Advisories | Goldlink | Goldmail | D2L | Safety | A-Z Index

Digital Commons @ East Tennessee State University
Home > STUDENT-WORKS > PROGRAM-ETD > ECED-ETD
Early Childhood Education Theses and Dissertations
If you are a graduate student submitting your thesis or dissertation, please click here to access the submission form.
Theses/Dissertations from 2024 2024
An Examination of Early Childhood Leadership in Public Elementary Schools: A Mixed Methods Study , Wesam Alshahrani
Design and Validation of a Test for Teachers: Measuring Knowledge of Trauma , Jennifer B. Bilbrey
Exploring Early Childhood Teachers’ Experiences in Teaching Multilingual Children in Public Mainstream Schools in Tennessee , Maria Dias
Theses/Dissertations from 2023 2023
Perceptions of Primary Caregivers About Managing Their Child’s Transition to Kindergarten: A Mixed-Methods Study , Kristy Lynn Castanon
Building Resilience: A Mixed Methods Exploration of Head Start Teachers Coping During the COVID-19 Pandemic , Ehichoya Edokhamhen
Exploration of Privilege and Preschool Teachers’ Demographics Associated with Teachers’ Self-Efficacy in Culturally Responsive Classroom Management , Katherine Madison
Examining Teachers' Referral and Placement Decisions of Hispanic Children for Gifted and Talented Programs , Guillermo I. Mendoza
Childhood Trauma in Early Care and Education: Understanding School Administrators’ Perceptions , Olawale Olubowale
Sound and Music Opportunities in Toddler Learning Environments , Sonia Akiko Yoshizawa
Theses/Dissertations from 2022 2022
An Investigation of the Relationship Between Teachers’ Personal Epistemologies and Their Self-Efficacy About Culturally Responsive Classroom Management , Tahani Ahmed
Early Detection of Atypical Motor and Neurobehavior of Infants at Risk Secondary to Opioid Exposure: A Prospective Study , Kara Boynewicz
The Impact of an Integrated STEM Collaborative Approach on Preservice Teachers’ Pedagogical Content Knowledge and Curricular Role Identity for Teaching Science , Qiuju Tian
Theses/Dissertations from 2021 2021
Student Collaboration: Early Childhood Teachers' Roles and Perspectives , Kimberly Ballantyne
The Impact of Natural Playscapes on Toddler Play , Laura J. Pearce
Familial Regulation of Young Children's TV Viewing in Ghana , Clara Puni-Nyamesem
Theses/Dissertations from 2020 2020
Determining if Classroom Pets as part of an Empathy-Based Intervention Affect Public Elementary School Students’ Empathy , Randa Dunlap
The Relationship Between the Amount of Time Spent in the Block Center and Gender Differences in Preschool Children’s Spatial Performance , Narges Sareh
Head Start Preschool Teachers’ Perceptions of Reggio Emilia Principles Practiced Within Their Own Setting: A Case Study , Tara Terry Voit
A Study of Empathy and Teacher Self-Efficacy Among Preservice Early Childhood Educators , Amy Wilson
Theses/Dissertations from 2019 2019
Arab-American Parents’ Views on the Use of Technology, Smartphones, and Touchscreen Devices with Infants, Toddlers and Preschoolers , Abidah Abutaleb
Seeing the World Differently. An Exploration of a Professional Development Model Bridging Science and Lay Cultures , Michael D. Garrett
Second-Grade Students’ Perceptions of Their Classrooms’ Physical Learning Environment , Tsitsi Nyabando
A Mixed Methods Exploration of East Tennessee Early Childhood Teachers’ Perceptions, Knowledge, Practices, and Resources of Critical Literacy , Rebekah Taylor
Theses/Dissertations from 2018 2018
The State of Outdoor Education in Northeast Tennessee: Preschool Teacher Attitudes Toward Outdoor Education , Cathy Landy
Teachers and Their Perceptions About Adaptive Skill Training Within an Early Childhood Comprehensive Development Classroom for Students with Intellectual Disabilities , Jennifer R. Lynberg
Preschool Teachers' Perceptions of Children Prenatally Exposed to Drugs , Brandie D. Maness
Gender Differences in Spatial Language During Preschool Small Group Geometry Activities , Winona Shue
Teachers’ Response to Infants’ Nonverbal Communication and Use of Response to Facilitate a Dialogue , Stephanie Stephens
The Effects of an Observation and Interpretation Intervention (COI/PALS) on Teachers’ Productive and Nonproductive Conversations with Preschool Children , Gina Joe Wohlford
Examining Contributors to Preschoolers’ Classroom Engagement using Structural Equation Modeling , Hongxia Zhao
Theses/Dissertations from 2017 2017
Parental Perceptions of Preschool-Age Children’s Literacy Development in a Rural Appalachian Community , Kimberly Austin
Levels of Feedback Observed in Kindergarten Classrooms: Perceptions and Reality , Jacqueline Johnson
Design and Validation of a Scale for Preschoolers: Measuring Nutrition Knowledge, Beliefs, and Behaviors , Michelle E. Johnson
Theses/Dissertations from 2016 2016
The Effects of Environmental Modifications and Visual Supports in the Home on Engagement and Challenging Behaviors in Children with Autism , Teresa L. Boggs
Teachers’ Perceptions of Intensive Professional Development on the Daily Five™ in Literacy Instruction: A Multiple Case Study Exploration , Lori A. Hamilton
Exploring Gesturing as a Natural Approach to Impact Stages of Second Language Development: A Multiple Baseline, Single Case Study of a Head Start Child , Guillermo I. Mendoza
Theses/Dissertations from 2015 2015
Determining if Custodial Grandparents of Pre-K - Third Grade Students Perceive Delivery of Information and Services Offered as Effective in Decreasing Early Chronic Absence , Kimberly S. Cassidy
Use of the Physical Classroom Environment as a Teaching and Learning Tool Including the Impact of the CCSSI in Kindergarten Through Third Grade Classrooms in Northeast Tennessee , Charity Hensley-Pipkin
Professional Learning Communities as a Professional Development Model Focusing on Instructional Practices Used to Teach Writing in Early Childhood , Jill T. Leonard
The Relationship Between an Affective Instructional Design, Children’s Attitudes Toward Mathematics, and Math Learning for Kindergarten-Age Children , Wendee B. White Mrs
Theses/Dissertations from 2014 2014
An Exploratory Critical Study of Questioning Strategies Posed by Early Childhood Teachers During Literacy Blocks , Angela H. Baker Ms.
Developing Mastery in Phonemic Awareness, Phonics, and Morphemic Awareness: A Multiple Case Study of Preservice Early Childhood Educators , Ruth Facun-Granadozo
Theses/Dissertations from 2012 2012
The Influences of Caregiver-Child Interactions and Temperament on Cortisol Concentrations of Toddlers in Full-Day Childcare , Helen Morris Lane
Theses/Dissertations from 2010 2010
Project 3rd Grade Environment: Descriptive Phenomenological Study of the Physical and Learning Environment in a Transformed 3rd Grade Classroom. , Charity Gail Hensley
Theses/Dissertations from 2008 2008
Inquire Within: The Connection between Teacher Training in Inquiry Learning Methodology and Classroom Practice. , Ariel Sky Ashe
Relationships between Primary Teacher Beliefs and Practice in the Primary Classrooms of a Small Urban School in East Tennessee. , Lindsay Collins Moore
Theses/Dissertations from 2007 2007
The Effects of Movement on Literacy. , Kathy S. Luppe
Theses/Dissertations from 2006 2006
Perceived Teacher Self-Efficacy in Early Childhood Settings: Differences between Early Childhood and Elementary Education Candidates. , Bradley Carroll Billheimer
Theses/Dissertations from 2004 2004
The Use of Rotation Model Sunday School. , Heather Renee Jones
The Relationship between the Use of Developmentally Appropriate Practice and the Inclusion of Product-Producing Art Activities in Infant Programs. , April D. Moore
Theses/Dissertations from 2003 2003
The Curricular Practices of Early Childhood Teachers Working in Public Sschool Primary Grades. , Elizabeth Ely Brading
Journaling as a Tool to Improve Story Comprehension for Kindergarten Students. , Carisa L. Carr
The Effects of Adult Interaction on Toddler Behavior in the Classroom. , Sarah Webb Hackney
Advanced Search
- Notify me via email or RSS
- Collections
- Disciplines
Author Corner
- Early Childhood Education Graduate Program
- Digital Scholarship Services
Sponsored by Charles C. Sherrod Library
Home | About | FAQ | My Account | Accessibility Statement
Privacy Copyright

- Customer Reviews
- Extended Essays
- IB Internal Assessment
- Theory of Knowledge
- Literature Review
- Dissertations
- Essay Writing
- Research Writing
- Assignment Help
- Capstone Projects
- College Application
- Online Class
Early Childhood Education Dissertation Topics: 20+ Ideas and Examples
by Antony W
February 19, 2022

Are you looking for some early childhood education dissertation topics but have no idea where to start? This guide is for you.
We understand that the best topics in this category of learning won’t come automatically during brainstorming. So some insights from can go a long way to help you identify the right topic ideas to consider for your project.
This guide is more than just a list of dissertation topics in early childhood education. It’s a guide in which we’ll go even further and look at:
- What early childhood education is
- How to choose early childhood education topics and
- Early childhood education dissertation topics
Let’s explore these subtopics even further to help you gain more insights into the topic:
What is Early Childhood Education?
Early childhood education is a teaching program that encompasses all form of formal and informal education provided to children of up to 8 years of age. Not only is this education significant to the current stage of the child. It also plays an important role of shaping them for later years in their lives.
- Informal education: Parents and caregivers are the major source of input that helps children’s early stage of development. In this case, parents are the first teachers, and it’s a crucial stage for children aged 0 to 2 years. Often, this is the point where a child develops a sense of self-awareness and attachment with parents.
- Formal education: Spanning between 2 to 8 years, formal early childhood education, which varies from state to state and from program to program, is a program that qualified teachers can provide in any relevant settings. Some of these settings include preschool, nursery schools, and kindergarten.
How to Choose Early Education Childhood Education Dissertation Topics
You never want to choose dissertation topics in early childhood education blindly. So it’s important to make sure you consider a few things before you conclude that a certain topic is worth working on.
Essentially, the topic you choose should be:
- Relevant: The topic you choose should be historic in kind and very relevant in its nature. You will have to identify research that already exist on the topic and then figure out how you can expand it.
- Specific: Does the topic have a specific scientific significance? If you can formulate the goals and objectives of the study, then the topic could be worth investigating.
- Practical: Your topic should be practical in the sense that it clearly explains who will benefit from the research and also explain the relevant area of application.
Early Childhood Education Dissertation Topics
Below are some of the examples of the early childhood education Dissertation topics that you should consider:
- Discuss a children's book about gender norms.
- How to Instill Early Leadership Skills in Children
- What are the difficulties that immigrant children face while attending classes alongside other children in mainstream classrooms?
- What are the advantages of early childhood education for children?
- Early learning provides opportunities.
- Evaluating the attributes of a good primary school teacher in early childhood education
- What is the best age to start exposing children to technology?
- Examine children's literature for patterns of prejudicial representation.
- What are the fundamental abilities of children in their early stages of development?
- Explain the various stages of structure play in early childhood.
- Explain and highlight the factors that influence teachers' levels of motivation.
- What hardships do young children face as they adapt to compulsory schooling?
- What are the roles of parents and teachers in instilling good ethics and morals in young children during early childhood education?
- What should be the primary focus of early developmental learning: academics or extracurricular activities?
- What are parents' concerns about their children attending school?
- What role does the student-teacher relationship play in ensuring that young children reach developmental milestones on time?
- The effect does seating arrangements in a classroom have on young students
- What role can teachers and parents play to combat the act of bullying among children in the young age?
- What is the value of primary education now when homeschooling is becoming more popular?
- How can the challenges of nation-building be addressed by developing a more effective curriculum for early childhood education?
- What are the benefits and drawbacks of instilling nationalist ideologies in young children?
- What is the significance of recess in school and how does it affect early learning?
- Explain the barriers to learning and the opportunities for young children from disadvantaged backgrounds.
- How to Ensure Young Children's Early Literacy
- Piaget's developmental stages
- What are common definitions of "good" and "bad" from the perspective of a young child; provide a thorough review.
- What are the potential advantages of a Montessori education?
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of mobile classroom applications in terms of increasing parent-student interaction?
- What is the impact of mandatory school uniforms; discuss both the educational benefits and drawbacks of mandatory school uniforms.
- Physical classes vs. online classes; weigh the benefits and drawbacks!
- Effective strategies for instilling etiquette in young students
- What are the advantages of homework?
- What are the limitations and risks of encouraging young children to develop a "sense of belonging" and "personal identity"?
- Determine an age-appropriate minimum level of social responsibility in young children.
- Describe effective behavior management techniques for young children.
- How do you instill self-worth in young children?
- The advantages of taking short breaks between long periods of study for young children
- What technologies and tools can be used to enhance and improve young children's learning experiences?
- Is the use of electronic whiteboards the future of education?
- What are the best techniques for teachers to use when providing experiential learning to preschool students versus primary school students?
- Language learning techniques that work for young children
- Should we encourage the inclusion of kids with learning disabilities in regular schools?
- Should pre-school curricula be defined by standardized educational mechanisms?
- How are children portrayed in the mainstream media?
- What are the pedagogical advantages of learning via the internet?
- What exactly is the theory of authoritarian management?
- What are the rules of online learning?
- Is online learning advantageous for young children?
- What exactly is gamified learning? Discuss the benefits and drawbacks.
It’s important to understand that these topic ideas are by no means an exhaustive list. Still, they make a good starting point to identify the right topic to work on as an early childhood education student.
About the author
Antony W is a professional writer and coach at Help for Assessment. He spends countless hours every day researching and writing great content filled with expert advice on how to write engaging essays, research papers, and assignments.
Education Thesis Topics

This page provides a comprehensive list of education thesis topics , designed to inspire and assist students in selecting the most suitable topic for their thesis. Whether you are pursuing a degree in education or looking to specialize in a specific area within the field, finding the right topic can be pivotal to your academic success and career trajectory. From exploring contemporary challenges in adult education to investigating innovative practices in educational technology, this list encompasses a broad range of areas tailored to meet diverse research interests and academic needs. Each category has been thoughtfully compiled to provide a rich variety of topics that reflect current trends and future directions in education. This resource aims to be an invaluable tool for students, guiding them through the process of topic selection by providing a structured and extensive range of possibilities.
1000 Education Thesis Topics and Ideas

Academic Writing, Editing, Proofreading, And Problem Solving Services
Get 10% off with 24start discount code, browse education thesis topics by category:, adult education thesis topics, art education thesis topics, comparative education thesis topics.
- Curriculum And Instruction Thesis Topics
Distance Education Thesis Topics
Early childhood education thesis topics, education policy thesis topics, educational leadership thesis topics, educational management thesis topics, educational psychology thesis topics, educational technology thesis topics, elementary education thesis topics, health education thesis topics, higher education thesis topics, international education thesis topics, language education thesis topics, mathematics education thesis topics, multicultural education thesis topics, music education thesis topics, online education thesis topics.
- Philosophy Of Education Thesis Topics
Physical Education Thesis Topics
Science education thesis topics, special education thesis topics, vocational education thesis topics.
- The impact of lifelong learning on career advancement in adults over 40.
- Analyzing the effectiveness of online versus traditional classroom settings for adult learners.
- Barriers to education in mature students and strategies for overcoming them.
- The role of adult education in fostering community development.
- The influence of cultural background on adult education participation.
- Adult literacy: Assessing the outcomes of government versus private sector programs.
- The effectiveness of adult education programs in reducing societal inequality.
- Integrating technology into adult education: Challenges and opportunities.
- How adult education programs can adapt to the changing needs of the workforce.
- Motivational strategies for returning students in adult education programs.
- The impact of adult education on mental health and well-being.
- Exploring the effectiveness of distance learning tools for adult education.
- Policy analysis of adult education funding in developing countries.
- The role of NGOs in promoting adult education in rural areas.
- Comparative analysis of adult education systems across different countries.
- The future of adult education in the age of artificial intelligence and automation.
- Career transitions through adult education: Case studies of success stories.
- Evaluating the impact of community colleges in adult education in the U.S.
- Adult education and its role in promoting environmental sustainability.
- The challenges of providing adult education to differently-abled learners.
- The effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on adult education and future implications.
- Utilizing gamification in adult education to enhance learning engagement.
- Strategies for integrating soft skills training in adult education curriculum.
- The role of adult education in mitigating the digital divide.
- Gender differences in adult education participation and outcomes.
- Exploring the role of libraries in supporting adult education.
- Assessing the economic impact of adult education programs.
- Challenges in standardizing curricula across adult education programs globally.
- Adult education as a tool for reducing recidivism in former inmates.
- The impact of social media on adult education and community building.
- Trends in funding adult education: A comparative study of OECD countries.
- Adult education for the elderly: Benefits and methodologies.
- The role of adult education in fostering political awareness and participation.
- Peer teaching and its effectiveness in adult education settings.
- The psychology of adult learning: How adults learn differently than younger students.
- Ethical considerations in adult education: A contemporary view.
- Collaborative learning environments in adult education: A case study approach.
- The impact of language barriers on adult education and strategies to overcome them.
- Exploring adaptive learning technologies in adult education.
- The role of adult education in promoting health awareness and lifestyle changes.
- The integration of digital media in art education: Implications for teaching and creativity.
- The role of art education in promoting multicultural understanding and appreciation.
- Evaluating the impact of art education on cognitive development in children.
- The use of virtual reality (VR) technology in art education classrooms.
- Art education and social justice: Teaching art as a form of activism.
- The decline of traditional art forms in education: Causes and effects.
- Strategies for incorporating contemporary artists into the art education curriculum.
- The role of public art in education: Engaging communities through school projects.
- Art education funding: Analyzing trends and predicting future directions.
- The impact of art education on emotional intelligence and empathy development.
- Collaborative art projects and their role in enhancing teamwork skills.
- The challenges of teaching art in digital environments: Teacher perspectives.
- Art therapy as an educational tool: Benefits and limitations.
- Cross-disciplinary approaches to art education: Combining art with science and technology.
- The role of art critiques in the educational process: Fostering critical thinking and feedback.
- The influence of cultural identity on art production and education.
- Sustainable practices in art education: Using recycled materials in art projects.
- Art education in rural vs. urban settings: A comparative analysis.
- The future of art education in the age of automation and AI-generated art.
- Gender representation in art education materials and its impact on students.
- The role of art education in addressing environmental issues through creative expressions.
- Assessment methods in art education: Moving beyond traditional grading.
- The effects of globalization on art education curricula.
- Inclusive education in the arts: Best practices for accommodating all students.
- Using art as a medium for language learning in multicultural classrooms.
- The historical evolution of art education and its relevance today.
- Art education and entrepreneurship: Preparing students for careers in the arts.
- The role of museums and galleries in contemporary art education.
- Art education and technology: Exploring new possibilities for interactive learning.
- The impact of government policies on art education.
- Art education leadership: Key skills and competencies for educators.
- The psychological benefits of engaging in art education.
- Parental involvement in art education: Effects on student outcomes.
- The balance between technique and creative expression in art education.
- Strategies for promoting lifelong learning through art.
- Art education for special needs students: Techniques and case studies.
- Exploring the concept of beauty in art education: A philosophical inquiry.
- The role of criticism in art education: Constructive vs. destructive feedback.
- The impact of social media on student art projects and their public reception.
- Exploring non-Western art traditions in Western art education settings.
- A comparative analysis of STEM education in Asian vs. Western countries.
- The impact of globalization on education systems: A study of developing vs. developed nations.
- Comparative study of teacher training programs across different countries.
- The influence of cultural factors on educational attainment in Scandinavian countries.
- Examining gender disparities in education within Middle Eastern and European contexts.
- The role of language policies in education: Comparisons between multilingual and monolingual states.
- Evaluating the outcomes of decentralized vs. centralized education systems.
- The effect of political instability on education quality in Sub-Saharan Africa compared to South America.
- A comparative analysis of approaches to special education in the US and Japan.
- Digital divide: Access to educational technology in rural vs. urban schools globally.
- Comparative effectiveness of online education platforms across different continents.
- The impact of refugee crises on education systems in host vs. origin countries.
- Education for sustainable development: Comparing curricula from Nordic countries to North American models.
- The role of private education in social mobility: A comparative international study.
- Comparative assessment of academic freedom in Asian universities vs. European universities.
- Exploring the integration of indigenous knowledge in formal education systems.
- The effectiveness of early childhood education programs in North America vs. Europe.
- A comparative analysis of educational responses to the COVID-19 pandemic.
- The role of religious education in secular vs. non-secular societies.
- Assessing the impact of international educational exchanges on student outcomes.
- Comparative studies on the implementation of educational policies for immigrant children.
- The evolution of vocational training systems in Germany compared to the United States.
- Comparative study on the impact of school uniforms on student behavior and performance.
- The influence of international assessments (PISA, TIMSS) on national education policies.
- Examining the role of non-governmental organizations in education across different political systems.
- Education and nationalism: A comparative study of curriculum content in post-Soviet states.
- The effects of tuition fees on higher education access in the UK and Germany.
- Comparative analysis of adult literacy programs in Africa and Asia.
- Assessing the role of educational technology in bridging learning gaps in low-income vs. high-income countries.
- Comparative effectiveness of bilingual education models in North America and Europe.
- The impact of cultural heritage on curriculum development in former colonial vs. colonizer countries.
- Examining student resilience in conflict zones: A comparative study.
- The role of sports in education: A comparative analysis between the US and UK.
- Comparing the impact of parental involvement in education in Eastern vs. Western cultures.
- The effectiveness of anti-bullying programs in schools across different countries.
- Comparative analysis of nutrition and health education in schools in Mediterranean vs. North American countries.
- The role of arts education in fostering social cohesion: A comparative study.
- Assessing the success of integration policies for students with disabilities in mainstream schools internationally.
- The effects of class size on educational outcomes: A comparative study.
- Comparing career counseling practices in high schools across different countries.
Curriculum and Instruction Thesis Topics
- The role of project-based learning in enhancing critical thinking skills.
- Evaluating the effectiveness of hybrid learning models post-COVID-19.
- The impact of standardized testing on curriculum development.
- Integrating sustainability education into the school curriculum: Methods and outcomes.
- The effectiveness of STEM curricula in fostering female participation in science and technology.
- Exploring the use of artificial intelligence in personalized learning environments.
- The challenges of implementing competency-based education in traditional schools.
- The impact of teachers’ instructional styles on student engagement and learning.
- Developing and evaluating anti-racist curriculum in secondary education.
- The use of virtual reality (VR) in simulating historical events for educational purposes.
- Assessing the impact of mindfulness education on student well-being and academic performance.
- Curriculum strategies for enhancing emotional intelligence in elementary schools.
- The role of feedback in the learning process: Implementing effective models.
- Strategies for integrating digital literacy into primary education curricula.
- The effects of bilingual instruction on cognitive development.
- Evaluating the long-term impacts of early childhood education curricula.
- The integration of coding and computational thinking across all school levels.
- Developing curricula for life skills education: Successes and challenges.
- The influence of parent-teacher partnerships on curriculum effectiveness.
- Assessing the efficacy of flipped classroom models in secondary education.
- Strategies for teaching critical media literacy in high schools.
- The role of the arts in promoting cross-curricular learning.
- Evaluating the inclusivity of curricula for multicultural classrooms.
- The impact of outdoor educational experiences on environmental awareness.
- Addressing the needs of gifted students through differentiated curriculum strategies.
- The challenges and outcomes of teaching global citizenship in schools.
- Implementing trauma-informed practices in curriculum and instruction.
- The effectiveness of peer tutoring programs integrated into the curriculum.
- Strategies for addressing learning loss due to school disruptions.
- The role of curriculum in shaping students’ attitudes towards diversity and inclusion.
- Evaluating the impact of social-emotional learning programs in urban schools.
- The influence of technology on modifying traditional teaching methodologies.
- The challenges of aligning vocational training with industry needs in high schools.
- Exploring the impact of teacher professional development on curriculum delivery.
- The role of student voice in curriculum planning and implementation.
- Assessing the effectiveness of health and wellness programs in school curricula.
- The impact of historical narratives in textbooks on student perception of history.
- The challenges and benefits of co-teaching models in inclusive classrooms.
- Implementing continuous assessment strategies in primary education.
- The role of school leadership in fostering curriculum innovation.
- The effectiveness of synchronous vs. asynchronous learning methods in distance education.
- Impact of AI-driven personalization on student outcomes in online courses.
- Barriers to effective communication in virtual classrooms and strategies for improvement.
- Analyzing dropout rates in online higher education programs.
- The role of virtual reality (VR) in enhancing engagement in distance learning environments.
- Assessing the quality and accreditation challenges in global online education.
- The evolution of mobile learning technologies and their impact on distance education.
- Cybersecurity challenges in distance learning systems and mitigation strategies.
- The influence of cultural diversity on learning outcomes in international online classrooms.
- Strategies for fostering a sense of community and collaboration among distance learners.
- The effectiveness of online professional development courses for teachers.
- Legal and ethical considerations in the administration of distance learning programs.
- The role of blockchain technology in securing academic records in distance education.
- Impact of social media integration on student engagement and learning in distance education.
- The use of big data analytics to improve learner retention rates in online courses.
- Adaptive learning technologies: Tailoring distance education to individual learner needs.
- Distance education as a tool for lifelong learning: Trends and effectiveness.
- The future of distance education: Predicting technology trends and educational practices.
- Designing effective course materials for visually impaired students in online formats.
- The impact of distance learning on traditional higher education business models.
- Evaluating the effectiveness of online language learning versus traditional methods.
- The role of e-portfolios in assessing student performance in distance education.
- The challenges of providing science labs in an online education format.
- Distance learning in rural areas: Accessibility challenges and technological solutions.
- Parental involvement in the distance education of younger students: Methods and impacts.
- The effectiveness of gamification in online education for enhancing motivation.
- Best practices for designing inclusive online courses for students with disabilities.
- The future of corporate training: The shift towards online learning platforms.
- Comparing student satisfaction in distance education vs. traditional classroom settings.
- The role of mentorship in online education: Impact on student success.
- Analyzing the impact of online education on adult learners’ career advancements.
- Distance education and global inequality: Access issues and scalable solutions.
- The role of distance education in emergency preparedness for educational institutions.
- Student privacy and data protection in online educational platforms.
- The impact of augmented reality (AR) tools on distance education.
- Pedagogical strategies for effective teaching in hybrid classrooms.
- The effectiveness of peer-to-peer learning networks in online education settings.
- Online education for environmental sustainability: Courses and student engagement.
- The challenges of cross-cultural communication in global virtual classrooms.
- Assessing the impact of regulatory frameworks on the growth of distance education.
- The impact of play-based learning on cognitive development in early childhood.
- Assessing the effectiveness of Montessori methods in early childhood education.
- The role of parental involvement in the early educational development of children.
- Integrating technology into early childhood classrooms: Tools and impacts.
- The influence of early childhood education on later academic and social outcomes.
- Developing emotional intelligence through early childhood education programs.
- The effects of outdoor learning experiences on young children’s environmental awareness.
- Nutrition and its impact on cognitive development in early childhood education settings.
- The role of music and arts in early childhood cognitive and emotional development.
- Addressing learning disabilities in early childhood: Detection and intervention strategies.
- The impact of socio-economic factors on access to quality early childhood education.
- Gender roles in early childhood education: Shaping perspectives from a young age.
- The effectiveness of bilingual education in early childhood development.
- Assessing the impact of teacher-student ratios on learning outcomes in preschools.
- Strategies for promoting literacy from an early age.
- The role of cultural diversity in early childhood education curricula.
- Evaluating the security and safety standards in early childhood education centers.
- The influence of childhood trauma on early educational experiences.
- The impact of COVID-19 on early childhood education: Challenges and innovations.
- Implementing STEM education in early childhood: Approaches and outcomes.
- The role of storytelling in emotional and language development in early childhood.
- Strategies for integrating special needs children in mainstream early childhood classrooms.
- The impact of digital media on attention spans and learning in young children.
- Parental expectations and their impact on early childhood education strategies.
- The effects of sleep on learning and behavior in early childhood education settings.
- Teacher training and its effectiveness in enhancing early childhood education.
- Assessing the impact of early childhood education on family dynamics.
- The role of feedback in the learning processes of early childhood.
- Ethical considerations in early childhood education research.
- Strategies for effective conflict resolution in early childhood education settings.
- The role of play in the socialization process of children in early education.
- Innovative approaches to language acquisition in early childhood education.
- The impact of preschool programs on social inequality.
- Cultural sensitivity training for educators in diverse early childhood classrooms.
- The effectiveness of health education in early childhood programs.
- Addressing the challenges of transitioning from early childhood education to primary school.
- The influence of siblings and peer interactions in early educational settings.
- The impact of maternal education levels on early childhood learning outcomes.
- Evaluating the role of educational toys in early learning environments.
- The use of augmented reality (AR) in interactive learning for young children.
- The impact of national education policies on achievement gaps in urban and rural schools.
- Evaluating the effectiveness of affirmative action in higher education admissions.
- The role of government policy in shaping teacher retention rates.
- Policy interventions to address the digital divide in remote learning.
- The consequences of standardized testing policies on curriculum flexibility.
- Comparative analysis of education policies for special needs students across different states.
- The effectiveness of early intervention policies in education for at-risk youth.
- The influence of immigration policies on public education systems.
- Analyzing the impact of school choice policies on public school demographics and performance.
- Policy measures to improve STEM education outcomes among underrepresented groups.
- The role of policy in integrating mental health support in schools.
- Effects of education policies on bilingual education and student language development.
- The impact of zero-tolerance policies on student behavior and school safety.
- Evaluating the success of policies aimed at reducing childhood obesity through school programs.
- The implications of homeschooling policies during and post-pandemic.
- Policy analysis of teacher certification standards across countries.
- The role of state policies in promoting environmental education.
- Analysis of funding equity in public schools under different educational policies.
- The impact of privacy laws on digital learning tools and student data.
- Policy strategies for enhancing parental engagement in public schools.
- The effects of minimum wage policies on the availability of qualified childcare workers.
- Evaluating the efficacy of policies aimed at integrating arts into the educational curriculum.
- The influence of non-profit organizations in shaping education policy.
- Policies to address teacher shortages in critical subject areas.
- The impact of trade policies on vocational education and training programs.
- Analyzing the role of public policies in combating academic dishonesty.
- The effect of nutrition policies on learning outcomes in schools.
- The impact of refugee education policies on local education systems.
- Education policy reforms for enhancing adult education and lifelong learning.
- The implications of international education policies for student mobility and exchange programs.
- Evaluating the impact of fiscal policies on higher education affordability.
- The role of education policies in fostering entrepreneurship education.
- The impact of climate change policies on education systems worldwide.
- Policy measures for managing teacher stress and burnout.
- The effectiveness of anti-bullying policies in schools.
- The role of policy in shaping sports education and physical activity in schools.
- The influence of policies on the adaptation of new technologies in education.
- Evaluating the success of gender-inclusive policies in educational institutions.
- The role of public policy in shaping early childhood education standards.
- The effectiveness of policies aimed at enhancing cybersecurity education in schools.
- The role of leadership in fostering a culture of innovation in schools.
- The impact of transformational leadership on teacher motivation and student performance.
- Strategies for educational leaders to manage change during technology integration.
- Leadership styles and their effects on school climate and culture.
- The role of educational leaders in promoting equity and inclusion within schools.
- Evaluating the effectiveness of leadership training programs for aspiring principals.
- The impact of school leadership on implementing sustainable practices.
- Leadership challenges in urban vs. rural school settings.
- The role of school leaders in crisis management and emergency preparedness.
- Strategies for effective stakeholder engagement by educational leaders.
- The impact of educational leadership on special education program success.
- Leadership and its role in shaping professional development for teachers.
- The influence of school leaders on fostering parent-teacher collaborations.
- The role of ethical leadership in educational institutions.
- Comparative analysis of educational leadership models across different countries.
- The impact of leadership on the adoption of digital textbooks and learning resources.
- Leadership strategies for combating teacher burnout and turnover.
- The role of educational leaders in policy advocacy and reform.
- Strategies for building and maintaining high-performance teams in education.
- The impact of leadership on student mental health initiatives.
- The effectiveness of distributed leadership in educational settings.
- Leadership in higher education: Managing faculty and student diversity.
- The role of school administrators in implementing anti-bullying policies.
- Evaluating the leadership practices in charter schools vs. public schools.
- The influence of leadership on enhancing school safety protocols.
- The role of leaders in developing ICT competencies within schools.
- Educational leadership in times of budget cuts: Strategies for maintaining quality education.
- The role of principals in fostering community partnerships for school improvement.
- Leadership decision-making processes in curriculum design and implementation.
- The effectiveness of servant leadership in educational settings.
- The challenges of leadership succession in schools and its impact on organizational continuity.
- The role of leadership in promoting physical education and wellness programs.
- How educational leaders influence the integration of global issues into the curriculum.
- Leadership and management of virtual and hybrid learning environments.
- The role of leadership in fostering student-led initiatives and governance.
- Evaluating the impact of educational leadership on national education performance standards.
- The role of leadership in the accreditation and quality assurance of educational programs.
- Leadership strategies for enhancing faculty development and scholarship.
- The role of educational leaders in managing conflicts among staff and students.
- Strategies used by leaders to enhance the reputation and competitiveness of educational institutions.
- The role of data analytics in improving school management decisions.
- Strategies for managing resource allocation in schools with limited budgets.
- The impact of leadership styles in educational management on school effectiveness.
- Evaluating the effectiveness of performance management systems in educational institutions.
- The challenges of implementing sustainable practices in school management.
- The role of school managers in fostering innovation and creativity in education.
- Management of teacher professional development and its impact on school improvement.
- The effectiveness of conflict resolution strategies in educational management.
- School management practices for handling multicultural education environments.
- The role of management in shaping the integration of technology in schools.
- Evaluating the impact of school management on student retention rates.
- The influence of school management on enhancing parental involvement in education.
- Strategies for effective crisis management in educational settings.
- The impact of educational management on implementing inclusive education policies.
- School branding and marketing: Management strategies for enhancing public perception.
- The challenges and strategies of financial management in private vs. public schools.
- The role of educational managers in compliance with national education standards.
- Managing staff turnover in educational institutions: Strategies and outcomes.
- The impact of educational management on special needs education programs.
- The role of strategic planning in educational management for long-term success.
- The effectiveness of communication strategies in educational management.
- Change management in schools: Approaches and resistance factors.
- The role of educational managers in facilitating digital learning environments.
- The impact of demographic changes on school management strategies.
- Managing the integration of non-traditional students in higher education institutions.
- The role of management in enhancing community engagement with schools.
- Educational management practices for promoting mental health awareness in schools.
- The challenges of managing cross-cultural teams in international schools.
- The role of educational managers in fostering ethical behavior and integrity.
- Evaluating the governance structures of educational institutions and their effectiveness.
- The impact of educational management on improving teaching quality.
- Strategies for managing large-scale assessments and evaluations in educational settings.
- The role of educational managers in navigating the politics of education reform.
- Management practices for enhancing the security and safety of educational environments.
- The effectiveness of mentorship programs managed by educational institutions.
- The role of management in handling the adoption of new educational curricula.
- Strategies for managing the transition from traditional to online education.
- The impact of educational management on promoting physical education and sports.
- Managing diversity and inclusion initiatives in educational settings.
- The challenges and outcomes of succession planning in educational leadership.
- The effects of psychological safety in classrooms on student learning outcomes.
- The impact of teacher-student relationships on student academic performance and well-being.
- Cognitive strategies that enhance learning retention in students with learning disabilities.
- The role of motivation in student engagement and achievement.
- Psychological implications of remote learning on elementary school students.
- The effectiveness of mindfulness and meditation programs in promoting student mental health.
- The role of parental involvement on children’s educational outcomes from a psychological perspective.
- Strategies for developing resilience in students facing academic failures.
- The impact of socio-economic status on children’s cognitive development and learning.
- Psychological assessments in schools: Their impact and implications for student development.
- The influence of peer relationships on academic motivation and performance.
- The role of emotional intelligence in leadership and group dynamics in schools.
- The impact of bullying on student mental health and academic outcomes.
- Strategies for addressing test anxiety among high school and college students.
- The psychological effects of praise vs. criticism on student motivation.
- The role of psychological counseling in managing student behavioral issues.
- The impact of learning environments on student psychological well-being.
- Psychological factors influencing the adoption of technology in education.
- The effects of childhood trauma on learning and academic performance.
- Strategies for supporting students with ADHD in educational settings.
- The role of cognitive biases in student learning and decision-making.
- The psychological impacts of extracurricular activities on student development.
- Understanding and managing the emotional aspects of teacher-student interactions.
- The effects of group work on individual student performance and social skills.
- The role of psychology in developing effective educational video games.
- Evaluating the psychological benefits of art and music education.
- The impact of sleep patterns on student learning and memory.
- Psychological theories of learning and their practical applications in the classroom.
- The influence of family dynamics on student academic achievements.
- The role of student self-efficacy in educational achievement and career aspirations.
- The psychological effects of social media use on student attention and learning.
- Strategies for enhancing parental engagement from a psychological perspective.
- The role of teacher feedback in shaping student self-concept and academic identity.
- Psychological perspectives on the challenges of bilingual education.
- The impact of psychological support services on student retention rates in universities.
- The role of psychology in understanding and addressing gender disparities in STEM fields.
- Psychological strategies for integrating special needs students in mainstream classrooms.
- The impact of racial and ethnic identity on educational experiences and outcomes.
- Psychological approaches to understanding and preventing academic dishonesty.
- The role of school psychologists in crisis intervention and management within schools.
- The impact of artificial intelligence on personalized learning environments.
- Evaluating the effectiveness of virtual reality (VR) in STEM education.
- The role of educational apps in enhancing early literacy skills.
- Blockchain technology in education: Implications for security and record-keeping.
- The efficacy of adaptive learning systems in improving student performance.
- The use of big data analytics to predict student learning outcomes and dropout risks.
- Gamification in education: Comparing engagement and learning outcomes across disciplines.
- The challenges and benefits of implementing BYOD (Bring Your Own Device) policies in schools.
- The impact of social media tools on collaborative learning and student engagement.
- Augmented reality (AR) applications in education: A tool for enhancing experiential learning.
- The effectiveness of online peer tutoring platforms on student achievement.
- Digital equity in education: Access to technology and its impact on learning disparities.
- The role of technology in facilitating continuous professional development for teachers.
- Online assessment tools: Their validity, reliability, and impact on educational outcomes.
- The influence of podcasting and audio resources on learning in higher education.
- The effects of screen time on cognitive development and academic performance in children.
- The role of e-books and digital libraries in fostering reading habits among students.
- Implementing smart classroom technologies: Benefits, challenges, and long-term outcomes.
- Technology integration in special education: Tools and strategies for inclusive learning.
- The impact of virtual labs on science education in remote learning environments.
- Wearable technology in education: Potential uses and implications for student learning.
- Evaluating the effectiveness of MOOCs (Massive Open Online Courses) in lifelong learning.
- Internet of Things (IoT) in education: Applications and future prospects.
- Cybersecurity education: Developing critical skills through technology-based curricula.
- The role of video conferencing tools in promoting international collaboration among students.
- The impact of cloud computing on collaboration and data management in schools.
- Analyzing the role of technology in transforming teacher-student interactions.
- The effectiveness of digital storytelling tools in enhancing narrative writing skills.
- The impact of technology on reducing educational disparities in rural areas.
- Student data privacy and ethical considerations in educational technology deployments.
- Mobile learning: Trends, effectiveness, and pedagogical implications.
- The influence of technology on homework practices and student time management.
- The effectiveness of digital feedback systems in improving student learning.
- The role of simulation software in professional and technical education.
- Technology-facilitated project-based learning: Case studies and outcomes.
- The challenges of integrating cutting-edge technologies into traditional curricula.
- Evaluating the long-term impacts of technology-enhanced collaborative learning environments.
- Technology in classroom management: Tools for enhancing disciplinary measures and student behavior monitoring.
- The effectiveness of assistive technologies in supporting dyslexic students.
- Exploring the potential of mixed reality environments in education.
- Evaluating the effectiveness of project-based learning in enhancing problem-solving skills in elementary students.
- Strategies for teaching advanced mathematical concepts to young learners through visual aids.
- Comparing phonics and whole language approaches to reading instruction in elementary education.
- The influence of multicultural curricula on fostering inclusivity and empathy among elementary students.
- The effects of parent-teacher partnerships on student academic achievement and social development.
- Implementing environmental sustainability education in elementary schools: methods and outcomes.
- Effective classroom management strategies for enhancing focus and discipline in young children.
- Assessing the role of regular physical activity in boosting academic performance and mental health in elementary-aged children.
- Integration of digital storytelling tools in elementary science education to enhance student engagement.
- Arts-based learning initiatives: Measuring their impact on creativity and academic success in the elementary classroom.
- Best practices for supporting ESL students in diverse elementary classrooms.
- The impact of reduced teacher-student ratios on personalized learning experiences in elementary schools.
- The role of modern school libraries in promoting digital literacy alongside traditional reading skills.
- Critical analysis of the reliance on standardized testing within elementary educational systems.
- Nutrition-focused school programs and their effects on concentration and academic performance in young students.
- Challenges and benefits of introducing STEM education in early grades.
- Utilizing children’s literature to teach ethics and social responsibility in elementary schools.
- Evaluating the efficacy of anti-bullying initiatives in elementary settings.
- Exploring the role of tablets and apps in developing early writing skills.
- Benefits of experiential outdoor education programs on environmental consciousness in elementary students.
- The educational benefits of structured play in developing cognitive and social skills in elementary pupils.
- Tailoring instruction to meet the needs of gifted students in mainstream elementary classrooms.
- Impact of comprehensive social-emotional learning programs on student behavior and academic outcomes.
- Designing effective strategies for elementary students with specific learning disabilities.
- Investigating the role of positive teacher feedback in shaping student self-perception and academic engagement.
- Analyzing parental pressure and its effects on academic stress in elementary-aged children.
- The role of interactive math games in enhancing numerical proficiency among elementary students.
- Assessing the effectiveness of peer tutoring in reading comprehension and literacy skills.
- The influence of school safety measures on creating a supportive learning environment for elementary learners.
- Cultural influences on teaching practices and curriculum design in diverse elementary classrooms.
- The impact of teacher training on instructional quality and student outcomes in early education.
- Evaluating the effectiveness of visual arts integration in elementary math and science curricula.
- The role of music education in improving cognitive development and academic performance in elementary students.
- Assessing the impact of technology-driven personalized learning environments on student engagement and learning outcomes.
- The effects of bilingual education programs on cognitive flexibility and language development in elementary students.
- Strategies for addressing behavioral issues in elementary classrooms through positive reinforcement.
- The role of community involvement in enhancing educational experiences in elementary schools.
- Investigating the effects of early intervention strategies for children at risk of educational failure.
- The benefits of a narrative approach to teaching history and social studies in elementary schools.
- Exploring the efficacy of mindfulness exercises in managing stress and enhancing focus among young students.
- The impact of school-based mental health programs on student well-being and academic performance.
- Evaluating the effectiveness of digital health education platforms in promoting adolescent health literacy.
- The role of health education in combating the rise of obesity among children and adolescents.
- Strategies for integrating mindfulness and stress reduction techniques into K-12 health curricula.
- Assessing the impact of nutrition education on dietary habits and health outcomes in primary schools.
- The effectiveness of anti-smoking campaigns targeted at young teens within school settings.
- The role of virtual reality (VR) simulations in enhancing health education on topics like CPR and first aid.
- Analyzing the influence of parental involvement in health education on children’s lifestyle choices.
- The effectiveness of peer education models for promoting sexual health among high school students.
- Challenges and opportunities in implementing mental health first aid training in schools.
- The impact of wearable fitness technology on physical education and student health outcomes.
- Evaluating community-based health education programs for their role in improving public health.
- The influence of social media on health behaviors in adolescents: Opportunities for educational interventions.
- Strategies for addressing health disparities through targeted school health education programs.
- The role of health education in prevention and management of adolescent drug abuse.
- Assessing the long-term impacts of health education on lifestyle diseases such as diabetes and hypertension.
- The effectiveness of school-based interventions for the management of asthma in children.
- The impact of culturally tailored health education programs on minority groups in schools.
- Evaluating the effectiveness of comprehensive reproductive health education in secondary schools.
- The role of schools in promoting environmental health education and awareness.
- The impact of health education interventions on preventing teenage pregnancies.
- Challenges in implementing health education curricula that accommodate students with disabilities.
- The role of gamification in enhancing engagement with health education content.
- Evaluating the impact of school gardens on health education and nutritional outcomes.
- The effectiveness of online health education tools in increasing student engagement and knowledge retention.
- The role of teacher training in the delivery of effective health education.
- Analyzing the policy landscape surrounding health education in schools across different states or countries.
- The impact of health education on reducing the stigma associated with mental health issues.
- The role of health education in fostering critical thinking about health news and media literacy.
- Evaluating the effectiveness of anti-bullying programs as a part of health education in schools.
- The influence of health education on changing attitudes towards vaccination among adolescents.
- The role of school health education in addressing the health needs of LGBTQ+ youth.
- Assessing the effectiveness of health education programs in rural vs. urban schools.
- The challenges of adapting health education programs to the digital age.
- The impact of experiential learning approaches in health education on student understanding and behaviors.
- The role of health educators in advocating for healthy school environments.
- Evaluating the effectiveness of interventions aimed at reducing sedentary behavior among students.
- The impact of nutrition and physical activity education on the academic performance of students.
- Strategies for promoting sun safety and skin cancer awareness in schools.
- The effectiveness of school-based dental health education programs in improving oral health behaviors.
- Evaluating the impact of online learning on student engagement in higher education.
- The effectiveness of competency-based education in university settings.
- Trends and challenges in managing diversity and inclusion on college campuses.
- The role of university leadership in fostering a culture of innovation.
- Assessing the financial sustainability of tuition-free college programs.
- The impact of international student enrollments on domestic education quality.
- Strategies for integrating mental health services into university student support systems.
- The effectiveness of academic advising in enhancing student retention and graduation rates.
- The role of technology in transforming traditional lecture-based learning in universities.
- The impact of COVID-19 on the globalization of higher education.
- Analyzing the shift towards STEM education in universities and its implications.
- The effectiveness of university partnerships with industry in preparing students for employment.
- Evaluating the impact of campus safety measures on student well-being.
- The role of social media in shaping university branding and student recruitment.
- Strategies for enhancing faculty development and teaching quality in higher education.
- The effectiveness of experiential learning programs in developing job-ready skills.
- Trends in higher education policy changes and their impact on institutional practices.
- The role of universities in promoting sustainable practices and environmental education.
- Assessing the impact of student loan policies on access to higher education.
- The influence of alumni networks on university development and student opportunities.
- The role of higher education in fostering entrepreneurial skills and mindsets.
- Challenges and strategies for delivering continuing education and professional development.
- The effectiveness of remedial programs in addressing college readiness gaps.
- Trends in higher education curriculum reform to meet evolving industry demands.
- The role of intercultural competencies in enhancing global readiness among graduates.
- Evaluating the effectiveness of hybrid learning models blending online and in-person instruction.
- The impact of artificial intelligence and automation on higher education curriculum and employment.
- Strategies for addressing gender disparities in academic leadership roles.
- The role of higher education in mitigating social inequality through accessible education.
- The effectiveness of wellness programs in improving student health and academic performance.
- The impact of microcredentialing and badge programs on professional development and lifelong learning.
- The challenges of maintaining academic integrity in an era of digital education.
- Evaluating the impact of student-centered learning environments on academic outcomes.
- The role of universities in fostering political and social engagement among students.
- Trends and challenges in the internationalization of higher education curricula.
- Assessing the effectiveness of peer mentoring programs in enhancing academic success.
- The role of higher education in promoting critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
- Evaluating the effectiveness of diversity training programs in universities.
- The impact of housing quality and availability on university student success.
- The role of accreditation standards in shaping educational quality in higher education institutions.
- Assessing the impact of global mobility on learning outcomes in international education.
- The effectiveness of international baccalaureate programs compared to national curricula.
- Trends in cross-cultural competency training for educators in international schools.
- The role of language barriers in shaping the international student experience.
- Strategies for integrating international students into domestic academic environments.
- The impact of political tensions on international educational collaborations.
- Evaluating the effectiveness of virtual exchange programs in fostering global understanding.
- The role of international education in promoting global citizenship and peace.
- Challenges and strategies in managing international higher education partnerships.
- Trends in student recruitment strategies by international universities.
- The impact of scholarship programs on promoting diversity in international education.
- The effectiveness of study abroad programs in enhancing intercultural communication skills.
- Assessing the financial sustainability of international branch campuses.
- The role of technology in facilitating international collaboration in education.
- Evaluating the impact of international education on career prospects and employability.
- The challenges of accrediting international educational programs across different countries.
- Trends in educational policy impacting international student visa regulations.
- The role of international education in mitigating cultural stereotypes.
- Strategies for enhancing the safety and security of international students abroad.
- The impact of international alumni networks on global engagement and development.
- Evaluating the role of international educational consultants in student success.
- The challenges of curriculum standardization across international educational systems.
- The impact of economic crises on international student mobility and enrollment.
- The effectiveness of international dual-degree programs in higher education.
- Trends in the use of English as a medium of instruction in non-English speaking countries.
- The role of international educational fairs in shaping global education trends.
- The impact of international education on local economies and cultural exchange.
- Strategies for supporting refugee and displaced students in international education systems.
- The challenges of ethical recruitment in international education.
- The effectiveness of multicultural teams in international school projects.
- Assessing the impact of cultural intelligence training on educators in international settings.
- Trends in governmental support for international education initiatives.
- The role of international education in fostering environmental awareness and action.
- Challenges in assessing the quality of international online education programs.
- The impact of global health crises on international education systems.
- Strategies for balancing nationalism and globalism in international education policies.
- The effectiveness of international peer mentorship programs.
- Trends in international education marketing and student engagement.
- The role of international education in promoting democratic values and social justice.
- Evaluating the impact of international educational exchanges on diplomatic relations.
- The impact of immersive technologies on second language acquisition.
- Strategies for integrating content and language integrated learning (CLIL) in multilingual classrooms.
- The role of motivation in second language learning success.
- Assessing the effectiveness of online language learning platforms versus traditional classroom settings.
- The impact of cultural immersion programs on language proficiency and cultural competence.
- Trends in bilingual education and its effects on cognitive development.
- The role of language in identity formation among multilingual students.
- Evaluating the effectiveness of early childhood language immersion programs.
- The impact of mother tongue-based multilingual education on learning outcomes.
- Strategies for overcoming language barriers in increasingly diverse educational settings.
- The effectiveness of language learning apps and tools: A comparative study.
- The role of teacher training in enhancing language teaching methodologies.
- The impact of study abroad programs on language proficiency and intercultural sensitivity.
- Trends in the assessment methods of second language proficiency.
- The influence of peer interaction in language learning environments.
- The role of artificial intelligence in personalized language learning experiences.
- Challenges and strategies for teaching less commonly taught languages.
- The effectiveness of heritage language programs in preserving linguistic diversity.
- The impact of globalization on language education policies and practices.
- Strategies for promoting linguistic diversity and inclusion in language education.
- The role of language in fostering global citizenship and international relations.
- Evaluating the impact of multiliteracy approaches in language education.
- The challenges of teaching language through online synchronous and asynchronous methods.
- The effectiveness of drama and role-play in enhancing language learning.
- The impact of social media on language learning and usage among students.
- Strategies for addressing language attrition among immigrant populations.
- The role of linguistic landscapes in language learning and cultural exposure.
- Assessing the socio-economic impacts of language education in multilingual societies.
- The influence of family language policies on bilingual education outcomes.
- Trends in language education funding and resource allocation.
- The effectiveness of language cafés and informal language learning environments.
- Challenges in standardizing language proficiency levels across educational systems.
- The role of languages in interdisciplinary education programs.
- The impact of language anxiety on learning outcomes and strategies for mitigation.
- Evaluating the effectiveness of language portfolios as a tool for language learning.
- The role of corrective feedback in second language acquisition.
- The impact of accent reduction programs on communication skills and social integration.
- Strategies for integrating language education with vocational training.
- The influence of linguistic relativity on second language learning processes.
- Evaluating the long-term retention of language skills post-education.
- Evaluating the impact of problem-based learning on mathematical problem-solving skills.
- The effectiveness of visual aids in enhancing understanding of complex mathematical concepts.
- Strategies for integrating technology in mathematics education to improve student engagement.
- The role of mathematical games and puzzles in primary education curriculum.
- Assessing the impact of flipped classrooms on student performance in high school mathematics.
- Trends in adaptive learning technologies for personalized mathematics instruction.
- The influence of teacher attitudes and beliefs on teaching methods in mathematics.
- The effectiveness of collaborative learning environments in mathematics education.
- The role of parental involvement in children’s mathematical development.
- Evaluating the impact of early intervention programs on mathematics achievement in at-risk students.
- Strategies for addressing math anxiety among middle school students.
- The effectiveness of hands-on activities versus traditional lectures in teaching mathematics.
- Assessing gender differences in mathematical achievement and attitudes.
- The role of formative assessment in enhancing learning outcomes in mathematics.
- The impact of professional development programs on mathematics teaching practices.
- Strategies for teaching mathematical concepts to students with learning disabilities.
- The influence of socio-economic factors on mathematics education outcomes.
- The effectiveness of inquiry-based mathematics education compared to traditional approaches.
- Trends in international comparisons of student achievement in mathematics.
- The role of language in understanding and solving mathematical problems.
- Evaluating the use of mathematical modeling in secondary education.
- The impact of STEM-focused schools on mathematics proficiency.
- Strategies for effective integration of statistics and probability in K-12 curricula.
- The role of cultural context in mathematics education and curriculum design.
- Assessing the long-term impacts of early childhood mathematics education.
- The effectiveness of online versus face-to-face tutoring in mathematics.
- Trends in teacher certification and its impact on mathematics education quality.
- The role of feedback in student learning and engagement in mathematics classes.
- Evaluating the effectiveness of peer teaching methods in mathematics.
- The impact of curriculum innovations on teaching and learning mathematics.
- Strategies for integrating ethical reasoning in mathematics education.
- The effectiveness of interdisciplinary approaches to teaching mathematics.
- The role of critical thinking skills in mathematics education.
- Assessing the effectiveness of remedial mathematics programs in higher education.
- Trends in the use of digital portfolios for assessing mathematics learning.
- The impact of international educational exchanges on mathematics teaching methods.
- Strategies for motivating underrepresented groups to pursue mathematics education.
- The influence of new curricular standards on mathematics education reform.
- Evaluating the role of competitions and awards in fostering interest in mathematics.
- The impact of augmented reality (AR) tools on spatial reasoning in geometry education.
- Evaluating the impact of multicultural curricula on racial and ethnic tolerance in schools.
- Strategies for integrating global perspectives into K-12 education systems.
- The effectiveness of teacher training programs in multicultural education competencies.
- Assessing the role of cultural exchange programs in promoting intercultural understanding among students.
- The influence of bilingual education on cultural identity and student achievement.
- Trends in multicultural education policies and their impact on educational equity.
- The role of community involvement in shaping multicultural education practices.
- Evaluating the effectiveness of anti-racism education in reducing bias and discrimination in schools.
- Strategies for addressing cultural conflicts in increasingly diverse classrooms.
- The impact of immigrant histories on curriculum design and teaching strategies.
- The effectiveness of cultural competency frameworks in teacher education.
- Assessing the role of indigenous knowledge systems in multicultural education.
- Trends in the representation of diverse cultures in school textbooks and media.
- The role of schools in fostering cultural preservation and appreciation among minority groups.
- Strategies for engaging parents from diverse backgrounds in the educational process.
- The impact of cultural diversity on classroom dynamics and learning outcomes.
- Evaluating the effectiveness of multicultural clubs and activities in promoting inclusivity.
- The role of intercultural communication training in teacher professional development.
- Assessing the challenges of teaching about sensitive cultural and historical issues.
- The effectiveness of international collaborations in enhancing multicultural understanding.
- Trends in multicultural counseling and guidance in educational settings.
- The role of arts education in promoting multicultural awareness and expression.
- Strategies for accommodating religious diversity in educational institutions.
- The impact of cultural festivals and events on community and school integration.
- Evaluating the role of language diversity in multicultural education settings.
- The effectiveness of storytelling and narrative in conveying multicultural values.
- Trends in educational technology for supporting multicultural education.
- The role of libraries in providing access to multicultural resources and fostering inclusivity.
- Assessing the impact of social justice education on student activism and awareness.
- Strategies for addressing socioeconomic disparities through multicultural education.
- The effectiveness of peer mentorship programs in enhancing multicultural understanding.
- The role of school leadership in promoting an inclusive school culture.
- Assessing the impact of educational policies on multicultural education practices.
- Strategies for using digital media to enhance multicultural learning experiences.
- The effectiveness of virtual reality (VR) simulations in teaching cultural empathy.
- Trends in government support for multicultural education initiatives.
- The role of language education in supporting multicultural communication skills.
- Assessing the impact of demographic changes on multicultural education needs.
- Strategies for integrating multicultural education into STEM fields.
- Evaluating the effectiveness of service learning projects in promoting multicultural competence.
- The impact of music education on cognitive development and academic performance in early childhood.
- Evaluating the effectiveness of digital tools and apps in teaching music theory and practice.
- The role of classical music training in enhancing memory and concentration in students.
- Trends in integrating world music into school curricula and its impact on cultural appreciation.
- The effectiveness of music therapy in special education settings for children with autism.
- Assessing the role of community music programs in fostering social cohesion and community engagement.
- The impact of school budget cuts on the quality and availability of music education programs.
- Strategies for teaching music in a multicultural classroom to enhance intercultural understanding.
- The role of music education in promoting emotional and mental health among adolescents.
- Evaluating the effectiveness of online music education vs. traditional face-to-face teaching methods.
- The influence of music competitions on student motivation and musical career aspirations.
- The impact of mentorship and role models in music education on student engagement and retention.
- Trends in music education policy changes and their impact on program sustainability.
- The effectiveness of adaptive music education tools for students with learning disabilities.
- The role of music in enhancing language acquisition and literacy skills.
- Assessing the impact of participatory music-making on teamwork and collaboration skills.
- The role of technology in transforming music composition and production education.
- Strategies for fostering creativity and innovation through music education.
- The impact of extracurricular music programs on student academic outcomes and school involvement.
- Evaluating the effectiveness of music education in reducing behavioral issues among at-risk youth.
- The role of music education in preserving cultural heritage and promoting cultural tourism.
- Trends in teacher training for music educators and its impact on teaching quality.
- The effectiveness of early musical training on lifelong musical engagement and appreciation.
- The impact of parental involvement in music education on children’s musical development.
- Assessing the role of music education in interdisciplinary learning environments.
- The effectiveness of music education in improving public speaking and presentation skills.
- The role of music education in enhancing spatial-temporal reasoning among students.
- Strategies for integrating music education into STEM fields to create STEAM curriculum.
- The impact of music festivals and live performances as educational tools in schools.
- Evaluating the sustainability of funding for music education programs in public schools.
- The role of peer teaching and learning in music education settings.
- Trends in the use of music technology in classroom settings and its educational outcomes.
- The effectiveness of music education in promoting positive youth development.
- Assessing the challenges of teaching diverse music genres in a standardized curriculum.
- The role of music education in enhancing multicultural understanding and global awareness.
- Strategies for overcoming challenges in access to music education in rural areas.
- The impact of competitive music environments on student psychology and learning outcomes.
- The effectiveness of community partnerships in enhancing music education opportunities.
- Trends in music copyright education for young musicians and educators.
- The role of music education in fostering entrepreneurial skills and career opportunities in the music industry.
- The effectiveness of online learning platforms in higher education: A comparative analysis.
- Strategies for enhancing student engagement in asynchronous online courses.
- The role of artificial intelligence in personalizing learning experiences in online education.
- Assessing the impact of digital divide on access to online education in underprivileged regions.
- Trends in the development and adoption of MOOCs (Massive Open Online Courses) across different disciplines.
- The effectiveness of online simulation tools in professional training and education.
- The role of online education in continuing professional development and lifelong learning.
- Strategies for combating academic dishonesty and plagiarism in online courses.
- The impact of virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) technologies on online education.
- Evaluating the pedagogical effectiveness of gamified elements in online learning environments.
- The influence of online peer collaboration on learning outcomes and student satisfaction.
- The role of online education in facilitating international education and global classrooms.
- Assessing the impact of online learning on traditional campus-based educational models.
- Trends in regulatory and accreditation challenges for online education programs.
- The effectiveness of online counseling and student support services in distance education.
- Strategies for integrating hybrid learning models in traditional educational institutions.
- The impact of mobile learning technologies on accessibility to education.
- The effectiveness of online teacher training programs in enhancing teaching quality.
- The role of community building in online education settings to enhance learning experiences.
- Evaluating the long-term career outcomes of graduates from online degree programs.
- The impact of social media on learning engagement in online educational settings.
- Strategies for ensuring equity and inclusion in online education environments.
- The role of open educational resources (OER) in reducing costs and improving access to education.
- Assessing the psychological effects of prolonged exposure to online learning environments.
- The effectiveness of online language learning programs in achieving fluency.
- Trends in the use of analytics and big data to improve student retention in online courses.
- The impact of online education on traditional faculty roles and teaching practices.
- The effectiveness of adaptive learning technologies in meeting diverse learner needs.
- Strategies for engaging parents in the online education of K-12 students.
- The role of online platforms in fostering interdisciplinary studies and research collaboration.
- Assessing the security and privacy concerns in online education platforms.
- The impact of cloud-based technologies on the scalability of online education.
- The role of certification and micro-credentialing in online education marketplaces.
- The effectiveness of virtual labs and experiments in science education online.
- Trends in the internationalization of online courses and degree programs.
- The impact of online education on reducing carbon footprints and promoting sustainability.
- Strategies for implementing effective feedback mechanisms in online learning.
- The effectiveness of multimedia and interactive content in online education.
- The role of online education in emergency preparedness and response training.
- Evaluating the future of online education in the post-pandemic era.
Philosophy of Education Thesis Topics
- Exploring the ethical dimensions of teacher-student relationships in modern educational settings.
- The role of pragmatism in shaping contemporary educational practices and policies.
- Critical theory and its implications for addressing social justice issues in education.
- The impact of constructivism on teaching methods and student learning outcomes.
- Analyzing the philosophy behind inclusive education and its implementation challenges.
- The influence of existentialism on student autonomy and personal development in education.
- The role of Confucian philosophy in shaping educational values and systems in East Asia.
- The impact of neoliberal policies on educational equity and access.
- Exploring the philosophical underpinnings of homeschooling and its growth in popularity.
- The role of education in democracy: Analyzing the contributions of John Dewey.
- The ethical implications of artificial intelligence and technology in education.
- The philosophy of lifelong learning and its relevance in the 21st century.
- Analyzing Paulo Freire’s pedagogy of the oppressed and its contemporary applications.
- The role of feminist theories in shaping gender education policies.
- The impact of postmodernism on curriculum design and educational objectives.
- Exploring the intersection of education and philosophy in the development of critical thinking skills.
- The role of virtue ethics in character education programs.
- The philosophical debates surrounding the commercialization of higher education.
- The influence of philosophical idealism on educational aspirations and outcomes.
- Nietzsche’s philosophy and its implications for educational motivation and excellence.
- The role of education in ethical and moral development according to Kantian philosophy.
- Analyzing the impact of Stoicism on resilience and stress management education.
- The role of Buddhist philosophy in promoting mindfulness and peace education.
- The philosophical foundations of experiential learning and its effectiveness.
- The implications of relativism for teaching multicultural and global education.
- The role of philosophy in defining the aims of scientific education.
- Analyzing the impact of libertarian educational theories on school choice and privatization.
- The ethics of care and its implications for educational practice and policy.
- The role of logical positivism in shaping approaches to scientific education.
- Analyzing the influence of Marxist philosophy on educational theory and classroom practice.
- The implications of phenomenology for understanding the educational experience.
- The role of educational philosophy in shaping environmental education.
- Exploring the philosophical basis for the integration of the arts in education.
- The role of philosophy in the debate over standardized testing and assessment.
- The implications of utilitarianism for educational policy and practice.
- Analyzing the philosophy of language and its implications for literacy education.
- The role of educational philosophy in teacher education and professional development.
- The impact of skepticism on promoting critical thinking and inquiry in education.
- The role of philosophy in shaping strategies for education during crises and emergencies.
- Analyzing the philosophical foundations of digital ethics in education.
- Assessing the impact of physical education on childhood obesity rates.
- The effectiveness of integrated technology in physical education: Wearables and fitness tracking.
- Strategies for promoting lifelong physical activity through school-based programs.
- The role of physical education in the psychological and social development of children.
- Evaluating gender differences in physical education participation and outcomes.
- The impact of school sports programs on academic performance and student behavior.
- Developing inclusive physical education curricula for students with disabilities.
- The role of physical education in addressing mental health issues among adolescents.
- Assessing the safety and risk management practices in school sports and physical education.
- The effectiveness of adventure-based learning programs in physical education.
- Trends in the professional development of physical education teachers.
- The impact of national standards on physical education curriculum development.
- Evaluating the role of competitive sports in physical education settings.
- The effectiveness of mindfulness and yoga programs integrated into physical education.
- The role of physical education in promoting healthy lifestyle choices among teenagers.
- Assessing the impact of extracurricular athletic programs on student engagement.
- The role of physical education in combating sedentary lifestyle trends among youth.
- Evaluating the efficacy of health and wellness education within physical education classes.
- The impact of community and parental involvement in physical education programs.
- Strategies for integrating cultural diversity into physical education programs.
- The effectiveness of physical education programs in rural vs. urban schools.
- Trends in adaptive sports programs within physical education for special needs students.
- The role of physical education in fostering team-building and leadership skills.
- Evaluating the impact of early childhood physical education on motor skill development.
- The role of physical education in the holistic development of students.
- Assessing the impact of budget cuts on physical education programs in public schools.
- The effectiveness of dance and movement programs as part of physical education.
- The role of physical education in reducing aggression and promoting peace among students.
- Strategies for enhancing student motivation and participation in physical education.
- The impact of outdoor education programs on environmental awareness and physical health.
- Evaluating the challenges and benefits of implementing cross-fit programs in high schools.
- The role of physical education in promoting gender equality and empowerment.
- Trends in physical education curricula focusing on non-traditional sports.
- The impact of coaching styles on student learning outcomes in physical education.
- Strategies for addressing the psychological barriers to physical activity among students.
- The role of physical education in promoting intercultural competence and understanding.
- Assessing the effectiveness of virtual and augmented reality tools in physical education.
- The impact of school policies on the provision and quality of physical education.
- Evaluating the long-term health impacts of physical education policies in schools.
- The role of physical education in preparing students for active and healthy aging.
- The effectiveness of inquiry-based learning approaches in enhancing student understanding of scientific concepts.
- Evaluating the impact of climate change education on students’ environmental behaviors and attitudes.
- The role of virtual reality (VR) simulations in teaching complex scientific phenomena.
- Strategies for integrating artificial intelligence (AI) into science curricula to foster problem-solving skills.
- Assessing the effectiveness of STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) integration in primary education.
- The impact of maker spaces and fab labs on innovation and creativity in science education.
- Trends in citizen science initiatives as tools for teaching and engaging students in scientific research.
- Evaluating gender disparities in science education and strategies to encourage female participation in STEM fields.
- The effectiveness of digital storytelling in teaching science to diverse student populations.
- The role of science education in promoting sustainability and understanding of ecological systems.
- Assessing the challenges and benefits of teaching controversial scientific topics (e.g., evolution, global warming) in schools.
- The impact of project-based learning on student engagement and retention in science subjects.
- Strategies for effective communication of scientific information in the age of misinformation.
- Evaluating the use of augmented reality (AR) tools for enhancing spatial reasoning in physics education.
- The role of science fairs and competitions in motivating students and fostering a love for science.
- The impact of remote and hybrid learning models on science education during and post-COVID-19.
- Assessing the professional development needs of science teachers in rapidly changing educational landscapes.
- The effectiveness of science education podcasts as a learning tool for high school students.
- Strategies for addressing the science achievement gap among underrepresented and low-income student groups.
- The role of outdoor education programs in teaching biological sciences and fostering environmental stewardship.
- Evaluating the effectiveness of interdisciplinary approaches to teaching science with technology and engineering.
- The impact of biotechnology education on student awareness and ethical perspectives towards genetic engineering.
- Trends in nanotechnology education and its integration into the science curriculum.
- The effectiveness of gamification in science education to enhance learning motivation and engagement.
- The role of mentoring programs in supporting underrepresented students in science fields.
- Assessing the impact of parental involvement on children’s science learning outcomes.
- The role of informal learning environments (museums, science centers) in supplementing formal science education.
- Evaluating the impact of international science collaborations in high school education.
- The challenges of adapting science curricula to include more local and indigenous knowledge systems.
- The effectiveness of flipped classrooms in fostering active learning in science education.
- Strategies for teaching complex scientific topics to students with learning disabilities.
- Assessing the role of peer instruction and collaborative learning in science education.
- The impact of science communication training for teachers on student outcomes.
- The role of artificial neural networks in modeling and simulation for science education.
- Trends in the use of machine learning to analyze educational data in science classrooms.
- Evaluating the impact of 3D printing technology on student understanding of molecular and cellular biology.
- The role of science education in fostering critical thinking and skepticism in an era of fake news.
- Strategies for enhancing science curriculum with real-world problem solving and innovation.
- The effectiveness of continuous assessment versus standardized tests in science education.
- The role of student-led research projects in promoting autonomous learning in science education.
- Evaluating the effectiveness of inclusive classrooms versus segregated settings for students with disabilities.
- The impact of assistive technologies on academic achievement for students with sensory impairments.
- Strategies for integrating social-emotional learning in special education curricula.
- Assessing the outcomes of early intervention programs for children with developmental delays.
- The role of parent-teacher collaboration in developing Individualized Education Programs (IEPs).
- Trends in teacher training for special education: Effectiveness and areas for improvement.
- The impact of Universal Design for Learning (UDL) on accessibility in education for special needs students.
- Strategies for addressing behavioral challenges in students with emotional and behavioral disorders.
- The effectiveness of speech therapy integrated within the school curriculum for students with speech impediments.
- Evaluating the transition programs for students with disabilities moving from secondary education to adulthood.
- The role of music therapy in enhancing communication and emotional expression in children with autism.
- Assessing the impact of legislative changes on the provision of special education services.
- The challenges and effectiveness of distance learning for students with special educational needs during the COVID-19 pandemic.
- Strategies for supporting students with learning disabilities in mainstream classrooms.
- The impact of peer tutoring on social skills development in children with special needs.
- Evaluating the use of augmented and virtual reality as educational tools for students with intellectual disabilities.
- The effectiveness of animal-assisted therapy in improving the well-being of students with special needs.
- Trends in funding for special education: Impacts and implications.
- The role of dietary interventions in managing symptoms of ADHD in school-aged children.
- Strategies for enhancing the motor skills of students with physical disabilities through adaptive physical education.
- The impact of bilingual education on students with learning disabilities.
- Evaluating the effectiveness of art therapy for students with emotional and psychological disorders.
- The challenges of assessing cognitive abilities in students with severe disabilities.
- The role of school counselors in supporting the mental health of special education students.
- Assessing the impact of sensory rooms on student behavior and learning outcomes.
- The effectiveness of professional development in autism spectrum disorders for general education teachers.
- Strategies for improving literacy skills among students with dyslexia.
- The impact of social stories and visual schedules in supporting students with autism in the classroom.
- Evaluating the long-term outcomes of students with disabilities who participate in life skills programs.
- The effectiveness of mindfulness and relaxation techniques in reducing anxiety in students with special needs.
- The role of technology in facilitating communication for non-verbal students.
- Strategies for involving students with disabilities in extracurricular activities.
- The impact of genetic counseling on parents of children with genetic disorders and its educational implications.
- Evaluating the role of educational psychologists in special education settings.
- The effectiveness of transition planning from school to employment for young adults with disabilities.
- The impact of community-based learning experiences on students with special needs.
- Strategies for addressing the shortage of qualified special education teachers.
- The role of early childhood intervention in preventing the escalation of special needs in later schooling.
- The impact of cultural and linguistic diversity on the delivery of special education services.
- Evaluating the effectiveness of behavior intervention plans for managing classroom behavior in students with emotional and behavioral disorders.
- The impact of vocational education on employment outcomes in the technology sector.
- Evaluating the effectiveness of apprenticeship programs in skilled trades.
- The role of vocational education in economic development within rural communities.
- Trends in vocational education policy changes and their impact on labor markets.
- The effectiveness of dual education systems combining vocational training and academic education.
- Assessing the role of industry partnerships in enhancing vocational training programs.
- The impact of digital transformation on vocational education and training (VET) curricula.
- Strategies for integrating soft skills training into vocational education programs.
- The role of vocational education in reducing youth unemployment rates.
- Evaluating gender disparities in access to vocational training and outcomes.
- The impact of vocational education on lifelong learning and career progression.
- Trends in vocational education for sustainable development and green jobs.
- The effectiveness of online and blended learning approaches in vocational education.
- The role of vocational education in supporting economic recovery post-COVID-19.
- Assessing the alignment of vocational training programs with current job market demands.
- The impact of vocational education on social inclusion and mobility.
- Strategies for improving the image and attractiveness of vocational education.
- The role of vocational education in supporting entrepreneurship and self-employment.
- Evaluating the effectiveness of vocational education in the hospitality and tourism industry.
- The impact of vocational training on the healthcare workforce and service delivery.
- Trends in vocational education for the creative arts and media sectors.
- The role of competency-based education in vocational training programs.
- The impact of international collaboration in vocational education on curriculum development.
- Evaluating the role of vocational education in the automotive industry’s shift to electric vehicles.
- Strategies for addressing the skills gap in manufacturing through vocational education.
- The role of vocational education in the digital economy and emerging sectors.
- Assessing the effectiveness of vocational education in culinary arts and food service management.
- The impact of vocational education on reducing recidivism through prison education programs.
- Trends in vocational education for the renewable energy sector.
- The effectiveness of vocational education in the retail and consumer services industry.
- The role of modular and flexible learning options in vocational education.
- Strategies for enhancing teacher training in vocational education settings.
- The impact of policy frameworks on the quality and delivery of vocational education.
- Evaluating the role of vocational education in enhancing workplace safety and occupational health.
- The effectiveness of vocational education in the agricultural sector.
- The role of vocational education in supporting older workers in workforce transitions.
- Assessing the impact of vocational education on community development and social welfare.
- Trends in vocational education for the entertainment and event management industry.
- The role of vocational education in fostering innovation and technology adoption.
- Evaluating the effectiveness of vocational education in the logistics and supply chain management industry.
We hope this extensive and carefully curated list of education thesis topics will serve as a springboard for your academic research. Each category has been designed to reflect the evolving landscape of educational inquiry, ensuring you can find a topic that not only interests you but also contributes to the field of education. As you peruse these options, consider how each topic might help you achieve your academic and professional goals. With this comprehensive resource, we aim to equip you with the tools to embark on a rewarding and insightful thesis writing journey.
The Range of Education Thesis Topics
Education is a dynamic field, constantly evolving in response to societal changes, technological advancements, and cultural shifts. The selection of a thesis topic in education is crucial, as it not only contributes to the academic development of students but also impacts the broader educational landscape. This in-depth article on education thesis topics explores the range of potential areas for scholarly research, highlighting the importance of choosing topics that are not only of personal interest but also of significant relevance to current issues, recent trends, and future directions in education. By delving into these dimensions, students can position their work to contribute meaningfully to ongoing conversations and innovations in the field. Whether you are examining traditional educational theories or exploring cutting-edge technologies, the goal remains the same: to enhance understanding and improve educational practices across diverse settings.
Current Issues in Education
The landscape of education is continually shaped by a variety of pressing issues that demand attention from educators, policymakers, and researchers. Education thesis topics that focus on these current issues are pivotal for students who aim to make meaningful contributions to the field. This section explores several significant challenges and areas of concern that are shaping educational discourse today.
- Educational Equity and Access: One of the critical areas within current education thesis topics is the persistent inequality in access to quality education. Disparities based on socioeconomic status, race, ethnicity, and geographical location significantly impact educational outcomes. Thesis topics in this area could explore strategies for improving access to high-quality education for underrepresented and disadvantaged groups, examining the effectiveness of policy interventions or the role of technology in bridging these gaps.
- Impact of Technology on Learning: The integration of technology in education has accelerated due to the global shift to online learning during the COVID-19 pandemic. Education thesis topics could investigate the long-term effects of remote learning on student academic performance and social skills, or explore the development of new pedagogical models that effectively integrate digital tools, addressing the digital divide and concerns over student data privacy and security.
- Mental Health in Educational Settings: Increasing awareness of mental health issues highlights the importance of supporting student well-being in educational environments. Education thesis topics can focus on evaluating the effectiveness of mental health programs in schools or exploring how educational settings can be designed to better support the mental health of both students and educators. This provides a fertile ground for thesis research aimed at developing effective support mechanisms.
- Curriculum Relevance and Reform: As the demands of the workforce evolve, there is a pressing need for curriculum reform to ensure that students are equipped with relevant skills for the future. Education thesis topics addressing these issues might involve examining the alignment of current curricula with the skills needed in today’s job market or evaluating the implementation and outcomes of curriculum innovations.
- Teacher Retention and Professional Development: Teacher turnover remains a significant issue in education, affecting the stability and quality of teaching. Education thesis topics in this area might include studies on the factors influencing teacher retention, the impact of teacher professional development on educational outcomes, or innovative strategies to enhance teacher engagement and satisfaction.
Addressing these education thesis topics through rigorous research not only contributes to academic growth but also plays a crucial role in shaping effective and responsive educational practices. Each of these areas offers a wealth of opportunities for developing thesis topics that can have a real-world impact, enhancing the educational experiences of learners and empowering educators across the globe.
Recent Trends in Education
Education is an ever-evolving field, with new methodologies, technologies, and philosophies continually reshaping the way knowledge is imparted and absorbed. Understanding these shifts is crucial for developing relevant education thesis topics. This section highlights some of the most significant recent trends in education that are influencing current research and teaching practices.
- Technology Integration: One of the prominent recent trends in education is the increased integration of technology in the classroom. Education thesis topics might explore how digital tools such as AI, VR, and cloud computing are transforming traditional teaching methodologies and student engagement. This trend has accelerated due to the necessity of remote learning during the COVID-19 pandemic, offering a rich area for investigation into its long-term effects on educational outcomes.
- Personalized Learning: Tailoring education to individual student needs and learning styles is becoming more feasible through data analytics and adaptive learning technologies. Recent trends in education suggest a move towards more personalized education, which is particularly relevant for thesis topics that investigate the effectiveness of these approaches in improving student learning and retention rates.
- Sustainability Education: As global awareness of environmental issues increases, so does the emphasis on sustainability within educational curricula. Recent trends in education highlight the integration of sustainability into all levels of education as a critical area of study. Education thesis topics could examine how sustainability is being taught in schools and its impact on student attitudes and behaviors towards the environment.
- Social and Emotional Learning (SEL): Another growing trend in the field of education is the focus on social and emotional learning. This trend emphasizes the importance of developing skills such as empathy, self-awareness, and emotional regulation. Education thesis topics could explore the integration of SEL into the curriculum, its effectiveness, and how it impacts academic and social outcomes.
- Inclusive Education: The push towards more inclusive educational practices that accommodate diverse learning needs, including those of students with disabilities, is a significant trend. Education thesis topics could focus on strategies for successful inclusion, the impact of inclusive policies on school culture, and student achievement.
- Lifelong Learning: The concept of lifelong learning has gained momentum, reflecting the continuous need for skill development in a rapidly changing world. Recent trends in education emphasize the importance of fostering lifelong learning habits, making it a compelling area for education thesis topics. These might investigate programs designed to encourage lifelong learning or evaluate methods for teaching skills that facilitate continuous personal and professional development.
Each of these recent trends in education provides a framework for valuable education thesis topics. By focusing on these areas, students can contribute to the dialogue on how best to adapt educational practices to meet the needs of today’s learners and tomorrow’s challenges.
Future Directions in Education
As we look towards the future, education continues to adapt to new challenges and opportunities. Identifying potential advancements and shifts within the field is crucial for students seeking to develop forward-thinking education thesis topics. This section explores several key areas that are likely to shape the future directions in education.
Integration of Emerging Technologies: One of the most anticipated future directions in education is the broader integration of emerging technologies such as blockchain, Internet of Things (IoT), and advanced artificial intelligence. Education thesis topics could explore how these technologies might revolutionize aspects of education management, security, personalized learning, and student assessment, offering new efficiencies and enhancing educational experiences.
- Global Education Systems: As globalization increases, there is a growing emphasis on global education frameworks that can provide consistent educational standards across borders. Future directions in education may involve the development of more unified global education policies and practices. Thesis topics might examine the impacts of these systems on local education traditions, student mobility, and international collaboration.
- Holistic Education Models: There is a shifting focus towards more holistic education models that emphasize not just academic skills but also physical health, mental well-being, and social responsibility. Future directions in education could see these models becoming more mainstream, with education thesis topics exploring the integration of holistic education practices in schools and their effects on student well-being and societal engagement.
- Decentralization of Education: The future might hold more decentralized education models, facilitated by technology, where learning is not confined to traditional classroom settings. Education thesis topics could investigate the potential of decentralized models to democratize access to education, personalize learning experiences, and reduce costs.
- Ethics and Education: As technology becomes more integrated into educational settings, ethical considerations regarding privacy, data security, and equality become increasingly important. Future directions in education will likely need to address these ethical challenges, providing rich areas for thesis research into best practices and regulatory frameworks.
- Lifelong and Lifewide Learning: The concept of lifelong learning is expected to expand into lifewide learning, where education spans multiple aspects of life and careers. Education thesis topics could focus on how educational institutions can support lifelong and lifewide learning paradigms, the impact on career development, and the implications for traditional educational pathways.
- Sustainability and Education: As environmental concerns continue to grow, future directions in education will increasingly need to integrate sustainability into all levels of education. Thesis topics might explore innovative ways to teach sustainability, the effectiveness of these educational programs, and their long-term impacts on environmental consciousness.
These future directions in education offer a broad array of possibilities for education thesis topics, each with the potential to significantly impact how education is delivered and experienced. By focusing on these emerging trends, students can position their research at the cutting edge of educational development, contributing valuable insights and solutions to the evolving challenges of the field.
In conclusion, the exploration of education thesis topics offers a window into the complex, ever-changing world of education. As this article has shown, engaging with current issues, embracing recent trends, and anticipating future directions are critical for students who wish to make impactful contributions through their research. From addressing the challenges of digital learning environments to enhancing strategies for inclusive education, the possibilities are vast and varied. By selecting a thesis topic that resonates with contemporary educational needs and future aspirations, students can contribute to the development of more effective, equitable, and innovative educational practices. Ultimately, the pursuit of these topics not only advances personal academic goals but also serves the larger purpose of enriching the educational experiences of learners around the globe.
Thesis Writing Services by iResearchNet
At iResearchNet, we understand that writing a thesis can be a daunting task. That’s why we’ve developed a range of custom writing services to assist students in navigating their academic challenges effectively. Whether you’re struggling with finding the right topic, conducting in-depth research, or crafting a compelling narrative, our expert team is here to help. We offer personalized support tailored to meet your specific needs, ensuring that each piece of work is not only comprehensive but also adheres to the highest academic standards.
- Expert Degree-Holding Writers: Our team consists of writers who hold advanced degrees in their respective fields. With their expertise, they bring a wealth of knowledge and a deep understanding of subject matter to ensure that your thesis is robust, well-researched, and scholarly. Each writer is committed to academic excellence and is skilled in both writing and critical analysis.
- Custom Written Works: Every thesis we help craft is started from scratch and tailored to the specific requirements of your assignment. We guarantee originality and a plagiarism-free approach, ensuring that your work is unique and meets the academic criteria of your institution.
- In-depth Research: Research is the cornerstone of every academic thesis. Our writers are proficient in conducting thorough research using a wide array of sources, including journals, books, and credible online resources. We ensure that all research is up-to-date and relevant, incorporating the latest findings and scholarly debates into your thesis.
- Custom Formatting (APA, MLA, Chicago/Turabian, Harvard): Understanding and applying the correct formatting style is crucial in academic writing. Our writers are experts in all major formatting styles and will ensure that your thesis meets the specific formatting requirements of your academic institution.
- Top Quality: Quality assurance is paramount at iResearchNet. We have a dedicated team of editors who ensure that each thesis is of the highest quality, free from errors, and polished to perfection. Our commitment to quality means that we consistently deliver work that is not only accurate but also impactful.
- Customized Solutions: We recognize that every student’s needs are unique. As such, our services are highly customized. Whether you need help with a specific chapter, statistical analysis, or a complete thesis, we tailor our services to fit your exact needs.
- Flexible Pricing: We offer competitive and flexible pricing models that cater to a range of budgets without compromising on quality. Our goal is to make professional writing assistance accessible to as many students as possible.
- Short Deadlines Up to 3 Hours: Facing a tight deadline? No problem. Our team is equipped to handle urgent orders, delivering comprehensive and high-quality work even on tight timelines.
- Timely Delivery: We understand the importance of deadlines in academic settings. Our team ensures that all work is completed and delivered within the agreed timeframe, allowing you to review the work and request any necessary revisions.
- 24/7 Support: Our support team is available around the clock to answer any questions or concerns you may have. Whether you need help placing an order or have a query about an existing order, our friendly support staff is always ready to assist you.
- Absolute Privacy: Your privacy and confidentiality are of utmost importance to us. All personal information and order details are kept confidential, and we ensure that your dealings with us are secure and private.
- Easy Order Tracking: Our user-friendly online platform allows you to track the progress of your order at any time. You can easily communicate with your writer, upload additional documents, and receive updates directly through your account.
- Money-Back Guarantee: We stand behind the quality of our work. If you are not satisfied with the final product, we offer a money-back guarantee, ensuring that you can order with confidence.
At iResearchNet, we are committed to supporting your academic journey with top-tier writing services. Our goal is to relieve the stress associated with thesis writing and to provide you with the tools you need to succeed. Trust us to help you achieve your academic goals through dedicated support, expert writing, and unwavering attention to detail. Let iResearchNet be your partner in navigating the complexities of academic writing.
Buy Your Custom-Written Thesis Today!
Ready to elevate your academic journey? Don’t let the challenges of thesis writing hold you back. At iResearchNet, we’re here to support you every step of the way with expert, customized writing services. Whether you’re struggling with topic selection, research, writing, or formatting, our team of degree-holding writers is ready to assist you.
Embrace the opportunity to work with professionals who understand your needs and are committed to your academic success. With our flexible pricing, timely delivery, and 24/7 support, you’re not just getting a service; you’re gaining a partner dedicated to helping you excel.
Don’t wait— order your custom thesis paper today ! Take advantage of our comprehensive services and ensure your thesis is of the highest quality. Visit us at iResearchNet to learn more and make your academic goals a reality. Join the many students who have successfully navigated their academic challenges with our help. Order now and make your academic journey smoother and more successful.
ORDER HIGH QUALITY CUSTOM PAPER


21 Early Childhood Education Essay Topics (Best Titles)
During your studies, the time to write an essay on early childhood education may come. We’ve compiled a list of good and creative early childhood education essay topics to help you fasten the process.
What is Early Childhood Education?
Early childhood education is described as education combined with child care services provided to young people from the time they are born until they reach the age of eight. When it comes to early childhood education, children participate in a variety of educational environments throughout their early childhood years. Whenever someone learns that you are a student majoring in education, they can’t help but wonder why you want to become a teacher. Isn’t it true that teachers are underpaid?
Due to their enthusiasm for all aspects of teaching, most aspiring teachers are completely immersed in the world of education before enrolling in even the first college course in their field. Consequently, many teacher candidates have difficulty narrowing their emphasis on a particular issue to do research for their thesis paper as a result of this. Fortunately, there is a diverse range of domains available within the field of education from which to pick from. When picking a field to investigate more, think about what motivates you the most as an instructor and how you can benefit from studying more about a specific issue in greater depth.
Early Childhood Education Essay Topics
When writing an essay on the importance of early childhood education, here are some of the best topics you can choose from.
1. How does poverty impact a child’s education?
In addition to the kid’s health and nutrition, parental mental and physical participation, a facilitating family environment, child care, as well as neighborhood and school environments, poverty can have an impact on a child’s developmental trajectory. As a result of these variables, a kid may develop feelings of self-doubt, disinterest, and inability to create a healthy educational environment.
So, what steps can we take to begin providing outreach to these stunted children? In order to address the numerous variables that contribute to the educational stagnation of low-income students, several alternatives must be explored.
To lessen or remove the financial divide between education and students, we must first ensure that funding is directly responsive to the needs of students and educational institutions.
I’ve witnessed personally the dearth of books, as well as outdated and usable technology, available to pupils. It is impossible to expect students to recall all of the necessary curriculum if they are not provided with adequate resources in school. If our own instructors are not equipped with the necessary resources to educate, how can we expect to prosper when presented with the opportunity to pursue higher education?
2. The use of Technology in early childhood learning.
There is a great deal of disagreement in the educational community about the use of electronics and multimedia in the classroom, particularly when it comes to early childhood education. Should children as young as three years old be allowed to use computers? What is the appropriate age for a youngster to learn how to use an iPad before learning how to use the bathroom on his or her own? When doing this research, researchers would look not only at the past, but also at the future, as technology becomes increasingly pervasive in children’s daily life. In light of the fact that these ideas are relatively new to the field of education, any research that is conducted on the benefits of using technology in the classroom will assist to define the future of teaching in contemporary society.
3. The relationship between early childhood education and literary skills in high school.
As a small child grows, his or her environment has a significant impact on the abilities that he or she acquires. The emergent literacy skills, that comprise phonological awareness, narrative awareness, alphabet knowledge, print concepts, vocabulary, and oral language, are part of the critical skills that will help these young learners prepare for their future.

It is possible to acquire these abilities through the home environment and early childhood school environments. Before kindergarten, children’s emergent literacy abilities are established, and they are predictive of a child’s later success in reading. There are a variety of elements that can influence whether or not a youngster is able to develop reading abilities.
4. Should the federal and state governments improve funding of early childhood learning?
Technology grants and philanthropic foundations are available to assist underserved communities. Because of its more user-friendly platforms, Apple initially had a monopoly on the market for educational applications of technology. For many educators, Apple continues to be the favored choice because of the discounts and additional possibilities that the company provides to its customers. Because of the numerous cross-platform software packages that have been produced, both Macintosh and Microsoft settings are increasingly being given equal access to current educational environments. Education decision-makers should remember that the future is unpredictable and that today’s smart buy may wind up on tomorrow’s garbage heap of obsolete technology, no matter which platform they chose.
5. Adverse Childhood Experiences and their Effects on High School Graduation Rates.
The shocking impact that adverse childhood experiences (ACEs) have on children and adults was shown in a landmark study that was initially published twenty years ago and has since gained widespread attention. Adults’ exposure to abuse, divorce, substance abuse, and other factors were found to be associated with a number of health risk factors, according to Andra et al (1998).

The Adverse Childhood Experiences (ACE) Study expanded our understanding of the long-term impacts of direct and indirect abuse, as well as the fact that children did not have to be abused themselves in order to suffer serious consequences to their physical, mental, and even social well-being in the long run.
6. The contribution of a child’s socioeconomic background to the success of early education.
In order for a child to acquire the necessary skills, his or her socioeconomic position must be taken into consideration. In addition, the child’s socioeconomic position will influence what resources are accessible at home and whether or not the parent or guardian is able to provide the child with the essential language and literacy exposure because they are constantly at work. Additionally, there are several other elements to consider, such as a child’s language handicap and prior adverse literacy experiences.
Therefore, to that extent, early childhood educators must conduct an in-depth investigation into the child’s family and community relationships in order to provide the best possible care. It is possible to use the outcomes of such investigations to optimize the teaching process and dissipate any negative connotations that may be detrimental to the child’s development.
On the other side, both the family and the community can work together to ensure the child’s future success in school and in the workplace. As a result, the educator must work to foster positive relationships with parents and members of the community for the children in his or her care.
7. Examining the benefits of daycare to young children
Early childhood educators, of course, are well aware of the significance of their work. Despite the fact that individuals may intuitively understand the relevance of early childhood education programs, research on the benefits of such programs places a quantifiable value on their significance, which has implications for funding. Participation in early education programs can have a variety of consequences for a kid.
Conducting longitudinal study on the potential future success of children in higher grades is essential to fully comprehending how a primary teacher’s efforts can result in long-term advantages for her students. This research can be done in a variety of ways.
The recognition of these consequences motivates teachers to do their best work every day and to constantly improve their approaches.
8. Does attending preschool improve a child’s vocabulary?
Following the completion of quality preschools, children have stronger self-regulation behavior and academic skills than their counterparts who do not participate in preschool. This is according to some new studies.
- Perks such as expanded vocabulary developed through socialization with other youngsters and a love of reading can provide children an advantage throughout their academic lives.
- By the time they reach high school, children who attend preschools where instructors receive additional training can still make academic gains of up to a quarter of a letter grade.
- With the start of a new school year in full swing, parents of preschool-aged children may be wondering whether or not sending their children to preschool makes a significant impact in their children’s development.
9. Contribution of early childhood learning to the cognitive development of young children.
In addition to assisting children in developing their individual cognitive, physical, emotional, and social skills, childhood care providers also assist instructors in responding to the unique requirements of each child in their care. One of the most important responsibilities of childhood care providers is to prepare children for school through curricula that assist children in developing their individual cognitive, physical, emotional, and social skills, and at the same time helps instructors respond to the unique requirements of each child in their care.
In this scenario, cognitive development is particularly important, since it provides youngsters with knowledge of topics such as measuring and patterns, forms and numbers, and counting strategies, among other things. The most effective way for children to develop in this area is through play.
As an example, a report from the Manitoba Early Learning and Childhood Curriculum Framework proposes that children’s cognitive and intellectual skills be developed through relevant activities – such as allowing them to experiment with a range of cardboard boxes and tube shapes.
10. The practices of early childhood teachers related to the use of dramatic play in learning environment.
A surprising finding from the research is that there is no single early childhood method that is intrinsically superior; rather, what matters most is that children are exposed to educational opportunities at the earliest feasible age. In spite of the fact that no single curriculum or pedagogical approach can be determined to be the most effective, children who participate in carefully planned, high-quality early childhood programs in which curriculum aims are specified and integrated across domains tend to learn more and are better prepared to master the complex demands of formal schooling.”
More essay topics on Early Childhood Education
11. The effects of school district policies on preventing maltreatment among early childhood learners.
12. The impacts of politics on the success of early childhood learning programs.
13. Exploring the problems of measuring the efficacy of ECE programs such as Head Start.
14. Evaluating the progress and transformation of early childhood learning.
15. Approaches to make early childhood curriculum effective.
16. What are the challenges facing early childhood learning in modern America?
ODU Digital Commons
Home > Education > Communication Disorders & Special Education > Early Childhood ETDs
Theses and Dissertations in Early Childhood Education
Theses/dissertations from 2023 2023.
Dissertation: Using Reciprocal Teaching Strategies to Improve Reading Comprehension For English as a Second Language Students With Learning Disabilities , Hana M. Almohamadi
Theses/Dissertations from 2015 2015
Dissertation: The Effects of Incorporating Interactive Questioning During Shared Electronic Book Reading on Preschoolers' Comprehension , Lynda Gail Salmon
Theses/Dissertations from 2014 2014
Dissertation: An Examination of Teachers' Writing Self-Efficacy, First-Grade Students' Attitudes and Self-Efficacy in Writing, and Students' Writing Behaviors , Julie Bridget Mary Dashiell
Dissertation: Recruiting, Engaging, and Retaining Low Income Parents in Community Parenting Programs: A Phenomenological Study , Jane Elyce Fuqua Glasgow
Dissertation: Using Interactive Reading Techniques with Word World to Enhance Emergent Literacy , James B. Godfrey
Dissertation: The Relationship of Mobility, Child Characteristics and School Characteristics to the Academic Achievement of Third Grade Students in a Predominantly Latino District , John Christopher Hicks
Theses/Dissertations from 2013 2013
Dissertation: How Counselors Are Trained to Work with Bisexual Clients in CACREP-Accredited Programs , Laurie Anne Bonjo
Dissertation: The Effect of Public Pre-Kindergarten Attendance on First Grade Reading and Social Achievement: A District Level Analysis , Michael James Haslip
Dissertation: Quality Profiles in Early Childhood: An Example From Virginia's Quality Rating Improvement System , Kathryn M. Squibb
Theses/Dissertations from 2011 2011
Dissertation: Kindergarten Teachers' Classroom Management Beliefs and Practices and Their Implications on Students' Social and Academic Outcomes , Lauren D. Florin
Theses/Dissertations from 2010 2010
Dissertation: A Hierarchical Examination of the Immigrant Achievement Gap: The Additional Explanatory Power of Nationality and Educational Selectivity Over Traditional Explorations of Race and Socioeconomic Status , Kathryn A. Simms
Theses/Dissertations from 2009 2009
Dissertation: The Impact of The 101s: A Guide to Positive Discipline Teacher Training on Teacher Interaction Practices, Teacher-Child Relationship Quality, School Adjustment, and Academic Outcomes in Kindergarten Classrooms in Bangkok, Thailand , Panadda Thanasetkorn
Dissertation: The Impact of The 101s: A Guide to Positive Discipline Parent Training: A Case Study of Kindergarteners and Their Parents in Bangkok, Thailand , Piyavalee Thanasetkorn
Theses/Dissertations from 2008 2008
Dissertation: The Impact of the 101s: A Guide to Positive Discipline Training on Teacher Interaction Practices, Attitudes, and Prosocial Skill Outcomes in Preschool Classrooms , Marie Louise Talayco Masterson
Advanced Search
- Notify me via email or RSS
- Collections
- Disciplines
- Author Guidelines
- Department of Communication Disorders & Special Education
- Other Digital Collections
- ODU Libraries
- Old Dominion University
Home | About | FAQ | My Account | Accessibility Statement
Privacy Copyright
Home > Departments > EDUCATION > EDUCATION_MASTERS_EARLYCHILDHOOD
Master's Theses & Capstones in Early Childhood
Submissions from 2024 2024.
Using an Interoception-Based Curriculum for Social-Emotional Learning in Preschool to increase Emotional Regulation , Montana Applegate
Using Small Groups to Support Mathematics Learning in Preschool , Katelyn Bradfield
Implementing Universal Design for Learning in the Inclusive Early Childhood Classroom , Lydia Bruns
Implementation of a Mental Health Consultation Program at an Early Childhood Education , Diana Buffington
Acquisition and Retention of Vocabulary Using Simplified Picture Word Inductive Model , Kodie Davis
Child Development Homes, Play-Based Learning, and Academic and Social-Emotional Skills , Hollie Fairholm
Alphabet Instruction in a Preschool Setting: Individualized or Large Group? , Kristen Guarino
Improving Elementary Literacy Achievement by Aligning Individual and Team Goals , Katie Hilby
Nature's Classroom: Outdoor Learning in Early Childhood , Kara Huberty
Improving Reading Interventions: A School Improvement Plan , Ivy Leitch
Improve Mentorship Through Meaningful Feedback and Coaching , Molly Montavon
Play Having Its Place in Early Childhood Education , Emily Streicher
School Improvement Plan: Enhancing Foundational Skills Instruction , Alexis Weber
Using Restorative Practices to Ensure Students Feel Seen, Heard, and Valued , Rylie Zyzda
Submissions from 2023 2023
Efficacy of Discrete Trial Training , Paula Ahlrich
Implementation of STAR to Support Students with Disabilities , Lexis Barkema
Conscious Discipline for Parent , Amber Brown
Social Emotional Learning in Early Childhood: A School Improvement Project , Madi Callan
Play Based Learning A School Improvement Plan , Kalee Chamberlin
Does Pre-Selected Technology-Based Games Improve Alphabet Knowledge in Preschoolers Compared to Peer Learning Small Groups? , Nicole Gray
Implementing Changes in Family Childcare Programs to Increase Social-Emotional Development and Decrease Negative Behavior , Julia Green
Student Inclusion in the Least Restrictive Environment , Jennifer Grossman
The Developing Independence of Toddlers , Maggie Harbaugh
Implementing Social-Emotional Supports with Coaching in a Preschool Program , Ashley Harvey
Promoting More Play in Kindergarten , Sarah Hofland
Preschool Approach to Teaching Alphabet Knowledge , Ashley Kreinbrink
Supporting Play in the Preschool Classroom with Visuals , Jessica Luetkemeier
Implementing Play-based Learning , Brooke Patton
SCCS Tinley Cultural Relationships School Improvement Plan , Rebecca D. Rael
Strengthening the Home and School Partnership: An Improvement Plan to Educate Parents on Child Development and School Initiatives , Jennifer N. Robinson
Addressing the Behavioral and Emotional Needs of Elementary School Students: A School Improvement Project , Katherine Ross
Developing Communication Skills in Preschoolers , Andrea Schlotman
Improving Trauma-Informed Practices in a School System , Maria Sloniker
Major Components Needed in a Literacy Curriculum to Promote Student Success , Brooke Smith
Improving Understanding of Mathematics Concepts in Kindergarten Students through Movement Integration , Kendall Stallings
Effects of Parental Involvement on Academics , Jessica Stamer
Foundational Literacy Programs Affect FAST Scores , Courtney Stekl
Improving Reading Comprehension and Vocabulary for English Language Learners , Rachael Vande Hoef
The Impact of Small-Group Multisensory Instructional Techniques on Kindergarteners’ Letter Sound Knowledge , Karly Walker
Using Restorative Practice to Decrease Behavior and Increase School Community , Kaylee West
Submissions from 2022 2022
The Positive Impact of Social and Emotional Learning , Alexi Allen
Preschoolers' Engagement In Physical Activity And The Ability To Gauge Risks And Challenges , Teresa Beyer
Can Play-Based Learning Provide Adequate Learning Experiences for Young Children? , Rachel Bienemann
Utilizing Mindfulness and Movement to Promote Executive Function and Self-Regulation , Sonia Bockoven
Professional Development Program Addressing Teachers’ Well-Being: A Natured-Based Intervention Approach , Carmen Chow
A Need for Social Emotional Instruction , Chelsea Cook
Social Emotional Learning Curriculum and Implementation at Saint Cecilia School , Rachel Eash
The Benefits of Parent-Teacher Collaboration on Achievement in the Preschool Classroom , Samantha Frye
Increasing Phonemic Awareness Instruction: A School Improvement Plan , Becca Gaffney
Building Executive Function and Self-Regulation in Preschool , Shawn Gorsett
The Value of Play-Based Learning in Early Childhood Classrooms , Courtney Hansmann
Improving Preschoolers’ Number Sense Using Computer Math Games , Justine Hosch
Implementing Self-Selected Outdoor Play for Preschoolers , Shannon Jensen
Effective Literacy Differentiated Instruction , Lauren Kahl
Playground Improvement Plan , Joan Ketelsen
Early Childhood Math Strategies , NiCole Merchant
The Research-Based Strategies to Help Trauma Students in a Preschool Classroom , Amber Murray
Effects of Differentiated Literacy Instruction in a Kindergarten Classroom , Brenda Nagel
Growing Independence Through the Use of Structured Work Systems , Skye Nicolls
The Expanding Expression Tool's Impact on Expressive Language in Preschool , Jill Owens
Sensory Rooms: Increasing Preschool Students’ Focus and Engagement in the Classroom , Tasha Pierce
Technology Enhances Literacy & Numeracy Skills in a Play-Based Preschool Classroom , Sarah Ringsdorf
Fine Motor Matters - A Plan to Improve Fine Motor Skills at the Early Childhood Level , Natasha Slater
Social and Emotional Skills Develop Through Play-Based Learning , April Welding
Effects of Using Hands-On Materials During Narrative Literacy Activities in the Preschool Classroom , Brittany White
Methods of Goal Selection , Molly Wickham
Family Centered Practices for Children Receiving Home Intervention Services , Jessica Winter
Submissions from 2021 2021
Technology Use in Early Childhood , Sandra Anderson
Brain Breaks Improve Student Behavior and Focus , Meghan M. Barker
The Vital Benefits of Play , Renata Bitoy
Outdoor Classroom/Natural Playground Space School Improvement Project , Holly Carlson
Impact of Technology Use on Early Childhood , Paige Davidson
Evidence-Based Best Practices for Kindergarten Reading , Rachel Dolehanty
Maintaining a Relational Classroom While Implementing TS GOLD , Leslie K. Gustafson
Social Interaction with Students Who Have a Visual Impairment in Early Childhood , Sarah Harms
The Implementation of Positive Behavior Supports and Interventions to Support and Encourage Appropriate Behavior and a Positive Climate in the School , Grace Hiveley
TCIT’s Impact on Various Challenging Behaviors , Emily Krakau
The Importance of Using Manipulatives in Math Class , Jennifer Lange
Technology to Increase Peer Interactions in Preschool , Angela McLean
How To Promote Self-Determination in Students with Disabilities , Elissa J. Meadows
How Adding Social Emotional Learning Impacts Preschool Student's Ability to Manage Their Behavior , Pamela Niemeyer
Explicit Literacy Instruction Focused on Letter Sounds vs. Letter Names and Student Educational Growth , Maria O'Dell
Increasing Family Engagement in a Preschool Program , Meghan Reiman
The Impact of Utilizing Learning Centers to Promote STEM Development in the Early Childhood Classroom , Crystal M. Riniker
Trauma-Informed Practices and Their Effects on Student Performance and Behaviors , Ashley Roberts
Parental Involvement in Education , Molly Schnekloth
Play It Again Mathematics , Michelle Sherman
The Importance of Physical Activity in Early Childhood Development , Kathleen Stuart
The Value of Play-Based Learning in Early Childhood Classrooms , Brandice TeGrootenhuis
Adverse Childhood Experiences and Creating a Culture of Support in the Classroom , Keisha Trimble
The Use of Social Stories to Teach Appropriate Social Skills to Create a Peaceful Classroom Environment , Kallie Turner
Examining Quality Inclusive Practices in Early Childhood Education , Laura Wagner
The Benefit of Inclusion in Early Childhood Classrooms , Taylor Webb
Teaching Early Literacy Skills in Preschool and Future Kindergarten Success , Amanda Wehrhan
Implementing Effective Inclusion in Prekindergarten , Jennifer L. Wenke
Comparison of Play-Based Learning versus Worksheets in English Language Arts Growth , Erin Wiskus
Submissions from 2020 2020
Effectiveness of Number Sense Instruction and Memorization of Math Facts , Katie Barnes
Children Living with Trauma , Maggie Boyd
Social Emotional Learning and Its Effects on Behaviors in the Kindergarten Classroom , Nicole Bruce
Executive Function and Self Regulation in Early Childhood , Jill Casey
Search the Site:
Advanced Search
- Notify me via email or RSS
- DeWitt Library
- Northwestern Review
Browse the Site
- Collections
- Disciplines
Meet the Authors
Home | About | FAQ | My Account | Accessibility Statement
Privacy Copyright

UKnowledge > College of Education > Early Childhood, Special Education, and Counselor Education > Theses & Dissertations
Theses and Dissertations--Early Childhood, Special Education, and Counselor Education
The Theses and Dissertations--Early Childhood, Special Education, and Counselor Education collection is formerly known as the Theses and Dissertations--Early Childhood, Special Education, and Rehabilitation Counseling collection.

Theses/Dissertations from 2024 2024
How Important is Parental Involvement and Engagement in Preschool , Emilee M. Dixon
USING NATURALISTIC LANGUAGE INTERVENTIONS TO INCREASE EXPRESSIVE COMMUNICATION OF AAC USERS WITH AUTISM , Kacey Eaton
Effect of Video Modeling and Teacher Praise on Turn-taking Behavior of Preschoolers in an Inclusive Setting , Happiness Efeturi
PIXELS OR PEOPLE: A COMPARISON OF THE DIFFERENITAL EFFECTS OF ANIMATED AND HUMAN VIDEO MODELS ON EXERCISE BEHAVIORS FOR HGH SCHOOL STUDENTS WITH INTELLECTUAL DISABILITY , Jade Alexis Fulkerson
CHILD LANGUAGE AND HAPPINESS BEHAVIORS: EVALUATING THE EFFECTS OF CAREGIVER COACHING , Ashlen Grubbs
Evaluating a Rapid Coaching Intervention Delivered Remotely: Teaching Naturalistic Language Strategies to a Parent of Child with Down Syndrome , Pallie Gullett
Training Paraprofessionals In The Implementation Of Aided Language Modeling With Individuals With Intellectual Disabilities And CCN , Julianne Hill
Group vs. Individual Video Modeling for Acquisition of Pilates for Individuals with Disabilities , Brittany Rounce
BUILDING INDEPENDENCE THROUGH STRUCTURED WORK SYSTEMS FOR STUDENTS WITH MODERATE TO SEVERE DISABILITIES , Maggie Smith
Theses/Dissertations from 2023 2023
EFFECTS OF VIDEO MODELING WITH VOICE-OVER NARRATION VERSUS NO VOICE-OVER NARRATION , Kennedy Carpenter
EVALUATING THE DIFFERENTIAL EFFECTS OF USING A TECHNOLOGY-BASED ANTECEDENT INTERVENTION IN COMPARISON TO A TECHNOLOGY-BASED TREATMENT PACKAGE , Rachel Fosnaught
ESTABLISHING SELF-INSTRUCTION SKILLS BY TEACHING MANDS FOR INFORMATIONAL INQUIRIES WITH INTELLIGENT VOICE ASSISTANTS USING PROGRESSIVE TIME DELAY , Taylor Rae Kelley
Comparing the Efficacy of Interventions Derived from Concurrent Operant Analysis and Indirect Assessment , Lane Marquardt
Comparing Indirect Assessment Results to a Direct Function Focused Preference Assessment to Identify Potential Reinforcers to Increase Task Completion in a School Setting , Kailee Joy Matthews
Self-Advocacy Training for Students with Complex Communication Needs using Time Delay and Generative Learning , Alexis Rai Patterson
ASYNCHRONOUS E-TRAINING AND COACHING TO INDONESIAN PARENTS: NATURALISTIC STRATEGIES TO SUPPORT LANGUAGE DEVELOPMENT OF CHILDREN WITH SOCIAL-COMMUNICATION DELAYS , Ndaru Prapti
EVALUATING A RAPID COACHING INTERVENTION THAT INCLUDES INTERDISCIPLINARY COLLABORATION: TEACHING A PARENT NATURALISTIC STRATEGIES , Lauren Reiss
Effects of Peer Training on the Use of Aided Language Modeling and AAC User Communicative Acts , Shelby Smith Sheets
DISABILITY LABEL AND LEAST RESTRICTIVE ENVIRONMENTS: GENERAL ELEMENTARY EDUCATION TEACHERS’ EXPERIENCES AND PERCEPTIONS , Sara Sheffler
A Comparative Analysis of Applied Behavior Analysis and the Montessori Method , Emily Webb
Theses/Dissertations from 2022 2022
Coaching and Training Paraprofessionals to Implement Communication Strategies in the Classroom with Students with Disabilities , Andrea Grace Antoniewicz
Interdisciplinary Collaboration: Using a Rapid Coaching Intervention to Teach Parents Naturalistic Strategies to Teach Communication , Rose Campbell
HOW DO PARENTS OF TYPICALLY DEVELOPING CHILDREN PERCEIVE AND INTERACT WITH CHILDREN WITH EXCEPTIONALITIES? , Zurisaday N. Decker
An Overview of Functional Communication Training for Registered Behavior Technicians , Christopher Dollinger
The Use of Video Modeling to Improve Transitions Within a Preschool Classroom , Amanda L. Duncan
Advanced Search
- Notify me via email or RSS
Browse by Author
- Collections
- Disciplines
Author Corner
- Submit Research
New Title Here
Below. --> connect.
- Law Library
- Special Collections
- Copyright Resource Center
- Graduate School
- Scholars@UK

- We’d like your feedback
Home | About | FAQ | My Account | Accessibility Statement
Privacy Copyright
University of Kentucky ®
An Equal Opportunity University Accreditation Directory Email Privacy Policy Accessibility Disclosures
- 2023 AERA in the News
- 2022 AERA in the News
- 2021 AERA In the News
- 2020 AERA In the News
- 2019 AERA In the News
- 2018 AERA In the News
- 2017 AERA In the News
- 2016 AERA In the News
- 2015 AERA In the News
- 2014 AERA In the News
- 2013 AERA In the News
- AERA Speaking Out on Major Issues
- 2023 AERA News Releases
- 2022 AERA News Releases
- 2021 AERA News Releases
- 2020 AERA News Releases
- 2019 AERA News Releases
- 2018 AERA News Releases
- 2017 AERA News Releases
- 2016 AERA News Releases
- 2015 AERA News Releases
- 2014 AERA News Releases
- 2013 AERA News Releases
- 2012 AERA News Releases
- 2011 News Releases
- 2010 News Releases
- 2009 News Releases
- 2008 News Releases
- 2007 News Releases
- 2006 News Releases
- 2005 News Releases
- 2004 News Releases
- AERA Research Archive
- Trending Topic Research Files
- Communication Resources for Researchers
- AERA Highlights Archival Issues
- AERA Video Gallery

Share
University of Minnesota Twin Cities
University digital conservancy, three essays in early childhood education, view/download file, persistent link to this item, journal title, journal issn, volume title, published date, description, collections, series/report number, funding information, isbn identifier, doi identifier, previously published citation, suggested citation.
Content distributed via the University Digital Conservancy may be subject to additional license and use restrictions applied by the depositor. By using these files, users agree to the Terms of Use . Materials in the UDC may contain content that is disturbing and/or harmful. For more information, please see our statement on harmful content in digital repositories .
- NAEYC Login
- Member Profile
- Hello Community
- Accreditation Portal
- Online Learning
- Online Store
Popular Searches: DAP ; Coping with COVID-19 ; E-books ; Anti-Bias Education ; Online Store

You are here
NAEYC provides the highest-quality resources on a broad range of important topics in early childhood. We’ve selected a few of our most popular topics and resources in the list below.
Still can’t find the topic you need? Check out our site search .
- Anti-Bias Education
- Back to School
- Common Core
- Coping with COVID-19
- Coping With Stress and Violence
- Developmentally Appropriate Practice (DAP)
- Dual Language Learners
- Family Engagement
- Guidance and Challenging Behaviors
- Recursos en Español
- Social and Emotional Development
- Summer Learning
- Technology and Media
- الموارد باللغة العربية
- منابع فارسی
Looking for a specific topic? Try using our search page! The new search allows you to filter by audience, age group of children, or topic.
- Research article
- Open access
- Published: 28 July 2022
Development of pre-service early childhood teachers’ technology integrations skills through a praxeological approach
- Taibe Kulaksız ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-7960-7440 1 &
- Mehmet Toran ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-3457-9113 2
International Journal of Educational Technology in Higher Education volume 19 , Article number: 36 ( 2022 ) Cite this article
5043 Accesses
5 Citations
4 Altmetric
Metrics details
How to improve and what should be carried out for pre-service teachers’ technological competencies for teaching purposes is still an important issue on the agenda of the higher education field. In light of this, we aimed to reflect the individual and collective technology integration knowledge and skills construction process of pre-service early childhood education teachers with democratic participation. We utilized the praxeological approach as a method and learning approach to reveal the reflections of the instructional technologies course. The participants in this study were 52 sophomore pre-service teachers in the early childhood education department. We collected the data from various sources such as interviews, portfolios, researchers’ field notes, e-mails, online course evaluation form. We carried out the thematic analysis method to analyze the data. The findings indicated that three main themes emerged as initial challenges, learning process, and learning outcomes during enhancement of pre-service early childhood teachers' technology integration knowledge and skills. As a result, the praxeological approach used in instructional technologies courses in teacher education programs leads to a crucial digital transformation to be ready to become future teachers.
Introduction
The use of technology in education has been getting increased. Although the use of technology in early childhood education (ECE) is controversial, it is helpful for children learning and development when it is used to create natural learning environments to meet their needs and for teaching purposes (Bolstad, 2004 ; Van Scoter et al., 2001 ). Accordingly, research on the effectiveness of technology in ECE has been produced positive results (Kerckaert et al., 2015 ). The various instructional technologies such as digital storybooks, and digital games, improve children's technical, literacy, social, math, problem-solving, and emotional skills (Bolstad, 2004 ; Contini et al., 2018 ; Morfoniou et al., 2020 ; Verbruggen et al., 2021 ; Zomer, 2014 ), therefore ECE teachers should mediate digital technologies wisely for children’s understandings (Segal-Drori & Ben Shabat, 2021 ). Technology also allows collaboration between children and children-adults (Bolstad, 2004 ). Furthermore, it is observed that digital competencies (e.g. digital citizenship) have been also included in preschool education programs (Lauricella et al., 2020 ). Being prepared for future learning and teaching scenarios is essential beyond focusing only on the present conditions of schools (Dong & Xu, 2020 ; Seufert et al., 2021 ). Therefore, technology knowledge and skills for educational purposes seem more important than all times for future ECE teachers.
On the other hand, teachers have low-level knowledge and skills about how to use technology in ECE (Contini et al., 2018 ; Martín et al., 2020 ; Masoumi, 2021 ; Öner, 2020 ). Moreover, studies reveal that some of them have negative attitudes towards technology use in ECE (Dong & Xu, 2020 ; Öner, 2020 ). However, Zilka's ( 2021 ) study indicated that pre-service teachers have positive attitudes, and they are more likely to integrate technology in ECE when they begin working more than in-service teachers. Therefore, technology integration in education of teacher candidates has required a systemic change in several ways discussed by Tondeur et al. ( 2012 ) such as technology planning and leadership, role models, collaboration, feedback, instructional design, authentic experiences. To complement this need, the praxeological approach, which refers to acquirement useful knowledge and skill as a transformation process (Pascal & Bertram, 2012 ), were taken into account to design an instructional technologies course for pre-service ECE teachers.
Theoretical background
Developing pre-service teachers’ technology integration knowledge and skills.
The studies show that pre-service teachers' knowledge and skills on technology integration increase with courses included in teacher education programs (Jung & Ottenbreit‐Leftwich, 2020 ; Neumann et al., 2021 ; Schina et al., 2020 ). Therefore, training seems like a key element to enhance pre-service teachers’ digital competence for education (Romero-Tena et al., 2020 ). However, ECE teacher education programs in terms of technology integration are still challenging, even if pre-service teachers have courses, they do not feel enough competent to transfer their knowledge and skills to the next implementations (Masoumi, 2021 ).
Besides, there are more factors linked to the construction process of technological knowledge and skills. Pre-service teachers' ability to integrate technology into ECE is closely related to their attitudes and their perception of the process (Zilka, 2021 ). Pre-service ECE teachers having low positive attitudes may not be aware of the role of technology in ECE, as their attitudes towards technology are related to information and communication technologies (ICT) usage, ICT professional training, and ICT skills (Dong & Xu, 2020 ). As the development of pre-service teachers' technology skills is affected by different factors as mentioned, these education programs for pre-service ECE teachers are more beyond merely acquiring digital skills (Masoumi, 2021 ). Hence, the non-negligible factors influencing their technology integration skills and knowledge should be also included in the pre-service teachers’ education programs.
Some approaches and strategies are suggested for pre-service teachers’ education in the context of technology. Tondeur et al. ( 2012 ) proposed a model called Synthesize Qualitative Data Model based on an intensive literature review. The model suggests the important elements for pre-service teachers’ preparation for technology in education like aligning theory and practice, teacher educators as role models, reflecting on attitudes about the role of technology in education, learning technology by design, collaborating with peers, scaffolding authentic technology experiences, moving from traditional assessment to continuous feedback. Polly and Byker ( 2020 ) also suggested collaborative experiences, appropriate scaffolds, and focused learning goals for pre-service teachers’ technological pedagogical content knowledge improvement by using the zone of proximal development. Providing quality examples, gaining experience in class, and feeling motivated and supported during design process strategies are valuable to improve the digital skills of pre-service teachers, however, the inclusion of these strategies in teacher education seems like a complex process (Howard et al., 2021 ).
However, the problems encountered from teacher education programs were reported as (Masoumi, 2021 ): (1) not engaging in activities unless they are compulsory, (2) not being aware of the importance of technology experience opportunities during the lessons, (3) not feeling comfortable using technology in education even after training, (4) the limitations of teacher educators about providing good examples and being a role model. So that, teacher education programs should concentrate on enhancing their perceptions of technology usability and providing context-specific examples and tools to develop technology-related skills to support of changing environments of the children (Dong & Xu, 2020 ; Xie et al., 2019 ). As a result, the development of technology integration for pre-service teachers is a dynamic and complex process, which shows the praxis side of the field. It involves not only focusing on knowledge and skills but also psychosocial change for them. Hence, in the light of the literature, instructional technologies course for pre-service ECE teachers was designed and developed holistically, with a praxeological approach as a social transformation process by considering context.
Praxeological approach
The views of research practice are required to change with a more participatory lens to address the ongoing challenges, troubles, and insufficiency that we face in studies, although practitioners' theory and practice and practice-based research have been widely accepted (Pascal & Bertram, 2012 ). In addition, the domination of the evidence-based paradigm research reveals the pre-determined outcomes of the studies, therefore, the process might be mainly undemocratic due to reliance on researcher(s) hands (Vandenbroeck et al., 2012 ). However, the praxeological approach overwhelms some limitations by picturing authentic complicated circumstances, in other words, the reality.
Praxeological perspective represents the mixture of action (praxis), reflection (phronesis), power (politics), and values (ethics) (Pascal & Bertram, 2012 ). According to Pascal and Bertram ( 2012 ), praxeological research has two purposes. The first purpose is to produce beneficial knowledge and skills, which are situated in a specific context with a participatory and democratic sense. The second purpose is to encourage the transformation process of building self-awareness and self-critique through an individualized path of the person. The strengths of this approach can be listed as follows (Pascal & Bertram, 2012 ); participants can define the way to advance themselves, take responsibility for their actions, stimulate collaborative learning, respond to questions regarding implementation, have transparent ethics and values. Another benefit of the praxeological approach provides an opportunity to advocate change and transformation by taking into account the identification of their context and pedagogical practice (Winterbottom & Mazzocco, 2016 ).
As a research method, praxeology occurs as an alternative method in educational studies to monitor change and construction of knowledge in a real environment (Formosinho & Oliveira-Formosinho, 2012 ). Also, the researcher(s) employing the praxeological method can reflect the complexity of the real context by setting various methods on revealing the participants' stories (Pascal & Bertram, 2012 ). Additionally, as an instructional strategy, praxeological learning provides a potential theoretical framework for teacher education programs to develop and support pre-service teachers’ pedagogical knowledge and skills by taking part in authentic experiences (Winterbottom & Mazzocco, 2016 ). Thus, the learning process allows students to overcome challenges collaboratively among their community, understand the diversity, voice their ideas (contrary instructor’s less), follow the process by assessing themselves, and put forward their particular goals (Winterbottom & Mazzocco, 2016 ).
The context of this study involves the elements of contemporary instructional technologies, technology integration in ECE, and pre-service ECE teachers' digital competencies. Under these current circumstances of the Covid-19 outbreak, accessibility of the technology has been maximized, the necessity of the technology integration in ECE became obvious, and taking the responsibility of own learning has come to the forefront. Therefore, neglected problems, as mentioned above by pre-service ECE teachers to enhance their competency was embodied in this study based on today’s needs. From this starting point, pre-service teachers revealed the course objectives collectively based on a prediction of the professional development on technology integration needs of today and future preschool teachers. The course was designed according to these objectives with the researchers by involving the pre-service teachers' suggestions about content, teaching methods and techniques, and assessment/evaluation approaches of the course. Thus, pre-service teachers were encouraged to experience possible professional development activities both individually and with their peers (as future colleagues). Therefore, this study is important to support technology integration in ECE teacher education and to expose a digital transformation process by eliminating the gap between theory and practice, which is frequently emphasized in teacher education studies.
Purpose of the research
This study aims to reflect the individual and collective technology integration knowledge and skills construction process of pre-service ECE teachers in the instructional technologies course within democratic participation.
In this context, the following research questions were sought answers:
What are the pre-service teachers' perceptions about technology in ECE at the beginning of the instructional technologies course?
How is the instructional design for the instructional technologies course that the pre-service teachers put forward collectively based on their perceptions?
How do the pre-service teachers' perceptions about technology in ECE change during the instructional technologies course?
How do pre-service teachers consider praxeological learning experience in instructional technologies course at the end of the semester?
This study employed a praxeological approach which aims to acquire directly useful knowledge and skills for participants and allows them to support their social transformation in the knowledge construction process (Pascal & Bertram, 2012 ). Praxeology was used as a research methodology since it provides an authentic procedure of learning within a socio-cultural context because of aligning with the participatory paradigm. In this way, both participants and researchers were located as subjects of the study to uncover the real environment without pre-determined interventions. Therefore, praxeology intertwined a research method and a learning approach naturally. In other words, in this study, instructional technologies course development based on a praxeological approach manifests itself in the concept of technology integration knowledge and skills of pre-service ECE teachers or vice versa.
Participants and context of the study
In Turkey, technology integration in ECE was not common until the need for emergency distance education emerged due to the lockdown of COVID-19. On the contrary, there has been a tendency to research and practice in this area. In line with these facts, this research was conducted in the instructional technologies course remotely. The nature of praxeological research requires participation, being democratic, and collaboration (Pascal & Bertram, 2012 ), therefore, both researchers and pre-service teachers are positioned as subjects of this study in allegiance with the praxeological method.
This study consists of 52 sophomore pre-service teachers (51 females, 1 male) in the early childhood education department, three of them took the course before. Their ages were between 19 and 32. The academic background of the group consisted of mandatory courses in teacher training program; which were pedagogical knowledge (e.g., introduction to early childhood education, educational psychology), pedagogical content knowledge (e.g. science education in early childhood, mathematics education in early childhood), and technological knowledge (limited with mandatory information technologies course) courses (exception, two students has graphic design background). Pre-service ECE teachers’ roles in this study -as agreed in the first week- are to follow up with the course, involving discussion and implementations, supporting peers, taking responsibility for their learning individually.
Another type of participant in this study is the researcher. While the first author is specialized in educational technology and acted as an instructor of the course, the second author is specialized in early childhood education and has been the advisor of the pre-service teachers for the past two years. As researchers, we followed Pascal and Bertram’s ( 2012 ) praxeological researcher’s guiding principles: (1) Value-driven, (2) Democratic and participatory, (3) Critical, (4) Subjective, (5) Methodologically rigorous, (6) Action-based. To do this, researchers were followed a value-driven approach that uncovers pre-service ECE teachers’ attitudes and beliefs regarding technology, advocates their voices for inclusion and collaboration, is critical and subjective for acknowledging multiple perspectives for equitability, and action-based research for creating a dynamic learning process of praxis. Therefore, the researchers encouraged the students to involve, criticize, support, create to comprehend the technology integration in ECE.
The starting point of the course design process
In the beginning, the instructional technologies course including instructional elements, such as content, learning goals, methods, assessment, was unclear as we adopted the praxeological approach. This uncertainty caused an ill-structured and dynamic process. However, before the semester, the researchers exchanged ideas about the students' academic backgrounds for the prediction of their expectations, which concluded with Fig. 1 as a starting point representing the outline of the course. Therefore, researchers’ experience and collaboration formed the basis of the research.
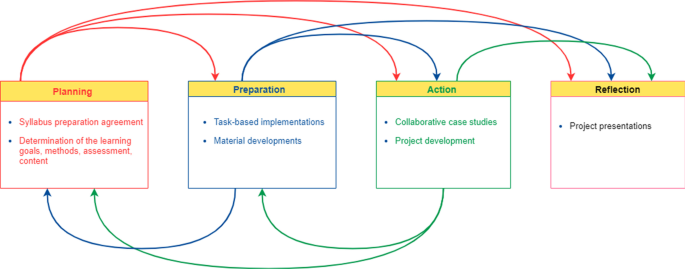
Overview of the instructional technologies course dynamics
In the first week, pre-service teachers' views on instructional technologies, their anticipations and goals about the course, their preferences in learning/teaching methods, and assessment-evaluation were asked. Also, the instructor’s and students' responsibilities were listed to achieve their goals. Encouraging democratic participation in course planning, these answers were collected anonymously with interactive presentations. The data were used to determine the goals, content, teaching method, and assessment-evaluation of the course in the following weeks shown in Additional file 1 .
On the other hand, praxeological learning involving planning, preparation, action, and reflection components, is a strategy to meet learning outcomes and content (Winterbottom & Mazzocco, 2016 ). As seen in Fig. 1 , planning, preparation, action, and reflection steps were performed consecutively, but also rotationally sometimes, which was shown by arrows, because of indetermination. Planning and preparation happened within 1–3 weeks, while preparation of the content, materials, and activities put in action during the remote lessons within 3–8 weeks. Collaborative activities and projects were mainly performed between 9 and 11 weeks. Lastly, the reflection part was included presentations and feedback. The course was carried out in two sections as A (N = 25) and B (N = 27) groups remotely.
Data collection process
Various qualitative data collection methods were used in this study following the praxeological approach to reflect the richness and complexity of that process (Pascal & Bertram, 2012 ). Therefore, every possible data source was included in the study. Video recordings (synchronous lectures), interactive slides, pre-service ECE teachers’ works (portfolios and projects), e-mails, researchers’ field notes, online course evaluation form, and semi-structured interview form were used as data collection tools.
Synchronous lectures were recorded as videos via a learning management system every week (N video = 30).
The first week of the semester, online interactive slides (Poll Everywhere) were used to collect pre-service ECE teachers’ opinions about course design anonymously.
Students’ works included two main elements as portfolio and project. Firstly, the digital materials and reports individually developed by pre-service ECE teachers were compiled as a portfolio with a self-assessment report (N portfolio = 52) and collected at the eight-week of the course. Secondly, the final project following the instructional design steps was developed individually or in groups of two (N project = 35) and gathered at twelve-week of the course.
E-mails of the pre-service ECE teachers between the lecturer/advisor of the course also followed during the semester to comprehend the off-line activities.
The researcher’s field notes were composed regarding the teaching/learning process in the course every week.
End of the semester, an Online Course Evaluation Form was designed via Google Forms to obtain anonymously pre-service ECE teachers' opinions and suggestions about course content, teaching method, learning environment, and also demographics (N form = 37).
A Semi-structured Interview Form (Additional file 2 ) consisting of 6 questions was designed to conduct interviews via Zoom online meeting platform about the learning experiences of the pre-service teachers 3–4 weeks after the course-end (N interview = 7).
Data analysis
Variety of the data collection tools, in other words, the multiple sources of data enabled the representations of the authentic experiences with enrichment of the context. Therefore, thematic analysis was used in this study to reveal the sense of data. This method concentrates on identifying, organizing, and representing the common meaning (theme) of the dataset in the context of research questions rather than specific meaning within single data (Braun & Clark, 2012 ). Braun and Clark’s ( 2012 ) six-phase approach was followed: (1) Familiarizing yourself with the data: It aims to get familiar with the dataset content which requires enough reading and re-reading until the researcher(s) absorption. (2) Generating initial codes: It defines the labelling of the content to describe the potential feature of the data regarding research questions. (3) Searching for themes: It is an evolving process by shifting the codes to the theme(s) to refine the dataset. (4) Reviewing potential themes: As an iterative process that emerged themes are reviewed to decide essential themes. (5) Defining and naming themes: The final themes were named and clarified the means of each theme by describing. (6) Producing the report: It means convincingly representing the themes to reflect the whole picture of the study.
The data analysis started with interviews by taking into account Braun and Clark's ( 2012 ) procedure. Firstly, the interviews were transcribed and read in detail line by line repeatedly. Secondly, the initial codes were created by one of the researchers. Afterwards, initial codes were re-examined by the other researcher, and final codes were decided together in order to resolve the disagreements in the last phase of the coding (Miles & Huberman, 1994 ). Thirdly, possible themes were emerged from the codes by using an inductive approach (Patton, 2002 ). Fourthly, all data were reviewed for consistency according to the possible themes for the last determination. Fifthly, the final themes were named and defined to be able to reflect the purpose and questions of the research. Sixthly, the final themes and definitions were reported with multiple data sources in the title of findings based on research questions. As a result, a good thematic analysis includes the themes which are a simple and singular focus, associated with each other without overlapping, and directly related to research questions (Braun & Clark, 2012 ). Therefore, our final analysis was presented by visualizing in the findings section as each theme built upon each other, which was connected to research questions.
Cresswell and Creswell’s ( 2018 ) suggested strategies about validity and reliability were followed to ensure the accuracy and credibility of the study. Various types of data were collected as evidence for the solid construction of the themes and consistency via triangulation. Thick descriptions and biases, within context and participants' background definition, were presented for the enrichment of each theme accompanied by direct quotations from different participants and data sources to delineate the findings. Furthermore, the first author of the study spent prolonged time because of conducting the course, while the second author involved the data analysis process as a peer debriefer to avoid biases of the first author. Lastly, transcription of the interviews, iterative reading, and comparison of the codes/themes during thematic analysis and final cross-checking and consensus were generated consistent findings.
The praxeological approach also guided the data collection and analysis in some aspects. The unclearness of the starting point of the research and update in progress capacity because of democratic participation yielded all possible sources to be considered as data collection tools. Then, these multiple sources contributed both to increase validity and reliability and to reflect research and learning/teaching progress in the course. Therefore, this approach allowed to be structured all the phenomena that emerged in the context of both research and educational activities with all their naturalness, and to reveal the reality at the maximum level.
Pre-service ECE teachers’ technology integration knowledge and skills development process in the context of instructional technologies course through praxeological approach was examined. As a result of the analysis of the data, three themes (Fig. 2 ) emerged as initial challenges, learning process, and learning outcomes given in detail as follows.
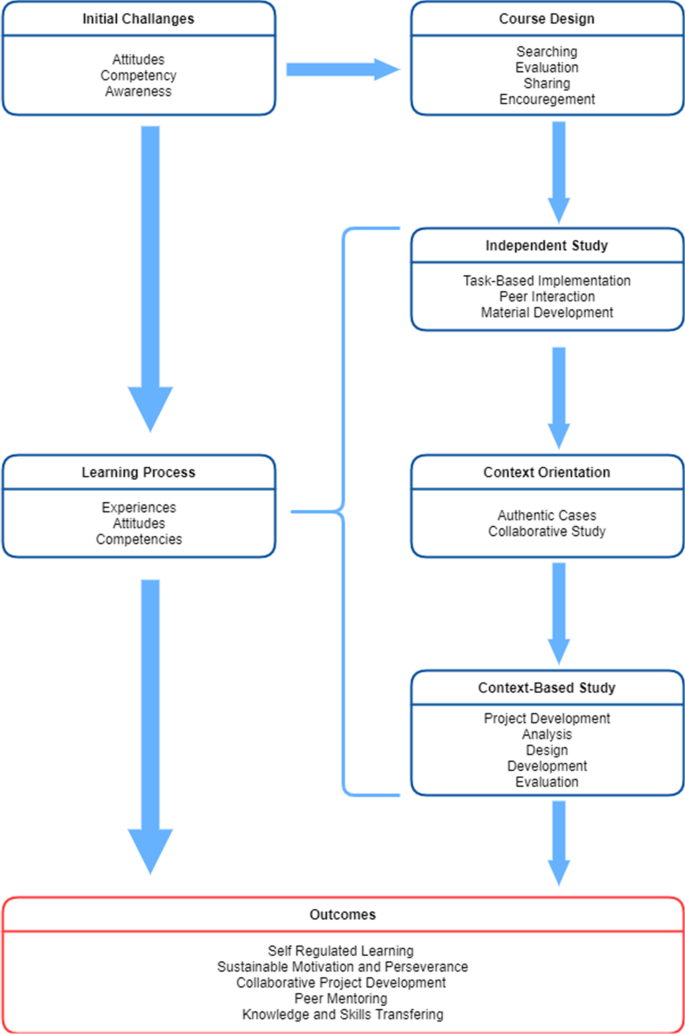
Instructional technologies course design based on praxeological approach
Initial challenges: what are the pre-service teachers' perceptions about technology in ECE at the beginning of the instructional technologies course?
The initial challenges that represent the pre-service teachers' perceptions about technology in ECE were attitudes, skills, and unawareness of educational technology as an answer to the first question of the research. These perceptions were revealed during a three-week course using the following activities.
The beginning of the course was partially dominated by syllabus preparation taking into account ethical issues in terms of decisions of learning goals, content, teaching/learning method, course evaluation. Therefore, a bond was aimed to be established regarding privacy and trust, so that pre-service teachers could freely express their thoughts. Sharing feelings was encouraged by the instructor, including online/offline communications. Syllabus preparation took three weeks, as pre-service teachers were not familiar with making decisions and taking responsibility for course content and teaching methods. During this time, pre-service teachers expressed their prior knowledge levels, wishes, and hesitations, depending on the strengthening of the established bond. It was observed that pre-service teachers were highly influenced by each other's ideas; they were afraid of sharing negative thoughts. The pre-service ECE teachers' suggestions for course content were mostly limited to the "technology" word due to the unfamiliarity of specific apps, which was considered as a clue for their low level of proficiency and awareness about teaching with technology. Also, it was determined that pre-service teachers had high expectations from the course, prefer experience-based teaching techniques, collaborative studies, product-oriented outputs (materials), and process-oriented assessments (projects, homework) for the course evaluation. In addition, the responsibilities of students and teachers were discussed to achieve the pre-determined goals. Anonymous answer from first-week interactive slides shared:
As a student, to participate effectively in the lesson and do the assigned tasks. As a teacher, to share your knowledge and experience with us in the most instructive way, to support problems quickly. (Anonymous, from interactive slides)
Lastly, the draft syllabus was reached with students' approvals, however, it was emphasized by the instructor that changes could be made in the scope of the syllabus in line with their demands and needs during the semester.
As a result of this phase, pre-service ECE teachers' initial challenges at the beginning of the instructional technologies course were revealed as attitudes, skills, and unawareness of educational technology. These emerged from the data collected during class discussions, anonymously answered questions presented in interactive slides, and interviews conducted. Their attitudes and competencies differed between technology and educational technology. Examining the attitudes of pre-service ECE teachers, they seemed biased and worried about technology, while they had positive attitudes and low self-efficacy regarding educational technology. P-3 mentioned her feelings at the interview:
I consider myself very inadequate about technology. Frankly, I was wondering about what to do. I was anxious ... I thought I would be unsuccessful. (P-3, from interview)
Meanwhile, pre-service teachers claimed that most of them had low technology and educational technology skills because of unfamiliarity and lack of awareness in the field. Some of them suffered even in the use of the basic functions of the devices (tablets, laptops) and the programs (Microsoft Word, PowerPoint). P-7 admitted at the interviews that:
I faced difficulties at some points due to the inability to adapt. I was not familiar with the common technologies. It was so hard for me. (P-7, from interview)
Moreover, it was revealed that pre-service teachers also had inadequacies in using technology in education, especially in the first few weeks of conducting online task-based implementations and individual material development studies. Although pre-service teachers considered themselves inadequate in the use of technology in education, it was observed frequently during in-class talks that they also had the curiosity and motivation about that. As P-1 mentioned about the necessity of the course during interviews:
We live in the technology age. We should not be left behind, and use technology effectively. But we did not know how to reach the kids over technology, indeed. (P-1, from interview)
Learning process: how is the instructional design for the instructional technologies course that the pre-service teachers put forward collectively based on their perceptions?
The learning process, in other words, the design of the course was constructed by pre-service ECE teachers collectively based on their decisions over their perceptions as attitudes, skills, and unawareness about technology integration in education. The instructional design of the course within democratic participation fulfilled the second research question.
The learning process lasted 14 weeks, consisting of four parts (see Additional file 1 ). Firstly, the introductory knowledge about the educational technology field was presented by the instructor in parallel with the syllabus design. Secondly, independent studies that include online task-based learning, group interactions, offline material development activities were employed. It was aimed to develop pre-service ECE teachers' technology knowledge, and have them experience the applications during the online part of the course. While they were divided into online break-out rooms, including 4–5 people, task-based implementation lists were provided to complete the task with peers and instructor support. Although they asked for support from the instructor during break-out room studies for the first several weeks, the support request declined over time as they became able to solve the problems by themselves (researcher’s notes, sixth week). As offline, they developed digital material based on the learning outcome(s) in the ECE curriculum in Turkey that they chose. Every week, volunteer pre-service ECE teachers shared their digital materials to get feedback and discuss them publicly. Thirdly, contextual orientation studies were conducted to adopt different educational environments for technology integration. To achieve this goal, students were given different authentic case studies to determine problems, assumptions, and alternative solutions during group discussions. Fourthly, pre-service ECE teachers (individually or in a two-person group) were required to develop digital materials using new applications (other than the ones they learned during the course) based on the methods of analysis, design, development, implementation, and evaluation steps. The implementation step was done if the pre-service ECE teachers had a chance to reach at least one target audience. Last four weeks, each project was presented and given feedback by the instructor and peers. These projects aimed to reflect their technology integration skills and knowledge and the ability to learn new programs by themselves.
Learning process: how do the pre-service teachers' perceptions about technology in ECE change during the instructional technologies course?
As a result of the learning process phase, the third research question was also answered. Pre-service teachers shed light on their learning process during the course in three components as attitudes, experience, and competencies. The instructional technologies course was designed by adopting a praxeological learning approach to allow them to be the subject of their learning journey. Therefore, it revealed that this self-designed course had a noticeable change in their attitudes, experience, and competencies regarding technology integration in ECE. It was stated by pre-service ECE teachers and also observed by instructors that the crucial experience in the course was active participation in the learning process. P-7 emphasized the importance of the relationship among the course participants at the interview that:
It was very good for us that our teacher shared this process with us, got our opinions, gave us feedback, evaluated our suggestions. It was quite good for us to have a collaborative interaction. (P-7, from interview)
At the same time, it was determined that peer mentoring and peer interaction were quite intense. Active participation, peer mentoring and interaction, and attitudes changing can be explained by the fact that pre-service ECE teachers hold decisive roles in the progress. Collaboration, sharing, helping each other, and solidarity have enabled the formation of collective learning, which amplified their learning responsibility. As voiced in the interview with P-1 is that:
The mentor [break-out room lead] was running the group. We were asking her/him, when we could not do some tasks, for example, “I couldn't do step 3 [in the task list]. How did you do?”. She/he showed us via screen-sharing how to do it. When the mentor was not able to do the task, she/he gave the screen-sharing to the one who did it. (P-1, from interview)
The collaborative studies had a positive impact on their educational technology competencies. It was reflected in their portfolios, researcher’s observations, and interviews with the participants that pre-service ECE teachers can carry out independent projects, design and develop digital materials, and make self-assessments. The initiatives taken by the pre-service teachers in the learning process have stimulated them to use educational technologies effectively and to learn by doing. The effect of the participants' accomplishments during the course was expressed as follows:
I was encouraged as I completed the project. I had been one who was unable. However, towards the end of the semester, I started helping my friends, giving ideas and feedback. Although I am incredibly prejudiced, I can say that practicing made me free from all my prejudices. (P-5, from interview) For me, the first two weeks and after were very important. As I accomplished things, I no longer fear the next application given by our teacher. (P-3, from interview)
Learning outcomes: how do pre-service teachers consider praxeological learning experience in instructional technologies course at the end of the semester?
The last research question answers at the end of the fourteen-week experience learning outcomes on pre-service ECE teachers were sustainable motivation and perseverance, self-regulated learning, collaborative project development, peer mentoring, and knowledge and skill transfer to different contexts. At the end of the semester, pre-service ECE teachers referred to the bond established during the semester as “warm”, and this bond helped to get these learning outcomes.
Pre-service ECE teachers’ studies, researchers’ observations, and interviews have clearly shown that their interest and attitudes regarding technology in education were increased. The findings indicated that their turning points were mostly noticed in the second or third independent studies. Therefore, it is possible to say that positive attitudes have eliminated prejudices and concerns, fostered their self-efficacy and awareness gradually, which was ended up in noticing the importance of perseverance and patience. As a result, pre-service ECE teachers have sustained their motivation because of the raising of awareness about technology use in education. Pre-service ECE teachers’ statements are as follows:
Before, technology integration in education was not necessary. I see it as a must now. (a self-evaluation statement, from a portfolio) ... production gave me a sense of pleasure, frankly... I think of everything as technology-oriented at the moment. Of course, if the facilities in the school are sufficient, I will definitely use technology, it (the course) has been very useful. (P-6, from interview) My first view of the course was that I started with bias. I ended this process with curiosity and perseverance. Now, I have an idea about how necessary technology is and how important it is in my future career. (anonymous, from online course evaluation form) I think that all prejudices against technological applications have been destroyed within the scope of this course thanks to the teacher's attitude. Even if I have difficulties in the first stages, I think this difficulty makes learning more permanent. (anonymous, from online course evaluation form)
The change in motivation and attitudes of pre-service ECE teachers also fostered them to transfer their practical experiences to the field. It was observed that pre-service ECE teachers could address potential problems by using technology in education, make plans, use new applications effectively for pedagogical purposes, and produce new and original pedagogical materials using applications. Also, it was frequently mentioned that taking an active role in the whole process and gaining experience increases the permanence of acquired knowledge and skills.
I started doing things in ten minutes that used to take two hours, and I really want to use in the future most of the apps I used. (P-2, from interview) While I was a beginner, I think I have mastered many things now. And at the same time, I had the opportunity to send the applications I made during the lesson to my friends' children. I had the opportunity to share the things I produced due to the pandemic. I started using those programs to do something new. In the family education class, I prepared family participation posters and invitation cards... (P-5, from interview)
The change of mentioned psychological factors led the pre-service ECE teachers to reach a level where they can learn on their own. Self-regulated learning about educational technology was often mentioned as “I can find/ search/ learn” in pre-service ECE teachers’ portfolios and project reports. The most important proof of this was the presentations of the final projects, including the materials they have developed with an application that they have not learned before.
I liked every step of the lesson very much. I am sorry that this lesson is over now. You [instructor] helped me a lot, especially with building self-confidence. Now I say that I can learn everything if I want. (anonymous, from online course evaluation form) Do not avoid learning applications. Knowing is freedom. When you need to do something in an application, the pleasure of doing it yourself without help cannot be described. Time will pass and maybe the applications we use now will get old. Do not neglect to follow the innovations, learn and try. (a suggestion herself in the future, from a final project self-assessment report) I really had a hard time choosing a suitable outcome for myself and designing a suitable material for the outcome. Although I had difficulty in the selection part, I think that I did not have that much difficulty while designing the materials. (a statement, from a final project self-assessment report)
The last, pre-service ECE teachers showed high collaborative skills about project/material development and the ability for peer mentoring as mentioned in the learning process section. So, it can be said that they can support their peer for curriculum studies, designing activity plans, learning new applications.
Discussion and implications
This research was aimed at developing the technology integration knowledge and skills of future pre-service ECE teachers. The instructional technologies course was created collectively based on a praxeological approach by the pre-service ECE teachers with the guidance of the instructor. As a result, it was revealed that pre-service teachers were not used to such teaching/learning methods, their content preferences for the course were decided on applications with visual and auditory elements because of the target audience. Also, they generally had a positive attitude towards technology in education, even though they had a negative attitude towards technology. At the end of the course, while enhancing their technology integration competencies, several learning outcomes were accomplished, such as self-regulated learning, collaborative project development, building sustainable motivation, peer mentoring, transferring acquired skills in different contexts. Therefore, it is possible to discuss the study results from two perspectives. The first one is about developing technology integration competencies of pre-service ECE teachers. Secondly, it concerns the contributions of the praxeological approach in terms of teacher education.
Pre-service ECE teachers’ technology integration skills development
First of all, it was observed in the praxeological designed course that low awareness, attitudes, and skills of pre-service ECE teachers towards instructional technologies were disincentive factors. Similarly, the studies show that attitudes and beliefs are significant factors for technology integration skills (Abbitt, 2011 ; Seufert et al., 2021 ; Tezci, 2011 ; Tondeur et al., 2017 ; Yerdelen-Damar et al., 2017 ). Also, observed prior knowledge levels differences of teachers were also a filter to think about the design of the course to subsume all participants. In this regard, one of the course’s aims became both raising awareness and developing a positive attitude towards instructional technologies while benefiting the individual differences. Additionally, participants were encouraged to the enhancement of their self-efficacy, and question effective technology use in ECE. Therefore, it is highly recommended to determine and include teaching/learning strategies about pre-service teachers' attitudes and awareness taking into account their pre-skills into instructional technologies training rather than focusing on only skill development in the training content.
It is emphasized that technology courses for pre-service ECE teachers should be customized with the technologies and applications by covering the purpose of the preschoolers' education (Masoumi, 2021 ; Xie et al., 2019 ). Accordingly, the learning process was structured with domain-specific technologies and scaffolding mechanisms (task-based lists and case studies) for content. The education provided takes the approach of introductory to speciality, taking into account the content suggested by the participants. The course was designed gradually to develop pre-service teachers' technology integration skills in ECE; applications utilization for general technology knowledge, learning outcome-oriented digital material design, and the adaptation of technologies to different educational contexts, respectively. This process internalizes the transition from technological knowledge to technological pedagogical content knowledge proposed by Koehler and Mishra ( 2005 ). Hence, since the learning process was experience-based, skill-oriented, and supportive to the attitude changing, pre-service ECE teachers were motivated to learn both individually and collectively through activities. Also, Neumann et al. ( 2021 ) indicated that detached courses for instructional technologies cannot represent the realities in the classrooms, therefore, practice-based courses should be offered. Current research also has recommended providing more learning opportunities and practical experiences for pre-service teachers in this regard (Howard et al., 2021 ; Masoumi, 2021 ; Neumann et al., 2021 ). It is suggested to design course content in which field-specific examples and practices are provided for the development of pre-service teachers' knowledge and skills in this field and to test their effectiveness. It is also advised to take into account the differences in technological knowledge, subject knowledge, and pedagogy knowledge of pre-service teachers in the design of these activities. For more details, it can be investigated how the pre-service teachers perceive field-specific applications in terms of usefulness, benefit, and easiness, and to determine the factors that affect their preferences in future research.
Considering the learning outcomes at the end of the learning process, it was observed that the pre-service ECE teachers' technology integration skills were improved. The most important changes were that they can predict alternatives, decide necessary material types based on learning outcomes, select appropriate applications and learn by themselves. Hence, at the educational technologies course end, the pre-service ECE teachers' lesson plans and materials became more detailed and they believe that this training is valuable for them in the future (Neumann et al., 2021 ). In addition, they reached some extra outcomes, such as collaborative studying, self-regulated learning, motivation and perseverance, peer mentoring, and transferring their knowledge. Online break-out room activities mediated computer-supported collaborative learning to reveal these outcomes. Although individual differences affect computer-supported collaborative learning, social sensitivity enables people to get together respectfully, constructively, and cohesively, so that equitable collaborations (Isohätälä et al., 2021 ). With this understanding, democratic participation was supported as well. Moreover, collaborative activities triggered their motives because of witnessing peers’ facing challenges and overcoming them. So that, the gained sustainable motivation and perseverance can pave the continuous learning of future ECE teachers to follow self-regulated professional development. Therefore, there is a need to investigate how computer-supported collaborative activities (in our case, it was break-out rooms) with peer mentoring leverage productivity and solidarity to attain new skills and knowledge. Furthermore, it is also suggested to examine online collaborative studies' ice breakers to foster active and democratic participation of the pre-service teachers.
Praxeological learning approach for teacher education
The praxeological-learning approach can make crucial contributions to teacher education in terms of many characteristics, such as taking responsibility, deciding on the purpose and process, respect for diversity; in short, being a democratic individual and a teacher. This study derived that pre-service ECE teachers’ motives made a substantial contribution because of being accustomed to this method over time to overcoming inabilities, hesitations, and prejudices. Furthermore, their perseverance manifested itself after the performance accomplishments, vicarious experiences, and peer support. Thanks to this flexible understanding, pre-service ECE teachers experienced the freedom of decision and the satisfaction of production-based study. Winterbottom and Mazzocco’s ( 2016 ) research results about teacher education also indicated that the pre-service teachers believed attendance of an experience of academic praxeological-learning develops pedagogical and social skills development and self-actualization. Hence, it can be inferred that they demonstrated improvement in different areas besides academic qualifications. However, the studies in the educational area focus more on measurable and predetermined questions and restricted results (Biesta, 2007 ; Pascal & Bertram, 2012 ; Vandenbroeck et al., 2012 ). Moreover, this issue narrows down the educational desirable opportunities, which makes the deficit of democratic education is apparent (Biesta, 2007 ). Therefore, this approach, without pre-determination of the continuum, allows all participants to equally engage in the research and educational paths.
On the other hand, this approach is discussed in specific for instructional technology education in teacher education programs. Although pre-service teachers are expected to have technology skills, contrary to popular belief, it is seen that they might not be enough digitally fluent (Martín et al., 2020 ). The fact indicates that pre-service teachers during their education need to be involved in a sort of transformation period to be able to have a digitally competent teacher mind map. Inasmuch as, teachers are expected to be able to show some roles such as “learner”, “leader”, “collaborator”, “designer” in digital educational settings (International Society for Technology in Education, 2021 ). Therefore, the praxeological approach in instructional technology education can provide wider opportunities for pre-service teachers to comprehend the nature of technological pedagogical content knowledge. For this reason, it seems important to uncover some teaching/learning strategies to ease integration of the initial challenges to the learning process within the courses designed with the praxeological-learning method in further research. Consequently, developing pre-service teachers’ digital competencies is a complex and multifaceted process to be needed detailed investigations (Howard et al., 2021 ; Masoumi, 2021 ; Tondeur et al., 2012 ), hence, we believe that the praxeological approach posits alternative ways in this context.
In conclusion, in this study, the praxeological approach was used in both the research and the teaching methods. Even if initial challenges were released as attitudes, awareness, and competencies, it was observed that pre-service ECE teachers took on their learning responsibilities as the subject of the learning process. Thus, they actively participated in the teaching process and positive changes took place in the attitudes, knowledge, and skills about the use of technology in education. Moreover, it was seen that pre-service teachers can learn on their own, design projects collectively, mentor their peers, and transfer knowledge and skills to different contexts at the end of the semester. It has been observed that they tend to continue these skills hereafter. As a result, the praxeological approach used in instructional technology education in teacher education programs leads to a crucial digital transformation to be ready to become future teachers. This course, including self and group learning activities, is also seen as a preliminary experience of future professional development training. Hopefully, this course will contribute to the construction process of their professional development as digitally competent future teachers.
Limitations
This study has some limitations both in terms of the implementation process and research methodology. On one hand, a few students did not have a computer during the course time, so that, they completed the semester with their mobile devices. To minimize the inequality of opportunity, offline support was provided and compatible mobile applications were suggested for them. Of course, it is possible to say that this approach was not suitable for a few students who preferred traditional education and considered this course tiring.
On the other hand, the nature of this research requires commitment and a bond between the participants and the instructor, however, this may lead to misrepresentations instead of reflecting actual results in real life (Pascal & Bertram, 2012 ). Nevertheless, to prevent this, the role of the second researcher stands as a filter during data collection and analysis. Also, democratic participation in the research does not follow the ordinary linear path to study, therefore, it makes it hard to conduct and conceptualize, and makes unpredictable (Vandenbroeck et al., 2012 ). Hence, we collected different types of data during the research, which assisted in the confirmation and comparison of the findings. The study is not generalizable as it was carried out in a contextualized subject-specific area and limited group, however; we consider it serves as a good example in this field. Considering the current circumstances, we believe that it’s high time to employ a praxeological approach in teacher education to tackle Biesta’s ( 2007 ) “democratic deficit” in education.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- Early childhood education
Abbitt, J. T. (2011). An investigation of the relationship between self-efficacy beliefs about technology integration and Technological Pedagogical Content Knowledge (TPACK) among preservice teachers. Journal of Digital Learning in Teacher Education, 27 (4), 134–143. https://doi.org/10.1080/21532974.2011.10784670
Article Google Scholar
Biesta, G. (2007). Why “what works” won’t work: Evidence-based practice and the democratic deficit in educational research. Educational Theory, 57 (1), 1–22.
Bolstad, R. (2004). The role and potential of ICT in early childhood education: A review of New Zealand and international literature . Ministry of Education.
Google Scholar
Braun, V., & Clarke, V. (2012). Thematic analysis. In H. Cooper (Ed.), Handbook of research methods in psychology: Research designs (Vol. 2, pp. 57–71). American Psychological Association.
Contini, A., Bertolini, C., Manera, L., Martin, I., Schlemmer, D., Kiefer, M., Nousiainen, T., Merjovaara, O., Gözen, G., & Pagano, A. (2018). Guidelines for digital storytelling in early childhood education [Project Report]. https://ec.europa.eu/programmes/erasmus-plus/project-result-content/fede56b0-7a42-4bde-9b4d-463871c653c2/GUIDELINE_English%20language.pdf
Creswell, J. W., & Creswell, J. D. (2018). Research design: Qualitative, quantitative, and mixed methods approaches (5th ed.). SAGE.
MATH Google Scholar
Dong, C., & Xu, Q. (2020). Pre-service early childhood teachers’ attitudes and intentions: Young children’s use of ICT. Journal of Early Childhood Teacher Education . https://doi.org/10.1080/10901027.2020.1726843
Formosinho, J., & Oliveira-Formosinho, J. (2012). Towards a social science of the social: The contribution of praxeological research. European Early Childhood Education Research Journal, 20 (4), 591–606. https://doi.org/10.1080/1350293X.2012.737237
Howard, S. K., Tondeur, J., Ma, J., & Yang, J. (2021). What to teach? Strategies for developing digital competency in preservice teacher training. Computers & Education, 165 , 104149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2021.104149
International Society for Technology in Education. (2021). ISTE standards for educators ISTE. https://www.iste.org/standards/iste-standards-for-teachers
Isohätälä, J., Näykki, P., Järvelä, S., Bakers, M. J., & Lund, K. (2021). Social sensitivity: A manifesto for CSCL research. International Journal of Computer-Supported Collaborative Learning, 16 , 289–299. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11412-021-09344-8
Jung, J., & Ottenbreit-Leftwich, A. (2020). Course-level modeling of preservice teacher learning of technology integration. British Journal of Educational Technology, 51 (2), 555–571. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjet.12840
Kerckaert, S., Vanderlinde, R., & van Braak, J. (2015). The role of ICT in early childhood education: Scale development and research on ICT use and influencing factors. European Early Childhood Education Research Journal, 23 (2), 183–199. https://doi.org/10.1080/1350293X.2015.1016804
Koehler, M. J., & Mishra, P. (2005). What happens when teachers design educational technology? The development of Technological Pedagogical Content Knowledge. Journal of Educational Computing Research, 32 (2), 131–152. https://doi.org/10.2190/0EW7-01WB-BKHL-QDYV
Lauricella, A. R., Herdzina, J., & Robb, M. (2020). Early childhood educators’ teaching of digital citizenship competencies. Computers & Education, 158 , 103989. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2020.103989
Martín, S. C., González, M. C., & Peñalvo, F. J. G. (2020). Digital competence of early childhood education teachers: Attitude, knowledge and use of ICT. European Journal of Teacher Education, 43 (2), 210–223. https://doi.org/10.1080/02619768.2019.1681393
Masoumi, D. (2021). Situating ICT in early childhood teacher education. Education and Information Technologies, 26 , 3009–3026. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-020-10399-7
Miles, M. B., & Huberman, A. M. (1994). Qualitative data analysis: An expanded sourcebook (2nd ed.). Sage.
Morfoniou, K., Voulgari, I., Sfyroera, M., & Gouscos, D. (2020). Digital games and the emergence of problem solving processes: A case study with preschool children. International Conference on the Foundations of Digital Games . https://doi.org/10.1145/3402942.3402991
Neumann, K. L., Alvarado-Albertorio, F., & Ramírez-Salgado, A. (2021). Aligning with practice: Examining the effects of a practice-based educational technology course on preservice teachers’ potential to teach with technology. TechTrends, 65 , 1027–1041. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11528-021-00672-y
Öner, D. (2020). The using technology and digital games in early childhood: An investigation of preschool teachers’ opinions. Inonu University Journal of the Graduate School of Education, 7 (14), 138–154. https://doi.org/10.29129/inujgse.715044
Pascal, C., & Bertram, T. (2012). Praxis, ethics and power: Developing praxeology as a participatory paradigm for early childhood research. European Early Childhood Education Research Journal, 20 (4), 477–492. https://doi.org/10.1080/1350293X.2012.737236
Patton, M. Q. (2002). Qualitative research & evaluation methods (3rd ed.). SAGE Publications.
Polly, D., & Byker, E. (2020). Considering the role of zone of proximal development and constructivism in supporting teachers’ TPACK and effective use of technology. Revista Educación a Distancia, 20 (64), 5. https://doi.org/10.6018/red.408661
Romero-Tena, R., Barragán-Sánchez, R., Llorente-Cejudo, C., & Palacios-Rodríguez, A. (2020). The challenge of initial training for early childhood teachers. A cross sectional study of their digital competences. Sustainability, 12 (11), 4782. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12114782
Schina, D., Esteve-González, V., Usart, M., Lázaro-Cantabrana, J.-L., & Gisbert, M. (2020). The integration of sustainable development goals in educational robotics: A teacher education experience. Sustainability, 12 (23), 10085. https://doi.org/10.3390/su122310085
Segal-Drori, O., & Ben Shabat, A. (2021). Preschoolers’ views on integration of digital technologies. Journal of Childhood, Education & Society, 2 (1), 29–42. https://doi.org/10.37291/2717638X.20212172
Seufert, S., Guggemos, J., & Sailer, M. (2021). Technology-related knowledge, skills, and attitudes of pre- and in-service teachers: The current situation and emerging trends. Computers in Human Behavior, 115 , 106552. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2020.106552
Tezci, E. (2011). Factors that influence pre-service teachers’ ICT usage in education. European Journal of Teacher Education, 34 (4), 483–499. https://doi.org/10.1080/02619768.2011.587116
Tondeur, J., van Braak, J., Ertmer, P. A., & Ottenbreit-Leftwich, A. (2017). Understanding the relationship between teachers’ pedagogical beliefs and technology use in education: A systematic review of qualitative evidence. Educational Technology Research and Development, 65 , 555–575. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11423-016-9481-2
Tondeur, J., van Braak, J., Sang, G., Voogt, J., Fisser, P., & Ottenbreit-Leftwich, A. (2012). Preparing pre-service teachers to integrate technology in education: A synthesis of qualitative evidence. Computers & Education, 59 (1), 134–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2011.10.009
Van Scoter, J., Ellis, D., & Railsback, J. (2001). Technology in early childhood education: Finding the balance . Northwest Regional Educational Laboratory.
Vandenbroeck, M., Roets, G., & Roose, R. (2012). Why the evidence-based paradigm in early childhood education and care is anything but evident. European Early Childhood Education Research Journal, 20 (4), 537–552. https://doi.org/10.1080/1350293X.2012.737238
Verbruggen, S., Depaepe, F., & Torbeyns, J. (2021). Effectiveness of educational technology in early mathematics education: A systematic literature review. International Journal of Child-Computer Interaction, 27 , 100220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijcci.2020.100220
Winterbottom, C., & Mazzocco, P. J. (2016). Reconstructing teacher education: A praxeological approach to pre-service teacher education. European Early Childhood Education Research Journal, 24 (4), 495–507. https://doi.org/10.1080/1350293X.2014.975940
Xie, K., Vongkulluksn, V. W., Justice, L. M., & Logan, J. A. R. (2019). Technology acceptance in context: Preschool teachers’ integration of a technology-based early language and literacy curriculum. Journal of Early Childhood Teacher Education, 40 (3), 275–295. https://doi.org/10.1080/10901027.2019.1572678
Yerdelen-Damar, S., Boz, Y., & Aydın-Günbatar, S. (2017). Mediated effects of technology competencies and experiences on relations among attitudes towards technology use, technology ownership, and self efficacy about Technological Pedagogical Content Knowledge. Journal of Science Education and Technology, 26 (4), 394–405. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10956-017-9687-z
Zilka, G. C. (2021). Attitudes of preservice kindergarten teachers toward the integration of computers and the reduction of the digital divide in kindergartens. Educational Technology Research and Development, 69 (2), 711–731. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11423-021-09982-
Zomer, R. N. (2014). Technology use in early childhood education: A review of the literature [Unpublished master's thesis]. University of Ontario.
Download references
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Distance Education Application and Research Center, University of Health Sciences, Hamidiye Campus, Selimiye Neighborhood, Tıbbiye Street, Nu:38, Üsküdar, 34668, Istanbul, Turkey
Taibe Kulaksız
Early Childhood Education Department, Istanbul Kültür University, Istanbul, Turkey
Mehmet Toran
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
TK: Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Data collection and analysis, Writing—original draft. MT: Conceptualization, Methodology, Conducting interviews, Analyzing interviews, Reporting. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Authors information
Taibe Kulaksız is an instructor at the Distance Education Application and Research Center at the University of Health Sciences. She holds a Ph.D. in Computer Education and Instructional Technologies. Her research focuses on technology integration in education, teacher education, instructional technology.
Mehmet Toran is an associate professor of early childhood education studies at Istanbul Kültür University. He holds his Ph.D. in Child Development and Education, and his research deals mainly with early childhood educator professional development, early childhood education curricula, early childhood education policy, and critical pedagogy.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Taibe Kulaksız .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1..
Learning process of the Instructional Technologies Course for pre-service ECE teachers.
Additional file 2.
Interview protocol.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Kulaksız, T., Toran, M. Development of pre-service early childhood teachers’ technology integrations skills through a praxeological approach. Int J Educ Technol High Educ 19 , 36 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s41239-022-00344-8
Download citation
Received : 08 November 2021
Accepted : 27 March 2022
Published : 28 July 2022
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s41239-022-00344-8
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Instructional technology
- Pre-service teachers
- Technology integration
- Praxeological research

TOP > Projects > ECEC around the World > [UNESCO] Report of the UNESCO "World Conference on Early Childhood Care and Education"
[UNESCO] Report of the UNESCO "World Conference on Early Childhood Care and Education"
On September 27-29, 2010, I participated in the "World Conference on Early Childhood Care and Education" held in Moscow, Russia, as a member of Japanese government delegation. This is a report of the discussions at the general and individual meetings.
The conference was sponsored by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO), and supported by the Association for the Development of Education in Africa (ADEA). The Government of Russian Federation and the City of Moscow served as the host country/city. In addition to the delegation from more than 130 countries, many people from international organizations and NGOs participated in the conference. The participants enthusiastically discussed the present situation and the problems of Early Childhood Education for three days.
This is the first world conference to focus on early childhood education. According to the staff of UNESCO, "in the field of education, a number of conferences and much discussion have taken place internationally on school education and lifelong education, but there has not been active discussion on early childhood education. The conference held this time is therefore expected to kindle active discussion in each country." With such an idea, this world conference was held in that hopes that the issues of early childhood education and care would become an important agenda in many countries.
The discussion at the conference revealed that many developed and developing countries have common problems with early childhood education. For example, as referred to in the title of the conference many countries do not know how the government should balance support for the two areas of education and care" in childhood.. Various opinions are also expressed in Japan on the balance between education and childcare, as typified by the issue of the unification of kindergartens and nursery schools.
Above all, the conference presentations stressed that providing high-quality education to all children is an issue related to human rights. In other words, one of the most important purposes of the conference was soliciting international agreement that "the access to education is a basic human right of children and that is necessary for the government of each country and the society as a whole to make efforts to improve early childhood education."
In addition, there was a considerable discussion on how to improve the quality of early childhood education and how the quality should be evaluated. When thinking about the quality of early childhood education, each country has different ideas about whether cognitive aspects (memory, acquisition and expression of knowledge, and concept development) or emotional aspects should be emphasized, and it finds the issue is very complicated. Moreover, as for the evaluation of the quality of education, some countries measure cognitive development by conforming to the so-called "achievement test," while other countries consider such assessment to be inappropriate for understanding the results of approaches toward preschool children. During the discussion, it was pointed out that three aspects: "educational quality," "quality of teachers and other educators," and "quality of programs" should be considered separately when looking at the quality of early childhood education
Before evaluating the content of education, however, there is the problem that early childhood education is not common in many developing countries. In this regard, UNESCO as a sponsor emphasized as their significant achievement that they had agreed to develop the "Child Development Index" based on the Conference discussions. The Index measures the present environment of children in each country and the degree of prevalence of early childhood education, by combining the indices of the mortality rate and low birth weight among children aged under 5 as well as the attendance rate at elementary school. Based on the index established in 1990 by the international NGO, "Save the Children UK," UNESCO will add some necessary items to advance the development of the index in cooperation with the specialists in statistics.
On the last day of the conference, "The Moscow Framework of Action" was adopted. "The Moscow Framework of Action" confirmed that "the lack of political commitment (to strengthen the support for early childhood education) and public funds, the difficulty in improving early childhood education, and the lack of outside support (such as development assistance) for its improvement" are major problems for today's early childhood education, particularly in the developing countries. In addition, it was pointed out that the promotion of international development assistance by developed countries and international organizations was essential, so that each country would increase financial support for early childhood education in developing countries.
During the conference, the importance of considering early childhood education from such perspectives as the improvement of the quality of basic education particularly in developing countries was pointed out. However, when developed countries including Japan consider the issues of early childhood education in their own country, they must notice a certain gap between the content of the discussion during the conference and the actual situation at home. In that sense, I felt difficulty in discussing a particular topic at an international conference, in which countries with various different situations participate.
For example, the conference this time was entitled "Early Childhood Care and Education." However, it seemed that many participants from developing countries were more likely to discuss the aspect of "care" on the basis of their common reality of poverty and poor sanitary conditions, although they were strongly aware of the importance of improving "education." This clearly reflects the social-economic realities of the developing countries.
Nevertheless, when comparing early childhood education in developed and developing countries, I strongly felt that they had many common issues, such as improving the quality of education; the importance ofevaluation method development; promoting a smooth transition from kindergarten to elementary school; and the lack of cooperation among government agencies. Regardless of whether the country is developing or developed, it was highlighted that the insufficient provision of public funds for the area of early childhood education is a big problem. Since this is a topic of current concern, I felt the need for further discussion on the financial issues of early childhood education both domestically and internationally.
Among thevarious presentations and reports, the keynote speech by Professor Jack P. Shonkoff of Harvard University at the general meeting on the first day of the Conference was extremely impressive. Based on the latest knowledge of brain science, he explained infant/child development in an easily comprehensible manner. What was most impressive was his remark: "it is only in the past 10 years that the discourses of traditional childrearing as practiced in various communities were proved to be scientifically correct". People have understood what they thought it was important instinctively and experientially, and have practiced it in each community. Professor Shonkoff pointed out that today's science plays an important role to prove the rightness of such practices. This indicates that when considering early childhood education and care, we should not always look for the new, but should learn from the experience and knowledge (or wisdom) inherited from each society. However, such experience and knowledge needs to be applied in the way suitable for the children in modern society.
The conference turned out to be extremely productive for me. I listened to discussions about early childhood education from the broad standpoint, and had the chance to exchange opinions with participants from many countries and institutions. In addition, it was a precious opportunity for me to rethink issues of early childhood education based on my specialty in international cooperation in education for developing countries.
- [Japan] Identifying Factor Structures and Determinants Involved in the Development of "Non" Cognitive Skills in Early Childhood
- [South Korea] Current Situation and Issues of Inclusive Education for Preschool Children in South Korea - II
- A Useful Comparison Table for Improving the Quality of ECEC--International Comparative Study on Free Preschool Education and Childcare (74th OMEP World Assembly and Conference)
Latest Posts
- [Aiming to Realize an Inclusive Society] An Inclusive World Realized by Art II: What Can We Do to Make Their Day in the Way They Desire?
- [Aiming to Realize an Inclusive Society] An Inclusive World Realized by Art I: We Do Not Want to Let Them Be Someone They Do Not Want to Be
- [Snuggling Up to Our Differences] Episode 8: There Is No Such Thing as a Bad Child
- [Parenting and Childcare in Germany - Insights from Berlin] Inclusive Education in Germany: A Japanese Perspective on Practices, Challenges, and Pathways to the Future
- ISS BERD Joint Research Project (JLSCP) Results of "2023 Fact-finding Survey on Children's Utilization of ICT": About 80% of School Children Enjoy Classes Using ICT Devices [Part2]
- ISS BERD Joint Research Project (JLSCP) Results of "2023 Fact-finding Survey on Children's Utilization of ICT": About 80% of School Children Enjoy Classes Using ICT Devices [Part 1]
- [Snuggling Up to Our Differences] Episode 7: Avoid Burying the Fun of Learning in Competition
- [Aiming to Realize an Inclusive Society] Providing an Environment Where Children Can Learn Things Independently and Proactively, Seeking to Enhance the "Ability to Become Happy"
- Seven-Year Follow-up Survey Data on the Reading Behaviors of Children from Elementary to High School: About 50% of children spend 0 min of their day reading books [Part 2]
- Early Childhood
- Elementary, Junior High, High School, and University
- International Comparisons
- Digital Media and Children
- Children's Rights and Well-being
- New Directions
- Full Paper Archive
- Research Data
- Latest Children's Issues
- Childrearing and Education
- About this Project
- Interactive Activities
- CRN History
- Publications
- Main navigation
- Main content
The Importance of High-Quality Early Childhood Education for Children and the Economy
- Lisa A. Nelson
- Michelle Volpe-Kohler
Early childhood education (ECE) has received increased attention since the pandemic given the impact of closures on children and families. Among other ways, access to high-quality ECE can affect the economy by supporting families' participation in the economy and paving the way for children to reach their full potential.
The views expressed in this report are those of the author(s) and are not necessarily those of the Federal Reserve Bank of Cleveland or the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System.
Early childhood education (ECE) can affect the economy in a variety of ways; for example, by allowing more parents of young children to participate in the labor force. It also can help prepare young children for future success in school, potentially impacting their longer-term educational trajectories and, by extension, the future US workforce. ECE, which refers to a range of programming for children prior to reaching school age (five years old), has received increased attention since the pandemic given the impact of closures—some temporary, some permanent—on children and families.
The state of childcare in the US is complex. The challenges for families can include affordability, accessibility, and quality. One specific issue that ECE programs face is maintaining a stable workforce. Recent research by the Cleveland Fed finds that “turnover among US childcare workers was about 65 percent higher than turnover in the median occupation in 2022, which creates challenges for the broader workforce.” In addition, the study finds that “currently, the number of childcare workers remains below prepandemic levels.” To help shed light on the importance of ECE and the childcare landscape in the Cleveland Fed’s district (Ohio, parts of Pennsylvania, Kentucky, and West Virginia), we talked to Jamie Remp . She’s a Cleveland Fed Community Advisory Council member and executive director of King's Daughters Childcare Center in West Virginia, and she shares below some of her experiences with running a childcare center.
Why is ECE important to the community that you serve and, more broadly, in the US?
Jamie: Research shows that the economy reaps the rewards when communities have quality ECE. Children who attended high-quality ECE programs are less likely to require remedial education or special services later, saving taxpayer dollars. Access to reliable childcare allows parents, particularly mothers, to participate in the workforce, boosting the economy. Early childhood programs encourage community engagement and parent support networks and can lead to stronger, more resilient communities.
In West Virginia, where I am based, 41 percent of children under six years old do not have access to childcare . So it’s a struggle to maintain access as well as high-quality standards.
How did the pandemic affect you or the services your organization provides?
Jamie: Pre-pandemic, ECE programs faced challenges such as finding quality teachers who would work for lower wages, high operating costs to meet licensing requirements, and a never-ending list of families in need of childcare. When the pandemic hit, thousands of programs had to close their doors; some closures were temporary, but others were permanent. Families were left scrambling to find alternate childcare options and businesses were struggling with employees unable to work.
Since the pandemic, our program has experienced much longer gaps in filling positions. The average turnaround time to hire one qualified staff member is almost six months. Hiring new staff requires background checks and training before a teacher can be placed in a classroom. Delays in hiring lead to the inability to enroll students—and even classroom closures—until teachers can be hired and trained.
In my experience, childcare staff often do the job of multiple people to keep their programs running. For instance, as executive director of a childcare program, I oversee the finances, grant-writing and fundraising, project management, and maintenance of the center, and often I am filling in the gaps where we are short on staff. The teachers at our center not only create and follow lesson plans for the children, but they also clean their classrooms and toys; do laundry (blanket, sheets, and towels); feed the children breakfast, lunch, and snacks; monitor naptime; and write up a daily newsletter for each child to communicate with parents.
What is high-quality ECE and why do you think it has an impact on children and your local economy?
Jamie: High-quality ECE programs have qualified and experienced teachers, lower student-teacher ratios, a stimulating learning environment, and a lot of family engagement and communication. During the crucial years from birth to age five, these programs can heavily impact the economic, health, and social outcomes for both individuals and society.
The findings of a study carried out by Professor James J. Heckman indicate that every dollar invested in high-quality, birth-to-five early childhood programs can deliver a 13 percent return on investment. This figure represents the highest rate of economic return of any workforce development initiative. The study analyzed several life outcomes throughout participants’ childhood and adulthood, including income, IQ, schooling, health, crime, and mothers’ incomes after returning to work through access to childcare.
Other research points to enhanced cognitive development in kids such as better memory and improved problem-solving abilities, as well as stronger social and emotional skills such as conflict resolution and empathy. High-quality childcare programs can also improve school readiness and narrow achievement gaps to the benefit of children from disadvantaged backgrounds.
The bottom line
The benefits of high-quality ECE for children and families can be wide-ranging, from stronger problem-solving skills in kids to helping to build more resilient communities. Access to high-quality ECE can support families’ participation in the economy and can pave the way for children to reach their full potential, contributing to a stronger economy for everyone.
Related resources
- CD Report: Using Worker Flows to Assess the Stability of the Early Childcare and Education Workforce, 2010-2022 (Cleveland Fed)
- Economic Commentary: Increasing the (Female) Labor Supply (Cleveland Fed)
- FedTalk: Access to Childcare and Labor Market Participation (Cleveland Fed)
- Why Equitable Access Matters to the Economy (Fed Communities)
- Examining Teacher Turnover in Early Care and Education (Minneapolis Fed)
- Early Childhood Development (Minneapolis Fed)

World Conference on Early Childhood Care and Education
for Transforming Early Childhood Care and Education

The World Conference had three main goals in the area of Early Childhood Care and Education (ECCE):
- To develop ambitious, relevant, and culturally appropriate policies
- To put in place effective and accountable systems, multi-stakeholder partnerships and services
- To increase and improve investment in this area as an essential and integral part of countries’ strategies for attaining lifelong learning societies and sustainable development.
Global Commitment for Early Childhood Care and Education
During the World Conference on Early Childhood Care and Education (WCECCE), 147 member states were represented, including 77 ministers and vice-ministers, culminating in a total attendance of 2,683 participants. All participating Member States adopted the Tashkent Declaration for Early Childhood Care and Education , committing to at least one year of free, compulsory pre-primary education for all.
The event provided a platform for countries to showcase national findings and engage in discussions regarding future commitments and the advancement of the Early Childhood Care and Education Agenda. UNESCO’s member states have pledged to invest at least 10% of their total education spending on pre-primary education.

"Investing in early childhood is crucial to reduce social inequalities, which begin even before birth. Increasing funding, both national and international, will make a difference for future generations."
A day at UNESCO’s preschool
UNESCO’s Assistant Director-General for Education, Stefania Giannini, explains the importance of giving all children a fair start in life
Evidence shows that a child’s early years are critical for shaping their ability to learn and build a foundation for their future

Thematic reports
- Promoting quality inclusion in early childhood care and education: inclusive practices for each and every child
- Building and strengthening the legal framework on ECCE rights: achievements, challenges and actions for change
- Early childhood care and education in emergencies
- Language acquisition in early years of childhood : the role of family and pre-primary education
Engagements
- Joint engagement document from ECCE Non-State Actors
Regional reports
- Arab States
- Asia and the Pacific
- Latin America and the Carribean (in Spanish)
- Sub-Saharan Africa
Conference bodies
- Programme Committee
- Drafting group members
- Bureau of the Conference
- Organising Committee
Media resources
- Social media pack
- Press release
- Media advisory
National statements
- Burkina Faso
- Guinée Bissau
- Japan
- Russian Federation
- Sierra Leone
- St Kitts and Nevis
- United Arab Emirates
Videos of the event
- Policy Day, Tuesday 15 November 2022 English - French - Russian
- Commitment Day, Wednesday 16 November 2022 English - French - Russian
Highlights of high-level sessions
- Session 1. Inclusion, quality and well-being
- Session 2. ECCE workforce and caregivers
- Session 3. Policy, governance and finance
- Session 4. Programme Innovations
Photo essays

Publications

The Conference is hosted by the Republic of Uzbekistan

Master of Arts in Teaching (MAT)

Master of Arts in Curriculum and Instruction
Education Dual Major
Health and economic benefits of breastfeeding quantified
Among half a million scottish infants, those exclusively breastfed were less likely to use healthcare services and incurred lower costs to the healthcare system.
Breastmilk can promote equitable child health and save healthcare costs by reducing childhood illnesses and healthcare utilization in the early years, according to a new study published this week in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Tomi Ajetunmobi of the Glasgow Centre for Population Health, Scotland, and colleagues.
Breastfeeding has previously been found to promote development and prevent disease among infants. In Scotland -- as well as other developed countries -- low rates of breastfeeding in more economically deprived areas are thought to contribute to inequalities in early childhood health. However, government policies to promote child health have made little progress and more evidence on the effectiveness of interventions may be needed.
In the new study, researchers used administrative datasets on 502,948 babies born in Scotland between 1997 and 2009. Data were available on whether or not infants were breastfed during the first 6-8 weeks, the occurrence of ten common childhood conditions from birth to 27 months, and the details of hospital admissions, primary care consultations and prescriptions.
Among all infants included in the study, 27% were exclusively breastfed, 9% mixed fed and 64% formula fed during the first 6-8 weeks of life. The rates of exclusively breastfed infants ranged from 45% in the least deprived areas to 13% in the most deprived areas.
The researchers found that, within each quintile of deprivation, exclusively breastfed infants used fewer healthcare services and incurred lower costs compared to infants fed any formula milk. On average, breastfed infants had lower average costs of hospital care per admission (£42) compared to formula-fed infants (£79) in the first six months of life and fewer GP consultations (1.72, 95% CI: 1.66 -- 1.79) than formula-fed infants (1.92 95% CI: 1.88 -- 1.94). At least £10 million of healthcare costs could have been avoided if all formula-fed infants had instead been exclusively breastfed for the first 6-8 weeks of life, the researchers calculated.
The authors conclude that breastfeeding has a significant health and economic benefit and that increasing breastfeeding rates in the most deprived areas could contribute to the narrowing of inequalities in the early years.
- Breastfeeding
- Infant's Health
- Today's Healthcare
- Health Policy
- Public Health
- Disaster Plan
- Poverty and Learning
- Education and Employment
- Early childhood education
- Upper respiratory tract infection
- Social inclusion
- Health science
- Evidence-based medicine
Story Source:
Materials provided by PLOS . Note: Content may be edited for style and length.
Journal Reference :
- Omotomilola Ajetunmobi, Emma McIntosh, Diane Stockton, David Tappin, Bruce Whyte. Levelling up health in the early years: A cost-analysis of infant feeding and healthcare . PLOS ONE , 2024; 19 (5): e0300267 DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0300267
Cite This Page :
Explore More
- The Case of the Missing Black Holes
- Adjusting Sunglasses for Your Windows
- Novel Gene-Editing Tool Created
- How Hummingbirds Hover With Such Accuracy
- Complete X and Y Chromosomes of Great Apes
- Moonlets Stuck Together Orbit 'Dinky' Asteroid
- Orchids Aid Seedlings Through Fungal Networks
- Precise Maps of the Moon's Surface
- Amazing Expertise of Scent Detection Dogs
- Getting to Grips With a Handy Extra Thumb
Trending Topics
Strange & offbeat.
Advertisement
Supported by
Optimistic About the War in Ukraine, Putin Unleashes a Purge at Home
Despite years of criticism, President Vladimir V. Putin has only now changed his defense minister and allowed high-level corruption arrests.
- Share full article

By Paul Sonne and Anatoly Kurmanaev
Reporting from Berlin
Periodic outcries over incompetence and corruption at the top of the Russian military have dogged President Vladimir V. Putin’s war effort since the start of his invasion of Ukraine in early 2022.
When his forces faltered around the Ukrainian capital, Kyiv, the need for change was laid bare. When they were routed months later outside the city of Kharkiv, expectations of a shake-up grew. And after the mercenary leader Yevgeny V. Prigozhin marched his men toward Moscow, complaining of deep rot and ineptitude at the top of the Russian force, Mr. Putin seemed obliged to respond.
But, at each turn, the Russian president avoided any major public moves that could have been seen as validating the criticism, keeping his defense minister and top general in place through the firestorm while shuffling battlefield commanders and making other moves lower on the chain.
Now, with the battlefield crises seemingly behind him and Mr. Prigozhin dead, the Russian leader has decided to act, changing defense ministers for the first time in more than a decade and allowing a number of corruption arrests among top ministry officials.
The moves have ushered in the biggest overhaul at the Russian Defense Ministry since the invasion began and have confirmed Mr. Putin’s preference for avoiding big, responsive changes in the heat of a crisis and instead acting at a less conspicuous time of his own choosing.
“We have to understand that Putin is a person who is stubborn and not very flexible,” said Abbas Gallyamov, a former Putin speechwriter who now lives outside Russia. “He believes that reacting too quickly and rapidly to a changing situation is a sign of weakness.”
The timing of Mr. Putin’s recent moves is most likely a sign that he has greater confidence about his battlefield prospects in Ukraine and his hold on political power as he begins his fifth term as president, experts say.
Russian forces are making gains in Ukraine , taking territory around Kharkiv and in the Donbas region, as Ukraine struggles with aid delays from the United States and strained reserves of ammunition and personnel . Top officials in the Kremlin are feeling optimistic.
“They likely judge the situation within the force as stable enough to punish some in the military leadership for its prior failures,” said Michael Kofman, an expert on the Russian military and a senior fellow at the Carnegie Endowment for International Peace.
Demand for change at the top of the Russian military has been pent up since the invasion’s earliest days, when stories circulated about Russian soldiers going to war without proper food and equipment and losing their lives while answering to feckless military leaders.
The anger crested with an aborted uprising led last year by Mr. Prigozhin , who died in a subsequent plane crash that U.S. officials have said was most likely a state-sanctioned assassination .
Mr. Prigozhin , a caterer turned warlord who grew rich on state contracts, was an unlikely messenger. But he put high-level corruption on the minds of Russia’s rank and file and the public more broadly, releasing profanity-laced tirades against Sergei K. Shoigu, then the defense minister, and Russia’s top uniformed officer, Gen. Valery V. Gerasimov. At one point, Mr. Prigozhin filmed himself in front of a pile of dead Russian fighters and denounced top officials for “rolling in fat” in their wood-paneled offices.
His subsequent failed mutiny showed that the problems festering in the Defense Ministry under Mr. Shoigu for over a decade had boiled over and that the populace craved renewal, said a person close to the ministry who spoke on the condition of anonymity in order to discuss sensitive topics.
The Russian leader now appears to be moving against the very officials that Mr. Prigozhin had been attacking.
The first harbinger of change arose last month with the arrest of Timur Ivanov , a protégé of Mr. Shoigu and the deputy defense minister in charge of military construction projects whom the Russian authorities have accused of taking a large bribe. He has denied wrongdoing. Mr. Ivanov previously attracted the attention of Aleksei A. Navalny’s Anti-Corruption Foundation for his and his wife’s conspicuously lavish lifestyle, including yacht rentals on the French Riviera.
Then, this month, days after Mr. Putin began his new term as president, the Kremlin announced that he had replaced Mr. Shoigu and chosen Andrei R. Belousov, one of his longtime economic advisers, as the new defense minister. Mr. Shoigu was moved to run the Russian Security Council, where he would still have access to the president but would have little direct control over money.
Mr. Belousov has no military experience . But he boasts a relatively clean image and a long government career untainted by large corruption scandals.
“If you want to win a war, corruption at a larger scale impacting the results on the battlefield is, in theory at least, not something you want,” said Maria Engqvist, the deputy head of Russia and Eurasia studies at the Swedish Defense Research Agency.
Still, Ms. Engqvist called high-level corruption in Russia “a feature, not a bug.”
“Corruption is a tool to gain influence, but it can also be used against you at any given time, depending on whether you say the wrong thing at the wrong time or make the wrong decision at the wrong time,” she said. “So you can be ousted with a reasonable explanation that the public can accept.”
Ms. Engqvist said the changes also raised questions about how long General Gerasimov would stay in his position as chief of the general staff and top battlefield commander in Ukraine.
The arrests at the Defense Ministry have gathered pace this month, with four more top generals and defense officials detained on corruption charges. Dmitri S. Peskov, the Kremlin spokesman, denied on Thursday that the arrests represented a “campaign.”
The corruption charges against top Defense Ministry officials have come alongside promises of greater financial and social benefits for the rank-and-file soldiers, an apparent attempt to improve morale and mollify populist critics.
Mr. Belousov used his first remarks after his nomination as defense minister to describe his plans to cut bureaucracy and improve access to health care and other social services for veterans of the war. And on Thursday, the speaker of Russia’s lower house of Parliament, Vyacheslav V. Volodin, and Finance Minister Anton G. Siluanov expressed support for exempting fighters in Ukraine from proposed income-tax increases.
The high-level arrests are unlikely to root out vast corruption in the Russian military establishment, but they could make top officials think twice before stealing at a particularly large scale, at least for a period, said Dara Massicot, a senior fellow at the Carnegie Endowment for International Peace.
“It will introduce a chill into the system and make everyone pause as they try to figure out the new code of accepted behavior,” Ms. Massicot said.
Beyond sending an anticorruption message, at least one of the arrests seemed to be aimed at settling a political score.
Maj. Gen. Ivan Popov, a top Russian commander who led forces holding off Ukraine’s counteroffensive, chided the Russian military leadership in a widely seen recording last year after he was removed from his post. He was apprehended on Tuesday on fraud charges, according to the state news agency TASS. He denied wrongdoing, his lawyer said.
“The bottom line is that the war exposed a lot of different problems — corruption, incompetence and openness to public expressions of insubordination — that the leadership feels a need to address,” said Samuel Charap, a senior political scientist at the RAND Corporation. “Now is a good time to do this, precisely because there isn’t a short-term acute risk on the battlefield.”
Paul Sonne is an international correspondent, focusing on Russia and the varied impacts of President Vladimir V. Putin’s domestic and foreign policies, with a focus on the war against Ukraine. More about Paul Sonne
Anatoly Kurmanaev covers Russia and its transformation following the invasion of Ukraine. More about Anatoly Kurmanaev
Our Coverage of the War in Ukraine
News and Analysis
Secretary of State Antony Blinken suggested that the Biden administration could be open to tolerating strikes by the Ukrainian military inside Russia using American-made weapons.
U.S. and allied intelligence officials are tracking an increase in low-level sabotage operations in Europe that they say are part of a Russian campaign to undermine support for Ukraine’s war effort.
Ukraine has begun releasing prisoners to serve in its army , part of a wider effort to rebuild a military that has been depleted by more than two years of war and is strained by relentless Russian assaults.
Zelensky Interview: In an interview with the New York Times, President Volodymyr Zelensky of Ukraine challenged the West over its reluctance to take bolder action.
Striking a Chord: A play based on a classic 19th-century novel, “The Witch of Konotop,” is a smash hit among Ukrainians who see cultural and historical echoes in the story of what they face after two years of war.
Europe’s Defense Industry: Russia’s invasion of Ukraine jolted Europe out of complacency about military spending. But the challenges are about more than just money .
How We Verify Our Reporting
Our team of visual journalists analyzes satellite images, photographs , videos and radio transmissions to independently confirm troop movements and other details.
We monitor and authenticate reports on social media, corroborating these with eyewitness accounts and interviews. Read more about our reporting efforts .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
An Exploratory Critical Study of Questioning Strategies Posed by Early Childhood Teachers During Literacy Blocks, Angela H. Baker Ms. PDF. Developing Mastery in Phonemic Awareness, Phonics, and Morphemic Awareness: A Multiple Case Study of Preservice Early Childhood Educators, Ruth Facun-Granadozo. Theses/Dissertations from 2012 PDF
Formal education: Spanning between 2 to 8 years, formal early childhood education, which varies from state to state and from program to program, is a program that qualified teachers can provide in any relevant settings. Some of these settings include preschool, nursery schools, and kindergarten.
Physical Education Thesis Topics. Assessing the impact of physical education on childhood obesity rates. The effectiveness of integrated technology in physical education: Wearables and fitness tracking. Strategies for promoting lifelong physical activity through school-based programs.
More essay topics on Early Childhood Education. 11. The effects of school district policies on preventing maltreatment among early childhood learners. 12. The impacts of politics on the success of early childhood learning programs. 13. Exploring the problems of measuring the efficacy of ECE programs such as Head Start.
Part of the Early Childhood Education Commons, and the Educational Methods Commons Recommended Citation Edwards, Michelle Lois, "Early Childhood Educators' Perspectives of Play in Preschool Classrooms" (2017). Dissertations. Paper 124. https://digitalcommons.wku.edu/diss/124 This Dissertation is brought to you for free and open access by ...
Dissertation: Quality Profiles in Early Childhood: An Example From Virginia's Quality Rating Improvement System, Kathryn M. Squibb. Theses/Dissertations from 2011 PDF. Dissertation: Kindergarten Teachers' Classroom Management Beliefs and Practices and Their Implications on Students' Social and Academic Outcomes, Lauren D. Florin
2) Nature-based Early Childhood Education 3) Social Emotional Learning 4) Technology-Based Learning 5) STEM/STEAM Education in ECE 6) Early Language and Literacy Development 7) Culturally Responsive Teaching, Practices and Approaches 8) Child-Centered Instruction 9) Developmentally Appropriate Practice 10) Family Engagement
A training framework for Early Childhood Education Care practitioners in facilitating transition from home to school. Chetty, Magesveri S. (University of Pretoria, 2021) The first five years in children's lives lay the foundation for their cognitive and social development and learning prowess over the course of their lives. In terms of global ...
Fine Motor Matters - A Plan to Improve Fine Motor Skills at the Early Childhood Level, Natasha Slater. PDF. Social and Emotional Skills Develop Through Play-Based Learning, April Welding. PDF. Effects of Using Hands-On Materials During Narrative Literacy Activities in the Preschool Classroom, Brittany White. PDF.
Thesis Presented to the Faculty ... Research confirms that instructional quality in early childhood education is a strong predictor of children's school-readiness and subsequent achievement. However, ... or investment of thought and effort necessary to comprehend ideas and master skills (Fredricks, Blumenfeld, & Paris, 2004). Both my ...
for this basic qualitative study explored early childhood educators' perspectives of the challenges of these practices. Using current research and the conceptual framework of critical race theory in education, research and interview questions were developed. Ten early educators were interviewed using the developed interview protocol. Four themes
The Theses and Dissertations--Early Childhood, Special Education, and Counselor Education collection is formerly known as the Theses and Dissertations--Early Childhood, Special Education, and Rehabilitation Counseling collection. Follow. Jump to: Theses/Dissertations from 2024 PDF. How ...
This research study examined family awareness of early childhood education (ECE) quality at two ECE programs in Anne Arundel County, Maryland. Both programs participated in the Maryland State Department of Education's (MSDE) field test of the quality rating and improvement system (QRIS) called Maryland EXCELS (MD EXCELS; n.d.) in 2012. These two
THESIS APPROVAL PRESCHOOL TEACHERS' EARLY PERCEPTIONS OF EDUCATION FOR SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT IN EARLY CHILDHOOD EDUCATION By Shannon S. Green A Thesis Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of Master of Science in the field of Early Childhood Education Approved by: Dr. Cathy Mogharreban, Chair Dr. Grant Miller
Early Education. Trending Topic Research File. Early education, including preschool, prekindergarten, and programs such as Head Start, is a robust area of education research. In recent years, AERA's journals - through research articles, essays, and book reviews and responses - have examined many aspects of the early education, including ...
This dissertation consists of three essays investigating children's early learning experiences in the United States. Specifically, I examine early learning achievement outcomes for immigrant children and low-income, minority children to identify early educational barriers and to reduce early achievement gaps. In addition, I focus on measurements that are often not included in early childhood ...
The TOP program that stresses social and academic skills for young children appears to have long-lasting benefits. After 5 years, these children were successful in school—academically, socially, and emotionally. Academic performance increased for children provided with high-quality, early learning.
NAEYC provides the highest-quality resources on a broad range of important topics in early childhood. We've selected a few of our most popular topics and resources in the list below. Still can't find the topic you need? Check out our site search. Anti-Bias Education; Back to School; Common Core; Coping with COVID-19; Coping With Stress and ...
early education (p. 2). These data suggest that the educational access needs of some, but not all, children with disabilities are being addressed by nations in order to fully achieve the goal of universal education (United Nations, 2008). Disparities in school enrollment may be related to the quality in educational programming.
Peer-review under responsibility of the organizing committee of ECCE 2016. doi: 10.1016/j.sbspro.2016.10.131 ScienceDirect Annual International Scientific Conference Early Childhood Care and Education, ECCE 2016, 12-14 May 2016, Moscow, Russia Impact of Mother Tongue on Children’s Learning Abilities in Early Childhood Classroom Anna V ...
The use of technology in education has been getting increased. Although the use of technology in early childhood education (ECE) is controversial, it is helpful for children learning and development when it is used to create natural learning environments to meet their needs and for teaching purposes (Bolstad, 2004; Van Scoter et al., 2001). ...
ECEC. On September 27-29, 2010, I participated in the "World Conference on Early Childhood Care and Education" held in Moscow, Russia, as a member of Japanese government delegation. This is a report of the discussions at the general and individual meetings. The conference was sponsored by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural ...
Early childhood education (ECE) can affect the economy in a variety of ways; for example, by allowing more parents of young children to participate in the labor force. It also can help prepare young children for future success in school, potentially impacting their longer-term educational trajectories and, by extension, the future US workforce.
The World Conference had three main goals in the area of Early Childhood Care and Education (ECCE): To develop ambitious, relevant, and culturally appropriate policies. To put in place effective and accountable systems, multi-stakeholder partnerships and services. To increase and improve investment in this area as an essential and integral part ...
The graduate program in Early Childhood and Childhood Education provides the education coursework and fieldwork required for initial and professional certification for Birth-Grade 6 in New York State and reciprocal states. Many of the undergraduate and graduate courses will be offered online, with fieldwork and student teaching in person. ...
Below are statements from early childhood education and child care providers in the field calling on the North Carolina General Assembly to make Governor Cooper's proposed early childhood education investments. "Our child care center is struggling to stay afloat. Your investment in early care and education will determine whether we sink or ...
Benjamin Balint is the author of "Kafka's Last Trial" and, most recently, "Bruno Schulz: An Artist, a Murder, and the Hijacking of History," winner of the National Jewish Book Award in ...
Breastmilk can promote equitable child health and save healthcare costs by reducing childhood illnesses and healthcare utilization in the early years, according to a new study published this week ...
In northeastern Ukraine, and in the part of Russia it touches, the war strains the emotions of people with relatives, and family histories, that span both sides.
Mr. Prigozhin, a caterer turned warlord who grew rich on state contracts, was an unlikely messenger.But he put high-level corruption on the minds of Russia's rank and file and the public more ...