- Search Search Please fill out this field.

Sowing the Seeds of the Crisis
Signs of trouble.
- Aug. 2007: The Beginning
- March 2008: Demise of Bear Stearns
- Sept. 2008: Fall of Lehman Brothers
The Aftermath
The bottom line, the 2007–2008 financial crisis in review.
Thomas J Catalano is a CFP and Registered Investment Adviser with the state of South Carolina, where he launched his own financial advisory firm in 2018. Thomas' experience gives him expertise in a variety of areas including investments, retirement, insurance, and financial planning.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/P2-ThomasCatalano-d5607267f385443798ae950ece178afd.jpg)
Pete Rathburn is a copy editor and fact-checker with expertise in economics and personal finance and over twenty years of experience in the classroom.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/E7F37E3D-4C78-4BDA-9393-6F3C581602EB-2c2c94499d514e079e915307db536454.jpeg)
- Guide to Stock Market Crashes
- October: The Month of Market Crashes?
- How Do Investors Lose Money When the Stock Market Crashes?
- Timeline of U.S. Stock Market Crashes
- October Effect
- Financial Crisis
- Circuit Breaker
- Plunge Protection Team
- Dutch Tulip Bulb Market Bubble
- Black Friday
- Bank Panic of 1907
- Stock Market Crash of 1929
- What Caused the Stock Market Crash of 1929
- Black Tuesday
- Black Thursday
- Stock Market Crash of 1987
- Black Monday
- What Caused Black Monday: The Stock Market Crash of 1987
- The 2007-2008 Financial Crisis in Review CURRENT ARTICLE
- The Fall of the Market in the Fall of 2008
- Components of the 2008 Bubble
- Financial Regulations: Glass-Steagall to Dodd-Frank
- Consequences of the Glass-Steagall Act Repeal
- Lessons from the 2008 Financial Crisis
- Major Players in the 2008 Financial Crisis: Where Are They Now?
- Too Big to Fail Banks: Where Are They Now?
The financial crisis of 2007–2008 was years in the making. By the summer of 2007, financial markets around the world were showing signs that the reckoning was overdue for a years-long binge on cheap credit. Two Bear Stearns hedge funds had collapsed, BNP Paribas was warning investors that they might not be able to withdraw money from three of its funds, and the British bank Northern Rock was about to seek emergency funding from the Bank of England.
Yet despite the warning signs, few investors suspected that the worst crisis in nearly eight decades was about to engulf the global financial system, bringing Wall Street's giants to their knees and triggering the Great Recession.
It was an epic financial and economic collapse that cost many ordinary people their jobs, their life savings, their homes, or all three.
Key Takeaways
- The 2007–2008 financial crisis developed gradually. Home prices began to fall in early 2006.
- In early 2007, subprime lenders began to file for bankruptcy.
- In June 2007, two big hedge funds failed, weighed down by investments in subprime loans.
- In August 2007, losses from subprime loan investments caused a panic that froze the global lending system.
- In September 2008 Lehman Brothers collapsed in the biggest U.S. bankruptcy ever.
- When the bubble burst, financial institutions were left holding trillions of dollars worth of near-worthless investments in subprime mortgages.
What Caused the 2008 Financial Crisis?
The 2008 financial crisis began with cheap credit and lax lending standards that fueled a housing bubble. When the bubble burst, the banks were left holding trillions of dollars of worthless investments in subprime mortgages. The Great Recession that followed cost many their jobs, their savings, and their homes.
The seeds of the financial crisis were planted during years of rock-bottom interest rates and loose lending standards that fueled a housing price bubble in the U.S. and elsewhere.
It began, as usual, with good intentions. Faced with the bursting of the dot-com bubble, a series of corporate accounting scandals, and the September 11 terrorist attacks , the Federal Reserve lowered the federal funds rate from 6.5% in May 2000 to 1% in June 2003. The aim was to boost the economy by making money available to businesses and consumers at bargain rates.
The result was an upward spiral in home prices as borrowers took advantage of the low mortgage rates. Even subprime borrowers , those with poor or no credit history, were able to realize the dream of buying a home.
The banks then sold those loans on to Wall Street banks, which packaged them into what were billed as low-risk financial instruments such as mortgage-backed securities and collateralized debt obligations (CDOs). Soon a big secondary market for originating and distributing subprime loans developed.
Fueling greater risk-taking among banks, the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) in October 2004 relaxed the net capital requirements for five investment banks—Goldman Sachs (NYSE: GS), Merrill Lynch (NYSE: MER), Lehman Brothers, Bear Stearns, and Morgan Stanley (NYSE: MS). That freed them to leverage their initial investments by up to 30 times or even 40 times.
Eventually, interest rates started to rise and homeownership reached a saturation point. The Fed started raising rates in June 2004, and two years later the Federal funds rate had reached 5.25%, where it remained until August 2007.
There were early signs of distress. By 2004, U.S. homeownership had peaked at 69.2%. Then, in early 2006, home prices started to fall .
This caused real hardship to many Americans. Their homes were worth less than they paid for them. They couldn't sell their houses without owing money to their lenders. If they had adjustable-rate mortgages, their costs were going up as their homes' values were going down. The most vulnerable subprime borrowers were stuck with mortgages they couldn't afford in the first place.
Subprime mortgage company New Century Financial made nearly $60 billion in loans in 2006, according to the Reuters news service. In 2007, it filed for bankruptcy protection.
As 2007 got underway, one subprime lender after another filed for bankruptcy. During February and March, more than 25 subprime lenders went under. In April, New Century Financial, which specialized in sub-prime lending, filed for bankruptcy and laid off half of its workforce.
By June, Bear Stearns stopped redemptions in two of its hedge funds, prompting Merrill Lynch to seize $800 million in assets from the funds.
Even these were small matters compared to what was to happen in the months ahead.
August 2007: The Dominoes Start to Fall
It became apparent by August 2007 that the financial markets could not solve the subprime crisis and that the problems were reverberating well beyond the U.S. borders.
The interbank market that keeps money moving around the globe froze completely, largely due to fear of the unknown. Northern Rock had to approach the Bank of England for emergency funding due to a liquidity problem. In October 2007, Swiss bank UBS became the first major bank to announce losses—$3.4 billion—from sub-prime-related investments.
In the coming months, the Federal Reserve and other central banks would take coordinated action to provide billions of dollars in loans to the global credit markets, which were grinding to a halt as asset prices fell. Meanwhile, financial institutions struggled to assess the value of the trillions of dollars worth of now-toxic mortgage-backed securities that were sitting on their books.
March 2008: The Demise of Bear Stearns
By the winter of 2008, the U.S. economy was in a full-blown recession and, as financial institutions' liquidity struggles continued, stock markets around the world were tumbling the most since the September 11 terrorist attacks.
In January 2008, the Fed cut its benchmark rate by three-quarters of a percentage point—its biggest cut in a quarter-century, as it sought to slow the economic slide.
The bad news continued to pour in from all sides. In February, the British government was forced to nationalize Northern Rock. In March, global investment bank Bear Stearns, a pillar of Wall Street that dated to 1923, collapsed and was acquired by JPMorgan Chase for pennies on the dollar.
September 2008: The Fall of Lehman Brothers
By the summer of 2008, the carnage was spreading across the financial sector. IndyMac Bank became one of the largest banks ever to fail in the U.S., and the country's two biggest home lenders, Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac, had been seized by the U.S. government.
Yet the collapse of the venerable Wall Street bank Lehman Brothers in September marked the largest bankruptcy in U.S. history, and for many became a symbol of the devastation caused by the global financial crisis.
That same month, financial markets were in free fall, with the major U.S. indexes suffering some of their worst losses on record. The Fed, the Treasury Department, the White House, and Congress struggled to put forward a comprehensive plan to stop the bleeding and restore confidence in the economy.
The Wall Street bailout package was approved in the first week of October 2008.
The package included many measures , such as a huge government purchase of "toxic assets," an enormous investment in bank stock shares, and financial lifelines to Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac.
$440 Billion
The amount spent by the government through the Troubled Asset Relief Program (TARP). It got back $442.6 billion after assets bought in the crisis were resold at a profit.
The public indignation was widespread. It appeared that bankers were being rewarded for recklessly tanking the economy. But it got the economy moving again. It also should be noted that the investments in the banks were fully recouped by the government, with interest.
The passage of the bailout package stabilized the stock markets, which hit bottom in March 2009 and then embarked on the longest bull market in its history.
Still, the economic damage and human suffering were immense. Unemployment reached 10%. About 3.8 million Americans lost their homes to foreclosures.
About Dodd-Frank
The most ambitious and controversial attempt to prevent such an event from happening again was the passage of the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act in 2010. On the financial side, the act restricted some of the riskier activities of the biggest banks, increased government oversight of their activities, and forced them to maintain larger cash reserves. On the consumer side, it attempted to reduce predatory lending.
By 2018, some portions of the act had been rolled back by the Trump Administration, although an attempt at a more wholesale dismantling of the new regulations failed in the U.S. Senate.
Those regulations are intended to prevent a crisis similar to the 2007–2008 event from happening again.
Which doesn't mean that there won't be another financial crisis in the future. Bubbles have occurred periodically at least since the 1630s Dutch Tulip Bubble .
The 2007–2008 financial crisis was a global event, not one restricted to the U.S. Ireland 's vibrant economy fell off a cliff. Greece defaulted on its international debts. Portugal and Spain suffered from extreme levels of unemployment. Every nation's experience was different and complex.
What Is a Mortgage-Backed Security?
A mortgage-backed security is similar to a bond. It consists of home loans bundled together and sold by the banks that lend the money to Wall Street investors. The point is to profit from the loan interest paid by the mortgage holders.
In the early 2000s, loan originators encouraged millions to borrow beyond their means to buy homes they couldn't afford. The loans were then sent on to investors in the form of mortgage-backed securities.
Inevitably, the homeowners who had borrowed beyond their means began to default. Housing prices fell and millions walked away from mortgages that cost more than the house was worth.
Who Is to Blame for the Great Recession?
Many economists place the greatest part of the blame on lax mortgage lending policies that allowed many consumers to borrow far more than they could afford. But there's plenty of blame to go around, including:
- The predatory lenders who marketed homeownership to people who could not possibly pay back the mortgages they were offered.
- The investment gurus who bought those bad mortgages and rolled them into bundles for resale to investors.
- The agencies who gave those mortgage bundles top investment ratings, making them appear to be safe.
- The investors who failed to check the ratings, or simply took care to unload the bundles to other investors before they blew up.
Which Banks Failed in 2008?
The total number of bank failures linked to the financial crisis cannot be revealed without first reporting this: No depositor in an American bank lost a penny to a bank failure.
That said, more than 500 banks failed between 2008 and 2015, compared to a total of 25 in the preceding seven years, according to the Federal Reserve of Cleveland. Most were small regional banks, and all were acquired by other banks, along with their depositors' accounts.
The biggest failures were not banks in the traditional Main Street sense but investment banks that catered to institutional investors. These notably included Lehman Brothers and Bear Stearns . Lehman Brothers was denied a government bailout and shut its doors. JPMorgan Chase bought the ruins of Bear Stearns on the cheap.
As for the biggest of the big banks, including JPMorgan Chase, Goldman Sachs, Bank of American, and Morgan Stanley, all were, famously, " too big to fail ." They took the bailout money, repaid it to the government, and emerged bigger than ever after the recession.
Who Made Money in the 2008 Financial Crisis?
A number of smart investors made money from the crisis, mostly by picking up pieces from the wreckage.
- Warren Buffett invested billions in companies including Goldman Sachs and General Electric out of a mix of motives that combined patriotism and profit.
- Hedge fund manager John Paulson made a lot of money betting against the U.S. housing market when the bubble formed, and then made a lot more money betting on its recovery after it hit bottom.
- Investor Carl Icahn proved his market-timing talent by selling and buying casino properties before, during, and after the crisis.
Bubbles occur all the time in the financial world. The price of a stock or any other commodity can become inflated beyond its intrinsic value. Usually, the damage is limited to losses for a few over-enthusiastic buyers.
The financial crisis of 2007–2008 was a different kind of bubble. Like only a few others in history, it grew big enough that, when it burst, it damaged entire economies and hurt millions of people, including many who were not speculating in mortgage-backed securities.
Govinfo.gov. " The Financial Crisis Inquiry Report ," Page 250.
U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission. " SEC Charges Two Former Bear Stearns Hedge Fund Managers with Fraud ."
Bank for International Settlements. " Reflections on Northern Rock: The Bank Run that Heralded the Global Financial Crisis ," Page 101.
Federal Reserve. " Open Market Operations Archive ."
Federal Reserve. " Open Market Operations ."
Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis. " All-Transactions House Price Index for the United States ."
Brookings. " The Origins of the Financial Crisis ," Pages 7–8.
Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis. " Homeownership Rate for the United States ."
Huduser.gov. " U.S. Housing Market Conditions - 4th Quarter 2006 ," Page 1 of PDF.
Reuters. " New Century Files for Chapter 11 Bankruptcy ."
U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission. " New Century Financial Corporation Files for Chapter 11; Announces Agreement to Sell Servicing Operations ."
Michael C. Hill. "Cannibal Capitalism," Page 44. John Wiley & Sons, 2012.
Lindsey K. Hanson and Timothy J. Essenburg. "The New Faces of American Poverty: A Reference Guide to the Great Recession," Page 18. ABC-CLIO, 2014.
UK Parliament. " The Nationalisation of Northern Rock ," Page 3.
U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission. " Bear Stearns: Merger Proposed—Your Vote Is Very Important ."
FDIC. " Failed Bank Information: Information for IndyMac Bank, F.S.B., and IndyMac Federal Bank, F.S.B., Pasadena, CA ."
Federal Housing Finance Agency. " History of Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac Conservatorships ."
U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission. " The Causes and Effects of the Lehman Brothers Bankruptcy ."
GovTrack. " Emergency Economic Stabilization Act of 2008 ."
U.S. Department of the Treasury. " Monthly Report to Congress - August 2018 ," Page 5.
Federal Reserve Bank of Chicago. " Have Borrowers Recovered from Foreclosures During the Great Recession? "
Govinfo.gov. " Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act ."
Govinfo.gov. " Executive Order 14036 of July 9, 2021 ," Pages 3, 12.
Federal Reserve Bank of Cleveland. " The Great Recession in Retrospect ."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/HenryPaulson_final-fc607bc124ca46b489afbca1c3b567b3.png)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
Find what you need to study
8.5 Global Economic Crisis: The Great Depression
3 min read • january 14, 2023
Bretnea Turner
Isabela Padilha Vilela
Great Britain, France, Russia, Belgium, and Germany saw the largest economic impacts of WWI. Nations were forced into a war of attrition . The new fighting style and weaponry of WWI caused extensive damage, more than any previous European war.
The expensive nature of the war forced nations into debt. The United States offered loans to its European allies during the war, expecting them to be paid afterwards. The Treaty of Versailles placed war reparations on Germany totaling 132 billion German marks (around $33 billion). This, coupled with their personal war debts, forced Germany into a period of hyperinflation when they were forced to print more money to cover their debts.
The US, under the direction of Charles Dawes , developed a plan in which the US would loan Germany money to pay off its debts. In return, the other European nations could pay off their debts to the US.
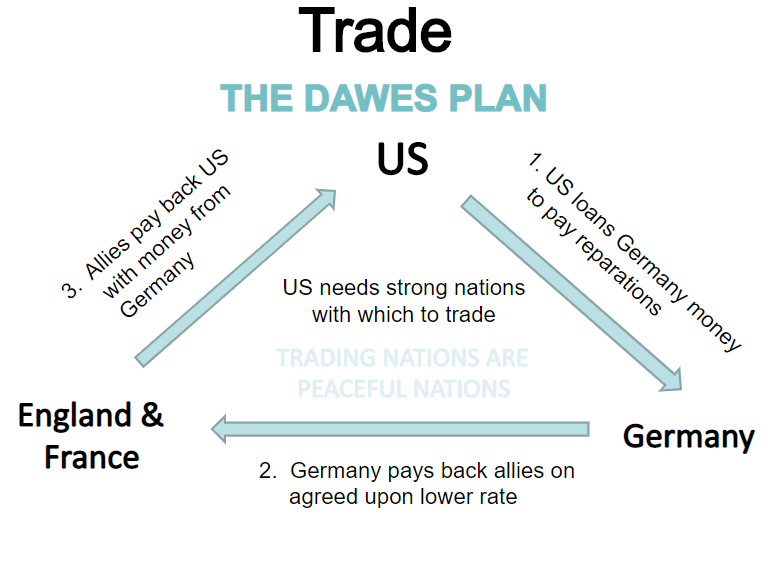
Dawes Plan . Photo courtesy of SlidePlayer.
US Stock Market Crash
In the United States, WWI had been an economic boom. Industry was more productive and the workforce had expanded in the wartime economy. This led to the outbreak of a consumer economy in the 1920s. Part of this consumer economy led to people investing in the stock market with expectations of making money. However, they didn’t invest the full amount required.
Most were buying on the margin : meaning they were only paying 10-20% of their investment and taking a loan out for the rest. When stock prices reached a peak, many began selling their stocks. As the DOW dropped after one day, a frenzy began and people started selling stocks quickly. The problem? People had only invested 10-20% of the cost. If they don’t make money, they can’t pay their loans back.
When banks began closing and the US Stock Market crashed in 1929, the US was unable to continue participating in the Dawes Plan and the Great Depression began, then exacerbated the hyperinflation already occurring in Europe.
Rise of Extremism
The extreme poverty that existed in Europe led to the rise of authoritarian leaders . People feared for their lives, their futures, and the futures of their nations. Men who had military backgrounds made strong speeches with rhetoric that matched the anger and frustrations of their populations, and promised to fix all that is wrong with their countries. They start gaining popularity in Italy, Spain, Germany, and even Russia. It is important to recognize that European Nations began to become very dependent on the U.S economy after WWI, so the nationalist rhetoric opposed this interconnectedness and preached self-sufficiency in the economy.
New Economic Theories
In order to revert this deep economic crisis, different economic ideologies began to gain popularity across the world. These new theories were often built as an alternative option to classical economics , and set the groundwork for heterodox economists .
Keynesianism - Deveoped by the British economist John Maynard Keynes , it consists of the idea that government intervention is important to maintain economic stability. Keynes emphasized the need to have a comprehensive fiscal set of policies that use government spending to expand the economy. His ideas highly influenced JFK in the United States to recover the US economy.
Cooperative Social action in Scandinavia - This set of policies emerged during the depression period in the Scandinavian countries, such as Denmark, Finland and Iceland. It consisted of cooperation between the government, employers and workers in achieving economic and social equality. This model has been praised for overcoming poverty and inequality and allowing for economic mobility (the capacity of citizens to ascend the social strata).
Popular Front policies in France - The popular front of France is a coalition of French left-wing political parties led by the PCF, the French Communist Party . Their economic policies aimed to reduce poverty and promote more equality through the nationalization of certain industries, the implementation of 40-hour workweeks and other social welfare programs.
All of these theories are a direct response to the tragic outcomes of war, and many of these policies endured until the late 20th Century.

Key Terms to Review ( 20 )
Authoritarian Leaders
Buying on the Margin
Charles Dawes
Classical Economics
Consumer Economy
Cooperative Social Action in Scandinavia
French Communist Party
German Marks
Great Depression
Heterodox Economists
Hyperinflation
John Maynard Keynes
Keynesianism
Popular Front Policies in France
Treaty of Versailles
US stock market crash
War of Attrition

About Fiveable
Code of Conduct
Terms of Use
Privacy Policy
CCPA Privacy Policy
AP Score Calculators
Study Guides
Practice Quizzes
Cram Events
Crisis Text Line
Help Center
Stay Connected
© 2024 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.
AP® and SAT® are trademarks registered by the College Board, which is not affiliated with, and does not endorse this website.
Top Ten Global Economic Challenges: An Assessment of Global Risks and Priorities
Subscribe to global connection.
February 1, 2007
To learn more about the critical issues and challenges facing the world today, explore 11 Global Debates , a collections of essays celebrating 10 years of research by the Global Economy and Development program at Brookings.
The beginning of 2007 offers a conflicting picture of the global economy for those trying to discern trends, challenges and opportunities. Concerns about energy security and climate sustainability are converging-finally bringing consensus in sight on the need for action in the United States, but prospects for breaking the global stalemate are still years away. While some developing countries are succeeding in bringing hundreds of millions out of poverty, too many are still mired in a doom spiral of conflict, poverty, and disease- despite the entry of new philanthropists, advocates and global corporations into the field of development. China’s projected 9.6 percent growth rate is sending ripples to the farthest reaches of the planet-creating opportunities but also significant risks. The United States remains in the “goldilocks” zone, but this is premised on continued borrowing from abroad at historically unprecedented rates while many Americans fret about widening inequality and narrowing opportunity. While the United States concentrates on civil war in the Middle East, most leaders in the region are preoccupied with putting an outsized cohort of young people to work and on the road to becoming productive citizens.
What are the most important challenges we face and what are the potential solutions? In Washington, D.C., where short-term political wrangling too often crowds out the harder and more important long-term challenges, this inaugural publication of Brookings Global Economy and Development seeks to put the spotlight squarely back on the most consequential issues demanding action. It seeks to size these issues, offering policymakers and leaders a concise and clear view of the critical challenges as viewed by leading experts in the field. From economic exclusion of youth in the Middle East to a pragmatic approach to energy and environmental security, this “top 10” is intended to mark core issues and shed light on opportunities and challenges with a broader and longer-term perspective.
When we gather a year from now, we would expect many of these challenges to remain front and central, but we would hope this publication would elevate their visibility and help sustain a dialogue on their resolution.
1. Energy and Environmental Security Warwick McKibbin and Peter Wilcoxen
Energy and environmental security has emerged as the primary issue on the global agenda for 2007. Consensus has recently been forged on the potential for long-term economic, national security and societal damage from insecure energy supplies and environmental catastrophe, as well as the intense need for technological advances that can provide low-polluting and secure energy sources. Yet despite growing global momentum, there is still little agreement on the best set of actions required to reduce global dependency on fossil fuels and greenhouse gas emissions. Confounding the international policy challenge is the disproportionate impact of high oil prices and global warming across nations, insulating some countries from immediate concern while forcing others to press for more rapid change.
2. Conflict and Poverty
Lael Brainard, Derek Chollet, Jane Nelson, Ngozi Okonjo-Iweala, and Susan Rice
In a world where boundaries and borders have blurred, and where seemingly distant threats can metastasize into immediate problems, the fight against global poverty has become a fight for global security. American policymakers, who traditionally have viewed security threats as involving bullets and bombs, are increasingly focused on the link between poverty and conflict: the Pentagon’s 2006 Quadrennial Defense Review focuses on fighting the “long war,” declaring that the U.S. military has a humanitarian role in “alleviating suffering, ? [helping] prevent disorder from spiraling into wider conflict or crisis.”
3. Competing in a New Era of Globalization
Lael Brainard, Robert Litan, and Wing Thye Woo
Is the new episode of globalization just another wave or a seismic shift? While individual elements feel familiar, the combined contours are unprecedented in scale, speed, and scope.
4. Global Imbalances
Barry Bosworth, Lael Brainard, Peter Blair Henry, Warwick McKibbin, Kenneth Rogoff, And Wing Thye Woo
Today’s interconnected world is in uncharted territory: the world’s sole hegemonic power, the United States, nurses an addiction to foreign capital, while up-and-coming powers such as China and oil exporters sustain surpluses of increasing magnitudes. Some worry that the world is at a tipping point, where only a dramatic shift in economic policy can alter the looming trajectory. Others see underlying structural factors perpetuating gross imbalances for a sustained period.
5. Rise of New Powers
Chong-En Bai, Erik Berglöf, Barry Bosworth, David de Ferranti, Clifford Gaddy, Xiao Geng, Homi Kharas, Santiago Levy, Leonardo Martinez-Diaz, Urjit Patel, Shang-Jin Wei, Wing Thye Woo
The rise of “emerging powers”-a group that usually includes the so-called BRICs (Brazil, Russia, India, and China), but which sometimes is applied more broadly to include South Africa, Mexico and others-is reshaping the global economy and, more gradually, international politics. Growing much faster than the rest of the world, these economies are changing the structure of international production and trade, the nature and direction of capital flows, and the patterns of natural resource consumption. At the same time, the growth of these countries is beginning to shift the global distribution of power forcing the great powers to come to terms with the reality that they will need to share management of international rules and systems in the coming decades.
6. Economic Exclusion in the Middle East
Navtej Dhillon, Caroline Moser, and Tarik Yousef
The Middle East has before it what could be one of the greatest demographic gifts in modern history-a potential economic windfall arising from a young and economically active workforce. Today, young people aged 15- to 24- years old account for 22 percent of the region’s total population, the highest regional average worldwide. With the right mix of policies, this demographic opportunity could be tapped to spur economic growth and promote stability.
7. Global Corporations, Global Impact
David Caprara and Jane Nelson
The private sector is becoming a significant player-indeed some might say the dominant player-in shaping the global economic and development agenda. Multinational corporations with operations that span the globe, and in some cases capacities and networks that match those of governments, have a particularly important role to play in helping to spread the opportunities and mitigating some of the risks of globalization.
8. Global Health Crises
Maria-Luisa Escobar, David de Ferranti, Jacques Van Der Gaag, Amanda Glassman, Charles Griffin, and Michael Kremer
From responding to the threat of pandemic flu to efforts to control the spread of HIV/AIDS, the world has begun to realize that global health issues are relevant for any citizen, regardless of nationality, residence or status. Despite improvements in the world’s collective ability to battle disease with advances in medicine and technology, global health needs remain unmet, making the entire world vulnerable to health crises. In particular, the poor continue to suffer disproportionately from inadequate health services, exacerbating their struggle out of poverty.
9. Global Governance Stalemate
Colin Bradford, Ralph Bryant, and Johannes Linn
Today’s global challenges-nuclear proliferation, the deadlock of global trade negotiations, the threat of pandemic flu, and the fight against global poverty-cannot be solved by yesterday’s international institutions. To resolve the world’s most pressing problems, which touch all corners of the globe, we must adapt our global governance approaches to be more representative and thus more effective by encouraging and enabling the key affected countries to take an active role in generating solutions.
10. Global Poverty: New Actors, New Approaches
Lael Brainard, Raj Desai, David de Ferranti, Carol Graham, Homi Kharas, Santiago Levy, Caroline Moser, Joe O’Keefe
The challenge of global poverty is more urgent than ever: over half the world’s population-nearly 3 billion people-lives on less than $2 per day; nearly 30,000 children die each day-about 11 million per year -because they’re too poor to survive. With such a toll, addressing poverty in new and more effective ways must be a priority for the global policy agenda. Fortunately, a variety of new actors are bringing new perspectives, new approaches and new energy to the challenge.
Related Content
Nancy Lindborg
July 31, 2017
October 5, 2016
Bruce Jones, Thomas Wright, Jeremy Shapiro, Robert Keane
February 25, 2014
Related Books
Lael Brainard, Abigail Jones, Nigel Purvis
July 15, 2009
Laurence Chandy, Hiroshi Kato, Homi Kharas
July 20, 2015
Nora Claudia Lustig
September 1, 1995
Development Financing Emerging Markets & Developing Economies Global Trade
Global Economy and Development
Middle East & North Africa
Climate and Energy Economics Project
Joshua Turner, Nicol Turner Lee
June 4, 2024
Tara Watson, Gabriela Goodman
Russell Wheeler, Kathryn Dunn Tenpas, Tracy Viselli, Adelle Patten
Global economy: Outlook worsens as global recession looms – IMF

Facebook Twitter Print Email
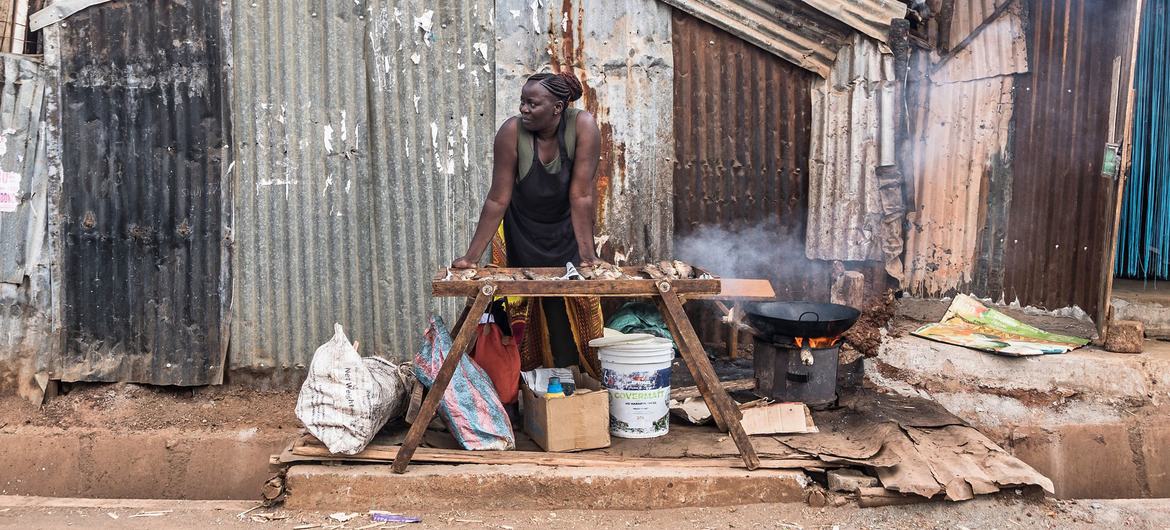
Still reeling from the COVID pandemic and Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, the global economy is facing an increasingly murky and uncertain outlook, according to the latest report released on Tuesday by the International Monetary Fund (IMF).
The World Economic Outlook Update July 2022: Gloomy and More Uncertain , highlights the significant consequences of the stalling of the world’s three main economic powerhouses – the United States, China and the major European economies.
The world may soon be teetering on the edge of a global recession – IMF economist
“The outlook has darkened significantly since April,” said Pierre-Olivier Gourinchas, IMF Economic Counsellor and Director of Research.
“The world may soon be teetering on the edge of a global recession, only two years after the last one”.
The baseline forecast for global growth is for it to slow from 6.1 per cent last year, to 3.2 per cent in 2022 – 0.4 per cent lower than forecast in the last Outlook update in April.
Three key economies
With higher-than-expected inflation – especially in the US and the largest European economies – global financial conditions are becoming tighter.
The global economy is slowing sharply. The war in Ukraine, rising energy and food prices, and supply-demand imbalances are feeding worldwide inflation. Find out how much this will affect global growth and what policymakers can do. https://t.co/ldMsaieJUU #WEO pic.twitter.com/rdHcvhY5cw IMF IMFNews
In the US, reduced household purchasing power and tighter monetary policy will drive growth down to 2.3 per cent this year and one percent next year, according to the outlook.
China’s slowdown has been worse than anticipated amid COVID-19 outbreaks and lockdowns, with negative effects from Russia’s invasion of Ukraine continuing.
Moreover, further lockdowns and a deepening real estate crisis there has pushed growth down to 3.3 per cent this year – the slowest in more than four decades, excluding the pandemic.
And in the Eurozone, growth has been revised down to 2.6 per cent this year and 1.2 percent in 2023, reflecting spillovers from the Ukraine war and tighter monetary policy.
“As a result, global output contracted in the second quarter of this year,” said Mr. Gourinchas.
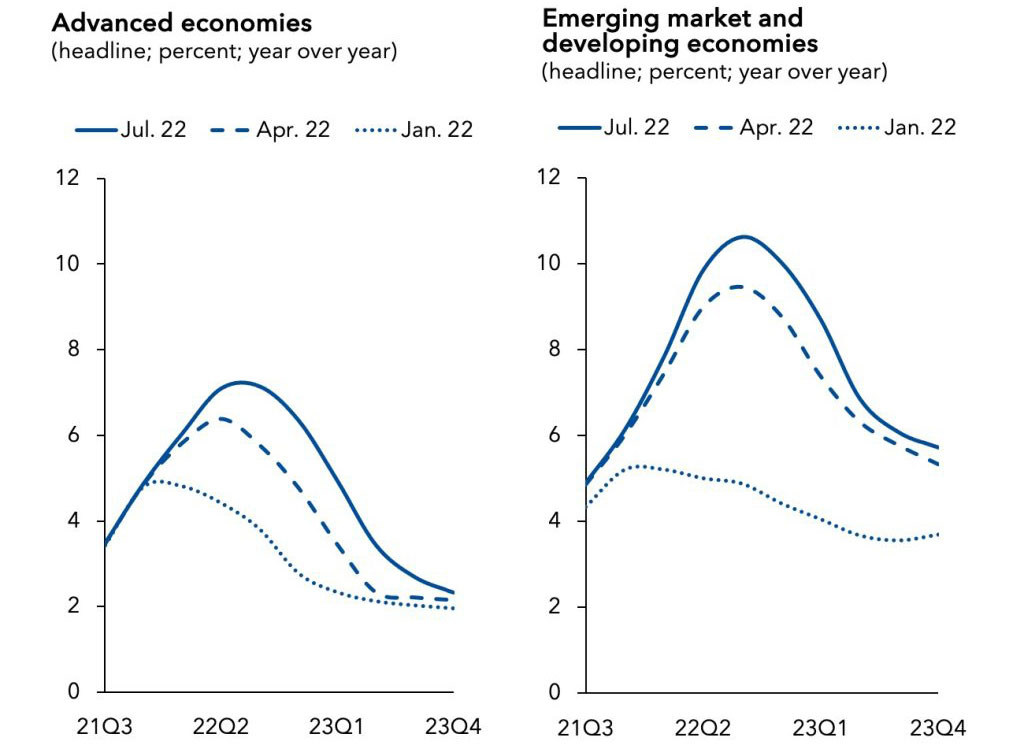
Despite the global slowdown, inflation has been revised up, in part due to rising food and energy prices.
This year it is anticipated to reach 6.6 per cent in advanced economies and 9.5 per cent in emerging market and developing economies – representing upward revisions of 0.9 and 0.8 percentage points respectively. And it is projected to remain elevated for longer.
Broadened inflation in many economies reflects “the impact of cost pressures from disrupted supply chains and historically tight labour markets,” the IMF official stated.
Downward risks
The report outlines some risks ahead, including that the war in Ukraine could end European gas supply from Russia altogether; rising prices could cause widespread food insecurity and social unrest; and geopolitical fragmentation may impede global trade and cooperation.
Inflation could remain stubbornly high if labour markets remain overly tight or inflation expectations are too optimistic and prove more costly than expected.
And renewed COVID-19 outbreaks and lockdowns threaten to further suppress China’s growth.
“In a plausible alternative scenario where some of these risks materialize…inflation will rise and global growth decelerate further to about 2.6 per cent this year and two per cent next year, a pace that growth has fallen below just five times since 1970,” said the IMF economist.
“Under this scenario, both the United States and the Euro area experience near-zero growth next year, with negative knock-on effects for the rest of the world”.
Destabilizing inflation
Current inflation levels represent a clear risk to macroeconomic stability , according to the outlook.
Responding to the situation, central banks in advanced economies are withdrawing monetary support faster than expected, while many in emerging market and developing economies began raising interest rates last year.
“The resulting synchronized monetary tightening across countries is historically unprecedented, and its effects are expected to bite, with global growth slowing next year and inflation decelerating,” said Mr. Gourinchas.
Policy priorities
While acknowledging that tighter monetary policy would have economic costs, the IMF official upheld that delaying it would only exacerbate hardship.
And hampered by difficulties in coordinating creditor agreements, how and whether debt can be restructured, remains unpredictable .
He argued that domestic policies responding to the impacts of high energy and food prices should focus on those most affected, without distorting prices.
“Governments should refrain from hoarding food and energy and instead look to unwind barriers to trade such as food export bans, which drive world prices higher,” advised the IMF official.
Meanwhile, mitigating climate change continues to require prompt multilateral action to limit emissions and raise investment to accelerate a “green transition”.
Policymakers are urged to ensure that measures are temporary and only cover energy shortfalls and climate policies.
Teetering on the edge
From climate transition and pandemic preparedness to food security and debt distress, multilateral cooperation is key , said the IMF economist.
“Amid great challenge and strife, strengthening cooperation remains the best way to improve economic prospects and mitigate the risk of geoeconomic fragmentation ,” he underscored.

- World Economic Outlook
- global economy
The Global Economic Outlook During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Changed World
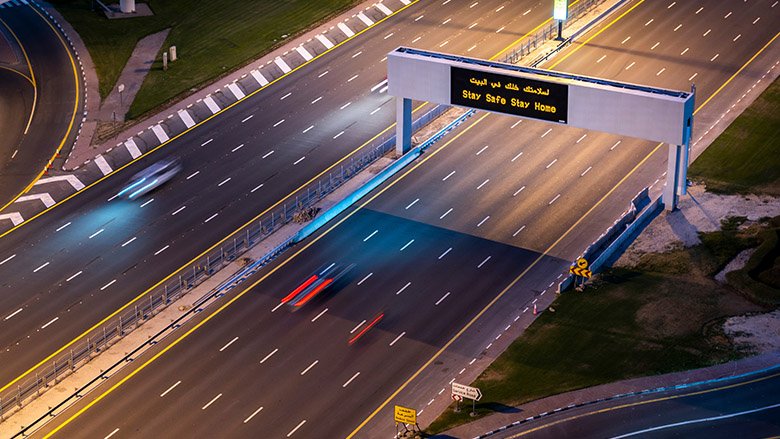

An empty highway in Dubai during the coronavirus pandemic. Above the highway, a sign reads "Stay Safe, Stay Home." © Mo Azizi/Shutterstock
The COVID-19 pandemic has spread with alarming speed, infecting millions and bringing economic activity to a near-standstill as countries imposed tight restrictions on movement to halt the spread of the virus. As the health and human toll grows, the economic damage is already evident and represents the largest economic shock the world has experienced in decades.
The June 2020 Global Economic Prospects describes both the immediate and near-term outlook for the impact of the pandemic and the long-term damage it has dealt to prospects for growth. The baseline forecast envisions a 5.2 percent contraction in global GDP in 2020, using market exchange rate weights—the deepest global recession in decades, despite the extraordinary efforts of governments to counter the downturn with fiscal and monetary policy support. Over the longer horizon, the deep recessions triggered by the pandemic are expected to leave lasting scars through lower investment, an erosion of human capital through lost work and schooling, and fragmentation of global trade and supply linkages.
The crisis highlights the need for urgent action to cushion the pandemic’s health and economic consequences, protect vulnerable populations, and set the stage for a lasting recovery. For emerging market and developing countries, many of which face daunting vulnerabilities, it is critical to strengthen public health systems, address the challenges posed by informality, and implement reforms that will support strong and sustainable growth once the health crisis abates.
Historic contraction of per capita income
The pandemic is expected to plunge most countries into recession in 2020, with per capita income contracting in the largest fraction of countries globally since 1870. Advanced economies are projected to shrink 7 percent. That weakness will spill over to the outlook for emerging market and developing economies, who are forecast to contract by 2.5 percent as they cope with their own domestic outbreaks of the virus. This would represent the weakest showing by this group of economies in at least sixty years.
Every region is subject to substantial growth downgrades. East Asia and the Pacific will grow by a scant 0.5%. South Asia will contract by 2.7%, Sub-Saharan Africa by 2.8%, Middle East and North Africa by 4.2%, Europe and Central Asia by 4.7%, and Latin America by 7.2%. These downturns are expected to reverse years of progress toward development goals and tip tens of millions of people back into extreme poverty.
Emerging market and developing economies will be buffeted by economic headwinds from multiple quarters: pressure on weak health care systems, loss of trade and tourism, dwindling remittances, subdued capital flows, and tight financial conditions amid mounting debt. Exporters of energy or industrial commodities will be particularly hard hit. The pandemic and efforts to contain it have triggered an unprecedented collapse in oil demand and a crash in oil prices. Demand for metals and transport-related commodities such as rubber and platinum used for vehicle parts has also tumbled. While agriculture markets are well supplied globally, trade restrictions and supply chain disruptions could yet raise food security issues in some places.

A possibility of even worse outcomes
Even this bleak outlook is subject to great uncertainty and significant downside risks. The forecast assumes that the pandemic recedes in such a way that domestic mitigation measures can be lifted by mid-year in advanced economies and later in developing countries, that adverse global spillovers ease during the second half of 2020, and that widespread financial crises are avoided. This scenario would envision global growth reviving, albeit modestly, to 4.2% in 2021.
However, this view may be optimistic. Should COVID-19 outbreaks persist, should restrictions on movement be extended or reintroduced, or should disruptions to economic activity be prolonged, the recession could be deeper. Businesses might find it hard to service debt, heightened risk aversion could lead to climbing borrowing costs, and bankruptcies and defaults could result in financial crises in many countries. Under this downside scenario, global growth could shrink by almost 8% in 2020.
Looking at the speed with which the crisis has overtaken the global economy may provide a clue to how deep the recession will be. The sharp pace of global growth forecast downgrades points to the possibility of yet further downward revisions and the need for additional action by policymakers in coming months to support economic activity.
A particularly concerning aspect of the outlook is the humanitarian and economic toll the global recession will take on economies with extensive informal sectors that make up an estimated one-third of the GDP and about 70% of total employment in emerging market and developing economies. Policymakers must consider innovative measures to deliver income support to these workers and credit support to these businesses.
Long-term damage to potential output, productivity growth
The June 2020 Global Economic Prospects looks beyond the near-term outlook to what may be lingering repercussions of the deep global recession: setbacks to potential output—the level of output an economy can achieve at full capacity and full employment—and labor productivity. Efforts to contain COVID-19 in emerging and developing economies, including low-income economies with limited health care capacity, could precipitate deeper and longer recessions—exacerbating a multi-decade trend of slowing potential growth and productivity growth. Many emerging and developing economies were already experiencing weaker growth before this crisis; the shock of COVID-19 now makes the challenges these economies face even harder.
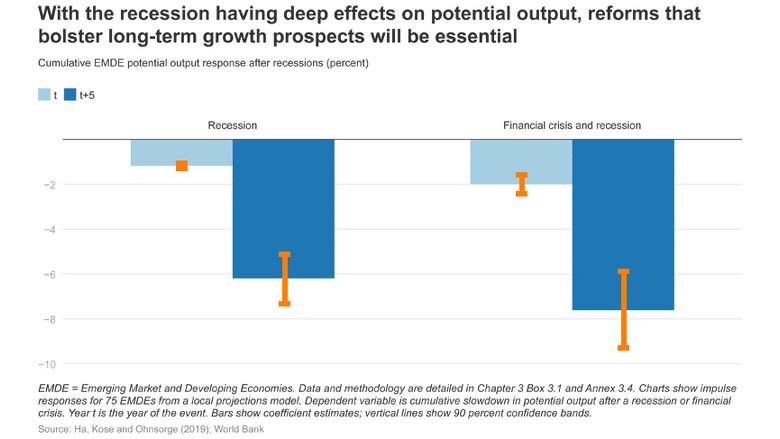
Another important feature of the current landscape is the historic collapse in oil demand and oil prices. Low oil prices are likely to provide, at best, temporary initial support to growth once restrictions to economic activity are lifted. However, even after demand recovers, adverse impacts on energy exporters may outweigh any benefits to activity in energy importers. Low oil prices offer an opportunity to oil producers to diversify their economies. In addition, the recent oil price plunge may provide further momentum to undertake energy subsidy reforms and deepen them once the immediate health crisis subsides.
In the face of this disquieting outlook, the immediate priority for policymakers is to address the health crisis and contain the short-term economic damage. Over the longer term, authorities need to undertake comprehensive reform programs to improve the fundamental drivers of economic growth once the crisis lifts.
Policies to rebuild both in the short and long-term entail strengthening health services and putting in place targeted stimulus measures to help reignite growth , including support for the private sector and getting money directly to people. During the mitigation period, countries should focus on sustaining economic activity with support for households, firms and essential services.
Global coordination and cooperation—of the measures needed to slow the spread of the pandemic, and of the economic actions needed to alleviate the economic damage, including international support—provide the greatest chance of achieving public health goals and enabling a robust global recovery.
- Global Economic Prospects
- Press release
- Download the report
- Download all data (Excel)
- Download charts (zip)
This site uses cookies to optimize functionality and give you the best possible experience. If you continue to navigate this website beyond this page, cookies will be placed on your browser. To learn more about cookies, click here .
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Elsevier - PMC COVID-19 Collection

A critical analysis of the impacts of COVID-19 on the global economy and ecosystems and opportunities for circular economy strategies
T. ibn-mohammed.
a Warwick Manufacturing Group (WMG), The University of Warwick, Coventry CV4 7AL, United Kingdom
K.B. Mustapha
b Faculty of Engineering and Science, University of Nottingham (Malaysia Campus), Semenyih, Selangor43500, Malaysia
c School of The Built Environment and Architecture, London South Bank University, London SE1 0AA, United Kingdom
K.A. Babatunde
d Faculty of Economics and Management, Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia, Bangi, Selangor43600, Malaysia
e Department of Economics, Faculty of Management Sciences, Al-Hikmah University, Ilorin, Nigeria
D.D. Akintade
f School of Life Sciences, University of Nottingham, Nottingham NG7 2UH United Kingdom
g Kent Business School, University of Kent, Canterbury CT2 7PE, United Kingdom
h Faculty of Economics, Kyushu University, 744 Motooka, Nishi-ku, Fukuoka 819-0395, Japan
M.M. Ndiaye
i Department of Industrial Engineering, College of Engineering, American University of Sharjah, Sharjah, UAE
F.A. Yamoah
j Department of Management, Birkbeck University of London, London WC1E 7JL United Kingdom
k Sheffield University Management School (SUMS), The University of Sheffield, Sheffield S10 1FL, United Kingdom
- • COVID-19 presents unprecedented challenge to all facets of human endeavour.
- • A critical review of the negative and positive impacts of the pandemic is presented.
- • The danger of relying on pandemic-driven benefits to achieving SDGs is highlighted.
- • The pandemic and its interplay with circular economy (CE) approaches is examined.
- • Sector-specific CE recommendations in a resilient post-COVID-19 world are outlined.
The World Health Organization declared COVID-19 a global pandemic on the 11th of March 2020, but the world is still reeling from its aftermath. Originating from China, cases quickly spread across the globe, prompting the implementation of stringent measures by world governments in efforts to isolate cases and limit the transmission rate of the virus. These measures have however shattered the core sustaining pillars of the modern world economies as global trade and cooperation succumbed to nationalist focus and competition for scarce supplies. Against this backdrop, this paper presents a critical review of the catalogue of negative and positive impacts of the pandemic and proffers perspectives on how it can be leveraged to steer towards a better, more resilient low-carbon economy. The paper diagnosed the danger of relying on pandemic-driven benefits to achieving sustainable development goals and emphasizes a need for a decisive, fundamental structural change to the dynamics of how we live. It argues for a rethink of the present global economic growth model, shaped by a linear economy system and sustained by profiteering and energy-gulping manufacturing processes, in favour of a more sustainable model recalibrated on circular economy (CE) framework. Building on evidence in support of CE as a vehicle for balancing the complex equation of accomplishing profit with minimal environmental harms, the paper outlines concrete sector-specific recommendations on CE-related solutions as a catalyst for the global economic growth and development in a resilient post-COVID-19 world.
1. Introduction
The world woke up to a perilous reality on the 11th of March, 2020 when the World Health Organization (WHO) declared novel coronavirus (COVID-19) a pandemic ( Sohrabi et al., 2020 ; WHO, 2020a ). Originating from Wuhan, China, cases rapidly spread to Japan, South Korea, Europe and the United States as it reached global proportions. Towards the formal pandemic declaration, substantive economic signals from different channels, weeks earlier, indicated the world was leaning towards an unprecedented watershed in our lifetime, if not in human history ( Gopinath, 2020 ). In series of revelatory reports ( Daszak, 2012 ; Ford et al., 2009 ; Webster, 1997 ), experts across professional cadres had long predicted a worldwide pandemic would strain the elements of the global supply chains and demands, thereby igniting a cross-border economic disaster because of the highly interconnected world we now live in. By all accounts, the emerging havoc wrought by the pandemic exceeded the predictions in those commentaries. At the time of writing, the virus has killed over 800,000 people worldwide ( JHU, 2020 ), disrupted means of livelihoods, cost trillions of dollars while global recession looms ( Naidoo and Fisher, 2020 ). In efforts to isolate cases and limit the transmission rate of the virus, while mitigating the pandemic, countries across the globe implemented stringent measures such as mandatory national lockdown and border closures.
These measures have shattered the core sustaining pillars of modern world economies. Currently, the economic shock arising from this pandemic is still being weighed. Data remains in flux, government policies oscillate, and the killer virus seeps through nations, affecting production, disrupting supply chains and unsettling the financial markets ( Bachman, 2020 ; Sarkis et al., 2020 ). Viewed holistically, the emerging pieces of evidence indicate we are at a most consequential moment in history where a rethink of sustainable pathways for the planet has become pertinent. Despite this, the measures imposed by governments have also led to some “accidental” positive effects on the environment and natural ecosystems. As a result, going forward, a fundamental change to human bio-physical activities on earth now appears on the spectrum of possibility ( Anderson et al., 2020 ). However, as highlighted by Naidoo and Fisher (2020) , our reliance on globalization and economic growth as drivers of green investment and sustainable development is no longer realistic. The adoption of circular economy (CE) – an industrial economic model that satisfies the multiple roles of decoupling of economic growth from resource consumption, waste management and wealth creation – has been touted to be a viable solution.
No doubt, addressing the public health consequences of COVID-19 is the top priority, but the nature of the equally crucial economic recovery efforts necessitates some key questions as governments around the world introduce stimulus packages to aid such recovery endeavours: Should these packages focus on avenues to economic recovery and growth by thrusting business as usual into overdrive or could they be targeted towards constructing a more resilient low-carbon CE? To answer this question, this paper builds on the extant literature on public health, socio-economic and environmental dimensions of COVID-19 impacts ( Gates, 2020b ; Guerrieri et al., 2020 ; Piguillem and Shi, 2020 ; Sohrabi et al., 2020 ), and examines its interplay with CE approaches. It argues for the recalibration and a rethink of the present global economic growth model, shaped by a linear economy system and sustained by profit-before-planet and energy-intensive manufacturing processes, in favour of CE. Building on evidence in support of CE as a vehicle for optimizing the complex equation of accomplishing profit while minimizing environmental damage, the paper outlines tangible sector-specific recommendations on CE-related solutions as a catalyst for the global economic boom in a resilient post-COVID-19 world. It is conceived that the “accidental” or the pandemic-induced CE strategies and behavioural changes that ensued during coronavirus crisis can be leveraged or locked in, to provide opportunities for both future resilience and competitiveness.
In light of the above, the paper is structured as follows. In Section 2 , the methodological framework, which informed the critical literature review is presented. A brief overview of the historical context of previous epidemics and pandemics is presented in Section 3 as a requisite background on how pandemics have shaped human history and economies and why COVID-19 is different. In Section 4 , an overview of the impacts (both negative and positive) of COVID-19 in terms of policy frameworks, global economy, ecosystems and sustainability are presented. The role of the CE as a constructive change driver is detailed in Section 5 . In Section 6 , opportunities for CE after COVID-19 as well as sector-based recommendations on strategies and measures for advancing CE are presented, leading to the summary and concluding remarks in Section 7.
A literature review exemplifies a conundrum because an effective one cannot be conducted unless a problem statement is established ( Ibn-Mohammed, 2017 ). Yet, a literature search plays an integral role in establishing many research problems. In this paper, the approach taken to overcome this conundrum involves searching and reviewing the existing literature in the specific area of study (i.e. impacts of COVID-19 on global economy and ecosystems in the context of CE). This was used to develop the theoretical framework from which the current study emerges and adopting this to establish a conceptual framework which then becomes the basis of the current review. The paper adopts the critical literature review (CLR) approach given that it entails the assessment, critique and synthetisation of relevant literature regarding the topic under investigation in a manner that facilitates the emergence of new theoretical frameworks and perspectives from a wide array of different fields ( Snyder, 2019 ). CLR suffers from an inherent weakness in terms of subjectivity towards literature selection ( Snyder, 2019 ), prompting Grant and Booth (2009) to submit that systematic literature review (SLR) could mitigate this bias given its strict criteria in literature selection that facilitates a detailed analysis of a specific line of investigation. However, a number of authors ( Morrison et al., 2012 ; Paez, 2017 ) have reported that SLR does not allow for effective synthesis of academic and grey literature which are not indexed in popular academic search engines like Google Scholar, Web-of-Science and Scopus. The current review explores the impacts of COVID-19 on the global economy and ecosystems and opportunities for circular economy strategies, rather than investigating a specific aspect of the pandemic. As such, adopting a CLR approach is favoured in realising the goal of the paper as it allows for the inclusion of a wide range of perspectives and theoretical underpinnings from different sources ( Greenhalgh et al., 2018 ; Snyder, 2019 ).
Considering the above, this paper employed archival data consisting of journal articles, documented news in the media, expert reports, government and relevant stakeholders’ policy documents, published expert interviews and policy feedback literature that are relevant to COVID-19 and the concept of CE. To identify the relevant archival data, we focused on several practical ways of literature searching using appropriate keywords that are relevant to this work including impact (positive and negative) of COVID-19, circular economy, economic resilience, sustainability, supply chain resilience, climate change, etc. After identifying articles and relevant documents, their contents were examined to determine inclusions and exclusions based on their relevance to the topic under investigation. Ideas generated from reading the resulting papers from the search were then used to develop a theoretical framework and a research problem statement, which forms the basis for the CLR. The impact analysis for the study was informed by the I = P × A × T model whereby the “impact” (I) of any group or country on the environment is a function of the interaction of its population size (P), per capita affluence (A), expressed in terms of real per capita GDP, as a valid approximation of the availability of goods and services and technology (T) involved in supporting each unit of consumption.
As shown in the methodological framework in Fig. 1 , the paper starts with a brief review of the impacts of historical plagues to shed more light on the link between the past and the unprecedented time, which then led to an overview of the positive and negative impacts of COVID-19. The role of CE as a vehicle for constructive change in the light of COVID-19 was then explored followed by the synthesis, analysis and reflections on the information gathered during the review, leading to sector-specific CE strategy recommendations in a post-COVID-19 world.

Methodological framework for the critical literature review.
3. A brief account of the socio-economic impacts of historical outbreaks
At a minimum, pandemics result in the twin crisis of stressing the healthcare infrastructure and straining the economic system. However, beyond pandemics, several prior studies have long noted that depending on latency, transmission rate, and geographic spread, any form of communicable disease outbreak is a potent vector of localized economic hazards ( Bloom and Cadarette, 2019 ; Bloom and Canning, 2004 ; Hotez et al., 2014 ). History is littered with a catalogue of such outbreaks in the form of endemics, epidemics, plagues and pandemics. In many instances, some of these outbreaks have hastened the collapse of empires, overwhelmed the healthcare infrastructure, brought social unrest, triggered economic dislocations and exposed the fragility of the world economy, with a knock-on effect on many sectors. Indeed, in the initial few months of COVID-19 pandemic, it has become more evident that natural, accidental or intentional biological threats or outbreak in any country now poses an unquantifiable risk to global health and the world economy ( Bretscher et al., 2020 ).
Saunders-Hastings and Krewski (2016) reported that there have been several pandemics over the past 100 years. A short but inexhaustible list of outbreaks of communicable diseases include ‘the great plague’ ( Duncan-Jones, 1996 ; Littman and Littman, 1973 ), the Justinian plague ( Wagner et al., 2014 ), the Black Death ( Horrox, 2013 ), the Third Plague pandemic ( Bramanti et al., 2019 ; Tan et al., 2002 ), the Spanish flu ( Gibbs et al., 2001 ; Trilla et al., 2008 ), HIV/AIDS ( De Cock et al., 2012 ), SARS ( Lee and McKibbin, 2004 ), dengue ( Murray et al., 2013 ), and Ebola ( Baseler et al., 2017 ), among others. The potency of each of these outbreaks varies. Consequently, their economic implications differ according to numerous retrospective analyses ( Bloom and Cadarette, 2019 ; Bloom and Canning, 2004 ; Hotez et al., 2014 ). For instance, the Ebola epidemic of 2013-2016 created socio-economic impact to the tune of $53 billion across West Africa, plummeted Sierra Leone's GDP in 2015 by 20% and that of Liberia by 8% between 2013 and 2014, despite the decline in death rates across the same timeframe ( Fernandes, 2020 ).
As the world slipped into the current inflection point, some of the historical lessons from earlier pandemics remain salutary, even if the world we live in now significantly differs from those of earlier period ( McKee and Stuckler, 2020 ). Several factors differentiate the current socio-economic crisis of COVID-19 from the previous ones ( Baker et al., 2020 ), which means direct simple comparisons with past global pandemics are impossible ( Fernandes, 2020 ). Some of the differentiating factors include the fact that COVID-19 is a global pandemic and it is creating knock-on effects across supply chains given that the world has become much more integrated due to globalisation and advancements in technology ( McKenzie, 2020 ). Moreover, the world has witnessed advances in science, medicine and engineering. The modest number of air travellers during past pandemics delayed the global spread of the virus unlike now where global travel has increased tremendously. From an economic impact perspective, interest rates are at record lows and there is a great imbalance between demand and supply of commodities ( Fernandes, 2020 ). More importantly, many of the countries that are hard hit by the current pandemic are not exclusively the usual low-middle income countries, but those at the pinnacle of the pyramid of manufacturing and global supply chains. Against this backdrop, a review of the impact of COVID-19 is presented in the next section.
4. COVID-19: Policy frameworks, global economy, ecosystems and sustainability
4.1. evaluation of policy frameworks to combat covid-19.
The strategies and policies adopted by different countries to cope with COVID-19 have varied over the evolving severity and lifetime of the pandemic during which resources have been limited ( Siow et al., 2020 ). It is instructive that countries accounting for 65% of global manufacturing and exports (i.e. China, USA, Korea, Japan, France, Italy, and UK) were some of the hardest to be hit by COVID-19 ( Baldwin and Evenett, 2020 ). Given the level of unpreparedness and lack of resilience of hospitals, numerous policy emphases have gone into sourcing for healthcare equipment such as personal protective equipment (PPE) and ventilators ( Ranney et al., 2020 ) due to global shortages. For ventilators, in particular, frameworks for rationing them along with bed spaces have had to be developed to optimise their usage ( White and Lo, 2020 ). Other industries have also been affected, with shocks to their existence, productivity and profitability ( Danieli and Olmstead-Rumsey, 2020 ) including the CE-sensitive materials extraction and mining industries that have been hit by disruption to their operations and global prices of commodities ( Laing, 2020 ).
As highlighted in subsequent sub-sections, one of the psychological impacts of COVID-19 is panic buying ( Arafat et al., 2020 ), which happens due to uncertainties at national levels (e.g. for scarce equipment) and at individual levels (e.g. for everyday consumer products). In both instances, the fragility, profiteering and unsustainability of the existing supply chain model have been exposed ( Spash, 2020 ). In fact, Sarkis et al. (2020) questioned whether the global economy could afford to return to the just-in-time (JIT) supply chain framework favoured by the healthcare sector, given its apparent shortcomings in dealing with much needed supplies. The sub-section that follow examines some of the macro and micro economic ramifications of COVID-19.
4.1.1. Macroeconomic impacts: Global productions, exports, and imports
One challenge faced by the healthcare industry is that existing best practices, in countries like the USA (e.g. JIT macroeconomic framework), do not incentivise the stockpiling of essential medical equipment ( Solomon et al., 2020 ). Although vast sums were budgeted, some governments (e.g. UK, India and USA) needed to take extraordinary measures to protect their supply chain to the extent that manufacturers like Ford and Dyson ventured into the ventilator design/production market ( Iyengar et al., 2020 ). The US, in particular activated the Defense Production Act to compel car manufacturers to shift focus on ventilator production ( American Geriatrics Society, 2020 ; Solomon et al., 2020 ) due to the high cost and shortage of this vital equipment. Hospitals and suppliers in the US were also forced to enter the global market due to the chronic shortfall of N95 masks as well as to search for lower priced equipment ( Solomon et al., 2020 ). Interestingly, the global production of these specialist masks is thought to be led by China ( Baldwin and Evenett, 2020 ; Paxton et al., 2020 ) where COVID-19 broke out, with EU's supply primarily from Malaysia and Japan ( Stellinger et al., 2020 ). Such was the level of shortage that the US was accused of ‘pirating’ medical equipment supplies from Asian countries intended for EU countries ( Aubrecht et al., 2020 ).
France and Germany followed suit with similar in-ward looking policy and the EU itself imposed restrictions on the exportation of PPEs, putting many hitherto dependent countries at risk ( Bown, 2020 ). Unsurprisingly, China and the EU saw it fit to reduce or waive import tariffs on raw materials and PPE, respectively ( Stellinger et al., 2020 ). Going forward, the life-threatening consequences of logistics failures and misallocation of vital equipment and products could breathe new life and impetus to technologies like Blockchain, RFID and IoT for increased transparency and traceability ( Sarkis et al., 2020 ). Global cooperation and scenario planning will always be needed to complement these technologies. In this regard, the EU developed a joint procurement framework to reduce competition amongst member states, while in the US, where states had complained that federal might was used to interfere with orders, a ventilator exchange program was developed ( Aubrecht et al., 2020 ). However, even with trade agreements and cooperative frameworks, the global supply chain cannot depend on imports – or donations ( Evenett, 2020 ) for critical healthcare equipment and this realisation opens doors for localisation of production with consequences for improvements in environmental and social sustainability ( Baldwin and Evenett, 2020 ). This can be seen in the case of N95 masks which overnight became in such high demand that airfreights by private and commercial planes were used to deliver them as opposed to traditional container shipping ( Brown, 2020 ).
As detailed in forthcoming sections, a significant reduction in emissions linked to traditional shipping was observed, yet there was an increase in use of airfreighting due to desperation and urgency of demand. Nevertheless, several countries are having to rethink their global value chains ( Fig. 2 ) as a result of realities highlighted by COVID-19 pandemic ( Javorcik, 2020 ). This is primarily because national interests and protectionism have been a by-product of COVID-19 pandemic and also because many eastern European/Mediterranean countries have a relative advantage with respect to Chinese exports. As shown in Fig. 2 , the global export share which each of these countries has, relative to China's share of the same exports (x-axis) is measured against the economies of countries subscribing to the European Bank for Reconstruction and Development (EBRD) (y-axis). For each product, the ideal is to have a large circle towards the top right-hand corner of the chart.

A summary of how some Eastern European / Mediterranean countries have advantages over China on certain exports – based on the Harmonized Commodity Description and Coding System from 2018, where export volume is represented by dot sizes in millions of USD; Source: Javorcik (2020) .
4.1.2. Microeconomic impacts: Consumer behaviour
For long, there has been a mismatch between consumerist tendencies and biophysical realities ( Spash, 2020 ). However, COVID-19 has further exacerbated the need to reflect on the social impacts of individual lifestyles. The behaviour of consumers, in many countries, was at some point alarmist with a lot of panic buying of food and sanitary products ( Sim et al., 2020 ). At private level, consumer sentiment is also changing. Difficult access to goods and services has forced citizens to re-evaluate purchasing patterns and needs, with focus pinned on the most essential items ( Company, 2020 ; Lyche, 2020 ). Spash (2020) argued that technological obsolescence of modern products brought about by rapid innovation and individual consumerism is also likely to affect the linear economy model which sees, for instance, mobile phones having an average life time of four years (two years in the US), assuming their manufacture/repair services are constrained by economic shutdown and lockdowns ( Schluep, 2009 ). On the other hand, a sector like healthcare, which could benefit from mass production and consumerism of vital equipment, is plagued by patenting. Most medical equipment are patented and the issue of a 3D printer's patent infringement in Italy led to calls for ‘Open Source Ventilators’ and ‘Good Samaritan Laws’ to help deal with global health emergencies like COVID-19 ( Pearce, 2020 ). It is plausible that such initiatives/policies could help address the expensive, scarce, high-skill and material-intensive production of critical equipment, via cottage industry production.
For perspective, it should be noted that production capacity of PPE (even for the ubiquitous facemasks) have been shown by COVID-19 to be limited across many countries ( Dargaville et al., 2020 ) with some countries having to ration facemask production and distribution in factories ( San Juan, 2020 ). Unsurprisingly, the homemade facemask industry has not only emerged for the protection of mass populations as reported by Livingston et al. (2020) , it has become critical for addressing shortages ( Rubio-Romero et al., 2020 ) as well as being part of a post-lockdown exit strategy ( Allison et al., 2020 ). A revival of cottage industry production of equipment and basic but essential items like facemasks could change the landscape of global production for decades, probably leading to an attenuation of consumerist tendencies.This pandemic will also impact on R&D going forward, given the high likelihood that recession will cause companies to take short-term views, and cancel long and medium-term R&D in favour of short-term product development and immediate cash flow/profit as was certainly the case for automotive and aerospace sectors in previous recessions.

4.2. Overview of the negative impacts of COVID-19
The negative effects have ranged from a severe contraction of GDP in many countries to multi-dimensional environmental and social issues across the strata of society. In many respects, socio-economic activities came to a halt as: millions were quarantined; borders were shut; schools were closed; car/airline, manufacturing and travel industries crippled; trade fairs/sporting/entertainment events cancelled, and unemployment claims reached millions while the international tourist locations were deserted; and, nationalism and protectionism re-surfaced ( Baker et al., 2020 ; Basilaia and Kvavadze, 2020 ; Devakumar et al., 2020 ; Kraemer et al., 2020 ; Thunstrom et al., 2020 ; Toquero, 2020 ). In the subsections that follow, an overview of some of these negative impacts on the global economy, environment, and society is presented.
4.2.1. Negative macroeconomic impact of COVID-19
Undoubtedly, COVID-19 first and foremost, constitutes a ferocious pandemic and a human tragedy that swept across the globe, resulting in a massive health crisis ( WHO, 2020b ), disproportionate social order ( UN DESA, 2020 ), and colossal economic loss ( IMF, 2020 ). It has created a substantial negative impact on the global economy, for which governments, firms and individuals scramble for adjustments ( Fernandes, 2020 ; Pinner et al., 2020 ; Sarkis et al., 2020 ; Sohrabi et al., 2020 ; Van Bavel et al., 2020 ). Indeed, the COVID-19 pandemic has distorted the world's operating assumptions, revealing the absolute lack of resilience of the dominant economic model to respond to unplanned shocks and crises ( Pinner et al., 2020 ). It has exposed the weakness of over-centralization of the complex global supply and production chains networks and the fragility of global economies, whilst highlighting weak links across industries( Fernandes, 2020 ; Guan et al., 2020 ; Sarkis et al., 2020 ). This has had a direct impact on employment and heightened the risk of food insecurity for millions due to lockdown and border restrictions ( Guerrieri et al., 2020 ). To some extent, some of the interventional measures introduced by governments across the world have resulted in the flattening of the COVID-19 curve (as shown in Fig. 3 ). This has helped in preventing healthcare systems from getting completely overwhelmed ( JHU, 2020 ), although as at the time of writing this paper, new cases are still being reported in different parts of the globe. Fernandes (2020) and McKibbin and Fernando (2020) reported thatthe socio-economic impact of COVID-19 will be felt for many months to come.

Daily confirmed new COVID-19 cases of the current 10 most affected countries based on a 5-day moving average. Valid as of August 31st, 2020 at 11:46 PM EDT ( JHU, 2020 ).
Guan et al. (2020) submitted that how badly and prolonged the recession rattles the world depends on how well and quickly the depth of the socio-economic implications of the pandemic is understood. IMF (2020) reported that in an unprecedented circumstance (except during the Great Depression), all economies including developed, emerging, and even developing will likely experience recession. In its April World Economic Outlook, IMF (2020) reversed its early global economic growth forecast from 3.3% to -3 %, an unusual downgrade of 6.3% within three months. This makes the pandemic a global economic shock like no other since the Great Depression and it has already surpassed the global financial crisis of 2009 as depicted in Fig. 4 . Economies in the advanced countries are expected to contract by -6.1% while recession in emerging and developing economies is projected (with caution) to be less adverse compared to the developed nations with China and India expected to record positive growth by the end of 2020. The cumulative GDP loss over the next year from COVID-19 could be around $9 trillion ( IMF, 2020 ).

Socioeconomic impact of COVID-19 lockdown: (a) Comparison of global economic recession due to COVID-19 and the 2009 global financial crisis; (b) Advanced economies, emerging and developing economies in recession; (c) the major economies in recession; (d) the cumulative economic output loss over 2020 and 2021. Note: Real GDP growth is used for economic growth, as year-on-year for per cent change ( IMF, 2020 ).
With massive job loss and excessive income inequality, global poverty is likely to increase for the first time since 1998 ( Mahler et al., 2020 ). It is estimated that around 49 million people could be pushed into extreme poverty due to COVID-19 with Sub-Sahara Africa projected to be hit hardest. The United Nations’ Department of Economic and Social Affairs concluded that COVID-19 pandemic may also increase exclusion, inequality, discrimination and global unemployment in the medium and long term, if not properly addressed using the most effective policy instruments ( UN DESA, 2020 ). The adoption of detailed universal social protection systems as a form of automatic stabilizers, can play a long-lasting role in mitigating the prevalence of poverty and protecting workers ( UN DESA, 2020 ).
4.2.2. Impact of COVID-19 on global supply chain and international trade
COVID-19 negatively affects the global economy by reshaping supply chains and sectoral activities. Supply chains naturally suffer from fragmentation and geographical dispersion. However, globalisation has rendered them more complex and interdependent, making them vulnerable to disruptions. Based on an analysis by the U.S. Institute for Supply Management, 75% of companies have reported disruptions in their supply chain ( Fernandes, 2020 ), unleashing crisis that emanated from lack of understanding and flexibility of the several layers of their global supply chains and lack of diversification in their sourcing strategies ( McKenzie, 2020 ). These disruptions will impact both exporting countries (i.e. lack of output for their local firms) and importing countries (i.e. unavailability of raw materials) ( Fernandes, 2020 ). Consequently, this will lead to the creation of momentary “manufacturing deserts” in which the output of a country, region or city drops significantly, turning into a restricted zone to source anything other than essentials like food items and drugs ( McKenzie, 2020 ). This is due to the knock-on effect of China's rising dominance and importance in the global supply chain and economy ( McKenzie, 2020 ). As a consequence of COVID-19, the World Trade Organization (WTO) projected a 32% decline in global trade ( Fernandes, 2020 ). For instance, global trade has witnessed a huge downturn due to reduced Chinese imports and the subsequent fall in global economic activities. This is evident because as of 25 th March 2020, global trade fell to over 4% contracting for only the second time since the mid-1980s ( McKenzie, 2020 ). Fig. 5 shows a pictorial representation of impact of pandemics on global supply chains based on different waves and threat levels.

Impact of pandemics on global supply chains. Adapted from Eaton and Connor (2020) .
4.2.3. Impact of COVID-19 on the aviation sector
The transportation sector is the hardest hit sector by COVID-19 due to the large-scale restrictions in mobility and aviation activities ( IEA, 2020 ; Le Quéré et al., 2020 ; Muhammad et al., 2020 ). In the aviation sector, for example, where revenue generation is a function of traffic levels, the sector has experienced flight cancellations and bans, leading to fewer flights and a corresponding immense loss in aeronautical revenues. This is even compounded by the fact that in comparison to other stakeholders in the aviation industry, when traffic demand declines, airports have limited avenues to reducing costs because the cost of maintaining and operating an airport remains the same and airports cannot relocate terminals and runaways or shutdown ( Hockley, 2020 ). Specifically, in terms of passenger footfalls in airports and planes, the Air Transport Bureau (2020) modelled the impact of COVID-19 on scheduled international passenger traffic for the full year 2020 under two scenarios namely Scenario 1 (the first sign of recovery in late May) and Scenario 2 (restart in the third quarter or later). Under Scenario 1, it estimated an overall reduction of: between 39%-56% of airplane seats; 872-1,303 million passengers, corresponding to a loss of gross operating revenues between ~$153 - $ 231 billion. Under Scenario 2, it predicted an overall drop of: between 49%-72% of airplane seats; 1,124 to 1,540 million passengers, with an equivalent loss of gross operating revenues between ~$198 - $ 273 billion. They concluded that the predicted impacts are a function of the duration and size of the pandemic and containment measures, the confidence level of customers for air travel, economic situations, and the pace of economic recovery ( Air Transport Bureau, 2020 ).
The losses incurred by the aviation industry require context and several other comparison-based predictions within the airline industry have also been reported. For instance, the International Civil Aviation Organization ICAO (2020) predicted an overall decline ininternational passengers ranging from 44% to 80% in 2020 compared to 2019. Airports Council International, ACI (2020) also forecasted a loss of two-fifths of passenger traffic and >$76 billion in airport revenues in 2020 in comparison to business as usual. Similarly, the International Air Transport Association IATA (2020) forecasted $113 billion in lost revenue and 48% drop in revenue passenger kilometres (RPKs) for both domestic and international routes ( Hockley, 2020 ). For pandemic scenario comparisons, Fig. 6 shows the impact of past disease outbreaks on aviation. As shown, the impact of COVID‐19 has already outstripped the 2003 SARS outbreak which had resulted in the reduction of annual RPKs by 8% and $6 billion revenues for Asia/Pacific airlines, for example. The 6‐month recovery path of SARS is, therefore, unlikely to be sufficient for the ongoing COVID-19 crisis ( Air Transport Bureau, 2020 ) but gives a backdrop and context for how airlines and their domestic/international markets may be impacted.

Impact of past disease outbreaks on aviation ( Air Transport Bureau, 2020 ).
Notably, these predictions are bad news for the commercial aspects of air travel (and jobs) but from the carbon/greenhouse gas emission and CE perspective, these reductions are enlightening and should force the airline industry to reflect on more environmentally sustainable models. However, the onus is also on the aviation industry to emphasise R&D on solutions that are CE-friendly (e.g. fuel efficiency; better use of catering wastes; end of service recycling of aircraft in sectors such as mass housing, or re-integrating airplane parts into new supply chains) and not merely investigating ways to recoup lost revenue due to COVID-19.
4.2.4. Impact of COVID-19 on the tourism industry
Expectedly, the impact of COVID-19 on aviation has led to a knock-on effect on the tourismindustry, which is nowadays hugely dependent on air travel. For instance, the United Nation World Tourism Organization UNWTO (2020) reported a 22% fall in international tourism receipts of $80 billion in 2020, corresponding to a loss of 67 million international arrivals. Depending on how long the travel restictions and border closures last, current scenario modelling indicated falls between 58% to 78% in the arrival of international tourists, but the outlook remains hugely uncertain. The continuous existence of the travel restrictions could put between 100 to 120 million direct tourism-related jobs at risk. At the moment, COVID-19 has rendered the sector worst in the historical patterns of international tourism since 1950 with a tendency to halt a 10-year period of sustained growth since the last global economic recession ( UNWTO, 2020 ). It has also been projected that a drop of ~60% in international tourists will be experienced this year, reducing tourism's contribution to global GDP, while affecting countries whose economy relies on this sector ( Naidoo and Fisher, 2020 ). Fig. 7 depicts the impact of COVID-19 on tourism in Q1 of 2020 based on % change in international tourists’ arrivals between January and March.

The impact of COVID-19 on tourism in quarter 1of 2020. Provisional data but current as of 31st August 2020 ( UNWTO, 2020 ).
4.2.5. Impact of COVID-19 on sustainable development goals
In 2015, the United Nations adopted 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) with the view to improve livelihood and the natural world by 2030, making all countries of the world to sign up to it. To succeed, the foundations of the SDGs were premised on two massive assumptions namely globalisation and sustained economic growth. However, COVID-19 has significantly hampered this assumption due to several factors already discussed. Indeed, COVID-19 has brought to the fore the fact that the SDGs as currently designed are not resilient to shocks imposed by pandemics. Prior to COVID-19, progress across the SDGs was slow. Naidoo and Fisher (2020) reported that two-thirds of the 169 targets will not be accomplished by 2030 and some may become counterproductive because they are either under threat due to this pandemic or not in a position to mitigate associated impacts.
4.3. Positive impact of COVID-19
In this section, we discussed some of the positive ramifications of COVID-19. Despite the many detrimental effects, COVID-19 has provoked some natural changes in behaviour and attitudes with positive influences on the planet. Nonetheless, to the extent that the trends discussed below were imposed by the pandemic, they also underscore a growing momentum for transforming business operations and production towards the ideal of the CE.
4.3.1. Improvements in air quality
Due to the COVID-19-induced lockdown, industrial activities have dropped, causing significant reductions in air pollution from exhaust fumes from cars, power plants and other sources of fuel combustion emissions in most cities across the globe, allowing for improved air quality ( Le Quéré et al., 2020 ; Muhammad et al., 2020 ). This is evident from the National Aeronautics and Space Administration ( NASA, 2020a ) and European Space Agency ( ESA, 2020 ) Earth Observatory pollution satellites showing huge reductions in air pollution over China and key cities in Europe as depicted in Fig. 8 . In China, for example, air pollution reduction of between 20-30% was achieved and a 20-year low concentration of airborne particles in India is observed; Rome, Milan, and Madrid experienced a fall of ~45%, with Paris recording a massive reduction of 54% ( NASA, 2020b ). In the same vein, the National Centre for Atmospheric Science, York University, reported that air pollutants induced by NO 2 fell significantly across large cities in the UK. Although Wang et al. (2020) reported that in certain parts of China, severe air pollution events are not avoided through the reduction in anthropogenic activities partially due to the unfavourable meteorological conditions. Nevertheless, these data are consistent with established accounts linking industrialization and urbanization with the negative alteration of the environment ( Rees, 2002 ).

The upper part shows the average nitrogen dioxide (NO 2 ) concentrations from January 1-20, 2020 to February 10-25, 2020, in China. While the lower half shows NO 2 concentrations over Europe from March 13 to April 13, 2020, compared to the March-April averaged concentrations from 2019 ( ESA, 2020 ; NASA, 2020a ).
The scenarios highlighted above reiterates the fact that our current lifestyles and heavy reliance on fossil fuel-based transportation systems have significant consequences on the environment and by extension our wellbeing. It is this pollution that was, over time, responsible for a scourge of respiratory diseases, coronary heart diseases, lung cancer, asthma etc.( Mabahwi et al., 2014 ), rendering plenty people to be more susceptible to the devastating effects of the coronavirus ( Auffhammer et al., 2020 ). Air pollution constitutes a huge environmental threat to health and wellbeing. In the UK for example, between ~28,000 to ~36,000 deaths/year was linked to long-term exposure to air pollutants ( PHE, 2020 ). However, the reduction in air pollution with the corresponding improvements in air quality over the lockdown period has been reported to have saved more lives than already caused by COVID-19 in China ( Auffhammer et al., 2020 ).
4.3.2. Reduction in environmental noise
Alongside this reduction in air pollutants is a massive reduction in environmental noise. Environmental noise, and in particular road traffic noise, has been identified by the European Environment Agency, EEA (2020) to constitute a huge environmental problem affecting the health and well-being of several millions of people across Europe including distortion in sleep pattern, annoyance, and negative impacts on the metabolic and cardiovascular system as well as cognitive impairment in children. About 20% of Europe's population experiences exposure to long-term noise levels that are detrimental to their health. The EEA (2020) submitted that 48000new cases of ischaemic heart disease/year and ~12000 premature deaths are attributed to environmental noise pollution. Additionally, they reported that ~22 million people suffer chronic high annoyance alongside ~6.5 million people who experienceextreme high sleep disturbance. In terms of noise from aircraft, ~12500 schoolchildren were estimated to suffer from reading impairment in school. The impact of noise has long been underestimated, and although more premature deaths are associated with air pollution in comparison to noise, however noise constitutes a bigger impact on indicators of the quality of life and mental health ( EEA, 2020 ).
A recent study on the aftereffect of COVID-19 pandemic on exercise rates across the globe concluded that reduced traffic congestions and by extension reduced noise and pollution has increased the rate at which people exercise as they leveraged the ensued pleasant atmosphere. Average, moderate, and passive (i.e. people who exercised once a week before COVID-19) athletes have seen the frequency of their exercise regime increased by 88%, 38%, and 156% respectively ( Snider-Mcgrath, 2020 ).
4.3.3. Increased cleanliness of beaches
Beaches constitute the interface between land and ocean, offering coastal protection from marine storms and cyclones ( Temmerman et al., 2013 ), and are an integral part of natural capital assets found in coastal areas ( Zambrano-Monserrate et al., 2018 ). They provide services (e.g. tourism, recreation) that are crucial for the survival of coastal communities and possess essential values that must be prevented against overexploitation ( Lucrezi et al., 2016 ; Vousdoukas et al., 2020 ). Questionable use to which most beaches have been subjected have rendered them pollution ridden ( Partelow et al., 2015 ). However, due to COVID-19-induced measures, notable changes in terms of the physical appearance of numerous beaches across the globe have been observed ( Zambrano-Monserrate et al., 2020 ).
4.3.4. Decline in primary energy use
Global energy demand during the first quarter of 2020 fell by ~3.8% compared to the first quarter of 2019, with a significant effect noticeable in March as control efforts heightened in North America and Europe ( IEA, 2020 ). The International Energy Agency (IEA) submitted that if curtailment measures in the form of restricted movement continue for long and economic recoveries are slow across different parts of the globe, as is progressively likely, annual energy demand will plummet by up to 6%, erasing the last five years energy demand growth. As illustrated in Fig. 9 , if IEA's projections become the reality, the world could experience a plunge in global energy use to a level not recorded in the last 70 years. The impact will surpass the effect of the 2008 financial crisis by a factor of more than seven times. On the other hand, if COVID-19 is contained earlier than anticipated and there is an early re-start of the economy at a successful rate, the fall in energy could be constrained to <4% ( IEA, 2020 ). However, a rough re-start of the economy characterised by supply chain disruptions and a second wave of infections in the second half of the year could further impede growth ( IEA, 2020 ).

Annual rate of change in primary energy demand, since 1900, with key events impacting energy demand highlighted ( IEA, 2020 ).
Coal was reported to have been hit the hardest by ~8% in comparison to the first quarter of 2019 due to the impact of COVID-19 in China whose economy is driven by coal, reduced gas costs, continued growth in renewables, and mild weather conditions. Oil demand was also strongly affected, plummeting by ~5% in the first quarter driven mainly by restrictions in mobility and aviation activities which constitute ~60% of global oil demand ( IEA, 2020 ). For instance, global road transport and aviation activities were respectively ~50% and 60% below the 2019 average. Global electricity demand declined by >20% during full lockdown restrictions, with a corresponding spill over effect on the energy mix. Accordingly, the share of renewable energy sources across the energy supply increased due to priority dispatch boosted by larger installed capacity and the fact that their outputs are largely unconstrained by demand ( IEA, 2020 ). However, there was a decline for all other sources of electricity including gas, coal and nuclear power ( IEA, 2020 ).
4.3.5. Record low CO 2 emissions
Unprecedented reduction in global CO 2 emissions is another positive effect that can be attributed to the COVID-19 pandemic.The massive fall in energy demand induced by COVID-19 accounted for the dramatic decline in global GHG emissions. The annual CO 2 emissions have not only been projected to fall at a rate never seen before, but the fall is also envisioned to be the biggest in a single year outstripping the fall experienced from the largest recessions of the past five decades combined ( IEA, 2020 ).The global CO 2 emissions are projected to decline by ~8% (2.6 GCO 2 ) to the levels of the last decade. If achieved, this 8% emissions reduction will result in the most substantial reduction ever recorded as it is expected to be six times larger than the milestone recorded during the 2009 financial crisis, ( Fig. 10 ). Characteristically, after an economic meltdown, the surge in emissions may eclipse the decline, unless intervention options to set the economy into recovery mode is based on cleaner and more resilient energy infrastructure ( IEA, 2020 ).

Global energy-related emissions (top) and annual change (bottom) in GtCO 2 , with projected 2020 levels highlighted in red. Other major events are indicated to provide a sense of scale ( IEA, 2020 ).
4.3.6. Boost in digitalisation
The COVID-19 pandemic has been described as an opportunity to further entrench digital transformation without the ‘digitalism’ which is an extreme and adverse form of connectedness ( Bayram et al., 2020 ). Protecting patients from unnecessary exposure was a driver for telemedicine ( Moazzami et al., 2020 ) and virtual care would become the new reality ( Wosik et al., 2020 ). The necessity for social distancing under lockdown circumstances has also highlighted the importance (and need) for remote working ( Dingel and Neiman, 2020 ; Omary et al., 2020 ), which has had implications for broadband connectivity ( Allan et al., 2020 ) as well as reductions in transportation-related pollution levels ( Spash, 2020 ). The impact of COVID-19 on remote working and digitalisation of work is expected to constitute long-term implications for reduced fossil fuel consumption due to mobility and commuting ( Kanda and Kivimaa, 2020 ). Besides, the survival and thriving of many small business restaurants during the lockdown period depended on whether they had a digital resilience, via online platforms, through which they could exploit the home delivery market via Uber Eats ( Raj et al., 2020 ). For consumers, the pandemic has seen a noticeable increase in online orders for food in many countries such as: Taiwan ( Chang and Meyerhoefer, 2020 ); Malaysia ( Hasanat et al., 2020 ); Germany ( Dannenberg et al., 2020 ) as well as Canada ( Hobbs, 2020 ).
4.4. Unsustainability of current economic and business models amidst COVID-19
It is interesting to observe that while COVID-19 has led to a very steep reduction in air pollution in advanced economies due to reduced economic activity imposed by the lockdown, this pandemic-driven positive impact is only temporary as they do not reflect changes in economic structures of the global economy ( Le Quéré et al., 2020 ). The changes are not due to the right decisions from governments in terms of climate breakdown policies and therefore should not be misconstrued as a climate triumph. More importantly, life in lockdown will not linger on forever as economies will need to rebuild and we can expect a surge in emissions again. To drive home the point, we conducted a decomposition analysis of key drivers (accelerators or retardants) of four global air pollutants using Logarithmic Mean Divisia Index (LMDI) framework ( Ang, 2005 ; Fujii et al., 2013 ), with the results shown in Fig. 11 . The drivers of the pollutants considered based on the production side of an economy include: (i) economic activity effect, given thatemissions can increase or decrease as a result of changes in the activity level of the entire economy; (ii) industrialeconomy structure effect, based on the fact thatthe growth in emissions is a function of the changes in the industrial activity composition; (iii) emissions intensity effect, which can be improvements or deteriorations at the sectoral level, depending on theenergy efficiency (e.g. cleaner production processes) of the sector; (iv) fuel mix or fuel dependency effect, given that its composition influences the amount of emissions; and (v) emission factors effect, because these factors, for different fuel types, changes over time due toswitching from fossil fuels to renewables, for example.

Drivers of representative four (4) global pollutants: a) CO 2 emissions; b) NO x emissions; c) SO x emissions; d) CO emissions. All data for the decomposition analysis of the four pollutants were obtained from the WIOD database ( Timmer et al., 2012 ).
As shown in Fig. 11 a, for example, between 1995 and 2009, global change in CO 2 emission was 32%, where economic activity (+48%) and emission factor (+2%) acted as accelerators, while economic structure (-8%), emission intensity (-9%) and fuel mix (-1%) acted as retardants, of the global CO 2 emission dynamics and trajectory.This implies that although economic activities, as expected, alongside emission factor drove up emissions, however, the upward effect of both drivers was offset by the combined improvements of other driving factors namely economic structure, emission intensity, and fuel mix. Indeed, cutting back on flying or driving less as we have experienced due to COVID-19 contributed to ~8% in emission reduction, however, zero-emissions cannot be attained based on these acts alone. Simply put, emissions reduction cannot be sustained until an optimal balance across the aforementioned drivers informed by structural changes in the economy is attained. As Gates (2020a) rightly stated – the world should be using more energy, not less, provided it is clean.
Characteristically, after an economic meltdown, like the global recession in 2008, there is a surge in emissions ( Feng et al., 2015 ; Koh et al., 2016 ). The current social trauma of lockdown and associated behavioural changes tends to modify the future trajectory unpredictably. However, social responses would not drive the profound and sustained reduction required to attain a low-carbon economy ( Le Quéré et al., 2020 ). This is evident given that we live on a planet interlinked by networked product supply chains, multidimensional production technologies, and non-linear consumption patterns ( Acquaye et al., 2017 ; Ibn-Mohammed et al., 2018 ; Koh et al., 2016 ). Additionally, post COVID-19, the society may suffer from green bounce back– there appears to be an increasing awareness of climate change and air pollution because of this pandemic (though the linkages are non-causal). On the one hand this might promote greener choices on behalf of consumers, but on the other it may result in increased car ownership (at the expense of mass transit), driving up emissions. As such, establishing approaches that ensure an optimal balance between quality of life and the environmental burden the planet can bear is pertinent, if the boundaries of environmental sustainability informed by the principles of low-carbon CE are to be extended. In the next section, the role of the CE as a potential strategy for combating pandemics such as COVID-19 is discussed.
5. The role of circular economy
For long, the central idea of the industrial economy rests on the traditional linear economic system of taking resources, making products from them, and disposing of the product at the end of life. Experts referred to this as “extract-produce-use-dump”, “take-make-waste”, or “take-make-dispose” energy flow model of industrial practice ( Geissdoerfer et al., 2017 ; Kirchherr et al., 2017 ; MacArthur, 2013 ). However, the unlimited use of natural resources with no concern for sustainability jeopardizes the elastic limit of the planet's resource supply. For instance, Girling (2011) submitted that ~90% of the raw materials used in manufacturing become waste before the final product leaves the production plant while ~80% of products manufactured are disposed of within the first 6 months of their life. Similarly, Hoornweg and Bhada-Tata (2012) reported that ~1.3 billion tonnes of solid waste with a corresponding cost implication of $205.4 billion/year is generated by cities across the globe and that such waste might grow to ~2.2 billion tonnes by 2025, with a corresponding rate of $375.5 billion. This is further compounded by the fact that at the global level, the demand for resources is forecasted to double by 2050 ( Ekins et al., 2016 ).
Against this backdrop, the search for an industrial economic model that satisfies the multiple roles of decoupling of economic growth from resource consumption, waste management and wealth creation, has heightened interests in concepts about circular economy ( Ekins et al., 2016 ; MacArthur, 2013 ).In theory, CE framework hinges on three principles: designing out waste, keeping products and materials in use and regenerating the natural systems ( MacArthur, 2013 ). Practically, CE is aimed at: (i) emphasizing environmentally-conscious manufacturing and product recovery ( Gungor and Gupta, 1999 ); (ii) promoting the avoidance of unintended ecological degradation in symbiotic cooperation between corporations, consumers and government ( Bauwens et al., 2020 ); and (iii) shifting the focus to a holistic product value chain and cradle-to-cradle life cycle via promotion of product repair/re-use and waste management ( Duflou et al., 2012 ; Lieder and Rashid, 2016 ; Rashid et al., 2013 ).
Given the current COVID-19 pandemic, there has never been a more adequate time to consider how the principles of CE could be translated into reality when the global economy begins to recover. This is pertinent because the pandemic has further exposed the limitations of the current dominant linear economy regarding how it is failing the planet and its inhabitants, and has revealed the global ecosystem's exposure to many risks including climate breakdown, supply chain vulnerabilities and fragility, social inequality and inherent brittleness ( Bachman, 2020 ; Sarkis et al., 2020 ). The pandemic continues to amplify the global interlinkages of humankind and the interdependencies that link our natural environment, economic, and social systems ( Haigh and Bäunker, 2020 ). In the subsections that follow, the potentials of CE as a tool for: (i) climate change mitigation; (ii) crafting a more resilient economy, and ; (iii) facilitating a socially just and inclusive society, is briefly discussed.
5.1. Circular economy as a tool for climate breakdown mitigation
As highlighted in Section 4.3.5 , a CO 2 emission reduction of 8%, which in real terms implies an equivalent of ~172 billion tCO 2 will be released instead of ~187 billion tCO 2 , is indeed unprecedented. Nevertheless, the peculiar conclusion from the lockdown is that it still entails emissions of 92% of the initial value while there was restrictions to mobility and other related leisure activities. Measures for mitigating climate change have often been presented dramatically as a "prohibition of the nice things of life", but as shown, a cut-off of such an amount of nice things only delivers an 8% reduction. More importantly, it comes at a heavy cost of between $3,200/tCO 2 and $5,400/tCO 2 in the US, for example, based on data from the Rhodium Group ( Gates, 2020a ). In other words, the shutdown is reducing emissions at a cost between 32 and 54 times the $100/tCO 2 deemed a reasonable carbon price by economists ( Gates, 2020a ). This suggests that a completely different approach to tackling climate issue is required.
Accordingly, there is the need for a system that calls for greater adoption of a more resilient low-carbon CE model, given the predictions by experts that climate breakdown and not COVID-19 will constitute the biggest threat to global health ( Hussey and Arku, 2020 ; Watts et al., 2018a ; Watts et al., 2018b ). International bodies and country-level environmental policies have highlighted the fact that a significant reduction in GHG emissions cannot be achieved by transitioning to renewables alone but with augmentation with CE strategies. The demands side CE strategies such as (i)material recirculation (more high-value recycling, less primary material production, lower emissions per tonne of material); (ii)product material efficiency (improved production process, reuse of components and designing products with fewer materials); (iii)circular business models (higher utilisation and longer lifetime of products through design for durability and disassembly, utilisation of long-lasting materials, improved maintenance and remanufacturing), could reduce emissions whilst contributing to climate change mitigation ( Enkvist et al., 2018 ). CE principles, when adopted in a holistic manner provide credible solutions to the majority of the structural weaknesses exposed by COVID-19, offering considerable opportunities in competitiveness and long-term reduced GHG emissions across value chains. Investments in climate-resilient infrastructure and the move towards circular and low-carbon economy future can play the dual role of job creation while enhancing environmental and economic benefits.
5.2. Circular economy as a vehicle for crafting more resilient economies
Haigh and Bäunker (2020) reported that if we muddle through every new crisis based on the current economic model, using short-term solutions to mitigate the impact, future shocks will continue to surpass capacities. It is, therefore, necessary to devise long-term risk-mitigation and sustainable fiscal thinking with the view to shift away from the current focus on profits and disproportionate economic growth. Resilience in the context of the CE largely pertains to having optimized cycles (i.e. products are designed for longevity and optimized for a cycle of disassembly and reuse that renders them easier to handle and transform). Some cycles can be better by being closed locally (e.g. many food items), and for other cycles, a global value chain could be a better option (e.g. rare earth elements). Due to globalization, all cycles have become organized at the global level, diminishing resilience. COVID-19 has further shown how some particular cycles had the wrong scale level, as such, the adoption of CE can be seen as an invitation to reconsider the optimal capacity of cycles.
Sustainability through resilience thinking would have a positive and lasting impact as reported by the Stockholm Resilience Centre (2016) , which concluded that prosperity and sustainability cannot be accomplished without building “ resilient systems that promote radical innovation in economic policy, corporate strategy, and in social systems and public governance”. It calls for sustainability through resilience thinking to become an overarching policy driver and encourages the application of the principles of such thinking to enhance social innovation. Haigh and Bäunker (2020) concluded that when resilience thinking is employed as a guide, all innovations emanating from circular thinking would extend beyond focusing mainly on boosting the market and competitiveness and recognise the general well-being of the populace as an equal goal. As the global economy recovers from COVID-19, it has become more apparent that there is a strong sense of interconnectedness between environmental, economic and social sustainability ( Bauwens et al., 2020 ).
5.3. Circular economy as a facilitator of a socially just and inclusive society
Advanced economies have mainly focused on maintaining the purchasing power of households through the establishment of the furlough scheme (in the UK, for example). Most developing countries have also adopted a similar approach through the integration of containment measures with a huge increase in social protection spending. However, these intervention strategies in response to the pandemic have further revealed the social injustice and inequality between countries and communities given that the deployment of such strategy in advanced economies could devastate developing countries and communities ( Ahmed et al., 2020 ; Haigh and Bäunker, 2020 ). Guan and Hallegatte (2020) revealed that developing and underdeveloped economies face tougher and more challenging situation in comparison to their developed counterparts, because even under the assumption that social protection systems could fully replace income and shield businesses from bankruptcy, maintaining access to essential commodities is impossible if the country is lacking in production capabilities in the first place. Furthermore, in the underdeveloped world, the idea of working from home is very difficult due to the lack of infrastructure and access to health facilities is severely cumbersome. As such, short-term fixes adopted by governments cannot adequately address deep-rooted inequality and social injustice.
Accordingly, Preston et al. (2019) submitted that CE has the potential to minimise prevailing pressures and struggles regarding conflicts due to imbalanced distribution of resources, through participatory forms of governance that entails the inclusion of local stakeholders in resource management initiatives. This can be achieved through the adoption of CE strategy such as closed-loop value chains, where wastes are transformed into resources with the view to not only reduce pollution but to simultaneously aid the pursuance of social inclusion objectives. A number of companies are already embracing this idea. For instance, under the Food Forward SA initiative, “ the world of excess is connected with the world of need ” through the recovery of edible surplus food from the consumer goods supply chain and gets redistributed to the local community. This ensures loops are closed and the needy receive nourishment ( Haigh and Bäunker, 2020 ). With sufficient investment in the CE, developing countries can leapfrog their developed counterparts in digital and materials innovation to integrate sustainable production and consumption and low-carbon developments at the core of their economies. Additionally, Stahel (2016) reported that another benefit of the CE as a facilitator of a socially just and inclusive society is that it is likely to be more labour-intensive due to the variety of end-of-life products and the high cost of automating their processing compared to manual work. As such, CE can enable the creation of local jobs and “reindustrialisation of regions” ( Stahel, 2019 ) through the substitution of: manpower for energy, materials for (local) labour, and local workshops for centralised factories ( Stahel, 2019 ), while boosting the repair economy and local micro industries. Of course, not everybody will see this as a benefit, and many would like to see more automation, not less. However, this is a political/economic argument, not an engineering or scientific one. In the next section, barriers to CE in general and in the context of COVID-19 is discussed.
5.4. Barriers to CE in the context of COVID-19
On the surface, the benefits of CE should be obvious as it strives for three wins in the three dimensions of social, economic and environment impacts through a symbiotic vision of reduced material usage, reduced waste generation, extending value retention in products and designing products for durability. However, limiting barriers obviating the success of CE have existed around technical implementation, behavioural change, financial and intellectual investments, policy and regulations, market dynamics, socio-cultural considerations as well as operational cost of transforming from the linear economy to one based on circularity ( Friant et al., 2020 ). In more concrete terms, the barriers dwell within the ecosystem of actors (and the interactions within the actors) involved in the move towards CE ( Lieder and Rashid, 2016 ).
Pre-COVID-19, Korhonen et al. (2018) enumerated six fundamental factors hindering the promise of CE: (i) thermodynamic factors (i.e. limit imposed by material and energy combustion in recycling/re-manufacturing); (ii) complexity of spatial and temporal boundaries (i.e. material and energy footprints for a product cannot be easily reduced to a point in space and time for an in-depth analysis of environmental impacts); (iii) interlink of governance and nation's economy; (iv) consumer and organizational inertia (i.e. reluctance to embrace new way of doing things due to uncertainty about the success of business models as well as fuzziness around organizational culture and management models that rely on CE); (v) fragile industrial ecosystems (featuring the difficulty of establishing and managing intra-/inter-organizational collaboration along with local/regional authorities); and (vi) lack of consensus on what the many Rs (re-use, recycle, recover, repurpose, repair, refurbish, remanufacture) embedded in CE framework really means ( Kirchherr et al., 2017 ). Challenges in data sharing between product end points and stakeholders, complexity in the supply chain with unclear details of product biography over time, and prohibitive start-up investment costs have also been identified as CE barrier in other climes ( Jaeger and Upadhyay, 2020 ; Manninen et al., 2018 ). Other issues along similar lines were captured in the work by several other authors including Galvão et al. (2020) , Kirchherr et al. (2018) , Govindan and Hasanagic (2018) , De Jesus and Mendonça (2018) and many more.
The paradox of COVID-19 is grounded on creating a once in a lifetime opportunity to re-examine the difficulty of some of these barriers, but it also unveiled a new set of challenges. For instance, the sharing economy models that have been hitherto hailed as exemplars of CE strategy is now perceived differently by many urban dwellers because of the behavioural change embedded in “social distancing”, which is necessary to limit the spread of the virus. Although if concepts such as “access over ownership” or “pay for performance” service have become fully operational, they could have constituted a significant solution to offer flexibility. Additionally, it has been argued that COVID-19 will ‘disrupt some disruptors’ peer-to-peer (P2P) providers such as Airbnb, which has reported a 4.16% drop in local bookings for every doubling new COVID-19 cases ( Hu and Lee, 2020 ). In transportation, demand from ride-sharing modes could increase due to commuters wanting to minimise exposure to COVID-19 in mass transport systems like buses and trains ( Chandra, 2020 ). However, the risks of human-to-human transmission of COVID-19 for passengers not wearing facemask have been noted ( Liu and Zhang, 2020 ), including when either passengers or drivers in ride-hailing and car-sharing disruptors like Uber do not wear facemasks ( Wong et al., 2020 ).
Reducing emissions, in the long run, requires large investments, from both the public and private sectors, in low-carbon technologies and infrastructure in terms of both innovation and diffusion ( OECD, 2018 ). Given the downturn of the global economy due to COVID-19, the prospects of significant low-carbon investments from the private sector have significantly reduced compared to pre-COVID-19. This view is not just limited to the private sector, but also to the public sector, as echoed by Naidoo and Fisher (2020) . Hence, post COVID-19, accelerating progress towards CE still requires: (i) a decisive legal and financial championships from local, regional and national authorities; (ii) innovation across multiple domains (product design, production technologies, business models, financing and consumer behaviours); (iii) governments to promote green logistics and waste management regulations with reasonable incentives to aid producers and manufacturers in minimizing loss while maximizing value. It is therefore recommended that governments provide the much-needed policy framework that will eliminate some of aforementioned barriers to facilitate the urgent transition to CE. Doing this will build resilience for community response to future pandemic and it also aligns with some of the existing roadmaps for resource efficiency ( European Commission, 2011 ).
6. Opportunities for circular economy post COVID-19
COVID-19 has instigated a focus on vibrant local manufacturing as an enabler of resilient economy and job creation; fostered behavioural change in consumers; triggered the need for diversification and circularity of supply chains, and evinced the power of public policy for tackling urgent socio-economic crises. As we rise to the challenges imposed by COVID-19, the question is no longer should we build back better, but how. Consequently, going forward, crafting a roadmap for a sustainable future is as much about the governmental will to forge a new path to socio-economic growth as it is about local businesses joining forces with the consumers to enable the transition to CE. As already documented in the earlier sections of this paper, governments around the world have deployed many financial policy instruments to combat the short-term consequences of COVID-19 pandemic. Still, in the long-term, the adoption of circular economy principles across various technological frontiers holds the promise to bring about a desired technical and behavioural change that will benefit many nations around the world.
Specifically, adopting the CE principle will alleviate some of the detrimental effects of COVID-19 pandemic in the future. To mention just a few: (i) a national level adoption of CE will reduce the over-reliance on one country as the manufacturing hub of the world; (ii) a systematic shift away from the traditional polluting, energy-intensive, manufacturing-driven economy to a CE, based on renewable energy, smart materials, smart re-manufacturing, and digital technology will strengthen the fight against pollution; and (iii) the transition to CE will also spur local job creation along several of the axes of societal needs (e.g. built environment, mobility, health, consumables, etc.). Accordingly, in the subsections that follow, an overview of recommendations as well as policy measures, incentives, and regulatory support for advancing sector-specific CE strategies in a post-COVID-19 world is presented.
6.1. Local manufacturing and re-manufacturing of essential medical accessories
Disruptions due to COVID-19 has been attributed to unprecedented demand, panic buying, and intentional hoarding of essential medical goods for profit ( Bradsher and Alderman, 2020 ; Fischer et al., 2020 ). The shortage of many items was so dire in many countries that the principle of CE, such as re-use, is already been unwittingly recommended ( Gondi et al., 2020 ), by respectable bodies such as the US Centres for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) ( Ranney et al., 2020 ). However, designed and produced from non-CE compliant processes, medical accessories such as PPE cannot be easily refurbished for re-use without leading to severe degradation in their efficiencies, as noticed for example, in the case of particulate respirators ( Liao et al., 2020 ). Accordingly, it is recommended that companies strive to establish competencies in eco-design and environmentally beneficial innovation to facilitate product re-use in the long run. Some of the desired competencies centre on design strategies for closing resource loops (e.g. designing for technological and biological cycles) as pioneered by McDonough and Braungart (2010) .
A detailed discussion of these competencies is also enunciated by Braungart et al. (2007) , where the authors differentiated between eco-efficiency (less desirable) and eco-effectiveness (the desired dream of CE), for companies to be compliant with the CE framework. Meanwhile, a starting point for companies to shift to eco-effectiveness at the product design level, which will facilitate product re-use, is to follow the five-step framework enumerated by Braungart et al. (2007) or to adopt the analytical framework to explore some of the key dimensions in eco-design innovations developed by Carrillo-Hermosilla et al. (2010) . During implementation, the preceding steps comport with the idea of eco-factories that take pride in design for effortless end-of-life product re-use and design for “upcycling” and remanufacturing ( Bocken et al., 2016 ; Herrmann et al., 2014 ; Ijomah, 2010 ), all of which falls under the umbrella of CE.
Another emerging evidence in favour of CE, also adopted inadvertently during this pandemic, is the ease with which several manufacturers have pivoted their factory floors to make different products in response to the shortage of medical accessories. Few examples of these companies in the UK include, but not limited to: AE Aerospace, which retooled its factory floor to produce milled parts for ventilators; Alloy Wire International re-purposed its machinery to make springs for ventilators; AMTICO (flooring manufacture) re-configured its production lines to make visors for front line workers; BAE Systems deployed its factory resources to produce and distribute over 40000 face shields; and BARBOUR (a clothing company) re-purposed to produce PPE for nurses ( Williamson, 2020 ).
6.2. CE strategies for managing hospital medical and general waste
Wastes generated by the healthcare industry (HCI) normally arouse concerns about operational, public, and environmental safety as a result of the awareness of the corrosive, hazardous, infectious, reactive, possibly radioactive, and toxic nature of the wastes’ composition ( Lee et al., 1991 ; Prüss-Üstün et al., 1999 ). Consequently, the management of the different categories of healthcare waste far removed from the traditional municipal wastes, falls under stringent national or local regulatory frameworks. Pre-COVID-19, the staggering scale of HCI waste is reported to reach into millions of tonnes per year and there have been many studies of national-level attempts at managing these wastes ( Da Silva et al., 2005 ; Insa et al., 2010 ; Lee et al., 1991 ; Oweis et al., 2005 ; Tudor et al., 2005 ). However, this problem is expected to worsen with the tremendous surge, in the last few months, in the volume of disposable medical hardware (PPE, masks, gloves, disposable gears worn by healthcare workers and sanitation workers as well as those contaminated by contacts with COVID-19 patients). Another allied problem is the troubling shift among consumers who now prioritize concerns for hygiene by leaning towards plastic packaging (e.g. in food delivery and grocery shopping) during this pandemic at the expense of environmental impacts ( Prata et al., 2020 ). Most of these products are derived from non-biodegradable plastics, and their disposal has not been given much thought. As a result, the management of these wastes has raised understandable angst in several quarters ( Klemeš et al., 2020 ; Xiao and Torok, 2020 ). Frustratingly, there is much less that can be done at the moment apart from devising judicious waste management policy for these potentially hazardous wastes.
The traditional steps concerning the treatment of HCI wastes (such as collection and separation, storage, transportation to landfill, and decontamination/disposal) suffer from many complications that make the management a challenging undertaking ( Windfeld and Brooks, 2015 ). To alleviate the complexity, the characterization of the physicochemical composition of HCI waste has become an important tool in devising crucial steps for setting up waste minimization and recycling programs ( Kaiser et al., 2001 ). This aligns with the objective of circular economy (CE), which prioritizes the prevention of waste, failing which it proposes the re-use/recyclability of materials from waste to close the loop.
Wong et al. (1994) reported that hospital wastes involve different types of materials: plastics (tubes, gloves, syringes, blood bags), metals (basins, aluminium cans), papers (towel papers, toilet papers, newspapers), cotton/textiles (drapes, table covers, diapers, pads, bandages), glass (bottles) etc. With this categorization in mind, a CE product design consideration that looks promising in the near future, as a way to avert some of the dangers that can be triggered by events such as COVID-19, is to increase the volume of recyclable materials and biodegradable bioplastics in the production of medical accessories. However, the reality is that not all medical gears and products can be derived from bio-plastics or recyclable materials, and some will inevitably continue to be fabricated with materials that need further downstream processing. Yet, the application of CE to the healthcare industry (HCI) remains a touchy subject. Understandably, health and safety concerns, as well as requirements to meet stringent regulations, tend to override the environmental gain from the 4R practice promoted by CE ( Kane et al., 2018 ). Nonetheless, the benefits of CE are starting to catch on in the HCI as a means of optimizing hospital supply chains and reduce overhead cost, all the while creating environmental benefits in the course of saving human lives.
Principally, the applications of CE in HCI, like in other fields, are tied to materials flow and an examination of the nature of wastes. Pioneering studies on hospital wastes characterizations ( Diaz et al., 2008 ; Eleyan et al., 2013 ; Özkan, 2013 ; Wong et al., 1994 ), revealed that close to 80% of the wastes can be classified as general wastes, while the remaining 20% falls under the infectious waste category ( WHO, 1998 ). A prevalent method of dealing with the two HCI waste categories has been incineration ( Wong et al., 1994 ). Although suitable for large volumes, incineration produces toxic pollutants such as heavy metals, dioxins, acid gases, and hydrogen chloride ( Yang et al., 2009 ). Consequently, pre-COVID-19, besides incineration, reducing or preventing the volume of wastes in both categories is also shaped by the adoption of green purchasing practices ( Wormer et al., 2013 ). While this may help in the short term, a holistic approach to confronting this problem is the adoption of CE, which can facilitate the shift towards eco-efficient HCI, starting with lifecycle evaluations of medical products to the proposal for re-usable medical instruments ( Cimprich et al., 2019 ; De Soete et al., 2017 ; Penn et al., 2012 ). Numerous CE strategies for healthcare waste management are detailed by Kane et al. (2018) and Voudrias (2018) . Undoubtedly, with COVID-19, there is an uptick in the percentage of waste under the infectious category due to hospitals taking various precautions to facilitate control of the pandemic ( Peng et al., 2020 ). Nevertheless, by subjecting the general waste category to proper sterilization procedure via any of thermal, microwave, bio-chemical sterilization, the huge potential from upcycling of the retrieved materials will edge towards fulfilling the promise of CE within the sector ( Yang et al., 2009 ).
6.3. Embracing resource efficiency in the construction and built environment
As with other economic sectors, COVID-19 has exposed the shortcomings of the built and natural environment's business-as-usual practices, highlighting the prevalence of poor-quality buildings, issues regarding affordability of decent housing and rigidity of the current building stocks ( EMF, 2020b ). Living in poor-quality houses and in small constricted energy inefficient homes, led to the in-house transmission of the virus in some cases ( Clair, 2020 ). This is particularly the case in poorer countries where inadequate access to sanitation amenities has prevented people from adopting best practices necessary for halting the transmission ( Andrew et al., 2020 ). These issues alongside the growing concern and awareness regarding the resource-wasting nature of the sector, present a strong case for rethinking it. The CE is well positioned to offer potential solutions to these problems.
CE can help balance behavioural challenges and opportunities from occupancy requirements. Humans spend up to 90% of their time indoors ( Marques et al., 2018 ; Pitarma et al., 2017 ). The pandemic has led to people spending more time at ‘home’ than at work, leading to massively underutilised office and business spaces, which is likely to increase due to on-going social distancing constraints ( Feber et al., 2020 ) or perhaps due to more organisation discovering the cost benefits of remote working. It is also plausible that upgrading of existing (or design of new) office and commercial spaces would require making them flexible and adaptable to cope with changing needs (e.g. occupant density, social distancing, ventilation, etc.) by using movable walls ( Carra and Magdani, 2017 ). Insufficient ventilation can increase the risk of infection to healthcare workers and susceptible patients in healthcare buildings, especially makeshift hospitals ( Chen and Zhao, 2020 ). The impact of these engineering measures on energy consumption of typical buildings and healthcare facilities needs to be considered because of social distancing measures, which may require a decrease in occupant density but an increase in ventilation rates. So, although energy recovery is high on the agenda for CE in the built environment ( Eberhardt et al., 2019 ), the additional requirement of more mechanical ventilation for less people will stretch the energy consumed by buildings. Some researchers have argued for buildings to avoid recirculation (essential for energy savings) and use 100% fresh outdoor air for mechanical ventilation systems ( Pinheiro and Luís, 2020 ). Such scenarios are likely to increase the adoption of renewable energy sources to support acceptable indoor air quality (IAQ).
The adoption of CE strategies such as material reuse and development of recycling infrastructure can facilitate value circulation and efficient use of resources within the built and natural environment, ensuring a more competitive and cost-effective post-COVID-19 recovery, while contributing to GHG emissions reduction and creating job opportunities ( EMF, 2020b ). For instance, a study by ARUP estimated that designing for steel reuse has the potential of generating savings of 6-27% and 9-43% for a warehouse and an office respectively, whilst constituting up to 25% savings on material costs ( SYSTEMIQ, 2017 ). The EU is leading in policy direction that would make it a legal requirement to introduce recycled content (i.e. material looping) in specific construction products, after the functionality and safety have been vetted ( European Commission, 2020 ). Such initiatives will encourage designers and researchers to incorporate material looping into their overall design strategy across the value chain to ensure they are fit for circulation ( Deloitte, 2020 ). This material looping has been shown to reduce disposal fees and generate new income streams from the secondary materials market ( Rios et al., 2015 ). It is an approach that would help reduce construction waste, which accounts for a third of all solid wastes in countries like India ( EMF, 2016 ). The adoption of digital material passports that supports end-to-end tracking of building materials has been reported by SYSTEMIQ (2017) to aid the identification of materials for reuse as they approach their end of first life, thereby allowing the longevity and encouraging tighter material looping.
COVID-19 in the context of CE will encourage prefabrication, design thinking and renovation. As the building industry moves towards the industrialisation of construction via prefabrication/offsite production, seven strategies have been suggested by Minunno et al. (2018) out of which the principle of designing for eventual disassembly and reuse is critical. With a combined smart and industrialised prefabrication (SAIP) process ( Abbas Elmualim et al., 2018 ), the intelligent performance and circularity of buildings can be boosted by advanced smart technologies ( Windapo and Moghayedi, 2020 ). The building of 1,000 bed Huoshenshan Hospital in Wuhan covering 34,000m 2 in ten days using modular pre-fabricated components, which can be disassembled and reused ( Zhou et al., 2020 ) has demonstrated the capability of the construction industry to deliver adaptable buildings in record time. But it is perhaps in the sphere of refurbishment and renovation that CE in the built environment would mostly be felt. A CE strategy that promotes repair and refurbishment is preferable to one which encourages recycling, since the economic and environmental value of a product is retained better by the former ( Sauerwein et al., 2019 ).
Renovation helps achieve carbon reduction targets while contributing to economic stimulation ( Ibn-Mohammed et al., 2013 ) . Retrofitting, refurbishing or repairing existing buildings leads to lower emission facilities, is less resource-intensive and more cost-effective than demolition or new construction ( Ardente et al., 2011 ; Ibn-Mohammed et al., 2014 ). Nevertheless, circular renovation of buildings must align with circular design thinking – as alluded to above, in terms of re-integrating materials back into the value chain – as well as the need to enhance material/product durability and energy efficiency ( Pomponi and Moncaster, 2017 ). In Europe, renovation of buildings decreases the residential sector's GHG emissions by 63%, with a reduction of up to 73% in the non-residential sector ( Artola et al., 2016 ). In meeting the emerging needs of the renovation sub-sector, digital infrastructure technologies (such as thermographic and infrared surveys, photogrammetry and 3D laser scanning, as well as BIM and Digital Twinning) will play a crucial role in ensuring the low carbon and energy-efficient future of the built environment ( ARUP, 2020 ).
6.4. Bio-cycle economy and the food sector
COVID-19 or not, the food sector is generally wasteful ( Dilkes-Hoffman et al., 2018 ), contributes to environmental degradation ( Beretta and Hellweg, 2019 ), disrupts nutrient flows due to the current linear nature of its value chain, thereby diminishing the nutritional quality of food ( Castañé and Antón, 2017 ). To address these issues, as part of a future resilience in the food sector, a number of CE levers applicable to the sector is highlighted: (i) closing nutrient loops through the adoption of regenerative agriculture ( Rhodes, 2017 ). The organic content of soil reflects its healthiness and propensity to produce nutritious crops. The adoption of regenerative agriculture can facilitate the preservation of soil health through returning organic matter to the soil in the form of food waste or composted by-products or digestates from treatment plants ( Sherwood and Uphoff, 2000 ); (ii) value recovery from organic nutrients through the adoption of anaerobic digestion facilities ( De Gioannis et al., 2017 ; Huang et al., 2017 ), which is related to controlled biogas production for onward injection into natural gas network or conversion to electrical energy ( Atelge et al., 2020 ; Monlau et al., 2015 ). This has the potential to transform ensuing methane from food waste into carbon-neutral energy; and (iii) the embrace of urban and peri-urban agriculture ( Ayambire et al., 2019 ; Lwasa et al., 2014 ; Opitz et al., 2016 ; Thebo et al., 2014 ), which entails the “ cultivation of crops and rearing of animals for food and other uses within and surrounding the boundaries of cities, including fisheries and forestry ”( EPRS, 2014 ). Indeed, by cultivating food in proximity to where it will be consumed, carbon footprint can be mitigated in numerous ways. For instance, through the adoption of urban agriculture, Lee et al. (2015) demonstrated GHG reduction of 11,668 t yr −1 in the transportation sector. The popularity of local farms has severely increased as a direct consequence of COVID-19, whereby people could experience the power of local food cycles and avoid perceived contamination risks in supermarkets. This will further bolster urban and peri-urban agriculture.
All the above-mentioned CE strategies will contribute towards the establishment of a better and more resilient future food system. However, in the context of COVID-19, transitioning to regenerative agricultural production processes and expanding food collection, redistribution and volarisation facilities constitute an integral part of a more resilient and healthy food system that allows greater food security and less wastage, post COVID-19 ( EMF, 2020a ). Investments towards accelerating regenerative agriculture offer economic benefits facilitated by reforms in food, land, and ocean use ( World Economic Forum, 2020 ). It also offer environmental benefits by supporting biologically active ecosystems ( EMF, 2020a ) and through numerous farming mechanisms including no-till farming, adoption of cover crops, crop rotations and diversification ( Ranganatha et al., 2020 ) as well as managed grazing for regenerative livestock rearing ( Fast Company, 2019 ). Similarly, expanding food collection, redistribution and volarisation facilities offers both economic and environmental benefits for the food system ( EMF, 2020a ). However, realising these benefits will require investment in: (i) physical infrastructure like cold chains that support the storage, processing, and supply of edible food, especially in low-income countries, and (ii) processing infrastructure for the collection and volarisation of waste food ( EMF, 2020a ). This will facilitate door-to-door waste food collection, offering avenues for municipal organic waste volarisation.
6.5. Opportunities for CE in the transport and mobility sector
Facilitating the movement of people, products and materials, transportation infrastructures are imperative to the success of circularity in the shift towards sustainable cities given its impact on the quality of life, the local environment and resource consumption ( Van Buren et al., 2016 ). As noted in an earlier section, the transport sector was one of the sectors most heavily impacted by COVID-19. Going forward, many CE strategies could be adopted as part of building a resilient transport sector. Development of compact city for effective mobility given their attributes in terms of being dense with mixed-use neighbourhoods and transit-oriented ( EMF, 2019 ), can create an enabling environment for both shared mobility options (e.g. trams, buses, ride-shares) and active mobility options (e.g. bicycling, walking) ( Chi et al., 2020 ; Shaheen and Cohen, 2020 ). This will help to re-organize urban fabric and promote intelligent use of transportation infrastructures ( Marcucci et al., 2017 ). However, the behavioural change embedded in “social distancing”, which is necessary to limit the contagion, may affect the perception of many urban dwellers about this. On the other hand, less compact cities require increased mobility infrastructure with a corresponding increase in operational vehicle use, leading to more traffic congestion, energy and resource depletion as well as pollution ( UN Habitat, 2013 ).
The use of urban freight strategies for effective reverse logistics and resource flows is also a viable CE strategy for the transport sector ( EMF, 2019 ) as it enables the provision of services in a manner that also supports similar priorities for economic growth, air quality, environmental noise and waste management ( Akgün et al., 2019 ; Kiba-Janiak, 2019 ). Beyond vehicles and infrastructure, the adoption of these strategies can enable the development of new technologies and practices such as virtualisation of products, digital manufacturing, waste collection, and sorting systems. Interestingly, innovative environmentally-friendly logistics solutions resting on the backbone of the CE framework are already materializing and being trialled in various capacities, including: urban consolidation centre (UCC) ( Johansson and Björklund, 2017 ), crowshipping ( Buldeo Rai et al., 2017a ; Rai et al., 2018 ) and off-hour delivery ( Gatta et al., 2019 ). UCC stresses the use of logistics facilities in city suburbs to ease good deliveries to customers ( Browne et al., 2005 ), while crowshipping is a collaborative measure that employs the use of free mobility resources to perform deliveries ( Buldeo Rai et al., 2017b ).
The availability of rich transport data (e.g. impacts of events on transport, commuter habits) and AI-enabled complex data processing technologies can be leveraged to inform the planning, management, and operations of transport networks over time. Real-time data can also be adopted for monitoring and for instant regulations of traffic flow based on route planning, dynamic pricing and parking space allocation. Noticeably, many of these innovative CE-related initiatives still need an efficient governance mechanism ( Janné and Fredriksson, 2019 ). However, coupling them with the deployment of environmentally efficient vehicles and superior technical solutions hinging on the internet-of-things will bring many nations closer to reaping the benefits of CE. Given that urban planning is most often within the remit of governmental agencies, they must therefore develop integrated pathways and strategies for urban mobility to ensure effective logistics and resource flows. Stakeholder engagements within the transport sector can also facilitate innovative solutions that enable better use of assets and big data solutions.
6.6. Sustaining improvements in air quality
Improvements in air quality is one of the positives recorded due to the COVID-19-imposed lockdown as transportation and industrial activities halted. To sustain such improvements, there is the need to facilitate a step change by ramping up the uptake of low emission vehicles through setting more ambitious targets for the embrace of electric vehicles, constructing more electric car charging points as well as encouraging low emissions fuels. This entails heightening investments in cleaner means of public transportation as well as foot and cycle paths for health improvements; redesigning of cities to ensure no proximity to highly polluting roads and the populace as well as preventing highly polluting vehicles from accessing populated areas using classifications such as clear air or low emission zones ( PHE, 2020 ).
Batteries constitute an integral part towards the decarbonisation of road transportation and support the move to a renewable energy system ( World Economic Forum, 2019 ). As such, it is important to establish a battery value chain that is circular, responsible and just, to realise the aforementioned transitions. This entails the identification of the ( World Economic Forum, 2019 ): (i) challenges inhibiting the scaling up of the battery value chain (e.g. battery production processes, risks of raw materials supplies); (ii) levers to mitigate the challenges such as a circular value chain (e.g. design for life extension, implementation of V1G and V2G and scaling up of electric shared and pooled mobility, coupling the transport and power sectors); sustainable business and technology (e.g. increasing the share of renewables and energy efficiency measures across the value chain, effective regulations and financial incentives to support value creation); and a responsible and just value chain based on a balanced view and interplay between environmental, social and economic factors. Indeed, cost-effective and sustainable batteries, as well as an enabling ecosystem for the deployment of battery-enabled renewable energy technologies backed with a dense infrastructure network for charging, will facilitate the transition towards broader acceptance of electric vehicles and by extension guarantees a sustained improvement in air quality ( Masiero et al., 2017 ; PHE, 2020 ; World Economic Forum, 2019 ).We recognize that if all cars are simply replaced by electricones, there will still be the same volume of traffic and an increased need for raw materials, posing significant social, environmental and integrity risks across its value chain. However, CE through the aforementioned levers can address these challenges and support the achievement of a sustainable battery value chain. This will entail lowering emission during manufacturing, eradicating human rights violations, ensuring safe working conditions across the value chain and improving reuse, recycling and remanufacturing ( World Economic Forum, 2019 ).
6.7. Digitalisation for supply chain resilience post COVID-19
Digitalisation of supply chains through leveraging disruptive digital technologies (DDTs) - technologies or tools underpinning smart manufacturing such as the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence, big data analytics, cloud computing and 3D printing - constitute an important step for companies to prepare for and mitigate against the disruptions and attain business resilience amidst global pandemics such as COVID-19. Circular supply chain value drivers’ entails elongation of useful lifespan and maximisation of asset utilisation. Intelligent assets value drivers entail gathering knowledge regarding the location, condition and availability of assets ( Morlet et al., 2016 ). Paring these drivers could provide a broad range of opportunities, which could change the nature of both products and business models, enabling innovation and value creation ( Antikainen et al., 2018 ; Morlet et al., 2016 ). For instance, big data analytics, when adopted properly can aid companies in streamlining their supplier selection processes; cloud-computing is currently being used to facilitate and manage supplier relationships; through automation and the IoT, logistics and shipping processes can be greatly enhanced ( McKenzie, 2020 ). Digitalisation enables predictive maintenance, preventing failures while extending the lifespan of a product across the supply chains. It therefore, constitutes an ideal vehicle for circular supply chains transitioning, providing opportunities to close material loops and improve processes ( Morlet et al., 2016 ; Pagoropoulos et al., 2017 ).
Indeed, COVID-19 has prompted renewed urgency in the adoption of automation and robotics towards mitigating against the disruptive impact on supply chains through restrictions imposed on people's movement. Numerous companies are taking advantage of this to automate their production lines. Prior to COVID-19, momentum towards adopting 5G mobile technology was mounting but delays caused by factors including anticipated use evaluations, security, competition and radio communications regulatory issues limited progress ( McKenzie, 2020 ). It is likely that the experience of COVID-19 may accelerate the provision of regulatory certainty for 5G, which will in turn fast-track the deployment of IoT-enabled devices for remote monitoring, to support supply chain resilience post COVID-19.
Despite the benefits of DDTs, tension exists between their potential benefits (i.e. ability to deliver measurable environmental benefits at an affordable cost), and the problems (i.e. heavy burden imposed during manufacturing and disposal phases of their lifecycle) they constitute, creating rebound effects. As such, the tension between the push for increasing digitalisation and the associated energy costs and environmental impacts should be investigated such that they do not exacerbate the existing problems of resource use and pollution caused by rapid obsolescence and disposal of products containing such technologies. This entails identifying, mapping and mitigating unintended consequences across their supply chains, whilst taking into account technological design embedded within green ethical design processes, to identify environmental sustainability hotspots, both in conception, application and end of life phases.
6.8. Policy measures, incentives and regulatory support for CE transitioning
Becque et al. (2016) in their analysis of the political economy of the CE identified six main types of policy intervention to facilitate, advance and guide the move to a CE by addressing either barriers that aim to fix the market and regulatory failures or encourage market activity. Some of the policy intervention options identified include: (i) education, information and awareness that entails the integration of CE and lifecycle systems thinking into educational curricula supported by public communication and information campaigns; (ii) setting up platforms for collaboration including public-private partnerships with ventures at the local, regional and national levels, encouraging information sharing as well as value chain and inter-sectoral initiatives, establishing research and development to facilitate breakthroughs in materials science and engineering, biomaterials systems etc.; (iii) introduction of sustainability initiatives in public procurement and infrastructure ; (iv) provision of business/financial/technical support schemes such as initial capital outlay, incentive programs, direct subsidies and financial guarantees as well as technical support, training, advice and demonstration of best practices; (v) regulatory frameworks such as regulation of products (including design), extension of warranties and product passports; strategies for waste management including standards and targets for collection and treatments, take-back systems and extended producer responsibility; strategies at the sectoral levels and associated targets for resource productivity and CE; consumer, competition, industry and trade regulations; introduction of standard carbon accounting standards and methodologies; and (vi) fiscal frameworks such as reductions of VAT or excise tax for products and services designed with CE principles.
7. Conclusion
COVID-19 has highlighted the environmental folly of ‘extract-produce-use-dump’ economic model of material and energy flows. Short-term policies to cope with the urgency of the pandemic are unlikely to be sustainable models in the long run. Nonetheless, they shed light on critical issues that deserve emphases, such as the clear link between environmental pollution and transportation/industrialization. The role of unrestricted air travel in spreading pandemics particularly the viral influenza types (of which COVID-19 is one) is not in doubt, with sectors like tourism and aviation being walloped (some airlines may never recover or return to profitability in a long time) due to reduced passenger volumes. The fallout will re-shape the aviation sector, which like tourism has been among the hardest to be hit economically, albeit with desirable outcomes for the reduction in adverse environmental impacts. Peer-to-peer (P2P) or sharing economy models (e.g. Uber, Airbnb) which have birthed a new generation of service providers and employees are found to be non-resilient to global systemic shocks.
The urgency of supply and demand led to a reduction in cargo shipping in favour of airfreights whose transatlantic cost/kg tripled overnight. This is matched by job losses, income inequalities, mass increase in global poverty levels and economic shocks across industries and supply chains. The practicability of remote working (once the domain of technology/service industries) has been tried and tested for specific industries/professions with its associated impacts on reduced commuting for workers. Remote healthcare/telemedicine/ and remote working, in general, is no longer viewed as unfeasible because it has been practiced with success over the best part of a four-month global lockdown period. There was a corresponding reduction in primary energy consumption due to the slowing and shutting down of production and economic activities, and the delivery of education remotely is also no longer questioned. The potential of automation, IoT, and robotics in improving manufacturing processes, as well as the use of cloud computing and big data analytics in streamlining supplier selection processes and management of supplier relationships and logistics are now better appreciated.
The inadequacies of modern healthcare delivery systems to cope with mass casualties and emergencies are universally acknowledged, primarily due to the incapacity of hospital JIT procurement process to provide essential medical and emergency supplies in vast quantities at short notice. This had deadly consequences with thousands of patients and healthcare workers paying the ultimate price for lack of planning and shortfalls in PPE inventory and critical care equipment. Protectionism and in-ward looking policies on exports and tariff reductions/waivers on the importation of raw materials and critical PPE have emphasized the importance of cooperation to cope with shortages, which evolved in tandem with profiteering, thereby emphasizing the role/need for cottage industries to help meet global production of essentials (facemasks, 3D printed parts/equipment, etc.). The increase in infectious hospital wastes due to the pandemic was necessitated by precautionary measures to control the transmission, but proper/advanced sterilization procedures via thermal, microwave, biochemical processes can help in upcycling discarded or retrieved materials and PPE.
Changes in consumer behaviour with social distancing have necessitated a huge increase in online purchasing, which has benefitted the big players but seriously harmed SMEs, who were not exploiting web-based product and service delivery. A CE-based resilience of the consumer food sector was found to require: (i) closing nutrient loops with the use of regenerative agriculture; (ii) value recovery from organic nutrients via anaerobic digestion facilities; (iii) adoption of urban and peri-urban agriculture; and (iv) expanding food collection, redistribution and volarisation facilities. It is believed that CE will facilitate a socially just and inclusive society,driven by the need for resilience and sustainability goals, which could see a rise in bio-economy and sharing economy (SE). The consequences of these would be felt in terms of global cooperation and mutual interests; long-term planning as well as the need to strike an optimum balance between dependence on outsourcing/importation and local manufacturing/productivity. A realignment of value chains is likely to occur because of countries with raw materials exploiting this pandemic for their sustainable growth, and a new world order not shaped by the technological superiority of super-powers is likely to emerge.
During the lockdown, offices and commercial spaces were massively underutilized and the need to increase ventilation rates, e.g. in hospitals is leading to more energy consumption. However, there are opportunities to (re)design buildings to have movable walls for adaptable use. The use of modular techniques for fast construction of buildings that can be disassembled and re-configured for new needs, as demonstrated in China, is likely to increase. Renovation and refurbishment will witness a renewed vigour as existing buildings get a new lease of life with reduced carbon emissions and new jobs being created. Nonetheless, integrating circularity (product durability, energy efficiency, recyclability, etc.) via design thinking is essential from the onset if all these potential benefits are to be achieved. Digital technologies will play a crucial role in ensuring the low carbon and energy-efficient future of the built environment.
Governments are recognizing the need for national-level CE policies in many aspects, such as: (a) reducing over-reliance on other manufacturing countries for essential goods as massive shortages forced the unwitting adoption of CE principles such as re-use; (b) intensive research into bio-based materials for the development of biodegradable products and the promotion of bio-economy; (c) legal framework for local, regional and national authorities to promote green logistics and waste management regulations which incentivize local production and manufacturing; and (d) development of compact smart cities for effective mobility (with social distancing considerations) as well as enabling environment for shared mobility options (e.g. ride-shares) and active mobility options (e.g. bicycling, walking).
Going forward, resilience thinking should guide lessons learnt and innovations emanating from circular thinking should target the general well-being of the populace and not merely focus on boosting the competitiveness, profitability or growth of businesses and national economies. The post-COVID-19 investments needed to accelerate towards more resilient, low carbon and circular economies should also be integrated into the stimulus packages for economic recovery being promised by governments, since the shortcomings in the dominant linear economic model are now recognized and the gaps to be closed are known.
Credit author statement
IMT, MKB and GJ conceived the idea. IMT developed the methodological notes. IMT, MKB, AZ & FH conducted the analysis. IMT, MKB, AZ, BKA, ADD, AA and FH designed the structure and outline of the paper. All authors contributed to the writing the paper, with comments and feedback from GJ and KSCL.
Declaration of Competing Interest
- Abbas Elmualim S.M., Chileshe N., Rameezdeen R. Construction and the circular economy: smart and industrialised prefabrication. Unmak. Waste Product. Consump. 2018:323. [ Google Scholar ]
- ACI Policy Brief – COVID-19: Relief measures to ensure the survival of the airport industry. Airport Council Int. 2020 [ Google Scholar ]
- Acquaye A., Feng K., Oppon E., Salhi S., Ibn-Mohammed T., Genovese A., Hubacek K. Measuring the environmental sustainability performance of global supply chains: A multi-regional input-output analysis for carbon, sulphur oxide and water footprints. J. Environ. Manag.187. 2017:571–585. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ahmed F., Ahmed N.e., Pissarides C., Stiglitz J. Why inequality could spread COVID-19. The Lancet Public Health. 2020; 5 :e240. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Air Transport Bureau . International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO); Montréal, Canada: 2020. Effects of Novel Coronavirus (COVID‐19) on Civil Aviation: Economic Impact Analysis. [ Google Scholar ]
- Akgün E.Z., Monios J., Rye T., Fonzone A. Influences on urban freight transport policy choice by local authorities. Transport Policy. 2019; 75 :88–98. [ Google Scholar ]
- Allan J., Donovan C., Ekins P., Gambhir A., Hepburn C., Robins N., Reay D., Shuckburgh E., Zenghelis D. A net-zero emissions economic recovery from COVID-19. COP26 Univ. Netw. Brief. 2020 April. [ Google Scholar ]
- Allison A.L., Ambrose-Dempster E., Domenech Aparsi T., Bawn M., Casas Arredondo M., Chau C., Chandler K., Dobrijevic D., Hailes H.C., Lettieri P. The environmental dangers of employing single-use face masks as part of a COVID-19 exit strategy. UCL Open. 2020 Preprint. [ Google Scholar ]
- American Geriatrics Society American Geriatrics Society (AGS) policy brief: COVID‐19 and nursing homes. J. American Geriatrics Society. 2020 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Anderson R.M., Heesterbeek H., Klinkenberg D., Hollingsworth T.D. How will country-based mitigation measures influence the course of the COVID-19 epidemic? The Lancet. 2020; 395 :931–934. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Andrew A., Armand A., Augsburg B., Taveras I.K. Challenges of adopting coronavirus precautions in low-income countries. The IFS, Inst. Fiscal Stud. 2020 [ Google Scholar ]
- Ang B.W. The LMDI approach to decomposition analysis: a practical guide. Energy Policy33. 2005:867–871. [ Google Scholar ]
- Antikainen M., Uusitalo T., Kivikytö-Reponen P. Digitalisation as an enabler of circular economy. Procedia CIRP. 2018; 73 :45–49. [ Google Scholar ]
- Arafat S.Y., Kar S.K., Marthoenis M., Sharma P., Apu E.H., Kabir R. Psychological underpinning of panic buying during pandemic (COVID-19) Psychiatry Res. 2020 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ardente F., Beccali M., Cellura M., Mistretta M. Energy and environmental benefits in public buildings as a result of retrofit actions. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev.15. 2011:460–470. [ Google Scholar ]
- Artola I., Rademaekers K., Williams R., Yearwood J. Study for the iTRE Committee, Commissioned by DG for Internal Policies Policy Department A. Vol. 72. 2016. Boosting building renovation: What potential and value for Europe. [ Google Scholar ]
- ARUP . ARUP; 2020. Transform and Reuse:Low-Carbon Futures for Existing Buildings. [ Google Scholar ]
- Atelge M., Atabani A., Banu J.R., Krisa D., Kaya M., Eskicioglu C., Kumar G., Lee C., Yildiz Y., Unalan S. A critical review of pretreatment technologies to enhance anaerobic digestion and energy recovery. Fuel. 2020; 270 [ Google Scholar ]
- Aubrecht, P., Essink, J., Kovac, M., Vandenberghe, A.-S., 2020. Centralized and decentralized responses to COVID-19 in federal systems: US and EU comparisons. Available at SSRN 3584182.
- Auffhammer M., Burke M., Burney J., Hsiang S., Lobell D., Roberts M., Schlenker W. COVID-19 reduces economic activity, which reduces pollution, which saves lives. Global Food, Environment and Economic Dynamics (G-FEED), United States. 2020 [ Google Scholar ]
- Ayambire R.A., Amponsah O., Peprah C., Takyi S.A. A review of practices for sustaining urban and peri-urban agriculture: Implications for land use planning in rapidly urbanising Ghanaian cities. Land Use Policy. 2019; 84 :260–277. [ Google Scholar ]
- Bachman D. COVID-19 could affect the global economy in three main ways. Deloitte. 2020 [ Google Scholar ]
- Baker S.R., Bloom N., Davis S.J., Terry S.J. National Bureau of Economic Research; 2020. Covid-induced economic uncertainty. [ Google Scholar ]
- Baldwin R., Evenett S. CEPR Press; London: 2020. Covid-19 and Trade Policy: Why turning inward won't work. [ Google Scholar ]
- Baseler L., Chertow D.S., Johnson K.M., Feldmann H., Morens D.M. The pathogenesis of ebola virus disease. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2017; 12 :387–418. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Basilaia G., Kvavadze D. Transition to Online Education in Schools during a SARS-CoV-2 Coronavirus (COVID-19) Pandemic in Georgia. Pedag. Res.5. 2020 [ Google Scholar ]
- Bauwens T., Hekkert M., Kirchherr J. Circular futures: what will they look like? Ecol. Econ.175. 2020 [ Google Scholar ]
- Bayram M., Springer S., Garvey C.K., Özdemir V. COVID-19 digital health innovation policy: A portal to alternative futures in the making. OMICS J. Integrat. Biol. 2020 [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Becque, R., Roy, N., Hamza-Goodacre, D., 2016. The Political Economy of the Circular Economy-lessons to date and questions for research. San Francisco, pp. 1-16.
- Beretta C., Hellweg S. Potential environmental benefits from food waste prevention in the food service sector. Resour. Conserv. Recycl.147. 2019:169–178. [ Google Scholar ]
- Bloom D.E., Cadarette D. Infectious disease threats in the 21st century: strengthening the global response. Front. Immunol.10. 2019:549. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bloom D.E., Canning D. Epidemics and economics. Interact. Glob. Chang. Hum. Health Scripta Varia. 2004; 106 :304–331. [ Google Scholar ]
- Bocken N.M., De Pauw I., Bakker C., van der Grinten B. Product design and business model strategies for a circular economy. J. Indust. Prod. Eng.33. 2016:308–320. [ Google Scholar ]
- Bown C.P. A CEPR Press; 2020. COVID-19: Demand spikes, export restrictions, and quality concerns imperil poor country access to medical supplies. VoxEU.org eBook, 31. [ Google Scholar ]
- Bradsher K., Alderman L. New York Times; 2020. The world needs masks. China makes them, but has been hoarding them. [ Google Scholar ]
- Bramanti B., Dean K.R., Walloe L., Chr Stenseth N. The third plague pandemic in Europe. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2019; 286 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Braungart M., McDonough W., Bollinger A. Cradle-to-cradle design: creating healthy emissions – a strategy for eco-effective product and system design. J. Clean. Prod.15. 2007:1337–1348. [ Google Scholar ]
- Bretscher, L., Hsu, A., Tamoni, A., 2020. The supply channel of uncertainty shocks and the cross-section of returns: evidence from the COVID-19 crisis. Available at SSRN 3588418.
- Browne M., Sweet M., Woodburn A., Allen J. Vol. 10. Transport Studies Group, University of Westminster; 2005. (Urban freight consolidation centres final report). [ Google Scholar ]
- Buldeo Rai H., Verlinde S., Merck J., Macharis C. Crowd logistics: an opportunity for more sustainable urban freight transport? Eur. Transp. Res. Rev. 2017; 9 (39) [ Google Scholar ]
- Buldeo Rai H., Verlinde S., Merckx J., Macharis C. Crowd logistics: an opportunity for more sustainable urban freight transport? Eur. Transp. Res. Rev.9. 2017:39. [ Google Scholar ]
- Carra G., Magdani N. Circular business models for the built environment. Arup BAM. 2017:1–44. [ Google Scholar ]
- Carrillo-Hermosilla J., Del Río P., Könnölä T. Diversity of eco-innovations: Reflections from selected case studies. J. Clean. Prod.18. 2010:1073–1083. [ Google Scholar ]
- Castañé S., Antón A. Assessment of the nutritional quality and environmental impact of two food diets: A Mediterranean and a vegan diet. J. Clean. Prod.167. 2017:929–937. [ Google Scholar ]
- Chandra, S., 2020. Speed, space and sustainability (3S) in transportation amid COVID-19 crisis. SSRN 3598501.
- Chang H.-H., Meyerhoefer C. National Bureau of Economic Research; 2020. COVID-19 and the Demand for Online Food Shopping Services: Empirical Evidence from Taiwan. [ Google Scholar ]
- Chen C., Zhao B. Makeshift hospitals for COVID-19 patients: where health-care workers and patients need sufficient ventilation for more protection. J. Hosp. Infect.105. 2020:98–99. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Chi M., George J.F., Huang R., Wang P. Unraveling sustainable behaviors in the sharing economy: An empirical study of bicycle-sharing in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020 [ Google Scholar ]
- Cimprich A., Santillán‐Saldivar J., Thiel C.L., Sonnemann G., Young S.B. Potential for industrial ecology to support healthcare sustainability: Scoping review of a fragmented literature and conceptual framework for future research. J. Indust. Ecol.23. 2019:1344–1352. [ Google Scholar ]
- Clair A. Social Market Foundation (SMF); 2020. Homes, health, and COVID-19: how poor housing adds to the hardship of the coronavirus crisis. Online. [ Google Scholar ]
- Company M. A global view of how consumer behavior is changing amid COVID-19. McKinsey. 2020 [ Google Scholar ]
- Da Silva C., Hoppe A., Ravanello M., Mello N. Medical wastes management in the south of Brazil. Waste Manag.25. 2005:600–605. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Danieli, A., Olmstead-Rumsey, J., 2020. Sector-specific shocks and the expenditure elasticity channel during the covid-19 crisis. Available at SSRN 3593514.
- Dannenberg, P., Fuchs, M., Riedler, T., Wiedemann, C., 2020. Digital transition by COVID‐19 pandemic? The German food online retail. Tijdschrift voor economische en sociale geografie. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ]
- Dargaville T., Spann K., Celina M. Opinion to address a potential personal protective equipment shortage in the global community during the COVID-19 outbreak. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2020 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Daszak P. Anatomy of a pandemic. The Lancet. 2012; 380 :1883–1884. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- De Cock K.M., Jaffe H.W., Curran J.W. The evolving epidemiology of HIV/AIDS. Aids. 2012; 26 :1205–1213. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- De Gioannis G., Muntoni A., Polettini A., Pomi R., Spiga D. Energy recovery from one-and two-stage anaerobic digestion of food waste. Waste Manag.68. 2017:595–602. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- De Jesus A., Mendonça S. Lost in transition? Drivers and barriers in the eco-innovation road to the circular economy. Ecol. Econ.145. 2018:75–89. [ Google Scholar ]
- De Soete W., Jiménez-González C., Dahlin P., Dewulf J. Challenges and recommendations for environmental sustainability assessments of pharmaceutical products in the healthcare sector. Green Chem.19. 2017:3493–3509. [ Google Scholar ]
- Deloitte . Deloitte; 2020. Understanding the sector impact of COVID-19: Engineering and Construction sector; p. 2. [ Google Scholar ]
- Devakumar D., Shannon G., Bhopal S.S., Abubakar I. Racism and discrimination in COVID-19 responses. The Lancet. 2020; 395 :1194. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Diaz L.F., Eggerth L., Enkhtsetseg S., Savage G. Characteristics of healthcare wastes. Waste Manag.28. 2008:1219–1226. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Dilkes-Hoffman L.S., Lane J.L., Grant T., Pratt S., Lant P.A., Laycock B. Environmental impact of biodegradable food packaging when considering food waste. J. Clean. Prod.180. 2018:325–334. [ Google Scholar ]
- Dingel J.I., Neiman B. National Bureau of Economic Research; 2020. How many jobs can be done at home? [ Google Scholar ]
- Duflou J.R., Sutherland J.W., Dornfeld D., Herrmann C., Jeswiet J., Kara S., Hauschild M., Kellens K. Towards energy and resource efficient manufacturing: A processes and systems approach. CIRP Anna.61. 2012:587–609. [ Google Scholar ]
- Duncan-Jones R.P. The impact of the Antonine plague. J. Roman Arch.9. 1996:108–136. [ Google Scholar ]
- Eaton J., Connor Y. How to strengthen your supply chain in the face of COVID-19 disruption: 8 Lessons for strengthening your supply chain today. Grant Thornton. 2020 Online. [ Google Scholar ]
- Eberhardt L.C.M., Birgisdottir H., Birkved M. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering. IOP Publishing; 2019. Potential of circular economy in sustainable buildings. [ Google Scholar ]
- EEA . Vol. 2020. Publications Office of the European Union; Luxembourg: 2020. pp. 1–104. (Environmental noise in Europe — 2020. European Environment Agency (EEA)). [ Google Scholar ]
- Ekins, P., Hughes, N., Brigenzu, S., Arden Clark, C., Fischer-Kowalski, M., Graedel, T., Hajer, M., Hashimoto, S., Hatfield-Dodds, S., Havlik, P., 2016. Resource efficiency: Potential and economic implications.
- Eleyan D., Al-Khatib I.A., Garfield J. System dynamics model for hospital waste characterization and generation in developing countries. Waste Manag. Res.31. 2013:986–995. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- EMF . Ellen MacArthur Foundation; London: 2016. Circular economy in India: Rethinking growth for long-term prosperity; p. 86. [ Google Scholar ]
- EMF . Ellen MacArthur Foundation; 2019. Planning effective transport of people, products and materials; p. 6. [ Google Scholar ]
- EMF . Ellen MacArthur Foundation; 2020. 10 circular investment opportunities to build back better: food sector; p. 13. [ Google Scholar ]
- EMF . Ellen MacArthur Foundation; London: 2020. 10 circular investment opportunities to build back better: The built environment; p. 10. [ Google Scholar ]
- Enkvist P., Klevnäs P., Teiwik A., Jönsson C., Klingvall S., Hellberg U. Material Economics Sverige AB; Stockholm, Sweden: 2018. The circular economy–a powerful force for climate mitigation: transformative innovation for prosperous and low-carbon industry. [ Google Scholar ]
- EPRS . European Parliamentary Research Service (EPRS); 2014. Urban And Peri-Urban Agriculture. [ Google Scholar ]
- ESA . European Space Agency (ESA); 2020. Air pollution remains low as Europeans stay at home. Online. [ Google Scholar ]
- European Commission . European Commission; 2011. The Roadmap to a Resource Efficient Europe; p. 26. [ Google Scholar ]
- European Commission . European Commission; 2020. EU Circular Economy Action Plan: A new Circular Economy Action Plan for a Cleaner and More Competitive Europe. [ Google Scholar ]
- Evenett S.J. Flawed prescription: Export curbs on medical goods won't tackle shortages. COVID-19 and Trade Policy: Why Turning Inward Won't Work. 2020; 49 [ Google Scholar ]
- Fast Company . Fast Company; 2019. Is it possible to raise a carbon-neutral cow? [ Google Scholar ]
- Feber D., Lingqvist O., Nordigården D. McKinsey & Company McKinsey & Company; 2020. Shaping the next normal of packaging beyond COVID-19; p. 6. [ Google Scholar ]
- Feng K., Davis S.J., Sun L., Hubacek K. Drivers of the US CO2 emissions 1997-2013. Nat. Commun.6. 2015 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Fernandes, N., 2020. Economic effects of coronavirus outbreak (COVID-19) on the world economy. Available at SSRN 3557504.
- Fischer R., Morris D.H., van Doremalen N., Sarchette S., Matson J., Bushmaker T., Yinda C.K., Seifert S., Gamble A., Williamson B. Assessment of N95 respirator decontamination and re-use for SARS-CoV-2. medRxiv. 2020 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ford T.E., Colwell R.R., Rose J.B., Morse S.S., Rogers D.J., Yates T.L. Using satellite images of environmental changes to predict infectious disease outbreaks. Emerg. Infect. Dis.15. 2009:1341. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Friant M.C., Vermeulen W.J., Salomone R. A typology of circular economy discourses: Navigating the diverse visions of a contested paradigm. Resour. Conserv. Recycl.161. 2020 [ Google Scholar ]
- Fujii H., Managi S., Kaneko S. Decomposition analysis of air pollution abatement in China: empirical study for ten industrial sectors from 1998 to 2009. J. Clean. Prod.59. 2013:22–31. [ Google Scholar ]
- Galvão G.D.A., Homrich A.S., Geissdoerfer M., Evans S., Ferrer P.S.s., Carvalho M.M. Towards a value stream perspective of circular business models. Resour. Conserv. Recycl.162. 2020 [ Google Scholar ]
- Gates B. COVID-19 is awful. Climate change could be worse. Clim. Coronavirus. 2020 GatesNotes. [ Google Scholar ]
- Gates B. Responding to Covid-19—a once-in-a-century pandemic? N. Engl. J. Med.382. 2020:1677–1679. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gatta V., Marcucci E., Delle Site P., Le Pira M., Carrocci C.S. Planning with stakeholders: Analysing alternative off-hour delivery solutions via an interactive multi-criteria approach. Res. Transp. Econ.73. 2019:53–62. [ Google Scholar ]
- Geissdoerfer M., Savaget P., Bocken N.M., Hultink E.J. The Circular Economy–A new sustainability paradigm? J. Clean. Prod.143. 2017:757–768. [ Google Scholar ]
- Gibbs M.J., Armstrong J.S., Gibbs A.J. Recombination in the hemagglutinin gene of the 1918" Spanish flu". Science. 2001; 293 :1842–1845. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Girling R. Random House; 2011. Rubbish!: Dirt on Our Hands and Crisis Ahead. [ Google Scholar ]
- Gondi S., Beckman A.L., Deveau N., Raja A.S., Ranney M.L., Popkin R., He S. Personal protective equipment needs in the USA during the COVID-19 pandemic. The Lancet. 2020 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gopinath G. Limiting the economic fallout of the coronavirus with large targeted policies. IMF. 2020 [ Google Scholar ]
- Govindan K., Hasanagic M. A systematic review on drivers, barriers, and practices towards circular economy: a supply chain perspective. Int. J. Prod. Res.56. 2018:278–311. [ Google Scholar ]
- Grant M.J., Booth A. A typology of reviews: an analysis of 14 review types and associated methodologies. Health Inform. Libr. J.26. 2009:91–108. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Greenhalgh T., Thorne S., Malterud K. Time to challenge the spurious hierarchy of systematic over narrative reviews? Eur. J. Clin. Invest. 2018; 48 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Guan, D., Hallegatte, S., 2020. The containment divide: COVID-19 lockdowns and basic needs in developing countries.
- Guan, D., Wang, D., Hallegatte, S., Huo, J., Li, S., Bai, Y., Lei, T., Xue, Q., Davis, S.J., Coffman, D.M., 2020. Global economic footprint of the COVID-19 pandemic.
- Guerrieri V., Lorenzoni G., Straub L., Werning I. National Bureau of Economic Research; 2020. Macroeconomic Implications of COVID-19: Can Negative Supply Shocks Cause Demand Shortages? [ Google Scholar ]
- Gungor A., Gupta S.M. Issues in environmentally conscious manufacturing and product recovery: a survey. Comp. Indust. Eng.36. 1999:811–853. [ Google Scholar ]
- Haigh, L., Bäunker, L., 2020. Covid-19 and the circular economy: opportunities and reflections.
- Hasanat M.W., Hoque A., Shikha F.A., Anwar M., Hamid A.B.A., Tat H.H. The impact of coronavirus (Covid-19) on e-business in Malaysia. Asian J. Multidiscipl. Stud.3. 2020:85–90. [ Google Scholar ]
- Herrmann C., Schmidt C., Kurle D., Blume S., Thiede S. Sustainability in manufacturing and factories of the future. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf.-Green Tech.1. 2014:283–292. [ Google Scholar ]
- Hobbs J.E. Food supply chains during the COVID‐19 pandemic. Can. J. Agricult. Econ./Revue canadienne d’agroeconomie. 2020 [ Google Scholar ]
- Hockley L. Coronavirus roundtable: How is the aviation industry responding to the COVID-19 pandemic? Int. Airport Rev. 2020 Online. [ Google Scholar ]
- Hoornweg, D., Bhada-Tata, P., 2012. What a waste: a global review of solid waste management.
- Horrox R. Manchester University Press; 2013. The Black Death. [ Google Scholar ]
- Hotez P.J., Alvarado M., Basáñez M.-G., Bolliger I., Bourne R., Boussinesq M., Brooker S.J., Brown A.S., Buckle G., Budke C.M. The global burden of disease study 2010: interpretation and implications for the neglected tropical diseases. PLoS Neglect. Tropic. Dis.8. 2014 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hu M.R., Lee A.D. Airbnb, COVID-19 risk and lockdowns: global evidence. COVID-19 Risk Lockdowns Glob. Evid. 2020 (April 30, 2020) [ Google Scholar ]
- Huang W., Zhao Z., Yuan T., Huang W., Lei Z., Zhang Z. Low-temperature hydrothermal pretreatment followed by dry anaerobic digestion: A sustainable strategy for manure waste management regarding energy recovery and nutrients availability. Waste Manag.70. 2017:255–262. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hussey L.K., Arku G. Are we ready for it? Health systems preparedness and capacity towards climate change-induced health risks: perspectives of health professionals in Ghana. Clim. Dev.12. 2020:170–182. [ Google Scholar ]
- IATA Air transport & COVID-19 coronavirus. Int. Air Transp. Assoc. 2020 www.airlines.iata.org [ Google Scholar ]
- Ibn-Mohammed T. Application of mixed-mode research paradigms to the building sector: a review and case study towards decarbonising the built and natural environment. Sustain. Cities Soc.35. 2017:692–714. [ Google Scholar ]
- Ibn-Mohammed T., Greenough R., Taylor S., Ozawa-Meida L., Acquaye A. Operational vs. embodied emissions in buildings—A review of current trends. Energy Build.66. 2013:232–245. [ Google Scholar ]
- Ibn-Mohammed T., Greenough R., Taylor S., Ozawa-Meida L., Acquaye A. Integrating economic considerations with operational and embodied emissions into a decision support system for the optimal ranking of building retrofit options. Build. Environ.72. 2014:82–101. [ Google Scholar ]
- Ibn-Mohammed T., Reaney I., Koh S., Acquaye A., Sinclair D., Randall C., Abubakar F., Smith L., Schileo G., Ozawa-Meida L. Life cycle assessment and environmental profile evaluation of lead-free piezoelectrics in comparison with lead zirconate titanate. J. Eur. Cer. Soc. 2018 [ Google Scholar ]
- ICAO Effects of novel coronavirus (COVID-19) on civil aviation: economic impact analysis. Unit. Aviat. 2020 [ Google Scholar ]
- IEA . International Energy Agency, IEA Publications; 2020. Global Energy Review 2020:The impacts of the COVID-19 crisis on global energy demand and CO2 emissions; pp. 1–56. [ Google Scholar ]
- Ijomah W.L. Proceedings of the Institution of Civil Engineers-Waste and Resource Management. Thomas Telford Ltd; 2010. The application of remanufacturing in sustainable manufacture; pp. 157–163. [ Google Scholar ]
- IMF . The International Monetary Fund (IMF); Washington, DC: 2020. World Economic Outlook: The Great Lockdown; p. 37. -37. [ Google Scholar ]
- Insa E., Zamorano M., López R. Critical review of medical waste legislation in Spain. Resour. Conserv. Recycl.54. 2010:1048–1059. [ Google Scholar ]
- Iyengar K., Bahl S., Vaishya R., Vaish A. Challenges and solutions in meeting up the urgent requirement of ventilators for COVID-19 patients. Diab. Metabol. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev. 2020 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Jaeger B., Upadhyay A. Understanding barriers to circular economy: cases from the manufacturing industry. J. Enterp. Inform. Manag. 2020 [ Google Scholar ]
- Janné M., Fredriksson A. Construction logistics governing guidelines in urban development projects. Constr. Innov. 2019 [ Google Scholar ]
- Javorcik B. Global supply chains will not be the same in the post-COVID-19 world. COVID-19 and Trade Policy: Why Turning Inward Won't Work. 2020; 111 [ Google Scholar ]
- JHU . Coronavirus Resource Center, Johns Hopkins University (JHU); 2020. MAPS & TRENDS: New Cases of COVID-19 In World Countries. [ Google Scholar ]
- Johansson H., Björklund M. Urban consolidation centres: retail stores’ demands for UCC services. Int. J. Phys. Distrib. Logist. Manag. 2017 [ Google Scholar ]
- Kaiser B., Eagan P.D., Shaner H. Solutions to health care waste: life-cycle thinking and“ green” purchasing. Environ. Health Perspect.109. 2001:205–207. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kanda W., Kivimaa P. What opportunities could the COVID-19 outbreak offer for sustainability transitions research on electricity and mobility? Energy Res. Soc. Sci.68. 2020 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kane G.M., Bakker C.A., Balkenende A.R. Towards design strategies for circular medical products. Resour. Conserv. Recycl.135. 2018:38–47. [ Google Scholar ]
- Kiba-Janiak M. EU cities’ potentials for formulation and implementation of sustainable urban freight transport strategic plans. Transp. Res. Procedia. 2019; 39 :150–159. [ Google Scholar ]
- Kirchherr J., Piscicelli L., Bour R., Kostense-Smit E., Muller J., Huibrechtse-Truijens A., Hekkert M. Barriers to the circular economy: evidence from the European Union (EU) Ecol. Econ.150. 2018:264–272. [ Google Scholar ]
- Kirchherr J., Reike D., Hekkert M. Conceptualizing the circular economy: An analysis of 114 definitions. Resour. Conserv. Recycl.127. 2017:221–232. [ Google Scholar ]
- Klemeš J.J., Fan Y.V., Tan R.R., Jiang P. Minimising the present and future plastic waste, energy and environmental footprints related to COVID-19. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev.127. 2020 -109883. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Koh S., Ibn-Mohammed T., Acquaye A., Feng K., Reaney I., Hubacek K., Fujii H., Khatab K. Drivers of US toxicological footprints trajectory 1998–2013. Sci. Rep.6. 2016:39514. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Korhonen J., Honkasalo A., Seppälä J. Circular economy: the concept and its limitations. Ecol. Econ.143. 2018:37–46. [ Google Scholar ]
- Kraemer M.U., Yang C.-H., Gutierrez B., Wu C.-H., Klein B., Pigott D.M., du Plessis L., Faria N.R., Li R., Hanage W.P. The effect of human mobility and control measures on the COVID-19 epidemic in China. Science. 2020; 368 :493–497. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Laing T. The economic impact of the Coronavirus 2019 (Covid-2019): Implications for the mining industry. Extract. Indust. Soc. 2020 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Le Quéré C., Jackson R.B., Jones M.W., Smith A.J., Abernethy S., Andrew R.M., De-Gol A.J., Willis D.R., Shan Y., Canadell J.G. Temporary reduction in daily global CO 2 emissions during the COVID-19 forced confinement. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2020:1–7. [ Google Scholar ]
- Lee C., Huffman G., Nalesnik R. Medical waste management. Environ. Sci. Tech.25. 1991:360–363. [ Google Scholar ]
- Lee G.-G., Lee H.-W., Lee J.-H. Greenhouse gas emission reduction effect in the transportation sector by urban agriculture in Seoul, Korea. Landscape and Urban Plan.140. 2015:1–7. [ Google Scholar ]
- Lee J.-W., McKibbin W.J. National Academies Press; Washington, DC: 2004. Estimating the global economic costs of SARS, Learning from SARS: preparing for the next disease outbreak: workshop summary; p. 92. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Liao L., Xiao W., Zhao M., Yu X., Wang H., Wang Q., Chu S., Cui Y. Can N95 respirators be reused after disinfection? How many times? ACS Nano. 2020 [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lieder M., Rashid A. Towards circular economy implementation: a comprehensive review in context of manufacturing industry. J. Clean. Prod.115. 2016:36–51. [ Google Scholar ]
- Littman R.J., Littman M.L. Galen and the Antonine plague. Am. J. Philol.94. 1973:243–255. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Liu X., Zhang S. COVID‐19: Face masks and human‐to‐human transmission. Influen. Other Respir. Virus. 2020 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Livingston E., Desai A., Berkwits M. Sourcing personal protective equipment during the COVID-19 pandemic. JAMA. 2020 [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lucrezi S., Saayman M., Van der Merwe P. An assessment tool for sandy beaches: A case study for integrating beach description, human dimension, and economic factors to identify priority management issues. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2016; 121 :1–22. [ Google Scholar ]
- Lwasa S., Mugagga F., Wahab B., Simon D., Connors J., Griffith C. Urban and peri-urban agriculture and forestry: Transcending poverty alleviation to climate change mitigation and adaptation. Urban Climate. 2014; 7 :92–106. [ Google Scholar ]
- Lyche, H., 2020. Might a disaster trigger a new circular-economy?
- Mabahwi N.A.B., Leh O.L.H., Omar D. Human health and wellbeing: Human health effect of air pollution. Procedia-Soc. Behav. Sci.153. 2014:221–229. [ Google Scholar ]
- MacArthur E. Ellen MacArthur Foundation; Cowes, UK: 2013. Towards the circular economy, economic and business rationale for an accelerated transition. [ Google Scholar ]
- Mahler D.G., Lakner C., Aguilar R.A.C., Wu H. World Bank; Washington, D.C., United States: 2020. The impact of COVID-19 (Coronavirus) on global poverty: Why Sub-Saharan Africa might be the region hardest hit. [ Google Scholar ]
- Manninen K., Koskela S., Antikainen R., Bocken N., Dahlbo H., Aminoff A. Do circular economy business models capture intended environmental value propositions? J. Clean. Prod.171. 2018:413–422. [ Google Scholar ]
- Marcucci E., Le Pira M., Carrocci C.S., Gatta V., Pieralice E. 2017 5th IEEE International Conference on Models and Technologies for Intelligent Transportation Systems (MT-ITS) IEEE; 2017. Connected shared mobility for passengers and freight: Investigating the potential of crowdshipping in urban areas; pp. 839–843. [ Google Scholar ]
- Marques G., Roque Ferreira C., Pitarma R. A system based on the internet of things for real-time particle monitoring in buildings. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health15. 2018 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Masiero G., Ogasavara M.H., Jussani A.C., Risso M.L. The global value chain of electric vehicles: A review of the Japanese, South Korean and Brazilian cases. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev.80. 2017:290–296. [ Google Scholar ]
- McDonough W., Braungart M. North point press; 2010. Cradle to cradle: Remaking the way we make things. [ Google Scholar ]
- McKee M., Stuckler D. If the world fails to protect the economy, COVID-19 will damage health not just now but also in the future. Nat. Med.26. 2020:640–642. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- McKenzie B. Beyond COVID-19: supply chain resilience holds key to recovery. Oxford Econ.24. 2020:20. [ Google Scholar ]
- McKibbin, W.J., Fernando, R., 2020. The global macroeconomic impacts of COVID-19: Seven scenarios.
- Minunno R., O'Grady T., Morrison G.M., Gruner R.L., Colling M. Strategies for applying the circular economy to prefabricated buildings. Buildings. 2018; 8 :125. [ Google Scholar ]
- Moazzami B., Razavi-Khorasani N., Moghadam A.D., Farokhi E., Rezaei N. COVID-19 and telemedicine: Immediate action required for maintaining healthcare providers well-being. J. Clin. Virol. 2020 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Monlau F., Sambusiti C., Antoniou N., Barakat A., Zabaniotou A. A new concept for enhancing energy recovery from agricultural residues by coupling anaerobic digestion and pyrolysis process. Appl. Energy. 2015; 148 :32–38. [ Google Scholar ]
- Morlet A., Blériot J., Opsomer R., Linder M., Henggeler A., Bluhm A., Carrera A. Ellen MacArthur Foundation; 2016. Intelligent assets: Unlocking the circular economy potential; pp. 1–25. [ Google Scholar ]
- Morrison A., Polisena J., Husereau D., Moulton K., Clark M., Fiander M., Mierzwinski-Urban M., Clifford T., Hutton B., Rabb D. The effect of English-language restriction on systematic review-based meta-analyses: a systematic review of empirical studies. Int. J. Tech. Assess. Health Care28. 2012:138. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Muhammad S., Long X., Salman M. COVID-19 pandemic and environmental pollution: A blessing in disguise? Sci. Total Environ. 2020 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Murray N.E.A., Quam M.B., Wilder-Smith A. Epidemiology of dengue: past, present and future prospects. Clin. Epidemiol.5. 2013:299. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Naidoo R., Fisher B. Nature Publishing Group; 2020. Reset Sustainable Development Goals for a pandemic world. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- NASA . National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA); 2020. Airborne Nitrogen Dioxide Plummets Over China. Online. [ Google Scholar ]
- NASA . NASA; 2020. Airborne Particle Levels Plummet in Northern India. [ Google Scholar ]
- OECD . OECD; Paris: 2018. Financing Climate Futures - Rethinking Infrastructure. [ Google Scholar ]
- Omary M.B., Eswaraka J., Kimball S.D., Moghe P.V., Panettieri R.A., Scotto K.W. The COVID-19 pandemic and research shutdown: staying safe and productive. J. Clin. Invest.130. 2020 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Opitz I., Berges R., Piorr A., Krikser T. Contributing to food security in urban areas: differences between urban agriculture and peri-urban agriculture in the Global North. Agricult. Hum. Val.33. 2016:341–358. [ Google Scholar ]
- Oweis R., Al-Widyan M., Al-Limoon O. Medical waste management in Jordan: A study at the King Hussein Medical Center. Waste Manag.25. 2005:622–625. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Özkan A. Evaluation of healthcare waste treatment/disposal alternatives by using multi-criteria decision-making techniques. Waste Manag. Res.31. 2013:141–149. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Paez A. Gray literature: An important resource in systematic reviews. J. Evid.‐Based Med.10. 2017:233–240. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Pagoropoulos A., Pigosso D.C., McAloone T.C. The emergent role of digital technologies in the Circular Economy: A review. Procedia CIRP. 2017; 64 :19–24. [ Google Scholar ]
- Partelow S., von Wehrden H., Horn O. Pollution exposure on marine protected areas: a global assessment. Mar. Pollut. Bull.100. 2015:352–358. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Paxton, N.C., Forrestal, D.P., Desselle, M., Kirrane, M., Sullivan, C., Powell, S.K., Woodruff, M.A., 2020. N95 respiratory masks for COVID-19: a review of the literature to inform local responses to global shortages.
- Pearce J.M. A review of open source ventilators for COVID-19 and future pandemics. F1000Research. 2020; 9 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Peng J., Wu X., Wang R., Li C., Zhang Q., Wei D. Medical waste management practice during the 2019-2020 novel coronavirus pandemic: Experience in a general hospital. Am. J. Infect. Control. 2020 S0196-6553(0120)30351-30355. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Penn E., Yasso S.F., Wei J.L. Reducing disposable equipment waste for tonsillectomy and adenotonsillectomy cases. Otolaryngol.–Head and Neck Surg.147. 2012:615–618. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- PHE . Public Health England (PHE); London: 2020. Review of interventions to improve outdoor air quality and public health; pp. 1–262. [ Google Scholar ]
- Piguillem F., Shi L. Einaudi Institute for Economics and Finance (EIEF); 2020. The optimal COVID-19 quarantine and testing policies, EIEF Working Papers Series 2004; p. 40. [ Google Scholar ]
- Pinheiro M.D., Luís N.C. COVID-19 Could Leverage a Sustainable Built Environment. Sustainability. 2020; 12 [ Google Scholar ]
- Pinner D., Rogers M., Samandari H. McKinsey & Company; 2020. McKinsey Quarterly: Addressing climate change in a post-pandemic world; pp. 1–6. [ Google Scholar ]
- Pitarma R., Marques G., Ferreira B.R. Monitoring indoor air quality for enhanced occupational health. J. Med. Syst.41. 2017 [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Pomponi F., Moncaster A. Circular economy for the built environment: A research framework. J. Clean. Prod.143. 2017:710–718. [ Google Scholar ]
- Prata J.C., Silva A.L.P., Walker T.R., Duarte A.C., Rocha-Santos T. COVID-19 pandemic repercussions on the use and management of plastics. Environ. Sci. Tech.54. 2020:7760–7765. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Preston F., Lehne J., Wellesley L. CHATAM HOUSE, The Royal Institute of International Affairs; London: 2019. An Inclusive Circular Economy; Priorities for Developing Countries, Priorities for Developing Countries; pp. 1–82. [ Google Scholar ]
- Prüss-Üstün A., Prüss A., Giroult E., Townend W.K., Rushbrook P., Organization W.H. World Health Organization; 1999. Safe Management of Wastes from Health-care Activities. [ Google Scholar ]
- Rai H.B., Verlinde S., Macharis C. Shipping outside the box. Environmental impact and stakeholder analysis of a crowd logistics platform in Belgium. J. Clean. Prod.202. 2018:806–816. [ Google Scholar ]
- Raj, M., Sundararajan, A., You, C., 2020. COVID-19 and Digital Resilience: Evidence from Uber Eats. arXiv preprint arXiv:2006.07204.
- Ranganatha J., Waite R., Searchinger T., Zionts J. World Resources Institute; 2020. Regenerative Agriculture: Good for Soil Health, but Limited Potential to Mitigate Climate Change. [ Google Scholar ]
- Ranney M.L., Griffeth V., Jha A.K. Critical supply shortages—the need for ventilators and personal protective equipment during the Covid-19 pandemic. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020 [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rashid A., Asif F.M., Krajnik P., Nicolescu C.M. Resource conservative manufacturing: an essential change in business and technology paradigm for sustainable manufacturing. J. Clean. Prod.57. 2013:166–177. [ Google Scholar ]
- Rees W.E. Footprint: our impact on Earth is getting heavier. Nature. 2002; 420 :267–268. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rhodes C.J. The imperative for regenerative agriculture. Sci. Progr.100. 2017:80–129. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rios F.C., Chong W.K., Grau D. Design for disassembly and deconstruction-challenges and opportunities. Procedia Eng.118. 2015:1296–1304. [ Google Scholar ]
- Rubio-Romero J.C., del Carmen Pardo-Ferreira M., García J.A.T., Calero-Castro S. Disposable masks: Disinfection and sterilization for reuse, and non-certified manufacturing, in the face of shortages during the COVID-19 pandemic. Safe. Sci. 2020 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- San Juan, D.M., 2020. Responding to COVID-19 through socialist (ic) measures: a preliminary review. Available at SSRN 3559398.
- Sarkis J., Cohen M.J., Dewick P., Schröder P. A brave new world: lessons from the COVID-19 pandemic for transitioning to sustainable supply and production. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sauerwein M., Doubrovski E., Balkenende R., Bakker C. Exploring the potential of additive manufacturing for product design in a circular economy. J. Clean. Prod.226. 2019:1138–1149. [ Google Scholar ]
- Saunders-Hastings P.R., Krewski D. Reviewing the history of pandemic influenza: understanding patterns of emergence and transmission. Pathogens. 2016; 5 :66. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Schluep M. UNEP; 2009. Recycling-from e-waste to resources: Sustainable innovation technology transfer industrial sector studies. [ Google Scholar ]
- Shaheen S., Cohen A. Elsevier; 2020. Mobility on demand (MOD) and mobility as a service (MaaS): early understanding of shared mobility impacts and public transit partnerships, Demand for Emerging Transportation Systems; pp. 37–59. [ Google Scholar ]
- Sherwood S., Uphoff N. Soil health: research, practice and policy for a more regenerative agriculture. Appl. Soil Ecol.15. 2000:85–97. [ Google Scholar ]
- Sim K., Chua H.C., Vieta E., Fernandez G. The anatomy of panic buying related to the current COVID-19 pandemic. Psychiatry Res. 2020 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Siow W.T., Liew M.F., Shrestha B.R., Muchtar F., See K.C. Springer; 2020. Managing COVID-19 in resource-limited settings: critical care considerations. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Snider-Mcgrath B. 2020. Exercise rates on the rise during COVID-19. [ Google Scholar ]
- Snyder H. Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines. J. Busi. Res.104. 2019:333–339. [ Google Scholar ]
- Sohrabi C., Alsafi Z., O’Neill N., Khan M., Kerwan A., Al-Jabir A., Iosifidis C., Agha R. World Health Organization declares global emergency: A review of the 2019 novel coronavirus (COVID-19) Int. J. Surg. 2020 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Solomon M.Z., Wynia M., Gostin L.O. Scarcity in the Covid‐19 pandemic. Hast. Cent. Rep.50. 2020:3. -3. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Spash C.L. ‘The economy'as if people mattered: revisiting critiques of economic growth in a time of crisis. Globalizations. 2020:1–18. [ Google Scholar ]
- Stahel W.R. The circular economy. Nature. 2016; 531 :435–438. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Stahel W.R. Routledge; 2019. The circular economy: A user's guide. [ Google Scholar ]
- Stellinger A., Berglund I., Isakson H. How trade can fight the pandemic and contribute to global health. COVID-19 and Trade Policy: Why Turning Inward Won't Work. 2020; 21 [ Google Scholar ]
- Stockholm Resilience Centre . Stockholm Resilience Centre, Stockholm University; Stockholm: 2016. Through resilience thinking towards sustainability and innovation: recommendations for policy makers in the EU; pp. 1–20. [ Google Scholar ]
- SYSTEMIQ . SUN Institute Environment & Sustainability in collaboration with The Ellen MacArthur Foundation; 2017. ACHIEVING ‘GROWTH WITHIN’: A €320-billion circular economy investment opportunity available to Europe up to 2025; p. 149. [ Google Scholar ]
- Tan J., Liu Y., Shen E., Zhu W., Wang W., Li R., Yang L. Towards<< the atlas of plague and its environment in the People's Republic of China>>: idea, principle and methodology of design and research results. Huan jing ke xue= Huanjing kexue. 2002; 23 :1–8. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Temmerman S., Meire P., Bouma T.J., Herman P.M., Ysebaert T., De Vriend H.J. Ecosystem-based coastal defence in the face of global change. Nature. 2013; 504 :79–83. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Thebo A., Drechsel P., Lambin E. Global assessment of urban and peri-urban agriculture: irrigated and rainfed croplands. Environ. Res. Lett.9. 2014 [ Google Scholar ]
- Thunstrom, L., Newbold, S., Finnoff, D., Ashworth, M., Shogren, J.F., 2020. The benefits and costs of flattening the curve for COVID-19. Available at SSRN 3561934.
- Timmer M., Erumban A., Gouma R., Los B., Temurshoev U., de Vries G., Arto I. The world input-output database (WIOD): contents, sources and methods. WIOD Background. 2012 document available at www. wiod. org 40. [ Google Scholar ]
- Toquero C. Challenges and opportunities for higher education amid the COVID-19 pandemic: The Philippine Context. Pedag. Res.5. 2020 [ Google Scholar ]
- Trilla A., Trilla G., Daer C. The 1918 “Spanish Flu” in Spain. Clin. Infect. Dis.47. 2008:668–673. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Tudor T., Noonan C., Jenkin L. Healthcare waste management: a case study from the National Health Service in Cornwall, United Kingdom. Waste Manag.25. 2005:606–615. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- UN DESA Everyone included: social impact of COVID-19. UN Depart. Econ. Soc. Aff. (UN DESA) 2020 [ Google Scholar ]
- UN Habitat . Taylor & Francis; 2013. Planning and design for sustainable urban mobility: Global report on human settlements 2013. [ Google Scholar ]
- UNWTO . World Tourism Organization; 2020. Impact assessment of the covid-19 outbreak on international tourism United Nation. [ Google Scholar ]
- Van Bavel J.J., Baicker K., Boggio P.S., Capraro V., Cichocka A., Cikara M., Crockett M.J., Crum A.J., Douglas K.M., Druckman J.N. Using social and behavioural science to support COVID-19 pandemic response. Nat. Hum. Behav. 2020:1–12. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Van Buren N., Demmers M., Van der Heijden R., Witlox F. Towards a circular economy: The role of Dutch logistics industries and governments. Sustainability. 2016; 8 :647. [ Google Scholar ]
- Voudrias, E.A., 2018. Healthcare waste management from the point of view of circular economy. [ PubMed ]
- Vousdoukas M.I., Ranasinghe R., Mentaschi L., Plomaritis T.A., Athanasiou P., Luijendijk A., Feyen L. Sandy coastlines under threat of erosion. Nat. Clim. Chang.10. 2020:260–263. [ Google Scholar ]
- Wagner D.M., Klunk J., Harbeck M., Devault A., Waglechner N., Sahl J.W., Enk J., Birdsell D.N., Kuch M., Lumibao C. Yersinia pestis and the Plague of Justinian 541–543 AD: a genomic analysis. Lancet Infect. Dis.14. 2014:319–326. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wang P., Chen K., Zhu S., Wang P., Zhang H. Severe air pollution events not avoided by reduced anthropogenic activities during COVID-19 outbreak. Resour. Conserv. Recycl.158. 2020 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Watts N., Amann M., Arnell N., Ayeb-Karlsson S., Belesova K., Berry H., Bouley T., Boykoff M., Byass P., Cai W. The 2018 report of the Lancet Countdown on health and climate change: shaping the health of nations for centuries to come. The Lancet. 2018; 392 :2479–2514. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Watts N., Amann M., Ayeb-Karlsson S., Belesova K., Bouley T., Boykoff M., Byass P., Cai W., Campbell-Lendrum D., Chambers J. The Lancet Countdown on health and climate change: from 25 years of inaction to a global transformation for public health. The Lancet. 2018; 391 :581–630. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Webster R.G. Predictions for future human influenza pandemics. J. Infect. Dis.176. 1997:S14–S19. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- White D.B., Lo B. A framework for rationing ventilators and critical care beds during the COVID-19 pandemic. JAMA. 2020 [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- WHO . 1998. Safe Management of Wastes from Health-Care Activities. 2014. [ Google Scholar ]
- WHO . World Health Organization; 2020. Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Pandemic. [ Google Scholar ]
- WHO, 2020b. Coronavirus disease (COVID-19): Situation Report – 107, pp. 1-17.
- Williamson J. Every UK manufacturer helping to produce PPE and equipment for NHS workers. The Manufacturer. 2020 [ Google Scholar ]
- Windapo A.O., Moghayedi A. Adoption of smart technologies and circular economy performance of buildings. Built Environ. Project Asset Manag. 2020 [ Google Scholar ]
- Windfeld E.S., Brooks M.S.-L. Medical waste management – A review. J. Environ. Manag.163. 2015:98–108. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wong H.J.Y., Deng Z., Yu H., Huang J., Leung C., Miao C. Proceedings of the Twenty-Ninth International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI-20)Demonstrations Track. 2020. A testbed for studying COVID-19 spreading in ride-sharing systems; pp. 5294–5296. [ Google Scholar ]
- Wong K.-F.V., Narasimhan R., Kashyap R., Fu J. Medical waste characterization. J. Environ. Health. 1994:19–25. [ Google Scholar ]
- World Economic Forum . World Economic Forum; Geneva: 2019. A Vision for a Sustainable Battery Value Chain in 2030: Unlocking the Full Potential to Power Sustainable Development and Climate Change Mitigation; pp. 1–52. [ Google Scholar ]
- World Economic Forum . World Economic Forum; 2020. New Nature Economy Report II: The Future of Nature and Business. [ Google Scholar ]
- Wormer B.A., Augenstein V.A., Carpenter C.L., Burton P.V., Yokeley W.T., Prabhu A.S., Harris B., Norton S., Klima D.A., Lincourt A.E. The green operating room: simple changes to reduce cost and our carbon footprint. Am. Surg.79. 2013:666–671. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wosik J., Fudim M., Cameron B., Gellad Z.F., Cho A., Phinney D., Curtis S., Roman M., Poon E.G., Ferranti J. Telehealth transformation: COVID-19 and the rise of virtual care. J. Am. Med. Inform. Assoc.27. 2020:957–962. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Xiao Y., Torok M.E. Taking the right measures to control COVID-19. The Lancet Infect. Dis.20. 2020:523–524. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Yang C., Peijun L., Lupi C., Yangzhao S., Diandou X., Qian F., Shasha F. Sustainable management measures for healthcare waste in China. Waste Manag. 2009; 29 :1996–2004. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Zambrano-Monserrate M.A., Ruano M.A., Sanchez-Alcalde L. Indirect effects of COVID-19 on the environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2020 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Zambrano-Monserrate M.A., Silva-Zambrano C.A., Ruano M.A. The economic value of natural protected areas in Ecuador: A case of Villamil Beach National Recreation Area. Ocean Coast. Manag.157. 2018:193–202. [ Google Scholar ]
- Zhou M., Chen Y., Su X., An L. Proceedings of the Institution of Civil Engineers-Civil Engineering. Thomas Telford Ltd; 2020. Rapid construction and advanced technology for a Covid-19 field hospital in Wuhan, China; pp. 1–29. [ Google Scholar ]
SouthAsiaSource
August 5, 2022
Bangladesh’s economic crisis: How did we get here?
By Ali Riaz

The International Monetary Fund (IMF)’s willingness to support Bangladesh’s request for a $4.5 billion bailout package over the next three years confirms that the country’s economy is facing a serious crisis.
It is the third country in the region, after Sri Lanka and Pakistan, that knocked on the door of the IMF in recent months. While the economic crises in Pakistan and Sri Lanka were widely reported in international media, Bangladesh’s situation flew under the radar for quite some time thanks to the government’s repeated denial of any impending crisis. Bangladeshi Prime Minister Sheikh Hasina’s government—for years— touted the economic success of the country and recently celebrated the opening of Bangladesh’s largest bridge as a symbol of its self-reliance.
The government claims that its request for “budget support,” an unrestricted loan with low interest which allows it to use the money as it wishes, is a preemptive measure and that the economy is not, in fact, in trouble .
This could not be further from the truth.
Huge financial woes
Dhaka’s search for financial support is not limited to the IMF. Besides requesting from the World Bank a one billion dollar loan, an estimated $2.5-3 billion have been solicited from several multilateral agencies and donor nations (such as the Japan International Cooperation Agency, or JICA) just this year.
Furthermore, considering that ongoing austerity measures including power cuts, restricted use of foreign currency, and fuel rationing are yet to make any major dent in the crisis, the government’s claim—that the country will weather shrinking foreign exchange reserves , a growing trade deficit , record inflation , daily depreciation of the local currency, and an intense energy crisis —is doubtful. As the IMF and other multilateral agencies open their purses to Bangladesh, it is also imperative to understand how the country arrived here.
The journey can tell us where the solution lies
Dhaka would like everyone to believe that the economic slowdown from the COVID-19 pandemic and the global impact of the Ukraine-Russia war are to be blamed for its current plight, but this only tells part of the story. The following statistics paint a far more worrisome picture:
- Bangladesh received at least $1.7 billion in loans from multilateral agencies by June 2020 , and by October 2021 it had borrowed at least three billion dollars from development partners as budget support to combat the adverse impacts of the pandemic.
- It is reported that budget support received from various multilateral agencies between 2019-2020 and 2021-2022 amounted to $5.8 billion.
- Dhaka received $732 million from the IMF as a balance of payment support and $1.4 billion from the World Bank to implement the countrywide vaccination program.
- It obtained sixty-one million doses of COVID-19 vaccines from the United States , free of cost.
- The government also offered various stimulus packages and repeatedly claimed that its economy not only turned around, but was on the road to a dramatic recovery, with such optimism echoed by the World Bank .
This information reveals two things—that the fallout from the pandemic should have been addressed in the past year with significant support from external sources, and that the government has been taking loans in recent years despite claims of robust economic growth.
What, then, prompted Bangladesh’s economic and financial crisis?
External factors notwithstanding, four domestic areas tied to government policies can be identified as sources of the present crisis:
- High cost of infrastructure projects, often described as “mega projects”
- Crisis in the banking sector due to widespread default of loans
- Waste of resources in the energy sector
- Capital flight
Unsustainable infrastructure spending Since coming to power in 2009, the Hasina government has undertaken several large infrastructure projects funded by various countries and multilateral agencies. These projects include the Padma Bridge, a nuclear power plant in Rooppur, Dhaka City Metro Rail, and Karnaphuli Tunnel, to name a few. Padma Bridge, one of the largest projects in the country, cost about $3.6 billion , which was previously estimated to be $1.16 billion in 2007. The ambitious nuclear power plant is costing Bangladesh $12.65 billion, and the actual amount to be spent will not be known until it is commissioned. The Metro Rail project ballooned to $3.3 billion from its original estimate of $2.1 billion. The cost of the underwater Karnaphuli Tunnel reached $1.03 billion, though originally estimated at $803 million.
Unfortunately, these are not exceptions, but patterns . In 2017, the World Bank noted that the cost of road construction in Bangladesh was the highest in the world. The cost overrun is largely because of overpricing of materials, corruption, and long delays.
Loan defaults and banking malpractice In addition, the banking sector, which has been in the news for quite some time, is crippled by large scams and non-performing loans . In 2019, when the Central Bank claimed that the total amount of defaulted loans was $11.11 billion, the IMF disputed this , saying that the true amount is more than double. The current official figure has been questioned by many on several grounds, however.
There is an explanation for this discrepancy —bad loans can be easily manipulated and hidden through write offs and changing the official definition of “bad loans” to skirt regulations.
In simple words, the Central Bank is alleged to have “cooked the books,” both in hopes of providing a rosy but inaccurate picture, as well as to benefit the incumbent and her inner circle. Corruption watchdog Transparency International Bangladesh said that “immense political pressure and illegal intervention by some large business groups” are the causes of an unabated increase in loan defaults.
This is not a new phenomenon, and though experts have been warning of such a situation for years, the Central Bank has not taken effective steps, instead changing policies to help the loan defaulters.
Corruption in the power sector In March 2022, the government celebrated its success in extending electricity coverage to the entire country. This, however, came at a high price.
The associated increase in electricity generation was largely due to the establishment of Quick Rental Power Plants (QRPPs) in the private sector. In 2009, it was said that these units were stopgap measures until a comprehensive, long-term solution was found. Increasingly, though, these units have become the mainstay of electricity generation, and not without suspicious beneficiaries.
In the past decade, the power sector received huge subsidies —between 2010 and 2021, the Power Development Board received $7.1 billion, while the Bangladesh Petroleum Corporation received three billion dollars between 2010 and 2015. Notably, this occurred while the prices of electricity and fuel hiked for consumers. Furthermore, the capacity charge provisions included in the contracts with Independent Power Producers, Rental Power Plants, and QRPPs force the government to pay these companies even when they did not provide any electricity.
These units are owned by companies connected to the government who are milking the system to their benefit. In the past decade, twelve companies received $5.5 billion as capacity charges . Additionally, the government has signed agreements with Indian energy company Adani which would require Bangladesh to pay annually $423.29 million and $11.01 billion over its lifetime of twenty-five years as capacity for its energy supply.
Capital flight In the past decade, as rampant corruption allowed a small group of people to amass large sums of money, Bangladesh witnessed widespread money laundering according to watchdog Global Financial Integrity. Between 2009 and 2018, annually $8.27 billion was siphoned through mis-invoicing of the values of import-export goods. The growth of deposits by Bangladeshis in Swiss banks in the past decade is indicative of capital flight. In 2021, it increased by 55.1 percent, reaching 871 million Francs ($912 million).
In conclusion
While these factors have contributed immensely to the unprecedented crisis Bangladesh is facing, I am neither suggesting that there are no other reasons, nor implying that they are mutually exclusive. Instead, these areas are intrinsically connected to the incumbent’s development policies and ideology. Therefore, Bangladesh’s pathway to the current economic crisis—leading to its arrival at the doorstep of the IMF—did not result solely from the pandemic and the Ukraine crisis. Instead, it was paved by the economic policies of the Hasina government and an unaccountable system of governance of the past decade.
Two consecutive fraudulent national elections, held in 2014 and 2018 , have created a de facto one party system with no checks and balances. As international lenders such as the IMF negotiate more loans for the current government, donors should understand that throwing more money at Dhaka will not bring an end to the crisis.
A bailout will only act as a bandaid. It may stop the bleeding for the moment, but there is no guarantee that it will magically solve the crisis without reforming an economic system tied deeply to the regime’s self-interested political vision.
Dr. Ali Riaz is a non-resident senior fellow with the Atlantic Council’s South Asia Center.

The South Asia Center is the hub for the Atlantic Council’s analysis of the political, social, geographical, and cultural diversity of the region. At the intersection of South Asia and its geopolitics, SAC cultivates dialogue to shape policy and forge ties between the region and the global community.
Related content

SouthAsiaSource Jul 6, 2022
Myanmar’s ‘Rohingya Genocide’: A conversation with Ronan Lee
By Atlantic Council
An interview between Rudabeh Shahid and Ronan Lee to discuss the difficulties in conducting the study and current book ban in Myanmar, post-coup Rohingya conditions, and wider repercussions for the South Asian region.

SouthAsiaSource May 12, 2022
Rising sea levels and the climate crisis in Bangladesh, the Maldives, and Sri Lanka
By South Asia Center
The South Asia Center brings together a panel of experts to discuss the effects of climate change on the economy, food and energy security, and migration in Bangladesh, the Maldives, and Sri Lanka.

SouthAsiaSource Feb 15, 2022
Revitalizing Pakistan-Bangladesh trade cooperation in pursuit of a free trade agreement
By Nida Gulzar
The expansion of cooperation and economic exchanges between Pakistan and Bangladesh is attainable if stakeholders from both sides work together.
Related Experts: Ali Riaz
Image: People buy handbags from a street vendor at the New Market area in Dhaka, Bangladesh January 24, 2021. REUTERS/Mohammad Ponir Hossain

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like According to this graph, US economic production increased from ______. Economic production is one indicator of economic depression. According to the graph, the depression began in __________, The withered leaves of industrial enterprise lie on every side; farmers find no markets for their produce; the savings of many years in ...
To pay reparations after World War I, Germany. printed more money. Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like US President Franklin D. Roosevelt was elected on his promise to improve economic conditions in America. In his first inaugural address, which he gave the day he came into office, he discussed the economic crisis.
Quizlet has study tools to help you learn anything. ... practice tests and expert-written solutions today. Flashcards. 1 / 17 Global Economic Crisis Assignment and Quiz. ... According to this graph, US economic production increased from _____. Economic production is one indicator of economic depression. According to the graph, the depression ...
US President Franklin D. Roosevelt was elected on his promise to improve economic conditions in America. In his first inaugural address, which he gave the day he came into office, he discussed the economic crisis. Which economic problems does President Roosevelt mention in this excerpt? Check all that apply.
The 2007-2008 financial crisis, or the global financial crisis ( GFC ), was the most severe worldwide economic crisis since the Great Depression. Predatory lending in the form of subprime mortgages targeting low-income homebuyers, [1] excessive risk-taking by global financial institutions, [2] a continuous buildup of toxic assets within banks ...
This is because banking or financial failures in one country will lead to crises in other countries, and thus will become internationalized rather than remaining isolated. This was the case with the Great Recession of 2008-2009, during which the financial crisis in the US subprime mortgage market led to a global economic meltdown. 5
WDR 2022 Chapter 1. Introduction. Chapter 1. The economic impacts of the COVID-19 crisis. The COVID-19 pandemic sent shock waves through the world economy and triggered the largest global economic crisis in more than a century. The crisis led to a dramatic increase in inequality within and across countries. Preliminary evidence suggests that ...
The 2007-2008 financial crisis was a global event, not one restricted to the U.S. Ireland 's vibrant economy fell off a cliff. Greece defaulted on its international debts. Portugal and Spain ...
Capitalism in crisis. On the morning of Thursday, October 24th, 1929 the New York stock market began a crash that would last four days. The fallout of that crash would last a decade. It started in the United States, but the Great Depression was an unprecedented, worldwide economic collapse. The ripple effects of "Black Thursday" would be ...
Great Depression. : The Great Depression was a severe worldwide economic depression that took place mostly during the 1930s. It began in the United States after a major fall in stock prices around September 29, 1929 (known as Black Tuesday), and became worldwide news with the stock market crash.
2. Conflict and Poverty. Lael Brainard, Derek Chollet, Jane Nelson, Ngozi Okonjo-Iweala, and Susan Rice. In a world where boundaries and borders have blurred, and where seemingly distant threats ...
The economic profession was taken by surprise as a seemingly negligible turmoil, in what was considered to be a rather remote segment of the US mortgage market, turned into a global financial and economic crisis from 2007 to 2008. The serious repercussions triggered by these events are still felt today. As a result, the crisis will likely ...
Finance & the Economy. Household Finance Parlay your profile into profits. Investing Putting the client's interest first at all times. Investing Don't be the greater fool. Investing Today's technology is always so yesterday. Investing Putting stock in bonds. Investing Fixed income; flexible choices.
The World Economic Outlook Update July 2022: Gloomy and More Uncertain, highlights the significant consequences of the stalling of the world's three main economic powerhouses - the United States, China and the major European economies. The world may soon be teetering on the edge of a global recession - IMF economist "The outlook has darkened significantly since April," said Pierre ...
Global Financial Crisis . by Marc Dobler, Simon Gray, Diarmuid Murphy, and . Bozena Radzewicz-Bak . IMF Working Papers describe research in progress by the author(s) and are published to elicit comments and to encourage debate. The views expressed in IMF Working Papers are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily represent the views of the ...
The pandemic is expected to plunge most countries into recession in 2020, with per capita income contracting in the largest fraction of countries globally since 1870. Advanced economies are projected to shrink 7 percent. That weakness will spill over to the outlook for emerging market and developing economies, who are forecast to contract by 2. ...
In its April World Economic Outlook, IMF (2020)reversed its early global economic growth forecast from 3.3% to -3 %, an unusual downgrade of 6.3% within three months. This makes the pandemic a global economic shock like no other since the Great Depression and it has already surpassed the global financial crisis of 2009 as depicted in Fig. 4.
Our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy-to-learn solution you can count on. Question: Which of the following variables were present in both the global financial crisis of 2008-2009 and the global economic crisis of 2020-2021? US exports exceeding imports A higher valued US dollar Increases in world trade A pandemic.
The International Monetary Fund (IMF)'s willingness to support Bangladesh's request for a $4.5 billion bailout package over the next three years confirms that the country's economy is facing a serious crisis.. It is the third country in the region, after Sri Lanka and Pakistan, that knocked on the door of the IMF in recent months. While the economic crises in Pakistan and Sri Lanka were ...