Editor's Choice: How AI Will Enhance Imaging Access and Analysis
- Kidney Donor and Recipient Outcomes May 23, 2024 Original Investigation Hypertension and Kidney Function After Living Kidney Donation Amit X. Garg, MD, PhD; Jennifer B. Arnold, BSc; Meaghan S. Cuerden, PhD; et al Editorial Prospectively Examining Outcomes After Living Kidney Donation: Informing the Altruist Elizabeth C. Lorenz, MD; Wolfgang C. Winkelmayer, MD, MPH, ScD
- Original Investigation Kidney Transplant Outcomes From Deceased Donors Who Received Dialysis Yumeng Wen, MD, PhD; Sherry G. Mansour, MD, MSc; Nityasree Srialluri, MD, MS, MHS; et al Editorial Expanding the Overton Window in Deceased Kidney Donor Eligibility—Enough to Make a Difference? Xingxing S. Cheng, MD, MS; Colin R. Lenihan, MB BCh BAO, PhD
- Audio Outcomes After Living Kidney Donation Amit X. Garg, MD, PhD, and Elizabeth C. Lorenz, MD, with host JAMA Associate Editor Wolfgang C. Winkelmayer, MD, MPH, ScD

Just Published
- Long-Term Outcomes From Prostate Cancer Active Surveillance Lisa F. Newcomb, PhD; et al. Original Investigation online first Lisa F. Newcomb, PhD; et al.
- Industry Payments to Physicians Endorsing Drugs and Devices on a Social Media Platform Sonia Persaud, MPH; et al. Research Letter online first Sonia Persaud, MPH; et al.
- Benefit of RAS Blockade in Heart Failure by Race Li Shen, MBChB, PhD; et al. Original Investigation online first Li Shen, MBChB, PhD; et al.
- Ransomware Attacks, ED Visits and Inpatient Admissions in Targeted and Nearby Hospitals Rahi Abouk, PhD; et al. Research Letter online first Rahi Abouk, PhD; et al.
- Shingles Vaccination in Medicare Part D After Inflation Reduction Act Elimination of Cost Sharing Dima M. Qato, PharmD, MPH, PhD; et al. Research Letter online first Dima M. Qato, PharmD, MPH, PhD; et al.
- US Journals’ Responsibility to Report on Public Health Crisis in Gaza Nadir Ijaz, MD; et al. Viewpoint online first Nadir Ijaz, MD; et al. Editor's Note
- The Texas Medical Board and the Futility of Medical Exceptions to Abortion Bans Elizabeth Sepper, JD, LLM; et al. Viewpoint online first Elizabeth Sepper, JD, LLM; et al.
- The Clinic Visit Mark Varvares, MD A Piece of My Mind online first Mark Varvares, MD
- Evidence Against Use of Nitrogen for the Death Penalty Philip E. Bickler, MD, PhD; et al. Viewpoint online first has multimedia Philip E. Bickler, MD, PhD; et al.
- Mimesis: Poetry and Imitating Medicine Rafael Campo, MD, MA Editor's Note online first Rafael Campo, MD, MA
- Review: Chronic Pruritus Daniel C. Butler, MD; et al. Review online first has active quiz has multimedia Daniel C. Butler, MD; et al.
- Accounting for Competing Risks in Clinical Research Peter C. Austin, PhD; et al. JAMA Guide to Statistics and Methods online first has active quiz Peter C. Austin, PhD; et al.
- Federal Trade Commission Actions on Prescription Drugs, 2000-2022 C. Joseph Ross Daval, JD; et al. Special Communication online first has active quiz has multimedia C. Joseph Ross Daval, JD; et al. Editorial
- Blood Testing for Phosphatidylethanol Areej Mazhar, DO; et al. JAMA Diagnostic Test Interpretation online first has active quiz Areej Mazhar, DO; et al.
- Causal Inference and Effects of Interventions From Observational Studies in Medical Journals Issa J. Dahabreh, MD, ScD; et al. Special Communication online first free access has active quiz Issa J. Dahabreh, MD, ScD; et al. Editor's Note
Latest from the USPSTF
- USPSTF Recommendation: Screening for Breast Cancer
- USPSTF Recommendation: Primary Care Interventions to Prevent Child Maltreatment
- USPSTF Recommendation: Screening for Speech and Language Delay and Disorders
- 81,898 Views USPSTF Recommendation: Screening for Breast Cancer
- 40,017 Views Causal Inference and Effects of Interventions From Observational Studies in Medical Journals
- 35,158 Views Aspirin vs Placebo as Adjuvant Therapy for Breast Cancer
- 34,413 Views Krill Oil for Knee Osteoarthritis
- 31,519 Views The Women’s Health Initiative Randomized Trials and Clinical Practice
- 28,010 Views Mortality in Patients Hospitalized for COVID-19 vs Influenza in Fall-Winter 2023-2024
- 25,153 Views Acetaminophen for Prevention and Treatment of Organ Dysfunction
- 22,637 Views Associations of Milestone Ratings and Certification Examination Scores With Patient Outcomes
- 22,260 Views Survival Benefit Associated With Participation in Clinical Trials of Anticancer Drugs
- 21,338 Views Why the Bird Flu Outbreak in Dairy Cows Matters
- 726 Citations Antibody Response to 2-Dose SARS-CoV-2 mRNA Vaccine Series in Solid Organ Transplant Recipients
- 717 Citations Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology Using Mendelian Randomization
- 631 Citations Pancreatic Cancer
- 623 Citations Updated Guidance on the Reporting of Race and Ethnicity in Medical and Science Journals
- 523 Citations Effect of 2 Inactivated SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines on Symptomatic COVID-19 Infection in Adults
- 448 Citations Association Between IL-6 Antagonists and Mortality Among Patients Hospitalized for COVID-19
- 414 Citations Association Between 3 Doses of mRNA COVID-19 Vaccine and Symptomatic Infection Caused by Omicron and Delta Variants
- 383 Citations Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis With Thrombocytopenia After Ad26.COV2.S Vaccination
- 382 Citations Association of COVID-19 mRNA Vaccination With Hospitalizations and Disease Severity
- 378 Citations Myocarditis Cases Reported After mRNA-Based COVID-19 Vaccination in the US From December 2020 to August 2021
- Register for email alerts with links to free full-text articles
- Access PDFs of free articles
- Manage your interests
- Save searches and receive search alerts
Research articles
Tislelizumab plus chemotherapy versus placebo plus chemotherapy as first line treatment for advanced gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction adenocarcinoma, epidural analgesia during labour and severe maternal morbidity, exposure to antibiotics during pregnancy or early infancy and risk of neurodevelopmental disorders, clinical and healthcare use outcomes after cessation of long term opioid treatment due to prescriber workforce exit, effect of the hpv vaccination programme on incidence of cervical cancer by socioeconomic deprivation in england, long acting progestogens vs combined oral contraceptive pill for preventing recurrence of endometriosis related pain, ultra-processed food consumption and all cause and cause specific mortality, comparative effectiveness of second line oral antidiabetic treatments among people with type 2 diabetes mellitus, efficacy of psilocybin for treating symptoms of depression, reverse total shoulder replacement versus anatomical total shoulder replacement for osteoarthritis, effect of combination treatment with glp-1 receptor agonists and sglt-2 inhibitors on incidence of cardiovascular and serious renal events, prenatal opioid exposure and risk of neuropsychiatric disorders in children, temporal trends in lifetime risks of atrial fibrillation and its complications, antipsychotic use in people with dementia, predicting the risks of kidney failure and death in adults with moderate to severe chronic kidney disease, impact of large scale, multicomponent intervention to reduce proton pump inhibitor overuse, esketamine after childbirth for mothers with prenatal depression, glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonist use and risk of thyroid cancer, use of progestogens and the risk of intracranial meningioma, delirium and incident dementia in hospital patients, derivation and external validation of a simple risk score for predicting severe acute kidney injury after intravenous cisplatin, quality and safety of artificial intelligence generated health information, large language models and the generation of health disinformation, 25 year trends in cancer incidence and mortality among adults in the uk, cervical pessary versus vaginal progesterone in women with a singleton pregnancy, comparison of prior authorization across insurers, diagnostic accuracy of magnetically guided capsule endoscopy with a detachable string for detecting oesophagogastric varices in adults with cirrhosis, ultra-processed food exposure and adverse health outcomes, added benefit and revenues of oncology drugs approved by the ema, exposure to air pollution and hospital admission for cardiovascular diseases, short term exposure to low level ambient fine particulate matter and natural cause, cardiovascular, and respiratory morbidity, optimal timing of influenza vaccination in young children, effect of exercise for depression, association of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease with cardiovascular disease and all cause death in patients with type 2 diabetes, duration of cpr and outcomes for adults with in-hospital cardiac arrest, clinical effectiveness of an online physical and mental health rehabilitation programme for post-covid-19 condition, atypia detected during breast screening and subsequent development of cancer, publishers’ and journals’ instructions to authors on use of generative ai in academic and scientific publishing, effectiveness of glp-1 receptor agonists on glycaemic control, body weight, and lipid profile for type 2 diabetes, neurological development in children born moderately or late preterm, invasive breast cancer and breast cancer death after non-screen detected ductal carcinoma in situ, all cause and cause specific mortality in obsessive-compulsive disorder, acute rehabilitation following traumatic anterior shoulder dislocation, perinatal depression and risk of mortality, undisclosed financial conflicts of interest in dsm-5-tr, effect of risk mitigation guidance opioid and stimulant dispensations on mortality and acute care visits, update to living systematic review on sars-cov-2 positivity in offspring and timing of mother-to-child transmission, perinatal depression and its health impact, christmas 2023: common healthcare related instruments subjected to magnetic attraction study, using autoregressive integrated moving average models for time series analysis of observational data, demand for morning after pill following new year holiday, christmas 2023: christmas recipes from the great british bake off, effect of a doctor working during the festive period on population health: experiment using doctor who episodes, christmas 2023: analysis of barbie medical and science career dolls, christmas 2023: effect of chair placement on physicians’ behavior and patients’ satisfaction, management of chronic pain secondary to temporomandibular disorders, christmas 2023: projecting complete redaction of clinical trial protocols, christmas 2023: a drug target for erectile dysfunction to help improve fertility, sexual activity, and wellbeing, christmas 2023: efficacy of cola ingestion for oesophageal food bolus impaction, conservative management versus laparoscopic cholecystectomy in adults with gallstone disease, social media use and health risk behaviours in young people, untreated cervical intraepithelial neoplasia grade 2 and cervical cancer, air pollution deaths attributable to fossil fuels, implementation of a high sensitivity cardiac troponin i assay and risk of myocardial infarction or death at five years, covid-19 vaccine effectiveness against post-covid-19 condition, association between patient-surgeon gender concordance and mortality after surgery, intravascular imaging guided versus coronary angiography guided percutaneous coronary intervention, treatment of lower urinary tract symptoms in men in primary care using a conservative intervention, autism intervention meta-analysis of early childhood studies, effectiveness of the live zoster vaccine during the 10 years following vaccination, effects of a multimodal intervention in primary care to reduce second line antibiotic prescriptions for urinary tract infections in women, pyrotinib versus placebo in combination with trastuzumab and docetaxel in patients with her2 positive metastatic breast cancer, association of dcis size and margin status with risk of developing breast cancer post-treatment, racial differences in low value care among older patients in the us, pharmaceutical industry payments and delivery of low value cancer drugs, rosuvastatin versus atorvastatin in adults with coronary artery disease, clinical effectiveness of septoplasty versus medical management for nasal airways obstruction, ultrasound guided lavage with corticosteroid injection versus sham lavage with and without corticosteroid injection for calcific tendinopathy of shoulder, early versus delayed antihypertensive treatment in patients with acute ischaemic stroke, mortality risks associated with floods in 761 communities worldwide, interactive effects of ambient fine particulate matter and ozone on daily mortality in 372 cities, association between changes in carbohydrate intake and long term weight changes, future-case control crossover analysis for adjusting bias in case crossover studies, association between recently raised anticholinergic burden and risk of acute cardiovascular events, suboptimal gestational weight gain and neonatal outcomes in low and middle income countries: individual participant data meta-analysis, efficacy and safety of an inactivated virus-particle vaccine for sars-cov-2, effect of invitation letter in language of origin on screening attendance: randomised controlled trial in breastscreen norway, visits by nurse practitioners and physician assistants in the usa, non-erosive gastro-oesophageal reflux disease and oesophageal adenocarcinoma, venous thromboembolism with use of hormonal contraception and nsaids, food additive emulsifiers and risk of cardiovascular disease, balancing risks and benefits of cannabis use, promoting activity, independence, and stability in early dementia and mild cognitive impairment, effect of home cook interventions for salt reduction in china, cancer mortality after low dose exposure to ionising radiation, effect of a smartphone intervention among university students with unhealthy alcohol use, long term risk of death and readmission after hospital admission with covid-19 among older adults, mortality rates among patients successfully treated for hepatitis c, association between antenatal corticosteroids and risk of serious infection in children, follow us on, content links.
- Collections
- Health in South Asia
- Women’s, children’s & adolescents’ health
- News and views
- BMJ Opinion
- Rapid responses
- Editorial staff
- BMJ in the USA
- BMJ in South Asia
- Submit your paper
- BMA members
- Subscribers
- Advertisers and sponsors
Explore BMJ
- Our company
- BMJ Careers
- BMJ Learning
- BMJ Masterclasses
- BMJ Journals
- BMJ Student
- Academic edition of The BMJ
- BMJ Best Practice
- The BMJ Awards
- Email alerts
- Activate subscription
Information
- Search by keyword
- Search by citation
Page 1 of 87
Associations of prenatal blood pressure trajectory and variability with child neurodevelopment at 2 years old
The patterns of blood pressure (BP) change throughout the pregnancy were related to adverse birth outcomes. However, little is known about the long-term effect of BP change patterns on child neurodevelopment. ...
- View Full Text
Clustering care pathways of people with alcohol dependence using a data linkage of routine data in Bremen, Germany
Although many individuals with alcohol dependence (AD) are recognized in the German healthcare system, only a few utilize addiction-specific treatment services. Those who enter treatment are not well character...
Comparison of children and adults in deep brain stimulation for Tourette Syndrome: a large-scale multicenter study of 102 cases with long-term follow-up
Deep brain stimulation (DBS) is a promising therapy for refractory Gilles de la Tourette syndrome (GTS). However, its long-term efficacy, safety, and recommended surgical age remain controversial, requiring ev...
Personalized therapy in endometriosis — based on ERα or ERβ expression
The original article was published in BMC Medicine 2023 21 :460
Specification curve analysis to identify heterogeneity in risk factors for dementia: findings from the UK Biobank
In 2020, the Lancet Commission identified 12 risk factors as priorities for prevention of dementia, and other studies identified APOE e4/e4 genotype and family history of Alzheimer’s disease strongly associated w...
The efficacy and safety of dalpiciclib, a cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitor, in patients with advanced head and neck mucosal melanoma harboring CDK4 amplification
Mucosal melanoma (MM) is a rare but devastating subtype of melanoma. Our previous studies have demonstrated robust anti-tumor effects of cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 (CDK 4/6) inhibitors in head and neck MM (HN...
Diabetes and further risk of cancer: a nationwide population-based study
Individuals with diabetes have a significantly higher risk of developing various forms of cancer, and the potential biological links between these two diseases are not completely understood.
Associations between vaping and self-reported respiratory symptoms in young people in Canada, England and the US
Prevalence of youth nicotine vaping has increased, heightening concerns around negative health effects. This study aimed to compare self-reported respiratory symptoms among youth by vaping behaviours.
Information technology-supported integrated health service for older adults in long-term care settings
To examine the effectiveness and safety of a data sharing and comprehensive management platform for institutionalized older patients.
The impact of major depressive disorder on glycaemic control in type 2 diabetes: a longitudinal cohort study using UK Biobank primary care records
This study evaluates longitudinal associations between glycaemic control, measured by mean and within-patient variability of glycated haemaglobin (HbA1c) levels, and major depressive disorder (MDD) in individu...
Healthy lifestyle change and all-cause and cancer mortality in the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition cohort
Healthy lifestyles are inversely associated with the risk of noncommunicable diseases, which are leading causes of death. However, few studies have used longitudinal data to assess the impact of changing lifes...
Safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics of TG103 injection in participants who are overweight or obese: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multiple-dose phase 1b study
TG103, a glucagon-like peptide-1 analog, is being investigated as an option for weight management. We aimed to determine the safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics of TG103 injection in p...
Association of heavy menstrual bleeding with cardiovascular disease in US female hospitalizations
Heavy menstrual bleeding (HMB) is a common menstrual disorder associated with multiple risk factors of cardiovascular disease (CVD) in women. In addition, HMB is often present with irregular menstruation (IM) ...
IL-2-free tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte therapy with PD-1 blockade demonstrates potent efficacy in advanced gynecologic cancer
Tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte (TIL) therapy has been restricted by intensive lymphodepletion and high-dose intravenous interleukin-2 (IL-2) administration. To address these limitations, we conducted preclinica...
ABO and Rhesus blood groups and multiple health outcomes: an umbrella review of systematic reviews with meta-analyses of observational studies
Numerous studies have been conducted to investigate the relationship between ABO and Rhesus (Rh) blood groups and various health outcomes. However, a comprehensive evaluation of the robustness of these associa...
Effectiveness of genetic feedback on alcohol metabolism to reduce alcohol consumption in young adults: an open-label randomized controlled trial
It is unclear whether brief interventions using the combined classification of alcohol-metabolizing enzymes aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 ( ALDH2 ) and alcohol dehydrogenase 1B ( ADH1B ) together with behavioral changes i...
Ruxolitinib plus standard of care in severe hospitalized adults with severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome (SFTS): an exploratory, single-arm trial
Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome (SFTS) is an emerging tick-borne infectious disease, and its morbidity and mortality are increasing. At present, there is no specific therapy available. An exacerbat...
Association between being large for gestational age and cardiovascular metabolic health in children conceived from assisted reproductive technology: a prospective cohort study
To the best of our knowledge, no study has investigated the potential joint effect of large for gestational age (LGA) and assisted reproductive technology (ART) on the long-term health of children.
Learning from sotorasib: risk of bias in confirmatory clinical studies of accelerated approved drugs and resolution strategies
Association of genetic variants related to combined lipid-lowering and antihypertensive therapies with risk of cardiovascular disease: 2 × 2 factorial mendelian randomization analyses.
Lipid-lowering drugs and antihypertensive drugs are commonly combined for cardiovascular disease (CVD). However, the relationship of combined medications with CVD remains controversial. We aimed to explore the...
Single-cell and spatial transcriptomics reveal metastasis mechanism and microenvironment remodeling of lymph node in osteosarcoma
Osteosarcoma (OS) is the most common primary malignant bone tumor and is highly prone to metastasis. OS can metastasize to the lymph node (LN) through the lymphatics, and the metastasis of tumor cells reestabl...
Exploratory biomarker analysis in the phase III L-MOCA study of olaparib maintenance therapy in patients with platinum-sensitive relapsed ovarian cancer
The prospective phase III multi-centre L-MOCA trial (NCT03534453) has demonstrated the encouraging efficacy and manageable safety profile of olaparib maintenance therapy in the Asian (mainly Chinese) patients ...
Learning together for better health using an evidence-based Learning Health System framework: a case study in stroke
In the context of expanding digital health tools, the health system is ready for Learning Health System (LHS) models. These models, with proper governance and stakeholder engagement, enable the integration of ...
Rethinking causal assumptions about maternal BMI, gestational weight gain, and adverse pregnancy outcomes
The aim of this study was to evaluate commonly assumed causal relationships between body mass index (BMI), gestational weight gain (GWG), and adverse pregnancy outcomes, which have formed the basis of guidelin...
Impact of mHealth interventions on maternal, newborn, and child health from conception to 24 months postpartum in low- and middle-income countries: a systematic review
Mobile health (mHealth) technologies have been harnessed in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs) to address the intricate challenges confronting maternal, newborn, and child health (MNCH). This review aspi...
Prevalence of diabetic cardiomyopathy in patients with type 2 diabetes in a large academic medical center
Diabetic cardiomyopathy (DbCM) is characterized by asymptomatic stage B heart failure (SBHF) caused by diabetes-related metabolic alterations. DbCM is associated with an increased risk of progression to overt ...
Modifiable lifestyle factors and lifetime risk of atrial fibrillation: longitudinal data from the Korea NHIS-HealS and UK Biobank cohorts
The reason for higher incidence of atrial fibrillation (AF) in Europe compared with East Asia is unclear. We aimed to investigate the association between modifiable lifestyle factors and lifetime risk of AF in...
Deprescribing of antidepressants: development of indicators of high-risk and overprescribing using the RAND/UCLA Appropriateness Method
Antidepressants are first-line medications for many psychiatric disorders. However, their widespread long-term use in some indications (e.g., mild depression and insomnia) is concerning. Particularly in older ...
Peripheral GFAP and NfL as early biomarkers for dementia: longitudinal insights from the UK Biobank
Peripheral glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) and neurofilament light chain (NfL) are sensitive markers of neuroinflammation and neuronal damage. Previous studies with highly selected participants have sho...
The Healthy Start scheme in England “is a lifeline for families but many are missing out”: a rapid qualitative analysis
Healthy Start (HS) is a government scheme in England, Wales and Northern Ireland that offers a financial payment card and free vitamins to families experiencing low income. Pregnant women and families with chi...
Supplementation with selenium and coenzyme Q 10 in an elderly Swedish population low in selenium — positive effects on thyroid hormones, cardiovascular mortality, and quality of life
Selenium-dependent deiodinases play a central role in thyroid hormone regulation and metabolism. In many European countries, insufficient selenium intake may consequently lead to adverse effects on thyroid fun...
A proposed simplified definition of metabolic syndrome in children and adolescents: a global perspective
Metabolic syndrome (MetS) is becoming prevalent in the pediatric population. The existing pediatric MetS definitions (e.g., the International Diabetes Federation (IDF) definition and the modified National Chol...
Glucose competition between endothelial cells in the blood-spinal cord barrier and infiltrating regulatory T cells is linked to sleep restriction-induced hyperalgesia
Sleep loss is a common public health problem that causes hyperalgesia, especially that after surgery, which reduces the quality of life seriously.
Floods and cause-specific mortality in the UK: a nested case-control study
Floods are the most frequent weather-related disaster, causing significant health impacts worldwide. Limited studies have examined the long-term consequences of flooding exposure.
Histology-specific standardized incidence ratio improves the estimation of second primary lung cancer risk
Lung cancer (LC) survivors are at increased risk for developing a second primary cancer (SPC) compared to the general population. While this risk is particularly high for smoking-related SPCs, the published st...
Driving delivery and uptake of catch-up vaccination among adolescent and adult migrants in UK general practice: a mixed methods pilot study
Migrants in the UK and Europe face vulnerability to vaccine-preventable diseases (VPDs) due to missed childhood vaccines and doses and marginalisation from health systems. Ensuring migrants receive catch-up va...
A randomized controlled trial of an app-based intervention on physical activity and glycemic control in people with type 2 diabetes
We investigated the effects of a physical activity encouragement intervention based on a smartphone personal health record (PHR) application (app) on step count increases, glycemic control, and body weight in ...
The effectiveness of a standardized tobacco cessation program on psychophysiological parameters in patients with addiction undergoing long-term rehabilitation: a quasi-experimental pilot study
Although there is a very high comorbidity between tobacco dependence and other addictive disorders, there are only few studies examining the implementation and outcomes of a tobacco cessation program in patien...
Toward evidence-based communication on overweight body mass index and mortality
Reducing overweight and obesity has been a longstanding focus of public health messaging and physician–patient interactions. Clinical guidelines by major public health organizations describe both overweight an...
Colon impairments and inflammation driven by an altered gut microbiota leads to social behavior deficits rescued by hyaluronic acid and celecoxib
The exact mechanisms linking the gut microbiota and social behavior are still under investigation. We aimed to explore the role of the gut microbiota in shaping social behavior deficits using selectively bred ...
First-trimester fetal size, accelerated growth in utero, and child neurodevelopment in a cohort study
Early pregnancy is a critical window for neural system programming; however, the association of first-trimester fetal size with children’s neurodevelopment remains to be assessed. This study aimed to explore t...
Suicide mortality following the implementation of tobacco packaging and pricing policies in Korea: an interrupted time-series analysis
To prevent tobacco use in Korea, the national quitline number was added to tobacco packages in December 2012, tobacco prices were raised by 80% in January 2015, and graphic health warning labels were placed on...
Correction: Identification of a novel bile marker clusterin and a public online prediction platform based on deep learning for cholangiocarcinoma
The original article was published in BMC Medicine 2023 21 :294
Correction: Autotaxin inhibition attenuates the aortic valve calcification by suppressing inflammation-driven fibro-calcific remodeling of valvular interstitial cells
The original article was published in BMC Medicine 2024 22 :122
Mini-dose methotrexate combined with methylprednisolone for the initial treatment of acute GVHD: a multicentre, randomized trial
There is an urgent unmet need for effective initial treatment for acute graft-versus-host disease (aGVHD) adding to the standard first-line therapy with corticosteroids after allogeneic haematopoietic stem cel...
Long-term assessment of the NHS hybrid closed-loop real-world study on glycaemic outcomes, time-in-range, and quality of life in children and young people with type 1 diabetes
Hybrid closed-loop (HCL) systems seamlessly interface continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) with insulin pumps, employing specialised algorithms and user-initiated automated insulin delivery. This study aimed to...
Osimertinib in combination with anti-angiogenesis therapy presents a promising option for osimertinib-resistant non-small cell lung cancer
Osimertinib has become standard care for epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-positive non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients whereas drug resistance remains inevitable. Now we recognize that the inter...
Efficacy and safety of tislelizumab plus lenvatinib as first-line treatment in patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: a multicenter, single-arm, phase 2 trial
Lenvatinib is widely used in treatment of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (uHCC), but the benefit of its combination with immunotherapy needs to be verified. This study evaluated the efficacy and safety ...
Impact of perioperative low-molecular-weight heparin therapy on clinical events of elderly patients with prior coronary stents implanted > 12 months undergoing non-cardiac surgery: a randomized, placebo-controlled trial
Little is known about the safety and efficacy of discontinuing antiplatelet therapy via LMWH bridging therapy in elderly patients with coronary stents implanted for > 12 months undergoing non-cardiac surgery. ...
A Pfs48/45-based vaccine to block Plasmodium falciparum transmission: phase 1, open-label, clinical trial
The stalling global progress in malaria control highlights the need for novel tools for malaria elimination, including transmission-blocking vaccines. Transmission-blocking vaccines aim to induce human antibod...
- Editorial Team
- Editorial Board
- Call for papers
- Editor’s choice
- Sign up for article alerts and news from this journal
- Manuscript editing services
Annual Journal Metrics
2022 Citation Impact 9.3 - 2-year Impact Factor 10.4 - 5-year Impact Factor 3.011 - SNIP (Source Normalized Impact per Paper) 3.447 - SJR (SCImago Journal Rank)
2023 Speed 6 days submission to first editorial decision for all manuscripts (Median) 145 days submission to accept (Median)
2023 Usage 6,375,113 downloads 24,228 Altmetric mentions
- More about our metrics
Announcements
medRxiv transfers
BMC Medicine is happy to consider manuscripts that have been, or will be, posted on a preprint server. Authors are able to submit their manuscripts directly from medRxiv , without having to re-upload files.
Registered reports
BMC Medicine is accepting Registered Reports. Find out more about this innovative format in our Submission Guidelines .
- Follow us on Twitter
BMC Medicine
ISSN: 1741-7015
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- General enquiries: [email protected]

Design and synthesis of novel factor XIa Inhibitors with bicyclic isoquinoline and naphthalene fragments
A study of alkene disulfonoxylation
- Shyam Sathyamoorthi
- Steven P. Kelley
Exploring nucleoside analogs: key targets in the viral life cycle - advancing strategies against SARS-CoV-2
- Roopal Garg
- Raveen Kumar
- Richa Srivastava
Design and synthesis of benzo[ d ]imidazo-6,7-dihydrobenzo[ d ] imidazo[2,1- b ]thiazol-8(5 H )-ones as potent anti-infective agents
- Rakesh K. Bollikanda
- Yana L. Esaulkova
- Srinivas Kantevari
Design and synthesis of indole-based elipticine analogues as topoisomerase IIβ inhibitors
- Mardia T. El Sayed
- Alaadin E. Sarhan
- Mamdouh M. Ali
Discovery of cytotoxic truncated vitamin D derivatives against both bortezomib‐sensitive and bortezomib‐resistant multiple myeloma phenotypes
- Mohamed O. Radwan
- Mikako Fujita
Correction: Bioassay-guided fractionations of Cannabis sativa extract and HPLC-assisted purifications of anti-proliferative active fractions lead to the isolation of 16 known and one new phytomolecule and their in-silico analysis
- Yedukondalu Nalli
- Sahil Bharti
- Mahendra Kumar Verma
Structural simplification and ester bond flipping lead to bis-benzodioxole derivatives as potential hypolipidemic and hepatoprotective agent
- Yundong Xie
Morpholinated curcuminoids against urinary bladder cancer cells: synthesis and anticancer evaluation
- Pawel Bakun
- Malgorzata Kucinska
- Tomasz Goslinski
Synthesis and in vitro biological activity of chalcone derivatives as potential antiparasitic agents
- Koketso J. Setshedi
- Richard M. Beteck
- Lesetja J. Legoabe
Discovery of HNPC-A188: a novel acaricide containing trifluoroethyl thioether and pyrimidin-4-amine
- Weidong Liu
The emergence of sulfo-click amidation in kinetic target-guided synthesis
- Prakash T. Parvatkar
- Roman Manetsch
Development of semisynthetic saponin immunostimulants
- Hyunjung Kim
- Pengfei Wang

A very promising antibiofilm activity against Candida albicans from an in vitro screening for antimicrobial, antibiofilm and antiproliferative activity of new synthesized 4-cinnamamido- and 2-phenoxyacedamido-1H-pyrazol-5-yl)benzamides
- Fabiana Plescia
- Valentina Catania
- Domenico Schillaci
Candida albicans ergosterol disorders as a consequence of the new sulfone derivative action mode
- Monika Staniszewska
- Michalina Kazek
- Zbigniew Ochal
Naturally occurring and artificially designed antimicrobial peptides: a comparative study of Mastoparan C and BP52
- Hai Bui Thi Phuong
- Huy Luong Xuan
Recent pharmacological insights about imidazole hybrids: a comprehensive review
- Samet Poyraz
- Metin Yıldırım
- Mehmet Ersatir
Synthesis of novel benzothieno-[3,2’- f ][1,3] oxazepines and their isomeric 2-oxo-2 H -spiro[benzothiophene-3,3’-pyrrolines] via 1,4-dipolar cycloaddition reaction and their evaluation as cytotoxic anticancer leads
- Mohammed M. Al-Mahadeen
- Areej M. Jaber
- Mutasem O. Taha
Folate-conjugated organic CO prodrugs: Synthesis and CO release kinetic studies
- Shameer M. Kondengadan
- Shubham Bansal
- Binghe Wang
Structure-activity relationships and pharmacokinetic evaluation of L-cystine diamides as L-cystine crystallization inhibitors for cystinuria
- Haifa Albanyan
- Amrik Sahota
Molecular hybridization method for obtaining paeonol-based fibrate derivatives with potent lipid-lowering and hepatoprotective activity
Role of natural secondary metabolites as HIF-1 inhibitors in cancer therapy
- Prem Shankar Mishra
- Rakhi Mishra
- Samiksha Dewangan
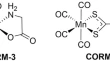
Characterization of the CO release properties of a common CO donor, CORM-401, in the context of its application in studying CO biology
- Nicola Bauer
Antitumor studies on celastrol and its derivatives as RORα agonists and RORγ inhibitors based on Alphafold reverse docking strategy
- Bangwen Yue

Phenoxyalkyl cyclic and acyclic amine derivatives: what do they teach us about scaffold-based drug design?
- Mohammad Mahdi Rezaeifar
- Ardavan Abiri
- Yaghoub Pourshojaei
Synthesis and anticancer activity of novel coumarin-stilbene hybrids with different hydrocarbon chains as linkers
- Lamya A. Al-lehaib
- Ehab M. M. Ali
- Reda M. El-Shishtawy
Vital residues-orientated rational design of butenolide inhibitors targeting Of ChtI
- Yun-Jiang Zi
- Hong-Xia Duan
Design, synthesis and antitumor activity evaluation of novel benzamide HDAC inhibitors
- Yepeng Luan
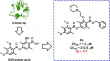
Design, synthesis, and in vitro biological evaluation of novel HDAC inhibitors bearing C-1 phenyl substituted tetrahydroisoquinoline Cap moiety as anti-tumor therapeutic agents
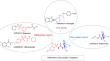
Diffractaic acid and its ethers as anti-respiratory syncytial virus agents
- Aleksandr S. Filimonov
- Diana U. Ismangulova
- Nariman F. Salakhutdinov
Synthesis, urease inhibitory and anticancer evaluation of glucosamine-sulfonylurea conjugates
- Ghadeer A. R. Y. Suaifan
- Mayadah Shehadeh
Motor and non-motor symptoms, drugs, and their mode of action in Parkinson’s disease (PD): a review
- Nancy Saini
- Neetu Singh
- Harvinder Singh Sohal
Evaluation of ortho -substituted Bis-Functionalized Triazoles as Tyrosinase Inhibitors: Modulating Dopamine Synthesis and Behavior in Zebrafish
- Shainaz Landge
- Vinoth Sittaramane
Bioassay-guided fractionations of Cannabis sativa extract and HPLC-assisted purifications of anti-proliferative active fractions lead to the isolation of 16 known and one new phytomolecule and their in-silico analysis
Design, synthesis, and biochemical and computational screening of novel oxindole derivatives as inhibitors of Aurora A kinase and SARS-CoV-2 spike/host ACE2 interaction
- Donatus B. Eni
- Joel Cassel
- Fidele Ntie-Kang
Evolution and challenges of opioids in pain management: Understanding mechanisms and exploring strategies for safer analgesics
- Toluwalope Temitope Bakare
- Henrietta Onyinye Uzoeto
- Olanrewaju Ayodeji Durojaye
Adenine derivatives as inhibitors of the casein kinase CK1delta enzyme
- Andrea Spinaci
- Catia Lambertucci
- Rosaria Volpini
Development of novel chalcone derivatives as multifunctional agents for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease
- Zhipei Sang
2-Styrylchromones as inhibitors of α-amylase and α-glucosidase enzymes for the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus
- Clementina M. M. Santos
- Carina Proença
- Eduarda Fernandes
Synthesis, characterization, and anticancer activity of syringaldehyde-derived chalcones against female cancers
- Qionghui Pan
- Huamao Yang
Synthesis and pharmacological activities of Schiff bases with some transition metal complexes: a review
- Kibrom Mezgebe
- Endale Mulugeta

The use of single-molecule FRET for the characterization of Holliday junctions containing human telomeric DNA: a methodological approach for nanoscale distance, mobility, and stability measurements
- Abeer F. R. Alanazi
- Shozeb Haider
- Gary N. Parkinson
Targeting disease with benzoxazoles: a comprehensive review of recent developments
- Abdulrahman Abdullahi
- Keng Yoon Yeong

Preliminary structure−activity relationships analysis on N-(3,5-dichlorophenyl)-4,5-dihydronaphtho[1,2-d]thiazol-2-amine, a disruptor of mycobacterial energetics
- Miriam Girardini
- Diana Machado
- Marco Pieroni
Insights on synthetic strategies and structure-activity relationship of donepezil and its derivatives
- Saraswati Patel
- Sonika Jain
- Jaya Dwivedi
Identification of novel benzoyl hydrazine derivatives as activators of neddylation pathway to inhibit the tumor progression in vitro
- Sumeng Guan
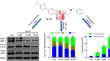
Selectivity of N(2) -substituted oxotriazinoindole aldose reductase inhibitors is determined by the interaction pattern with Pro301-Arg312 loop of aldehyde reductase
- Lucia Kováčiková
- Sunil Gaikwad
- Milan Štefek
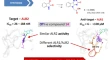
Novel biologically active pyridine derivatives: Synthesis, structure characterization, in vitro antimicrobial evaluation and structure-activity relationship
- Mohamed A. Elsayed
- Alshaimaa M. Elsayed
- Farid M. Sroor
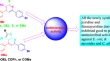
Benzocaine- N -acylindoline conjugates: synthesis and antiviral activity against Coxsackievirus B3
- Alexandrina S. Volobueva
- Anton A. Shetnev
- Sergey V. Baykov
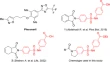
Exploring the latest breakthroughs in rhodesain inhibitors for African trypanosomiasis
- Diego Eidy Chiba
- Guilherme Felipe dos Santos Fernandes
- Cauê Benito Scarim

- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
- Search by keyword
- Search by citation
Page 1 of 503
Associations of psychological factors with atherosclerosis and cardiovascular health in middle-age: the population-based Swedish CArdioPulmonary bioImage study (SCAPIS)
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a major global health issue, primarily caused by atherosclerosis. Psychological factors may play a role in the development and progression of CVD. However, the relationship betw...
- View Full Text
Impact of COVID-19 pandemic responses on tuberculosis incidence: insights from Shantou, China
Various measures taken against the COVID-19 pandemic are not only effective in reducing the spread of the disease, but also lead to some unexpected results. This article regarded these measures as an intervent...
Global burden of pertussis in 204 countries and territories, from 1990 to 2019: results from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019
This study aimed to examine the impact of pertussis on the global, regional, and national levels between 1990 and 2019.
The cross-sectional correlation between the oxidative balance score and cardiometabolic risk factors and its potential correlation with longitudinal mortality in patients with cardiometabolic risk factors
This study analyzes the correlation between oxidative balance score (OBS), cardiometabolic risk factors (CMRFs), and mortality in individuals with CMRFs.
Long-term effects of climate factors on dengue fever over a 40-year period
Dengue fever stands as one of the most extensively disseminated mosquito-borne infectious diseases worldwide. While numerous studies have investigated its influencing factors, a gap remains in long-term analys...
Gender disparities in all-cause mortality among individuals with early-onset cardiovascular diseases
Gender disparities in mortality among individuals with early-onset cardiovascular disease (CVD) remain uncertain. This study aimed to investigate gender differences in all-cause mortality and identify influenc...
Knowledge, attitudes, and practices toward cardiovascular complications among end-stage renal disease patients undergoing maintenance hemodialysis
This study aimed to investigate the knowledge, attitudes, and practices (KAP) toward cardiovascular complications among end-stage renal disease patients undergoing maintenance hemodialysis.
Effort-reward imbalance and common mental disorders among public sector employees of Iran: a cross-sectional analysis
The effort-reward imbalance (ERI) model is a widely used theoretical model to measure stress in the workplace. The objective of this study was to investigate the relationship between ERI and three common menta...
Hospitalization information and burden of pediatric inpatients in transport accidents
Transport accidents are one of the leading causes of child morbidity and mortality worldwide and represent a significant public health burden. This study aimed to investigate the hospitalization information an...
State of mental health, sleep status, and the interaction with health-related quality of life in HIV-infected Chinese patients during the COVID-19 pandemic
To describe how mental health and sleep status influence the health-related quality of life (HRQOL) of people living with HIV/AIDS (PLWHA) during the novel coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, and to ...
Dose-response association of obesity and risk of mental health among tehranian residents: result of a cross-sectional study
Obesity and mental health issues are two of the most prevalent global public health issues for a significant portion of people. The purpose of this study was to investigate the relationship between obesity ind...
Factors associated with depressive symptoms among cancer patients: a nationwide cross-sectional study
Research on factors contributing to depressive symptoms in cancer patients at a national level, encompassing a comprehensive set of variables was limited. This study aimed to address this gap by identifying th...
Situation analysis on the integration of refractive error services provided by optometrists into the national health services in Kenya
Even though the burden of uncorrected refractive error could potentially be addressed through innovative and cost-effective approaches, integration of the services into the National Health Services (NHS) is de...
Work & life stress experienced by professional workers during the pandemic: a gender-based analysis
The COVID-19 pandemic impacted work and home life exacerbating pre-existing stressors and introducing new ones. These impacts were notably gendered. In this paper, we explore the different work and home life r...
Ethnic disparities in complete and partial molar pregnancy incidence: a retrospective analysis of arab and jewish women in single medical center
Molar pregnancies, encompassing complete and partial moles, represent a rare and enigmatic gestational disorder with potential ethnic variations in incidence. This study aimed to investigate relations of ethni...
Does integrated health management within a county medical consortium improve rural type 2 diabetic patients’ self-management behavior and quality of life? An empirical analysis from Eastern China
Levels of self-management behaviors (SMB) and quality of life (QoL) are suboptimal in Chinese adults with type 2 diabetes (T2D), especially in rural China. Integrated health management within a county medical ...
Social contact patterns during the early COVID-19 pandemic in Norway: insights from a panel study, April to September 2020
During the COVID-19 pandemic, many countries adopted social distance measures and lockdowns of varying strictness. Social contact patterns are essential in driving the spread of respiratory infections, and cou...
Survival and disease burden analyses of occupational pneumoconiosis during 1958–2021 in Huangshi city, China: a retrospective cohort study
Pneumoconiosis, a chronic disease stemming from prolonged inhalation of dust particles, stands as a significant global burden of occupational diseases. This study aims to investigate the survival outcomes of p...
Prioritization of ethical concerns regarding HIV molecular epidemiology by public health practitioners and researchers
HIV molecular epidemiology (HIV ME) can support the early detection of emerging clusters of new HIV infections by combining HIV sequence data routinely obtained during the clinical treatment of people living w...
Evaluation of knowledge, attitude, practices and effectiveness of menstrual hygiene interventions in rural schools from Lilongwe, Malawi
Menstrual hygiene management (MHM) is associated with the menstrual process in women and adolescent girls who face cultural and financial challenges in rural areas of many developing countries. As part of the ...
Primary health care challenges: insights from older people with multimorbidity in Malawi – a qualitative study
The global population is undergoing a significant surge in aging leading to increased susceptibility to various forms of progressive illnesses. This phenomenon significantly impacts both individual health and ...
The diabetes mellitus multimorbidity network in hospitalized patients over 50 years of age in China: data mining of medical records
Many diabetes mellitus (DM) patients suffer from multimorbidity. Understanding the DM multimorbidity network should be given priority. The purpose of this study is characterize the DM multimorbidity network in...
The interaction of occupational stress and job burnout on depressive symptoms in railway workers in Fuzhou city
To explore the relationship between occupational stress, burnout and depressive symptoms among railroad workers in Fuzhou, and to analyze the interaction of burnout and occupational stress on depressive symptoms.
Retrospective analysis of mortality among children under 5 years of age in Huangshi over the period 2002–2022, China
The United Nations’ Millennium Development Goals and Sustainable Development Goals both underscore the critical need to reduce the under-five mortality rate globally. China has made remarkable progress in decr...
Effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on the rates of adverse birth outcomes and fetal mortality in Japan: an analysis of national data from 2010 to 2022
Although the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic affected trends of multiple health outcomes in Japan, there is a paucity of studies investigating the effect of the pandemic on adverse birth outcomes ...
Sleep quality mediates the effect of medical social support on depression symptoms in patients with HIV/AIDS
The purpose of our study is to further understanding of the depression symptoms of HIV/AIDS patients in Guilin, Guangxi via exploring whether there is a mediating effect of sleep quality on medical-social supp...
The effect of information provision on consumers’ risk perceptions of, support for a ban, and behavioral intention towards the preventive use of antibiotics in food animals
Antibiotics have been widely used in feed and drinking water for food animals to prevent them from getting sick. Such preventive use of antibiotics has become a contributor to increasing antibiotic resistance ...
Knowledge level and constructs of the theory of planned behaviour (TPB) to the practice of unsafe abortion among postnatal mothers attending Mkonze health center, Dodoma Region, Tanzania
Unsafe abortion is now a global agenda because 45% of all global abortions are unsafe, and 97% are occurring in developing countries. In Tanzania, one million reproductive-aged women face unplanned pregnancies...
Cost-effectiveness of drug consumption rooms in France: a modelling study
People who inject drugs (PWID) experience many health problems which result in a heavy economic and public health burden. To tackle this issue, France opened two drug consumption rooms (DCRs) in Paris and Stra...
An updated scoping review of migrant health research in Ireland
One in five people living in Ireland is a migrant. Understanding the distinctive health needs of this diverse population is essential to provide evidence-based, culturally sensitive primary care services. The ...
The impact of an innovative community-based peer-led intervention on uptake and coverage of sexual and reproductive health services among adolescents and young people 15–24 years old: results from the Yathu Yathu cluster randomised trial
The Yathu Yathu (“For Us, By Us”) cluster-randomized trial (CRT) evaluated a peer-led community-based sexual and reproductive health(SRH) intervention implemented to address persistent barriers to SRH service ...
Epidemiological characteristics of asthma-COPD overlap, its association with all-cause mortality, and the mediating role of depressive symptoms: evidence from NHANES 2005–2018
Asthma-COPD overlap (ACO) is a distinct and intricate respiratory condition that requires specific attention and management. The objective of this cohort study was to examine the epidemiological characteristic...
Utilizing disease transmission and response capacities to optimize covid-19 control in Malaysia
Public Health Social Measures (PHSM) such as movement restriction movement needed to be adjusted accordingly during the COVID-19 pandemic to ensure low disease transmission alongside adequate health system cap...
Socioeconomic inequalities in pandemic-induced psychosocial stress in different life domains among the working-age population
Psychosocial stress is considered a risk factor for physical and mental ill-health. Evidence on socioeconomic inequalities with regard to the psychosocial consequences of the COVID-19 pandemic in Germany is st...
Individual and community-level factors associated with repeat induced abortion among women in Ghana: a multivariable complex sample logistic regression analysis of 2017 Ghana maternal health survey
Repeat induced abortion is a serious public health issue that has been linked to adverse maternal health outcomes. However, knowledge about repeat induced abortion and its associated factors among reproductive...
Existing psychological supportive care interventions for cervical cancer patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Cervical cancer patients commonly experience psychological supportive care needs, necessitating diverse interventions to enhance psychological well-being and alleviate physical symptoms. This systematic review...
Developing and planning country-specific integrated knowledge translation strategies: experiences from the GELA project in Malawi, Nigeria, and South Africa
The G lobal E vidence, L ocal A daptation (GELA) project aims to maximise the impact of research on poverty-related diseases by increasing researchers’ and decision-makers’ capacity to use global research to develop ...
Effectiveness of a community-based participatory health promotion intervention to address knowledge, attitudes and practices related to intimate partner violence: a quasi-experimental study
Intimate partner violence is the most common form of violence experienced by women. It has detrimental consequences. A range of determinants cause intimate partner violence and to reduce it, effective interven...
Correction to: Healthcare-seeking of medical students: the effect of socio-demographic factors, health behaviour and health status – a cross-sectional study in Hungary
The original article was published in BMC Public Health 2023 23 :2126
The effects of mindfulness-based interventions on alleviating academic burnout in medical students: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Mindfulness-based interventions have been tested to be the effective approach for preventing/reducing burnout in medical students. Therefore, this systematic review and meta-analysis aimed to synthesize the sc...
Predictive models for delay in medical decision-making among older patients with acute ischemic stroke: a comparative study using logistic regression analysis and lightGBM algorithm
To explore the factors affecting delayed medical decision-making in older patients with acute ischemic stroke (AIS) using logistic regression analysis and the Light Gradient Boosting Machine (LightGBM) algorit...

Association of parental depression with adolescent children’s psychological well-being and health behaviors
Parental depression is a significant problem that negatively affects parents’ welfare and influences family dynamics, children’s academic and health behaviors, and mental health. However, there is limited evid...
Correction: social media influence on COVID-19 vaccine perceptions among University students: a Malawi case study
The original article was published in BMC Public Health 2024 24 :1312
Effect of capacity building interventions on classroom teacher and early childhood educator perceived capabilities, knowledge, and attitudes relating to physical activity and fundamental movement skills: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Capacity building may play an important role in improving classroom teachers’ and early childhood educators’ (ECE) capacity to implement physical activity and FMS interventions. Capacity building is the develo...
Predicting higher child BMI z-score and obesity incidence in Malaysia: a longitudinal analysis of a dynamic cohort study
To target public health obesity prevention, we need to predict who might become obese i.e. predictors of increasing Body Mass Index (BMI) or obesity incidence. Predictors of incidence may be distinct from more...
Trends in socio-demographic characteristics and substance use among high school learners in a selected district in Limpopo Province, South Africa
Substance use is an escalating public health problem in South Africa resulting in risky behaviours and poor educational attainment among adolescents. There is a huge battle to overcome substance use among lear...
Association of Life's Essential 8 with all-cause mortality and risk of cancer: a prospective cohort study
No study has concentrated on the association of LE8 with cancer risk and death. We aim to examine the association of LE8 with death and cancer.
The effects of cognitive leisure activities on frailty transitions in older adults in China: a CHARLS-Based longitudinal study
In an effort to identify factors associated with frailty transitions that trigger a significant difference in preventing and postponing the progression of frailty, questions regarding the role of cognitive lei...
Assessing trends and burden of occupational exposure to asbestos in the United States: a comprehensive analysis from 1990 to 2019
This study aimed to analyze the trends and burden of occupational exposure to asbestos in the United States (U.S.) from 1990 to 2019, focusing on mortality rates, geographic distribution, age and sex patterns,...
Youth not engaged in education, employment, or training: a discrete choice experiment of service preferences in Canada
Prior research has showed the importance of providing integrated support services to prevent and reduce youth not in education, employment, or training (NEET) related challenges. There is limited evidence on N...
Important information
Editorial board
For authors
For editorial board members
For reviewers
- Manuscript editing services
Annual Journal Metrics
2022 Citation Impact 4.5 - 2-year Impact Factor 4.7 - 5-year Impact Factor 1.661 - SNIP (Source Normalized Impact per Paper) 1.307 - SJR (SCImago Journal Rank)
2023 Speed 32 days submission to first editorial decision for all manuscripts (Median) 173 days submission to accept (Median)
2023 Usage 24,332,405 downloads 24,308 Altmetric mentions
- More about our metrics
Peer-review Terminology
The following summary describes the peer review process for this journal:
Identity transparency: Single anonymized
Reviewer interacts with: Editor
Review information published: Review reports. Reviewer Identities reviewer opt in. Author/reviewer communication
More information is available here
- Follow us on Twitter
BMC Public Health
ISSN: 1471-2458
- General enquiries: [email protected]
Suggestions or feedback?
MIT News | Massachusetts Institute of Technology
- Machine learning
- Social justice
- Black holes
- Classes and programs
Departments
- Aeronautics and Astronautics
- Brain and Cognitive Sciences
- Architecture
- Political Science
- Mechanical Engineering
Centers, Labs, & Programs
- Abdul Latif Jameel Poverty Action Lab (J-PAL)
- Picower Institute for Learning and Memory
- Lincoln Laboratory
- School of Architecture + Planning
- School of Engineering
- School of Humanities, Arts, and Social Sciences
- Sloan School of Management
- School of Science
- MIT Schwarzman College of Computing
Scientists identify mechanism behind drug resistance in malaria parasite
Press contact :.

Previous image Next image
Share this news article on:
Related links.
- Peter Dedon
- Antimicrobial Resistance Interdisciplinary Research Group
- Singapore-MIT Alliance for Research and Technology (SMART)
- Department of Biological Engineering
Related Topics
- Drug resistance
- Antibiotics
- Biological engineering
- Drug development
- International initiatives
- Collaboration
Related Articles

Satellite-based method measures carbon in peat bogs

Newly discovered bacterial communication system aids antimicrobial resistance

SMART launches research group to advance AI, automation, and the future of work

A novel combination therapy counters antibiotic-resistant Mycobacterium abscessus infections
Previous item Next item
More MIT News

Noubar Afeyan PhD ’87 gives new MIT graduates a special assignment
Read full story →

President Sally Kornbluth’s charge to the Class of 2024

Commencement address by Noubar Afeyan PhD ’87

Microscopic defects in ice influence how massive glaciers flow, study shows

Getting to systemic sustainability

New MIT-LUMA Lab created to address climate challenges in the Mediterranean region
- More news on MIT News homepage →
Massachusetts Institute of Technology 77 Massachusetts Avenue, Cambridge, MA, USA
- Map (opens in new window)
- Events (opens in new window)
- People (opens in new window)
- Careers (opens in new window)
- Accessibility
- Social Media Hub
- MIT on Facebook
- MIT on YouTube
- MIT on Instagram
Scientists develop visual tool to help people group foods based on their levels of processing
Fralin Biomedical Research Institute at VTC scientists studying ultra-processed foods have created a new tool for assessing the rewarding and reinforcing properties of foods that make up 58 percent of calories consumed in the United States. The foods have been linked to a wide range of negative health outcomes.
The research, which was published in April in the journal Appetite , provides a collection of carefully curated images of minimally processed and ultra-processed foods matched on 26 characteristics, including macronutrients, sodium, dietary fiber, calories, price, and visual characteristics such as a color and portion size.
The work was based on the NOVA classification system -- "nova" means new in Portuguese -- which groups foods into four categories based on their level of processing. Nutrition researchers at the University of São Paulo in Brazil developed the scale while studying the country's sharp increase in obesity rates.
The scale has its detractors.
"A major criticism of the NOVA scale is that it's difficult to use or that foods are classified differently by different people," said Alexandra DiFeliceantonio, corresponding author and assistant professor at the Fralin Biomedical Research Institute. "We found that people with education in nutrition generally agreed on the food classifications, providing some data that it might not be a valid criticism."
What they did
The NOVA system assigns food to four categories: unprocessed or minimally processed, such as fresh fruit, legumes, or plain yogurt; processed culinary ingredients, such as cooking oils, butter, and salt; processed foods, which combine the two above through simple methods suc as cheese, canned vegetables, or freshly baked bread; and ultra-processed foods, such as soft drinks, flavored yogurt, processed meat, and most packaged breads, made through industrial processing and additives rarely found in a home pantry.
To develop the picture set, a team of psychologists, neuroscientists, and registered dietitians selected foods to represent either minimally processed or ultra-processed foods.
The foods were prepared in a lab, visually represented through professional photography, and controlled for consistency. Researchers also gathered price, food weights, and nutritional information -- calories, macronutrients, sodium, and dietary fiber -- for the food in each image.
Study participants rated images across a range of qualities to generate a final set of 28 pictures matched across 26 characteristics. To objectively measure NOVA classification, researchers recruited 67 nutrition professionals and asked them to classify the foods as minimally or ultra-processed.
"With this food picture set we can start to infer that any differences between food pictures is due to the degree of food processing, and not all these other factors that we know are potentially impactful," said Zach Hutelin, the study's lead author and a Fralin Biomedical Research Institute-based graduate student in the translational biology, medicine and health Ph.D. program.
Why this matters
Ultra-processed foods are linked with increased risk of developing obesity, Type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and cancer. They represent more than half of calories consumed in the United States, Canada, and the United Kingdom and have been identified as a global threat to public health.
"There is very little experimental research on ultra-processed foods, and part of what's been holding us back is better tools for measuring and assessing their effects," said DiFeliceantonio, who is also associate director of the Fralin Biomedical Research Institute's Center for Health Behaviors Research. "The more tools we can provide, the more we can learn."
The Virginia Tech team is making the pictures and associated data accessible through the Virginia Tech Data Repository of the Virginia Tech University Libraries. This will allow scientists to test hypotheses in behavioral economic and neuroimaging studies.
In the DiFeliceantonio lab, the photos are being used with functional MRI to reveal associated brain activity, with the images isolating the effects of food processing from other characteristics.
The study was funded by a National Science Foundation graduate research fellowship, the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases of the National Institutes of Health, and a grant from the Seale Innovation Fund, which supports innovative pilot research projects at the Fralin Biomedical Research Institute. DiFeliceantonio received a grant from the fund to investigate metabolic, neural, and behavioral data to better understand how our brains process nutrient availability and food preference.
- Staying Healthy
- Cholesterol
- Diet and Weight Loss
- Food and Agriculture
- Agriculture and Food
- Food groups
- Mediterranean diet
- Genetically modified food
- Low-carb diets
- Raw food diet
Story Source:
Materials provided by Virginia Tech . Original written by Leigh Anne Kelley. Note: Content may be edited for style and length.
Journal Reference :
- Zach Hutelin, Monica Ahrens, Mary Elizabeth Baugh, Mary E. Oster, Alexandra L. Hanlon, Alexandra G. DiFeliceantonio. Creation and validation of a NOVA scored picture set to evaluate ultra-processed foods. . Appetite , 2024; 198: 107358 DOI: 10.1016/j.appet.2024.107358
Cite This Page :
Explore More
- Extinct Saber-Toothed Cat On Texas Coast
- Some Black Holes Survive in Globular Clusters
- People Altering Decomposition in Waterways
- Historic Iceberg Surges
- Food Groups Based On Level of Processing
- Computer Vision, Machine Learning Aid Driving
- Most Distant Known Galaxy
- A New Dinosaur from Zimbabwe
- The Case of the Missing Black Holes
- Menstrual Periods Arriving Earlier
Trending Topics
Strange & offbeat.
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
Your Health
- Treatments & Tests
- Health Inc.
- Public Health
Plastic junk? Researchers find tiny particles in men's testicles

Researchers have detected microplastics in human testicles. Volodymyr Zakharov/Getty Images hide caption
Researchers have detected microplastics in human testicles.
Whether it's our bloodstream, brain, or lungs, microscopic fragments of plastic seem to turn up every time scientists scour a new corner of the human body.
The male reproductive organs are no exception.
New research published this month finds microplastics can build up in the testicles of humans and dogs — raising more questions about the potential health impacts of these particles.
Animal studies have shown exposure to microplastics can impact sperm quality and male fertility, but scientists are still in the early stages of translating this work to human health.
"Microplastics are everywhere," says Dr. John Yu , a toxicologist in the College of Nursing at the University of New Mexico and lead author of the study. "The quantification of those microplastics in humans is the first step to understanding its potential adverse effects."

For the first time, researchers find microplastics deep in the lungs of living people
When he set out to do the study, Yu didn't expect microplastics would have penetrated the male reproductive system so extensively, given the tight blood-tissue barrier around those organs. To his surprise, the research team unearthed a wide range and heavy concentration of microplastics in the testicles of about two dozen men and close to 50 dogs.
The results may also be relevant to a well-documented global decline in sperm count and other problems related to male fertility. This trend has been linked to a host of environmental and lifestyle factors, including certain endocrine-disrupting chemicals found in plastics.
The growing numbers of studies like this one are "compelling and should be a wake up call for policymakers," says Tracey Woodruff , director of the Environmental Research and Translation for Health Center at the University of California, San Francisco.
How much and what kind of plastics were in the testicles?
This is the largest study to measure how much of these microplastics that permeate the water, food and even air end up in the most intimate recesses of male reproductive anatomy.
It follows a smaller analysis, published last year by a team in China, that detected microplastics in about half a dozen human testicles and in semen.
For the current study, researchers at the University of New Mexico collected the testicles from autopsies of people ranging in age from 16 to 88 and from nearly 50 dogs after they were neutered at local veterinary clinics.
Dogs can function as "sentinel" animals for disease and harmful chemical exposure because they're so embedded in the human environment, plus canine spermatogenesis is more similar to the human process of producing sperm than lab rats, says Yu.

Researchers find a massive number of plastic particles in bottled water
Instead of trying to count each microplastic particle, the researchers were able to quantify the total amount of plastic by dissolving all the biological tissue and separating out the solids.
About 75% of what remained was plastic.
Polyethylene , or PE, made up a large portion of that. It's the most widely used plastic in the world, showing up in packaging, bags and any number of products.
Matthew Campen , who has examined these tiny particles up close, describes them as "shard-like, stabby bits" because of the way they've become "old and brittle and fragmented."
"What they do in the body, we don't know," says Campen, a professor at the UNM College of Pharmacy and one of the authors of the study, "Obviously, little tiny particles can disrupt the way cells behave."
Polyvinyl chloride — what's in PVC piping — emerged as another prominent culprit and was the second most common in the dog testicles. Vinyl chloride is classified as a carcinogen and long-term exposure, for example in drinking water, can increase the risk of cancer.
What's more, Yu and his team found a correlation between lower sperm count in the dog testicles and the presence of PVC (the analysis couldn't be done on the human samples because of how they had been stored).
There was also an association between greater levels of PVC and decreased weight of the testicles. The same was seen with Polyethylene terephthalate , or PET, another common source of plastic, which recent research suggests may be harmful.
Woodruff says weight is a somewhat "crude" marker for the effects on testicular health, although it's frequently used by regulatory agencies to evaluate the impacts of chemicals.
Implications?
The research comes with many caveats and cannot prove microplastics directly cause problems with male fertility. Nonetheless, Yu says the results are "concerning" and lay the foundation for more targeted studies on the "relationship between microplastic exposure and its potential impact on sperm."
An emerging body of evidence suggests microplastics can have toxic effects on reproductive health .
In a 2022 review of the evidence for the state of California, Woodruff and her colleagues concluded that microplastics were "suspected" to harm sperm quality and testicular health, but she says that may soon tip over from "suspected" to "likely" because more high-quality studies are being published.
"In the history of looking at chemical or environmental health issues, at the beginning you see these indicators of health harms and then those that have some type of evidence behind them just tend to grow," says Woodruff, "I anticipate we're just going to see more health harms from these microplastics."
In the University of New Mexico study, the concentration of microplastics in human testicles was on average three times higher than in dogs.
Campen says there are still many unknowns, like what specific concentration would pose a threat to health, or how that might vary depending on the kind of microplastic or where they accumulate in the body.
"We're just at the tip of the iceberg," says Campen, who has used this same technique to quantify the levels of microplastics in other tissues and organs.
The amount in the testicles is considerably higher than what was discovered in placenta, and second to what they observed in the brain, says Yu.
Exactly how the microplastics are making their way into the testicles requires further study. Campen suspects they could be "hitchhiking" through the gut via tiny fat particles that get metabolized and then fan out across the body.
It's plausible the build-up of microplastics in the testicles could affect reproductive health in any number of ways. Yu says microplastics could physically disrupt spermatogenesis, mess with the barrier between the testicles, or be a vehicle for harmful chemicals.
They could lead to inflammation and cause oxidative stress, which down the road might affect fertility, says Dr. Sarah Krzastek , a urologist at Virginia Commonwealth University.
"It's probably one more piece of the puzzle of things that are contributing to declines in male fertility over the years as these environmental exposures keep accumulating," she says, "We don't know the clinical ramifications of that yet."
Richard Lea , a reproductive biologist at the University of Nottingham, calls the findings "alarming."
"Having something unnatural like that in the testes is not particularly good news for good reproductive health," says Lea.
In his lab, Lea has found that exposure to phthalates , which are chemicals that can leach from plastics, can reduce the ability of sperm to swim and increase the fragmentation of DNA in the sperm head. This is one likely contributor to the decline in sperm quality in household dogs over the last several decades, a trend that mirrors what's seen in humans.
Of course, the testicles are just one part of the male reproductive system.
Lea says there's now research showing these chemical contaminants can affect the hormonal control of reproduction, at different levels in the body, including in the brain.
How to study a substance that is ubiquitous
Dr. Shanna Swan , a reproductive epidemiologist who has documented the global decline in sperm count, says she's concerned about the accumulation of microplastics. But it's not yet clear finding them in the testicles rather than other parts of the body is more worrisome from the standpoint of reproductive health.
For example in her work, she's looked at how prenatal exposure to endocrine-disrupting chemicals like phthalates can affect male reproductive function and "lead to lifetime of reproductive damage."
Swan says a limitation running through many of the recent studies on microplastics is that the samples may be inadvertently exposed to microplastics in the environment and that leads to skewed impressions of what was actually present in the person.
She notes there were similar quality control issues nearly a quarter century ago when scientists first started measuring phthalates in human tissues.
"I think there have to be a lot of caveats saying this is really the beginning," says Swan, a professor at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, "It's suggestive, it's important, and it's preliminary."
The University of New Mexico researchers developed a quality control process to protect the samples from being accidentally exposed to microplastics as much as possible. Campen says there's so much plastic in the human body, the amount that might contaminate the samples is "trivial."
More broadly, though, he acknowledges the field faces some huge challenges moving forward — especially as they try to draw a stronger link between these tiny particles and a decline in reproductive health or disease.
"A lot of the problem is they're so ubiquitous. There are no proper controls anymore. Right? Everybody's exposed," he says.
- men's reproductive health
- plastic pollution
- microplastics
- reproductive health
- endocrine disrupters
- Mission, Facts and Figures
- Deans, Chairs and Staff
- Leadership Council
- Dean in the News
- Get Involved
- DEIB Mission
- Message from DEIB Associate Dean
- News and Media
- Reading Lists
- The Yale and Slavery Research Project
- Photo Gallery
- Winslow Medal
- Coat of Arms & Mace
- $50 Million Challenge
- For Pandemic Prevention and Global Health
- For Understanding the Health Impacts of Climate Change
- For Health Equity and Justice
- For Powering Health Solutions through Data Science
- For Future Leaders
- For Faculty Leaders
- For Transformational Efforts
- Data, Leadership, and Collaboration at the School of Public Health
- An abiding love for Yale turns into a lasting gift – in 15 minutes
- Endowed Professorship Created at Critical Time for Yale School of Public Health
- Brotherly encouragement spurs gift to support students
- Prestipino creates opportunities for YSPH students, now and later
- Alumna gives back to the school that “opened doors” in male-dominated field
- For Public Health, a Broad Mission and a Way to Amplify Impact
- Couple Endows Scholarship to Put Dreams in Reach for YSPH Students
- A Match Made at YSPH
- A HAPPY Meeting of Public Health and the Arts
- Generous Gift Bolsters Diversity & Inclusion
- Alumni Donations Aid Record Number of YSPH Students
- YSPH’s Rapid Response Fund Needs Donations – Rapidly
- Podiatric Medicine and Orthopedics as Public Health Prevention
- Investing in Future Public Health Leaders
- Support for Veterans and Midcareer Students
- Donor Eases Burden for Policy Students
- A Personal Inspiration for Support of Cancer Research
- Reducing the Burden of Student Debt
- Learning About Global Health Through Global Travel
- A Meeting in Dubai, and a Donation to the School
- Rapid Response Fund
- Planned Giving
- Testimonials
- Faculty, Postdoc Jobs
- For the Media
- Issues List
- PDF Issues for Download
- Editorial Style Guide
- Social Media
- Shared Humanity Podcast
- Health & Veritas Podcast
- Accreditation
- Faculty Directory by Name
- Career Achievement Awards
- Annual Research Awards
- Teaching Spotlights
- Biostatistics
- Chronic Disease Epidemiology
- Climate Change and Health Concentration
- Environmental Health Sciences
- Epidemiology of Microbial Diseases
- Global Health
- Health Policy and Management
- Maternal and Child Health Promotion Track
- Public Health Modeling Concentration
- Regulatory Affairs Track
- Social & Behavioral Sciences
- U.S. Health Justice Concentration
- Why Public Health at Yale
- Events and Contact
- What Does it Take to be a Successful YSPH Student?
- How to Apply and FAQs
- Incoming Student Gateway
- Traveling to Yale
- Meet Students and Alumni
- Past Internship Spotlights
- Student-run Organizations
- MS and PhD Student Leaders
- Staff Spotlights
- Life in New Haven
- Libraries at Yale
- The MPH Internship Experience
- Practicum Course Offerings
- Summer Funding and Fellowships
- Downs Fellowship Committee
- Stolwijk Fellowship
- Climate Change and Health
- Career Management Center
- What You Can Do with a Yale MPH
- MPH Career Outcomes
- MS Career Outcomes
- PhD Career Outcomes
- Employer Recruiting
- Tuition and Expenses
- External Funding and Scholarships
- External Fellowships for PhD Candidates
- Alumni Spotlights
- Bulldog Perks
- Stay Involved
- Board of Directors
- Emerging Majority Affairs Committee
- Award Nomination Form
- Board Nomination Form
- Alumni Engagement Plus
- Mentorship Program
- The Mentoring Process
- For Mentors
- For Students
- Recent Graduate Program
- Transcript and Verification Requests
- Applied Practice and Student Research
- Competencies and Career Paths
- Applied Practice and Internships
- Student Research
- Seminar and Events
- Competencies and Career paths
- Why the YSPH Executive MPH
- Message from the Program Director
- Two-year Hybrid MPH Schedule
- The Faculty
- Student Profiles
- Newsletter Articles
- Approved Electives
- Physicians Associates Program
- Joint Degrees with International Partners
- MS in Biostatistics Standard Pathway
- MS Implementation and Prevention Science Methods Pathway
- MS Data Sciences Pathway
- Internships and Student Research
- Competencies
- Degree Requirements - Quantitative Specialization
- Degree Requirements - Clinical Specialization
- Degree Requirements- PhD Biostatistics Standard Pathway
- Degree Requirements- PhD Biostatistics Implementation and Prevention Science Methods Pathway
- Meet PhD Students in Biostatistics
- Meet PhD Students in CDE
- Degree Requirements and Timeline
- Meet PhD Students in EHS
- Meet PhD Students in EMD
- Meet PhD Students in HPM
- Degree Requirements - PhD in Social and Behavioral Sciences
- Degree Requirements - PhD SBS Program Maternal and Child Health Promotion
- Meet PhD Students in SBS
- Differences between MPH and MS degrees
- Academic Calendar
- Translational Alcohol Research Program
- Molecular Virology/Epidemiology Training Program (MoVE-Kaz)
- For Public Health Practitioners and Workforce Development
- Course Description
- Instructors
- Registration
- Coursera Offerings
- Non-degree Students
- International Initiatives & Partnerships
- NIH-funded Summer Research Experience in Environmental Health (SREEH)
- Summer International Program in Environmental Health Sciences (SIPEHS)
- 2022 Student Awards
- APHA Annual Meeting & Expo
- National Public Health Week (NPHW)
- Leaders in Public Health
- YSPH Dean's Lectures
- The Role of Data in Public Health Equity & Innovation Conference
- Innovating for the Public Good
- Practice- and community-based research and initiatives
- Practice and community-based research and initiatives
- Activist in Residence Program
- Publications
- Health Care Systems and Policy
- Heart Disease and Stroke
- Panels, Seminars and Workshops (Recordings)
- Rapid Response Fund Projects
- SalivaDirect™
- Emerging Infections Program - COVID-NET
- Public Health Modeling Unit Projects
- HIV-AIDS-TB
- The Lancet 2023 Series on Breastfeeding
- 'Omics
- News in Biostatistics
- Biostatistics Overview
- Seminars and Events
- Seminar Recordings
- Statistical Genetics/Genomics, Spatial Statistics and Modeling
- Causal Inference, Observational Studies and Implementation Science Methodology
- Health Informatics, Data Science and Reproducibility
- Clinical Trials and Outcomes
- Machine Learning and High Dimensional Data Analysis
- News in CDE
- Nutrition, Diabetes, Obesity
- Maternal and Child Health
- Outcomes Research
- Health Disparities
- Women's Health
- News in EHS
- EHS Seminar Recordings
- Climate change and energy impacts on health
- Developmental origins of health and disease
- Environmental justice and health disparities
- Enviromental related health outcomes
- Green chemistry solutions
- Novel approaches to assess environmental exposures and early markers of effect
- 1,4 Dioxane
- Reproducibility
- Tissue Imaging Mass Spectrometry
- Alcohol and Cancer
- Olive Oil and Health
- Lightning Talks
- News in EMD
- Antimicrobial Resistance
- Applied Public Health and Implementation Science
- Emerging Infections and Climate Change
- Global Health/Tropical Diseases
- HIV and Sexually Transmitted Infections
- Marginalized Population Health & Equity
- Pathogen Genomics, Diagnostics, and Molecular Epidemiology
- Vector-borne and Zoonotic Diseases
- Disease Areas
- EMD Research Day
- News in HPM
- Health Systems Reform
- Quality, Efficiency and Equity of Healthcare
- Substance Abuse and Mental Health
- Modeling: Policy, Operations and Disease
- Pharmaceuticals, Vaccines and Medical Devices
- Health and Wellbeing
- News in SBS
- Aging Health
- Community Engagement
- Health Equity
- Mental Health
- Reproductive Health
- Sexuality and Health
- Nutrition, Exercise
- Stigma Prevention
- Community Partners
- For Public Health Practitioners
- Reports and Publications
- Fellows Stipend Application
- Agency Application
- Past Fellows
- PHFP in the News
- Frequently Asked Questions
- International Activity
- Research Publications
- Grant Listings
- Modeling Analyses
- 3 Essential Questions Series
INFORMATION FOR
- Prospective Students
- Incoming Students
- myYSPH Members
2024 Top Research Awards Announced
Yale School of Public Health (YSPH) Associate Dean of Research Melinda Irwin Wednesday announced the recipients of this year’s top research awards.
“Congratulations to the YSPH faculty who were awarded YSPH Research Prizes for manuscripts published in 2023,” said Irwin, Susan Dwight Bliss Professor of Epidemiology (Chronic Diseases). “YSPH faculty published more than 1,100 papers in 2023, and these six papers were recognized for their novel approaches and significant findings, focused on critically important public health issues (e.g., opioid use disorder, environmental carcinogens, breastfeeding) using novel methods and approaches such as electronic medical record data of health outcomes linked to residential addresses’ drinking water supplies and incubating colorectal cancer organoids with PFAS resulting in expression of metastasis-related proteins. “
Here is a list of this year’s award winners:
YSPH Early Career Investigator Research Prize
Liew, Z., Meng, Q., Yan, Q., Schullehner, J., Hansen, B., Kristiansen, S. M., Voutchkova, D. D., Olsen, J., Ersbøll, A. K., Ketzel, M., Raaschou-Nielsen, O., & Ritz, B. R. (2023). Association Between Estimated Geocoded Residential Maternal Exposure to Lithium in Drinking Water and Risk for Autism Spectrum Disorder in Offspring in Denmark. JAMA Pediatrics .
Dr. Liew and his team conducted a nationwide nested case-control study using medical records to capture ASD diagnoses in Denmark, and then created a model to estimate lithium levels in drinking water supplies linked to every residential address in Denmark. They are the first to report a novel association between maternal exposure to lithium in drinking water and child ASD. The study findings have been widely reported in the media, including the New York Times, CNN, and NBC.
YSPH Investigator Research Prize
Yize Zhao, Changgee Chang, Jingwen Zhang & Zhengwu Zhang. Genetic Underpinnings of Brain Structural Connectome for Young Adults . Journal of the American Statistical Association .
With the primary goal of her paper to uncover genetic underpinnings to brain structural connectome variations among young adult populations, Dr. Zhao developed an innovative Bayesian analytical framework and identified genetic biomarkers and validated the reliability of these scientific findings with an external database. The developed methods are readily applicable for use in biobanks and brain imaging genetic landmark studies, which offers a great potential for understanding the genetic bases and directing intervention targets for neurological and psychiatric research for public health outcomes.
YSPH Team Science Prize
Robert Heimer and Lauretta Grau from YSPH
Receipt of opioid use disorder treatments prior to fatal overdoses and comparison to no treatment in Connecticut, 2016–17 . Heimer R, Black AC, Lin H, Grau LE, Fiellin DA, Howell BA, Hawk K, D’Onofrio G, Becker WC. Drug and Alcohol Dependence .
Dr. Heimer and team compiled and merged state agency data on opioid overdose deaths and exposures to opioid use disorder treatment to determine incidence rates following exposure to different treatment modalities. Exposure to treatment reduced the relative risk by 38% compared to non-medication treatment. These findings have been presented to statewide advisory boards, and in February Dr. Heimer presented the results at the federal level to an interagency group convened by the Office of National Drug Control Policy, with the goal of expanding access to OUD treatment.
Caroline Johnson and other YSPH faculty members Krystal Pollitt and Lingeng Lu
Zheng, J., Sun, B., Berardi, D., Lu, L., Yan, H., Zheng, S., Aladelokun, O., Xie, Y., Cai, Y., Godri Pollitt, K. J., Khan, S. A., & Johnson, C. H. (2023). Perfluorooctanesulfonic Acid and Perfluorooctanoic Acid Promote Migration of Three-Dimensional Colorectal Cancer Spheroids . Environmental Science & Technology .
PFAS are widespread environmental contaminants that accumulate in the environment and body, and are found in man-made products such as cosmetics, cookware, food packaging, and carpets. Even though PFAS have been linked to cancer, and recently classified as Group 1 carcinogens, there has been limited research on the effects of these chemicals in colorectal cancer (CRC). Dr. Caroline Johnson and her team found that when CRC human organoids are incubated with occupational exposure levels of PFOS, they exhibit increased motility and expression of metastasis-related proteins. Their study was the first to show that PFAS can elicit a metastatic phenotype in CRC cells when PFAS were at levels comparable to those seen in the blood of those occupationally exposed, such as firefighters.
YSPH Impact Research Prize
Rafael Pérez-Escamilla
Rafael Pérez-Escamilla, Cecília Tomori, Sonia Hernández-Cordero, Phillip Baker, Aluisio J D Barros, France Bégin, Donna J Chapman, Laurence M Grummer-Strawn, David McCoy, Purnima Menon, Paulo Augusto Ribeiro Neves, Ellen Piwoz, Nigel Rollins, Cesar G Victora, Linda Richter, on behalf of the 2023 Lancet Breastfeeding Series Group* Breastfeeding: crucially important, but increasingly challenged in a market-driven world . Lancet .
This article has been cited over 140 times since it was published in February 2023. The article involved scholars from around the world working together for over two years updating the evidence on breastfeeding benefits, and evidence-based approaches to protect, promote, and support breastfeeding on a large scale, heavily considering the economic, social, political, and commercial determinants of infant feeding. The article is based on a strong and innovative conceptual framework and is informed by original data analyses of large epidemiological studies, as well as eight systematic reviews and one meta-analysis commissioned by the World Health Organization. This work is already having a strong impact in reshaping breastfeeding initiatives, policies, and programs across the globe.
David Paltiel and Gregg Gonsalves
Paltiel AD, Ahmed AR, Jin EY, McNamara M, Freedberg KA, Neilan AM, and Gonsalves GS. Increased HIV transmissions with reduced insurance coverage for HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis: Potential consequences of Braidwood Management v. Becerra . Open Forum Infectious Diseases
This study evaluates the potential public health consequences of a recent U.S. federal court ruling that deemed it unconstitutional for the Affordable Care Act to require employers to cover HIV prevention with pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP). The authors found that this ruling could result in more than 2,000 preventable HIV infections in the coming year alone. In the 24 hours following publication, the paper achieved an Altimetric score of 149. It received widespread national attention, including coverage in the New York Times, the Boston Globe, and the American Journal of Managed Care. The paper was selected as a Best of 2023 by the editors-in-chief of the journals of the Infectious Disease Society of America. Their paper was the central analytic element of several friend-of-the-court (amicus) briefs filed with the U.S. Court of Appeals for the Fifth Circuit, urging reversal of the lower court ruling, including the HIV Medicine Association and National Alliance of State and Territorial AIDS Directors, the American Public Health Association, the Yale Law School, and others.
- Recognitions
Featured in this article
- Melinda Irwin, PhD, MPH Associate Dean of Research and Susan Dwight Bliss Professor of Epidemiology (Chronic Diseases); Deputy Director (Public Health), Yale Center for Clinical Investigation; Deputy Director, Yale Cancer Center
- Zeyan Liew, PhD, MPH Assistant Professor of Epidemiology (Environmental Health)
- Yize Zhao, PhD Associate Professor of Biostatistics
- Robert Heimer, PhD Professor of Epidemiology (Microbial Diseases) and of Pharmacology; Affiliated Faculty, Yale Institute for Global Health
- Lauretta Grau, PhD Research Scientist in Epidemiology (Microbial Diseases)
- Caroline Helen Johnson, PhD Associate Professor of Epidemiology (Environmental Health Sciences)
- Krystal Pollitt, PhD, P.Eng. Associate Professor of Epidemiology (Environmental Health); Affiliated Faculty, Yale Institute for Global Health
- Lingeng Lu, MD, PhD Research Scientist in Epidemiology (Chronic Diseases)
- Rafael Pérez-Escamilla, PhD Professor of Public Health (Social and Behavioral Sciences); Director, Office of Public Health Practice; Affiliated Faculty, Yale Institute for Global Health; Director, YSPH Global Health Concentration; Director, Maternal and Child Health Promotion (MCHP) Program
- A. David Paltiel, MBA, PhD Professor of Public Health (Health Policy), Professor of Management, and Professor in the Institution for Social and Policy Studies; Co-director, Public Health Modeling Concentration; Affiliated Faculty, Yale Institute for Global Health
- Gregg Gonsalves, PhD Associate Professor of Epidemiology (Microbial Diseases); Associate (Adjunct) Professor of Law, Yale Law School; Affiliated Faculty, Program in Addiction Medicine; Co-Director, Global Health Justice Partnership; Affiliated Faculty, Yale Institute for Global Health
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Cannabis Tops Alcohol as Americans’ Daily Drug of Choice
A new study shows a growing number of people are regularly using cannabis, while frequent alcohol consumption has remained stable.

By Christina Caron
For the first time on record, cannabis has outpaced alcohol as the daily drug of choice for Americans.
In 2022 there were 17.7 million people who reported using cannabis either every day or nearly every day, compared with 14.7 million who reported using alcohol with the same frequency, according to a study, published on Wednesday in the journal Addiction that analyzed data from the U.S. National Survey on Drug Use and Health.
While far more people drink than use cannabis, drinking frequently has become slightly less common than it was around 15 years ago, the study found. But the proportion of people in the U.S. who use cannabis frequently has increased 15-fold in the three decades since 1992, when daily cannabis use hit a low point.
Cannabis legalization has also rapidly accelerated since the ’90s. The drug is now legal for recreational use in 24 states and Washington, D.C. , and for medical use in 38 states and D.C.
The sharp increase in the prevalence of high-frequency cannabis use over the last three decades might partly be attributed to a growing acceptance of the drug, said Jonathan P. Caulkins, a professor of public policy at Heinz College at Carnegie Mellon University. And because the survey data was self-reported, people may now feel more comfortable disclosing how often they use it.
Even so, “I don’t think that for most daily or near-daily users it is a health-promoting activity,” he added. “For some, it’s truly harmful.”
Several experts who were not involved in the research said the study’s findings were concerning. Those in favor of legalizing cannabis have argued that making the drug widely available would draw people away from the harms of alcohol, said Beatriz Carlini, a research associate professor in the psychiatry department of the University of Washington in Seattle.
But the study’s data, which shows only a slight decline in frequent alcohol use, suggests this has not been the case.
“It is disheartening,” she said.
Dr. Carlini and others noted that the concentrations of THC, the psychoactive component in marijuana, have increased dramatically over the years.
In 1995, the concentration of THC in cannabis samples seized by the Drug Enforcement Administration was about 4 percent. By 2021, it was about 15 percent . And now cannabis manufacturers are extracting THC to make oils, edibles, wax, sugar-size crystals and glass-like products called shatter with THC levels that can exceed 95 percent.
In the last decade , research has shown that frequent cannabis use — and particularly the use of high-potency products with levels of THC greater than 10 percent — is a risk factor for the onset of schizophrenia and other psychotic disorders.
“But that isn’t to say that use less frequent — monthly or yearly — is necessarily safe,” said Dr. Michael Murphy, an assistant professor of psychiatry at Harvard Medical School and a psychiatrist at McLean Hospital in Belmont, Mass.
“As we see higher rates of cannabis use in young people, I expect to see higher rates of psychotic disorders,” he said.
The risks of developing psychotic symptoms are higher for those who use cannabis before age 25, people who use it frequently, those with a genetic predisposition (for example, a parent or sibling with a psychotic disorder) or individuals who experienced stressful events like abuse, poverty or neglect during childhood.
In states that have legalized cannabis for recreational use, anyone 21 and over can purchase it.
Those who use cannabis frequently are also at risk of developing cannabis addiction as well as cannabinoid hyperemesis syndrome, a condition that causes recurrent vomiting, the experts said.
This latest study arrives on the heels of the Biden administration’s move last week to downgrade marijuana from the most restrictive category of drugs, known as Schedule I, to Schedule III, which includes drugs thought to have a low-to-moderate risk of abuse.
The survey did not collect information about the concentrations of THC in the products purchased by frequent users or note how often the respondents used cannabis each day.
“A lot of people go home and have a vape after work or take a gummy to go to sleep at night,” said Aaron Smith, the co-founder and chief executive of the National Cannabis Industry Association. He didn’t see that kind of casual daily use as a problem, he added.
At the same time, there may be young people who are using throughout the day “and are exposing themselves to a lot more THC than those people who are just taking a puff a day,” said Ziva D. Cooper, the director of the Center for Cannabis and Cannabinoids at the University of California, Los Angeles. “The mental health and the physical health outcomes are probably going to vary drastically when you look at those different groups of people.”
Christina Caron is a Times reporter covering mental health. More about Christina Caron
U.S. Girls Are Beginning Periods Earlier
By Dennis Thompson HealthDay Reporter

WEDNESDAY, May 29, 2024 (HealthDay News) -- U.S. girls are getting their periods at younger ages, a new study has found.
Girls born between 2000 and 2005 started their periods at an average age of 11.9 years -- a half year earlier than the average age of 12.5 years for girls born between 1950 and 1969, researchers reported May 29 in the journal JAMA Network Open .
The latest generation was also more likely to start menstruation early (15.5% versus 8.6%) and very early (1.4% versus 0.6%), results show.
Early onset of menstruation “is associated with higher risk of adverse health outcomes, such as cardiovascular disease and cancer,” said researcher Zifan Wang , a postdoctoral research fellow with the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health in Boston.
U.S. Cities With the Most Homelessness

The researchers found that all women are experiencing earlier menstruation, but that those who are poor or a racial minority were even more likely to start their periods at a younger age.
“To address these health concerns -- which our findings suggest may begin to impact more people, with disproportionate impact on already disadvantaged populations -- we need much more investment in menstrual health research,” Wang said.
For the study, researchers analyzed data on more than 71,000 women participating in a large-scale health study. The researchers divided the women into five age brackets: born between 1950-1969, 1970-1979, 1980-1989, 1990-1999 and 2000-2005.
A girl’s first menstrual period was defined as early if it occurred before age 11, very early if it occurred younger than age 9 and late if it came at age 16 or older.
Researchers found that as birth year increased, the average age of a girl’s first period decreased.
They also found it is taking girls longer for their menstrual cycle to become regular.
A girl’s weight appears to partially explain why periods are starting earlier, researchers said. In other words, childhood obesity -- already known to be a risk factor for early puberty -- could be contributing to earlier menstruation.
Other possible explanations include dietary patterns, stress, adverse childhood experiences and environmental factors like air pollution and chemicals that disrupt hormones.
More information
The Office on Women’s Health has more about menstrual cycles .
SOURCE: Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, news release, May 29, 2024
Copyright © 2024 HealthDay . All rights reserved.
Join the Conversation
Tags: women's health
America 2024

Health News Bulletin
Stay informed on the latest news on health and COVID-19 from the editors at U.S. News & World Report.
Sign in to manage your newsletters »
Sign up to receive the latest updates from U.S News & World Report and our trusted partners and sponsors. By clicking submit, you are agreeing to our Terms and Conditions & Privacy Policy .
You May Also Like
The 10 worst presidents.
U.S. News Staff Feb. 23, 2024

Cartoons on President Donald Trump
Feb. 1, 2017, at 1:24 p.m.

Photos: Obama Behind the Scenes
April 8, 2022

Photos: Who Supports Joe Biden?
March 11, 2020

Key Reactions to Trump’s Guilty Verdict
Lauren Camera and Laura Mannweiler May 30, 2024

Trump's Convicted: What's Next?
Lauren Camera May 30, 2024

Trump Guilty in Historic Trial

What to Know: Human Cases of Bird Flu
Cecelia Smith-Schoenwalder May 30, 2024

How’s Biden Doing With Young Voters?

Q1 Economic Growth Revised Downward
Tim Smart May 30, 2024

An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List

Benefits and harms of medical cannabis: a scoping review of systematic reviews
Misty pratt.
1 Knowledge Synthesis Group, Ottawa Methods Centre, Ottawa Hospital Research Institute, The Ottawa Hospital, General Campus, 501 Smyth Road, Ottawa, Ontario K1H 8 L6 Canada
Adrienne Stevens
2 TRIBE Graduate Program, University of Split School of Medicine, Split, Croatia
Micere Thuku
Claire butler.
3 Department of Pharmacology and Therapeutics, McGill University, Montreal, Quebec H3A 2B4 Canada
Becky Skidmore
4 Ottawa, Canada
L. Susan Wieland
5 Center for Integrative Medicine, University of Maryland School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD USA
Mark Clemons
6 School of Epidemiology and Public Health, University of Ottawa, 451 Smyth Road, Ottawa, Ontario K1H 8 M5 Canada
7 Division of Medical Oncology and Department of Medicine, University of Ottawa, Ottawa, Canada
Salmaan Kanji
8 Department of Pharmacy, The Ottawa Hospital, Ottawa, Canada
9 Clinical Epidemiology Program, The Ottawa Hospital Research Institute, Ottawa, Canada
Brian Hutton
Associated data.
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article (and its supplementary information files).
There has been increased interest in the role of cannabis for treating medical conditions. The availability of different cannabis-based products can make the side effects of exposure unpredictable. We sought to conduct a scoping review of systematic reviews assessing benefits and harms of cannabis-based medicines for any condition.
A protocol was followed throughout the conduct of this scoping review. A protocol-guided scoping review conduct. Searches of bibliographic databases (e.g., MEDLINE®, Embase, PsycINFO, the Cochrane Library) and gray literature were performed. Two people selected and charted data from systematic reviews. Categorizations emerged during data synthesis. The reporting of results from systematic reviews was performed at a high level appropriate for a scoping review.
After screening 1975 citations, 72 systematic reviews were included. The reviews covered many conditions, the most common being pain management. Several reviews focused on management of pain as a symptom of conditions such as multiple sclerosis (MS), injury, and cancer. After pain, the most common symptoms treated were spasticity in MS, movement disturbances, nausea/vomiting, and mental health symptoms. An assessment of review findings lends to the understanding that, although in a small number of reviews results showed a benefit for reducing pain, the analysis approach and reporting in other reviews was sub-optimal, making it difficult to know how consistent findings are when considering pain in general. Adverse effects were reported in most reviews comparing cannabis with placebo (49/59, 83%) and in 20/24 (83%) of the reviews comparing cannabis to active drugs. Minor adverse effects (e.g., drowsiness, dizziness) were common and reported in over half of the reviews. Serious harms were not as common, but were reported in 21/59 (36%) reviews that reported on adverse effects. Overall, safety data was generally reported study-by-study, with few reviews synthesizing data. Only one review was rated as high quality, while the remaining were rated of moderate ( n = 36) or low/critically low ( n = 35) quality.
Conclusions
Results from the included reviews were mixed, with most reporting an inability to draw conclusions due to inconsistent findings and a lack of rigorous evidence. Mild harms were frequently reported, and it is possible the harms of cannabis-based medicines may outweigh benefits.
Systematic review registration
The protocol for this scoping review was posted in the Open Access ( https://ruor.uottawa.ca/handle/10393/37247 ).
Interest in medical applications of marijuana ( Cannabis sativa ) has increased dramatically during the past 20 years. A 1999 report from the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine supported the use of marijuana in medicine, leading to a number of regulatory medical colleges providing recommendations for its prescription to patients [ 1 ]. An updated report in 2017 called for a national research agenda, improvement of research quality, improvement in data collection and surveillance efforts, and strategies for addressing barriers in advancing the cannabis agenda [ 2 ].
Proponents of medical cannabis support its use for a highly varied range of medical conditions, most notably in the fields of pain management [ 3 ] and multiple sclerosis [ 4 ]. Marijuana can be consumed by patients in a variety of ways including smoking, vaporizing, ingesting, or administering sublingually or rectally. The plant consists of more than 100 known cannabinoids, the main ones of relevance to medical applications being tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD) [ 5 ]. Synthetic forms of marijuana such as dronabinol and nabilone are also available as prescriptions in the USA and Canada [ 6 ].
Over the last decade, there has been an increased interest in the use of medical cannabis products in North America. It is estimated that over 3.5 million people in the USA are legally using medical marijuana, and a total of USD$6.7 billion was spent in North America on legal marijuana in 2016 [ 7 ]. The number of Canadian residents with prescriptions to purchase medical marijuana from Health Canada–approved growers tripled from 30,537 in 2015 to near 100,000 in 2016 [ 8 ]. With the legalization of recreational-use marijuana in parts of the USA and in Canada in October 2018, the number of patients using marijuana for therapeutic purposes may become more difficult to track. The likely increase in the numbers of individuals consuming cannabis also necessitates a greater awareness of its potential benefits and harms.
Plant-based and plant-derived cannabis products are not monitored as more traditional medicines are, thereby increasing the uncertainty regarding its potential health risks to patients [ 3 ]. While synthetic forms of cannabis are available by prescription, different cannabis plants and products contain varied concentrations of THC and CBD, making the effects of exposure unpredictable [ 9 ]. While short-lasting side effects including drowsiness, loss of short-term memory, and dizziness are relatively well known and may be considered minor, other possible effects (e.g., psychosis, paranoia, anxiety, infection, withdrawal) may be more harmful to patients.
There remains a considerable degree of clinical equipoise as to the benefits and harms of marijuana use for medical purposes [ 10 – 13 ]. To understand the extent of synthesized evidence underlying this issue, we conducted a scoping review [ 14 ] of systematic reviews evaluating the benefits and/or harms of cannabis (plant-based, plant-derived, and synthetic forms) for any medical condition. We located and mapped systematic reviews to summarize research that is available for consideration for practice or policy questions in relation to medical marijuana.
A scoping review protocol was prepared and posted to the University of Ottawa Health Sciences Library’s online repository ( https://ruor.uottawa.ca/handle/10393/37247 ). We used the PRISMA for Scoping Reviews checklist to guide the reporting of this report (see Additional file 1 ) [ 15 ].
Literature search and process of study selection
An experienced medical information specialist developed and tested the search strategy using an iterative process in consultation with the review team. Another senior information specialist peer-reviewed the strategy prior to execution using the PRESS Checklist [ 16 ]. We searched seven Ovid databases: MEDLINE®, including Epub Ahead of Print and In-Process & Other Non-Indexed Citations, Embase, Allied and Complementary Medicine Database, PsycINFO, the Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, the Database of Abstracts of Reviews of Effects, and the Health Technology Assessment Database. The final peer-reviewed search strategy for MEDLINE was translated to the other databases (see Additional file 2 ). We performed the searches on November 3, 2017.
The search strategy incorporated controlled vocabulary (e.g., “Cannabis,” “Cannabinoids,” “Medical Marijuana”) and keywords (e.g., “marijuana,” “hashish,” “tetrahydrocannabinol”) and applied a broad systematic review filter where applicable. Vocabulary and syntax were adjusted across the databases and where possible animal-only and opinion pieces were removed, from the search results.
Gray literature searching was limited to relevant drug and mental health databases, as well as HTA (Health Technology Assessment) and systematic review databases. Searching was guided by the Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health’s (CADTH) checklist for health-related gray literature (see Additional file 3 ). We performed searches between January and February 2018. Reference lists of overviews were searched for relevant systematic reviews, and we searched for full-text publications of abstracts or protocols.
Management of all screening was performed using Distiller SR Software ® (Evidence Partners Inc., Ottawa, Canada). Citations from the literature search were collated and de-duplicated in Reference Manager (Thomson Reuters: Reference Manager 12 [Computer Program]. New York: Thomson Reuters 2011), and then uploaded to Distiller. The review team used Distiller for Levels 1 (titles and abstracts) and 2 (full-text) screening. Pilot testing of screening questions for both levels were completed prior to implementation. All titles and abstracts were screened in duplicate by two independent reviewers (MT and MP) using the liberal accelerated method [ 17 ]. This method requires only one reviewer to assess an abstract as eligible for full-text screening, and requires two reviewers to deem the abstract irrelevant. Two independent reviewers (MT and MP) assessed full-text reports for eligibility. Disagreements during full-text screening were resolved through consensus, or by a third team member (AS). The process of review selection was summarized using a PRISMA flow diagram (Fig. (Fig.1) 1 ) [ 18 ].

PRISMA-style flow diagram of the review selection process
Review selection criteria
English-language systematic reviews were included if they reported that they investigated harms and/or benefits of medical or therapeutic use of cannabis for adults and children for any indication. Definitions related to medical cannabis/marijuana are provided in Table Table1. 1 . We also included synthetic cannabis products, which are prescribed medicines with specified doses of THC and CBD. Reviews of solely observational designs were included only in relation to adverse effects data, in order to focus on the most robust evidence available. We considered studies to be systematic reviews if at least one database was searched with search dates reported, at least one eligibility criterion was reported, the authors had assessed the quality of included studies, and there was a narrative or quantitative synthesis of the evidence. Reviews assessing multiple interventions (both pharmacological and complementary and alternative medicine (CAM) interventions) were included if the data for marijuana studies was reported separately. Published and unpublished guidelines were included if they conducted a systematic review encompassing the criteria listed above.
Context for the use of cannabis-related terms during the review selection process
We excluded overviews of systematic reviews, reviews in abstract form only, and review protocols. We further excluded systematic reviews focusing on recreational, accidental, acute, or general cannabis use/abuse and interventions such as synthetic cannabinoids not approved for therapeutic use (e.g., K2 or Spice).
Data collection and quality assessment
All data were collected electronically in a pre-developed form using Microsoft Excel software (Microsoft Corporation, Seattle, USA). The form was pilot tested on three included reviews by three people. One reviewer (MP or CB) independently extracted all data, and a second reviewer (MT) verified all of the items collected and checked for any omitted data. Disagreements were resolved by consensus and consultation with a third reviewer if necessary. A data extraction form with the list of included variables is provided in Additional file 4 . All collected data has also been made available in the online supplemental materials associated with this report.
Quality assessment of systematic reviews was performed using the AMSTAR-2 [ 20 ] tool. One reviewer (MP or CB) independently assessed quality, while a second reviewer (MT) verified the assessments. Disagreements were resolved by consensus and consultation with a third reviewer if necessary. The tool consists of 16 items in total, with four critical domains and 12 non-critical domains. The AMSTAR-2 tool is not intended to generate an overall score, and instead allows for an overall rating based on weaknesses in critical domains. Reviews were rated as high (no critical flaws with zero or one non-critical flaw), moderate (no critical flaws with ≥ 1 non-critical flaw), low (one critical flaw with/without non-critical weakness), or critically low (> 1 critical flaw with/without non-critical weakness) quality.
Evidence synthesis
We used a directed content analytic approach [ 21 ] with an initial deductive framework [ 22 ] that allowed flexibility for inductive analysis if refinement or development of new categorization was needed. The framework used to categorize outcome data results is outlined in Table Table2. 2 . Where reviews had a mix of narrative and quantitative data, results from meta-analyses were prioritized over count data or study-by-study data. The extraction and reporting of data results was performed at a high level and did not involve an in-depth evaluation, which is appropriate for a scoping review [ 14 ]. Review authors’ conclusions and/or recommendations were extracted and reported narratively.
Outcome result categorization
Changes from the study protocol
For feasibility, we decided to limit the inclusion of systematic reviews of only observational study designs to those that addressed adverse events data. All other steps of the review were performed as planned.
Search findings
The PRISMA flow diagram describing the process of review selection is presented in Fig. Fig.1. 1 . After duplicates were removed, the search identified a total of 1925 titles and abstracts, of which 47 references were located through the gray literature search. Of the total 1925 citations assessed during Level 1 screening, 1285 were deemed irrelevant. We reviewed full-text reports for the 640 reviews of potential relevance, and of these, 567 were subsequently excluded, leaving a total of 72 systematic reviews that were included; the associated data collected are provided in Additional file 5 . A listing of the reports excluded during full-text review is provided in Additional file 6 .
Characteristics of included reviews
There were 63 systematic reviews [ 4 , 19 , 23 – 83 ] and nine guidelines with systematic reviews [ 84 – 92 ]. Overall, 27 reviews were performed by researchers in Europe, 16 in the USA, 15 in Canada, eight in Australia, two in Brazil, and one each in Israel, Singapore, South Africa, and China. Funding was not reported in 29 (40%) of the reviews, and the remaining reviews received funding from non-profit or academic ( n = 20; 28%), government ( n = 14; 19%), industry ( n = 3; 4%), and mixed ( n = 1; 1%) sources. Five reviews reported that they did not receive any funding for the systematic review. Tables Tables3, 3 , ,4, 4 , ,5, 5 , ,6, 6 , ,7, 7 , ,8, 8 , ,9, 9 , ,10, 10 , ,11, 11 , ,12, 12 , and and13 13 provide an overview of the characteristics of the 72 included systematic reviews.
Multiple sclerosis
MS multiple sclerosis, NICE National Institute for Health and Care Excellence, No . number, NR not reported, NRS numerical rating scale, QoL quality of life, RMI Rivermead Mobility Index, SBS study-by-study, VAS visual analog scale
*A colon indicates that there were separate analyses for each comparator
Movement disorders
HD Huntington’s disease, MS multiple sclerosis, NR not reported, PD Parkinson’s disease, SBS study-by-study, SCL-90R Symptoms Checklist-90 Revised, QoL quality of life, STSSS Shapiro Tourette Syndrome Severity Scale, THC tetrahydrocannabinol, TS-CGI Tourette Syndrome Clinical Global Impressions, TSSL Tourette’s Syndrome Symptom List (patient rated), VAS visual analog scale, YGTSS Yale Global Tic Severity Scale
AE : adverse effect, NICE National Institute for Health and Care Excellence, NNT numbers needed to treat, NP neuropathic pain, NR not reported, QoL quality of life, QST quantitative sensory testing, SBS study-by-study, VAS visual analog scale
*A colon indicates that there were separate analyses for each comparator; a “+” sign indicates placebo was combined with another comparator
AE adverse effect, NP neuropathic pain, NR not reported, NRS numerical rating scale, QoL quality of life, THC tetrahydrocannabinol, SIGN Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network, SBS study-by-study
Rheumatic disease
AE adverse event, FM fibromyalgia, NR not reported, NRS numerical rating scale, OA osteoarthritis, RA rheumatoid arthritis, SBS study-by-study
NP neuropathic pain, NR not reported, QoL quality of life, SBS study-by-study
Mental health
PTSD posttraumatic stress disorder, SBS study-by-study
NP neuropathic pain, NR not reported, SBS study-by-study
Neurological conditions
AE adverse effect, ALS amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, CADTH Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health, NR not reported
Various conditions
AE adverse effect, AD Alzheimer’s disease, ALS amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, CADTH Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health, CGI-C Clinical Global Impression of Change scale, COPD Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease, FIQ fibromyalgia impact questionnaire, FM fibromyalgia, HD Huntington’s disease, IBD inflammatory bowel disease, MS multiple sclerosis, NP neuropathic pain, NR not reported, PD Parkinson’s disease, PTSD posttraumatic stress disorder, RA rheumatoid arthritis, SBS study-by-study, SCI spinal cord injury
Other conditions
CADTH Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health, IBS irritable bowel syndrome, NR not reported, QoL quality of life, SBS study-by-study, VAS visual analog scale
The reviews were published between 2000 and 2018 (median year 2014), and almost half (47%) were focused solely on medical cannabis. Four (6%) reviews covered both medical and other cannabis use (recreational and substance abuse), 19 (26%) reported multiple pharmaceutical interventions (cannabis being one), six (8%) reported various CAM interventions (cannabis being one), and nine (13%) were mixed pharmaceutical and CAM interventions (cannabis being one). Multiple databases were searched by almost all of the reviews (97%), with Medline/PubMed or Embase common to all.
Cannabis use
Figure Figure2 2 illustrates the different cannabis-based interventions covered by the included reviews. Plant-based cannabis consists of whole plant products such as marijuana or hashish. Plant-derived cannabinoids are active constituents of the cannabis plant, such as tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), cannabidiol (CBD), or a combination of THC:CBD (also called nabiximols, under the brand name Sativex) [ 3 ]. Synthetic cannabinoids are manufactured rather than extracted from the plant and include drugs such as nabilone and dronabinol.

Review coverage of the various cannabis-based interventions
Twenty-seven reviews included solely interventions from plant-derived cannabinoids, 10 studied solely synthetic cannabinoids, and eight included solely studies on plant-based cannabis products. Twenty-four reviews covered a combination of different types of cannabis, and the remaining three systematic reviews did not report which type of cannabinoid was administered in the included studies.
The systematic reviews covered a wide range of conditions and illnesses, the most notable being pain management. Seventeen reviews looked at specific types of pain including neuropathic [ 31 , 42 , 62 , 69 , 85 , 90 ], chronic [ 26 , 32 , 52 , 58 , 80 ], cancer [ 84 , 87 ], non-cancer [ 41 , 68 ], and acute [ 38 ] types of pain (one review covered all types of pain) [ 65 ]. Twenty-seven reviews (38%) also focused on management of pain as a symptom of conditions such as multiple sclerosis (MS) [ 6 , 23 , 27 , 43 , 46 , 52 , 63 , 85 , 92 ], injury [ 29 , 35 , 36 , 69 ], cancer [ 37 , 43 , 65 , 88 ], inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) [ 28 ], rheumatic disease (RD) [ 49 , 51 , 73 ], diabetes [ 68 – 70 ], and HIV [ 48 , 53 , 67 ]. In Fig. Fig.3, 3 , the types of illnesses addressed by the set of included reviews are graphically represented, with overlap between various conditions and pain. Some systematic reviews covered multiple diseases, and therefore the total number of conditions represented in Fig. Fig.3 3 is greater than the total number of included reviews.

Conditions or symptoms across reviews that were treated with cannabis. IBD inflammatory bowel disease, MS multiple sclerosis, RD rheumatic disease
One review included a pediatric-only population, in the evaluation of marijuana for nausea and vomiting following chemotherapy [ 54 ]. Although trials in both adult and child populations were eligible for thirteen (18%) reviews, only two additional reviews included studies in children; these reviews evaluated cannabis in cancer [ 60 ] and a variety of conditions [ 25 ]. Many of the reviews ( n = 25, 35%) included only adults ≥ 18 years of age. Almost half of the reviews ( n = 33, 46%) did not report a specific population for inclusion.
Cannabis was prescribed for a wide range of medical issues. The indication for cannabis use is illustrated in Fig. Fig.4. 4 . Pain management ( n = 27) was the most common indication for cannabis use. A number of reviews sought to address multiple disease symptoms ( n = 12) or explored a more holistic treatment for the disease itself ( n = 11). After pain, the most common symptoms being treated with cannabis were spasticity in MS, movement disturbances (such as dyskinesia, tics, and spasms), weight or nausea/vomiting, and mental health symptoms.

Indications for cannabis use across included reviews
Figure Figure5 5 summarizes the breadth of outcomes analyzed in the included reviews. The most commonly addressed outcomes were withdrawal due to adverse effects, “other pain,” neuropathic pain, spasticity, and the global impression of the change in clinical status. Many outcomes were reported using a variety of measures across reviews. For example, spasticity was measured both objectively (using the Ashworth scale) and subjectively (using a visual analog scale [VAS] or numerical rating scale [NRS]). Similarily, outcomes for pain included VAS or NRS scales, reduction in pain, pain relief, analgesia, pain intensity, and patient assessment of change in pain.

Quality of the systematic reviews
Quality assessments of the included reviews based upon AMSTAR-2 are detailed in Additional file 7 and Additional file 8 . Only one review was rated as high quality [ 45 ]. All other reviews were deemed to be of moderate ( n = 36) or low/critically low ( n = 35) methodological quality. Assessments for the domains deemed of critical importance for determining quality ratings are described below.
Only 20% of reviews used a comprehensive search strategy; another 47% were given a partial score because they had not searched the reference lists of the included reviews, trial registries, gray literature, and/or the search date was older than 2 years. The remaining reviews did not report a comprehensive search strategy.
Over half of the reviews (51%) used a satisfactory technique for assessing risk of bias (ROB) of the individual included studies, while 35% were partially satisfactory because they had not reported whether allocation sequence was truly random and/or they had not assessed selective reporting. The remaining reviews did not report a satisfactory technique for assessing ROB.
Most reviews (71%) could not be assessed for an appropriate statistical method for combining results in a meta-analysis, as they synthesized study data narratively. Approximately 19% of reviews used an appropriate meta-analytical approach, leaving 10% that used inappropriate methods.
The final critical domain for the AMSTAR-2 determines whether review authors accounted for ROB in individual studies when discussing or interpreting the results of the review. The majority of reviews (83%) did so in some capacity.
Mapping results of included systematic reviews
We mapped reviews according to authors’ comparisons, the conditions or symptoms they were evaluating, and the categorization of the results (see Table Table2). 2 ). In some cases, reviews contributed to more than one comparison (e.g., cannabis versus placebo or active drug). As pain was the most commonly addressed outcome, we mapped this outcome separately from all other endpoints. This information is shown for all reviews and then restricted to reviews of moderate-to-high quality (as determined using the AMSTAR-2 criteria): cannabis versus placebo (Figs. (Figs.6 6 and and7), 7 ), cannabis versus active drugs (Figs. (Figs.8 8 and and9), 9 ), cannabis versus a combination of placebo and active drug (Figs. (Figs.10 10 and and11), 11 ), one cannabis formulation versus other (Figs. (Figs.12 12 and and13), 13 ), and cannabis analyzed against all other comparators (Fig. (Fig.14). 14 ). Details on how to read the figures are provided in the corresponding figure legends. The median number of included studies across reviews was four, and ranged from one to seventy-nine (not shown in figures).

Cannabis vs. placebo. Authors’ presentations of the findings were mapped using the categorization shown in Table Table2. 2 . According to the reviews’ intended scope for the condition being treated, outcomes were mapped into “pain,” “non-pain outcomes,” and “adverse events.” For each condition and outcome pair (i.e., each row in the grid), the number of reviews reporting findings is shown according to the results categorization. For pain, reviews numbered in different categories signal discordant findings across those reviews. For non-pain outcomes, reviews presenting findings in the different categories would signal different results for different outcomes, as well as discordant findings within and across reviews. Adverse events are grouped as a whole and “favors intervention” would be interpreted as a decrease in events with cannabis when compared with the control group. Favors int = favors intervention; Favors Ctrl = favors control; Not stat sig = not statistically significant

Cannabis vs. placebo, high and moderate quality reviews. Authors’ presentations of the findings were mapped using the categorizations shown in Table Table2. 2 . According to the reviews’ intended scope for the condition being treated, outcomes were mapped into “pain,” “non-pain outcomes,” and “adverse events.” For each condition and outcome pair (i.e., each row in the grid), the number of reviews reporting findings is shown according to the results categorization. For pain, reviews numbered in different categories signal discordant findings across those reviews. For non-pain outcomes, reviews presenting findings in the different categories would signal different results for different outcomes, as well as discordant findings within and across reviews. Adverse events are grouped as a whole and “favors intervention” would be interpreted as a decrease in events with cannabis when compared with the control group. Favors int = favors intervention; Favors Ctrl = favors control; Not stat sig = not statistically significant

Cannabis vs. active drugs. Authors’ presentations of the findings were mapped using the categorizations shown in Table Table2. 2 . According to the reviews’ intended scope for the condition being treated, outcomes were mapped into “pain,” “non-pain outcomes,” and “adverse events.” For each condition and outcome pair (i.e., each row in the grid), the number of reviews reporting findings is shown according to the results categorization. For pain, reviews numbered in different categories signal discordant findings across those reviews. For non-pain outcomes, reviews presenting findings in the different categories would signal different results for different outcomes, as well as discordant findings within and across reviews. Adverse events are grouped as a whole and “favors intervention” would be interpreted as a decrease in events with cannabis when compared with the control group. Favors int = favors intervention; Favors Ctrl = favors control; Not stat sig = not statistically significant

Cannabis vs. active drugs, high and moderate quality reviews. Authors’ presentations of the findings were mapped using the categorizations shown in Table Table2. 2 . According to the reviews’ intended scope for the condition being treated, outcomes were mapped into “pain,” “non-pain outcomes,” and “adverse events.” For each condition and outcome pair (i.e., each row in the grid), the number of reviews reporting findings is shown according to the results categorization. For pain, reviews numbered in different categories signal discordant findings across those reviews. For non-pain outcomes, reviews presenting findings in the different categories would signal different results for different outcomes, as well as discordant findings within and across reviews. Adverse events are grouped as a whole and “favors intervention” would be interpreted as a decrease in events with cannabis when compared with the control group. Favors int = favors intervention; Favors Ctrl = favors control; Not stat sig = not statistically significant

Cannabis vs. placebo + active drug. Authors’ presentations of the findings were mapped using the categorizations shown in Table Table2. 2 . According to the reviews’ intended scope for the condition being treated, outcomes were mapped into “pain,” “non-pain outcomes,” and “adverse events.” For each condition and outcome pair (i.e., each row in the grid), the number of reviews reporting findings is shown according to the results categorization. For pain, reviews numbered in different categories signal discordant findings across those reviews. For non-pain outcomes, reviews presenting findings in the different categories would signal different results for different outcomes, as well as discordant findings within and across reviews. Adverse events are grouped as a whole and “favors intervention” would be interpreted as a decrease in events with cannabis when compared with the control group. Favors int = favors intervention; Favors Ctrl = favors control; Not stat sig = not statistically significant

Cannabis vs. placebo + active drug, high and moderate quality reviews. Authors’ presentations of the findings were mapped using the categorizations shown in Table Table2. 2 . According to the reviews’ intended scope for the condition being treated, outcomes were mapped into “pain,” “non-pain outcomes,” and “adverse events.” For each condition and outcome pair (i.e., each row in the grid), the number of reviews reporting findings is shown according to the results categorization. For pain, reviews numbered in different categories signal discordant findings across those reviews. For non-pain outcomes, reviews presenting findings in the different categories would signal different results for different outcomes, as well as discordant findings within and across reviews. Adverse events are grouped as a whole and “favors intervention” would be interpreted as a decrease in events with cannabis when compared with the control group. Favors int = favors intervention; Favors Ctrl = favors control; Not stat sig = not statistically significant

One cannabis formulation vs. other. Authors’ presentations of the findings were mapped using the categorizations shown in Table Table2. 2 . According to the reviews’ intended scope for the condition being treated, outcomes were mapped into “pain,” “non-pain outcomes,” and “adverse events.” For each condition and outcome pair (i.e., each row in the grid), the number of reviews reporting findings is shown according to the results categorization. For pain, reviews numbered in different categories signal discordant findings across those reviews. For non-pain outcomes, reviews presenting findings in the different categories would signal different results for different outcomes, as well as discordant findings within and across reviews. Adverse events are grouped as a whole and “favors intervention” would be interpreted as a decrease in events with cannabis when compared with the control group. Favors int = favors intervention; Favors Ctrl = favors control; Not stat sig = not statistically significant

One cannabis formulation vs. other, high and moderate quality reviews. Authors’ presentations of the findings were mapped using the categorizations shown in Table Table2. 2 . According to the reviews’ intended scope for the condition being treated, outcomes were mapped into “pain,” “non-pain outcomes,” and “adverse events.” For each condition and outcome pair (i.e., each row in the grid), the number of reviews reporting findings is shown according to the results categorization. For pain, reviews numbered in different categories signal discordant findings across those reviews. For non-pain outcomes, reviews presenting findings in the different categories would signal different results for different outcomes, as well as discordant findings within and across reviews. Adverse events are grouped as a whole and “favors intervention” would be interpreted as a decrease in events with cannabis when compared with the control group. Favors int = favors intervention; Favors Ctrl = favors control; Not stat sig = not statistically significant

Cannabis vs. all comparators combined. Authors’ presentations of the findings were mapped using the categorizations shown in Table Table2. 2 . According to the reviews’ intended scope for the condition being treated, outcomes were mapped into “pain,” “non-pain outcomes,” and “adverse events.” For each condition and outcome pair (i.e., each row in the grid), the number of reviews reporting findings is shown according to the results categorization. For pain, reviews numbered in different categories signal discordant findings across those reviews. For non-pain outcomes, reviews presenting findings in the different categories would signal different results for different outcomes, as well as discordant findings within and across reviews. Adverse events are grouped as a whole and “favors intervention” would be interpreted as a decrease in events with cannabis when compared with the control group. Favors int = favors intervention; Favors Ctrl = favors control; Not stat sig = not statistically significant
Cannabis versus placebo
Most reviews (59/72, 82%) compared cannabis with placebo. Of these reviews, 34 (58%) addressed pain outcomes and 47 (80%) addressed non-pain outcomes, with most outcomes addressed by three reviews or fewer (Fig. (Fig.6). 6 ). Some reviews had a mix of quantitative syntheses and study-by-study data reported (13/59, 22%), while another group of reviews (14/59, 24%) only reported results study-by-study. Overall, 24% (14/59) of the cannabis versus placebo reviews had only one included study.
- i. Reviews focused on addressing pain across conditions. In most cases, findings were discordant across reviews for the pain outcomes measured. For chronic non-cancer pain, however, two reviews favored cannabis over placebo for decreasing pain. One review assessing acute pain for postoperative pain relief found no difference between various cannabinoid medications and placebo. The distribution of findings was similar when restricting to moderate-to-high-quality reviews.
- ii. Reviews focused on treating a condition or family of related conditions . Various results were observed for pain. For MS and HIV/AIDS, one review each reported quantitative results favoring cannabis for decreased pain but with other reviews reporting results study-by-study, it is difficult to know, broadly, how consistent those findings are. For cancer, two reviews reported results favoring cannabis for decreased pain. For rheumatic disease, findings are discordant between two reviews, and another two reviews reported results study-by-study. One review that included studies of MS or paraplegia found no difference in pain between groups. For treating injury, one review showed that the placebo group had less pain and one review reported data study-by-study. No reviews addressed pain in movement disorders, neurological conditions, and IBD.
For those reviews assessing pain as part of a focus on treating a range of conditions, two showed cannabis reduced pain [ 43 , 52 ], but one showed mixed results depending on how pain was measured [ 43 ]. These reviews covered several different conditions, including injury, chronic pain, rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, fibromyalgia, HIV/AIDS, cancer, and MS or paraplegia.
When restricting to moderate-to-high-quality reviews, only one review each in multiple sclerosis and HIV/AIDS with a study-by-study analysis on pain remained. One review on cancer favored cannabis for pain reduction. Findings remained the same for MS or paraplegia and rheumatic disease. No review for injury and paint outcomes was of higher quality.
- 2. Non-pain outcomes
The types of non-pain outcomes included in the reviews varied by condition/illness. The most commonly reported outcomes (see Fig. Fig.5 5 for overall outcomes) when comparing cannabis to placebo included muscle- or movement-related outcomes ( n = 20), quality of life ( n = 14), and sleep outcomes ( n = 10).
There was no consistent pattern for non-pain outcomes either within or across medical conditions. Many ( n = 24, 33%) reviews assessing non-pain outcomes reported the results of those analyses study-by-study. Conflicting results are observed in some cases due to the use of different measures, such as different ways of quantifying spasticity in patients with multiple sclerosis [ 56 , 91 ]. One review each addressing neurological conditions [ 50 ] (outcome: muscle cramps) and MS/paraplegia [ 27 ] (outcomes: spasticity, spasm, cognitive function, daily activities, motricity, and bladder function) showed no difference between groups.
- 3. Adverse effects
Adverse effects were reported in most reviews comparing cannabis with placebo (49/59, 83%). Most adverse events were reported study-by-study, with few reviews ( n = 16/59, 27%) conducting a narrative or quantitative synthesis. Serious adverse effects were reported in 21/59 (36%) reviews, and minor adverse effects were reported in 30/59 (51%) reviews. The remaining reviews did not define the difference between serious and minor adverse events. The most commonly reported serious adverse events included psychotic symptoms ( n = 6), severe dysphoric reactions ( n = 3), seizure ( n = 3), and urinary tract infection ( n = 2). The most commonly reported minor adverse events included somnolence/drowsiness ( n = 28), dizziness ( n = 27), dry mouth ( n = 20), and nausea ( n = 18). Many reviews ( n = 37/59, 63%) comparing cannabis to placebo reported both neurocognitive and non-cognitive adverse effects. Withdrawals due to adverse events were reported in 22 (37%) reviews.
Of the moderate-/high-quality reviews, adverse effect analyses were reported in reviews on pain, multiple sclerosis, cancer, HIV/AIDS, movement disorders, rheumatic disease, and several other conditions. Two reviews on pain showed fewer adverse events with cannabis for euphoria, events linked to alternations in perception, motor function, and cognitive function, withdrawal due to adverse events, sleep, and dizziness or vertigo [ 58 , 90 ]. One review on MS showed that there was no statistically significant difference between cannabis and placebo for adverse effects such as nausea, weakness, somnolence, and fatigue [ 91 ], while another review on MS/paraplegia reported fewer events in the placebo group for dizziness, somnolence, nausea, and dry mouth [ 27 ]. Within cancer reviews, one review found no statistically significant difference between cannabis and placebo for dysphoria or sedation but reported fewer events with placebo for “feeling high,” and fewer events with cannabis for withdrawal due to adverse effects [ 40 ]. In rheumatic disease, one review reported fewer total adverse events with cannabis and found no statistically significant difference between cannabis and placebo for withdrawal due to adverse events [ 51 ].
Cannabis versus other drugs
Relatively fewer reviews compared cannabis with active drugs ( n = 23/72, 32%) (Fig. (Fig.8). 8 ). Many of the reviews did not synthesize studies quantitatively, and results were reported study-by-study. The most common conditions in reviews comparing cannabis to active drugs were pain, cancer, and rheumatic disease. Comparators included ibuprofen, codeine, diphenhydramine, amitriptyline, secobarbital, prochlorperazine, domperidone, metoclopramide, amisulpride, neuroleptics, isoproterenol, megestrol acetate, pregabalin, gabapentin, and opioids.
- i. Reviews focused on addressing pain across conditions. When comparing across reviews, a mix of results are observed (see Fig. Fig.8), 8 ), and some were reported study-by-study. One review found no statistically significant difference between cannabinoids and codeine for nociceptive pain, postoperative pain, and cancer pain [ 65 ]. Another review favored “other drugs” (amitriptyline and pregabalin) over cannabinoids for neuropathic pain [ 90 ]. The distribution of findings was similar when restricting to moderate-to-high-quality reviews.
- ii. Reviews focused on treating a condition or family of related conditions. One review on cancer compared cannabinoids and codeine or secobarbital and reported pain results study-by-study. Another review on fibromyalgia comparing synthetic cannabinoids with amitriptyline also reported pain data study-by-study [ 39 ].
- Non-pain outcomes
Two reviews on cancer favored cannabinoids over active drugs (prochlorperazine, domperidone, metoclopramide, and neuroleptics) for patient preference and anti-emetic efficacy [ 40 , 60 ]. Non-pain outcomes were reported study-by-study for the outcome of sleep in neuropathic pain [ 90 ] and rheumatic disease [ 39 , 49 ]. In a review covering various conditions (pain, MS, anorexia, cancer, and immune deficiency), results were unclear or indeterminate for subjective measures of sleep [ 46 ].
Adverse effects were reported in 20/24 (83%) of the reviews comparing cannabis to active drugs, and only 6/20 (30%) reported a narrative or quantitative synthesis. Many reviews that reported narrative data did not specify whether adverse effects could be attributed to a placebo or active drug comparator.
Of the moderate-to-high-quality reviews, two pain reviews found no statistically significant difference for cannabis compared to codeine or amitriptyline for withdrawals due to adverse events [ 65 , 90 ]. Results from one cancer review were mixed, with fewer adverse events for cannabis (compared to prochlorperazine, domperidone, or metoclopramide) or no difference between groups, depending on the type of subgroup analysis that was conducted [ 40 ].
Cannabis + active drugs versus placebo + active drugs
Two reviews compared cannabis with placebo cannabis in combination with an active drug (opioids and gabapentin) (Figs. (Figs.10 10 and and11). 11 ). Both were scored to be of moderate quality. Although one review showed that cannabis plus opioids decreased chronic pain [ 80 ], another review on pain in MS included only a single study [ 81 ], precluding the ability to determine concordance of results. Cannabis displayed varied effects on non-pain outcomes, including superiority of placebo over cannabis for some outcomes. One review reported withdrawal due to adverse events study-by-study and also reported that side effects such as nausea, drowsiness, and dizziness were more frequent with higher doses of cannabinoids (data from two included studies) [ 80 ].
Cannabis versus other cannabis comparisons
Six (8%) reviews compared different cannabis formulations or doses (Figs. (Figs.12 12 and and13). 13 ). Almost all were reported as study-by-study results, with two reviews including only one RCT. One review for PTSD found only observational data [ 33 ] and another review on anxiety and depression combined data from one RCT with cross-sectional study data [ 19 ]. A single review on MS reported a narrative synthesis that found a benefit for spasticity. However, it was unclear if the comparator was placebo or THC alone [ 56 ]. Four reviews reported adverse effects study-by-study, with a single review comparing side effects from different dosages; in this review, combined extracts of THC and CBD were better tolerated than extracts of THC alone [ 56 ].
Cannabis versus all comparators
One review combined all comparators for the evaluation (Fig. (Fig.14). 14 ). The review (combining non-users, placebo and ibuprofen) covered a range of medical conditions and was rated as low quality [ 30 ]. No adverse effects were evaluated for this comparison.
Mapping the use of quality assessment and frameworks to interpret the strength of evidence
Although 83% of reviews incorporated risk of bias assessments in their interpretation of the evidence, only 11 (15%) reviews used a framework such as GRADE to evaluate important domains other than risk of bias that would inform the strength of the evidence.
Mapping authors’ conclusions or recommendations
Most reviews (43/72 60%) indicated an inability to draw conclusions, whether due to uncertainty, inconsistent findings, lack of (high quality) evidence, or focusing their conclusion statement on the need for more research. Almost 15% of reviews (10/72) reported recommendations or conclusions that included some uncertainty. One review (1%) provided a statement of the extent of the strength of the evidence, which differed according to outcome.
Eleven reviews provided clearer conclusions (14%). Four indicated that cannabis was not effective or not cost-effective compared to placebo in relation to multiple sclerosis, acute pain, cancer, and injury. Three reviews addressing various conditions provided varying conclusions: one stated cannabis was not effective, one indicated it was modestly safe and effective, and one concluded that cannabis was safe and efficacious as short-term treatment; all reviews were of low quality. The three remaining reviews stated moderate or modest effects for improving chronic pain, compared with placebo or other analgesia; two of those reviews were of medium AMSTAR-2 quality, and one used the GRADE framework for interpreting the strength of the evidence.
The eight remaining included reviews (11%) did not provide a clear conclusion statement or reported only limitations.
Mapping authors’ limitations of the research
Several of the reviews indicated that few studies, small sample sizes, short duration of treatment, and issues related to outcomes (e.g., definition, timing, and types) were drawbacks to the literature. Some reviews noted methodological issues with and heterogeneity among studies as limitations. A few authors stated that restricting eligibility to randomized trials, English-language studies, or full publications may have affected their review results.
With the increasing use of medical cannabis, an understanding of the landscape of available evidence syntheses is needed to support evidence-informed decision-making, policy development, and to inform a research agenda. In this scoping review, we identified 72 systematic reviews evaluating medical cannabis for a range of conditions and illnesses. Half of the reviews were evaluated as being of moderate quality, with only one review scoring high on the AMSTAR-2 assessment tool.
There was disparity in the reported results across reviews, including non-synthesized (study-by-study) data, and many were unable to provide a definitive statement regarding the effectiveness of cannabis (as measured by pain reduction or other relevant outcomes), nor the extent of increased side effects and harms. This is consistent with the limitations declared in general across reviews, such as the small numbers of relevant studies, small sample sizes of individual studies, and methodological weaknesses of available studies. This common theme in review conclusions suggests that while systematic reviews may have been conducted with moderate or high methodological quality, the strength of their conclusions are driven by the availability and quality of the relevant underlying evidence, which was often found to be limited.
Relatively fewer reviews addressed adverse effects associated with cannabis, except to narratively summarize study level data. Although information was provided for placebo-controlled comparisons, none of the comparative effectiveness reviews quantitatively assessed adverse effects data. For the placebo-controlled data, although the majority of adverse effects were mild, the number of reviews reporting serious adverse effects such as psychotic symptoms [ 25 , 42 ] and suicidal ideation [ 68 , 85 ] warrants caution.
A mix of reviews supporting and not supporting the use of cannabis, according to authors’ conclusions, was identified. Readers may wish to consider the quality of the reviews, the use of differing quality assessment tools, additional considerations covered by the GRADE framework, and the potential for spin as possible reasons for these inconsistencies. It is also possible that cannabis has differing effects depending on its type (e.g., synthetic), dose, indication, the type of pain being evaluated (e.g., neuropathic), and the tools used for outcome assessment, which can be dependent on variations in condition. Of potential interest to readers may be a closer examination of the reviews evaluating chronic pain, in order to locate the source(s) of discordance. For example, one review was deemed of moderate quality, used the GRADE framework, and rated the quality of evidence for the effectiveness of cannabis for reducing neuropathic pain as moderate, suggesting that further investigation of cannabis for neuropathic pain may be warranted [ 80 ]. The exploration aspects outlined in this paragraph are beyond the purview of scoping review methodology; a detailed assessment of the reviews, including determining the overlap of included studies among similar reviews, potential reasons for the observed discordance of findings, what re-analysis of study-by-study analyses would yield, and an undertaking of missing GRADE assessments would fall outside the bounds of a scoping review and require the use of overview methodology [ 14 ].
Our findings are consistent with a recently published summary of cannabis-based medicines for chronic pain management [ 3 ]. This report found inconsistent results in systematic reviews of cannabis-based medicines compared to placebo for chronic neuropathic pain, pain management in rheumatic diseases and painful spasms in MS. The authors also concluded that cannabis was not superior to placebo in reducing cancer pain. Four out of eight included reviews scored high on the original AMSTAR tool. The variations between the two tools can be attributed to the differences in our overall assessments. Lastly, the summary report included two reviews that were not located in our original search due to language [ 93 ] and the full-text [ 94 ] of an abstract [ 95 ] that was not located in our search.
This scoping review has identified a plethora of synthesized evidence in relation to medical cannabis. For some conditions, the extent of review replication may be wasteful. Many reviews have stated that additional trials of methodologically robust design and, where possible, of sufficient sample size for precision, are needed to add to the evidence base. This undertaking may require the coordination of multi-center studies to ensure adequate power. Future trials may also help to elucidate the effect of cannabis on different outcomes.
Given authors’ reporting of issues in relation to outcomes, future prospective trials should be guided by a standardized, “core” set of outcomes to strive for consistency across studies and ensure relevance to patient-centered care. Development of those core outcomes should be developed using the Core Outcome Measures in Effectiveness Trials (COMET) methodology [ 96 ], and further consideration will need to be made in relation to what outcomes may be common across all cannabis research and which outcomes are condition-specific. With maturity of the evidence base, future systematic reviews should seek and include non-journal-published (gray literature) reports and ideally evaluate any non-English-language papers; authors should also adequately assess risk of bias and undertake appropriate syntheses of the literature.
The strengths of this scoping review include the use of an a priori protocol, peer-reviewed search strategies, a comprehensive search for reviews, and consideration of observational designs for adverse effects data. For feasibility, we restricted to English-language reviews, and it is unknown how many of the 39 reviews in other languages that we screened would have met our eligibility criteria. The decision to limit the inclusion of reviews of observational data to adverse effects data was made during the process of full-text screening and for pragmatic reasons. We also did not consider a search of the PROSPERO database for ongoing systematic reviews; however, in preparing this report, we performed a search and found that any completed reviews were already considered for eligibility or were not available at the time of our literature search. When charting results, we took a broad perspective, which may be different than if these reviews were more formally assessed during an overview of systematic reviews.
Cannabis-based medicine is a rapidly emerging field of study, with implications for both healthcare practitioners and patients. This scoping review is intended to map and collate evidence on the harms and benefits of medical cannabis. Many reviews were unable to provide firm conclusions on the effectiveness of medical cannabis, and results of reviews were mixed. Mild adverse effects were frequently but inconsistently reported, and it is possible that harms may outweigh benefits. Evidence from longer-term, adequately powered, and methodologically sound RCTs exploring different types of cannabis-based medicines is required for conclusive recommendations.
Supplementary information
Acknowledgements.
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
Authors’ contributions.
MP, AS, and BH drafted the initial version of the report. BS designed and implemented the literature search. MP, MT, and CB contributed to review of abstracts and full texts as well as data collection. MP, AS, and BH were responsible for analyses. All authors (MP, AS, MT, CB, BS, SW, MC, SK, BH) contributed to interpretation of findings and revision of drafts and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Research reported in this publication was supported by the National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health of the National Institutes of Health under award number R24AT001293. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health.
Availability of data and materials
Ethics approval and consent to participate, consent for publication, competing interests.
BH has previously received honoraria from Cornerstone Research Group for provision of methodologic advice related to the conduct of systematic reviews and meta-analysis. All other authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Contributor Information
Misty Pratt, Email: ac.irho@ttarpim .
Adrienne Stevens, Email: ac.irho@snevetsda .
Micere Thuku, Email: ac.irho@ukuhtm .
Claire Butler, Email: ac.irho@reltublc .
Becky Skidmore, Email: moc.sregor@eromdiksb .
L. Susan Wieland, Email: moc.liamg@dnaleiwsl .
Mark Clemons, Email: ac.hot@snomelcm .
Salmaan Kanji, Email: ac.hot@ijnaks .
Brian Hutton, Email: ac.irho@nottuhb .
Supplementary information accompanies this paper at 10.1186/s13643-019-1243-x.
How to make money from medical research and donations
- You can make thousands of dollars by donating some time or body parts to science.
- But these procedures are not all painless, and not everyone can participate.
- Below is a short list, though be warned: these strategies aren't all easy money.

Get dysentery. Play cards with someone who has the flu . Or, spend 45 days trapped in a tiny apartment with three total strangers.
These are just a few of the many ways you can get paid for helping out with scientific research. If you want to aid the science community and potentially save some lives while making a little extra cash, there are some unconventional options to consider.
Below is a short list, though be warned: these strategies aren't all exactly easy money.
Sell your blood plasma
Payout (per donation): around $50
Plasma is the largest component in human blood. It's a protein-rich liquid that contains mostly water but is also filled with enzymes, antibodies, and salts. This gooey, sticky yellow-ish stuff can be used to create therapies that treat people with blood clotting disorders, autoimmune diseases, and even burn victims. Donating plasma is often called "the gift of life" since treatments for some conditions can't be made synthetically and require this kind of human contribution.
During plasma donation, blood is drawn and an automated machine separates the plasma from other blood components, which are returned to the donor. Plasma donation pay varies from site to site, but the average payout is typically around $50 per donation. You can donate safely roughly once a month, according to the American Red Cross , and a typical session takes less than two hours. Find a licensed and certified plasma center near you.
Donate your sex cells
Payout for eggs (per donation): usually $10,000 to $12,000;
Payout for sperm (per donation): typically $35-$150
Egg and sperm donation can allow couples who have trouble conceiving naturally to become parents by using a donor's sex cells. But the time commitment and risk involved in a woman's egg donation is far steeper than what a man goes through donating his sperm.
In the United States, egg donors generally net around $10,000-$12,000. Weill Cornell outlines the standard steps for egg donation , which requires about a four-week time commitment.
During the egg donation cycle, patients are injected with fertility drugs so that the ovaries make more mature eggs than normal. (Eligible women are generally between the ages of 21 and 30). The egg retrieval procedure takes about 20 minutes but may require several days of recovery. Donors should be aware of the risks involved (largely related to the hormones used) before signing up.
Related stories
Men are generally paid anywhere from $35 to $150 per sperm donation, according to The Sperm Bank of California , but sperm donation can really start to add up if you regularly donate samples (many programs require a six-month or one-year donation commitment).
Donors should bear in mind that even if they choose to donate anonymously, sperm and egg donation is never really 100% incognito. Your DNA always knows who you are.
Spend 45 days on a fake spaceship
Payout: $160/day
NASA will pay you to spend 45 days traveling in space. Well, sort of.
You'll actually be on the ground the whole time in Houston, Texas, but you'll be locked inside a model space capsule (650 square feet) along with three strangers. This simulation is designed to study what being cooped up for a very long time inside a spaceship might do to a person, both physically and mentally. NASA wants to check this out thoroughly before they start sending astronauts on missions to Mars, or to explore faraway asteroids.
Participants in NASA's human research program share a capsule with each other that includes some workspace for doing lab experiments, a little kitchen table for eating meals that are just like what's served aboard the International Space Station, plus an exercise bike and some free weights. There's no internet, but you do get your own little cozy sleeping pod on the top floor.
The fake astronauts "on board" the capsule in May and June of 2024 include an aerospace engineering professor, a US Air Force Reserve member, a commercial pilot, and a biomedical engineer.
And that mission is nothing compared to NASA's CHAPEA Mars simulation , which keeps recruits in a simulated habitat of the red planet for 378 days. (NASA declined to comment on how much CHAPEA pays).
Take part in a clinical trial
Payout: Varies by program
The National Institutes of Health run a searchable database, ClincalTrials.gov , that rounds up human clinical studies ongoing around the world. Participants may be guinea pigs for new medical products, like drugs to treat high blood pressure, or they take part in observational research, like a study that records the effects of different lifestyles on heart health.
Subjects are generally paid to participate in such clinical trials, and most of the time, the bigger the risk, the bigger the reward. For example, a participant in one study in which participants were exposed to dysentery-causing bacteria was paid over $7,000, while a single blood draw or lab visit for a more straightforward study may only be worth $100 or so.
If you do decide to enroll in a study, choose wisely and carefully because not all of the studies on the site are regulated or evaluated for safety by the US Food and Drug Administration.
Enroll in a psychological study
Paid psychological studies, such as those that examine human behavior and brain function, may not generate as high of a return as clinical trials, but they are generally lower risk and require a shorter time commitment.
Most research universities keep an online database of studies so people can easily sign up. For example, here's a list of the most recent paid research studies offered by New York University . At NYU, you can make $12 an hour playing video games, and receive a $50 bonus if you're good at it.
Give your dead body to science
Payout: free cremation
This last idea is sort of morbid, but if you're worried about being a bother when you're dead, you can donate your body to science . This helps with various types of research and education.
Places like BioGift and Science Care will cover the costs of cremation, which can run upwards of $2,000.
- Main content
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
Medicinal chemistry articles within Nature Chemistry
Article | 20 May 2024
Discovery of N–X anomeric amides as electrophilic halogenation reagents
Electrophilic halogenation approaches often suffer from low reactivity and chemoselectivity when it comes to complex compounds. Now a class of halogenating reagents based on anomeric amides that can halogenate complex bioactive molecules with diverse functional groups and heterocycles has been developed. The higher reactivity of these anomeric amide reagents is attributed to the energy stored in the pyramidalized nitrogen.
- & Phil S. Baran
Article 16 May 2024 | Open Access
Machine learning designs new GCGR/GLP-1R dual agonists with enhanced biological potency
Engineering new ligands that specifically target multiple G protein-coupled receptors with desired activity profiles requires time-consuming and expensive cycles of design-make-test-analyse work. Now it has been shown that limited experimental data can be used to train sophisticated machine learning models to accurately predict the activity of previously uncharacterized peptide ligand variants.
- Anna M. Puszkarska
- , Bruck Taddese
- & Lucy J. Colwell
Research Briefing | 08 February 2024
A protein-templated selection approach for the identification of full ligands from DNA-encoded libraries
A protein-templated selection approach has been developed for the discovery of full ligands from dual-pharmacophore DNA-encoded libraries by incorporating fragment linking into the selection process. The performance of this method was demonstrated with selections against protein–protein interaction and protein–DNA interaction targets, through which potent and selective inhibitors were identified.
Article | 07 February 2024
Protein-templated ligand discovery via the selection of DNA-encoded dynamic libraries
Dual-pharmacophore DNA-encoded chemical libraries enable the identification of two synergistic binders for a biological target, but subsequent linking of this pair is required to obtain a full ligand, which can be challenging. Here we report a protein-templated selection of DNA-encoded dynamic library that can identify full ligands from fragment libraries without the need for subsequent fragment linking.
- , Wenyin Shen
- & Xiaoyu Li
In Your Element | 06 February 2024
Redefining peptide therapeutics with semaglutide
Thomas Kruse and Søren Østergaard reflect on the development of the GLP-1 analogue, semaglutide, which is reshaping peptide therapeutics in type 2 diabetes, weight management, and beyond.
- Thomas Kruse
- & Søren Østergaard
Thesis | 20 December 2023
Given the fraught history of fluorine, Michelle Francl wonders what made medicinal chemists consider fluorine derivatives?
- Michelle Francl
Article | 19 December 2023
Molecular jackhammers eradicate cancer cells by vibronic-driven action
In contrast to photothermal therapy requiring high powers over extended times and photodynamic therapy being abrogated by inhibitors of reactive oxygen species, actuation of vibronic modes in single molecules—molecular jackhammers—can now induce efficient cancer cell death. Here, the mechanical disassembly of cell membranes is characterized as the underlying mechanism by which this vibronic-driven action promotes necrotic cell death.
- Ciceron Ayala-Orozco
- , Diego Galvez-Aranda
- & James M. Tour
Article 23 November 2023 | Open Access
Enabling late-stage drug diversification by high-throughput experimentation with geometric deep learning
Late-stage functionalization of complex drug molecules is challenging. To address this problem, a discovery platform based on geometric deep learning and high-throughput experimentation was developed. The computational model predicts binary reaction outcome, reaction yield and regioselectivity with low error margins, enabling the functionalization of complex molecules without de novo synthesis.
- David F. Nippa
- , Kenneth Atz
- & Gisbert Schneider
Research Briefing | 10 November 2023
In vitro selection of covalent aptamers with sulfur(VI) fluoride exchange chemistry
To develop covalent inhibitors with high potency and low off-target effects, combinatorial approaches that search for candidates from large libraries are desired. Here, sulfur(VI) fluoride exchange (SuFEx) in vitro selection is established for the evolution of covalent aptamers from trillions of SuFEx-modified oligonucleotides. Through this technique, covalent aptamers with optimally balanced selectivity and reactivity are identified.
Article | 26 October 2023
Programmable late-stage functionalization of bridge-substituted bicyclo[1.1.1]pentane bis-boronates
The bicyclo[1.1.1]pentane (BCP) motif has drawn increasing attention recently in drug discovery. Now, a programmable bis-functionalization strategy has been developed to modularly access bridge-substituted BCP scaffolds, based on the inherent chemoselectivity of BCP bis-boronates (3° > 2°). This strategy should enable further structure–activity relationship studies of BCP-containing drug candidates and open the door to unexplored chemical space.
- Yangyang Yang
- , Jet Tsien
- & Tian Qin
Article | 31 August 2023
Discovering covalent inhibitors of protein–protein interactions from trillions of sulfur(VI) fluoride exchange-modified oligonucleotides
Covalent inhibitors offer high potency but their potential is hindered by off-target reactivity. Now, an in vitro selection method has been developed to enable the discovery of covalent inhibitors from trillions of oligonucleotides endowed with the sulfur(VI) fluoride exchange chemistry. This strategy generates covalent inhibitors of protein–protein interactions with optimally balanced selectivity and reactivity.
- , Kaining Zhang
- & Yu Xiang
Pervasive transcriptome interactions of protein-targeted drugs
Now a reactivity-based RNA profiling strategy can measure the global off-target transcriptome interactions of small-molecule drugs at single-nucleotide resolution. Using this approach, three FDA-approved drugs were evaluated, uncovering pervasive drug–RNA interactions and interactions that perturb RNA functions in cells.
- Linglan Fang
- , Willem A. Velema
- & Eric T. Kool
News & Views | 05 July 2023
Anticancer platinum-based photo-oxidants in a new light
Pharmacologically inactive prodrugs that can be activated by near-infrared light are attractive candidates for clinical applications. Now, platinum-based photo-oxidants have been shown to eradicate tumours in mice with a new mode of action.
- Gloria Vigueras
- & Gilles Gasser
Article | 03 July 2023
A DNA-encoded chemical library based on chiral 4-amino-proline enables stereospecific isozyme-selective protein recognition
The design and construction of a stereo-defined DNA-encoded chemical library, featuring the four different 4-amino-proline stereoisomers as a central scaffold, has now enabled the discovery of potent ligands to proteins of pharmaceutical interest. Parallel screening with closely related isoforms (anti-targets) facilitated the isolation of hits with high selectivity ratios.
- Sebastian Oehler
- , Laura Lucaroni
- & Gabriele Bassi
Article 05 June 2023 | Open Access
2-Oxabicyclo[2.1.1]hexanes as saturated bioisosteres of the ortho -substituted phenyl ring
The ortho -substituted phenyl ring is a basic structural element in chemistry. Now, 2-oxabicyclo[2.1.1]hexanes have been developed as saturated bioisosteres of the ortho -substituted phenyl ring with improved physicochemical properties. Replacement of the phenyl ring with 2-oxabicyclo[2.1.1]hexanes in marketed agrochemicals fluxapyroxad and boscalid improved water solubility, reduced lipophilicity and retained bioactivity.
- Aleksandr Denisenko
- , Pavel Garbuz
- & Pavel K. Mykhailiuk
Article | 30 March 2023
OregonFluor enables quantitative intracellular paired agent imaging to assess drug target availability in live cells and tissues
Water-soluble, cell-permeable, inert fluorescent tags called OregonFluors have been developed to withstand environmental changes while resistant towards non-specific binding with subcellular structures. These tags enable quantitative imaging of drug target availability in cells and tissues, providing a route for the future assessment of personalized therapies.
- Lei G. Wang
- , Antonio R. Montaño
- & Summer L. Gibbs
Article | 03 October 2022
Practical synthesis of the therapeutic leads tigilanol tiglate and its analogues
Tigilanol tiglate is a therapeutic lead for the treatment of a broad range of cancers. Now, it has been shown that tigilanol tiglate can be synthesized in a time and step economical fashion from phorbol—its naturally abundant biosynthetic precursor. This synthesis provides rapid access to analogues with unprecedented protein kinase C binding activity.
- Paul A. Wender
- , Zachary O. Gentry
- & Edward Njoo
Article | 26 September 2022
Total synthesis of structurally diverse pleuromutilin antibiotics
General synthetic methods to access pleuromutilin antibiotics are limited due to their complex carbocyclic skeleton. Now, a synthetic platform has been developed to access structurally diverse pleuromutilins with variations at the quaternary C12 position and hydrindanone cores. Seventeen structurally distinct derivatives were prepared and evaluated against a panel of Gram-positive and -negative bacteria.
- Olivia Goethe
- , Mikaela DiBello
- & Seth B. Herzon
News & Views | 29 July 2022
Warhead assembly in a lethal pathogen
Malleicyprols are highly reactive polyketides responsible for virulence in some pathogenic bacteria. Now, the enzyme that constructs the cyclopropanol warhead of malleicyprols has been identified. This enzyme could represent a useful target for developing new antivirulence therapeutics.
- Elijah Abraham
- & Rebecca A. Butcher
News & Views | 01 July 2022
ortho -Quinone drugs go pro
Antibody-mediated delivery of therapeutics has been primarily limited to agents containing amine, alcohol or thiol functional groups. Now, an approach has been developed to create stable and bio-reversible prodrugs that mask ortho -quinones. Drug release requires both protease activation followed by acid-assisted elimination.
- Thomas Pillow
Article 27 June 2022 | Open Access
Controlled masking and targeted release of redox-cycling ortho -quinones via a C–C bond-cleaving 1,6-elimination
A strategy for protecting redox-active ortho -quinones, which show promise as anticancer agents but suffer from redox-cycling behaviour and systemic toxicity, has been developed. The ortho -quinones are derivatized to redox-inactive para -aminobenzyl ketols. Upon amine deprotection, an acid-promoted, self-immolative C–C bond-cleaving 1,6-elimination releases the redox-active hydroquinone. The strategy also enables conjugation to a carrier for targeted delivery of ortho -quinone species.
- Lavinia Dunsmore
- , Claudio D. Navo
- & Gonçalo J. L. Bernardes
Review Article | 05 May 2022
Multistep enzyme cascades as a route towards green and sustainable pharmaceutical syntheses
Enzymes, either purified or as whole-cell biocatalysts, can be concatenated into catalytic cascades and used to produce pharmaceutically relevant molecules. This Review discusses the advantages and requirements of multistep enzyme cascades and also highlights how they can be harnessed to achieve highly sustainable and cost-efficient syntheses.
- Ana I. Benítez-Mateos
- , David Roura Padrosa
- & Francesca Paradisi
Perspective | 04 February 2022
Strategies for developing DNA-encoded libraries beyond binding assays
DNA-encoded libraries can be applied in a diverse range of applications beyond simple binding assays. This Perspective covers the recent progress in using DNA-encoded chemical libraries to investigate complex biological targets and discusses their potential to identify structures that elicit function or possess other useful properties.
- Yiran Huang
- , Yizhou Li
News & Views | 27 January 2022
Simple strategy towards amide bioisosteres
Aryl aminooxetanes are used as amide bioisosteres in drug discovery but there are limited strategies for synthesizing them. Now, an approach has been developed that simplifies the synthesis of these privileged motifs, enabling a broad range of amines to be used.
- Malcolm P. Huestis
- & Jack A. Terrett
News & Views | 05 January 2022
A hydroxide lock for metallo-β-lactamases
It is extremely difficult to design a broad-spectrum inhibitor for metallo-β-lactamases (MBLs) due to the diversity in the active site. Now, indole-2-carboxylates have been developed as broad-spectrum inhibitors for MBLs. These inhibitors take advantage of key elements of both MBL substrates and products and work by locking a hydroxide.
- & Hongzhe Sun
Article | 13 December 2021
Imitation of β-lactam binding enables broad-spectrum metallo-β-lactamase inhibitors
The efficacy of carbapenem antibiotics can be compromised by metallo-β-lactamases, but a high-throughput screen followed by optimization has now enabled the discovery of indole-2-carboxylates (InCs) as potent broad-spectrum metallo-β-lactamase inhibitors. The results highlight the potential of InC–carbapenem combinations for clinical use as well as mechanism-guided approaches to combatting globally disseminated antibiotic resistant mechanisms.
- Jürgen Brem
- , Tharindi Panduwawala
- & Christopher J. Schofield
Article | 06 December 2021
A mating mechanism to generate diversity for the Darwinian selection of DNA-encoded synthetic molecules
DNA-encoded libraries facilitate the discovery of ligands that interact with biomolecules but such technologies do not take full advantage of the principles of Darwinian selection. Now, libraries of conformationally constrained peptides ( D suprabodies) have been assembled using a strategy that allows for iterative cycles of selection, amplification and diversification. This method was validated with selections against streptavidin and PD-L1.
- Balayeshwanth R. Vummidi
- , Lluc Farrera-Soler
- & Nicolas Winssinger
Article | 10 June 2021
Switching on prodrugs using radiotherapy
Prodrugs offer one route to treat cancer, but they require activation once they have been delivered to the tumour. Now, a simultaneous chemo-radiotherapy strategy has been demonstrated in mice that uses gamma or X-ray irradiation to locally activate an anticancer prodrug.
- , Yichuan Zhang
- & Mark Bradley
News & Views | 01 June 2021
Expanding the effectiveness of screening
DNA-encoded libraries are a powerful tool to identify hit compounds for drug discovery. Now, two papers have reported new advances in this technology. One paper reports a method to screen for binders inside a living cell, and the other investigates the effects of stereo- and regiochemistry on ligand discovery.
- Minsoo Song
- & Gil Tae Hwang
Article | 08 April 2021
Stereo- and regiodefined DNA-encoded chemical libraries enable efficient tumour-targeting applications
A DNA-encoded chemical library based on regio- and stereoisomers of phenylalanine has been synthesized and used for affinity-based selections against multiple target proteins. This approach led to the isolation and validation of potent ligands capable of CAR T-cell activation and tumour targeting.
- Nicholas Favalli
- , Gabriele Bassi
- & Dario Neri
News & Views | 30 March 2021
Designing in vivo active DNAzymes
The therapeutic applications of DNAzymes are limited because of their low effectiveness in vivo. Now, a promising approach for constructing DNAzymes that show high gene-silencing efficiency in mammalian cells has been developed. This approach incorporates chemical modifications into an existing DNAzyme scaffold.
- & Chuanzheng Zhou
News & Views | 29 January 2021
The liberating force of ultrasound
Sophisticated drug delivery systems are as essential to modern medicine as drugs themselves. Now, polymer mechanochemistry in sonicated solutions has been used to activate drugs in three different systems. These results offer a promising approach that can be tailored to diverse molecular structures of modern pharmaceuticals.
- Roman Boulatov
Article | 21 December 2020
Selection of DNA-encoded chemical libraries against endogenous membrane proteins on live cells
A method to label membrane proteins with a DNA tag has been developed that enables the selection of DNA-encoded chemical libraries against endogenous membrane proteins on live cells. As a demonstration, a 30-million-compound DNA-encoded chemical library is screened against folate receptor, carbonic anhydrase 12 and epidermal growth factor receptor on live cells.
- , Ling Meng
News & Views | 23 September 2020
Protein targeting with SAF(er) electrophiles
Electrophilic groups that undergo sulfur-exchange chemistry with protein nucleophiles can serve as the functional basis of chemical proteomic probes. A new addition to this class, sulfuramidimidoyl fluoride (SAF), which can be included in an array of covalent small molecule probes, exhibits a unique reactivity profile with proteins.
- Thomas E. Speltz
- & Raymond E. Moellering
Article | 24 August 2020
Design of a small molecule that stimulates vascular endothelial growth factor A enabled by screening RNA fold–small molecule interactions
A selection-based screen has now revealed preferences in small-molecule chemotypes that bind RNA as well as preferences in the RNA motifs that bind small molecules. Analysis of these data enabled the design of a small molecule that selectively binds a non-coding microRNA and upregulates expression of vascular endothelial growth factor A.
- Hafeez S. Haniff
- , Laurent Knerr
- & Matthew D. Disney
Comment | 10 July 2020
Harder, better, faster
The gap between fundamental academic research and the applied industrial research that is necessary to ensure real-world applications can be bridged by engaging in well-defined collaborative academia–industry projects and fostering better communication between the scientists involved in them.
- Danielle Schultz
- & Louis-Charles Campeau
Correspondence | 18 June 2020
Crowdsourcing drug discovery for pandemics
- John Chodera
- , Alpha A. Lee
- & Frank von Delft
Thesis | 13 March 2020
A chemist’s cup of tea
Michelle Francl dips into the science of making tea.
Article | 16 December 2019
Repurposing human kinase inhibitors to create an antibiotic active against drug-resistant Staphylococcus aureus , persisters and biofilms
Screening commercial kinase inhibitors for antibacterial activity identified the anticancer drug sorafenib as a major hit. Subsequent structure–activity optimization created a new antibacterial analogue with high potency against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus , including challenging persisters and biofilms, as well as demonstrating efficacy in an in vivo mouse model. The mode of action involves stimulation of protein secretion and inhibition of menaquinone biosynthesis.
- , Elena Kunold
- & Stephan A. Sieber
Article | 28 October 2019
Expedited mapping of the ligandable proteome using fully functionalized enantiomeric probe pairs
A set of enantioprobes—photoreactive, clickable fragment pairs differing only in absolute stereochemistry—have been used to provide a robust and streamlined chemical proteomic map of small-molecule/protein interactions in human cells. More than 170 stereoselective fragment–protein interactions were discovered and shown to occur at functional sites on proteins from diverse classes.
- , Melissa M. Dix
- & Benjamin F. Cravatt
Article | 23 September 2019
Targeted photoredox catalysis in cancer cells
Current photodynamic therapy photosensitizers require oxygen; however, tumours are often hypoxic. Now, an organoiridium complex with an unusually high redox potential, which is effective in normoxia and hypoxia, has been developed. The organoiridium complex kills cancer cells by an immunogenic apoptotic mechanism involving efficient photocatalytic oxidation of NADH to NAD radicals, and reduction of cytochrome c .
- Huaiyi Huang
- , Samya Banerjee
- & Peter J. Sadler
Fungal indole alkaloid biogenesis through evolution of a bifunctional reductase/Diels–Alderase
The complete biosynthesis of the fungal indole alkaloid malbrancheamide, which culminates in an intramolecular [4+2] hetero-Diels–Alder cyclization to produce the bicyclo[2.2.2]diazaoctane scaffold, has now been discovered. Chemical synthesis and protein structural analysis were used to provide mechanistic insight into this enzyme-dependent diastereo- and enantioselective cycloaddition.
- Qingyun Dan
- , Sean A. Newmister
- & Robert M. Williams
Perspective | 02 September 2019
Towards the online computer-aided design of catalytic pockets
The shape complementarity between the active site of a catalyst and a substrate influences how effectively a reaction can be catalysed. Computational tools can be used to visualize the shape around the active centre of a range of catalysts and the application of such approaches to rationalize the behaviour of known catalysts — and to design new ones — is discussed.
- Laura Falivene
- & Luigi Cavallo
News & Views | 13 May 2019
Diverse engineering
Methods for generating molecular diversity provide a route to screen a wider section of chemical space, to discover compounds with useful biological properties. Now, a complexity-to-diversity strategy has enabled the discovery of a multi-cyclic structure from a complex natural product that induces ferroptotic cell death in cancer cells.
- Tatiana Cañeque
- & Raphaël Rodriguez
Article | 13 May 2019
Diverse compounds from pleuromutilin lead to a thioredoxin inhibitor and inducer of ferroptosis
A set of stereochemically complex and structurally diverse compounds were created from the diterpene natural product pleuromutilin using the complexity-to-diversity strategy. Phenotypic screening identified a compound that induces rapid ferroptotic death of cancer cells. Experiments to probe the mechanism revealed the compound to be an inhibitor of thioredoxin.
- Evijola Llabani
- , Robert W. Hicklin
- & Paul J. Hergenrother
Article | 10 December 2018
Rapamycin-inspired macrocycles with new target specificity
Rapamycin and FK506 are macrocycles that contain an FKBP-binding domain and an effector domain responsible for interacting with their respective targets, mTOR and calcineurin. Now, a 45,000-compound macrocycle library has been synthesized by fusing oligopeptides with synthetic FKBP-binding domains. Screening and subsequent optimization yielded a highly potent FKBP-dependent inhibitor of hENT1.
- , Sam Y. Hong
- & Jun O. Liu
Article | 08 October 2018
Inhibiting amyloid-β cytotoxicity through its interaction with the cell surface receptor LilrB2 by structure-based design
Inhibiting the interaction between amyloid-β (Aβ) and a neuronal cell surface receptor, LilrB2, could offer a potential route for treating Alzheimer’s disease. Now, binding sites between Aβ and LilrB2 have been discovered and computational selection has identified inhibitors that block this binding site. Cell-penetrating inhibitors were found to block the Aβ–LilrB2 interaction and limit Aβ-induced cytotoxicity.
- , Woo Shik Shin
- & Lin Jiang
News & Views | 20 September 2018
A positive positive to negative
The structure of an antibiotic that is effective against Gram-positive bacteria, but not against Gram-negative bacteria, has now been modified to improve its effectiveness against Gram-negative bacteria. The approach could help broaden the spectrum of activity of other antibiotics.
- Jed F. Fisher
- & Shahriar Mobashery
Article | 10 September 2018
Chromopynones are pseudo natural product glucose uptake inhibitors targeting glucose transporters GLUT-1 and -3
New natural-product-inspired molecules are often limited by their only partial coverage of biologically relevant chemical space. Combining fragments of natural products has now been shown to yield pseudo natural products, which — while still being inspired by natural products — populate previously unexplored areas of chemical space and have novel biological activities.
- George Karageorgis
- , Elena S. Reckzeh
- & Herbert Waldmann
Editorial | 21 June 2018
Ring binders
Encoded chemical libraries can be used to screen a vast array of compounds against a protein target to identify potent binders. A collection of articles in this issue discuss different methods to increase the chemical space sampled by encoded macrocycle libraries and the advantages that such libraries offer for discovering new drug leads.
Browse broader subjects
- Drug discovery
Browse narrower subjects
- Chemical libraries
- Cheminformatics
- Computational chemistry
- Drug delivery
- Drug discovery and development
- Lead optimization
- Pharmacology
- Structure-based drug design
- Target identification
- Target validation
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The New England Journal of Medicine (NEJM) is a weekly general medical journal that publishes new medical research and review articles, and editorial opinion on a wide variety of topics of ...
JAMA - The Latest Medical Research, Reviews, and Guidelines. Home New Online Issues For Authors. Editor's Choice: How AI Will Enhance Imaging Access and Analysis. Kidney Donor and Recipient OutcomesMay 23, 2024Original Investigation Hypertension and Kidney Function After Living Kidney Donation Amit X. Garg, MD, PhD; Jennifer B. Arnold, BSc ...
Medical research articles from across Nature Portfolio. Medical research involves research in a wide range of fields, such as biology, chemistry, pharmacology and toxicology with the goal of ...
Medicinal Research Reviews is an essential resource for researchers around the world. Our top-ranked medicinal chemistry journal features timely, critical reviews and opinion-based articles that cover the full range of medicinal research to which our authors have made significant contributions.
The proportions of term or late preterm births after exposure to early antenatal corticosteroids, and outcomes. August 2, 2023. Can't find what you're looking for? Continue to all research articles. Original research studies that can improve decision making in clinical medicine, public health, health care policy, medical education, or ...
Advanced. Journal List. PubMed Central ® (PMC) is a free full-text archive of biomedical and life sciences journal literature at the U.S. National Institutes of Health's National Library of Medicine (NIH/NLM)
Neglecting sex and gender in research is a public-health risk The data are clear: taking sex and gender into account in research and using that knowledge to change health care could benefit ...
1. Introduction. Breakthroughs in Medicinal Chemistry: New Targets and Mechanisms, New Drugs, New Hopes is a series of Editorials that is published on a biannual basis by the Editorial Board of the Medicinal Chemistry section of the journal Molecules.In these Editorials, we highlight in brief reports (of about one hundred words) a number of recently published articles that describe crucial ...
Here, the authors investigate the fluctuations of physiological indices along aging trajectories and observed a characteristic decrease in the organism state recovery rate. Timothy V. Pyrkov ...
Volume 44, Issue 1. Pages: 1-452. January 2024. Medicinal Research Reviews is a top-ranked medicinal chemistry journal featuring critical reviews and opinion articles in medicinal research.
Sleep loss is a common public health problem that causes hyperalgesia, especially that after surgery, which reduces the quality of life seriously. Yulin Huang, Rui Xu, Qi Liu, Xiao Zhang, Yanting Mao, Yan Yang, Xiaoping Gu, Yue Liu and Zhengliang Ma. BMC Medicine 2024 22 :189.
Medicinal Chemistry. Trust ACS to bring you experimental and theoretical studies across a broad range of medicinal chemistry, including compound design and optimization, biological evaluation, molecular mechanistic understanding of drug delivery and drug delivery systems, imaging agents, and pharmacology and translational science of both small ...
Figure 5. Temporal evolution on medical plants publications for Top 12 countries. The first group is the leaders of this research, China and India, with between 800 and 1100 publications per year. China led the research from 1996 to 2010, and from this year to 2016, the leader was India, after which it returned to China.
Medicinal Chemistry Research is a journal focused on the publication of novel findings in drug design, drug discovery, and mechanisms of action of biologically active compounds.. Offers prompt publication of experimental achievements. Covers chemical biological relationships, especially on: structure-activity relationships, investigations of biochemical and pharmacological targets of drug ...
Jian Ma. Ruvishika S. Jayawardena. Original Research Article 04 January 2024 Pages: 308 - 313. 1. 2. …. 87. Next. Medicinal Chemistry Research is a journal focused on the publication of novel findings in drug design, drug discovery, and mechanisms of action of ...
3.3 million articles on ScienceDirect are open access. Articles published open access are peer-reviewed and made freely available for everyone to read, download and reuse in line with the user license displayed on the article. ScienceDirect is the world's leading source for scientific, technical, and medical research.
Medicinal chemistry articles from across Nature Portfolio. Medicinal chemistry deals with the design, optimization and development of chemical compounds for use as drugs. It is inherently a ...
Asthma-COPD overlap (ACO) is a distinct and intricate respiratory condition that requires specific attention and management. The objective of this cohort study was to examine the epidemiological characteristic... Meng Zhu and An Chen. BMC Public Health 2024 24 :1423. Research Published on: 28 May 2024.
The research sets the foundation for the development of better tools to study RNA modifications and their role in resistance while simultaneously opening new avenues for drug development. RNA-modifying enzymes, especially those linked to resistance, are currently understudied, and they are attractive targets for the development of new and more ...
2.1. Coriolus versicolor (L.) Quél. Coriolus versicolor, commonly known as tunzhi in China or turkey tail, has always been used as a "magic herb" in Asian regions and particularly in China, where ancient formulations based on this mushroom have been and are still widely used to promote good health, strength, and longevity [10,11].Thousands of years ago in China, its medicinal properties ...
The research, which was published in April in the journal Appetite, provides a collection of carefully curated images of minimally processed and ultra-processed foods matched on 26 characteristics ...
The male reproductive organs are no exception. New research published this month finds microplastics can build up in the testicles of humans and dogs — raising more questions about the potential ...
May 23, 2024. Yale School of Public Health (YSPH) Associate Dean of Research Melinda Irwin Wednesday announced the recipients of this year's top research awards. "Congratulations to the YSPH faculty who were awarded YSPH Research Prizes for manuscripts published in 2023," said Irwin, Susan Dwight Bliss Professor of Epidemiology (Chronic ...
May 23, 2024. For the first time on record, cannabis has outpaced alcohol as the daily drug of choice for Americans. In 2022 there were 17.7 million people who reported using cannabis either every ...
More than 150 research applications for studies into cannabis were pending before the FDA as of March, according to a recent letter from two congressional lawmakers to the U.S. health secretary ...
Medicinal chemistry articles within Nature. Featured. Article | 22 May 2024. ... Research articles News Opinion Research Analysis Careers ...
For the study, researchers analyzed data on more than 71,000 women participating in a large-scale health study. The researchers divided the women into five age brackets: born between 1950-1969 ...
Adverse effects were reported in most reviews comparing cannabis with placebo (49/59, 83%) and in 20/24 (83%) of the reviews comparing cannabis to active drugs. Minor adverse effects (e.g., drowsiness, dizziness) were common and reported in over half of the reviews. Serious harms were not as common, but were reported in 21/59 (36%) reviews that ...
Donate your sex cells. Iryna Inshyna/Shutterstock. Payout for eggs (per donation): usually $10,000 to $12,000; Payout for sperm (per donation): typically $35-$150. Advertisement. Egg and sperm ...
Read the latest Research articles in Medicinal chemistry from Nature Chemistry. Skip to main content. ... Medicinal chemistry articles within Nature Chemistry. Featured. Article | 20 May 2024.