Use Our Free A/B Testing Hypothesis Generator . Never Miss Key Elements From Your Hypotheses. Get Big Conversion Lifts.
Observation, inadvertent impact.


Streamline Your Hypothesis Generation Research with Custom Templates the Pros Use.
Have questions about a/b testing hypotheses, what is a hypothesis.
Many people define a hypothesis as an “educated guess”.
To be more precise, a properly constructed hypothesis predicts a possible outcome to an experiment or a test where one variable (the independent one ) is tweaked and/or modified and the impact is measured by the change in behavior of another variable (generally the dependent one).
A hypothesis should be specific (it should clearly define what is being altered and what is the expected impact), data-driven (the changes being made to the independent variable should be based on historic data or theories that have been proven in the past), and testable (it should be possible to conduct the proposed test in a controlled environment to establish the relationship between the variables involved, and disprove the hypothesis - should it be untrue.)
What is the Cost of a Hastily Assembled Hypothesis?
According to an analysis of over 28,000 tests run using the Convert Experiences platform, only 1 in 5 tests proves to be statistically significant.
While more and more debate is opening up around sticking to the concept of 95% statistical significance, it is still a valid rule of thumb for optimizers who do not want to get into the fray with peeking vs. no peeking, and custom stopping rules for experiments.
There might be a multitude of reasons why a test does not reach statistical significance. But framing a tenable hypothesis that already proves itself logistically feasible on paper is a better starting point than a hastily assembled assumption.
Moreover, the aim of an A/B test may be to extract a learning, but some learnings come with heavy costs. 26% decrease in conversion rates to be specific.
A robust hypothesis may not be the answer to all testing woes, but it does help prioritisation of possible solutions and leads testing teams to pick low hanging fruits.
How is an A/B Testing Hypothesis Different?
An A/B test should be treated with the same rigour as tests conducted in laboratories. That is an easy way to guarantee better hypotheses, more relevant experiments, and ultimately more profitable optimization programs.
The focus of an A/B test should be on first extracting a learning , and then monetizing it in the form of increased registration completions, better cart conversions and more revenue.
If that is true, then an A/B test hypothesis is not very different from a regular scientific hypothesis. With a couple of interesting points to note:
- Most scientific hypotheses proceed with one independent variable and one dependent variable, for the sake of simplicity. But in A/B tests, there might be changes made to several independent variables at the same time. Under such circumstances it is good to explore the relationship between the independent variables to make sure that they do not inadvertently impact one another. For example changing both the value proposition and button copy of a landing page to determine improvement in click through or completion rates is tricky. Reaching a point where the browser is compelled to click the button could easily have been impacted by the value proposition (as in a strong hook and heading). So what caused the improvement in the dependent variable? Was it the change to the first element or the second one?
- The concept of Operational Definition is non-negotiable in most laboratory experiments. And comes baked with the question of ethics or morality. Operation Definition is the specific process that will be used to quantify the change in the value/behavior of the independent variable in the test. As an example, if a test wishes to measure the level of frustration that subjects experience when they are exposed to certain stimuli, researchers must be careful to define exactly how they will measure the output or frustration. Should they allow the test subjects to act out, in which case they may hurt or harm other individuals. Or should they use a non-invasive technique like an fMRI scan to monitor brain activity and collect the needed data. In A/B tests however, since data is collected through relatively inanimate channels like analytics dashboards, generally little thought is spared to Operational Definition and the impact of A/B testing on the human subjects (site traffic in this case).
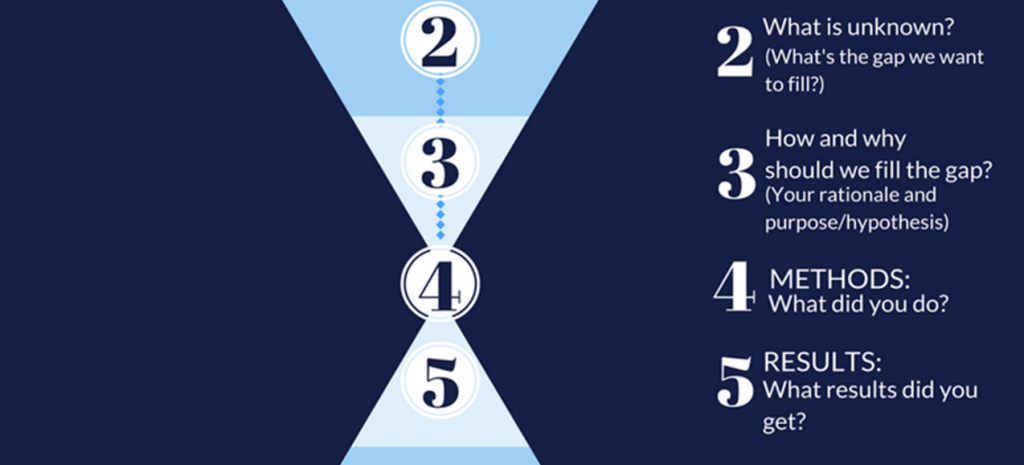
The 5 Essential Parts of an A/B Testing Hypothesis
A robust A/B testing hypothesis should be assembled in 5 key parts:

1. OBSERVATION
This includes a clear outline of the problem (the unexplained phenomenon) observed and what it entails. This section should be completely free of conjecture and rely solely on good quality data - either qualitative and/or quantitative - to bring a potential area of improvement to light. It also includes a mention of the way in which the data is collected.
Proper observation ensures a credible hypothesis that is easy to “defend” later down the line.

2. EXECUTION
This is the where, what, and the who of the A/B test. It specifies the change(s) you will be making to site element(s) in an attempt to solve the problem that has been outlined under “OBSERVATION”. It serves to also clearly define the segment of site traffic that will be exposed to the experiment.
Proper execution guidelines set the rhythm for the A/B test. They define how easy or difficult it will be to deploy the test and thus aid hypothesis prioritization .

This is where you make your educated guess or informed prediction. Based on a diligently identified OBSERVATION and EXECUTION guidelines that are possible to deploy, your OUTCOME should clearly mention two things:
- The change (increase or decrease) you expect to see to the problem or the symptoms of the problem identified under OBSERVATION.
- The Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) you will be monitoring to gauge whether your prediction has panned out, or not.
In general most A/B tests have one primary KPI and a couple of secondary KPIs or ways to measure impact. This is to ensure that external influences do not skew A/B test results and even if the primary KPI is compromised in some way, the secondary KPIs do a good job of indicating that the change is indeed due to the implementation of the EXECUTION guidelines, and not the result of unmonitored external factors.

4. LOGISTICS
An important part of hypothesis formulation, LOGISTICS talk about what it will take to collect enough clean data from which a reliable conclusion can be drawn. How many unique tested visitors, what is the statistical significance desired, how many conversions is enough and what is the duration for which the A/B test should run? Each question on its own merits a blog or a lesson. But for the sake of convenience, Convert has created a Free Sample Size & A/B/N Test Duration Calculator .
Set the right logistical expectations so that you can prioritise your hypotheses for maximum impact and minimum effort .

5. INADVERTENT IMPACT
This is a nod in the direction of ethics in A/B testing and marketing, because experiments involve humans and optimizers should be aware of the possible impact on their behavior.
Often a thorough analysis at this stage can modify the way impact is measured or an experiment is conducted. Or Convert certainly hopes that this will be the case in future. Here’s why ethics do matter in testing.
Now Organize, Prioritise & Learn from Your Hypotheses.
Try convert experiences in free trial & access compass beta - our hypothesis management platform., always working to improve outcomes..
Start Your 15 -Day Free Trial Right Now. No Credit Card Required
Important. Please Read.
- Check your inbox for the password to Convert’s trial account.
- Log in using the link provided in that email.
This sign up flow is built for maximum security. You’re worth it!

Research Hypothesis Generator
Generate research hypotheses with ai.
- Academic Research: Formulate a hypothesis for your thesis or dissertation based on your research topic and objectives.
- Data Analysis: Generate a hypothesis to guide your data collection and analysis strategy.
- Market Research: Develop a hypothesis to guide your investigation into market trends and consumer behavior.
- Scientific Research: Create a hypothesis to direct your experimental design and data interpretation.
New & Trending Tools
In-cite ai reference generator, legal text refiner, job search ai assistant.
Research Hypothesis Generator Online
- ️👍 Hypothesis Maker: the Benefits
- ️🔎 How to Use the Tool?
- ️🕵️ What Is a Research Hypothesis?
- ️⚗️ Scientific Method
- ️🔗 References
👍 Hypothesis Maker: the Benefits
Here are the key benefits of this null and alternative hypothesis generator.
🔎 Hypothesis Generator: How to Use It?
Whenever you conduct research, whether a 5-paragraph essay or a more complex assignment, you need to create a hypothesis for this study.
Clueless about how to create a good hypothesis?
No need to waste time and energy on this small portion of your writing process! You can always use our hypothesis creator to get a researchable assumption in no time.
To get a ready-made hypothesis idea, you need to:
- State the object of your study
- Specify what the object does
- Lay out the outcome of that activity
- Indicate the comparison group
Once all data is inserted into the fields, you can press the “Generate now” button and get the result from our hypothesis generator for research paper or any other academic task.
🕵️ What Is a Research Hypothesis?
A hypothesis is your assumption based on existing academic knowledge and observations of the surrounding natural world.

It also involves a healthy portion of intuition because you should arrive at an interesting, commonsense question about the phenomena or processes you observe.
The traditional formula for hypothesis generation is an “if…then” statement, reflecting its falsifiability and testability.
What do these terms mean?
- Testability means you can formulate a scientific guess and test it with data and analysis.
- Falsifiability is a related feature, allowing you to refute the hypothesis with data and show that your guess has no tangible support in real-world data.
For example, you might want to hypothesize the following:
If children are given enough free play time, their intelligence scores rise quicker.
You can test this assumption by observing and measuring two groups – children involved in much free play and those who don’t get free play time. Once the study period ends, you can measure the intelligence scores in both groups to see the difference, thus proving or disproving your hypothesis, which will be testing your hypothesis. If you find tangible differences between the two groups, your hypothesis will be proven, and if there is no difference, the hypothesis will prove false.
Null and Alternative Hypothesis
As a rule, hypotheses are presented in pairs in academic studies, as your scientific guess may be refuted or proved. Thus, you should formulate two hypotheses – a null and alternative variant of the same guess – to see which one is proved with your experiment.

The alternative hypothesis is formulated in an affirmative form, assuming a specific relationship between variables. In other words, you hypothesize that the predetermined outcome will be observed if one condition is met.
Watching films before sleep reduces the quality of sleep.
The null hypothesis is formulated in a negative form, suggesting that there is no association between the variables of your interest. For example:
Watching films before sleep doesn’t affect the quality of sleep.
⚗️ Creating a Hypothesis: the Key Steps
The development and testing of multiple hypotheses are the basis of the scientific method .
Without such inquiries, academic knowledge would never progress, and humanity would remain with a limited understanding of the natural world.
How can you contribute to the existing academic base with well-developed and rigorously planned scientific studies ? Here is an introduction to the empirical method of scientific inquiry.
Step #1: Observe the World Around You
Look around you to see what’s taking place in your academic area. If you’re a biology researcher, look into the untapped biological processes or intriguing facts that nobody has managed to explain before you.
What’s surprising or unusual in your observations? How can you approach this area of interest?
That’s the starting point of an academic journey to new knowledge.
Step #2: Ask Questions
Now that you've found a subject of interest, it's time to generate scientific research questions .
A question can be called scientific if it is well-defined, focuses on measurable dimensions, and is largely testable.
Some hints for a scientific question are:
- What effect does X produce on Y?
- What happens if the intensity of X’s impact reduces or rises?
- What is the primary cause of X?
- How is X related to Y in this group of people?
- How effective is X in the field of C?
As you can see, X is the independent variable , and Y is the dependent variable.
This principle of hypothesis formulation is vital for cases when you want to illustrate or measure the strength of one variable's effect on the other.
Step #3: Generate a Research Hypothesis
After asking the scientific question, you can hypothesize what your answer to it can be.
You don't have any data yet to answer the question confidently, but you can assume what effect you will observe during an empirical investigation.
For example, suppose your background research shows that protein consumption boosts muscle growth.
In that case, you can hypothesize that a sample group consuming much protein after physical training will exhibit better muscle growth dynamics compared to those who don’t eat protein. This way, you’re making a scientific guess based on your prior knowledge of the subject and your intuition.
Step #4: Hold an Experiment
With a hypothesis at hand, you can proceed to the empirical study for its testing. As a rule, you should have a clearly formulated methodology for proving or disproving your hypothesis before you create it. Otherwise, how can you know that it is testable? An effective hypothesis usually contains all data about the research context and the population of interest.
For example:
Marijuana consumption among U. S. college students reduces their motivation and academic achievement.
- The study sample here is college students.
- The dependent variable is motivation and academic achievement, which you can measure with any validated scale (e.g., Intrinsic Motivation Inventory).
- The inclusion criterion for the study's experimental group is marijuana use.
- The control group might be a group of marijuana non-users from the same population.
- A viable research methodology is to ask both groups to fill out the survey and compare the results.
Step #5: Analyze Your Findings
Once the study is over and you have the collected dataset, it's time to analyze the findings.
The methodology should also delineate the criteria for proving or disproving the hypothesis.
Using the previous section's example, your hypothesis is proven if the experimental group reveals lower motivational scores and has a lower GPA . If both groups' motivation and GPA scores aren't statistically different, your hypothesis is false.
Step #6: Formulate Your Conclusion
Using your study's hypothesis and outcomes, you can now generate a conclusion . If the alternative hypothesis is proven, you can conclude that marijuana use hinders students' achievement and motivation. If the null hypothesis is validated, you should report no identified relationship between low academic achievement and weed use.
Thank you for reading this article! Note that if you need to conduct a business analysis, you can try our free tools: SWOT , VRIO , SOAR , PESTEL , and Porter’s Five Forces .
❓ Research Hypothesis Generator FAQ
❓ what is a research hypothesis.
A hypothesis is a guess or assumption you make by looking at the available data from the natural world. You assume a specific relationship between variables or phenomena and formulate that supposition for further testing with experimentation and analysis.
❓ How to write a hypothesis?
To compose an effective hypothesis, you need to look at your research question and formulate a couple of ways to answer it. The available scientific data can guide you to assume your study's outcome. Thus, the hypothesis is a guess of how your research question will be answered by the end of your research.
❓ What is the difference between prediction and hypothesis?
A prediction is your forecast about the outcome of some activities or experimentation. It is a guess of what will happen if you perform some actions with a specific object or person. A hypothesis is a more in-depth inquiry into the way things are related. It is more about explaining specific mechanisms and relationships.
❓ What makes a good hypothesis?
A strong hypothesis should indicate the dependent and independent variables, specifying the relationship you assume between them. You can also strengthen your hypothesis by indicating a specific population group, an intervention period, and the context in which you'll hold the study.
🔗 References
- What is and How to Write a Good Hypothesis in Research?
- Research questions, hypotheses and objectives - PMC - NCBI
- Developing the research hypothesis - PubMed
- Alternative Hypothesis - SAGE Research Methods
- Alternative Hypothesis Guide: Definition, Types and Examples

- How it Works
- Member Area
“Write your paper 10x faster”
The #1 AI Research Tool for Students, Teachers, Scholars, and those in Academia
Generate study guides, outlines, research topics, key findings, hypotheses, and exam questions in seconds..
Streamline your planning and preparation with the top AI-generated answers for your specific academic field.

How Research Panda Works
1. pick the research template, 2. fill out the form in less than 2 minutes, 3. generate your academic content.

Save Hours and Days of Research Work

What You Get
Topic and idea selection.
Retrieve topics and subtopics, a longside possible ideas to e nforce and expand upon. Simplify and expand any topic or subtopic of reference.
Brainstorm and Outline Build
Have a thought flow built out s o you’re not mentally stuck. C reate a concrete outline and structure f or your research paper.
Research Questions, Gaps, and Hypothesis Generator
Based on a topic and keywords, g et a list of questions, gaps in research, a nd possible hypotheses t o utilize.
Methodology and Techniques Creator
Explain how the qualitative or quantitive approach can be used to address the topic. Get the top data collection practices.
Research Paper and Article Locator
Literature Review – Based on a given topic and keywords, p roduce articles for reference.
Summary and Analysis Generator
Get the main arguments and key findings of a given text. Describe the theoretical framework and methodology used.
Personal Study Guide and Plan Build
Create a step-by-step c omprehensive guide and plan b ased on y our timeframe to study.
Exam Preparation Creator
Generate multiple choice questions based on your given research topic
…ranging in various difficulties.
Book Summarizer
Give the title and author. Condense books into concise and comprehensive summaries for effortless learning.
Lesson Plan Generator
Structured lesson plans for any subject, idea, course, or concept. Just plug in the topic and grade level. AI will provide the rest.
Educational Handout Writer
Efficiently create comprehensive handouts encompassing all the essential information about a particular topic, concept, or subject area for both yourself and a student.
Gaps in Understanding Identifier
Provide your own understanding of a given topic, idea, or concept. An analysis will take place pointing out the gaps in knowledge of the said topic.
Bonus #1: The Quick Learner
Pick the topic, keywords, and main points you want to focus on and learn about. Be broad or specific as need be. Use the 80/20 principle to learn faster than ever.
Bonus #2: The Proofreader
Improvise your writing. Proofread, correct, and get tailored feedback to what you need to do to better your writing. This detailed feedback will give you the steps needed to take next.
Bonus #3: The Detailer
Completely understand a topic, idea, or research point. Have a concept broken down to have a strong mental grasp on it, being able to speak and write on it intelligently.
Why Research Panda?

Enhance your planning and preparation process through the power of comprehensive AI. Discover streamlined templates for study guides and receive tailored writing prompts and answers for each section of your paper that cater to your specific academic field. Research Panda was built for the academic .
Pick a Plan
Optimize your research and writing, get all the ai research tools, built for students, teachers, scholars, and academics.

1. Topic Selection and
Idea Generator
2. Brainstorm and Outline Generator
3. Research Questions, Research Gaps,
and Hypothesis Generator
4. Methodology and Technique Generator
5. Research Paper
and Article Locator Generator
6. Summary and Analysis Generator
7. Study Guide and Plan Generator
8. Exam Preparation Generator
Research Panda works for education levels ranging from high school students to doctoral academics. Nevertheless, it is for any academic looking to further their research in any given field.
Research Panda is capable of generating educational guides, study plans, academic content, and much more. If you can think it, Research Panda can create it. This includes materials related to mathematics, English Language Arts (reading, writing, grammar), science (biology, chemistry, physics), social Studies (history, geography, civics, economics), computer science, political science, and any subject you work in.
To use Research Panda, simply click one of the membership options above to “Try for 3 Days Free” to access the sign up page. From there, you can give Research Panda detailed instructions using any of the 8+ premium AI tools. Once you’ve generated your first AI content, go ahead and edit it to your liking, and copy it for your research use.
Yes! All Research Panda users get unlimited usage and access to all AI tools as long as they are a member. This means you can create as many guides, handouts, article reviews, outlines, and academic content as you’d like.
We offer a 3-day free trial with both membership tiers, Monthly and Quarterly. If you are not 100% satisfied, no worries! Just cancel before your free trial ends. Because of the work in the upkeep of Research Panda, we do not offer any refunds.
Feel free to send us a message using the form below! We will get back to you within 48 hours.
Get in Touch
©2023 by ResearchPanda.io | All Rights Reserved | Site Built by Nathan Schweikart

Create structured research hypotheses
AI Generators in Science and Research

🔬✍️ Formulate precise, well-founded hypotheses for your studies and scientific work. Explore the potential of your research!
Provide additional feedback
Discover the power of a well-formulated hypothesis with our Research Hypothesis Generator. In the world of scientific research, a solid, relevant hypothesis is the foundation on which any study is built.
🧪 Structured and precise
A well-defined hypothesis can guide your experiments and set the course for your discoveries. Our generator provides you with structured proposals based on your field and subject.
🌌 For all areas
Whether you're in biology, physics or the social sciences, we've got you covered. adapted our tool to meet the diversity of research needs.
💭 Refine Your Thinking
With our help, crystallize your idea into a clear, logical hypothesis. Each proposal is designed to stimulate your thinking and enrich your scientific approach.
Similar publications :

Popular generators:

Create Limitless with Generator AI
Immerse yourself in a world where every idea is instantly transformed into reality. Generator AI brings your boldest visions to life in the blink of an eye.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Methodology
- How to Write a Strong Hypothesis | Guide & Examples
How to Write a Strong Hypothesis | Guide & Examples
Published on 6 May 2022 by Shona McCombes .
A hypothesis is a statement that can be tested by scientific research. If you want to test a relationship between two or more variables, you need to write hypotheses before you start your experiment or data collection.
Table of contents
What is a hypothesis, developing a hypothesis (with example), hypothesis examples, frequently asked questions about writing hypotheses.
A hypothesis states your predictions about what your research will find. It is a tentative answer to your research question that has not yet been tested. For some research projects, you might have to write several hypotheses that address different aspects of your research question.
A hypothesis is not just a guess – it should be based on existing theories and knowledge. It also has to be testable, which means you can support or refute it through scientific research methods (such as experiments, observations, and statistical analysis of data).
Variables in hypotheses
Hypotheses propose a relationship between two or more variables . An independent variable is something the researcher changes or controls. A dependent variable is something the researcher observes and measures.
In this example, the independent variable is exposure to the sun – the assumed cause . The dependent variable is the level of happiness – the assumed effect .
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Step 1: ask a question.
Writing a hypothesis begins with a research question that you want to answer. The question should be focused, specific, and researchable within the constraints of your project.
Step 2: Do some preliminary research
Your initial answer to the question should be based on what is already known about the topic. Look for theories and previous studies to help you form educated assumptions about what your research will find.
At this stage, you might construct a conceptual framework to identify which variables you will study and what you think the relationships are between them. Sometimes, you’ll have to operationalise more complex constructs.
Step 3: Formulate your hypothesis
Now you should have some idea of what you expect to find. Write your initial answer to the question in a clear, concise sentence.
Step 4: Refine your hypothesis
You need to make sure your hypothesis is specific and testable. There are various ways of phrasing a hypothesis, but all the terms you use should have clear definitions, and the hypothesis should contain:
- The relevant variables
- The specific group being studied
- The predicted outcome of the experiment or analysis
Step 5: Phrase your hypothesis in three ways
To identify the variables, you can write a simple prediction in if … then form. The first part of the sentence states the independent variable and the second part states the dependent variable.
In academic research, hypotheses are more commonly phrased in terms of correlations or effects, where you directly state the predicted relationship between variables.
If you are comparing two groups, the hypothesis can state what difference you expect to find between them.
Step 6. Write a null hypothesis
If your research involves statistical hypothesis testing , you will also have to write a null hypothesis. The null hypothesis is the default position that there is no association between the variables. The null hypothesis is written as H 0 , while the alternative hypothesis is H 1 or H a .
Hypothesis testing is a formal procedure for investigating our ideas about the world using statistics. It is used by scientists to test specific predictions, called hypotheses , by calculating how likely it is that a pattern or relationship between variables could have arisen by chance.
A hypothesis is not just a guess. It should be based on existing theories and knowledge. It also has to be testable, which means you can support or refute it through scientific research methods (such as experiments, observations, and statistical analysis of data).
A research hypothesis is your proposed answer to your research question. The research hypothesis usually includes an explanation (‘ x affects y because …’).
A statistical hypothesis, on the other hand, is a mathematical statement about a population parameter. Statistical hypotheses always come in pairs: the null and alternative hypotheses. In a well-designed study , the statistical hypotheses correspond logically to the research hypothesis.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2022, May 06). How to Write a Strong Hypothesis | Guide & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 14 May 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/research-methods/hypothesis-writing/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, operationalisation | a guide with examples, pros & cons, what is a conceptual framework | tips & examples, a quick guide to experimental design | 5 steps & examples.
- Affiliate Program

- UNITED STATES
- 台灣 (TAIWAN)
- TÜRKIYE (TURKEY)
- Academic Editing Services
- - Research Paper
- - Journal Manuscript
- - Dissertation
- - College & University Assignments
- Admissions Editing Services
- - Application Essay
- - Personal Statement
- - Recommendation Letter
- - Cover Letter
- - CV/Resume
- Business Editing Services
- - Business Documents
- - Report & Brochure
- - Website & Blog
- Writer Editing Services
- - Script & Screenplay
- Our Editors
- Client Reviews
- Editing & Proofreading Prices
- Wordvice Points
- Partner Discount
- Plagiarism Checker
- APA Citation Generator
- MLA Citation Generator
- Chicago Citation Generator
- Vancouver Citation Generator
- - APA Style
- - MLA Style
- - Chicago Style
- - Vancouver Style
- Writing & Editing Guide
- Academic Resources
- Admissions Resources

How to Write a Research Hypothesis: Good & Bad Examples
What is a research hypothesis?
A research hypothesis is an attempt at explaining a phenomenon or the relationships between phenomena/variables in the real world. Hypotheses are sometimes called “educated guesses”, but they are in fact (or let’s say they should be) based on previous observations, existing theories, scientific evidence, and logic. A research hypothesis is also not a prediction—rather, predictions are ( should be) based on clearly formulated hypotheses. For example, “We tested the hypothesis that KLF2 knockout mice would show deficiencies in heart development” is an assumption or prediction, not a hypothesis.
The research hypothesis at the basis of this prediction is “the product of the KLF2 gene is involved in the development of the cardiovascular system in mice”—and this hypothesis is probably (hopefully) based on a clear observation, such as that mice with low levels of Kruppel-like factor 2 (which KLF2 codes for) seem to have heart problems. From this hypothesis, you can derive the idea that a mouse in which this particular gene does not function cannot develop a normal cardiovascular system, and then make the prediction that we started with.
What is the difference between a hypothesis and a prediction?
You might think that these are very subtle differences, and you will certainly come across many publications that do not contain an actual hypothesis or do not make these distinctions correctly. But considering that the formulation and testing of hypotheses is an integral part of the scientific method, it is good to be aware of the concepts underlying this approach. The two hallmarks of a scientific hypothesis are falsifiability (an evaluation standard that was introduced by the philosopher of science Karl Popper in 1934) and testability —if you cannot use experiments or data to decide whether an idea is true or false, then it is not a hypothesis (or at least a very bad one).
So, in a nutshell, you (1) look at existing evidence/theories, (2) come up with a hypothesis, (3) make a prediction that allows you to (4) design an experiment or data analysis to test it, and (5) come to a conclusion. Of course, not all studies have hypotheses (there is also exploratory or hypothesis-generating research), and you do not necessarily have to state your hypothesis as such in your paper.
But for the sake of understanding the principles of the scientific method, let’s first take a closer look at the different types of hypotheses that research articles refer to and then give you a step-by-step guide for how to formulate a strong hypothesis for your own paper.
Types of Research Hypotheses
Hypotheses can be simple , which means they describe the relationship between one single independent variable (the one you observe variations in or plan to manipulate) and one single dependent variable (the one you expect to be affected by the variations/manipulation). If there are more variables on either side, you are dealing with a complex hypothesis. You can also distinguish hypotheses according to the kind of relationship between the variables you are interested in (e.g., causal or associative ). But apart from these variations, we are usually interested in what is called the “alternative hypothesis” and, in contrast to that, the “null hypothesis”. If you think these two should be listed the other way round, then you are right, logically speaking—the alternative should surely come second. However, since this is the hypothesis we (as researchers) are usually interested in, let’s start from there.
Alternative Hypothesis
If you predict a relationship between two variables in your study, then the research hypothesis that you formulate to describe that relationship is your alternative hypothesis (usually H1 in statistical terms). The goal of your hypothesis testing is thus to demonstrate that there is sufficient evidence that supports the alternative hypothesis, rather than evidence for the possibility that there is no such relationship. The alternative hypothesis is usually the research hypothesis of a study and is based on the literature, previous observations, and widely known theories.
Null Hypothesis
The hypothesis that describes the other possible outcome, that is, that your variables are not related, is the null hypothesis ( H0 ). Based on your findings, you choose between the two hypotheses—usually that means that if your prediction was correct, you reject the null hypothesis and accept the alternative. Make sure, however, that you are not getting lost at this step of the thinking process: If your prediction is that there will be no difference or change, then you are trying to find support for the null hypothesis and reject H1.
Directional Hypothesis
While the null hypothesis is obviously “static”, the alternative hypothesis can specify a direction for the observed relationship between variables—for example, that mice with higher expression levels of a certain protein are more active than those with lower levels. This is then called a one-tailed hypothesis.
Another example for a directional one-tailed alternative hypothesis would be that
H1: Attending private classes before important exams has a positive effect on performance.
Your null hypothesis would then be that
H0: Attending private classes before important exams has no/a negative effect on performance.
Nondirectional Hypothesis
A nondirectional hypothesis does not specify the direction of the potentially observed effect, only that there is a relationship between the studied variables—this is called a two-tailed hypothesis. For instance, if you are studying a new drug that has shown some effects on pathways involved in a certain condition (e.g., anxiety) in vitro in the lab, but you can’t say for sure whether it will have the same effects in an animal model or maybe induce other/side effects that you can’t predict and potentially increase anxiety levels instead, you could state the two hypotheses like this:
H1: The only lab-tested drug (somehow) affects anxiety levels in an anxiety mouse model.
You then test this nondirectional alternative hypothesis against the null hypothesis:
H0: The only lab-tested drug has no effect on anxiety levels in an anxiety mouse model.
How to Write a Hypothesis for a Research Paper
Now that we understand the important distinctions between different kinds of research hypotheses, let’s look at a simple process of how to write a hypothesis.
Writing a Hypothesis Step:1
Ask a question, based on earlier research. Research always starts with a question, but one that takes into account what is already known about a topic or phenomenon. For example, if you are interested in whether people who have pets are happier than those who don’t, do a literature search and find out what has already been demonstrated. You will probably realize that yes, there is quite a bit of research that shows a relationship between happiness and owning a pet—and even studies that show that owning a dog is more beneficial than owning a cat ! Let’s say you are so intrigued by this finding that you wonder:
What is it that makes dog owners even happier than cat owners?
Let’s move on to Step 2 and find an answer to that question.
Writing a Hypothesis Step 2:
Formulate a strong hypothesis by answering your own question. Again, you don’t want to make things up, take unicorns into account, or repeat/ignore what has already been done. Looking at the dog-vs-cat papers your literature search returned, you see that most studies are based on self-report questionnaires on personality traits, mental health, and life satisfaction. What you don’t find is any data on actual (mental or physical) health measures, and no experiments. You therefore decide to make a bold claim come up with the carefully thought-through hypothesis that it’s maybe the lifestyle of the dog owners, which includes walking their dog several times per day, engaging in fun and healthy activities such as agility competitions, and taking them on trips, that gives them that extra boost in happiness. You could therefore answer your question in the following way:
Dog owners are happier than cat owners because of the dog-related activities they engage in.
Now you have to verify that your hypothesis fulfills the two requirements we introduced at the beginning of this resource article: falsifiability and testability . If it can’t be wrong and can’t be tested, it’s not a hypothesis. We are lucky, however, because yes, we can test whether owning a dog but not engaging in any of those activities leads to lower levels of happiness or well-being than owning a dog and playing and running around with them or taking them on trips.
Writing a Hypothesis Step 3:
Make your predictions and define your variables. We have verified that we can test our hypothesis, but now we have to define all the relevant variables, design our experiment or data analysis, and make precise predictions. You could, for example, decide to study dog owners (not surprising at this point), let them fill in questionnaires about their lifestyle as well as their life satisfaction (as other studies did), and then compare two groups of active and inactive dog owners. Alternatively, if you want to go beyond the data that earlier studies produced and analyzed and directly manipulate the activity level of your dog owners to study the effect of that manipulation, you could invite them to your lab, select groups of participants with similar lifestyles, make them change their lifestyle (e.g., couch potato dog owners start agility classes, very active ones have to refrain from any fun activities for a certain period of time) and assess their happiness levels before and after the intervention. In both cases, your independent variable would be “ level of engagement in fun activities with dog” and your dependent variable would be happiness or well-being .
Examples of a Good and Bad Hypothesis
Let’s look at a few examples of good and bad hypotheses to get you started.
Good Hypothesis Examples
Bad hypothesis examples, tips for writing a research hypothesis.
If you understood the distinction between a hypothesis and a prediction we made at the beginning of this article, then you will have no problem formulating your hypotheses and predictions correctly. To refresh your memory: We have to (1) look at existing evidence, (2) come up with a hypothesis, (3) make a prediction, and (4) design an experiment. For example, you could summarize your dog/happiness study like this:
(1) While research suggests that dog owners are happier than cat owners, there are no reports on what factors drive this difference. (2) We hypothesized that it is the fun activities that many dog owners (but very few cat owners) engage in with their pets that increases their happiness levels. (3) We thus predicted that preventing very active dog owners from engaging in such activities for some time and making very inactive dog owners take up such activities would lead to an increase and decrease in their overall self-ratings of happiness, respectively. (4) To test this, we invited dog owners into our lab, assessed their mental and emotional well-being through questionnaires, and then assigned them to an “active” and an “inactive” group, depending on…
Note that you use “we hypothesize” only for your hypothesis, not for your experimental prediction, and “would” or “if – then” only for your prediction, not your hypothesis. A hypothesis that states that something “would” affect something else sounds as if you don’t have enough confidence to make a clear statement—in which case you can’t expect your readers to believe in your research either. Write in the present tense, don’t use modal verbs that express varying degrees of certainty (such as may, might, or could ), and remember that you are not drawing a conclusion while trying not to exaggerate but making a clear statement that you then, in a way, try to disprove . And if that happens, that is not something to fear but an important part of the scientific process.
Similarly, don’t use “we hypothesize” when you explain the implications of your research or make predictions in the conclusion section of your manuscript, since these are clearly not hypotheses in the true sense of the word. As we said earlier, you will find that many authors of academic articles do not seem to care too much about these rather subtle distinctions, but thinking very clearly about your own research will not only help you write better but also ensure that even that infamous Reviewer 2 will find fewer reasons to nitpick about your manuscript.
Perfect Your Manuscript With Professional Editing
Now that you know how to write a strong research hypothesis for your research paper, you might be interested in our free AI proofreader , Wordvice AI, which finds and fixes errors in grammar, punctuation, and word choice in academic texts. Or if you are interested in human proofreading , check out our English editing services , including research paper editing and manuscript editing .
On the Wordvice academic resources website , you can also find many more articles and other resources that can help you with writing the other parts of your research paper , with making a research paper outline before you put everything together, or with writing an effective cover letter once you are ready to submit.
Online Hypothesis Generator
Add the required information into the fields below to build a list of well-formulated hypotheses.
- If patients follow medical prescriptions, then their condition will improve.
- If patients follow medical prescriptions, then their condition will show better results.
- If patients follow medical prescriptions, then their condition will show better results than those who do not follow medical prescriptions.
- H0 (null hypothesis) - Attending most lectures by first-year students has no effect on their exam scores.
- H1 (alternative hypothesis) - Attending most lectures by first-year students has a positive effect on their exam scores.
* Hint - choose either null or alternative hypothesis
⭐️ Hypothesis Creator: the Benefits
- 🔎 How to Use the Tool?
- 🤔 What Is a Hypothesis?
- 👣 Steps to Generating a Hypothesis
- 🔍 References
🔎 Hypothesis Generator: How to Use It?
The generation of a workable hypothesis is not an easy task for many students. You need to research widely, understand the gaps in your study area, and comprehend the method of hypothesis formulation to the dot. Lucky for you, we have a handy hypothesis generator that takes hours of tedious work out of your study process.
To use our hypothesis generator, you’ll need to do the following:
- Indicate your experimental group (people, phenomena, event)
- Stipulate what it does
- Add the effect that the subject’s activities produce
- Specify the comparison group
Once you put all this data into our online hypothesis generator, click on the “Generate hypothesis” tab and enjoy instant results. The tool will come up with a well-formulated hypothesis in seconds.
🤔 What Is a Research Hypothesis?
A hypothesis is a claim or statement you make about the assumed relationship between the dependent and independent variables you're planning to test. It is formulated at the beginning of your study to show the direction you will take in the analysis of your subject of interest.
The hypothesis works in tandem with your research purpose and research question , delineating your entire perspective.
For example, if you focus on the quality of palliative care in the USA , your perspective may be as follows.
This way, your hypothesis serves as a tentative answer to your research question, which you aim to prove or disprove with scientific data, statistics, and analysis.
Hypothesis Types
In most scholarly studies, you’ll be required to write hypotheses in pairs – as a null and alternative hypothesis :
- The alternative hypothesis assumes a statistically significant relationship between the identified variables. Thus, if you find that relationship in the analysis process, you can consider the alternative hypothesis proven.
- A null hypothesis is the opposite; it assumes that there is no relationship between the variables. Thus, if you find no statistically significant association, the null hypothesis is considered proven.

A handy example is as follows:
You are researching the impact of sugar intake on child obesity. So, based on your data, you can either find that the number of sugar spoons a day directly impacts obesity or that the sugar intake is not associated with obesity in your sample. The hypotheses for this study would be as follows:
ALTERNATIVE
There is a relationship between the number of sugar spoons consumed daily and obesity in U.S. preschoolers.
There is no relationship between the number of sugar spoons consumed daily and obesity in U.S. preschoolers.
Besides, hypotheses can be directional and non-directional by type:
- A directional hypothesis assumes a cause-and-effect relationship between variables, clearly designating the assumed difference in study groups or parameters.
- A non-directional hypothesis , in turn, only assumes a relationship or difference without a clear estimate of its direction.
NON-DIRECTIONAL
Students in high school and college perform differently on critical thinking tests.
DIRECTIONAL
College students perform better on critical thinking tests that high-school students.
👣 How to Make a Hypothesis in Research
Now let’s cover the algorithm of hypothesis generation to make this process simple and manageable for you.

Step #1: Formulate Your Research Question
The first step is to create a research question . Study the topic of interest and clarify what aspect you're fascinated about, wishing to learn more about the hidden connections, effects, and relationships.
Step #2: Research the Topic
Next, you should conduct some research to test your assumption and see whether there’s enough published evidence to back up your point. You should find credible sources that discuss the concepts you’ve singled out for the study and delineate a relationship between them. Once you identify a reasonable body of research, it’s time to go on.
Step #3: Make an Assumption
With some scholarly data, you should now be better positioned to make a researchable assumption.
For instance, if you find out that many scholars associate heavy social media use with a feeling of loneliness, you can hypothesize that the hours spent on social networks will directly correlate with perceived loneliness intensity.
Step #4: Improve Your Hypothesis
Now that you have a hypothesis, it’s time to refine it by adding context and population specifics. Who will you study? What social network will you focus on? In this example, you can focus on the student sample’s use of Instagram .
Step #5: Try Different Phrasing
The final step is the proper presentation of your hypothesis. You can try several variants, focusing on the variables, correlations , or groups you compare.
For instance, you can say that students spending 3+ hours on Instagram every day are lonelier than their peers. Otherwise, you can hypothesize that heavy social media use leads to elevated feelings of loneliness.
👀 Null Hypothesis Examples
If you’re unsure about how to generate great hypotheses, get some inspiration from the list of examples formulated by our writing pros.
Thank you for reading this article! If you’re planning to analyze business issues, try our free templates: PEST , PESTEL , SWOT , SOAR , VRIO , and Five Forces .
❓ Hypothesis Generator FAQ
❓ what does hypothesis mean.
A hypothesis in an essay or a larger research assignment is your claim or prediction of the relationship you assume between the identified dependent and independent variables. You share an assumption that you’re going to test with research and data analysis in the later sections of your paper.
❓ How to create a hypothesis?
The first step to formulating a good hypothesis is to ask a question about your subject of interest and understand what effects it may experience from external sources or how it changes over time. You can identify differences between groups and inquire into the nature of those distinctions. In any way, you need to voice some assumption that you’ll further test with data; that assumption will be your hypothesis for a study.
❓ What is a null and alternative hypothesis?
You need to formulate a null and alternative hypothesis if you plan to test some relationship between variables with statistical instruments. For example, you might compare a group of students on an emotional intelligence scale to determine whether first-year students are less emotionally competent than graduates. In this case, your alternative hypothesis would state that they are, and a null hypothesis would say that there is no difference between student groups.
❓ What does it mean to reject the null hypothesis?
A null hypothesis assumes that there is no difference between groups or that the dependent variables don't have any sizable impact on the independent variable. If your null hypothesis gets rejected, it means that your alternative hypothesis has been proved, showing that there is a tangible difference or relationship between your variables.
🔗 References
- How to Write a Hypothesis in 6 Steps - Grammarly
- The Hypothesis in Science Writing
- Hypothesis Definition & Examples - Simply Psychology
- Hypothesis Examples: Different Types in Science and Research
- Forming a Good Hypothesis for Scientific Research
Navigation Menu
Search code, repositories, users, issues, pull requests..., provide feedback.
We read every piece of feedback, and take your input very seriously.
Saved searches
Use saved searches to filter your results more quickly.
To see all available qualifiers, see our documentation .
- Notifications
An AI Tool for Automated Research Question and Hypothesis Generation from a given Scientific Literature
bhaskatripathi/HypothesisHub
Folders and files, repository files navigation, hypothesishub.
HypothesisHub is an AI Tool for the Automated Generation of Research Questions and Hypotheses from Scientific Literature. It applies a chain of reasoning to scientific literature to generate questions and hypotheses. OpenAI and Langchain serve as the underlying technologies for the tool.
- Generates research questions from a given scientific literature
- Generates a null hypothesis (H0) and an alternate hypothesis (H1) for each research question
- Handles cases where either H0 or H1 is not present
- Automatically generates missing H1 using the LLMChain if needed
- Negates hypothesis statement if H0 is missing
Sequence Diagram

Please give a star if you like this project and find it useful.
Star History
- Jupyter Notebook 100.0%
History Hypothesis Generator
If you’re searching for a hypothesis generator, you’re in the right place! With this free online tool, you’ll easily make a hypothesis from a question or from scratch.
Need a hypothesis for your history paper? This automatic hypothesis generator will save your time and nerves! Follow these 3 steps:
- ❓ Definitions
- 💡 What’s This Tool?
🔬 How to Generate a Hypothesis from a Question?
- ✅ Characteristics
- ✍️ Examples
🔗 References
❓ hypothesis in history: definitions.
In high school or college, you might need to develop a historical hypothesis for your academic paper or any other project. In the sections below, we have explained what it means for this subject.
What Is a Hypothesis?
A hypothesis is a statement or proposed explanation for a phenomenon. For it to be scientific, researchers should be able to test it.
The words “hypothesis” and “ theory ” are often used interchangeably. However, they are not the same. In exact science, a hypothesis needs to be provable to become a theory. In the non-scientific environment, the word is used more loosely.
What about a Hypothesis in History?
A historical hypothesis consists of:
- Attitudes that demonstrate relations between variables.
It is a proposed explanation for a phenomenon different from recorded facts , which is useful when:
- the existing evidence is limited,
- no recognized historical methodology is available,
- or researchers want to examine a specific aspect of a historical event.
A reasonable hypothesis should give a straightforward answer with substantial explanatory power . If you also need a unique idea to write about, check our list of history topics .
Hypothesis vs. Theory
💡 hypothesis maker: what it is.
An automatic hypothesis generator is a tool that can save you time and energy. It uses advanced AI technology to create an appropriate assumption:
- The generator analyzes the variables you have input into the cycle.
- Then, it formulates the relations between them.
- Finally, it generates a hypothesis that you can use for your paper.
Our history hypothesis generator is a straightforward tool. You can use it whenever you need help inventing or wording your idea. It’s free and available all the time!
At a particular stage of your research, you will need to generate a hypothesis from a research question. A hypothesis is a statement that you will further test.
To do that, you need to take five steps:
- Define independent and dependent variables.
- Brainstorm ideas to explain the question.
- Choose the most convincing explanation.
- Formulate a statement based on this explanation.
- Check if the claim is testable in a scientific study.
✅ How to Make a Good Hypothesis in History
So that you don’t get confused when developing your historical hypothesis, let’s see what characteristics a successful one should obtain:
✍️ History Hypothesis Maker: Examples
So, you’ve read about the characteristics of a good hypothesis in history. Now you may be wondering what one actually looks like. In this section, we have listed some examples based on sample academic papers .
Italian industrial capacities were underutilized, while other Axis partners exploited their capabilities. Such countries as Hungary, Bulgaria, and Slovakia even granted loans to Nazi Germany. The WWII could have ended differently if German-Italian cooperation had been more efficient.
People from dominant racial groups deny racism because they are ignorant of human history. At the same time, minorities see the issue differently. They are aware of the records and experience systemic racism in the present.
Islamic Art has features distinctive from the Platonic influence on Islamic thought. Thus, there is a philosophical explanation of why it follows the principles of order and harmony.
The world ignored the Korean crisis in 1948 due to the situation in Germany and the deterioration of Soviet-American relations.
Thanks for reading!
If you’re working on a history paper, try out our automatic hypothesis generator. It will come up with great ideas and save you a lot of time. Use our tips and examples to make your paper and research better. Besides, share it with other students who may need our advice.
Updated: May 17th, 2024
- Hypothesis-Based Research | Michigan Tech
- A Brief Guide to Writing a History Paper | Harvard College
- Hypothesis Formulation | Boston University
- Developing a Hypothesis | Pressbooks
World’s #1 Research Paper Generator
Over 5,000 research papers generated daily
Have an AI Research and write your Paper in just 5 words
See it for yourself: get your free research paper started with just 5 words, how smodin makes research paper writing easy, instantly find sources for any sentence.
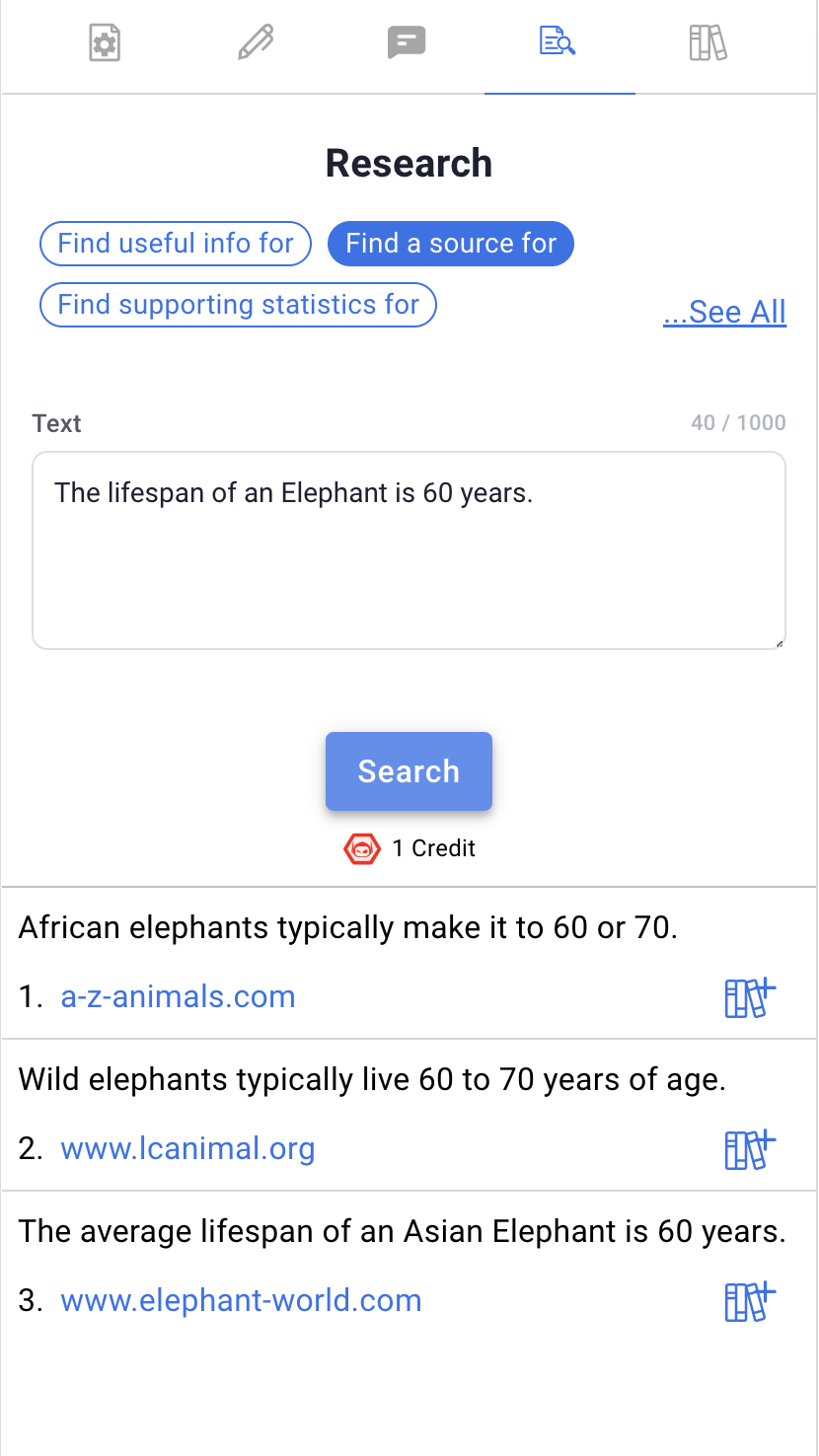
Our AI research tool in the research paper editor interface makes it easy to find a source or fact check any piece of text on the web. It will find you the most relevant or related piece of information and the source it came from. You can quickly add that reference to your document references with just a click of a button. We also provide other modes for research such as “find support statistics”, “find supporting arguments”, “find useful information”, and other research methods to make finding the information you need a breeze. Make research paper writing and research easy with our AI research assistant.
Easily Cite References
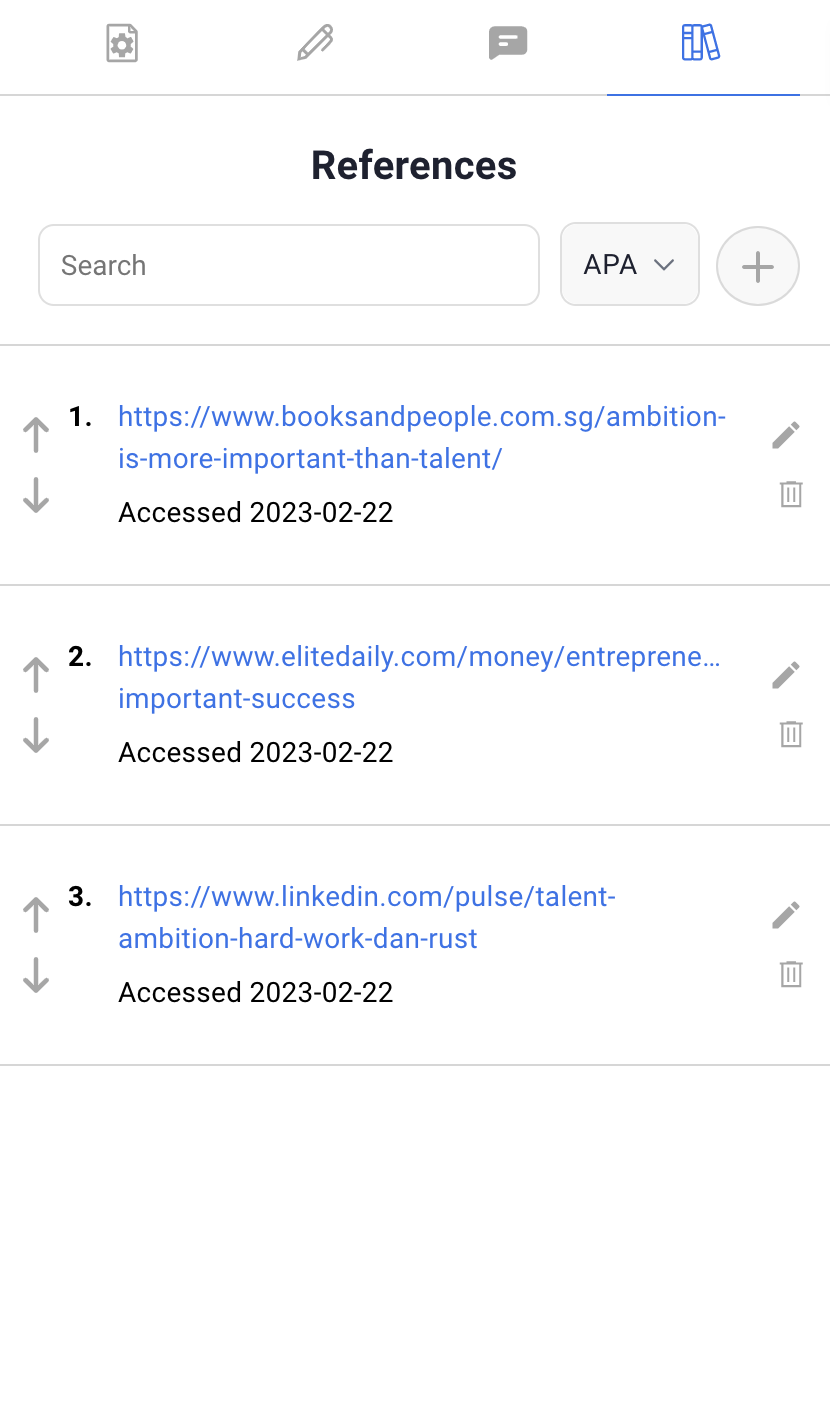
Our research paper generator makes citing references in MLA and APA styles for web sources and references an easy task. The research paper writer works by first identifying the primary elements in each source, such as the author, title, publication date, and URL, and then organizing them in the correct format required by the chosen citation style. This ensures that the references are accurate, complete, and consistent. The product provides helpful tools to generate citations and bibliographies in the appropriate style, making it easier for you to document your sources and avoid plagiarism. Whether you’re a student or a professional writer, our research paper generator saves you time and effort in the citation process, allowing you to focus on the content of your work.
Free AI Research Paper Generator & Writer - Say Goodbye to Writer's Block!
Are you struggling with writer's block? Even more so when it comes to your research papers. Do you want to write a paper that excels, but can't seem to find the inspiration to do so? Say goodbye to writer's block with Smodin’s Free AI Research Paper Generator & Writer!
Smodin’s AI-powered tool generates high-quality research papers by analyzing millions of papers and using advanced algorithms to create unique content. All you need to do is input your topic, and Smodin’s Research Paper generator will provide you with a well-written paper in no time.
Why Use Smodin Free AI Research Paper Generator & Writer?
Writing a research paper can be a complicated task, even more so when you have limited time and resources. A research paper generator can help you streamline the process, by quickly finding and organizing relevant sources. With Smodin's research paper generator, you can produce high-quality papers in minutes, giving you more time to focus on analysis and writing
Benefits of Smodin’s Free Research Paper Generator
- Save Time: Smodin AI-powered generator saves you time by providing you with a well-written paper that you can edit and submit.
- Quality Content: Smodin uses advanced algorithms to analyze millions of papers to ensure that the content is of the highest quality.
- Easy to Use: Smodin is easy to use, even if you're not familiar with the topic. It is perfect for students, researchers, and professionals who want to create high-quality content.
How to Write a Research Paper?
All you need is an abstract or a title, and Smodin’s AI-powered software will quickly find sources for any topic or subject you need. With Smodin, you can easily produce multiple sections, including the introduction, discussion, and conclusion, saving you valuable time and effort.
Who can write a Research Paper?
Everyone can! Smodin's research paper generator is perfect for students, researchers, and anyone else who needs to produce high-quality research papers quickly and efficiently. Whether you're struggling with writer's block or simply don't have the time to conduct extensive research, Smodin can help you achieve your goals.
Tips for Using Smodin's Research Paper Generator
With our user-friendly interface and advanced AI algorithms, you can trust Smodin's paper writer to deliver accurate and reliable results every time. While Smodin's research paper generator is designed to be easy to use, there are a few tips you can follow to get the most out of Smodinl. First, be sure to input a clear and concise abstract or title to ensure accurate results. Second, review and edit the generated paper to ensure it meets your specific requirements and style. And finally, use the generated paper as a starting point for your research and writing, or to continue generating text.
The Future of Research Paper Writing
As technology continues to advance, the future of research paper writing is likely to become increasingly automated. With tools like Smodin's research paper generator, researchers and students can save time and effort while producing high-quality work. Whether you're looking to streamline your research process or simply need a starting point for your next paper, Smodin's paper generator is a valuable resource for anyone interested in academic writing.
So why wait? Try Smodin's free AI research paper generator and paper writer today and experience the power of cutting-edge technology for yourself. With Smodin, you can produce high-quality research papers in minutes, saving you time and effort while ensuring your work is of the highest caliber.
© 2024 Smodin LLC
Innovative Statistics Project Ideas for Insightful Analysis
Table of contents
- 1.1 AP Statistics Topics for Project
- 1.2 Statistics Project Topics for High School Students
- 1.3 Statistical Survey Topics
- 1.4 Statistical Experiment Ideas
- 1.5 Easy Stats Project Ideas
- 1.6 Business Ideas for Statistics Project
- 1.7 Socio-Economic Easy Statistics Project Ideas
- 1.8 Experiment Ideas for Statistics and Analysis
- 2 Conclusion: Navigating the World of Data Through Statistics
Diving into the world of data, statistics presents a unique blend of challenges and opportunities to uncover patterns, test hypotheses, and make informed decisions. It is a fascinating field that offers many opportunities for exploration and discovery. This article is designed to inspire students, educators, and statistics enthusiasts with various project ideas. We will cover:
- Challenging concepts suitable for advanced placement courses.
- Accessible ideas that are engaging and educational for younger students.
- Ideas for conducting surveys and analyzing the results.
- Topics that explore the application of statistics in business and socio-economic areas.
Each category of topics for the statistics project provides unique insights into the world of statistics, offering opportunities for learning and application. Let’s dive into these ideas and explore the exciting world of statistical analysis.
Top Statistics Project Ideas for High School
Statistics is not only about numbers and data; it’s a unique lens for interpreting the world. Ideal for students, educators, or anyone with a curiosity about statistical analysis, these project ideas offer an interactive, hands-on approach to learning. These projects range from fundamental concepts suitable for beginners to more intricate studies for advanced learners. They are designed to ignite interest in statistics by demonstrating its real-world applications, making it accessible and enjoyable for people of all skill levels.
Need help with statistics project? Get your paper written by a professional writer Get Help Reviews.io 4.9/5
AP Statistics Topics for Project
- Analyzing Variance in Climate Data Over Decades.
- The Correlation Between Economic Indicators and Standard of Living.
- Statistical Analysis of Voter Behavior Patterns.
- Probability Models in Sports: Predicting Outcomes.
- The Effectiveness of Different Teaching Methods: A Statistical Study.
- Analysis of Demographic Data in Public Health.
- Time Series Analysis of Stock Market Trends.
- Investigating the Impact of Social Media on Academic Performance.
- Survival Analysis in Clinical Trial Data.
- Regression Analysis on Housing Prices and Market Factors.
Statistics Project Topics for High School Students
- The Mathematics of Personal Finance: Budgeting and Spending Habits.
- Analysis of Class Performance: Test Scores and Study Habits.
- A Statistical Comparison of Local Public Transportation Options.
- Survey on Dietary Habits and Physical Health Among Teenagers.
- Analyzing the Popularity of Various Music Genres in School.
- The Impact of Sleep on Academic Performance: A Statistical Approach.
- Statistical Study on the Use of Technology in Education.
- Comparing Athletic Performance Across Different Sports.
- Trends in Social Media Usage Among High School Students.
- The Effect of Part-Time Jobs on Student Academic Achievement.
Statistical Survey Topics
- Public Opinion on Environmental Conservation Efforts.
- Consumer Preferences in the Fast Food Industry.
- Attitudes Towards Online Learning vs. Traditional Classroom Learning.
- Survey on Workplace Satisfaction and Productivity.
- Public Health: Attitudes Towards Vaccination.
- Trends in Mobile Phone Usage and Preferences.
- Community Response to Local Government Policies.
- Consumer Behavior in Online vs. Offline Shopping.
- Perceptions of Public Safety and Law Enforcement.
- Social Media Influence on Political Opinions.
Statistical Experiment Ideas
- The Effect of Light on Plant Growth.
- Memory Retention: Visual vs. Auditory Information.
- Caffeine Consumption and Cognitive Performance.
- The Impact of Exercise on Stress Levels.
- Testing the Efficacy of Natural vs. Chemical Fertilizers.
- The Influence of Color on Mood and Perception.
- Sleep Patterns: Analyzing Factors Affecting Sleep Quality.
- The Effectiveness of Different Types of Water Filters.
- Analyzing the Impact of Room Temperature on Concentration.
- Testing the Strength of Different Brands of Batteries.
Easy Stats Project Ideas
- Average Daily Screen Time Among Students.
- Analyzing the Most Common Birth Months.
- Favorite School Subjects Among Peers.
- Average Time Spent on Homework Weekly.
- Frequency of Public Transport Usage.
- Comparison of Pet Ownership in the Community.
- Favorite Types of Movies or TV Shows.
- Daily Water Consumption Habits.
- Common Breakfast Choices and Their Nutritional Value.
- Steps Count: A Week-Long Study.
Business Ideas for Statistics Project
- Analyzing Customer Satisfaction in Retail Stores.
- Market Analysis of a New Product Launch.
- Employee Performance Metrics and Organizational Success.
- Sales Data Analysis for E-commerce Websites.
- Impact of Advertising on Consumer Buying Behavior.
- Analysis of Supply Chain Efficiency.
- Customer Loyalty and Retention Strategies.
- Trend Analysis in Social Media Marketing.
- Financial Risk Assessment in Investment Decisions.
- Market Segmentation and Targeting Strategies.
Socio-Economic Easy Statistics Project Ideas
- Income Inequality and Its Impact on Education.
- The Correlation Between Unemployment Rates and Crime Levels.
- Analyzing the Effects of Minimum Wage Changes.
- The Relationship Between Public Health Expenditure and Population Health.
- Demographic Analysis of Housing Affordability.
- The Impact of Immigration on Local Economies.
- Analysis of Gender Pay Gap in Different Industries.
- Statistical Study of Homelessness Causes and Solutions.
- Education Levels and Their Impact on Job Opportunities.
- Analyzing Trends in Government Social Spending.
Experiment Ideas for Statistics and Analysis
- Multivariate Analysis of Global Climate Change Data.
- Time-Series Analysis in Predicting Economic Recessions.
- Logistic Regression in Medical Outcome Prediction.
- Machine Learning Applications in Statistical Modeling.
- Network Analysis in Social Media Data.
- Bayesian Analysis of Scientific Research Data.
- The Use of Factor Analysis in Psychology Studies.
- Spatial Data Analysis in Geographic Information Systems (GIS).
- Predictive Analysis in Customer Relationship Management (CRM).
- Cluster Analysis in Market Research.
Conclusion: Navigating the World of Data Through Statistics
In this exploration of good statistics project ideas, we’ve ventured through various topics, from the straightforward to the complex, from personal finance to global climate change. These ideas are gateways to understanding the world of data and statistics, and platforms for cultivating critical thinking and analytical skills. Whether you’re a high school student, a college student, or a professional, engaging in these projects can deepen your appreciation of how statistics shapes our understanding of the world around us. These projects encourage exploration, inquiry, and a deeper engagement with the world of numbers, trends, and patterns – the essence of statistics.
Readers also enjoyed

WHY WAIT? PLACE AN ORDER RIGHT NOW!
Just fill out the form, press the button, and have no worries!
We use cookies to give you the best experience possible. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Our hypothesis maker is a simple and efficient tool you can access online for free. If you want to create a research hypothesis quickly, you should fill out the research details in the given fields on the hypothesis generator. Below are the fields you should complete to generate your hypothesis:
AI-powered research hypothesis generator. ... Copy and paste the hypothesis into your research proposal, paper, or project documentation. FAQ. Is HyperWrite's Hypothesis Maker free to use? Yes, HyperWrite offers a free trial for users to try the Hypothesis Maker. For unlimited access, you can choose the Premium Plan for $19.99/mo or Ultra for ...
Create null (H0) and alternative (H1) hypotheses based on a given research question and dataset. HyperWrite's Hypothesis Generator is a powerful AI tool that helps you create null and alternative hypotheses for your research. This tool takes a given research question and dataset and generates hypotheses that are clear, concise, and testable. By utilizing the latest AI models, it simplifies the ...
The Convert A/B testing hypothesis generator is a free tool to create credible hypotheses that drive big conversion lifts. ... But framing a tenable hypothesis that already proves itself logistically feasible on paper is a better starting point than a hastily assembled assumption. ... I research and/or hypothesize experiments.
Create a research hypothesis based on a provided research topic and objectives. Introducing HyperWrite's Research Hypothesis Generator, an AI-powered tool designed to formulate clear, concise, and testable hypotheses based on your research topic and objectives. Leveraging advanced AI models, this tool is perfect for students, researchers, and professionals looking to streamline their research ...
Here are the key benefits of this null and alternative hypothesis generator. 👌 User-friendly. Use the prompts and examples to write a hypothesis. 🎯 Tunable. The more details you add, the more accurate result you'll get. 🌐 Online. No need to download any software with this hypothesis writer. 🆓 No payments.
Kick-start your research endeavors with EssayGPT's hypothesis generator by these steps: 1. Start by by indicating the positive or negative trajectory of your hypothesis in the "Effect" section. 2. Then, enter specifics of the experimental group in the "Who (what)" field. 3.
The #1 AI Research Tool for Students, Teachers, Scholars, and those in Academia. Generate Study Guides, Outlines, Research Topics, Key Findings, Hypotheses, and Exam Questions. In Seconds. Streamline your planning and preparation with the top AI-generated answers for your specific academic field. Try it now for FREE.
6. Write a null hypothesis. If your research involves statistical hypothesis testing, you will also have to write a null hypothesis. The null hypothesis is the default position that there is no association between the variables. The null hypothesis is written as H 0, while the alternative hypothesis is H 1 or H a.
A well-defined hypothesis can guide your experiments and set the course for your discoveries. Our generator provides you with structured proposals based on your field and subject. 🌌 For all areas. Whether you're in biology, physics or the social sciences, we've got you covered. adapted our tool to meet the diversity of research needs.
3. Simple hypothesis. A simple hypothesis is a statement made to reflect the relation between exactly two variables. One independent and one dependent. Consider the example, "Smoking is a prominent cause of lung cancer." The dependent variable, lung cancer, is dependent on the independent variable, smoking. 4.
Step 5: Phrase your hypothesis in three ways. To identify the variables, you can write a simple prediction in if … then form. The first part of the sentence states the independent variable and the second part states the dependent variable. If a first-year student starts attending more lectures, then their exam scores will improve.
Another example for a directional one-tailed alternative hypothesis would be that. H1: Attending private classes before important exams has a positive effect on performance. Your null hypothesis would then be that. H0: Attending private classes before important exams has no/a negative effect on performance.
Create Faster With AI. Try it Risk-Free. Stop wasting time and start creating high-quality content immediately with power of generative AI. Get started for free. Best AI Content Generator & Copywriting Assistant. Generate a hypothesis for your research or project in seconds! Use it for Free.
If your null hypothesis was rejected, this result is interpreted as "supported the alternate hypothesis." Stating results in a research paper We found a difference in average height between men and women of 14.3cm, with a p-value of 0.002, consistent with our hypothesis that there is a difference in height between men and women.
A research hypothesis is your proposed answer to your research question. The research hypothesis usually includes an explanation ("x affects y because …"). A statistical hypothesis, on the other hand, is a mathematical statement about a population parameter. Statistical hypotheses always come in pairs: the null and alternative hypotheses.
Research Paper Generator; Contact phone +1 866 372-2910. Order Now Login. Home page Writing Tools Hypothesis Generator. Online Hypothesis Generator. ... This research hypothesis generator was made for students. 💫 Intuitive: Follow the prompts and look at the examples if needed.
Generates research questions from a given scientific literature; Generates a null hypothesis (H0) and an alternate hypothesis (H1) for each research question; Handles cases where either H0 or H1 is not present; Automatically generates missing H1 using the LLMChain if needed; Negates hypothesis statement if H0 is missing
The generator analyzes the variables you have input into the cycle. Then, it formulates the relations between them. Finally, it generates a hypothesis that you can use for your paper. Our history hypothesis generator is a straightforward tool. You can use it whenever you need help inventing or wording your idea.
Step 1: Introduce your topic. Step 2: Describe the background. Step 3: Establish your research problem. Step 4: Specify your objective (s) Step 5: Map out your paper. Research paper introduction examples. Frequently asked questions about the research paper introduction.
AI-based structure prediction is an amazing research accelerator and hypothesis generator. We very much look forward to new implementations that will incorporate post-translational modifications, small molecules, and protein-nucleic acid interactions! Fast-forwarding to testable hypotheses.
Our research paper generator makes citing references in MLA and APA styles for web sources and references an easy task. The research paper writer works by first identifying the primary elements in each source, such as the author, title, publication date, and URL, and then organizing them in the correct format required by the chosen citation style.
1.2 Statistics Project Topics for High School Students. 1.3 Statistical Survey Topics. 1.4 Statistical Experiment Ideas. 1.5 Easy Stats Project Ideas. 1.6 Business Ideas for Statistics Project. 1.7 Socio-Economic Easy Statistics Project Ideas. 1.8 Experiment Ideas for Statistics and Analysis. 2 Conclusion: Navigating the World of Data Through ...