Overpopulation Essay
500 words essay on overpopulation.
Overpopulation refers to an undesirable condition in which the number of existing human being exceeds the actual carrying capacity of the earth. It has many causes which range from a decline in the death rate to early marriages and more. The overpopulation essay will throw light on this issue.


Ill-Effects of Overpopulation
The ill-effects of overpopulation are quite severe. The first one is that natural resources deplete at a faster level. Our planet can produce only a limited amount of water and food . Thus, overpopulation causes environmental damage including deforestation, pollution, etc.
Similarly, there is the degradation of the environment which happens because of the overuse of resources like coal, oil, natural gases and more. As a result, the quality of air also gets affected in this manner.
In developing countries, overpopulation puts a strain on resources. Thus, it gives rise to conflicts and tension. It also causes more diseases that become harder to control. Next up, we have the issue of unemployment.
Moreover, it rises due to overpopulation. There is more number of people than job opportunities. As a result, unemployment gives rise to crimes like theft and more. We also have pandemics and epidemics which happen due to overpopulation.
It is because overcrowded and unhygienic living gives rise to infectious diseases . Another ill-effect is malnutrition and starvation. When there are scarce resources, these diseases will likely to be on the rise.
Most importantly, we have a shortage of water which makes it tougher for people to get access to clean water. Similarly, lower life expectancy also happens because of the boom in population, especially in less-developed nations.
We also witness faster climate change as nations continue to develop their industrial capacities. Thus, they emit industrial waste which gives rise to global temperatures . It will keep getting worse if things are not checked immediately.
Solutions of Overpopulation
There are many solutions which we may take up to prevent overpopulation. The best measure is family planning to keep the overpopulation check. In order to do that, one can ensure proper spacing between the births of the children.
Further, limiting the number of children as per income and resources must also be important. Similarly, it is essential to increase resources. The government must make the horrors of overpopulation reach the public through the use of media.
Moreover, better education can help implement social change which can curb overpopulation. Next up, knowledge of sex education must be made mandatory in schools so students learn young about everything they need to know.
Most importantly, it is essential to empower women so they can break out of poverty. This way, they can learn about reproductive health and make better decisions. Another solution can be government incentives.
Many governments of countries already have various policies which relate to tax exemptions for curbing overpopulation. For instance, some waive a certain part of income tax for married couples with one or two children.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
Conclusion of Overpopulation Essay
All in all, overpopulation is no less than a curse that poses a permanent threat to the development of any country. It is essential to stop the flood of population. In order to do that, one must indulge in proper family planning and creating balance in society for a better world.
FAQ of Overpopulation Essay
Question 1: What is the main cause of overpopulation?
Answer 1: It is believed that the main cause of overpopulation is poverty. When there is a lack of education resource which coupled with high death rates, it results in impoverished areas witnessing large booms in population.
Question 2: How is overpopulation affecting the world?
Answer 2: Overpopulation is affecting the world as it is outpacing the ability of the planet earth to support it. It also has environmental and economic outcomes which range from the impacts of over-farming on global warming.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

- How Do Overpopulation and Overconsumption Damage the Environment?…

How Do Overpopulation and Overconsumption Damage the Environment? What You Need to Know
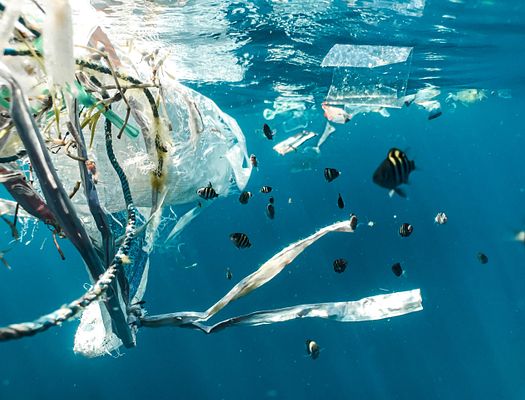
Overpopulation of the earth is a major problem on its own , but it also leads directly to other serious environmental impacts. One of those issues is overconsumption, especially of single-use products that damage the environment, slow the ability of the earth to renew its resources, and contribute to climate change.
What Is Overconsumption and Why Is It so Bad?
Overconsumption is, simply, individuals consuming more resources than they need and that the earth can provide. This extreme behavior also prevents the natural renewal of resources due to the speed of consumption. It is particularly a problem in the global North, where the populace tends to have more money available for leisure and convenience.
Download Our Free White Paper
This is not to say that nonbiodegradable consumables aren’t a problem in the global South, but the major offenders tend to be in places like the United States. Especially dangerous to the environment are single-use, disposable plastic items like bags, cups, etc. These items do not break down in the soil, and they can prevent the earth from naturally replenishing its valuable resources.
The United States alone uses over 1 trillion disposable items related to food each year. These items can end up in bodies of water and cause damage to sea creatures as well as pollute the water itself. Large cities in the global North are the main source of the problem. Many of these cities have huge populations, and the concentration of people and wealth in a relatively small area is disastrous to the environment, as it leads to overconsumption quickly. According to one report , “The United States contributes more to this deluge than any other nation, generating about 287 pounds of plastics per person. Overall, the United States produced 42 million metric tons of plastic waste — almost twice as much as China, and more than the entire European Union combined.”
China, currently the world’s most populous nation, is one of the worst polluters in the world, behind the United States. As China’s economy has grown, so has the trend toward overconsumption. China has not done much to curtail the profligate habits of its citizens, and the country has some of the highest carbon emissions of any nation in the world.
Other nations are guilty of indulgence, pollution and overconsumption too. The tiny Middle Eastern nation of Qatar ranks near the top in the world in terms of carbon emissions per capita. Its citizens consume so much that, if their consumption rate was replicated all over the world, five earths would be required to provide enough resources to cover the consumption.
We don’t have five earths, we only have one, with 8 Billion people who will call the earth home by the end of the year.
Overconsumption and Overpopulation Exacerbate One Another’s Impact
Overconsumption is partly caused by the increasing population in many areas around the world. Larger populations require more food, water , and energy, and consequently tax the earth’s ability to replace used resources. Overpopulation depletes wildlife to dangerously low levels. Overfishing has ruined many formerly fertile fishing grounds. Increased use of agriculture displaced many wild animal species, sometimes resulting in their extinction. According to National Geographic , “by 1989, when about 90 million tonnes (metric tons) of fish were taken from the ocean, the industry had hit its high point, and yields have declined or stagnated ever since. Fisheries for the most sought-after species, like orange roughly, Chilean sea bass, and bluefin tuna, have collapsed for lack of fish. In 2003, a scientific report estimated that industrial fishing had reduced the number of large ocean fish to just 10 percent of their pre-industrial population.” The destruction of wetlands is particularly impactful, as their biodiversity is very high.
Every human deserves clean water, clear air, and space to live—a fair amount of Earth’s resources. These are basic human rights. There are no “right” or “wrong” people to inhabit our planet, but we must all work together to change our current population trajectory, which has us on track to hit nearly 11 billion people by 2100, a capacity our world simply cannot handle while providing adequately for all inhabitants.
On the other hand, humanity’s growing population has introduced invasive species into areas where they can do serious damage to the environment. Species introduced into areas through human migration and travel often have no natural predators, allowing them to expand their numbers quickly. This may cause the depletion in population of other species in the area. Invasive insects can damage native plants, while invasive plants can choke out other indigenous plant species. In places like New York, it is estimated invasive species, like the emerald ash borer, will kill off 1.4 million street trees by 2050. In fact according to the British Ecological Society , 90% of the 1.4 million trees deaths forecasted in the study are predicted to be caused by the emerald ash borer ( Agrilus planipennis ), which is expected to kill virtually all ash trees in more than 6000 urban areas. The ash borer can be tied directly to overconsumption and overabundant free-market policies, as the destroyer of trees arrived accidently on trade goods and cargo shipped from Asia to the United States.

Larger populations demand more resources of all kinds, and this includes the use of fossil fuels. Because fossil fuel technology is older and well-established, it tends to be cheaper than alternative sources. Some nations cannot afford the costs associated with cleaner, renewal energy sources.
Increased use of fossil fuels results in more carbon emissions and more environmental damage. This, combined with the inevitable process of deforestation that occurs in overpopulated areas, multiplies the effect of fossil fuel use, does additional harm to the environment, and prevents natural renewal of resources.
Overconsumption cannot be separated from overpopulation. If the world’s population became more sustainable—or our practices more environmentally-friendly—there could be enough resources available for all humans to thrive.
But with an already-burgeoning population that will continue to grow for decades, the need to conserve resources is so great that even a small degree of overconsumption becomes a major problem. Reducing consumption across the world can help in the short term, but the long-term problem remains the rate of population growth. Let’s work on addressing these issues together, because no single problem is solvable if we go at them alone.
We’re Focused on Making an Impact. Learn More About Our Work.
Global sustainability.


45,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today
Meet top uk universities from the comfort of your home, here’s your new year gift, one app for all your, study abroad needs, start your journey, track your progress, grow with the community and so much more.

Verification Code
An OTP has been sent to your registered mobile no. Please verify

Thanks for your comment !
Our team will review it before it's shown to our readers.

- School Education /
Essay on Overpopulation in 500 Words

- Updated on
- Dec 28, 2023

Essay on Overpopulation: Today, there are a total of 8.1 billion people in the world. This is a result of overpopulation and studies suggest that in the next 25 years, this number will reach 10 billion. This is overpopulation or overabundance, where our environment cannot offer resources to such large amounts of people. Overpopulation is not limited to humans only. It can be of any species living in a particular habitat.
India, China, and the USA are the three most populated countries in the world, which account for a total of 40% of the global population. Population plays a major role in a country’s development. However, if there is overpopulation, it will hamper developmental activities and there will be fewer resources available. This will eventually lead to higher food prices, making survival difficult for everyone.
Also Read: World Population Day 2023
Also Read: Essay on India of My Dreams
Causes of Overpopulation
There are various causes of overpopulation, such as lack of education, high birth rates, primitive medical facilities, illiteracy, lack of employment opportunities, etc. Most of these factors are prevalent in developing and underdeveloped countries.
High birth rates contribute significantly to overpopulation. Factors such as lack of access to family planning, cultural norms, and a high infant mortality rate can encourage families to have more children.
Lack of education and poverty lead to higher population growth. People belonging to communities where education is limited, are not aware of or have access to family planning methods.
In many places, cultural and religious beliefs influence reproductive choices. Some families have several children, which is part of their social norm or is encouraged by religious teachings.
Another major cause of overpopulation is migration. People move to areas with better economic prospects, leading to population density issues in those regions.
Also Read: Essay on Education
Also Read: Essay on New Education in 500 Words
Consequences of Overpopulation
In one way or another, all the problems the world is facing today are related to overpopulation. Say it war, overuse of resources, slow developmental activities, carbon emission, global warming, etc.
Natural resources are depleting at a faster rate than ever. As the population increases, the demand for food and energy resources also increases. Overpopulation contributes to climate change, loss of biodiversity, and other environmental issues.
As humans, we need houses, which are established by cutting down forests and other natural resources. This results in a loss of biodiversity. Rapid urbanization causes problems such as inadequate housing, insufficient infrastructure, traffic congestion, and increased pollution in urban areas.
A rapidly growing population can outstrip job opportunities, resulting in high levels of unemployment. This can lead to social unrest and economic instability.
The overpopulation myth ~ Make babies, not war 🙏 pic.twitter.com/3JaLbDbHd2 — Oddvin (@enterfx) December 16, 2023
How to Deal With Overpopulation
Educating people about the causes and effects of overpopulation is one of the best ways to deal with overpopulation. Studies show that people who have access to proper medical and healthcare facilities have better family planning measures.
Promoting and educating women and girls about reproduction is very important. Educated women tend to have fewer children and this will make them socially and economically more empowered. Encouraging women to participate in the workforce and decision-making processes can be another way to deal with overpopulation.
Offering job opportunities and promoting green sustainable development will allow people to understand the effects of overpopulation on the environment.
The world is our home and we are its protector. Overpopulation is putting a lot of strain on the natural environment, and it needs to be addressed in a civilised way. We need to make sure there is enough for everyone and that we are fulfilling our duty to Mother Nature.
Ans: The major causes of overpopulation are high birth rate, lack of education and illiteracy, poverty, cultural and religious beliefs, etc.
Ans: Some of the least populated countries are Iceland, Suriname, Mongolia, San Marino, Liechtenstein, and Palau.
Ans: Overpopulation is a phenomenon where a particular species exceeds the carrying capacity of the environment. The global population has increased by 1.2 billion in the last 20 years. This was the biggest population boom, putting a heavy strain on the natural environment. Overpopulation is majorly caused in developing countries, because of factors like lack of education and illiteracy, higher birth rates, poverty, etc. Proper government actions are required to address overpopulation, such as educational and family planning programs, women empowerment, job opportunities, etc.
Related Articles
For more information on such informative articles for your school, visit our essay writing page and follow Leverage Edu .
Shiva Tyagi
With an experience of over a year, I've developed a passion for writing blogs on wide range of topics. I am mostly inspired from topics related to social and environmental fields, where you come up with a positive outcome.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Contact no. *

Connect With Us

45,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today.

Resend OTP in

Need help with?
Study abroad.
UK, Canada, US & More
IELTS, GRE, GMAT & More
Scholarship, Loans & Forex
Country Preference
New Zealand
Which English test are you planning to take?
Which academic test are you planning to take.
Not Sure yet
When are you planning to take the exam?
Already booked my exam slot
Within 2 Months
Want to learn about the test
Which Degree do you wish to pursue?
When do you want to start studying abroad.
January 2024
September 2024
What is your budget to study abroad?

How would you describe this article ?
Please rate this article
We would like to hear more.
Have something on your mind?

Make your study abroad dream a reality in January 2022 with
India's Biggest Virtual University Fair

Essex Direct Admission Day
Why attend .

Don't Miss Out
Home — Essay Samples — Sociology — Population Growth — Overpopulation, Its Causes And Effects
Overpopulation, Its Causes and Effects
- Categories: Population Growth
About this sample

Words: 1510 |
Published: Jan 28, 2021
Words: 1510 | Pages: 3 | 8 min read

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Verified writer
- Expert in: Sociology

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
2 pages / 1131 words
5 pages / 2441 words
1 pages / 1427 words
2 pages / 701 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Population Growth
Overpopulation is a phenomenon whereby the population of a certain region or area exceeds the carrying capacity of the environment. The term is often used in reference to human populations, and it can have far-reaching impacts [...]
China is the most populous country in the world, with a population of over 1.4 billion people. The population pyramid of China has undergone significant changes over the past few decades, reflecting the country's demographic [...]
Examine the links between population growth and increased greenhouse gas emissions, focusing on potential mitigative actions.The issue of overpopulation and its contributions to climate change is a complex and urgent matter that [...]
In conclusion, the evolution of human population growth has been a complex and multifaceted process influenced by a variety of historical events. The transition from a nomadic lifestyle to settled agriculture, the rise of cities [...]
Hans starts of talking about how astounded he was when his teacher in school told him that the world population had become three billion people; back in 1960. Rosling explains that instead of using digital technology; he is [...]
Overpopulation is an undesirable condition where the number of existing human population exceeds the carrying capacity of Earth. This scenario can be illustrated in case such as, for example a square feet normally can placed [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Facts Views Vis Obgyn
- v.5(4); 2013
The world population explosion: causes, backgrounds and projections for the future
J. van bavel.
Centre for Sociological Research / Family & Population Studies (FaPOS), Faculty of Social Sciences, University of Leuven, Parkstraat 45 bus 3601, 3000 Leuven, Belgium.
At the beginning of the nineteenth century, the total world population crossed the threshold of 1 billion people for the first time in the history of the homo sapiens sapiens. Since then, growth rates have been increasing exponentially, reaching staggeringly high peaks in the 20th century and slowing down a bit thereafter. Total world population reached 7 billion just after 2010 and is expected to count 9 billion by 2045. This paper first charts the differences in population growth between the world regions. Next, the mechanisms behind unprecedented population growth are explained and plausible scenarios for future developments are discussed. Crucial for the long term trend will be the rate of decline of the number of births per woman, called total fertility. Improvements in education, reproductive health and child survival will be needed to speed up the decline of total fertility, particularly in Africa. But in all scenarios, world population will continue to grow for some time due to population momentum. Finally, the paper outlines the debate about the consequences of the population explosion, involving poverty and food security, the impact on the natural environment, and migration flows.
Key words: Fertility, family planning, world population, population growth, demographic transition, urbanization, population momentum, population projections.
Introduction
In the year 1900, Belgium and the Philippines had more or less the same population, around 7 million people. By the year 2000, the population of the Western European monarchy had grown to 10 million citizens, while the South East Asian republic at the turn of the century already counted 76 million citizens. The population of Belgium has since then exceeded 11 million citizens, but it is unlikely that this number will rise to 12 million by the year 2050. The population of the Philippines on the other hand will continue to grow to a staggering 127 million citizens by 2050, according to the demographic projections of the United Nations (UN 2013).
The demographic growth rate of the Philippines around the turn of the century (2% a year) has already created enormous challenges and is clearly unsustainable in the long term: such growth implies a doubling of the population every 35 years as a consequence of which there would be 152 million people by 2035, 304 million by 2070, and so on. Nobody expects such a growth to actually occur. This contribution will discuss the more realistic scenarios for the future.
Even the rather modest Belgian demographic growth rate around the turn of this century (0.46%) is not sustainable in the long term. In any case, it exceeds by far the average growth rate of the human species (homo sapiens sapiens) that arose in Africa some 200.000 years ago. Today, earth is inhabited by some 7 billion people. To achieve this number in 200.000 years, the average yearly growth rate over this term should have been around 0.011% annually (so 11 extra human beings per 1.000 human beings already living on earth). The current Belgian growth rate would imply that our country would have grown to 7 billion in less than 1500 years.
The point of this story is that the current growth numbers are historically very exceptional and untenable in the long term. The demographic growth rates are indeed on the decline worldwide and this paper will attempt to explain some of the mechanisms behind that process. That doesn’t change the fact, however, that the growth remains extraordinarily high and the decline in some regions very slow. This is especially the case in Sub Saharan Africa. In absolute numbers, the world population will continue to grow anyway for quite some time as a result of demographic inertia. This too will be further clarified in this paper.
The evolution of the world population in numbers
In order to be sustainable, the long term growth rate of the population should not differ much from 0%. That is because a growth rate exceeding 0% has exponential implications. In simple terms: if a combination of birth and growth figures only appears to cause a modest population growth initially, then this seems to imply an explosive growth in the longer term.
Thomas R. Malthus already acquired this point of view by the end of the 18th century. In his famous “Essay on the Principle of Population” (first edition in 1789), Malthus argues justly that in time the growth of the population will inevitably slow down, either by an increase of the death rate or by a decrease of the birth rate. On a local scale, migration also plays an important role.
It is no coincidence that Malthus’ essay appeared in England at the end of the 18th century. After all, the population there had started to grow at a historically unseen rate. More specifically the proletariat had grown immensely and that worried the intellectuals and the elite. Year after year, new demographic growth records were recorded.
At the beginning of the 19th century, the number of 1 billion people was exceeded for the first time in history. Subsequently growth accelerated and the number of 2 billion people was already surpassed around 1920. By 1960, another billion had been added, in 40 instead of 120 years time. And it continued to go even faster: 4 billion by 1974, 5 billion by 1987, 6 billion by 1999 and 7 billion in 2011 ( Fig. 1 ).

This will certainly not stop at the current 7 billion. According to the most recent projections by the United Nations, the number of 8 billion will probably be exceeded by 2025, and around 2045 there will be more than 9 billion people 1 . The further one looks into the future, the more uncertain these figures become, and with demography on a world scale one must always take into account a margin of error of a couple of tens of millions. But according to all plausible scenarios, the number of 9 billion will be exceeded by 2050.
Demographic growth was and is not equally distributed around the globe. The population explosion first occurred on a small scale and with a relatively moderate intensity in Europe and America, more or less between 1750 and 1950. From 1950 on, a much more substantial and intensive population explosion started to take place in Asia, Latin America and Africa ( Fig. 2 ). Asia already represented over 55% of the world population in 1950 with its 1.4 billion citizens and by the year 2010 this had increased to 4.2 billion people or 60%. Of those people, more than 1.3 billion live in China and 1.2 billion in India, together accounting for more than one third of the world population.

In the future, the proportion of Asia will come down and that of Africa will increase. Africa was populated by some 230 million people around 1950, or 9% of the world population. In 2010 there were already more than 1 billion Africans or 15% of the world population. According to UN projections, Africa will continue to grow at a spectacular rate up to 2.2 billion inhabitants in 2050 or 24% of the world population. The proportion of Europe, on the other hand, is evolving in the opposite direction: from 22% of the world population in 1950, over 11% in 2010 to an expected mere 8% in 2050. The population of Latin America has grown and is growing rapidly in absolute terms, but because of the strong growth in Asia and especially Africa, the relative proportion of the Latin American population is hardly increasing (at most from 6 to 8%). The proportion of the population in North America, finally, has decreased slightly from 7 to 5% of the world population.
What these figures mainly come down to in practice is that the population size in especially the poor countries is increasing at an unprecedented rate. At the moment, more than 5.7 billion people, or more than 80% of humanity, are living in what the UN categorise as a developing country. By 2050, that number would – according to the projections – have increased to 8 billion people or 86% of the world population. Within this group of developing countries, the group of least developed countries, the poorest countries so to speak, is growing strongly: from 830 million now, up to an expected 1.7 billion in 2050. This comprises very poor countries such as Somalia, Sudan, Liberia, Niger or Togo in Africa; Afghanistan, Bangladesh or Myanmar in Asia; and Haiti in the Caribbean.
The growth of the world population goes hand in hand with global urbanisation: while around the year 1950 less than 30% of people lived in the cities, this proportion has increased to more than 50%. It is expected that this proportion will continue to grow to two thirds around 2050. Latin America is the most urbanised continent (84%), closely followed by North America (82%) and at a distance by Europe (73%). The population density has increased intensely especially in the poorest countries: from 9 people per square km in 1950 to 40 people per square km in 2010 (an increase by 330%) in the poorest countries, while this figure in the rich countries increased from 15 to 23 people per square km (a 50% growth). In Belgium, population density is 358 people per square km and in the Netherlands 400 people per square km; in Rwanda this number is 411, in the Palestinian regions 666 and in Bangladesh an astonishing 1050.
Although the world population will continue to grow in absolute figures for some time – a following paragraph will explain why – the growth rate in percentages in all large world regions is decreasing. In the richer countries, the yearly growth rate has already declined to below 0.3%. On a global scale, the yearly growth rate of more than 2% at the peak around 1965 decreased to around 1% now. A further decline to less than 0.5% by 2050 is expected. In the world’s poorest countries, the demographic growth is still largest: at present around 2.2%. For these countries, a considerable decrease is expected, but the projected growth rate would not fall below 1.5% before 2050. This means, as mentioned above, a massive growth of the population in absolute figures in the world’s poorest countries.
Causes of the explosion: the demographic transition
The cause of, first, the acceleration and, then, the deceleration in population growth is the modern demographic transition: an increasingly growing group of countries has experienced a transition from relatively high to low birth and death rates, or is still in the process of experiencing this. It is this transition that is causing the modern population explosion. Figure 3 is a schematic and strongly simplified representation of the modern demographic transition.

In Europe, the modern demographic transition started to take place in the middle of the 18th century. Until then, years of extremely high death rates were quite frequent. Extremely high crisis mortality could be the consequence of epidemic diseases or failed harvests and famine, or a combination of both. As a consequence of better hygiene and a better transportation infrastructure (for one, the canals and roads constructed by Austria in the 18th century), amongst other reasons, crisis mortality became less and less frequent. Later on in the 19th century, child survival began to improve. Vaccination against smallpox for example led to an eradication of the disease, with the last European smallpox pandemic dating from 1871. This way, not only the years of crisis mortality became less frequent, but also the average death rate decreased, from an average 30 deaths per 1000 inhabitants in the beginning of the 19th century to around 15 deaths per 1000 citizens by the beginning of the 20th century. In the meantime, the birth rate however stayed at its previous, high level of 30-35 births per 1000 inhabitants.
The death rate went down but the birth rate still didn’t: this caused a large growth in population. It was only near the end of the nineteenth century (a bit earlier in some countries, later in others) that married couples in large numbers started to reduce their number of children. By the middle of the 20th century, the middle class ideal of a two children household had gained enormous popularity and influence. The reaction by the Church, for example in the encyclical Humanae Vitae (1968), came much too late to bring this evolution to a halt.
As a consequence of widespread family planning – made even easier in the sixties by modern hormonal contraceptives – the birth rate started declining as well and the population tended back towards zero growth. Nowadays the end of this transition process has been more than achieved in all European countries, because the fertility has been below replacement level for several decades (the replacement level is the fertility level that would in the long term lead to a birth rate identical to the death rate, if there would be no migration) 2 .
That the population explosion in the developing countries since the second half of the 20th century was so much more intense and massive, is a consequence of the fact that in those countries, the process of demographic transition occurred to a much more extreme extent and on a much larger scale. On the one hand, mortality decreased faster than in Europe. After all, in Europe the decline in mortality was the result of a gradual understanding of the importance of hygiene and afterwards the development of new medical insights. These insights of course already existed at the start of the demographic transitions in Asian, Latin American and African regions, whereby the life expectancy in these regions could grow faster. On the other hand, the total fertility – the average number of children per woman – at the start of the transition was a lot higher in many poor regions than it initially was in Europe. For South Korea, Brasil and the Congo, for example, the total fertility rate shortly after the Second World War (at the start of their demographic transition) is estimated to be 6 children per woman. In Belgium this number was close to 4.5 children per woman by the middle of the nineteenth century. In some developing regions, the fertility and birth rate decreased moderately to very fast, but in other regions this decline took off at an exceptionally sluggish pace – this will be further explained later on. As a consequence of these combinations of factors, in most of these countries the population explosion was much larger than it had been in most European countries.
Scenarios for the future
Nonetheless, the process of demographic transition has reached its second phase in almost all countries in the world, namely the phase of declining fertility and birth rates. In a lot of Asian and Latin American countries, the entire transition has taken place and the fertility level is around or below the replacement level. South Korea for example is currently at 1.2 children per woman and is one of the countries with the lowest fertility levels in the world. In Iran and Brasil the fertility level is currently more or less equal to Belgium’s, that is 1.8 to 1.9 children per woman.
Crucial to the future evolution of the population is the further evolution of the birth rate. Scenarios for the future evolution of the size and age of the population differ according to the hypotheses concerning the further evolution of the birth rate. The evolution of the birth rate is in turn dependent on two things: the further evolution of the total fertility rate (the average number of children per woman) in the first place and population momentum in the second. The latter is a concept I will later on discuss in more detail. The role of the population momentum is usually overlooked in the popular debates, but is of utmost importance in understanding the further evolution of the world population. Population momentum is the reason why we are as good as certain that the world population will continue to grow for a while. The other factor, the evolution of the fertility rate, is much more uncertain but of critical importance in the long term. The rate at which the further growth of the world population can be slowed down is primarily dependent on the extent to which the fertility rates will continue to decline. I will further elaborate on this notion in the next paragraph. After that, I will clarify the notion of population momentum.
Declining fertility
Fertility is going down everywhere in the world, but it’s going down particularly slowly in Africa. A further decline remains uncertain there. Figure 4 shows the evolution per world region between 1950 and 2010, plus the projected evolution until 2050. The numbers before 2010 illustrate three things. First of all, on all continents there is a decline going on. Secondly, this decline is not equal everywhere. And thirdly: the differences between the continents remain large in some cases. Asia and Latin America have seen a similar decline in fertility: from 5.9 children per woman in 1950 to 2.5 at the start of the 21st century. Europe and North America had already gone through the largest part of their demographic transition by the 1950’s. Their fertility level has been below replacement levels for years. Africa has indeed seen a global decrease of fertility, but the average number of children is still at an alarmingly high level: the fertility merely decreased from 6.7 to 5.1 children per woman.

These continental averages hide a huge underlying diversity in fertility paths. Figure 5 attempts to illustrate this for a number of countries. Firstly let us consider two African countries: the Congo and Niger. As was often the case in Europe in the 19th century, fertility was first on the rise before it started declining. In the Congo this decrease was more extensive, from around 6 children in 1980 to 4 children per woman today, and a further decline to just below three is expected in the next thirty years. Niger is the country where the fertility level remains highest: from 7 it first rose to an average of just below 8 children per woman in the middle of the 1980’s, before decreasing to just above 6.5 today. For the next decades a decline to 4 children per woman is expected. But that is not at all certain: it is dependent on circumstances that will be further explained in a moment. The demographic transition is after all not a law of nature but the result of human actions and human institutions.

Around 1950, Pakistan and Iran had more or less the same fertility level as Niger, but both countries have seen a considerable decline in the meantime. In Pakistan the level decreased slowly to the current level of 3 children per woman. In Iran the fertility decreased more abruptly, faster and deeper to below the replacement level – Iran today has one of the lowest fertility levels in the world, and a further decline is expected. The Iranian Revolution of 1978 played a crucial role in the history of Iran (Abassi-Shavazi et al., 2009): it brought better education and health care, two essential ingredients for birth control.
Brasil was also one of the countries with very high fertility in the 1950’s – higher than the Congo, for example. The decrease started earlier than in Iran but happened more gradually. Today both countries have the same total fertility, below the replacement level.
Child mortality, education and family planning
Which factors cause the average number of children to go down? The literature concerning explanations for the decrease in fertility is vast and complex, but two factors emerge as crucial in this process: education and child survival.
Considering child survival first: countries combining intensive birth control with very high child mortality are simply non-existent. The statistical association between the level of child mortality and fertility is very tight and strong: in countries with high child mortality, fertility is high, and vice versa. This statistical correlation is very strong because the causal relation goes in both directions; with quick succession of children and therefore a lot of children to take care for, the chances of survival for the infants are lower than in those families with only a limited number of children to take care of – this is a fortiori the case where infrastructure for health care is lacking. A high fertility level thus contributes to a high child mortality. And in the other direction: where survival chances of children improve, the fertility will go down because even those households with a lower number of children have increasing confidence in having descendants in the long term.
It is crucial to understand that the decline in child mortality in the demographic transition always precedes the decline in fertility. Men, women and families cannot be convinced of the benefits of birth control if they don’t have confidence in the survival chances of their children. Better health care is therefore essential, and a lack of good health care is one of the reasons for a persistently high fertility in a country like Niger.
Education is another factor that can cause a decline in fertility. This is probably the most important factor, not just because education is an important humanitarian goal in itself (apart from the demographic effects), but also because with education one can kill two birds with one stone: education causes more birth control but also better child survival (recently clearly demonstrated by Smith-Greenaway (2013), which in its turn will lead to better birth control. The statistical correlation between level of education and level of fertility is therefore very strong.
Firstly, education enhances the motivation for birth control: if parents invest in the education of their children, they will have fewer children, as has been demonstrated. Secondly, education promotes a more forward-looking lifestyle: it will lead people to think on a somewhat longer term, to think about tomorrow, next week and next month, instead of living for the day. This attitude is necessary for effective birth control. Thirdly, education also increases the potential for effective contraception, because birth control doesn’t just happen, especially not when efficient family planning facilities are not or hardly accessible or when there are opposing cultural or family values.
The influence of education on birth control has been demonstrated in a vast number of studies (James et al., 2012). It starts with primary education, but an even larger effect can be attained by investment in secondary education (Cohen, 2008). In a country like Niger, for example, women who didn’t finish primary school have on average 7.8 children. Women who did finish primary school have on average 6.7 children, while women who finished secondary school “only” have 4.6 children ( Fig. 6 ). The fertility of Niger would be a lot lower if more women could benefit from education. The tragedy of that country is that too many people fall in the category of those without a degree of primary school, with all its demographic consequences.

One achieves with education therefore a plural beneficial demographic effect on top of the important objective of human emancipation in itself. All this is of course not always true but depends on which form of “education”; I assume that we’re talking about education that teaches people the knowledge and skills to better take control of their own destiny.
It is one thing to get people motivated to practice birth control but obtaining actual effective contraception is quite another matter. Information concerning the efficient use of contraceptives and increasing the accessibility and affordability of contraceptives can therefore play an important role. There are an estimated 215 million women who would want to have contraception but don’t have the means (UNFPA, 2011). Investments in services to help with family planning are absolutely necessary and could already have great results in this group of women. But it’s no use to put the cart before the horse: if there is no intention to practice birth control, propaganda for and accessibility of contraception will hardly have any effect, as was demonstrated in the past. In Europe the lion’s share of the decline in fertility was realized with traditional methods, before the introduction of hormonal contraception in the sixties. There is often a problem of lack of motivation for birth control on the one hand, as a result of high child mortality and low schooling rates, and a lack of power in women who may be motivated to limit fertility but are confronted with male resistance on the other (Blanc, 2011; Do and Kurimoto, 2012). Empowerment of women is therefore essential, and education can play an important role in that process as well.
Population momentum
Even if all the people would suddenly practice birth control much more than is currently considered possible, the world population would still continue to grow for a while. This is the consequence of population momentum, a notion that refers to the phenomenon of demographic inertia, comparable to the phenomenon of momentum and inertia in the field of physics. Demographic growth is like a moving train: even when you turn off the engine, the movement will continue for a little while.
The power and direction of population momentum is dependent on the age structure of the population. Compare the population pyramids of Egypt and Germany ( Fig. 7 ). The one for Egypt has a pyramidal shape indeed, but the one for Germany looks more like an onion. As a consequence of high birth rates in the previous decades, the largest groups of Egyptians are to be found below the age of forty; the younger, the more voluminous the generation. Even if the current and future generations of Egyptians would limit their fertility strongly (as is indeed the case), the birth rate in Egypt would still continue to rise for quite some time, just because year after year more and more potential mothers and fathers reach the fertile ages. Egypt therefore clearly has a growth momentum.

Germany on the other hand has a negative or shrinking momentum: even if the younger generations of Germans would have a larger num ber of children than the generation of their own parents, the birth rate in Germany would still continue to decrease because fewer and fewer potential mothers and fathers reach the fertile ages.
The population momentum on a global scale is positive: even if fertility would decrease overnight to the replacement level, the world population would continue to grow with 40% (from 7 billion to 9.8 billion). Only the rich countries have a shrinking momentum, that is -3%. For Europe the momentum is -7%. The population momentum for the poorest countries in the world is +44%, that of Sub Saharan Africa +46% (Espenshade et al., 2011).
Consequences of the population explosion
The concerns about the consequences of population explosion started in the sixties. Milestone publications were the 1968 book The Population bomb by biologist Paul Ehrlich, the report of the Club of Rome from 1972 (The Limits to Growth) and the first World Population Plan of Action of the UN in 1974 among others.
In the world population debate, the general concerns involve mainly three interconnected consequences of the population explosion: 1) the growing poverty in the world and famine; 2) the exhaustion and pollution of natural resources essential to human survival; and 3) the migration pressure from the poor South to the rich North (Van Bavel, 2004).
Poverty and famine
The Malthusian line of thought continues to leave an important mark on the debate regarding the association between population growth and poverty: Malthus saw an excessive population growth as an important cause of poverty and famine. Rightfully this Malthusian vision has been criticized a lot. One must after all take the reverse causal relation into account as well: poverty and the related social circumstances (like a lack of education and good health care for children) contribute to high population growth as well.
Concerning famine: the production of food has grown faster since 1960 than the world population has, so nowadays the amount of food produced per person exceeds that which existed before the population explosion (Lam, 2011). The problem of famine isn’t as much an insufficient food production as it is a lack of fair distribution (and a lack of sustainable production, but that’s another issue). Often regions with famine have ecological conditions permitting sufficient production of food, provided the necessary investments in human resources and technology are made. The most important cause of famine is therefore not the population explosion. Famine is primarily a consequence of unequal distribution of food, which in turn is caused by social-economic inequality, lack of democracy and (civil) war.
Poverty and famine usually have mainly political and institutional causes, not demographic ones. The Malthusian vision, that sees the population explosion as the root of all evil, therefore has to be corrected ( Fig. 8 ). Rapid population growth can indeed hinder economical development and can thus pave the way for poverty. But this is only part of the story. As mentioned, poverty is also an underlying cause of rapid population growth. Social factors are at the base of both poverty and population growth. It’s those social factors that require our intervention: via investments in education and (reproductive) health care.

Impact on the environment
The impact of the population explosion on the environment is unquestionably high, but the size of the population represents only one aspect of this. In this regard it can be useful to keep in mind the simple I=PAT scheme: the ecological footprint or impact on the environment (I) can be regarded as the product of the size of the population (P), the prosperity or consumption level (A for affluence) and the technology used (T). The relationship between each of these factors is more complex than the I=PAT scheme suggests, but in any case the footprint I of a population of 1000 people is for example dependent on how many of those people drive a car instead of a bike, and of the emission per car of the vehicle fleet concerned.
The ecological footprint of the world population has increased tremendously the past decades and the growth of the world population has obviously played an important role in this. The other factors in the I=PAT scheme have however played a relatively bigger role than the demographic factor P. The considerable increase in the Chinese ecological footprint of the past decades for example, is more a consequence of the increased consumption of meat than of population growth (Peters et al., 2007; Liu et al., 2008). The carbon dioxide emission of China grew by 82% between 1990 and 2003, while the population only increased by 11% in that same period. A similar story exists for India: the population grew by less than 23% between 1990 and 2003, while the emission of carbon dioxide increased by more than 83% (Chakravarty et al., 2009). The consumption of water and meat in the world is increasing more rapidly than the population 3 . The consumption of water per person is for example threefold higher in the US than in China (Hoekstra and Chapagain, 2007). The African continent has at present the same number of inhabitants as Europe and North America together, over 1 billion. But the total ecological footprint of Europeans and Americans is many times higher than that of Africans (Ewing et al., 2010). Less than 18% of the world population is responsible for over 50% of the global carbon dioxide emission (Chakravarty et al., 2009).
If we are therefore concerned about the impact of the world population on the environment, we can do something about it immediately by tackling our own overconsumption: it’s something we can control and it has an immediate effect. In contrast, we know of the population growth that it will continue for some time anyhow, even if people in poor countries would practice much more birth control than we consider possible at present.
The population explosion has created an increasing migration pressure from the South to the North – and there is also important migration within and between countries in the South. But here as well the message is: the main responsibility doesn’t lie with the population growth but with economic inequality. The primary motive for migration was and is economic disparity: people migrate from regions with no or badly paid labour and a low standard of living to other regions, where one hopes to find work and a higher standard of living (Massey et al., 1993; Hooghe et al., 2008; IMO, 2013). Given the permanent population growth and economical inequality, a further increasing migration pressure is to be expected, irrespective of the national policies adopted.
It is sometimes expected that economic growth and increasing incomes in the South will slow down the migration pressure, but that remains to be seen. After all, it isn’t usually the poorest citizens in developing countries that migrate to rich countries. It is rather the affluent middle class in poor countries that have the means to send their sons and daughters to the North – an investment that can raise a lot of money via remittances to the families in the country of origin (IMO, 2013). There is after all a considerable cost attached to migration, in terms of money and human capital. Not everyone can bear those costs: to migrate you need brains, guts and money. With growing economic development in poor countries, an initial increase in migration pressure from those countries would be expected; the association between social-economic development and emigration is not linearly negative but follows the shape of a J turned upside down: more emigration at the start of economic development and a decline in emigration only with further development (De Haas, 2007).
7 Billion and counting… What is to be done?
A world population that needed some millennia before reaching the number of 1 billion people, but then added some billions more after 1920 in less than a century: the social, cultural, economic and ecological consequences of such an evolution are so complex that they can lead to fear and indifference at the same time. What kind of constructive reaction is possible and productive in view of such an enormous issue?
First of all: we need to invest in education and health care in Africa and elsewhere, not just as a humanitarian target per se but also because it will encourage the spread of birth control. Secondly, we need to encourage and support the empowerment of women, not just via education but also via services for reproductive health. This has triple desirable results for demographics: it will lead to more and more effective birth control, which in itself has a positive effect on the survival of children, which in turn again facilitates birth control.
Thirdly: because of the positive population momentum, the world population will certainly continue to grow in absolute figures, even though the yearly growth rate in percentages is already on the decline for several years. The biggest contribution we could make therefore, with an immediate favourable impact for ourselves and the rest of the world, is to change our consumption pattern and deal with the structural overconsumption of the world’s richest countries.
(1) Unless otherwise specified, all figures in this paragraph are based on the United Nations World Population Prospects, the 2012 Revision, http://esa.un.org/wpp/ . Concerning projections for the future, I reported the results of the Medium Variant. Apart from this variant, there are also high and low variants (those relying on scenarios implying respectively an extremely high and extremely low growth of the population) and a variant in which the fertility rates are fixed at the current levels. It is expected that the actual number will be somewhere between the highest and lowest variant and will be closest to the medium variant. That’s why I only report this latter value.
(2) In demography, the term «fertility» refers to the actual number of live births per women. By contrast, the term fecundity refers to reproductive capacity (irrespective of actual childbearing), see Habbema et al. (2004).
(3) See http://www.unwater.org/water-cooperation-2013/water-cooperation/facts-and-figures
- Abbasi-Shavazi MJ, McDonald P, Chavoshi M. Dordrecht: Springer; 2009. The Fertility Transition in Iran. Revolution and Reproduction. [ Google Scholar ]
- Blanc AK. The effect of power in sexual relationships on sexual and reproductive health: an examination of the evidence. Stud Fam Plan. 2001; 32 :189–213. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Chakravarty S, Chikkatur A, de Coninck H, et al. Sharing global CO2 emission reductions among one billion high emitters. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2009; 106 :11884–11888. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cohen JE. Make secondary education universa. Nature. 2008; 456 :572–573. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- De Haas H. International migration, remittances and development: myths and facts. Third World Quarterly. 2007; 26 :1269–1284. [ Google Scholar ]
- Do M, Kurimoto N. Women’s Empowerment and Choice of Contraceptive Methods in Selected African Countries. Int Perspect Sex Reprod Health. 2012; 38 :23–33. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Espenshade TJ, Olgiati AS, Levin S. On nonstable and stable population momentum. Demography. 2011; 48 :1581–1599. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ewing B, Moore D, Goldfinger S, Oursler A, et al. Oakland, CA: Global Footprint Network; Ecological Footprint Atlas 2010. [ Google Scholar ]
- Habbema JDF, Collins J, Leridon H, et al. Towards less confusing terminology in reproductive medicine: a proposal. Hum Reprod. 2004; 19 :1497–1501. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hoekstra AY, Chapagain AK. Water footprints of nations: Water use by people as a function of their consumption pattern. Water Resources Management. 2007; 21 :35–48. [ Google Scholar ]
- Hooghe M, Trappers A, Meuleman B, et al. Migration to European countries: A structural explanation of patterns, 1980-2004. International Migration Review. 2008; 42 :476–504. [ Google Scholar ]
- IMO. World Migration Report 2013. Genève, CH: International Organization for Migration; 2013. [ Google Scholar ]
- Vienna Yearbook of Population Research. 2012; 10 [ Google Scholar ]
- Lam D. How the world survived the population bomb: lessons from 50 years of extraordinary demographic history. Demography. 2011; 48 :1231–1262. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Liu J, Yang H, Savenije HHG. China’s move to higher-meat diet hits water security. 2008. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Livi-Bacci M. A Concise History of World Population. 3rd ed. Cambridge (Mass.): Blackwell; 2001. [ Google Scholar ]
- Massey , DS , Arango J, Hugo G, et al. Theories of international migration: a review and appraisal. Population and Development Review. 1993; 19 :431–466. [ Google Scholar ]
- Peters GP, Weber CL, Guan D, et al. China’s Growing CO 2 Emissions - A Race between Increasing Consumption and Efficiency Gains. Environ Sci Technol. 2007; 41 [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Smith-Greenaway E. Maternal reading skills and child mortality in Nigeria: a reassessment of why education matters. Demography. 2013; 50 :1551–1561. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- UNFPA. The State of World Population 2011. People and Possibilities in a World of 7 Billion. New York: United Nations; [ Google Scholar ]
- UN. World Population Prospects. The 2012 Revision. Volume I : Comprehensive Tables. New York: United Nations; 2013. [ Google Scholar ]
- Van Bavel, J. De wereldbevolkingsexplosie en duurzame ontwikkeling: een veldoverzicht. Tijdschrift voor Sociologie. 2004; 25 :227–245. [ Google Scholar ]
- IELTS Scores
- Life Skills Test
- Find a Test Centre
- Alternatives to IELTS
- General Training
- Academic Word List
- Topic Vocabulary
- Collocation
- Phrasal Verbs
- Writing eBooks
- Reading eBook
- All eBooks & Courses
- Sample Essays
- Overpopulation Essay
IELTS Overpopulation Essay
This model essay is about overpopulation in cities . You specifically have to talk about the problems of overpopulation, and suggest some solutions to this problem.
Note that this question specifically asks you what governments and individuals can do.
Here is the question:
Overpopulation of urban areas has led to numerous problems.
Identify one or two serious ones and suggest ways that governments and individuals can tackle these problems.
Organising a Problems & Solutions Essay
Note that this overpopulation essay question specifically asks you what governments and individuals can do.

You MUST, therefore, write about what both of these can do in order to fully answer the question.
Note as well that you must talk about serious problems.
The easiest way to organize a problems and solutions essay is as follows:
Body 1: Problems
Body 2: Solutions
In this essay, a separate paragraph has been written about government and individual solutions, so it is organized as follows:
Body 2: Solutions - Government
Body 3: Solutions - Individuals
Model Essay
You should spend about 40 minutes on this task.
Write about the following topic:
Give reasons for your answer and include any relevant examples from your own experience or knowledge.
Write at least 250 words.
IELTS Overpopulation Essay - Sample Answer
Many countries of the world are currently experiencing problems caused by rapidly growing populations in urban areas, and both governments and individuals have a duty to find ways to overcome these problems.
Overpopulation can lead to overcrowding and poor quality housing in many large cities. Poorly heated or damp housing could cause significant health problems, resulting in illness, such as bronchitis or pneumonia. Another serious consequence of overcrowding is a rising crime rate as poor living conditions may lead young people in particular to take desperate measures and turn to crime or drugs.
In terms of solutions, I believe the government should be largely responsible. Firstly, it is vital that the state provides essential housing and healthcare for all its citizens. Secondly, setting up community projects to help foster more community spirit and help keep young people off the street is a good idea. For example, youth clubs or evening classes for teenagers would keep them occupied. Finally, more effective policing of inner city areas would also be beneficial.
Naturally, individuals should also try to address these problems. One way is to put pressure on the government to ensure they tackle the problems by, for instance, forming action groups to lobby the government and request intervention and adequate funding. They could also form Neighbourhood Watch areas to try and help reduce the high levels of crime.
Therefore, it is clear that the problems caused by overpopulation in urban areas are very serious. Yet if governments and individuals share a collective responsibility, then it may well become possible to offer some solutions.
(260 words)
<<< Back
Next >>>
More Problems & Solutions Essays:
IELTS Problem Solution Essay Example: Why is immigration problematic?
This problem solution essay example is about the increasing number of professionals who are leaving their own poorer countries to work in developed countries

Competing for Jobs Essay
Competing for Jobs Essay: This is a model essay about the problems arising when older people have to compete with younger people for jobs. you need to write about the problems that arise if older people have to compete for jobs with younger people.
Any comments or questions about this page or about IELTS? Post them here. Your email will not be published or shared.
Would you prefer to share this page with others by linking to it?
- Click on the HTML link code below.
- Copy and paste it, adding a note of your own, into your blog, a Web page, forums, a blog comment, your Facebook account, or anywhere that someone would find this page valuable.
Band 7+ eBooks
"I think these eBooks are FANTASTIC!!! I know that's not academic language, but it's the truth!"
Linda, from Italy, Scored Band 7.5

IELTS Modules:
Other resources:.
- All Lessons
- Band Score Calculator
- Writing Feedback
- Speaking Feedback
- Teacher Resources
- Free Downloads
- Recent Essay Exam Questions
- Books for IELTS Prep
- Useful Links

Recent Articles
IELTS Bundle Writing eBooks: 30% Off
Jun 01, 24 09:55 AM

House Sitting
May 31, 24 03:59 AM

Key Phrases for IELTS Speaking: Fluency and Coherence
May 26, 24 06:52 AM
Important pages
IELTS Writing IELTS Speaking IELTS Listening IELTS Reading All Lessons Vocabulary Academic Task 1 Academic Task 2 Practice Tests
Connect with us
Before you go...
Check out the ielts buddy band 7+ ebooks & courses.

Copyright © 2022- IELTSbuddy All Rights Reserved
IELTS is a registered trademark of University of Cambridge, the British Council, and IDP Education Australia. This site and its owners are not affiliated, approved or endorsed by the University of Cambridge ESOL, the British Council, and IDP Education Australia.

Public Health and Overpopulation: The United Nations Takes Action
With the world’s population rising faster than ever before, will our population growth outpace our resource reserves? How can the dangerous effects of overpopulation be managed without diminishing the major improvements in our quality of life that come about thanks to population growth?
The UN projects that over half of the Earth’s population growth in the next three decades will occur in the continent of Africa. This is due to the fact that, from 2010 to 2015, Africa’s population grew at a rate of 2.55 percent annually, with the continent still maintaining the highest pace of population growth among other continents. The UN predicts that, behind Africa, Asia will be the second greatest donor to future international population growth, with an expected addition of approximately one billion people by 2050. In contrast, within every European nation, fertility rates are currently below the population replacement level, which is approximately two children per woman. In most of Europe, fertility rates have remained beneath replacement level for decades. The global population grew fourfold in the past 100 years, so what impact could increased population growth have in the future? Will there be mass-migration? Overcrowding in already densely populated or resource-rich areas? Poor living conditions and sanitation similar to Industrial Revolution era slums?
The global population is currently rising at a steady rate. The number of humans existing on Earth has never been as high as it is now. In 1800, Earth had approximately 1 billion inhabitants, which rose to 2.3 billion in 1940, then 3.7 billion in 1970, and approximately 7.5 billion today. In the last five decades, Earth has experienced an extreme population boom. This phenomenon is known as overpopulation, where the condition in which the amount of humans currently existing on Earth outstrips future resource availability and earth’s carrying capacity. Throughout human history, birth and death rates have always counterbalanced each other, which ensured that Earth had a maintainable population growth level. However, in the 1960s, the global population increased at an unparalleled rate. This brought about a variety of apocalyptic predictions, most prominently, a revival of the Malthusian trap panic.
Paul R. Ehrlich’s 1968 novel, The Population Bomb , eerily echoes Thomas R. Malthus’s landmark 1798 Essay on the Principle of Population . Ehrlich’s novel proposes theories regarding potential outcomes for when agricultural growth does not keep pace with population growth. Ultimately his theories say that the world’s food supply will inevitably become inadequate for feeding the general population, whose numbers would continue to swell until famine, disease epidemics, war, or other calamities took root. These Malthusian predictions about out-of-control population growth have resulted in a variety of detrimental global impacts, particularly the emergence of extreme reproductive control measures, which have taken center stage on an international scale. Today, despite the fact that population scientists mostly agree that Malthus’s forecasts were overblown, the lingering prevalence of these fears have contributed to millions of forced sterilizations in Mexico, Bolivia, Peru, Indonesia, Bangladesh and India, as well as China’s two-child policy . Overall, this has left many wondering whether extreme population growth projections are legitimate or merely groundless panic perpetuated by alarmists.
The Demographic Transition
In reality, rising birth rates and population booms are components of a four-step process called the demographic transition, which the Earth is currently undergoing. Most developed nations have already made this transition, but other countries are currently experiencing this change. In the 1700s, the entire world was undergoing the first stage of the demographic transition. During this time, the continent of Europe was in even poorer condition than the modern-day definition of a developing region, and was afflicted with inferior public health, sustenance, and medical facilities. Birth rates were higher; however, death rates were also higher. For this reason, population growth remained largely stagnant.
Statistically, in the 1700s, women birthed four to six children. However, on average, only two survived to adulthood. When the Industrial Revolution began in Great Britain in the mid-18th century, the Earth experienced the most significant shift in human lifestyles since the Agricultural Revolution. The Industrial Revolution altered every aspect of society, and fostered a greater sense of global interconnectedness. For example, many peasants became factory workers, manufactured products became widely available due to mass production, and countless scientific advancements improved existing methods of transportation, communication, and medicine.
Gradually, this economic development created a middle class and, after the work of union activists, ultimately raised the standard of living and health care for the impoverished labor demographic. Thus began the second transition stage. The increased availability of better foodstuffs, sanitation, and medicine directly contributed to lower death rates, causing a population explosion that doubled Great Britain’s population from 1750 to 1850. In the past, families tended to have more children because not all were expected to survive, but when child mortality rates decreased, the third transition stage was launched. This stage involves reduced conception rates and slowing population growth. Ultimately, a balance was established, with fewer deaths and births, creating a stable population growth rate and signifying the attainment of the fourth and final stage of the demographic transition.
Even as birth rates have decreased dramatically, Earth’s population is still rising at an alarming rate because the humans conceived during the population boom of the 1970s and 1980s are currently having more children; however, the current average number of children per family remains two and a half, while it was five during the late 1970s. As this generation ages and its fertility diminishes, the rate of population growth will likely continue to decrease in every nation. Most of the world’s countries have reached the fourth stage of the demographic transition. In approximately 80 years, developed countries will experience a reduction in fertility from over six children to fewer than three children. Malaysia and South Africa reached this point in 34 years, Bangladesh in 20 years, and Iran in 10 years. If developing countries are afforded more support, they will reach this point much faster.
Overall, most scientists postulate that human population growth will eventually come to an end, and the UN predicts that Earth’s population will not exceed twelve billion. Some of the major causes of population growth are reduced infant mortality rates, increased lifespans, higher fertility rates, advances in science and technology, and improved access to proper medical care. With the UN’s continued assistance, concurrent with overpopulation, the development level of the global community will increase, and the number of people living in poverty will decrease. Nonetheless, an ever-expanding human population is an immense social and economic challenge that necessitates the alignment of different national interests, especially with regards to reproductive rights, resource availability, and environmental concerns.
The United Nations Takes Action
In 1969, the United Nations Population Fund (UNFPA) was established in order to lead the UN in implementing population programs fundamentally based on the notion of family planning, or the “human right of individuals and couples to freely determine the size of their families” without governmental interference or legislation. In 1994, at the International Conference on Population and Development in Cairo, Egypt, the designated objectives of the UNFPA were determined in greater depth. It was decided that the UNFPA would specifically focus on the gender and human rights elements of population issues; consequently, the UN Population Fund was granted the lead role in aiding nations in fulfilling the Conference’s Programme of Action.
The three most significant sections of the UN Population Fund mandate are “Reproductive Health,” “Gender Equality,” and “Population and Development.” The United Nations Population Division (UNPD) works to confront the interconnected global issues posed by population growth, which is primarily fueled by rising fertility rates, increased longevity, and greater international migration. The UN produces the official demographic approximations and predictions for every country and all regions of the world. The UNFPA specifically addresses global population by compiling data and statistics regarding migration, fertility, marriage, regional development, urbanization, world population projections, and national population policies.
In November 2012, the UNFPA declared family planning a global human right; however, approximately 12 percent of 15 to 49-year-old women internationally are not afforded access to family planning. This is considered an egregious modern-day human rights infringement. The UNFPA aids various UN bodies like the Commission on Population and Development, and endorses the implementation of the Programme of Action undertaken by the International Conference on Population and Development (IPCD) in 1994. The UNFPA has been successful in urging international cooperation on the issue of securing family planning as a human right, pushing the UN to hold three conferences concerning the issue of population, along with two special sessions of the General Assembly and a summit in 2019 .
The Way Forward
Ultimately, apocalyptic population growth fears are overblown, and as such, draconian population control regulations are unnecessary. We have witnessed progress on an international scale in this area, perhaps most notably with China revoking its infamous, longstanding one-child policy just seven years ago. However, a broader global focus on guaranteeing family planning as a human right remains essential. In the words of economist Julian Simon, “Whatever the rate of population growth is, historically it has been that the food supply increases at least as fast, if not faster.” Since Ehrlich’s initial fear-mongering regarding an overpopulation-induced Armageddon, the planet’s population has more than doubled . However, annually, famine deaths have dropped by millions. Today’s famines are war-induced, not caused by natural resource consumption. As production rose, prices fell and calorie consumption increased, which decreased malnutrition worldwide. In Simon’s words, human ingenuity is the “ ultimate resource .” Therefore, the enactment of heavy-handed population-control regulations is not only abhorrent, but is also irrational and unsupported by scientific evidence.

Sophia Scott
Sophia Scott is a staff writer for the Harvard International Review. She is interested in global health & health equity, along with the intersections between science and policy.
Recent Posts
Germany's energy crisis: europe's leading economy is falling behind.
Russian Narrative: Constitutional Amendments, Civilizationism and Multipolarity
Nickel and Dimed: The Green Metal Gamble in New Caledonia
In Comparative Perspective: Interview with COFR President Emeritus Richard Haass
Bloodied Blossoms: Can Afghanistan Grow Past Its Opioid Industry?
You Might Be Interested In
Defying dictatorships: an interview with garry kasparov, cambodia’s triumph and tragedy: the un’s greatest experiment 30 years on, on atlantic alliances and autocrats: an interview with jeanne shaheen.
The Effects of Overpopulation
Global problems affect the life not only of certain individuals but the society in general. One of the global dilemmas that can consequently lead to the severe outcome is overpopulation. The major purpose of the paper is to discuss the problem of overpopulation, highlight the risks and environmental problems, as well as make an accent on the ways of regulation this issue.
As a matter of fact, overpopulation is a modern ecological problem. According to the recent researches, the number of people increases every year with tremendous speed. In 1900, the population reached the point of 1,5 billion of people whereas by 1960 the population has already doubled. Moreover, by 1999, the population doubled again (Pettorelli 543).
Every person consumes a lot of resources, and overpopulation is considered to be a threat. The only solution is birth control and improvement of the quality of life. The human overpopulation takes place in those countries where the population is bigger than food and water resources.
However, birth control encounters many obstacles. Among them are the following, namely negative reaction of the society, the enormous role of religion that encourages having many children, primitive communal forms of living, illiteracy and ignorance, poor development of medicine, and other. Thus, the countries of the third world are the most vulnerable in relation to the overpopulation.
Environmental problem, overpopulation, and underdevelopment are directly linked to a possible threat of lack of the resources in the nearest future. The majority of countries that experience a rapid increase in population have poorly developed agricultural segment.
The solution is to boost the productivity. However, the increase in usage of fertilizers, pesticides, and chemicals leads to a deterioration of the ecological situation and increasing concentrations of substances that are harmful to human food (Coallier 61). The interference of a human being into ecology leads to the lack of water that is good for drinking. In case people do not address the issue, a number of questions will arise, namely:
- Landfills and pollution of the surface of the planet;
- The destruction of the forests;
- Shortage of mineral resources;
- Hazardous impact on the marine ecosystem;
- Air and water pollution with CO2 emissions (Bourne 375).
The only solution that will mitigate the impact of the over population is the birth control programs. The demographic situation in the Eastern World has already reached the point when the government found it essential to interfere. In the number of states, the measures directed to the reduction of the population were vital for implementation. One of the examples is China, which established the principle one child for one family.
The objective of the government was to control overpopulation. The average number of children who were born in China from one woman decreased from about 5 to 1 (Coallier 83). Thus, the restriction policy was successful, and the government reached the goal. The government encourages families to have one child; however, with the birth of the second baby, the family will be liable to pay a fee.
Throughout the history, the number of people was always controlled by wars and epidemics. Every time the number of people decreased, the society experienced rapid development. Nevertheless, nowadays, the society has already gained a significant experience that can be used in the treatment of different diseases. Thus, there are almost no factors that would significantly decrease the number of people.
In conclusion, it should be stressed that the situation regarding the overpopulation demands the solution. The issue should receive the priority not only on the governmental but global levels as well. Overpopulation can lead to severe consequences and become the reason for the destruction of the planet and humanity.
Works Cited
Bourne, Debra. “Overpopulation.” Companion Animal 20.7 (2015): 373-381. Web. 24 Apr. 2016.
Coallier, Julien. Overpopulation Revisited a Global Perspective . Hillsborough: Lulu, 2015. Print.
Pettorelli, Nathalie. “Climate Change as a Main Driver of Ecological Research.” Journal of Applied Ecology 49.3 (2012): 542-545. Web. 24 Apr. 2016.
Cite this paper
- Chicago (N-B)
- Chicago (A-D)
StudyCorgi. (2020, January 13). The Effects of Overpopulation. https://studycorgi.com/the-effects-of-overpopulation/
"The Effects of Overpopulation." StudyCorgi , 13 Jan. 2020, studycorgi.com/the-effects-of-overpopulation/.
StudyCorgi . (2020) 'The Effects of Overpopulation'. 13 January.
1. StudyCorgi . "The Effects of Overpopulation." January 13, 2020. https://studycorgi.com/the-effects-of-overpopulation/.
Bibliography
StudyCorgi . "The Effects of Overpopulation." January 13, 2020. https://studycorgi.com/the-effects-of-overpopulation/.
StudyCorgi . 2020. "The Effects of Overpopulation." January 13, 2020. https://studycorgi.com/the-effects-of-overpopulation/.
This paper, “The Effects of Overpopulation”, was written and voluntary submitted to our free essay database by a straight-A student. Please ensure you properly reference the paper if you're using it to write your assignment.
Before publication, the StudyCorgi editorial team proofread and checked the paper to make sure it meets the highest standards in terms of grammar, punctuation, style, fact accuracy, copyright issues, and inclusive language. Last updated: November 10, 2023 .
If you are the author of this paper and no longer wish to have it published on StudyCorgi, request the removal . Please use the “ Donate your paper ” form to submit an essay.
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Human Overpopulation: Causes and Effects in Developing Countries

This research paper outlines the causes and effects of human overpopulation, focusing in developing countries. The primary cause of this problems includes low mortality rates coupled with high birth rates. The exponential influx in human overpopulation has had negative effects on both the economic stability and environment of the affected countries. In addition to the causes and effects discussed, potential solutions are proposed to assist in the mitigation of the problem.
Related Papers
Ritu Mahendru
Egyptian STEM schools
Mina Eskandar
Over-population is a great Problem for many countries. This research looks into all possible solutions for this problem. World population has jumped from about 2.5 billion in 1951 to 7.8 billion in April 2020 , 212% increase. Over-population has been an issue for many countries especially in Africa, as Africa has the highest fertility rate ,children per woman, and Africans are low on resources especially for those who live in the middle of Africa ,in other words, near the equator, Because of its hot weather and being low on water, it is optimum environment for spreading diseases and droughts which its direct relation to overpopulation was later discovered resulting in lack of resources and slowness of economy development. Human Resources management has important terminology which need to be understood before getting into our main topic: fertility rate is the average children per woman, birth rate is the average number of children born per year and death rate is the number of deaths per year, natural change is the birth rate minus the death rate . Social Scientists have many theories on what causes over-population, Some suggest that poverty is the main cause of over-population as it is seen in most poor countries like in Africa unlike rich countries in Europe. They suggest that families try to overcome their poor condition by having more children. But other scientists argue that it can be correlation and something else is causing both of them. They suggest that it is a high death rates. Also, through comparing between poor Countries and rich Countries, it can be notice that in poor countries, death rates are high as of that most families give birth to many children. There are other suggested causes like lack of education and child labor. Over-population can cause many serious problems especially for poor countries. For example, It can cause lack of water in developing countries because as the population grow, water consumption increases. For countries that do not have a fresh stable water source, This can lead to droughts and lower life expectancy. Also, population growth could cause Extinction of wild life and pollution because forests and natural environments for various animals are cut down to free more space for buildings and cities. green house effect was learned in (CH.2.11) about and learned In (ES.2.10) about the role of plants in stabilizing the carbon dioxide percentage and the role of forest in keeping biodiversity in (BI.2.12). For These reasons, Countries tried to solve this issue, because of its significant impact on the economy and the productivity. Some of these solutions were the “one-child-policy” and “two-child-policy” tried by China to control population growth using the law. The Results of them were very fast. Other places tried to control over-population by focusing on education especially for girls like in Europe in the 19 th century. To conclude, This research will focus on these prior solutions and others and discuss why they work.
International Journal of Science, Technology and Society
Casmir Onyeneke
Overpopulation is an immensely dangerous problem that does not affect only individual countries but worldwide. It has many causes such as immigration; early marriages, poor medical access, and education are the main reasons to be indicated. While it has many reasons why the earth faces overcrowded, overpopulation's effects are considered a perilous crisis more than itself. In the past, researchers have explored how to stop this rising problem even though; they have tried several ways from mass sterilization to awarding families with no child. None of these approaches worked instead, people tend to have more children and take this dangerous risk. Therefore, depletion of natural resources, rise in pollution, epidemics, and other diseases are the main consequences of overpopulation which this literature review has discussed. Even though scientists and nature activists have argued about the effects of overcrowding on the earth, humankind, and health, there is no right solution taken by us: humans as a creator of this crisis. Furthermore, this research will concentrate on the possible effects of overpopulation on the earth, health, and human kind. Plus, it suggests some possible solutions. Significantly, it illustrates how overpopulation will impact natural resources and human health.
Sandu Szilveszter
The purpose of this paper is to shed light on the overpopulation issue of India and propose recommendations on how to overcome it. First, the paper summarizes the crucial demographic conditions and where India stands by numbers. Then the article presents the development of the state approach to the issue starting from the early years of independence up to the current policies. It does so by scrutinizing its cultural, economic and social factors and implications of overpopulation and identifies socioeconomic backwardness, early marriages and family norms, lack of adequate health care infrastructure and education as the correlated and interdependent features supporting the trend of overpopulation. The authors come up with three recommendations to tackle the issue – women empowerment, education and industrialization.
Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series B: Biological Sciences
Wolfgang Lutz
The 20th century has seen unprecedented growth of the human population on this planet. While at the beginning of the century the Earth had an estimated 1.6 billion inhabitants, this number grew to 6.1 billion by the end of the century, and further significant growth is a near certainty. This paper tries to summarize what factors lie behind this extraordinary expansion of the human population and what population growth we can expect for the future. It discusses the concept of demographic transition and the preconditions for a lasting secular fertility decline. Recent fertility declines in all parts of the world now make it likely that human population growth will come to an end over the course of this century, but in parts of the developing world significant population growth is still to be expected over the coming decades. The slowing of population growth through declining birth rates, together with still increasing life expectancy, will result in a strong ageing of population age s...
Joseph A Heath
Analysis of how to tackle this issue. Written in spring 2016.
Environmental and Resource Economics
john Cleland
Thandolwenkosi Mthembu
Rapid population growth has been a topic of contestation on a socio-economic, statistical and environmental stance. It has proven to be a great cause for concern in much literature with regards to resource scarcity and the earth’s capacity to withstand the impact thereof, it’s hindrance to economic and social development and it’s threat to global political stability. It is important to note that 80 percent of the world’s population is found in low income countries (Hewitt) and in as much as it has been proven that population growth is exponential in these areas, it has not been resolved that one is poor because they have many children. Quite the opposite has been argued of which recent literature on the relationship between population and development has illustrated. When looking specifically at overpopulation in relation to development, there are two standpoints. The first one sees population growth being the barrier to sustainable development efforts as a whole, and much like the Malthusian Theory it urges control over population growth. The other standpoint denounces claims that overpopulation is the cause of social and economic development problems, but says it is a symptom of it. This essay will be looking at both standpoints so as to critically evaluate whether overpopulation really is the principle cause of development problems.
Manjula G. K
Arthur L. Griffith
RELATED PAPERS
Alfredo Gorio
Pakistan Journal of Medical and Health Sciences
Dr Yasha Sajjad
Jurnal IPTA
Drs. I Made Sendra, M.Si.
MARIA GEMA QUINTERO LIMA
Current Psychology
Zeynep Karataş
RESEARCH PAPER
sarita satpathy
History of European Ideas
Sylvana Tomaselli
Proceedings INNODOCT/20. International Conference on Innovation, Documentation and Education
Lúcia Grave Magueta
Romania within the European Union: the Integration Quality Desideratum under the Proactivity Condition
Laurentiu Oprescu
solunumhastaliklari.org
Mehmet Ali OKUR
De Moderne Tijd
Marita Mathijsen
hgjtrgg hjjghyfg
Precambrian Research
Caetano Juliani
Ankit Kumar
Alexandre Fernandes
Marcio Roberto Silva
JURNAL ECONOMINA
Afifah nuryani Nuryani
Applied Psycholinguistics
Marc Sebrechts
E+M Ekonomie a management
Rizwan Raheem Ahmed
Gorgias Press eBooks
Yohai Hakak
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024

Essay on Overpopulation
To guarantee a future for our planet, it’s essential that we strive for sustainability in all of our practices. Whether it is in business, industry, or even the everyday decisions and habits in our lives. We must be vocal and proactive in preserving the earth’s resources and advocating for sustainable practices. One of the major concerns affecting the sustainability of the planet is population. The increase in population is leading to several problems. Therefore, today we will focus on the effects of overpopulation on our planet in detail.
Short and Long Overpopulation Essay in English
Here, we are presenting long and short essays on Overpopulation in English for students under word limits of 100 – 150 Words, 200 – 250 words, and 500 – 600 words. This topic is useful for students of classes 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, and 12 in English. These provided essays on Overpopulation will help you to write effective essays, paragraphs, and speeches on this topic.
Overpopulation Essay 10 Lines (100 – 150 Words)
1) Overpopulation is a very disastrous problem in the world nowadays.
2) It increases pressure on resources such as food, water, shelter, and energy.
3) Overpopulation also contributes to global warming.
4) Overpopulation reduces the quality of life and affects the quality of the environment.
5) Overpopulation affects the education system and causes overcrowding in schools and universities.
6) It limits spaces for individuals to enjoy outdoor activities, such as parks and beaches.
7) Overpopulation leads to increased competition for jobs and wages.
8) It makes it difficult for people to receive healthcare and other essential services.
9) Government runs several policies to control the population.
10) Overpopulation is a major concern that should be controlled as soon as possible.
Short Essay on Overpopulation (250 – 300 Words)
Introduction
Overpopulation is a global issue that affects our lives and will continue to do so until some action is taken. To put it in simple terms, it is a situation where the number of people living in an area is significantly higher than the amount of resources available to them. As population growth continues to spiral and more people are born than die in a given area, overpopulation inevitably increases.
Consequences of Overpopulation
The consequences of overpopulation are far-reaching and deadly. In densely populated cities, finite resources become increasingly scarce as industrialization and urbanization increase. This causes competition over resources and pressure on water, energy, and food supplies. Stressful living conditions only add to the problem as people battle overcrowding in housing as well as in workplaces and public spaces. This struggle to survive can lead to mental and physical health problems, aggression, and crime.
Impact of Overpopulation on the Environment
The environment also suffers greatly under overpopulation. With more people consuming resources and creating waste, there is an increased demand for space, energy, and materials. This often leads to habitat destruction, air and water pollution, and the depletion of natural resources. It is also believed that the human population is partly responsible for climate change as a result of the increase in emissions from transport, agriculture, and industry.
Overpopulation is an urgent, complex, and universal issue that needs to be tackled now to ensure our planet’s future. We must prioritize our wellbeing of us while carefully managing our resources so that no one is disproportionately affected by the consequences of human population growth.
Long Essay on Overpopulation (500 Words)
The global population has increased exponentially over the past century. Overpopulation is a major concern for the world, as it has a wide range of impacts on the environment, economy, health, and more. It is therefore important to understand the various implications of overpopulation and take steps to mitigate them.
Impact of Overpopulation on Global Scale
On a global scale, overpopulation can create large-scale environmental issues. As the number of people on the planet increases, so does the number of resources required to sustain them. This can lead to deforestation as more trees are cut down to provide materials for housing, and increased pollution due to additional waste being created. In addition, it creates the issue of food insecurity as more people are competing for access to limited resources.
Impact of Overpopulation on National Level
On a national level, overpopulation can lead to economic problems. As the population increases, it becomes more difficult to produce enough jobs and create enough income opportunities to support everyone. This in turn can lead to higher unemployment, higher taxes, and poorer living standards. In addition, due to population pressure, public services such as healthcare, transportation, and education can suffer from underinvestment, leading to poorer quality and inaccessibility for those who need it the most.
Impact of Overpopulation on Personal Level
On a personal level, being part of an overpopulated society can have many negative impacts. Crowding can lead to greater stress due to reduced personal space, more noise and air pollution, and decreased access to recreational areas. In addition, it can lead to greater competition for resources such as food and housing, resulting in rising prices and poverty rates.
Solutions for Overpopulation
While overpopulation has serious implications for our planet, there are steps we can take to mitigate this issue. Governments can implement and promote family planning programs to help families have better access to modern contraception and reproductive health care. In addition, comprehensive sex education can be used to promote responsible and informed decision-making on the part of individuals. On an environmental level, we can take steps to reduce our consumption of resources, adopt cleaner energy sources, and implement programs that promote environmental protection.
Overpopulation in India
India is one of the most populous countries in the world, with a population of more than 140 crore people. The country is struggling to meet the needs of its rapidly growing population. Overpopulation is an issue that India needs to address urgently. This can be done through education and better access to family planning services. Awareness campaigns need to be conducted to educate people about the consequences of overpopulation. Furthermore, the government needs to provide incentives for family planning and reproductive health care needs to be made accessible to everyone.
Overpopulation is a global issue with a wide range of societal and environmental implications. It is therefore important to understand the various impacts of overpopulation and to take steps to reduce, mitigate, and address them. With the proper solutions in place, it is possible to ensure that our planet can sustain its population in a way that is healthy and beneficial to all.
I hope the above-provided essay on overpopulation will be helpful for everyone to know the impact of the increasing population on our planet.
FAQs: Frequently Asked Questions on Overpopulation
Ans. The primary causes of overpopulation in India are declining death rates, increased life expectancy, and deep-seated cultural and religious values that favor high birth rates. Additionally, poverty and a lack of education and access to family planning methods also contribute to overpopulation.
Ans. The long-term effects of overpopulation in India are a decrease in the quality of life due to increased shortages of healthcare, food, clean water, and jobs and an increased risk of environmental damage and resource depletion.
Ans. In 2023, China is considered the most populous country in the world.
Ans. Vatican City is the least populated country in the world in 2023.
Ans. In 2023, the population of India counts to 1,380,004,385.
Related Posts
Essay on digital india, cashless india essay, essay on child is father of the man, essay on causes, effects and prevention of corona virus, essay on dr. sarvepalli radhakrishnan, durga puja essay, essay on summer vacation, essay on my plans for summer vacation, essay on holiday.
Impacts of Overpopulation on the Environment Application Essay
- To find inspiration for your paper and overcome writer’s block
- As a source of information (ensure proper referencing)
- As a template for you assignment
Introduction
Major impacts on the environment resulting from overpopulation, works cited.
Overpopulation may be described as a situation where a habitat holds a larger number of organisms than it should. The human population has been increasing at extreme rates in last few decades with an estimated three births every day (Connor 2006). Overpopulation has continued affecting the environment negatively over these years. Many human activities are not environment friendly and overpopulation does not make the situation any better.
One of the major ways in which overpopulations affects the environment is through water pollution. As many people move to urban areas to seek employment, the amount of sewage waste tends to increase. Such wastes are carelessly disposed off such that they finally find their way into water bodies in their untreated condition.
Some of the main contributors of water pollution are industries and open mines whose waste water contains chemical substances and other materials such as heavy metals which cannot be purified. Overexploitation in oceans through overfishing causes imbalance in the ecosystem of the coastal areas and results to lower populations of fish and other aquatic organisms (Stancheva 2003).
Eventually, all these wastes and sediments find their way into the ocean and since the ocean is important in regulating climate, the overall climate is affected which may lead to economical problems. In addition, the ocean helps to prevent global warming through absorption of some percentage of the carbon dioxide released into the atmosphere by human activities. Destruction of the ocean through overexploitation, therefore, limits this function.
Besides polluting the water, there is also the problem of overconsumption which limits the supply of this precious commodity. Lack of adequate water also affects the environment since water is essential in maintaining a balanced ecosystem through its use by plants and animals (Vinelli 2003).
Degradation of soil is another major impact of overpopulation. As the population increases, so does the demand for food production to cater for the growing population. This then leads to exploitation of lands that are not suitable for cultivation such as hilly areas and hilly lands whose cultivation leads to erosion and consequent loss of nutrients.
This need for more land for cultivation leads to certain agricultural practices that are not environment friendly such as slash-and-burn cultivation which lead to deforestation. Similarly, overpopulation calls for higher energy production. This leads to exploitation of wood for fuel production and hence resulting to deforestation.
Other primary causes of deforestation are construction of roads and residential houses to cater for the increasing population. The general impact of all the effects mentioned above is the decrease in biodiversity (Fears 2009). As the natural habitats are destroyed, many wildlife species have been displaced and many died due to changes in the environment resulting from pressure due to human overexploitation of the environment.
All of these issues indicate that the natural resources that humans ignore and misuse are of great importance to them. Some of these impacts on the environment resulting from human overexploitation of natural resources may be permanent or last for long periods of time (Nahle 2003).
If these trends continue, the environmental conditions will intensify since it is no doubt that the human population will continue increasing in the recent past. Sustainable approaches should, therefore, be taken to conserve the natural resources in order to counteract these adverse impacts
Connor, S. “ Overpopulation ‘is main threat to planet’ ”. 2006. Web.
Fears, N. “The effect of overpopulation on the environment and our sustainability”. 2009. Web.
Nahle, N. “Current effects of overpopulation”. 2003. Web.
Stancheva, T. “ Effects of overpopulation on the environment ”, 2003.Web.
Vinelli, G. “Environmental effects of population”. 2003. Web.
- Overpopulation Effects on the Environment
- Overpopulation Benefits
- The Problem of Overpopulation
- Solar growth in USA
- Environmental Controversy: Population Growth and Soil Fertility
- Energy Conservation
- Essay on Bhopal – The Gas Leak Tragedy
- The Climatic Condition of San Francisco and Key West
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2018, October 10). Impacts of Overpopulation on the Environment. https://ivypanda.com/essays/impacts-of-overpopulation-on-the-environment/
"Impacts of Overpopulation on the Environment." IvyPanda , 10 Oct. 2018, ivypanda.com/essays/impacts-of-overpopulation-on-the-environment/.
IvyPanda . (2018) 'Impacts of Overpopulation on the Environment'. 10 October.
IvyPanda . 2018. "Impacts of Overpopulation on the Environment." October 10, 2018. https://ivypanda.com/essays/impacts-of-overpopulation-on-the-environment/.
1. IvyPanda . "Impacts of Overpopulation on the Environment." October 10, 2018. https://ivypanda.com/essays/impacts-of-overpopulation-on-the-environment/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Impacts of Overpopulation on the Environment." October 10, 2018. https://ivypanda.com/essays/impacts-of-overpopulation-on-the-environment/.

Overpopulation in World Essay in English for Children and Students

Table of Contents
Overpopulation refers to a situation where the number of humans in a particular place becomes more than the carrying capacity of that particular place. In a broader perspective the term overpopulation is also used for planet earth, because of the incessant rise in human population.
Fill Out the Form for Expert Academic Guidance!
Please indicate your interest Live Classes Books Test Series Self Learning
Verify OTP Code (required)
I agree to the terms and conditions and privacy policy .
Fill complete details
Target Exam ---
There are various factors responsible for overpopulation like – low mortality rate; better public amenities; availability of food and habitat etc. A few social factors like illiteracy, poverty and no family planning are also responsible for overpopulation in developing or underdeveloped nations.
Long and Short Essay on Overpopulation in World in English
Below we have provided long and short essay on overpopulation in world. These overpopulation in world essay have been written in simple language covering all the vital topics under the heading overpopulation.
After going through the following essays you will know the causes of overpopulation in world; causes of overpopulation in India and other developing countries; what are the social effects of overpopulation; effects of overpopulation on health; what are the solutions of overpopulation etc.
Short Essay on Overpopulation in World (200 words) – Essay 1
Overpopulation is the overcrowding of earth due to unregulated population growth of humans. There are many economical and social factors leading to overpopulation. It could result from low mortality rate, high birth rate, illiteracy, lack of family planning, large scale migration etc. Also, depletion of natural resources at one place results in overpopulation at some other place, where the resources are abundant.
An improvement in the past century in basic healthcare facilities and amenities has led to a decline in mortality rate, thus causing the population to grow consistently and is set to continue growing in to the next century.
Overpopulation, despite being a significant global issue, doesn’t get its due consideration. Still not much is being done by the world, to regulate population or to counter its effects. Overpopulation can serious hamper the growth of a nation, causing issues like – unemployment, scarcity of resources, habitat destruction and law and order problems among others.
Necessary steps must be taken to keep the world population under control, so that no place on earth gets overcrowded with humans and become scarce in vital resources, making survival difficult. Along with the mentioned effects, overpopulation also indirectly affects the environment up to large extent.

Essay on Causes of Overpopulation in World (300 words) – Essay 2
Introduction
Overpopulation is the growing cause of concern throughout the world. It refers to an increase in population over a specific area, so much so, that the particular area becomes overcrowded, beyond its natural capacity. There are many reasons for overpopulation will we will discuss further in the essay.
Causes of Overpopulation in World
There could be various factors causing overpopulation in the world. Large scale immigration of people from one place to another because of political, communal or other issues may cause overpopulation at a particular place. People migrate to neighboring country to escape political upheaval or military conflicts on their own soil.
There is also a trend of migration from underdeveloped or developing countries to the developed nations. Mostly, labour class undertakes such migration in search of better financial opportunities. This migration however causes the population of the host nation to swell up.
Another significant factor that has been contributing to the population growth in the world is high life expectancy due to better medical facilities and development in medical science. People, today are dying less due to diseases, those had been claimed millions of lives in the past century.
Causes of Overpopulation in India and other Developing Countries
The main causes for overpopulation in India and other similar developing countries differ slightly from that of the world. Overpopulation in India is caused by factors like poverty, ignorance, lack of family planning, child labour, and reduced mortality rate, interstate immigration etc.
Poverty in India is considered to be one of the prime causes of overpopulation. Poverty leads to illiteracy and lack of awareness on issues like – contraceptive use and family planning; this, leading to a uncontrolled population growth in deprived areas.
The cause of overpopulation in the world is many and they differ from place to place. At one place migration might causing it, at another place it might have been caused due to poverty. Whatever the cause may be, we must take necessary steps to reduce overpopulation.
Essay on Effects of Overpopulation in World (400 words) – Essay 3
There are many effects of overpopulation in the world. Overpopulation in a place causes scarcity of available resources leading to deprivation and poverty. Moreover, it also causes unemployment, as the number of persons in need of a particular job, large outgrows the total number of actual vacancies. Two of the most common effects of overpopulation- social and health are discussed below.
Effects of Overpopulation in World
- Social Effects of Overpopulation
There are a variety of social effects of overpopulation, ranging from, poverty, unemployment, poor hygienic conditions and a scarcity of resources for a community. When the population of a particular area rises beyond the destined capacity of that place, then a number of changes in the society are witnessed.
For example, if a fresh water resource is used by more people than it can sustain; then such situation often results in conflicts. People tend to fight with each other over the use of resources.
Overpopulation also leads to scarcity of food and unemployment, causing large scale poverty, hunger and poor hygiene.
- Effects of Overpopulation on Health
Overpopulation also has an adverse effect on health of an individual, due to scarcity of food and other resources. The food and other resources, those had been available in abundance, become scarce, when the population of a place grows beyond a specific limit. Moreover, overpopulation is directly related to unemployment and latter could be directly associated to malnutrition and depleting health conditions.
Many people living in a crowded area also results in habitat destruction, reducing the quality of air and other vital parameters, resulting in poor health condition. As more people start living in an area, it becomes imperative to cut down trees and clear vegetation to make houses for them. Thus, begins the vicious cycle of materialistic growth compromising the health and fitness of humans.
People residing in populated areas are often seen living in poor health and hygienic conditions with no access to basic health amenities, clean air and clean water.
Overpopulation in area causes evident social and health effects on the individuals and the society as a whole. From poor health and hygiene conditions to natural resource depletion, unemployment and increase in criminal activities – overpopulation has a hand in all these adversities. It therefore becomes important that we take necessary remedial measures before the populations goes beyond the specified limit.
Essay on Solutions of Overpopulation in World (500 words) – Essay 4
The problem of overpopulation is grave, but as every problem has a solution, so overpopulation too has solutions; though, it may take some time before the results are evident, but the effort would be worth it. Below, the solutions for overpopulation in the world, India and other developing countries along with the government’s efforts in reducing overpopulation are discussed below.
Solutions of Overpopulation in World
Solutions to eliminate overpopulation in the world are discussed below. For the convenience of understanding, in this heading we will discuss the matter of overpopulation only in developed countries.
The main reason behind the concentration of population over a particular area in developed countries is the availability of resources and better growth opportunities. People tend to concentrate over the place where irrigation, water, electricity and other amenities are available in abundance. Necessary efforts must be made by the respective government to make the basic public amenities to the people in their native place of residence.
Any political or military conflict must be resolved quickly by the intervention of world community to prevent cross border migration and population complications at other places.
Solution of Overpopulation in India and other Developing Countries
The main causes of overpopulation in India and other countries are poverty, illiteracy and lack of basic knowledge about family planning. Majority of population in India and other developing nations, still reside in villages, where they lack basic education and other facilities than the cities.
People residing in villages still shy from talking on issues like family planning and use of contraceptives is considered a taboo. Therefore, awareness through education seems to be the only appropriate solution for a developing country like India.
People must be told about the significance of family planning and that shying away from it will only aggravate their financial crisis and reduce their social status. It is indeed more economical and practical to feed a family of four than a family of six or ten members. Also, they must be insisted to use contraceptives and that it is necessary for their family’s welfare and overall health.
What is Government doing about Overpopulation?
The government’s agenda to eliminate overpopulation include acting up on the root causes – education and health care. Despite making a number of reforms in these two sectors, the government is also making efforts to make people aware of family planning. A well trained team of doctors and paramedical staff in the primary health centers across the country are educating people about the advantages of a small family and its overall effects on the nation’s growth.
They also teach people about the use of contraceptives to eliminate the possibility of conception. The government is also distributing free contraceptives to remote locations through the PHCs.
The most important solutions to overpopulation are education and awareness of people. The more educated and aware the people are, the more remote will be the possibility of overpopulation. The government has made considerable effort towards keeping the population under control but a lot more still needed to be done.

Long Essay on Overpopulation in World (600 words) – Essay 5
Overpopulation in the world is a global phenomenon and is more evident in developing and underdeveloped countries. Even the developed countries witness a large influx of migratory population from the developing and under developed countries. In the following essay we will discuss on the causes of overpopulation, the problems of overpopulation, state of overpopulation in India and other developing countries and the solution of overpopulation.
What Causes Overpopulation?
1) Illiteracy
Illiteracy is one of the main causes of overpopulation in any country over the world. The countries lacking on the front of education have more population growth than others.
2) Lack of Awareness
Lack of public awareness about family planning issues is one of the prime reasons for overpopulation. People are not aware of the effects of overpopulation and its effects on the society and nation. The act is in disregard to their own financial constraints.
3) Poor Health Facilities
Poor condition of basic health amenities is also a prime cause of overpopulation. Absence of a medical professional and non availability of contraceptives, leads to incessant growth in population.
Problems related to the Overpopulation
1) Resources Depletion
Overpopulation causes the depletion of resources over a particular area. As the number of people using a specific resource increases, its fast consumption results in rapid depletion. Vital resource like food and water become scarce in case of overpopulation. Even the basic health and transport facilities become rare.
2) Unemployment
Unemployment is one of the most severe consequences of overpopulation. If the number of people in an area increases beyond limit; however, the number of vacancies in different sectors, by and large remain the same, thereby increasing unemployment. Thus, unemployment becomes a significant ill effect of overpopulation.
Poverty is the next consequence of unemployment caused by overpopulation. However, poverty is also related to scarcity resources and basic amenities of health and education, caused by overpopulation. A crowded place will always have poor employment opportunities, leading to poverty. It is considered as one of the most prominent consequences of population explosion, by the economists of the world.
4) Poor Law and Order
Factors like poverty, unemployment, depletion of natural resources result in poor law and order condition. People fight with each other over vital resources like water and food. Unemployment leads to poverty forcing people to take up illegal professions of robbery and theft, to meet their requirements.
Overpopulation in India and other Developing Countries
Overpopulation in India and similar developing countries is a great cause of concern, as it has many adverse effects on the nation’s progress and growth. All the development loses its sheen due to overpopulation. The state of public transport system and other basic amenities degrades quickly due to large number of people using them.
Overpopulation Solutions
Making the people aware of the ill effects of overpopulation is the most significant method to eliminate the latter. This awareness must be brought by education and advertising through different modes of communication. When people understand that the quality of life depends on the total number of family members, and the lesser the members the more good the finances will be; the fight against overpopulation will become much easier.
Overpopulation leads to various social, economical and developmental issues. It is therefore imperative that the world comes together on the issue of overpopulation and take necessary steps towards eliminating it. Unless the population of the world is kept under control, it would not be possible to achieve the development that the world seeks.
More Information:
- Essay on World Population Day
- Essay on Population
- Essay on Population Growth
- Essay on Family Planning in India
- Paragraph on Population
Related content
Talk to our academic expert!
Language --- English Hindi Marathi Tamil Telugu Malayalam
Get access to free Mock Test and Master Class
Register to Get Free Mock Test and Study Material
Offer Ends in 5:00
Overpopulation Reconsidered: A Decentralized Approach
Overpopulation has been a concern for a long time, sparking debates about humanity’s future, resource scarcity, and environmental degradation. The temptation to resort to centralized control measures is significant. However, a closer examination reveals two major problems with such an approach.
The ethical problem
The violation of individual rights is the first issue. As Murray Rothbard explains in ‘The Ethics Of Liberty,’ individuals have an inherent right to own themselves and their property. Any violation of this right is unethical and unjust. Therefore, no entity, be it an individual or an organization, should have the authority to claim ownership over the entire human population and dictate its size.
We’ve seen the devastating effects of ignoring this ethical principle throughout history, with authoritarian regimes implementing harsh measures in the name of population control. These actions have led to violations of individual rights and immense human suffering, including forced sterilizations and coercive family planning policies.
The knowledge problem
Consider the story of “The Population Bomb,” a book published in 1968 that predicted dire consequences if population growth was not immediately curbed. However, the book’s predictions failed to materialize, largely because they did not account for the innovation and entrepreneurial solutions that humans can generate. This failure underscores the inadequacy of centralized power in addressing the complexities of population dynamics.
This brings us to the second problem, as Friedrich Hayek explained in his renowned essay ‘The use of knowledge in society’. In this essay he highlights the challenge of centralized planning due to the dispersed nature of information in society. He argues that central authorities lack the necessary knowledge to make optimal decisions for everyone. Instead, decentralized decision-making and the price mechanism can allocate resources more efficiently based on individuals’ localized knowledge and preferences. This emphasizes the superiority of market-based solutions over top-down planning in addressing societal challenges.
But is deciding the human population’s size an economic issue? Do Hayek’s insights apply to this? Contrary to what many might assume, economics is not just about money or financial transactions; it encompasses the study of human action in the face of scarcity. Population decisions involve individuals and families making choices about resource allocation, consumption patterns, and future planning. These decisions have profound economic implications, as they determine labor supply, demand for goods and services, and the distribution of wealth and resources within a society. Population dynamics not only influence productivity, innovation, and economic growth over time but also serve as catalysts for entrepreneurial action, constantly creating new information and solutions. As individuals and families navigate decisions regarding resource allocation, consumption patterns, and future planning, they engage in entrepreneurial endeavors that address emerging challenges, including environmental concerns. Understanding how these decisions are made within the framework of decentralized knowledge and market signals is crucial for comprehending the broader economic landscape. Entrepreneurial solutions play a pivotal role in this process, driving adaptation and innovation in response to changing population dynamics and market demands.
That’s why while interventionism may not seem to be tyrannical and terrifying, it causes problems by distorting market signals and blocking essential information and can lead to harmful results. For example, in the case of population, subsidies and social programs artificially cushion individuals from the true costs of their decisions, which makes it impossible to calculate the price of having children and all possible alternatives, disrupting the natural feedback mechanisms of the market. This distortion prevents the market from effectively coordinating human action, leading to the potential for both overpopulation and underpopulation.
But it doesn’t end there; intervention-induced distortion triggers a relentless cycle of population issues and governmental meddling. China serves as a poignant example of this cycle, where the one-child policy initially aimed at controlling population growth led to unintended consequences, including a rapidly aging population and negative population growth. And now their solution to this new problem that was created by intervention is more intervention, without considering the possibility that the new interventions could lead to new unintended consequences.
The tale of “The Population Bomb” and other similar failed predictions demonstrate that no centralized power possesses the necessary knowledge to determine the optimal size of the human population.
In conclusion, the debate surrounding overpopulation underscores the need for a reevaluation of centralized approaches in favor of decentralized solutions rooted in individual freedom and market principles. By rejecting top-down interventions that infringe on individual rights and fail to address the complexities of population dynamics, we pave the way for a more ethical and effective approach to managing population challenges.
Entrepreneurial action, driven by decentralized knowledge and market signals, plays a crucial role in addressing not only population concerns but also broader societal issues, including environmental sustainability. By empowering individuals to make decisions for themselves, we foster innovation, adaptation, and resilience in the face of evolving demographic trends.
As we navigate the complexities of population growth, let us embrace the principles of liberty and free enterprise, recognizing that true progress lies in the hands of individuals, not centralized authorities. By doing so, we can forge a path toward a future where human dignity and prosperity are preserved for generations to come.
The Mises Institute is a non-profit organization that exists to promote teaching and research in the Austrian School of economics, individual freedom, honest history, and international peace, in the tradition of Ludwig von Mises and Murray N. Rothbard.
Non-political, non-partisan, and non-PC, we advocate a radical shift in the intellectual climate, away from statism and toward a private property order. We believe that our foundational ideas are of permanent value, and oppose all efforts at compromise, sellout, and amalgamation of these ideas with fashionable political, cultural, and social doctrines inimical to their spirit.
Helping Christians think about the myth of overpopulation

Research Fellow
November 17, 2022
Recently, viewers were given a new season of “The Crown,” the Netflix series that chronicles the life of Queen Elizabeth. In the wake of her death earlier this year, the season is all the more interesting because of the new monarch who sits on the throne, her son, King Charles III. Charles is being dubbed the “ climate king .” His concern for the environment has led to controversial mentions of overpopulation in the past. But, where does this idea come from, and how should Christians think about it?
The myth of overpopulation
In 1968, Stanford entomologist Paul Ehrlich published The Population Bomb , warning that the earth was overpopulated and that millions of people would starve to death. His doomsday warning did not come true. Starvation has occurred on much smaller scales, due largely to government mismanagement and corruption, not overpopulation.
Yet the myth of overpopulation persists. Ecologist Emma Olliff of the U.K.-based group Population Matters recently said , “More of us is only going to make (the environment) worse. This kind of reasoning was famously cited by Prince Harry and Meghan Markle, who are choosing to have only two children because of global overpopulation.
At the 2020 World Economic Forum in Davos, famed primatologist Dr. Jane Goodall said that human population growth is responsible for most environmental problems. Goodall stated, “All these (environmental) things we talk about wouldn’t be a problem if there was the size of the population that there was 500 years ago.” Apparently, Goodall pines for the good ol’ days when the average life expectancy was around 40 years of age and infant mortality was around 20%.
Human life is not the problem, and human death is not the solution. Since the publication of The Population Bomb , several books have debunked the myth of overpopulation, including The Myth of Over-Population (1969) R.J. Rushdoony, Fewer (2004) by Ben Wattenberg, and Population Control (2008) by Steven Mosher. Governments in Japan, Finland, Italy, and Australia (to name a few) are now paying people to have babies.
Currently, no European country has a population replacement rate of 2.1 babies per woman. Globally, many countries are below the replacement rate , including China (1.7), Brazil (1.7), Canada (1.5), Puerto Rico (1.1), Thailand (1.5), and Chile (1.7).
In 1968, the fear was global starvation. In 2020, humans wasted an estimated 1.6 billion tons of food at a cost of $1.2 trillion dollars annually. In 1968 the fear was overpopulation. In 2020, under-populated towns and cities paid people to move there.
Dangers of the myth
Overpopulation is an old myth. Catastrophic predictions about human population and food shortage go back (at least) to 19th-century Anglican pastor and economist Thomas Robert Malthus. In his book An Essay on the Principle of Population, Malthus argued that human population would outpace food production. Malthus advocated preventative measures such as family planning, late marriages, and celibacy.
Global overpopulation is not only a myth; it is a dangerous myth. Bernie Sanders said that abortion is an important way of addressing global overpopulation. National Public Radio (NPR) has even reported on the research of journalist Mei Fong, who in her book One Child (2016), estimated that China’s one-child policy led to 30 million forced abortions.
In popular culture, Thanos (of the Marvel Universe) channels his inner Malthus in 2018’s “Avengers: Infinity War,” saying, “The universe is finite, its resources finite, if life is left unchecked, life will cease to exist.” This is the same faulty logic (and bad theology) peddled by Malthus, Ehrlich, Goodall, and Sanders. Unlike in the Marvel Universe, the “bad guys” aren’t always so easy to spot.
A Christian response
God created marriage between a man and a woman, commanded human procreation, and placed the family as the primary building block of human flourishing in a world that he equipped to accommodate human growth (Gen 1:26-28). He did this, in part, by creating humans with a capacity to solve problems using science and technology. As global population has grown, standards of living and life expectancy have increased while infant mortality and extreme poverty have decreased. Human population growth is not the problem.
There are a variety of possible ways that Christians can respond to the myth of overpopulation. First, Christians do best when telling the true biblical story of creation, fall, redemption, and restoration. Christians can place the growth of population into the storyline of Scripture where it is a good thing, not a problem to be corrected. It is part of God’s command to fill the earth and steward it.
Second, local churches can promote and support healthy and normative patterns of human flourishing by offering biblical counseling and parenting services, supporting pregnancy resource centers and adoption and foster care ministries, and by welcoming children and those with special needs into the worship service. In so doing, they evidence that the family is essential to God’s plan for flourishing and the Church has a vested interest in helping strengthen this building block of society.
Third, Christians cannot allow the sin of materialism to go unchecked. That amounts to aiding and abetting the enemy. Human population growth is only a problem if one accepts the lie that joy, identity, and comfort are found in unchecked consumption and material possessions. There is nothing inherently wrong with living in a large home, owning recreational vehicles, retiring early, or sending your kids to the best schools. However, such things are not the biblical picture of success or an indication of God’s favor and blessing. Christians are to be those who steward the created world, not those who intentionally put off God-ordained gifts because they are controlled by the things of this world.
Conclusion
Ideas have consequences. Most tragically, the idea of overpopulation has resulted in global mass murder, including calls for expanding abortion access in developing nations where population growth is higher. It is a myth that continues to be used to justify both abortion and suicide. Christians who believe in the sanctity and goodness of human life should expose the myth of overpopulation for what it often is: A pretext for murder and justification for opposing a biblical view of children,family, and procreation.
Related Content

Hope for Our Neighbor
When Eric Costanzo was first installed as pastor at South Tulsa Baptist Church in...

Hope in cooperation
As the pro-life movement adapts to a post-Roe America, many are finding more attention...

Gospel hope on a politically charged college campus
When Elizabeth graduated from a small Baptist college and began pursuing her master’s degree...

Explainer: 5 additional federal regulations the ERLC is pushing back against
Over the past month, the Biden administration has finalized numerous problematic rules that undermine...

Explainer: USCIRF releases 2024 religious freedom report and observes 25th anniversary of IRFA
On May 1, 2024, the United States Commission on International Religious Freedom (USCIRF) released...

Ethical and Theological Considerations on IVF from the Southern Baptist Convention
1. What do Southern Baptists believe about life, marriage, and family? Scripture clearly speaks...
Understanding the Side Effects of Birth Control: a Comprehensive Overview
This essay is about the side effects of birth control and how they impact users. It explains the various side effects associated with hormonal methods like pills, patches, injections, and IUDs, such as nausea, weight gain, mood swings, and the risk of blood clots. The essay also covers non-hormonal methods like copper IUDs, condoms, and diaphragms, noting potential issues like heavier menstrual bleeding and allergic reactions. It highlights the importance of personalized medical advice and careful consideration of individual health histories when choosing a birth control method. The essay emphasizes that while side effects exist, many people use birth control without significant problems.
How it works
Contraception, also referred to as birth control, has transformed the landscape of reproductive health, empowering individuals to exert greater autonomy over their fertility and family planning endeavors. Nevertheless, akin to any pharmaceutical intervention, birth control methodologies harbor potential side effects. It is imperative to comprehend these conceivable repercussions to facilitate judicious decision-making regarding contraceptive utilization. This discourse furnishes an exposition on the side effects associated with diverse birth control modalities, accentuating the indispensability of tailored medical counsel.
Hormonal contraceptive modalities, encompassing pills, patches, injections, and intrauterine devices (IUDs), rank amongst the preeminent contraceptive methodologies.
These modalities operate by modulating the body’s hormonal milieu to thwart ovulation. Despite their efficacy, they engender an array of side effects. For instance, many women encounter manifestations such as nausea, breast tenderness, and headaches upon commencement of hormonal contraceptive pill regimens. These manifestations typically ameliorate subsequent to several months as the body acclimates. However, certain individuals may manifest more pronounced reactions, such as mood fluctuations, weight gain, and diminished libido, which can markedly impinge upon their quality of life.
The birth control patch and injection entail commensurate side effects to the pill, albeit their administration modalities can exacerbate specific issues. The patch, for instance, can precipitate cutaneous irritation at the site of application. The injection, administered tri-monthly, has been correlated with weight gain and osteoporosis with protracted usage. It is imperative for individuals contemplating these alternatives to engage in comprehensive discussions regarding their medical history and lifestyle preferences with a healthcare professional to discern the optimal modality.
Non-hormonal birth control modalities, inclusive of copper IUDs, condoms, and diaphragms, proffer alternatives for individuals either contraindicated or disinclined to employ hormonal contraception. Copper IUDs, notwithstanding their efficacy, may incite augmented menstrual hemorrhage and intensified cramping, particularly in the initial months post-insertion. Condoms and diaphragms lack systemic side effects but can elicit allergic reactions or irritation in select users. Additionally, their efficacy is contingent upon meticulous adherence to correct usage, constituting a caveat for certain individuals.
An eminent concern with hormonal birth control pertains to the heightened propensity for thromboembolic phenomena. Estrogen-containing contraceptives, encompassing combination pills and select patches, can augment the peril of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE). Although the overall incidence is relatively modest, it escalates within specific demographics, such as smokers and women exceeding 35 years of age. Progestin-only modalities, such as the mini-pill or hormonal IUDs, portend a diminished risk of thromboembolic events and may thus represent a safer alternative for those predisposed to risk factors.
An additional pivotal consideration is the ramifications of birth control on mental well-being. Certain users delineate mood fluctuations, depression, or anxiety concomitant with hormonal contraceptives. Inquiry into this realm remains ongoing, and while empirical evidence is disparate, it underscores the exigency for individuals to monitor their mental well-being vigilantly and articulate any concerns to their healthcare provider. Transitioning to an alternative contraceptive modality may sometimes assuage these manifestations.
Prolonged utilization of birth control precipitates queries regarding its repercussions on fertility and overall health. Generally, fertility rebounds to baseline expeditiously following discontinuation of hormonal contraceptives, albeit some individuals may necessitate several months for resumption. Scrutiny concerning cancer susceptibility has also been extensive. Hormonal contraception has evinced a propensity to abate the hazard of ovarian and endometrial cancers whilst marginally amplifying the peril of breast and cervical malignancies. These perils and benefits warrant meticulous consideration and discourse with a healthcare practitioner.
It is imperative to underscore that notwithstanding the possibility of side effects, myriad individuals avail themselves of birth control sans significant complications. The advantages of averting unintended pregnancies and mitigating menstrual-related maladies frequently outweigh the conceivable drawbacks for numerous users. Nevertheless, experiences may vary substantially from individual to individual, accentuating the necessity to approach birth control as an individualized health decision.
In summation, cognizance of birth control side effects constitutes a linchpin in effectuating enlightened decisions regarding contraception. Hormonal and non-hormonal methodologies each harbor distinctive potential side effects, ranging from benign and transient to more grave concerns. Tailored medical counsel is indispensable in navigating these alternatives, ensuring individuals can ascertain the most suitable and efficacious modality commensurate with their requisites. Transparent communication with healthcare providers and sustained abreastment with the latest research can empower individuals to manage and ameliorate side effects, thereby fostering enhanced health outcomes and heightened contentment with their elected mode of birth control.
Kindly bear in mind that this essay serves as a launchpad for further introspection and investigation. For bespoke guidance and adherence to academic conventions, contemplate soliciting the services of professionals at EduBirdie.
Cite this page
Understanding the Side Effects of Birth Control: A Comprehensive Overview. (2024, May 28). Retrieved from https://papersowl.com/examples/understanding-the-side-effects-of-birth-control-a-comprehensive-overview/
"Understanding the Side Effects of Birth Control: A Comprehensive Overview." PapersOwl.com , 28 May 2024, https://papersowl.com/examples/understanding-the-side-effects-of-birth-control-a-comprehensive-overview/
PapersOwl.com. (2024). Understanding the Side Effects of Birth Control: A Comprehensive Overview . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/understanding-the-side-effects-of-birth-control-a-comprehensive-overview/ [Accessed: 3 Jun. 2024]
"Understanding the Side Effects of Birth Control: A Comprehensive Overview." PapersOwl.com, May 28, 2024. Accessed June 3, 2024. https://papersowl.com/examples/understanding-the-side-effects-of-birth-control-a-comprehensive-overview/
"Understanding the Side Effects of Birth Control: A Comprehensive Overview," PapersOwl.com , 28-May-2024. [Online]. Available: https://papersowl.com/examples/understanding-the-side-effects-of-birth-control-a-comprehensive-overview/. [Accessed: 3-Jun-2024]
PapersOwl.com. (2024). Understanding the Side Effects of Birth Control: A Comprehensive Overview . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/understanding-the-side-effects-of-birth-control-a-comprehensive-overview/ [Accessed: 3-Jun-2024]
Don't let plagiarism ruin your grade
Hire a writer to get a unique paper crafted to your needs.

Our writers will help you fix any mistakes and get an A+!
Please check your inbox.
You can order an original essay written according to your instructions.
Trusted by over 1 million students worldwide
1. Tell Us Your Requirements
2. Pick your perfect writer
3. Get Your Paper and Pay
Hi! I'm Amy, your personal assistant!
Don't know where to start? Give me your paper requirements and I connect you to an academic expert.
short deadlines
100% Plagiarism-Free
Certified writers

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Overpopulation is a highly unfavorable condition characterized by the total number of people on Earth exceeding its carrying capacity. Overpopulation is caused by positive changes in people's welfare: better health care, higher life expectancy, reduced rates of mortality, etc. Technological advances improving the quality of life and ...
The overpopulation essay will throw light on this issue. Ill-Effects of Overpopulation. The ill-effects of overpopulation are quite severe. The first one is that natural resources deplete at a faster level. Our planet can produce only a limited amount of water and food. Thus, overpopulation causes environmental damage including deforestation ...
The Causes of Overpopulation. Today the Earth is home to over 8 billion people. By 2100 the population is on track to hit 10.8 billion, according to the United Nations — and that's assuming steady fertility declines in many countries.Interestingly, if extra progress is made in women's reproductive self-determination, and fertility falls more than the United Nations assumes is likely, the ...
Causes of Overpopulation. Although different scholars point to different factors that influence population growth, the core ones remain the same. These factors include the following: Advances in food production and agriculture; Advances in industry and production; Advances in medicine; and. Poor family planning (Barbier 92).
This essay explores the complex issues of overpopulation, analyzing its root causes and significant effects on the environment and society and outlining workable strategies to lessen its effects. Recognizing and treating overpopulation is essential to building a sustainable future for future generations in a world where human footprints are ...
This essay explores the multifaceted aspects of overpopulation, analyzing its causes, effects, and potential solutions through essays of varying lengths. The root of overpopulation can often be traced to factors such as improved healthcare leading to lower mortality rates, high birth rates in certain regions, and migration due to various socio ...
The consequences of overpopulation can be far-reaching and impactful. One significant consequence is economic challenges, including unemployment, poverty, and rising living costs. As populations grow, competition for natural resources and job opportunities can increase, leading to economic instability and inequality. ... This essay has explored ...
Secondly, it is necessary to rethink the life of inmates in prison. The Problem of Overpopulation. The purpose of this paper is to examine the causes and effects of overpopulation, potential threats to society, and the ecosystem, as well as the ways to overcome the problem. The Challenges of Overpopulation: Vertical Cities.
Overconsumption is partly caused by the increasing population in many areas around the world. Larger populations require more food, water, and energy, and consequently tax the earth's ability to replace used resources. Overpopulation depletes wildlife to dangerously low levels. Overfishing has ruined many formerly fertile fishing grounds.
Essay on Overpopulation: Today, there are a total of 8.1 billion people in the world. This is a result of overpopulation and studies suggest that in the next 25 years, this number will reach 10 billion. This is overpopulation or overabundance, where our environment cannot offer resources to such large amounts of people.
The effects of overpopulation are quite severe. The first of these is the depletion of resources. The Earth can only produce a limited amount of water and food, which is falling short of the current needs. Most of the environmental damage seen in the last fifty-odd years is because of the growing number of people on the planet.
Get original essay. Overpopulation is a bothersome condition where the quantity of existing human populace surpasses the conveying limit of Earth. Overpopulation is brought about by a number of elements. Decreased death rate, better medical offices, and exhaustion of valuable resources are many of the causes which results in overpopulation.
The concerns about the consequences of population explosion started in the sixties. Milestone publications were the 1968 book The Population bomb by biologist Paul Ehrlich, the report of the Club of Rome from 1972 (The Limits to Growth) and the first World Population Plan of Action of the UN in 1974 among others.
Overpopulation can lead to overcrowding and poor quality housing in many large cities. Poorly heated or damp housing could cause significant health problems, resulting in illness, such as bronchitis or pneumonia. Another serious consequence of overcrowding is a rising crime rate as poor living conditions may lead young people in particular to ...
The global population is currently rising at a steady rate. The number of humans existing on Earth has never been as high as it is now. In 1800, Earth had approximately 1 billion inhabitants, which rose to 2.3 billion in 1940, then 3.7 billion in 1970, and approximately 7.5 billion today. In the last five decades, Earth has experienced an ...
15 essay samples found. Overpopulation occurs when the number of people living in a certain area exceeds the carrying capacity of the environment. Essays could delve into the causes and effects of overpopulation, its impact on resource scarcity and environmental degradation, or the policies and strategies for managing population growth.
One of the examples is China, which established the principle one child for one family. The objective of the government was to control overpopulation. The average number of children who were born in China from one woman decreased from about 5 to 1 (Coallier 83). Thus, the restriction policy was successful, and the government reached the goal.
This research paper outlines the causes and effects of human overpopulation, focusing in developing countries. The primary cause of this problems includes low mortality rates coupled with high birth rates. The exponential influx in human overpopulation has had negative effects on both the economic stability and environment of the affected ...
Overpopulation will become less likely as society becomes more aware and aware. Despite significant government efforts to control the population, much more needs to be done. Overpopulation Problems Essay . Overpopulation is a widespread problem that is exacerbated in developing and underdeveloped countries.
The world' s population has touched a mark of 7.3 billion in 2015 and could attain growth le vel of 9-12. billion before the year 2050 which suggest that the impact of overpopulation can ...
Overpopulation Essay 10 Lines (100 - 150 Words) 1) Overpopulation is a very disastrous problem in the world nowadays. 2) It increases pressure on resources such as food, water, shelter, and energy. 3) Overpopulation also contributes to global warming. 4) Overpopulation reduces the quality of life and affects the quality of the environment.
Lack of adequate water also affects the environment since water is essential in maintaining a balanced ecosystem through its use by plants and animals (Vinelli 2003). Degradation of soil is another major impact of overpopulation. As the population increases, so does the demand for food production to cater for the growing population.
Essay on Effects of Overpopulation in World (400 words) - Essay 3. Introduction. There are many effects of overpopulation in the world. Overpopulation in a place causes scarcity of available resources leading to deprivation and poverty. Moreover, it also causes unemployment, as the number of persons in need of a particular job, large outgrows ...
In conclusion, the debate surrounding overpopulation underscores the need for a reevaluation of centralized approaches in favor of decentralized solutions rooted in individual freedom and market principles. By rejecting top-down interventions that infringe on individual rights and fail to address the complexities of population dynamics, we pave ...
Overpopulation is an old myth. Catastrophic predictions about human population and food shortage go back (at least) to 19th-century Anglican pastor and economist Thomas Robert Malthus. In his book An Essay on the Principle of Population, Malthus argued that human population would outpace food production. Malthus advocated preventative measures ...
It explains the various side effects associated with hormonal methods like pills, patches, injections, and IUDs, such as nausea, weight gain, mood swings, and the risk of blood clots. The essay also covers non-hormonal methods like copper IUDs, condoms, and diaphragms, noting potential issues like heavier menstrual bleeding and allergic reactions.