- IAS Preparation
- UPSC Preparation Strategy
- Cashless Economy

Cashless Economy in India - UPSC GS-III Notes
When the transactions in an economy are not heavily based on the money notes, coins or any other physical form of money but are aided by the use of credit cards, debit cards and prepaid payment instruments, such an economy is called cashless economy.
The cashless Economy in India has been amplified with the Indian Government’s initiative of Digital India . This is a flagship programme with a vision to transform India into a digitally empowered society and knowledge economy.
The topic, ‘Cashless Economy’ is important for GS-III Indian Economy of the IAS Exam . This article will talk about it, the types of cash transfer modes, UPI and more.
Table of Contents:
Cashless Economy in India – UPSC Notes:- Download PDF Here
What is a Cashless Economy?
Cashless Economy can be defined as a situation in which the flow of cash within an economy is non-existent and all transactions must be through electronic channels such as direct debit, credit cards, debit cards, electronic clearing, and payment systems such as Immediate Payment Service (IMPS), National Electronic Funds Transfer (NEFT) and Real-Time Gross Settlement (RTGS) in India.
To know the Difference Between RTGS and NEFT , visit the linked article
Highlights of Cashless Economy in India
- Post Demonetization , the Centre is making a big push for online and card-based transactions in the country to achieve its target of becoming a largely cashless economy.
- The rapid growth of e-payment startups in the country.
- Launch of Unified Payments Interface (UPI) to facilitate cashless transactions.
- The Covid-19 pandemic fueled a massive shift towards digital transactions in India aligning with the prime minister’s vision of a Digital India. In fact, according to the National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI) data, payments on UPI in June 2020 hit an all-time high of 1.34 billion in terms of volume with transactions worth nearly Rs 2.62 lakh crore.
Cashless Economy – Types of Cashless Modes and Payments
There are various cashless payment modes and these are mentioned below:
Mobile wallet: It is basically a virtual wallet available on your mobile phone. You can store cash in your mobile to make online or offline payments. Various service providers offer these wallets via mobile apps, which is to be downloaded on the phone. You can transfer the money into these wallets online using credit/debit card or Net banking. This means that every time you pay a bill or make a purchase online via the wallet, you won’t have to furnish your card details. You can use these to pay bills and make online purchases.
Plastic money: It includes credit, debit and prepaid cards. The latter can be issued by banks or non-banks and it can be physical or virtual. These can be bought and recharged online via Net banking and can be used to make online or point-of-sale (PoS) purchases, even given as gift cards. Cards are used for three primary purposes – for withdrawing money from ATMs, making online payments and swiping for purchases or payments at PoS terminals at merchant outlets like shops, restaurants, fuel pumps etc.
Net banking : It does not involve any wallet and is simply a method of online transfer of funds from one bank account to another bank account, credit card, or a third party. You can do it through a computer or mobile phone. Log in to your bank account on the internet and transfer money via national electronic funds transfer (NEFT), real-time gross settlement (RTGS) or immediate payment service (IMPS), all of which come at a nominal transaction cost.
The cashless economy in India is being promoted through various platforms and applications which provide easy methods of funds transfer and payments:

Cashless Economy – Prepaid Payment Instrument
The RBI classifies every mode of cashless fund transfer using cards or mobile phones as ‘prepaid payment instrument’ . They can be issued as smart cards, magnetic stripe cards, Net accounts, Net wallets, mobile accounts, mobile wallets or paper vouchers. They are classified into four types:
- Open Wallets : These allow you to buy goods and services, withdraw cash at ATMs or banks and transfer funds. These services can only be jointly launched in association with a bank. Apart from the usual merchant payments, it also allows you to send money to any mobile number linked with a bank account. M-Pesa by Vodafone is an example.
- Semi-Open Wallets : You cannot withdraw cash or get it back from these wallets. In this case, a customer has to spend what he loads. For example, Airtel Money/Ola Money is a semi-open wallet, which allows you to transact with merchants having a contract with Airtel/Ola.
- Closed Wallets : This is quite popular with e-commerce companies; wherein a certain amount of money is locked with the merchant in case of a cancellation or return of the product or gift cards. Flipkart and Book My Show wallets are an example.
- Semi-Closed Wallets : These wallets do not permit cash withdrawals or redemption, but it allows you to buy goods and services from listed vendors and perform financial services at listed locations. Paytm is an example.
Read in detail about the Fiscal Policy in India at the linked article.
Advantages of a Cashless Economy in India
- The main advantage of a cashless society in India is that a record of all economic transactions through electronic means makes it almost impossible to sustain black economies or underground markets that often prove damaging to national economies. This reduces the chances of black money entering the system. It is also much riskier to conduct criminal transactions. An economy that is largely cash-based facilitates a rampant underground market which abets criminal activities such as drug trafficking, human trafficking, terrorism, extortion etc. Cashless transactions make it difficult to launder money for such nefarious activities.
- Circulation of Fake Currency notes can be curbed.
- Increase Tax base: It is difficult to avoid the proper payment of due taxes in a cashless society, such violations are likely to be greatly reduced. The increased tax base would result in greater revenue for the state and greater amount available to fund the welfare programmes.
- Digital transactions bring in better transparency, scalability and accountability.
- Digital transactions are convenient and improve market efficiency
- It will eliminate the risks associated with carrying and transporting huge amounts of cash
- The cashless economy will reduce the production of paper currency and coins. This will save a lot of production cost in turn.
- A lot of data transfer happens due to the cashless transaction. This data will help the government plan for future expenses such as housing, energy management, etc from the pattern of the data transmission.

Challenges in transitioning to a Cashless society
- Acceptance infrastructure and digital inclusion: Lack of adequate infrastructure is a major hurdle in setting up a cashless economy. Inefficient banking systems, poor digital infrastructure, poor internet connectivity, lack of robust digital payment interface and poor penetration of PoS terminals are some of the issues that need to be overcome. Increasing smartphone penetration, boosting internet connectivity and building a secure, seamless payments infrastructure is a prerequisite to transition into a cashless economy.
- Financial Inclusion – For a cashless economy to take off the primary precondition that should exist is that there should be universal financial inclusion. Every individual must have access to banking facilities and should hold a bank account with debit/credit card and online banking facilities. Read more about Financial Inclusion in the linked article.
- Digital and Financial Literacy – Ensuring financial and digital inclusion alone are not sufficient to transition to a cashless economy. The citizens should also be made aware of the financial and digital instruments available and how to transact using them.
- Cyber Security – Digital infrastructure is highly vulnerable to cyber-attacks, cyber frauds, phishing and identity theft. Off late cyber-attacks have become more sophisticated and organised and poses a clear and present danger. Hence establishing secure and resilient payment interfaces is a prerequisite for going cashless. This includes enhanced defences against attacks, data protection, addressing privacy concerns, robust surveillance to pre-empt attacks and institutionalised cybersecurity architecture.
- Changing habits and attitude – Indian economy functions primarily on cash due to lack of penetration of e-payment modes, digital illiteracy of e-payment and cashless transaction methods and thirdly habit of handling cash as a convenience. In this scenario, the ideal thing to do is to make people adopt e-payments in an incremental fashion and spread awareness to initiate behavioural change in habits and attitude.
- Urban-Rural Divide – While urban centres mostly enjoy high-speed internet connectivity, semi-urban and rural areas are deprived of a stable net connection. Therefore, even though India has more than 200 million smartphones, it is still some time away for rural India to seamlessly transact through mobile phones. Even with regard to the presence of ATM’s, PoS terminals and bank branches there exists a significant urban-rural divide and bridging this gap is a must to enable a cashless economy.
To understand the Digital Divide in India , candidates can visit the linked article. This will also give them a brief idea of the areas of improvement to make India a cashless economy.
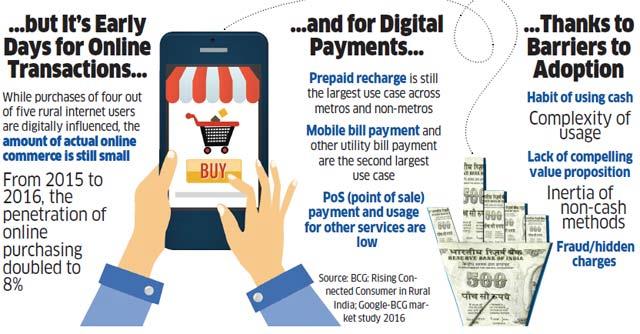
Is India Ready for a cashless economy?
The difficulty in going digital is exemplified by the data on debit card usage — over 85% (in volume) and 94% (in value) of all debit card usage is at ATMs for the purpose of withdrawing cash. The principal purpose for cards in an Indian context is thus a means to withdraw cash. The exponential growth in debit cards (over 600 million) is a direct consequence of the financial inclusion drive that led to the opening of over 170 million bank accounts. Though the move put plastic money into the hands of millions, effectively it has only shifted cash withdrawals from banks to ATMs, which was not quite the intent.
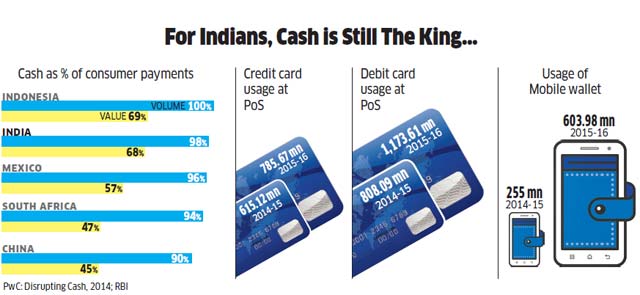
India’s Cash to GDP ratio:
As calls for going cashless grows louder in India, a key challenge being faced at the global level is to check the continuing rise in the total value of the currency in circulation and its share in the overall GDP , a trend particularly seen in the US, Switzerland and Euro area.
Such a continuing rise in the circulation of currencies for economic activities could well be a major impediment in the transformation to a cashless and digital economy.
India’s cash to GDP ratio — an indicator of the amount of cash being used in the economy — is around 12 to 13%, which is much higher than major economies including the US, the UK and Euro area but below that of Japan (about 18%).
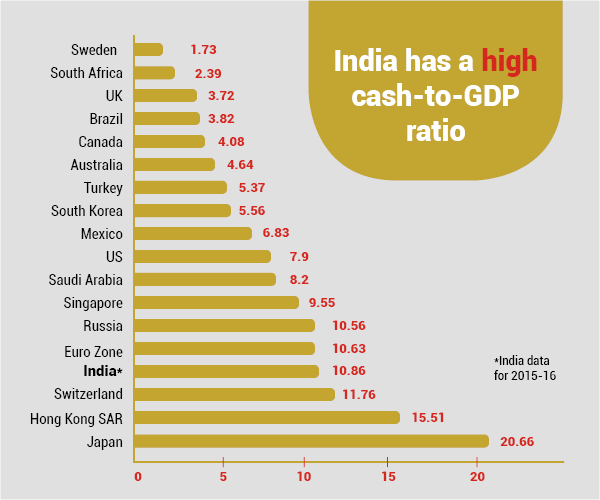
Cashless Economy in India & The Challenges ahead
Typically in India, a cashless economy may take a bit longer to be adaptable. The challenges with regard to the same have been discussed below:
- A large part of the population does not have access to debit cards and smartphones, which is why they prefer to make transactions in cash
- The maximum population uses debit cards to withdraw money rather than paying directly through it
- People are not entirely aware and educated about the cashless methods of payment
- As per the survey and data collected, only 26% has access to the internet and choose online payments as an option for transactions
- Making the people aware of the privacy and security under cashless transactions is another challenge for the government. As the cashless economy in India is also taking time to recover as people do not trust the privacy terms of the online portals, platforms and applications
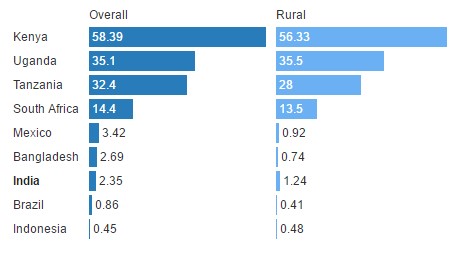
Penetration of Mobile Accounts
Cashless Economy and Government Initiatives
- Paytm had witnessed 5 million daily usage post demonetisation as opposed to their average transaction of three million. It also saw a 700% increase in the overall traffic and a 1000% increase in the amount of money added to its account in the first two days of post-demonetization. Ola Money too saw a 1500% increase in its e-wallet.
- Payment service providers (PSPs) to provide the interface between the payer and the payee. Unlike wallets, here the payer and the payee can use two different PSPs.
- Banks will provide the underlying accounts. In some cases, the bank and the PSP may be the same.
- NPCI will act as the central switch by ensuring Virtual Payment Address (VPA) resolution, affecting credit and debit transactions through IMPS.
- Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT): It is a scheme that was launched by the Government of India to transfer the benefits and subsidies of various social welfare schemes like LPG subsidy, Old Age Pension, Scholarship, MGNREGA , etc. directly to the bank account of the beneficiaries. This allowed for the penetration of digital banking into rural India.
- The Centre has set up a committee headed by NITI Aayog CEO Amitabh Kant, to formulate a strategy to expedite the process of transforming India into a cashless economy.
- The panel is tasked with identifying various bottlenecks that are affecting access to digital payments.
- The panel will engage regularly with all stakeholders – Central ministries, regulators, state governments, district administration, local bodies, trade and industry associations to promote adoption of digital payment systems.
- The idea is to establish and monitor an implementation framework with strict timelines to ensure that nearly 80% of the transactions in India moves to the digital-only platform
- The committee will also try to estimate the costs involved in various digital payments options and oversee the implementation of these measures to make such transactions between the government and citizens cheaper than cash-based transactions.
- Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana , one of the biggest financial inclusion initiatives in the world, was launched in 2014. It is a national mission on financial inclusion which has an integrated approach to bring about comprehensive financial inclusion and provide banking services to all households within the country. This scheme ensures access to a range of financial services like availability of basic savings, bank accounts, access to need-based credit, insurance and pension. It has played a significant role in the opening of bank accounts for the poor.
- The terms of reference of the committee include identifying global best practices for implementing an economy primarily based on digital payments and examine the possibility of adopting these global standards in the Indian context.
- The panel will also outline measures for rapid expansion and adoption of the system of digital payments like cards (Debit, Credit and pre-paid), Digital-wallets/ e-wallets, internet banking, Unified Payments Interface (UPI), banking apps, etc. and shall broadly come up with the roadmap to be implemented in one year.
- Ratan Watal panel on digital payments
The panel, headed by former finance secretary Ratan Watal, was constituted in August to suggest ways to encourage India’s movement towards a cashless economy.
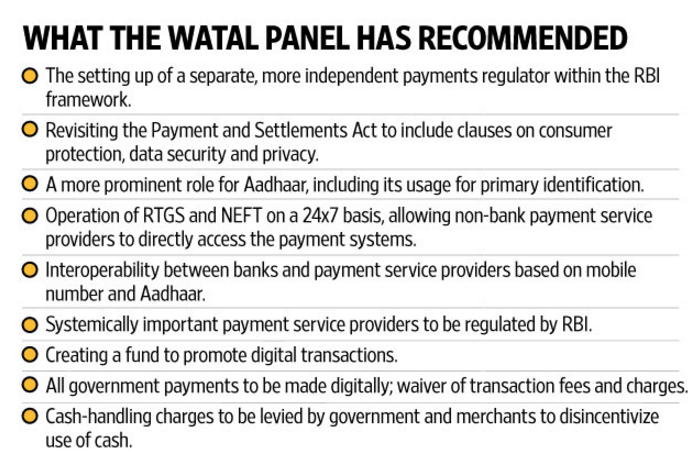
Way Forward
India must learn from other countries in the developing world, which have managed to reduce their dependence on cash even while bringing in more people in the folds of the formal banking system. Kenya has been a well-documented success story, where mobile money has spread much faster and deeper than in India. Kenyan households with access to mobile money were able to manage negative economic shocks (like job loss, death of livestock or problems with harvests) better than those without access to mobile money.
The path forward is clear:
- Invest in building the required financial and digital infrastructure
- A nationwide financial and digital literacy campaign accompanied by a medium-term strategy to improve access to, and awareness of, electronic payments. Targeted financial education programs can improve financial skills and credit management, and increase account ownership.
- the government must undertake the herculean task of changing attitudes towards digital payments among customers and merchants
- Put in place all necessary cybersecurity measures
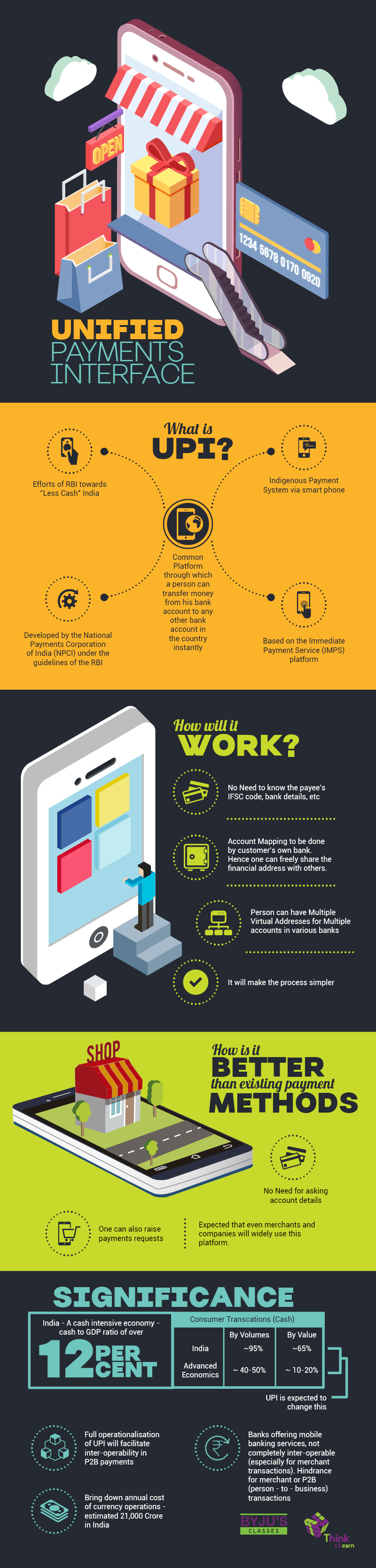
Cashless Economy – What is United Interface Payments (UPI)?
How to Approach the topic ‘Cashless Economy in India’ for UPSC
- Economics – Learn about UPI, Payments Modes etc.
- Current Affairs – Check on important editorials related to the Indian economy.
General Studies III:
- Indian Economy
- Cashless Economy – a probable essay topic
Practice Questions:
- Which of the following committees dealt with digital payments?
- Urjit Patel committee
- Bimal Jalan committee
- Ratan Watal committee
- Nachiket Mor committee
- Critically Discuss the benefits of India transitioning into a cashless economy. Does India possess the required prerequisites?
Frequently Asked Questions on Cashless Economy in India
Q 1. what is cashless economy and is india ready for cashless economy, q 2. how is cashless economy beneficial.
Related Links:
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
IAS 2024 - Your dream can come true!
Download the ultimate guide to upsc cse preparation.
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- Cashless India Essay

An Introduction to Cashless India
A cashless India is the first step towards making the dream of digital India a reality. In this cashless India essay, we will be talking about the meaning of ‘cashless’, the different alternatives for our monetary system, and the disadvantages and advantages of a country going fully cashless and digital in its economy. The following cashless India essay in English is for students studying in class 5 and above. The language here has been kept simple for a better understanding of young students. This essay on the cashless economy in India would enable young students to write an essay on the cashless economy in India on their own.
As we know that cashless India is the new India and with the decision made by our honourable prime minister to demonetize money used previously, this concept of going cashless has become very popular. Although there are some disadvantages of going cashless, along with that there are more benefits as well. In this essay, you will know about everything that will help you to get better information about the concept of India going cashless.
Essay on Cashless India
On the evening of November 8, 2016, at 8 P.M., Narendra Modi, the Prime Minister of India announced the demonetization of 500 and 1000 rupees notes in India. That historic decision had many reasons. One of the reasons was laying the stepping stone towards the dream of a cashless India.
The traditional form of monetary transactions happens with the exchange of physical hard cash between people. Cashless India is going to make it almost redundant. This idea has got a huge amount of push due to the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, given the concerns with the exchange of physical cash. There are a lot of advantages to going cashless. Remember that everything has a positive as well as a negative aspect. It is not that there won't be any disadvantages of going cashless but the thing is that you tend to find the ways by which you can prevent these disadvantages from harming you. All that you need to do is be more careful. As we all know, prevention is always better than cure.
First of all, let’s understand the meaning of a cashless economy. A cashless economy is one in which the liquid transactions through the system happen with the exchange of plastic currency or through digital currency. ATM debit and credit cards are plastic currency and online payments come under digital currency. The advent of blockchain technology has redefined the meaning of a cashless economy through bitcoins. A decentralized system of finance is defined by the concept of bitcoins, but we are not focusing on that in this particular essay on cashless India. We are more focused to discuss why India needs to go cashless and what are the benefits that will come with India taking on this new change. This essay provides you with information on the advantages and disadvantages of the digital payment system also. It is not that you are not going to face any problem in online transactions, you must have heard that a coin has two sides and just like that, this topic of cashless India also has both pros and cons. Let’s move on to the pros and cons of a digital payment system.
We can see the Three Main Advantages of Cashless India.
Reduction of Black Money
Black money is the money that is earned but not accounted for in taxes. That money is hidden by people from paying taxes. This black money is an illegal instrument in an economy that is capable of reducing a government down to bankruptcy. The cashless economy will ensure there’s no black money since unlike hard cash digital money cannot be hidden. At least there is no way yet that could make the hiding possible. Digital money enables governments to track all transactions in an economy that helps keep the income authentic and transparent. The technology behind the digital economy has to be well updated and sturdy though.
Transparency
India has corruption inbred in its system starting from the ministerial level to the watchman level. And it exists due to the lack of transparency in our monetary system. In an economy that is as big as India, transparency is a huge issue. We have learned of scandals like the CWG or 2g scams or the Rafale Jet scams over the years, and these scams are a result of the lack of transparency in transactions. It’s a shame that a small cashless economy in India essay would never do justice to the topic since it will never be enough to write about all of the corruption scandals India has had since its independence. Corruptions of this scale could be brought down to a large extent if we could achieve that dream of a cashless economy throughout. And it's possible because the origin and endpoint of a transaction could easily be tracked in a cashless economy and that’s the biggest advantage.
There are Two Major Disadvantages of Cashless India.
Online Theft
With the improving technology every day, there’s a rampant increase in online cheating and fraud episodes. If the government is unable to achieve sturdy and not-possible-to-hack digital systems, in a country like India with a 135 crore population, it is completely impossible to make the economy cashless. People are still afraid of making big transactions online after watching the reports of online thefts on national news channels.
Infrastructure, or the Lack of it
Not just the government infrastructure, it requires infrastructure on an individual level too. A gadget or a smartphone, data connectivity, and electricity for charging the phones regularly are the basic requirements for making online transactions possible. These are privileges that exist mostly in urban India and most of rural India is still deprived of these privileges. The government should first fix this before even dreaming of making a cashless India possible.
The Government of India took the whole country by storm by announcing the demonetization on 8th November 2016. 500- and 1000-rupees notes were no longer legal tender. This move was aimed at getting rid of the black money in the economy that was largely used to fund criminals and terrorists and formed a parallel economy. The acute shortage of cash led to long queues outside ATMs and banks trying to withdraw cash or exchange notes. This was all to initiate the fruition of a dream of cashless India.
With the enormous amount of technological revolutions happening, it is close to impossible to find people without a smartphone in these times. Almost every citizen possesses a smartphone. The ease of transaction through interfaces like GooglePay or PhonePe or Paytm has never been more seamless than this. The Indian government has also introduced interfaces like UPI or Unified Payments Interface for hassle-free digital transactions that are fully cashless.
In recent years, we have been asked to be in very less contact with each other. This is because of the communicable diseases of Covid-19 that have seen an adverse effect throughout India. For this reason, online payments have recently been the most popular means of transaction. The money will directly get transferred to the account of the user from our account; all you need to do is just download the app that you can use for the transaction.
In the end, the demonetization step became crucial to start a cashless economy in the country. It has paved the way towards an economy in India that is defined by greater transparency and convenience and ease in monetary transactions.

FAQs on Cashless India Essay
1. Which Country is fully cashless?
There are a lot of benefits of going cashless and most of the benefits are discussed over here. Now the world is more focused on how to go cashless as they are well aware of the advantages that they will have after going cashless. This is the reason that most of the countries are seeking some changes and making constant efforts to make their country cashless. Going cashless will improve technologies and will also increase your economy. That is also one of the main reasons why this world is more focused on going cashless. Sweden could achieve a near cashless economy in the world.
2. Name the different Digital Currencies in the world?
Just as in terms of cash, we have rupees or dollars or pounds and so on. In the same way, it is not like only one kind of digital currency is used throughout the whole world. There are different kinds of currencies that the world uses for online transactions. Litecoin, Bitcoin, Ethereum are some of them that were found to be in existence as of 2020. You need to have good knowledge about these currencies and then you can easily transfer the money.
3. What are the apps that you can use to transfer money directly into another person's account in India?
In India going cashless is the new normal. People are using online money apps such as Google pay, Paytm, Payz app, PhonePe to make the transactions directly through their phone and bank account but when we talk about the currencies being used currently, Indians are more preferably using bitcoins as their online currency. India is now making efforts to go cashless and increase its economy.
4. How much is India cashless now?
In recent years, at the time of Corona, it was advised to people not to make contact with each other. It was at that time that the cashless India concept was created and the apps like Google Pay etc came into existence. The app was introduced in India before it came into use. In the covid time, most people used the cashless way of payment. The census has proved that 37% of India has not paid using cash since the Corona times.
5. Is it possible to have cashless India anytime sooner?
Given the regency usage and increased usage of the apps such as Google pay and Paytm and the increase in the number of vendors who have accepted this method of online payment, the more India can be cashless. The most difficult thing will be to make the people of India agree to use these online methods of payment and move toward increasing the other economy of India. India too can be cashless; it is just that we need to create awareness among people regarding this.
- Business Today
- India Today
- India Today Gaming
- Cosmopolitan
- Harper's Bazaar
- Brides Today
- Aajtak Campus

- Magazine Cover Story Editor's Note Deep Dive Interview The Buzz
- BT TV Market Today Easynomics Drive Today BT Explainer
- Market Today Trending Stocks Indices Stocks List Stocks News Share Market News IPO Corner
- Tech Today Unbox Today Authen Tech Tech Deck Tech Shorts
- Money Today Tax Investment Insurance Tools & Calculator
- Mutual Funds
- Industry Banking IT Auto Energy Commodities Pharma Real Estate Telecom
- Visual Stories

INDICES ANALYSIS
Mutual funds.
- Cover Story
- Editor's Note
- Market Today
- Drive Today
- BT Explainer
- Trending Stocks
- Stocks List
- Stocks News
- Share Market News
- Unbox Today
- Authen Tech
- Tech Shorts
- Tools & Calculator
- Commodities
- Real Estate
- Election with BT
- Economic Indicators
- BT-TR GCC Listing
How India can become a cashless economy
Targeted incentives will encourage consumers and merchants to consider moving away from cash. this might be achieved by reducing the cost of digital payments, introducing cash-handling charges or restricting the use of cash above certain thresholds.
- Updated Jul 23, 2021, 4:42 PM IST

The steps and the global case studies India can undertake to move towards a cashless society
Increased penetration of internet and banking system: Approximately 45% to 50% of the Indian population still doesn't have internet access, and approximately 20% of the population does not have access to a bank account. There is a lot of ground to be covered for India to become completely cashless, and steps need to be taken to increase the penetration in both these areas. Establish the right incentives: Targeted incentives will encourage consumers and merchants to consider moving away from cash. This might be achieved by reducing the cost of digital payments, introducing cash-handling charges or restricting the use of cash above certain thresholds (the EU is currently considering this measure).
Also Read: Cash Splash
For example, in Sweden, a consortium of banks launched a free mobile payments app, which was adopted by almost 50% of the population within four years of launch.
PromptPay, the electronic payment service under the Thai government's e-payment plan, encouraged usage by removing charges for online banking. Governments and companies might also consider consumer-friendly schemes such as weekly prize drawings based on transaction IDs or systems with specific demographics in mind. Strong data security and regulations: The year 2020 saw one of the largest numbers of data breaches in the world and in India. The total number of brute force attacks against remote desktop protocol jumped from about one million during early 2020 to about three million mid-2020.
By early 2021, the average jumped to about nine million attacks. Organisations in India lost about $2 million per breach on an average in 2020. Hence, in order to truly go cashless, a strong data security infrastructure is the key enabler and should encompass all the internet, mobile, and e-payment technologies.
Further, targeted and proportional regulation can strengthen confidence in electronic payments and enforce financial inclusion. Initiatives such as rapid dispute resolution mechanisms, licencing schemes, and fee caps have typically been highly effective in boosting the uptake of cashless solutions.
Also Read: NHAI transitions to 100% cashless toll via compulsory FASTags The measures adopted by a few of the global economies that are moving towards a cashless society are as follows: - Sweden: Sweden has the most aggressive policy to become cashless. Many Swedish retailers do not accept cash and only 20% of all transactions in Sweden are made in cash. There is also a popular payment application called Swish, which enables instant money transfers between people.
Sweden has also rolled out an array of policies encouraging cashless payments, from eliminating infrastructures such as ATMs to establishing enabling measures such as electronic know-your-customer (e-KYC) capabilities and real-time payments to granting stores the right to refuse cash. A tangential impact has been a surge in tax receipts, with the value-added tax rising nearly 30% over five years.
Also Read: Paytm earmarks Rs 50 cr for cashback programme to celebrate six years of Digital India Poland: Cashless Poland, the public-private foundation in Poland aims to popularise cashless payments in the country. The foundation offers free point of sale (POS) devices through partner banks to business owners in order to encourage the latter to accept cashless payments. The foundation has already helped over 200,000 companies to start accepting cards and mobile payments. South Korea: South Korea saw accelerating adoption of digital payments after introducing end-of-year tax credits for up to 30% of spending on debit cards. Australia: The Reserve Bank of Australia has taken action to address the high cost of digital payments, capping interchange fees and putting a ceiling on card surcharges for small businesses.
The moves led to a $11 billion decline in merchant payment costs and an acceleration in the growth of card transactions. A similar cap in the US in 2011 led to an 8% rise in credit card usage.
(The author is Managing Director, Duff & Phelps.)
- #Indian economy
- #cashless economy
- #cashless society
- #digitisation
- #digital economy
TOP STORIES

- Advertise with us
- Privacy Policy
- Terms and Conditions
- Press Releases
Copyright©2024 Living Media India Limited. For reprint rights: Syndications Today

Add Business Today to Home Screen
Cashless Economy – Is India Ready for Transformation?
From Current Affairs Notes for UPSC » Editorials & In-depths » This topic
To make India a cashless economy, during the Union Budget 2019-20 , the Finance Minister had stated that 2% tax deducted at source will be levied on cash withdrawals that exceed Rs.1 crore in a year from the bank account to discourage the practice of making business payments through cash transactions. The government had also said that the businesses with an annual turnover of over Rs.50 crore can offer low-cost digital modes of payments and no charges or Merchant Discount Rate will be imposed on them or their customers. This is a noteworthy move by the government of India to incentivize people to adapt to the emerging cashless economy. Transforming the cash-dependent India into a cashless economy is proving to a great challenge for the Indian government given the size of the informal sector within the Indian economy. It is estimated that nearly 90% of all transactions in the Indian economy is dependent on cash. This is due to the large informal sector that employs 90% of the workforce. India cannot become cashless unless this mammoth sector adapts to the digital payments. Incentivizing the people alone is not sufficient. The government needs to develop the supporting infrastructures and technologies for India to become a cashless economy while also providing awareness to its people.

This topic of “Cashless Economy – Is India Ready for Transformation?” is important from the perspective of the UPSC IAS Examination , which falls under General Studies Portion.

What is a cashless economy?
- Cashless economy is the term that is used to describe the situation wherein the flow of cash doesn’t exist within the economy and that all the transactions are undertaken through electronic channels.
- This can include cash transfer through credit and debit cards, direct debit, and electronic clearing and payment systems such as Immediate Payment Services (IMPS), National Electronic Funds Transfer (NEFT) and Real-Time Gross Settlement (RTGS) in India.
Express Learning Programme (ELP)
- Optional Notes
- Study Hacks
- Prelims Sureshots (Repeated Topic Compilations)
- Current Affairs (Newsbits, Editorials & In-depths)
- Ancient Indian History
- Medieval Indian History
- Modern Indian History
- Post-Independence Indian History
- World History
- Art & Culture
- Geography (World & Indian)
- Indian Society & Social Justice
- Indian Polity
- International Relations
- Indian Economy
- Environment
- Agriculture
- Internal Security
- Disasters & its Management
- General Science – Biology
- General Studies (GS) 4 – Ethics
- Syllabus-wise learning
- Political Science
- Anthropology
- Public Administration
SIGN UP NOW
Why should India transform into a cashless economy?
India should shift to a cashless economy. The reasons for this statement are as follows:
- Cash is expensive: A significant amount of time and money is needed to print the currency. RBI has spent Rs.32.1 billion on printing the currency. The effort is also needed to steer the money through the system and to the consumers. Also, there is the cost for the setting up of and maintaining of the ATMs. Furthermore, the paper currencies have shelf-life after which it needs to be replaced. It is estimated that the direct cost of running a cash-based economy is about 0.25% of India’s GDP.
- Cash is the driver of the shadow economy : Cash is difficult to trace. Its transaction provides secrecy enabling the people to carry out illegal activities like tax evasion, black money , etc. In 2007, currency in circulation was almost on par with the bank deposits. However, in the last three years, the currency with Indians was more than the bank deposits by 50%. According to the government data, the amount of black money (unaccounted money) in India is 15-16 lakh crores. The unaccounted money is used to finance the shadow economy that is running parallel to the government as it finances illegal activities terrorist activities, purchasing votes, smuggling, betting, trafficking, etc.
- Enables financial inclusion and increased tax revenues : A cashless economy mandates all citizens to have bank accounts. This will ensure a higher financial inclusion rate. It will also guarantee transparency in the transaction of money within the economy – minimizing the possibility of tax evasion exponentially. Even the beneficiaries of various government schemes can easily be identified and taken care of by the government.
Prelims Sureshots – Most Probable Topics for UPSC Prelims
A Compilation of the Most Probable Topics for UPSC Prelims, including Schemes, Freedom Fighters, Judgments, Acts, National Parks, Government Agencies, Space Missions, and more. Get a guaranteed 120+ marks!
What are the measures taken by the Indian government?
- Demonetisation : Demonetisation drive has not curbed the black money. However, it had nudged India towards being a cashless economy. It has become a radical ‘reform’ to transform India into a cashless economy. Paytm had witnessed 5 million daily usage post demonetisation as opposed to their average transaction of three million. It also saw a 700% increase in the overall traffic and a 1000% increase in the amount of money added to its account in the first two days of post-demonetisation. Ola Money too saw a 1500% increase in its e-wallet.
- Apart from demonetisation, the government has undertaken various other measures to reduce people’s dependence on cash in recent years.
- Some of them are as follows:
- Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana , one of the biggest financial inclusion initiatives in the world, was launched in 2014. It is a national mission on financial inclusion which has an integrated approach to bring about comprehensive financial inclusion and provide banking services to all households within the country. This scheme ensures access to a range of financial services like availability of basic savings, bank accounts, access to need-based credit, insurance and pension. It has played a significant role in the opening of bank accounts for the poor.
- Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT): It is a scheme that was launched by the Government of India to transfer the benefits and subsidies of various social welfare schemes like LPG subsidy, Old Age Pension, Scholarship, MGREGA, etc. directly to the bank account of the beneficiaries. This allowed for the penetration of digital banking into rural India.
- Unified Payment Interface (UPI): It is a system that powers multiple bank accounts into a single mobile application (of any participating banks), merging several banking features, seamless fund routing, and merchant payments into one hood. This makes digital transactions a simplified process. Transaction via UPI had increased the monthly transaction from nil to 754 million in less than 3 years.
- GST: The implementation of GST has encouraged businesses to opt for cashless transactions.
- Financial Literacy Centres: The RBI and Finance Ministry have established the Financial Literacy Centres (FLCs), a keystone of the PMJDY. This initiative has provided financial education programmes to spread awareness of banking products and benefits.
- The RBI has also provided licences to open new-age small finance banks and payment banks which are expected to give a push to financial inclusion and bring in innovative banking solutions.
- Other promotions like e-banking, debit and credit cards, card-swipe or PoS machines and digital wallets have made the transition to cashless economy easier.
What are the factors that determine the transition to the cashless economy?
Several factors determine the transition to the cashless economy. They are as follows:
- Awareness and skills related to banking and e-transactions
- Technological developments to support the cashless economy
- Government interventions to promote the transition.
Indications in India of transition to the cashless economy are as follows:
- Mobile wallets have significant market traction in India in recent times.
- Banks and related service providers have invested highly to improve security and ease of cash transactions.
- As previously mentioned, the Government of India is undertaking various measures to incentivize the population to shift to the cashless economy while also discouraging the cash payments.
- In India, as per the 2011 census, more households had mobile phones than toilets. 58% of households had mobile phones while 47% had toilets within the houses in 2011. 5 years later, the gap between the two has widened as the march of telecom connectivity has outpaced the march of water connectivity in the country. According to fresh data from a nationally representative household survey, the proportion of households with toilets has increased while the proportion of those with mobile phones has grown even more sharply. This shows the increased potential of the Indian economy to transform into a cashless economy if the government intervenes.
- India’s current economic situation has created a crucial turning point. If this situation is handled correctly, there is a high probability of India becoming a cashless economy.
What are the challenges that India might face while transferring to the cashless economy?
- Lack of adequate infrastructure and technology within the Indian society : India, a country with a vast area, currently has only 2.3 lakhs ATMs and 14 lakhs Point of Sale (POS). This is much too low when compared to other countries like the UK, France, Australia, and Brazil as they have three or four times that of India. Moreover, the ATMs are concentrated in urban areas and they are scarce in suburban and rural areas.
- Limited usage of credit/debit cards : India has a user base of 750 million cards. Ideally, its usage on PoS should be at least 375 million transactions per month, on the assumption that the customers, on average use the card at least once in two months on the POS terminal. But according to the RBI data, the volume of POS and e-commerce transactions together for all banks is about 130 million against the 765 million on the ATM channel as of 2016.
- The penetration of mobile internet is very low in rural India : Making India a cashless economy is highly difficult in the current scenario as rural India has poor internet connectivity. Also, the awareness and knowledge related to digital transactions are limited in rural areas.
- Indian economy is cash-dependent: India is much dependent on cash, so much so, that the MNCs like Amazon had to include “cash on delivery” to penetrate the Indian market. The rate of cash to GDP is the highest in India (12.42%). In other large economies, the average cash to GDP ratio is 5%. In fact, the year 2015 saw 78% of all consumer payments in cash in India. On the other hand, during the same period, it was 20% and 25% in the US and the UK. India is also the 4 th largest user of cash in the world. This shows India is not fast enough to adapt to the current era, the one that is dominated by technological innovations and developments. Rural India’s adaptation to new technologies is slow. This is a major concern for India’s aspiration to become a cashless economy.
What can be the way forward?
- Targeted financial education drive can be undertaken by the government to improve the knowledge of e-transactions to the public, even the illiterate.
- The banks must make sure that the transaction fee is either free or affordable to all.
- The banks must encourage the opening of zero balance accounts to encourage the poor to make use of the bank accounts.
- The government must improve internet connectivity in rural India and other isolated regions .
- Supporting infrastructures must be assured like the availability of ATMs in the rural and suburban areas as the availability of bank accounts alone cannot address the problem of India being overly dependent on cash.
Conclusion:
According to a report by Google India and Boston Consulting Group, by 2020, $500 billion worth of transactions would take place online. This means that the increase will be 10 folds. Furthermore, cash-based transactions would fall by 40% in the coming years. The online transactions have increased 20 times in the last 6 years. This data is before the demonetisation. While observing the recent situation, it is evident that India is well-equipped to adapt to the slow-paced shift towards the cashless economy.
GET MONTHLY COMPILATIONS
Related Posts

Banking Regulation (Amendment) Bill, 2020 – Need, Features, Limitation...

IMF Bailout- Working, Pros & Cons

There was a problem reporting this post.
Block Member?
Please confirm you want to block this member.
You will no longer be able to:
- See blocked member's posts
- Mention this member in posts
Please allow a few minutes for this process to complete.


Press ESC to close

Benefits of Cashless Economy: Is India Ready for a Cashless Economy?
On 8th November 2016, India underwent the process of demonetization. The 500 and 1000 notes were declared banned. A new set of notes were then pushed out but after a long while. In the gap between the note ban and the arrival of new notes, one payment method started to shine. E-wallets and cashless transactions were now spreading.
United Payments Interface or UPI was launched. This connected bank accounts to your mobile number and enabled users to have a bank to bank transfers at the tip of their fingers. It was launched in 2016 by the National Payments Corporation of India and is also recognized as a mode of payment by RBI.
What is a Cashless Economy?
You must wonder what a cashless economy is? An economy in which transactions of cash are less and transactions mainly take place on credit cards, debit cards, e-wallets, or any digital payments.
This is a much cheaper method and will also help control excess inflation caused by the overprinting of money for circulation in the economy. It will also help in the rapid development of Digital India which is a program launched by the government of India in 2015.
Is India Ready for a Cashless Economy?
A very big question lies in front of everyone. Is India ready for a cashless economy? The answer is relative to most people. Some believe that India is ready for it and some believe that India is not.
The Government of India has a strong belief in the fact that India can transform itself. Since most people are connected with a smartphone in India, it is very usable and will help India move towards a paperless society. The government also announced a few incentives for cashless transactions to promote it.
Merits and Demerits of Cashless Economy
A paperless economy has its own merits and demerits.
The benefits of a cashless economy are
- Reduction in cost : the cost of printing and circulating money into the economy is cut down
- More transparency : since most e-wallets and digital payments require KYC, and this helps the RBI to track transactions.
- Convenience : e-transactions are convenient for both banks and customers. This kind of transactions can take place in any corner of the world, 24*7*365
- Offers : Lots of e-wallets give exciting offers like cash backs on transactions. Cashback is an offer where people get back a certain amount on their transactions
- Rapid development : Due to the high demand for digital needs, India has seen rapid development in many parts of the country.
- Control on black money : digital transactions have proven to cut down the black money problem in India due to higher transparency in transactions
The Demerits of Cashless Economy
- Not enough reach: The digital India platform has not reached a lot of parts in rural India. Many villages are yet to have the rapid development seen in the digital infrastructure.
- Lack of digitalization : Not everyone in India has a smartphone, around 14 people out of 100 in India lack a smartphone
- Cyberattack : Due to digitalization, the chance of hacking and cyber attacks on your phone is very high.
- Bad servers : Many UPI users have trouble in transactions due to bad servers very often. This can put people in big problems at times
Also Read : What is the Minimum Age to be the Governor of a State? Things You Should Know for UPSC Exam
Curbing of Black Money
India has a very big and well-known issue of corruption and black money. Reports claim that India has more than 1 trillion dollars of black money in Swiss replica watch banks alone. Most sources of black money are by evading tax on income and property. India has tried many ways to avoid black money but none have proven to work.
It is highly believed that a cashless economy can help control the black money issues in India as these transactions can be recorded and monitored by the RBI. This will also in turn help widen the tax base as people try to avoid paying taxes.
You are required to connect your pan card through KYC for e-wallet transactions thus tying you up with the government control.
Many e-wallets like Paytm, Amazon Pay and etc. Give the users exciting offers like cashback,
Cashback is an offer where users get a certain amount from the total transaction or as per the terms and conditions.
There is generally a maximum amount which a person can get through cashback on purchases but in recent times companies have also allowed cashback on money transfer from bank to bank or through UPI.
The amount received on cash backs is not the same throughout companies. Some offer higher chances of getting cashback while some give higher amounts. Most new users get assured cashback on their first transactions.
Companies also give a certain amount to referrals. For example, if you invite a friend to use their app, you will be rewarded as well as your friend on their first transaction. So, a win-win situation!
Know Your Customer
Know Your Customer, also called KYC, is a process where the customer verifies his or her identity with the bank through official government identity cards before they get into business or contract with you.
RBI has made KYC compulsory to avail maximum benefits of E-wallets, without KYC a customer cannot use the complete ability of the wallet.
It is compulsory for banks to comply with Know Your Customer norms and also make sure that they do not hassle customers for the same.
In recent times, E-Know Your Customer has become the need of the hour. You can get a minimum Know Your Customer done by just adding your PAN card details into various websites and they will be verified later through their own system of checking.
It is recommended that you go through the Know Your Customer policies of each website before entering details and also be aware of fraudulent websites or unauthorized websites. Make sure that the bank or wallet is complying with RBI and its norms.
Digital India
Digital India is a campaign launched by the Government of India to help the rapid development of digital infrastructure in India especially in the rural parts of the country. It was launched in 2015 to convert India into a digitally empowered society and a knowledge economy.
Under this campaign, a program called cashless India was launched which is looking to convert India into a cashless economy. It ties various payment methods with the government, trying to make it official and a well-built system.
They are conducting programs to spread awareness and on the importance and the need for digitization of payments in India. Most of these programs are for the rural parts of India, which are underdeveloped in digital infrastructure.
You can learn more about the program through the official website of Cashless India.
With a change in the world, there is a need for development in the economy of India. India has started to aim at a cashless economy. This does have its own benefits and demerits which are discussed in detail in the blog. The movement has a lot to offer to help customers and get customers enrolled in paperless transactions.
It has helped to control the black money in India and is giving the government more control over transaction records and helping to improve the tax base of the country.
Also Read : IAS Preparation Strategy for Beginners: Boost your UPSC Preparation Today

#DigitalIndia. Was that a thing before Narendra Modi came up with it?
I’m amazed, I have to admit. Rarely do I come across a blog that’s equally educative and entertaining, and let me tell you, you’ve hit the nail on the head. The problem is an issue that too few men and women are speaking intelligently about. I’m very happy that I came across this in my search for something concerning this.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Share Article:
You might also like

Liberalised Remittance Scheme UPSC: UPSC Current Affairs Notes

What is Indo-Pacific Economic Framework? Understanding IPEF Notes for UPSC

Manipur Violence UPSC: Let’s Check Out the Reason for Manipur Violence for the UPSC Exam!
Other stories, what is the minimum age to be a member of rajya sabha guide on rajya sabha for upsc, ias preparation strategy for beginners: boost your upsc preparation today.
Forgot your password?
Lost your password? Please enter your email address. You will receive mail with link to set new password.
Back to login

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Cashless Economy can be defined as a situation in which the flow of cash within an economy is non-existent and all transactions must be through electronic channels such as direct debit, credit cards, debit cards, electronic clearing, and payment systems such as Immediate Payment Service (IMPS), National Electronic Funds Transfer (NEFT) and Real-Time Gross Settlement (RTGS) in India.
In this cashless India essay, we will be talking about the meaning of 'cashless', the different alternatives for our monetary system, and the disadvantages and advantages of a country going fully cashless and digital in its economy. The following cashless India essay in English is for students studying in class 5 and above.
The steps and the global case studies India can undertake to move towards a cashless society. Increased penetration of internet and banking system: Approximately 45% to 50% of the Indian ...
Indian economy is cash-dependent: India is much dependent on cash, so much so, that the MNCs like Amazon had to include "cash on delivery" to penetrate the Indian market. The rate of cash to GDP is the highest in India (12.42%). In other large economies, the average cash to GDP ratio is 5%. In fact, the year 2015 saw 78% of all consumer ...
India's transition to a cashless economy needs more focus on behavioral change (as observed during demonetization). The government is moving in the right direction as supply of digital infrastructure will eventually create demand for digitalization. This can have a multiplier effect on the economy. Sweden and China are leading in digitization.
An economy that is majorly cash-based gives advantages to criminal activities like terrorism, human trafficking, drug trafficking, etc. In a Cashless Economy, the circulation of fake currency notes can be reduced. It would lead to an increase in the tax base, as it is difficult to avoid proper payment in a cashless society.
The benefits of a cashless economy are. Reduction in cost: the cost of printing and circulating money into the economy is cut down. More transparency: since most e-wallets and digital payments require KYC, and this helps the RBI to track transactions. Convenience: e-transactions are convenient for both banks and customers.
Published: December 20, 2016 5:48am EST. Indians have turned to digital payment following demonetisation. RAJAT GUPTA/EPA. It was a move that could have brought India's economy to a shuddering ...
Benefits of a Cashless India. 1. Financial Inclusion and Accessibility. Increased Reach: Digital transactions facilitate financial inclusion by reaching remote and underserved areas where traditional banking infrastructure may be lacking. Empowering the Unbanked: Mobile wallets and digital payment platforms enable individuals with limited access to formal banking services, fostering economic ...
A cashless India offers numerous benefits. Firstly, it aids in curbing corruption and black money as all transactions are recorded, making it difficult for illegal transactions to go unnoticed. Secondly, it promotes financial inclusion by bringing the unbanked population into the formal banking system. Thirdly, it is convenient as it eliminates ...
So said Narendra Modi, doubling up as the nation's digital evangelist-in-chief. Appropriately, he "said" this via a tweet. PM Modi's November 8 surprise demonetising Rs 500 and Rs 1,000 notes, effectively took 86 per cent of cash out of circulation in an economy that is close to 90 per cent reliant on cash.
Let's discuss today if India is ready to be a cashless economy. Cashless transactions really came into effect after demonetization announced by PM in 2016. The historic decision illegalised 86% of cash overnight. This decision encouraged the market for companies like Paytm, and their finances have been increasing since the last couple of years.
Going cashless helps to curb corruption hence increases the economic growth of the country. With the demonetization that took place in 2016, a large step was taken to initiate this concept. According to Union defense minister after demonetization the crime rates in Mumbai has dropped to half.
Published: Feb 12, 2019. Cashless India is a mission launched by the Government of India led by Prime Minister Narendra Modi to lower the dependency of Indian economy on cash and to bring hoards of stashed black money lying unused into the banking system. The country commence upon this transition to a cashless economy when the government took ...
Cashless India Essay 5 (300 words) Cashless India is a recently introduced phenomenon targeted to bring a sea change in the country's economy by the Indian government, transforming the cash-based economy into cashless through digital means. However, still there are various challenges to be addressed if we want to make India cashless in true ...
How to Approach the topic 'Cashless Economy in India' for UPSC Prelims: Economics - Learn about UPI, Payments Modes etc. Current Affairs - Check on important editorials related to the Indian economy. General Studies III: Indian Economy Essay: Cashless Economy - a probable essay topic Related Links:
effort to move towards a cashless transaction economy by minimizing the use of corporal cash. A Cashless economy is a situation in which all the financial transactions are made by digital currencies rather than physical currencies. Cashless India means the cashless transaction. y the 2010's cash had become actively disfavored in some kinds of
INTRODUCTION- Cashless India is a mission launched by the Government of India led by Prime Minister Narendra Modi to reduce the dependency of the Indian economy on cash and to bring hoards of ...
Advantages and Disadvantages of Cashless Economy: Since the pastimes, India has always been categorized under the niche of a cash-based economy. The government seized all black money, undeclared commodities, and the recent Covid pandemic compelled contactless mortgages and boosted cashless transactions. The government initially planned the natural route for the cashless economy in 2006 by […]
Read our special report on India's economy Read our report on how Narendra Modi sweet-talks the nation India, the world's fastest-growing big country, is expanding at an annual rate of 6-7%.
Cashless India is a mission launched by the Government of India led by Prime Minister Narendra Modi to reduce dependency of Indian economy on cash and to bring hoards of stashed black money lying unused into the banking system. The country embarked upon this transition to a cashless economy when the government took the revolutionary step of demonetization of old currency notes of Rs 500 and Rs ...
Why should India transform into a cashless economy? India should shift to a cashless economy. The reasons for this statement are as follows: Cash is expensive: A significant amount of time and money is needed to print the currency. RBI has spent Rs.32.1 billion on printing the currency. The effort
New topics added every week. Yes, India is ready for a cashless economy. According to TRAI, as on 30 September 2016, 82 out of 100 citizens in India owned a mobile phone. The evolution of the telecom ecosystem, with significant reduction in call and data rates, along with the prices of smart phones, is propelling the shift to a cashless economy.
Cashless India Speech for ASL in English for 1 and 2 Minute, Essay 100 Words, Quotes, Essay in 200 Words, Project, Questions and Disadvantages for Class 12. ... the concept of a cashless economy in India is concentrated around the need to transform the country into a society, which is digitally empowered and enabled by several modes of cashless ...