Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Methodology
- Types of Variables in Research | Definitions & Examples

Types of Variables in Research | Definitions & Examples
Published on 19 September 2022 by Rebecca Bevans . Revised on 28 November 2022.
In statistical research, a variable is defined as an attribute of an object of study. Choosing which variables to measure is central to good experimental design .
You need to know which types of variables you are working with in order to choose appropriate statistical tests and interpret the results of your study.
You can usually identify the type of variable by asking two questions:
- What type of data does the variable contain?
- What part of the experiment does the variable represent?
Table of contents
Types of data: quantitative vs categorical variables, parts of the experiment: independent vs dependent variables, other common types of variables, frequently asked questions about variables.
Data is a specific measurement of a variable – it is the value you record in your data sheet. Data is generally divided into two categories:
- Quantitative data represents amounts.
- Categorical data represents groupings.
A variable that contains quantitative data is a quantitative variable ; a variable that contains categorical data is a categorical variable . Each of these types of variable can be broken down into further types.
Quantitative variables
When you collect quantitative data, the numbers you record represent real amounts that can be added, subtracted, divided, etc. There are two types of quantitative variables: discrete and continuous .
Categorical variables
Categorical variables represent groupings of some kind. They are sometimes recorded as numbers, but the numbers represent categories rather than actual amounts of things.
There are three types of categorical variables: binary , nominal , and ordinal variables.
*Note that sometimes a variable can work as more than one type! An ordinal variable can also be used as a quantitative variable if the scale is numeric and doesn’t need to be kept as discrete integers. For example, star ratings on product reviews are ordinal (1 to 5 stars), but the average star rating is quantitative.
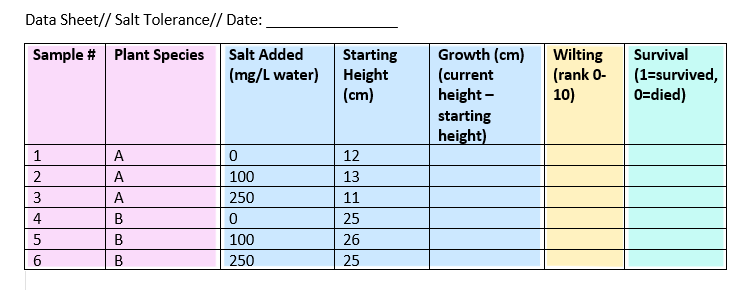
Example data sheet
To keep track of your salt-tolerance experiment, you make a data sheet where you record information about the variables in the experiment, like salt addition and plant health.
To gather information about plant responses over time, you can fill out the same data sheet every few days until the end of the experiment. This example sheet is colour-coded according to the type of variable: nominal , continuous , ordinal , and binary .
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Experiments are usually designed to find out what effect one variable has on another – in our example, the effect of salt addition on plant growth.
You manipulate the independent variable (the one you think might be the cause ) and then measure the dependent variable (the one you think might be the effect ) to find out what this effect might be.
You will probably also have variables that you hold constant ( control variables ) in order to focus on your experimental treatment.
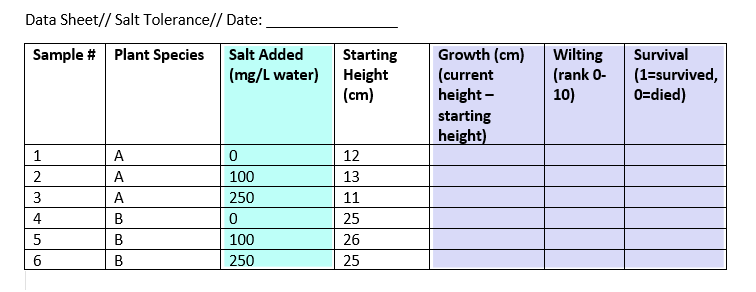
In this experiment, we have one independent and three dependent variables.
The other variables in the sheet can’t be classified as independent or dependent, but they do contain data that you will need in order to interpret your dependent and independent variables.
What about correlational research?
When you do correlational research , the terms ‘dependent’ and ‘independent’ don’t apply, because you are not trying to establish a cause-and-effect relationship.
However, there might be cases where one variable clearly precedes the other (for example, rainfall leads to mud, rather than the other way around). In these cases, you may call the preceding variable (i.e., the rainfall) the predictor variable and the following variable (i.e., the mud) the outcome variable .
Once you have defined your independent and dependent variables and determined whether they are categorical or quantitative, you will be able to choose the correct statistical test .
But there are many other ways of describing variables that help with interpreting your results. Some useful types of variable are listed below.
A confounding variable is closely related to both the independent and dependent variables in a study. An independent variable represents the supposed cause , while the dependent variable is the supposed effect . A confounding variable is a third variable that influences both the independent and dependent variables.
Failing to account for confounding variables can cause you to wrongly estimate the relationship between your independent and dependent variables.
Discrete and continuous variables are two types of quantitative variables :
- Discrete variables represent counts (e.g., the number of objects in a collection).
- Continuous variables represent measurable amounts (e.g., water volume or weight).
You can think of independent and dependent variables in terms of cause and effect: an independent variable is the variable you think is the cause , while a dependent variable is the effect .
In an experiment, you manipulate the independent variable and measure the outcome in the dependent variable. For example, in an experiment about the effect of nutrients on crop growth:
- The independent variable is the amount of nutrients added to the crop field.
- The dependent variable is the biomass of the crops at harvest time.
Defining your variables, and deciding how you will manipulate and measure them, is an important part of experimental design .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
Bevans, R. (2022, November 28). Types of Variables in Research | Definitions & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 3 June 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/research-methods/variables-types/
Is this article helpful?
Rebecca Bevans
Other students also liked, a quick guide to experimental design | 5 steps & examples, quasi-experimental design | definition, types & examples, construct validity | definition, types, & examples.
Independent and Dependent Variables
Saul Mcleod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul Mcleod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
On This Page:
In research, a variable is any characteristic, number, or quantity that can be measured or counted in experimental investigations . One is called the dependent variable, and the other is the independent variable.
In research, the independent variable is manipulated to observe its effect, while the dependent variable is the measured outcome. Essentially, the independent variable is the presumed cause, and the dependent variable is the observed effect.
Variables provide the foundation for examining relationships, drawing conclusions, and making predictions in research studies.
Independent Variable
In psychology, the independent variable is the variable the experimenter manipulates or changes and is assumed to directly affect the dependent variable.
It’s considered the cause or factor that drives change, allowing psychologists to observe how it influences behavior, emotions, or other dependent variables in an experimental setting. Essentially, it’s the presumed cause in cause-and-effect relationships being studied.
For example, allocating participants to drug or placebo conditions (independent variable) to measure any changes in the intensity of their anxiety (dependent variable).
In a well-designed experimental study , the independent variable is the only important difference between the experimental (e.g., treatment) and control (e.g., placebo) groups.
By changing the independent variable and holding other factors constant, psychologists aim to determine if it causes a change in another variable, called the dependent variable.
For example, in a study investigating the effects of sleep on memory, the amount of sleep (e.g., 4 hours, 8 hours, 12 hours) would be the independent variable, as the researcher might manipulate or categorize it to see its impact on memory recall, which would be the dependent variable.
Dependent Variable
In psychology, the dependent variable is the variable being tested and measured in an experiment and is “dependent” on the independent variable.
In psychology, a dependent variable represents the outcome or results and can change based on the manipulations of the independent variable. Essentially, it’s the presumed effect in a cause-and-effect relationship being studied.
An example of a dependent variable is depression symptoms, which depend on the independent variable (type of therapy).
In an experiment, the researcher looks for the possible effect on the dependent variable that might be caused by changing the independent variable.
For instance, in a study examining the effects of a new study technique on exam performance, the technique would be the independent variable (as it is being introduced or manipulated), while the exam scores would be the dependent variable (as they represent the outcome of interest that’s being measured).
Examples in Research Studies
For example, we might change the type of information (e.g., organized or random) given to participants to see how this might affect the amount of information remembered.
In this example, the type of information is the independent variable (because it changes), and the amount of information remembered is the dependent variable (because this is being measured).
For the following hypotheses, name the IV and the DV.
1. Lack of sleep significantly affects learning in 10-year-old boys.
IV……………………………………………………
DV…………………………………………………..
2. Social class has a significant effect on IQ scores.
DV……………………………………………….…
3. Stressful experiences significantly increase the likelihood of headaches.
4. Time of day has a significant effect on alertness.
Operationalizing Variables
To ensure cause and effect are established, it is important that we identify exactly how the independent and dependent variables will be measured; this is known as operationalizing the variables.
Operational variables (or operationalizing definitions) refer to how you will define and measure a specific variable as it is used in your study. This enables another psychologist to replicate your research and is essential in establishing reliability (achieving consistency in the results).
For example, if we are concerned with the effect of media violence on aggression, then we need to be very clear about what we mean by the different terms. In this case, we must state what we mean by the terms “media violence” and “aggression” as we will study them.
Therefore, you could state that “media violence” is operationally defined (in your experiment) as ‘exposure to a 15-minute film showing scenes of physical assault’; “aggression” is operationally defined as ‘levels of electrical shocks administered to a second ‘participant’ in another room.
In another example, the hypothesis “Young participants will have significantly better memories than older participants” is not operationalized. How do we define “young,” “old,” or “memory”? “Participants aged between 16 – 30 will recall significantly more nouns from a list of twenty than participants aged between 55 – 70” is operationalized.
The key point here is that we have clarified what we mean by the terms as they were studied and measured in our experiment.
If we didn’t do this, it would be very difficult (if not impossible) to compare the findings of different studies to the same behavior.
Operationalization has the advantage of generally providing a clear and objective definition of even complex variables. It also makes it easier for other researchers to replicate a study and check for reliability .
For the following hypotheses, name the IV and the DV and operationalize both variables.
1. Women are more attracted to men without earrings than men with earrings.
I.V._____________________________________________________________
D.V. ____________________________________________________________
Operational definitions:
I.V. ____________________________________________________________
2. People learn more when they study in a quiet versus noisy place.
I.V. _________________________________________________________
D.V. ___________________________________________________________
3. People who exercise regularly sleep better at night.
Can there be more than one independent or dependent variable in a study?
Yes, it is possible to have more than one independent or dependent variable in a study.
In some studies, researchers may want to explore how multiple factors affect the outcome, so they include more than one independent variable.
Similarly, they may measure multiple things to see how they are influenced, resulting in multiple dependent variables. This allows for a more comprehensive understanding of the topic being studied.
What are some ethical considerations related to independent and dependent variables?
Ethical considerations related to independent and dependent variables involve treating participants fairly and protecting their rights.
Researchers must ensure that participants provide informed consent and that their privacy and confidentiality are respected. Additionally, it is important to avoid manipulating independent variables in ways that could cause harm or discomfort to participants.
Researchers should also consider the potential impact of their study on vulnerable populations and ensure that their methods are unbiased and free from discrimination.
Ethical guidelines help ensure that research is conducted responsibly and with respect for the well-being of the participants involved.
Can qualitative data have independent and dependent variables?
Yes, both quantitative and qualitative data can have independent and dependent variables.
In quantitative research, independent variables are usually measured numerically and manipulated to understand their impact on the dependent variable. In qualitative research, independent variables can be qualitative in nature, such as individual experiences, cultural factors, or social contexts, influencing the phenomenon of interest.
The dependent variable, in both cases, is what is being observed or studied to see how it changes in response to the independent variable.
So, regardless of the type of data, researchers analyze the relationship between independent and dependent variables to gain insights into their research questions.
Can the same variable be independent in one study and dependent in another?
Yes, the same variable can be independent in one study and dependent in another.
The classification of a variable as independent or dependent depends on how it is used within a specific study. In one study, a variable might be manipulated or controlled to see its effect on another variable, making it independent.
However, in a different study, that same variable might be the one being measured or observed to understand its relationship with another variable, making it dependent.
The role of a variable as independent or dependent can vary depending on the research question and study design.
Related Articles

Research Methodology
Qualitative Data Coding

What Is a Focus Group?

Cross-Cultural Research Methodology In Psychology

What Is Internal Validity In Research?

Research Methodology , Statistics
What Is Face Validity In Research? Importance & How To Measure

Criterion Validity: Definition & Examples

Variables in Research | Types, Definiton & Examples

Introduction
What is a variable, what are the 5 types of variables in research, other variables in research.
Variables are fundamental components of research that allow for the measurement and analysis of data. They can be defined as characteristics or properties that can take on different values. In research design , understanding the types of variables and their roles is crucial for developing hypotheses , designing methods , and interpreting results .
This article outlines the the types of variables in research, including their definitions and examples, to provide a clear understanding of their use and significance in research studies. By categorizing variables into distinct groups based on their roles in research, their types of data, and their relationships with other variables, researchers can more effectively structure their studies and achieve more accurate conclusions.

A variable represents any characteristic, number, or quantity that can be measured or quantified. The term encompasses anything that can vary or change, ranging from simple concepts like age and height to more complex ones like satisfaction levels or economic status. Variables are essential in research as they are the foundational elements that researchers manipulate, measure, or control to gain insights into relationships, causes, and effects within their studies. They enable the framing of research questions, the formulation of hypotheses, and the interpretation of results.
Variables can be categorized based on their role in the study (such as independent and dependent variables ), the type of data they represent (quantitative or categorical), and their relationship to other variables (like confounding or control variables). Understanding what constitutes a variable and the various variable types available is a critical step in designing robust and meaningful research.
ATLAS.ti makes complex data easy to understand
Turn to our powerful data analysis tools to make the most of your research. Get started with a free trial.
Variables are crucial components in research, serving as the foundation for data collection , analysis , and interpretation . They are attributes or characteristics that can vary among subjects or over time, and understanding their types is essential for any study. Variables can be broadly classified into five main types, each with its distinct characteristics and roles within research.
This classification helps researchers in designing their studies, choosing appropriate measurement techniques, and analyzing their results accurately. The five types of variables include independent variables, dependent variables, categorical variables, continuous variables, and confounding variables. These categories not only facilitate a clearer understanding of the data but also guide the formulation of hypotheses and research methodologies.
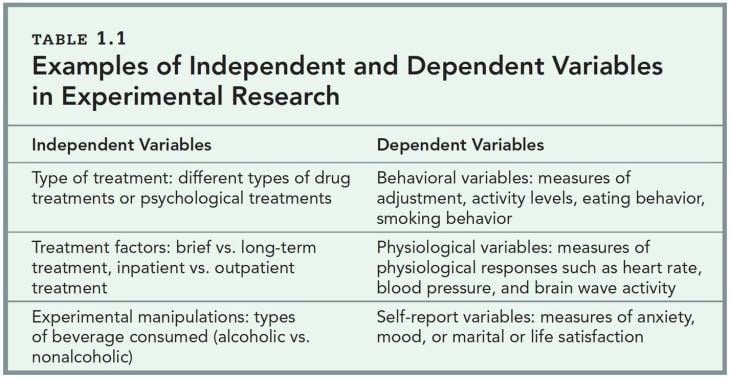
Independent variables
Independent variables are foundational to the structure of research, serving as the factors or conditions that researchers manipulate or vary to observe their effects on dependent variables. These variables are considered "independent" because their variation does not depend on other variables within the study. Instead, they are the cause or stimulus that directly influences the outcomes being measured. For example, in an experiment to assess the effectiveness of a new teaching method on student performance, the teaching method applied (traditional vs. innovative) would be the independent variable.
The selection of an independent variable is a critical step in research design, as it directly correlates with the study's objective to determine causality or association. Researchers must clearly define and control these variables to ensure that observed changes in the dependent variable can be attributed to variations in the independent variable, thereby affirming the reliability of the results. In experimental research, the independent variable is what differentiates the control group from the experimental group, thereby setting the stage for meaningful comparison and analysis.
Dependent variables
Dependent variables are the outcomes or effects that researchers aim to explore and understand in their studies. These variables are called "dependent" because their values depend on the changes or variations of the independent variables.
Essentially, they are the responses or results that are measured to assess the impact of the independent variable's manipulation. For instance, in a study investigating the effect of exercise on weight loss, the amount of weight lost would be considered the dependent variable, as it depends on the exercise regimen (the independent variable).
The identification and measurement of the dependent variable are crucial for testing the hypothesis and drawing conclusions from the research. It allows researchers to quantify the effect of the independent variable , providing evidence for causal relationships or associations. In experimental settings, the dependent variable is what is being tested and measured across different groups or conditions, enabling researchers to assess the efficacy or impact of the independent variable's variation.
To ensure accuracy and reliability, the dependent variable must be defined clearly and measured consistently across all participants or observations. This consistency helps in reducing measurement errors and increases the validity of the research findings. By carefully analyzing the dependent variables, researchers can derive meaningful insights from their studies, contributing to the broader knowledge in their field.
Categorical variables
Categorical variables, also known as qualitative variables, represent types or categories that are used to group observations. These variables divide data into distinct groups or categories that lack a numerical value but hold significant meaning in research. Examples of categorical variables include gender (male, female, other), type of vehicle (car, truck, motorcycle), or marital status (single, married, divorced). These categories help researchers organize data into groups for comparison and analysis.
Categorical variables can be further classified into two subtypes: nominal and ordinal. Nominal variables are categories without any inherent order or ranking among them, such as blood type or ethnicity. Ordinal variables, on the other hand, imply a sort of ranking or order among the categories, like levels of satisfaction (high, medium, low) or education level (high school, bachelor's, master's, doctorate).
Understanding and identifying categorical variables is crucial in research as it influences the choice of statistical analysis methods. Since these variables represent categories without numerical significance, researchers employ specific statistical tests designed for a nominal or ordinal variable to draw meaningful conclusions. Properly classifying and analyzing categorical variables allow for the exploration of relationships between different groups within the study, shedding light on patterns and trends that might not be evident with numerical data alone.
Continuous variables
Continuous variables are quantitative variables that can take an infinite number of values within a given range. These variables are measured along a continuum and can represent very precise measurements. Examples of continuous variables include height, weight, temperature, and time. Because they can assume any value within a range, continuous variables allow for detailed analysis and a high degree of accuracy in research findings.
The ability to measure continuous variables at very fine scales makes them invaluable for many types of research, particularly in the natural and social sciences. For instance, in a study examining the effect of temperature on plant growth, temperature would be considered a continuous variable since it can vary across a wide spectrum and be measured to several decimal places.
When dealing with continuous variables, researchers often use methods incorporating a particular statistical test to accommodate a wide range of data points and the potential for infinite divisibility. This includes various forms of regression analysis, correlation, and other techniques suited for modeling and analyzing nuanced relationships between variables. The precision of continuous variables enhances the researcher's ability to detect patterns, trends, and causal relationships within the data, contributing to more robust and detailed conclusions.
Confounding variables
Confounding variables are those that can cause a false association between the independent and dependent variables, potentially leading to incorrect conclusions about the relationship being studied. These are extraneous variables that were not considered in the study design but can influence both the supposed cause and effect, creating a misleading correlation.
Identifying and controlling for a confounding variable is crucial in research to ensure the validity of the findings. This can be achieved through various methods, including randomization, stratification, and statistical control. Randomization helps to evenly distribute confounding variables across study groups, reducing their potential impact. Stratification involves analyzing the data within strata or layers that share common characteristics of the confounder. Statistical control allows researchers to adjust for the effects of confounders in the analysis phase.
Properly addressing confounding variables strengthens the credibility of research outcomes by clarifying the direct relationship between the dependent and independent variables, thus providing more accurate and reliable results.
Beyond the primary categories of variables commonly discussed in research methodology , there exists a diverse range of other variables that play significant roles in the design and analysis of studies. Below is an overview of some of these variables, highlighting their definitions and roles within research studies:
- Discrete variables : A discrete variable is a quantitative variable that represents quantitative data , such as the number of children in a family or the number of cars in a parking lot. Discrete variables can only take on specific values.
- Categorical variables : A categorical variable categorizes subjects or items into groups that do not have a natural numerical order. Categorical data includes nominal variables, like country of origin, and ordinal variables, such as education level.
- Predictor variables : Often used in statistical models, a predictor variable is used to forecast or predict the outcomes of other variables, not necessarily with a causal implication.
- Outcome variables : These variables represent the results or outcomes that researchers aim to explain or predict through their studies. An outcome variable is central to understanding the effects of predictor variables.
- Latent variables : Not directly observable, latent variables are inferred from other, directly measured variables. Examples include psychological constructs like intelligence or socioeconomic status.
- Composite variables : Created by combining multiple variables, composite variables can measure a concept more reliably or simplify the analysis. An example would be a composite happiness index derived from several survey questions .
- Preceding variables : These variables come before other variables in time or sequence, potentially influencing subsequent outcomes. A preceding variable is crucial in longitudinal studies to determine causality or sequences of events.

Master qualitative research with ATLAS.ti
Turn data into critical insights with our data analysis platform. Try out a free trial today.

- How it works

Types of Variables – A Comprehensive Guide
Published by Carmen Troy at August 14th, 2021 , Revised On October 26, 2023
A variable is any qualitative or quantitative characteristic that can change and have more than one value, such as age, height, weight, gender, etc.
Before conducting research, it’s essential to know what needs to be measured or analysed and choose a suitable statistical test to present your study’s findings.
In most cases, you can do it by identifying the key issues/variables related to your research’s main topic.
Example: If you want to test whether the hybridisation of plants harms the health of people. You can use the key variables like agricultural techniques, type of soil, environmental factors, types of pesticides used, the process of hybridisation, type of yield obtained after hybridisation, type of yield without hybridisation, etc.
Variables are broadly categorised into:
- Independent variables
- Dependent variable
- Control variable
Independent Vs. Dependent Vs. Control Variable
The research includes finding ways:
- To change the independent variables.
- To prevent the controlled variables from changing.
- To measure the dependent variables.
Note: The term dependent and independent is not applicable in correlational research as this is not a controlled experiment. A researcher doesn’t have control over the variables. The association and between two or more variables are measured. If one variable affects another one, then it’s called the predictor variable and outcome variable.
Example: Correlation between investment (predictor variable) and profit (outcome variable)
What data collection best suits your research?
- Find out by hiring an expert from ResearchProspect today!
- Despite how challenging the subject may be, we are here to help you.
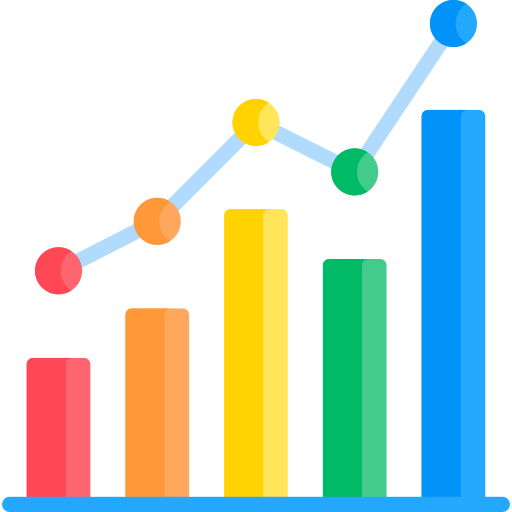
Types of Variables Based on the Types of Data
A data is referred to as the information and statistics gathered for analysis of a research topic. Data is broadly divided into two categories, such as:
Quantitative/Numerical data is associated with the aspects of measurement, quantity, and extent.
Categorial data is associated with groupings.
A qualitative variable consists of qualitative data, and a quantitative variable consists of a quantitative variable.
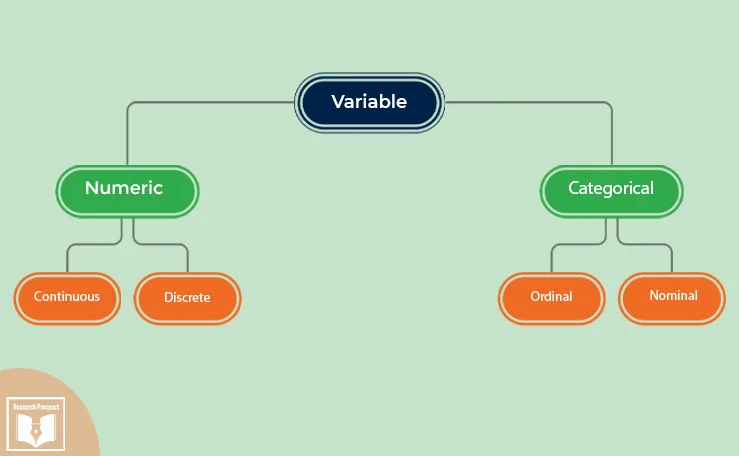
Quantitative Variable
The quantitative variable is associated with measurement, quantity, and extent, like how many . It follows the statistical, mathematical, and computational techniques in numerical data such as percentages and statistics. The research is conducted on a large group of population.
Example: Find out the weight of students of the fifth standard studying in government schools.
The quantitative variable can be further categorised into continuous and discrete.
Categorial Variable
The categorical variable includes measurements that vary in categories such as names but not in terms of rank or degree. It means one level of a categorical variable cannot be considered better or greater than another level.
Example: Gender, brands, colors, zip codes
The categorical variable is further categorised into three types:
Note: Sometimes, an ordinal variable also acts as a quantitative variable. Ordinal data has an order, but the intervals between scale points may be uneven.
Example: Numbers on a rating scale represent the reviews’ rank or range from below average to above average. However, it also represents a quantitative variable showing how many stars and how much rating is given.
Not sure which statistical tests to use for your data?
Let the experts at researchprospect do the daunting work for you..
Using our approach, we illustrate how to collect data, sample sizes, validity, reliability, credibility, and ethics, so you won’t have to do it all by yourself!
Other Types of Variables
It’s important to understand the difference between dependent and independent variables and know whether they are quantitative or categorical to choose the appropriate statistical test.
There are many other types of variables to help you differentiate and understand them.
Also, read a comprehensive guide written about inductive and deductive reasoning .
- Entertainment
- Online education
- Database management, storage, and retrieval
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the 10 types of variables in research.
The 10 types of variables in research are:
- Independent
- Confounding
- Categorical
- Extraneous.
What is an independent variable?
An independent variable, often termed the predictor or explanatory variable, is the variable manipulated or categorized in an experiment to observe its effect on another variable, called the dependent variable. It’s the presumed cause in a cause-and-effect relationship, determining if changes in it produce changes in the observed outcome.
What is a variable?
In research, a variable is any attribute, quantity, or characteristic that can be measured or counted. It can take on various values, making it “variable.” Variables can be classified as independent (manipulated), dependent (observed outcome), or control (kept constant). They form the foundation for hypotheses, observations, and data analysis in studies.
What is a dependent variable?
A dependent variable is the outcome or response being studied in an experiment or investigation. It’s what researchers measure to determine the effect of changes in the independent variable. In a cause-and-effect relationship, the dependent variable is presumed to be influenced or caused by the independent variable.
What is a variable in programming?
In programming, a variable is a symbolic name for a storage location that holds data or values. It allows data storage and retrieval for computational operations. Variables have types, like integer or string, determining the nature of data they can hold. They’re fundamental in manipulating and processing information in software.
What is a control variable?
A control variable in research is a factor that’s kept constant to ensure that it doesn’t influence the outcome. By controlling these variables, researchers can isolate the effects of the independent variable on the dependent variable, ensuring that other factors don’t skew the results or introduce bias into the experiment.
What is a controlled variable in science?
In science, a controlled variable is a factor that remains constant throughout an experiment. It ensures that any observed changes in the dependent variable are solely due to the independent variable, not other factors. By keeping controlled variables consistent, researchers can maintain experiment validity and accurately assess cause-and-effect relationships.
How many independent variables should an investigation have?
Ideally, an investigation should have one independent variable to clearly establish cause-and-effect relationships. Manipulating multiple independent variables simultaneously can complicate data interpretation.
However, in advanced research, experiments with multiple independent variables (factorial designs) are used, but they require careful planning to understand interactions between variables.
You May Also Like
A survey includes questions relevant to the research topic. The participants are selected, and the questionnaire is distributed to collect the data.
A confounding variable can potentially affect both the suspected cause and the suspected effect. Here is all you need to know about accounting for confounding variables in research.
Textual analysis is the method of analysing and understanding the text. We need to look carefully at the text to identify the writer’s context and message.
USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

- How It Works
Independent and Dependent Variables
This guide discusses how to identify independent and dependent variables effectively and incorporate their description within the body of a research paper.
A variable can be anything you might aim to measure in your study, whether in the form of numerical data or reflecting complex phenomena such as feelings or reactions. Dependent variables change due to the other factors measured, especially if a study employs an experimental or semi-experimental design. Independent variables are stable: they are both presumed causes and conditions in the environment or milieu being manipulated.
Identifying Independent and Dependent Variables
Even though the definitions of the terms independent and dependent variables may appear to be clear, in the process of analyzing data resulting from actual research, identifying the variables properly might be challenging. Here is a simple rule that you can apply at all times: the independent variable is what a researcher changes, whereas the dependent variable is affected by these changes. To illustrate the difference, a number of examples are provided below.
- The purpose of Study 1 is to measure the impact of different plant fertilizers on how many fruits apple trees bear. Independent variable : plant fertilizers (chosen by researchers) Dependent variable : fruits that the trees bear (affected by choice of fertilizers)
- The purpose of Study 2 is to find an association between living in close vicinity to hydraulic fracturing sites and respiratory diseases. Independent variable: proximity to hydraulic fracturing sites (a presumed cause and a condition of the environment) Dependent variable: the percentage/ likelihood of suffering from respiratory diseases
Confusion is possible in identifying independent and dependent variables in the social sciences. When considering psychological phenomena and human behavior, it can be difficult to distinguish between cause and effect. For example, the purpose of Study 3 is to establish how tactics for coping with stress are linked to the level of stress-resilience in college students. Even though it is feasible to speculate that these variables are interdependent, the following factors should be taken into account in order to clearly define which variable is dependent and which is interdependent.
- The dependent variable is usually the objective of the research. In the study under examination, the levels of stress resilience are being investigated.
- The independent variable precedes the dependent variable. The chosen stress-related coping techniques help to build resilience; thus, they occur earlier.
Writing Style and Structure
Usually, the variables are first described in the introduction of a research paper and then in the method section. No strict guidelines for approaching the subject exist; however, academic writing demands that the researcher make clear and concise statements. It is only reasonable not to leave readers guessing which of the variables is dependent and which is independent. The description should reflect the literature review, where both types of variables are identified in the context of the previous research. For instance, in the case of Study 3, a researcher would have to provide an explanation as to the meaning of stress resilience and coping tactics.
In properly organizing a research paper, it is essential to outline and operationalize the appropriate independent and dependent variables. Moreover, the paper should differentiate clearly between independent and dependent variables. Finding the dependent variable is typically the objective of a study, whereas independent variables reflect influencing factors that can be manipulated. Distinguishing between the two types of variables in social sciences may be somewhat challenging as it can be easy to confuse cause with effect. Academic format calls for the author to mention the variables in the introduction and then provide a detailed description in the method section.
Unfortunately, your browser is too old to work on this site.
For full functionality of this site it is necessary to enable JavaScript.

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
Margin Size
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

2.2: Concepts, Constructs, and Variables
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 26212

- Anol Bhattacherjee
- University of South Florida via Global Text Project
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
We discussed in Chapter 1 that although research can be exploratory, descriptive, or explanatory, most scientific research tend to be of the explanatory type in that they search for potential explanations of observed natural or social phenomena. Explanations require development of concepts or generalizable properties or characteristics associated with objects, events, or people. While objects such as a person, a firm, or a car are not concepts, their specific characteristics or behavior such as a person’s attitude toward immigrants, a firm’s capacity for innovation, and a car’s weight can be viewed as concepts.
Knowingly or unknowingly, we use different kinds of concepts in our everyday conversations. Some of these concepts have been developed over time through our shared language. Sometimes, we borrow concepts from other disciplines or languages to explain a phenomenon of interest. For instance, the idea of gravitation borrowed from physics can be used in business to describe why people tend to “gravitate” to their preferred shopping destinations. Likewise, the concept of distance can be used to explain the degree of social separation between two otherwise collocated individuals. Sometimes, we create our own concepts to describe a unique characteristic not described in prior research. For instance, technostress is a new concept referring to the mental stress one may face when asked to learn a new technology.
Concepts may also have progressive levels of abstraction. Some concepts such as a person’s weight are precise and objective, while other concepts such as a person’s personality may be more abstract and difficult to visualize. A construct is an abstract concept that is specifically chosen (or “created”) to explain a given phenomenon. A construct may be a simple concept, such as a person’s weight , or a combination of a set of related concepts such as a person’s communication skill , which may consist of several underlying concepts such as the person’s vocabulary , syntax , and spelling . The former instance (weight) is a unidimensional construct , while the latter (communication skill) is a multi-dimensional construct (i.e., it consists of multiple underlying concepts). The distinction between constructs and concepts are clearer in multi-dimensional constructs, where the higher order abstraction is called a construct and the lower order abstractions are called concepts. However, this distinction tends to blur in the case of unidimensional constructs.
Constructs used for scientific research must have precise and clear definitions that others can use to understand exactly what it means and what it does not mean. For instance, a seemingly simple construct such as income may refer to monthly or annual income, before-tax or after-tax income, and personal or family income, and is therefore neither precise nor clear. There are two types of definitions: dictionary definitions and operational definitions. In the more familiar dictionary definition, a construct is often defined in terms of a synonym. For instance, attitude may be defined as a disposition, a feeling, or an affect, and affect in turn is defined as an attitude. Such definitions of a circular nature are not particularly useful in scientific research for elaborating the meaning and content of that construct. Scientific research requires operational definitions that define constructs in terms of how they will be empirically measured. For instance, the operational definition of a construct such as temperature must specify whether we plan to measure temperature in Celsius, Fahrenheit, or Kelvin scale. A construct such as income should be defined in terms of whether we are interested in monthly or annual income, before-tax or after-tax income, and personal or family income. One can imagine that constructs such as learning , personality , and intelligence can be quite hard to define operationally.
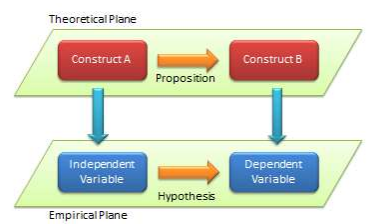
A term frequently associated with, and sometimes used interchangeably with, a construct is a variable. Etymologically speaking, a variable is a quantity that can vary (e.g., from low to high, negative to positive, etc.), in contrast to constants that do not vary (i.e., remain constant). However, in scientific research, a variable is a measurable representation of an abstract construct. As abstract entities, constructs are not directly measurable, and hence, we look for proxy measures called variables. For instance, a person’s intelligence is often measured as his or her IQ ( intelligence quotient ) score , which is an index generated from an analytical and pattern-matching test administered to people. In this case, intelligence is a construct, and IQ score is a variable that measures the intelligence construct. Whether IQ scores truly measures one’s intelligence is anyone’s guess (though many believe that they do), and depending on whether how well it measures intelligence, the IQ score may be a good or a poor measure of the intelligence construct. As shown in Figure 2.1, scientific research proceeds along two planes: a theoretical plane and an empirical plane. Constructs are conceptualized at the theoretical (abstract) plane, while variables are operationalized and measured at the empirical (observational) plane. Thinking like a researcher implies the ability to move back and forth between these two planes.
Depending on their intended use, variables may be classified as independent, dependent, moderating, mediating, or control variables. Variables that explain other variables are called independent variables , those that are explained by other variables are dependent variables , those that are explained by independent variables while also explaining dependent variables are mediating variables (or intermediate variables), and those that influence the relationship between independent and dependent variables are called moderating variables . As an example, if we state that higher intelligence causes improved learning among students, then intelligence is an independent variable and learning is a dependent variable. There may be other extraneous variables that are not pertinent to explaining a given dependent variable, but may have some impact on the dependent variable. These variables must be controlled for in a scientific study, and are therefore called control variables .
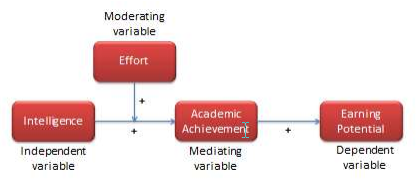
To understand the differences between these different variable types, consider the example shown in Figure 2.2. If we believe that intelligence influences (or explains) students’ academic achievement, then a measure of intelligence such as an IQ score is an independent variable, while a measure of academic success such as grade point average is a dependent variable. If we believe that the effect of intelligence on academic achievement also depends on the effort invested by the student in the learning process (i.e., between two equally intelligent students, the student who puts is more effort achieves higher academic achievement than one who puts in less effort), then effort becomes a moderating variable. Incidentally, one may also view effort as an independent variable and intelligence as a moderating variable. If academic achievement is viewed as an intermediate step to higher earning potential, then earning potential becomes the dependent variable for the independent variable academic achievement , and academic achievement becomes the mediating variable in the relationship between intelligence and earning potential. Hence, variable are defined as an independent, dependent, moderating, or mediating variable based on their nature of association with each other. The overall network of relationships between a set of related constructs is called a nomological network (see Figure 2.2). Thinking like a researcher requires not only being able to abstract constructs from observations, but also being able to mentally visualize a nomological network linking these abstract constructs.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- J Korean Med Sci
- v.37(16); 2022 Apr 25

A Practical Guide to Writing Quantitative and Qualitative Research Questions and Hypotheses in Scholarly Articles
Edward barroga.
1 Department of General Education, Graduate School of Nursing Science, St. Luke’s International University, Tokyo, Japan.
Glafera Janet Matanguihan
2 Department of Biological Sciences, Messiah University, Mechanicsburg, PA, USA.
The development of research questions and the subsequent hypotheses are prerequisites to defining the main research purpose and specific objectives of a study. Consequently, these objectives determine the study design and research outcome. The development of research questions is a process based on knowledge of current trends, cutting-edge studies, and technological advances in the research field. Excellent research questions are focused and require a comprehensive literature search and in-depth understanding of the problem being investigated. Initially, research questions may be written as descriptive questions which could be developed into inferential questions. These questions must be specific and concise to provide a clear foundation for developing hypotheses. Hypotheses are more formal predictions about the research outcomes. These specify the possible results that may or may not be expected regarding the relationship between groups. Thus, research questions and hypotheses clarify the main purpose and specific objectives of the study, which in turn dictate the design of the study, its direction, and outcome. Studies developed from good research questions and hypotheses will have trustworthy outcomes with wide-ranging social and health implications.
INTRODUCTION
Scientific research is usually initiated by posing evidenced-based research questions which are then explicitly restated as hypotheses. 1 , 2 The hypotheses provide directions to guide the study, solutions, explanations, and expected results. 3 , 4 Both research questions and hypotheses are essentially formulated based on conventional theories and real-world processes, which allow the inception of novel studies and the ethical testing of ideas. 5 , 6
It is crucial to have knowledge of both quantitative and qualitative research 2 as both types of research involve writing research questions and hypotheses. 7 However, these crucial elements of research are sometimes overlooked; if not overlooked, then framed without the forethought and meticulous attention it needs. Planning and careful consideration are needed when developing quantitative or qualitative research, particularly when conceptualizing research questions and hypotheses. 4
There is a continuing need to support researchers in the creation of innovative research questions and hypotheses, as well as for journal articles that carefully review these elements. 1 When research questions and hypotheses are not carefully thought of, unethical studies and poor outcomes usually ensue. Carefully formulated research questions and hypotheses define well-founded objectives, which in turn determine the appropriate design, course, and outcome of the study. This article then aims to discuss in detail the various aspects of crafting research questions and hypotheses, with the goal of guiding researchers as they develop their own. Examples from the authors and peer-reviewed scientific articles in the healthcare field are provided to illustrate key points.
DEFINITIONS AND RELATIONSHIP OF RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
A research question is what a study aims to answer after data analysis and interpretation. The answer is written in length in the discussion section of the paper. Thus, the research question gives a preview of the different parts and variables of the study meant to address the problem posed in the research question. 1 An excellent research question clarifies the research writing while facilitating understanding of the research topic, objective, scope, and limitations of the study. 5
On the other hand, a research hypothesis is an educated statement of an expected outcome. This statement is based on background research and current knowledge. 8 , 9 The research hypothesis makes a specific prediction about a new phenomenon 10 or a formal statement on the expected relationship between an independent variable and a dependent variable. 3 , 11 It provides a tentative answer to the research question to be tested or explored. 4
Hypotheses employ reasoning to predict a theory-based outcome. 10 These can also be developed from theories by focusing on components of theories that have not yet been observed. 10 The validity of hypotheses is often based on the testability of the prediction made in a reproducible experiment. 8
Conversely, hypotheses can also be rephrased as research questions. Several hypotheses based on existing theories and knowledge may be needed to answer a research question. Developing ethical research questions and hypotheses creates a research design that has logical relationships among variables. These relationships serve as a solid foundation for the conduct of the study. 4 , 11 Haphazardly constructed research questions can result in poorly formulated hypotheses and improper study designs, leading to unreliable results. Thus, the formulations of relevant research questions and verifiable hypotheses are crucial when beginning research. 12
CHARACTERISTICS OF GOOD RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
Excellent research questions are specific and focused. These integrate collective data and observations to confirm or refute the subsequent hypotheses. Well-constructed hypotheses are based on previous reports and verify the research context. These are realistic, in-depth, sufficiently complex, and reproducible. More importantly, these hypotheses can be addressed and tested. 13
There are several characteristics of well-developed hypotheses. Good hypotheses are 1) empirically testable 7 , 10 , 11 , 13 ; 2) backed by preliminary evidence 9 ; 3) testable by ethical research 7 , 9 ; 4) based on original ideas 9 ; 5) have evidenced-based logical reasoning 10 ; and 6) can be predicted. 11 Good hypotheses can infer ethical and positive implications, indicating the presence of a relationship or effect relevant to the research theme. 7 , 11 These are initially developed from a general theory and branch into specific hypotheses by deductive reasoning. In the absence of a theory to base the hypotheses, inductive reasoning based on specific observations or findings form more general hypotheses. 10
TYPES OF RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
Research questions and hypotheses are developed according to the type of research, which can be broadly classified into quantitative and qualitative research. We provide a summary of the types of research questions and hypotheses under quantitative and qualitative research categories in Table 1 .
Research questions in quantitative research
In quantitative research, research questions inquire about the relationships among variables being investigated and are usually framed at the start of the study. These are precise and typically linked to the subject population, dependent and independent variables, and research design. 1 Research questions may also attempt to describe the behavior of a population in relation to one or more variables, or describe the characteristics of variables to be measured ( descriptive research questions ). 1 , 5 , 14 These questions may also aim to discover differences between groups within the context of an outcome variable ( comparative research questions ), 1 , 5 , 14 or elucidate trends and interactions among variables ( relationship research questions ). 1 , 5 We provide examples of descriptive, comparative, and relationship research questions in quantitative research in Table 2 .
Hypotheses in quantitative research
In quantitative research, hypotheses predict the expected relationships among variables. 15 Relationships among variables that can be predicted include 1) between a single dependent variable and a single independent variable ( simple hypothesis ) or 2) between two or more independent and dependent variables ( complex hypothesis ). 4 , 11 Hypotheses may also specify the expected direction to be followed and imply an intellectual commitment to a particular outcome ( directional hypothesis ) 4 . On the other hand, hypotheses may not predict the exact direction and are used in the absence of a theory, or when findings contradict previous studies ( non-directional hypothesis ). 4 In addition, hypotheses can 1) define interdependency between variables ( associative hypothesis ), 4 2) propose an effect on the dependent variable from manipulation of the independent variable ( causal hypothesis ), 4 3) state a negative relationship between two variables ( null hypothesis ), 4 , 11 , 15 4) replace the working hypothesis if rejected ( alternative hypothesis ), 15 explain the relationship of phenomena to possibly generate a theory ( working hypothesis ), 11 5) involve quantifiable variables that can be tested statistically ( statistical hypothesis ), 11 6) or express a relationship whose interlinks can be verified logically ( logical hypothesis ). 11 We provide examples of simple, complex, directional, non-directional, associative, causal, null, alternative, working, statistical, and logical hypotheses in quantitative research, as well as the definition of quantitative hypothesis-testing research in Table 3 .
Research questions in qualitative research
Unlike research questions in quantitative research, research questions in qualitative research are usually continuously reviewed and reformulated. The central question and associated subquestions are stated more than the hypotheses. 15 The central question broadly explores a complex set of factors surrounding the central phenomenon, aiming to present the varied perspectives of participants. 15
There are varied goals for which qualitative research questions are developed. These questions can function in several ways, such as to 1) identify and describe existing conditions ( contextual research question s); 2) describe a phenomenon ( descriptive research questions ); 3) assess the effectiveness of existing methods, protocols, theories, or procedures ( evaluation research questions ); 4) examine a phenomenon or analyze the reasons or relationships between subjects or phenomena ( explanatory research questions ); or 5) focus on unknown aspects of a particular topic ( exploratory research questions ). 5 In addition, some qualitative research questions provide new ideas for the development of theories and actions ( generative research questions ) or advance specific ideologies of a position ( ideological research questions ). 1 Other qualitative research questions may build on a body of existing literature and become working guidelines ( ethnographic research questions ). Research questions may also be broadly stated without specific reference to the existing literature or a typology of questions ( phenomenological research questions ), may be directed towards generating a theory of some process ( grounded theory questions ), or may address a description of the case and the emerging themes ( qualitative case study questions ). 15 We provide examples of contextual, descriptive, evaluation, explanatory, exploratory, generative, ideological, ethnographic, phenomenological, grounded theory, and qualitative case study research questions in qualitative research in Table 4 , and the definition of qualitative hypothesis-generating research in Table 5 .
Qualitative studies usually pose at least one central research question and several subquestions starting with How or What . These research questions use exploratory verbs such as explore or describe . These also focus on one central phenomenon of interest, and may mention the participants and research site. 15
Hypotheses in qualitative research
Hypotheses in qualitative research are stated in the form of a clear statement concerning the problem to be investigated. Unlike in quantitative research where hypotheses are usually developed to be tested, qualitative research can lead to both hypothesis-testing and hypothesis-generating outcomes. 2 When studies require both quantitative and qualitative research questions, this suggests an integrative process between both research methods wherein a single mixed-methods research question can be developed. 1
FRAMEWORKS FOR DEVELOPING RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
Research questions followed by hypotheses should be developed before the start of the study. 1 , 12 , 14 It is crucial to develop feasible research questions on a topic that is interesting to both the researcher and the scientific community. This can be achieved by a meticulous review of previous and current studies to establish a novel topic. Specific areas are subsequently focused on to generate ethical research questions. The relevance of the research questions is evaluated in terms of clarity of the resulting data, specificity of the methodology, objectivity of the outcome, depth of the research, and impact of the study. 1 , 5 These aspects constitute the FINER criteria (i.e., Feasible, Interesting, Novel, Ethical, and Relevant). 1 Clarity and effectiveness are achieved if research questions meet the FINER criteria. In addition to the FINER criteria, Ratan et al. described focus, complexity, novelty, feasibility, and measurability for evaluating the effectiveness of research questions. 14
The PICOT and PEO frameworks are also used when developing research questions. 1 The following elements are addressed in these frameworks, PICOT: P-population/patients/problem, I-intervention or indicator being studied, C-comparison group, O-outcome of interest, and T-timeframe of the study; PEO: P-population being studied, E-exposure to preexisting conditions, and O-outcome of interest. 1 Research questions are also considered good if these meet the “FINERMAPS” framework: Feasible, Interesting, Novel, Ethical, Relevant, Manageable, Appropriate, Potential value/publishable, and Systematic. 14
As we indicated earlier, research questions and hypotheses that are not carefully formulated result in unethical studies or poor outcomes. To illustrate this, we provide some examples of ambiguous research question and hypotheses that result in unclear and weak research objectives in quantitative research ( Table 6 ) 16 and qualitative research ( Table 7 ) 17 , and how to transform these ambiguous research question(s) and hypothesis(es) into clear and good statements.
a These statements were composed for comparison and illustrative purposes only.
b These statements are direct quotes from Higashihara and Horiuchi. 16
a This statement is a direct quote from Shimoda et al. 17
The other statements were composed for comparison and illustrative purposes only.
CONSTRUCTING RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
To construct effective research questions and hypotheses, it is very important to 1) clarify the background and 2) identify the research problem at the outset of the research, within a specific timeframe. 9 Then, 3) review or conduct preliminary research to collect all available knowledge about the possible research questions by studying theories and previous studies. 18 Afterwards, 4) construct research questions to investigate the research problem. Identify variables to be accessed from the research questions 4 and make operational definitions of constructs from the research problem and questions. Thereafter, 5) construct specific deductive or inductive predictions in the form of hypotheses. 4 Finally, 6) state the study aims . This general flow for constructing effective research questions and hypotheses prior to conducting research is shown in Fig. 1 .

Research questions are used more frequently in qualitative research than objectives or hypotheses. 3 These questions seek to discover, understand, explore or describe experiences by asking “What” or “How.” The questions are open-ended to elicit a description rather than to relate variables or compare groups. The questions are continually reviewed, reformulated, and changed during the qualitative study. 3 Research questions are also used more frequently in survey projects than hypotheses in experiments in quantitative research to compare variables and their relationships.
Hypotheses are constructed based on the variables identified and as an if-then statement, following the template, ‘If a specific action is taken, then a certain outcome is expected.’ At this stage, some ideas regarding expectations from the research to be conducted must be drawn. 18 Then, the variables to be manipulated (independent) and influenced (dependent) are defined. 4 Thereafter, the hypothesis is stated and refined, and reproducible data tailored to the hypothesis are identified, collected, and analyzed. 4 The hypotheses must be testable and specific, 18 and should describe the variables and their relationships, the specific group being studied, and the predicted research outcome. 18 Hypotheses construction involves a testable proposition to be deduced from theory, and independent and dependent variables to be separated and measured separately. 3 Therefore, good hypotheses must be based on good research questions constructed at the start of a study or trial. 12
In summary, research questions are constructed after establishing the background of the study. Hypotheses are then developed based on the research questions. Thus, it is crucial to have excellent research questions to generate superior hypotheses. In turn, these would determine the research objectives and the design of the study, and ultimately, the outcome of the research. 12 Algorithms for building research questions and hypotheses are shown in Fig. 2 for quantitative research and in Fig. 3 for qualitative research.

EXAMPLES OF RESEARCH QUESTIONS FROM PUBLISHED ARTICLES
- EXAMPLE 1. Descriptive research question (quantitative research)
- - Presents research variables to be assessed (distinct phenotypes and subphenotypes)
- “BACKGROUND: Since COVID-19 was identified, its clinical and biological heterogeneity has been recognized. Identifying COVID-19 phenotypes might help guide basic, clinical, and translational research efforts.
- RESEARCH QUESTION: Does the clinical spectrum of patients with COVID-19 contain distinct phenotypes and subphenotypes? ” 19
- EXAMPLE 2. Relationship research question (quantitative research)
- - Shows interactions between dependent variable (static postural control) and independent variable (peripheral visual field loss)
- “Background: Integration of visual, vestibular, and proprioceptive sensations contributes to postural control. People with peripheral visual field loss have serious postural instability. However, the directional specificity of postural stability and sensory reweighting caused by gradual peripheral visual field loss remain unclear.
- Research question: What are the effects of peripheral visual field loss on static postural control ?” 20
- EXAMPLE 3. Comparative research question (quantitative research)
- - Clarifies the difference among groups with an outcome variable (patients enrolled in COMPERA with moderate PH or severe PH in COPD) and another group without the outcome variable (patients with idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension (IPAH))
- “BACKGROUND: Pulmonary hypertension (PH) in COPD is a poorly investigated clinical condition.
- RESEARCH QUESTION: Which factors determine the outcome of PH in COPD?
- STUDY DESIGN AND METHODS: We analyzed the characteristics and outcome of patients enrolled in the Comparative, Prospective Registry of Newly Initiated Therapies for Pulmonary Hypertension (COMPERA) with moderate or severe PH in COPD as defined during the 6th PH World Symposium who received medical therapy for PH and compared them with patients with idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension (IPAH) .” 21
- EXAMPLE 4. Exploratory research question (qualitative research)
- - Explores areas that have not been fully investigated (perspectives of families and children who receive care in clinic-based child obesity treatment) to have a deeper understanding of the research problem
- “Problem: Interventions for children with obesity lead to only modest improvements in BMI and long-term outcomes, and data are limited on the perspectives of families of children with obesity in clinic-based treatment. This scoping review seeks to answer the question: What is known about the perspectives of families and children who receive care in clinic-based child obesity treatment? This review aims to explore the scope of perspectives reported by families of children with obesity who have received individualized outpatient clinic-based obesity treatment.” 22
- EXAMPLE 5. Relationship research question (quantitative research)
- - Defines interactions between dependent variable (use of ankle strategies) and independent variable (changes in muscle tone)
- “Background: To maintain an upright standing posture against external disturbances, the human body mainly employs two types of postural control strategies: “ankle strategy” and “hip strategy.” While it has been reported that the magnitude of the disturbance alters the use of postural control strategies, it has not been elucidated how the level of muscle tone, one of the crucial parameters of bodily function, determines the use of each strategy. We have previously confirmed using forward dynamics simulations of human musculoskeletal models that an increased muscle tone promotes the use of ankle strategies. The objective of the present study was to experimentally evaluate a hypothesis: an increased muscle tone promotes the use of ankle strategies. Research question: Do changes in the muscle tone affect the use of ankle strategies ?” 23
EXAMPLES OF HYPOTHESES IN PUBLISHED ARTICLES
- EXAMPLE 1. Working hypothesis (quantitative research)
- - A hypothesis that is initially accepted for further research to produce a feasible theory
- “As fever may have benefit in shortening the duration of viral illness, it is plausible to hypothesize that the antipyretic efficacy of ibuprofen may be hindering the benefits of a fever response when taken during the early stages of COVID-19 illness .” 24
- “In conclusion, it is plausible to hypothesize that the antipyretic efficacy of ibuprofen may be hindering the benefits of a fever response . The difference in perceived safety of these agents in COVID-19 illness could be related to the more potent efficacy to reduce fever with ibuprofen compared to acetaminophen. Compelling data on the benefit of fever warrant further research and review to determine when to treat or withhold ibuprofen for early stage fever for COVID-19 and other related viral illnesses .” 24
- EXAMPLE 2. Exploratory hypothesis (qualitative research)
- - Explores particular areas deeper to clarify subjective experience and develop a formal hypothesis potentially testable in a future quantitative approach
- “We hypothesized that when thinking about a past experience of help-seeking, a self distancing prompt would cause increased help-seeking intentions and more favorable help-seeking outcome expectations .” 25
- “Conclusion
- Although a priori hypotheses were not supported, further research is warranted as results indicate the potential for using self-distancing approaches to increasing help-seeking among some people with depressive symptomatology.” 25
- EXAMPLE 3. Hypothesis-generating research to establish a framework for hypothesis testing (qualitative research)
- “We hypothesize that compassionate care is beneficial for patients (better outcomes), healthcare systems and payers (lower costs), and healthcare providers (lower burnout). ” 26
- Compassionomics is the branch of knowledge and scientific study of the effects of compassionate healthcare. Our main hypotheses are that compassionate healthcare is beneficial for (1) patients, by improving clinical outcomes, (2) healthcare systems and payers, by supporting financial sustainability, and (3) HCPs, by lowering burnout and promoting resilience and well-being. The purpose of this paper is to establish a scientific framework for testing the hypotheses above . If these hypotheses are confirmed through rigorous research, compassionomics will belong in the science of evidence-based medicine, with major implications for all healthcare domains.” 26
- EXAMPLE 4. Statistical hypothesis (quantitative research)
- - An assumption is made about the relationship among several population characteristics ( gender differences in sociodemographic and clinical characteristics of adults with ADHD ). Validity is tested by statistical experiment or analysis ( chi-square test, Students t-test, and logistic regression analysis)
- “Our research investigated gender differences in sociodemographic and clinical characteristics of adults with ADHD in a Japanese clinical sample. Due to unique Japanese cultural ideals and expectations of women's behavior that are in opposition to ADHD symptoms, we hypothesized that women with ADHD experience more difficulties and present more dysfunctions than men . We tested the following hypotheses: first, women with ADHD have more comorbidities than men with ADHD; second, women with ADHD experience more social hardships than men, such as having less full-time employment and being more likely to be divorced.” 27
- “Statistical Analysis
- ( text omitted ) Between-gender comparisons were made using the chi-squared test for categorical variables and Students t-test for continuous variables…( text omitted ). A logistic regression analysis was performed for employment status, marital status, and comorbidity to evaluate the independent effects of gender on these dependent variables.” 27
EXAMPLES OF HYPOTHESIS AS WRITTEN IN PUBLISHED ARTICLES IN RELATION TO OTHER PARTS
- EXAMPLE 1. Background, hypotheses, and aims are provided
- “Pregnant women need skilled care during pregnancy and childbirth, but that skilled care is often delayed in some countries …( text omitted ). The focused antenatal care (FANC) model of WHO recommends that nurses provide information or counseling to all pregnant women …( text omitted ). Job aids are visual support materials that provide the right kind of information using graphics and words in a simple and yet effective manner. When nurses are not highly trained or have many work details to attend to, these job aids can serve as a content reminder for the nurses and can be used for educating their patients (Jennings, Yebadokpo, Affo, & Agbogbe, 2010) ( text omitted ). Importantly, additional evidence is needed to confirm how job aids can further improve the quality of ANC counseling by health workers in maternal care …( text omitted )” 28
- “ This has led us to hypothesize that the quality of ANC counseling would be better if supported by job aids. Consequently, a better quality of ANC counseling is expected to produce higher levels of awareness concerning the danger signs of pregnancy and a more favorable impression of the caring behavior of nurses .” 28
- “This study aimed to examine the differences in the responses of pregnant women to a job aid-supported intervention during ANC visit in terms of 1) their understanding of the danger signs of pregnancy and 2) their impression of the caring behaviors of nurses to pregnant women in rural Tanzania.” 28
- EXAMPLE 2. Background, hypotheses, and aims are provided
- “We conducted a two-arm randomized controlled trial (RCT) to evaluate and compare changes in salivary cortisol and oxytocin levels of first-time pregnant women between experimental and control groups. The women in the experimental group touched and held an infant for 30 min (experimental intervention protocol), whereas those in the control group watched a DVD movie of an infant (control intervention protocol). The primary outcome was salivary cortisol level and the secondary outcome was salivary oxytocin level.” 29
- “ We hypothesize that at 30 min after touching and holding an infant, the salivary cortisol level will significantly decrease and the salivary oxytocin level will increase in the experimental group compared with the control group .” 29
- EXAMPLE 3. Background, aim, and hypothesis are provided
- “In countries where the maternal mortality ratio remains high, antenatal education to increase Birth Preparedness and Complication Readiness (BPCR) is considered one of the top priorities [1]. BPCR includes birth plans during the antenatal period, such as the birthplace, birth attendant, transportation, health facility for complications, expenses, and birth materials, as well as family coordination to achieve such birth plans. In Tanzania, although increasing, only about half of all pregnant women attend an antenatal clinic more than four times [4]. Moreover, the information provided during antenatal care (ANC) is insufficient. In the resource-poor settings, antenatal group education is a potential approach because of the limited time for individual counseling at antenatal clinics.” 30
- “This study aimed to evaluate an antenatal group education program among pregnant women and their families with respect to birth-preparedness and maternal and infant outcomes in rural villages of Tanzania.” 30
- “ The study hypothesis was if Tanzanian pregnant women and their families received a family-oriented antenatal group education, they would (1) have a higher level of BPCR, (2) attend antenatal clinic four or more times, (3) give birth in a health facility, (4) have less complications of women at birth, and (5) have less complications and deaths of infants than those who did not receive the education .” 30
Research questions and hypotheses are crucial components to any type of research, whether quantitative or qualitative. These questions should be developed at the very beginning of the study. Excellent research questions lead to superior hypotheses, which, like a compass, set the direction of research, and can often determine the successful conduct of the study. Many research studies have floundered because the development of research questions and subsequent hypotheses was not given the thought and meticulous attention needed. The development of research questions and hypotheses is an iterative process based on extensive knowledge of the literature and insightful grasp of the knowledge gap. Focused, concise, and specific research questions provide a strong foundation for constructing hypotheses which serve as formal predictions about the research outcomes. Research questions and hypotheses are crucial elements of research that should not be overlooked. They should be carefully thought of and constructed when planning research. This avoids unethical studies and poor outcomes by defining well-founded objectives that determine the design, course, and outcome of the study.
Disclosure: The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Author Contributions:
- Conceptualization: Barroga E, Matanguihan GJ.
- Methodology: Barroga E, Matanguihan GJ.
- Writing - original draft: Barroga E, Matanguihan GJ.
- Writing - review & editing: Barroga E, Matanguihan GJ.

What are Examples of Variables in Research?
Table of contents, introduction.
In writing your thesis, one of the first terms that you encounter is the word variable. Failure to understand the meaning and the usefulness of variables in your study will prevent you from doing excellent research. What are variables, and how do you use variables in your research?
I explain this key research concept below with lots of examples of variables commonly used in a study.
You may find it challenging to understand just what variables are in research, especially those that deal with quantitative data analysis. This initial difficulty about variables becomes much more confusing when you encounter the phrases “dependent variable” and “independent variable” as you go deeper in studying this vital concept of research, as well as statistics.
Understanding what variables mean is crucial in writing your thesis proposal because you will need these in constructing your conceptual framework and in analyzing the data that you have gathered.
Therefore, it is a must that you should be able to grasp thoroughly the meaning of variables and ways on how to measure them. Yes, the variables should be measurable so that you will use your data for statistical analysis.
I will strengthen your understanding by providing examples of phenomena and their corresponding variables below.
Definition of Variable
Variables are those simplified portions of the complex phenomena that you intend to study. The word variable is derived from the root word “vary,” meaning, changing in amount, volume, number, form, nature, or type. These variables should be measurable, i.e., they can be counted or subjected to a scale.
The next section provides examples of variables related to climate change , academic performance, crime, fish kill, crop growth, and how content goes viral. Note that the variables in these phenomena can be measured, except the last one, where a bit more work is required.
Examples of Variables in Research: 6 Phenomena
The following are examples of phenomena from a global to a local perspective. The corresponding list of variables is given to illustrate how complex phenomena can be broken down into manageable pieces for better understanding and to subject the phenomena to research.
Phenomenon 1: Climate change
Examples of variables related to climate change :
- temperature
- the amount of carbon emission
- the amount of rainfall
Phenomenon 2: Crime and violence in the streets
Examples of variables related to crime and violence :
- number of robberies
- number of attempted murders
- number of prisoners
- number of crime victims
- number of laws enforcers
- number of convictions
- number of carnapping incidents
Phenomenon 3: Poor performance of students in college entrance exams
Examples of variables related to poor academic performance :
- entrance exam score
- number of hours devoted to studying
- student-teacher ratio
- number of students in the class
- educational attainment of teachers
- teaching style
- the distance of school from home
- number of hours devoted by parents in providing tutorial support
Phenomenon 4: Fish kill
Examples of variables related to fish kill :
- dissolved oxygen
- water salinity
- age of fish
- presence or absence of parasites
- presence or absence of heavy metal
- stocking density
Phenomenon 5: Poor crop growth
Examples of variables related to poor crop growth :
- the amount of nitrogen in the soil
- the amount of phosphorous in the soil
- the amount of potassium in the ground
- frequency of weeding
- type of soil

Phenomenon 6: How Content Goes Viral
- interesting,
- surprising, and
- causing physiological arousal.
Notice in the above variable examples that all the factors listed under the phenomena can be counted or measured using an ordinal, ratio, or interval scale, except for the last one. The factors that influence how content goes viral are essentially subjective.
But researchers devised ways to measure those variables by grouping the respondents’ answers on whether content is positive, interesting, prominent, among others (see the full description here ).
Thus, the variables in the last phenomenon represent the nominal scale of measuring variables .
The expected values derived from these variables will be in terms of numbers, amount, category, or type. Quantified variables allow statistical analysis . Variable descriptions, correlations, or differences are then determined.
Difference Between Independent and Dependent Variables
Which of the above examples of variables are the independent and the dependent variables?
Independent Variables
The independent variables are those variables that may influence or affect the other variable, i.e., the dependent variable.
For example, in the second phenomenon, i.e., crime and violence in the streets, the independent variables are the number of law enforcers. If there are more law enforcers, it is expected that it will reduce the following:
- number of robberies,
- number of attempted murders,
- number of prisoners,
- number of crime victims, and
- the number of carnapping incidents.
The five variables listed under crime and violence in the streets as the theme of a study are all dependent variables.
Dependent Variables
The dependent variable, as previously mentioned, is the variable affected or influenced by the independent variable.
For example, in the first phenomenon on climate change, temperature as the independent variable influences sea level rise, the dependent variable. Increased temperature will cause the expansion of water in the sea. Thus, sea-level rise on a global scale will occur.
I will leave the classification of the other variables to you. Find out whether those are independent or dependent variables. Note, however, that some variables can be both independent or dependent variables, as the context of the study dictates.
Finding the relationship between variables
How will you know that one variable may cause the other to behave in a certain way?
Finding the relationship between variables requires a thorough review of the literature . Through a review of the relevant and reliable literature, you will find out which variables influence the other variable. You do not just guess relationships between variables. The entire process is the essence of research.
At this point, I believe that the concept of the variable is now clear to you. Share this information with your peers, who may have difficulty in understanding what the variables are in research.
Related Posts

Regression Analysis: 5 Steps and 4 Applications

Data Analysis: Five Essential Steps to Ensure Data Integrity, Accuracy, and Reliability
How to write the conceptual framework in a research proposal, about the author, patrick regoniel.
Dr. Regoniel, a faculty member of the graduate school, served as consultant to various environmental research and development projects covering issues and concerns on climate change, coral reef resources and management, economic valuation of environmental and natural resources, mining, and waste management and pollution. He has extensive experience on applied statistics, systems modelling and analysis, an avid practitioner of LaTeX, and a multidisciplinary web developer. He leverages pioneering AI-powered content creation tools to produce unique and comprehensive articles in this website.
128 Comments
Your question is unclear to me Biyaminu. What do you mean? If you want to cite this, see the citation box after the article.
- Pingback: Quantitative Research Design: 4 Common Ways to Gather Your Data Efficiently October 15, 2020
Dear Calvin, when you state your research objectives that’s where you will know if you need to use variables or not.
Great work. I’d just like to know in which situations are variables not used in scientific research please. thank you.
- Pingback: Nonparametric Tests: 8 Important Considerations Before Using Them October 11, 2020
I salute your work, before I was have no enough knowledge about variable I think I was claimed from my lecturers, but the real meaning I was in the mid night. thanks
Thank you very much for your nice NOTE! I have a question: Can you please give me any examples of variables in students’ indiscipline?
A well articulated exposition! Pls, I need a simple guide on the variables of the following topic : IMPACT OF TAX REFORMS ON REVENUE GENERATION IN NIGERIA: A CASE STUDY OF KOGI STATE. THANKS A LOT.
thanks for the explanation a bout variables. keep on posting information a bout reseach on my email.
This was extremely helpful and easy to digest
Dear Hamse, That depends on what variables you are studying. Are you doing a study on cause and effect?
Dear Sophia and Hamse,
As I mentioned earlier, please read the last part of the above article on how to determine the dependent and independent variables.
CHALLENGES FACING DEVELOPMENT OF COOPERATIVE MOVEMENT IN TANA RIVER COUNTY
What is the IV and DV of this Research topic?
You can see in the last part of the above article an explanation about dependent and independent variables.
Dear Maur, what you just want to do is to describe the challenges. No need for a conceptual framework.
Hey, I really appreciate your explanation however I’m having a hard time figuring out the IV and DV on the topic about fish kill, can you help me?
I am requested to write 50 variables in my research as per my topic which is about street vending. I am really clueless.
Hi Regoniel…your articles are much more guiding….pls am writing my thesis on impact of insurgency on Baga Road fish market Maiduguri.
How will my conceptual framework looks like What do I need to talk on
Dear Alhaji, just be clear about what you want to do. Your research question must be clearly stated before you build your conceptual framework.
- Pingback: How to Analyze Frequency Data | SimplyEducate.Me December 4, 2018
Thanks so much ! This article is so much simple to my understanding. A friend of my referred me to this site and I am so greatful. Please Sir, when writing the dependent and independent variables should it be in a table form ?
Dear Grace, Good day. I don’t understand what you mean. But if your school requires that the independent and dependent variables be written in table form, I see no problem with that. It’s just a way for you to clearly show what variables you are analyzing. And you need to justify that.
Can you please give me what are the possible variables in terms of installation of street lights along barangay roads of calauan, laguna: an assessment?
Hello sir, sorry to bother you but what are the guidelines for writing a good report
Guidelines for writing a good research report?
SimplyEducate.Me Privacy Policy

Today's Hours
- Centre College Grace Doherty Library
- ACTIVE Library Website
Information Literacy Instruction
Formulate a research topic.
- Find Information
- Evaluate Information
- Use Information
- Chicago/Turabian
- Citation Tools
- Exercises to Build Research Skills
- Choose a topic
- Narrow your topic
- Develop a research question
- State your working thesis or hypothesis
Choosing a topic
The hardest part of research is getting started! Choosing a topic can be challenging, especially in introductory classes, when you don't really know much about the subject. The most important thing to remember is this: you are doing research, so don't make a statement about what you want to prove and then go looking for evidence to support your claim. Instead, start out with an interest, read some articles on the topic and then take a stance on the subject based on what you have learned.
Here are some tips to get you started when choosing a topic:
1. Think about the topics in your class that have interested you so far. Or, if it is the beginning of the semester, think about what you expect the course will cover and what you expect to enjoy about the class. When you added this class, what made you think it might be interesting?
2. Flip through your textbooks and look for chapter titles or subheadings that interest you.
3. Look at a magazine or journal in your subject area and look for interesting articles that might inspire you.
4. Think about controversies or current events in your subject area. Could they lead to a potential research question? If you don't know any controversies or current events for your subject, Google "Controversies in XYZ," "Disagreements in XYZ," or "Current hot topics in XYX" and see if something you find interests you.
5. Think about what you’re studying in other classes. Are there interesting ways in which they might intersect with or relate to this class?
5. Brainstorm with your classmates. Talking to each other is a good way to figure out what interests you.
Some things to consider when choosing a topic:
How long does your paper need to be?
A shorter paper will need a more narrowly focused idea. A longer paper will allow for a more complex exploration of a topic. How much time do you have?
If you have several weeks, it’s likely your instructor is expecting you to do a lot of research.
Do you need a a particular number or type of references?
Scholarly books and articles take time to write and publish, so topics focused narrowly on a very recent event can be problematic. If you need primary sources, choosing a topic focused on a region whose language you do not speak will be difficult.
Narrowing your topic
When you first begin working on a writing assignment, it is fine to start out with a really broad idea. For example, if you are writing a paper for an introductory computer science class, you might want to focus on cyber security because that is the work field you plan to enter. That is a good starting point - choosing to do more research on an aspect of your future profession is a great idea. But cyber security is too broad of a topic.
How do you know if your topic is too broad?
Here are some strategies you might use to decide if your topic is too broad:
1. Type the topic (like cyber security) into a library search engine. If you get thousands of results, your topic is probably too broad. Look at some of the titles of those results to get an idea of "sub-topics" you might focus on.
2. If you type the topic into a search engine and you find whole books are written on the topic, it is definitely too broad. But scan the chapter titles of several of those books to get an idea of something more specific to focus on.
3. Sit down and brainstorm all the different angles you might take on your topic (ex. cyber security: encryption methods, types of malware, device security, types a social engineering etc). If you can list lots of different angles, any one of those might be a good way to narrow your topic - but it definitely needs to be narrower.
Why is it a big deal if my topic is too broad? Doesn't that make it easier to find lots of information?
Finding lots of information may make you feel more comfortable at first, but here are some reasons why its important to make sure you topic is narrow enough:
1. If your topic is too broad you'll have so much information to include in your paper that you won't know how to organize it or even where to start.
2. If your topic is too broad, your reader may expect you to talk about aspects of the topic that you never address.
3. If your topic is too broad, you'll have to write more pages than your instructor assigned to cover everything you need to say. Most instructors won't accept that. Or they may take off points for it. So, you'll end up having to cut material you took time to write in order to make your paper fit the proper length.
4. If your topic is too broad, you will spend a lot of time finding articles or gathering data you will never use because you eventually have to cut material as in #3 above.
5. If your topic is too broad, it will be difficult to identify and apply the proper methods needed to analyze all the information/data you gather.
So,in short, making sure your topic is properly narrow saves you from wasting a lot of time!
How can you narrow your topic?
We suggest two great ways to narrow your topic:
1. One option is to ask yourself who, what, where, when, why and how questions about your topic. Using cyber security as an example of a "too broad" topic, we can ask who? (what countries are responsible for hacking? who performs hacking for corporate espionage?) and how? (types of malware, types of social engineering) and where? (on networks, computers, phones, smart devices). If we were writing a historical overview of cyber security, we might have narrowed our focus by asking "when". Then our topic might have narrowed like this: A comparison of how hacking has evolved since the dawn of the Internet of Things (ex. smart refrigerators, coffee pots etc).
Below is a video of how this might work using an example from an American history class:
2. A second option is to create a concept map. To create a concept map, write down your broad topic in the middle of a piece of paper. Then brainstorm associated ideas. The terms you write down will likely be good directions to take when narrowing your topic. Here is an example of a concept map:

Here is a video showing how to develop a concept map and use it to create a research statement:
So, returning to our example of cyber security, we might finally decide to write about user education (who? - users) to prevent phishing attacks (what? - phishing attacks)?
What is a research question?
Once you have done enough research to narrow your topic to something manageable, you are probably ready to formulate your research question. For college-level research, you will start out with a question, look at all the evidence and then draw a conclusion based on that evidence. Therefore, your research must begin with a research question - a statement that identifies what you are going to study.
How do you formulate a research question?
To formulate your research question you might:
1. Start with the topic that you have decided upon and then list all the questions that you'd like answered about it yourself. Brainstorm, alone or with another student or with your professor, on all the questions the topic raises in your mind.
2. For beginning researchers, a good way to identify possible research questions is to look at previous studies on the topic. While reading the research studies, look for places where the authors of the studies mention "more research is needed" or "XYZ angle was not included in this study." These statements might indicate gaps in the current research.
3. Another way to use existing studies is to identify a type of study that has been done on one population, but not another. For example, referring again to our computer science research project on which types of user education mitigate social engineering attacks, what if your preliminary research showed there have been many studies on "white collar" workers but none that focused on "blue collar" workers. A study that focused on blue collar workers might offer a new angle for research.
4. A final way to use existing research studies to identify a research question is to look for indications of controversy. If numerous recent studies mention a particular angle of research on the topic is controversial, that indicates there is still a need for study on that angle.
What are the characteristics of a good research question?
Your individual classes will address in depth the characteristics of a good research question in your discipline. We can make a few generalizations about good research questions at the introductory level here. A good research question:
1. Can be answered objectively, with evidence. It is not solely value-based.
2. Can be answered with evidence that already exists or with evidence that can be gathered through experimentation you can design.
3. Is adequately focused.
4. Is significant.
What is all this about being able to test and analyze? Or in other words: A quick introduction to the concept of Methodology
The type of methodology you will use for your research depends greatly on your field of study. Biologists, economists, historians, literature scholars - they all have vastly different methods of gathering evidence that suit their fields. For now, it would help to understand that in some fields, especially the humanities (literature, history, religion etc), research is often "qualitative." Qualitative research focuses on relationships between people or texts. It seeks to to understand people's beliefs, experiences, attitudes, behavior, and interactions in a non-numeric way. For example, a scholar of literature might exam a wide body of medieval texts to answer the question: How was the LGBTQ+ community portrayed in the writings of a certain author. To answer that question, the scholar will examine a body of texts for all references to LGBTQ+ characters or interactions and how they were portrayed/perceived by other characters. They will then draw a conclusion based on that evidence on the perception of LGBTQ+ characters by that author in that time period.
Physical and social scientists (ex. biologists, psychologists, economists), in contrast, typically conduct quantitative research . Quantitative research emphasizes objective measurements and the statistical, mathematical, or numerical analysis of data collected through direct experiments, polls, questionnaires, and surveys, or by manipulating pre-existing statistical data using computational techniques. Your goal in conducting quantitative research study is to determine the relationship between one thing [an independent variable] and another [a dependent or outcome variable] within a population. Quantitative research designs are either descriptive [subjects usually measured once] or experimental [subjects measured before and after a treatment]. A descriptive study establishes only associations between variables; an experimental study establishes causality.
You will focus on discipline-appropriate methodologies in your classes, but having at least this introduction will help you understand why certain questions aren't really research questions - they can't be tested and they don't allow for analysis or conclusions.
Babbie, Earl R. The Practice of Social Research . 12th ed. Belmont, CA: Wadsworth Cengage, 2010; Brians, Craig Leonard et al. Empirical Political Analysis: Quantitative and Qualitative Research Methods . 8th ed. Boston, MA: Longman, 2011; McNabb, David E. Research Methods in Public Administration and Nonprofit Management: Quantitative and Qualitative Approaches . 2nd ed. Armonk, NY: M.E. Sharpe, 2008; Quantitative Research Methods . Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Singh, Kultar. Quantitative Social Research Methods . Los Angeles, CA: Sage, 2007.
Once you have developed your research question and you have done some preliminary reading on your topic, you are ready to form your thesis statement or hypothesis. Depending on your discipline, your thesis or hypothesis will have very specific requirements. You will learn about those requirements in your classes. Here, we will make a general introduction to the thesis or hypothesis statement.
A thesis statement may be seen in quantitative, qualitative, and mixed methods research.
A thesis statement is a short, direct sentence that summarizes the main point or claim of an essay or research paper. It It is developed, supported, and explained in the body of the essay or research report by means of examples and evidence.
A good thesis statement:
- is stated in declarative form.
- tells the reader how you will interpret the significance of the subject matter under discussion.
- is a road map for the paper; in other words, it tells the reader what to expect from the rest of the paper.
- directly answers the research question.
- makes a claim that others might dispute and that you will support with evidence.
The following is an example of a strong thesis statement in the context of the introduction paragraphs of a history paper:

Ritchie, Daniel. “War, Religion and Anti-Slavery Ideology: Isaac Nelson’s Radical Abolitionist Examination of the American Civil War.” Historical Research , vol. 89, no. 246, Nov. 2016, pp. 799–823. EBSCOhost , doi:10.1111/1468-2281.12134.
Hypotheses are typically used in quantitative research.
A hypothesis is a formal statement that predicts a measurable relationship between two or more variables. A well stated, researchable hypothesis:
- Is stated in declarative form
- Uses precise terminology and is stated as concisely as possible
- Aligns with the research question and problem statement and is consistent with known fact, previous research and theory
- Is testable
- Is a statement of relationship between variables
Types of variables:
To properly formulate a hypothesis, it is helpful to understand the different types of variables that it must operationalize:
Dependent variable : the target organism; who or what is affected. Independent variable: who or what will affect the target organism; the variable the researcher will manipulate to see if it will make the dependent variable change. Control variable(s ): variables that must be held constant to ensure that the independent variable is the only variable affecting the dependent variable.
Types of hypothesis
There are several types of hypotheses that you might formulate:
Simple hypothesis - predicts the relationship between a single independent variable (IV) and a single dependent variable (DV).
For example: Computer-based training (IV) is associated with lower susceptibility to social engineering attacks (DV).
Complex hypothesis - predicts the relationship between two or more independent variables, and two or more dependent variables.
For example: The implementation of a computer-based training program (IV) will result in (DV):
decreased user susceptibility to social engineering attacks; increased user confidence in the ability to recognize social engineering attacks;
Null hypotheses - the hypothesis that there is no significant correlation or difference between specified populations, any observed difference being due to sampling or experimental error.
For example: Computer-based training will have no significant effect on susceptibility to social engineering attacks.
Directional hypothesis - predicts positive or negative correlation or change.
For example:
There is a positive correlation between user education and user confidence in the ability to recognize a social engineering attack. Users receiving computer-based training will succumb less frequently to phishing attacks than users who do not receive training.
Nondirectional hypothesis - predicts the independent variable will affect the dependent variable, but the direction of the effect is not specified.
For example: There will be a difference in how users trained by computer-based methods and face-to-face training methods respond to social engineering attacks. (As opposed to: Users trained with face-to-face methods will succumb to fewer social engineering attacks than users trained with computer-based methods).
- << Previous: Home
- Next: Find Information >>
- Last Updated: Nov 15, 2023 2:28 PM
- Subjects: For Faculty/Staff , Library Orientation
- URL: https://library.centre.edu/ILI
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Applying Critical Thinking
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
Importance of Narrowing the Research Topic
Whether you are assigned a general issue to investigate, must choose a problem to study from a list given to you by your professor, or you have to identify your own topic to investigate, it is important that the scope of the research problem is not too broad, otherwise, it will be difficult to adequately address the topic in the space and time allowed. You could experience a number of problems if your topic is too broad, including:
- You find too many information sources and, as a consequence, it is difficult to decide what to include or exclude or what are the most relevant sources.
- You find information that is too general and, as a consequence, it is difficult to develop a clear framework for examining the research problem.
- A lack of sufficient parameters that clearly define the research problem makes it difficult to identify and apply the proper methods needed to analyze it.
- You find information that covers a wide variety of concepts or ideas that can't be integrated into one paper and, as a consequence, you trail off into unnecessary tangents.
Lloyd-Walker, Beverly and Derek Walker. "Moving from Hunches to a Research Topic: Salient Literature and Research Methods." In Designs, Methods and Practices for Research of Project Management . Beverly Pasian, editor. ( Burlington, VT: Gower Publishing, 2015 ), pp. 119-129.
Strategies for Narrowing the Research Topic
A common challenge when beginning to write a research paper is determining how and in what ways to narrow down your topic . Even if your professor gives you a specific topic to study, it will almost never be so specific that you won’t have to narrow it down at least to some degree [besides, it is very boring to grade fifty papers that are all about the exact same thing!].
A topic is too broad to be manageable when a review of the literature reveals too many different, and oftentimes conflicting or only remotely related, ideas about how to investigate the research problem. Although you will want to start the writing process by considering a variety of different approaches to studying the research problem, you will need to narrow the focus of your investigation at some point early in the writing process. This way, you don't attempt to do too much in one paper.
Here are some strategies to help narrow the thematic focus of your paper :
- Aspect -- choose one lens through which to view the research problem, or look at just one facet of it [e.g., rather than studying the role of food in South Asian religious rituals, study the role of food in Hindu marriage ceremonies, or, the role of one particular type of food among several religions].
- Components -- determine if your initial variable or unit of analysis can be broken into smaller parts, which can then be analyzed more precisely [e.g., a study of tobacco use among adolescents can focus on just chewing tobacco rather than all forms of usage or, rather than adolescents in general, focus on female adolescents in a certain age range who choose to use tobacco].
- Methodology -- the way in which you gather information can reduce the domain of interpretive analysis needed to address the research problem [e.g., a single case study can be designed to generate data that does not require as extensive an explanation as using multiple cases].
- Place -- generally, the smaller the geographic unit of analysis, the more narrow the focus [e.g., rather than study trade relations issues in West Africa, study trade relations between Niger and Cameroon as a case study that helps to explain economic problems in the region].
- Relationship -- ask yourself how do two or more different perspectives or variables relate to one another. Designing a study around the relationships between specific variables can help constrict the scope of analysis [e.g., cause/effect, compare/contrast, contemporary/historical, group/individual, child/adult, opinion/reason, problem/solution].
- Time -- the shorter the time period of the study, the more narrow the focus [e.g., restricting the study of trade relations between Niger and Cameroon to only the period of 2010 - 2020].
- Type -- focus your topic in terms of a specific type or class of people, places, or phenomena [e.g., a study of developing safer traffic patterns near schools can focus on SUVs, or just student drivers, or just the timing of traffic signals in the area].
- Combination -- use two or more of the above strategies to focus your topic more narrowly.
NOTE: Apply one of the above strategies first in designing your study to determine if that gives you a manageable research problem to investigate. You will know if the problem is manageable by reviewing the literature on your more narrowed problem and assessing whether prior research is sufficient to move forward in your study [i.e., not too much, not too little]. Be careful, however, because combining multiple strategies risks creating the opposite problem--your problem becomes too narrowly defined and you can't locate enough research or data to support your study.
Booth, Wayne C. The Craft of Research . Fourth edition. Chicago, IL: The University of Chicago Press, 2016; Coming Up With Your Topic. Institute for Writing Rhetoric. Dartmouth College; Narrowing a Topic. Writing Center. University of Kansas; Narrowing Topics. Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Strategies for Narrowing a Topic. University Libraries. Information Skills Modules. Virginia Tech University; The Process of Writing a Research Paper. Department of History. Trent University; Ways to Narrow Down a Topic. Contributing Authors. Utah State OpenCourseWare.
- << Previous: Reading Research Effectively
- Next: Broadening a Topic Idea >>
- Last Updated: May 30, 2024 9:38 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide
1000+ FREE Research Topics & Title Ideas
If you’re at the start of your research journey and are trying to figure out which research topic you want to focus on, you’ve come to the right place. Select your area of interest below to view a comprehensive collection of potential research ideas.

Research Topic FAQs
What (exactly) is a research topic.
A research topic is the subject of a research project or study – for example, a dissertation or thesis. A research topic typically takes the form of a problem to be solved, or a question to be answered.
A good research topic should be specific enough to allow for focused research and analysis. For example, if you are interested in studying the effects of climate change on agriculture, your research topic could focus on how rising temperatures have impacted crop yields in certain regions over time.
To learn more about the basics of developing a research topic, consider our free research topic ideation webinar.
What constitutes a good research topic?
A strong research topic comprises three important qualities : originality, value and feasibility.
- Originality – a good topic explores an original area or takes a novel angle on an existing area of study.
- Value – a strong research topic provides value and makes a contribution, either academically or practically.
- Feasibility – a good research topic needs to be practical and manageable, given the resource constraints you face.
To learn more about what makes for a high-quality research topic, check out this post .
What's the difference between a research topic and research problem?
A research topic and a research problem are two distinct concepts that are often confused. A research topic is a broader label that indicates the focus of the study , while a research problem is an issue or gap in knowledge within the broader field that needs to be addressed.
To illustrate this distinction, consider a student who has chosen “teenage pregnancy in the United Kingdom” as their research topic. This research topic could encompass any number of issues related to teenage pregnancy such as causes, prevention strategies, health outcomes for mothers and babies, etc.
Within this broad category (the research topic) lies potential areas of inquiry that can be explored further – these become the research problems . For example:
- What factors contribute to higher rates of teenage pregnancy in certain communities?
- How do different types of parenting styles affect teen pregnancy rates?
- What interventions have been successful in reducing teenage pregnancies?
Simply put, a key difference between a research topic and a research problem is scope ; the research topic provides an umbrella under which multiple questions can be asked, while the research problem focuses on one specific question or set of questions within that larger context.
How can I find potential research topics for my project?
There are many steps involved in the process of finding and choosing a high-quality research topic for a dissertation or thesis. We cover these steps in detail in this video (also accessible below).
How can I find quality sources for my research topic?
Finding quality sources is an essential step in the topic ideation process. To do this, you should start by researching scholarly journals, books, and other academic publications related to your topic. These sources can provide reliable information on a wide range of topics. Additionally, they may contain data or statistics that can help support your argument or conclusions.
Identifying Relevant Sources
When searching for relevant sources, it’s important to look beyond just published material; try using online databases such as Google Scholar or JSTOR to find articles from reputable journals that have been peer-reviewed by experts in the field.
You can also use search engines like Google or Bing to locate websites with useful information about your topic. However, be sure to evaluate any website before citing it as a source—look for evidence of authorship (such as an “About Us” page) and make sure the content is up-to-date and accurate before relying on it.
Evaluating Sources
Once you’ve identified potential sources for your research project, take some time to evaluate them thoroughly before deciding which ones will best serve your purpose. Consider factors such as author credibility (are they an expert in their field?), publication date (is the source current?), objectivity (does the author present both sides of an issue?) and relevance (how closely does this source relate to my specific topic?).
By researching the current literature on your topic, you can identify potential sources that will help to provide quality information. Once you’ve identified these sources, it’s time to look for a gap in the research and determine what new knowledge could be gained from further study.
How can I find a good research gap?
Finding a strong gap in the literature is an essential step when looking for potential research topics. We explain what research gaps are and how to find them in this post.
How should I evaluate potential research topics/ideas?
When evaluating potential research topics, it is important to consider the factors that make for a strong topic (we discussed these earlier). Specifically:
- Originality
- Feasibility
So, when you have a list of potential topics or ideas, assess each of them in terms of these three criteria. A good topic should take a unique angle, provide value (either to academia or practitioners), and be practical enough for you to pull off, given your limited resources.
Finally, you should also assess whether this project could lead to potential career opportunities such as internships or job offers down the line. Make sure that you are researching something that is relevant enough so that it can benefit your professional development in some way. Additionally, consider how each research topic aligns with your career goals and interests; researching something that you are passionate about can help keep motivation high throughout the process.
How can I assess the feasibility of a research topic?
When evaluating the feasibility and practicality of a research topic, it is important to consider several factors.
First, you should assess whether or not the research topic is within your area of competence. Of course, when you start out, you are not expected to be the world’s leading expert, but do should at least have some foundational knowledge.
Time commitment
When considering a research topic, you should think about how much time will be required for completion. Depending on your field of study, some topics may require more time than others due to their complexity or scope.
Additionally, if you plan on collaborating with other researchers or institutions in order to complete your project, additional considerations must be taken into account such as coordinating schedules and ensuring that all parties involved have adequate resources available.
Resources needed
It’s also critically important to consider what type of resources are necessary in order to conduct the research successfully. This includes physical materials such as lab equipment and chemicals but can also include intangible items like access to certain databases or software programs which may be necessary depending on the nature of your work. Additionally, if there are costs associated with obtaining these materials then this must also be factored into your evaluation process.
Potential risks
It’s important to consider the inherent potential risks for each potential research topic. These can include ethical risks (challenges getting ethical approval), data risks (not being able to access the data you’ll need), technical risks relating to the equipment you’ll use and funding risks (not securing the necessary financial back to undertake the research).
If you’re looking for more information about how to find, evaluate and select research topics for your dissertation or thesis, check out our free webinar here . Alternatively, if you’d like 1:1 help with the topic ideation process, consider our private coaching services .

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
- Privacy Policy

Home » 500+ Qualitative Research Titles and Topics
500+ Qualitative Research Titles and Topics
Table of Contents

Qualitative research is a methodological approach that involves gathering and analyzing non-numerical data to understand and interpret social phenomena. Unlike quantitative research , which emphasizes the collection of numerical data through surveys and experiments, qualitative research is concerned with exploring the subjective experiences, perspectives, and meanings of individuals and groups. As such, qualitative research topics can be diverse and encompass a wide range of social issues and phenomena. From exploring the impact of culture on identity formation to examining the experiences of marginalized communities, qualitative research offers a rich and nuanced perspective on complex social issues. In this post, we will explore some of the most compelling qualitative research topics and provide some tips on how to conduct effective qualitative research.
Qualitative Research Titles
Qualitative research titles often reflect the study’s focus on understanding the depth and complexity of human behavior, experiences, or social phenomena. Here are some examples across various fields:
- “Understanding the Impact of Project-Based Learning on Student Engagement in High School Classrooms: A Qualitative Study”
- “Navigating the Transition: Experiences of International Students in American Universities”
- “The Role of Parental Involvement in Early Childhood Education: Perspectives from Teachers and Parents”
- “Exploring the Effects of Teacher Feedback on Student Motivation and Self-Efficacy in Middle Schools”
- “Digital Literacy in the Classroom: Teacher Strategies for Integrating Technology in Elementary Education”
- “Culturally Responsive Teaching Practices: A Case Study in Diverse Urban Schools”
- “The Influence of Extracurricular Activities on Academic Achievement: Student Perspectives”
- “Barriers to Implementing Inclusive Education in Public Schools: A Qualitative Inquiry”
- “Teacher Professional Development and Its Impact on Classroom Practice: A Qualitative Exploration”
- “Student-Centered Learning Environments: A Qualitative Study of Classroom Dynamics and Outcomes”
- “The Experience of First-Year Teachers: Challenges, Support Systems, and Professional Growth”
- “Exploring the Role of School Leadership in Fostering a Positive School Culture”
- “Peer Relationships and Learning Outcomes in Cooperative Learning Settings: A Qualitative Analysis”
- “The Impact of Social Media on Student Learning and Engagement: Teacher and Student Perspectives”
- “Understanding Special Education Needs: Parent and Teacher Perceptions of Support Services in Schools
Health Science
- “Living with Chronic Pain: Patient Narratives and Coping Strategies in Managing Daily Life”
- “Healthcare Professionals’ Perspectives on the Challenges of Rural Healthcare Delivery”
- “Exploring the Mental Health Impacts of COVID-19 on Frontline Healthcare Workers: A Qualitative Study”
- “Patient and Family Experiences of Palliative Care: Understanding Needs and Preferences”
- “The Role of Community Health Workers in Improving Access to Maternal Healthcare in Rural Areas”
- “Barriers to Mental Health Services Among Ethnic Minorities: A Qualitative Exploration”
- “Understanding Patient Satisfaction in Telemedicine Services: A Qualitative Study of User Experiences”
- “The Impact of Cultural Competence Training on Healthcare Provider-Patient Communication”
- “Navigating the Transition to Adult Healthcare Services: Experiences of Adolescents with Chronic Conditions”
- “Exploring the Use of Alternative Medicine Among Patients with Chronic Diseases: A Qualitative Inquiry”
- “The Role of Social Support in the Rehabilitation Process of Stroke Survivors”
- “Healthcare Decision-Making Among Elderly Patients: A Qualitative Study of Preferences and Influences”
- “Nurse Perceptions of Patient Safety Culture in Hospital Settings: A Qualitative Analysis”
- “Experiences of Women with Postpartum Depression: Barriers to Seeking Help”
- “The Impact of Nutrition Education on Eating Behaviors Among College Students: A Qualitative Approach”
- “Understanding Resilience in Survivors of Childhood Trauma: A Narrative Inquiry”
- “The Role of Mindfulness in Managing Work-Related Stress Among Corporate Employees: A Qualitative Study”
- “Coping Mechanisms Among Parents of Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder”
- “Exploring the Psychological Impact of Social Isolation in the Elderly: A Phenomenological Study”
- “Identity Formation in Adolescence: The Influence of Social Media and Peer Groups”
- “The Experience of Forgiveness in Interpersonal Relationships: A Qualitative Exploration”
- “Perceptions of Happiness and Well-Being Among University Students: A Cultural Perspective”
- “The Impact of Art Therapy on Anxiety and Depression in Adult Cancer Patients”
- “Narratives of Recovery: A Qualitative Study on the Journey Through Addiction Rehabilitation”
- “Exploring the Psychological Effects of Long-Term Unemployment: A Grounded Theory Approach”
- “Attachment Styles and Their Influence on Adult Romantic Relationships: A Qualitative Analysis”
- “The Role of Personal Values in Career Decision-Making Among Young Adults”
- “Understanding the Stigma of Mental Illness in Rural Communities: A Qualitative Inquiry”
- “Exploring the Use of Digital Mental Health Interventions Among Adolescents: A Qualitative Study”
- “The Psychological Impact of Climate Change on Young Adults: An Exploration of Anxiety and Action”
- “Navigating Identity: The Role of Social Media in Shaping Youth Culture and Self-Perception”
- “Community Resilience in the Face of Urban Gentrification: A Case Study of Neighborhood Change”
- “The Dynamics of Intergenerational Relationships in Immigrant Families: A Qualitative Analysis”
- “Social Capital and Economic Mobility in Low-Income Neighborhoods: An Ethnographic Approach”
- “Gender Roles and Career Aspirations Among Young Adults in Conservative Societies”
- “The Stigma of Mental Health in the Workplace: Employee Narratives and Organizational Culture”
- “Exploring the Intersection of Race, Class, and Education in Urban School Systems”
- “The Impact of Digital Divide on Access to Healthcare Information in Rural Communities”
- “Social Movements and Political Engagement Among Millennials: A Qualitative Study”
- “Cultural Adaptation and Identity Among Second-Generation Immigrants: A Phenomenological Inquiry”
- “The Role of Religious Institutions in Providing Community Support and Social Services”
- “Negotiating Public Space: Experiences of LGBTQ+ Individuals in Urban Environments”
- “The Sociology of Food: Exploring Eating Habits and Food Practices Across Cultures”
- “Work-Life Balance Challenges Among Dual-Career Couples: A Qualitative Exploration”
- “The Influence of Peer Networks on Substance Use Among Adolescents: A Community Study”
Business and Management
- “Navigating Organizational Change: Employee Perceptions and Adaptation Strategies in Mergers and Acquisitions”
- “Corporate Social Responsibility: Consumer Perceptions and Brand Loyalty in the Retail Sector”
- “Leadership Styles and Organizational Culture: A Comparative Study of Tech Startups”
- “Workplace Diversity and Inclusion: Best Practices and Challenges in Multinational Corporations”
- “Consumer Trust in E-commerce: A Qualitative Study of Online Shopping Behaviors”
- “The Gig Economy and Worker Satisfaction: Exploring the Experiences of Freelance Professionals”
- “Entrepreneurial Resilience: Success Stories and Lessons Learned from Failed Startups”
- “Employee Engagement and Productivity in Remote Work Settings: A Post-Pandemic Analysis”
- “Brand Storytelling: How Narrative Strategies Influence Consumer Engagement”
- “Sustainable Business Practices: Stakeholder Perspectives in the Fashion Industry”
- “Cross-Cultural Communication Challenges in Global Teams: Strategies for Effective Collaboration”
- “Innovative Workspaces: The Impact of Office Design on Creativity and Collaboration”
- “Consumer Perceptions of Artificial Intelligence in Customer Service: A Qualitative Exploration”
- “The Role of Mentoring in Career Development: Insights from Women in Leadership Positions”
- “Agile Management Practices: Adoption and Impact in Traditional Industries”
Environmental Studies
- “Community-Based Conservation Efforts in Tropical Rainforests: A Qualitative Study of Local Perspectives and Practices”
- “Urban Sustainability Initiatives: Exploring Resident Participation and Impact in Green City Projects”
- “Perceptions of Climate Change Among Indigenous Populations: Insights from Traditional Ecological Knowledge”
- “Environmental Justice and Industrial Pollution: A Case Study of Community Advocacy and Response”
- “The Role of Eco-Tourism in Promoting Conservation Awareness: Perspectives from Tour Operators and Visitors”
- “Sustainable Agriculture Practices Among Smallholder Farmers: Challenges and Opportunities”
- “Youth Engagement in Climate Action Movements: Motivations, Perceptions, and Outcomes”
- “Corporate Environmental Responsibility: A Qualitative Analysis of Stakeholder Expectations and Company Practices”
- “The Impact of Plastic Pollution on Marine Ecosystems: Community Awareness and Behavioral Change”
- “Renewable Energy Adoption in Rural Communities: Barriers, Facilitators, and Social Implications”
- “Water Scarcity and Community Adaptation Strategies in Arid Regions: A Grounded Theory Approach”
- “Urban Green Spaces: Public Perceptions and Use Patterns in Megacities”
- “Environmental Education in Schools: Teachers’ Perspectives on Integrating Sustainability into Curricula”
- “The Influence of Environmental Activism on Policy Change: Case Studies of Grassroots Campaigns”
- “Cultural Practices and Natural Resource Management: A Qualitative Study of Indigenous Stewardship Models”
Anthropology
- “Kinship and Social Organization in Matrilineal Societies: An Ethnographic Study”
- “Rituals and Beliefs Surrounding Death and Mourning in Diverse Cultures: A Comparative Analysis”
- “The Impact of Globalization on Indigenous Languages and Cultural Identity”
- “Food Sovereignty and Traditional Agricultural Practices Among Indigenous Communities”
- “Navigating Modernity: The Integration of Traditional Healing Practices in Contemporary Healthcare Systems”
- “Gender Roles and Equality in Hunter-Gatherer Societies: An Anthropological Perspective”
- “Sacred Spaces and Religious Practices: An Ethnographic Study of Pilgrimage Sites”
- “Youth Subcultures and Resistance: An Exploration of Identity and Expression in Urban Environments”
- “Cultural Constructions of Disability and Inclusion: A Cross-Cultural Analysis”
- “Interethnic Marriages and Cultural Syncretism: Case Studies from Multicultural Societies”
- “The Role of Folklore and Storytelling in Preserving Cultural Heritage”
- “Economic Anthropology of Gift-Giving and Reciprocity in Tribal Communities”
- “Digital Anthropology: The Role of Social Media in Shaping Political Movements”
- “Migration and Diaspora: Maintaining Cultural Identity in Transnational Communities”
- “Cultural Adaptations to Climate Change Among Coastal Fishing Communities”
Communication Studies
- “The Dynamics of Family Communication in the Digital Age: A Qualitative Inquiry”
- “Narratives of Identity and Belonging in Diaspora Communities Through Social Media”
- “Organizational Communication and Employee Engagement: A Case Study in the Non-Profit Sector”
- “Cultural Influences on Communication Styles in Multinational Teams: An Ethnographic Approach”
- “Media Representation of Women in Politics: A Content Analysis and Audience Perception Study”
- “The Role of Communication in Building Sustainable Community Development Projects”
- “Interpersonal Communication in Online Dating: Strategies, Challenges, and Outcomes”
- “Public Health Messaging During Pandemics: A Qualitative Study of Community Responses”
- “The Impact of Mobile Technology on Parent-Child Communication in the Digital Era”
- “Crisis Communication Strategies in the Hospitality Industry: A Case Study of Reputation Management”
- “Narrative Analysis of Personal Stories Shared on Mental Health Blogs”
- “The Influence of Podcasts on Political Engagement Among Young Adults”
- “Visual Communication and Brand Identity: A Qualitative Study of Consumer Interpretations”
- “Communication Barriers in Cross-Cultural Healthcare Settings: Patient and Provider Perspectives”
- “The Role of Internal Communication in Managing Organizational Change: Employee Experiences”
Information Technology
- “User Experience Design in Augmented Reality Applications: A Qualitative Study of Best Practices”
- “The Human Factor in Cybersecurity: Understanding Employee Behaviors and Attitudes Towards Phishing”
- “Adoption of Cloud Computing in Small and Medium Enterprises: Challenges and Success Factors”
- “Blockchain Technology in Supply Chain Management: A Qualitative Exploration of Potential Impacts”
- “The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Personalizing User Experiences on E-commerce Platforms”
- “Digital Transformation in Traditional Industries: A Case Study of Technology Adoption Challenges”
- “Ethical Considerations in the Development of Smart Home Technologies: A Stakeholder Analysis”
- “The Impact of Social Media Algorithms on News Consumption and Public Opinion”
- “Collaborative Software Development: Practices and Challenges in Open Source Projects”
- “Understanding the Digital Divide: Access to Information Technology in Rural Communities”
- “Data Privacy Concerns and User Trust in Internet of Things (IoT) Devices”
- “The Effectiveness of Gamification in Educational Software: A Qualitative Study of Engagement and Motivation”
- “Virtual Teams and Remote Work: Communication Strategies and Tools for Effectiveness”
- “User-Centered Design in Mobile Health Applications: Evaluating Usability and Accessibility”
- “The Influence of Technology on Work-Life Balance: Perspectives from IT Professionals”
Tourism and Hospitality
- “Exploring the Authenticity of Cultural Heritage Tourism in Indigenous Communities”
- “Sustainable Tourism Practices: Perceptions and Implementations in Small Island Destinations”
- “The Impact of Social Media Influencers on Destination Choice Among Millennials”
- “Gastronomy Tourism: Exploring the Culinary Experiences of International Visitors in Rural Regions”
- “Eco-Tourism and Conservation: Stakeholder Perspectives on Balancing Tourism and Environmental Protection”
- “The Role of Hospitality in Enhancing the Cultural Exchange Experience of Exchange Students”
- “Dark Tourism: Visitor Motivations and Experiences at Historical Conflict Sites”
- “Customer Satisfaction in Luxury Hotels: A Qualitative Study of Service Excellence and Personalization”
- “Adventure Tourism: Understanding the Risk Perception and Safety Measures Among Thrill-Seekers”
- “The Influence of Local Communities on Tourist Experiences in Ecotourism Sites”
- “Event Tourism: Economic Impacts and Community Perspectives on Large-Scale Music Festivals”
- “Heritage Tourism and Identity: Exploring the Connections Between Historic Sites and National Identity”
- “Tourist Perceptions of Sustainable Accommodation Practices: A Study of Green Hotels”
- “The Role of Language in Shaping the Tourist Experience in Multilingual Destinations”
- “Health and Wellness Tourism: Motivations and Experiences of Visitors to Spa and Retreat Centers”
Qualitative Research Topics
Qualitative Research Topics are as follows:
- Understanding the lived experiences of first-generation college students
- Exploring the impact of social media on self-esteem among adolescents
- Investigating the effects of mindfulness meditation on stress reduction
- Analyzing the perceptions of employees regarding organizational culture
- Examining the impact of parental involvement on academic achievement of elementary school students
- Investigating the role of music therapy in managing symptoms of depression
- Understanding the experience of women in male-dominated industries
- Exploring the factors that contribute to successful leadership in non-profit organizations
- Analyzing the effects of peer pressure on substance abuse among adolescents
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with disabilities in the workplace
- Understanding the factors that contribute to burnout among healthcare professionals
- Examining the impact of social support on mental health outcomes
- Analyzing the perceptions of parents regarding sex education in schools
- Investigating the experiences of immigrant families in the education system
- Understanding the impact of trauma on mental health outcomes
- Exploring the effectiveness of animal-assisted therapy for individuals with anxiety
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful intergenerational relationships
- Investigating the experiences of LGBTQ+ individuals in the workplace
- Understanding the impact of online gaming on social skills development among adolescents
- Examining the perceptions of teachers regarding technology integration in the classroom
- Analyzing the experiences of women in leadership positions
- Investigating the factors that contribute to successful marriage and long-term relationships
- Understanding the impact of social media on political participation
- Exploring the experiences of individuals with mental health disorders in the criminal justice system
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful community-based programs for youth development
- Investigating the experiences of veterans in accessing mental health services
- Understanding the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on mental health outcomes
- Examining the perceptions of parents regarding childhood obesity prevention
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful multicultural education programs
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with chronic illnesses in the workplace
- Understanding the impact of poverty on academic achievement
- Exploring the experiences of individuals with autism spectrum disorder in the workplace
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful employee retention strategies
- Investigating the experiences of caregivers of individuals with Alzheimer’s disease
- Understanding the impact of parent-child communication on adolescent sexual behavior
- Examining the perceptions of college students regarding mental health services on campus
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful team building in the workplace
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with eating disorders in treatment programs
- Understanding the impact of mentorship on career success
- Exploring the experiences of individuals with physical disabilities in the workplace
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful community-based programs for mental health
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with substance use disorders in treatment programs
- Understanding the impact of social media on romantic relationships
- Examining the perceptions of parents regarding child discipline strategies
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful cross-cultural communication in the workplace
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with anxiety disorders in treatment programs
- Understanding the impact of cultural differences on healthcare delivery
- Exploring the experiences of individuals with hearing loss in the workplace
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful parent-teacher communication
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with depression in treatment programs
- Understanding the impact of childhood trauma on adult mental health outcomes
- Examining the perceptions of college students regarding alcohol and drug use on campus
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful mentor-mentee relationships
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with intellectual disabilities in the workplace
- Understanding the impact of work-family balance on employee satisfaction and well-being
- Exploring the experiences of individuals with autism spectrum disorder in vocational rehabilitation programs
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful project management in the construction industry
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with substance use disorders in peer support groups
- Understanding the impact of mindfulness meditation on stress reduction and mental health
- Examining the perceptions of parents regarding childhood nutrition
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful environmental sustainability initiatives in organizations
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with bipolar disorder in treatment programs
- Understanding the impact of job stress on employee burnout and turnover
- Exploring the experiences of individuals with physical disabilities in recreational activities
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful strategic planning in nonprofit organizations
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with hoarding disorder in treatment programs
- Understanding the impact of culture on leadership styles and effectiveness
- Examining the perceptions of college students regarding sexual health education on campus
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful supply chain management in the retail industry
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with personality disorders in treatment programs
- Understanding the impact of multiculturalism on group dynamics in the workplace
- Exploring the experiences of individuals with chronic pain in mindfulness-based pain management programs
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful employee engagement strategies in organizations
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with internet addiction disorder in treatment programs
- Understanding the impact of social comparison on body dissatisfaction and self-esteem
- Examining the perceptions of parents regarding childhood sleep habits
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful diversity and inclusion initiatives in organizations
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with schizophrenia in treatment programs
- Understanding the impact of job crafting on employee motivation and job satisfaction
- Exploring the experiences of individuals with vision impairments in navigating public spaces
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful customer relationship management strategies in the service industry
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with dissociative amnesia in treatment programs
- Understanding the impact of cultural intelligence on intercultural communication and collaboration
- Examining the perceptions of college students regarding campus diversity and inclusion efforts
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful supply chain sustainability initiatives in organizations
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with obsessive-compulsive disorder in treatment programs
- Understanding the impact of transformational leadership on organizational performance and employee well-being
- Exploring the experiences of individuals with mobility impairments in public transportation
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful talent management strategies in organizations
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with substance use disorders in harm reduction programs
- Understanding the impact of gratitude practices on well-being and resilience
- Examining the perceptions of parents regarding childhood mental health and well-being
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful corporate social responsibility initiatives in organizations
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with borderline personality disorder in treatment programs
- Understanding the impact of emotional labor on job stress and burnout
- Exploring the experiences of individuals with hearing impairments in healthcare settings
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful customer experience strategies in the hospitality industry
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with gender dysphoria in gender-affirming healthcare
- Understanding the impact of cultural differences on cross-cultural negotiation in the global marketplace
- Examining the perceptions of college students regarding academic stress and mental health
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful supply chain agility in organizations
- Understanding the impact of music therapy on mental health and well-being
- Exploring the experiences of individuals with dyslexia in educational settings
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful leadership in nonprofit organizations
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with chronic illnesses in online support groups
- Understanding the impact of exercise on mental health and well-being
- Examining the perceptions of parents regarding childhood screen time
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful change management strategies in organizations
- Understanding the impact of cultural differences on international business negotiations
- Exploring the experiences of individuals with hearing impairments in the workplace
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful team building in corporate settings
- Understanding the impact of technology on communication in romantic relationships
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful community engagement strategies for local governments
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in treatment programs
- Understanding the impact of financial stress on mental health and well-being
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful mentorship programs in organizations
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with gambling addictions in treatment programs
- Understanding the impact of social media on body image and self-esteem
- Examining the perceptions of parents regarding childhood education
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful virtual team management strategies
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with dissociative identity disorder in treatment programs
- Understanding the impact of cultural differences on cross-cultural communication in healthcare settings
- Exploring the experiences of individuals with chronic pain in cognitive-behavioral therapy programs
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful community-building strategies in urban neighborhoods
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with alcohol use disorders in treatment programs
- Understanding the impact of personality traits on romantic relationships
- Examining the perceptions of college students regarding mental health stigma on campus
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful fundraising strategies for political campaigns
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with traumatic brain injuries in rehabilitation programs
- Understanding the impact of social support on mental health and well-being among the elderly
- Exploring the experiences of individuals with chronic illnesses in medical treatment decision-making processes
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful innovation strategies in organizations
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with dissociative disorders in treatment programs
- Understanding the impact of cultural differences on cross-cultural communication in education settings
- Examining the perceptions of parents regarding childhood physical activity
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful conflict resolution in family relationships
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with opioid use disorders in treatment programs
- Understanding the impact of emotional intelligence on leadership effectiveness
- Exploring the experiences of individuals with learning disabilities in the workplace
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful change management in educational institutions
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with eating disorders in recovery support groups
- Understanding the impact of self-compassion on mental health and well-being
- Examining the perceptions of college students regarding campus safety and security measures
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful marketing strategies for nonprofit organizations
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with postpartum depression in treatment programs
- Understanding the impact of ageism in the workplace
- Exploring the experiences of individuals with dyslexia in the education system
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with anxiety disorders in cognitive-behavioral therapy programs
- Understanding the impact of socioeconomic status on access to healthcare
- Examining the perceptions of parents regarding childhood screen time usage
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful supply chain management strategies
- Understanding the impact of parenting styles on child development
- Exploring the experiences of individuals with addiction in harm reduction programs
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful crisis management strategies in organizations
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with trauma in trauma-focused therapy programs
- Examining the perceptions of healthcare providers regarding patient-centered care
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful product development strategies
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with autism spectrum disorder in employment programs
- Understanding the impact of cultural competence on healthcare outcomes
- Exploring the experiences of individuals with chronic illnesses in healthcare navigation
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful community engagement strategies for non-profit organizations
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with physical disabilities in the workplace
- Understanding the impact of childhood trauma on adult mental health
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful supply chain sustainability strategies
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with personality disorders in dialectical behavior therapy programs
- Understanding the impact of gender identity on mental health treatment seeking behaviors
- Exploring the experiences of individuals with schizophrenia in community-based treatment programs
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful project team management strategies
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with obsessive-compulsive disorder in exposure and response prevention therapy programs
- Understanding the impact of cultural competence on academic achievement and success
- Examining the perceptions of college students regarding academic integrity
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful social media marketing strategies
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with bipolar disorder in community-based treatment programs
- Understanding the impact of mindfulness on academic achievement and success
- Exploring the experiences of individuals with substance use disorders in medication-assisted treatment programs
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with anxiety disorders in exposure therapy programs
- Understanding the impact of healthcare disparities on health outcomes
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful supply chain optimization strategies
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with borderline personality disorder in schema therapy programs
- Understanding the impact of culture on perceptions of mental health stigma
- Exploring the experiences of individuals with trauma in art therapy programs
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful digital marketing strategies
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with eating disorders in online support groups
- Understanding the impact of workplace bullying on job satisfaction and performance
- Examining the perceptions of college students regarding mental health resources on campus
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful supply chain risk management strategies
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with chronic pain in mindfulness-based pain management programs
- Understanding the impact of cognitive-behavioral therapy on social anxiety disorder
- Understanding the impact of COVID-19 on mental health and well-being
- Exploring the experiences of individuals with eating disorders in treatment programs
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful leadership in business organizations
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with chronic pain in cognitive-behavioral therapy programs
- Understanding the impact of cultural differences on intercultural communication
- Examining the perceptions of teachers regarding inclusive education for students with disabilities
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with depression in therapy programs
- Understanding the impact of workplace culture on employee retention and turnover
- Exploring the experiences of individuals with traumatic brain injuries in rehabilitation programs
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful crisis communication strategies in organizations
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with anxiety disorders in mindfulness-based interventions
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with chronic illnesses in healthcare settings
- Understanding the impact of technology on work-life balance
- Exploring the experiences of individuals with learning disabilities in academic settings
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful entrepreneurship in small businesses
- Understanding the impact of gender identity on mental health and well-being
- Examining the perceptions of individuals with disabilities regarding accessibility in public spaces
- Understanding the impact of religion on coping strategies for stress and anxiety
- Exploring the experiences of individuals with chronic illnesses in complementary and alternative medicine treatments
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful customer retention strategies in business organizations
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with postpartum depression in therapy programs
- Understanding the impact of ageism on older adults in healthcare settings
- Examining the perceptions of students regarding online learning during the COVID-19 pandemic
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful team building in virtual work environments
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with gambling disorders in treatment programs
- Exploring the experiences of individuals with chronic illnesses in peer support groups
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful social media marketing strategies for businesses
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with ADHD in treatment programs
- Understanding the impact of sleep on cognitive and emotional functioning
- Examining the perceptions of individuals with chronic illnesses regarding healthcare access and affordability
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with borderline personality disorder in dialectical behavior therapy programs
- Understanding the impact of social support on caregiver well-being
- Exploring the experiences of individuals with chronic illnesses in disability activism
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful cultural competency training programs in healthcare settings
- Understanding the impact of personality disorders on interpersonal relationships
- Examining the perceptions of healthcare providers regarding the use of telehealth services
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with dissociative disorders in therapy programs
- Understanding the impact of gender bias in hiring practices
- Exploring the experiences of individuals with visual impairments in the workplace
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful diversity and inclusion programs in the workplace
- Understanding the impact of online dating on romantic relationships
- Examining the perceptions of parents regarding childhood vaccination
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful communication in healthcare settings
- Understanding the impact of cultural stereotypes on academic achievement
- Exploring the experiences of individuals with substance use disorders in sober living programs
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful classroom management strategies
- Understanding the impact of social support on addiction recovery
- Examining the perceptions of college students regarding mental health stigma
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful conflict resolution in the workplace
- Understanding the impact of race and ethnicity on healthcare access and outcomes
- Exploring the experiences of individuals with post-traumatic stress disorder in treatment programs
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful project management strategies
- Understanding the impact of teacher-student relationships on academic achievement
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful customer service strategies
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with social anxiety disorder in treatment programs
- Understanding the impact of workplace stress on job satisfaction and performance
- Exploring the experiences of individuals with disabilities in sports and recreation
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful marketing strategies for small businesses
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with phobias in treatment programs
- Understanding the impact of culture on attitudes towards mental health and illness
- Examining the perceptions of college students regarding sexual assault prevention
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful time management strategies
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with addiction in recovery support groups
- Understanding the impact of mindfulness on emotional regulation and well-being
- Exploring the experiences of individuals with chronic pain in treatment programs
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful conflict resolution in romantic relationships
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with autism spectrum disorder in social skills training programs
- Understanding the impact of parent-child communication on adolescent substance use
- Examining the perceptions of parents regarding childhood mental health services
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful fundraising strategies for non-profit organizations
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with chronic illnesses in support groups
- Understanding the impact of personality traits on career success and satisfaction
- Exploring the experiences of individuals with disabilities in accessing public transportation
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful team building in sports teams
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with chronic pain in alternative medicine treatments
- Understanding the impact of stigma on mental health treatment seeking behaviors
- Examining the perceptions of college students regarding diversity and inclusion on campus.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

500+ Economics Research Topics

500+ Educational Research Topics

500+ Nursing Research Topic Ideas

300+ Controversial Research Topics

300+ Communication Research Topics

500+ Environmental Research Topics
SYSTEMATIC REVIEW article
This article is part of the research topic.
Reviews in Gastroenterology 2023
Electrogastrography Measurement Systems and Analysis Methods Used in Clinical Practice and Research: Comprehensive Review Provisionally Accepted

- 1 VSB-Technical University of Ostrava, Czechia
The final, formatted version of the article will be published soon.
Electrogastrography (EGG) is a non-invasive method with high diagnostic potential for the prevention of gastroenterological pathologies in clinical practice. In this paper, a review of the measurement systems, procedures, and methods of analysis used in electrogastrography is presented. A critical review of historical and current literature is conducted, focusing on electrode placement, measurement apparatus, measurement procedures, and time-frequency domain methods of filtration and analysis of the non-invasively measured electrical activity of the stomach.As a result a total of 129 relevant articles with primary aim on experimental diet were reviewed in this study. Scopus, PubMed and Web of Science databases were used to search for articles in English language, according to the specific query and using PRISMA method. The research topic of electrogastrography has been continuously growing in popularity since the first measurement by professor Alvarez 100 years ago and there are many researchers and companies interested in EGG nowadays. Measurement apparatus and procedures are still being developed in both commercial and research settings. There are plenty variable electrode layouts, ranging from minimal numbers of electrodes for ambulatory measurements to very high numbers of electrodes for spatial measurements. Most authors used in their research anatomically approximated layout with 2 active electrodes in bipolar connection and commercial electrogastrograph with sampling rate of 2 or 4 Hz. Test subjects were usually healthy adults and diet was controlled. However, evaluation methods are being developed at a slower pace and usually the signals are classified only based on dominant frequency. The main review contributions include the overview of spectrum of measurement systems and procedures for electrogastrography developed by many authors, but a firm medical standard has not yet been defined. Therefore, it is not possible to use this method in clinical practice for objective diagnosis.
Keywords: electrogastrography, non-invasive method, Measurement systems, Electrode placement, Measurement apparatus, Signal processing
Received: 19 Jan 2024; Accepted: 03 Jun 2024.
Copyright: © 2024 Oczka, Augustynek, Penhaker and Kubicek. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY) . The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) or licensor are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
* Correspondence: Dr. Jan Kubicek, VSB-Technical University of Ostrava, Ostrava, 708 33, Moravian-Silesian Region, Czechia
People also looked at

COMMENTS
Examples. Discrete variables (aka integer variables) Counts of individual items or values. Number of students in a class. Number of different tree species in a forest. Continuous variables (aka ratio variables) Measurements of continuous or non-finite values. Distance.
While the independent variable is the " cause ", the dependent variable is the " effect " - or rather, the affected variable. In other words, the dependent variable is the variable that is assumed to change as a result of a change in the independent variable. Keeping with the previous example, let's look at some dependent variables ...
Types of Variables in Research. Types of Variables in Research are as follows: Independent Variable. This is the variable that is manipulated by the researcher. It is also known as the predictor variable, as it is used to predict changes in the dependent variable. Examples of independent variables include age, gender, dosage, and treatment type ...
Independent vs. Dependent Variables | Definition & Examples. Published on February 3, 2022 by Pritha Bhandari.Revised on June 22, 2023. In research, variables are any characteristics that can take on different values, such as height, age, temperature, or test scores. Researchers often manipulate or measure independent and dependent variables in studies to test cause-and-effect relationships.
Dependent Variable The variable that depends on other factors that are measured. These variables are expected to change as a result of an experimental manipulation of the independent variable or variables. It is the presumed effect. Independent Variable The variable that is stable and unaffected by the other variables you are trying to measure.
The Role of Variables in Research. In scientific research, variables serve several key functions: Define Relationships: Variables allow researchers to investigate the relationships between different factors and characteristics, providing insights into the underlying mechanisms that drive phenomena and outcomes. Establish Comparisons: By manipulating and comparing variables, scientists can ...
Examples. Discrete variables (aka integer variables) Counts of individual items or values. Number of students in a class. Number of different tree species in a forest. Continuous variables (aka ratio variables) Measurements of continuous or non-finite values. Distance.
In research, the independent variable is manipulated to observe its effect, while the dependent variable is the measured outcome. Essentially, the independent variable is the presumed cause, and the dependent variable is the observed effect. Variables provide the foundation for examining relationships, drawing conclusions, and making ...
Compare the independent variable and dependent variable in research. See other types of variables in research, including confounding and extraneous variables. Updated: 11/21/2023
Examples of categorical variables include gender (male, female, other), type of vehicle (car, truck, motorcycle), or marital status (single, married, divorced). These categories help researchers organize data into groups for comparison and analysis. Categorical variables can be further classified into two subtypes: nominal and ordinal.
A data is referred to as the information and statistics gathered for analysis of a research topic. Data is broadly divided into two categories, such as: ... A control variable in research is a factor that's kept constant to ensure that it doesn't influence the outcome. By controlling these variables, researchers can isolate the effects of ...
Here is a simple rule that you can apply at all times: the independent variable is what a researcher changes, whereas the dependent variable is affected by these changes. To illustrate the difference, a number of examples are provided below. The purpose of Study 1 is to measure the impact of different plant fertilizers on how many fruits apple ...
As shown in Figure 2.1, scientific research proceeds along two planes: a theoretical plane and an empirical plane. Constructs are conceptualized at the theoretical (abstract) plane, while variables are operationalized and measured at the empirical (observational) plane. Thinking like a researcher implies the ability to move back and forth ...
The purpose of research is to describe and explain variance in the world, that is, variance that. occurs naturally in the world or chang e that we create due to manipulation. Variables are ...
Variables are important to understand because they are the basic units of the information studied and interpreted in research studies. Researchers carefully analyze and interpret the value (s) of each variable to make sense of how things relate to each other in a descriptive study or what has happened in an experiment. previous next.
Thus, the research question gives a preview of the different parts and variables of the study meant to address the problem posed in the research question.1 An excellent research question clarifies the research writing while facilitating understanding of the research topic, objective, scope, and limitations of the study.5
Introduction. Definition of Variable. Examples of Variables in Research: 6 Phenomena. Phenomenon 1: Climate change. Phenomenon 2: Crime and violence in the streets. Phenomenon 3: Poor performance of students in college entrance exams. Phenomenon 4: Fish kill. Phenomenon 5: Poor crop growth. Phenomenon 6: How Content Goes Viral.
If numerous recent studies mention a particular angle of research on the topic is controversial, that indicates there is still a need for study on that angle. ... Control variable(s): variables that must be held constant to ensure that the independent variable is the only variable affecting the dependent variable. Types of hypothesis.
Type-- focus your topic in terms of a specific type or class of people, places, or phenomena [e.g., a study of developing safer traffic patterns near schools can focus on SUVs, or just student drivers, or just the timing of traffic signals in the area]. Combination -- use two or more of the above strategies to focus your topic more narrowly.
Be sure to have at least two independent variables for proposed research paper. The topic proposal should include the following four items which serve as . . . In a study to determine whether how long a student sleeps affects test scores. the independent variable is the length of time spent sleeping while the dependent variable is the test score.
1000+ FREE Research Topics & Title Ideas. If you're at the start of your research journey and are trying to figure out which research topic you want to focus on, you've come to the right place. Select your area of interest below to view a comprehensive collection of potential research ideas. AI & Machine Learning. Blockchain & Cryptocurrency.
Quantitative research involves collecting and analyzing numerical data to identify patterns, trends, and relationships among variables. This method is widely used in social sciences, psychology, economics, and other fields where researchers aim to understand human behavior and phenomena through statistical analysis. If you are looking for a quantitative research topic, there are numerous areas ...
Qualitative Research Topics. Qualitative Research Topics are as follows: Understanding the lived experiences of first-generation college students. Exploring the impact of social media on self-esteem among adolescents. Investigating the effects of mindfulness meditation on stress reduction. Analyzing the perceptions of employees regarding ...
Understanding the mechanisms by which the combination of green marketing components fosters local sustainable development is crucial for global regions in achieving the United Nations' sustainable development goals. Utilizing panel data from China's provinces from 2011 to 2022, this study employs the DEA model to assess both the static and dynamic efficiencies of sustainable development ...
With the emerging of virtual coupling technologies, the concept of train platoon, where different vehicles can be flexibly and dynamically grouped or decoupled, has become a hot research topic. In this study, we investigate the scheduling of train platoons for urban rail networks with time-dependent demand to mitigate passenger inconvenience. We propose a mixed-integer linear programming (MILP ...
The research topic of electrogastrography has been continuously growing in popularity since the first measurement by professor Alvarez 100 years ago and there are many researchers and companies interested in EGG nowadays. Measurement apparatus and procedures are still being developed in both commercial and research settings.