

85 Critical Thinking Questions to Carefully Examine Any Information
There might be affiliate links on this page, which means we get a small commission of anything you buy. As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases. Please do your own research before making any online purchase.
The ability to think critically will often determine your success in life.
Let’s face it. Every day, we are bombarded by news, social media updates, and an avalanche of information. If you take all of this at face value, it’s easy to be deceived, misled or ripped off.
That’s why it’s important to develop a mindset that focuses on critical thinking . This is a skill that needs to be developed in the classroom. But it’s also a valuable life skill.
With that in mind, the following post will share 85 critical thinking questions you can use to increase your awareness about different problems by carefully examining available information.
Let’s get started…
Table of Contents
What Are Critical Thinking Questions?
Critical thinking questions are inquiries that help you think rationally and clearly by understanding the link between different facts or ideas. These questions create a seemingly endless learning process that lets you critique, evaluate, and develop a depth of knowledge about a given subject. Moreover, you get to reinforce your viewpoints or see things in a new way.
We make decisions every day, whether at work or home. Adopting logical, rational, and practical approaches in addressing various issues requiring critical thinking is essential in decision-making. Therefore, before arriving at a decision, always ask yourself relevant questions and carefully analyze the matter’s pros and cons.
Critical Thinking Questions When in an Argument
When you make an argument using a critical thinking approach, you focus on justified claims that are valid and based on evidence. It helps one establish a strong argument.
- Do I disagree with the other person? Might the person I'm arguing with be misinformed on what they are saying?
- Would I be comfortable saying what I am telling him/her if I was in front of a group of people?
- What would happen if I lose this argument? Is engaging in this argument worth my time and energy? How will I feel if I lose?
- Is there room for ambiguity or misinterpretation? Are we arguing because I didn't make my point explicit? Should I take my time to understand his school of thought?
- Do I need some rest before saying something? Am I arguing because of other reasons other than the issues at hand? Do I need to take some time and cool down?

- Is it more important that I’m right? Am I trying to ask to prove an unnecessary point?
- Is this argument inductive, deductive, or abductive? Is it a weak or strong argument that I need to engage in? Is it compelling or sound?
- Is my opponent sincere? Given that they are wrong, are they willing to admit that they are wrong? Can they depend on available evidence, wherever it leads?
- Are my opponents only trying to shift their burden to me? What is the best way to prove them wrong without making them feel bad?
- Are the people I'm arguing with only interested in winning, or are they trying to pass some information across and help me discover the truth?
Critical Thinking Questions When Reading a Book
When you read a book, you probably ask yourself many “why” questions. Why is this a problem? Why did the character say that? Why is this important? The most challenging part of reading a book is assessing the information you are reading. These questions can help.
- If I learn only two things from this book, what will they be? How will they help me? How will I apply them in my daily life?
- What message are the authors trying to pass across? Are they making suggestions or providing evidence for their arguments?
- Given that almost every book is about solving problems, what is the most prevalent issue that the author is trying to solve?
- What is the author’s writing style? What strategy or master plan does the author employ to convey his/her main ideas throughout the book?
- Do I have background information about the book’s topic? If so, how is what the author is saying different from what I already know?
- What didn’t I understand from the book? Should I re-read the book to understand everything the writer is trying to convey?
- Which sections of the book do I love the most, and why? Generally, do I like this book? Should I look for more books that are written by the same author?
- If I had a chance to meet this book’s author, what questions would I ask him/her? What would I tell the writer about the book? Is it a great book worth recommending to your friends and family members?
- Who are the main characters of the book? If there is only one main character, what overarching goal does the character accomplish?
- In what ways did the protagonist change from the start of the book to the end? What caused the changes? Was the protagonist reckless in some ways? Which ways?
Critical Thinking Questions to Spot a Scam
Asking questions when you feel that a fraud or a scam is being presented to you is a good way to stretch your critical thinking muscles. Are you being emailed or messaged by a stranger? Or maybe there are other red flags you are unsure about. If so, ask these questions.
- Does it seem to be too good to be true? Is this stranger pushy or trying to lure me into making a poor decision?
- When trying out online dating: Is my new “friend” professing strong feelings towards me although we’ve only interacted for a few hours?
- Why is a stranger calling me to ask about my Social Security Number (SSN), personal contact information, or bank details while claiming they are from the bank or a phone company?
- When buying products online, why does the seller ask me to pay for goods using an insecure payment option like Bitcoin or money order?
- Does the email I have received have any spelling or grammatical errors? Is the language used overly formal or informal?
- If I do a quick search about the exact words of the email I received, does Google indicate it's a fraud or scam?
- Why should a stranger manipulate me using obvious questions like “Would you want to be rich or poor?” While they already know the answer?
- Is the email asking me to download an attachment? Or click a link to some insecure website?
- Is the person trying to make me feel selfish or guilty for not sending them money, whether for a donation or buying a product?
- Is the stranger portraying a sense of urgency and using pressure tactics? Are they telling me that their family member needs urgent medical attention?
Critical Thinking Questions About Your Life
It can also help to ask yourself a few critical thinking questions about your life. This way, you can gather basic information and uncover solutions to problems you might not have otherwise thought of.
- Where do I wish to be in a few years, probably two, three, or five years? What short-term and long-term goals should I set?
- What have I achieved so far from the time I set my previous goals? What should I be grateful for?
- Do I have any values that guide me in life? If so, what are these values? Am I always true to these values?
- Am I always worried about what people around me think? Can I act independently without the need to meet social expectations?
- What should people say about me at my funeral? Would they talk about how good I made them feel or how rich and flashy I was?
- If I wasn't afraid of anyone or anything, what would I have done? What if I didn't have any fear in me?
- If today was my last day, what extraordinary thing would I do? Can I do it right now?
- What should I do with the things that matter the most to me?
- What things will make the greatest difference in my future life if I take action now?
- How should I react when I feel unwanted by the people I love the most? Should I tell them?

Critical Thinking Questions for a Debate or Discussion
When you are in the middle of a debate or discussion, you need to know that what you are saying is fact, have evidence to support your claim, and position yourself as an expert in what you are saying. Here are some critical thinking questions to ask when you are in a debate or discussion.
- Is there fairness in this discussion? Is the moderator supporting one side? Do they want to make one side look stupid or wrong?
- What is the aim of this discussion? Is there a major problem that needs to be solved? If so, how can I help solve it?
- Who are the people affected by this discussion? If they were here, what would they say?
- Do my views on this discussion matter? If I raise my point, will I be redundant?
- What am I supposed to learn from this debate, and how can I use what I have learned in my daily life?
- Does the audience seem to be biased towards one side? Are they booing one side? What can I do even if it's our opponents being booed?
- Who are the discussion panel members? What views have they held about this kind of discussion or any other related discussions in the past?
- How can I make my point without being ambiguous? Before I speak, should I take down some notes to avoid any confusion during my speech?
- Am I ready to apologize if I make a mistake during the discussion? If so, what are the limits?
- What information does my team, or I need before this discussion?
Critical Thinking Questions About Lying
Admitting when you are wrong, choosing not to cheat, and sharing constructive feedback are all ways to show your honesty. Here are some critical thinking skills to ask regarding lying.
- Will the lie hurt those I am telling, or will it help them? What if being honest might cause my friend unnecessary pain?
- Should I be the one telling this person a lie, or I let someone else do it?
- Will I be the one hurt if I tell this lie? Will my friend feel I am a betrayer? Will it affect our friendship?
- Do they answer my questions in detail, or are they always trying to ignore and dodge the main problem?
- What if I ask these people the same question using different terms and wording? Will they give me the same response?
- Did the tone of my friend suddenly change after I asked him/her this question? Do they sound louder, faster, or slower compared to how they usually speak?
- Does this person have something to gain by lying to me? What is their motive?
- Does this person take a sudden pause or hesitate more than usual when responding to my question?
- When I look at these people's faces, do their facial expressions match what they say?
- Should I believe this person or not? What are my intuitions? Does it look like they are telling the truth?
- Do they blink like other days when I ask them questions? Are they always trying to avoid direct eye contact?
- Why do they seem uncomfortable when it’s just a normal conversation?
Critical Thinking Questions When Presented With a Claim
Critical thinking is much more than just evaluating whether a claim is true or not. It also means a critical thinker reflects on what follows from true claims.
- What does this claim mean, and what are its implications? What if it's a false claim?
- Which of my morals, values, or beliefs do I have to give up to accept this claim?
- Do professionals in this field agree or disagree with the claim that has been made?
- Do they have evidence to back their claim? Which is the most robust evidence to support the claim?
- What argument can I come up with to refute this claim? Or what is the best view that can support this claim?
- Who is the primary source of the claim being made? Is the basis of the claim reliable?
- Is it a claim, or it's just an opinion?
- Is the claim likely to be 100% false, true, or partially true?
- Am I allowed to refute the claim and table my evidence, or is it one-sided?
Critical Thinking Interview Questions
Critical thinking skills are valuable in any industry or field and for almost all roles. During a job interview, you will be asked questions so the potential employer can assess your skills and see how you use logic. Your critical thinking ability is just one vital part that can play into your professional development.
- Is there a time you had to convince someone to use an alternate approach to solve a problem?
- Have you ever had to make a difficult decision quickly?
- How would you handle a situation where your supervisor handled something wrong or made a mistake?
- What is one of the most difficult decisions you have ever had to make at work?
- How would you solve a disagreement between coworkers when approaching a project?
- Can you describe a time when you anticipated a problem ahead of time and took the appropriate steps to stop the problem from becoming an issue?
- If you discover a cheaper way to do something or a better solution to a problem and try to explain it to your supervisor, but they don’t understand, what do you do?
Critical Thinking Questions for Kids
We can’t leave the kids out either. Critical thinking questions for kids get them thinking and talking. It also allows a parent to get to know their child better.
- How many grains of sand do you think are on the beach?
- What would happen if it stopped raining?
- Do you think there is life on other planets?
- Should children be able to set their own bedtimes?
- How would you describe what a tree looks like without saying green or leaves?
- Can you name five different emotions?
- Can you talk for five minutes without uttering “um?”
What Are the Basic Principles of Critical Thinking?
Your critical thinking skills involve gathering complete information, understanding and defining terms, questioning the methods by which we get facts, questioning the conclusions, and looking for hidden assumptions and biases.
Additionally, we can’t expect to find all of the answers, and we need to take the time to examine the big picture of it all.
Here are the basic principles:
- Disposition: Someone with critical thinking skills is often skeptical, open-minded, and practices fair-mindedness. They can look at different viewpoints and change positions if the evidence and reason lead them to do so.
- Criteria: In order to think critically, one must also apply criteria. Certain conditions must be met before someone believes in something. The information needs to be from credible sources.
- Argument: An argument is simply a statement or proposition that is shown with supporting evidence. When you use your critical thinking skills, you identify, evaluate, and construct your argument.
- Reasoning: With critical thinking comes reasoning. You must examine logical relationships among the statements being made.
- Point of View: Critical thinkers can see things from different perspectives and different points of view.
What Are Good Analysis Questions?
Analysis is a part of critical thinking that allows you to examine something carefully. Someone with analytical skills can examine the information presented, understand what that information means, and then properly explain that information to others. Analysis in critical thinking provides more clarity on the information you process.
When analyzing, you may ask yourself, “how do I know this,” how would I solve this problem,” and “why does it matter?”
Why Is Critical Thinking an Important Skill?
Critical thinking skills allow you to express thoughts, ideas, and beliefs in a better way. It also leads to improved communication while allowing others to understand you better. Critical thinking fosters creativity and encourages out-of-the-box thinking. This is a skill that can be applied to many different areas of your life.
For example, knowing the answers to critical thinking questions for a job interview will better prepare you for the interview. Many employers, during questioning, are likely to ask you critical thinking questions to assess if you have the ability to evaluate information effectively so you can make more informed decisions.
Final Thoughts on Critical Thinking Questions
Although it's common to get torn between making two or more choices, nobody wants to make the wrong decision. The only thing you can do to avoid this is use critical thinking questions to examine your situation. The answers to these questions will help you make informed decisions and help you comprehend crucial matters in your life.
Want to learn more about critical thinking and decision-making using a real-life example? Here is how Jeff Bezos uses critical thinking to make some of the most challenging life decisions.
Finally, if you want to ask better questions, then watch this short, 20-minute course to learn how to have a great conversation with virtually anyone .

- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
Critical Thinking Is About Asking Better Questions
- John Coleman

Six practices to sharpen your inquiry.
Critical thinking is the ability to analyze and effectively break down an issue in order to make a decision or find a solution. At the heart of critical thinking is the ability to formulate deep, different, and effective questions. For effective questioning, start by holding your hypotheses loosely. Be willing to fundamentally reconsider your initial conclusions — and do so without defensiveness. Second, listen more than you talk through active listening. Third, leave your queries open-ended, and avoid yes-or-no questions. Fourth, consider the counterintuitive to avoid falling into groupthink. Fifth, take the time to stew in a problem, rather than making decisions unnecessarily quickly. Last, ask thoughtful, even difficult, follow-ups.
Are you tackling a new and difficult problem at work? Recently promoted and trying to both understand your new role and bring a fresh perspective? Or are you new to the workforce and seeking ways to meaningfully contribute alongside your more experienced colleagues? If so, critical thinking — the ability to analyze and effectively break down an issue in order to make a decision or find a solution — will be core to your success. And at the heart of critical thinking is the ability to formulate deep, different, and effective questions.
- JC John Coleman is the author of the HBR Guide to Crafting Your Purpose . Subscribe to his free newsletter, On Purpose , follow him on Twitter @johnwcoleman, or contact him at johnwilliamcoleman.com.
Partner Center
- Grades 6-12
- School Leaders
Enter Today's Teacher Appreciation Giveaway!
100+ Critical Thinking Questions for Students To Ask About Anything
Critical thinkers question everything.

In an age of “fake news” claims and constant argument about pretty much any issue, critical thinking skills are key. Teach your students that it’s vital to ask questions about everything, but that it’s also important to ask the right sorts of questions. Students can use these critical thinking questions with fiction or nonfiction texts. They’re also useful when discussing important issues or trying to understand others’ motivations in general.
“Who” Critical Thinking Questions
Questions like these help students ponder who’s involved in a story and how the actions affect them. They’ll also consider who’s telling the tale and how reliable that narrator might be.
- Is the protagonist?
- Is the antagonist?
- Caused harm?
- Is harmed as a result?
- Was the most important character?
- Is responsible?
- Is most directly affected?
- Should have won?
- Will benefit?
- Would be affected by this?

- Makes the decisions?
“What” Critical Thinking Questions
Ask questions that explore issues more deeply, including those that might not be directly answered in the text.
- Background information do I know or need to know?
- Is the main message?
- Are the defining characteristics?

- Questions or concerns do I have?
- Don’t I understand?
- Evidence supports the author’s conclusion?
- Would it be like if … ?
- Could happen if … ?
- Other outcomes might have happened?
- Questions would you have asked?
- Would you ask the author about … ?
- Was the point of … ?
- Should have happened instead?
- Is that character’s motive?
- Else could have changed the whole story?

- Can you conclude?
- Would your position have been in that situation?
- Would happen if … ?
- Makes your position stronger?
- Was the turning point?
- Is the point of the question?
- Did it mean when … ?
- Is the other side of this argument?
- Was the purpose of … ?
- Does ______ mean?
- Is the problem you are trying to solve?
- Does the evidence say?
- Assumptions are you making?
- Is a better alternative?
- Are the strengths of the argument?
- Are the weaknesses of the argument?
- Is the difference between _______ and _______?
“Where” Critical Thinking Questions
Think about where the story is set and how it affects the actions. Plus, consider where and how you can learn more.
- Would this issue be a major problem?
- Are areas for improvement?
- Did the story change?
- Would you most often find this problem?

- Are there similar situations?
- Would you go to get answers to this problem?
- Can this be improved?
- Can you get more information?
- Will this idea take us?
“When” Critical Thinking Questions
Think about timing and the effect it has on the characters or people involved.
- Is this acceptable?
- Is this unacceptable?

- Does this become a problem?
- Is the best time to take action?
- Will we be able to tell if it worked?
- Is it time to reassess?
- Should we ask for help?
- Is the best time to start?
- Is it time to stop?
- Would this benefit society?

- Has this happened before?
“Why” Critical Thinking Questions
Asking “why” might be one of the most important parts of critical thinking. Exploring and understanding motivation helps develop empathy and make sense of difficult situations.
- Is _________ happening?
- Have we allowed this to happen?
- Should people care about this issue?

- Is this a problem?
- Did the character say … ?
- Did the character do … ?
- Is this relevant?
- Did the author write this?
- Did the author decide to … ?
- Is this important?
- Did that happen?
- Is it necessary?
- Do you think I (he, she, they) asked that question?
- Is that answer the best one?
- Do we need this today?
“How” Critical Thinking Questions
Use these questions to consider how things happen and whether change is possible.
- Do we know this is true?
- Does the language used affect the story?
- Would you solve … ?
- Is this different from other situations?

- Is this similar to … ?
- Would you use … ?
- Does the location affect the story?
- Could the story have ended differently?
- Does this work?
- Could this be harmful?
- Does this connect with what I already know?
- Else could this have been handled?
- Should they have responded?

- Would you feel about … ?
- Does this change the outcome?
- Did you make that decision?
- Does this benefit you/others?
- Does this hurt you/others?
- Could this problem be avoided?
More Critical Thinking Questions
Here are more questions to help probe further and deepen understanding.
- Can you give me an example?

- Do you agree with … ?
- Can you compare this with … ?
- Can you defend the actions of … ?
- Could this be interpreted differently?
- Is the narrator reliable?
- Does it seem too good to be true?

- Is ______ a fact or an opinion?
What are your favorite critical thinking questions? Come exchange ideas on the WeAreTeachers HELPLINE group on Facebook .
Plus, check out 10 tips for teaching kids to be awesome critical thinkers ., you might also like.

5 Critical Thinking Skills Every Kid Needs To Learn (And How To Teach Them)
Teach them to thoughtfully question the world around them. Continue Reading
Copyright © 2024. All rights reserved. 5335 Gate Parkway, Jacksonville, FL 32256

How it works
For Business
Join Mind Tools
Article • 8 min read
Critical Thinking
Developing the right mindset and skills.
By the Mind Tools Content Team
We make hundreds of decisions every day and, whether we realize it or not, we're all critical thinkers.
We use critical thinking each time we weigh up our options, prioritize our responsibilities, or think about the likely effects of our actions. It's a crucial skill that helps us to cut out misinformation and make wise decisions. The trouble is, we're not always very good at it!
In this article, we'll explore the key skills that you need to develop your critical thinking skills, and how to adopt a critical thinking mindset, so that you can make well-informed decisions.
What Is Critical Thinking?
Critical thinking is the discipline of rigorously and skillfully using information, experience, observation, and reasoning to guide your decisions, actions, and beliefs. You'll need to actively question every step of your thinking process to do it well.
Collecting, analyzing and evaluating information is an important skill in life, and a highly valued asset in the workplace. People who score highly in critical thinking assessments are also rated by their managers as having good problem-solving skills, creativity, strong decision-making skills, and good overall performance. [1]
Key Critical Thinking Skills
Critical thinkers possess a set of key characteristics which help them to question information and their own thinking. Focus on the following areas to develop your critical thinking skills:
Being willing and able to explore alternative approaches and experimental ideas is crucial. Can you think through "what if" scenarios, create plausible options, and test out your theories? If not, you'll tend to write off ideas and options too soon, so you may miss the best answer to your situation.
To nurture your curiosity, stay up to date with facts and trends. You'll overlook important information if you allow yourself to become "blinkered," so always be open to new information.
But don't stop there! Look for opposing views or evidence to challenge your information, and seek clarification when things are unclear. This will help you to reassess your beliefs and make a well-informed decision later. Read our article, Opening Closed Minds , for more ways to stay receptive.
Logical Thinking
You must be skilled at reasoning and extending logic to come up with plausible options or outcomes.
It's also important to emphasize logic over emotion. Emotion can be motivating but it can also lead you to take hasty and unwise action, so control your emotions and be cautious in your judgments. Know when a conclusion is "fact" and when it is not. "Could-be-true" conclusions are based on assumptions and must be tested further. Read our article, Logical Fallacies , for help with this.
Use creative problem solving to balance cold logic. By thinking outside of the box you can identify new possible outcomes by using pieces of information that you already have.
Self-Awareness
Many of the decisions we make in life are subtly informed by our values and beliefs. These influences are called cognitive biases and it can be difficult to identify them in ourselves because they're often subconscious.
Practicing self-awareness will allow you to reflect on the beliefs you have and the choices you make. You'll then be better equipped to challenge your own thinking and make improved, unbiased decisions.
One particularly useful tool for critical thinking is the Ladder of Inference . It allows you to test and validate your thinking process, rather than jumping to poorly supported conclusions.
Developing a Critical Thinking Mindset
Combine the above skills with the right mindset so that you can make better decisions and adopt more effective courses of action. You can develop your critical thinking mindset by following this process:
Gather Information
First, collect data, opinions and facts on the issue that you need to solve. Draw on what you already know, and turn to new sources of information to help inform your understanding. Consider what gaps there are in your knowledge and seek to fill them. And look for information that challenges your assumptions and beliefs.
Be sure to verify the authority and authenticity of your sources. Not everything you read is true! Use this checklist to ensure that your information is valid:
- Are your information sources trustworthy ? (For example, well-respected authors, trusted colleagues or peers, recognized industry publications, websites, blogs, etc.)
- Is the information you have gathered up to date ?
- Has the information received any direct criticism ?
- Does the information have any errors or inaccuracies ?
- Is there any evidence to support or corroborate the information you have gathered?
- Is the information you have gathered subjective or biased in any way? (For example, is it based on opinion, rather than fact? Is any of the information you have gathered designed to promote a particular service or organization?)
If any information appears to be irrelevant or invalid, don't include it in your decision making. But don't omit information just because you disagree with it, or your final decision will be flawed and bias.
Now observe the information you have gathered, and interpret it. What are the key findings and main takeaways? What does the evidence point to? Start to build one or two possible arguments based on what you have found.
You'll need to look for the details within the mass of information, so use your powers of observation to identify any patterns or similarities. You can then analyze and extend these trends to make sensible predictions about the future.
To help you to sift through the multiple ideas and theories, it can be useful to group and order items according to their characteristics. From here, you can compare and contrast the different items. And once you've determined how similar or different things are from one another, Paired Comparison Analysis can help you to analyze them.
The final step involves challenging the information and rationalizing its arguments.
Apply the laws of reason (induction, deduction, analogy) to judge an argument and determine its merits. To do this, it's essential that you can determine the significance and validity of an argument to put it in the correct perspective. Take a look at our article, Rational Thinking , for more information about how to do this.
Once you have considered all of the arguments and options rationally, you can finally make an informed decision.
Afterward, take time to reflect on what you have learned and what you found challenging. Step back from the detail of your decision or problem, and look at the bigger picture. Record what you've learned from your observations and experience.
Critical thinking involves rigorously and skilfully using information, experience, observation, and reasoning to guide your decisions, actions and beliefs. It's a useful skill in the workplace and in life.
You'll need to be curious and creative to explore alternative possibilities, but rational to apply logic, and self-aware to identify when your beliefs could affect your decisions or actions.
You can demonstrate a high level of critical thinking by validating your information, analyzing its meaning, and finally evaluating the argument.
Critical Thinking Infographic
See Critical Thinking represented in our infographic: An Elementary Guide to Critical Thinking .

You've accessed 1 of your 2 free resources.
Get unlimited access
Discover more content
Snyder's hope theory.
Cultivating Aspiration in Your Life
Mindfulness in the Workplace
Focusing the Mind by Staying Present
Add comment
Comments (1)
priyanka ghogare

Gain essential management and leadership skills
Busy schedule? No problem. Learn anytime, anywhere.
Subscribe to unlimited access to meticulously researched, evidence-based resources.
Join today and save on an annual membership!
Sign-up to our newsletter
Subscribing to the Mind Tools newsletter will keep you up-to-date with our latest updates and newest resources.
Subscribe now
Business Skills
Personal Development
Leadership and Management
Member Extras
Most Popular
Latest Updates

Better Public Speaking

How to Build Confidence in Others
Mind Tools Store
About Mind Tools Content
Discover something new today
How to create psychological safety at work.
Speaking up without fear
How to Guides
Pain Points Podcast - Presentations Pt 1
How do you get better at presenting?
How Emotionally Intelligent Are You?
Boosting Your People Skills
Self-Assessment
What's Your Leadership Style?
Learn About the Strengths and Weaknesses of the Way You Like to Lead
Recommended for you
The science of a good night's sleep infographic.
Infographic Transcript
Infographic
Business Operations and Process Management
Strategy Tools
Customer Service
Business Ethics and Values
Handling Information and Data
Project Management
Knowledge Management
Self-Development and Goal Setting
Time Management
Presentation Skills
Learning Skills
Career Skills
Communication Skills
Negotiation, Persuasion and Influence
Working With Others
Difficult Conversations
Creativity Tools
Self-Management
Work-Life Balance
Stress Management and Wellbeing
Coaching and Mentoring
Change Management
Team Management
Managing Conflict
Delegation and Empowerment
Performance Management
Leadership Skills
Developing Your Team
Talent Management
Problem Solving
Decision Making
Member Podcast
- Our Mission
Using Student-Generated Questions to Promote Deeper Thinking
Asking students to create their own questions has a powerful impact on learning. Plus, 5 tips to encourage high-quality questions.

You’ve seen a penny hundreds, if not thousands, of times. But can you draw one from memory?
In a famous decades-old study , adults were asked to draw a U.S. penny without any aids. Although they were confident that they knew what a penny looked like, their performance on the test was “remarkably poor.” And when shown pennies with slightly different characteristics, such as misplaced text or with Lincoln’s portrait facing the wrong direction, few were able to identify the inaccuracies.
It’s a maddening quirk of human memory: We’re often convinced that we know something, but upon closer examination, it’s just an illusion. And this, of course, is no surprise to teachers, who often encounter students who overestimate how well they know a topic.
Understanding how people learn and reliably commit things to memory is what prompted psychology professor Mirjam Ebersbach and her colleagues at the University of Kassel to study how students prepare for an exam, and what strategies yielded the optimal improvements in student learning.
In a recent study , Ebersbach and her research team randomly assigned 82 university students to one of three groups. In the restudy group, students simply revisited and restudied the material from a lesson in their psychology course. In the testing group, students studied the material and then took a short 10-question quiz. In the last group, students studied the same material and then created their own probing questions.
One week later, all of the students took a test on the material. Students in the restudy group scored an average of 42 percent on the test, while students in the testing and generating questions groups both scored 56 percent—an improvement of 14 percentage points, or the equivalent of a full letter grade.
“Question generation promotes a deeper elaboration of the learning content,” Ebersbach told Edutopia. “One has to reflect what one has learned and how an appropriate knowledge question can be inferred from this knowledge.”
Stronger Memory Traces
Why is generating questions so effective? Past studies reveal that learning strategies that require additional cognitive effort— retrieval practice, elaboration, concept mapping , or drawing , for example—encourage students to process the material more deeply and consider it in new contexts, generating additional memory traces that aid retention.
Yet the most commonly used strategies are also the least effective. In the study, students filled out a survey identifying the learning strategies they typically used when studying for exams. By far, they said that taking notes and restudying were their go-to strategies—a surprisingly common finding that’s been regularly reported in the research . Less than half as many mentioned practice tests, and only one student among 82 mentioned generating questions.
Passive strategies such as rereading or highlighting passages are “superficial” and may even impair long‐term retention, Ebersbach explained. “This superficial learning is promoted by the illusion of knowledge, which means that learners often have the impression after the reading of a text, for instance, that they got the messages. However, if they are asked questions related to the text (or are asked to generate questions relating to the text), they fail because they lack a deeper understanding,” she told Edutopia.
That lasting “impression” of success makes it hard to convince people that rereading and underlining are, in fact, suboptimal approaches. They register the minor benefits as major improvements and hold fast to the strategies, even when the research reveals that we’re wrong.
Getting Students to Generate Productive Questions in Class
While generating questions is an effective study strategy, it also can be adapted into a classroom activity, whether online or in person.
Here are five ideas to incorporate student-generated questions into your classroom.
Teach students how to ask good questions: At first, it can be difficult for students to generate their own questions, and many will start with simple yes/no or factual prompts. To encourage better questions, ask students to think about and focus on some of the tougher or more important concepts they encountered in the lesson, and then have them propose questions that start with “explain” or that use “how” and “why” framing. Direct your students to road-test their questions by answering them themselves: Do the questions lead to longer, more substantive answers, or can they be answered with a simple “yes” or “no”?
A bonus: Students who propose questions and then answer them to test their soundness are also relearning the materials more deeply themselves. Very sneaky.
Play Jeopardy! : Research shows that active learning strategies, such as using the format of the popular game show Jeopardy! to review concepts, not only boosts student engagement but also increases academic performance. You can involve students by asking them to write the questions themselves.
To create the game, specialized software isn’t even necessary: The researchers in the study used the wiki feature in the class’s learning management system to create a 6x5 table with each cell containing a question. Similarly, you can use PowerPoint or Google Slides to create the Jeopardy! game grid. Here’s a handy template .
Have students create their own test and quiz questions: Is it cheating if students write the questions to the exam? In a 2014 study , researchers evaluated a strategy whereby students not only developed the learning materials for the class but also wrote a significant part of the exams. The result? A 10 percentage point increase in the final grade, attributed largely to an increase in student engagement and motivation. Popular tools like Kahoot and Quizlet are fun and convenient ways to create quizzes, no matter if your classroom is in person, hybrid, or virtual.
Improve class-wide discussions: In a 2018 study , students were asked to write questions based on Bloom’s taxonomy; questions ranged from lower-order true/false and multiple-choice questions to challenging questions that required analysis and synthesis. The students not only enjoyed the exercise—many called it a “rewarding experience”—but also scored 7 percentage points higher on the final exam, compared with their peers in other classes.
Use some class time to identify the characteristics of higher-order questions; then collect student questions and discuss some of the more challenging ones as a group.
Get at ‘driving questions’: For Andrew Miller, a former high school teacher and current administrator at an international pre-K–12 school, taking a page out of project-based learning and asking students to create driving questions —such as “Why do leaves have different shapes?”—not only enhances their understanding of the topic but also “creates interest and a feeling of challenge” that can draw in even the most reluctant students.

Critical Thinking Questions That Will Blow Your Mind
- February 10, 2018

What would it be like if every decision you made didn’t involve your personal feelings or over-emotional reactions? What if your perspective was always balanced and decisions completely informed? Is it not time that you used critical thinking questions to become the more levelheaded, cool, and calm person you want to be?
Being a critical thinker enables you to take a neutral perspective on an idea or scenario and gives you the power of true choice. Being free from manipulation or emotional ties to your decision will allow you to make the most beneficial choice in any circumstance.
In critical thinking, we are taught to question everything. However, the question behind the question is; what questions should you be asking? Before we go into the critical matter of the exact questions, we should first look at the manner in which these critical thinking questions should be asked. After this article, you will be a wizard at asking critical thinking questions.

The Standard of Questions You Should Ask
Although the actual questions will be very important to critical thinking, the emphasis and purpose of these questions will determine how effective the questions will be. You must first know how to question before you know what and which critical thinking questions to ask.
1. Open-ended questioning
As a critical thinker, you cannot allow whomever or whatever you are questioning to give you the smallest amount of information for your questions. Yes or No answers can really drag out the process of getting the answers and information that you want.
Asking questions that will not only give you the answers you are looking for but also open up a heap more information than you were searching for. Ask open-ended questions such as the following:
- “What is the purpose of this scenario?” Instead of: “Is this the purpose of this scenario?”
- “What is your favorite thing about this scenario?” Instead of: “Is this your favorite thing about this scenario?”
2. Avoid leading questions
Being a critical thinker is about escaping your bias and seeing things outside of your personal perspective . It is thus very important to avoid leading the question, in an area you want it to go.
Keep your questions as neutral as possible and don’t allow any definitive language to creep into the question. Such as using the following:
- “What is your take on the healthiest diet there is?” Instead of: “Don’t you think the vegan diet is the healthiest diet?”
- “What is the condition of the country at the moment?” Instead of: “How bad is the condition of the country at the moment?”
3. Specify the boundaries of your questions
As much as leading a question can be a hindrance to what you want, so can leaving the question too open, and invite unnecessary information to be given. Critical thinking is about being objective, but it still needs a direction and focus in which you apply your critical thinking.
Make sure that you set up an accurate framework in which your questions can be answered. Being too broad makes the process of getting answers inefficient and drawn out. Try asking questions like:
- “Who is your favorite male tennis player in the United States?” Instead of: “Who is your favorite tennis player?”
- “If you could live anywhere in South East Asia, where would that be?” Instead of: “If you could live anywhere, where would that be?”
4. Funnel the questions until you get the answer you were looking for
When questions remain shallow, it is easy for the sources of information you are questioning to mislead and avoid giving you the information that you want.
Do not set up the path of questions beforehand, but rather make sure that you dig deeper after each question in the direction of information that you really want. Once you have your answer, then move back to broader questioning in order to get a better picture of the whole once again.
5. All the answers to your question must be based on facts and well supported from many different sources
Make sure that you don’t give into hearsay. Find the studies, the science, and ample testimonials before you accept the information that you have been given.
Look into many different and unrelated sources to see if the information matches up. Look at the other side of the argument and validate their claims.

Methods of Critical Thinking Questions
1. the 5 w’s and the h.
These are the absolute basics of critical thinking. The Who, What, Where, When, Why, and How are foundational questions that are taught over and over in journalism, investigation, and research.
They are the base from which every critical analysis should be created. You would apply these questions as follows:
- …would benefit?
- …would this harm?
- …is responsible?
- …has researched this before?
- …is the other perspective?
- …would be the challenges?
- …are the strengths?
- …is the key subject?
- …would this problem reside?
- …are there similar situations?
- …can more information be found?
- …can this be improved on?
- …is this acceptable and unacceptable?
- …could this be implemented?
- …would we be able to measure the results?
- …is it time to stop this action?
- …is this a problem?
- …is this relevant?
- …should this be known about?
- …is there a need for this?
- …is this different from anything else similar to it?
- …it functions?
- … is this the truth about it?
- …could it harm anyone?
2. Agenda and method questioning
These two areas of questioning may have already been covered through the 5 W’s and the H. However, it is beneficial to emphasize the angle from which this questioning comes.
The first one is questioning the agenda. This is aimed at figuring out how people could benefit from a situation or idea. This agenda can place all the information received in context.
For instance, if a company was contributing to a charity and their agenda was to improve their image against the damage done by that company, then the contributions would be much less charitable and much more about publicity.
Questions that would help clarify the agenda would be:
- What is the person or organization involved trying to accomplish?
- What issues or problems are raised by the person or organization involved?
- What data, what experiences, what evidence is given?
- Is the person or organization involved thinking about the environment?
- Is the person’s or organization’s thinking justified as far as we can see from our perspective?
- And how do they justify it from their perspective?
- How can we enter their perspective to appreciate what they have to say?
The second aspect of this is questioning the method. As a critical thinker, this makes the outcomes of every situation and idea questionable, which is exactly the point of critical thinking.
Too many times the outcome of a specific method is the focus of debate, without clarifying if that outcome has validity.
Questions that would help clarify the Method would be:
- I s the person or organization involved willing to fundamentally rethink their methods of creating a certain outcome?
- Has the person or organization involved thought about how the method will work going into the future?
- To what extent has the method been tested?
- Is there any other method that could be used to produce this outcome and what would be the implications of this method?
- Is the person or organization involved willing to allow this method to be tested?
- In what other situation has this method been used and how effective was it?
3. Inquiry process
The inquiry process is exactly that; a process. It does entail certain questions but the power of this process resides in the way the process is conducted.
This process is the standard of research and creates an order in which you can follow, uncovering the information that you seek. Although the terminology may change for each step of the process, the essence of what needs to be done remains the same.
The process is divided as follows:
- Ask (Pose Question)
- Investigate (Find Resources)
- Create (interpret/ Synthesise)
- Discuss (Report findings)
- Reflect (follow the process backward)
4. Bloom’s taxonomy
Bloom’s taxonomy was created by Dr. Benjamin Bloom , a psychologist in the 1950’s. Bloom’s work was to create a better form of learning through more focus on analysis and evaluation.
Bloom’s taxonomy is very much Maslow’s hierarchy of needs to critical thinking. The original Bloom’s taxonomy encompasses:
- What is the subject?
- When did it happen?
Comprehension:
- How would you compare the subject?
- Explain the subject in your own words?
Application
- What examples can you find of the subject?
- What approach would you use to solve the problem?
- What inference can you make from the information?
- How would you classify or categorize the subject?
- How would you compare the information?
- What was the value or importance of the information?
Creation or Synthesis
- Can you propose an alternative interpretation of the information?
- What might happen if you…?

Bloom’s Taxonomy has since been revised. In 2001 a group of cognitive psychologists, curriculum theorists and instructional researchers, and testing and assessment specialists change the titles of each level to make a more dynamic approach to the system.
The titles were revised to:
- Recognizing
- Recalling
- Interpreting
- Exemplifying
- Classifying
- Summarizing
- Inferring
- Comparing
- Explaining
- Executing
- Implementing
- Differentiating
- Organizing
- Attributing
- Checking
- Critiquing
- Generating
- Planning
- Producing
In the process of the revision, the authors broke the knowledge area into its own taxonomy:
Factual Knowledge
- Knowledge of terminology
- Knowledge of specific details and elements
Conceptual Knowledge
- Knowledge of classifications and categories
- Knowledge of principles and generalizations
- Knowledge of theories, models, and structures
Procedural Knowledge
- Knowledge of subject-specific skills and algorithms
- Knowledge of subject-specific techniques and methods
- Knowledge of criteria for determining when to use appropriate procedures
Metacognitive Knowledge
- Strategic Knowledge
- Knowledge about cognitive tasks, including appropriate contextual and conditional knowledge
- Self-knowledge
If you want to know more about the reasoning behind the revision click here .
5. Integral questioning
Integral theory was created by Ken Wilber (author of A Brief History of Everything ) and has become one of the most useful structures of evaluation in this era. The integral model is a reference structure in which you can objectively see all areas of a specific subject.
This method goes hand in glove with the practice of critical thinking. Applying the method into question form will bring out the following analysis:
Quadrants: this is the evaluation of each viewpoint of a certain subject.
- What does a specific person involved think or feel about the subject?
- What studies and tests have been done on the subject?
- What do the people as a whole feel or think about the subject?
- What does the industry of the subject say on the subject?
Lines: These are the areas of understanding of factors involved in the matter.
- What are the different areas of life expressed in this subject?
- What factors are involved in the situation or subject?
- To what area of understanding does is the subject appeal to?
Levels: This deals with a hierarchical standard of a certain area of the subject.
- To what level of understanding does is a subject appeal?
- How complex or advanced is this subject?
- What standard of knowledge needs to be obtained to understand this subject?
State: This refers to a fleeting state of being in which the subject can be seen in.
- In what state of mind was the person involved in when reviewing the subject?
- In what state of mind was the person involved in when the situation occurred?
- Is the information given contextual to a certain situation?
Types: This is a division of experiences based on traits that could affect perspective.
- How would someone who is completely different from the person involved perceive the situation?
- What different types of people were involved in the situation?
- How could this subject be received differently by a different cultural reference?
Question Everything
You now possess all that you need to start becoming a critical thinker and asking critical thinking questions. The only way to engrain the above processes and questions to become a critical thinker is to practice. You might need to refer to this article consistently at first, but after time you will become a natural and healthy critical thinker.
This video may help to ignite your passion for questioning everything:
Read more on critical thinking by checking out these related articles and resources:
- How to Solve the Biggest Problems With Critical Thinking
- Critical Thinking Examples That Wil Influence the World Around You
Recommended Free Masterclass For You

Discover Powerful Hacks to Unlock Your Superbrain to Learn Faster, Comprehend More and Forget Less
Join the foremost expert in memory improvement and brain performance, Jim Kwik, in a free masterclass that will dive into the one skill you will ever need — learning how to learn Reserve My Free Spot Now

Irina Yugay
You Might Also Like

Brian Klaas believes embracing chaos is key to growth—here’s why

The thousand-yard stare is a cry for help—here’s how to break free from it

The Burnt Toast Theory is all over TikTok—here’s what it is & why it’s a blessing in disguise

How to overcome fear: 3 no-fail strategies to take back control

How to take notes: 5 methods to help turbocharge your learning

Can you REALLY develop a spidey sense? Science says yes (and here’s how)
Get started.
- Try Mindvalley for Free
- Free Masterclasses
- Coaching Certifications
- Vishen Lakhiani
- The Mindvalley Show
- Partnerships
- In English 🇺🇸
- En Español 🇪🇸
- Mindvalley Events
- Mindvalley Coach
- Mindvalley For Business

Fact-Checking: Our Process
Mindvalley is committed to providing reliable and trustworthy content.
We rely heavily on evidence-based sources, including peer-reviewed studies and insights from recognized experts in various personal growth fields. Our goal is to keep the information we share both current and factual.
The Mindvalley fact-checking guidelines are based on:
- Content Foundation: Our articles build upon Mindvalley’s quest content, which are meticulously crafted and vetted by industry experts to ensure foundational credibility and reliability.
- Research and Sources: Our team delves into credible research, ensuring every piece is grounded in facts and evidence, offering a holistic view on personal growth topics.
- Continuous Updates: In the dynamic landscape of personal development, we are committed to keeping our content fresh. We often revisit and update our resources to stay abreast of the latest developments.
- External Contributions: We welcome insights from external contributors who share our passion for personal transformation and consciousness elevation.
- Product Recommendations and Affiliations: Recommendations come after thoughtful consideration and alignment with Mindvalley’s ethos, grounded in ethical choices.
To learn more about our dedication to reliable reporting, you can read our detailed editorial standards .
K-12 Resources By Teachers, For Teachers Provided by the K-12 Teachers Alliance
- Teaching Strategies
- Classroom Activities
- Classroom Management
- Technology in the Classroom
- Professional Development
- Lesson Plans
- Writing Prompts
- Graduate Programs
Effective Critical-Thinking Questions to Use in Class
Jessica shaffer.
- May 17, 2021

What is Critical Thinking?
Critical thinking does not have just one definition, but one way to explain it is that it is “thinking about one’s thinking.” A critical thinker does not always take things at face value and will question ideas to further understand them. Critical thinkers also have the ability to see past the surface of something, and they possess important skills such as the ability to analyze, interpret, make inferences, and problem-solve. Critical thinkers also tend to be inquisitive about many issues, have a concern to remain well-informed, and embrace and even seek out critical thinking opportunities. Simply stated, critical thinkers think deep thoughts.
What is the Importance of Critical Thinking for Students?
Back in the day, school was different! Honestly, even a year ago, school was far different than it is now, but there is currently so much more emphasis on the “why” and the “how” than just knowing what the answer is. Critical thinking skills are important for students because of the curricula they are exposed to. “Right there” questions are few and far between and students have to rely on their own ability to dig deeper and read between the lines. There is a lot of emphasis placed on college and career readiness, and part of that is to prepare students to problem solve when there is no apparent answer.
Critical thinking provides students opportunities to acquire the higher-level thinking skills that will be needed for career and beyond. It is important to teach students at a young age that you cannot find the answer to everything in a book or through Google. You have to look within yourself to find many answers and, most importantly, justify why that is your answer. There are many ways teachers can incorporate these types of questions throughout the day, you just have to change your mindset a bit!
Critical Thinking Questions to Use in Class
A teacher will ask questions that usually contain one of the following components: who, what, where, when, how, or why. Using good questioning techniques is important and not always as difficult as it seems. Just changing the way that you start a question can change the way students think about an answer or solution. For example, instead of asking students “Who stole the pizza?”, ask students, “Why would that character want to steal the pizza?”
A critical thinking question should aim to make you think. It should lead students to ponder the answer and discuss possible solutions. Critical thinking questions can even lead to disagreements and arguments that can turn into an impressive teachable moment.
One way to incorporate a solid critical thinking question into a math lesson is to have the students solve a problem, and then ask students how they solved the problem. You can have the students talk it out or have each student write down a written explanation and then share it out. Either of these techniques gives various perspectives on how to solve the same problems and can help students to develop math sense.
Another way to incorporate critical thinking questions into math is to present a problem that is solved incorrectly and have students analyze the mistake. Students will have to solve for the correct answer and determine where the mistake occurred. To make this even more challenging, present a word problem or a multi-step story problem to further present critical thinking challenges.
Making inferences is generally one of the most difficult skills for students to learn. This is where students must use their critical thinking skills to understand what is not written or observed. Students must use evidence and couple it with reasoning skills to form a conclusion. A basic example would be looking at a photograph of a dog holding a leash in its mouth and coming to the conclusion that the dog would like to go for a walk.
Morning journals for students can present the perfect opportunity to enhance critical thinking skills. Instead of asking basic questions with basic answers, create questions that force students to think outside the box. For example, ask the question, “Is creativity something that can be measured? Should it be?” Instead of asking what creativity is and giving an example, this question makes a student pause and think about the answer before beginning to respond. These are the types of questions that can frustrate students “in a good way.”
A great way to encourage critical thinking in ELA is to ask students to write an alternate ending to a story. This promotes creativity and deep thinking. Then, students can explain how changing the ending of the story could have an impact on not just the novel, but the world. Encouraging students to think on a more global level also encourages a higher-level of thinking as well as a better understanding of the culture of the world, not just the small bubble they reside in.
Science is a subject perfect for inquiry! Having students think as an engineer would is a critical thinking skill at it’s finest. Students have to design a solution, test it, and then design an even better solution in order to combat weaknesses in the original design. This can be applied at any grade level.
A terrific way to incorporate critical thinking in Social Studies is similar to ELA by changing the outcome of important events in history. For example, have students discuss how our lives would be different if the Civil War had been won by the South. How would it have changed subsequent events in our history and what would life be like today? The opportunities are endless.
Ending Thoughts
All in all, teachers can create many opportunities each and every day for students to use critical thinking skills. It is as simple as starting the day off with a critical thinking question and changing certain techniques. Even if you ask the students a basic question, follow it up with something that requires more depth of thought. As the great Albert Einstein once said, “Education is not the learning of facts, but the training of the mind to think.” Force students to think about their thinking, and get them ready for the real world!
- #CriticalThinking , #TeachingStrategies
More in Teaching Strategies

Explaining the 5 Pillars of Reading
Reading is a fundamental skill that shapes the way we learn and communicate….

A Guide to Supporting Students with Bad Grades
Supporting students who are struggling academically as an educator can be challenging. Poor grades often…

Learning Where You Live: The Power of Place-Based Education
Place-based learning is an innovative approach that engages students in their community. By…

Write On! Fun Ways to Help Kids Master Pencil Grip
Teaching children proper pencil grip will lay the foundation for successful writing. Holding…
17 Types of Questions for Teachers in the Classroom

Questions are the foundation of almost any class, but knowing when to ask the right ones may require some pre-planning. Educators can use different types of questions in teaching to check on a student’s understanding, spark discussion, or help others learn from their peers.
Of course, you may have the perfect list of questions to ask, but keeping students engaged and talking can become another hurdle. We’ll go over different strategies for designing effective questions and how to handle various situations, such as incorrect answers or silence. Plus, we’ll show you how tech like Poll Everywhere can help you engage your students with interactive presentations and questions .
How to design effective and engaging questions (and get students to respond)
Keeping students engaged while you ask questions designed to measure their level of understanding is an art. Here are some steps you can take to thoughtfully craft different types of questions for your classroom:
Planning what types of questions to ask
- Choose a goal for asking questions: This helps you decide which types of questions used in teaching are best for your needs.
- Decide what course material to base questions on: It’s better to choose content you feel is important to the overall learning objectives noted in your lesson plan.
- Plan critical questions ahead of time: While it’s okay to formulate questions as the class progresses, it’s important to plan questions you deem essential to gauging students’ learning or prompting critical thinking ahead of time.
- Adapt questions to students’ knowledge levels: Make sure your questions challenge your students' understanding of newly presented topics or assess their foundational knowledge—using a diagnostic assessment before and after the semester can help gauge current knowledge.
- Use a variety of question types: Using a variety of question types—even for the same concept—can help students better grasp the course material by prompting them to think about their answers in different ways. Using Bloom’s Taxonomy to develop multiple levels of questions for the same topic is helpful.
- Anticipate possible answers: This helps you ensure the phrasing of your question isn’t too vague or misleading, as well as whether the questions match your learning objectives.
Asking questions
- Phrase questions clearly: Ensure your questions are unambiguous and are phrased logically so students don’t misunderstand or end up more confused.
- Allow time to process the question: Don’t be afraid of silence—it likely means your students are contemplating the question and thinking through their responses. You should always wait a moment for students to process the question before rephrasing or assuming they don’t understand.
- Avoid including the answer in your questions: If you’re assessing students’ comprehension, including the answer in your question defeats the purpose and likely won’t encourage engagement.
- Vary the types of questions you ask: By varying the questions you use in your teaching, you can prompt students to think about the material in different ways.
Assessing student responses
- Follow student responses with reflection: A reflective statement (e.g., “It sounds like…” or “What did you mean when you said…?”) helps you show you’re listening and double-check your understanding of the response.
- Ask students to elaborate: Similar to making a reflective statement, you can outright request that a student elaborate on their response. This can help you really dig into their level of comprehension and may also help other students who are listening in by giving them insight into their peers’ thinking processes.
- Know how you’ll handle incorrect answers: Have a game plan in place in case students answer incorrectly. This not only reduces the chance of confusion but also helps you confidently guide the discussion so students can come to the correct answer and understand why their original answer was incorrect.
- Encourage other students to chime in: Turn a one-way conversation into a discussion by inviting others to offer their opinions or state if they agree or disagree (and why).
- Use positive reinforcement: Make students feel confident and glad they responded by smiling, using positive statements, nodding, and making eye contact. This positive reinforcement can help students feel safe when responding—or when asking questions.
- Keep track of who’s responded: While some students are eager to offer their two cents, others may be more reluctant. You can create a more inclusive and inviting discussion by allowing a variety of students to share. If you teach a hybrid class, be sure to include both in-person and remote students as well.
3 strategies for addressing incorrect answers or surface-level understanding
If your students don’t respond with a satisfactory answer, you can take advantage of that time to help students understand what they got wrong and what the correct answer is. Three different strategies for guiding students to a better understanding of the topic include probing, redirecting, and refocusing.
- Probing: The probing strategy encourages students to use critical thinking to analyze their answers. This may involve uncovering relationships by comparing and contrasting different concepts, or instructors can ask students to clarify their ideas by providing examples. Additionally, educators can help students pinpoint assumptions used to justify their answers.
- Redirecting: By using redirection carefully, you can invite other students to correct a peer’s incorrect answers. This strategy also encourages more students to participate in the discussion by asking if they agree with the answer or if they can provide an example to support the answer. Just be sure to lay out ground rules before opening up a discussion based on one student’s thoughts to avoid unnecessary conflict.
- Refocusing: Instructors can refocus students if their answer doesn’t quite fit with the content being discussed. For example, let’s say you ask, “What’s one way our modern food system is making people sick?” and a student responds with, “Doesn’t it encourage us to overeat?”—you might refocus the discussion to discuss how not all calories are nutritionally equal by asking, “Yes, but what if we’re talking about not just caloric intake but nutritional intake as well?”
How to use Bloom’s Taxonomy to craft engaging questions
Bloom’s Taxonomy is a framework intended to define different levels of learning and help teachers assess student progress. You can use this concept to develop questions that assess students’ levels of understanding. According to Bloom’s Taxonomy, there are six different levels of understanding: remember, understand, apply, analyze, evaluate, and create.
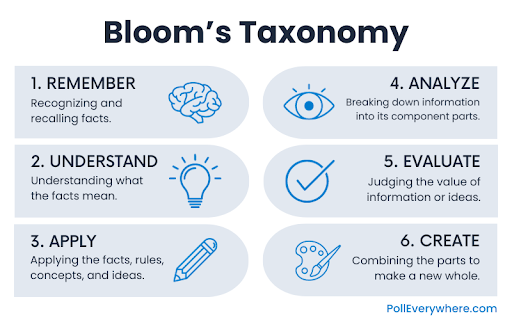
Remember, understand, and apply questions are typically used to assess learners’ comprehension to see whether anyone needs additional assistance grasping the course content. Analyze, evaluate, and create questions are more often used to encourage deeper critical thinking and problem-solving, or to spark discussions.
If you start with higher-level questions associated with the analyze, evaluate, and create levels and students aren’t sure of the answer, asking a follow-up question related to the lower levels of remember, understand, and apply can help you judge whether your learners understand the course material or not.
Here are some examples to help you craft your own questions based on Bloom’s Taxonomy:
- Can you describe ____?
- When did ____ happen?
- Which is true/false, ____ or ____?
- What does ____ mean?
- How would you show ____?
- How would you compare/contrast ____?
- What’s the main idea of ____?
- What would happen if ____?
- How would you state ____ in your own words?
- Which statements support ____?
- Do you know of another instance where ____?
- What examples can you think of to support ____?
- How would you use ____?
- How would you solve ____ using what you’ve learned?
- What questions would you ask to better understand ____?
- Why do you think ____?
- What conclusions can you draw about ____?
- Why did ____ changes occur?
- What’s the theme of ____?
- How is ____ similar to ____?
- What’s your opinion of ____ and why?
- How would you handle ____?
- Is there a better solution to ____?
- What information would you use to support the view of ____?
- Why was ____ better than ____?
- Can you see a possible solution for ____?
- What alternative can you propose for ____?
- How would you test ____?
- What would you predict is the outcome of ____?
- What new/unique uses can you come up with for ____?
What to do if students don’t respond to questions
Possibly one of the worst nightmares any instructor can have is asking a question and being met with silence. But with a few simple strategies you can turn silence into learning opportunities:
- Rephrase the question: Chances are your students don’t understand the question or aren’t sure what you’re looking for. In this case, rephrasing the question to clarify could help clear up the confusion. For example, let’s say you ask your students, “How would you define a project?” You can reword the question by asking, “In what ways are projects different from processes?”
- Prompt with information: You might be able to jog students’ memories or thinking by providing information or context. For example, if students cannot answer “How do you calculate the circumference of a circle?” you could break the question down by asking “How do you calculate the radius of a circle?”
Why is it important to use engaging questions while teaching?
At a minimum, crafting thoughtful questions can help you judge whether your class comprehends the concepts presented in the course. Additionally, strategically designing questions can improve students’ learning comprehension by helping them think critically and creatively as well as encouraging them to engage with the course content.
Questions, credibility, and feedback are all aspects of communication that can improve student engagement. A 2021 study published in the Frontiers in Psychology journal found a “strong dynamic between the aspects of academic engagement and teacher caring, credibility, feedback, and communication style.” Additionally, one study participant noted that an instructor’s credibility actually improves if they don’t always know the answers to all questions.
17 effective types of questions in teaching
Planning out your questions for each lesson also involves considering what types of questions you’ll ask. There are numerous question types and each one may elicit a different response from students. Here are some more effective types of questions to use in teaching that encourage critical thinking and creativity:
A type of rhetorical question, display questions help educators check on students’ ability to retrieve information.
- How much of the body’s oxygen consumption does the brain account for?
- Who wrote “The Faerie Queene?”

2. Referential
A referential question is used when the person asking the question doesn’t know the answer. These types of questions may be helpful to instructors when gathering student feedback about course materials and activities—or to create personal connections by checking in on how students are doing.
- Overall, do you feel this class was beneficial?
- How was your weekend?
Factual questions, also called explicit questions, call on students to answer using information pulled directly from reading assignments. Educators can use factual questions to understand whether students understand the concepts presented in the readings.
Factual questions are an essential starting point for students to expand on the information they’ve learned with critical thinking.
- Which art movement is Salvador Dali associated with?
- Who designed the Sagrada Familia in Barcelona, Spain?
4. Convergent
These types of questions ask students to pull together ideas and information from different sources and synthesize them to create a logical answer. Convergent questions are ideal for problem-solving activities.
- What was the common theme in last week’s reading?
- How would you describe this current event in one word?
5. Divergent
The opposite of convergent questions, divergent questions don’t have a single answer. These types of questions are best used to inspire creative responses and encourage students to consider different points of view, ideas, and scenarios.
- How do you think Edgar Allen Poe would have ended “The Tell-Tale Heart” if his main character didn’t confess?
- How do you think the US might be different if the assassination of John F. Kennedy never took place?
6. Evaluative
An evaluative question requires students to think of a response based on their opinion. These questions can prompt students to think critically about readings or discussions and draw connections to their own experiences or ideals.
- What do you think about Captain Ahab’s mission to find the white whale?
- Do you agree with what the author said in this paper about animal rights?
Open-ended questions are essential to prompt students to think critically about their answers. Open questions can’t be answered with a simple “Yes” or “No,” making them a powerful tool for inspiring discussion.
- What is the main purpose of the United Nations?
- What’s one major breakthrough we’ve had in science over the last 10 years?
Learn more: Marquise McGraw, Ph.D., a professional lecturer at American University, gets students involved in discussions using Poll Everywhere. Find out his personal strategies for engaging everyone —even students who are normally too shy to share—in classroom discussions.
If instructors are trying to get a student to provide more information about their answer, they can use probing questions to prompt students to clarify, justify, or elaborate on their thoughts.
- What information helped you come to that conclusion?
- Who might disagree with your answer?
9. Multiple choice
One of the most common types of questions, multiple-choice questions provide options for students to choose from when answering. Usually, multiple-choice questions have one correct answer, but alternatives include prompting students to choose the option that’s wrong out of a list of correct options or offering an “All of the above” option.
Multiple-choice questions can improve student participation by making it easier for them to respond. Tech like Poll Everywhere further enhances this accessibility by allowing students to answer using their cell phones—or answer anonymously if the instructor chooses to set up the question that way.
- Which project document includes the description, owner, source, priority, and status of product requirements? a) The project charter b) The requirements traceability matrix c) The scope management plan d) The work breakdown structure
- How are tertiary colors created? a) Mixing equal amounts of two secondary colors b) Mixing unequal amounts of two primary colors c) Mixing three primary colors d) All of the above
Focal questions encourage students to pick a side and support their position with logical reasoning. These can be helpful in inspiring students to consider alternative points of view or schools of thought.
- Do you think all US citizens should have to sign up for the draft? Why or why not?
- Do you believe it was within the right of the US Supreme Court to overturn Roe v. Wade? Why or why not?
Physicist Enrico Fermi is the namesake of the Fermi question, which requires students to estimate an answer based on limited information. You may recognize this type of question from articles covering Google’s unconventional approach to interviewing potential new employees, as Fermi questions require creative thinking and the ability to work through a problem.
- Why are manhole covers round?
- How would you explain how the internet works to a seven-year-old?
Thunk questions are intended to encourage students to pause and look at what might normally be a common, benign concept in a different light. (Fun fact: The term “thunk” is based on the irregular form of the verb “think.”)
- If your pet could talk, what would it say about you?
- What’s the difference between knowing and believing?
13. Hypothetical
Hypothetical questions use the good old “What if…” structure to prompt students to consider a scenario and how they would react or feel. Hypothetical questions inspire creativity, problem-solving, and critical thinking.
- What if Europeans never reached North or South America, how would the world be different?
- What do you think life would be like if dinosaurs never went extinct?
14. Ethical
Educators can present students with moral dilemmas using ethical questions. These types of questions don’t have a right or wrong answer but do require students to think critically about why they believe their answer is correct. Ethical questions are excellent discussion starters.
- Do you think countries should be able to claim other planets as their own?
- Should we take care of workers whose jobs are replaced by AI?
15. Application
Instructors can use application questions to encourage students to apply newly gained knowledge related to the course. By using information they’ve learned in class and applying it to real-world situations, students can achieve a higher level of comprehension.
- What are some examples of media bias you’ve seen recently?
- How would you demonstrate Newton’s first law using objects on your desk or in the classroom?
- Using what you know about cognitive bias, how would you design a website landing page that converts leads?
16. Affective
You can encourage students to engage with course content on a more personal level by using affective questions. These types of questions ask students about their feelings toward a topic and how it relates to their values.
Poll Everywhere’s numeric rating scale allows educators to present affective questions in a friendly way. Ask students to rate how they feel about an issue using a scale from one to five, then ask if anyone wants to chime in with the reasoning behind their rating to kick the discussion off.
- How do you feel about the author’s portrayal of Lenny?
- Is the use of imagination in art important to you?
These types of questions are used to gauge your students’ understanding of a topic all at the same time. By using hinge questions, you can decide whether the day’s class should continue going over the topic or if you can move on to the next lesson.
- Which of the following examples represents an allegory?
- Which of the following is an example of soft news?
3 types of ineffective questions to avoid (or use carefully)
Along with the 17 types of effective questions above, there are three more types of questions that can become problematic if not used carefully.
- Binary: Also called a closed question, a binary question is usually answered with “Yes” or No” or variations thereof. These questions typically force students to choose a side and are more effective if there’s no right or wrong answer or if you probe for additional information.
- Leading: Leading questions are problematic because they suggest the correct or desired answer. An example of a leading question is, “How satisfied were you with the class?”
- Loaded: These types of questions include an implicit assumption about the respondent. An example of a loaded question is, “How many times did you cheat on your exams during the semester?”
Poll Everywhere makes gauging student understanding effective and engaging
Getting students to participate in discussions or even ask their own questions is challenging. Designing effective questions based on your desired outcomes or learning objectives keeps you one step ahead of in-class conversations. However, you should also be ready to guide discussions back on topic if students take off on tangents or a respectful debate becomes a heated argument.
Tech like Poll Everywhere can help you present your questions in an engaging format that invites all students to participate. With the ability to ask and share any type of question using Poll Everywhere, including multiple-choice, you can quickly and easily inspire and guide discussions that all students are excited to participate in.
Related articles

10+ Critical Thinking Questions to Build Your Skills
What is critical thinking for leaders, why do you need critical thinking skills at work, critical thinking questions for managers and teams, critical thinking questions for decision-making and planning, critical thinking questions for team building, thinking, critically, critical thinking questions faqs.
Other Related Blogs
- Problem-solving: In any workplace, there are bound to be problems that arise. Critical thinking enables employees to analyze the problem from different angles, identify the root cause, and develop effective solutions.
- Decision-making: Critical thinking is crucial when making important decisions. Employees with strong critical thinking skills can better weigh the pros and cons of various options, anticipate potential outcomes, and make informed decisions.
- Innovation: Critical thinking enables employees to think outside the box and develop innovative solutions to problems. Employees can identify new and creative ways to approach problems by examining the situation from different perspectives.
- Communication: Effective communication is essential in any workplace. Critical thinking helps employees to communicate their ideas clearly and persuasively. It also enables employees to listen actively, ask insightful questions, and respond thoughtfully.
- Time management: In fast-paced work environments, employees must make decisions quickly. Critical thinking lets employees quickly analyze information and make informed decisions without sacrificing quality.

What problem or issue are we trying to solve, and what are the underlying causes?
A manager leads a team that needs help meeting its sales targets. Rather than simply increasing sales numbers, the manager first tries to understand the issue’s root causes. After conducting research and analysis, the manager identifies that the team needs more sales training and skills to engage with potential customers effectively . With this understanding, the manager can develop targeted training and coaching programs to improve the team’s sales skills, ultimately leading to better sales performance.
What are the potential consequences of different courses of action, and how can I mitigate risks?
A manager is considering launching a new product line. Before making a decision, the manager should evaluates the consequences of different courses of action. They consider factors such as market demand, production costs, and potential profitability, as well as potential risks such as supply chain disruptions or low sales volume. With this understanding, the manager then develops strategies to mitigate risks and maximize the chances of success. By taking a thoughtful and strategic approach to decision-making, the manager can increase the chances of success and minimize potential negative consequences.
What data do I need to make an informed decision, and how can I ensure its accuracy and reliability?
A manager is considering expanding into a new market. To make an informed decision, the manager needs data on market size, consumer demographics, competitor analysis, and potential regulatory barriers. The manager then works to ensure the accuracy and reliability of this data, which involves validating sources, cross-checking data against multiple sources, and engaging experts in the field to provide additional insights.
What are the potential unintended consequences of the actions, and how can I minimize them?
A manager is considering implementing a new cost-cutting measure, such as reducing employee benefits. While this may help the organization save money in the short term, it could also have unintended consequences, such as reduced employee morale and increased turnover. To minimize these unintended consequences, the manager could consider alternative cost-cutting measures or work to mitigate the impact on employees by providing additional support or incentives.
How can I test the assumptions and hypotheses, and what metrics can I measure success?
A manager is considering launching a new product. The manager has assumptions about the market demand for the product, customer preferences, and production costs. To test these assumptions, the manager conducts market research, analyzes customer feedback, and conducts cost-benefit analyses to determine the product’s viability. The manager then sets metrics for success, such as sales targets or customer satisfaction ratings, and tracks these metrics over time to determine if the product is meeting expectations.
How can I anticipate and prepare for potential roadblocks or obstacles and develop contingency plans?
A manager oversees the development of a new product dependent on a key supplier for a critical component. The manager anticipates potential roadblocks, such as delays or quality issues with the supplier, and develops contingency plans to identify alternate suppliers or develop in-house capabilities for the component. In addition to developing contingency plans, the manager also communicates and aligns these plans with relevant stakeholders, including team members and leadership. It helps ensure everyone is on the same page and prepared to pivot if necessary.
How can I learn from past experiences and mistakes and apply those lessons to the current situation?
A manager oversaw a marketing campaign that failed to generate the desired results. After analyzing the campaign, the manager identified that the messaging was unclear and did not effectively communicate the product’s value proposition. When planning a new campaign for a similar product, the manager could apply the lessons learned by ensuring the messaging is clear and effectively communicates the value proposition.
- 7 Top Skills Every Hiring Manager Should Possess
- How to do a Self-evaluation in Performance Reviews? (With 7 Examples)
- 5 Types of Conflict Resolution Styles: Which one is yours?
- Coaching Employee with Negative Attitude to turn them around in 5 easy steps
- Performance Conversations: Building a Path to Growth and Success
- Types of Negotiations: Your Ultimate Toolkit for Effective Communication
- Learn To Effectively face and handle Different Decision Making Scenarios with 30 tips
- The Top 10 Team Management Tasks You Should Start Today
- How Succession Planning And Leadership Development Go Hand-in-Hand With 5 Examples
- Managing Employee Benefits for Small Business: A Complete Guide
How can I leverage our team’s diverse perspectives and expertise to generate creative solutions?
A manager is tasked with improving customer satisfaction ratings. The manager could convene a cross-functional team, including representatives from sales, customer service, marketing, and product development. The team could then use brainstorming sessions or design thinking techniques to generate creative solutions, drawing on their diverse perspectives and expertise to create innovative ideas. By involving the team in the solution process, the manager not only taps into the collective knowledge and experience of the team but also increases buy-in and engagement around the solution.
What is the long-term impact of my decisions, and how can I ensure they align with our organization’s mission and values?
A manager overseeing a manufacturing operation may need to make decisions about sourcing raw materials or disposing of waste products. By considering the long-term impact of these decisions, the manager could work to identify suppliers who prioritize sustainability and implement practices that reduce waste and minimize environmental harm.
How can we effectively communicate our decisions to the team to gain buy-in and support?
A manager observes that their team feels disconnected from the work being done daily. Upon thinking, the manager understands that the team needs to be made aware of the rationale behind decisions made by the management. They can explore various communication strategies and channels to ensure team members understand the rationale behind decisions.
What feedback mechanisms can we implement to regularly assess and enhance our processes?
A manager observes little performance improvement even after reviews and appraisals are over. They conclude that the feedback mechanisms are insufficient as they work infrequently and without coordination for follow-ups. It helps them search for better processes to implement with their team.
Suprabha Sharma
Suprabha, a versatile professional who blends expertise in human resources and psychology, bridges the divide between people management and personal growth with her novel perspectives at Risely. Her experience as a human resource professional has empowered her to visualize practical solutions for frequent managerial challenges that form the pivot of her writings.
Test your critical thinking skills for free to start growing.
The free critical thinking assessment helps managers discover the hurdles to their growth.
How do you encourage critical thinking in employees?
How can teams improve critical thinking skills, what are critical thinking questions, what are 3 important things to consider in critical thinking.

6 Steps to Beat Common Critical Thinking Barriers at Work
How to develop the 8 conceptual skills every manager needs, 7 ways to develop critical thinking skills as a manager, 5 steps to excellent strategic thinking skills for managers.
Classroom Q&A
With larry ferlazzo.
In this EdWeek blog, an experiment in knowledge-gathering, Ferlazzo will address readers’ questions on classroom management, ELL instruction, lesson planning, and other issues facing teachers. Send your questions to [email protected]. Read more from this blog.
Eight Instructional Strategies for Promoting Critical Thinking

- Share article
(This is the first post in a three-part series.)
The new question-of-the-week is:
What is critical thinking and how can we integrate it into the classroom?
This three-part series will explore what critical thinking is, if it can be specifically taught and, if so, how can teachers do so in their classrooms.
Today’s guests are Dara Laws Savage, Patrick Brown, Meg Riordan, Ph.D., and Dr. PJ Caposey. Dara, Patrick, and Meg were also guests on my 10-minute BAM! Radio Show . You can also find a list of, and links to, previous shows here.
You might also be interested in The Best Resources On Teaching & Learning Critical Thinking In The Classroom .
Current Events
Dara Laws Savage is an English teacher at the Early College High School at Delaware State University, where she serves as a teacher and instructional coach and lead mentor. Dara has been teaching for 25 years (career preparation, English, photography, yearbook, newspaper, and graphic design) and has presented nationally on project-based learning and technology integration:
There is so much going on right now and there is an overload of information for us to process. Did you ever stop to think how our students are processing current events? They see news feeds, hear news reports, and scan photos and posts, but are they truly thinking about what they are hearing and seeing?
I tell my students that my job is not to give them answers but to teach them how to think about what they read and hear. So what is critical thinking and how can we integrate it into the classroom? There are just as many definitions of critical thinking as there are people trying to define it. However, the Critical Think Consortium focuses on the tools to create a thinking-based classroom rather than a definition: “Shape the climate to support thinking, create opportunities for thinking, build capacity to think, provide guidance to inform thinking.” Using these four criteria and pairing them with current events, teachers easily create learning spaces that thrive on thinking and keep students engaged.
One successful technique I use is the FIRE Write. Students are given a quote, a paragraph, an excerpt, or a photo from the headlines. Students are asked to F ocus and respond to the selection for three minutes. Next, students are asked to I dentify a phrase or section of the photo and write for two minutes. Third, students are asked to R eframe their response around a specific word, phrase, or section within their previous selection. Finally, students E xchange their thoughts with a classmate. Within the exchange, students also talk about how the selection connects to what we are covering in class.
There was a controversial Pepsi ad in 2017 involving Kylie Jenner and a protest with a police presence. The imagery in the photo was strikingly similar to a photo that went viral with a young lady standing opposite a police line. Using that image from a current event engaged my students and gave them the opportunity to critically think about events of the time.
Here are the two photos and a student response:
F - Focus on both photos and respond for three minutes
In the first picture, you see a strong and courageous black female, bravely standing in front of two officers in protest. She is risking her life to do so. Iesha Evans is simply proving to the world she does NOT mean less because she is black … and yet officers are there to stop her. She did not step down. In the picture below, you see Kendall Jenner handing a police officer a Pepsi. Maybe this wouldn’t be a big deal, except this was Pepsi’s weak, pathetic, and outrageous excuse of a commercial that belittles the whole movement of people fighting for their lives.
I - Identify a word or phrase, underline it, then write about it for two minutes
A white, privileged female in place of a fighting black woman was asking for trouble. A struggle we are continuously fighting every day, and they make a mockery of it. “I know what will work! Here Mr. Police Officer! Drink some Pepsi!” As if. Pepsi made a fool of themselves, and now their already dwindling fan base continues to ever shrink smaller.
R - Reframe your thoughts by choosing a different word, then write about that for one minute
You don’t know privilege until it’s gone. You don’t know privilege while it’s there—but you can and will be made accountable and aware. Don’t use it for evil. You are not stupid. Use it to do something. Kendall could’ve NOT done the commercial. Kendall could’ve released another commercial standing behind a black woman. Anything!
Exchange - Remember to discuss how this connects to our school song project and our previous discussions?
This connects two ways - 1) We want to convey a strong message. Be powerful. Show who we are. And Pepsi definitely tried. … Which leads to the second connection. 2) Not mess up and offend anyone, as had the one alma mater had been linked to black minstrels. We want to be amazing, but we have to be smart and careful and make sure we include everyone who goes to our school and everyone who may go to our school.
As a final step, students read and annotate the full article and compare it to their initial response.
Using current events and critical-thinking strategies like FIRE writing helps create a learning space where thinking is the goal rather than a score on a multiple-choice assessment. Critical-thinking skills can cross over to any of students’ other courses and into life outside the classroom. After all, we as teachers want to help the whole student be successful, and critical thinking is an important part of navigating life after they leave our classrooms.

‘Before-Explore-Explain’
Patrick Brown is the executive director of STEM and CTE for the Fort Zumwalt school district in Missouri and an experienced educator and author :
Planning for critical thinking focuses on teaching the most crucial science concepts, practices, and logical-thinking skills as well as the best use of instructional time. One way to ensure that lessons maintain a focus on critical thinking is to focus on the instructional sequence used to teach.
Explore-before-explain teaching is all about promoting critical thinking for learners to better prepare students for the reality of their world. What having an explore-before-explain mindset means is that in our planning, we prioritize giving students firsthand experiences with data, allow students to construct evidence-based claims that focus on conceptual understanding, and challenge students to discuss and think about the why behind phenomena.
Just think of the critical thinking that has to occur for students to construct a scientific claim. 1) They need the opportunity to collect data, analyze it, and determine how to make sense of what the data may mean. 2) With data in hand, students can begin thinking about the validity and reliability of their experience and information collected. 3) They can consider what differences, if any, they might have if they completed the investigation again. 4) They can scrutinize outlying data points for they may be an artifact of a true difference that merits further exploration of a misstep in the procedure, measuring device, or measurement. All of these intellectual activities help them form more robust understanding and are evidence of their critical thinking.
In explore-before-explain teaching, all of these hard critical-thinking tasks come before teacher explanations of content. Whether we use discovery experiences, problem-based learning, and or inquiry-based activities, strategies that are geared toward helping students construct understanding promote critical thinking because students learn content by doing the practices valued in the field to generate knowledge.

An Issue of Equity
Meg Riordan, Ph.D., is the chief learning officer at The Possible Project, an out-of-school program that collaborates with youth to build entrepreneurial skills and mindsets and provides pathways to careers and long-term economic prosperity. She has been in the field of education for over 25 years as a middle and high school teacher, school coach, college professor, regional director of N.Y.C. Outward Bound Schools, and director of external research with EL Education:
Although critical thinking often defies straightforward definition, most in the education field agree it consists of several components: reasoning, problem-solving, and decisionmaking, plus analysis and evaluation of information, such that multiple sides of an issue can be explored. It also includes dispositions and “the willingness to apply critical-thinking principles, rather than fall back on existing unexamined beliefs, or simply believe what you’re told by authority figures.”
Despite variation in definitions, critical thinking is nonetheless promoted as an essential outcome of students’ learning—we want to see students and adults demonstrate it across all fields, professions, and in their personal lives. Yet there is simultaneously a rationing of opportunities in schools for students of color, students from under-resourced communities, and other historically marginalized groups to deeply learn and practice critical thinking.
For example, many of our most underserved students often spend class time filling out worksheets, promoting high compliance but low engagement, inquiry, critical thinking, or creation of new ideas. At a time in our world when college and careers are critical for participation in society and the global, knowledge-based economy, far too many students struggle within classrooms and schools that reinforce low-expectations and inequity.
If educators aim to prepare all students for an ever-evolving marketplace and develop skills that will be valued no matter what tomorrow’s jobs are, then we must move critical thinking to the forefront of classroom experiences. And educators must design learning to cultivate it.
So, what does that really look like?
Unpack and define critical thinking
To understand critical thinking, educators need to first unpack and define its components. What exactly are we looking for when we speak about reasoning or exploring multiple perspectives on an issue? How does problem-solving show up in English, math, science, art, or other disciplines—and how is it assessed? At Two Rivers, an EL Education school, the faculty identified five constructs of critical thinking, defined each, and created rubrics to generate a shared picture of quality for teachers and students. The rubrics were then adapted across grade levels to indicate students’ learning progressions.
At Avenues World School, critical thinking is one of the Avenues World Elements and is an enduring outcome embedded in students’ early experiences through 12th grade. For instance, a kindergarten student may be expected to “identify cause and effect in familiar contexts,” while an 8th grader should demonstrate the ability to “seek out sufficient evidence before accepting a claim as true,” “identify bias in claims and evidence,” and “reconsider strongly held points of view in light of new evidence.”
When faculty and students embrace a common vision of what critical thinking looks and sounds like and how it is assessed, educators can then explicitly design learning experiences that call for students to employ critical-thinking skills. This kind of work must occur across all schools and programs, especially those serving large numbers of students of color. As Linda Darling-Hammond asserts , “Schools that serve large numbers of students of color are least likely to offer the kind of curriculum needed to ... help students attain the [critical-thinking] skills needed in a knowledge work economy. ”
So, what can it look like to create those kinds of learning experiences?
Designing experiences for critical thinking
After defining a shared understanding of “what” critical thinking is and “how” it shows up across multiple disciplines and grade levels, it is essential to create learning experiences that impel students to cultivate, practice, and apply these skills. There are several levers that offer pathways for teachers to promote critical thinking in lessons:
1.Choose Compelling Topics: Keep it relevant
A key Common Core State Standard asks for students to “write arguments to support claims in an analysis of substantive topics or texts using valid reasoning and relevant and sufficient evidence.” That might not sound exciting or culturally relevant. But a learning experience designed for a 12th grade humanities class engaged learners in a compelling topic— policing in America —to analyze and evaluate multiple texts (including primary sources) and share the reasoning for their perspectives through discussion and writing. Students grappled with ideas and their beliefs and employed deep critical-thinking skills to develop arguments for their claims. Embedding critical-thinking skills in curriculum that students care about and connect with can ignite powerful learning experiences.
2. Make Local Connections: Keep it real
At The Possible Project , an out-of-school-time program designed to promote entrepreneurial skills and mindsets, students in a recent summer online program (modified from in-person due to COVID-19) explored the impact of COVID-19 on their communities and local BIPOC-owned businesses. They learned interviewing skills through a partnership with Everyday Boston , conducted virtual interviews with entrepreneurs, evaluated information from their interviews and local data, and examined their previously held beliefs. They created blog posts and videos to reflect on their learning and consider how their mindsets had changed as a result of the experience. In this way, we can design powerful community-based learning and invite students into productive struggle with multiple perspectives.
3. Create Authentic Projects: Keep it rigorous
At Big Picture Learning schools, students engage in internship-based learning experiences as a central part of their schooling. Their school-based adviser and internship-based mentor support them in developing real-world projects that promote deeper learning and critical-thinking skills. Such authentic experiences teach “young people to be thinkers, to be curious, to get from curiosity to creation … and it helps students design a learning experience that answers their questions, [providing an] opportunity to communicate it to a larger audience—a major indicator of postsecondary success.” Even in a remote environment, we can design projects that ask more of students than rote memorization and that spark critical thinking.
Our call to action is this: As educators, we need to make opportunities for critical thinking available not only to the affluent or those fortunate enough to be placed in advanced courses. The tools are available, let’s use them. Let’s interrogate our current curriculum and design learning experiences that engage all students in real, relevant, and rigorous experiences that require critical thinking and prepare them for promising postsecondary pathways.

Critical Thinking & Student Engagement
Dr. PJ Caposey is an award-winning educator, keynote speaker, consultant, and author of seven books who currently serves as the superintendent of schools for the award-winning Meridian CUSD 223 in northwest Illinois. You can find PJ on most social-media platforms as MCUSDSupe:
When I start my keynote on student engagement, I invite two people up on stage and give them each five paper balls to shoot at a garbage can also conveniently placed on stage. Contestant One shoots their shot, and the audience gives approval. Four out of 5 is a heckuva score. Then just before Contestant Two shoots, I blindfold them and start moving the garbage can back and forth. I usually try to ensure that they can at least make one of their shots. Nobody is successful in this unfair environment.
I thank them and send them back to their seats and then explain that this little activity was akin to student engagement. While we all know we want student engagement, we are shooting at different targets. More importantly, for teachers, it is near impossible for them to hit a target that is moving and that they cannot see.
Within the world of education and particularly as educational leaders, we have failed to simplify what student engagement looks like, and it is impossible to define or articulate what student engagement looks like if we cannot clearly articulate what critical thinking is and looks like in a classroom. Because, simply, without critical thought, there is no engagement.
The good news here is that critical thought has been defined and placed into taxonomies for decades already. This is not something new and not something that needs to be redefined. I am a Bloom’s person, but there is nothing wrong with DOK or some of the other taxonomies, either. To be precise, I am a huge fan of Daggett’s Rigor and Relevance Framework. I have used that as a core element of my practice for years, and it has shaped who I am as an instructional leader.
So, in order to explain critical thought, a teacher or a leader must familiarize themselves with these tried and true taxonomies. Easy, right? Yes, sort of. The issue is not understanding what critical thought is; it is the ability to integrate it into the classrooms. In order to do so, there are a four key steps every educator must take.
- Integrating critical thought/rigor into a lesson does not happen by chance, it happens by design. Planning for critical thought and engagement is much different from planning for a traditional lesson. In order to plan for kids to think critically, you have to provide a base of knowledge and excellent prompts to allow them to explore their own thinking in order to analyze, evaluate, or synthesize information.
- SIDE NOTE – Bloom’s verbs are a great way to start when writing objectives, but true planning will take you deeper than this.
QUESTIONING
- If the questions and prompts given in a classroom have correct answers or if the teacher ends up answering their own questions, the lesson will lack critical thought and rigor.
- Script five questions forcing higher-order thought prior to every lesson. Experienced teachers may not feel they need this, but it helps to create an effective habit.
- If lessons are rigorous and assessments are not, students will do well on their assessments, and that may not be an accurate representation of the knowledge and skills they have mastered. If lessons are easy and assessments are rigorous, the exact opposite will happen. When deciding to increase critical thought, it must happen in all three phases of the game: planning, instruction, and assessment.
TALK TIME / CONTROL
- To increase rigor, the teacher must DO LESS. This feels counterintuitive but is accurate. Rigorous lessons involving tons of critical thought must allow for students to work on their own, collaborate with peers, and connect their ideas. This cannot happen in a silent room except for the teacher talking. In order to increase rigor, decrease talk time and become comfortable with less control. Asking questions and giving prompts that lead to no true correct answer also means less control. This is a tough ask for some teachers. Explained differently, if you assign one assignment and get 30 very similar products, you have most likely assigned a low-rigor recipe. If you assign one assignment and get multiple varied products, then the students have had a chance to think deeply, and you have successfully integrated critical thought into your classroom.

Thanks to Dara, Patrick, Meg, and PJ for their contributions!
Please feel free to leave a comment with your reactions to the topic or directly to anything that has been said in this post.
Consider contributing a question to be answered in a future post. You can send one to me at [email protected] . When you send it in, let me know if I can use your real name if it’s selected or if you’d prefer remaining anonymous and have a pseudonym in mind.
You can also contact me on Twitter at @Larryferlazzo .
Education Week has published a collection of posts from this blog, along with new material, in an e-book form. It’s titled Classroom Management Q&As: Expert Strategies for Teaching .
Just a reminder; you can subscribe and receive updates from this blog via email (The RSS feed for this blog, and for all Ed Week articles, has been changed by the new redesign—new ones won’t be available until February). And if you missed any of the highlights from the first nine years of this blog, you can see a categorized list below.
- This Year’s Most Popular Q&A Posts
- Race & Racism in Schools
- School Closures & the Coronavirus Crisis
- Classroom-Management Advice
- Best Ways to Begin the School Year
- Best Ways to End the School Year
- Student Motivation & Social-Emotional Learning
- Implementing the Common Core
- Facing Gender Challenges in Education
- Teaching Social Studies
- Cooperative & Collaborative Learning
- Using Tech in the Classroom
- Student Voices
- Parent Engagement in Schools
- Teaching English-Language Learners
- Reading Instruction
- Writing Instruction
- Education Policy Issues
- Differentiating Instruction
- Math Instruction
- Science Instruction
- Advice for New Teachers
- Author Interviews
- Entering the Teaching Profession
- The Inclusive Classroom
- Learning & the Brain
- Administrator Leadership
- Teacher Leadership
- Relationships in Schools
- Professional Development
- Instructional Strategies
- Best of Classroom Q&A
- Professional Collaboration
- Classroom Organization
- Mistakes in Education
- Project-Based Learning
I am also creating a Twitter list including all contributors to this column .
The opinions expressed in Classroom Q&A With Larry Ferlazzo are strictly those of the author(s) and do not reflect the opinions or endorsement of Editorial Projects in Education, or any of its publications.
Sign Up for EdWeek Update
Edweek top school jobs.

Sign Up & Sign In

85 Fun Critical Thinking Questions for Kids & Teens

Have you ever thought about using fun questions to practice critical thinking?
Students may need a little guidance to think their way through questions that lack straightforward answers.
But it is that process that is important!
How the Right Questions Encourage Critical Thinking
Every parent knows how natural it is for children to ask questions.
It should be encouraged. After all, asking questions helps with critical thinking.
As they grow older, however, training them to answer questions can be equally beneficial.
Posing questions that encourage kids to analyze, compare, and evaluate information can help them develop their ability to think critically about tough topics in the future.
Of course, critical thinking questions for kids need to be age-appropriate—even better if you can mix a little fun into it!
That’s what I hope to help you with today. I’ve organized the questions below into three different ages groups:
- Upper elementary
- Middle school
- High school

Get a Question-Based Critical Thinking Exercise—Free!
Introduce critical thinking gently & easily with thought-provoking exercises.
Upper Elementary
Students in upper elementary grades can be reluctant to put themselves out there, especially with answers that seem weird.
In some cases, such hesitancy is actually fear of differing from their peers (and a barrier to critical thinking ).
But that’s exactly why it’s important to practice answering ambiguous questions.
We want our children to stand firm for their beliefs—not cave to peer pressure.
Additionally, students may feel uneasy about answering serious questions, uncertain of tackling “big” problems.
However, with careful use of creative questions for kids, it’s possible to engage even the most reluctant children in this age group.
The idea is to simply get them interested in the conversation and questions asked.
If you have an especially reserved student, try starting with the funny critical thinking questions.
Humor is a natural icebreaker that can make critical thinking questions more lighthearted and enjoyable.
Of course, most younger kids just like to be silly, so playing upon that can keep them active and engaged.
With that said, here are some great questions to get you started:
1. Someone gives you a penguin. You can’t sell it or give it away. What do you do with it?
2. What would it be like if people could fly?
3. If animals could talk, what question would you ask?
4. If you were ice cream, what kind would you be and why?
5. Do you want to travel back in time? If yes, how far back would you go? If no, why not?
6. What could you invent that would help your family?
7. If you could stay up all night, what would you do?
8. What does the man on the moon do during the day?
9. What makes something weird or normal?
10. Can you describe the tastes “salty” and “sweet” without using those words?
11. What does it feel like to ride a rollercoaster?
12. What makes a joke funny?
13. What two items would you take if you knew you would be stranded on an island and why?
14. Do you have a favorite way of laughing?
15. What noise makes you cringe and cover your ears? Why?
16. If you could be the parent for the day, what would you do?
17. If you could jump into your favorite movie and change the outcome, which one would you pick and why?
18. If you could be invisible for a day, what would you do?
19. What makes a day “perfect”?
20. If you owned a store, what kind of products would you sell?
21. If your parents were your age, would you be friends with them?
22. Would you still like your favorite food if it tasted the same as always, but now had an awful smell?
23. What would you do if you forgot to put your shoes on before leaving home?
24. Who would you be if you were a cartoon character?
25. How many hot dogs do you think you could eat in one sitting?
26. If you could breathe under water, what would you explore?
27. At what age do you think you stop being a kid?
28. If you had springs in your legs, what would you be able to do?
29. Can you describe the color blue to someone if they’re blind?
Middle School
At this point, students start to acquire more complex skills and are able to form their own conclusions based on the information they’re given.
However, we can’t expect deep philosophical debates with 12 and 13 year olds.
That said, as parent-teachers, we can certainly begin using more challenging questions to help them examine and rationalize their thought processes.
Browse the fun critical thinking questions below for students in this age range.
You might be surprised to see how receptive middle school kids can be to such thought-provoking (yet still fun) questions .
30. What would happen if it really did rain cats and dogs?
31. What does it mean to be lucky?
32. If you woke up in the middle of a dream, where would you be?
33. Is it ever okay to lie? Why or why not?
34. If you were solely responsible for creating laws, what one law would you make?
35. What makes a person a good friend?
36. What do you think is the most important skill you can take into adulthood?
37. If you had to give up lunch or dinner, which would you choose? Why?
38. How much money would you need to be considered rich?
39. If you knew you wouldn’t get caught, would you cheat on a test?
40. If you could live anywhere in the world, where would that be?
41. What is your greatest strength? How is that an asset?
42. If you had an opportunity to visit the International Space Station, would you do it?
43. Is it better to keep the peace or speak your mind?
44. Imagine yourself as your favorite animal. How would you spend your day?
45. Would you be friends with someone who didn’t have the same values as you?
46. How much screen time do you think is too much?
47. Can you describe your favorite color without naming it?
48. If you suddenly became blind, would you see things differently?
49. Would you ever go skydiving?
50. Describe the time you were the happiest in your life. Why did this make you happy?
51. If you had a million dollars, what would you do?
52. If you had to move to a new city, would you change how you present yourself to others?
53. What do you need to do in order to be famous?
54. If you could rewrite the ending of your favorite book or movie, what changes would you make?
55. How would you tackle a huge goal?
56. How would you sell ice to an eskimo in Alaska successfully?
57. What makes you unique?
High School
Critical thinking takes on an entirely different role once students reach high school.
At this age, they have a greater sense of right and wrong (and what makes things so) as well as a better understanding of the world’s challenges.
Guiding teens to delve deeper and contemplate such things is an important part of developing their reasoning and critical thinking skills.

Whether it’s fun questions about hypothetical superpowers or tough critical thinking questions about life, older teens typically have what it takes to think their way to a logical conclusion .
Of course, use your discernment as you choose discussion topics, but here are some questions to help get you started:
58. How can you avoid [common problem] in the future?
59. Do you think it’s okay to take a life in order to save 5, 10, 20 or more people?
60. If you could go back and give your younger self advice, what would it be?
61. Is it better to give or receive a gift?
62. How important is it to be financially secure? Why?
63. If it was up to you, what one rule would you change in your family?
64. What would you do if a group of friends wanted to do something that you thought was a bad idea?
65. How do you know that something is a fact rather than an opinion?
66. What would it take to get you to change your mind?
67. What’s the most important thing in your life?
68. If money were of no concern, what job would you choose and why?
69. How do you know if you’re happy?
70. Do you think euthanasia is moral?
71. What is something you can do today that you weren’t able to do a year ago?
72. Is social media a good thing or not?
73. Is it right to keep animals in a zoo?
74. How does your attitude affect your abilities?
75. What would you do if you found out a friend was doing something dangerous?
76. If you could have any superpower, what would it be? Why?
77. What will life on Earth look like in 50 years?
78. Which is more important, ending world hunger or global warming?
79. Is it a good idea to lower the voting age to 16? Why or why not?
80. If the electrical power went out today, how would you cook if using wood wasn’t an option?
81. If you could magically transport yourself to any other place, where would that be and why?
82. When should teenagers be able to stay out all night?
83. Does the number zero actually exist?
84. What defines a generous person?
85. Does an influential person influence everyone?
Feel free to print out these fun critical thinking questions and incorporate them into your homeschool week!

will your children recognize truth?
About the author.
Jordan Mitchell

19 Short Stories and Questions For Critical Thinking
Apr 2, 2024
There have been rumblings in different online teacher groups recently about replacing novels with short stories and informational articles in middle and high school English classrooms. I have to admit I was shocked when I first read the comments because I am a book lover at heart, but since then, I’ve considered that there are several pros and cons to this approach.
Short stories and other smaller texts can provide a briefer timeline to complete tasks, and this process is helpful when there is already SO MUCH curriculum to cover. Short stories and related activities can also be more engaging for our students because of the exposure to diverse voices and themes! Using short stories and lessons provides students with amazing choices to meet their needs and preferences!
On the other hand, incorporating mainly short stories and other shorter passages means students’ already-pressed attention spans (as a result of social media influences and pervasive sources of technology) are reinforced. Plus, students miss out on the more complex stories within longer pieces of fiction that are, dare I say, life-altering! A novel can provide opportunities for sustained reading and layers for analysis that shorter pieces of literature like short stories and related texts cannot offer.
Ultimately, no matter where you find yourself on the issue, I think we can all agree that short stories and their counterparts can be vital, effective, and helpful in the modern classroom!
Continue reading for 19 Short Stories and Questions For Critical Thinking!!
Need help with Test Prep ? Check out this FREE Pack of 3 Test Prep Activities to help students achieve success on standardized tests!

Table of Contents
19 Short Stories and Questions – Suggestions for Teaching Them
You don’t need to remove all novels to be able to include short stories and smaller passages like vignettes, articles, and narratives; there’s a time and place for all genres! But if you’re thinking about ways to include more short stories and fun activities, check out this list of 19 varied short stories and critical thinking questions as well as suggestions for teaching them in middle school and high school.
1. “The Most Dangerous Game”
“The Most Dangerous Game” is one of my absolute favorite short stories and overall plots to teach! This suspenseful short story by Richard Connell follows the harrowing ordeal of Sanger Rainsford, a skilled hunter who becomes the prey of a deranged aristocrat named General Zaroff. Stranded on Zaroff’s secluded island, Rainsford must outwit the cunning general in a deadly game of survival, where the stakes are life and death.

SUGGESTIONS FOR TEACHING:
- You could focus on the setting (description of time and place) and examine how the setting changes throughout the story.
- Students could learn about the plot (major events in the story) and list the major events and evidence as they read.
- Define foreshadowing (hints for what will happen by the end of the story) and encourage students to hypothesize about what will happen after every page.
- Analyze the character development (how a character changes over time) of Rainsford and highlight his traits/actions as you read along.
CRITICAL THINKING QUESTIONS:
- How does the setting contribute to the tension and suspense in the story?
- How does the author use foreshadowing? How does the author hint at the danger Rainford is facing?
- What inferences can you make about the main character and the changes he undergoes from the beginning to the end of the story?
If you want to teach plot elements and plot analysis , check out this lesson bundle for the story , which includes comprehension quizzes and a variety of activities!
2. “An Occurrence at Owl Creek Bridge”
Ambrose Bierce’s story is a gripping tale set during the American Civil War, where a Southern civilian named Peyton Farquhar faces execution by hanging after attempting to sabotage a Union railroad bridge. As Farquhar falls through the trapdoor, time seems to stretch, and he experiences a surreal moment, only to realize his grim reality.
Integrating historical texts with other short stories and passages like “An Occurrence at Owl Creek Bridge” will make history come more alive and relevant for our students!
- Teach about irony (when the opposite occurs from what is expected) and how it plays a role throughout the story.
- Explain the term characterization (how a character is depicted) by looking at direct and indirect references while reading with your students.
- Discuss the major themes (messages) of the story and how they connect to our modern era within a Socratic Seminar.
- How does the author use characterization to convey Peyton Farquhar’s thoughts, emotions, and motivations?
- What is the purpose of irony in this story? How does its use affect the reader’s interpretation and understanding of events?
- What is the significance in our contemporary/real world of the themes of the story, including reality and fantasy, the passage of time, and the consequences of actions?
Ensure students’ understanding of the story with this set of reading questions that are perfect for state test prep, too !

3. “The Masque of the Red Death”
This chilling tale from Edgar Allan Poe is set in a secluded abbey where Prince Prospero and his wealthy guests attempt to escape a deadly plague known as the Red Death. Despite their isolation efforts, the guests are confronted with their own mortality as a mysterious figure in a blood-red mask appears.
If you have not read any short stories and poems from Poe, this story is a perfect journey into the horror genre!
- The setting (description of time and place) plays a MAJOR role in the story, so following the Prince from room to room and highlighting the imagery (description that connects to the five senses) is very important when reading.
- If you have not introduced mood (emotion intended for the reader to experience), this story is PERFECT for delineating its progression from start to finish.
- As students read, you might guide them through identifying various examples of symbolism (object, person, or place that represents something else); each room, objects within, and the “antagonist” is symbolic in some way!
- How does the author convey the tone of the story? How would you, as the reader, describe the story’s mood?
- What role does the plot structure (focus on the different rooms) play in shaping the reader’s understanding of the story?
- What is the purpose of the symbolism in the story such as the clock and the masked figure?
Check out this EASY-TO-TEACH bundle , you can practice with your students, so they will feel more confident analyzing higher-level language in “The Masque of the Red Death!”
4. “The Cask of Amontillado”
Another chilling tale from Poe is the classic story “The Cask of Amontillado.” This one is set during Carnival in an unnamed Italian city. The plot centers on a man seeking revenge on a ‘friend’ he believes has insulted him. If your students are anything like mine, they will relish the ending particularly!
This is just one more of Poe’s short stories and tales that will capture the mind of every reader!
- As you plan for this short story, be sure to encourage your students to analyze the changing setting (description of time and place); following Fortunato from scene to scene will help your students track what is really going on.
- This story is the perfect moment to teach about dialogue (conversation within someone=internal and/or between someone and someone/thing else=external); Montresor certainly means more than what he SEEMS to say!
- You might also offer a mini-lesson on the 3 types of irony and how each plays a role in the story: verbal (when a person says the opposite of what is really intended), situational (an action occurs that is the opposite from what the reader expects), and dramatic (a character expects a result, but the opposite occurs and the audience can tell what will happen)!
- Describe Montresor. What are his motives and personality?
- What inferences can you make about Montresor’s mindset based on his dialogue?
- What is the purpose of the family’s motto and the carnival atmosphere?
Check out this Short Story Activity & Quiz Bundle for Edgar Allan Poe’s “The Cask of Amontillado,” which contains questions and answers modeled after various reading standardized tests as well as pre-quiz reading comprehension questions, graphic organizers, and a writing activity to get students thinking critically about this classic short story involving REVENGE!
Want 7 more teaching ideas for one of Poe’s epic short stories and questions to go with it? Click below!

5. “To Build a Fire”
This story by Jack London describes the treacherous journey of a man through the harsh Yukon wilderness during extreme cold. Despite warnings and the company of a loyal dog, the man’s arrogance and underestimation of nature’s power lead to a tragic end.
Short stories and ideas related to survival in nature are still relevant today! Who knows when you might get lost on a hike or crashland in no man’s land?
- This story is PERFECT for a bit of literary analysis (examining the impact of various ideas, elements, or themes within a piece of literature); you could hone in on literary devices, characterization, theme, etc.!
- Integrating clips from survival shows will help students see connections to the world and extend their thinking by comparing (recognizing similarities) and contrasting (recognizing differences) varied experiences!
- Write a short narrative about surviving 24 hours in a different setting (description of time and place).
- How does the author use irony? Provide an example and explain.
- What real-world connections can be made between this story and our contemporary life?
- What is the story’s message about preparedness and respecting nature?
Grab these engaging short stories and activities to make teaching this Jack London story stress-free!
6. “The Cactus”
Told from the point of view of a young man at his former lover’s wedding, the narrator retells their story. Like most of O. Henry’s short stories and texts, this one has a twist that involves the titular cactus plant.
The ending will end in a bit of fun for your students!
- Introduce diction (word choice) and its impact within the story by hyperfocusing on specific words within the story . Students can look up definitions, locate synonyms, create their own sentences, replace the words, etc.
- Investigate twist endings (unexpected finish to a story); before reading the end of the story, ask students to guess why the girl “rejected” him. Some students may know the answer before reading it!
- Describe the main characters. What similarities and differences are evident? How does this affect the story’s action?
- What inferences can you make about Trysdale and his feelings about love and marriage?
- What are the real and symbolic meanings of the cactus?
This resource packed with questions and answers, graphic organizers, and writing activities is sure to get your students thinking about this love story driven by misconceptions.

7. “After Twenty Years”
This tale of friendship and betrayal focuses on the reunion of two old friends after twenty years apart on a New York City street corner. As they reminisce, something is revealed that demonstrates the reality of their bond as well as the choices they’ve made in life.
If you have not read O. Henry’s short stories and incorporated character analysis yet, this is your chance! The story is not long and can be completed in one to two class periods!
- Sometimes, we ask students to visualize (create a picture) in their minds, but why not give them the opportunity to use their artistic skills to draw the two characters?
- As students read, annotate for a description of each character; then, students can do a character analysis (investigation of the characters’ similarities and differences).
- What type of irony is used in the story? How does its use affect your interpretation and understanding of the story?
- How does the urban setting contribute to the mood of the story?
- What is the story’s message about friendship and loyalty?
Examine the links between loyalty and duty with this set of resources designed specifically for this O. Henry story.
8. “The Lottery”
“The Lottery” is the quintessential short story for middle school or high school English! Shirley Jackson’s “The Lottery” tells the story of an annual ritual that takes place in a seemingly idyllic town. When the townsfolk gather for the lottery drawing, a shocking turn of events demonstrates the dark side of human nature and their ties to (outdated) traditions.
- Introduce the terms suspense (uncertainty and/or excitement leading up to a major event) and tension (anxiety or uneasy feelings experienced by characters). While reading, identify evidence that relates to each of these concepts and chat/write about their impact on meaning and plot.
- Teach title (the name of the text) analysis. The title of “The Lottery” is perfect for teaching the impact of the title and audience expectations. Before reading, students may write what they believe the story will be about based on the title. After reading, students can complete a quick write responding to their previous expectations! You can do a text analysis for all short stories and poems!
- What role does the plot structure play in building suspense and tension? (Consider the revelation of the lottery’s ‘prize’ in particular.)
- What social commentary is being made through the story and its characters?
- Describe Mr. Summers, Tessie, and Old Man Warner. What does the story reveal about their role in the community and their feelings about the lottery?
Give yours elf a breath of fresh air with this NO PREP curriculum that integrates test prep within the teaching of literature by using Shirley Jackson’s quintessential story!

9. “The Pedestrian”
This Ray Bradbury story follows a lone walker in a futuristic society in which everyone else is consumed by technology, particularly the television. One evening, the walker encounters a police car that questions his unusual behavior and the end is quite unexpected! (Most of Bradbury’s short stories and texts connect to the future and technology in some way!)
- This story exemplifies Dystopian Literature (texts that include a supposedly perfect future society marred in some way by governmental or societal oppression). Using this story to introduce this type of literature is always fun for students because they will easily make connections to other dystopic short stories and poems!
- Teach about mood (the emotional impact of a story’s description/action). The goal is to get students to deepen their critical thinking skills by recognizing how the mood changes and the purpose for that change!
- How does the author use foreshadowing and suspense to build the mood of the story?
- What is the central theme of the story? How might it connect with our current world?
- What similes and metaphors does Bradbury use to describe the community and its members? What is notable about these comparisons?
With this resource about Bradbury’s “The Pedestrian,” you can just print and teach the lesson and activities with EASE!
10. “The Gift of the Magi”
This 1905 story by O. Henry relays a tale about a couple struggling to make ends meet. Throughout the story, they both figure out gifts to buy one another for Christmas and realize what love truly means!
- Review character traits (how a character is depicted internally and externally). Log the traits of each character within the story and how they are important to the meaning of the story.
- Extend (move beyond the text) critical thinking skills by encouraging students to think and write about other people. If they had $1,000 to spend on someone else, how would they spend the money and why?

- How would you describe Della and Jim, and their relationship?
- What values do the characters have, when you consider their actions and decisions?
- Explain how dramatic irony is used in the story. Is it necessary? Is it effective? Why or why not?
This tale is a great addition to your short stories and questions unit around the winter holidays! Save yourself time at that time of the year with this lesson bundle .
11. “The Monkey’s Paw”
“The Monkey’s Paw” is a classic horror story about the White family who come into possession of a mystical monkey’s paw that grants three wishes. Despite warnings, they use it and then face devastating consequences as a result.
- Teach about the elements of the horror/suspense genre (Ex. Scary movies are typically dark, stormy, surprising, morbid, etc.).
- Create a thematic statement (message relayed by the text in a complete sentence). There is no perfectly created theme (message) unless it is directly stated by the author; however, students can create a theme by supporting their ideas with evidence from the story!
- What is the main theme of the story? Or how does the author communicate the themes of greed or fate? Is one stronger than the other?
- Are Mr. and Mrs. White more alike or different from one another? How do you know?
- Should we be afraid of the unknown? What message does the story share? Do you agree or disagree?
Examine W.W. Jacobs’ classic story with this set of questions and answers along with rigorous reading and writing activities . While it is ideal for a spooky season, the story is valuable for its ability to hook readers any time of year!
12. “Lamb to the Slaughter”
This classic story with a killer plot twist is about a woman who kills her husband and gets away with murder thanks to cooking a leg of lamb!
- You could introduce the plot elements (exposition, rising action, climax, falling action, resolution), encourage students to identify major events to fit each element and write down textual evidence to support their ideas.
- Complete a film analysis (examination of film techniques and their effects) to compare/contrast the short story with the classic Alfred Hitchcock television episode.
- What is Mary Maloney’s state of mind? Does it remain the same or does it change throughout the story? Explain.
- Is the resolution of the story satisfying? Why or why not? Why do you think the author ended it as he did?
- How does irony contribute to the theme of deception in the story? Explain.
Spice up your middle school English or high school English class with this short stories and activities bundle for Dahl’s famous story!
13. “The Tell-Tale Heart”
Poe’s classic psychological thriller is narrated by an unnamed protagonist who insists on their sanity while recounting how they murdered an old man. The narrator is haunted by the sound of the victim’s beating heart, which ultimately drives him to confess to the crime despite not originally being a suspect.
- Teach symbolism (object, person, or place that represents something else) by focusing on the heart and eye . The author used these symbols in various ways!
- Investigate psychology (the study of the human mind) as a part of the story. Determine what is fact and what is fiction within the narrator’s mind.
- What does the story reveal about the human psyche?
- What is the deeper meaning of the two key symbols in the story – the beating heart and the eye of the old man?
- What role do the narrator’s inner thoughts play in the development of the plot?

This Short Story Comprehension Bundle offers quick (and effective!) ways to assess students’ learning and understanding of the story. It’s easy to use and will no doubt save you time too!
14. “The Scarlet Ibis”
Emotional short stories and their counterparts have a place as well in English classrooms! This short story by James Hurst about two brothers is a heartbreaking must-read. Through flashbacks, the unnamed narrator tells the life story of his younger sickly brother William Armstrong, who is nicknamed Doodle. And the end…well, you’ll see.
- Define and explain the purpose of a flashback (referring back to the past within a story). Think about the implications of never thinking back on the past or always thinking about the past.
- Complete a comparison chart between Doodle and the Ibis as you read along. Then, students can create a visual of each after they have ready by using their own evidence!
- What is the meaning of the story’s title and the presence of a scarlet ibis in the story?
- What is the central theme of the story? How do the events of the story support this chosen theme?
- How does the author use personification for the storm? What effect does this have on the story?
This flexible resource features critical thinking questions and answers as well as writing and reading activities for students to explore Hurst’s heartbreaking story.
15. “The Veldt”
This science fiction story by Ray Bradbury was first published as “The World the Children Made” and it is quite fitting as a title! The story focuses on a futuristic world in which a video screen can be controlled and it turns out to be more than simple virtual reality! By the story’s conclusion, the world the children made is the downfall of their parents.
- Compare and contrast “The Veldt” with “The Pedestrian,” two short stories and dystopic texts by Ray Bradbury. Analyze the similarities and differences of both short stories and create a thematic statement that connects to both texts!
- Make connections to our current reality in the 21st century. Locate research about the implications of technology on young people and integrate this information as you discuss this short story.
- How does the author address the theme of technology versus humanity in the story? Do you agree with this commentary? Why or why not?
- How does the nursery reflect the personalities of Wendy and Peter in this story?
- Do you know the story of Peter Pan and his friend Wendy? What connections can you make between it and this story by Ray Bradbury?
Ray Bradbury’s classic short stories and similar passages are the BEST to teach in middle and high school English! With so much to dive into, they are sure to be a hit with your students. Grab this set of activities to extend your students’ engagement with rigorous reading and writing activities about “The Veldt.”
16. “The Necklace”
A woman who longs for a life of luxury and elegance beyond her means faces consequences when she loses a borrowed necklace. Guy de Maupassant’s story ends with a twist that has the reader question the value of material possessions.
- I love comparing this short story with O. Henry’s “The Gift of the Magi.” You might choose to focus on the theme, characterization, setting, etc.
- Summarize (writing about the main idea with details) each chunk of the story as you read with your students. Instead of asking students to write a paragraph, you could ask students to create each summary in only one sentence.
- The story explores vanity, deception, and the consequences of striving for social status. Which theme do you think is the most important? Explain with support from the story.
- Is Mathilde Loisel a likable character? Does this change during the story? Does it matter if the reader likes her? Why or why not?
- What clues does the author provide throughout the story that foreshadow the twist at the story’s end?
Focus on the standards with this Short Story Lesson Bundle for “The Necklace” by Guy de Maupassant!
Need help with implementing activities for “The Necklace?” See below!

17. “A Vendetta”
Guy de Maupassant’s late-19th-century story is all about REVENGE. A mother is obsessed with creating a plan to avenge her son’s murder and she then puts the plan into action with a morbid outcome.
- There are so many texts that involve REVENGE! Why not use this concept as a focus for a thematic unit (texts linked to a similar concept and/or message)? You could read “A Poison Tree,” “The Cask of Amontillado,” and “Lamb to the Slaughter” as well as “A Vendetta” with the intention of writing about all 4 for a comparison/contrast paper, presentation, or seminar.
- Analyze the development (how a character changes over time) of the mother and the dog throughout the story; you might annotate for similarities and differences as well as their motivations!
- What comment is the story making about the nature (or need) for justice? Do you agree or disagree? Why or why not?
- What similes and metaphors does the author use to communicate the main character’s feelings about the vendetta?
- How does the author use details to explain the main character’s thoughts, feelings, and motivation?
Add these activities for this lesser-known work to your short story plans. It’s sure to keep things fresh for your short stories and activities unit!
18. “Thank You, Ma’am” (also known as “Thank You, M’am”)
This heartfelt story by Langston Hughes tells the story of Luella, an older woman in the neighborhood, who is nearly robbed by a young man named Roger. In response to Roger, Luella brings him back to her home and treats him with an abundance of kindness, which has a profound effect on Roger.
This tale is at the top of the list for the BEST short stories and passages for upper middle and younger high school students!
- Introduce perspective and/or point of view (how a story is told: 1st, 2nd, 3rd omniscient, 3rd limited, 3rd objective). Students might rewrite the story from another perspective or extend the story using the perspective of one of the main characters.
- Review plot elements with a focus on the exposition (introduction to the characters, setting, and conflict), climax (highest point of interest/turning point of the story), and resolution (how the story is concluded and/or resolved in some way.) You could assign an activity surrounding each concept: visualization of the scene, a journal response to the event, or a short response focused on how the element is important to the overall theme!

- Do you believe in second chances? What does the story say about second chances?
- How might the climax of the story also be seen as the turning point in Roger’s life?
- How would you describe Mrs. Luella Bates Washington Jones? Are her actions expected or unexpected in the story? Consider from Roger’s and the reader’s point of view.
Click to check out all of the details for this BUNDLE with differentiated options , which includes a Test Prep Quiz (with varied options), Venn Diagrams, Graphic Organizers, and Writing Responses!!
19. “Click Clack the Rattle Bag”
This short story by Neil Gaiman is creepy and fun in the best ways possible! The narrator is taking care of his girlfriend’s little brother and walking him to bed when the child asks for a story. Instead of the narrator sharing a story, the boy shares about the Click Clacks who drink their prey and leave behind rattling bodies. The end is too good to be missed!
Short stories and plots like those in “Click Clack the Rattle Bag” will most certainly engage even your most struggling learners!
- We all know that test prep can be tough as many reading passages are, well, boring! Why not accomplish some test prep with your students and incorporate 5 standardized test-related questions ? You could focus on theme, structure, order of events, characterization, etc.!
- Help students make inferences (acknowledging and hypothesizing about the impact of details that are not directly referenced or stated) as the scene moves along. Students can analyze the change in the setting, the little boy himself, the story the boy is telling, and specific phrases from the story.
- What details in the story contribute to its eerie atmosphere or mood? Or what figurative language devices does Neil Gaiman use to create a sense of suspense in the story?
- How does the author use ambiguity in the story? Is it effective or not? Explain.
- What inferences can you make about the relationship between the narrator and the young boy?

This “Click Clack the Rattle Bag” Quiz Pack for middle and high school students uses the Common Core standards and contains questions and answers modeled after various state standardized tests! Make teaching this amazing short story by Neil Gaiman SIMPLE & EASY!
Why should we incorporate more short stories and activities in our teaching?
While I would never advocate replacing all novels with short stories and smaller texts, there is still something to be said about spending quality time with short stories and excerpts.
Including short stories and standards-based activities is an ideal option to improve reading comprehension and develop skills, especially in middle and high school English classes!
SHORT STORIES AND ACTIVITIES RESOURCES:

This Short Stories and Test Prep Questions ULTIMATE BUNDLE with Lessons, Quizzes, and Activities uses the Common Core standards with reading comprehension QUESTIONS and ANSWERS for 18 short stories such as “The Most Dangerous Game,” “The Monkey’s Paw,” “The Tell-Tale Heart,” “After Twenty Years,” “The Gift of the Magi,” “The Veldt,” “The Lottery,” “The Pedestrian,” etc. modeled after various state reading exams.
Make teaching short stories and activities SIMPLE & EASY!
Just PRINT & TEACH with engaging short stories and lessons!!
Need more fun ideas for teaching short stories and corresponding activities? Check out my store Kristin Menke-Integrated ELA Test Prep !

Hi, I’m KRISTIN!
I primarily focus on integrating multiple disciplines and subjects. The goal is to make teaching simplified and effective!
Let's Connect
- Follow Follow
Click below to download “13 Simple Strategies to make test prep a breeze!”
A Creative Thinking Skills Recharge with 49 Powerful Questions
Tools , Creativity , Idea Magnets , Collaboration
I’m fascinated with how to expand your creative thinking skills through powerful questions . My fascination goes back years. Since starting Brainzooming, we’ve especially seen how the right questions make it easier for people to generate ideas they wouldn’t otherwise imagine.
While working by myself on our marketing plan, I realized a new way to think about creative thinking questions. When you don’t have anyone around to help push your thinking , creative thinking questions stand in for the person who routinely asks, “ Hey, have you thought about it THIS way?”
When I was a corporate marketing VP, multiple people would dependably and constructively challenge my thinking. Some were co-workers; others worked at our advertising agency or were freelancers in our marketing department. No matter where they lived organizationally, asking me if I’d thought about something in a different way was ALWAYS valuable.

As an entrepreneur, you don’t necessarily have a big team to engage for creative thinking. That’s where, when you are working solo, the right question can stretch your creative thinking in dramatic directions. A question can be the perfect vehicle to challenge and expand your thinking in highly productive ways. I think of great questions as providing detours to creativity and strategic thinking. They make you go a different route than you'd originally considered.
Are you recharging your creative thinking skills with these new questions?

If you could use the help of a surrogate for that Have you thought about it THIS way person, download a FREE copy of our latest Idea Magnets eBook with questions to lead to amazing ideas .
We developed the questions in the eBook from our experiences with Brainzooming clients and studying creative thinking skills of well-known innovators. These creative thinking questions will stretch, shift, constrain, exaggerate, and re-orient your thinking to help you boost your creativity, EVEN IF you are working all by yourself.
I’d love for you to enjoy the benefits of the same resource we’re using to grow our business!
And when you get 49 Questions , let us know how you put it to work to boost your creative thinking skills! – Mike Brown
You Might Also Like:

Convergent Thinking Week - When Is It Better to Go with What You Have?

Sports Strategy Lessons Week - Yes, I’m Bluffing . . . Don’t You Think?

Strategic Thinking - 5 Stories Worth Clicking this Week
Date published: 01/08/19
Zoom your brain!
Enter your email address for emails bursting with creativity.
Brainzooming Topics
- Analysis (87)
- Blogging (244)
- Branding (419)
- Career (360)
- Change your character (32)
- Collaboration (952)
- Communication (661)
- Competitive Strategy (121)
- Compilations (116)
- Creative Quickies (56)
- Creativity (1012)
- Diversity (134)
- Events (262)
- Facebook (116)
- Fun Strategic Planning (52)
- Google Fiber (28)
- Guest author (199)
- Humor (114)
- Idea Magnets (131)
- Implementation (994)
- Innovation (966)
- Insights (334)
- Market Research (82)
- Marketing (377)
- Offered Without Comment (33)
- Performance (1180)
- Social media (416)
- Strategic Planning (324)
- Strategic Thinking (1374)
- Strategy (1108)
- Tools (1423)
- Twitter (252)
- Video (127)
- March 2024 (1)
- February 2024 (1)
- January 2024 (9)
- December 2023 (3)
- November 2023 (2)
- October 2023 (2)
- September 2023 (1)
- August 2023 (1)
- July 2023 (3)
- June 2023 (2)
- May 2023 (3)
- April 2023 (7)
- March 2023 (12)
- February 2023 (6)
- January 2023 (6)
- December 2022 (3)
- November 2022 (1)
- October 2022 (1)
- September 2022 (1)
- August 2022 (5)
- July 2022 (1)
- June 2022 (3)
- April 2022 (1)
- March 2022 (7)
- February 2022 (3)
- July 2021 (1)
- April 2021 (1)
- March 2021 (11)
- February 2021 (1)
- January 2021 (4)
- December 2020 (3)
- October 2020 (1)
- July 2020 (1)
- June 2020 (2)
- May 2020 (1)
- April 2020 (3)
- March 2020 (6)
- February 2020 (7)
- January 2020 (7)
- December 2019 (3)
- November 2019 (4)
- October 2019 (9)
- September 2019 (4)
- August 2019 (7)
- July 2019 (6)
- June 2019 (11)
- May 2019 (1)
- February 2019 (12)
- January 2019 (16)
- December 2018 (5)
- November 2018 (16)
- October 2018 (4)
- September 2018 (5)
- August 2018 (9)
- July 2018 (13)
- June 2018 (18)
- May 2018 (6)
- April 2018 (8)
- March 2018 (7)
- February 2018 (14)
- January 2018 (16)
- December 2017 (7)
- November 2017 (10)
- October 2017 (7)
- September 2017 (9)
- August 2017 (9)
- July 2017 (12)
- June 2017 (14)
- May 2017 (20)
- April 2017 (14)
- March 2017 (19)
- February 2017 (20)
- January 2017 (18)
- December 2016 (5)
- November 2016 (10)
- October 2016 (10)
- September 2016 (11)
- August 2016 (14)
- July 2016 (11)
- June 2016 (10)
- May 2016 (12)
- April 2016 (13)
- March 2016 (20)
- February 2016 (21)
- January 2016 (17)
- December 2015 (14)
- November 2015 (16)
- October 2015 (22)
- September 2015 (16)
- August 2015 (18)
- July 2015 (18)
- June 2015 (19)
- May 2015 (19)
- April 2015 (21)
- March 2015 (22)
- February 2015 (20)
- January 2015 (18)
- December 2014 (14)
- November 2014 (17)
- October 2014 (18)
- September 2014 (17)
- August 2014 (16)
- July 2014 (19)
- June 2014 (17)
- May 2014 (18)
- April 2014 (21)
- March 2014 (20)
- February 2014 (22)
- January 2014 (21)
- December 2013 (17)
- November 2013 (19)
- October 2013 (23)
- September 2013 (21)
- August 2013 (22)
- July 2013 (22)
- June 2013 (20)
- May 2013 (21)
- April 2013 (22)
- March 2013 (19)
- February 2013 (20)
- January 2013 (22)
- December 2012 (20)
- November 2012 (20)
- October 2012 (23)
- September 2012 (10)
- August 2012 (22)
- July 2012 (20)
- June 2012 (23)
- May 2012 (23)
- April 2012 (19)
- March 2012 (20)
- February 2012 (19)
- January 2012 (22)
- December 2011 (15)
- November 2011 (18)
- October 2011 (21)
- September 2011 (22)
- August 2011 (23)
- July 2011 (23)
- June 2011 (22)
- May 2011 (24)
- April 2011 (18)
- March 2011 (22)
- February 2011 (22)
- January 2011 (23)
- December 2010 (21)
- November 2010 (19)
- October 2010 (19)
- September 2010 (18)
- August 2010 (22)
- July 2010 (20)
- June 2010 (20)
- May 2010 (20)
- April 2010 (21)
- March 2010 (23)
- February 2010 (22)
- January 2010 (21)
- December 2009 (13)
- November 2009 (18)
- October 2009 (19)
- September 2009 (18)
- August 2009 (20)
- July 2009 (19)
- June 2009 (23)
- May 2009 (20)
- April 2009 (18)
- March 2009 (21)
- February 2009 (23)
- January 2009 (26)
- December 2008 (19)
- November 2008 (21)
- October 2008 (22)
- September 2008 (20)
- August 2008 (21)
- July 2008 (20)
- June 2008 (19)
- May 2008 (18)
- April 2008 (22)
- March 2008 (19)
- February 2008 (21)
- January 2008 (22)
- December 2007 (15)
- November 2007 (5)
- October 2007 (6)
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
Don't Miss a Post! Subscribe
- Guest Posts

- Educational AI
- Edtech Tools
- Edtech Apps
- Teacher Resources
- Special Education
- Edtech for Kids
- Buying Guides for Teachers

Educators Technology
Innovative EdTech for teachers, educators, parents, and students
Question of the Day Examples
By Med Kharbach, PhD | Last Update: May 25, 2024

The importance of questioning in the classroom cannot be overstated, as it is a fundamental tool for fostering engagement, critical thinking, and deeper understanding. According to Patrícia Albergaria Almeida (2012), effective classroom questioning shifts the focus from teacher-centered to student-centered learning, encouraging higher-order thinking and active participation. Almeida’s research highlights that while teachers ask a high volume of questions—between 300 and 400 daily—students ask significantly fewer, typically only one question per week. This disparity underscores the need for greater awareness and strategies to promote student questioning, as it is vital for uncovering students’ conceptual understanding and reasoning processes.
Similarly, Rodolfo A. Neirotti (2021) emphasizes that questioning is crucial for understanding and exploring the world around us. Questions drive curiosity and foster an analytical mindset, allowing students to connect new information with prior knowledge and make sense of complex concepts. Neirotti argues that questioning helps improve interactions, stimulate creativity, and support scientific inquiry, which are essential for intellectual growth and problem-solving.
In today’s post, I compiled an extensive list of Question of the Day examples that you can use with your students or colleagues to spark engagement, foster critical thinking, and promote a dynamic learning environment. These questions are carefully categorized to cover diverse themes, including Cultural Appreciation, Environmental Awareness, Historical Perspectives, STEM Curiosities, Creative Expression, Global Citizenship, Philosophical Inquiry, Health and Wellness, Innovative Thinking, and Interpersonal Skills.
Question of The Day Examples
Here are some engaging “Question of the Day” prompts to spark curiosity and foster a dynamic learning environment.
1. Cultural Appreciation

Understanding and appreciating diverse cultures is essential in our interconnected world. This category encourages students to explore traditions, customs, and values from various cultures, fostering a sense of global awareness and respect. Through these questions, students will learn about the richness of cultural diversity and the importance of inclusivity.
- What is one tradition from another culture that you find interesting and why?
- How do different cultures celebrate the New Year?
- Can you name a traditional dish from another country and describe it?
- What are some common cultural symbols from around the world?
- How do various cultures honor their ancestors?
- What is a unique holiday celebrated in another country?
- How do different cultures approach education?
- What is one art form unique to a specific culture?
- How do people in different countries greet each other?
- What are some traditional clothing items from different cultures?
- How do various cultures celebrate weddings?
- What are some unique musical instruments from around the world?
- How do different cultures celebrate coming-of-age ceremonies?
- What is a popular sport in another country that is less known here?
- How do various cultures view and use traditional medicine?
2. Environmental Awareness

Our planet faces numerous environmental challenges, and it’s crucial to raise awareness about sustainability and conservation. This category focuses on questions that highlight the significance of protecting our environment. Students will explore topics like climate change, recycling, and renewable energy, inspiring them to take action towards a greener future.
- What is one simple way you can reduce your carbon footprint?
- How does recycling help the environment?
- What are the effects of deforestation on wildlife?
- How does pollution affect marine life?
- What are the benefits of using renewable energy sources?
- How can planting trees help combat climate change?
- What are the consequences of plastic waste in the oceans?
- How can we conserve water in our daily lives?
- What are some endangered species and why are they at risk?
- How does composting benefit the environment?
- What is the importance of biodiversity?
- How do oil spills impact the environment?
- What are some ways to promote sustainable agriculture?
- How does urbanization affect natural habitats?
- What role do bees play in our ecosystem?
Related: 100 Engaging Philosophical Questions for Kids
3. Historical Perspectives

History offers invaluable lessons and insights into our present and future. This category prompts students to delve into significant historical events and figures, encouraging them to think critically about the past. By understanding history, students can better appreciate the complexities of the world and the progress we’ve made.
- What is one historical event you would like to witness and why?
- How did the invention of the printing press change the world?
- What are some lessons we can learn from ancient civilizations?
- How did the Industrial Revolution impact society?
- What is the significance of the Magna Carta?
- How did the discovery of electricity revolutionize life?
- What are the key causes of the World Wars?
- How did the civil rights movement shape modern society?
- What is the impact of the Renaissance on art and culture?
- How did explorers like Christopher Columbus change the world?
- What is the historical significance of the Great Wall of China?
- How did the Cold War influence global politics?
- What can we learn from the fall of the Roman Empire?
- How did the Space Race affect technological advancement?
- What was the impact of the Silk Road on trade and culture?
4. STEM Curiosities

Science, Technology, Engineering, and Math (STEM) are fields that drive innovation and shape our future. This category is designed to spark curiosity and interest in STEM topics. Through these questions, students will explore fascinating concepts and recent advancements, encouraging them to think like scientists and engineers.
- How do vaccines work to protect us from diseases?
- What are black holes and why are they important to study?
- How does coding contribute to creating video games?
- What are some recent breakthroughs in renewable energy?
- How does 3D printing work and what are its uses?
- What is the role of DNA in heredity?
- How do self-driving cars navigate and avoid obstacles?
- What are the benefits and risks of artificial intelligence?
- How does the internet work?
- What are the basic principles of quantum physics?
- How do weather satellites predict storms?
- What are some cutting-edge materials used in construction?
- How do we measure the distance between stars?
- What are the applications of nanotechnology in medicine?
- How does the human brain process information?
5. Creative Expression

Creativity is a vital part of personal and academic growth. This category inspires students to express themselves artistically and imaginatively. Whether through art, music, writing, or design, these questions encourage students to explore their creative potential and understand the value of artistic expression.
- If you could create a new art form, what would it be?
- How does music influence your mood and creativity?
- What story would you tell if you wrote a book?
- How would you design a dream home?
- What inspires you to create art?
- If you could compose a song, what would it be about?
- How would you direct a movie with no dialogue?
- What is your favorite way to express yourself creatively?
- If you could build a sculpture out of any material, what would you use?
- How do colors influence your artwork?
- What role does creativity play in solving everyday problems?
- How would you choreograph a dance to tell a story?
- If you could design a video game, what would its theme be?
- How do different cultures influence artistic styles?
- What would you paint if you had a giant canvas and no restrictions?
6. Global Citizenship

Being a responsible global citizen means understanding and addressing global issues. This category promotes awareness of topics like human rights, global health, and social justice. Through these questions, students will learn about their role in the global community and how they can contribute to a more equitable world.
- How can we support fair trade practices globally?
- What are the impacts of global warming on different regions of the world?
- How can we help refugees in our communities?
- What are the benefits of learning a second language?
- How do international organizations like the UN help maintain peace?
- What are some ways to reduce global poverty?
- How does access to education vary around the world?
- What is the importance of protecting human rights?
- How can we promote gender equality globally?
- What are the effects of global health crises on different countries?
- How does global trade affect local economies?
- What role can individuals play in combating climate change?
- How does cultural exchange benefit global understanding?
- What are the consequences of deforestation in the Amazon rainforest?
- How can we support clean water initiatives worldwide?
7. Philosophical Inquiry

Philosophy encourages deep, critical thinking about life’s fundamental questions. This category challenges students to consider philosophical ideas and ethical dilemmas. By engaging with these questions, students will develop their reasoning skills and explore different perspectives on complex issues.
- What is the meaning of happiness?
- Do humans have free will?
- What is the nature of reality?
- Is there such a thing as absolute truth?
- What is the purpose of life?
- Can we ever truly know another person’s mind?
- What makes an action morally right or wrong?
- Is it possible to achieve true equality?
- What is the value of art in society?
- Can machines possess consciousness?
- What is the role of government in our lives?
- How do we define beauty?
- Is there life after death?
- What are the limits of human knowledge?
- How do we determine what is just?
8. Health and Wellness

Promoting health and wellness is essential for a balanced life. This category focuses on questions that encourage students to think about their physical and mental well-being. Topics include nutrition, exercise, mindfulness, and stress management, helping students develop healthy habits and self-awareness.
- What are the benefits of a balanced diet?
- How does exercise impact mental health?
- What are some effective stress management techniques?
- Why is sleep important for overall health?
- How can mindfulness improve daily life?
- What are the signs of a healthy friendship?
- How does staying hydrated affect your body?
- What are the benefits of spending time in nature?
- How can setting goals improve mental health?
- What role does laughter play in well-being?
- How can you create a personal wellness plan?
- What are the benefits of practicing gratitude?
- How does music influence your mood?
- What is the importance of regular medical check-ups?
- How can volunteering boost your happiness?
9. Innovative Thinking

Innovation drives progress and solves problems. This category encourages students to think creatively and entrepreneurially. Through these questions, students will explore ways to address challenges and create new opportunities, fostering a mindset of innovation and proactive problem-solving.
- What problem in your community would you like to solve with an invention?
- How can we make renewable energy more accessible?
- What new technology could improve education?
- How can design thinking be applied to everyday problems?
- What is an example of an innovative solution to a global issue?
- How can we use technology to reduce food waste?
- What startup idea do you think would succeed today?
- How can we promote entrepreneurship in young people?
- What is the future of transportation?
- How can we make healthcare more affordable and effective?
- What role does creativity play in innovation?
- How can businesses become more environmentally sustainable?
- What is the next big thing in technology?
- How can we encourage more women in STEM fields?
- What innovative approach could solve the housing crisis?
10. Interpersonal Skills

Effective communication and strong interpersonal skills are key to personal and professional success. This category helps students develop social skills, empathy, and leadership qualities. These questions encourage students to reflect on their interactions with others and improve their ability to collaborate and connect.
- How can you show empathy in a conversation?
- What are some effective ways to resolve conflicts?
- How can you improve your active listening skills?
- What are the benefits of giving and receiving constructive feedback?
- How can you build trust in a team?
- What are some ways to practice effective communication?
- How do you handle difficult conversations?
- What are the qualities of a good leader?
- How can you be more assertive without being aggressive?
- What role does body language play in communication?
- How can you improve your public speaking skills?
- How do you build and maintain healthy relationships?
- What are some strategies for networking?
- How can you be a better collaborator?
- What are the benefits of understanding different communication styles?
Related: Attendance Questions for Your Class
Importance of Questions in Learning
For those interested in exploring the significance of questions in educational settings, several key research papers provide valuable insights and practical strategies. For instances, Robin Alexander’s “Towards Dialogic Teaching” (2005) emphasizes the role of dialogue and questioning in fostering a more interactive and engaging classroom environment. Allison and Shrigley (1986) discuss techniques for teaching children to ask operational questions in science, highlighting the importance of inquiry-based learning. On their part, Arzi and White (1986) explore the types and impacts of students’ questions in science education, offering a research-based perspective on promoting student curiosity.
Similarly, Paul Black and colleagues (2002) in “Working Inside the Black Box” focus on how questioning and formative assessment can enhance learning outcomes. Blosser (1995) provides practical advice on asking effective questions, while Browne and Keeley (1998) offer a guide to critical thinking through the art of questioning. Carlsen (1991) analyzes classroom questioning from a sociolinguistic perspective, providing a deeper understanding of its dynamics.
For a problem-based learning approach, Chin and Chia (2004) demonstrate how student questions drive knowledge construction. Penick, Crow, and Bonnsteter (1996) argue that questions are fundamental to effective science teaching while Rop (2002) investigates the meaning and impact of student inquiry questions from the teacher’s viewpoint.
As for Rosenshine, Meister, and Chapman (1996), they provided an extensive review of intervention studies on teaching students to generate questions. Finally, Shodell (1995) advocates for a question-driven classroom to stimulate student engagement and learning.
These resources collectively underscore the transformative power of questioning in education, offering both theoretical insights and practical approaches to enhance teaching and learning.

- Almeida, P. A. (2012). Can I ask a question? the importance of classroom questioning. Procedia – Social and Behavioral Sciences , 31, 634-63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2011.12.116.
- Alexander, R. (2005). Towards dialogic teaching . York, UK: Dialogos.
- Allison, A.W., & Shrigley, R.L. (1986). Teaching children to ask operational questions in science. Science Education , 70, 73–80.
- Arzi, H.J. & White, R.T. (1986). Questions on students’ questions. Research in Science Education , 16, 82–91.
- Black, P., Harrison, C., Lee, C., Marshall, B., & Wiliam, D. (2002). Working inside the black box: Assessment for learning in the classroom . London: King’s College London
- Blosser, P.E. (1995). How to ask the right questions. Arlington , VA: National Science Teachers Association
- Browne, M.N., & Keeley, S.M. (1998). Asking the right questions: A guide to critical thinking. Englewood Cliffs , NJ: Prentice Hall.
- Carlsen, W.S. (1991). Questioning in classrooms: A sociolinguistic perspective. Review of Educational Research , 61, 157–178.
- Chin, C., & Chia, L.G. (2004). Problem-based learning: Using students’ questions to drive knowledge construction. Science Education , 88, 707–727.
- Chin, C., & Osborne, J. (2008). Students’ questions: a potential resource for teaching and learning science. Studies in Science Education , 44, 1-39.
- Neirotti, R. A. (2021). The importance of asking questions and doing things for a reason. Braz J Cardiovasc Surg , 36(1): I-II. doi: 10.21470/1678-9741-2021-0950 . PMID: 33594859; PMCID: PMC7918389.
- Penick, J.E., Crow, L.W., & Bonnsteter, R.J. (1996). Questions are the answers. Science Teacher , 63, 26–29.
- Rop, C.J. (2002). The meaning of student inquiry questions: A teacher’s beliefs and responses. International Journal of Science Education , 24(7), 717–736.
- Rosenshine, B., Meister, C., & Chapman, S. (1996). Teaching students to generate questions: A review of the intervention studies. Review of Educational Research , 66, 181–221.
- Shodell, M. (1995). The question-driven classroom. American Biology Teacher , 57, 278–281.

Join our mailing list
Never miss an EdTech beat! Subscribe now for exclusive insights and resources .

Meet Med Kharbach, PhD
Dr. Med Kharbach is an influential voice in the global educational technology landscape, with an extensive background in educational studies and a decade-long experience as a K-12 teacher. Holding a Ph.D. from Mount Saint Vincent University in Halifax, Canada, he brings a unique perspective to the educational world by integrating his profound academic knowledge with his hands-on teaching experience. Dr. Kharbach's academic pursuits encompass curriculum studies, discourse analysis, language learning/teaching, language and identity, emerging literacies, educational technology, and research methodologies. His work has been presented at numerous national and international conferences and published in various esteemed academic journals.

Join our email list for exclusive EdTech content.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Critical thinking questions are inquiries that help you think rationally and clearly by understanding the link between different facts or ideas. These questions create a seemingly endless learning process that lets you critique, evaluate, and develop a depth of knowledge about a given subject. Moreover, you get to reinforce your viewpoints or ...
Questions to Provoke Critical Thinking. Varying question stems can sustain engagement and promote critical thinking. The timing, sequence and clarity of questions you ask students can be as important as the type of question you ask. The table below is organized to help formulate questions provoking gradually higher levels of thinking.
Critical thinking is becoming a lost art in modern society. Far too many people never develop their ability to step back and look at their own beliefs and assumptions with a questioning mind. Here are some questions and examples for how to boost your critical thinking capabilities. 1) Why is this topic important or controversial to people?
The Ultimate Cheat Sheet For Digital Thinking by Global Digital Citizen Foundation is an excellent starting point for the 'how' behind teaching critical thinking by outlining which questions to ask. It offers 48 critical thinking questions useful for any content area or even grade level with a little re-working/re-wording. Enjoy the list!
Question Stems Framed Around Bloom's Taxonomy. by TeachThought Staff. While critical thinking is a foundation rather than a brick, how you build that foundation depends on the learning process itself: exposing students to new thinking and promoting interaction with that thinking in a gradual release of responsibility approach.
Types Of Questions For Teaching. Clarifying Question: A question meant to clarify something-either a question asked by the teacher to clarify the answer a student gives or what the student thinks or a question asked by the student to the teacher to clarify something (a statement, a task, a question, etc.) Probing Questions: A probing question ...
At the heart of critical thinking is the ability to formulate deep, different, and effective questions. For effective questioning, start by holding your hypotheses loosely. Be willing to ...
Students can use these critical thinking questions with fiction or nonfiction texts. They're also useful when discussing important issues or trying to understand others' motivations in general. ... We also work with a network of over 500 teacher writers and contributors to create the articles you see on our site. Learn more about writing ...
Thinking critically involves applying reason and logic to assess arguments and come to your own conclusions. Instead of reciting facts or giving a textbook answer, critical thinking skills encourage students to move beyond knowing information and get to the heart of what they really think and believe. 15 Questions to Encourage Critical Thinking ...
Critical thinking involves rigorously and skilfully using information, experience, observation, and reasoning to guide your decisions, actions and beliefs. It's a useful skill in the workplace and in life. You'll need to be curious and creative to explore alternative possibilities, but rational to apply logic, and self-aware to identify when ...
Students in the restudy group scored an average of 42 percent on the test, while students in the testing and generating questions groups both scored 56 percent—an improvement of 14 percentage points, or the equivalent of a full letter grade. "Question generation promotes a deeper elaboration of the learning content," Ebersbach told Edutopia.
Methods of Critical Thinking Questions. 1. The 5 W's and the H. These are the absolute basics of critical thinking. The Who, What, Where, When, Why, and How are foundational questions that are taught over and over in journalism, investigation, and research. They are the base from which every critical analysis should be created.
A critical thinking question should aim to make you think. It should lead students to ponder the answer and discuss possible solutions. Critical thinking questions can even lead to disagreements and arguments that can turn into an impressive teachable moment. One way to incorporate a solid critical thinking question into a math lesson is to ...
The benefits of critical thinking are that it can help you: Question assumptions; Make better decisions; Exercise curiosity; Create compelling arguments; Reflect on yourself and your life. What's more, critical thinking and problem solving often go hand-in-hand. Employers are always looking for people who possess both skills. Critical ...
Here are some more effective types of questions to use in teaching that encourage critical thinking and creativity: 1. Display. A type of rhetorical question, display questions help educators check on students' ability to retrieve information. Examples:
Critical thinking is the ability to effectively analyze information and form a judgment. To think critically, you must be aware of your own biases and assumptions when encountering information, and apply consistent standards when evaluating sources. Critical thinking skills help you to: Identify credible sources. Evaluate and respond to arguments.
The Power of Questions for Critical Thinking. What Socrates discovered some 2,500 years ago was the power of questions to make others think. In his book Blink, Malcolm Gladwell shows that much of our thought life takes place behind the closed door of our subconscious. As a result, we often don't know why we do, feel, or think the way we do.
Communication: Effective communication is essential in any workplace. Critical thinking helps employees to communicate their ideas clearly and persuasively. It also enables employees to listen actively, ask insightful questions, and respond thoughtfully. Time management: In fast-paced work environments, employees must make decisions quickly.
Students grappled with ideas and their beliefs and employed deep critical-thinking skills to develop arguments for their claims. Embedding critical-thinking skills in curriculum that students care ...
Critical thinking questions are a great way to help you learn and get to the heart of many matters. ... As an EFL teacher, he took full responsibility for planning and delivering lessons, frequently employing creative and diverse questions to engage the children in conversation. Learn more about Tom on our About page. LinkedIn.
Humor is a natural icebreaker that can make critical thinking questions more lighthearted and enjoyable. Of course, most younger kids just like to be silly, so playing upon that can keep them active and engaged. With that said, here are some great questions to get you started: 1. Someone gives you a penguin.
Students can look up definitions, locate synonyms, create their own sentences, replace the words, etc. Investigate twist endings (unexpected finish to a story); before reading the end of the story, ask students to guess why the girl "rejected" him. Some students may know the answer before reading it! CRITICAL THINKING QUESTIONS:
These creative thinking questions will stretch, shift, constrain, exaggerate, and re-orient your thinking to help you boost your creativity, EVEN IF you are working all by yourself. I'd love for you to enjoy the benefits of the same resource we're using to grow our business! And when you get 49 Questions, let us know how you put it to work ...
The importance of questioning in the classroom cannot be overstated, as it is a fundamental tool for fostering engagement, critical thinking, and deeper understanding. According to Patrícia Albergaria Almeida (2012), effective classroom questioning shifts the focus from teacher-centered to student-centered learning, encouraging higher-order thinking and active participation. Almeida's ...