

225+ Action Research Topics In Education (Updated 2023)
Action research in education offers a powerful tool for educators to actively engage in improving their teaching practices and student outcomes. By combining research and action, this approach encourages teachers to become reflective practitioners and agents of change within their classrooms and schools. Action research topics in education encompass a wide range of issues that educators can investigate to address specific challenges and enhance their instructional strategies.
From examining the impact of technology integration to exploring innovative assessment methods, action research empowers teachers to develop evidence-based solutions tailored to their unique educational contexts. By conducting small-scale studies, educators can gather data, analyze it, and implement targeted interventions to make tangible improvements in student learning.
In this blog, we will delve into a variety of action research topics in education, exploring how they can empower educators to drive meaningful change and foster a dynamic and effective learning environment for their students.
Table of Contents
Format of action research paper in education

Please note that this table provides a general outline and can be customized based on the specific requirements and guidelines of your research paper.
| 300+ For College Students (Updated 2023) |
What to consider while selecting action research topics in education
When selecting action research topics in education, it is important to consider several factors to ensure that your research is meaningful, relevant, and feasible. Here are some key considerations to keep in mind:
Personal Interest
Choose action research topics in education that genuinely interests you. When you are passionate about the subject matter, you will be more motivated and engaged throughout the research process.
Educational Context
Consider the specific educational context in which you work or are interested in. Reflect on the challenges, needs, or areas of improvement within that context. Your research should address a problem or issue that is relevant and impactful within the educational setting.
Research Gap
Review existing literature and research in your chosen area to identify any gaps or unanswered questions. Select action research topics in education that contributes to the existing knowledge base and fills a research gap.
Feasibility
Evaluate the feasibility of conducting the research within the available resources, time frame, and constraints. Consider factors such as access to participants, data collection methods, ethical considerations, and potential support from colleagues or institutions.
Relevance and Impact
Choose action research topics in education that have practical implications and can lead to positive changes in teaching practices, student learning, or educational policies. Aim for research that can make a difference in the educational field.
Collaboration Opportunities
Consider if there are opportunities for collaboration with colleagues, researchers, or educational organizations. Collaborative research can provide additional support, expertise, and diverse perspectives.
Ethical Considerations
Ensure that your research topic aligns with ethical guidelines and regulations. Consider the potential impact on participants and ensure their rights, privacy, and confidentiality are protected.
Remember, selecting an action research topic is an important decision, so take the time to thoroughly evaluate and choose a topic that aligns with your goals and the needs of the educational community you serve.
200+ Action research topics in education
- The impact of technology integration on student engagement in the classroom.
- Strategies to improve reading comprehension in elementary school students.
- Enhancing parental involvement in student learning and academic success.
- Investigating the effectiveness of cooperative learning strategies in promoting peer interaction and collaboration.
- Addressing the achievement gap in mathematics between different student groups.
- Examining the impact of inclusive education on the academic and social development of students with disabilities.
- Enhancing critical thinking skills through project-based learning.
- Implementing differentiated instruction to meet the diverse needs of students in the classroom.
- Investigating the effects of homework on student learning and academic performance.
- Promoting positive classroom behavior and reducing disruptive behaviors.
- Assessing the effectiveness of teacher feedback in improving student writing skills.
- Strategies to promote a growth mindset and enhance student motivation.
- Examining the impact of physical activity on student concentration and academic performance.
- Enhancing teacher-student relationships and its impact on student engagement and achievement.
- Investigating the effects of arts integration on student creativity and academic achievement.
- Strategies to support English language learners in mainstream classrooms.
- Examining the impact of peer tutoring on student learning and academic achievement.
- Enhancing teacher collaboration and its impact on instructional practices and student outcomes.
- Investigating the effectiveness of inquiry-based science instruction in promoting student understanding.
- Promoting gender equity in STEM education.
- Examining the impact of mindfulness practices on student well-being and academic success.
- Strategies for reducing test anxiety and promoting test-taking skills.
- Investigating the effects of the classroom environment on student learning and engagement.
- Enhancing student self-regulation skills through metacognitive strategies.
- Promoting multicultural education and inclusivity in the classroom.
- Examining the impact of flipped classroom models on student learning outcomes.
- Strategies for integrating technology effectively in early childhood education.
- Investigating the effects of outdoor education on student engagement and academic achievement.
- Enhancing teacher professional development programs to improve instructional practices.
- Promoting environmental education and sustainable practices in schools.
- Examining the impact of social-emotional learning programs on student behavior and well-being.
- Strategies for supporting students with ADHD in the classroom.
- Investigating the effects of classroom management strategies on student behavior and academic performance.
- Enhancing parental involvement in early childhood education settings.
- Promoting digital literacy skills among students.
- Examining the impact of peer assessment on student learning and achievement.
- Strategies for fostering creativity and innovation in the classroom.
- Investigating the effects of inclusive literature on promoting empathy and cultural understanding.
- Enhancing the use of formative assessment in the classroom.
- Promoting critical media literacy skills among students.
- Examining the impact of outdoor learning on student engagement and academic achievement.
- Strategies for promoting positive social skills and reducing bullying in schools.
- Investigating the effects of flexible seating arrangements on student behavior and learning outcomes.
- Enhancing the use of educational technology in special education settings.
- Promoting student self-efficacy and academic motivation.
- Examining the impact of project-based learning on student problem-solving skills.
- Strategies for promoting positive school climate and student well-being.
- Investigating the effects of parental involvement on student homework completion and academic performance.
- Enhancing teacher feedback practices to improve student learning and achievement.
- Promoting inclusive practices for students with diverse cultural backgrounds.
- Examining the impact of arts education on student creativity and academic success.
- Strategies for supporting students with learning disabilities
- Investigating the effects of gamification on student motivation and engagement.
- Enhancing collaborative learning in online education settings.
- Promoting effective study habits and time management skills among students.
- Examining the impact of parental involvement on early literacy skills development.
- Strategies for promoting positive teacher-student relationships in high school settings.
- Investigating the effects of mindfulness practices on reducing stress and anxiety in students.
- Enhancing student self-esteem and self-confidence through targeted interventions.
- Promoting gender equality in science education.
- Examining the impact of teacher-led professional learning communities on instructional practices and student outcomes.
- Strategies for supporting students with autism spectrum disorder in inclusive classrooms.
- Investigating the effects of project-based learning on student problem-solving skills in mathematics.
- Enhancing cultural competency among educators to meet the needs of diverse student populations.
- Promoting digital citizenship and online safety education.
- Examining the impact of restorative justice practices on reducing disciplinary incidents and promoting a positive school climate.
- Strategies for integrating social justice education across the curriculum.
- Investigating the effects of parental involvement on student transitions from elementary to middle school.
- Enhancing teacher collaboration for effective interdisciplinary instruction.
- Promoting global citizenship and cross-cultural understanding in the classroom.
- Examining the impact of music education on student cognitive development and academic performance.
- Strategies for supporting students with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in mainstream classrooms.
- Investigating the effects of cooperative learning strategies on improving students’ social skills.
- Enhancing the use of educational technology for students with visual impairments.
- Promoting inclusive practices for students with diverse learning needs.
- Examining the impact of teacher-led professional development on instructional practices and student outcomes.
- Strategies for promoting positive classroom behavior in early childhood settings.
- Investigating the effects of growth mindset interventions on student resilience and academic achievement.
- Enhancing parent-teacher communication for improved student support and academic success.
- Promoting environmental sustainability education in primary schools.
- Examining the impact of outdoor play on children’s physical and cognitive development.
- Strategies for supporting students with English language learning difficulties.
- Investigating the effects of mindfulness practices on reducing test anxiety in students.
- Enhancing the use of educational technology for students with learning disabilities.
- Promoting critical thinking and problem-solving skills in mathematics education.
- Examining the impact of peer mentoring programs on student academic and social-emotional development.
- Strategies for creating inclusive classrooms for students with hearing impairments.
- Investigating the effects of student-led conferences on student ownership of learning.
- Enhancing the use of formative assessment for personalized instruction.
- Promoting positive classroom discourse and student participation.
- Examining the impact of outdoor experiential learning on student environmental awareness and action.
- Strategies for supporting students with emotional and behavioral disorders in inclusive settings.
- Investigating the effects of teacher self-reflection on instructional practices and student outcomes.
- Enhancing the use of assistive technology for students with physical disabilities.
- Promoting media literacy education to develop critical media consumers.
- Examining the impact of service-learning on student civic engagement and social responsibility.
- Strategies for creating inclusive classrooms for students with specific learning disabilities.
- Investigating the effects of inquiry-based science instruction on student scientific inquiry skills.
- Enhancing teacher-parent partnerships for collaborative support of student learning.
- Promoting cultural diversity education in secondary schools.
- Examining the impact of cooperative learning on student academic achievement in science education.
- Strategies for promoting inclusive practices for students with speech and language disorders.
- Investigating the effects of flipped classroom models on student engagement and learning outcomes in social studies.
- Enhancing teacher feedback practices to improve student writing skills in English language arts.
- Promoting social-emotional learning through mindfulness-based interventions in elementary schools.
- Examining the impact of project-based learning on student creativity and problem-solving skills in the arts.
- Strategies for supporting students with executive functioning difficulties in the classroom.
- Investigating the effects of differentiated instruction on student motivation and academic achievement in mathematics.
- Enhancing parental involvement in supporting early literacy development at home.
- Promoting inclusive practices for students with physical disabilities in physical education classes.
- Examining the impact of teacher-student relationships on student attendance and classroom behavior.
- Strategies for promoting positive peer relationships and reducing social isolation in middle school.
- Investigating the effects of drama-based pedagogy on student engagement and understanding in literature studies.
- Enhancing the use of educational technology for students with learning difficulties in computer science education.
- Promoting character education and ethical decision-making in schools.
- Examining the impact of teacher self-efficacy on instructional practices and student outcomes.
- Strategies for supporting students with English language learning difficulties in content area classes.
- Investigating the effects of arts integration on student motivation and academic achievement in history education.
- Enhancing family-school partnerships for students with special educational needs.
- Promoting critical digital literacy skills for responsible online information consumption.
- Examining the impact of inclusive physical education on student attitudes towards fitness and physical activity.
- Strategies for supporting students with dyslexia in reading instruction.
- Investigating the effects of outdoor education on student environmental attitudes and behaviors.
- Enhancing the use of educational technology for students with autism spectrum disorder.
- Promoting career readiness and employability skills in high school education.
- Examining the impact of parent-led reading interventions on early literacy skills in kindergarten.
- Strategies for promoting positive teacher-student relationships in online learning environments.
- Investigating the effects of arts integration on student creativity and academic achievement in science education.
- Enhancing teacher collaboration for effective co-teaching in inclusive classrooms.
- Promoting global perspectives and intercultural understanding in social studies education.
- Examining the impact of cooperative learning on student social skills and peer relationships.
- Strategies for supporting students with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in physical education classes.
- Investigating the effects of project-based learning on student problem-solving skills in computer science.
- Enhancing cultural competence among educators for working with diverse student populations.
- Promoting digital citizenship and online safety in digital media literacy education.
- Examining the impact of restorative practices on reducing disciplinary incidents and fostering a positive school climate.
- Strategies for supporting students with emotional and behavioral challenges in mainstream classrooms.
- Investigating the effects of growth mindset interventions on student academic resilience in mathematics education.
- Enhancing parent-teacher communication for effective student support and academic success.
- Promoting environmental sustainability education in secondary schools.
- Examining the impact of outdoor experiential learning on student STEM (science, technology, engineering, and mathematics) interest and career aspirations.
- Strategies for creating inclusive classrooms for students with visual impairments.
- Investigating the effects of student-led conferences on student self-evaluation and goal setting.
- Enhancing the use of formative assessment for personalized instruction in physical education.
- Promoting positive classroom management strategies.
- Examining the impact of cooperative learning on student academic achievement in foreign language education.
- Strategies for promoting inclusive practices for students with autism spectrum disorder in inclusive classrooms.
- Investigating the effects of blended learning models on student engagement and learning outcomes in mathematics.
- Enhancing teacher feedback practices to improve student oral communication skills in language arts.
- Promoting social-emotional learning through mindfulness-based interventions in high schools.
- Examining the impact of project-based learning on student creativity and problem-solving skills in technology education.
- Strategies for supporting students with learning difficulties in inclusive science classrooms.
- Investigating the effects of differentiated instruction on student motivation and academic achievement in social studies.
- Enhancing parental involvement in supporting numeracy development at home.
- Promoting inclusive practices for students with sensory impairments in inclusive classrooms.
- Examining the impact of teacher-student relationships on student motivation and academic achievement in physical education.
- Strategies for promoting positive peer relationships and reducing bullying in high schools.
- Investigating the effects of arts integration on student motivation and academic achievement in mathematics education.
- Enhancing the use of educational technology for students with learning difficulties in science education.
- Promoting character education and ethical decision-making in elementary schools.
- Examining the impact of teacher self-efficacy on instructional practices and student outcomes in music education.
- Strategies for supporting students with English language learning difficulties in mathematics classes.
- Investigating the effects of arts integration on student creativity and academic achievement in social-emotional learning.
- Enhancing family-school partnerships for students with special educational needs in inclusive settings.
- Promoting critical digital literacy skills for responsible online communication in language arts education.
- Examining the impact of inclusive physical education on student attitudes towards physical fitness and well-being.
- Strategies for supporting students with dyscalculia in mathematics instruction.
- Investigating the effects of outdoor education on student environmental knowledge and sustainability practices.
- Enhancing the use of educational technology for students with hearing impairments in inclusive classrooms.
- Promoting career exploration and development in middle school education.
- Examining the impact of parent-led science experiments on student interest and learning outcomes in science education.
- Strategies for promoting positive teacher-student relationships in virtual learning environments.
- Investigating the effects of arts integration on student creativity and academic achievement in language arts.
- Enhancing teacher collaboration for effective co-planning and instructional delivery in inclusive classrooms.
- Promoting global citizenship and cultural competence in foreign language education.
- Examining the impact of cooperative learning on student social-emotional development and well-being.
- Strategies for supporting students with physical disabilities in adaptive physical education classes.
- Investigating the effects of project-based learning on student problem-solving skills in engineering education.
- Enhancing cultural competence among educators for working with diverse student populations in social studies.
- Promoting digital literacy skills for responsible online research and information evaluation.
- Examining the impact of restorative practices on reducing conflicts and promoting positive relationships in middle schools.
- Strategies for supporting students with emotional and behavioral challenges in inclusive classrooms.
- Investigating the effects of growth mindset interventions on student academic resilience in language arts.
- Enhancing parent-teacher communication for effective collaboration and student support in mathematics education.
- Promoting environmental sustainability education in primary schools through cross-curricular integration.
- Examining the impact of outdoor experiential learning on student ecological literacy and environmental stewardship.
- Strategies for creating inclusive classrooms for students with cognitive impairments.
- Investigating the effects of student-led conferences on student self-reflection and goal-setting in science education.
- Enhancing the use of formative assessment for personalized instruction in social studies.
- Promoting positive classroom management strategies for students with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).
- Examining the impact of cooperative learning on student academic achievement in physical sciences.
- Strategies for promoting inclusive practices for students with speech and language difficulties in inclusive classrooms.
- Investigating the effects of blended learning models on student engagement and learning outcomes in language arts.
- Enhancing teacher feedback practices to improve student presentation skills in communication studies.
- Promoting social-emotional learning through mindfulness-based interventions in middle schools.
- Examining the impact of project-based learning on student creativity and problem-solving skills in fine arts.
- Strategies for supporting students with learning difficulties in inclusive social-emotional learning programs.
- Investigating the effects of differentiated instruction on student motivation and academic achievement in physical education.
- Enhancing parental involvement in supporting STEM (science, technology, engineering, and mathematics) education at home.
- Promoting inclusive practices for students with intellectual disabilities in inclusive classrooms.
- Examining the impact of teacher-student relationships on student motivation and academic achievement in music education.
- Strategies for promoting positive peer relationships and fostering social-emotional development in high schools.
- Investigating the effects of arts integration on student motivation and academic achievement in physical sciences.
- Enhancing the use of educational technology for students with learning difficulties in social studies education.
- Promoting character education and ethical decision-making in secondary schools.
- Examining the impact of teacher self-efficacy on instructional practices and student outcomes in physical education.
- Strategies for supporting students with English language learning difficulties in science classes.
- Investigating the effects of arts integration on student creativity and academic achievement in physical education.
- Enhancing family-school partnerships for students with special educational needs in inclusive physical education settings.
- Promoting critical digital literacy skills for responsible online communication in social studies education.
- Strategies for supporting students with dysgraphia in writing instruction.
- Investigating the effects of outdoor education on student environmental knowledge and sustainable practices in science education.
- Enhancing the use of educational technology for students with visual impairments in inclusive classrooms.
- Promoting career exploration and development in high school education.
- Examining the impact of parent-led math activities on student interest and learning outcomes in mathematics education.
- Investigating the effects of arts integration on student creativity and academic achievement in social sciences.
- Enhancing teacher collaboration for effective co-planning and instructional delivery in inclusive physical education settings.
- Promoting global citizenship and cultural competence in history education.
- Examining the impact of cooperative learning on student social-emotional development and well-being in language arts.
- Strategies for supporting students with physical disabilities in inclusive arts education classes.
- Investigating the effects of project-based learning on student problem-solving skills in computer programming education.
- Enhancing cultural competence among educators for working with diverse student populations in mathematics education.
- Promoting digital literacy skills for responsible online communication and information sharing.
- Examining the impact of restorative practices on reducing conflicts and promoting positive relationships in high schools.
- Strategies for supporting students with emotional and behavioral challenges in inclusive language arts classrooms.
- Investigating the effects of growth mindset interventions on student academic resilience in social sciences.
- Enhancing parent-teacher communication for effective collaboration and student support in science education.
- Promoting environmental sustainability education in elementary schools through interdisciplinary integration.
Tips to write appealing action research paper in education
Here are some tips to write an appealing action research paper in education:
- Select a Relevant and Engaging Topic: Choose action research topics in education that is relevant to the field of education and aligns with your interests and goals. Select a topic that has practical implications and can contribute to improving educational practices.
- Clearly Define the Problem: Clearly define the problem or issue you want to address through your action research. Provide a concise and focused problem statement that highlights the specific area you aim to investigate.
- Set Clear Objectives: State clear and measurable objectives for your research. Identify what you want to achieve through your study and how you plan to measure your outcomes.
- Conduct a Literature Review: Conduct a thorough review of existing literature related to your research topic. Identify gaps in current knowledge and highlight how your research will contribute to filling those gaps.
- Use a Rigorous Research Design: Choose an appropriate research design that aligns with your research objectives. Consider whether a quantitative, qualitative, or mixed-methods approach is most suitable for your study.
- Collect and Analyze Data: Collect relevant data through appropriate methods, such as surveys, interviews, observations, or document analysis. Use rigorous data analysis techniques to derive meaningful findings from your data.
- Reflect and Take Action: Reflect on your findings and consider their implications for educational practice. Based on your findings, develop actionable recommendations or interventions that can be implemented to address the identified problem.
- Write Clearly and Concisely: Present your research in a clear and concise manner. Use appropriate academic language and structure your paper logically. Clearly explain your methodology, findings, and conclusions.
- Support Findings with Evidence: Use evidence from your data analysis to support your findings and conclusions. Use graphs, charts, or quotes from participants to enhance the credibility of your research.
- Discuss Limitations and Future Directions: Acknowledge the limitations of your study and discuss areas for future research. Address any potential biases or challenges that may have influenced your findings.
- Consider the Audience: Keep in mind the intended audience for your research paper, which may include educators, researchers, or policymakers. Write in a way that engages and appeals to your target audience.
- Revise and Edit: Proofread your paper for any grammatical or spelling errors. Revise your content to ensure clarity and coherence. Seek feedback from peers or mentors to improve the quality of your paper.
Remember, an appealing action research paper in education is one that not only presents valuable findings but also offers practical insights and recommendations for improving educational practices.
In conclusion, action research topics in education provide a powerful framework for addressing real-world issues and improving teaching and learning practices. This research approach empowers educators to take an active role in identifying challenges, implementing interventions, and evaluating their impact within their own classrooms or educational settings.
By engaging in systematic inquiry, educators can generate valuable insights, evidence-based strategies, and meaningful changes that positively influence student outcomes. Action research promotes a reflective and collaborative approach, encouraging teachers to continuously refine their instructional methods, adapt to diverse student needs, and create inclusive learning environments.
Ultimately, action research in education empowers educators to be agents of change, fostering innovation and improvement in education while enhancing student engagement, achievement, and well-being.
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
200+ List of Topics for Action Research in the Classroom

In the dynamic landscape of education, teachers are continually seeking innovative ways to enhance their teaching practices and improve student outcomes. Action research in the classroom is a powerful tool that allows educators to investigate and address specific challenges, leading to positive changes in teaching methods and learning experiences.
Selecting the right topics from the list of topics for action research in the classroom is crucial for ensuring meaningful insights and improvements. In this blog post, we will explore the significance of action research in the classroom, the criteria for selecting impactful topics, and provide an extensive list of potential research areas.
Understanding: What is Action Research
Table of Contents
Action research is a reflective process that empowers teachers to systematically investigate and analyze their own teaching practices. Unlike traditional research, action research is conducted by educators within their own classrooms, emphasizing a collaborative and participatory approach.
This method enables teachers to identify challenges, implement interventions, and assess the effectiveness of their actions.
How to Select Topics From List of Topics for Action Research in the Classroom
Choosing the right topic is the first step in the action research process. The selected topic should align with classroom goals, address students’ needs, be feasible to implement, and have the potential for positive impact. Teachers should consider the following criteria when selecting action research topics:
- Alignment with Classroom Goals and Objectives: The chosen topic should directly contribute to the overall goals and objectives of the classroom. Whether it’s improving student engagement, enhancing learning outcomes, or fostering a positive classroom environment, the topic should align with the broader educational context.
- Relevance to Students’ Needs and Challenges: Effective action research addresses the specific needs and challenges faced by students. Teachers should identify areas where students may be struggling or where improvement is needed, ensuring that the research directly impacts the learning experiences of the students.
- Feasibility and Practicality: The feasibility of the research is crucial. Teachers must choose topics that are practical to implement within the constraints of the classroom setting. This includes considering available resources, time constraints, and the level of support from school administrators.
- Potential for Positive Impact: The ultimate goal of action research is to bring about positive change. Teachers should carefully assess the potential impact of their research, aiming for improvements in teaching methods, student performance, or overall classroom dynamics.
List of Topics for Action Research in the Classroom
- Impact of Mindfulness Practices on Student Focus
- The Effectiveness of Peer Tutoring in Mathematics
- Strategies for Encouraging Critical Thinking in History Classes
- Using Gamification to Enhance Learning in Science
- Investigating the Impact of Flexible Seating Arrangements
- Assessing the Benefits of Project-Based Learning in Language Arts
- The Influence of Classroom Decor on Student Motivation
- Examining the Use of Learning Stations for Differentiation
- Implementing Reflective Journals to Enhance Writing Skills
- Exploring the Impact of Flipped Classroom Models
- Analyzing the Effects of Homework on Student Performance
- The Role of Positive Reinforcement in Classroom Behavior
- Investigating the Impact of Classroom Libraries on Reading Proficiency
- Strategies for Fostering a Growth Mindset in Students
- Assessing the Benefits of Cross-Curricular Integration
- Using Technology to Enhance Vocabulary Acquisition
- The Impact of Outdoor Learning on Student Engagement
- Investigating the Relationship Between Attendance and Academic Success
- The Role of Parental Involvement in Homework Completion
- Assessing the Impact of Classroom Rituals on Community Building
- Strategies for Increasing Student Participation in Discussions
- Exploring the Influence of Classroom Lighting on Student Alertness
- Investigating the Impact of Daily Agendas on Time Management
- The Effectiveness of Socratic Seminars in Social Studies
- Analyzing the Use of Graphic Organizers for Concept Mapping
- Implementing Student-Led Conferences for Goal Setting
- Examining the Effects of Mind Mapping on Information Retention
- The Influence of Classroom Temperature on Academic Performance
- Investigating the Benefits of Cooperative Learning Strategies
- Strategies for Addressing Test Anxiety in Students
- Assessing the Impact of Positive Affirmations on Student Confidence
- The Use of Literature Circles to Enhance Reading Comprehension
- Exploring the Effects of Classroom Noise Levels on Concentration
- Investigating the Benefits of Cross-Grade Collaborations
- Analyzing the Impact of Goal Setting on Student Achievement
- Implementing Interactive Notebooks for Conceptual Understanding
- The Effectiveness of Response to Intervention (RTI) Programs
- Strategies for Integrating Social-Emotional Learning (SEL)
- Investigating the Impact of Classroom Discussions on Critical Thinking
- The Role of Brain Breaks in Enhancing Student Focus
- Assessing the Benefits of Inquiry-Based Learning in Science
- Exploring the Effects of Music on Studying and Retention
- Investigating the Use of Learning Contracts for Individualized Learning
- The Influence of Classroom Colors on Mood and Learning
- Strategies for Promoting Collaborative Problem-Solving
- Analyzing the Impact of Flexible Scheduling on Student Productivity
- The Effectiveness of Mindful Breathing Exercises on Stress Reduction
- Investigating the Benefits of Service Learning Projects
- The Role of Peer Assessment in Improving Writing Skills
- Exploring the Impact of Field Trips on Cultural Competency
- Assessing the Benefits of Personalized Learning Plans
- Strategies for Differentiating Instruction in Large Classrooms
- Investigating the Influence of Teacher-Student Relationships on Learning
- The Effectiveness of Vocabulary Games in Foreign Language Classes
- Analyzing the Impact of Classroom Discussions on Civic Engagement
- Implementing Goal-Setting Strategies for Test Preparation
- The Role of Classroom Celebrations in Building a Positive Environment
- Strategies for Enhancing Student Reflection and Metacognition
- Investigating the Effects of Positive Behavior Supports (PBS)
- The Influence of Classroom Humor on Student Engagement
- Assessing the Benefits of Student-Led Research Projects
- Exploring the Impact of Timed vs. Untimed Tests on Anxiety
- Investigating the Use of Educational Podcasts for Learning
- The Effectiveness of Debate Activities in Developing Persuasive Skills
- Analyzing the Impact of Mindful Walking Breaks on Concentration
- Strategies for Promoting Digital Citizenship in the Classroom
- The Role of Visualization Techniques in Mathematics Learning
- Assessing the Benefits of Classroom Agreements for Behavior
- Exploring the Effects of Goal-Setting in Physical Education
- Investigating the Influence of Classroom Seating Charts on Behavior
- The Effectiveness of Peer Editing in Improving Writing Skills
- Strategies for Integrating Cultural Competency in History Lessons
- Analyzing the Impact of Classroom Pets on Student Well-Being
- The Role of Morning Meetings in Building Classroom Community
- Investigating the Benefits of Using Learning Centers in Elementary Schools
- Exploring the Effects of Virtual Reality in Geography Education
- Assessing the Impact of Homework Choice on Student Motivation
- Strategies for Promoting Growth Mindset in Mathematics
- The Influence of Classroom Layout on Group Collaboration
- Investigating the Benefits of Mindful Listening Practices
- The Effectiveness of Using Real-World Examples in Science Lessons
- Analyzing the Impact of Student-Led Assessments on Accountability
- Exploring the Use of Learning Contracts for Student Responsibility
- Investigating the Benefits of Teaching Digital Literacy Skills
- Strategies for Implementing Peer Mentoring Programs
- The Role of Graphic Novels in Promoting Literacy
- Assessing the Impact of Flexible Grouping in Mathematics Classes
- The Effectiveness of Using Storytelling for Conceptual Understanding
- Investigating the Influence of Classroom Rituals on Attendance
- Exploring the Benefits of Mindfulness Practices in Physical Education
- Strategies for Integrating Social Justice Education in the Curriculum
- Analyzing the Impact of Goal-Setting on Homework Completion
- The Role of Classroom Mindfulness Activities in Stress Reduction
- Investigating the Benefits of Using Educational Apps for Vocabulary
- The Effectiveness of Using Drama in History Lessons
- Assessing the Impact of Classroom Routines on Time Management
- Exploring the Influence of Teacher-Student Rapport on Academic Achievement
- Strategies for Promoting Active Listening Skills in the Classroom
- Investigating the Benefits of Using Concept Mapping in Science
- The Role of Classroom Socratic Seminars in Developing Critical Thinking
- Assessing the Impact of Mindful Eating Practices on Student Focus
- Exploring the Effects of Flipped Learning in Physical Education
- Investigating the Benefits of Using Educational Games for Math Fluency
- The Effectiveness of Peer Assessment in Art Classes
- Strategies for Fostering Creativity in Science Education
- Analyzing the Impact of Morning Stretches on Student Alertness
- The Role of Classroom Discussions in Enhancing Social Studies Learning
- Investigating the Benefits of Using Augmented Reality in History Lessons
- Assessing the Impact of Growth Mindset Interventions on Test Anxiety
- Strategies for Incorporating Environmental Education in the Curriculum
- The Effectiveness of Using Conceptual Maps in Literature Analysis
- Exploring the Influence of Classroom Lighting on Reading Comprehension
- Investigating the Benefits of Using Learning Apps for Language Acquisition
- The Role of Classroom Experiments in Science Education
- Analyzing the Impact of Mindful Breathing Exercises on Test Performance
- Strategies for Promoting Collaborative Problem-Solving in Mathematics
- Assessing the Benefits of Mindfulness Practices in Physical Education
- Exploring the Effects of Flexible Seating on Student Collaboration
- Investigating the Influence of Homework Choice on Student Motivation
- The Effectiveness of Using Educational Podcasts for History Learning
- Strategies for Integrating Sustainability Education Across Subjects
- Analyzing the Impact of Mindful Writing Practices on Language Arts Skills
- The Role of Peer Teaching in Enhancing Understanding of Complex Concepts
- Investigating the Benefits of Using Digital Storytelling in Literature Classes
- The Effectiveness of Inquiry-Based Learning in Social Studies
- Assessing the Impact of Student-Led Book Clubs on Reading Engagement
- Strategies for Incorporating Financial Literacy in Mathematics Education
- Exploring the Influence of Classroom Decor on Science Interest
- Investigating the Benefits of Mindful Movement Breaks in the Classroom
- The Role of Reflection Journals in Developing Critical Thinking Skills
- Analyzing the Impact of Virtual Field Trips on Geography Learning
- Strategies for Promoting Inclusive Physical Education Practices
- Assessing the Benefits of Using Educational Board Games for Learning
- The Effectiveness of Mindfulness Practices in Foreign Language Classes
- Investigating the Influence of Classroom Rituals on Academic Rigor
- Exploring the Impact of Student-Led Conferences on Goal Setting
- The Role of Mindful Listening Practices in Improving Communication Skills
- Investigating the Benefits of Using Educational Apps for Science Exploration
- Analyzing the Effectiveness of Socratic Seminars in Philosophy Classes
- Strategies for Promoting Gender Equity in STEM Education
- Assessing the Impact of Classroom Celebrations on Student Well-Being
- The Effectiveness of Using Debate Activities in Language Arts
- Exploring the Influence of Positive Affirmations on Classroom Climate
- Investigating the Benefits of Using Concept Mapping in History Essays
- Strategies for Incorporating Media Literacy in Social Studies
- Analyzing the Impact of Mindful Reflection Practices on Homework Completion
- The Role of Peer Collaboration in Enhancing Artistic Skills
- Investigating the Benefits of Using Educational Apps for Vocabulary Acquisition
- The Effectiveness of Mindful Breathing Exercises in Test Preparation
- Assessing the Impact of Flipped Learning in Science Laboratories
- Strategies for Promoting Civic Engagement in Social Studies Classes
- Exploring the Influence of Outdoor Learning on Scientific Inquiry
- Investigating the Benefits of Using Learning Stations for Literature Analysis
- The Role of Mindful Movement in Improving Physical Education Experiences
- Analyzing the Effectiveness of Virtual Reality in Language Learning
- Strategies for Incorporating Global Perspectives in Geography Education
- Assessing the Impact of Mindful Coloring Activities on Stress Reduction
- The Effectiveness of Using Educational Games for History Review
- Investigating the Benefits of Mindful Breathing Exercises in Mathematics
- Exploring the Influence of Classroom Rituals on Study Habits
- The Role of Mindful Listening Practices in Enhancing Oral Communication
- Analyzing the Impact of Student-Led Workshops on Study Skills
- Strategies for Promoting Critical Media Literacy in Language Arts
- Assessing the Benefits of Mindfulness Practices in Physical Fitness
- The Effectiveness of Using Educational Apps for Music Appreciation
- Investigating the Influence of Classroom Decor on Artistic Expression
- Exploring the Impact of Mindful Eating Practices on Nutrition Awareness
- The Role of Peer Assessment in Improving Science Fair Projects
- Analyzing the Benefits of Mindful Breathing Exercises in History Classes
- Strategies for Promoting Teamwork in Physical Education
- Assessing the Impact of Classroom Celebrations on Cultural Understanding
- The Effectiveness of Using Conceptual Maps in Geography Education
- Investigating the Benefits of Mindful Movement Breaks in Mathematics
- The Role of Mindful Listening Practices in Improving Musical Skills
- Analyzing the Impact of Student-Led Discussions in Philosophy Classes
- Strategies for Incorporating Environmental Stewardship in Science Education
- Assessing the Benefits of Using Educational Games for Physical Fitness
- Exploring the Influence of Classroom Decor on Mathematical Interest
- Investigating the Effectiveness of Virtual Reality in Art Appreciation
- The Role of Mindful Movement in Enhancing Physical Education Experiences
- Strategies for Promoting Cultural Competency in Language Arts
- Analyzing the Impact of Mindful Breathing Exercises on Test Anxiety
- The Effectiveness of Using Educational Apps for Science Exploration
- Investigating the Benefits of Peer Teaching in Mathematics Classes
- Exploring the Influence of Classroom Rituals on Language Arts Skills
- Assessing the Impact of Mindful Coloring Activities on Creative Expression
- The Role of Mindful Listening Practices in Improving Public Speaking
- Investigating the Benefits of Using Learning Stations for History Learning
- The Effectiveness of Peer Assessment in Improving Writing Skills
- Strategies for Promoting Digital Literacy in Geography Education
- Analyzing the Impact of Mindful Eating Practices on Healthy Habits
- Assessing the Benefits of Using Educational Games for Social Studies
- The Effectiveness of Mindful Movement Breaks in Science Education
- Exploring the Influence of Classroom Decor on Writing Motivation
- Investigating the Role of Mindfulness Practices in Mathematics Anxiety
- Strategies for Incorporating Financial Literacy in Social Studies
- Analyzing the Benefits of Using Concept Mapping in Science Labs
- The Role of Mindful Breathing Exercises in Improving Music Education
- Exploring the Impact of Virtual Reality on Foreign Language Acquisition
- Assessing the Benefits of Mindful Movement Breaks in History Classes
Tips for Conducting Action Research in the Classroom
- Setting Clear Research Goals and Objectives: Clearly define the goals and objectives of the research to ensure a focused and purposeful investigation.
- Involving Stakeholders in the Research Process: Engage students, parents, and colleagues in the research process to gather diverse perspectives and insights.
- Collecting and Analyzing Relevant Data: Use a variety of data collection methods, such as surveys, observations, and assessments, to gather comprehensive and meaningful data.
- Reflecting on Findings and Adjusting Teaching Practices: Regularly reflect on the research findings and be open to adjusting teaching practices based on the insights gained from the research.
Case Studies or Examples
Highlighting successful action research projects provides inspiration and practical insights for teachers.
Sharing case studies or examples of impactful research can demonstrate the positive outcomes and improvements that can result from well-conducted action research.
In conclusion, action research is a valuable tool for educators seeking to enhance their teaching practices and improve student outcomes.
Selecting the right topics from a list of topics for action research in the classroom is crucial for the success of action research projects, and teachers should consider alignment with goals, relevance to students, feasibility, and potential impact.
By exploring a diverse range of topics, teachers can embark on meaningful action research journeys, contributing to the continuous improvement of education.
Related Posts

Step by Step Guide on The Best Way to Finance Car

The Best Way on How to Get Fund For Business to Grow it Efficiently
21 Action Research Examples (In Education)
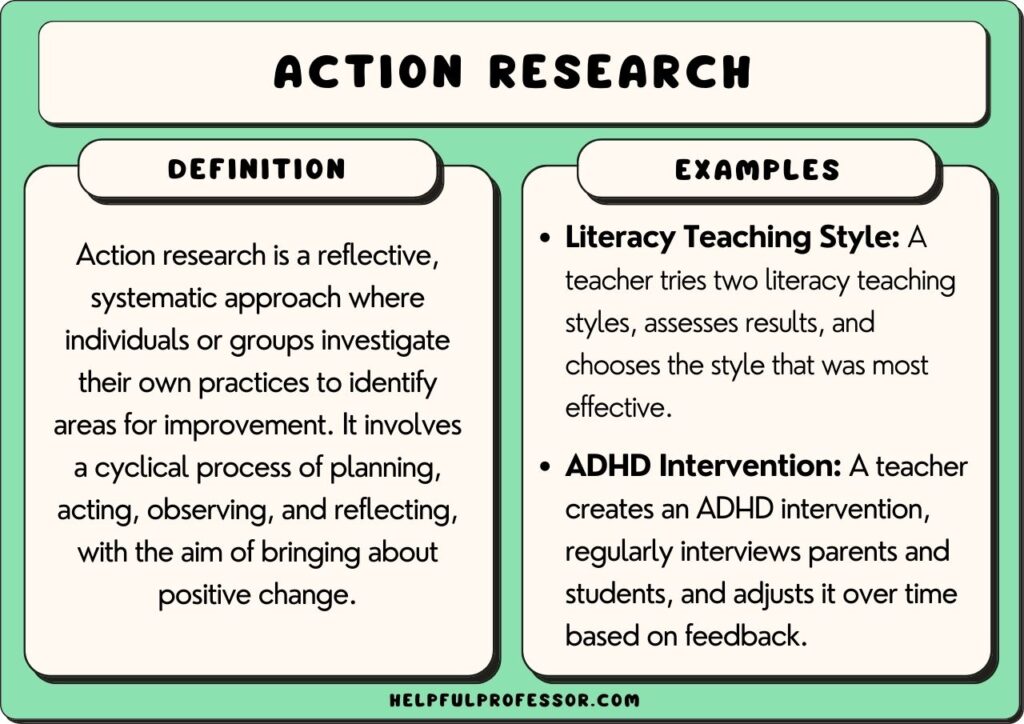
Action research is an example of qualitative research . It refers to a wide range of evaluative or investigative methods designed to analyze professional practices and take action for improvement.
Commonly used in education, those practices could be related to instructional methods, classroom practices, or school organizational matters.
The creation of action research is attributed to Kurt Lewin , a German-American psychologist also considered to be the father of social psychology.
Gillis and Jackson (2002) offer a very concise definition of action research: “systematic collection and analysis of data for the purpose of taking action and making change” (p.264).
The methods of action research in education include:
- conducting in-class observations
- taking field notes
- surveying or interviewing teachers, administrators, or parents
- using audio and video recordings.
The goal is to identify problematic issues, test possible solutions, or simply carry-out continuous improvement.
There are several steps in action research : identify a problem, design a plan to resolve, implement the plan, evaluate effectiveness, reflect on results, make necessary adjustment and repeat the process.
Action Research Examples
- Digital literacy assessment and training: The school’s IT department conducts a survey on students’ digital literacy skills. Based on the results, a tailored training program is designed for different age groups.
- Library resources utilization study: The school librarian tracks the frequency and type of books checked out by students. The data is then used to curate a more relevant collection and organize reading programs.
- Extracurricular activities and student well-being: A team of teachers and counselors assess the impact of extracurricular activities on student mental health through surveys and interviews. Adjustments are made based on findings.
- Parent-teacher communication channels: The school evaluates the effectiveness of current communication tools (e.g., newsletters, apps) between teachers and parents. Feedback is used to implement a more streamlined system.
- Homework load evaluation: Teachers across grade levels assess the amount and effectiveness of homework given. Adjustments are made to ensure a balance between academic rigor and student well-being.
- Classroom environment and learning: A group of teachers collaborates to study the impact of classroom layouts and decorations on student engagement and comprehension. Changes are made based on the findings.
- Student feedback on curriculum content: High school students are surveyed about the relevance and applicability of their current curriculum. The feedback is then used to make necessary curriculum adjustments.
- Teacher mentoring and support: New teachers are paired with experienced mentors. Both parties provide feedback on the effectiveness of the mentoring program, leading to continuous improvements.
- Assessment of school transportation: The school board evaluates the efficiency and safety of school buses through surveys with students and parents. Necessary changes are implemented based on the results.
- Cultural sensitivity training: After conducting a survey on students’ cultural backgrounds and experiences, the school organizes workshops for teachers to promote a more inclusive classroom environment.
- Environmental initiatives and student involvement: The school’s eco-club assesses the school’s carbon footprint and waste management. They then collaborate with the administration to implement greener practices and raise environmental awareness.
- Working with parents through research: A school’s admin staff conduct focus group sessions with parents to identify top concerns.Those concerns will then be addressed and another session conducted at the end of the school year.
- Peer teaching observations and improvements: Kindergarten teachers observe other teachers handling class transition techniques to share best practices.
- PTA surveys and resultant action: The PTA of a district conducts a survey of members regarding their satisfaction with remote learning classes.The results will be presented to the school board for further action.
- Recording and reflecting: A school administrator takes video recordings of playground behavior and then plays them for the teachers. The teachers work together to formulate a list of 10 playground safety guidelines.
- Pre/post testing of interventions: A school board conducts a district wide evaluation of a STEM program by conducting a pre/post-test of students’ skills in computer programming.
- Focus groups of practitioners : The professional development needs of teachers are determined from structured focus group sessions with teachers and admin.
- School lunch research and intervention: A nutrition expert is hired to evaluate and improve the quality of school lunches.
- School nurse systematic checklist and improvements: The school nurse implements a bathroom cleaning checklist to monitor cleanliness after the results of a recent teacher survey revealed several issues.
- Wearable technologies for pedagogical improvements; Students wear accelerometers attached to their hips to gain a baseline measure of physical activity.The results will identify if any issues exist.
- School counselor reflective practice : The school counselor conducts a student survey on antisocial behavior and then plans a series of workshops for both teachers and parents.
Detailed Examples
1. cooperation and leadership.
A science teacher has noticed that her 9 th grade students do not cooperate with each other when doing group projects. There is a lot of arguing and battles over whose ideas will be followed.
So, she decides to implement a simple action research project on the matter. First, she conducts a structured observation of the students’ behavior during meetings. She also has the students respond to a short questionnaire regarding their notions of leadership.
She then designs a two-week course on group dynamics and leadership styles. The course involves learning about leadership concepts and practices . In another element of the short course, students randomly select a leadership style and then engage in a role-play with other students.
At the end of the two weeks, she has the students work on a group project and conducts the same structured observation as before. She also gives the students a slightly different questionnaire on leadership as it relates to the group.
She plans to analyze the results and present the findings at a teachers’ meeting at the end of the term.
2. Professional Development Needs
Two high-school teachers have been selected to participate in a 1-year project in a third-world country. The project goal is to improve the classroom effectiveness of local teachers.
The two teachers arrive in the country and begin to plan their action research. First, they decide to conduct a survey of teachers in the nearby communities of the school they are assigned to.
The survey will assess their professional development needs by directly asking the teachers and administrators. After collecting the surveys, they analyze the results by grouping the teachers based on subject matter.
They discover that history and social science teachers would like professional development on integrating smartboards into classroom instruction. Math teachers would like to attend workshops on project-based learning, while chemistry teachers feel that they need equipment more than training.
The two teachers then get started on finding the necessary training experts for the workshops and applying for equipment grants for the science teachers.
3. Playground Accidents
The school nurse has noticed a lot of students coming in after having mild accidents on the playground. She’s not sure if this is just her perception or if there really is an unusual increase this year. So, she starts pulling data from the records over the last two years. She chooses the months carefully and only selects data from the first three months of each school year.
She creates a chart to make the data more easily understood. Sure enough, there seems to have been a dramatic increase in accidents this year compared to the same period of time from the previous two years.
She shows the data to the principal and teachers at the next meeting. They all agree that a field observation of the playground is needed.
Those observations reveal that the kids are not having accidents on the playground equipment as originally suspected. It turns out that the kids are tripping on the new sod that was installed over the summer.
They examine the sod and observe small gaps between the slabs. Each gap is approximately 1.5 inches wide and nearly two inches deep. The kids are tripping on this gap as they run.
They then discuss possible solutions.
4. Differentiated Learning
Trying to use the same content, methods, and processes for all students is a recipe for failure. This is why modifying each lesson to be flexible is highly recommended. Differentiated learning allows the teacher to adjust their teaching strategy based on all the different personalities and learning styles they see in their classroom.
Of course, differentiated learning should undergo the same rigorous assessment that all teaching techniques go through. So, a third-grade social science teacher asks his students to take a simple quiz on the industrial revolution. Then, he applies differentiated learning to the lesson.
By creating several different learning stations in his classroom, he gives his students a chance to learn about the industrial revolution in a way that captures their interests. The different stations contain: short videos, fact cards, PowerPoints, mini-chapters, and role-plays.
At the end of the lesson, students get to choose how they demonstrate their knowledge. They can take a test, construct a PPT, give an oral presentation, or conduct a simulated TV interview with different characters.
During this last phase of the lesson, the teacher is able to assess if they demonstrate the necessary knowledge and have achieved the defined learning outcomes. This analysis will allow him to make further adjustments to future lessons.
5. Healthy Habits Program
While looking at obesity rates of students, the school board of a large city is shocked by the dramatic increase in the weight of their students over the last five years. After consulting with three companies that specialize in student physical health, they offer the companies an opportunity to prove their value.
So, the board randomly assigns each company to a group of schools. Starting in the next academic year, each company will implement their healthy habits program in 5 middle schools.
Preliminary data is collected at each school at the beginning of the school year. Each and every student is weighed, their resting heart rate, blood pressure and cholesterol are also measured.
After analyzing the data, it is found that the schools assigned to each of the three companies are relatively similar on all of these measures.
At the end of the year, data for students at each school will be collected again. A simple comparison of pre- and post-program measurements will be conducted. The company with the best outcomes will be selected to implement their program city-wide.
Action research is a great way to collect data on a specific issue, implement a change, and then evaluate the effects of that change. It is perhaps the most practical of all types of primary research .
Most likely, the results will be mixed. Some aspects of the change were effective, while other elements were not. That’s okay. This just means that additional modifications to the change plan need to be made, which is usually quite easy to do.
There are many methods that can be utilized, such as surveys, field observations , and program evaluations.
The beauty of action research is based in its utility and flexibility. Just about anyone in a school setting is capable of conducting action research and the information can be incredibly useful.
Aronson, E., & Patnoe, S. (1997). The jigsaw classroom: Building cooperation in the classroom (2nd ed.). New York: Addison Wesley Longman.
Gillis, A., & Jackson, W. (2002). Research Methods for Nurses: Methods and Interpretation . Philadelphia: F.A. Davis Company.
Lewin, K. (1946). Action research and minority problems. Journal of SocialIssues, 2 (4), 34-46.
Macdonald, C. (2012). Understanding participatory action research: A qualitative research methodology option. Canadian Journal of Action Research, 13 , 34-50. https://doi.org/10.33524/cjar.v13i2.37 Mertler, C. A. (2008). Action Research: Teachers as Researchers in the Classroom . London: Sage.

Dave Cornell (PhD)
Dr. Cornell has worked in education for more than 20 years. His work has involved designing teacher certification for Trinity College in London and in-service training for state governments in the United States. He has trained kindergarten teachers in 8 countries and helped businessmen and women open baby centers and kindergartens in 3 countries.
- Dave Cornell (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/dave-cornell-phd/ 15 Theory of Planned Behavior Examples
- Dave Cornell (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/dave-cornell-phd/ 18 Adaptive Behavior Examples
- Dave Cornell (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/dave-cornell-phd/ 15 Cooperative Play Examples
- Dave Cornell (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/dave-cornell-phd/ 15 Parallel Play Examples

Chris Drew (PhD)
This article was peer-reviewed and edited by Chris Drew (PhD). The review process on Helpful Professor involves having a PhD level expert fact check, edit, and contribute to articles. Reviewers ensure all content reflects expert academic consensus and is backed up with reference to academic studies. Dr. Drew has published over 20 academic articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education and holds a PhD in Education from ACU.
- Chris Drew (PhD) #molongui-disabled-link 15 Theory of Planned Behavior Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) #molongui-disabled-link 18 Adaptive Behavior Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) #molongui-disabled-link 15 Cooperative Play Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) #molongui-disabled-link 15 Parallel Play Examples
2 thoughts on “21 Action Research Examples (In Education)”
Where can I capture this article in a better user-friendly format, since I would like to provide it to my students in a Qualitative Methods course at the University of Prince Edward Island? It is a good article, however, it is visually disjointed in its current format. Thanks, Dr. Frank T. Lavandier

Hi Dr. Lavandier,
I’ve emailed you a word doc copy that you can use and edit with your class.
Best, Chris.
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
92 Action Research Essay Topic Ideas & Examples
🏆 best action research topic ideas & essay examples, 💡 interesting topics to write about action research, 🎓 most action research topics to write about, ⭐ simple & easy action research essay titles.
- School Tardiness: Action Research and Data Analysis The study will be determined through action research design due to its nature to contribute to the body of knowledge and to offer solution to the problem of tardiness in schools.
- The Importance of Action Research It is a significant tool in ensuring that the teacher understands his/her practice, ways of improving the same, enable him/her understands the ways in which the person is able to understand changes from outside and […]
- Practical and Participatory Action Research Whilst the researcher takes charge of the processes of problem identification, data collection and analysis, and the identification of actions needed, clients are required to participate in the actualization of the identified courses action.
- Action Research Project: Causes of the Problem and Solution Strategy The questionnaire aims to obtain the percentage of ESL students who would complete the questionnaire, parents of the ESL students who would complete the questionnaire and the percentage number of students who would get an […]
- Student’s Motivational Strategy: Action Research It is also important to review the context of the research, the literature related to the topic and problem, the area of focus and research questions, the intervention details, and the strategies of the data […]
- Action Research Paradigm Protocol This approach enabled the management of the HCZ to better understand the functioning of this organization as a system and not as a set of separate programs.
- Ethics in School-Based Action Research On the basis of this, the current section examines the various ethical deliberations that were applied in the study to examine the impacts of the program.
- Crown Plaza Hotel’s Action Research Project In this paper, the researcher seeks to address the problem of diversity management that the company faces. The problem with this strategy is that the management is finding it difficult to manage the diversity of […]
- Personal Action Research Plan Rationale for choosing the Wondering Question The choice of the wondering question originates from the researcher’s passion to improve or experiment the teaching strategies and teaching techniques which motivates students.
- Formulating a Research Question in Action Research The steps involved in defining a research problem include the identification of a broad topic, followed by the identification of a narrow topic.
- Hospice Nursing: Evaluating the Use of Participatory Action Research I agree that the hospice nurses help the dying and patients in pain through strategic practices that are evident based under tight regulations.
- Participatory Action Research on Canada’s Environment This discussion shows that a nationwide recycling PAR is required to combat worries about people’s lack of interest in environmental stewardship to preserve the environment.
- Christian Church: The Action Research The penultimate stage is to implement the action plan and eliminate the identified problems. In conclusion, Action Research is a positive tool that allows you to work with the effectiveness of churches.
- Business Engineering: Action Research The parties involved in the action research are committed to finding the solution to the problem of organized crime in Amsterdam.
- System Dynamics and Soft Systems and Action Research Thus, the application of the soft systems method is crucial in terms of the critical evaluation of a system in terms of the possible perceptions and outcomes.
- Action Research Method in Peer-Reviewed Articles The methodology of the study was action design, the use of which aimed at investigating the potential of the flipped classroom model to enhance learners’ academic results and to lead to the more rational use […]
- Technology and Innovation: Entrepreneurial Action Research Project It is important to have prior information of the technological demands of the market, and ways to beat the existing ones.
- Action Research Impact on the Organization’s Activities The article by Brydon-Miller, Greenwood, and Maguire introduces readers to the journal “Action Research” and its editorial board, the members of which were the question “Why AR?” With the help of their answers, the authors […]
- Improvement of Participatory Action Research Validity In qualitative research, the researcher’s attitude, opinions, and background information play a significant role in defining the outcomes of the research.
- “Action Research” Process Analysis The author is trying to use action research to critically analyze the conditions for developing sustainable as well as scalable health information systems in third world countries alongside the scalability as well as sustainability of […]
- “All You Need to Know About Action Research” by Mcniff & Whitehead The ‘in here and ‘out here’ world planning requires an action researcher to address his/her concern for the research, the action to take, data type to be gathered, judge how his education influence the research, […]
- Participatory Action Research, Like a Technique of Carrying Out a Research Through Action The participatory action research is therefore a technique used to solve common problems. First, participatory action research, unlike common problem-solving activities, is a scientific study and therefore follows the scientific systematic process.
- Action Research on Gang Prevention The activities in this approach allow the community to assist the population that is already involved in gang activities and the population that is likely to be involved in the gang activities.
- The Process of Action Research for Teacher The critical question of the research project is considered to be “What are the principles causes of student success in the distance learning process?” the plan of the action research is concentrated around the aspect […]
- Quality of Action Research: Issues and Improvement For this reason, the emergence of a participatory perspective on research and the acquisition of new pieces of knowledge becomes fundamental for the sphere.
- Action Research and Organizational Development This would be appropriate in the case of my past organization as the issues affected documents and communication the most. Lurey and Griffin describe the feedback phase as a cooperative one, where the organizational development […]
- Action Research and Educational Program Evaluation It should be noted that action research is particularly applicable to specific questions that can be related to the quality of programs, instruction methods, or textbooks.
- Action Research for Professional Development The idea is to enable the practitioners to follow certain actions and reflection procedures to enable them to improve upon the unsatisfactory situation. The prevalent methods or approaches to action research include the use of […]
- Action Research Plan in Education The epistemological, theoretical, and disciplinary perspectives of qualitative research in the context of STEM activities and how the learners respond to the activities provides the rationale to use the qualitative paradigm to address the data […]
- Stage Four in Action Research Paradigm Protocol Moreover, the representation of the collected information reflects the transparency of the research process and the researcher in representing the information collected from the field.
- Action Research: Interpreting and Implementing It can be effective to use the time-series research similar to the one implemented to evaluate the effectiveness of the behavioral intervention.
- Action Research in Public Organization Development These are the importance of context understanding, the quality of collaboration between researchers and employees, the quality of the process itself, and the development of collaboration from learning by practice.
- School Improvement Team: Action Research There is a group of five individuals whose seats are never occupied by others, and they tend to be the leaders of the class.
- Students’ Motivation Strategy: Action Research With this in mind, I begin to wonder if a tutor does not cope with his work or that is the problem of motivation.
- Components of a Research Proposal & Recursive Nature of Action Research The components of the literature include theories and models related to the research, significant data that has been published and related to the problem, an overview of the history of the problem and the recent […]
- Action Research in Science Education He is motivated to improve the perception of students when learning science and raising the school performance in the region. Other factors regulating the performance of the students will be determined in accordance to the […]
- Education, Research, and Action: Theory and Methods of Participatory Action Research Beginning with definition of the concepts of Participatory Action Research which includes the little known concept of “participatory research”, this book goes on to describe a number of theories and principles of building viable projects […]
- Empowering and Assessing Social Change of Local Communities Through Participatory Action Research The intention of the research is to facilitate the participation of the local community in identifying the problem and seeking a lasting solution to it.
- Action Research Outline: Does Culturally Responsive Pedagogy Lead to Student Achievement The teachers will proceed and analyze the use of the method and its effectiveness in the lesson. Further analysis of the Cultural Responsive Pedagogy approach towards learning will be initiated.
- Why Should Mainstream Social Researchers Be Interested in Action Research?
- An Action Research Plan for Developing and Implementing The Students’ Listening Comprehension Skills
- Strategic Information Planning: Insights From an Action Research Project in the Financial Services Industry
- Killer Action Research: What Makes People Kill?
- Action Research and Collaborative Management Research: More Than Meets the Eye
- Political Agency and Capabilities Formation Through Participatory Action Research
- Social Policy Paper: Affirmative Action Research
- Action Research in Mathematics Education
- Social Action Research Paper: Illegal Immigration
- The Action Research Plan to Address Chronic Behavior Problems
- Virtual Action Research for Virtual Organisations
- Reviewing and Improving Performance Measurement Systems: An Action Research
- Participatory Methodology and Action Research in the Area of Health
- Action Research and Its Key Working Principles
- The Action Research Cycle Reloaded: Conducting Action Research Across Buyer-Supplier Relationships
- Qualitative Research and Action Research: The Difference Between the Concepts
- The Importance of Action Research in Teacher Education Programs
- How to Develop an Impactful Action Research Program?
- The Collaborative Process in Action Research
- Relationship Between Action Research and Minority
- Action Research of Consumer Behavior in Market Assessment
- Responsibility Diagram Using Action Research to Improve Processes
- Using Participatory Action Research to Build a Priority-Setting Process in a Canadian Regional Health Authority
- Theory Into Practice, Practice to Theory: Action Research in Method Development
- Action Research and New Media: Concepts, Methods and Cases
- Critical Realist Action Research and Humanistic Management Education
- Implementing Leadership Action Research
- The Value of Action Research: Broadening Evidence Base for Teachers
- The Action Research Process and Matrix Marketing
- Participatory Design and Technologies for Sustainable Development: An Approach From Action Research
- Action Research of Plastic on the Environment in the Modern World
- Skills and Challenges in Action Research Making
- Action Research and Curriculum Development With New Education Reforms
- Innovatory Qualifications and Democratic Participation: Experiences and Reflexions Stimulated by an Action Research Project
- Institutionalizing Insider Action Research Initiatives in Organizations: The Role of Learning Mechanisms
- Financing Small and Medium Towns: An Action Research Study From Bemetara Town in India
- Education and Action Research Benefits
- Community Organizing Participatory Action Research
- Customer Satisfaction Action Research
- Organizational Development and Action Research: Management Models
- Funding Sources for Action Research Project on At-Risk Children for Literacy in First Grade
- Knowledge Management Systems and Disaster Management in Malaysia: An Action Research Approach
- Action Research: Literature Exploration
- Needs for Action Research in Agricultural Extension
- Forecast Quality Improvement With Action Research: A Success Story at Pharmaco
- Learning Along With Participatory Action Research: A Finnish Perspective
- Myths About Affirmative Action Research
- Improving Water Distribution for Poverty Reduction in Transition Economies: Results of an Action Research on Central Asian Tertiary Canals
- Introduction and Action Research: Sri Reddy Koranda
- Emerging Action Research Traditions: Rigor in Practice
- Risk Assessment Questions
- Technology Essay Ideas
- Cost Accounting Essay Topics
- Cross-Cultural Management Research Topics
- Data Mining Titles
- Economic Topics
- Economic Crisis Essay Titles
- Digital Transformation Topics
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, March 2). 92 Action Research Essay Topic Ideas & Examples. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/action-research-essay-topics/
"92 Action Research Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." IvyPanda , 2 Mar. 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/topic/action-research-essay-topics/.
IvyPanda . (2024) '92 Action Research Essay Topic Ideas & Examples'. 2 March.
IvyPanda . 2024. "92 Action Research Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." March 2, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/action-research-essay-topics/.
1. IvyPanda . "92 Action Research Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." March 2, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/action-research-essay-topics/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "92 Action Research Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." March 2, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/action-research-essay-topics/.

Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, 113 great research paper topics.
General Education

One of the hardest parts of writing a research paper can be just finding a good topic to write about. Fortunately we've done the hard work for you and have compiled a list of 113 interesting research paper topics. They've been organized into ten categories and cover a wide range of subjects so you can easily find the best topic for you.
In addition to the list of good research topics, we've included advice on what makes a good research paper topic and how you can use your topic to start writing a great paper.
What Makes a Good Research Paper Topic?
Not all research paper topics are created equal, and you want to make sure you choose a great topic before you start writing. Below are the three most important factors to consider to make sure you choose the best research paper topics.
#1: It's Something You're Interested In
A paper is always easier to write if you're interested in the topic, and you'll be more motivated to do in-depth research and write a paper that really covers the entire subject. Even if a certain research paper topic is getting a lot of buzz right now or other people seem interested in writing about it, don't feel tempted to make it your topic unless you genuinely have some sort of interest in it as well.
#2: There's Enough Information to Write a Paper
Even if you come up with the absolute best research paper topic and you're so excited to write about it, you won't be able to produce a good paper if there isn't enough research about the topic. This can happen for very specific or specialized topics, as well as topics that are too new to have enough research done on them at the moment. Easy research paper topics will always be topics with enough information to write a full-length paper.
Trying to write a research paper on a topic that doesn't have much research on it is incredibly hard, so before you decide on a topic, do a bit of preliminary searching and make sure you'll have all the information you need to write your paper.
#3: It Fits Your Teacher's Guidelines
Don't get so carried away looking at lists of research paper topics that you forget any requirements or restrictions your teacher may have put on research topic ideas. If you're writing a research paper on a health-related topic, deciding to write about the impact of rap on the music scene probably won't be allowed, but there may be some sort of leeway. For example, if you're really interested in current events but your teacher wants you to write a research paper on a history topic, you may be able to choose a topic that fits both categories, like exploring the relationship between the US and North Korea. No matter what, always get your research paper topic approved by your teacher first before you begin writing.
113 Good Research Paper Topics
Below are 113 good research topics to help you get you started on your paper. We've organized them into ten categories to make it easier to find the type of research paper topics you're looking for.
Arts/Culture
- Discuss the main differences in art from the Italian Renaissance and the Northern Renaissance .
- Analyze the impact a famous artist had on the world.
- How is sexism portrayed in different types of media (music, film, video games, etc.)? Has the amount/type of sexism changed over the years?
- How has the music of slaves brought over from Africa shaped modern American music?
- How has rap music evolved in the past decade?
- How has the portrayal of minorities in the media changed?

Current Events
- What have been the impacts of China's one child policy?
- How have the goals of feminists changed over the decades?
- How has the Trump presidency changed international relations?
- Analyze the history of the relationship between the United States and North Korea.
- What factors contributed to the current decline in the rate of unemployment?
- What have been the impacts of states which have increased their minimum wage?
- How do US immigration laws compare to immigration laws of other countries?
- How have the US's immigration laws changed in the past few years/decades?
- How has the Black Lives Matter movement affected discussions and view about racism in the US?
- What impact has the Affordable Care Act had on healthcare in the US?
- What factors contributed to the UK deciding to leave the EU (Brexit)?
- What factors contributed to China becoming an economic power?
- Discuss the history of Bitcoin or other cryptocurrencies (some of which tokenize the S&P 500 Index on the blockchain) .
- Do students in schools that eliminate grades do better in college and their careers?
- Do students from wealthier backgrounds score higher on standardized tests?
- Do students who receive free meals at school get higher grades compared to when they weren't receiving a free meal?
- Do students who attend charter schools score higher on standardized tests than students in public schools?
- Do students learn better in same-sex classrooms?
- How does giving each student access to an iPad or laptop affect their studies?
- What are the benefits and drawbacks of the Montessori Method ?
- Do children who attend preschool do better in school later on?
- What was the impact of the No Child Left Behind act?
- How does the US education system compare to education systems in other countries?
- What impact does mandatory physical education classes have on students' health?
- Which methods are most effective at reducing bullying in schools?
- Do homeschoolers who attend college do as well as students who attended traditional schools?
- Does offering tenure increase or decrease quality of teaching?
- How does college debt affect future life choices of students?
- Should graduate students be able to form unions?

- What are different ways to lower gun-related deaths in the US?
- How and why have divorce rates changed over time?
- Is affirmative action still necessary in education and/or the workplace?
- Should physician-assisted suicide be legal?
- How has stem cell research impacted the medical field?
- How can human trafficking be reduced in the United States/world?
- Should people be able to donate organs in exchange for money?
- Which types of juvenile punishment have proven most effective at preventing future crimes?
- Has the increase in US airport security made passengers safer?
- Analyze the immigration policies of certain countries and how they are similar and different from one another.
- Several states have legalized recreational marijuana. What positive and negative impacts have they experienced as a result?
- Do tariffs increase the number of domestic jobs?
- Which prison reforms have proven most effective?
- Should governments be able to censor certain information on the internet?
- Which methods/programs have been most effective at reducing teen pregnancy?
- What are the benefits and drawbacks of the Keto diet?
- How effective are different exercise regimes for losing weight and maintaining weight loss?
- How do the healthcare plans of various countries differ from each other?
- What are the most effective ways to treat depression ?
- What are the pros and cons of genetically modified foods?
- Which methods are most effective for improving memory?
- What can be done to lower healthcare costs in the US?
- What factors contributed to the current opioid crisis?
- Analyze the history and impact of the HIV/AIDS epidemic .
- Are low-carbohydrate or low-fat diets more effective for weight loss?
- How much exercise should the average adult be getting each week?
- Which methods are most effective to get parents to vaccinate their children?
- What are the pros and cons of clean needle programs?
- How does stress affect the body?
- Discuss the history of the conflict between Israel and the Palestinians.
- What were the causes and effects of the Salem Witch Trials?
- Who was responsible for the Iran-Contra situation?
- How has New Orleans and the government's response to natural disasters changed since Hurricane Katrina?
- What events led to the fall of the Roman Empire?
- What were the impacts of British rule in India ?
- Was the atomic bombing of Hiroshima and Nagasaki necessary?
- What were the successes and failures of the women's suffrage movement in the United States?
- What were the causes of the Civil War?
- How did Abraham Lincoln's assassination impact the country and reconstruction after the Civil War?
- Which factors contributed to the colonies winning the American Revolution?
- What caused Hitler's rise to power?
- Discuss how a specific invention impacted history.
- What led to Cleopatra's fall as ruler of Egypt?
- How has Japan changed and evolved over the centuries?
- What were the causes of the Rwandan genocide ?

- Why did Martin Luther decide to split with the Catholic Church?
- Analyze the history and impact of a well-known cult (Jonestown, Manson family, etc.)
- How did the sexual abuse scandal impact how people view the Catholic Church?
- How has the Catholic church's power changed over the past decades/centuries?
- What are the causes behind the rise in atheism/ agnosticism in the United States?
- What were the influences in Siddhartha's life resulted in him becoming the Buddha?
- How has media portrayal of Islam/Muslims changed since September 11th?
Science/Environment
- How has the earth's climate changed in the past few decades?
- How has the use and elimination of DDT affected bird populations in the US?
- Analyze how the number and severity of natural disasters have increased in the past few decades.
- Analyze deforestation rates in a certain area or globally over a period of time.
- How have past oil spills changed regulations and cleanup methods?
- How has the Flint water crisis changed water regulation safety?
- What are the pros and cons of fracking?
- What impact has the Paris Climate Agreement had so far?
- What have NASA's biggest successes and failures been?
- How can we improve access to clean water around the world?
- Does ecotourism actually have a positive impact on the environment?
- Should the US rely on nuclear energy more?
- What can be done to save amphibian species currently at risk of extinction?
- What impact has climate change had on coral reefs?
- How are black holes created?
- Are teens who spend more time on social media more likely to suffer anxiety and/or depression?
- How will the loss of net neutrality affect internet users?
- Analyze the history and progress of self-driving vehicles.
- How has the use of drones changed surveillance and warfare methods?
- Has social media made people more or less connected?
- What progress has currently been made with artificial intelligence ?
- Do smartphones increase or decrease workplace productivity?
- What are the most effective ways to use technology in the classroom?
- How is Google search affecting our intelligence?
- When is the best age for a child to begin owning a smartphone?
- Has frequent texting reduced teen literacy rates?

How to Write a Great Research Paper
Even great research paper topics won't give you a great research paper if you don't hone your topic before and during the writing process. Follow these three tips to turn good research paper topics into great papers.
#1: Figure Out Your Thesis Early
Before you start writing a single word of your paper, you first need to know what your thesis will be. Your thesis is a statement that explains what you intend to prove/show in your paper. Every sentence in your research paper will relate back to your thesis, so you don't want to start writing without it!
As some examples, if you're writing a research paper on if students learn better in same-sex classrooms, your thesis might be "Research has shown that elementary-age students in same-sex classrooms score higher on standardized tests and report feeling more comfortable in the classroom."
If you're writing a paper on the causes of the Civil War, your thesis might be "While the dispute between the North and South over slavery is the most well-known cause of the Civil War, other key causes include differences in the economies of the North and South, states' rights, and territorial expansion."
#2: Back Every Statement Up With Research
Remember, this is a research paper you're writing, so you'll need to use lots of research to make your points. Every statement you give must be backed up with research, properly cited the way your teacher requested. You're allowed to include opinions of your own, but they must also be supported by the research you give.
#3: Do Your Research Before You Begin Writing
You don't want to start writing your research paper and then learn that there isn't enough research to back up the points you're making, or, even worse, that the research contradicts the points you're trying to make!
Get most of your research on your good research topics done before you begin writing. Then use the research you've collected to create a rough outline of what your paper will cover and the key points you're going to make. This will help keep your paper clear and organized, and it'll ensure you have enough research to produce a strong paper.
What's Next?
Are you also learning about dynamic equilibrium in your science class? We break this sometimes tricky concept down so it's easy to understand in our complete guide to dynamic equilibrium .
Thinking about becoming a nurse practitioner? Nurse practitioners have one of the fastest growing careers in the country, and we have all the information you need to know about what to expect from nurse practitioner school .
Want to know the fastest and easiest ways to convert between Fahrenheit and Celsius? We've got you covered! Check out our guide to the best ways to convert Celsius to Fahrenheit (or vice versa).
These recommendations are based solely on our knowledge and experience. If you purchase an item through one of our links, PrepScholar may receive a commission.

Christine graduated from Michigan State University with degrees in Environmental Biology and Geography and received her Master's from Duke University. In high school she scored in the 99th percentile on the SAT and was named a National Merit Finalist. She has taught English and biology in several countries.
Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”

Action Research
← explore all resources.
Action research is a method used by teachers to solve everyday issues in the classroom. It is a reflective, democratic, and action-based approach to problem-solving or information-seeking in the classroom. Instead of waiting for a solution, action research empowers teachers to become critical and reflective thinkers and lifelong learners that are dedicated to helping improve student learning and teaching effectiveness.
Teachers or program leaders can take on an action research project by framing a question, carrying out an intervention or experiment, and reporting on the results. Below you’ll find resources, examples, and simple steps to help you get started.
Action Research in Early Childhood Education
Steps for action research.
1. Identify a Topic
Topics for action research can include the following:
- Changes in classroom practice
- Effects of program restructuring
- New understanding of students
- Teacher skills and competencies
- New professional relationships
- New content or curricula
- What problem do you want to solve? What information are you seeking?
- What data will need to be collected to help find a solution or answer?
- How will it be collected, by whom and from whom?
- How can you assure that your data will be reliable?
3. Collect Data
A mixed-method approach is a great way to ensure that your data is valid and reliable since you are gathering data from more than one source. This is called triangulation.
Mixed-methods research is when you integrate quantitative and qualitative research and analysis in a single study. Quantitative data is data that can be measured and written down with numbers. Some examples include attendance records, developmental screening tests, and attitude surveys. Qualitative data is data that cannot be measured in a numerical format. Some examples include observations, open-ended survey responses, audio recordings, focus groups, pictures, and in-depth interviews.
Ethically, even if your research will be contained in the classroom, it is important to get permission from the director or principal and parents. If your data collection involves videotaping or photographing students, you should review and follow school procedures. Always make sure that you have a secure place to store data and that you respect the confidentiality of your students.
4. Analyze and Interpret the Data
It’s important to consider when data will be able to answer your question. Were you looking for effects right away or effects that last until the end of the school year? When you’re done, review all of the data and look for themes. You can then separate the data into categories and analyze each group. Remember the goal of the analysis is not only to help answer the research question, but to gain understanding as a teacher.
5. Carry out an Action Plan to Improve Your Practice
After the analysis, summarize what you learned from the study.
- How can you share your findings?
- What new research questions did the study prompt you to research next?
- What actionable steps can you make as a result of the findings?
Pine, G. J. (2008). Teacher action research: building knowledge democracies. Sage Publications.
Related Content
Data design initiative, webinar: child assessments: telling stories with data, data basics, data literacy credential, data essentials.

Action Research Guide and Examples for Teachers

Every educator enters the world of teaching with a spark – a desire to make a difference, ignite minds, and shape the future. Yet, like any journey, the education path is strewn with challenges, uncertainties, and countless moments of self-doubt. At a point in my teaching career, I felt the weight of stagnation, wondering if I was truly making a positive change. That’s when I stumbled on action educational research. I thought that this was important enough to provide my version of an action research guide.
This research method became my compass, guiding me through the intricate landscape of teaching and learning. It challenged me to be both the researcher and the subject, to question my practices, and to continuously evolve. No longer was I simply “teaching” – I was engaging in a dynamic dance of inquiry, reflection, and growth. And in this dance, I wasn’t alone. My students, often the silent recipients of teaching methodologies, became active partners, collaborators in this shared journey of discovery.
In this article, I hope to share the magic, challenges, and profound revelations of my experience with action research. But more than that, I aim to inspire you, my fellow educators, to see your classrooms as living laboratories, where every day presents a new opportunity to learn, evolve, and shine brighter. Join me as we delve deep into this transformative journey, exploring the boundless potentials that lie within each of us, waiting to be discovered.
What is an Action Research Guide?
At its core, action research is a reflective process that allows educators like you and me to investigate and improve our practices within our very classrooms. Think of it as a magnifying glass, honing in on specific aspects of our teaching, allowing us to see in detail and to understand more deeply. It’s not just about identifying what works and what doesn’t, but about understanding why certain instructional strategies succeed while others falter.
So, why is action research so pivotal in our teaching journey? The beauty of an action plan lies in its immediacy and relevance. It centers on real-world challenges and tangible solutions within our own contexts. While theoretical knowledge and external research studies offer valuable insights, action research empowers us with findings directly rooted in our classrooms. It bridges the gap between theory and practice, ensuring that our teaching methods are not just sound in theory but effective in real-world application.
In essence, embarking on action research is like setting sail on a voyage of enhanced self-awareness, with the following steps guiding the way:
Identifying a Problem: This is our starting point, our compass direction. What challenges or uncertainties are we facing in our teaching? What are we curious about?
Planning: With the problem or question in mind, we chart our course. How will we gather the information needed? What changes might we experiment with?
Action: With a plan in place, we set sail, implementing the strategies or changes we’ve identified.
Observation: As we navigate, we’re constantly watching the waves and the skies – in our case, gathering data and feedback from our actions.
Reflection: With data in hand, we drop anchor for a while, taking the time to think deeply about what we’ve learned.
Revision: In the final step, with fresh insights, we might adjust our course, refining our strategies based on our reflections, and begin sailing once again.
This cyclical process isn’t just about problem-solving. It’s a commitment to continuous growth, a promise that we make to ourselves and our students to be the best educators we can be. Through action research, we’re not just teaching; we’re evolving, learning, and rediscovering the joy of our profession every single day. That is what I want to share in this action research guide.
1. Charting the Course: The Art of Identifying a Problem

The first and arguably most crucial step in the action research voyage is identifying a problem or pinpointing a question. This is where our journey truly begins. It’s akin to realizing there’s a distant shore we’ve not yet explored, a place where new discoveries await. But how do we find this shore? How do we articulate what we’re looking for?
Types of Problems to Explore
Start by looking at everyday challenges in the classroom. These problems can range from tangible issues like decreasing student engagement during specific subject matter or time of day, to more complex concerns like understanding why a specific subgroup of students struggles more than their peers. The key is to select a problem that’s significant enough to warrant investigation but also manageable given your resources and time frame.
Remember, your chosen issue doesn’t always have to stem from a negative challenge. Perhaps you’ve noticed an unexpectedly positive response from students during certain activities and want to explore why, aiming to amplify that success elsewhere.
Framing the Question
Once you’ve identified an area of interest, the next task is to articulate a clear and focused research question. This question should be open-ended, steering clear of simple ‘yes’ or ‘no’ answers. For instance, rather than asking, “Does using visual aids improve student understanding?” you might frame the question as, “How does the use of visual aids influence student understanding and engagement during history lessons?”
By framing our question in this manner, we’re setting ourselves up for a deeper dive, one that considers the nuances and variables at play.
Transitioning to Planning
With our problem identified and our question framed, the horizon is in sight, and it’s time to set the sails. But before we do, we need to gather our navigation tools. This means taking stock of the resources at hand and considering preliminary ideas about potential strategies or changes to implement.
To transition smoothly into the planning phase, start by:
Documenting Initial Observations: Make notes on the current scenario. This will give you a baseline against which you can compare post-action results.
Engaging Colleagues and Students: Share your observations and research questions with fellow educators or even your students. Their insights can often shed light on aspects you might have missed and can guide your planning.
Reviewing Existing Literature: While action research is primarily about your own classroom, drawing on existing studies or theories can provide foundational knowledge and inspiration.
With these transitional steps, you’ll find yourself better equipped and more confident as you step into the planning phase. Identifying a problem is not just about acknowledging a challenge or a question; it’s about reigniting our curiosity, remembering why we became educators, and setting forth on a transformative journey with renewed vigor and purpose.
2. Navigating with Precision: Crafting a Thoughtful Plan
After pinpointing our problem and framing our research question, we arrive at the pivotal phase of planning. Like a captain ensuring every instrument, map, and crew member is in place before setting sail, an educator’s plan is their beacon, illuminating the path ahead and minimizing unforeseen challenges.
Elements of a Robust Plan
Objective and Clear Goals : Start by defining what success looks like for your action research. Whether it’s an improvement in student achievement, better participation, or more positive feedback, having a clear goal will guide your every step.
Methods for Data Collection: Decide on the tools you’ll use to gather information. This could be student assessments, student surveys , observation notes, or even video recordings. The method should align with the research question and be practical to implement.
Timeline: Construct a realistic timeline for your research. Define when you’ll start and finish the action, when you’ll collect data, and when you’ll analyze and reflect.
Resources: Identify any additional resources you may need. This could include technology, external expertise, or supplementary teaching materials.
Feedback Mechanisms: Plan for periodic checkpoints where you can gather interim feedback, either from students, peers, or through self-reflection.
Ensuring Success in Planning
Collaboration: Engage with fellow educators, seeking their insights or feedback on your plan. A second set of eyes can often identify potential pitfalls or areas of improvement.
Flexibility: While planning is essential, rigidly adhering to a plan without room for adjustment can be counterproductive. Be prepared to tweak your approach based on ongoing observations.
Alignment with Broader Curriculum: Ensure your action research plan doesn’t divert too significantly from the curriculum or educational goals. It should complement and enhance the broader educational objectives.
Knowing When the Plan is Ready for Action
Clarity and Vision: You should be able to succinctly explain your plan and its purpose to a colleague or even a student. If you can articulate it clearly, it’s a good sign you’ve thought it through.
Feasibility Check: Ensure that your plan is realistic. Do you have the resources, time, and support needed?
Positive Anticipation: If, after all the drafting and redrafting, you find yourself excited and optimistic about implementing your plan, it’s a good indicator that you’re ready to move forward.
Remember, a plan isn’t just a roadmap; it’s a promise – a commitment to our students and ourselves. It represents our dedication to enhancing our teaching practices and ensuring our best student outcomes. When the planning phase is executed with thoroughness and passion, the subsequent steps in our action research journey become more manageable and incredibly rewarding.
3. Setting Sail: The Vital Phase of Action in the Classroom

With our compass set and our maps drawn out, we step into the heart of our action research journey: the Action phase. This is the stage where our planning comes to life, our theories meet reality, and our classroom becomes the laboratory of educational innovation. Here, the rubber meets the road.
What Does Action Look Like in the Classroom?
Implementation of Action Research Guide: At its core, the action phase involves bringing the planned strategies or changes into the classroom. This could mean introducing a new teaching technique, using a different form of technology, adjusting classroom seating arrangements, or integrating new types of learning materials.
Active Observation: As these strategies unfold, it’s vital to maintain an active observation stance. This means not just teaching but keenly watching and noting the students’ reactions, participation levels, and engagement.
Openness to Feedback: The action phase isn’t about getting everything right on the first try. It’s about learning and adapting. Be open to feedback, both from students and peers, and be prepared to make minor adjustments along the way.
Maintaining Consistency: While flexibility is crucial, it’s equally important to give your strategies enough time to truly take effect. Consistency ensures that the observed results are genuinely a product of the changes you’ve implemented.
Specifics of Implementing the Plan
Start with Clear Communication: Before diving in, communicate your intentions to your students. Let them know that you’re trying something new and that their feedback is crucial. This not only sets expectations but also fosters a collaborative environment.
Document Everything: Maintain a journal or a digital log to document daily observations, challenges, successes, and any unexpected occurrences. This documentation will be invaluable during the reflection phase.
Seek Peer Support: If possible, invite a fellow educator to observe a class session. Their external perspective can offer invaluable insights and provide an objective viewpoint on the efficacy of your strategies.
Stay Adaptable: If a particular strategy isn’t working as anticipated, don’t be disheartened. Remember, the action phase is as much about learning what doesn’t work as it is about discovering what does.
Maintain Student-Centricity: Always prioritize the well-being and learning experience of your students. Ensure that any adjustments made during the action phase align with the best interests of the learners.
In essence, the action phase is where our dedication, passion, and commitment are truly tested. But it’s also where we, as educators, experience the profound joy of discovery, the exhilaration of innovation, and the satisfaction of seeing our plans come to life. As we navigate the waters of our classrooms, every challenge encountered and every success celebrated enriches our journey, making us not just better classroom teachers but lifelong learners.
4. Observing with Intention: The Critical Lens of Data Collection
The canvas of our action research becomes vibrant as we immerse ourselves in the action phase, but the true depth of our insights emerges through the lens of observation. Observing is more than just watching; it’s a meticulous process of data collection, allowing us to gather evidence of our action’s impact. In this intricate dance of teaching and learning, observation is our spotlight, shedding light on both the expected and the unexpected outcomes of our efforts.
How Teachers Should Gather Data
Stay Organized: Organize your observation tools in advance. Whether it’s a digital tool, a journal, or a structured survey, having them readily available ensures you capture data efficiently.
Consistent Timing: Choose specific times for your observations. Consistency will help you understand patterns and changes over a period.
Diversify Data Collection Methods: To gain a holistic understanding, use a mix of observation tools and methods. This ensures you’re capturing a well-rounded snapshot of classroom dynamics.
Types of Data to Collect
Qualitative Data
Anecdotal Records: Keep a journal where you note down specific incidents, conversations, or behaviors that stood out during the lesson. This offers insights into individual student experiences and reactions.
Student Feedback: Collect feedback from students about their experiences. This can be done informally through discussions or formally through structured feedback forms.
Peer Observations: Invite fellow educators to your class and ask for their feedback. Their perspective can offer new insights or validate your observations.
Reflective Journaling: End each day with a personal reflection. How did you feel the lesson went? Were there surprises? What went well, and what could be improved?
Quantitative Data
Assessment Scores: Track students’ performance on tests or quizzes. This provides measurable evidence of learning outcomes.
Attendance and Participation Rates: Monitor if there’s a change in attendance or participation. Increased engagement or attendance could be a sign of positive reception to your strategies.
Time Tracking: Measure the time students take for specific tasks or the time spent on certain activities. This can show if students are becoming more efficient or if they are more engrossed in particular activities.
Surveys with Scaled Responses: Use surveys where students can rate statements on a scale (e.g., 1-5). This provides quantitative data on students’ perceptions and feelings.
Additional Considerations for the Observation Phase
Maintain Objectivity: As invested as you are in the outcome, strive for objectivity. Your aim is to understand the genuine impact of your actions, whether positive, negative, or neutral.
Ensure Confidentiality: If gathering feedback or noting specific student behaviors, ensure that data is kept confidential. Respect privacy and use data ethically.
Stay Open-Minded: Be prepared for unexpected outcomes. Sometimes, the most unexpected observations lead to the most profound insights.
Observation, when approached with diligence and intention, unveils the intricacies of our classroom dynamics. It offers us a mirror to see the results of our actions, a window into our students’ experiences, and a telescope to envision the future course of our teaching journey.
5. The Harbor of Insight: Delving into the Reflection Stage
As our action research guide begins to reach its crescendo, we find ourselves anchored at the reflection stage—a moment of pause, introspection, and insight. Like a traveler pouring over the pages of a travel journal, the educator now sifts through the collected data, seeking to understand, interpret, and ultimately chart the way forward. The reflection stage isn’t merely an endpoint; it’s a springboard for future journeys, a compass recalibration, ensuring our teaching sails are ever aligned with the winds of effective pedagogy.
Data Analysis
Descriptive Analysis : Begin by taking a broad view of your data. Lay out all the qualitative research and quantitative information and look for obvious trends, patterns, or standout points.
Comparative Analysis: Compare the data from different points in time. How have things changed from the start to the end of your research? Look for improvements, regressions, or constants.
Pattern Recognition: Especially with qualitative data, search for recurring themes or sentiments. Are students consistently expressing a particular feeling or opinion? Do certain topics or methods evoke similar reactions across the board?
Statistical Analysis: For quantitative data, employ basic statistical tools (mean, median, mode, standard deviation) to get a clearer sense of your results. Tools like spreadsheets can assist in visualizing data trends.
What to Do with the Data
Document Your Findings: Craft a comprehensive report or journal entry detailing your findings. This not only helps in organizing your thoughts but serves as a valuable resource for future reference or sharing with peers.
Evaluate Against Objectives: Revisit the goals you set during the planning stage. Have these been met, exceeded, or not reached? Understanding this alignment helps in measuring the success of your action research.
Seek External Perspectives: Share your findings with fellow educators, mentors, or even students. Their insights can offer additional interpretations or validate your conclusions.
Consider the Broader Implications: Think beyond the confines of your classroom. How might your findings impact the wider school community, curriculum planning, or even educational theory?
Guiding Questions for Deeper Reflection
- How do the results align with my initial expectations?
- Were there any surprises in the data? What might have caused them?
- What were the challenges encountered, and how were they addressed?
- How have my students truly benefited (or not) from the implemented changes?
- What have I, as an educator, learned about myself, my teaching style, and my students through this process?
- Given another opportunity, what would I do differently? What would I retain?
Reflection is a potent tool, transforming raw data into actionable insights. It challenges us, reaffirms our beliefs, or offers a fresh perspective. But, above all, the reflection stage celebrates the spirit of action research in education—the relentless pursuit of betterment, the unwavering commitment to growth, and the heartfelt dedication to our students’ success. With every cycle of reflection, we don’t just become better educators; we amplify our impact, one classroom at a time.
6. Recharting the Course: Embracing the Power of Revision
With reflection complete, the map of our action research is fully sketched, brimming with insights and discoveries. But like any map of uncharted territories, revisions are inevitable, even welcome. The revision stage is the alchemy of action research, where past learnings are transmuted into the gold of future strategies. It’s not just about identifying what went wrong, but more crucially, about envisioning how things can be even better.
Revising with Purpose
Identify Areas of Improvement: Using the findings from the reflection phase, pinpoint specific areas that did not meet expectations or had unintended outcomes. Highlight these as primary candidates for revision.
Revisit Goals: Sometimes, it’s not the strategy but the goal that might need reconsideration. Ensure your objectives remain relevant to the ever-evolving classroom dynamics.
Integrate Feedback: Take into account the feedback from students, peers, and your self-reflections. Feedback is the cornerstone for any revision process.
Seek External Resources: Dive into educational literature, attend workshops, or collaborate with fellow educators. Bringing in external insights can provide fresh perspectives for your revisions.
Feeding Back into Another Round of Action Research
Starting Anew, Armed with Knowledge: The revision essentially kickstarts a new cycle of action research. But this time, you’re not starting from scratch. You’re armed with past insights, making your next cycle more refined.
Refined Questioning: With the data and reflections from the previous cycle, you can frame more specific research questions, addressing nuances you might have missed earlier.
Iterative Process: Understand that action research is iterative. Each cycle of revision and implementation brings you closer to an optimal strategy. It’s about continuous improvement, not instantaneous perfection.
Building a Repository: With each iteration, you’re essentially adding to a repository of teaching strategies, observations, and reflections. This becomes an invaluable resource, not just for you but for any educator looking to embark on a similar journey.
Important Considerations for the Revision Stage
Embrace Change with Positivity: Revision isn’t an admission of failure. It’s a celebration of growth. Approach it with optimism and view it as an opportunity.
Maintain Student-Centricity: Always keep the students at the heart of your revisions. Any changes you introduce should foremost benefit their learning experience.
Pace Yourself: While the enthusiasm to correct and implement can be overwhelming, ensure you’re giving yourself ample time for revisions. Hasty changes might not yield the desired results.
Document the Process: Just as with the initial action research, document every step of your revision process. This creates a trail of your evolution as an educator and can be insightful for future reflections.
Revision, in essence, is the heartbeat of action research. It embodies the spirit of adaptability, resilience, and continuous learning. Each revision is a testament to an educator’s unwavering commitment to excellence, a nod to the belief that while perfection might be elusive, the next step is always worthwhile. And as the cycle recommences, each iteration, informed by the last, pushes the boundaries of what’s possible in our classrooms, one revision at a time.
10 Types of Action Research Projects That Might Interest Teachers

- Differentiated Instruction: Research how implementing differentiated instruction strategies affects student engagement and understanding in a mixed-ability classroom.
- Incorporating Technology: Explore the effects of integrating technology (like tablets or specific educational apps) on student motivation and comprehension in a particular subject.
- Mindfulness and Student Behavior: Investigate the impact of daily mindfulness exercises on student behavior, attention span, and emotional well-being.
- Homework’s True Value: Study the correlation between the amount/type of homework given and students’ academic performance and stress levels.
- Effects of Outdoor Education: Explore how outdoor education can improve student confidence, behavior, and overall demeanor.
- Peer Tutoring and Collaboration: Research the effects of peer tutoring or cooperative learning structures on students’ academic achievements and social skills.
- Reading Strategies for Struggling Readers: Investigate the effectiveness of specific reading interventions on improving the fluency and comprehension of struggling readers.
- Feedback Methods: Explore the impact of various feedback methods (written comments, grades, peer feedback) on students’ academic performance and their perceptions about learning.
- Culturally Responsive Teaching: Research the outcomes of implementing culturally responsive teaching methods on the engagement and achievement of students from diverse backgrounds.
- Classroom Environment and Learning: Examine how changes in the classroom environment (e.g., seating arrangements, use of visuals, ambient noise) influence students’ concentration, participation, and overall learning experiences.
Each of these projects can help educators better understand their students, teaching methods, and overall classroom dynamics. By analyzing and reflecting upon the results, teachers can refine their practices to better meet the unique ways our students learn.
An Example of Action Research Project for Differentiated Instruction
Action research project plan: differentiated instruction in social sciences.
1. Introduction:
Purpose: To enhance student learning and engagement by tailoring instruction to meet individual needs.
Rationale: Observations indicate a range of abilities and learning styles within the classroom. A differentiated instruction approach may better cater to this diversity, ensuring all students are given an equitable opportunity to succeed.
2. Research Question:
How does the implementation of differentiated instruction strategies impact student engagement, understanding, and achievement in a mixed-ability classroom?
3. Data Sources:
Pre-assessment Surveys: Administer surveys to gauge students’ prior knowledge, learning preferences, and interests related to the topic at hand.
Lesson Observations: Use a checklist or journal to record levels of student engagement and participation during differentiated activities.
Student Feedback: Use informal discussions, suggestion boxes, or structured feedback forms to gather students’ perceptions of the differentiated activities.
Assessments: Compare performance on standardized tests or assignments before and after the introduction of differentiated strategies.
Teacher Reflection Journal: Maintain a daily or weekly journal to record personal observations, challenges, successes, and unexpected outcomes.
4. Differentiated Strategies to Implement:
Content Differentiation: Provide materials at varying reading levels, offer video/audio resources, and use graphic organizers.
Process Differentiation: Introduce tiered assignments where students can choose tasks based on complexity, conduct group activities tailored to different skill levels, and offer choice boards.
Product Differentiation: Allow students to showcase understanding in various ways (e.g., presentations, written reports, art projects, group projects, project-based learning, research paper).
5. Implementation Timeline:
Week 1: Administer pre-assessment surveys and conduct baseline observations.
Week 2-4: Gradually introduce differentiated strategies, starting with content differentiation.
Week 5-7: Incorporate process differentiation while continuing to monitor and adjust content differentiation based on feedback.
Week 8-10: Introduce product differentiation. Continue all forms of differentiation, making adjustments as needed.
Week 11: Administer post-assessment tests and gather student feedback.
Week 12: Analyze data, reflect on findings, and start drafting the research report.
6. Analysis:
Compare pre and post-assessment scores to gauge academic growth.
Analyze observation checklists to determine patterns in engagement and participation.
Use student feedback to understand their perceptions and experiences.
Reflect on teacher (the action researcher) journal entries to identify challenges, successes, and areas for future exploration.
7. Conclusion and Future Steps:
Summarize key findings, insights, and implications of implementing differentiated instruction.
Outline actionable steps for further refining and expanding the use of differentiated strategies based on the findings.
Consider collaborating with colleagues or attending professional development workshops for additional strategies and insights.
8. Share and Collaborate:
Present findings at school meetings or professional development sessions.
Collaborate with other educators to expand on successful strategies and brainstorm solutions for challenges.
Consider publishing findings in educational journals or sharing on teacher platforms to contribute to the wider educational community’s knowledge.
By following this plan, teachers can systematically investigate the potential benefits of differentiated instruction in their classrooms, allowing them to tailor their teaching methods to better serve all students.
Concluding the Action Research Guide: Refining Education One Cycle at a Time
The realm of education is in perpetual motion, driven by an unyielding quest for methods that can uplift, inspire, and catalyze effective learning. Action research emerges as an invaluable instrument in this quest. By weaving an intricate tapestry of questioning, planning, action, observation, reflection, and revision, action research empowers educators to actively sculpt their instructional practices, honing them in response to real-time classroom dynamics.
From the initial stages of identifying pertinent issues—be it the challenges of differentiated instruction, the integration of technology, or the nuances of classroom environment—to the iterative cycles of revision and reimplementation, participatory action research is a testament to educators’ proactive and adaptive spirit. It’s not merely about identifying what works but understanding why something works and how it can be improved.
Every phase, from the clarity of planning to the meticulousness of observation and the introspection of reflection, fortifies the foundation upon which educators build their strategies. The revision phase, integral to the cyclical nature of the action research process, underscores the philosophy that education is not static; it evolves, mirroring students’ dynamic needs and aspirations.
In essence, action research topics in education is both a journey and a destination. As a journey, it offers educators a structured pathway to navigate the intricate corridors of pedagogy, seeking betterment at every turn. As a destination, it culminates in classrooms where both teaching and learning are optimized, where educators, armed with insights and refined strategies, are better equipped to steer their students towards success.
In wrapping up our exploration, it’s clear that the action research cycle is not a mere academic exercise but a potent catalyst for transformative change in elementary schools, middle school, and secondary schools. It beckons educators worldwide to adopt a mindset of continuous improvement, forever striving, forever refining, and forever reimagining the horizons of what’s possible in our classroom practices.
For more on action research, consider Action Research: A Guide for the Teacher Researcher by Geoffrey Mills.
Join our Community!
Sign up for our weekly roundup of new content on The Cautiously Optimistic Teacher. We don’t spam! Read our privacy policy for more info.
Check your inbox or spam folder to confirm your subscription.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- What Is Action Research? | Definition & Examples
What Is Action Research? | Definition & Examples
Published on January 27, 2023 by Tegan George . Revised on January 12, 2024.
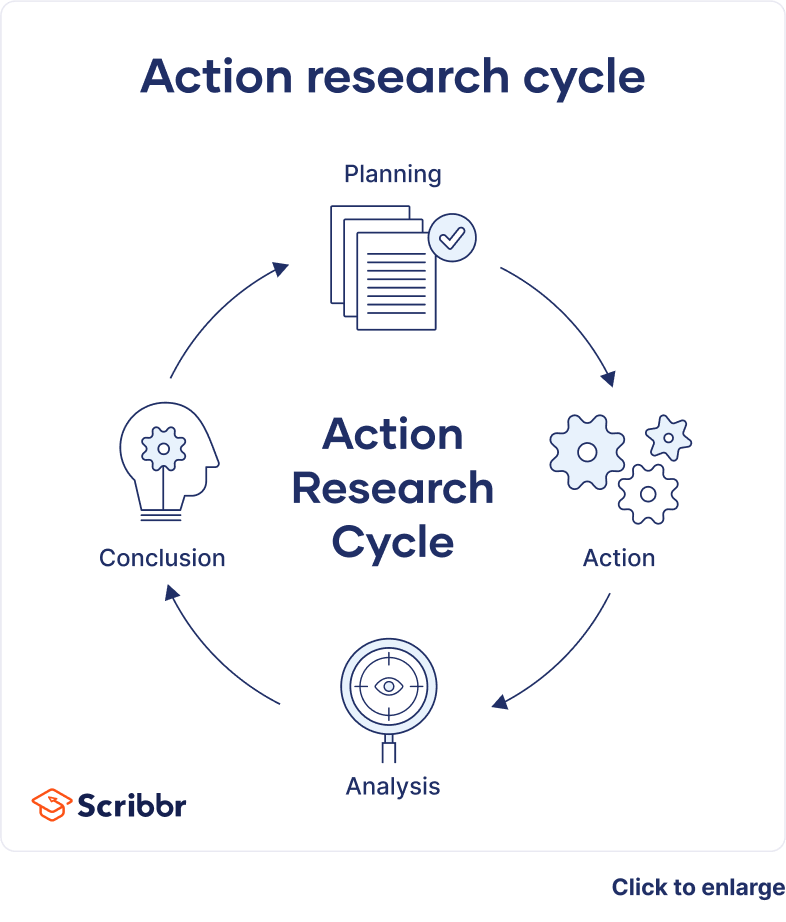
Table of contents
Types of action research, action research models, examples of action research, action research vs. traditional research, advantages and disadvantages of action research, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about action research.
There are 2 common types of action research: participatory action research and practical action research.
- Participatory action research emphasizes that participants should be members of the community being studied, empowering those directly affected by outcomes of said research. In this method, participants are effectively co-researchers, with their lived experiences considered formative to the research process.
- Practical action research focuses more on how research is conducted and is designed to address and solve specific issues.
Both types of action research are more focused on increasing the capacity and ability of future practitioners than contributing to a theoretical body of knowledge.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Action research is often reflected in 3 action research models: operational (sometimes called technical), collaboration, and critical reflection.
- Operational (or technical) action research is usually visualized like a spiral following a series of steps, such as “planning → acting → observing → reflecting.”
- Collaboration action research is more community-based, focused on building a network of similar individuals (e.g., college professors in a given geographic area) and compiling learnings from iterated feedback cycles.
- Critical reflection action research serves to contextualize systemic processes that are already ongoing (e.g., working retroactively to analyze existing school systems by questioning why certain practices were put into place and developed the way they did).
Action research is often used in fields like education because of its iterative and flexible style.
After the information was collected, the students were asked where they thought ramps or other accessibility measures would be best utilized, and the suggestions were sent to school administrators. Example: Practical action research Science teachers at your city’s high school have been witnessing a year-over-year decline in standardized test scores in chemistry. In seeking the source of this issue, they studied how concepts are taught in depth, focusing on the methods, tools, and approaches used by each teacher.
Action research differs sharply from other types of research in that it seeks to produce actionable processes over the course of the research rather than contributing to existing knowledge or drawing conclusions from datasets. In this way, action research is formative , not summative , and is conducted in an ongoing, iterative way.
| Action research | Traditional research | |
|---|---|---|
| and findings | ||
| and seeking between variables | ||
As such, action research is different in purpose, context, and significance and is a good fit for those seeking to implement systemic change.
Action research comes with advantages and disadvantages.
- Action research is highly adaptable , allowing researchers to mold their analysis to their individual needs and implement practical individual-level changes.
- Action research provides an immediate and actionable path forward for solving entrenched issues, rather than suggesting complicated, longer-term solutions rooted in complex data.
- Done correctly, action research can be very empowering , informing social change and allowing participants to effect that change in ways meaningful to their communities.
Disadvantages
- Due to their flexibility, action research studies are plagued by very limited generalizability and are very difficult to replicate . They are often not considered theoretically rigorous due to the power the researcher holds in drawing conclusions.
- Action research can be complicated to structure in an ethical manner . Participants may feel pressured to participate or to participate in a certain way.
- Action research is at high risk for research biases such as selection bias , social desirability bias , or other types of cognitive biases .
If you want to know more about statistics , methodology , or research bias , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Normal distribution
- Degrees of freedom
- Null hypothesis
- Discourse analysis
- Control groups
- Mixed methods research
- Non-probability sampling
- Quantitative research
- Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Research bias
- Rosenthal effect
- Implicit bias
- Cognitive bias
- Selection bias
- Negativity bias
- Status quo bias
Action research is conducted in order to solve a particular issue immediately, while case studies are often conducted over a longer period of time and focus more on observing and analyzing a particular ongoing phenomenon.
Action research is focused on solving a problem or informing individual and community-based knowledge in a way that impacts teaching, learning, and other related processes. It is less focused on contributing theoretical input, instead producing actionable input.
Action research is particularly popular with educators as a form of systematic inquiry because it prioritizes reflection and bridges the gap between theory and practice. Educators are able to simultaneously investigate an issue as they solve it, and the method is very iterative and flexible.
A cycle of inquiry is another name for action research . It is usually visualized in a spiral shape following a series of steps, such as “planning → acting → observing → reflecting.”
Sources in this article
We strongly encourage students to use sources in their work. You can cite our article (APA Style) or take a deep dive into the articles below.
George, T. (2024, January 12). What Is Action Research? | Definition & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved June 9, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/methodology/action-research/
Cohen, L., Manion, L., & Morrison, K. (2017). Research methods in education (8th edition). Routledge.
Naughton, G. M. (2001). Action research (1st edition). Routledge.
Is this article helpful?
Tegan George
Other students also liked, what is an observational study | guide & examples, primary research | definition, types, & examples, guide to experimental design | overview, steps, & examples, get unlimited documents corrected.
✔ Free APA citation check included ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
- QuestionPro

- Solutions Industries Gaming Automotive Sports and events Education Government Travel & Hospitality Financial Services Healthcare Cannabis Technology Use Case NPS+ Communities Audience Contactless surveys Mobile LivePolls Member Experience GDPR Positive People Science 360 Feedback Surveys
- Resources Blog eBooks Survey Templates Case Studies Training Help center
Home Market Research Research Tools and Apps
Action Research: What it is, Stages & Examples

The best way to get things accomplished is to do it yourself. This statement is utilized in corporations, community projects, and national governments. These organizations are relying on action research to cope with their continuously changing and unstable environments as they function in a more interdependent world.
In practical educational contexts, this involves using systematic inquiry and reflective practice to address real-world challenges, improve teaching and learning, enhance student engagement, and drive positive changes within the educational system.
This post outlines the definition of action research, its stages, and some examples.
Content Index
What is action research?
Stages of action research, the steps to conducting action research, examples of action research, advantages and disadvantages of action research.
Action research is a strategy that tries to find realistic solutions to organizations’ difficulties and issues. It is similar to applied research.
Action research refers basically learning by doing. First, a problem is identified, then some actions are taken to address it, then how well the efforts worked are measured, and if the results are not satisfactory, the steps are applied again.
It can be put into three different groups:
- Positivist: This type of research is also called “classical action research.” It considers research a social experiment. This research is used to test theories in the actual world.
- Interpretive: This kind of research is called “contemporary action research.” It thinks that business reality is socially made, and when doing this research, it focuses on the details of local and organizational factors.
- Critical: This action research cycle takes a critical reflection approach to corporate systems and tries to enhance them.
All research is about learning new things. Collaborative action research contributes knowledge based on investigations in particular and frequently useful circumstances. It starts with identifying a problem. After that, the research process is followed by the below stages:
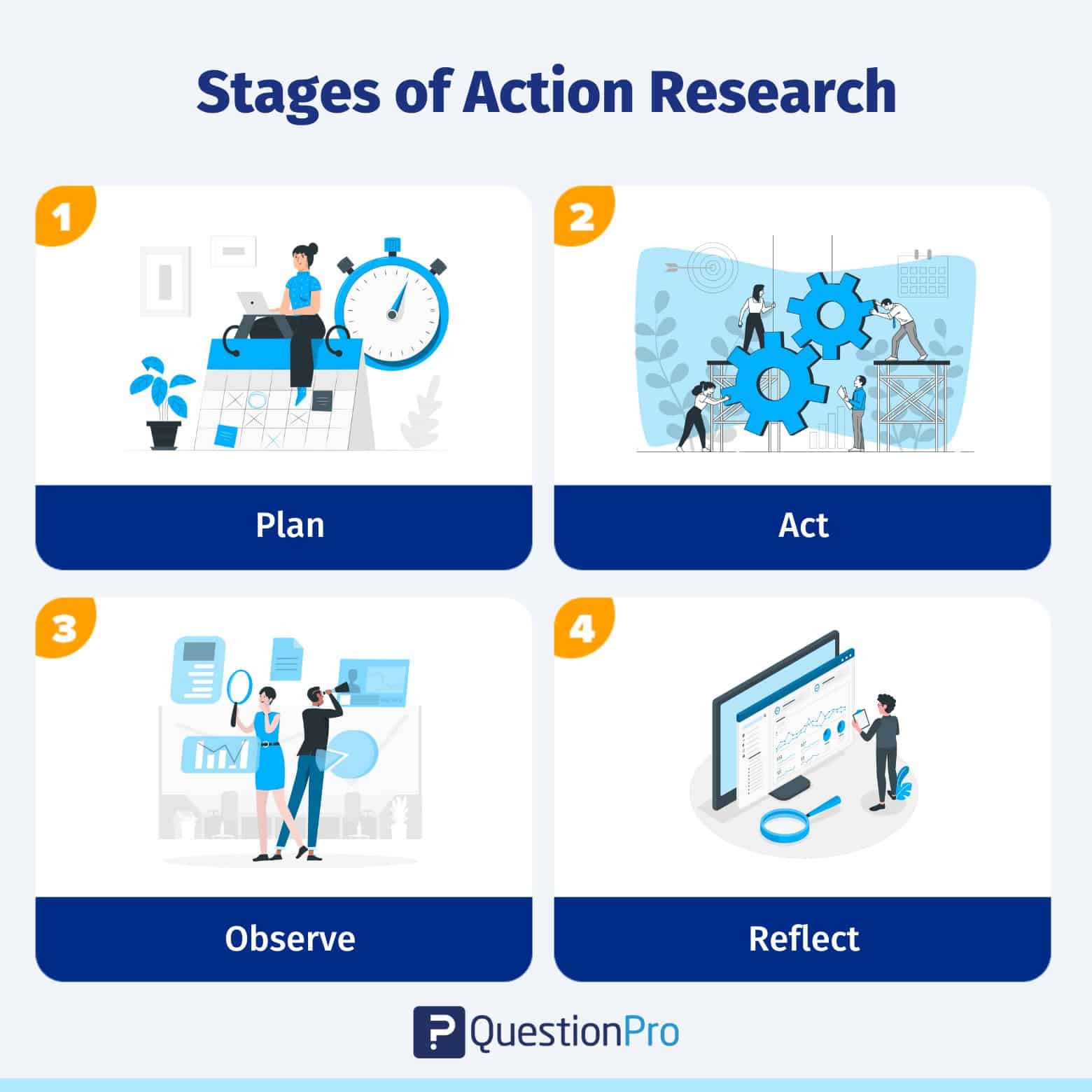
Stage 1: Plan
For an action research project to go well, the researcher needs to plan it well. After coming up with an educational research topic or question after a research study, the first step is to develop an action plan to guide the research process. The research design aims to address the study’s question. The research strategy outlines what to undertake, when, and how.
Stage 2: Act
The next step is implementing the plan and gathering data. At this point, the researcher must select how to collect and organize research data . The researcher also needs to examine all tools and equipment before collecting data to ensure they are relevant, valid, and comprehensive.

Stage 3: Observe
Data observation is vital to any investigation. The action researcher needs to review the project’s goals and expectations before data observation. This is the final step before drawing conclusions and taking action.
Different kinds of graphs, charts, and networks can be used to represent the data. It assists in making judgments or progressing to the next stage of observing.
Stage 4: Reflect
This step involves applying a prospective solution and observing the results. It’s essential to see if the possible solution found through research can really solve the problem being studied.
The researcher must explore alternative ideas when the action research project’s solutions fail to solve the problem.
Action research is a systematic approach researchers, educators, and practitioners use to identify and address problems or challenges within a specific context. It involves a cyclical process of planning, implementing, reflecting, and adjusting actions based on the data collected. Here are the general steps involved in conducting an action research process:
Identify the action research question or problem
Clearly define the issue or problem you want to address through your research. It should be specific, actionable, and relevant to your working context.
Review existing knowledge
Conduct a literature review to understand what research has already been done on the topic. This will help you gain insights, identify gaps, and inform your research design.
Plan the research
Develop a research plan outlining your study’s objectives, methods, data collection tools, and timeline. Determine the scope of your research and the participants or stakeholders involved.
Collect data
Implement your research plan by collecting relevant data. This can involve various methods such as surveys, interviews, observations, document analysis, or focus groups. Ensure that your data collection methods align with your research objectives and allow you to gather the necessary information.
Analyze the data
Once you have collected the data, analyze it using appropriate qualitative or quantitative techniques. Look for patterns, themes, or trends in the data that can help you understand the problem better.
Reflect on the findings
Reflect on the analyzed data and interpret the results in the context of your research question. Consider the implications and possible solutions that emerge from the data analysis. This reflection phase is crucial for generating insights and understanding the underlying factors contributing to the problem.
Develop an action plan
Based on your analysis and reflection, develop an action plan that outlines the steps you will take to address the identified problem. The plan should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART goals). Consider involving relevant stakeholders in planning to ensure their buy-in and support.
Implement the action plan
Put your action plan into practice by implementing the identified strategies or interventions. This may involve making changes to existing practices, introducing new approaches, or testing alternative solutions. Document the implementation process and any modifications made along the way.
Evaluate and monitor progress
Continuously monitor and evaluate the impact of your actions. Collect additional data, assess the effectiveness of the interventions, and measure progress towards your goals. This evaluation will help you determine if your actions have the desired effects and inform any necessary adjustments.
Reflect and iterate
Reflect on the outcomes of your actions and the evaluation results. Consider what worked well, what did not, and why. Use this information to refine your approach, make necessary adjustments, and plan for the next cycle of action research if needed.
Remember that participatory action research is an iterative process, and multiple cycles may be required to achieve significant improvements or solutions to the identified problem. Each cycle builds on the insights gained from the previous one, fostering continuous learning and improvement.
Explore Insightfully Contextual Inquiry in Qualitative Research
Here are two real-life examples of action research.
Action research initiatives are frequently situation-specific. Still, other researchers can adapt the techniques. The example is from a researcher’s (Franklin, 1994) report about a project encouraging nature tourism in the Caribbean.
In 1991, this was launched to study how nature tourism may be implemented on the four Windward Islands in the Caribbean: St. Lucia, Grenada, Dominica, and St. Vincent.
For environmental protection, a government-led action study determined that the consultation process needs to involve numerous stakeholders, including commercial enterprises.
First, two researchers undertook the study and held search conferences on each island. The search conferences resulted in suggestions and action plans for local community nature tourism sub-projects.
Several islands formed advisory groups and launched national awareness and community projects. Regional project meetings were held to discuss experiences, self-evaluations, and strategies. Creating a documentary about a local initiative helped build community. And the study was a success, leading to a number of changes in the area.
Lau and Hayward (1997) employed action research to analyze Internet-based collaborative work groups.
Over two years, the researchers facilitated three action research problem -solving cycles with 15 teachers, project personnel, and 25 health practitioners from diverse areas. The goal was to see how Internet-based communications might affect their virtual workgroup.
First, expectations were defined, technology was provided, and a bespoke workgroup system was developed. Participants suggested shorter, more dispersed training sessions with project-specific instructions.
The second phase saw the system’s complete deployment. The final cycle witnessed system stability and virtual group formation. The key lesson was that the learning curve was poorly misjudged, with frustrations only marginally met by phone-based technical help. According to the researchers, the absence of high-quality online material about community healthcare was harmful.
Role clarity, connection building, knowledge sharing, resource assistance, and experiential learning are vital for virtual group growth. More study is required on how group support systems might assist groups in engaging with their external environment and boost group members’ learning.
Action research has both good and bad points.
- It is very flexible, so researchers can change their analyses to fit their needs and make individual changes.
- It offers a quick and easy way to solve problems that have been going on for a long time instead of complicated, long-term solutions based on complex facts.
- If It is done right, it can be very powerful because it can lead to social change and give people the tools to make that change in ways that are important to their communities.
Disadvantages
- These studies have a hard time being generalized and are hard to repeat because they are so flexible. Because the researcher has the power to draw conclusions, they are often not thought to be theoretically sound.
- Setting up an action study in an ethical way can be hard. People may feel like they have to take part or take part in a certain way.
- It is prone to research errors like selection bias , social desirability bias, and other cognitive biases.
LEARN ABOUT: Self-Selection Bias
This post discusses how action research generates knowledge, its steps, and real-life examples. It is very applicable to the field of research and has a high level of relevance. We can only state that the purpose of this research is to comprehend an issue and find a solution to it.
At QuestionPro, we give researchers tools for collecting data, like our survey software, and a library of insights for any long-term study. Go to the Insight Hub if you want to see a demo or learn more about it.
LEARN MORE FREE TRIAL
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQ’s)
Action research is a systematic approach to inquiry that involves identifying a problem or challenge in a practical context, implementing interventions or changes, collecting and analyzing data, and using the findings to inform decision-making and drive positive change.
Action research can be conducted by various individuals or groups, including teachers, administrators, researchers, and educational practitioners. It is often carried out by those directly involved in the educational setting where the research takes place.
The steps of action research typically include identifying a problem, reviewing relevant literature, designing interventions or changes, collecting and analyzing data, reflecting on findings, and implementing improvements based on the results.
MORE LIKE THIS

Life@QuestionPro: The Journey of Kristie Lawrence
Jun 7, 2024

How Can I Help You? — Tuesday CX Thoughts
Jun 5, 2024

Why Multilingual 360 Feedback Surveys Provide Better Insights
Jun 3, 2024

Raked Weighting: A Key Tool for Accurate Survey Results
May 31, 2024
Other categories
- Academic Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assessments
- Brand Awareness
- Case Studies
- Communities
- Consumer Insights
- Customer effort score
- Customer Engagement
- Customer Experience
- Customer Loyalty
- Customer Research
- Customer Satisfaction
- Employee Benefits
- Employee Engagement
- Employee Retention
- Friday Five
- General Data Protection Regulation
- Insights Hub
- Life@QuestionPro
- Market Research
- Mobile diaries
- Mobile Surveys
- New Features
- Online Communities
- Question Types
- Questionnaire
- QuestionPro Products
- Release Notes
- Research Tools and Apps
- Revenue at Risk
- Survey Templates
- Training Tips
- Uncategorized
- Video Learning Series
- What’s Coming Up
- Workforce Intelligence
education, community-building and change
What is action research and how do we do it?
In this article, we explore the development of some different traditions of action research and provide an introductory guide to the literature.
Contents : what is action research · origins · the decline and rediscovery of action research · undertaking action research · conclusion · further reading · how to cite this article . see, also: research for practice ., what is action research.
In the literature, discussion of action research tends to fall into two distinctive camps. The British tradition – especially that linked to education – tends to view action research as research-oriented toward the enhancement of direct practice. For example, Carr and Kemmis provide a classic definition:
Action research is simply a form of self-reflective enquiry undertaken by participants in social situations in order to improve the rationality and justice of their own practices, their understanding of these practices, and the situations in which the practices are carried out (Carr and Kemmis 1986: 162).
Many people are drawn to this understanding of action research because it is firmly located in the realm of the practitioner – it is tied to self-reflection. As a way of working it is very close to the notion of reflective practice coined by Donald Schön (1983).
The second tradition, perhaps more widely approached within the social welfare field – and most certainly the broader understanding in the USA is of action research as ‘the systematic collection of information that is designed to bring about social change’ (Bogdan and Biklen 1992: 223). Bogdan and Biklen continue by saying that its practitioners marshal evidence or data to expose unjust practices or environmental dangers and recommend actions for change. In many respects, for them, it is linked into traditions of citizen’s action and community organizing. The practitioner is actively involved in the cause for which the research is conducted. For others, it is such commitment is a necessary part of being a practitioner or member of a community of practice. Thus, various projects designed to enhance practice within youth work, for example, such as the detached work reported on by Goetschius and Tash (1967) could be talked of as action research.
Kurt Lewin is generally credited as the person who coined the term ‘action research’:
The research needed for social practice can best be characterized as research for social management or social engineering. It is a type of action-research, a comparative research on the conditions and effects of various forms of social action, and research leading to social action. Research that produces nothing but books will not suffice (Lewin 1946, reproduced in Lewin 1948: 202-3)
His approach involves a spiral of steps, ‘each of which is composed of a circle of planning, action and fact-finding about the result of the action’ ( ibid. : 206). The basic cycle involves the following:
This is how Lewin describes the initial cycle:
The first step then is to examine the idea carefully in the light of the means available. Frequently more fact-finding about the situation is required. If this first period of planning is successful, two items emerge: namely, “an overall plan” of how to reach the objective and secondly, a decision in regard to the first step of action. Usually this planning has also somewhat modified the original idea. ( ibid. : 205)
The next step is ‘composed of a circle of planning, executing, and reconnaissance or fact-finding for the purpose of evaluating the results of the second step, and preparing the rational basis for planning the third step, and for perhaps modifying again the overall plan’ ( ibid. : 206). What we can see here is an approach to research that is oriented to problem-solving in social and organizational settings, and that has a form that parallels Dewey’s conception of learning from experience.
The approach, as presented, does take a fairly sequential form – and it is open to a literal interpretation. Following it can lead to practice that is ‘correct’ rather than ‘good’ – as we will see. It can also be argued that the model itself places insufficient emphasis on analysis at key points. Elliott (1991: 70), for example, believed that the basic model allows those who use it to assume that the ‘general idea’ can be fixed in advance, ‘that “reconnaissance” is merely fact-finding, and that “implementation” is a fairly straightforward process’. As might be expected there was some questioning as to whether this was ‘real’ research. There were questions around action research’s partisan nature – the fact that it served particular causes.
The decline and rediscovery of action research
Action research did suffer a decline in favour during the 1960s because of its association with radical political activism (Stringer 2007: 9). There were, and are, questions concerning its rigour, and the training of those undertaking it. However, as Bogdan and Biklen (1992: 223) point out, research is a frame of mind – ‘a perspective that people take toward objects and activities’. Once we have satisfied ourselves that the collection of information is systematic and that any interpretations made have a proper regard for satisfying truth claims, then much of the critique aimed at action research disappears. In some of Lewin’s earlier work on action research (e.g. Lewin and Grabbe 1945), there was a tension between providing a rational basis for change through research, and the recognition that individuals are constrained in their ability to change by their cultural and social perceptions, and the systems of which they are a part. Having ‘correct knowledge’ does not of itself lead to change, attention also needs to be paid to the ‘matrix of cultural and psychic forces’ through which the subject is constituted (Winter 1987: 48).
Subsequently, action research has gained a significant foothold both within the realm of community-based, and participatory action research; and as a form of practice-oriented to the improvement of educative encounters (e.g. Carr and Kemmis 1986).
Exhibit 1: Stringer on community-based action research
A fundamental premise of community-based action research is that it commences with an interest in the problems of a group, a community, or an organization. Its purpose is to assist people in extending their understanding of their situation and thus resolving problems that confront them….
Community-based action research is always enacted through an explicit set of social values. In modern, democratic social contexts, it is seen as a process of inquiry that has the following characteristics:
• It is democratic , enabling the participation of all people.
• It is equitable , acknowledging people’s equality of worth.
• It is liberating , providing freedom from oppressive, debilitating conditions.
• It is life enhancing , enabling the expression of people’s full human potential.
(Stringer 1999: 9-10)
Undertaking action research
As Thomas (2017: 154) put it, the central aim is change, ‘and the emphasis is on problem-solving in whatever way is appropriate’. It can be seen as a conversation rather more than a technique (McNiff et. al. ). It is about people ‘thinking for themselves and making their own choices, asking themselves what they should do and accepting the consequences of their own actions’ (Thomas 2009: 113).
The action research process works through three basic phases:
Look -building a picture and gathering information. When evaluating we define and describe the problem to be investigated and the context in which it is set. We also describe what all the participants (educators, group members, managers etc.) have been doing.
Think – interpreting and explaining. When evaluating we analyse and interpret the situation. We reflect on what participants have been doing. We look at areas of success and any deficiencies, issues or problems.
Act – resolving issues and problems. In evaluation we judge the worth, effectiveness, appropriateness, and outcomes of those activities. We act to formulate solutions to any problems. (Stringer 1999: 18; 43-44;160)
The use of action research to deepen and develop classroom practice has grown into a strong tradition of practice (one of the first examples being the work of Stephen Corey in 1949). For some, there is an insistence that action research must be collaborative and entail groupwork.
Action research is a form of collective self-reflective enquiry undertaken by participants in social situations in order to improve the rationality and justice of their own social or educational practices, as well as their understanding of those practices and the situations in which the practices are carried out… The approach is only action research when it is collaborative, though it is important to realise that action research of the group is achieved through the critically examined action of individual group members. (Kemmis and McTaggart 1988: 5-6)
Just why it must be collective is open to some question and debate (Webb 1996), but there is an important point here concerning the commitments and orientations of those involved in action research.
One of the legacies Kurt Lewin left us is the ‘action research spiral’ – and with it there is the danger that action research becomes little more than a procedure. It is a mistake, according to McTaggart (1996: 248) to think that following the action research spiral constitutes ‘doing action research’. He continues, ‘Action research is not a ‘method’ or a ‘procedure’ for research but a series of commitments to observe and problematize through practice a series of principles for conducting social enquiry’. It is his argument that Lewin has been misunderstood or, rather, misused. When set in historical context, while Lewin does talk about action research as a method, he is stressing a contrast between this form of interpretative practice and more traditional empirical-analytic research. The notion of a spiral may be a useful teaching device – but it is all too easy to slip into using it as the template for practice (McTaggart 1996: 249).
Further reading
This select, annotated bibliography has been designed to give a flavour of the possibilities of action research and includes some useful guides to practice. As ever, if you have suggestions about areas or specific texts for inclusion, I’d like to hear from you.
Explorations of action research
Atweh, B., Kemmis, S. and Weeks, P. (eds.) (1998) Action Research in Practice: Partnership for Social Justice in Education, London: Routledge. Presents a collection of stories from action research projects in schools and a university. The book begins with theme chapters discussing action research, social justice and partnerships in research. The case study chapters cover topics such as: school environment – how to make a school a healthier place to be; parents – how to involve them more in decision-making; students as action researchers; gender – how to promote gender equity in schools; writing up action research projects.
Carr, W. and Kemmis, S. (1986) Becoming Critical. Education, knowledge and action research , Lewes: Falmer. Influential book that provides a good account of ‘action research’ in education. Chapters on teachers, researchers and curriculum; the natural scientific view of educational theory and practice; the interpretative view of educational theory and practice; theory and practice – redefining the problem; a critical approach to theory and practice; towards a critical educational science; action research as critical education science; educational research, educational reform and the role of the profession.
Carson, T. R. and Sumara, D. J. (ed.) (1997) Action Research as a Living Practice , New York: Peter Lang. 140 pages. Book draws on a wide range of sources to develop an understanding of action research. Explores action research as a lived practice, ‘that asks the researcher to not only investigate the subject at hand but, as well, to provide some account of the way in which the investigation both shapes and is shaped by the investigator.
Dadds, M. (1995) Passionate Enquiry and School Development. A story about action research , London: Falmer. 192 + ix pages. Examines three action research studies undertaken by a teacher and how they related to work in school – how she did the research, the problems she experienced, her feelings, the impact on her feelings and ideas, and some of the outcomes. In his introduction, John Elliot comments that the book is ‘the most readable, thoughtful, and detailed study of the potential of action-research in professional education that I have read’.
Ghaye, T. and Wakefield, P. (eds.) CARN Critical Conversations. Book one: the role of the self in action , Bournemouth: Hyde Publications. 146 + xiii pages. Collection of five pieces from the Classroom Action Research Network. Chapters on: dialectical forms; graduate medical education – research’s outer limits; democratic education; managing action research; writing up.
McNiff, J. (1993) Teaching as Learning: An Action Research Approach , London: Routledge. Argues that educational knowledge is created by individual teachers as they attempt to express their own values in their professional lives. Sets out familiar action research model: identifying a problem, devising, implementing and evaluating a solution and modifying practice. Includes advice on how working in this way can aid the professional development of action researcher and practitioner.
Quigley, B. A. and Kuhne, G. W. (eds.) (1997) Creating Practical Knowledge Through Action Research, San Fransisco: Jossey Bass. Guide to action research that outlines the action research process, provides a project planner, and presents examples to show how action research can yield improvements in six different settings, including a hospital, a university and a literacy education program.
Plummer, G. and Edwards, G. (eds.) CARN Critical Conversations. Book two: dimensions of action research – people, practice and power , Bournemouth: Hyde Publications. 142 + xvii pages. Collection of five pieces from the Classroom Action Research Network. Chapters on: exchanging letters and collaborative research; diary writing; personal and professional learning – on teaching and self-knowledge; anti-racist approaches; psychodynamic group theory in action research.
Whyte, W. F. (ed.) (1991) Participatory Action Research , Newbury Park: Sage. 247 pages. Chapters explore the development of participatory action research and its relation with action science and examine its usages in various agricultural and industrial settings
Zuber-Skerritt, O. (ed.) (1996) New Directions in Action Research , London; Falmer Press. 266 + xii pages. A useful collection that explores principles and procedures for critical action research; problems and suggested solutions; and postmodernism and critical action research.
Action research guides
Coghlan, D. and Brannick, D. (2000) Doing Action Research in your own Organization, London: Sage. 128 pages. Popular introduction. Part one covers the basics of action research including the action research cycle, the role of the ‘insider’ action researcher and the complexities of undertaking action research within your own organisation. Part two looks at the implementation of the action research project (including managing internal politics and the ethics and politics of action research). New edition due late 2004.
Elliot, J. (1991) Action Research for Educational Change , Buckingham: Open University Press. 163 + x pages Collection of various articles written by Elliot in which he develops his own particular interpretation of action research as a form of teacher professional development. In some ways close to a form of ‘reflective practice’. Chapter 6, ‘A practical guide to action research’ – builds a staged model on Lewin’s work and on developments by writers such as Kemmis.
Johnson, A. P. (2007) A short guide to action research 3e. Allyn and Bacon. Popular step by step guide for master’s work.
Macintyre, C. (2002) The Art of the Action Research in the Classroom , London: David Fulton. 138 pages. Includes sections on action research, the role of literature, formulating a research question, gathering data, analysing data and writing a dissertation. Useful and readable guide for students.
McNiff, J., Whitehead, J., Lomax, P. (2003) You and Your Action Research Project , London: Routledge. Practical guidance on doing an action research project.Takes the practitioner-researcher through the various stages of a project. Each section of the book is supported by case studies
Stringer, E. T. (2007) Action Research: A handbook for practitioners 3e , Newbury Park, ca.: Sage. 304 pages. Sets community-based action research in context and develops a model. Chapters on information gathering, interpretation, resolving issues; legitimacy etc. See, also Stringer’s (2003) Action Research in Education , Prentice-Hall.
Winter, R. (1989) Learning From Experience. Principles and practice in action research , Lewes: Falmer Press. 200 + 10 pages. Introduces the idea of action research; the basic process; theoretical issues; and provides six principles for the conduct of action research. Includes examples of action research. Further chapters on from principles to practice; the learner’s experience; and research topics and personal interests.
Action research in informal education
Usher, R., Bryant, I. and Johnston, R. (1997) Adult Education and the Postmodern Challenge. Learning beyond the limits , London: Routledge. 248 + xvi pages. Has some interesting chapters that relate to action research: on reflective practice; changing paradigms and traditions of research; new approaches to research; writing and learning about research.
Other references
Bogdan, R. and Biklen, S. K. (1992) Qualitative Research For Education , Boston: Allyn and Bacon.
Goetschius, G. and Tash, J. (1967) Working with the Unattached , London: Routledge and Kegan Paul.
McTaggart, R. (1996) ‘Issues for participatory action researchers’ in O. Zuber-Skerritt (ed.) New Directions in Action Research , London: Falmer Press.
McNiff, J., Lomax, P. and Whitehead, J. (2003) You and Your Action Research Project 2e. London: Routledge.
Thomas, G. (2017). How to do your Research Project. A guide for students in education and applied social sciences . 3e. London: Sage.
Acknowledgements : spiral by Michèle C. | flickr ccbyncnd2 licence
How to cite this article : Smith, M. K. (1996; 2001, 2007, 2017) What is action research and how do we do it?’, The encyclopedia of pedagogy and informal education. [ https://infed.org/mobi/action-research/ . Retrieved: insert date] .
© Mark K. Smith 1996; 2001, 2007, 2017
Last Updated on December 7, 2020 by infed.org

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
4 Preparing for Action Research in the Classroom: Practical Issues
ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS
- What sort of considerations are necessary to take action in your educational context?
- How do you facilitate an action plan without disrupting your teaching?
- How do you respond when the unplanned happens during data collection?
An action research project is a practical endeavor that will ultimately be shaped by your educational context and practice. Now that you have developed a literature review, you are ready to revise your initial plans and begin to plan your project. This chapter will provide some advice about your considerations when undertaking an action research project in your classroom.
Maintain Focus
Hopefully, you found a lot a research on your topic. If so, you will now have a better understanding of how it fits into your area and field of educational research. Even though the topic and area you are researching may not be small, your study itself should clearly focus on one aspect of the topic in your classroom. It is important to maintain clarity about what you are investigating because a lot will be going on simultaneously during the research process and you do not want to spend precious time on erroneous aspects that are irrelevant to your research.
Even though you may view your practice as research, and vice versa, you might want to consider your research project as a projection or megaphone for your work that will bring attention to the small decisions that make a difference in your educational context. From experience, our concern is that you will find that researching one aspect of your practice will reveal other interconnected aspects that you may find interesting, and you will disorient yourself researching in a confluence of interests, commitments, and purposes. We simply want to emphasize – don’t try to research everything at once. Stay focused on your topic, and focus on exploring it in depth, instead of its many related aspects. Once you feel you have made progress in one aspect, you can then progress to other related areas, as new research projects that continue the research cycle.
Identify a Clear Research Question
Your literature review should have exposed you to an array of research questions related to your topic. More importantly, your review should have helped identify which research questions we have addressed as a field, and which ones still need to be addressed . More than likely your research questions will resemble ones from your literature review, while also being distinguishable based upon your own educational context and the unexplored areas of research on your topic.
Regardless of how your research question took shape, it is important to be clear about what you are researching in your educational context. Action research questions typically begin in ways related to “How does … ?” or “How do I/we … ?”, for example:
Research Question Examples
- How does a semi-structured morning meeting improve my classroom community?
- How does historical fiction help students think about people’s agency in the past?
- How do I improve student punctuation use through acting out sentences?
- How do we increase student responsibility for their own learning as a team of teachers?
I particularly favor questions with I or we, because they emphasize that you, the actor and researcher, will be clearly taking action to improve your practice. While this may seem rather easy, you need to be aware of asking the right kind of question. One issue is asking a too pointed and closed question that limits the possibility for analysis. These questions tend to rely on quantitative answers, or yes/no answers. For example, “How many students got a 90% or higher on the exam, after reviewing the material three times?
Another issue is asking a question that is too broad, or that considers too many variables. For example, “How does room temperature affect students’ time-on-task?” These are obviously researchable questions, but the aim is a cause-and-effect relationship between variables that has little or no value to your daily practice.
I also want to point out that your research question will potentially change as the research develops. If you consider the question:
As you do an activity, you may find that students are more comfortable and engaged by acting sentences out in small groups, instead of the whole class. Therefore, your question may shift to:
- How do I improve student punctuation use through acting out sentences, in small groups ?
By simply engaging in the research process and asking questions, you will open your thinking to new possibilities and you will develop new understandings about yourself and the problematic aspects of your educational context.
Understand Your Capabilities and Know that Change Happens Slowly
Similar to your research question, it is important to have a clear and realistic understanding of what is possible to research in your specific educational context. For example, would you be able to address unsatisfactory structures (policies and systems) within your educational context? Probably not immediately, but over time you potentially could. It is much more feasible to think of change happening in smaller increments, from within your own classroom or context, with you as one change agent. For example, you might find it particularly problematic that your school or district places a heavy emphasis on traditional grades, believing that these grades are often not reflective of the skills students have or have not mastered. Instead of attempting to research grading practices across your school or district, your research might instead focus on determining how to provide more meaningful feedback to students and parents about progress in your course. While this project identifies and addresses a structural issue that is part of your school and district context, to keep things manageable, your research project would focus the outcomes on your classroom. The more research you do related to the structure of your educational context the more likely modifications will emerge. The more you understand these modifications in relation to the structural issues you identify within your own context, the more you can influence others by sharing your work and enabling others to understand the modification and address structural issues within their contexts. Throughout your project, you might determine that modifying your grades to be standards-based is more effective than traditional grades, and in turn, that sharing your research outcomes with colleagues at an in-service presentation prompts many to adopt a similar model in their own classrooms. It can be defeating to expect the world to change immediately, but you can provide the spark that ignites coordinated changes. In this way, action research is a powerful methodology for enacting social change. Action research enables individuals to change their own lives, while linking communities of like-minded practitioners who work towards action.
Plan Thoughtfully
Planning thoughtfully involves having a path in mind, but not necessarily having specific objectives. Due to your experience with students and your educational context, the research process will often develop in ways as you expected, but at times it may develop a little differently, which may require you to shift the research focus and change your research question. I will suggest a couple methods to help facilitate this potential shift. First, you may want to develop criteria for gauging the effectiveness of your research process. You may need to refine and modify your criteria and your thinking as you go. For example, we often ask ourselves if action research is encouraging depth of analysis beyond my typical daily pedagogical reflection. You can think about this as you are developing data collection methods and even when you are collecting data. The key distinction is whether the data you will be collecting allows for nuance among the participants or variables. This does not mean that you will have nuance, but it should allow for the possibility. Second, criteria are shaped by our values and develop into standards of judgement. If we identify criteria such as teacher empowerment, then we will use that standard to think about the action contained in our research process. Our values inform our work; therefore, our work should be judged in relation to the relevance of our values in our pedagogy and practice.
Does Your Timeline Work?
While action research is situated in the temporal span that is your life, your research project is short-term, bounded, and related to the socially mediated practices within your educational context. The timeline is important for bounding, or setting limits to your research project, while also making sure you provide the right amount of time for the data to emerge from the process.
For example, if you are thinking about examining the use of math diaries in your classroom, you probably do not want to look at a whole semester of entries because that would be a lot of data, with entries related to a wide range of topics. This would create a huge data analysis endeavor. Therefore, you may want to look at entries from one chapter or unit of study. Also, in terms of timelines, you want to make sure participants have enough time to develop the data you collect. Using the same math example, you would probably want students to have plenty of time to write in the journals, and also space out the entries over the span of the chapter or unit.
In relation to the examples, we think it is an important mind shift to not think of research timelines in terms of deadlines. It is vitally important to provide time and space for the data to emerge from the participants. Therefore, it would be potentially counterproductive to rush a 50-minute data collection into 20 minutes – like all good educators, be flexible in the research process.
Involve Others
It is important to not isolate yourself when doing research. Many educators are already isolated when it comes to practice in their classroom. The research process should be an opportunity to engage with colleagues and open up your classroom to discuss issues that are potentially impacting your entire educational context. Think about the following relationships:
Research participants
You may invite a variety of individuals in your educational context, many with whom you are in a shared situation (e.g. colleagues, administrators). These participants may be part of a collaborative study, they may simply help you develop data collection instruments or intervention items, or they may help to analyze and make sense of the data. While the primary research focus will be you and your learning, you will also appreciate how your learning is potentially influencing the quality of others’ learning.
We always tell educators to be public about your research, or anything exciting that is happening in your educational context, for that matter. In terms of research, you do not want it to seem mysterious to any stakeholder in the educational context. Invite others to visit your setting and observe your research process, and then ask for their formal feedback. Inviting others to your classroom will engage and connect you with other stakeholders, while also showing that your research was established in an ethic of respect for multiple perspectives.
Critical friends or validators
Using critical friends is one way to involve colleagues and also validate your findings and conclusions. While your positionality will shape the research process and subsequently your interpretations of the data, it is important to make sure that others see similar logic in your process and conclusions. Critical friends or validators provide some level of certification that the frameworks you use to develop your research project and make sense of your data are appropriate for your educational context. Your critical friends and validators’ suggestions will be useful if you develop a report or share your findings, but most importantly will provide you confidence moving forward.
Potential researchers
As an educational researcher, you are involved in ongoing improvement plans and district or systemic change. The flexibility of action research allows it to be used in a variety of ways, and your initial research can spark others in your context to engage in research either individually for their own purposes, or collaboratively as a grade level, team, or school. Collaborative inquiry with other educators is an emerging form of professional learning and development for schools with school improvement plans. While they call it collaborative inquiry, these schools are often using an action research model. It is good to think of all of your colleagues as potential research collaborators in the future.
Prioritize Ethical Practice
Try to always be cognizant of your own positionality during the action research process, its relation to your educational context, and any associated power relation to your positionality. Furthermore, you want to make sure that you are not coercing or engaging participants into harmful practices. While this may seem obvious, you may not even realize you are harming your participants because you believe the action is necessary for the research process.
For example, commonly teachers want to try out an intervention that will potentially positively impact their students. When the teacher sets up the action research study, they may have a control group and an experimental group. There is potential to impair the learning of one of these groups if the intervention is either highly impactful or exceedingly worse than the typical instruction. Therefore, teachers can sometimes overlook the potential harm to students in pursuing an experimental method of exploring an intervention.
If you are working with a university researcher, ethical concerns will be covered by the Institutional Review Board (IRB). If not, your school or district may have a process or form that you would need to complete, so it would beneficial to check your district policies before starting. Other widely accepted aspects of doing ethically informed research, include:
Confirm Awareness of Study and Negotiate Access – with authorities, participants and parents, guardians, caregivers and supervisors (with IRB this is done with Informed Consent).
- Promise to Uphold Confidentiality – Uphold confidentiality, to your fullest ability, to protect information, identity and data. You can identify people if they indicate they want to be recognized for their contributions.
- Ensure participants’ rights to withdraw from the study at any point .
- Make sure data is secured, either on password protected computer or lock drawer .
Prepare to Problematize your Thinking
Educational researchers who are more philosophically-natured emphasize that research is not about finding solutions, but instead is about creating and asking new and more precise questions. This is represented in the action research process shown in the diagrams in Chapter 1, as Collingwood (1939) notes the aim in human interaction is always to keep the conversation open, while Edward Said (1997) emphasized that there is no end because whatever we consider an end is actually the beginning of something entirely new. These reflections have perspective in evaluating the quality in research and signifying what is “good” in “good pedagogy” and “good research”. If we consider that action research is about studying and reflecting on one’s learning and how that learning influences practice to improve it, there is nothing to stop your line of inquiry as long as you relate it to improving practice. This is why it is necessary to problematize and scrutinize our practices.
Ethical Dilemmas for Educator-Researchers
Classroom teachers are increasingly expected to demonstrate a disposition of reflection and inquiry into their own practice. Many advocate for schools to become research centers, and to produce their own research studies, which is an important advancement in acknowledging and addressing the complexity in today’s schools. When schools conduct their own research studies without outside involvement, they bypass outside controls over their studies. Schools shift power away from the oversight of outside experts and ethical research responsibilities are shifted to those conducting the formal research within their educational context. Ethics firmly grounded and established in school policies and procedures for teaching, becomes multifaceted when teaching practice and research occur simultaneously. When educators conduct research in their classrooms, are they doing so as teachers or as researchers, and if they are researchers, at what point does the teaching role change to research? Although the notion of objectivity is a key element in traditional research paradigms, educator-based research acknowledges a subjective perspective as the educator-researcher is not viewed separately from the research. In action research, unlike traditional research, the educator as researcher gains access to the research site by the nature of the work they are paid and expected to perform. The educator is never detached from the research and remains at the research site both before and after the study. Because studying one’s practice comprises working with other people, ethical deliberations are inevitable. Educator-researchers confront role conflict and ambiguity regarding ethical issues such as informed consent from participants, protecting subjects (students) from harm, and ensuring confidentiality. They must demonstrate a commitment toward fully understanding ethical dilemmas that present themselves within the unique set of circumstances of the educational context. Questions about research ethics can feel exceedingly complex and in specific situations, educator- researchers require guidance from others.
Think about it this way. As a part-time historian and former history teacher I often problematized who we regard as good and bad people in history. I (Clark) grew up minutes from Jesse James’ childhood farm. Jesse James is a well-documented thief, and possibly by today’s standards, a terrorist. He is famous for daylight bank robberies, as well as the sheer number of successful robberies. When Jesse James was assassinated, by a trusted associate none-the-less, his body travelled the country for people to see, while his assailant and assailant’s brother reenacted the assassination over 1,200 times in theaters across the country. Still today in my hometown, they reenact Jesse James’ daylight bank robbery each year at the Fall Festival, immortalizing this thief and terrorist from our past. This demonstrates how some people saw him as somewhat of hero, or champion of some sort of resistance, both historically and in the present. I find this curious and ripe for further inquiry, but primarily it is problematic for how we think about people as good or bad in the past. Whatever we may individually or collectively think about Jesse James as a “good” or “bad” person in history, it is vitally important to problematize our thinking about him. Talking about Jesse James may seem strange, but it is relevant to the field of action research. If we tell people that we are engaging in important and “good” actions, we should be prepared to justify why it is “good” and provide a theoretical, epistemological, or ontological rationale if possible. Experience is never enough, you need to justify why you act in certain ways and not others, and this includes thinking critically about your own thinking.
Educators who view inquiry and research as a facet of their professional identity must think critically about how to design and conduct research in educational settings to address respect, justice, and beneficence to minimize harm to participants. This chapter emphasized the due diligence involved in ethically planning the collection of data, and in considering the challenges faced by educator-researchers in educational contexts.
Planning Action
After the thinking about the considerations above, you are now at the stage of having selected a topic and reflected on different aspects of that topic. You have undertaken a literature review and have done some reading which has enriched your understanding of your topic. As a result of your reading and further thinking, you may have changed or fine-tuned the topic you are exploring. Now it is time for action. In the last section of this chapter, we will address some practical issues of carrying out action research, drawing on both personal experiences of supervising educator-researchers in different settings and from reading and hearing about action research projects carried out by other researchers.
Engaging in an action research can be a rewarding experience, but a beneficial action research project does not happen by accident – it requires careful planning, a flexible approach, and continuous educator-researcher reflection. Although action research does not have to go through a pre-determined set of steps, it is useful here for you to be aware of the progression which we presented in Chapter 2. The sequence of activities we suggested then could be looked on as a checklist for you to consider before planning the practical aspects of your project.
We also want to provide some questions for you to think about as you are about to begin.
- Have you identified a topic for study?
- What is the specific context for the study? (It may be a personal project for you or for a group of researchers of which you are a member.)
- Have you read a sufficient amount of the relevant literature?
- Have you developed your research question(s)?
- Have you assessed the resource needed to complete the research?
As you start your project, it is worth writing down:
- a working title for your project, which you may need to refine later;
- the background of the study , both in terms of your professional context and personal motivation;
- the aims of the project;
- the specific outcomes you are hoping for.
Although most of the models of action research presented in Chapter 1 suggest action taking place in some pre-defined order, they also allow us the possibility of refining our ideas and action in the light of our experiences and reflections. Changes may need to be made in response to your evaluation and your reflections on how the project is progressing. For example, you might have to make adjustments, taking into account the students’ responses, your observations and any observations of your colleagues. All this is very useful and, in fact, it is one of the features that makes action research suitable for educational research.
Action research planning sheet
In the past, we have provided action researchers with the following planning list that incorporates all of these considerations. Again, like we have said many times, this is in no way definitive, or lock-in-step procedure you need to follow, but instead guidance based on our perspective to help you engage in the action research process. The left column is the simplified version, and the right column offers more specific advice if need.
Figure 4.1 Planning Sheet for Action Research
| My topic of research is about … | |
| Why do you wish to research this topic | |
| Are your plans realistic, doable, and/or supported? | |
| Write down a working title. What is your research question or aspect you are intending to study? What do you know and not know about your topic of study? | |
| Who will be involved in the research? What is the timeline? What ethical procedures do you need? | |
| Where will I search for literature? | |
| What data do you need to collect? Why do you need each of them? | |
| What are the possible outcomes of my research? | |
| What is your research question? |
Action Research Copyright © by J. Spencer Clark; Suzanne Porath; Julie Thiele; and Morgan Jobe is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
DepEd Action Research Topics and Sample Titles
DepEd Action Research is a process of systematic, reflective inquiry to improve educational practices or resolve problems in any operating unit (i.e. school, classroom, office).
The research topic/area should be taken from Basic Education Research Agenda under the following themes: teaching and learning, child protection, human resource development, and governance themes: disaster risk reduction management, gender and development, and inclusive education.
READ: Action Research in Education: What You Need to Know
Table of Contents
Areas of Research
The area of research differs based on the levels of governance. All research proposals must be anchored on the following thematic areas:
- improving access to education
- improving the quality of education
- improving governance
Table 1 below outlines the areas of research that the National, Regional Office, Division Office, and school shall undertake.
Table 1. Proposed areas of research, per level of governance
READ: DepEd Order No. 43, s. 2015
| Level of Governance | Areas of Research | Maximum amount | Who can avail? | Where to Submit? | Duration of the Research |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| National | research that would inform policy and decision making at the national level; program development and implementation; program evaluation; process evaluation and impact study | Not more than PhP500,000 per research | Regular DepEd employees with SG not below 11; qualified external research institutions | Policy Research and Development Division-Central Office (PRD-CO) | Maximum of 1 year |
| Region, Division, District | research that would improve contextualization and implementation of policy in the region, division and district; program development and process and program evaluation | Not more than PhP150,000 per research | Regular employees of DepEd RO, SDO and Districts with SG not below 11 | Policy, Planning and Research Division-Regional OfficefPPRD-RO | |
| Schools | action research that would improve teaching and learning and school governance; matters arising from SIP analysis and Learning Action Cells sessions that require further investigation | Not more than PhP30,000 per research | Regular school heads, teachers and qualified non teaching personnel | Maximum of 6 months |
DepEd Research Proposals should also follow the prescribed outline/format stipulated in the Research Management Guidelines.
Proponent/s (maximum of three) along with his/her or their proposal should submit the following documents to the Schools Division Research Committee (SDRC) for final evaluation using the rubrics attached:
ACCEPTANCE AND APPROVAL SHEET
Research proposal application form and endorsement of immediate supervisor, declaration of absence of conflict of interest, declaration of anti-plagiarism, sample deped action research topics and titles.
| ACTION RESEARCHES |
|---|
| The Plight of Teachers on One Time Monthly Salary Release: Financial Literacy and Survival |
| Improving Mathematics Performance Through the Use of Differentiated Instruction of Grade Four Ginto in Teacherph Elementary School |
| Examining Teachers' Technological Pedagogical Knowledge (Tpk): Basis for Conduct of Technology-Driven Instruction Enhancement Program |
| Maximizing Parents' Involvement in Monitoring Students' Performance in School |
| The Impact of Communicative Language Teaching Strategies in Solving English Oral Communication Learning Deficiency |
| Looking Through the Lens of Differently-Abled Teachers in Antipolo City: Experiences, Challenges, Aspirations |
| Delving into the Implementation of School-Based Management (Sbm) in the Schools Division of Antipolo City |
| Assessment on the Level of Awareness and Preparedness of the Public and Private Secondary Schools of Antipolo City in the Implementation of Disaster Risk Reduction Management Program |
| Level of Preparedness of Antipolo District Teachers Towards Airborne Diseases and Viruses: A Basis for Contingency Planning |
| Ang Epekto ng Paggamit ng Cellphone ng mga Mag-aaral ng Baitang 10 sa Mataas na Paaralang Pambansa ng TeacherPH |
| Challenges of Grade 1 Teachers in Mother Tongue Based-Multilingual Education Among Elementary Schools of Antipolo City |
| Teacher- Researchers' Engagements and Challenges in Antipolo City Division: Research Program and Policy Recommendations |
| The Plight of Financially-Challenged Teachers in Antipolo City Division |
| Understanding Multi-Grade Teachers' Life Changing Experiences: A Phenomenological Analysis |
| Quality Assurance Technical Assistance Monitoring and Evaluation (QATAME) of Training: Results Utilization for Enhancement in the Schools Division of Antipolo City |
| Teachers' Research Competencies and Attitudes: Capability Building Program for Antipolo City Division |
| The Research Capability of Senior High School Research Teachers in the Division of Antipolo City |
| Braving the Waves: Lived Experiences of School Heads Assigned in Island Schools |
| Job Satisfaction of Public Elementary Schools Teachers |
| Impacts and Challenges of Banner Projects in Antipolo City: Stufflebeam's Context-Input-Process- Product (IPP) Evaluation Model |
| Challenges Encountered by Multigrade Teachers in the Implementation of Budget of Work of Daily Lesson Log: Basis for Intervention Scheme and Plan |
| Strengthening Parent's Participation Through Awards Recognition (SPPAR) Approach: Incentives. Benefits, and Contribution to Quality Education |
| Ethnomathematics in the Cultural Activities of Badjaos in Tandag City: An Ethnographic Case Study Approach |
| Students with Good Mathematical Ability: A Grounded Theory |
| Scientific Calculator Literacy of Grade 11 Students |
| Utilization of Information Communication Technology (ICT) Among Public Elementary Schools of Antipolo District 11 |
| The Effects of Flipped Classroom Learning Model on the Performance of Grade 8 Students in Solving Non-routine Mathematical Problems |
| Impact of Merging of Classes |
| Predictors of the Competencies of Technical-Vocational and Livelihood of Grade 12 Students in Selected Schools of Antipolo City |
| Spiritual needs and Religious beliefs in relation to Language and Science Education of Secondary Students in Sibagat, Philippines: Implication for Strengthening the Spiritual and Religious Program in the Curriculum |
| Saturday Mathematics Program: Its Effect to Selected Students of Trento District |
| The Effect of the Scaffolding Strategy on the Performance of Grade 9 Students in Solving Word Problems in Math |
| Attitudes Towards Mathematics and Achievement in Problem-Solving among Grade 11 Students |
| Modules in 21st Century Literature |
| Resource Materials in English for Academic and Professional Purposes |
| Difficulties Encountered by the Grade IV Mathematics Teachers in Teaching Pupils Exposed to MTB-MLE |
| Challenges of the MTB-MLE Exposed Pupils: Basis for Setting of Classroom Learning Goals |
| Exploring the School-based Management (SBM) Implementation in the Schools Division of Agusan del Sur: Basis for Policy Recommendation |
| Assessment on the Management of Public Secondary |
| School Canteens in Compliance of DepEd Order No. 08, s. 2007: Basis for an Intervention Plan |
| The Participation of Stakeholders in the Management of Newly-opened Schools with IP Learners in the Division of Agusan del Sur |
| Development of Strategic Intervention Material (SIM) in Science 7 Using Braille Method and Tactile Graphics for Visually Impaired Learners |
| Community Linkages and Professional Engagement among Junior and Senior High School Teachers in DRRM Resources Development |
| ICT-enhanced Mathematics Instruction in Public Senior High Schools: Basis for Developing District-wide Information and Communication Technology Training |
| Reaching the Standards: School Head's Performance Management Response to Challenges in Implementing PPST for Year One |
| Beyond Four Walls: Education Behind Bars of Antipolo City Division |
| Motivational Teaching Strategies among Secondary School Mathematics Teachers of Antipolo Districts |
| Management of Fund Utilization among Public Elementary and Secondary Schools of Antipolo District |
| Action Research Competence of School Heads and Teachers of Antipolo City Division |
| The Journey of a Single Father; Its Untold Pains and Dreams |
| Beyond The Four Walls: Education Behind Bars (EBB) In Antipolo City |
| Text-based Learning Resource Evaluation in Private schools: Basis for Policy Formulation |
| The Use of 1 Story Book per Week for the Development of Reading Comprehension Among Kindergarten |
| The Effect of Gadgets in the Learning Behavior of Grade 4 Learners |
| Learner Adversity in Multiplication and Division of Whole Numbers |
| The Effectiveness of Integrating ICT In Teaching AP Grade 5 on Pupils Learning Outcomes |
| The relationships between ALS Learner's Attendance and the Result of ALE Test Of BPOSA |
| Play-based learning VS computer-based learning In improving the reading skills of Kindergarten Learners |
| The Effectiveness of Quipper school in Teaching Mathematics in Grade 5 |
| The Effects of using Manipulative Towards Mastery of Multiplication of whole numbers Of Grade 6 Pupils |
| Social Media trends sa Pangkatang Gawain ng Mga mag-aaral sa Pagtalakay sa panitikan |
| The Interest Level of CSN in the Integration Of Job Coaching in Special Education |
| The Effects of Using Online games (Application) In Teaching Grammar and Vocabulary |
| Integration of Interactive games in teaching students With Autism |
| The Use of day-out Fishing Vocabulary in Enhancing the Reading Comprehension Skills of Grade 3 Pupils in Science |
| The Challenges of SHS ABM Grade 11 Transferee students to the School Performance of CMSHS |
| The Effectiveness of Training Modules in Increasing the RSPC and NSPC Winners of SDO-Mandaluyong City |
| Time Allotment for ESP: A limit to Maximize Learning |
| Factors Affecting the Interest Level of Pupils in Learning EPP/TLE |
| Paggamit ng Cartoon sa Pagtuturo ng Noli Me Tangere sa Baitang Siyam |
| The Effects of Utilizing Manipulative Materials in recognition of Numbers among Kindergarten Learners |
| The Use of short stem Questions in Araling Panlipunan Quarterly Evaluation Test for the MPS Increment |
| Time Allotment for ESP: A Limit to Maximize Learning for Grade 2 in JFMS |
| Factors that affect Learners' Poor Skill Performance in EPP/TLE |
| Improving the Reading Comprehension Skills of Grade 6 Pupils through Reading Remediation Using Short Reading Selections |
| Relationship between reading Comprehension Skills and Problem Solving |
| The Use of Ted Talks in Improving the Public Speaking Skills of Grade 10 Learners in English |
| The Effectiveness of DAP-ELLN in Improving The Reading Skills of Grade 1 learners |
| Manipulative Materials and Worksheet activities for Kindergarten Pupils: A Comparative assessment |
| Paggamit ng Big Book sa Pagkatuto ng mga Mag-aaral sa Ikatlong Baitang |
| Parents/Guardians as Paraprofessional Educators in the Inclusive Setting of JFMS |
| The Filipino Short Story: It's Effect on the Reading Comprehension of the Grade 6 Learners |
| Kindergarten Learners' Emotional stability in Learning Basic Math Skills |
| Difficulties of Learners in Science |
| Reading and Comprehension Skills of Grade 7 Learners in relation to their Academic Performance |
| Improving the Skills of Grade 7 Students in BPP (Bread and Pastry Production) through Blended Approach |
| Non-Cognitive Factors Affecting the Academic of Student-Athletes |
| Development of Interactive Strategic Intervention Materials as an Instructional Tool towards Improvement of Least Learned Skills in English |
| The relationship between the Reading Performance of the Learners to their Academic Performance |
| The Use of Extended Activities to Improve the English Performance of Grade 8 Students |
| Factors Affecting learners' Performance In MAPEH |
| Pagbuo ng Mungkahing Pangremedyal Na Gawain sa Pagsulat ng ibat-ibang Uri Ng Sulatin |
| The attitude of Grade 10 Students Towards Learning Mathematics |
| The Effectiveness of COT-RPMS in the Teaching Performance of Teachers |
| The effect of Whole Brain Approach to Improve The Academic Performance of Grade 12 Students In Social Science Subjects (Core) |
| The Challenges in Using Quipper as a Learning for Senior High school Teachers and Students of IBIS |
| Spiral progression Curriculum of Science in SHS: Effectiveness to the Comprehension of SHS Students |
| Effectiveness of Araling Panlipunan Intervention and Review Program (APIR) Towards the Increase of Quarterly MPS in AP Grade 8 |
| Improving the Academic Performance of Grade 6 Learners of ATRRES in Math through Project Mandaluyong Mathematics Circle- Division Remediation and Enhancement of Aptitude in Math (Project MMC-DREAM) |
| Epekto ng Kultura ng mga Banyaga sa mg Mag-aaral Sa ngayon |
| The Effects of Computer-Aided Instruction in Teaching Araling Panlipunan 5 in Pupils' Learning Outcomes |
| Play-Based Teaching Approach to Facilitate Pupils Learning in Aralinq Panlipunan 3 |
| Using Sound Blending To Acquire Reading Skills in the Early Grades |
| Contextualizing Lesson Plans in EnSciMa 3: Improving the Learning Performance of the Subanen Learners |
| Interactive Computer-Assisted Instruction: Enhancing Mathematics Teaching Among Grade 9 Students |
| Using SIM in Enhancing Grade 8 Students Level of Performance in Science |
| Play-Based Word Translation Activities: An Intervention to Improve Reading Comprehension |
| School Stakeholders Values Formation Program |
| CIS Life Laboratory Rooted with Learning Organic Agriculture and Mushroom Cultivation |
| Influence of Socio-Economic Status on the Academic Performance of 4 P's Student-Beneficiaries |
| Project CARE: Exploring CIS Action Research Experience |
| Developing C-V-C Word Recognition Skills Using Repetitive Exercises and Drill |
| Twenty-minute Habit Through Word Wall Activities |
| Doing Arts Approach in Teaching Elementary Science |
| Project LURE: Improving First Graders Reading Comprehension |
| Effectiveness of Senior Hgh School (SHS) Immersion Program on National Certification (NC) II Assessment |
| Reward System. An Intervention Addressing Dropout |
| Influence of School-based feeding Program on Class Performance |
| Using Teacher-Pupil: A Reading Intervention |
| Ka-TITSER: SLAC Program in Improving Teacher Quality of SHS Teachers |
| Mathematics Problem Solving Interventions for Grade 2 and Grade 3 Pupils |
| FuReAct: A Reading Intervention |
| OPLAN Search for Children With Special Needs: Basis for Opening SPED Classes |
| Repetition Rate: Factors and Possible Interventions |
| Project BETRead: A Remedial Reading Program |
| Reducing the Number of Repeaters Through Homeschooling |
| Influence of Parental Support on Students Dropout Rate: The Mediating Effect of Students Motivation |
| LOVE: Close Monitoring of Learners At-Risk of Dropping Out. |
| Enhancing the Reading Ability of Grade 3 Pupils |
| Word Recognition, Comprehension and Fluency Through Multimedia Instruction for Multi-Grade Pupils |
| Drill: Enhancing Multiplication and Division Operation Skills |
| Overcoming Reading Difficulties Through Phonological and Phonemic Activities |
| Photonary: Increasing Pupils' Word Recognition Skills |
| Exploring the Mathematics Problem Solving Skills of Grade 4 Pupils |
| Improving Reading Through Reciprocal Teaching Approach |
| Reading-At-Noon Program: Improving Reading Comprehension |
| Improving Mathematics Performance Through Games and Graphic Organizers |
| Promoting Parents' Awareness on Phonetics: An Aid To Learners' Reading Proficiency |
| Sing-Along Learning Using Technology: Improves Memorization in Multiplication Tables |
| Innovative Reading Intervention Scheme: A Tool in Improving Reading and Vocabulary Words |
| Teachers' Assessment Practices in the Classroom: basis for Intervention |
| Illustrated Stories: Preferable Reading Material in Sustaining Reading Interest of Pupils |
| Information Communication Technology Competence of Teachers: An Exploratory Study |
| Impact of Instruction in High Repetition Rate Among Male Students |
| Teacher's Challenges in Doing Action Research: Basis for Intervention |
| Students' Evaluation of SHS Teachers' Teaching Performance: Basis for Curriculum Enhancement and Training |
| Exploring the Level of Pupil's Motivation Through Enhanced Q8A Technique |
| The Role of Teachers and Parents in Honing Students' Hidden Skills |
| Using Comic Strips in Improving Comprehension Skills of Intermediate Graders |
| Effectiveness of Remedial Reading Programs Among First Graders |
| Using Semantic Webbing in Improving Reading Comprehension |
| Using Dimensional Approach in Enhancing Reading Comprehension |
| Reading Materials: Improving Reading Ability of Third Graders |
| Pictoword Application: An Aid in Enhancing the Learners' Vocabulary and Spelling Skills |
| Operational Use of Parent-Teacher Conference Report Document Among Public Elementary Educators |
| Redefining Strategies and Approaches in Solving Reading Difficulties of Third Graders |
| Using the Art of Digital Storytelling in Improving the Reading and Listening Comprehension Skills |
| Using Songs As A Tool in Improving the Listening and Comprehension Skills in English |
| Ready to Mingle: Exploring Aging Attitudes Through Puppet Making Study |
| Effects of Teacher-Mediated Echo Communication Game On Expressive Language of Children With Autism |
| Blended Learning: Social Media As A Learning Tool |
| Using Academic Games in Teaching Fundamentals of Accountancy, Business and Management (FABM 1) in Senior High School |
| Developing the Professional Ethics of Neophyte Teachers of Looc National High School: A Modular Approach |
| Improving Family Earthquake Preparedness Through the Use of Community Lecture |
| Utilizing Computer-Based Assessment for Self- Paced Learners in Computer System Servicing NCII |
| Motivational Strategies in Strengthening Cooperation of Faculty and Staff During Fire Drills |
| PARAVARTYA YOJAYET: Solving Simple Equations Using Vedic Math |
| Grassroots Innovations for Sustainable Development Towards Competent Football Athletes |
| Effects of Multimedia Assisted Instruction on Academic Performance in English: A Case Study |
| Using ICT Generated Word Game in Increasing Vocabulary Skills of Seventh Graders |
| Integrating Video Clips in Science Class In Promoting Climate Change Awareness |
| Word-Recognition Practice: Its Impact on the Development of Pupils' Listening Comprehension |
| Platooning: A Strategy on Increasing Pupils' Performance in English- Science-Mathematics- (EnSciMa) Learning Areas |
| Kaguro Ko, Kaagapay Ker. Addressing the Mentoring Barriers As Experienced by Master Teachers |
| Using Electronic Forms on Fast-Tracking the School Maintenance and Other Operating Expenses (MOOE) |
| Improving Family Earthquake Preparedness Through the Use of Community Lecture |
| Effectiveness of Using Activity Sheets in Teaching Science Among Seventh Graders |
| Remedial Reading Intervention Through Reviving Fuller Lesson Approach |
| Assessment on Schools' Physical Condition: Basis for DRRM Action Plan |
| Using CODEVS in Developing Automaticity in Reading Among Elementary Pupils |
| Using Guided Choral Reading (GCR) in Improving Reading Fluency of Fourth Graders |
| Using Manipulative Materials in Teaching Mathematics Fundamental Operations |
| Using Five Finger Retell (FFR) in Enhancing the Reading Comprehension Skill of Fifth Graders |
| Instituting Storylandia in Intensifying Word Recognition and Accuracy Towards Answering Comprehension Questions |
| Institutionalizing Project CLEAN As a Solid Waste Management in School Through SPG Involvement |
| Situational Factors Influencing Learners Motivation in Developing the Skills in Speaking English as a Second Language |
| B-Home Sign Model: Making Addition and Subtraction of Integers Easy |
| Standard Process of Teaching Noting Details in Decreasing the Number of Frustration Readers |
| An Action Research on Improving Teachers' Assessment Skills and Behaviour Towards Performance -Based Classroom Assessment |
| Translation of English to Filipino and Mother Tongue to Improve Reading Comprehension |
| Improving Reading Comprehension Through Multimedia Assisted Instruction |
| Program LURE: Improving the Reading Comprehension of First Graders |
| Oral Drill: Improving the Pronunciation Skills of Sixth Graders |
| Effectiveness of Innovation Techniques in Teaching Science |
| Reading Comprehension on Understanding Cause and Effect Relationship |
| Information Communication Technology Competence of Elementary Teachers: An Exploratory Study |
| Research Writing Capabilities of Teachers: An Exploratory Study |
| Utilization of E-Classroom: Its Effect to Teaching-Learning in EPP |
| School-Based Counseling: Its Effect on the Emotional Recovery of Bullied Learners |
| Home Visitation: Its Effect on Learners with Misbehavior |
| Remedial Reading Program: An Intervention for Reading Skills Among Grade Six Pupils of Mantiguib Elementary School |
| Using Graphics, Video Clips and Localized Stories: Its Effect On the Reading Comprehension Level of English VI Pupils in San Isidro Elementary School |
| Active Learning Plan: A Strategy Combined with Simplified Lesson to Increase Students' Focus and Performance in Mathematics |
| Behavior Modification and Enhancement Program: Its Effect to the Edukasyon sa Pagpapakatao Learning Performance of Intermediate Pupils |
| Improvised Materials in Science: Its Effect on Self-Efficacy and Creativity of Grade Three Pupils |
| Creativity, Computation and Reasoning (C-C-R) Strategy: Its Effects on Mathematics Performance |
| Weekend Information Communications Technology Training Program: Its Effect on Teachers Computer Literacy Skills |
| Anti-Bullying Campaign: Its Effect on Learners' Behavior |
| Differentiating Instruction Through Workbook in Science 5: An Instructional Support for the 21st Century Teachers |
| Contextualized Language Module and Students' English Proficiency and Attitude Towards the English Language |
All DepEd Action Research to be conducted must be related to the nature of work, would improve teaching and learning, access and school governance, and matters arising from the SIP analysis and Learning Action Cells sessions that require further investigation.
Revised Guidelines for the Basic Education Research Fund (BERF)
DepEd Research Management Guidelines
Mark Anthony Llego
Mark Anthony Llego, hailing from the Philippines, has made a profound impact on the teaching profession by enabling thousands of teachers nationwide to access crucial information and engage in meaningful exchanges of ideas. His contributions have significantly enhanced their instructional and supervisory capabilities, elevating the quality of education in the Philippines. Beyond his domestic influence, Mark's insightful articles on teaching have garnered international recognition, being featured on highly respected educational websites in the United States. As an agent of change, he continues to empower teachers, both locally and internationally, to excel in their roles and make a lasting difference in the lives of their students, serving as a shining example of the transformative power of knowledge-sharing and collaboration within the teaching community.
86 thoughts on “DepEd Action Research Topics and Sample Titles”
Good day po, ask permission po yo have a copy of a qualitative research paper thank you…
Hello po! Can you send me a copy of sample Action Research related to Enhancing Mathematical Basic operations. Thank you po and God bless you
Kindly send samples of these researches sir/madam?Thankyou very much. 1.Word-Recognition Practice: Its Impact on the Development of Pupils’ Listening Comprehension 2.The Use of 1 Story Book per Week for the Development of Reading Comprehension Among Kindergarten
3. Play-based learning VS computer-based learning In improving the reading skills of Kindergarten Learners Using Manipulative materials in teaching mathematics fundamental operations. 4. Improving mathematics performance through games and graphics organizers 5.Drill: Enhancing multiplication and division operation skills
Hello good morning. Can I ask a sample of action research?
Good Day! Can I ask the following research for my reference? Thank you po.
1. Strengthening Parent’s Participation Through Awards Recognition (SPPAR) Approach: Incentives. Benefits, and Contribution to Quality Education 2. Improving the Reading Comprehension Skills of Grade 6 Pupils through Reading Remediation Using Short Reading Selections 3. Improving Reading Comprehension Through Multimedia Assisted Instruction. 4. Twenty-minute habit through word wall activities.
Can I have a copy of the action research ” The Effectiveness of COT-RPMS in the Teaching Performance of Teachers” for reference sir. Thank you and more power!
Good pm sir. Can i ask for a sample copy for the following Action Reasearch for my reference? 1. Remedial Reading Intervention Through Reviving Fuller Lesson Approach 2. Institutionalizing Project CLEAN As a Solid Waste Management in School Through SPG Involvement
May I request a sample action research here? I would like to read and learn para may may magawa din yung mga guro na gustong maka gawa ng AR.
Greetings! Sir Mark Anthony Llego, I would like to ask if it is okay with you to copy your ideas in your Action Research Because I need it for our Action Research also in our Field Study 2.
Good day! May I ask for the copy of the research
Effectiveness of Araling Panlipunan Intervention and Review Program Towards the Increase of Quarterly MPS for Elementary Pupils
The Effects of Computer-Aided Instruction in Teaching Araling Panlipunan for Pupils’ Learning Outcomes
Have a blessed day Sir Mark. I humbly ask for a sample research for reference lng po. Effectiveness of COT-RPMS in the Teaching Performance of Teachers. or any research on governance po. Thank you ang God bless po!
Hello Po. Could you please give me an example of this research. “Institutionalizing Project CLEAN As a Solid Waste Management in School Through SPG Involvement”
Good day po! Can I ask help po to the author of Action Research name below to support may on going researcch about numeracy gap. Drill: Enhancing Multiplication and Division Operation skills
Thanks Sir Mark . God bless po
Good day po. Can I ask the following following research for my reference? 1.Reward System. An Intervention Addressing Dropout. 2.Maximizing Parents’ Involvement in Monitoring Students’ Performance in School. Maraming salamat po.
GOOD EVENING PERMISSION TO THE OWNER OF THIS AR The relationships between ALS Learner’s Attendance and the Result of ALE Test Of BPOSA. may i ask soft copy for this please. thanks sir/mam.
Good day po sir Mark… Pwede po ba makahingi ng sample action research related po sa UTILIZATION OF INSTUCTIONAL MULTIMEDIA: ITS EFFECT ON THE COMPREHENSION LEVEL OF STRUGGLING LEARNERS IN ENGLISH as my reference po. Salamat po
Hello po. Can I ask for the sample of this action researches for reference?
1. The attitude of Grade 10 Students Towards Learning Mathematics
2. An Action Research on Improving Teachers’ Assessment Skills and Behaviour Towards Performance -Based Classroom Assessment
Good day. It’s a great privilege that i know you. Can you help me materialize my action research? I am interested on Oplan search for children with special needs: Basis for opening SPED classes. Thank you…
Good day. It’s a great privilege that i know you. Can you help me materialize my action research? I am interested on Oplan search for children with special needs: Basis for opening SPED classes.
Hi Po, can I ask a permission to get a copy of your research ” The effect of Gadgets in the Learning Behavior of Grade 4 Learners” Thank you po
Good Day and Mabuhay! can I have a sample copy on institutionalizing Project CLEAN as a Solid Waste Management in School Through the SPG Involvement
Good day! May I have a copy of the following research for reference? 1.Improving the Reading Comprehension Skills of Grade 6 pupils through Reading Remediation Using Short Reading Selection 2. Drill:Enhancing Multiplication and Division Operation Skills 3. Reading Materials:Improving Reading Ability of Third Graders
Good day po! Can I ask the copy of this researches for my reference?
1. Word Recognition, Comprehension and Fluency Through Multimedia Instruction for Multi-Grade Pupils 2. The Impact of Communicative Language Teaching Strategies in Solving English Oral Communication Learning Deficiency 3. Translation of English to Filipino and Mother Tongue to Improve Reading Comprehension 4. Using Sound Blending To Acquire Reading Skills in the Early Grades 5. Pictoword Application: An Aid in Enhancing the Learners’ Vocabulary and Spelling Skills
Thank you po and God bless
Hello Sir/Ma’am. Can I ask a copy of the following action research for reference. Thank you po in advance. 1.Improving the Reading Comprehension Skills of Grade 6 Pupils through Reading Remediation Using Short Reading Selections 2. Improving Reading Comprehension Through Multimedia Assisted Instruction
Good day po Sir Llego.
A very helpful information to all who wish to conduct researches.
May I request permission to have a copy from the owner of the research “Maximizing Parents’ Involvement in Monitoring Students Performance in School” and “Play-Based Word Translation Activities: An Intervention to Improve Reading Comprehension” for reference.
Good day Ma’am/Sir! Can I have this copy of, “Improving the reading skill of Grade 6 Pupils through Reading Remediation using short reading selection?”. Thank you and God bless.
Hello po Madam/sir:
Please share me a soft of the research “Understanding Multi-Grade Teachers’ Life Changing Experiences: A Phenomenological Analysis….Thank u sir and More power and blessings to come…God Bless po…
Good day Ma’am/Sir, Can I have the copy of the following research for reference. Thank you.
1. Improving Mathematics Performance Through the Use of Differentiated Instruction of Grade Four Ginto in Teacherph Elementary School 2. Saturday Mathematics Program: Its Effect to Selected Students of Trento District 3. Scientific Calculator Literacy of Grade 11 Students
May I ask permission who owns this Studies/ Research
1. The Plight of Teachers on One Time Monthly Salary Release: Financial Literacy and Survival. 2. Delving into the Implementation of School-Based Management (Sbm) in the Schools Division of Antipolo City
Good evening.Can you share a copy of the ff research? Badly needed for reference only. 1. Improving the Reading Comprehension Skills of Grade 6 Pupils through Reading Remediation Using Short Reading Selections 2. The Effect of Gadgets in the Learning Behavior of Grade 4 Learners 3. Improving Reading Comprehension Through Multimedia Assisted Instruction Thank you po and god bless❤️❤️
I want to learn more on writing action research. Can I ask for a latest action research proposal with complete parts?
Hi, good day po Sir! Can I ask a copy of this Action Research ” The Effect of Gadgets in the Learning Behavior of Grade IV Learners”?
Hi Sir! May I request for a copy of this reseaech entitled, Using Songs As A Tool in Improving the Listening and Comprehension Skills in English Thank you in advance.
Good day! Can I ask if you can give me a sample of Research Question about “Post Assessment on Mathematical Skills of Grade 10 students after Modular Distance Learning” Hoping for your response. Thank you in advance.
Good day po. Can I ask the following following research for my reference? 1. Using Manipulative materials in teaching mathematics fundamental operations. 2. Improving mathematics performance through games and graphics organizers 3.Drill: Enhancing multiplication and division operation skills 4. Twenty-minute habit through word wall activities
Thank you and Keep safe!
Good day po. Can I ask copy of Word-Recognition Practice: Its Impact on the Development of Pupils’ Listening Comprehension as sample Action Research po sana? Thank you in advance.
Good day po. Can I request a copy for reference about 1. ” The Attitude of Elem Teachers towards Inclusive Education” 2. Improving the skills of G7 students in BPP through Blended Approach…My permission to the owner. Thank you so much
good morning po can i ask a copy of the sample research about Difficulties Encountered by the Grade IV Mathematics teacher in Teaching pupils exposed to MTB-MLE
Good day po. Can I ask a copy of Action Research about Teacher’s Challenges in Doing Action Research:Basis for Intervension. and The Effectiveness of COT-RPMS in the Teaching Performance of Teachers Thank you and More Power Sir!
Hello good day po Sir! Can I ask a copy of this Action Research ” The Effect of Gadgets in the Learning Behavior of Grade IV Learners”?
Hi Sir, Can I ask for the copy of thirls research for reference. Thank you.
Challenges of Grade 1 Teachers in Mother Tongue Based-Multilingual Education Among Elementary Schools of Antipolo City
Good day ! Can I ask the research for a reference? Effectiveness of Using Activity Sheets in Teaching Science Among Seventh Graders
Thank you po
Pwede po makahingi ng copy ng research abot Using Five Finger Retell (FFR) in Enhancing the Reading Comprehension Skill of Fifth Graders. For reference po. Tnak you
Good day Ma’am/Sir, Can I have the copy of the following research for reference. Thank you😊
1. Home Visitation: Its Effect on Learners with Misbehavior 2. Improving the Reading Comprehension Skills of Grade 6 Pupils through Reading Remediation Using Short Reading Selections 3. The Effect of Gadgets in the Learning Behavior of Grade 4 Learners 4. Improving Reading Comprehension Through Multimedia Assisted Instruction
The Filipino Short Story: It’s Effect on the Reading Comprehension of the Grade 6 Learners
Good day po, may I ask a permission to access or have a soft copy of the action research in titled “Improving Mathematics Performance Through Games and Graphic Organizers” for reference purposes po. Thank you.
Good day po This is mary ann may l ask permission to share to me a soft copy of this AR . Improving Mathematics Performance Through the Use of Differentiated Instruction of Grade Four Ginto in Teacherph Elementary School Thank you & more power.
Improving Mathematics Performance Through the Use of Differentiated Instruction of Grade Four Ginto in Teacherph Elementary School
Hi sir/mam. Pwede po bang humingi ng copy ng action research ninyo about The Effect of Gadgets in the Learning Behavior of Grade 4 Learners
Thank you po. Guide lng po.
hello po may asking permission po sa author or owner po sa research factors affecting learners’ performance in mapeh pashare nman po plss?
Institutionalizing Project CLEAN As a Solid Waste Management in School Through SPG Involvement.. can you give me a copy po fore reference purposes..god bless po.
Good day. Can you give me a copy of action research for reference po. tnx in advance..
hello sir can i have a copy of this research PROMOTING PARENTS’ AWARENESS ON PHONETICS: AN AID TO LEARNERS READING PROFICIENCY
Can I have the copy of this research:
Remedial Reading Program : An intervention for reading skill
My I ask permission who own this Studies/ Research.
1. The Effects of Computer-Aided Instruction in Teaching Araling Panlipunan 5 in Pupils’ Learning Outcomes 2. Research Writing Capabilities of Teachers: An Exploratory Study
Thank you po.
Sir can i can have a sample copy of this research entitled ‘the effective of using online games in teaching grammar and vocabulary. It will help me a lot..
Thank you so much sir..
Good day sir, can I access this sample action Research for reference “Innovative Reading Intervention Scheme: A Tool in Improving Reading and Vocabulary Words” Thank you po
Good day sir can I ask this research for my reference Thank you po. *Play based learning versus computer based learning in improving the reading skills in kindergarten
Good Day! Sir, can I have access to this topic “Attitudes of Elementary Teachers Towards Inclusive Education” for my reference. Thanks..
Hello sir. Can I have a copy of this Topic for reference sir. Innovative Reading Intervention Scheme: A Tool in Improving Reading and Vocabulary Words
good day po mam and sir,
asking permission of copy of action research Improving Mathematics Performance Through the Use of Differentiated Instruction of Grade Four? for my reference po. thank you in advance god bless
Good day po! Can I ask the research for a reference? Effectiveness of Using Activity Sheets in Teaching Science Among Seventh Graders
Good day sir, Can i ask a sample of the Factors affecting learners’ performance in MAPEH??Most specifically online classes?
Can i ask for a reference regarding this research topic: Contextualized Language Module and Students’ English Proficiency and Attitude Towards the English Language. Thank you so much!
Can i ask sample of action resesrch?
Hello sir. Would you please share me a copy of action research about vocabulary enrichment? Thank you sir .
Good day, Sir, with your permission po can I have a copy of the following Action Research for reference po sana. 1. Blended Learning: Social Media as A Learning Tool. 2. institutionalizing Project CLEAN as a Solid Waste Management in School Through the SPG Involvement 3. The Effect of Computer-Aided Instruction in Teaching Araling Panlipunan in Pupils Learning Outcome
Good Day! Can I ask the following research for my reference?
The Effect of the Scaffolding Strategy on the Performance of Grade 9 Students in Solving Word Problems in Math
Thank you so much po❤️ God Bless????
Hello Ma’am/Sir! Can I have the copy of this research:
Using ICT Generated Word Game in Increasing Vocabulary Skills of Seventh Graders
Hello Ma’am/Sir! Can I have the copy of this research:
Innovative Reading Intervention Scheme: A Tool in Improving Reading and Vocabulary Words
Hello po! Who can provide and share a sampleof action research for my title: Using the Art of Digital Story telling to Improve the Reading and Listening Comprehension Skills of Grade 4 Pupils
Good day po can i ask sample topic about teaching and learning strategies action research
Good Day Sir, can I access and use this sample action research? badly need po for our FIELD study for review and critique lang sana huhu hopefully ma notice.
Good Day, po! Can I ask the following research for my reference??
1.Challenges of Grade 1 Teachers in Mother Tongue Based-Multilingual Education Among Elementary Schools of Antipolo City
2. The Effect of the Scaffolding Strategy on the Performance of Grade 9 Students in Solving Word Problems in Math
3. The Use of 1 Story Book per Week for the Development of Reading Comprehension Among Kindergarten
4. Play-based learning VS computer-based learning In improving the reading skills of Kindergarten Learners
Thank you so much po, I really need it????
Can I ask a sample of action research title?
Good day po… Can I ask the following research for reference? 1. Effectiveness of Innovation Techniques in Teaching Science 2. Effectiveness of Using Activity Sheets in Teaching Science Among Seventh Graders
Thank you and God bless.
Good day po ma’am. may may nakuha na po ba kaung references tungkol sa mga reaserch topics po ninyo na iyan? Maari po bang pashare ma’am. Maraming Salamat po.
Good Day po
1. The Effects of Computer-Aided Instruction in Teaching Araling Panlipunan 5 in Pupils’ Learning Outcomes 2. Research Writing Capabilities of Teachers: An Exploratory Study
Sir mark, may i ask sample of action research, governance po.tnx po
Hello sir may permission who owns this research Factors affecting learners’ performance in MAPEH
non-cognitive factors affecting the academic of student-athletes
Can I ask a sample of Action Research?
i hope sir mark that you can help me in my action research
I’m happy sir Mark Anthony Llego for the information about Action Research.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Can't find what you're looking for.
We are here to help - please use the search box below.
- NAEYC Login
- Member Profile
- Hello Community
- Accreditation Portal
- Online Learning
- Online Store
Popular Searches: DAP ; Coping with COVID-19 ; E-books ; Anti-Bias Education ; Online Store
How to Do Action Research in Your Classroom

You are here
This article is available as a pdf. please see the link on the right..
















IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
May 27, 2023 by Gurpreet Kumar. Action research in education offers a powerful tool for educators to actively engage in improving their teaching practices and student outcomes. By combining research and action, this approach encourages teachers to become reflective practitioners and agents of change within their classrooms and schools.
Choosing the right topic is the first step in the action research process. The selected topic should align with classroom goals, address students' needs, be feasible to implement, and have the potential for positive impact. Teachers should consider the following criteria when selecting action research topics:
A comprehensive list of research topics and ideas in education, along with a list of existing dissertations & theses covering education. About Us; Services. 1-On-1 Coaching. ... Write on action research topic, using guidance and counseling to address unwanted teenage pregnancy in school. Reply. Samson ochuodho on January 6, 2024 at 5:59 pm
The methods of action research in education include: conducting in-class observations. taking field notes. surveying or interviewing teachers, administrators, or parents. using audio and video recordings. The goal is to identify problematic issues, test possible solutions, or simply carry-out continuous improvement.
The study will be determined through action research design due to its nature to contribute to the body of knowledge and to offer solution to the problem of tardiness in schools. Benefits of Action Research in Education. Giving teachers the power to design and implement their research work improves the overall performance of the students.
The goal of this handbook is to address the needs of educators new to the benefits and processes of Action Research by providing step-by-step guidelines for implementing Action Research projects for the purpose of examining and refining literacy practices to improve student performance.
113 Great Research Paper Topics. One of the hardest parts of writing a research paper can be just finding a good topic to write about. Fortunately we've done the hard work for you and have compiled a list of 113 interesting research paper topics. They've been organized into ten categories and cover a wide range of subjects so you can easily ...
Action research is a method used by teachers to solve everyday issues in the classroom. It is a reflective, democratic, and action-based approach to problem-solving or information-seeking in the classroom. Instead of waiting for a solution, action research empowers teachers to become critical and reflective thinkers and lifelong learners that ...
The Center for Collaborative Action research suggests a process of framing questions by recognizing a problem, identifying a possible solution, and anticipating outcomes. Examples, sample topics, and discussion about action research in education using drawings, interviews, and other data sources to study teaching and learning.
Action Research Guide and Examples for Teachers. Every educator enters the world of teaching with a spark - a desire to make a difference, ignite minds, and shape the future. Yet, like any journey, the education path is strewn with challenges, uncertainties, and countless moments of self-doubt. At a point in my teaching career, I felt the ...
Further, they should be of interest to the researcher and have the potential to lead to improved student learning. Action Research Topics Using Drawings: sample Action Research topics using drawings as a primary data source. Action Research Examples: examples of Action Research by practicing teachers using a wide variety of research methodologies.
Action research is a process for improving educational practice. Its methods involve action, evaluation, and reflection. It is a process to gather evidence to implement change in practices. Action research is participative and collaborative. It is undertaken by individuals with a common purpose.
Action research is a research method that aims to simultaneously investigate and solve an issue. In other words, as its name suggests, action research conducts research and takes action at the same time. It was first coined as a term in 1944 by MIT professor Kurt Lewin.A highly interactive method, action research is often used in the social ...
Stage 1: Plan. For an action research project to go well, the researcher needs to plan it well. After coming up with an educational research topic or question after a research study, the first step is to develop an action plan to guide the research process. The research design aims to address the study's question.
The action research process works through three basic ... but it is all too easy to slip into using it as the template for practice (McTaggart 1996: ... the learner's experience; and research topics and personal interests. Action research in informal education. Usher, R., Bryant, I. and Johnston, R. (1997) Adult Education and the Postmodern ...
An action research project is a practical endeavor that will ultimately be shaped by your educational context and practice. Now that you have developed a literature review, you are ready to revise your initial plans and begin to plan your project. This chapter will provide some advice about your considerations when undertaking an action ...
Action research really is that simple. The word research often conjures up images of scientists in white lab coats, or of academics spending decades of their lives in the pursuit of the proof of their theory. The implication of research is that it is rigorous, that it takes forever, that it is difficult, and that it is a lot of hard work.
DepEd Action Research is a process of systematic, reflective inquiry to improve educational practices or resolve problems in any operating unit (i.e. school, classroom, office). The research topic/area should be taken from Basic Education Research Agenda under the following themes: teaching and learning, child protection, human resource ...
Home How to Do Action Research in Your Classroom. This article is available as a PDF. Please see the link on the right. Audience: Faculty, Teacher. Topics: Other Topics, Research, Teacher Research. Advertisement. Advertisement. Action research can introduce you to the power of systematic reflection on your practice.
In conducting action research, we structure routines for the continuous confrontation of problems regarding the health of school communities using data. These routines represent the five essential stages of the action research cycle. They include the following. 1. Identifying a problem area. The first step is to identify a unique problem.
Finding and choosing a strong research topic is the critical first step when it comes to crafting a high-quality dissertation, thesis or research project. If you've landed on this post, chances are you're looking for a healthcare-related research topic, but aren't sure where to start. Here, we'll explore a variety of healthcare-related research ideas and topic thought-starters across a ...
We've listed several potential action research topics in education that relate to our research methodology of using drawings to study science teaching and learning. There are many other action research topics in education that may require a different approach. The sample questions below are provided to get you thinking about how you might use ...
Topics & Ideas: Ecological Science. The impact of land-use change on species diversity and ecosystem functioning in agricultural landscapes. The role of disturbances such as fire and drought in shaping arid ecosystems. The impact of climate change on the distribution of migratory marine species.
The Food Research an Action Center reports one in 11 kids who receive free or reduced-price lunch during the school year, are at risk for summer hunger, the food bank said. ABC7 Chicago is now ...
Positive thinking often starts with self-talk. Self-talk is the endless stream of unspoken thoughts that run through your head. These automatic thoughts can be positive or negative. Some of your self-talk comes from logic and reason. Other self-talk may arise from misconceptions that you create because of lack of information or expectations due ...
2729. Last week, Microsoft released the new Bing, which is powered by artificial intelligence software from OpenAI, the maker of the popular chatbot ChatGPT. Ruth Fremson/The New York Times. By ...