
- Search Search Search …
- Search Search …

Critical Thinking Models: A Comprehensive Guide for Effective Decision Making

Critical thinking models are valuable frameworks that help individuals develop and enhance their critical thinking skills . These models provide a structured approach to problem-solving and decision-making by encouraging the evaluation of information and arguments in a logical, systematic manner. By understanding and applying these models, one can learn to make well-reasoned judgments and decisions.

Various critical thinking models exist, each catering to different contexts and scenarios. These models offer a step-by-step method to analyze situations, scrutinize assumptions and biases, and consider alternative perspectives. Ultimately, the goal of critical thinking models is to enhance an individual’s ability to think critically, ultimately improving their reasoning and decision-making skills in both personal and professional settings.
Key Takeaways
- Critical thinking models provide structured approaches for enhancing decision-making abilities
- These models help individuals analyze situations, scrutinize assumptions, and consider alternative perspectives
- The application of critical thinking models can significantly improve one’s reasoning and judgment skills.
Fundamentals of Critical Thinking

Definition and Importance
Critical thinking is the intellectual process of logically, objectively, and systematically evaluating information to form reasoned judgments, utilizing reasoning , logic , and evidence . It involves:
- Identifying and questioning assumptions,
- Applying consistent principles and criteria,
- Analyzing and synthesizing information,
- Drawing conclusions based on evidence.
The importance of critical thinking lies in its ability to help individuals make informed decisions, solve complex problems, and differentiate between true and false beliefs .
Core Cognitive Skills
Several core cognitive skills underpin critical thinking:
- Analysis : Breaking down complex information into smaller components to identify patterns or inconsistencies.
- Evaluation : Assessing the credibility and relevance of sources, arguments, and evidence.
- Inference : Drawing conclusions by connecting the dots between analyzed information.
- Synthesis : Incorporating analyzed information into a broader understanding and constructing one’s argument.
- Logic and reasoning : Applying principles of logic to determine the validity of arguments and weigh evidence.
These skills enable individuals to consistently apply intellectual standards in their thought process, which ultimately results in sound judgments and informed decisions.
Influence of Cognitive Biases
A key aspect of critical thinking is recognizing and mitigating the impact of cognitive biases on our thought processes. Cognitive biases are cognitive shortcuts or heuristics that can lead to flawed reasoning and distort our understanding of a situation. Examples of cognitive biases include confirmation bias, anchoring bias, and availability heuristic.
To counter the influence of cognitive biases, critical thinkers must be aware of their own assumptions and strive to apply consistent and objective evaluation criteria in their thinking process. The practice of actively recognizing and addressing cognitive biases promotes an unbiased and rational approach to problem-solving and decision-making.
The Critical Thinking Process

Stages of Critical Thinking
The critical thinking process starts with gathering and evaluating data . This stage involves identifying relevant information and ensuring it is credible and reliable. Next, an individual engages in analysis by examining the data closely to understand its context and interpret its meaning. This step can involve breaking down complex ideas into simpler components for better understanding.
The next stage focuses on determining the quality of the arguments, concepts, and theories present in the analyzed data. Critical thinkers question the credibility and logic behind the information while also considering their own biases and assumptions. They apply consistent standards when evaluating sources, which helps them identify any weaknesses in the arguments.
Values play a significant role in the critical thinking process. Critical thinkers assess the significance of moral, ethical, or cultural values shaping the issue, argument, or decision at hand. They determine whether these values align with the evidence and logic they have analyzed.
After thorough analysis and evaluation, critical thinkers draw conclusions based on the evidence and reasoning gathered. This step includes synthesizing the information and presenting a clear, concise argument or decision. It also involves explaining the reasoning behind the conclusion to ensure it is well-founded.
Application in Decision Making
In decision making, critical thinking is a vital skill that allows individuals to make informed choices. It enables them to:
- Analyze options and their potential consequences
- Evaluate the credibility of sources and the quality of information
- Identify biases, assumptions, and values that may influence the decision
- Construct a reasoned, well-justified conclusion
By using critical thinking in decision making, individuals can make more sound, objective choices. The process helps them to avoid pitfalls like jumping to conclusions, being influenced by biases, or basing decisions on unreliable data. The result is more thoughtful, carefully-considered decisions leading to higher quality outcomes.
Critical Thinking Models
Critical thinking models are frameworks that help individuals develop better problem-solving and decision-making abilities. They provide strategies for analyzing, evaluating, and synthesizing information to reach well-founded conclusions. This section will discuss four notable models: The RED Model, Bloom’s Taxonomy, Paul-Elder Model, and The Halpern Critical Thinking Assessment.
The RED Model
The RED Model stands for Recognize Assumptions, Evaluate Arguments, and Draw Conclusions. It emphasizes the importance of questioning assumptions, weighing evidence, and reaching logical conclusions.
- Recognize Assumptions: Identify and challenge assumptions that underlie statements, beliefs, or arguments.
- Evaluate Arguments: Assess the validity and reliability of evidence to support or refute claims.
- Draw Conclusions: Make well-reasoned decisions based on available information and sound reasoning.
The RED Model helps individuals become more effective problem solvers and decision-makers by guiding them through the critical thinking process ^(source) .
Bloom’s Taxonomy
Bloom’s Taxonomy is a hierarchical model that classifies cognitive skills into six levels of complexity. These levels are remembering, understanding, applying, analyzing, evaluating, and creating. By progressing through these levels, individuals can develop higher-order thinking skills.
- Remembering: Recall information or facts.
- Understanding: Comprehend the meaning of ideas, facts, or problems.
- Applying: Use knowledge in different situations.
- Analyzing: Break down complex topics or problems into sub-parts.
- Evaluating: Assess the quality, relevance, or credibility of information, ideas, or solutions.
- Creating: Combine elements to form a new whole, generate new ideas, or solve complex issues.
Paul-Elder Model
The Paul-Elder Model introduces the concept of “elements of thought,” focusing on a structured approach to critical thinking. This model promotes intellectual standards, such as clarity, accuracy, and relevance. It consists of three stages:
- Critical Thinking: Employ the intellectual standards to problem-solving and decision-making processes.
- Elements of Thought: Consider purpose, question at issue, information, interpretation and inference, concepts, assumptions, implications, and point of view.
- Intellectual Traits: Develop intellectual traits, such as intellectual humility, intellectual empathy, and intellectual perseverance.
This model fosters a deeper understanding and appreciation of critical thinking ^(source) .
The Halpern Critical Thinking Assessment
The Halpern Critical Thinking Assessment is a standardized test developed by Diane Halpern to assess critical thinking skills. The evaluation uses a variety of tasks to measure abilities in core skill areas, such as verbal reasoning, argument analysis, and decision making. Pearson, a leading publisher of educational assessments, offers this test as a means to assess individuals’ critical thinking skills ^(source) .
These four critical thinking models can be used as frameworks to improve and enhance cognitive abilities. By learning and practicing these models, individuals can become better equipped to analyze complex information, evaluate options, and make well-informed decisions.
Evaluating Information and Arguments
In this section, we will discuss the importance of evaluating information and arguments in the process of critical thinking, focusing on evidence assessment, logic and fallacies, and argument analysis.
Evidence Assessment
Evaluating the relevance, accuracy, and credibility of information is a vital aspect of critical thinking. In the process of evidence assessment, a thinker should consider the following factors:
- Source reliability : Research and understand the expertise and credibility of the source to ensure that biased or inaccurate information is not being considered.
- Currency : Check the date of the information to make sure it is still relevant and accurate in the present context.
- Objectivity : Analyze the information for potential bias and always cross-reference it with other credible sources.
When practicing critical thinking skills, it is essential to be aware of your own biases and make efforts to minimize their influence on your decision-making process.
Logic and Fallacies
Logic is crucial for deconstructing and analyzing complex arguments, while identifying and avoiding logical fallacies helps maintain accurate and valid conclusions. Some common fallacies to watch out for in critical thinking include:
- Ad Hominem : Attacking the person making the argument instead of addressing the argument itself.
- Strawman : Misrepresenting an opponent’s argument to make it easier to refute.
- False Dilemma : Presenting only two options when there may be multiple viable alternatives.
- Appeal to Authority : Assuming a claim is true simply because an authority figure supports it.
Being aware of these fallacies enables a thinker to effectively evaluate the strength of an argument and make sound judgments accordingly.
Argument Analysis
Analyzing an argument is the process of evaluating its structure, premises, and conclusion while determining its validity and soundness. To analyze an argument, follow these steps:
- Identify the premises and conclusion : Determine the main point is being argued, how it is related and substance of the argument.
- Evaluate the validity : Assess whether the conclusion logically follows from the premises and if the argument’s structure is sound.
- Test the soundness : Evaluate the truth and relevance of the premises. This may require verifying the accuracy of facts and evidence, as well as assessing the reliability of sources.
- Consider counter-arguments : Identify opposing viewpoints and counter-arguments, and evaluate their credibility to gauge the overall strength of the original argument.
By effectively evaluating information and arguments, critical thinkers develop a solid foundation for making well-informed decisions and solving problems.
Enhancing Critical Thinking
Strategies for improvement.
To enhance critical thinking, individuals can practice different strategies, including asking thought-provoking questions, analyzing ideas and observations, and being open to different perspectives. One effective technique is the Critical Thinking Roadmap , which breaks critical thinking down into four measurable phases: execute, synthesize, recommend, and communicate. It’s important to use deliberate practice in these areas to develop a strong foundation for problem-solving and decision-making. In addition, cultivating a mindset of courage , fair-mindedness , and empathy will support critical thinking development.
Critical Thinking in Education
In the field of education, critical thinking is an essential component of effective learning and pedagogy. Integrating critical thinking into the curriculum encourages student autonomy, fosters innovation, and improves student outcomes. Teachers can use various approaches to promote critical thinking, such as:
- Employing open-ended questions to stimulate ideas
- Incorporating group discussions or debates to facilitate communication and evaluation of viewpoints
- Assessing and providing feedback on student work to encourage reflection and improvement
- Utilizing real-world scenarios and case studies for practical application of concepts
Developing a Critical Thinking Mindset
To truly enhance critical thinking abilities, it’s important to adopt a mindset that values integrity , autonomy , and empathy . These qualities help to create a learning environment that encourages open-mindedness, which is key to critical thinking development. To foster a critical thinking mindset:
- Be curious : Remain open to new ideas and ask questions to gain a deeper understanding.
- Communicate effectively : Clearly convey thoughts and actively listen to others.
- Reflect and assess : Regularly evaluate personal beliefs and assumptions to promote growth.
- Embrace diversity of thought : Welcome different viewpoints and ideas to foster innovation.
Incorporating these approaches can lead to a more robust critical thinking skillset, allowing individuals to better navigate and solve complex problems.
Critical Thinking in Various Contexts
The workplace and beyond.
Critical thinking is a highly valued skill in the workplace, as it enables employees to analyze situations, make informed decisions, and solve problems effectively. It involves a careful thinking process directed towards a specific goal. Employers often seek individuals who possess strong critical thinking abilities, as they can add significant value to the organization.
In the workplace context, critical thinkers are able to recognize assumptions, evaluate arguments, and draw conclusions, following models such as the RED model . They can also adapt their thinking to suit various scenarios, allowing them to tackle complex and diverse problems.
Moreover, critical thinking transcends the workplace and applies to various aspects of life. It empowers an individual to make better decisions, analyze conflicting information, and engage in constructive debates.
Creative and Lateral Thinking
Critical thinking encompasses both creative and lateral thinking. Creative thinking involves generating novel ideas and solutions to problems, while lateral thinking entails looking at problems from different angles to find unique and innovative solutions.
Creative thinking allows thinkers to:
- Devise new concepts and ideas
- Challenge conventional wisdom
- Build on existing knowledge to generate innovative solutions
Lateral thinking, on the other hand, encourages thinkers to:
- Break free from traditional thought patterns
- Combine seemingly unrelated ideas to create unique solutions
- Utilize intuition and intelligence to approach problems from a different perspective
Both creative and lateral thinking are essential components of critical thinking, allowing individuals to view problems in a holistic manner and generate well-rounded solutions. These skills are highly valued by employers and can lead to significant personal and professional growth.
In conclusion, critical thinking is a multifaceted skill that comprises various thought processes, including creative and lateral thinking. By embracing these skills, individuals can excel in the workplace and in their personal lives, making better decisions and solving problems effectively.
Overcoming Challenges
Recognizing and addressing bias.
Cognitive biases and thinking biases can significantly affect the process of critical thinking . One of the key components of overcoming these challenges is to recognize and address them. It is essential to be aware of one’s own beliefs, as well as the beliefs of others, to ensure fairness and clarity throughout the decision-making process. To identify and tackle biases, one can follow these steps:
- Be self-aware : Understand personal beliefs and biases, acknowledging that they may influence the interpretation of information.
- Embrace diverse perspectives : Encourage open discussions and invite different viewpoints to challenge assumptions and foster cognitive diversity.
- Reevaluate evidence : Continuously reassess the relevance and validity of the information being considered.
By adopting these practices, individuals can minimize the impact of biases and enhance the overall quality of their critical thinking skills.
Dealing with Information Overload
In today’s world, information is abundant, and it can become increasingly difficult to demystify and make sense of the available data. Dealing with information overload is a crucial aspect of critical thinking. Here are some strategies to address this challenge:
- Prioritize information : Focus on the most relevant and reliable data, filtering out unnecessary details.
- Organize data : Use tables, charts, and lists to categorize information and identify patterns more efficiently.
- Break down complex information : Divide complex data into smaller, manageable segments to simplify interpretation and inferences.
By implementing these techniques, individuals can effectively manage information overload, enabling them to process and analyze data more effectively, leading to better decision-making.
In conclusion, overcoming challenges such as biases and information overload is essential in the pursuit of effective critical thinking. By recognizing and addressing these obstacles, individuals can develop clarity and fairness in their thought processes, leading to well-informed decisions and improved problem-solving capabilities.
Measuring Critical Thinking
Assessment tools and criteria.
There are several assessment tools designed to measure critical thinking, each focusing on different aspects such as quality, depth, breadth, and significance of thinking. One example of a widely used standardized test is the Watson-Glaser Critical Thinking Appraisal , which evaluates an individual’s ability to interpret information, draw conclusions, and make assumptions. Another test is the Cornell Critical Thinking Tests Level X and Level Z , which assess an individual’s critical thinking skills through multiple-choice questions.
Furthermore, criteria for assessing critical thinking often include precision, relevance, and the ability to gather and analyze relevant information. Some assessors utilize the Halpern Critical Thinking Assessment , which measures the application of cognitive skills such as deduction, observation, and induction in real-world scenarios.
The Role of IQ and Tests
It’s important to note that intelligence quotient (IQ) tests and critical thinking assessments are not the same. While IQ tests aim to measure an individual’s cognitive abilities and general intelligence, critical thinking tests focus specifically on one’s ability to analyze, evaluate, and form well-founded opinions. Therefore, having a high IQ does not necessarily guarantee strong critical thinking skills, as critical thinking requires additional mental processes beyond basic logical reasoning.
To build and enhance critical thinking skills, individuals should practice and develop higher-order thinking, such as critical alertness, critical reflection, and critical analysis. Using a Critical Thinking Roadmap , such as the four-phase framework that includes execution, synthesis, recommendation, and the ability to apply, individuals can continuously work to improve their critical thinking abilities.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main steps involved in the paul-elder critical thinking model.
The Paul-Elder Critical Thinking Model is a comprehensive framework for developing critical thinking skills. The main steps include: identifying the purpose, formulating questions, gathering information, identifying assumptions, interpreting information, and evaluating arguments. The model emphasizes clarity, accuracy, precision, relevance, depth, breadth, logic, and fairness throughout the critical thinking process. By following these steps, individuals can efficiently analyze and evaluate complex ideas and issues.
Can you list five techniques to enhance critical thinking skills?
Here are five techniques to help enhance critical thinking skills:
- Ask open-ended questions : Encourages exploration and challenges assumptions.
- Engage in active listening: Focus on understanding others’ viewpoints before responding.
- Reflect on personal biases: Identify and question any preconceived notions or judgments.
- Practice mindfulness: Develop self-awareness and stay present in the moment.
- Collaborate with others: Exchange ideas and learn from diverse perspectives.
What is the RED Model of critical thinking and how is it applied?
The RED Model of critical thinking consists of three key components: Recognize Assumptions, Evaluate Arguments, and Draw Conclusions. To apply the RED Model, begin by recognizing and questioning underlying assumptions, being aware of personal biases and stereotypes. Next, evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of different arguments, considering evidence, logical consistency, and alternative explanations. Lastly, draw well-reasoned conclusions that are based on the analysis and evaluation of the information gathered.
How do the ‘3 C’s’ of critical thinking contribute to effective problem-solving?
The ‘3 C’s’ of critical thinking – Curiosity, Creativity, and Criticism – collectively contribute to effective problem-solving. Curiosity allows individuals to explore various perspectives and ask thought-provoking questions, while Creativity helps develop innovative solutions and unique approaches to challenges. Criticism, or the ability to evaluate and analyze ideas objectively, ensures that the problem-solving process remains grounded in logic and relevance.
What characteristics distinguish critical thinking from creative thinking?
Critical thinking and creative thinking are two complementary cognitive skills. Critical thinking primarily focuses on analyzing, evaluating, and reasoning, using objectivity and logical thinking. It involves identifying problems, assessing evidence, and drawing sound conclusions. Creative thinking, on the other hand, is characterized by the generation of new ideas, concepts, and approaches to solve problems, often involving imagination, originality, and out-of-the-box thinking.
What are some recommended books to help improve problem-solving and critical thinking skills?
There are several books that can help enhance problem-solving and critical thinking skills, including:
- “Thinking, Fast and Slow” by Daniel Kahneman: This book explores the dual process theory of decision-making and reasoning.
- “The 5 Elements of Effective Thinking” by Edward B. Burger and Michael Starbird: Offers practical tips and strategies for improving critical thinking skills.
- “Critique of Pure Reason” by Immanuel Kant: A classic philosophical work that delves into the principles of reason and cognition.
- “Mindware: Tools for Smart Thinking” by Richard E. Nisbett: Presents a range of cognitive tools to enhance critical thinking and decision-making abilities.
- “The Art of Thinking Clearly” by Rolf Dobelli: Explores common cognitive biases and errors in judgment that can affect critical thinking.
You may also like

Critical Thinking Vs Analytical Thinking
It’s easy to confuse critical and analytical thinking as one, but they’re not the same. While there are similarities, you will realize […]

Online Learning and Critical Thinking: How to Choose the Right Course
Online learning gives more people access to education because of its convenience. It allows those with little time to take courses that […]

Critical thinking and Decision making
Have you ever wondered about critical thinking and decision making, and how these two concepts link to represent a common process of […]

Critical thinking and Relationships: How critical thinking can help your relationships in life.
Everyone always says that communication is key – especially for couples. And in this modern age of passive communication, this is certainly […]
- A Model for the National Assessment of Higher Order Thinking
- International Critical Thinking Essay Test
- Online Critical Thinking Basic Concepts Test
- Online Critical Thinking Basic Concepts Sample Test
Consequential Validity: Using Assessment to Drive Instruction
Translate this page from English...
*Machine translated pages not guaranteed for accuracy. Click Here for our professional translations.

Critical Thinking Testing and Assessment
The purpose of assessment in instruction is improvement. The purpose of assessing instruction for critical thinking is improving the teaching of discipline-based thinking (historical, biological, sociological, mathematical, etc.) It is to improve students’ abilities to think their way through content using disciplined skill in reasoning. The more particular we can be about what we want students to learn about critical thinking, the better we can devise instruction with that particular end in view.

The Foundation for Critical Thinking offers assessment instruments which share in the same general goal: to enable educators to gather evidence relevant to determining the extent to which instruction is teaching students to think critically (in the process of learning content). To this end, the Fellows of the Foundation recommend:
that academic institutions and units establish an oversight committee for critical thinking, and
that this oversight committee utilizes a combination of assessment instruments (the more the better) to generate incentives for faculty, by providing them with as much evidence as feasible of the actual state of instruction for critical thinking.
The following instruments are available to generate evidence relevant to critical thinking teaching and learning:
Course Evaluation Form : Provides evidence of whether, and to what extent, students perceive faculty as fostering critical thinking in instruction (course by course). Machine-scoreable.
Online Critical Thinking Basic Concepts Test : Provides evidence of whether, and to what extent, students understand the fundamental concepts embedded in critical thinking (and hence tests student readiness to think critically). Machine-scoreable.
Critical Thinking Reading and Writing Test : Provides evidence of whether, and to what extent, students can read closely and write substantively (and hence tests students' abilities to read and write critically). Short-answer.
International Critical Thinking Essay Test : Provides evidence of whether, and to what extent, students are able to analyze and assess excerpts from textbooks or professional writing. Short-answer.
Commission Study Protocol for Interviewing Faculty Regarding Critical Thinking : Provides evidence of whether, and to what extent, critical thinking is being taught at a college or university. Can be adapted for high school. Based on the California Commission Study . Short-answer.
Protocol for Interviewing Faculty Regarding Critical Thinking : Provides evidence of whether, and to what extent, critical thinking is being taught at a college or university. Can be adapted for high school. Short-answer.
Protocol for Interviewing Students Regarding Critical Thinking : Provides evidence of whether, and to what extent, students are learning to think critically at a college or university. Can be adapted for high school). Short-answer.
Criteria for Critical Thinking Assignments : Can be used by faculty in designing classroom assignments, or by administrators in assessing the extent to which faculty are fostering critical thinking.
Rubrics for Assessing Student Reasoning Abilities : A useful tool in assessing the extent to which students are reasoning well through course content.
All of the above assessment instruments can be used as part of pre- and post-assessment strategies to gauge development over various time periods.
Consequential Validity
All of the above assessment instruments, when used appropriately and graded accurately, should lead to a high degree of consequential validity. In other words, the use of the instruments should cause teachers to teach in such a way as to foster critical thinking in their various subjects. In this light, for students to perform well on the various instruments, teachers will need to design instruction so that students can perform well on them. Students cannot become skilled in critical thinking without learning (first) the concepts and principles that underlie critical thinking and (second) applying them in a variety of forms of thinking: historical thinking, sociological thinking, biological thinking, etc. Students cannot become skilled in analyzing and assessing reasoning without practicing it. However, when they have routine practice in paraphrasing, summarizing, analyzing, and assessing, they will develop skills of mind requisite to the art of thinking well within any subject or discipline, not to mention thinking well within the various domains of human life.
For full copies of this and many other critical thinking articles, books, videos, and more, join us at the Center for Critical Thinking Community Online - the world's leading online community dedicated to critical thinking! Also featuring interactive learning activities, study groups, and even a social media component, this learning platform will change your conception of intellectual development.

- Teaching Tips
A Brief Guide for Teaching and Assessing Critical Thinking in Psychology
In my first year of college teaching, a student approached me one day after class and politely asked, “What did you mean by the word ‘evidence’?” I tried to hide my shock at what I took to be a very naive question. Upon further reflection, however, I realized that this was actually a good question, for which the usual approaches to teaching psychology provided too few answers. During the next several years, I developed lessons and techniques to help psychology students learn how to evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of scientific and nonscientific kinds of evidence and to help them draw sound conclusions. It seemed to me that learning about the quality of evidence and drawing appropriate conclusions from scientific research were central to teaching critical thinking (CT) in psychology.
In this article, I have attempted to provide guidelines to psychology instructors on how to teach CT, describing techniques I developed over 20 years of teaching. More importantly, the techniques and approach described below are ones that are supported by scientific research. Classroom examples illustrate the use of the guidelines and how assessment can be integrated into CT skill instruction.
Overview of the Guidelines
Confusion about the definition of CT has been a major obstacle to teaching and assessing it (Halonen, 1995; Williams, 1999). To deal with this problem, we have defined CT as reflective thinking involved in the evaluation of evidence relevant to a claim so that a sound or good conclusion can be drawn from the evidence (Bensley, 1998). One virtue of this definition is it can be applied to many thinking tasks in psychology. The claims and conclusions psychological scientists make include hypotheses, theoretical statements, interpretation of research findings, or diagnoses of mental disorders. Evidence can be the results of an experiment, case study, naturalistic observation study, or psychological test. Less formally, evidence can be anecdotes, introspective reports, commonsense beliefs, or statements of authority. Evaluating evidence and drawing appropriate conclusions along with other skills, such as distinguishing arguments from nonarguments and finding assumptions, are collectively called argument analysis skills. Many CT experts take argument analysis skills to be fundamental CT skills (e.g., Ennis, 1987; Halpern, 1998). Psychology students need argument analysis skills to evaluate psychological claims in their work and in everyday discourse.
Some instructors expect their students will improve CT skills like argument analysis skills by simply immersing them in challenging course work. Others expect improvement because they use a textbook with special CT questions or modules, give lectures that critically review the literature, or have students complete written assignments. While these and other traditional techniques may help, a growing body of research suggests they are not sufficient to efficiently produce measurable changes in CT skills. Our research on acquisition of argument analysis skills in psychology (Bensley, Crowe, Bernhardt, Buchner, & Allman, in press) and on critical reading skills (Bensley & Haynes, 1995; Spero & Bensley, 2009) suggests that more explicit, direct instruction of CT skills is necessary. These results concur with results of an earlier review of CT programs by Chance (1986) and a recent meta-analysis by Abrami et al., (2008).
Based on these and other findings, the following guidelines describe an approach to explicit instruction in which instructors can directly infuse CT skills and assessment into their courses. With infusion, instructors can use relevant content to teach CT rules and concepts along with the subject matter. Directly infusing CT skills into course work involves targeting specific CT skills, making CT rules, criteria, and methods explicit, providing guided practice in the form of exercises focused on assessing skills, and giving feedback on practice and assessments. These components are similar to ones found in effective, direct instruction approaches (Walberg, 2006). They also resemble approaches to teaching CT proposed by Angelo (1995), Beyer (1997), and Halpern (1998). Importantly, this approach has been successful in teaching CT skills in psychology (e.g., Bensley, et al., in press; Bensley & Haynes, 1995; Nieto & Saiz, 2008; Penningroth, Despain, & Gray, 2007). Directly infusing CT skill instruction can also enrich content instruction without sacrificing learning of subject matter (Solon, 2003). The following seven guidelines, illustrated by CT lessons and assessments, explicate this process.
Seven Guidelines for Teaching and Assessing Critical Thinking
1. Motivate your students to think critically
Critical thinking takes effort. Without proper motivation, students are less inclined to engage in it. Therefore, it is good to arouse interest right away and foster commitment to improving CT throughout a course. One motivational strategy is to explain why CT is important to effective, professional behavior. Often, telling a compelling story that illustrates the consequences of failing to think critically can motivate students. For example, the tragic death of 10-year-old Candace Newmaker at the hands of her therapists practicing attachment therapy illustrates the perils of using a therapy that has not been supported by good empirical evidence (Lilienfeld, 2007).
Instructors can also pique interest by taking a class poll posing an interesting question on which students are likely to have an opinion. For example, asking students how many think that the full moon can lead to increases in abnormal behavior can be used to introduce the difference between empirical fact and opinion or common sense belief. After asking students how psychologists answer such questions, instructors might go over the meta-analysis of Rotton and Kelly (1985). Their review found that almost all of the 37 studies they reviewed showed no association between the phase of the moon and abnormal behavior with only a few, usually poorly, controlled studies supporting it. Effect size over all studies was very small (.01). Instructors can use this to illustrate how psychologists draw a conclusion based on the quality and quantity of research studies as opposed to what many people commonly believe. For other interesting thinking errors and misconceptions related to psychology, see Bensley (1998; 2002; 2008), Halpern (2003), Ruscio (2006), Stanovich (2007), and Sternberg (2007).
Attitudes and dispositions can also affect motivation to think critically. If students lack certain CT dispositions such as open-mindedness, fair-mindedness, and skepticism, they will be less likely to think critically even if they have CT skills (Halpern, 1998). Instructors might point out that even great scientists noted for their powers of reasoning sometimes fail to think critically when they are not disposed to use their skills. For example, Alfred Russel Wallace who used his considerable CT skills to help develop the concept of natural selection also believed in spiritualistic contact with the dead. Despite considerable evidence that mediums claiming to contact the dead were really faking such contact, Wallace continued to believe in it (Bensley, 2006). Likewise, the great American psychologist William James, whose reasoning skills helped him develop the seeds of important contemporary theories, believed in spiritualism despite evidence to the contrary.
2. Clearly state the CT goals and objectives for your class
Once students are motivated, the instructor should focus them on what skills they will work on during the course. The APA task force on learning goals and objectives for psychology listed CT as one of 10 major goals for students (Halonen et al., 2002). Under critical thinking they have further specified outcomes such as evaluating the quality of information, identifying and evaluating the source and credibility of information, recognizing and defending against thinking errors and fallacies. Instructors should publish goals like these in their CT course objectives in their syllabi and more specifically as assignment objectives in their assignments. Given the pragmatic penchant of students for studying what is needed to succeed in a course, this should help motivate and focus them.
To make instruction efficient, course objectives and lesson objectives should explicitly target CT skills to be improved. Objectives should specify the behavior that will change in a way that can be measured. A course objective might read, “After taking this course, you will be able to analyze arguments found in psychological and everyday discussions.” When the goal of a lesson is to practice and improve specific microskills that make up argument analysis, an assignment objective might read “After successfully completing this assignment, you will be able to identify different kinds of evidence in a psychological discussion.” Or another might read “After successfully completing this assignment, you will be able to distinguish arguments from nonarguments.” Students might demonstrate they have reached these objectives by showing the behavior of correctly labeling the kinds of evidence presented in a passage or by indicating whether an argument or merely a claim has been made. By stating objectives in the form of assessable behaviors, the instructor can test these as assessment hypotheses.
Sometimes when the goal is to teach students how to decide which CT skills are appropriate in a situation, the instructor may not want to identify specific skills. Instead, a lesson objective might read, “After successfully completing this assignment, you will be able to decide which skills and knowledge are appropriate for critically analyzing a discussion in psychology.”
3. Find opportunities to infuse CT that fit content and skill requirements of your course
To improve their CT skills, students must be given opportunities to practice them. Different courses present different opportunities for infusion and practice. Stand-alone CT courses usually provide the most opportunities to infuse CT. For example, the Frostburg State University Psychology Department has a senior seminar called “Thinking like a Psychologist” in which students complete lessons giving them practice in argument analysis, critical reading, critically evaluating information on the Internet, distinguishing science from pseudoscience, applying their knowledge and CT skills in simulations of psychological practice, and other activities.
In more typical subject-oriented courses, instructors must find specific content and types of tasks conducive to explicit CT skill instruction. For example, research methods courses present several opportunities to teach argument analysis skills. Instructors can have students critically evaluate the quality of evidence provided by studies using different research methods and designs they find in PsycINFO and Internet sources. This, in turn, could help students write better critical evaluations of research for research reports.
A cognitive psychology teacher might assign a critical evaluation of the evidence on an interesting question discussed in textbook literature reviews. For example, students might evaluate the evidence relevant to the question of whether people have flashbulb memories such as accurately remembering the 9-11 attack. This provides the opportunity to teach them that many of the studies, although informative, are quasi-experimental and cannot show causation. Or, students might analyze the arguments in a TV program such as the fascinating Nova program Kidnapped by Aliens on people who recall having been abducted by aliens.
4. Use guided practice, explicitly modeling and scaffolding CT.
Guided practice involves modeling and supporting the practice of target skills, and providing feedback on progress towards skill attainment. Research has shown that guided practice helps student more efficiently acquire thinking skills than unguided and discovery approaches (Meyer, 2004).
Instructors can model the use of CT rules, criteria, and procedures for evaluating evidence and drawing conclusions in many ways. They could provide worked examples of problems, writing samples displaying good CT, or real-world examples of good and bad thinking found in the media. They might also think out loud as they evaluate arguments in class to model the process of thinking.
To help students learn to use complex rules in thinking, instructors should initially scaffold student thinking. Scaffolding involves providing product guidelines, rules, and other frameworks to support the process of thinking. Table 1 shows guidelines like those found in Bensley (1998) describing nonscientific kinds of evidence that can support student efforts to evaluate evidence in everyday psychological discussions. Likewise, Table 2 provides guidelines like those found in Bensley (1998) and Wade and Tavris (2005) describing various kinds of scientific research methods and designs that differ in the quality of evidence they provide for psychological arguments.
In the cognitive lesson on flashbulb memory described earlier, students use the framework in Table 2 to evaluate the kinds of evidence in the literature review. Table 1 can help them evaluate the kinds of evidence found in the Nova video Kidnapped by Aliens . Specifically, they could use it to contrast scientific authority with less credible authority. The video includes statements by scientific authorities like Elizabeth Loftus based on her extensive research contrasted with the nonscientific authority of Bud Hopkins, an artist turned hypnotherapist and author of popular books on alien abduction. Loftus argues that the memories of alien abduction in the children interviewed by Hopkins were reconstructed around the suggestive interview questions he posed. Therefore, his conclusion that the children and other people in the video were recalling actual abduction experiences was based on anecdotes, unreliable self-reports, and other weak evidence.
Modeling, scaffolding, and guided practice are especially useful in helping students first acquire CT skills. After sufficient practice, however, instructors should fade these and have students do more challenging assignments without these supports to promote transfer.
5. Align assessment with practice of specific CT skills
Test questions and other assessments of performance should be similar to practice questions and problems in the skills targeted but differ in content. For example, we have developed a series of practice and quiz questions about the kinds of evidence found in Table 1 used in everyday situations but which differ in subject matter from practice to quiz. Likewise, other questions employ research evidence examples corresponding to Table 2. Questions ask students to identify kinds of evidence, evaluate the quality of the evidence, distinguish arguments from nonarguments, and find assumptions in the examples with practice examples differing in content from assessment items.
6. Provide feedback and encourage students to reflect on it
Instructors should focus feedback on the degree of attainment of CT skill objectives in the lesson or assessment. The purpose of feedback is to help students learn how to correct faulty thinking so that in the future they monitor their thinking and avoid such problems. This should increase their metacognition or awareness and control of their thinking, an important goal of CT instruction (Halpern, 1998).
Students must use their feedback for it to improve their CT skills. In the CT exercises and critical reading assignments, students receive feedback in the form of corrected responses and written feedback on open-ended questions. They should be advised that paying attention to feedback on earlier work and assessments should improve their performance on later assessments.
7. Reflect on feedback and assessment results to improve CT instruction
Instructors should use the feedback they provide to students and the results of ongoing assessments to ‘close the loop,’ that is, use these outcomes to address deficiencies in performance and improve instruction. In actual practice, teaching and assessment strategies rarely work optimally the first time. Instructors must be willing to tinker with these to make needed improvements. Reflection on reliable and valid assessment results provides a scientific means to systematically improve instruction and assessment.
Instructors may find the direct infusion approach as summarized in the seven guidelines to be efficient, especially in helping students acquire basic CT skills, as research has shown. They may especially appreciate how it allows them to take a scientific approach to the improvement of instruction. Although the direct infusion approach seems to efficiently promote acquisition of CT skills, more research is needed to find out if students transfer their skills outside of the classroom or whether this approach needs adjustment to promote transfer.
Table 1. Strengths and Weaknesses of Nonscientific Sources and Kinds of Evidence
Table 2. Strengths and Weaknesses of Scientific Research Methods/Designs Used as Sources of Evidence
Abrami, P. C., Bernard, R. M., Borokhovhovski, E., Wade, A., Surkes, M. A., Tamim, R., et al., (2008). Instructional interventions affecting critical thinking skills and dispositions: A stage 1 meta-analysis. Review of Educational Research, 4 , 1102–1134.
Angelo, T. A. (1995). Classroom assessment for critical thinking. Teaching of Psychology , 22(1), 6–7.
Bensley, D.A. (1998). Critical thinking in psychology: A unified skills approach. Pacific Grove, CA: Brooks/Cole.
Bensley, D.A. (2002). Science and pseudoscience: A critical thinking primer. In M. Shermer (Ed.), The Skeptic encyclopedia of pseudoscience. (pp. 195–203). Santa Barbara, CA: ABC–CLIO.
Bensley, D.A. (2006). Why great thinkers sometimes fail to think critically. Skeptical Inquirer, 30, 47–52.
Bensley, D.A. (2008). Can you learn to think more like a psychologist? The Psychologist, 21, 128–129.
Bensley, D.A., Crowe, D., Bernhardt, P., Buckner, C., & Allman, A. (in press). Teaching and assessing critical thinking skills for argument analysis in psychology. Teaching of Psychology .
Bensley, D.A. & Haynes, C. (1995). The acquisition of general purpose strategic knowledge for argumentation. Teaching of Psychology, 22 , 41–45.
Beyer, B.K. (1997). Improving student thinking: A comprehensive approach . Boston: Allyn & Bacon.
Chance, P. (1986) Thinking in the classroom: A review of programs . New York: Instructors College Press.
Ennis, R.H. (1987). A taxonomy of critical thinking dispositions and abilities. In J. B. Baron & R. F. Sternberg (Eds.). Teaching thinking skills: Theory and practice (pp. 9–26). New York: Freeman.
Halonen, J.S. (1995). Demystifying critical thinking. Teaching of Psychology, 22 , 75–81.
Halonen, J.S., Appleby, D.C., Brewer, C.L., Buskist, W., Gillem, A. R., Halpern, D. F., et al. (APA Task Force on Undergraduate Major Competencies). (2002) Undergraduate psychology major learning goals and outcomes: A report. Washington, DC: American Psychological Association. Retrieved August 27, 2008, from http://www.apa.org/ed/pcue/reports.html .
Halpern, D.F. (1998). Teaching critical thinking for transfer across domains: Dispositions, skills, structure training, and metacognitive monitoring. American Psychologist , 53 , 449–455.
Halpern, D.F. (2003). Thought and knowledge: An introduction to critical thinking . (3rd ed.). Mahwah, NJ: Erlbaum.
Lilienfeld, S.O. (2007). Psychological treatments that cause harm. Perspectives on Psychological Science , 2 , 53–70.
Meyer, R.E. (2004). Should there be a three-strikes rule against pure discovery learning? The case for guided methods of instruction. American Psychologist , 59 , 14–19.
Nieto, A.M., & Saiz, C. (2008). Evaluation of Halpern’s “structural component” for improving critical thinking. The Spanish Journal of Psychology , 11 ( 1 ), 266–274.
Penningroth, S.L., Despain, L.H., & Gray, M.J. (2007). A course designed to improve psychological critical thinking. Teaching of Psychology , 34 , 153–157.
Rotton, J., & Kelly, I. (1985). Much ado about the full moon: A meta-analysis of lunar-lunacy research. Psychological Bulletin , 97 , 286–306.
Ruscio, J. (2006). Critical thinking in psychology: Separating sense from nonsense. Belmont, CA: Wadsworth.
Solon, T. (2007). Generic critical thinking infusion and course content learning in introductory psychology. Journal of Instructional Psychology , 34(2), 972–987.
Stanovich, K.E. (2007). How to think straight about psychology . (8th ed.). Boston: Pearson.
Sternberg, R.J. (2007). Critical thinking in psychology: It really is critical. In R. J. Sternberg, H. L. Roediger, & D. F. Halpern (Eds.), Critical thinking in psychology. (pp. 289–296) . Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press.
Wade, C., & Tavris, C. (2005) Invitation to psychology. (3rd ed.). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall.
Walberg, H.J. (2006). Improving educational productivity: A review of extant research. In R. F. Subotnik & H. J. Walberg (Eds.), The scientific basis of educational productivity (pp. 103–159). Greenwich, CT: Information Age.
Williams, R.L. (1999). Operational definitions and assessment of higher-order cognitive constructs. Educational Psychology Review , 11 , 411–427.
Excellent article.
Interesting and helpful!
APS regularly opens certain online articles for discussion on our website. Effective February 2021, you must be a logged-in APS member to post comments. By posting a comment, you agree to our Community Guidelines and the display of your profile information, including your name and affiliation. Any opinions, findings, conclusions, or recommendations present in article comments are those of the writers and do not necessarily reflect the views of APS or the article’s author. For more information, please see our Community Guidelines .
Please login with your APS account to comment.
About the Author
D. Alan Bensley is Professor of Psychology at Frostburg State University. He received his Master’s and PhD degrees in cognitive psychology from Rutgers University. His main teaching and research interests concern the improvement of critical thinking and other cognitive skills. He coordinates assessment for his department and is developing a battery of instruments to assess critical thinking in psychology. He can be reached by email at [email protected] Association for Psychological Science December 2010 — Vol. 23, No. 10

Student Notebook: Five Tips for Working with Teaching Assistants in Online Classes
Sarah C. Turner suggests it’s best to follow the golden rule: Treat your TA’s time as you would your own.
Teaching Current Directions in Psychological Science
Aimed at integrating cutting-edge psychological science into the classroom, Teaching Current Directions in Psychological Science offers advice and how-to guidance about teaching a particular area of research or topic in psychological science that has been
European Psychology Learning and Teaching Conference
The School of Education of the Paris Lodron University of Salzburg is hosting the next European Psychology Learning and Teaching (EUROPLAT) Conference on September 18–20, 2017 in Salzburg, Austria. The main theme of the conference
Privacy Overview

- Productivity
- Thoughtful learning
Become a better critical thinker with these 7 critical thinking exercises

Critical thinking is a skill you can use in any situation. Whether you're a student, entrepreneur, or business executive, critical thinking can help you make better decisions and solve problems.
But learning critical thinking skills isn't always an easy task. Many tools, techniques, and strategies are available, and choosing the right one can be challenging. Vague suggestions on the internet like "read more" aren't very helpful, and elaborate business examples don’t apply to many of us.
As average problem-solvers, we need actionable thinking exercises to improve our critical thinking skills and enhance our thinking processes. Regularly performing exercises that specifically stretch our decision-making and reasoning skills is the most effective method of improving our thinking abilities.
This article will explore several exercises that will help you develop critical thinking skills. Whether you are preparing for an exam, making an influential decision for your business, or going about your daily life, these fun activities can build your reasoning skills and creative problem-solving abilities.
Boost your logical thinking skills and start practicing a critical mindset with these 10 critical thinking exercises.
A Quick Look at Critical Thinking
As a thoughtful learner, you likely already understand the basics of critical thinking, but here's a quick refresher.
Critical thinking involves analyzing problems or issues objectively and rationally. Critical thinkers are able to understand their own biases and assumptions, as well as those of others. They’re also able to see the world from a different point of view and understand how their experiences impact their thinking.
Developing critical thinking skills is essential because it allows us to see things from multiple perspectives, identify biases and errors in reasoning, and be open to possible solutions. Making informed decisions is easier when we have a better understanding of the world around us.
Why We Need to Practice Critical Thinking

We aren't born with critical thinking skills, and they don’t naturally develop beyond survival-level thinking. To master critical thinking, we must practice it and develop it over time.
However, learning to think critically isn't as easy as learning to ride a bicycle. There aren't any step-by-step procedures to follow or supportive guides to fall back on, and it is not taught in public schools consistently or reliably. To ensure students' success, teachers must know higher-order thinking skills (HOTS) and how to teach them, research says.
Unfortunately, although teachers understand the importance of HOTS and attempt to teach it, studies show that their capacity to measure students' HOTS is low. Educator and author Dr. Kulvarn Atwal says, "It seems that we are becoming successful at producing students who are able to jump through hoops and pass tests."
As critical thinking skills become more important in higher grades, some students find it challenging to understand the concept of critical thinking. To develop necessary thinking skills, we must set aside our assumptions and beliefs. This allows us to explore and question topics from a "blank page" point of view and distinguish fact from opinion.
Be the first to try it out!
We're developing ABLE, a powerful tool for building your personal knowledge, capturing information from the web, conducting research, taking notes, and writing content.
7 Critical Thinking Exercises To Improve Your Critical Thinking Skills

The good news is that by assessing, analyzing, and evaluating our thought processes, we can improve our skills. Critical thinking exercises are key to this improvement. Our critical thinking builds and improves with regular practice, just like a muscle that gets stronger with use.
If you want to become a better critical thinker , here are some critical thinking exercises to try:
Exercise #1: The Ladder of Inference
You can exercise your critical thinking skills by using the Ladder of Inference model . This thinking model was developed by renowned organizational psychologist Chris Argyris. Each rung on the ladder of inference represents a step you take to arrive at your conclusions.
The decision-making process starts when we are faced with a problem or situation. As soon as we observe something problematic or important, we presume what is causing it, and then we use that assumption to draw conclusions. Based on those conclusions, we take action.
For example, say you're at a party and see a friend across the room. You catch their eye and wave, but they turn and walk away. Using the ladder, you might climb the rungs as follows:
- Observe that your friend walked away.
- Select a few details of the situation, including your wave and your assumption that they saw you.
- Meaning is attached based on the environment, making you think your friend must have other people to talk to at the party.
- Assumptions are made based on that meaning, assuming that means your friend doesn’t like you as much as them.
- Conclusions are drawn from the assumption, and you determine that your friend must be mad at you or doesn't want you to be at the party.
- Beliefs are formed, making you think you're not welcome.
- Action is taken, and you leave the party.
In this example, you started with a situation (someone walking away at a crowded party) and made a series of inferences to arrive at a conclusion (that the person is mad at you and doesn't want you there).
The Ladder of Inference can be a helpful tool to frame your thinking because it encourages you to examine each step of your thought process and avoid jumping to conclusions. It's easy to make assumptions without realizing it, as in this scene. Perhaps your friend never even saw you wave from across the crowded room.

Exercise #2: The Five Whys
The "Five Whys" technique is an analytical skill that can help you uncover the source of a problem. The activity was created by Sakichi Toyoda, the founder of Toyota, and consists of repeatedly asking “why?” when a problem is encountered to determine its root cause.
This exercise can be difficult because knowing if you've discovered the source of your problem is challenging. The "five" in "Five Whys" is just a guideline — you may need to ask more. When you can't ask anything else, and your response is related to the original issue, you've probably arrived at the end.
Even if you need several rounds of questioning, just keep going. The important part that helps you practice critical thinking is the process of asking "why?" and uncovering the deeper issues affecting the situation.
For instance, say you're trying to figure out why your computer keeps crashing.
- You ask " why ," and the answer is that there's a software problem.
- Why? Because the computer keeps running out of memory.
- Why? Because too many programs are running at the same time.
- Why? Because too many browser tabs are open .
- Why? Because multitasking is fragmenting your focus, you're doing too many things at once.
In this example, working through the "why's" revealed the underlying cause. As a result, you can find the best solution, which is concentrating on just one thing at a time.
Exercise #3: Inversion

Inversion is another critical thinking exercise that you can use in any situation. Inversion is sort of like taking on the role of the devil's advocate. In this exercise, adopt the opposite view of whatever issue you're exploring and consider the potential arguments for that side. This will help broaden your critical thinking skills and enable you to see other perspectives on a situation or topic more clearly.
For example, let's say you're thinking about starting your own business. Using inversion, you would explore all of the potential arguments for why starting your own business is bad. This might include concerns like:
- You could end up in debt.
- The business might fail.
- It's a lot of work.
- You might not have time for anything else.
By exploring these potentially adverse outcomes, you can identify the potential risks involved in starting your own business and make a more sound decision. You might realize that now is not the right time for you to become an entrepreneur. And if you do start the company, you'll be better prepared to deal with the issues you identified when they occur.
Exercise #4: Argument Mapping
Argument mapping can be a beneficial exercise for enhancing critical thinking skills. Like mind mapping, argument mapping is a method of visually representing an argument's structure. It helps analyze and evaluate ideas as well as develop new ones.
In critical thinking textbooks, argument diagramming is often presented to introduce students to argument constructions. It can be an effective way to build mental templates or schema for argument structures, which researchers think may make critical evaluation easier .
Argument maps typically include the following:
- Conclusion: What is being argued for or against
- Premises: The reasons given to support the conclusion
- Inferences: The connections made between the premises and conclusion
The argument map should be as clear and concise as possible, with a single word or phrase representing each element. This will help you make connections more easily. After the map is completed, you can use it to identify any weak points in the argument. If any areas aren't well-supported, additional premises can be added.
Argument mapping can be applied to any situation that requires critical thinking skills. The more time you take to map out an argument, the better you'll understand how the pieces fit together. Ultimately, this will help you think more creatively and critically, and make more informed decisions.
Exercise #5: Opinion vs. Fact
Critical thinking activities that focus on opinions and facts are particularly valuable and relevant new learning opportunities. Our constantly-connected world makes it easy to confuse opinions and facts , especially with sensationalist news articles and click-bait headlines.
How can you tell a fact from an opinion? Facts are generally objective and established, whereas opinions are subjective and unproven. For example, "the cloud is in the air" is a fact. "That dress looks good on you" is an opinion.
Practice your critical thinking skills by reading or listening to the news. See if you can identify when someone is stating an opinion rather than a fact. Ask yourself the following questions:
- Who is saying what? What reasons might be behind their statements?
- Does the claim make sense? Who would disagree with it and why?
- How can you tell if the data is reliable? Can it be fact-checked? Has it been shared by other credible publishers?
- How do you know whether or not the presenter is biased? What kind of language is being used?
This powerful exercise can train your mind to start asking questions whenever presented with a new claim. This will help you think critically about the information you're taking in and question what you're hearing before accepting it as truth.
Exercise #6: Autonomy of an Object
In her book " The Critical Thinking Tool Kit ," Dr. Marlene Caroselli describes a critical thinking exercise called "Living Problems, Lively Solutions." This exercise uses the autonomy of an object as a problem-solving tool to find a possible solution.
To do this, you'll personify your problem and place it in another context — a different time or place. This allows you to uncover unique solutions to the problem that might be tied to your mental associations with that setting.
For example, if your problem is poor time management , you might personify the issue as a thief of your time. The idea of a thief could make you think of jail, which might prompt thoughts of locking up specific distractions in your life. The idea of jail could also make you think of guards and lead you to the possible solution of checking in with an accountability buddy who can make sure you're sticking to your schedule.
The autonomy-of-object technique works because it stimulates thoughts you wouldn’t have considered without the particular context in which you place the problem.
Exercise #7: The Six Thinking Hats
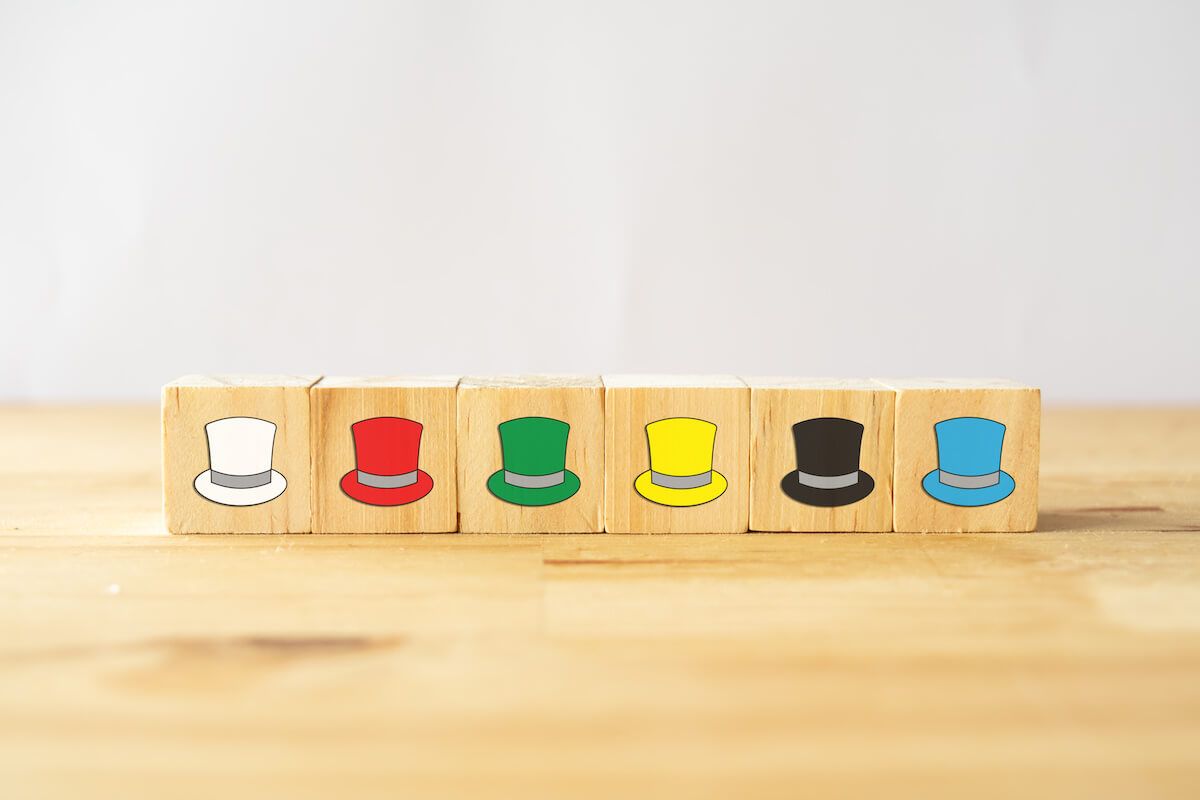

Designed by Edward de Bono, the Six Thinking Hats is a critical thinking exercise that was created as a tool for groups to use when exploring different perspectives on an issue. When people use other thinking processes, meetings can become challenging rather than beneficial.
To help teams work more productively and mindfully, de Bono suggests dividing up different styles of thinking into six categories, represented as hats:
- The white hat is objective and focuses on facts and logic
- The red hat is intuitive, focusing on emotion and instinct
- The black hat is cautious and predicts negative outcomes
- The yellow hat is optimistic and encourages positive outcomes
- The green hat is creative, with numerous ideas and little criticism
- The blue hat is the control hat used for management and organization
With each team member wearing a different hat, a group can examine an issue or problem from many different angles, preventing one viewpoint (or individual) from dominating the meeting or discussion. This means that decisions and solutions reached using the Six Thinking Hats approach will likely be more robust and effective, and everyone’s creative thinking skills will benefit.
Train Your Brain With Critical Thinking Exercises
Using critical thinking regularly in various situations can improve our ability to evaluate and analyze information. These seven critical thinking exercises train your brain for better critical thinking skills . With daily practice, they can become habits that will help you think more critically each day.
Improve your critical thinking with ABLE
Ask better questions and get better answers with ABLEs integrated web search, annotation and note-taking features. Check how ABLE helps you to improve your critical thinking.
I hope you have enjoyed reading this article. Feel free to share, recommend and connect 🙏
Connect with me on Twitter 👉 https://twitter.com/iamborisv
And follow Able's journey on Twitter: https://twitter.com/meet_able
And subscribe to our newsletter to read more valuable articles before it gets published on our blog.
Now we're building a Discord community of like-minded people, and we would be honoured and delighted to see you there.

Straight from the ABLE team: how we work and what we build. Thoughts, learnings, notes, experiences and what really matters.
Read more posts by this author
follow me :
Mental models: 13 thinking tools to boost your problem-solving skills
7 note-taking strategies to improve your study skills.

What is abstract thinking? 10 activities to improve your abstract thinking skills

5 examples of cognitive learning theory (and how you can use them)
0 results found.
- Aegis Alpha SA
- We build in public
Building with passion in
Want a daily email of lesson plans that span all subjects and age groups?
Subjects all subjects all subjects the arts all the arts visual arts performing arts value of the arts back business & economics all business & economics global economics macroeconomics microeconomics personal finance business back design, engineering & technology all design, engineering & technology design engineering technology back health all health growth & development medical conditions consumer health public health nutrition physical fitness emotional health sex education back literature & language all literature & language literature linguistics writing/composition speaking back mathematics all mathematics algebra data analysis & probability geometry measurement numbers & operations back philosophy & religion all philosophy & religion philosophy religion back psychology all psychology history, approaches and methods biological bases of behavior consciousness, sensation and perception cognition and learning motivation and emotion developmental psychology personality psychological disorders and treatment social psychology back science & technology all science & technology earth and space science life sciences physical science environmental science nature of science back social studies all social studies anthropology area studies civics geography history media and journalism sociology back teaching & education all teaching & education education leadership education policy structure and function of schools teaching strategies back thinking & learning all thinking & learning attention and engagement memory critical thinking problem solving creativity collaboration information literacy organization and time management back, filter by none.
- Elementary/Primary
- Middle School/Lower Secondary
- High School/Upper Secondary
- College/University
- TED-Ed Animations
- TED Talk Lessons
- TED-Ed Best of Web
- Under 3 minutes
- Under 6 minutes
- Under 9 minutes
- Under 12 minutes
- Under 18 minutes
- Over 18 minutes
- Algerian Arabic
- Azerbaijani
- Cantonese (Hong Kong)
- Chinese (Hong Kong)
- Chinese (Singapore)
- Chinese (Taiwan)
- Chinese Simplified
- Chinese Traditional
- Chinese Traditional (Taiwan)
- Dutch (Belgium)
- Dutch (Netherlands)
- French (Canada)
- French (France)
- French (Switzerland)
- Kurdish (Central)
- Luxembourgish
- Persian (Afghanistan)
- Persian (Iran)
- Portuguese (Brazil)
- Portuguese (Portugal)
- Spanish (Argentina)
- Spanish (Latin America)
- Spanish (Mexico)
- Spanish (Spain)
- Spanish (United States)
- Western Frisian
sort by none
- Longest video
- Shortest video
- Most video views
- Least video views
- Most questions answered
- Least questions answered

How could so many people support Hitler?
Lesson duration 05:10
193,231 Views

Can you solve the magical maze riddle?
Lesson duration 04:51
352,149 Views

How to make smart decisions more easily
Lesson duration 05:16
1,110,590 Views

Can you solve a mystery before Sherlock Holmes?
Lesson duration 05:17
475,285 Views

Can you solve the secret assassin society riddle?
Lesson duration 05:01
706,544 Views

How to overcome your mistakes
Lesson duration 04:52
911,157 Views

Can you solve the cursed dice riddle?
Lesson duration 04:31
706,176 Views

Why some people don't have an inner monologue
Lesson duration 12:03
2,782,947 Views

Science vs. Pseudoscience
Lesson duration 05:48
351,334 Views
Can you solve the time traveling car riddle?
Lesson duration 05:18
633,869 Views

This one weird trick will get you infinite gold
Lesson duration 05:08
1,022,869 Views

How to quit your job — without ruining your career - Gala Jackson
Lesson duration 06:13
106,482 Views

What if you experienced every human life in history?
Lesson duration 05:21
2,824,673 Views

How to design climate-resilient buildings - Alyssa-Amor Gibbons
Lesson duration 14:12
43,353 Views

The case for free, universal basic services - Aaron Bastani
Lesson duration 19:09
80,348 Views

Can you steal the most powerful wand in the wizarding world?
Lesson duration 05:20
766,548 Views

History vs. Thomas Jefferson
463,365 Views

The best way to apologize (according to science)
Lesson duration 05:06
1,457,707 Views

How do we determine the value of a life?
Lesson duration 06:06
727,851 Views

What’s the smartest age?
Lesson duration 04:53
1,571,760 Views

The Boltzmann brain paradox
Lesson duration 05:40
1,139,314 Views

The 4 greatest threats to the survival of humanity
Lesson duration 05:24
486,693 Views

Can you outsmart the college admissions fallacy?
Lesson duration 06:17
817,024 Views

Can you solve the fortress riddle?
Lesson duration 05:23
1,223,777 Views
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
A Short Guide to Building Your Team’s Critical Thinking Skills
- Matt Plummer

Critical thinking isn’t an innate skill. It can be learned.
Most employers lack an effective way to objectively assess critical thinking skills and most managers don’t know how to provide specific instruction to team members in need of becoming better thinkers. Instead, most managers employ a sink-or-swim approach, ultimately creating work-arounds to keep those who can’t figure out how to “swim” from making important decisions. But it doesn’t have to be this way. To demystify what critical thinking is and how it is developed, the author’s team turned to three research-backed models: The Halpern Critical Thinking Assessment, Pearson’s RED Critical Thinking Model, and Bloom’s Taxonomy. Using these models, they developed the Critical Thinking Roadmap, a framework that breaks critical thinking down into four measurable phases: the ability to execute, synthesize, recommend, and generate.
With critical thinking ranking among the most in-demand skills for job candidates , you would think that educational institutions would prepare candidates well to be exceptional thinkers, and employers would be adept at developing such skills in existing employees. Unfortunately, both are largely untrue.
- Matt Plummer (@mtplummer) is the founder of Zarvana, which offers online programs and coaching services to help working professionals become more productive by developing time-saving habits. Before starting Zarvana, Matt spent six years at Bain & Company spin-out, The Bridgespan Group, a strategy and management consulting firm for nonprofits, foundations, and philanthropists.
Partner Center
- Blogs @Oregon State University
Teaching With Writing: The WIC Newsletter
Critical thinking: multiple models for teaching and learning (abridged), excerpts from critical thinking: multiple models for teaching and learning.
By Aubrae Vanderpool and Tracy Ann Robinson
“A great truth wants to be criticized, not idolized.”
The development of critical thinking skills increasingly is being identified not only as an essential component of writing courses but even more broadly, as a desired outcome of an undergraduate education. In this article, adapted from a paper by Aubrae Vanderpool that focuses on critical thinking in first-year writing classes, we take a look at what critical thinking means, offer some strategies and suggestions for incorporating critical thinking pedagogy into subject-matter courses, and comment on assessment issues and strategies.
Critical Thinking Defined…Or Not…
For some critical thinking has a lot to do with understanding one’s own perspective and those of others. Another model [of critical thinking] is dialectic, an idea or work is critiqued in a way that produces a counter-perspective and ultimately leads to a synthesis. For some critical thinking evokes a synthetic or inductive model based on testing evidence and making arguments. The exercise of reflective judgment is also a form of critical thinking. (“Critical Thinking and Broad Knowledge”)
While widely accepted as an educational imperative, critical thinking, as the above statement (excerpted from meeting notes for a Critical Thinking dialogue group at Western Washington University) indicates, is quite variously conceived and described. . . . Clearly, however, how an institution or department defines this intellectual practice will influence where in the curriculum critical thinking is taught, how it is taught, and, equally importantly, how it is assessed. For those in the process of formulating a working definition, familiarity with the following widely utilized models may serve as a helpful starting point.
Bloom’s Taxonomy
According to Benjamin Bloom’s Taxonomy of Educational Objectives (1956)—a cross-disciplinary model for developing higher-order thinking in students—learning how to think critically involves the mastery of six increasingly complex cognitive skills: knowledge (i.e., possession of specific facts or pieces of information) , comprehension, application, analysis, synthesis, and evaluation . See sidebar for details.
Bloom’s Taxonomy conceives critical thinking mastery as a sequential process, that is, one cannot move to the next cognitive tier without successfully negotiating the previous level. (“Teaching Critical Thinking”). Thus, some view the taxonomy as “a set of microlevel skills which may be used in critical thinking but do not represent critical thinking” (French and Rhoder 195). Philosopher Richard Paul objects to the taxonomy’s product-oriented conceptualization of thinking as a “one-way hierarchy” as opposed to thinking being a process that involves the recursive use of interrelated skills (French and Rhoder 195). Nonetheless, Bloom’s Taxonomy has been and continues to be an influential model for those developing critical thinking programs, as its inclusion in the Dartmouth College Composition Center’s critical thinking web page attests (Gocsik).
Knowledge: the remembering (recalling) of appropriate, previously learned terminology/specific facts/ways and means of dealing with specifics (conventions, trends and sequences, classifications and categories, criteria, methodology)/universals and abstractions in a field (principles and generalizations, theories and structures). defines; describes; enumerates; identifies; labels; lists; matches; names; reads; records; reproduces; selects; states; views.
Comprehension: Grasping (understanding) the meaning of informational materials. classifies; cites; converts; describes; discusses; estimates; explains; generalizes; gives examples; makes sense out of; paraphrases; restates (in own words); summarizes; traces; understands.
Application: The use of previously learned information in new and concrete situations to solve problems that have single or best answers. acts; administers; articulates; assesses; charts; collects; computes; constructs; contributes; controls; determines; develops; discovers; establishes; extends; implements; includes; informs; instructs; operationalizes; participates; predicts; prepares; preserves; produces; projects; provides; relates; reports; shows; solves; teaches; transfers; uses; utilizes.
Analysis: The breaking down of informational materials into their component parts, examining (and trying to understand the organizational structure of) such information to develop divergent conclusions by identifying motives or causes, making inferences, and/or finding evidence to support generalizations. breaks down; correlates; diagrams; differentiates; discriminates; distinguishes; focuses; illustrates; infers; limits; outlines; points out; prioritizes; recognizes; separates; subdivides.
Synthesis: Creatively or divergently applying prior knowledge and skills to produce a new or original whole. adapts; anticipates; categorizes; collaborates; combines; communicates; compares; compiles; composes; contrasts; creates; designs; devises; expresses; facilitates; formulates; generates; incorporates; individualizes; initiates; integrates; intervenes; models; modifies; negotiates; plans; progresses; rearranges; reconstructs; reinforces; reorganizes; revises; structures; substitutes; validates.
Evaluation: Judging the value of material based on personal values/opinions, resulting in an end product, with a given purpose, without real right or wrong answers. appraises; compares & contrasts; concludes; criticizes; critiques; decides; defends; interprets; judges; justifies; reframes; supports.
SOURCE: http://faculty.washington.edu/krumme/guides/bloom.html (no longer available)
Beyer’s evaluative thinking model
Barry Beyer, a prominent contemporary thinking skills theorist and teacher, interprets critical thinking as a more specifically evaluative activity than Bloom’s Taxonomy would imply:
Critical thinking is not making decisions or solving problems. It is not the same as reflective thinking, creative thinking, or conceptualizing. Each of these other types of thinking serves a specific purpose. We make decisions in order to choose among alternatives. We solve problems when we encounter an obstacle to a preferred condition. We engage in creative or conceptual thinking to invent or improve things. Critical thinking serves a purpose quite different from these other types of thinking. (Beyer 1995, 8)
For Beyer, the crux of critical thinking is criteria : “ The word critical in critical thinking comes from the Greek word for criterion, kriterion , which means a benchmark for judging” (Beyer 1995, 8-9). Thus, critical (or, to use Beyer’s preferred term, evaluative) thinking provides the means to assess the “accuracy, authenticity, plausibility, or sufficiency of claims” (Beyer 1995, 10).
Beyer asserts that critical thinking involves 10 cognitive operations, which can be employed in any sequence or combination as needed for the thinking task at hand:
- Distinguishing between verifiable facts and value claims
- Distinguishing relevant from irrelevant information, claims, or reasons
- Determining the factual accuracy of a statement
- Determining the credibility of a source
- Identifying ambiguous claims or arguments
- Identifying unstated assumptions
- Detecting bias
- Recognizing logical fallacies
- Recognizing logical inconsistencies in a line of reasoning
- Determining the strength of an argument or claim (Beyer 1988, 57)
Further, Beyer argues that successful critical thinking requires “complex and often simultaneous interaction” of the following six elements:
o Dispositions. Critical thinkers develop habits of mind that “guide and sustain critical thinking”, including skepticism, fairmindedness, openmindedness, respect for evidence and reasoning, respect for clarity and precision, ability to consider different points of view, and a willingness to alter one’s position when reason and evidence call for such a shift.
o Criteria . Critical thinkers know about and have the ability to construct appropriate benchmarks for judging the issue at hand.
o Argument —defined as “a proposition with its supporting evidence and reasoning.” Critical thinkers are skillful at constructing, identifying, and evaluating the strength of arguments.
o Reasoning —the “cement that holds an argument together.” Critical thinkers determine the strength and validity of a conclusion by examining the soundness of the inductive or deductive process through which the conclusion was reached.
o Point of View. Critical thinkers are aware of their own point of view and capable of examining other points of view in order to better evaluate an issue.
o Procedures for applying criteria and judging. Critical thinkers have a repertoire of strategies appropriate to the subject matter and type of judgment to be made (Beyer 1995, 10-20)
In other words, critical thinkers habitually question the authenticity of anything that confronts them to ascertain exactly the extent to which it is an authentic instance of what it purports to be. In addition, they make judgments based on certain standards or other measures that serve as criteria for plausibility and truthfulness. And they pay special attention to the reasons and reasoning that undergird conclusions and claims.” (Beyer 1995, 22)
Critical thinking as a divergent process
While Beyer depicts critical thinking as a “ con vergent,” narrowing process, others prefer to view it as a di vergent, expanding, exploratory practice (French and Rhoder, 184-85) —a way to open up new solutions as well as evaluate those that have already been identified. For example, consider this statement from Peter Taylor of the UMass/Boston Graduate College of Education’s Critical and Creative Thinking Program. (In February, 2001, Taylor led a critical thinking workshop at OSU, sponsored jointly by the College of Liberal Arts’ Center for Excellence in Teaching, Learning, and Research, the Center for Water and Environmental Sustain-ability, and the Office of Academic Affairs; and organized by Anita Helle [English] and Denise Lach [CWest].)
My sense of critical thinking […] depends on inquiry being informed by a strong sense of how things could be otherwise. I want students to see that they understand things better when they have placed established facts, theories, and practices in tension with alternatives . Critical thinking at this level should not depend on students rejecting conventional accounts, but they do have to move through uncertainty. Their knowledge is, at least for a time, destabilized; what has been established cannot be taken for granted.
This view suggests a much closer connection between critical and creative thinking than Beyer, for instance, would subscribe to. However, many of the concerns that underlie the current interest in furthering college students’ critical thinking skills recognize and affirm this connection.
Teaching Considerations and Strategies
. . . B. Lehman and D. Hayes propose the following strategies for promoting critical thinking in the classroom:
o Help students recognize what they already know about a topic. [For suggestions, see next section.]
o Help students learn to recognize their biases and keep an open mind about the topic. Have students list and share opinions on the subject, but postpone evaluation until more information is gathered.
o Formulate open-ended questions to help students analyze, synthesize, and evaluate the topic.
o Guide students in finding and using diverse sources to explain and support their ideas.
o Have students check the validity of sources and qualifications of authors.
o Help students see there is no single, final authority. By reading several sources on the same topic, students will discover that information is often conflicting and contradictory.
o Help students develop criteria for evaluation. As students learn to support their opinions with logical thinking and comparison of sources, they [develop] critical thinking skills. (Smith 350) . . . .
The Writing–Critical Thinking Connection
For centuries, the rhetorical assumption about language was that “one first finds knowledge and then puts it into words” (Bizzell, Herzberg, and Reynolds 1)—in other words, thinking always precedes writing or speaking. Today, however, we recognize that “knowledge is actually created by words” (Bizzell, Herzberg, and Reynolds 1) and that writing and thinking are recursive, interdependent processes that promote and enhance one another.
James Sheridan points out that “the act of generating written discourse is not merely a result of critical thinking but also a stimulus to new thinking and new discoveries” (52). This claim echoes Linda Flower’s assertion that “writing is a generative act—a process of not just ‘expressing’ but ‘making’ meaning” (193-94). The fact is that “when students write, they cannot remain passive players in the learning game” (Gocsik-source no longer available). As Peter Elbow suggests, “writing helps us achieve the perennially difficult task of standing outside our own thinking” (27). Hence, the concept of “writing to learn,” which has become so integral to Writing Across the Curriculum courses and programs.
Using writing to uncover knowledge
As well as using writing to reinforce and integrate new information, writing can be a way of discovering existing knowledge. Many critical thinking experts advocate beginning any new learning unit by identifying what students already know (but often don’t know they know) about the topic. This strategy promotes critical thinking and active learning by allowing students to “establish a context for new information and share ideas with others” (Smith 350). Two writing strategies that can assist in this discovery process are freewriting and the “write-and-pass” exercise:
Freewriting. Describing freewriting as an activity that “helps students break the writing-is-grammar chain [, which] stultifies the freedom and risk-taking necessary for innovative critical thinking” (53), James Sheridan suggests the process has only two r equirements:
( 1) “You cannot stop writing during the 10-minute exercise.” (2) “You are forbidden to think. [. . .] Write whatever comes into your right (or left) hand. You must keep on writing. Even if you say ‘I don’t know what to write,’ write that. You cannot scratch your head. You cannot gaze pensively at the ceiling. Just write. You are not responsible for what you say; your hand is doing it all. Say anything. Say ‘This is the worst exercise I ever heard of and I can’t believe they’re paying this guy good bucks to have us do it.’ Yell, scream, shout, kick (in written words). Say anything, but keep writing” (52)
With unfocused freewriting, students write about whatever they want. With focused , or directed , freewriting, students are given a topic or question to write on.
Write-and-pass. Another informal writing assignment that helps students discover what they already know is to ask them to spend a few minutes writing everything they can think of about a given topic or question (for example, “What is critical thinking?”). After several minutes, students pass what they’ve written to the person next to them, and that person reads and expands on the original response. The process is repeated a few more times; generally, with each pass, adding new information becomes more challenging.. The exercise provides a way both for students to focus their thoughts on a particular topic and to benefit from one another’s stores of knowledge.
Assessing Critical Thinking: Current Models
[A]n informed choice of an approach to assessing critical thinking can be made only after faculty have [asked and answered] these questions: What do we think critical thinking is? How do the critical thinking skills, processes, and strategies work together, and what aspects or combinations of them do we wish to assess? What are our students like? What are their motivations [and] environments? What are our assumptions relative to the knowledge and abilities that students need prior to engaging in college-level critical thinking? (Carpenter and Doig 34-35)
Carpenter and Doig’s observation comes from a 1988 review of assessment instruments developed for specific critical thinking courses and programs. Alternatively, the rubric developed in 2002 by Washington State University’s Critical Thinking Project can be used in subject-matter courses across the curriculum that focus on critical thinking. This rubric includes the following criteria for student writing:
- Identifies and summarizes the problem/question at issue.
- Identifies and presents the student’s own perspective and position as it is important to the analysis of the issue.
- Identifies and considers other salient perspectives and positions that are important to the analysis of the issue.
- Identifies and assesses the key assumptions.
- Identifies and assesses the quality of supporting data/evidence and provides additional data/evidence related to the issue.
- Identifies and considers the influence of the context (e.g. cultural/social, scientific, educational, economic, technological, ethical, political, personal, and so on) on the issue.
- Identifies and assesses conclusions, implications, and consequences. “Critical Thinking Rubric” no longer available online.
Each item in the rubric includes a description of what would be considered “scant” vs “substantially developed” coverage of that item. The Washington State Critical Thinking Project website is no longer available online.
A Final Note
In this article, we have focused on what Kerry S. Walters describes as the “logicistic” model of critical thinking—that is (according to Walters) “the unwarranted assumption that good thinking is reducible to logical thinking” (1). In Re-Thinking Reason: New Perspectives in Critical Thinking , Walters explores an alternative model being forwarded by an emerging “second-wave” of critical thinking research and pedagogy. Second-wave advocates argue that while “logical skills are essential functions of good thinking, […] so are non-analytic ones such as imagination and intuition, and the good thinker knows how to utilize both types” (2). This reconception of critical thinking is grounded in current scholarship in the fields of philosophy, psychology, education, feminist theory, and critical pedagogy; Walters’s book serves as an introduction to and dialogue among some of the proponents and practitioners of this alternative. While beyond the scope of this article, the second-wave perspective on critical thinking deserves our serious attention and consideration as well.
This article was previously published in entirety in Teaching with Writing , Winter 2004.
Works Cited (some sources no longer available)
Beyer, Barry K. Critical Thinking. Bloomington, IN: Phi Delta Kappa Educational Foundation, 1995.
________. Developing a Thinking Skills Program. Boston: Allyn and Bacon, 1988.
Bizzell, Patricia, Bruce Hertzberg, and Nedra Reynolds. The Bedford Bibliography for Teachers of Writing. 5th Ed. Boston: Bedford/St. Martin’s, 2000.
Carpenter, C. Blaine, and James C. Doig. “Assessing Critical Thinking Across the Curriculum.” Assessing Student’s Learning 34 (Summer 1988): 33-46.
“Critical Thinking and Broad Knowledge Meeting Notes.” 2 Nov. 2001. Center for Instructional Innovation, Western Washington University. 4 March 2003. http://pandora.cii.wwu.edu/gened/dialogue/critical_notes_nov.htm Source no longer available.
Elbow, Peter. “Teaching Two Kinds of Thinking by Teaching Writing.” Re-Thinking Reason: New Perspectives in Critical Thinking . Ed. Kerry S. Walters. Albany: SUNY Press, 1994. 25-31.
Flower, Linda. “Taking Thought: The Role of Conscious Processing in the Making of Meaning.” Thinking, Reasoning, and Writing. Ed. Elaine P. Maimon, Barbara F. Nodine, and Finbarr W. O’Connor. NY: Longman, 1989. 185-212.
French, Joyce N. and Carol Rhoder. Teaching Thinking Skills: Theory and Practice. NY: Garland, 1992.
Gocsik, Karen. “Teaching Critical Thinking.: 1997 Dartmouth College Composition Center. Source no longer available.
Scriven, Michael and Richard Paul. “Defining Critical Thinking.” Draft Statement for the National Council for Excellence in Critical Thinking. Foundation for Critical Thinking. 27 Feb. 2003. <http://www.criticalthinking.org/pages/definint-critical-thinking/766>
Sheridan, James J. “Skipping on the Brink of the Abyss: Teaching Thinking Through Writing.” Cr itical Thinking: Educational Imperative. Ed. Cynthia A. Barnes. New Directions for Community Colleges, No. 77. San Francisco: Jossey-Bass, 1992. 51-61.
Smith, Carl B. “Two Approaches to Critical Thinking.” The Reading Teacher 4.4 (Dec. 1990): 350-51.
Stewart, Ruth. “Teaching Critical Thinking in First-Year Composition: Sometimes More Is More.” Teaching English at the Two-Year College 29 (Dec. 2001): 162-171.
Taylor, Peter. “We Know More Than We Are, At First, Prepared To Acknowledge: Journeying to Develop Critical Thinking.” 12 March 2003 <http://www.faculty.umb.edu/pjt/journey.html>
Walters, Kerry S. Re-Thinking Reason: New Perspectives in Critical Thinking. Albany: SUNY Press, 1994.

Comments are closed.
Contact Info

3 Activities to Enhance Your Evaluation in Critical Thinking
This set of exercises may help enhance critical thinking..
Posted July 9, 2021 | Reviewed by Devon Frye
Back in January, I posted a piece on this blog asking if any readers wanted to develop their critical thinking as a kind of New Year’s Resolution. Following some rather positive feedback, I added a second set of exercises on "analysis."
The third set of exercises in this sequence, regarding "evaluation," can be found below. If you’re interested in enhancing your critical thinking skills, please start with the first set of exercises and then the second, before jumping into this next set. Remember, when we are given opportunities to think about our thinking, we are engaging our metacognitive processes; and that’s a foundational part of critical thinking!
Evaluate arguments on a topic from articles online regarding a current social problem.
Exercise 1:
Find two examples of each type of evidence from the articles you’ve read and evaluate the credibility of the proposition. That is, is the source reliable? Can it be trusted? If not, why? Remember, personal experience and "common belief" statements are among the worst sources for credible information, so be on the lookout for those!
Assess the evidence based on the following factors:
- Anecdotal Evidence/Personal Experience
- Common Belief/Sense Statements
- Expert Opinion
- Statistical Evidence
- Research Data
Exercise 2:
Of course, there is more to "evaluation" than an assessment of credibility. In critical thinking, we must also evaluate the relevance, logic, balance, and bias among the propositions of support and refutation. Think about the articles you read and try answering the following questions in light of your reading:
- Is there any information presented that is irrelevant to the central claim that the article is trying to make?
- Is the overall argument imbalanced in any way?
- Is the overall argument biased in any way?
- Does the argument exclude important arguments?
- Are there hidden assumptions that need to be made more explicit?
Exercise 3:
Finally, consider whether the reasoning presented within these articles is strong enough, in light of your evaluations, to support the conclusion(s) drawn. Are there other reasonable conclusions possible? Again, consider the credibility, relevance, bias, balance, and logic of the information presented in the articles in the context of your consideration.
These activities are a great way to start working on the critical thinking skill of evaluation, as they help you to assess the strength and weaknesses of an argument through each proposition. Depending on how thorough your evaluation was, considering the credibility, relevance, logical strength and both balance and bias of the network of proposition within an argument should give you confidence when inferring a conclusion. In Exercise 4, we will delve further into the skill of inference.

Christopher Dwyer, Ph.D., is a lecturer at the Technological University of the Shannon in Athlone, Ireland.
- Find Counselling
- Find a Support Group
- Find Online Therapy
- United Kingdom
- Asperger's
- Bipolar Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Eating Disorders
- Passive Aggression
- Personality
- Goal Setting
- Positive Psychology
- Stopping Smoking
- Low Sexual Desire
- Relationships
- Child Development
- Therapy Center NEW
- Diagnosis Dictionary
- Types of Therapy

Understanding what emotional intelligence looks like and the steps needed to improve it could light a path to a more emotionally adept world.
- Emotional Intelligence
- Gaslighting
- Affective Forecasting
- Neuroscience
Critical thinking definition

Critical thinking, as described by Oxford Languages, is the objective analysis and evaluation of an issue in order to form a judgement.
Active and skillful approach, evaluation, assessment, synthesis, and/or evaluation of information obtained from, or made by, observation, knowledge, reflection, acumen or conversation, as a guide to belief and action, requires the critical thinking process, which is why it's often used in education and academics.
Some even may view it as a backbone of modern thought.
However, it's a skill, and skills must be trained and encouraged to be used at its full potential.
People turn up to various approaches in improving their critical thinking, like:
- Developing technical and problem-solving skills
- Engaging in more active listening
- Actively questioning their assumptions and beliefs
- Seeking out more diversity of thought
- Opening up their curiosity in an intellectual way etc.
Is critical thinking useful in writing?
Critical thinking can help in planning your paper and making it more concise, but it's not obvious at first. We carefully pinpointed some the questions you should ask yourself when boosting critical thinking in writing:
- What information should be included?
- Which information resources should the author look to?
- What degree of technical knowledge should the report assume its audience has?
- What is the most effective way to show information?
- How should the report be organized?
- How should it be designed?
- What tone and level of language difficulty should the document have?
Usage of critical thinking comes down not only to the outline of your paper, it also begs the question: How can we use critical thinking solving problems in our writing's topic?
Let's say, you have a Powerpoint on how critical thinking can reduce poverty in the United States. You'll primarily have to define critical thinking for the viewers, as well as use a lot of critical thinking questions and synonyms to get them to be familiar with your methods and start the thinking process behind it.
Are there any services that can help me use more critical thinking?
We understand that it's difficult to learn how to use critical thinking more effectively in just one article, but our service is here to help.
We are a team specializing in writing essays and other assignments for college students and all other types of customers who need a helping hand in its making. We cover a great range of topics, offer perfect quality work, always deliver on time and aim to leave our customers completely satisfied with what they ordered.
The ordering process is fully online, and it goes as follows:
- Select the topic and the deadline of your essay.
- Provide us with any details, requirements, statements that should be emphasized or particular parts of the essay writing process you struggle with.
- Leave the email address, where your completed order will be sent to.
- Select your prefered payment type, sit back and relax!
With lots of experience on the market, professionally degreed essay writers , online 24/7 customer support and incredibly low prices, you won't find a service offering a better deal than ours.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
to match the titles, numbering, and lettering in the Lesson Plan. Training Activities contain detailed descriptions of the activities as well as step-by-step tips for preparing, presenting, and processing the activities. The description also specifies the Training Content that accompanies the activity, and the time and materials required.
In decision making, critical thinking is a vital skill that allows individuals to make informed choices. It enables them to: Analyze options and their potential consequences. Evaluate the credibility of sources and the quality of information. Identify biases, assumptions, and values that may influence the decision.
The purpose of assessing instruction for critical thinking is improving the teaching of discipline-based thinking (historical, biological, sociological, mathematical, etc.) It is to improve students' abilities to think their way through content using disciplined skill in reasoning. The more particular we can be about what we want students to ...
Instructional interventions affecting critical thinking skills and dispositions: A stage 1 meta-analysis. Review of Educational Research, 4, 1102-1134. Angelo, T. A. (1995). Classroom assessment for critical thinking. Teaching of Psychology, 22(1), 6-7. Bensley, D.A. (1998). Critical thinking in psychology: A unified skills approach.
The development of critical thinking has been the topic of many educational articles recently. Numerous instructional methods exist to promote thought and active learning in the classroom, including case studies, discussion methods, written exercises, questioning techniques, and debates. Three methods—questioning, written exercises, and ...
Exercise #1: The Ladder of Inference. You can exercise your critical thinking skills by using the Ladder of Inference model. This thinking model was developed by renowned organizational psychologist Chris Argyris. Each rung on the ladder of inference represents a step you take to arrive at your conclusions.
The 3CA (Concept Maps, Critical Thinking, Collaboration, and Assessment) model is a competencycentered approach to instruction in which students learn patterns of critical thinking. The model has four components: (a) concept maps are a visual method for displaying information as nodes with connecting links; the nodes are visual representation of
Critical thinking is one of the most frequently discussed higher order skills, believed to play a central role in logical thinking, decision making, and problem solving (Butler, 2012; Halpern, 2003).It is also a highly contentious skill in that researchers debate about its definition; its amenability to assessment; its degree of generality or specificity; and the evidence of its practical ...
case histories and collaborate on computer-based learning activities. On the basis of assessment data, we conclude that the OLM helped exercise science students de- ... critical thinking model was selected for the present study, and the instructor-assessed student critical ... the five stages, skills, and activities of the critical thinking ...
Activity 1: Identify the role each statement, or proposition, plays in the piece - for example, the central claim; core reasons and core objections (for the central claim); as well as supporting ...
Activity 3. Finish your analysis by asking yourself: 1. Was the author of the original article, for the most part, being subjective or objective? 2. If any objective propositions were presented ...
Anecdotal Evidence/Personal Experience. Common Belief/Sense Statements. Expert Opinion. Statistical Evidence. Research Data. Exercise 2: Of course, there is more to "evaluation" than an assessment ...
Development of critical thinking skills in college students is a goal for many college instructors in higher education who seek to prepare their students for postgraduate, real-world situations (7, 8, 26).Despite the importance of these skills, the unfortunate reality is that many college graduates lack the ability to think critically (8, 15, 29, 28), partially owing to 1) large class sizes ...
TED-Ed lessons on the subject Critical Thinking. TED-Ed celebrates the ideas of teachers and students around the world. Discover hundreds of animated lessons, create customized lessons, and share your big ideas. ... Thinking & Learning Can you steal the most powerful wand in the wizarding world? Lesson duration 05:20 765,721 Views. 06:13 ...
Using these models, they developed the Critical Thinking Roadmap, a framework that breaks critical thinking down into four measurable phases: the ability to execute, synthesize, recommend, and ...
Critical thinking skills are increasingly necessary for success in professional health care careers. Changes in the contemporary healthcare system in the United States arguably make these critical thinking skills more important than they have ever been, as clinicians are required on a daily basis to evaluate multiple bits of information about patients with multiple-systemic health concerns and ...
Other Critical Thinking Activities. Jigsaw—Developing Community and Disseminating Knowledge: Learners take on the role of "experts" or "specialists" of a particular topic. Then a panel of experts is assembled to get the larger picture. K-W-L Charts—Assessing What We Know/What We Still Want to Learn: Charts to document "What I Know ...
Another model [of critical thinking] is dialectic, an idea or work is critiqued in a way that produces a counter-perspective and ultimately leads to a synthesis. For some critical thinking evokes a synthetic or inductive model based on testing evidence and making arguments. The exercise of reflective judgment is also a form of critical thinking.
6. Start a Debate. In this activity, the teacher can act as a facilitator and spark an interesting conversation in the class on any given topic. Give a small introductory speech on an open-ended topic. The topic can be related to current affairs, technological development or a new discovery in the field of science.
Expert Opinion. Statistical Evidence. Research Data. Exercise 2: Of course, there is more to "evaluation" than an assessment of credibility. In critical thinking, we must also evaluate the ...
Instructor David White. Cite this lesson. Critical thinking involves looking at facts and considering information from different perspectives. Review some exercises, strategies, and activities to ...
Share via: Critical thinking, as described by Oxford Languages, is the objective analysis and evaluation of an issue in order to form a judgement. Active and skillful approach, evaluation, assessment, synthesis, and/or evaluation of information obtained from, or made by, observation, knowledge, reflection, acumen or conversation, as a guide to ...