seems hard, you can still hire a theme essay writer or expert and pay for your essay to get perfect results.
A thematic essay should be brief and free of wordiness. As the paper’s author, you should concentrate on one sub-topic or argument. The number of body paragraphs for confirming each assertion or outlining the reasoning of the thematic essay might vary. Such variation depends on the intricacy of the topics.
This section strengthens the thesis rather than merely restating it. Therefore, avoid introducing fresh information not covered in the text. Instead, summarize the data discussed in the paper and quickly review the central assertions.
How to Write a Thematic Essay?
Here are the tricks to learn how to write a theme-based essay:
Before writing your paper, find all the source elements and materials you will utilize. Some of the preparation elements may include:
- Reading literature abstract
- Recordings from results of discussions
- Your consideration of the paper’s theme
- Finding the perfect topics
Process all the available materials (arguments, reasoning, and organization) properly to get supporting evidence to support your topics.
When going through source materials, take notes. Taking notes helps you pay more attention to the content you are reading to gain crucial information related to your topic. From the notes, you can easily filter what is relevant and generate your understanding of the literary devices you are using.
Write a Perfect Thematic Essay Introduction
When developing a perfect intro, include a brief description of your approach and understanding of the topic. Mention your goals or what you will cover in the thematic essay. Additionally, include a literary device that plays an important role in the task.
Generate the Main Section
The main part of your paper assumes the generation of the paper’s analysis. It entails the paper’s primary information. At this stage, you should describe your topics.
Develop a Perfect Thematic Essay Conclusion and edit your work
This section is fundamental when you are writing a theme essay. Include a summary of your analysis while writing this section. Make it brief.
After writing the theme essay, review it again to fix any mistakes. You can also give the paper to a friend to confirm any errors. Sometimes you can go online and type, “I want to edit my essay, please help.” You will get online resources to help you fix your professional essay. These resources help individuals edit their theme-based essays to perfection.
How to Write a Thematic Essay: Thematic Essay Example
Here is a sample thematic paper that you can work with:
How is the dog-human relationship portrayed in the Call of the Wild novel?
Dogs are men’s best friends with connected feelings. However, this is a cliché since everyone knows dogs’ role in our lives. We can have police dogs, hunting dogs, guide dogs, herding dogs, etc. This isn’t different from the roles that bucks play. Usually, human beings reciprocate the devotion offered to them with friendship. But is the friendship that humans provide sufficient for the adoration that the dog gives? In Call of the wild, there is a human that shows that humans can provide more than companionship and friendship.
At the start of the Call of the wild, we can see that the crucial part that Buck plays to the Miller family exceeds that of a pet. Buck is relied upon to be a pretty reliable protector and companion. Elmo and Buck were consistent protectors and hunters. No wonder their owner treated them well. However, one expression showed Buck the fierce side of life.
We see how humans tend to treat dogs ruthlessly. They forced the dogs to pull very heavy weights even though they were tired and cold. Moreover, the dogs weren’t compensated sufficiently with food and sleep even though they worked hard each day.
Later on, John Thornton saves Buck and his friends. And for the first time, these dogs experienced true love, the love they were missing while under the care of Judge Miller. Therefore, Buck heads back to Thornton with total devotion. After a while, Thornton dies. Buck joins a pack of wolves. But even when in the pack, Buck always returns to where Thornton died to mourn his loving master.
At the end of the story, we can see that death and time aren’t a hindrance for dogs to show their feelings to their master. Indeed, dogs offer more than love to their masters.
What is a good hook for a thematic essay?
A good hook for a thematic paper should be intriguing to grab the reader’s attention. Moreover, it should introduce the main subject for the theme essay.
How to Write a Thesis for a Thematic Essay?
To write the thesis statement, you should capture the following elements:
- Author (if you know them)
- A simple reference to a certain conflict in the story
What is a Perfect Topic Sentence for a Thematic Paper?
A strong topic sentence should be clear and indicate what to expect in the entire paper. However, it should be brief to avoid giving everything away. Moreover, you should review multiple topics to find the right one.
What is the difference between a Theme Essay and a Research Paper?
A theme paper is short and only includes around five paragraphs. Research papers tend to be pretty long, reaching around eight pages. However, as an author, you can gain help in both of these papers using online writing help by Papersowl . The company has experts who work on your paper and ensure you get perfect results.
- Free unlimited checks
- All common file formats
- Accurate results
- Intuitive interface
Readers also enjoyed

WHY WAIT? PLACE AN ORDER RIGHT NOW!
Just fill out the form, press the button, and have no worries!
We use cookies to give you the best experience possible. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy.

- Customer Reviews
- Extended Essays
- IB Internal Assessment
- Theory of Knowledge
- Literature Review
- Dissertations
- Essay Writing
- Research Writing
- Assignment Help
- Capstone Projects
- College Application
- Online Class

How to Write a Thematic Essay: The Complete Guide
by Antony W
September 12, 2022

In this guide, you'll learn exactly how to write a thematic essay step-by-step.
Thematic essays, or theme essays, require you to really examine a literary object such as a book, journal, paper, or other art form and pick out the main ideas (themes).
You will then explain how these themes are brought on and what literary devices are used to do that.
Key Takeaways
To write an outstanding theme essay, you should:
- Select a literary work to base your thematic analysis on.
- Choose a primary theme.
- Identify supporting evidence and literary devices used.
- Plan and outline the essay.
- Write the first draft.
- Edit and proofread your work for submission.
What is a Thematic Essay?

A thematic essay is a one in which you identify the main idea (theme) expressed in a chosen literary object and explore how the writer of that literature chooses to address that theme through various literary devices.
The devices can be metaphors, hyperbole, imagery, allegory, and many others.
Writing a thematic analysis essay is a great way to learn how to pick out themes in the literature you read as well as how to improve your writing skills.
A thematic essay will be at least five paragraphs long , but usually longer depending on the complexity of the work being reviewed.
You can write a thematic essay based on a book, a speech, a magazine article, a video, audio, or any other art form.
Choosing a Theme for a Thematic Essay
Choosing the main idea or theme of such a work is not a straightforward process.
It is highly subjective, and what you consider the main theme in a book may not be somebody else’s.
You have to make sure that what you pick as your main theme is fully supported throughout the book and makes significant appearances in most chapters, if not all of them.
How to Write a Thematic Essay Step by Step
Writing a thematic essay is easy. You just have to:
1. Choose a Literary Object
If your instructor does not provide the topic, think back to a book or article that made a strong impression to you, or think about your favorite pieces of literature.
Another option is to brainstorm. Brainstorming hardly fails, especially if you incorporate the help of your friends and even your instructor.
Collect different ideas and be sure to write each of them down, no matter how unlikely they sound. From there, eliminate most of these the following criteria:
- The topic should be interesting and captivating. Avoid those that are too common and overly used in academia unless you can provide a fresh twist or insight.
- The topic needs to have one or more important themes running through.
- It should be a literary work that is relatively well known and in the public domain.
- Some of the shorter works are best because they guarantee your essay won’t be too long.
This process will likely leave you with one or two possible topics, but make sure to confirm with your instructor that what you choose to focus on is acceptable.
2. Find a Relevant Theme
A theme is a significant idea that recurs throughout the literary work you have chosen. You can think of it as the main message the author is trying to pass across.
There are major and minor themes differentiated by how much attention the author gives to each.
For the best outcome, your theme should be one of the major themes addressed throughout the work.
There are a few things you can do to figure out what major themes are present:
- As you read the work, note and write down what tone, setting, language styles, and characterization the writer is using.
- What is the plot of the book and what does it lead to? Think about what you would tell somebody else about the book.
- Identify who the protagonist (main character) is and what they represent. Do they change at all in the book?
For example, in Harper Lee’s To Kill a Mockingbird, Atticus Finch does not change and represents morality, love, fairness, and good reason to the end.
- Put yourself in the author’s shoes and observe from their point of view. What message do you think they want to pass on as the most important?
3. Pick Material for the Essay
Read through the book again with the main theme in mind.
See how the author plays with it, what literary devices are used to highlight their thematic approach, and write down all these for reference.
What you are doing at this stage is a literary analysis.
The tools in the author’s hands include character development, mood, setting, irony, allegory, simile, alliteration, symbolism, metaphor, among many others.
Think about how effective these tools are in shining the light upon the main theme. It helps to read between the lines as well because sometimes the most important thing is what the author leaves unsaid.
4. Planning: Thematic Essay Outline
A thematic essay is very simple and straightforward. Like most essays, it will have an introduction, body, and conclusion.
Each of these parts should be considered carefully in the planning stage and map out which ideas will go where.
Introduction
The introduction serves to catch the reader’s interest, set the background, and mention what exactly you intend to discuss in the essay.
The first one or two sentences should be a hook, that is, a statement that will be intriguing enough to make the reader want to keep reading. It can be a clever observation, a surprising statement, or even a relevant question.
Second, provide a very brief background on which to build your essay.
However, you will be assuming that the reader has already read the literary work that is the subject of the essay. So you don’t have to give too much detail.
In winding up the introductory, write your thesis statement . This is a one-sentence statement that tells the reader what your essay is about.
However, don’t say it like this: “My thesis statement is ... “ Instead, let the introduction flow and link smoothly up to this point.
Body paragraphs
You will have three or more body paragraphs detailing your arguments about the main theme. In a thematic essay, each of the body paragraphs will be focusing on one literary device and how it is useful in presenting the theme message.
As with most essays, body paragraphs will follow the TEEL format.
- Topic Sentence : The introductory sentence introduces the idea that the paragraph is about. Think of it as a mini-thesis statement. The rest of the paragraph will be explaining and supporting this one statement.
- Explanation: Explain your topic idea clearly.
- Evidence : Give compelling evidence for your claims. It can be a quote, a direct observation, similar use of the same method elsewhere in the book, a citation from an authoritative work, etc.
- Link : Show how the idea you just described links with the rest of the essay and thesis statement. Again, you won’t say, “this idea relates to my thesis statement because …” Instead, let the whole paragraph flow smoothly and seamlessly.
The number of body paragraphs will depend on how much evidence you have collected. However, make sure to keep within the reasonable word count parameters as given by your instructor.
Recap the main arguments in your body and restate your thesis statement.
The purpose of the conclusion is to give your “take-home” argument, what you feel the reader should retain from the whole work.
Customize your theme essay outline accordingly; don’t make it as generic as this example here.
Fill it with details like what ideas you will include in your first paragraph, what your thesis statement will be, and what your introduction hook is. With this thematic essay format, you are now ready to do the write-up.
5. Write the Essay
With a good outline, writing a thematic essay becomes a piece of cake. You will simply be fleshing out the template.
6. Proofreading and Revision
Make sure to read through your essay at least twice.
Note how well your ideas flow, how the arguments and evidence presented link back to the thesis statement, and of course, clear any grammatical errors.
Thematic Essay Writing Help
If you don’t have the time to read your subject thoroughly and analytically, you can hire Help for Assessment’s essay writing service . We have a suitable writer that can help you get the assignment completed on time.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. how do you start a theme essay.
The introduction of your theme essay should be an intriguing hook about the subject you wish to discuss.
Ensure the hook is concise and strong enough to grab your reader’s attention.
2. What are the Elements of a Thematic Essay?
The elements of a thematic essay are the introduction, body paragraphs, and the conclusion.
Ensure the introduction includes a thesis statement. The body paragraphs should support the thesis using relevant examples, evidence, and arguments.
Lastly, the conclusion should be logical enough to tie everything together at the end.
3. What is the Main Point of a Thematic Essay?
The main point of a thematic essay is to identify themes from a source, present a theme statement, and address a specific issue within the requirement of the assignment.
About the author
Antony W is a professional writer and coach at Help for Assessment. He spends countless hours every day researching and writing great content filled with expert advice on how to write engaging essays, research papers, and assignments.
How to Write a History Essay with Outline, Tips, Examples and More

Samuel Gorbold
Before we get into how to write a history essay, let's first understand what makes one good. Different people might have different ideas, but there are some basic rules that can help you do well in your studies. In this guide, we won't get into any fancy theories. Instead, we'll give you straightforward tips to help you with historical writing. So, if you're ready to sharpen your writing skills, let our history essay writing service explore how to craft an exceptional paper.
What is a History Essay?
A history essay is an academic assignment where we explore and analyze historical events from the past. We dig into historical stories, figures, and ideas to understand their importance and how they've shaped our world today. History essay writing involves researching, thinking critically, and presenting arguments based on evidence.
Moreover, history papers foster the development of writing proficiency and the ability to communicate complex ideas effectively. They also encourage students to engage with primary and secondary sources, enhancing their research skills and deepening their understanding of historical methodology. Students can benefit from utilizing essay writers services when faced with challenging assignments. These services provide expert assistance and guidance, ensuring that your history papers meet academic standards and accurately reflect your understanding of the subject matter.
History Essay Outline
.png)
The outline is there to guide you in organizing your thoughts and arguments in your essay about history. With a clear outline, you can explore and explain historical events better. Here's how to make one:
Introduction
- Hook: Start with an attention-grabbing opening sentence or anecdote related to your topic.
- Background Information: Provide context on the historical period, event, or theme you'll be discussing.
- Thesis Statement: Present your main argument or viewpoint, outlining the scope and purpose of your history essay.
Body paragraph 1: Introduction to the Historical Context
- Provide background information on the historical context of your topic.
- Highlight key events, figures, or developments leading up to the main focus of your history essay.
Body paragraphs 2-4 (or more): Main Arguments and Supporting Evidence
- Each paragraph should focus on a specific argument or aspect of your thesis.
- Present evidence from primary and secondary sources to support each argument.
- Analyze the significance of the evidence and its relevance to your history paper thesis.
Counterarguments (optional)
- Address potential counterarguments or alternative perspectives on your topic.
- Refute opposing viewpoints with evidence and logical reasoning.
- Summary of Main Points: Recap the main arguments presented in the body paragraphs.
- Restate Thesis: Reinforce your thesis statement, emphasizing its significance in light of the evidence presented.
- Reflection: Reflect on the broader implications of your arguments for understanding history.
- Closing Thought: End your history paper with a thought-provoking statement that leaves a lasting impression on the reader.
References/bibliography
- List all sources used in your research, formatted according to the citation style required by your instructor (e.g., MLA, APA, Chicago).
- Include both primary and secondary sources, arranged alphabetically by the author's last name.
Notes (if applicable)
- Include footnotes or endnotes to provide additional explanations, citations, or commentary on specific points within your history essay.
History Essay Format
Adhering to a specific format is crucial for clarity, coherence, and academic integrity. Here are the key components of a typical history essay format:
Font and Size
- Use a legible font such as Times New Roman, Arial, or Calibri.
- The recommended font size is usually 12 points. However, check your instructor's guidelines, as they may specify a different size.
- Set 1-inch margins on all sides of the page.
- Double-space the entire essay, including the title, headings, body paragraphs, and references.
- Avoid extra spacing between paragraphs unless specified otherwise.
- Align text to the left margin; avoid justifying the text or using a centered alignment.
Title Page (if required):
- If your instructor requires a title page, include the essay title, your name, the course title, the instructor's name, and the date.
- Center-align this information vertically and horizontally on the page.
- Include a header on each page (excluding the title page if applicable) with your last name and the page number, flush right.
- Some instructors may require a shortened title in the header, usually in all capital letters.
- Center-align the essay title at the top of the first page (if a title page is not required).
- Use standard capitalization (capitalize the first letter of each major word).
- Avoid underlining, italicizing, or bolding the title unless necessary for emphasis.
Paragraph Indentation:
- Indent the first line of each paragraph by 0.5 inches or use the tab key.
- Do not insert extra spaces between paragraphs unless instructed otherwise.
Citations and References:
- Follow the citation style specified by your instructor (e.g., MLA, APA, Chicago).
- Include in-text citations whenever you use information or ideas from external sources.
- Provide a bibliography or list of references at the end of your history essay, formatted according to the citation style guidelines.
- Typically, history essays range from 1000 to 2500 words, but this can vary depending on the assignment.

How to Write a History Essay?
Historical writing can be an exciting journey through time, but it requires careful planning and organization. In this section, we'll break down the process into simple steps to help you craft a compelling and well-structured history paper.
Analyze the Question
Before diving headfirst into writing, take a moment to dissect the essay question. Read it carefully, and then read it again. You want to get to the core of what it's asking. Look out for keywords that indicate what aspects of the topic you need to focus on. If you're unsure about anything, don't hesitate to ask your instructor for clarification. Remember, understanding how to start a history essay is half the battle won!
Now, let's break this step down:
- Read the question carefully and identify keywords or phrases.
- Consider what the question is asking you to do – are you being asked to analyze, compare, contrast, or evaluate?
- Pay attention to any specific instructions or requirements provided in the question.
- Take note of the time period or historical events mentioned in the question – this will give you a clue about the scope of your history essay.
Develop a Strategy
With a clear understanding of the essay question, it's time to map out your approach. Here's how to develop your historical writing strategy:
- Brainstorm ideas : Take a moment to jot down any initial thoughts or ideas that come to mind in response to the history paper question. This can help you generate a list of potential arguments, themes, or points you want to explore in your history essay.
- Create an outline : Once you have a list of ideas, organize them into a logical structure. Start with a clear introduction that introduces your topic and presents your thesis statement – the main argument or point you'll be making in your history essay. Then, outline the key points or arguments you'll be discussing in each paragraph of the body, making sure they relate back to your thesis. Finally, plan a conclusion that summarizes your main points and reinforces your history paper thesis.
- Research : Before diving into writing, gather evidence to support your arguments. Use reputable sources such as books, academic journals, and primary documents to gather historical evidence and examples. Take notes as you research, making sure to record the source of each piece of information for proper citation later on.
- Consider counterarguments : Anticipate potential counterarguments to your history paper thesis and think about how you'll address them in your essay. Acknowledging opposing viewpoints and refuting them strengthens your argument and demonstrates critical thinking.
- Set realistic goals : Be realistic about the scope of your history essay and the time you have available to complete it. Break down your writing process into manageable tasks, such as researching, drafting, and revising, and set deadlines for each stage to stay on track.

Start Your Research
Now that you've grasped the history essay topic and outlined your approach, it's time to dive into research. Here's how to start:
- Ask questions : What do you need to know? What are the key points to explore further? Write down your inquiries to guide your research.
- Explore diverse sources : Look beyond textbooks. Check academic journals, reliable websites, and primary sources like documents or artifacts.
- Consider perspectives : Think about different viewpoints on your topic. How have historians analyzed it? Are there controversies or differing interpretations?
- Take organized notes : Summarize key points, jot down quotes, and record your thoughts and questions. Stay organized using spreadsheets or note-taking apps.
- Evaluate sources : Consider the credibility and bias of each source. Are they peer-reviewed? Do they represent a particular viewpoint?
Establish a Viewpoint
By establishing a clear viewpoint and supporting arguments, you'll lay the foundation for your compelling historical writing:
- Review your research : Reflect on the information gathered. What patterns or themes emerge? Which perspectives resonate with you?
- Formulate a thesis statement : Based on your research, develop a clear and concise thesis that states your argument or interpretation of the topic.
- Consider counterarguments : Anticipate objections to your history paper thesis. Are there alternative viewpoints or evidence that you need to address?
- Craft supporting arguments : Outline the main points that support your thesis. Use evidence from your research to strengthen your arguments.
- Stay flexible : Be open to adjusting your viewpoint as you continue writing and researching. New information may challenge or refine your initial ideas.
Structure Your Essay
Now that you've delved into the depths of researching historical events and established your viewpoint, it's time to craft the skeleton of your essay: its structure. Think of your history essay outline as constructing a sturdy bridge between your ideas and your reader's understanding. How will you lead them from point A to point Z? Will you follow a chronological path through history or perhaps dissect themes that span across time periods?
And don't forget about the importance of your introduction and conclusion—are they framing your narrative effectively, enticing your audience to read your paper, and leaving them with lingering thoughts long after they've turned the final page? So, as you lay the bricks of your history essay's architecture, ask yourself: How can I best lead my audience through the maze of time and thought, leaving them enlightened and enriched on the other side?
Create an Engaging Introduction
Creating an engaging introduction is crucial for capturing your reader's interest right from the start. But how do you do it? Think about what makes your topic fascinating. Is there a surprising fact or a compelling story you can share? Maybe you could ask a thought-provoking question that gets people thinking. Consider why your topic matters—what lessons can we learn from history?
Also, remember to explain what your history essay will be about and why it's worth reading. What will grab your reader's attention and make them want to learn more? How can you make your essay relevant and intriguing right from the beginning?
Develop Coherent Paragraphs
Once you've established your introduction, the next step is to develop coherent paragraphs that effectively communicate your ideas. Each paragraph should focus on one main point or argument, supported by evidence or examples from your research. Start by introducing the main idea in a topic sentence, then provide supporting details or evidence to reinforce your point.
Make sure to use transition words and phrases to guide your reader smoothly from one idea to the next, creating a logical flow throughout your history essay. Additionally, consider the organization of your paragraphs—is there a clear progression of ideas that builds upon each other? Are your paragraphs unified around a central theme or argument?
Conclude Effectively
Concluding your history essay effectively is just as important as starting it off strong. In your conclusion, you want to wrap up your main points while leaving a lasting impression on your reader. Begin by summarizing the key points you've made throughout your history essay, reminding your reader of the main arguments and insights you've presented.
Then, consider the broader significance of your topic—what implications does it have for our understanding of history or for the world today? You might also want to reflect on any unanswered questions or areas for further exploration. Finally, end with a thought-provoking statement or a call to action that encourages your reader to continue thinking about the topic long after they've finished reading.
Reference Your Sources
Referencing your sources is essential for maintaining the integrity of your history essay and giving credit to the scholars and researchers who have contributed to your understanding of the topic. Depending on the citation style required (such as MLA, APA, or Chicago), you'll need to format your references accordingly. Start by compiling a list of all the sources you've consulted, including books, articles, websites, and any other materials used in your research.
Then, as you write your history essay, make sure to properly cite each source whenever you use information or ideas that are not your own. This includes direct quotations, paraphrases, and summaries. Remember to include all necessary information for each source, such as author names, publication dates, and page numbers, as required by your chosen citation style.
Review and Ask for Advice
As you near the completion of your history essay writing, it's crucial to take a step back and review your work with a critical eye. Reflect on the clarity and coherence of your arguments—are they logically organized and effectively supported by evidence? Consider the strength of your introduction and conclusion—do they effectively capture the reader's attention and leave a lasting impression? Take the time to carefully proofread your history essay for any grammatical errors or typos that may detract from your overall message.
Furthermore, seeking advice from peers, mentors, or instructors can provide valuable insights and help identify areas for improvement. Consider sharing your essay with someone whose feedback you trust and respect, and be open to constructive criticism. Ask specific questions about areas you're unsure about or where you feel your history essay may be lacking. If you need further assistance, don't hesitate to reach out and ask for help. You can even consider utilizing services that offer to write a discussion post for me , where you can engage in meaningful conversations with others about your essay topic and receive additional guidance and support.
History Essay Example
In this section, we offer an example of a history essay examining the impact of the Industrial Revolution on society. This essay demonstrates how historical analysis and critical thinking are applied in academic writing. By exploring this specific event, you can observe how historical evidence is used to build a cohesive argument and draw meaningful conclusions.

FAQs about History Essay Writing
How to write a history essay introduction, how to write a conclusion for a history essay, how to write a good history essay.
Samuel Gorbold , a seasoned professor with over 30 years of experience, guides students across disciplines such as English, psychology, political science, and many more. Together with EssayHub, he is dedicated to enhancing student understanding and success through comprehensive academic support.

- Plagiarism Report
- Unlimited Revisions
- 24/7 Support
- New Visions Social Studies Curriculum
- Curriculum Development Team
- Content Contributors
- Getting Started: Baseline Assessments
- Getting Started: Resources to Enhance Instruction
- Getting Started: Instructional Routines
- Unit 9.1: Global 1 Introduction
- Unit 9.2: The First Civilizations
- Unit 9.3: Classical Civilizations
- Unit 9.4: Political Powers and Achievements
- Unit 9.5: Social and Cultural Growth and Conflict
- Unit 9.6: Ottoman and Ming Pre-1600
- Unit 9.7: Transformation of Western Europe and Russia
- Unit 9.8: Africa and the Americas Pre-1600
- Unit 9.9: Interactions and Disruptions
- Unit 10.0: Global 2 Introduction
- Unit 10.1: The World in 1750 C.E.
- Unit 10.2: Enlightenment, Revolution, and Nationalism
- Unit 10.3: Industrial Revolution
- Unit 10.4: Imperialism
- Unit 10.5: World Wars
- Unit 10.6: Cold War Era
- Unit 10.7: Decolonization and Nationalism
- Unit 10.8: Cultural Traditions and Modernization
- Unit 10.9: Globalization and the Changing Environment
- Unit 10.10: Human Rights Violations
- Unit 11.0: US History Introduction
- Unit 11.1: Colonial Foundations
- Unit 11.2: American Revolution
- Unit 11.3A: Building a Nation
- Unit 11.03B: Sectionalism & the Civil War
- Unit 11.4: Reconstruction
- Unit 11.5: Gilded Age and Progressive Era
- Unit 11.6: Rise of American Power
- Unit 11.7: Prosperity and Depression
- Unit 11.8: World War II
- Unit 11.9: Cold War
- Unit 11.10: Domestic Change
- Resources: Regents Prep: Global 2 Exam
- Regents Prep: Framework USH Exam: Regents Prep: US Exam
- Find Resources
According to the State of New York, there are 20 themes that are found amongst the curriculum guides & suggested content for the New York State U.S. History & Government course. This Teacher's Guide lists the themes that have been repeated on the Regents exam starting with the those most frequently asked, provides the prompts that have been used in the past and suggested topics that will help students prepare for the exam.
Teacher Feedback
Please comment below with questions, feedback, suggestions, or descriptions of your experience using this resource with students.
If you found an error in the resource, please let us know so we can correct it by filling out this form .
- How to Write a Thematic Essay
- How to Write a Thematic Essay: A Step-by-Step Guide + Topics

- Thematic Essay Definition
Thematic Essay Topics: How to Choose
- Best Thematic Essay Topics
- Thematic Essay Outline
- Introduction
- Body Paragraphs
How to Write a Good Thematic Essay
- Thematic Essay Format
Thematic Essay Example
- Final Thoughts
- People Also Ask
1. How do you write a thesis for a thematic essay?
- 2. When do I need to write a thematic essay?
3. Which book should I write a thematic essay on?
Thematic essay definition .
The initial step in writing this type of academic paper is to have a question, "What is a thematic essay?" answered. According to the definition, it's a piece of writing based on a particular question or theme . When working on this paper, a student is supposed to reveal and develop the central theme in a specific literature work using various literary devices such as metaphor , personification, comparison, and other techniques. The thematic essay's primary purpose is to identify and disclose the main subject discussed in work. A student needs to use evidence, facts, and examples gathered from primary and secondary sources . As a professional writer, you should relate various facts. Use credible sources; otherwise, you may confuse your reader with wrong facts.
The first step requires coming up with a good thematic essay topic. If you have a theme assigned by your professor, consider yourself super lucky. But for those students who don't have any topic to write about, our top writers have prepared helpful tips and unique ideas to get you started. Keep in mind these simple guidelines:
- Focus on social issues. Commonly, a thematic essay is associated with social problems in different periods of human civilization.
- Refer to literature pieces. Use appropriate materials and references suggested by the professor to come up with an unusual topic.
- Choose a compelling theme. Understand your potential audience and define the most acceptable and strong idea which would engage an ordinary reader.
- Find the angle. Consider the issue's pros and cons, and find the turning point, which will guide you in the right way.
Still don't know what to write about in your thematic essay? Take it easy – the topic ideas listed below will come in handy. Or look through other topics such as sociology topics , etc in our database.
Best Thematic Essay Topics
There is a great variety of thematic essay topics that can be used to write an impressive work. Some of the most common subjects are related to history regents. Feel free to choose out of the following US history regents thematic essay topics:
- Years of the Great Depression
- Era of Progress in the United States of America
- Consequences of the Civil War
- Racism in the USA
- Slavery on the territory of Northern America
- Expansion of the US
As for the global regents thematic essay topics, you may consider the following ideas:
- Belief systems
- Global changes
- Environmental issues
- Economic affairs
- Alterations in the political life
- Cultural affairs
- Intellectual development
- Technological advancements
Now let's discuss the thematic essay structure and see what points to include as you do your assignment.
Thematic Essay Outline
Introduction .
To write a thematic essay introduction, you'll need to include four key components:
- Intriguing beginning
- Background information on topic
- Clear explanation of your primary subject
- Thesis statement
Body Paragraphs
Body part should follow a coherent thematic essay outline. Remember to structure your paper using these key elements:
- Topic sentence presenting your argument
- Supporting evidence (literary devices)
- Examples that prove your argument
Conclusion
A good thematic essay conclusion should be brief, logical and effective. Typically, a concluding paragraph should resonate with the thesis statement and contain such information:
- Rephrased thesis statement
- Brief summary of main arguments
- Final thoughts for further exploration
Now that you know what key elements an excellent theme paper should include let's dig deeper into the entire writing process.
As mentioned earlier, writing a thematic essay should start with unveiling the central theme of a book or novel. Basically, the whole process is all about interpreting this main subject with the help of relevant evidence . To make it easier, we invite you to look through the guide on how to write a thematic essay that stands out.
- Highlight the central theme . After you choose a literary work, determine its central theme. Think about the main idea an author tried to convey. This step requires reading between the lines and finding all main points. Once you identify literary devices used to communicate the main message, try to recognize the work's overall significance.
- Craft a thesis statement. It is the most crucial part amongst all components of the entire paper. A thesis statement is a brief claim introducing your position on the central theme. This single sentence has more significance than other sentences – remember that you will need to prove a thesis with supporting evidence.
- Write a captivating introduction. The opening paragraph of your writing should explain the theme's significance and grab the reader's attention. Highlight the main purpose of your research and offer some information on the subject. Finally, include a previously written thesis to give your audience an idea of what claim you will be supporting.
- Work on the body paragraphs. The text's main body contains at least three paragraphs that develop research and start with the topic sentence — argument. Like in an argumentative essay , they present the evidence, some examples, and proven facts. Each body paragraph should focus on at least one literary device. Use only trustworthy informative sources to support the arguments. Conduct some analysis to verify your claim.
- Write a powerful conclusion. To conclude a thematic essay, summarize the main points discussed in the body paragraphs. Your objective is to write a brief review of the work. As you write the closing paragraph, make sure that all questions were answered. Provide some food for thoughts and encourage the audience to do further research on the chosen subject.
Thematic Essay Format
Once you have your thematic essay shovel-ready, make sure that the proper essay format is followed. There are three most common academic formatting styles: APA, MLA, and Chicago. Ensure that you cite all sources and compose a reference page according to specific formatting requirements . Stick to a particular style from cover to cover; otherwise, a professor may decrease your grade.
If you wonder how a complete thematic assignment looks like, do not hesitate to dive deep into the following extracts attached below. Feel free to use these samples for your reference.
Final Thoughts
Hopefully, this writing guide was of great help. But if you need professional academic backing, look no further! Whether you have a tight deadline or aren't sure how to write a thematic essay properly, count on expert essay help. With reliable academic assistance, you can be sure that your paper will be in line with the highest educational standards. Order an essay now and have a top-notch work delivered before the deadline is up.
People Also Ask
A good thesis statement must contain the literary work’s title and author. Besides, you should provide background information on the central theme. As you write a thematic thesis, give a brief overview on how the author reveals this theme in the work.
2. When do I need to write a thematic essay?
As a college student, you will need to write a thematic essay for the US History Regents exam. It’s a mandatory requirement, so make sure that you have carefully read our guide on how to write an A+ thematic essay.
Any book that has a theme would work. Thematic essays are composed to show the central theme of a chosen work through evidence. As clear from the definition, you can even choose a short story or poetry to discuss the main idea. However, picking a book that has a powerful theme and bunch of literary devices would be best of all.
Expect nothing less than a tasty collection of IB extended essays and topics as you read this article.The International Baccalaureate (IB) is a globally recognized educational program established to offer studying opportunities to high-school students. Most applicants mostly choose the IB Diploma Pr...
It isn't as easy as ABC to write an argumentative essay if you don’t know how to write it. Such a paper's critical elements are a balanced evaluation of the problem, robust evidence gathered from credible sources, and a persuasive tone. Doing all the stuff can be pretty time-consuming. However, if y...
Writing a persuasive essay is one of many tasks that students need to perform while studying. You need to know how to write a persuasive essay. One of the primary purposes of such an assignment is to determine the students' writing skills and ability to convince. Other goals include the demonstratio...

How to write an introduction for a history essay

Every essay needs to begin with an introductory paragraph. It needs to be the first paragraph the marker reads.
While your introduction paragraph might be the first of the paragraphs you write, this is not the only way to do it.
You can choose to write your introduction after you have written the rest of your essay.
This way, you will know what you have argued, and this might make writing the introduction easier.
Either approach is fine. If you do write your introduction first, ensure that you go back and refine it once you have completed your essay.
What is an ‘introduction paragraph’?
An introductory paragraph is a single paragraph at the start of your essay that prepares your reader for the argument you are going to make in your body paragraphs .
It should provide all of the necessary historical information about your topic and clearly state your argument so that by the end of the paragraph, the marker knows how you are going to structure the rest of your essay.
In general, you should never use quotes from sources in your introduction.
Introduction paragraph structure
While your introduction paragraph does not have to be as long as your body paragraphs , it does have a specific purpose, which you must fulfil.
A well-written introduction paragraph has the following four-part structure (summarised by the acronym BHES).
B – Background sentences
H – Hypothesis
E – Elaboration sentences
S - Signpost sentence
Each of these elements are explained in further detail, with examples, below:
1. Background sentences
The first two or three sentences of your introduction should provide a general introduction to the historical topic which your essay is about. This is done so that when you state your hypothesis , your reader understands the specific point you are arguing about.
Background sentences explain the important historical period, dates, people, places, events and concepts that will be mentioned later in your essay. This information should be drawn from your background research .
Example background sentences:
Middle Ages (Year 8 Level)
Castles were an important component of Medieval Britain from the time of the Norman conquest in 1066 until they were phased out in the 15 th and 16 th centuries. Initially introduced as wooden motte and bailey structures on geographical strongpoints, they were rapidly replaced by stone fortresses which incorporated sophisticated defensive designs to improve the defenders’ chances of surviving prolonged sieges.
WWI (Year 9 Level)
The First World War began in 1914 following the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand. The subsequent declarations of war from most of Europe drew other countries into the conflict, including Australia. The Australian Imperial Force joined the war as part of Britain’s armed forces and were dispatched to locations in the Middle East and Western Europe.
Civil Rights (Year 10 Level)
The 1967 Referendum sought to amend the Australian Constitution in order to change the legal standing of the indigenous people in Australia. The fact that 90% of Australians voted in favour of the proposed amendments has been attributed to a series of significant events and people who were dedicated to the referendum’s success.
Ancient Rome (Year 11/12 Level)
In the late second century BC, the Roman novus homo Gaius Marius became one of the most influential men in the Roman Republic. Marius gained this authority through his victory in the Jugurthine War, with his defeat of Jugurtha in 106 BC, and his triumph over the invading Germanic tribes in 101 BC, when he crushed the Teutones at the Battle of Aquae Sextiae (102 BC) and the Cimbri at the Battle of Vercellae (101 BC). Marius also gained great fame through his election to the consulship seven times.
2. Hypothesis
Once you have provided historical context for your essay in your background sentences, you need to state your hypothesis .
A hypothesis is a single sentence that clearly states the argument that your essay will be proving in your body paragraphs .
A good hypothesis contains both the argument and the reasons in support of your argument.
Example hypotheses:
Medieval castles were designed with features that nullified the superior numbers of besieging armies but were ultimately made obsolete by the development of gunpowder artillery.
Australian soldiers’ opinion of the First World War changed from naïve enthusiasm to pessimistic realism as a result of the harsh realities of modern industrial warfare.
The success of the 1967 Referendum was a direct result of the efforts of First Nations leaders such as Charles Perkins, Faith Bandler and the Federal Council for the Advancement of Aborigines and Torres Strait Islanders.
Gaius Marius was the most one of the most significant personalities in the 1 st century BC due to his effect on the political, military and social structures of the Roman state.
3. Elaboration sentences
Once you have stated your argument in your hypothesis , you need to provide particular information about how you’re going to prove your argument.
Your elaboration sentences should be one or two sentences that provide specific details about how you’re going to cover the argument in your three body paragraphs.
You might also briefly summarise two or three of your main points.
Finally, explain any important key words, phrases or concepts that you’ve used in your hypothesis, you’ll need to do this in your elaboration sentences.
Example elaboration sentences:
By the height of the Middle Ages, feudal lords were investing significant sums of money by incorporating concentric walls and guard towers to maximise their defensive potential. These developments were so successful that many medieval armies avoided sieges in the late period.
Following Britain's official declaration of war on Germany, young Australian men voluntarily enlisted into the army, which was further encouraged by government propaganda about the moral justifications for the conflict. However, following the initial engagements on the Gallipoli peninsula, enthusiasm declined.
The political activity of key indigenous figures and the formation of activism organisations focused on indigenous resulted in a wider spread of messages to the general Australian public. The generation of powerful images and speeches has been frequently cited by modern historians as crucial to the referendum results.
While Marius is best known for his military reforms, it is the subsequent impacts of this reform on the way other Romans approached the attainment of magistracies and how public expectations of military leaders changed that had the longest impacts on the late republican period.
4. Signpost sentence
The final sentence of your introduction should prepare the reader for the topic of your first body paragraph. The main purpose of this sentence is to provide cohesion between your introductory paragraph and you first body paragraph .
Therefore, a signpost sentence indicates where you will begin proving the argument that you set out in your hypothesis and usually states the importance of the first point that you’re about to make.
Example signpost sentences:
The early development of castles is best understood when examining their military purpose.
The naïve attitudes of those who volunteered in 1914 can be clearly seen in the personal letters and diaries that they themselves wrote.
The significance of these people is evident when examining the lack of political representation the indigenous people experience in the early half of the 20 th century.
The origin of Marius’ later achievements was his military reform in 107 BC, which occurred when he was first elected as consul.
Putting it all together
Once you have written all four parts of the BHES structure, you should have a completed introduction paragraph. In the examples above, we have shown each part separately. Below you will see the completed paragraphs so that you can appreciate what an introduction should look like.
Example introduction paragraphs:
Castles were an important component of Medieval Britain from the time of the Norman conquest in 1066 until they were phased out in the 15th and 16th centuries. Initially introduced as wooden motte and bailey structures on geographical strongpoints, they were rapidly replaced by stone fortresses which incorporated sophisticated defensive designs to improve the defenders’ chances of surviving prolonged sieges. Medieval castles were designed with features that nullified the superior numbers of besieging armies, but were ultimately made obsolete by the development of gunpowder artillery. By the height of the Middle Ages, feudal lords were investing significant sums of money by incorporating concentric walls and guard towers to maximise their defensive potential. These developments were so successful that many medieval armies avoided sieges in the late period. The early development of castles is best understood when examining their military purpose.
The First World War began in 1914 following the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand. The subsequent declarations of war from most of Europe drew other countries into the conflict, including Australia. The Australian Imperial Force joined the war as part of Britain’s armed forces and were dispatched to locations in the Middle East and Western Europe. Australian soldiers’ opinion of the First World War changed from naïve enthusiasm to pessimistic realism as a result of the harsh realities of modern industrial warfare. Following Britain's official declaration of war on Germany, young Australian men voluntarily enlisted into the army, which was further encouraged by government propaganda about the moral justifications for the conflict. However, following the initial engagements on the Gallipoli peninsula, enthusiasm declined. The naïve attitudes of those who volunteered in 1914 can be clearly seen in the personal letters and diaries that they themselves wrote.
The 1967 Referendum sought to amend the Australian Constitution in order to change the legal standing of the indigenous people in Australia. The fact that 90% of Australians voted in favour of the proposed amendments has been attributed to a series of significant events and people who were dedicated to the referendum’s success. The success of the 1967 Referendum was a direct result of the efforts of First Nations leaders such as Charles Perkins, Faith Bandler and the Federal Council for the Advancement of Aborigines and Torres Strait Islanders. The political activity of key indigenous figures and the formation of activism organisations focused on indigenous resulted in a wider spread of messages to the general Australian public. The generation of powerful images and speeches has been frequently cited by modern historians as crucial to the referendum results. The significance of these people is evident when examining the lack of political representation the indigenous people experience in the early half of the 20th century.
In the late second century BC, the Roman novus homo Gaius Marius became one of the most influential men in the Roman Republic. Marius gained this authority through his victory in the Jugurthine War, with his defeat of Jugurtha in 106 BC, and his triumph over the invading Germanic tribes in 101 BC, when he crushed the Teutones at the Battle of Aquae Sextiae (102 BC) and the Cimbri at the Battle of Vercellae (101 BC). Marius also gained great fame through his election to the consulship seven times. Gaius Marius was the most one of the most significant personalities in the 1st century BC due to his effect on the political, military and social structures of the Roman state. While Marius is best known for his military reforms, it is the subsequent impacts of this reform on the way other Romans approached the attainment of magistracies and how public expectations of military leaders changed that had the longest impacts on the late republican period. The origin of Marius’ later achievements was his military reform in 107 BC, which occurred when he was first elected as consul.
Additional resources

What do you need help with?
Download ready-to-use digital learning resources.

Copyright © History Skills 2014-2024.
Contact via email
- Paper writing help
- Buy an Essay
- Pay for essay
- Buy Research Paper
- Write My Research Paper
- Research Paper Help
- Custom Research Paper
- Custom Dissertation
- Dissertation Help
- Buy Dissertation
- Dissertation Writer
- Write my Dissertation
- How it works
If You Don’t Know How to Write a Thematic Essay, Just Don’t Sweat It And Use Our Tips!

It can be extremely difficult to cope with assignments, especially when we mean papers. It can be a real epic because it consumes a huge amount of time, and a real problem is when you don’t know how to write a thematic essay. Obviously, it can be all-consuming, and if you don’t have trouble writing and expressing yourself, you are very lucky.
So, a lack of time is a real problem, that’s why many students face difficulties while writing a thematic essay paper. Some students don’t have time for writing because they have to work due to some reasons or help their families and relatives. They may be involved in various fascinating activities or barely understand what should be done with a thematic paper. It is very hard to blame them because time is precious, and there are a lot of things that are important or even vital and must be done. No one likes wasting time.
What Is a Thematic Essay?
It is obvious, that students may deal with different essays. All of them require special knowledge to write them properly. So, a thematic essay is an example of the numerous types that students face every single day. There are special requirements and standards that are applicable to this kind of assignment. First of all, you have to understand a thematic essay definition and what your task is.
Well, what is a thematic essay? Basically, it is any writing where a central problem, normally a critical problem or a historic issue, is described by the author. So, it means that a learner has to express their point of view on an acute problem by using special literary techniques and standards. Naturally, it should be well-structured and clear for reading and understanding. If you fully understand how to cope with this issue or if you are really keen on writing, you are really lucky because it isn’t a problem for you at all.
Other seniors are forced to fight for their happiness. It is explicit that you cannot write anything duly if you don’t understand how you should do so or if you don’t actually get a theme. This issue is crucial if you need to write a good thematic essay. So, you are forced to understand it to write it in a befitting way. Actually, the main idea of such work is to develop critical thinking and teach a student to analyze and develop information. It is really important nowadays, regarding the fact that we have to deal with outreach. So, it is crucial to use common sense to survive.
Ways To Describe a Central Theme Creatively Different In a Thematic Essay
It sometimes appears to be very hard to choose a good topic. The problem is that many people have different attitudes to life and various situations. It means that it is harder to find a theme that can interest many people. That’s why it is important to grab your audience’s attention by thinking a bit differently than it usually happens.
It’s no use thinking over thematic paper writing if you haven’t defined your theme yet. It means that you need to specify the essence idea you are going to highlight. In other words, you express your opinion. It’s a good idea to look at your main subject. It provides common guidance on what you have to express. As you see, the difference between the first and the second is that a subject is the matter in hand whereas the main theme is your attitude and opinion that you express on that matter. Moreover, look through the used literature as it can give you comprehension of your theme. Apart from this, try to imagine situations where the main theme can be applicable or acceptable. Your attitude towards those ‘real examples’ will help you to develop an idea.
Thematic Essay Outline
Let’s make it clear that the construction of this work is similar to other papers. Well, let’s look at a thematic summary sample of the core construction. So, there are three main parts: the introduction, main body, and conclusion. Whereas one paragraph is enough for your introduction and conclusion, the main body should include at least three paragraphs. Thus, the total number of paragraphs should be five or even more. It’s quite a common procedure that is widely approved in practice, and it’s a good idea to keep it.
Your Thematic Essay Introduction
This part is very important because it should motivate your audience to continue reading or listening to your thematic essay paper. So, it should be captivating. The introduction includes historical background, arguments for or against of the discussed problem, thesis statement. If you want to create a strong introduction, don’t forget about your thesis statement.
An introduction shouldn’t be too long as it can make readers get bored. Every sentence should be level-headed. Apart from this, don’t forget to outline your further steps and statements that you are going to highlight. Thus, a thematic summary example of the introduction looks as follows: historical background (if any), arguments, thesis statement , your further steps. 5-8 sentences are more than enough because you have to be brief and precise here.
Body Paragraphs
Here you have to highlight those statements and arguments that you have pointed out in your introduction. One argument is for one paragraph. It means, that you have to have at least three arguments. Don’t put more than 6 arguments because it makes your ‘piece of art’ a bit boring. Open up the most interesting and the strongest arguments in your last paragraphs of the main body. It makes you more persuasive and convincing.
A Thematic Essay Conclusion
The principal idea of this part is to restate your arguments. It means that you have to summarize briefly all the statements represented in the main body. Please mark that a conclusion doesn’t presuppose adding new arguments to your work. You just need to outline all your previous statements and express your brief attitude. Thus, you reaffirm constructively important key statements to clarify your opinion. Voila! Now you have a well-structured thematic summary sample that can be used in most cases!
A Thematic Essay Format

How To Write a Thematic Essay For English?
It is not a secret that literature and languages require our special attention because we may need to use a full spectrum of literary devices to express our thoughts and satisfy our professors. As it has been told before, the core steps are similar. It means that you have to have a common structure: an introduction, main body, and conclusion. First of all, you have to clearly understand what are you asked to write about. Don’t be afraid to ask your teachers or mates for further clarification. Once you have understood your task, just start writing. When you finish a couple of paragraphs, summarize them to create a thesis statement.
Don’t make your thesis statement too broad. One or two sentences are more than enough. It mustn’t be a question. It should be an affirmative sentence or sentences that reveal the main line of your argumentation system. If you don’t understand how to write a perfect thematic essay for English you can look through similar samples on the Internet .
Thematic Summary Example
It presupposes the understanding of what the author wanted to tell. So, answering this question helps with specifying the desired summary. In this case, a summary is an outline of your main theme. Look at this thematic summary sample of The Hunger Games by Suzanne Collins.
‘The future. A despotic state organizes annually demonstration survival games that are being watched live by the whole world. The lot fell upon young Katniss and Peeta secretly enamored of her. They have known each other since childhood, but they have to become enemies now because the inviolable law of the Hunger Games states that only one out of twenty-four must survive. Judges don’t care who is the winner. The sight is the matter!’
As you see, this thematic summary example outlines the essence idea and later on, you can add ideas of love, class, community, revolution, stoicism in order to develop and finalize the idea.
How To Write a Thematic Essay For US History?
You are aware of the main structure. It’s time to make a draft where you outline the main statements. It’s a good idea to use quotes to emphasize statements. Your draft is a good way to develop an effective writing strategy in order to avoid weak points and make your paper well-structured. Thus, your draft looks like a theme analysis essay that helps to build a connected argumentation system. If you don’t know how to write a well-structured thematic essay with quotes for US history, you can ask professionals to assist.
A Global Regents Thematic Essay
Everything works here as usual. You need to pick up a topic and develop it. So, don’t forget to describe the historical circumstances, explain policies, practices, traditions, beliefs or challenges that were at that point in time. Explain undertaken measures and actions and discuss how the essence idea influenced further generations or how a situation has been changed since then. Don’t forget to use the general essay structure .
Thematic Essay Topics
Let’s imagine that you need a theme analysis essay , what would you choose? Take a closer look at topics that may be interesting.
Topics on Cultural Studies and Religious Doctrines
- Dualistic cosmology in Zoroastrianism
- The main aspects of Islam and Judaism confrontation
- Christianity as the world’s global power
Science and Technology
- What is the aim of planetary science?
- 3D-printers and their perspectives
- How were discoveries of space affected by the Cold War?
Essays on Nationalism
- European nationalism: historical prerequisites
- The prerequisites and consequences of the Civil War
- International conflicts grounded on nationalism
Geography Topics
- Greta Thunberg phenomenon: consequences of global warming
- The impact of a geographic location
- Space satellites and their assistance in solving geographic issues
Human Rights
- The significance of the suffragettes’ movement
- The US policy on refugees
- Human rights on the Internet
Wrap Things Up
Proofread your paper for any grammatical, spelling and other mistakes. Make sure that you have analyzed the problem and answered all the questions. Make your paper well-structured and readable. Rewrite your draft with all corrections if needed.
The UK National Charity for History
Password Sign In
Become a Member | Register for free
Essay Writing
Student Guides

- Add to My HA Add to folder Default Folder [New Folder] Add
History is not just about writing lots of essays! It is also about discussion, debate and evidence. However, there will be, as with many other subjects at A-Level, some essays to write - but it is not as tough as it looks. Essay writing is a skill that you will get better at over time, but you might find the guide below useful to help you along.
How to Write a History Essay
- Are you new to the 6th form?
- Are you already in the 6th form but worried about your essay writing skills?
- Are you moving on to study history at university?
Then this could be just what you need! This guide will not help you to get outstanding grades - that is up to you, but it will prepare you with the skills that you need to produce that masterpiece!
Key Features: The Must Haves
A-Level/Undergraduate essays should contain the following features; although it depends on the type of essay you are writing as to how far you go; for example, a personal study or dissertation will require a great deal of historiography and referencing, whereas class essays may require less. If you are unsure as to how much your teacher will expect, it is best to ask!
A well considered argument - This is VERY important to get right. It means that you will need to make sure that you clearly state your line of argument and do it convincingly. At the same time, you will also need to give full coverage to other factors/opinions/arguments that are at play - even if it is to rubbish them!
Reference to the question
An introduction
A middle - the substantive part of the essay, where you present the evidence and arguments
A conclusion
Footnotes and bibliography
Before You Start...
The key to success in any history essay is preparation. This not only includes focussed and wide reading around the topic, but also your preparation of your thoughts and arguments. Richard Harris, experienced history teacher and now lecturer in education at Southampton University provides a very good starting point for essay writing. His plan is designed to get you thinking and planning your structure before you write. You can find a copy of this planning sheet at the end of the guide.
1) Considered Argument
The key to providing a considered argument is to read widely! What is the historiography (views of different historians) surrounding the topic? What evidence is there to support different lines of argument? Your job is firstly to present these lines of argument.
Secondly, you should critically evaluate these views and evidence as you explain them. Is there evidence to counteract? By providing a considered argument - what we don't mean is that you sit on the fence! Every essay MUST have an argument, but by considered, we simply mean that you should be prepared to consider other arguments/factors, other than your own view, even if it is to critically evaluate them and dismiss their importance! But you must be convincing and be prepared to examine them fully.
At A level, the mark-schemes tend to be stepped into 5 different levels; you cannot progress beyond level 2/3 if you do not provide a well considered argument! The examiner wants to see what your opinion is, but they also want to know that you have not just "plucked" this opinion from nowhere - they want to see that you have considered the topic fully, taken account of all of the views and arguments before making your judgement. Therefore, you should stick to your line of argument throughout, but you should clearly evaluate other points of view, showing your reader how and why they are less valuable arguments than your own.
2) Reference to the question
Where possible you should show how the evidence you are presenting links back to the question. You should refer back to the question wherever a link or piece of evidence provides some clues to help formulate an answer. This should help you to avoid going off track. Always think as you are writing "does this paragraph help to present the evidence to support my line of argument or help me to answer the question?"
3) The Introduction
The introduction should set the scene. It should be short and snappy, no more than a few lines, but they are very important as you need to hook your reader in. There should be some very brief background detail to the question. You should also include some brief historiography - what is the main debate among historians about this issue? Who is saying what? You should also at this point wish to state what YOUR argument is going to be.
You should then refer back to the question by stating how you are going to measure/argue your case; a good way to do this is by referring back to the question itself. It should help you to get the question straight in your own mind too and give you some direction. For example, if you have a question asking you how significant an event was, you need to explain what is meant by significance and how you will measure this.
E.g. 'How significant was the Reichstag Fire in the Nazi revolution?'
When this question is analysed, bit by bit it helps us to explain to our reader what the essay intends to cover.
4) The Middle
This is the substantive part of the essay. This is the bit where you have to present the evidence and arguments. It should predominantly contain your analysis/argument but you must also look at the counter-arguments and the views of historians.
- Present evidence in a balanced way: You should present your argument/response to the question clearly and effectively, using the views of historians and other evidence to back up the points you make. On the other side, you should also consider the arguments against your own and critically evaluate them in order to show why they are less important/plausible than your own.
- Present your evidence in a logical order : Try to avoid jumping around. Make a plan before you write that organizes your evidence logically. This could either be in themes or in chronological order.
- Include analysis: You must make sure that you don't just fall into the trap of presenting evidence without analysis. This reads more like a list! When presenting a piece of evidence or the view of a historian, don't forget to critically analyse. Is the evidence reliable? Is the view of the historian reliable or are they writing from a specific viewpoint? Are there different interpretations? What do you think? Is it a valid point?
- Refer often to the title: Don't forget to link your points back to the question where possible. It will help your essay and your reader stay focused on the answer to the question!
How to Structure Paragraphs:
It is important to structure your points within the scaffolding of the paragraph well. A good way to do this is to PEE all over your paragraphs!!!
Of course, don't take this literally and ruin your essay - what we mean is to use the PEE formula:
E - Example
E - Explanation.
This is a good habit to get into and a good way to provide structure. Simply make your point, give an example or piece of evidence to back it up, then explain it. What is the context? How or why is it significant/insignificant? How does it fit into the topic? How does it help to answer the question?
Test yourself:
See if you can spot the PEE on this paragraph which forms part of an answer to the question "Was Edward IV a new monarch?"
"Edward's power did not increase at the expense of the nobility; a key criteria for new monarch status. Edward continued the tradition of letting powerful magnates rule the peripheral regions of the country, such as the North and Wales. This resulted in the creation of a number of large power bases including the Herberts in Wales, Gloucester in the North, the Percys in the eastern marshes and the Woodvilles in London. This was largely due to the small number of noble creations in his reign - he only made nine promotions to high nobility. On the one hand this shows that he was in form control as he had sufficient power and stability without having to make lots of noble creations to gain support, yet on the other hand he was creating a volatile situation as rivalries built up between powerful factions and Edward was cresting a potentially explosive situation which only he could control."
5) Conclusion
This is the end of the essay. This is the bit where you are expected to answer the question! Here you should sum up in a couple of sentences what your argument is, and why it is the most plausible explanation, being careful to remind the reader of supportive evidence. Finally, you should put the essay in context. Explain the wider context to the question. It might be that there are longer-term or under the surface issues that need further exploration, or it may be that there is a bigger picture in play. By putting your answer in context, we don't mean just adding some extra facts about the period at the end - your setting in context should display your broader understanding of the period. A good example of this is when a student was writing about the Golden Age of Spain:
"In conclusion, the extent to whether this period can be deemed as a "Golden Age" ultimately rests on the context of the time. Although it is true to say that Spain was making advances in several areas, in terms of power, unity, wealth, economy, culture, empire and discovery. The extent of religious and racial persecution however, could be deemed as less golden in terms of morality, even if both policies were successful in terms of strengthening Spain's power base. In the wider context of the time, Spain's achievements seem less golden than they may at first appear. We have to remember that this period saw the Renaissance. The Renaissance affected practically every area of life at the time, and was a new dawn of discovery and thinking - Leonardo Da Vinci, William Harvey, Martin Luther, Copernicus and Galileo were but a few of the characters that shaped the time; therefore, if Spain had a golden age, so too did many other countries."
- Re-state your argument using the key words from the title
- Be confident in your argument
- Hint at a broader context
- What other issues would you explore, given more time?
6) Footnotes and Bibliography
At A-Level and undergraduate level, you will be expected to footnote your essays. Because you are not expected to do this at GCSE, this may be a new skill for you, but it is very easy!
What are footnotes?
When you quote evidence or the views of a historian from a book or periodical, you are expected to let your reader know where you got this evidence from, so that if they wished (very few would) they could go and check your evidence. You can do this by including citations or footnotes.
How to Footnote
The process of footnoting is slightly different on different computer programs and may differ again if you are using a MAC, but the process is the same, even if you are handwriting.
Footnotes should be numbered and should either appear at the bottom of the page on which they are cited or in a list at the end of the essay. They should include the following information:
1.) Author's name (surname first)
2.) Date and place of publication (found on the first page of the book usually)
3.) Title of book (in italics)
4.) Page reference.
How to footnote on the computer
If you have Microsoft Office, the simplest way to insert a footnote is by going to the references section on the tool-bar and then following the instructions above. If you are using an earlier version of Office, you should click on insert and then select footnote from the list.
Below is an example to illustrate what a footnote should look like:
"Leo, the holy pope in Rome, passed away; and in this year there was a great pestilence among cattle than man could remember for many years..." [1]
Footnote extras
- If the book is a collection of articles or a reproduction of primary source material, it will not have an author, but an editor instead. If the main name on the book is an editor, you need to write the letters (ed.) next to the name.
- If your next footnote in the sequence is from the same book, but a different page, you do not need to write out all of the information again, you can simply write the word "Ibid" which means same source and then cite the page number. However, you should only do this once in any given sequence. If you have 3 quotes in a row from the same book, the third time, you should write out the information again.
What is a bibliography?
A bibliography is the list of books that you have used to help you write your essay. This may include books that you have quoted from or used as part of your reading.
You should always include a bibliography at the end of your essay which lists the books that you have used. You can use the same format as you would for footnotes. Below is a sample to show you how it should look.
1.) Campbell, J (ed) Cambridge 1982 - The Anglo-Saxons
2.) Swanton, M (ed) J.M Dent 1997 - The Anglo-Saxon Chronicle
The Harvard Footnote System
Another option to make sure you have referenced correctly is to use the simpler Harvard system. This may be a preferred method for the writing of normal class essays, although for a personal study, the use of traditional footnoting is still recommended. Harvard referencing uses the author and the date of the work in the main body of the text, and then has a reference list at the end of the essay which contains the references cited in alphabetical order by author. The reference list contains the full details of the book or journal cited. Because you only refer to a shortened form of works in the main essay (author, date) your essay doesn't get filled with too much reference material. The use of the author/date shorthand does make it easy to locate works in the reference list.
An example from the main body of a text:
Within the last ten years, teachers who have attended INSET courses have reported that the courses have helped to increase their competence and confidence in using IT (see, for example, Higham and Morris, 1993; ESRC 1990), yet despite the fact that the passing years have presented opportunities for more teachers to increase their skills in IT, weaknesses identified by McCoy (1992) seem to be still evident (Gillmon, 1998; Goldstein 1997). This suggests that we need to look for explanations other than attendance at INSET courses for the reasons for the apparently poor state of teachers' competence and confidence in IT.
In this text the author is citing entire works by other researchers to support her argument. Notice the use of brackets and the author/s and dates of all works.
Another example from the main body of a text:
One resource provided in the secondary speech genre is the "posited author" (Bakhtin, 1981, p. 312).
Here the quotation is a direct one so a page number has been added. Quotations of no more than two sentences can be incorporated into the main text and marked off with quotation marks, but if you quote a longer passage it must be placed in a separate paragraph and indented from the left and right margins of the main text.
_______________
[1] Swanton, Michael (ed), J.M Dent 1997, The Anglo-Saxon Chronicle, pg. 185
Attached files:
- Essay Planning Sheet 54.5 KB Word document
- How to write a synoptic essay
- A-level 'how to' guides
OCR homepage
Administration
- Active Results
- Interchange
- Submit for Assessment
- Teach Cambridge
- ExamBuilder
- Online Support Centre
Main navigation
Five key things to remember for a level historical themes - mike goddard.
Most of our A Level history centres are about to start teaching unit 3, historical themes. Its approach is unique to the OCR specification, and so many teachers new to our specification won’t have taught thematic history at A Level before. This unit is worth 40% of the overall grade, so here are five key things to remember to help make it a success:
About the author

Mike is a history subject specialist and has worked at OCR on the history portfolio since 2007. Previously he has held roles at Cambridge International Examinations and for an educational publisher. Mike has a degree in Economic and Social History from the University of York and a Masters in Modern History from UCL. In his spare time he enjoys crosswords and snooker.

How to Structure a History Essay – Illustrated Guide

To write an excellent college-level history paper, you’ll need a structure that will help you organize your facts and ideas.
In this guide, first I’ll give you three effective ways to organize your historical essay.
And then I’ll show you how to further outline your larger sections in case you have to write one of those bigger papers.
As a result, you’ll be able to:
- Organize your thoughts
- Get ideas out of your head quickly
- Write a well-organized essay without getting stuck
Let’s dive right in!
Let’s Pick Our Historical Subject and Setting
To have a productive guide, we need our subject (the What) and the setting (the When) to use throughout the techniques and examples.
Let’s pick our subject and setting.
The antagonism between the United States and the United Kingdom in the quest for petroleum in the Middle East.
Middle Eastern oil was a big factor in the early 20th century, and the two countries have quite a history of rivalry in the quest for this precious resource.
This rivalry escalated between World War I and World War II.
Oil was especially important in the two world wars when war machines began to play a crucial role in warfare. It was also important in between the wars when the motor car industry exploded.
Let’s write out our full thesis (main point) so that we know what exactly we’re discussing in this essay we want to structure.
Our Sample Thesis
“ The antagonism between the United States and the United Kingdom in the quest for petroleum in the Middle East escalated between World War I and World War II.”
Now that we know what this history paper will be about, let’s look at three very effective ways to structure such an essay.
1. Structure Your Essay Chronologically
A chronological structure is the most intuitive way to organize a historical essay because in it you simply proceed from earlier to later events as they happened in history.
History books are usually organized this way. And it’s a fine way to structure your paper. It is also a pretty simple and straightforward way.
Our structure for this essay about petroleum would look something like this:

By the way, I usually choose to divide my essays into three main sections. Three is a very practical number when it comes to writing essays.
Besides, number three works very well for our example because we have three shorter periods – during WWI, in between the wars, and during WWII.
But you can use three sections with any subject and setting. This means you will have three supporting ideas for your main point.
You’ll see how easy it is to do as you read the rest of the guide.
What Happens In Each Section
I’ll give you several great ideas on how to structure each of your sections later in the guide. But for now, you can see the clear focus of each section.
Each one is devoted to a definite time period. You just need to make sure that you stick to what belongs in each section as you write it.
As you write your first section, make sure you focus only on what happened between the US and the UK during WWI, or between the years of 1914 and 1918.
This approach gives you a clear direction. Once you’re done with this period, proceed to the next. And then do the final section where you focus only on the period between 1941 and 1945.
Let’s move on to the next way to structure a historical essay.
2. Structure Your Essay Thematically
No matter what historical subject you write about, your essay will have certain themes. For example, an essay about war can include the themes of warfare strategy, financing of the military operations, or the treatment of civilians.
If you have a good idea of your themes, then maybe arranging your essay thematically is the right approach for your paper.
In our example, since petroleum played such an important role in the early 20th century, several themes come to mind:
- We can discuss why the demand for oil increased in each country or situation.
- We can talk about the scarcity of oil and why it was hard to come by at the time.
- And we can discuss the actual process of rivalry or quest for oil .
Here is what our structure would look like:

Again, we have three main sections. And we’ll have a distinct subject in each one.
Note that our thesis, our main point about the antagonism between the two nations stays the same regardless of the structure we choose to organize our evidence.
In other words, you can use one of these structures to organize any history essay or to support any thesis.
To organize your essay thematically, you’ll need just three themes. Make a list of several themes about your subject and just pick three.
Pick those themes about which you feel the most knowledgeable and competent to write. This structure will work especially well for you if you already have a few themes in mind when you begin.
We’re ready for our next way to structure a history paper.
3. Use a Compare/Contrast Structure
This structure can work for any subject, if you choose to compare things. Or, use it whenever your professor asks you to write a comparative paper. In any case, this is a great option.
Here is what a basic comparative structure can look like:

In this essay, we would simply have two sections.
In the first section, we would discuss everything that pertains to the United States and its Middle East oil policy.
And in the second section, we can discuss the United Kingdom’s oil policy in the region.
As a result, the similarities and differences between the oil policies of these countries will become apparent.
This is a very basic way to write a comparative historical essay. In a minute, I’ll show you a better, more advanced way to organize such a paper.
But now you have three simple and effective ways to structure your history essay. And it’s time to dig a level deeper and see how to organize content within the main sections of these structures.
How to Organize Your Ideas by Combining These Structures
Yes, I’ve saved the best for last. I’ve kept you in suspense a little. And that’s because we had to lay a solid foundation first.
Now that you know how to use chronology, themes, and comparison to structure your historical essay, you can simply combine these methods to create a complete outline.
By the way, if you need help with writing essays in general, I wrote this great tutorial for beginners .
Let’s look at the ways you can create a structure within a structure, using the methods you already know.
Combine Chronology with Themes
To use this combination, simply structure your essay chronologically first. And then use themes within each main section to create another level of organization.
This can really help you put every thought, every idea in place. Let’s see what the main structure would look like:

As you can see, we still have our three main sections arranged chronologically.
But now, within each of the sections, we also have a structure arranged by theme. Our three themes are the demand, the scarcity, and the quest for oil.
And all we need to do is have three little subsections in each section. Each subsection can have one or more paragraphs, depending on how big your paper needs to be.
Here’s what a complete outline of this essay might look like.
Sample History Essay Outline
- Introductory sentence.
- Thesis statement.
- The demand for oil rose during WWI due to war machines
- Oil remained a scarce resource for a number of reasons
- The US and the UK competed for Middle Eastern drilling sites
- The demand for oil rose due to the auto industry
- The US and the UK continued to compete for Middle Eastern oil
- The demand for oil rose again during WWII due to war strategy
- The US and the UK raised the stakes in their quest for petroleum
When you have this level of clarity about your essay, writing it becomes easy. It’s even easier when you do your math in terms of the number of words you need.
How to Meet Your Word Count Requirement
Let’s say that you need to write a 2,000-word essay. Here is how your basic math would work.
- Introduction Paragraph ( 100 words )
- 200 words about the demand for oil
- 200 words about the scarcity of oil
- 200 words about the quest for oil
- 200 words (demand)
- 200 words (scarcity)
- 200 words (quest)
- Conclusion ( 100 words )
If you add up all the words, you get 2,000.
Your giant paper becomes a collection of smaller essays that you can easily handle, one by one.
Let’s explore the next way of combining structures.
Combine Themes with Chronology
This sounds the same, but is in fact different. In this case, your main structure is not chronological but thematic.
In other words, you arrange your main sections by theme, and then organize your subsections chronologically. Here is what this would look like:

We basically switched Chronology and Themes around and made our thematic structure the main one, and the chronological the supporting one.
I don’t give you this option just to play with content. Instead, I want to make you see that you have many ways of organizing the same material.
Just pick a structure that you like and stick to it. Your material will often give you hints as to how you should organize your information and what structure would work best.
Now, as promised, I’ll give you the best way to organize your essay if you opt for a comparative structure.
The Best Comparative Structure for a History Essay
Earlier, I showed you how to divide a comparative essay into two main sections:
That way you can simply talk about one subject completely, and then talk about the other one completely. And that’s how comparison becomes apparent.
But it’s not the best way to do it for an important reason. You see, by the time your reader gets to the end of the first section, she has already forgotten what you were talking about in the beginning.
That’s because when you have only two sections, they are pretty long.
And now, as the reader goes through the second section, she has to keep referring back to the first section to see the similarities and differences.
This is why it is much better to structure your comparative essay either chronologically or thematically, and then use compare and contrast within subsections.
This way, you have three main sections instead of two. And it is much easier to see the similarities and differences when discussing them one next to another.
Let me illustrate.

As you can see, in this structure, we arrange the main content chronologically. And we compare the US with the UK within each main section.
This is just much easier for a reader to digest. This is also easier to write because you as a writer have an easier time following your own comparisons.
Here is how you would use a thematic structure with comparison:

In this case, we again have three main sections, this time arranged by theme. And then we simply compare the US and the UK in whatever terms appropriate within each section.
I hope this guide was helpful.
If you’re a visual learner and would enjoy this lesson on video, here you are:
I also wrote a great tutorial on how to write a thesis statement that you might want to read next.
I wish you all the best with your history essay. Let me know how it went in the comments.
Tutor Phil is an e-learning professional who helps adult learners finish their degrees by teaching them academic writing skills.
Recent Posts
How to Write an Essay about Why You Want to Become a Nurse
If you're eager to write an essay about why you want to become a nurse, then you've arrived at the right tutorial! An essay about why you want to enter the nursing profession can help to...
How to Write an Essay about Why You Deserve a Job
If you're preparing for a job application or interview, knowing how to express why you deserve a role is essential. This tutorial will guide you in crafting an effective essay to convey this...

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Keep the main body logical, so that every paragraph is somehow connected to the previous and the next ones. Step 5. Create a Thematic Essay Conclusion. A strong thematic essay conclusion should highlight all important points from tyourhe essay while avoiding adding new facts or evidence.
An outline serves as the roadmap for your essay, helping you organize your thoughts and ideas in a logical manner. Step 1: Identify the Theme. Start by identifying the theme or central idea that you will explore in your essay. This theme will serve as the foundation for your entire piece. Step 2: Brainstorm Ideas.
A theme is a specific point the author is making about said subject. So, find the talking point that is most commonly being brought up. This will be the focal point of the essay. 3. Read between the lines: After finding the most suitable subject, decipher what main point the author is trying to make.
(a.k.a., Making) History At first glance, writing about history can seem like an overwhelming task. History's subject matter is immense, encompassing all of human affairs in the recorded past — up until the moment, that is, that you started reading this guide. Because no one person can possibly consult all of these records, no work of ...
Thematic writing is a staple of high school English and college writing courses. The idea behind thematic writing is to create a piece that uses a theme to tie together different ideas or topics. Thematic writing can be used for essays, short stories, novels, and even non-fiction pieces. In academic writing, thematic essays often center on a ...
US History Thematic Essay. In this essay, there will be fewer words that address the reader. The purpose of this writing is to present a balanced analysis of a topic based on facts, explaining a topic in a logical and straightforward manner. US History thematic essay example topics: Major movements in U.S. history; Major advances in U.S. history
1. Identify a Central Theme. The audience can determine the central theme of a thematic essay from a thesis statement or an overview of topic statements. Basically, writing a well-composed thesis statement must explicitly mention the central theme or implicitly hint at the central theme.
Rather, it requires explication. It requires, as well, that you connect it to your thesis. Remember that you bring evidence in support of your thesis and evidence that's evidence that does not serve that purpose should be excluded. (4) Weave your thesis throughout the body of your essay - Once delineated in your introduction, be sure to weave ...
A thematic essay should be brief and free of wordiness. As the paper's author, you should concentrate on one sub-topic or argument. The number of body paragraphs for confirming each assertion or outlining the reasoning of the thematic essay might vary. Such variation depends on the intricacy of the topics.
If you understand how each part works and fits into the overall essay, you are well on the way to creating a great assessment piece. Most essays will require you to write: 1 Introduction Paragraph. 3 Body Paragraphs. 1 Concluding Paragraph.
Writing a thematic essay is easy. You just have to: 1. Choose a Literary Object. If your instructor does not provide the topic, think back to a book or article that made a strong impression to you, or think about your favorite pieces of literature. Another option is to brainstorm.
Body paragraph 1: Introduction to the Historical Context. Provide background information on the historical context of your topic. Highlight key events, figures, or developments leading up to the main focus of your history essay. Body paragraphs 2-4 (or more): Main Arguments and Supporting Evidence.
Table of contents. When to use thematic analysis. Different approaches to thematic analysis. Step 1: Familiarization. Step 2: Coding. Step 3: Generating themes. Step 4: Reviewing themes. Step 5: Defining and naming themes. Step 6: Writing up.
Count on your personal experience: A theme that resonates in your life will make the best essay. You are likely to go into depth as the issue affects your lifestyle. Note down your ideas: Some ideas that come to your mind may seem useless. However, note down every idea as they may seem important at the latest.
According to the State of New York, there are 20 themes that are found amongst the curriculum guides & suggested content for the New York State U.S. History & Government course. This Teacher's Guide lists the themes that have been repeated on the Regents exam starting with the those most frequently asked, provides the prompts that have been ...
A thematic essay paper outline is supposed to lead a writer flawlessly through the entire writing process and prevent from being stuck. The paper should stick to the typical five paragraph essay outline: an introductory paragraph, 3 body paragraphs and a conclusion. Don't think that writing an outline is just a waste of time.
1. Background sentences. The first two or three sentences of your introduction should provide a general introduction to the historical topic which your essay is about. This is done so that when you state your hypothesis, your reader understands the specific point you are arguing about. Background sentences explain the important historical ...
Stay focused in order not to miss important things that may help you to write your essay. Differentiate the theme from the subject of the work under analysis. The general topic of the conversation is a subject. For example: love, hate, or brevity. A theme is more specific and is based on the subject.
Thus, your draft looks like a theme analysis essay that helps to build a connected argumentation system. If you don't know how to write a well-structured thematic essay with quotes for US history, you can ask professionals to assist. A Global Regents Thematic Essay. Everything works here as usual. You need to pick up a topic and develop it.
The key to success in any history essay is preparation. This not only includes focussed and wide reading around the topic, but also your preparation of your thoughts and arguments. Richard Harris, experienced history teacher and now lecturer in education at Southampton University provides a very good starting point for essay writing.
As the 'helicopter' approach suggests, synthesis is the key driver for the thematic essays. The AS/A Level History A mark scheme shows that a fully developed synthesis supporting a substantiated judgement is expected in the best answers. Synthesis simply means the ability to draw out and use evidence from over the period to support an argument.
Select a relevant topic. First sentence should be a hook statement. A good hook statement will grab the reader's attention instantly. Provide necessary background information after the hook statement. This will help the readers to better understand your claims in the rest of the text. Now add a thesis statement.
Pick those themes about which you feel the most knowledgeable and competent to write. This structure will work especially well for you if you already have a few themes in mind when you begin. We're ready for our next way to structure a history paper. 3. Use a Compare/Contrast Structure.