- Companies & Schools

Should you discuss mental health issues in your college essay?
by Erica L. Meltzer | Oct 20, 2018 | Blog , College Essays | 6 comments
Image ©Nickshot, Adobe Stock
Note, January 2022: This post was written in 2018, before the start of the Covid-19 pandemic. Obviously, many things have changed since then, not least the amount of psychological pressure that many high school students have experienced. Clearly, some of the boundaries and expectations surrounding acceptable/advisable topics for admissions essays have shifted, and applicants undoubtedly have more leeway in discussing mental-health issues than they did in the past. That said, I would still caution against making this subject the exclusive focus of your essay(s). If it happens to be relevant—and it very well might be, given the events of the last couple of years— then you should focus on discussing it in a mature way that conveys qualities such as empathy and resilience, and that demonstrates your ability to reflect insightfully on what may have been very difficult situations.
As regular readers of my blog may know, I periodically trawl the forums over at College Confidential to see what’s trending. Recently, I’ve noticed a concerning uptick in the number of students asking whether it’s appropriate for them to write about mental health issues, most frequently ADD and/or anxiety, in their college applications.
So the short answer: don’t do it.
The slightly longer version:
If you’re concerned about a drop in grades or an inconsistent transcript, talk to your guidance counselor. If these types of issues are addressed, the GC’s letter is the most appropriate place for them. If, for any reason, the GC is unable/unwilling to discuss them and the issues had a significant impact on your performance in school that unequivocally requires explanation, you can put a brief, matter of fact note in the “is there any additional information you’d like us to know?” section, but think very carefully about how you present it. Do not write your main essay about the issue.
The full version:
To understand why these topics should generally be avoided, you need to understand what information colleges are actually seeking to gain from the personal statement. Although it is technically a personal narrative, it is, in a sense, also a persuasive essay: its purpose is to convey what sets you apart from the thousands of others with equally good grades and scores, and to suggest whether you have qualities that make you more likely to thrive at university x than the other 10 or 15 or even 20 applicants clamoring for that spot.
Now, whether such thing can actually be determined from 650 words (with which some students receive significant help) is of course questionable; however, the bottom line is that, adcoms are looking for students who will be successful in college. Discussing one’s inability to focus or intense aversion to social situations does not exactly inspire confidence, even if a student insists those problems have been overcome. Leaving home, dealing with professors and roommates and more challenging classes… Those are all major stressors. There is a tacit understanding that of course some students will flame out, have breakdowns, etc., but adcoms are understandably hesitant to admit anyone who is already at a higher risk for those issues. You want them to be excited about the prospect of admitting you, not debate whether you’ll really be able to handle college. (In fact, I had multiple students with various issues who were not truly ready for college and who did flame out — colleges have good reason to take these things seriously.)
This concern goes beyond any particular student’s well-being: graduation rates get factored into rankings, and every student who doesn’t make it through drags that statistic just a little bit lower. If a student does develop serious problems while on campus, there are also potential legal/liability issues involved, and no school wants to deliberately court those.
Besides, if your grades are iffy, it is extremely difficult not to sound as if you are making excuses. You are much better off talking about an experience or interest that will make them look past the transcript and think, “Hey, I really like this kid.” And the reality is that if your grades are that iffy, you’re probably not a competitive candidate at super-selective colleges anyway. These schools are looking for applicants who are on the way to fulfilling their potential, not for ones who need to explain away chronic underachievement.
In addition, one thing applicants — and sometimes their parents — have difficulty wrapping their heads around is the sheer number of applications the average admissions officer has encountered. Situations that may seem extreme and dramatic to adolescents who have recently confronted them may in fact have already been experienced — and written about — by thousands of other applicants. A 17-year old may believe that describing their anxiety in morbid detail will make them seem complex and introspective, but more likely it will only come off as overwrought and trite.
I know that might sound harsh, but please remember that admissions officers are coming at this process with no pre-existing knowledge of you as a person, only a few minutes to spend on your essay, and hundreds of other applications to get through. They are also under intense pressure to ensure that the appropriate demographics targets are being met and all the various institutional constituencies (coaches, development office, orchestra conductor) are being satisfied. They’re not ogres, and they’ll try to give you the benefit of the doubt, but if yours is the fifth essay about overcoming anxiety they’ve seen in the last 48 hours, they will look at it and reflexively think, “oh, another one of these.” That is not a first impression you want to make.
Now, are there exceptions? Yes, of course, but they are rare. In all the time I did college admissions work, I had exactly one student successfully discuss anxiety in an essay. It was, however, introduced in the context of a family tragedy that had profoundly shaped the student’s life; given that background, the discussion seemed natural and matter of fact rather than overdramatized. Even so, I made the student take a good week to think about whether that topic was truly the one they wanted to write about.
Ultimately, of course, the decision is yours, and the choice depends on the larger story you want to tell as well as your ability as a writer, but these topics are so difficult to pull off well that you are best off avoiding them if you can (particularly if you don’t have access to someone with a lot of admissions experience who can review your essay). Find another topic/ experience that you enjoy writing about (and that others are likely to enjoy reading about); that presents you as someone interesting and thoughtful; and that suggest you are ready to thrive in college.
If you really are concerned about your ability to function in college, most schools have plenty of resources for you to take advantage of (academic support, counseling center, etc.). But those are things to investigate after you get admitted. Before that, don’t go out of your way to fly red flags where none are warranted.
Why is Dyslexia ok to mention on an essay, but overcoming selective mutism is not?
Dyslexia is a learning disability that lends itself to proof that it has been overcome through excellent scores in reading and writing. It’s not easy to overcome or cope with dyslexia so an essay showing how a student did it demonstrates their tenacity and resourcefulness. Grades and scores are proof that the dyslexia will not be a problem in college, while the essay can highlight the characteristics that led to the student’s success and which will serve them well in college.
I wrote about how my dog helped me overcome me ending my life/depression and moving to another school is that too common
Thanks for the tips and perspective. It seems like common sense to me as a parent and tutor, but now I have an “established author” to cite!
I want to write about how depression had change me. But my grades and statistics are all great. Is this okay to write? My bad mental health somehow didn’t manage to get to the others parts of my life.
Is it okay to write about how despite psychosis I could manage to get good grades?
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Currently you have JavaScript disabled. In order to post comments, please make sure JavaScript and Cookies are enabled, and reload the page. Click here for instructions on how to enable JavaScript in your browser.
Yes, add me to your mailing list.
Sign up for the Question of the Day
Question of the Day
Complete SAT/ACT Grammar Rules
Complete GMAT Sentence Correction Rules
AP English Comp Terms, Condensed
10 Tips for Acing SAT Reading
Commas With Names and Titles, Simplified
Why You Won’t Go to Harvard on a National Merit Scholarship
Recent Posts
- Why are SAT and ACT English benchmarks so low?
- “However” vs. “though”: similar, but not the same
- Statement regarding the recent website outage
- Digital SAT math timing, Common Core, and the “deep understanding” trap
- “SAT® Vocabulary: A New Approach” for the Digital SAT is now available!
Posts by Category
- ACT English/SAT Writing (36)
- ACT Essay (8)
- ACT Reading (22)
- College Admissions (44)
- College Essays (2)
- English Proficiency Exams (1)
- Financial Aid (2)
- General Tips (35)
- Grammar (SAT & ACT) (27)
- Issues in Education (69)
- Parents (13)
- Phonics (26)
- Questions (1)
- Reading (SAT & ACT) (20)
- Reading Wars (7)
- SAT Critical Reading (Old Test) (52)
- SAT Essay (13)
- SAT Grammar (Old Test) (30)
- SAT Reading (12)
- SAT vs. ACT (5)
- Students (10)
- Test Optional (1)
- The Digital SAT (12)
- The Mental Game (18)
- The New SAT (59)
- The Science of Reading (9)
- Time Management (7)
- Tutor Interviews (9)
- Tutoring (27)
- Tutors (16)
- Uncategorized (10)
- Vocabulary (17)
Favorite Links
Barry Garelick on Common Core Math
Cogito Zero Sum
Hannah Arendt on The Crisis in Education
Critical Thinking: Why is it So Hard to Teach?
A Don’s Life (Mary Beard’s Blog)
Educational Jargon Generator
EduBabble Bingo
English is Not Normal
Everybody is Stupid Except You
The Fluency Factory
Gary Saul Morson on Anna Karenina
How I Rewired My Brain to Become Fluent in Math
Letter Against Learning Styles
Mercedes Schneider’s EduBlog
MIT Admissions Blog
Reflections on Liberal Education
The Revenge of K-12 Education
Seven Myths About Education
Silent StopWatch (for standardized tests)
The Usefulness of Brief Instruction in Reading Comprehension Strategies
What David Coleman Doesn’t Know About Literature
Why a Great Individual is Better than a Good Team
Students Get Real About Mental Health—and What They Need from Educators
Explore more.
- Perspectives
- Student Support
M ental health issues among college students have skyrocketed . From 2013 to 2021, the number of students who reported feelings of depression increased 135 percent, and the number of those with one or more mental health problems doubled. Simply put, the well-being of our students is in jeopardy.
To deepen our understanding of this crisis, we asked 10 students to speak candidly about their mental health. We learned that the issues they face are uniquely theirs and yet collectively ours. We hope these responses will inform your teaching and encourage you to create safe classroom spaces where students feel seen and supported.
Students Share Their Mental Health Struggles—and What Support They Need
We asked these students and recent graduates, In what ways has your mental health affected your college experience, and how can professors better support you? Here’s what they had to say.

Elizabeth Ndungu, graduate student in the School of Professional Studies at Columbia University, United States: My mental health has affected me deeply, and I have sought therapy (which is a big thing for me, as I was born and raised in Africa and therapy is a “Western” concept). I’m a caregiver, so unexpected medical emergencies happen a lot, which mentally stresses me out. However, my professors have given me the time I need to perform my best. They’ve listened.
In general, I think professors can better support students by
Observing and reaching out to students if they notice a pattern of behavior.
Being kind. Giving a student a second chance may very well change their life for the better.
Being supportive. Remember students’ names, learn one unique thing about them that’s positive, or connect with them on LinkedIn or other social media platforms and show them that they have a mentor.
I think schools can better support students by
Admitting diverse students. Don’t just say it—do it. Seek out ways to make the school population more DEIA (diversity, equity, inclusion, accessibility) friendly, especially at historically white colleges. Inclusivity should be everywhere.
Making DEIA initiatives a priority. If you are educating organizations’ next leaders, make sure DEIA initiatives are in each program and cohort. Each of our classes should be tied to knowledge, strategy, and DEIA and its impact.
Raising awareness around mental health. Provide onsite and remote resources for mental assistance, automate low complexity tasks that will cause stress to students, invest in your staff and resources, and ensure that they are happy. Because dealing with unhappy staff will make unhappy students.

Pritish Dakhole, sophomore studying engineering at Birla Institute of Technology and Science, Pilani, India: Mental health is still stigmatized in India. We do not have easy access to therapy sessions, and it is a difficult topic to talk about with family. Thankfully, the scenario is changing.
I have been affected both positively and negatively by my mental health. Positively, because I have become more open-minded and perceptive. Negatively, because it has drained my will to continue, made me tired from all the overthinking, and made me turn to harmful addictions to distract myself from the pain.
Professors and schools could provide better support through
Webinars and meetings that make students aware of the issues they face and how to tackle them.
Group sessions—preferably anonymous—to remove fear.
Feedback systems so that the college is made aware of the problems that lead to a bad mental state.
Flexible education systems that allow students to take breaks during periods of excessive burnout.

Ocean Ronquillo-Morgan, Class of ’21, studied computer science and business administration at the University of Southern California, United States: In February 2021, I called 911 twice in the span of two weeks. I thought I was dying. I felt confused, felt like my body was about to give way, then I called the paramedics. They hooked me up to an EKG and checked my pulse. It was the first time in my life that I experienced panic attacks.
I don’t think anything else could have been done at the classroom level besides extending deadlines in extenuating circumstances. That’s the unfortunate nature of post-education institutions—you still need to make it “fair” for all students.

Alberto Briones, Class of ’22, studied operations and information management at Northern Illinois University, United States: Mental health can be a touchy subject. I have experienced depression and anxiety, but just thinking about all the things I could miss in life if I gave up is what gave me the strength to keep going.
Something professors can do to support students’ mental health is give students time to study between tests. Sometimes professors schedule tests on the same day, and suddenly students must study for three or four exams, all in the same day. It becomes overwhelming and they have to prioritize what tests they need to study more for.

Anjali Bathra Ravikumar, sophomore studying management information systems at The University of Texas at Austin, United States: It is stressful to be an international student at a competitive university in a competitive major. I often find myself having breakdowns and calling my parents in a panic about my future. The relatively restricted job opportunities because of my visa status and uncertainty about whether I’ll be able to forge the career that I want are major reasons behind this.
I have noticed that a lot of my international-student friends are constantly hustling as well, since we feel that we always need to be 10 steps ahead and cannot afford to slow down.
The best thing that a professor can do for me is provide as much guidance as possible in their respective field. Most of my professors have done that. This helps weed out some of the doubts that I have about potential career paths and gives me better clarity about the future. I feel that I cannot ask for more since I don’t expect everyone to be informed of what life is like for an international student.
Schools, on the other hand, can do a lot for us, such as tailor career management resources, offer international student group counseling (I attended one session and it was very liberating), provide financial relief (this is the absolute best thing that can be done for us) during rough times such as COVID-19. For example, when millions of international students had to take online classes during the pandemic, schools could have offered reduced tuition rates.
Something else that can seem small but goes a long way is using inclusive language in university announcements and communication. Most of the emails that we receive from the university feel more tailored to or are directly addressing in-state students (especially when major changes were happening at the beginning of the pandemic), and it is natural for us to feel left out. It might be a simple thing, but a couple of lines at the end of each email announcement with links addressing our specific concerns would make a lot of difference to us since we wouldn’t have to do our own research to figure out what it means for us.
EDUCATE YOURSELF BEFORE DIVING INTO MENTAL HEALTH TALKS
Starting a mental health conversation with students before we are prepared can be harmful. Here’s some advice from “ It’s Time We Talk About Mental Health in Business Classrooms ” by Bahia El Oddi, founder of Human Sustainability Inside Out, and Carin-Isabel Knoop, executive director of the Case Research and Writing Group at Harvard Business School, on how to get ready for these critical conversations.
Learn to talk about mental health. Enhance your mental health literacy through free resources such as the Learn Mental Health Literacy course (specifically for educators), the World Health Organization , and the National Institute of Mental Health . Consult the CDC for language about mental and behavioral health and the American Psychiatry Association for ways to describe individuals presenting with potential mental health disorders .
Reflect on your own biases. Consider how your own story—being raised by a parent with a mental health disorder, for example—may influence how you react and relate to others. Determine your level of openness to discussing the struggles you or your loved ones face or have faced. While it is possible to discuss mental health in the classroom without these anecdotes or personal connections, the courage to be open about your own past can have a transformative effect on classroom discussion.
Understand students may need extra support. Make yourself accessible and approachable to your students from the start so you can establish trust early. Advise them to seek professional help when necessary.

Nick Neral, Class of ’18, studied marketing management at the University of Akron, United States: At the end of my first year of college, I decided to stop participating in Division I athletics and my mental health plummeted. After calling our campus counseling center and waiting six weeks for my first intake appointment, I was told I couldn’t start therapy for two more months, but I could get medication within a couple of days.
After getting prescriptions for an SSRI and Xanax, I never heard from another clinician at my school again. They had no clue if I got the meds, if I took them, how I was doing, and whether I was on campus every day.
When my mental health was at its poorest, I was very disconnected from my classes. I went to, I think, five or six out of 30 finance classes I had during the semester.
I think professors are in this mindset that 20 percent of the class will naturally excel, a majority will do well enough, and a small chunk probably can’t be saved. Sometimes we don’t need saving in the classroom, we just need professors looking out for our well-being. There’s more to the story when a kid doesn’t show up to 80 percent of their classes.
My experience—and seeing others go through similar events—led me to create a platform where therapists can create content and free resources at forhaley.com . Anyone can filter through the content based on how they’re feeling and what’s going on in their life without paying anything or creating an account.

Shreyas Gavit, Class of ’20 in the MBA program at Oakland University, United States: Mental health has affected me because I’ve been depressed and feel trapped; I can’t just go to my home country and come back to the United States whenever I need to. Instead, I have to wait on visa dates, which are a total mess.
Schools and professors could provide more guidance in understanding how immigration has been affected due to COVID-19.

Nigel Hammett, Class of ’19, studied industrial and systems engineering at North Carolina Agricultural & Technical State University, United States: Throughout college I faced mental stress—not only from school, like everyone, but also from many constant family issues going on back home that required my energy. At times, I learned how to push through my feelings and submerge myself in my schoolwork, although I should have unpacked my trauma and handled it in a more mature way.
Students need an environment that encourages inclusive, candid dialogue around how we are feeling. There’s a correlation between social and mental health to overall success in our respective careers.

Alek Nybro, Class of ’21, studied marketing at St. Edward’s University, United States: Anxiety shows up differently for every person. I consider myself to be high functioning. This means when the going gets tough, I dig down and keep pushing, but often to extents that aren’t physically, emotionally, or mentally healthy.
In school, I didn’t know when to step back and take a break. That’s probably my biggest regret about my college years.
Professors could help students by making everything iterative. There shouldn’t be a final grade for assignments or projects. If you want to go back and revise something for a better grade, you should be able to do so.

Patrick Mandiraatmadja, first-year graduate student studying technology management at Columbia University, United States: There are times when I have felt overwhelmed by the number of deadlines and exams crammed into a specific week or few days. I always want to put in my best effort to study, which can lead to less sleep and more anxiety. Then college becomes more about getting through assignments and exams just for the sake of it and less about the learning.
Because of the amount of work or busy work, I have less opportunity to go out and do the things that make me feel alive and excited about life—whether it’s being with friends, exploring my city, exercising, involving myself with professional and social networks outside of school, or simply taking a walk and enjoying my day.
Students want to know that our professors and schools care. Part of that is providing an environment where we can talk about our personal struggles. I also think professors and schools should update the policies on homework, assignments, and exams. Sometimes we may push through and neglect our mental health, not taking the time to care for ourselves, just to get through that homework or finish that exam. The added pressure causes us increased anxiety; it’s no wonder today’s young people are some of the most anxious and unmotivated compared to previous generations.
What We Learned from These Students
These students and young alumni offer an honest glimpse into how mental health struggles have affected their college experiences. Although every student faces their own unique—and sometimes complicated—challenges, we are learning that sometimes the best response is the simplest one.
We must show our students that we care. So lend an empathetic ear, offer that deadline extension, and turn your classroom into a safe haven for open discussion. Your students need it.
Special thanks to Justin Nguyen , founder of Declassified Media , for connecting HBP to these students and young alumni who volunteered to share their experiences.
Help shape our coverage: These students spoke candidly; now it’s your turn. What are the biggest challenges you face in addressing student mental health in and out of the classroom? What experiences have stood out to you? Let us know .
Elizabeth Ndungu is a graduate student in the School of Professional Studies at Columbia University.
Pritish Dakhole is a sophomore studying engineering at Birla Institute of Technology and Science in Pilani, India.
Ocean Ronquillo-Morgan is a member of the University of Southern California’s Class of ’21.
Alberto Briones is a member of Northern Illinois University’s Class of ’22.
Anjali Bathra Ravikumar is a sophomore at The University of Texas at Austin.
Nick Neral studied marketing management at the University of Akron and is a member of the Class of ’18.
Shreyas Gavit studied in the MBA program at Oakland University and graduated as a member of the Class of ’20.
Nigel Hammett studied industrial and systems engineering at North Carolina A&T State University and graduated as a member of Class of ’19.
Alek Nybro studied marketing at St. Edward’s University and graduated as a member of the Class of ’21.
Patrick Mandiraatmadja is a first-year graduate student studying technology management at Columbia University.
Related Articles
We use cookies to understand how you use our site and to improve your experience, including personalizing content. Learn More . By continuing to use our site, you accept our use of cookies and revised Privacy Policy .
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
Why Are College Students So Depressed?
It may not always feel like the best four years of your life
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Andreswd / Getty Images
Symptoms of Depression in College Students
What percentage of college students experience depression, what really causes depression in college students, impact of depression on academic and personal life, coping with depression in college, treatments for depression in college students, how schools can help.
Depression is one of the most common mental health conditions and affects people of all ages, including college students. It impacts thoughts, feelings, and behaviors and is characterized by persistent sadness and loss of interest in once-enjoyable activities.
This condition is prevalent on college campuses, affecting an estimated 53% of students at some point.
"College students are a vulnerable population who are faced with a range of new and often wonderful—yet sometimes stressful—experiences," explains Randall Dwenger, MD , the chief medical officer at Mountainside Treatment Center. He also notes that people who have a predisposition to depression typically start to display symptoms during their early 20s.
Depression can take a toll on many aspects of a young person's life, including academic performance, social life, and physical health. It can also increase their risk of substance abuse and co-occurring mental health conditions.
For this reason, it is crucial to recognize the signs of depression in college students and provide tools, resources, and support that can help.
At a Glance
College students are faced with multiple stressors like living on their own for the first time, meeting new people, and taking a rigorous course load. All of these changes happen at one time and cause major stress.
Any symptoms—both mild and severe—can affect college students' performance and mental health.
Fortunately, help is available and schools have also stepped in to address mental health concerns.
"Even mild symptoms may significantly interfere with academic and social functioning," explains Amy Mezulis, PhD , a licensed clinical psychologist and chief clinical officer of Joon. She also notes that it can lead to symptoms such as trouble concentrating, fatigue , and low energy, which can make it tough for students to keep up with academic work.
Randall Dwenger, MD
Some students may experience frustration with themselves at not being able to keep up with the challenges of living independently: balancing academics, social life, and tasks of daily living. These frustrations turned inward may present as depression.
Symptoms of depression that college students may experience include:
- Feeling sad, low, or "empty"
- Loss of interest in previously enjoyed activities
- Difficulty concentrating and making decisions
- Missing class
- Poor grades
- Not having the motivation to finish assignments
- Poor self-care and personal hygiene
- Using drugs or alcohol to cope with difficult emotions
- Irritability or restlessness
- Guilt, helplessness, or hopelessness
- Lack of energy or fatigue
- Feelings of worthlessness
- Reduced physical activity
- Changes in sleep habits and appetite
- Thoughts of self-harm or suicide
If you are having suicidal thoughts, contact the National Suicide Prevention Lifeline at 988 for support and assistance from a trained counselor. If you or a loved one are in immediate danger, call 911.
For more mental health resources, see our National Helpline Database .
Unfortunately, it isn’t easy to predict which students will excel and which will struggle with all the changes and challenges that college brings.
“Some students may experience frustration with themselves at not being able to keep up with the challenges of living independently: balancing academics, social life, and tasks of daily living. These frustrations turned inward may present as depression,” Dr. Dwenger says.
In one study that involved interviewing college students about their experiences, students suggested that depression affected many academic areas, including their effort, ability to focus, and time management.
Struggling with motivation and falling behind on academic work were common themes.
"[Depression] can definitely be a drain on focus because if I’m having a particularly bad episode, it’s hard to do anything at all," one student explained.
For some students, falling behind in classes can make depression feel even worse. "Once you start falling behind, then the depression kicks in, it will make me think less of myself for that. Then it’s even harder to catch up. As the things pile up, it gets more difficult to pull myself out of [the depression]," another student told researchers.
Depression rates among U.S. college students are at an all-time high and growing. According to one internet-based survey, 44% reported that they currently have symptoms of depression, and 15% said they had considered suicide in the past year.
A 2022 study published in the Journal of Affective Disorders examined data from the national Healthy Minds study between the years 2013 and 2021. The researchers found that there has been a steady, consistent decline in the mental health of college students throughout the United States, amounting to a 135% increase in depression over the course of those eight years.
Between 2013 and 2021, the number of college students who met the diagnostic criteria for one or more mental disorders doubled.
Such numbers are sobering, but the survey also found some positive indicators; more students are participating in therapy, and fewer are turning to alcohol to cope with their mental health problems. Unfortunately, the increasing rates of depression may also be outpacing the resources that are available to treat it.
And while the COVID-19 pandemic was associated with significant increases in rates of depression, the survey data shows that these increases are part of a larger trend and not simply attributable to a singular pandemic-era dip in mental well-being.
For students to get the help they need, researchers, public health experts, and academic institutions need to learn more about why students are struggling with depression. By identifying the factors that play a role, they can offer better interventions and develop prevention programs to combat depression in college students.
Leaving home for the first time can be an exciting but also challenging time for many students. It can be a time of self-discovery and personal growth, but it can also be stressful, anxiety-provoking, and isolating for many.
The following are just some of the common factors that can play a role in the onset of depression among college-age students.
Transitions and Adjustments
"The transition to college can be a big change, both academically and socially," explains Laura Erickson-Schroth, MD , chief medical officer of The Jed Foundation (JED). Going to college often means leaving behind social connections and support and starting over in a new environment.
For most students, college is their first experience living away from home. Moving out, adjusting to a new environment, and forging new social connections can contribute to stress that can play a part in causing depression, Dr. Erickson-Schroth says.
Students are also dealing with a lot of pressure to perform well. This stress can affect well-being and contribute to feelings of inadequacy and helplessness.
Relationships and Social Pressures
Students also face the pressure of fitting in with their peers in a new setting. They may feel disconnected from their old friends and struggle to form new friendships in an unfamiliar environment. This lack of social support may contribute to depression.
The college years can also be a time to forge new relationships with friends and romantic partners, but this can also be a source of conflict and strife. Arguments with roommates, losing touch with old friends, and problems in romantic relationships can sometimes leave college students feeling distressed.
Financial Stress
Paying for school and managing living expenses can create additional pressures. College is the first time many young people have had to deal with this type of financial pressure, and it can create feelings of stress that can play a part in the onset of depression.
Dr. Erickson-Schroth notes that students from lower-income households experience more financial stress, including struggles related to finding stable housing, food, and healthcare.
Surveys suggest that three out of every five college students face some type of insecurity related to essential needs.
Social activities and academic demands can contribute to poor sleep habits. Depression and sleep have a bidirectional relationship. Irregular or poor sleep habits are linked to the onset of depression, but depression can make sleeping more difficult. Sleep disturbances are also associated with an increased risk of suicidal ideation.
Research has also found that 82% of college students who experience suicidal thinking also experience sleep disturbances.
Substance Use
Some students may experiment with alcohol and drugs in college, in some cases as a way to cope with negative emotions and stress. Unfortunately, such substance use is also associated with increased depressive symptoms.
Other Hurdles
Dr. Erickson-Schroth notes that some young adults face additional challenges that can make them more susceptible to depression.
"Youth of color who attend college at predominantly white institutions (PWIs) often experience microaggressions and have trouble finding spaces where they feel they can be themselves," she explains.
Research also suggests that LGBTQIA+ students, financially insecure students, and lower-division students have a higher risk of experiencing more severe depression.
Generational Challenges
The COVID-19 pandemic also played a role in fueling struggles that many college students have experienced over the past few years. Dr. Dwenger notes that the social disruptions caused by the pandemic left many students struggling without the tools, resources, and coping skills they needed to navigate what is already a tricky period in most people's lives.
"Many experienced a sort of “whiplash” in adjusting back to in-person learning and resuming social interactions," he explains.
Unique global concerns facing today's generation of college students can also contribute to depression. This can include environmental worries, climate anxiety , political turmoil, social justice issues, and other concerns.
The political minefield, losses in terms of personal freedoms and choice, and issues of diversity may inspire some young people into action and activism, but these issues can also bring feelings of pessimism and hopelessness to many.
The high rates of depression among college students negatively affect physical health, mental well-being, academic success, and interpersonal relationships . These effects can be distressing and far-reaching. They can also potentially interfere with a student's long-term academic and professional goals.
One of the most immediate effects of depression in college students is its effect on academic performance, attendance, and participation. Depression makes it harder to concentrate, reduces motivation to learn, and even makes it hard for students to attend class sessions.
The toll on a student's academic life can be severe. It can lead to poor test performance and bad grades, which even jeopardize a student's ability to graduate and, for those depending on academic scholarships, impair their ability to keep their form of financial support.
Declining grades and poor feedback from instructors can worsen the feelings of hopelessness and inadequacy that many students are already struggling with.
Life Outside of School
Depression also makes it more challenging for students to enjoy many of the experiences that are often associated with college. Extracurricular activities, social events, and hobbies that they used to enjoy lose their appeal. This often means that they stop participating in these activities altogether.
Because social withdrawal is another common symptom of depression, making important connections and getting the social support they need becomes even more of a challenge. As a result, a student with depression may feel disconnected from their friends, roommates, family members, and college community.
Physical Health
Depression can also affect a college student's physical health. When people are depressed, they also experience increases in stress hormones such as adrenaline and cortisol .
This stress response is associated with a variety of health effects, including impaired immunity. Periods of prolonged stress associated with depression can also elevate the risk of health problems such as autoimmune conditions, cardiovascular disease, high blood pressure, and gastrointestinal disorders.
It is also common for people with depression to experience a variety of physical symptoms, including back pain, stomach upset, reduced psychomotor activity, and joint pain.
If you are a college student struggling with depression, there are a few things that you can do that may help make it easier to cope.
Make a Plan
Dr. Erickson-Schroth suggests proactive plans for how you'll take care of your mental health before college begins.
"Make a list of some of the potential challenges you may face. This could include finding community, adjusting to living in a new place away from family and friends, keeping up with a different level of academic work, or getting the right amount of good nutrition, exercise, and sleep," she explains.
Once you have a list, brainstorm some ways you'll tackle these challenges. This can include checking out resources your school might offer and leaning on tactics that have worked for you in the past.
Try Behavioral Activation
Dr. Mezulis says that one of the best ways to manage depression is to use a strategy known as behavioral activation . It involves scheduling activities that help promote a positive mood and well-being, even if you might not necessarily feel in the mood.
The idea is that doing things that are good for us and that we typically enjoy will give us opportunities to feel effective, socially connected, and happy, thus improving our mood.
This includes scheduling things like social events, exercise, and even daily tasks like doing your laundry and homework. Start by taking stock of some of your daily habits and look for ways to schedule activities that will support your emotional well-being:
- Make it a habit to go to bed and wake up at the same time each day
- Eat a balanced diet
- Utilize relaxation techniques to cope with stress
- Start a mindfulness or meditation practice
- Get regular physical activity
- Seek support from family, friends, professors, advisors, and others
While there are many strategies you can use on your own to improve your mental health and ability to cope, it is important to seek professional help if your symptoms have lasted longer than two weeks and/or are making it difficult to function in your daily life. Treatment options can include on- or off-campus options.
Talking to a mental health professional at your school's counseling center or student health services can be a great place to start. They can provide further options about mental health services that are available on-campus or refer you to off-campus providers.
Your doctor or therapist may recommend a few different options to treat your depression. Because depression is complex and influenced by a number of factors, research suggests that a combination of therapy and medication is often the most effective treatment approach.
During talk therapy , you can discuss the challenges you are facing with a professional. Your therapist can help you gain insights, improve relationships, and develop new coping skills.
There are different types of therapy that can help, including cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) , which focuses on changing negative thoughts; interpersonal therapy (IPT) , which focuses on improving relationships; and dialectical behavior therapy (DBT) , which improves thoughts, emotions, and relationships.
There are also medications that can help people find relief from symptoms of depression. Antidepressants that are commonly prescribed include Prozac (fluoxetine), Paxil (paroxetine), Zoloft (sertraline), Celexa (citalopram), and Lexapro (escitalopram).
Some antidepressants carry a black box warning of an increased risk of suicide in young people under the age of 25. This risk tends to be highest when treatment is first initiated, so young people should be monitored for signs of increased suicidal thinking or behavior while taking antidepressant medication.
Resources for Professional Help
Dr. Dwenger recommends reaching out for professional support sooner rather than later. "Don’t try to hide it when you find yourself falling behind or missing commitments. All colleges have Student Services that include mental health services, academic guidance, and many resources both on campus and off," he suggests.
While all colleges offer different services, you might be able to access mental health services at the following locations:
- Student Support Services : Offers a range of services for academic and personal development and may provide counseling services
- Counseling Center : Provides counseling services to students experiencing mental health concerns
- Student Health Center : Offers a variety of health services to students, including mental health care
- Psychology Clinic : Provides psychological services to students and community members
Some colleges and universities may also offer teletherapy services. Other places to turn if you are experiencing depression include your resident advisor (RA), academic advisor, a trusted professor, or campus helpline.
While colleges and universities offer resources to combat depression, evidence suggests that around 60% of students are unaware of these options.
Dr. Erickson-Schroth says every college should have a comprehensive plan designed to address aspects of student mental health. Such plans should include strategies that make student mental health a priority:
- Ways to promote social connections: Strategies for promoting social connections include improving student coping skills, identifying students at risk, providing mental health and crisis support, and encouraging help-seeking
- Staff mental health training: Training can help higher education faculty feel empowered, informed, and knowledgeable when it comes to helping students with mental health problems
- Peer training programs: These can be particularly helpful since students are more likely to turn to their peers instead of other adults.
- Community-building spaces: These can help students build connections, including LGBTQIA+ centers and clubs for students of color.
You don't have to be a mental health professional to have a positive impact on your students' emotional well-being. You just need to pay attention, listen, and connect students to help if they need it.
Colleges and universities must offer comprehensive support for students experiencing depression. Recognizing the signs of this condition can allow students to better access resources that can help support their well-being and recovery.
Schools can help by promoting depression awareness and working to combat the stigma that might prevent students from seeking help.
Frequently Asked Questions
While depression does not have a single cause, stress is a common factor that plays a major role in causing depression in college students. Coping with many different new challenges, including moving away from home, juggling new responsibilities, dealing with roommates, and adjusting to all of these transitions, can be stressful for many people.
Students who have mental health conditions such as depression may experience interruptions in their life that make it difficult to manage their normal daily needs and achieve their educational goals. If you have been diagnosed with depression or another psychiatric illness, you can request that your school make reasonable accommodations. Such accommodations may include more time to complete assignments or additional time on exams.
Liu XQ, Guo YX, Zhang WJ, Gao WJ. Influencing factors, prediction and prevention of depression in college students: A literature review . World J Psychiatry . 2022;12(7):860-873. doi:10.5498/wjp.v12.i7.860
American Psychiatric Association (APA). Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders . 5th ed, text revision. Washington, D.C.; 2022.
Mohammed TF, Gin LE, Wiesenthal NJ, Cooper KM. The experiences of undergraduates with depression in online science learning environments . CBE Life Sci Educ . 2022;21(2):ar18. doi:10.1187/cbe.21-09-0228
Healthy Minds Network. The Healthy Minds Study: 2021-2022 Data Report .
Lipson SK, Zhou S, Abelson S, et al. Trends in college student mental health and help-seeking by race/ethnicity: Findings from the national healthy minds study, 2013–2021 . Journal of Affective Disorders . 2022;306:138-147. doi:10.1016/j.jad.2022.03.038
Ettman CK, Cohen GH, Abdalla SM, et al. Persistent depressive symptoms during COVID-19: a national, population-representative, longitudinal study of U.S. adults . The Lancet Regional Health - Americas . 2022;5:100091. doi:10.1016/j.lana.2021.100091)
The Hope Center for College, Community, and Justice. The Hope Center Student Basic Needs Survey .
Fang H, Tu S, Sheng J, Shao A. Depression in sleep disturbance: A review on a bidirectional relationship, mechanisms and treatment . J Cell Mol Med . 2019;23(4):2324-2332. doi:10.1111/jcmm.14170
Brüdern J, Hallensleben N, Höller I, et al. Sleep disturbances predict active suicidal ideation the next day: an ecological momentary assessment study . BMC Psychiatry . 2022;22(1):65. doi:10.1186/s12888-022-03716-6
Becker SP, Dvorsky MR, Holdaway AS, Luebbe AM. Sleep problems and suicidal behaviors in college students . J Psychiatr Res . 2018;99:122-128. doi:10.1016/j.jpsychires.2018.01.009
Brenner P, Brandt L, Li G, DiBernardo A, Bodén R, Reutfors J. Substance use disorders and risk for treatment resistant depression: a population-based, nested case-control study . Addiction . 2020;115(4):768-777. doi:10.1111/add.14866
Busch CA, Mohammed TF, Nadile EM, Cooper KM. Aspects of online college science courses that alleviate and exacerbate undergraduate depression . PLoS One . 2022;17(6):e0269201. Published 2022 Jun 1. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0269201
Konturek PC, Brzozowski T, Konturek SJ. Stress and the gut: pathophysiology, clinical consequences, diagnostic approach and treatment options . J Physiol Pharmacol . 2011;62(6):591-9.
National Institute of Mental Health. Depression .
Cuijpers P, Sijbrandij M, Koole SL, Andersson G, Beekman AT, Reynolds CF. Adding psychotherapy to antidepressant medication in depression and anxiety disorders: a meta-analysis . World Psychiatry . 2014;13(1):56-67. doi:10.1002/wps.20089
Inside Higher Ed. Lack of awareness causes students to fall through the cracks .
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
What are your chances of acceptance?
Calculate for all schools, your chance of acceptance.
Your chancing factors
Extracurriculars.
Should You Talk About Mental Health in College Essays?
This article was written based on the information and opinions presented by Shravya Kakulamarri in a CollegeVine livestream. You can watch the full livestream for more info.
What’s Covered:
What are you required to disclose in your application.
- Should You Include Mental Health History in Your Application?
How to Talk about Mental Health in College Applications
Taking care of your health in college.
Many students wonder if they should discuss mental health or disability in their college applications. Mental health history or a disability might be an integral part of who a student is, but that doesn’t necessarily make it relevant to a college application. Keep in mind that it is actually illegal for colleges to ask for these types of details about your life because it can be considered discrimination. So, colleges will never directly ask if you’ve had any sort of mental health issue or if you’ve ever had a disability. Based on this reason alone, you are not required to disclose mental or physical health concerns on your application.
Disclosing your mental or physical health is strictly a matter of personal choice. If you leave out this information, it is not lying and 100% within your legal right to do so.
Should You Include Mental Health History in Your Application?
Before you choose whether to disclose your history of mental health or disability, you should think about the purpose of a college application. Everything that you put in your college application should contribute to an overall positive image of who you are as a student and member of the community.
You usually don’t want to hide integral parts of who you are, but you also don’t want to be sharing challenges that are not going to strengthen your application. This is true not only for mental health or disabilities but also for academics, extracurriculars, and other experiences. Normally, students don’t bring up the time that they got a C or D in a class on their application. Everything that you include on your application should paint the most positive image of you possible. You always want to put your best foot forward and keep the focus on your strengths.
You don’t want colleges to doubt your ability to succeed and perform well under pressure. If you mention any mental health concerns, they might use that as a way to question if you will do well at their school and be able to handle their rigorous course load. While colleges are supportive of their students’ mental health challenges and provide resources and services, you don’t want their first impression of you on your application to be something that makes them uncertain of your abilities. So, keep this in mind when deciding whether to disclose your mental health history.
If you decide to include your mental health or disability history in your application , there are specific aspects of your experience that you should focus on. Rather than talking about the mental illness itself, focus more on the recovery and management aspects and what you have learned from the experience.
Discuss things like how you have grown and the coping methods that you have cultivated due to the experience. These will give the admissions officer an idea of the types of strategies that you’ll likely use in college anytime that you encounter a stressful situation.
Overall, if you choose to talk about mental health in your applications, focus on the learning and growth that you’ve gained because of it.
Mental health is an important part of your well-being, and it’s essential to start good habits in high school . This way, you’ll be better prepared to cope when you face new challenges in college. You’ll likely be experiencing living on your own for the first time and have new responsibilities without the same support system that you had at home. It’s crucial to learn how to take care of your mental health early.
Fortunately, most students will have many resources at college to help them through mental health challenges. If you’re dealing with any mental health struggles, there is usually an office of wellness where you can schedule a time to see a therapist. This is usually provided with your school’s health insurance. If this is something that you are concerned about for your college experience, make sure to look into what mental health resources each college provides before applying.
Related CollegeVine Blog Posts

Calculate for all schools
Your chance of acceptance, your chancing factors, extracurriculars, college essay on depression.
I've been dealing with depression for a while and I feel like it's played a big part in shaping who I am today. Is it a good idea to write my college essay about it? Will admissions officers view it negatively? Any insights would be appreciated.
Writing about depression in your college essay can be a powerful and meaningful way to share your personal experiences and reflect on your growth. However, it's essential to approach the topic thoughtfully and carefully, as mental health is a sensitive subject.
1. Focus on growth and resilience: Instead of primarily describing your struggles with depression, emphasize how you've navigated those challenges and grown as a result. Discuss coping strategies, support systems, and other positive changes you've made that have helped you move forward.
2. Show self-awareness: Demonstrate an understanding of your situation and acknowledge your progress, while still recognizing that recovering from depression is an ongoing journey. This can give college admissions officers a sense of maturity and emotional intelligence on your part.
3. Keep it relevant to your college goals: Connect your experiences with depression to your educational and career aspirations. Perhaps overcoming depression has influenced your choice of major, or it has motivated you to engage in volunteer work or other extracurricular activities.
4. Seek feedback from trusted individuals: Ask someone you trust, like a teacher or counselor, to review your essay and provide input. Their perspectives can ensure that you're discussing depression sensitively and that your essay is appropriate for college admissions officers.
5. Be cautious of oversharing: While it's important to be genuine and authentic, avoid revealing deeply personal or disturbing details about your mental health struggles. Some admissions officers may not be comfortable with this level of disclosure, and it could overshadow your accomplishments and other positive aspects of your application.
In summary, writing about depression in your college essay is a personal choice. If you can present your experiences in a thoughtful, growth-focused manner, and connect your journey to your future goals, then it may be a powerful and effective essay topic. However, always consider seeking feedback from trusted individuals to ensure you are addressing the topic appropriately.
About CollegeVine’s Expert FAQ
CollegeVine’s Q&A seeks to offer informed perspectives on commonly asked admissions questions. Every answer is refined and validated by our team of admissions experts to ensure it resonates with trusted knowledge in the field.
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Guest Essay
I Edited Mental Illness Out of My College Applications. I’m Not Alone.

By Emi Nietfeld
Ms. Nietfeld is the author of a memoir, “Acceptance.”
When I applied to college in the 2009-10 school year, I wasn’t worried about my grades or extracurriculars. Instead, I agonized over a dilemma that’s familiar to more students than ever as the Common Application deadline looms: What should I disclose about my mental health?
As I wrote my applications, my past was both my greatest asset and my biggest liability. I’d spent time in foster care and homeless, circumstances that made me attractive to the handful of selective universities that offered full scholarships to low-income students — my only hope at avoiding crushing loans. In an applicant pool filled with squash champions, concert organists and third-generation double legacies, I had my story.
But my experiences also affected me and my academic record in ways that weren’t so appealing: Like approximately 80 percent of current foster youths and many former ones, I had serious mental health diagnoses, including post-traumatic stress disorder, depression, anxiety and disordered eating. From ages 13 to 15, I was hospitalized repeatedly. Before being placed in a foster home, I spent nine months in a locked treatment center. I’d attended four to eight high schools, depending on how you counted. How could I possibly explain all that?
Officially, colleges say that students can share as much about their mental health as feels comfortable. But in practice, it seems clear that schools are nervous about accepting adolescents who divulge psychiatric histories. That perception is reinforced by high-profile lawsuits alleging discrimination against students with mental health disabilities, including an ongoing suit against Yale University and a similar one settled by Stanford University in 2019.
“We have all read the headlines of students on college campuses who have either harmed others or harmed themselves,” said Kat Cohen, a private admissions consultant who helped me, pro bono, with my applications. “These are the things that colleges worry about if they admit someone who is not stable.”
These mixed messages are forcing more and more students to make impossible choices amid a teenage mental health crisis. Should applicants play it safe and conceal their emotional troubles — even when it means leaving low grades and gaps in transcripts unexplained? Or should they tell the truth and risk getting flagged as a liability?
For those with mental health conditions, college admissions are unfairly arduous, an injustice that has long-lasting ramifications for both students and society. Many teenagers with psychological disorders end up at lower-quality schools than they could have attended otherwise, affecting their career options and earning potential. And since elite universities produce a disproportionate number of politicians and managers, society loses out by having fewer people in power who deeply understand mental illness and how it intersects with almost every major issue.
“In the age of Instagram activists, I thought it wouldn’t be as bad,” Jia Suo, a high school senior from Sugar Land, Texas, told me about the stigma of mental illness. “But when I got out of my treatment center my junior year, it’s not an exaggeration to say that I lost every single one of my friends.”
After an inpatient program for suicidal ideation (a diagnosis Ms. Suo attributes to normal angst misinterpreted by doctors), she did not receive credit for the classwork she did there. Looking at her grades — C’s and incompletes in a transcript filled with A’s — she figured she must have been given a zero for every missed assignment. She said she reached out to her guidance counselor and homebound teacher but was told it was too late and there was nothing they could do.
Initially, Ms. Suo wanted to explain herself in her college application essay. She wrote a personal statement about how her institutionalization motivated her to study law after meeting girls who had been sex trafficked and boys who languished in the facility for months waiting for foster homes.
But sharing her struggles was risky. A family friend who worked in admissions advised her, “Say you slacked off junior year.” Ms. Suo crossed her dream school, Cornell, off her list and has instead applied to 17 colleges without any explanation for the sudden drop in G.P.A. She resents that her brush with psychiatry will shape what college she attends, but it feels safer to talk about her institutionalization in The New York Times than in her applications. “I’m OK with the whole world knowing about it, but at the same time I just know the stigma they’re going to have at colleges about this.” In three months, when Ms. Suo gets the final acceptance and rejection letters, she’ll know the true impact.
When I applied to college, Ms. Cohen — Dr. Kat, as I and her other clients call her — advised the opposite approach at first. “You have to be extremely explicit,” I remember her warning me. “Otherwise they’ll have no idea how bad things were.” This surprised me. Until that point, the adults around me made me feel my symptoms were evidence of what was wrong with me, not evidence of what was wrong with my circumstances. Though I was deeply ashamed, when I applied to Yale early, I attached a timeline detailing my mom’s hoarding and my overmedication, culminating with me regaining my emotional stability as a scholarship student at boarding school.
I was rejected. My school guidance counselor called Yale’s admissions office and relayed to me that though my grades and test scores were similar to other applicants’, as she put it in an email to me, “regarding the past issues, the list was daunting.” Dr. Kat also queried her network and surmised that Yale wanted to minimize its risk after several high-profile on-campus suicides of college students around the country. “It was just T.M.I.,” she told me — too much information.
A spokeswoman for Yale this month said in a statement to The New York Times that she could not discuss my case because admission files are confidential. But she did say, “This account of an admissions decision from over a decade ago is at odds with our admissions practices and philosophy,” adding that Yale’s admissions process is “holistic.”
She continued, “The admissions committee does not discriminate against any applicant for health reasons.”
For my next round of applications, I wrote a simple explanation for why I had changed schools and thereby excised three years of my life: the diagnoses, the drugs, the self-inflicted scars. I became a parallel person who’d gone through the same things but come out unscathed. I hit “submit,” applying to 10 schools, including Harvard.
While I waited, I lived in fear of being found out. In my dreams, admissions officers interrogated me. They called me a liar and a cheater.
But after three months of nightmares, on April 1, 2010, I got into Harvard.
I screamed when I opened the email; I danced in the rain. Then guilt fogged the world. Harvard accepted 7 percent of applicants that spring. I felt alternate versions of myself trailing me, fates in which I hadn’t been able to hide my past and it haunted me into adulthood.
I spoke to current and former admissions officers this fall, seeking answers to the question that had mystified me as a teenager: How much should students talk about mental health on their college applications? Echoing the advice of other professionals, Claudia Marroquin, the dean of admissions at Bowdoin College, implied that applicants should not feel pressure to disclose. Pressed for more specifics, she told me that students “have to feel comfortable with what they’re sharing.” This platitude made me seethe with frustration: Even if I was comfortable sharing everything, I suspected that the colleges were not comfortable hearing it. The students I interviewed all sensed there was a line, but few of us were lucky enough to know where it lay.
Only Dr. Kat was willing to speak candidly. In the years since she initially advised me to discuss my struggles in detail, she has realized that this approach may be unwise.
“Without exception,” she said, “reading a personal statement about the applicant’s mental health struggles — that’s going to immediately raise a red flag unless it can really be contextualized as something that the student has triumphed over.”
She emphasized that mental health had to be handled on “a case-by-case basis,” ideally in close consultation with the student’s school guidance counselor.
But that, too, is fraught. At 16, I sought out Dr. Kat’s help because even at a private boarding school, my counselor didn’t have the bandwidth to give me the personal attention I needed. The pro bono services I received would’ve cost more than $16,000 in 2009 dollars. When I spoke to students about their experiences, far greater than the variety of emotional issues was the range in support. Even at Ms. Suo’s affluent suburban school, a single counselor could juggle more than 400 students at a time. Students with less help turn to YouTube gurus and Discord servers where peers workshop their essays.
Favour Osisioma, who immigrated from Nigeria to rural Tennessee at 13, started 2020 on track to attend an elite school. Then Covid hit. She found herself caretaker for her two younger siblings — the three of them remote-learning on one computer while their mom worked 100-hour weeks and Ms. Osisioma worked part time at McDonald’s. “I felt that it was my job to bring my family out of poverty,” she said. Her grades fell, escalating the anxiety she’d had before the pandemic into paralyzing panic attacks. She remembers an adviser saying, “‘I never expected you to disappoint me in this way.’”
Ms. Osisioma agonized over how to explain this to colleges. “I was trying to get the perfect words,” she said. “But I wasn’t sure anyone would see me and think, ‘This is an attractive package.’” In her senior year, she won a number of accolades, including a prestigious Coca-Cola scholarship. A video crew surprised her at school with a jumbo check.
“I remember coming home and putting it down in my room and still crying because I didn’t know what to say in my applications about the anxiety.” At the time, a single guidance counselor was assisting 800 students with everything from class scheduling to college counseling. Staring at her Yale application, Ms. Osisioma watched the deadline tick past and became so overwhelmed that she couldn’t walk and felt herself going in and out of consciousness. She had to see a neurologist to rule out seizures. She ended up attending college a year later than planned at the University of Tennessee at Martin. She’s a university scholar there and enjoys her classes but feels a long way from where she hoped she’d be.
Meanwhile, prep schools often employ former admissions officers as counselors, with caseloads closer to 30 students. Jessica Smith, the director of college counseling at Westtown School in Pennsylvania, said she takes pains to protect “students’ private business.” She added, “Even when a psychiatric crisis affects a transcript, there’s a lot I can control about how much it shows up.”
Jaimi Salone, now in their final quarter at Stanford, benefited from this kind of advice while a student at the Blake School in Minneapolis, which they attended on scholarship. In their essay, they wrote frankly about depression, anxiety and shame after their mom’s cancer diagnosis and eventual death — providing context for why they “did not look like what was expected of a Stanford admit,” with a 3.06 G.P.A. and many absences. But at the suggestion of their college counselor, they omitted their sophomore-year hospitalization. “Is it lying to not include?” they wondered. “What is considered an accurate representation of me as a student when I actually do have mental health issues?”
Even after they got in, the stress stayed. “I was worried my admissions would be revoked if other information came out.”
My Harvard application taught me what was acceptable to share and what was not. I sensed that colleges wanted a pristine survivor who was not marred by trauma. At 16, I didn’t realize that it is impossible to emerge from certain hardships unscathed; the perfect overcomer is a fantasy that some young people are coached into creating. This illusion can do great damage. I saw that I was not that person, which caused me deep shame.
Effective admissions policies require grasping how mental illness manifests in different students’ lives. The same crisis that leads to an outpouring of support for a wealthy child might cause a foster youth to be sent to a locked facility, prescribed antipsychotics and forced to change schools. Stigma varies widely across communities, affecting how teenagers view their struggles and what leeway they get from adults. Some kids are far less likely to be diagnosed and treated; others receive superfluous labels and get overmedicated. Understanding these disparities is crucial in the face of worsening adolescent mental health and ever more competitive standards at the colleges that produce an outsize share of leaders.
For a decade, I believed my story was an anomaly, but every year that seems less and less true. There are so many young people unable to hide their crises. We all lose out if this disqualifies them from a better future.
Emi Nietfeld ( @eminietfeld ) is the author of a memoir, “ Acceptance .”
The Times is committed to publishing a diversity of letters to the editor. We’d like to hear what you think about this or any of our articles. Here are some tips . And here’s our email: [email protected] .
Follow The New York Times Opinion section on Facebook , Twitter (@NYTopinion) and Instagram .
An earlier version of this article misspelled the name of a city in Texas. It is Sugar Land, not Sugarland.
How we handle corrections
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Front Psychiatry
Family and Academic Stress and Their Impact on Students' Depression Level and Academic Performance
1 School of Mechatronics Engineering, Daqing Normal University, Daqing, China
2 School of Marxism, Heilongjiang University, Harbin, China
Jacob Cherian
3 College of Business, Abu Dhabi University, Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates
Noor Un Nisa Khan
4 Faculty of Business Administration, Iqra University Karachi Pakistan, Karachi, Pakistan
Kalpina Kumari
5 Faculty of Department of Business Administration, Greenwich University Karachi, Karachi, Pakistan
Muhammad Safdar Sial
6 Department of Management Sciences, COMSATS University Islamabad (CUI), Islamabad, Pakistan
Ubaldo Comite
7 Department of Business Sciences, University Giustino Fortunato, Benevento, Italy
Beata Gavurova
8 Faculty of Mining, Ecology, Process Control and Geotechnologies, Technical University of Kosice, Kosice, Slovakia
József Popp
9 Hungarian National Bank–Research Center, John von Neumann University, Kecskemét, Hungary
10 College of Business and Economics, University of Johannesburg, Johannesburg, South Africa
Associated Data
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Current research examines the impact of academic and familial stress on students' depression levels and the subsequent impact on their academic performance based on Lazarus' cognitive appraisal theory of stress. The non-probability convenience sampling technique has been used to collect data from undergraduate and postgraduate students using a modified questionnaire with a five-point Likert scale. This study used the SEM method to examine the link between stress, depression, and academic performance. It was confirmed that academic and family stress leads to depression among students, negatively affecting their academic performance and learning outcomes. This research provides valuable information to parents, educators, and other stakeholders concerned about their childrens' education and performance.
Introduction
Higher education institutions (HEIs) are believed to be one of the strongest pillars in the growth of any nation ( 1 ). Being the principal stakeholder, the performance of HEIs mainly relies on the success of its students ( 2 ). To successfully compete in the prevailing dynamic industrial environment, students are not only supposed to develop their knowledge but are also expected to have imperative skills and abilities ( 3 ). In the current highly competitive academic environment, students' performance is largely affected by several factors, such as social media, academic quality, family and social bonding, etc. ( 4 ). Aafreen et al. ( 2 ) stated that students continuously experience pressure from different sources during academic life, which ultimately causes stress among students.
Stress is a common factor that largely diminishes individual morale ( 5 ). It develops when a person cannot handle their inner and outer feelings. When the stress becomes chronic or exceeds a certain level, it affects an individual's mental health and may lead to different psychological disorders, such as depression ( 6 ). Depression is a worldwide illness marked by feelings of sadness and the inability to feel happy or satisfied ( 7 ). Nowadays, it is a common disorder, increasing day by day. According to the World Health Organization ( 8 , 9 ), depression was ranked third among the global burden of disease and predicted to take over first place by 2030.
Depression leads to decreased energy, difficulty thinking, concentrating, and making career decisions ( 6 ). Students are a pillar of the future in building an educated society. For them, academic achievement is a big goal of life and can severely be affected if the students fall prey to depression ( 10 , 11 ). There can be several reasons for this: family issues, exposure to a new lifestyle in colleges and universities, poor academic grades, favoritism by teachers, etc. Never-ending stress or academic pressure of studies can also be a chief reason leading to depression in students ( 12 ). There is a high occurrence of depression in emerging countries, and low mental health literacy has been theorized as one of the key causes of escalating rates of mental illness ( 13 ).
Several researchers, such as ( 6 , 14 , 15 ) have studied stress and depression elements from a performance perspective and reported that stress and depression negatively affect the academic performance of students. However, Aafreen et al. ( 2 ) reported contradictory results and stated that stress sharpens the individual's mind and reflexes and enables workers to perform better in taxing situations. Ardalan ( 16 ) conducted a study in the United States (US). They reported that depression is a common issue among students in the US, and 20 percent of them may have a depressive disorder spanning 12 months or more. It affects students' mental and physical health and limits their social relationships and professional career.
However, the current literature provides mixed results on the relationship between stress and performance. Therefore, the current research investigates stress among students from family and academic perspectives using Lazaru's theory which describes stress as a relation between an individual and his environment and examines how it impacts students' depression level, leading to their academic performance. Most of the available studies on stress and depression are from industrial perspectives, and limited attention is paid to stress from family and institutional perspectives and examines its impact on students' depression level, leading to their academic performance, particularly in Pakistan, the place of the study. Besides, the present study follows a multivariate statistical technique, followed by structural equation modeling (SEM) to examine the relationship between stated variables which is also a study's uniqueness.
This paper is divided into five main sections. The current section provided introduction, theoretical perspective, and background of the study. In the second section, a theoretical framework, a detailed literature review and research hypotheses of the underlying relationships are being proposed. In the third and fourth section, methodology and analysis have been discussed. Finally, in the last section, the conclusion, limitations, implications, and recommendations for future research have been proposed.
Theory and Literature
The idea of cognitive appraisal theory was presented in 1966 by psychologist Richard Lazarus in Psychological Stress and Coping Process. According to this theory, appraisal and coping are two concepts that are central to any psychological stress theory. Both are interrelated. According to the theory, stress is the disparity between stipulations placed on the individuals and their coping resources ( 17 ). Since its first introduction as a comprehensive theory ( 18 ), a few modifications have been experienced in theory later. The recent adaptation states that stress is not defined as a specific incitement or psychological, behavioral, or subjective response. Rather, stress is seen as a relation between an individual and his environment ( 19 ). Individuals appraise the environment as significant for their well-being and try to cope with the exceeding demands and challenges.
Cognitive appraisal is a model based on the idea that stress and other emotional processes depend on a person's expectancies regarding the significance and outcome of an event, encounter, or function. This explains why there are differences in intensity, duration, and quality of emotions elicited in people in response to the environment, which objectively, are equal for all ( 18 ). These appraisals may be influenced by various factors, including a person's goals, values, motivations, etc., and are divided into primary and secondary appraisals, specific patterns of which lead to different kinds of stress ( 20 ). On the other hand, coping is defined as the efforts made by a person to minimize, tolerate, or master the internal and external demands placed on them, a concept intimately related to cognitive appraisal and, therefore, to the stress-relevant person-environment transactions.
Individuals experience different mental and physiological changes when encountering pressure, such as stress ( 21 , 22 ). The feelings of stress can be either due to factors in the external environment or subjective emotions of individuals, which can even lead to psychological disorders such as anxiety and depression. Excess stress can cause health problems. A particularly negative impact has been seen in students due to the high level of stress they endure, affecting their learning outcomes. Various methods are used to tackle stress. One of the methods is trying to pinpoint the causes of stress, which leads us to different terms such as family stress and academic stress. The two factors, stress and depression, have greatly impacted the students' academic performances. This research follows the Lazarus theory based on stress to examine the variables. See the conceptual framework of the study in Figure 1 .

Conceptual framework.
Academic Stress
Academic issues are thought to be the most prevalent source of stress for college students ( 23 ). For example, according to Yang et al. ( 24 ), students claimed that academic-related pressures such as ongoing study, writing papers, preparing for tests, and boring professors were the most important daily problems. Exams and test preparation, grade level competitiveness, and gaining a big quantity of knowledge in a short period of time all contribute to academic pressure. Perceived stress refers to a condition of physical or psychological arousal in reaction to stressors ( 25 , 26 ). When college students face excessive or negative stress, they suffer physical and psychological consequences. Excessive stress can cause health difficulties such as fatigue, loss of appetite, headaches, and gastrointestinal issues. Academic stress has been linked to a variety of negative effects, including ill health, anxiety, depression, and poor academic performance. Travis et al. ( 27 ), in particular, discovered strong links between academic stress and psychological and physical health.
Family Stress
Parental participation and learning effect how parents treat their children, as well as how they handle their children's habits and cognitive processes ( 28 ). This, in turn, shapes their children's performance and behaviors toward them. As a result, the parent-child relationship is dependent on the parents' attitudes, understanding, and perspectives. When parents have positive views, the relationship between them and their children will be considerably better than when they have negative attitudes. Parents respond to unpleasant emotions in a variety of ways, which can be classified as supportive or non-supportive ( 29 ). Parents' supportive reactions encourage children to explore their emotions by encouraging them to express them or by assisting them in understanding and coping with an emotion-eliciting scenario. Non-supportive behaviors, such as downplaying the kid's emotional experience, disciplining the child, or getting concerned by the child's display, transmit the child the message that expressing unpleasant emotions is inappropriate and unacceptable. Supportive parental reactions to unpleasant emotions in children have been linked to dimensions of emotional and social competence, such as emotion comprehension and friendship quality. Non-supportive or repressive parental reactions, on the other hand, have been connected to a child's stored negative affect and disordered behaviors during emotion-evoking events, probably due to an inability or unwillingness to communicate unpleasant sentiments ( 30 , 31 ).
Academic Stress and Students' Depression Levels
Generally, it is believed that mental health improves as we enter into adulthood, and depression disorder starts to decline between the age of 18 and 25. On the other hand, excessive depression rates are the highest pervasiveness during this evolution ( 15 ), and many university students in the particular screen above clinical cut-off scores for huge depression ( 14 , 32 ). Afreen et al. ( 2 ) stated that 30% of high school students experience depression from different perspectives. This means a major chunk of fresh high school graduates are more likely to confront depression or are more vulnerable to encountering depression while enrolling in the university. As the students promote to a higher level of education, there are many factors while calculating the stress like, for example, the syllabus is tough to comprehend, assignments are quite challenging with unrealistic deadlines, and accommodation problems for the students who are shifted from other cities, etc. ( 33 ). Experiences related to university can also contribute while studying depression. The important thing to consider is depression symptoms vary from time to time throughout the academic years ( 34 ); subjective and objective experiences are directly connected to the depression disorder ( 6 ), stress inherent in the university situation likely donates to the difference in university students' depressing experiences.
Stress negatively impacts students' mental peace, and 42.3% of students of Canadian university respondents testified devastating levels of anxiety and stress ( 35 , 36 ). Moreover, there were (58.1%) students who stated academic projects are too tough to handle for them. In Germany, Bulgaria, and Poland, a huge sample of respondents consider assignments a burden on their lives that cannot stand compared to relationships or any other concern in life ( 14 ).
In several countries, university students were studied concerning stress, and results show that depression disorder and apparent anxiety are correlated to educational needs and demands ( 37 ). In their cross-sectional study conducted on a sample of 900 Canadian students, Lörz et al. ( 38 ) concluded that strain confronted due to academic workload relatively has high bleak symptoms even after controlling 13 different risk affecting factors for depression (e.g., demographic features, abusive past, intellectual way, and personality, currently experienced stressful trials in life, societal support). Few have exhibited that students who are tired of educational workload or the students who name them traumatic tend to have more depressing disorders ( 15 ).
These relations can be described by examining the stress and coping behaviors that highlight the role of positive judgments in the stress times ( 39 ), containing the Pancer and colleagues' university modification framework ( 40 , 41 ). The evaluation concept includes examining the circumstances against the available resources, for instance, the effectiveness of coping behavior and societal support. As per these frameworks, if demand is considered unapproachable and resources are lacking, confronted stress and interrelated adverse effects will be high, conceivably giving birth to difficulties in an adjustment like mental instability. Stress triggering situations and the resources in the educational area led to excessive workload, abilities, and study and enhanced time managing skills.
Sketching the overall evaluation frameworks, Pancer et al. ( 40 ) established their framework to exhibit the constructive and damaging adjustment results for the university students dealing with the academic challenges. They stated that while students enroll in the university, they evaluate all the stress-related factors that students confront. They consider them manageable as long as they have sufficient resources. On the other hand, if the available resources do not match the stress factors, it will surely result in a negative relationship, which will lead students to experience depression for sure. Based on the given arguments, the researcher formulates the following hypothesis:
- H1: Increased academic stress results in increased depression levels in students.
Family Stress and Students' Depression Levels
According to Topuzoglu et al. ( 42 ), 3% to 16.9% of individuals are affected by depression worldwide. There are fewer chances for general people to confront depression than university students ( 43 , 44 ). In Mirza et al.'s ( 45 ) study, 1/3 of students encounter stress and depression (a subjective mean occurrence of 30.6%) of all participant students, which suggests students have a 9% higher rate of experiencing depression than general people. Depression can destroy life; it greatly impacts living a balanced life. It can impact students' personal and social relationships, educational efficiency, quality of life, affecting their social and family relationships, academic productivity, and bodily operations ( 46 , 47 ). This declines their abilities, and they get demotivated to learn new things, resulting in unsatisfactory performances, and it can even result in university dropouts ( 48 ). Depression is a continuous substantial risk aspect for committing suicide for university students ( 49 ); thus, it is obliged to discover the factors that can give rise to students' depression.
Seventy-five percentage of students in China of an intermediate school are lucky enough to enroll in higher education. The more students pursue higher education, the more they upsurge for depression (in 2002, the depression rate was 5 to 10%, 2011 it rises 24 to 38%) ( 5 ). Generally, University students' age range is late teens to early twenties, i.e., 18–23 years. Abbas ( 50 ) named the era of university students as “post-adolescence. Risk factors for teenage depression have several and complicated problems of individual characteristics and family and educational life ( 51 ). Amongst the huge depression factors, relationship building with family demands a major chunk of attention and time since factors like parenting and family building play an important role in children's development ( 52 , 53 ). Halonen et al. ( 54 ) concluded that factors like family binding play a major role in development, preservation, and driving adolescent depression. Generally speaking, depressed teenagers tend to have a weaker family relationship with their parents than non-depressed teenagers.
There are two types of family risk factors, soft and hard. Hard factors are encountered in families with a weak family building structure, parents are little to no educated at all, and of course, the family status (economically). Several studies have proved that students of hard risk factors are more likely to encounter depression. Firstly, students from broken families have low confidence in every aspect of life, and they are weak at handling emotional breakdowns compared to students from complete and happy families ( 55 – 57 ). Secondly, the university students born in educated families, especially mothers (at least a college degree or higher degree), are less likely to confront depression than the university students born in families with little to no educated families. Secondly, children born with educated mothers or mothers who at least have a college degree tend to be less depressive than the children of less-educated mothers ( 58 ). However, Parker et al. and Mahmood et al. ( 59 , 60 ) stated a strong relationship between depression and mothers with low literacy levels.
On the other hand, Chang et al. ( 46 ) couldn't prove the authentication of this relationship in university students. Thirdly, university students who belong to lower class families tend to have more unstable mental states and are more likely to witness depression than middle or upper-class families ( 61 ). Jadoon et al. and Abbas et al. ( 62 , 63 ) said that there is no link between depression and economic status. Their irrelevance can be because medical students often come from educated and wealthy families and know their jobs are guaranteed as soon as they graduate. Therefore, the relationship between the hard family environment and depression can be known by targeting a huge audience, and there are several factors to consider while gauging this relationship.
The soft family environment is divided into clear factors (parenting style example, family guidelines, rules, the parent with academic knowledge, etc.) and implied factors (family norm, parent-child relationship, communication within the family, etc.). The soft factor is the key factor within the family that cannot be neglected while studying the teenagers' mental state or depression. Families make microsystems within the families, and families are the reason to build and maintain dysfunctional behavior by multiple functional procedures ( 64 ). Amongst the soft family environmental factors, consistency and struggles can be helpful while forecasting the mental health of teenagers. The youth of broken families, family conflict, weak family relationships, and marital issues, especially unhappy married life, are major factors for youth depression ( 65 ). Ruchkin et al. ( 66 ) stated that African Americans usually have weak family bonding, and their teenagers suffer from depression even when controlling for source bias. Whereas, few researchers have stated, family unity is the most serious factor while foreseeing teenagers' depression. Eaton noted that extreme broken family expressions might hurt emotionality and emotional regulation ( 67 , 68 ).
Social circle is also considered while studying depression in teenagers ( 69 – 71 ). The traditional Pakistani culture emphasizes collectivism and peace and focuses on blood relations and sensitive sentiments. Adolescents with this type of culture opt to get inspired by family, but students who live in hostels or share the room with other students lose this family inspiration. This transformation can be a big risk to encounter depression ( 72 ). Furthermore, in Pakistan securing employment is a big concern for university students. If they want a good job in the future, they have to score good grades and maintain GPA from the beginning. They have to face different challenges all at once, like aggressive educational competition, relationships with peers and family, and of course the biggest employment stress all alone. The only source for coping with these pressures is the family that can be helpful for fundings. If the students do not get ample support the chances are of extreme depression. The following hypothesis is suggested:
- H2: Increased family stress level results in increased depression levels in students.
Students' Depression Levels and Students' Academic Performance
University students denote many people experiencing a crucial conversion from teenagers to adulthood: a time that is generally considered the most traumatic time in one's ( 73 ). This then gets accumulated with other challenges like changes in social circle and exams tension, which possibly puts students' mental health at stake. It has been concluded that one-third of students experience moderate to severe depression in their entire student life ( 74 ). This is the rate that can be increased compared to the general people ( 75 , 76 ). Students with limited social-class resources tend to be more helpless. Additionally, depressed students in attainable-focused environments (for instance, higher academic institutes) are likely to score lower grades with a sense of failure and more insufficient self-assurance because they consider themselves failures, find the world unfair, and have future uncertainties. Furthermore, students with low self-esteem are rigid to take on challenging assignments and projects, hence they are damaging their educational career ( 77 ).
Depression can be defined as a blend of physical, mental, bodily processes, and benightedness which can make themselves obvious by symptoms like, for example, poor sleep schedule, lack of concentration, ill thoughts, and state of remorse ( 78 , 79 ). But, even after such a huge number of depressions in students and the poor academic system, research has not explored the effect of depression on educational performance. A study has shown that the relationship between emotional stability and academic performance in university students and financial status directly results in poor exam performance. As the study further concluded, it was verified depression is an independent factor ( 80 ). Likewise, students suffering from depression score poor grades, but this relationship vanished if their depression got treated. Apart from confidence breaking, depression is a big failure for their academic life. Students with depression symptoms bunk more classes, assessments, and assignments. They drop courses if they find them challenging than non-depressed peers, and they are more likely to drop out of university completely ( 81 ). Students suffering from depression can become ruthless, ultimately affecting their educational performance and making them moody ( 82 ).
However, it has been stated that the association between anxiety and educational performance is even worse and ambiguous. At the same time, some comprehensive research has noted that the greater the anxiousness, the greater the student's performance. On the other hand, few types of research have shown results where there is no apparent relationship between anxiety and poorer academic grades ( 83 ). Ironically, few studies have proposed that a higher anxiety level may improve academic performance ( 84 , 85 ). Current research by Khan et al. ( 86 ) on the undergraduate medical students stated that even though the high occurrence of huge depression between the students, the students GPA is unharmed. Therefore, based on given differences in various research findings, this research is supposed to find a more specific and clear answer to the shared relationship between students' depression levels and academic performance. Based on the given arguments, the researcher formulates the following hypothesis:
- H3: Students' depression level has a significant negative effect on their academic performance.
Methodology
Target population and sampling procedure.
The target audience of this study contains all male and female students studying in the public, private, or semi-government higher education institutions located in Rawalpindi/Islamabad. The researchers collected data from undergraduate and postgraduate students from the management sciences, engineering, and computer science departments. The sampling technique which has been used is the non-probability sampling technique. A questionnaire was given to the students, and they were requested to fill it and give their opinion independently. The questionnaire is based on five points Likert scale.
However, stress and depression are the most common issue among the students, which affects their learning outcomes adversely. A non-probability sampling technique gathered the data from February 2020 to May 2020. The total questionnaires distributed among students were 220, and 186 responses were useful. Of which 119 respondents were females, 66 males, and 1 preferred not to disclose. See Table 1 for detailed demographic information of respondents.
Respondent's demographic profile.
Measurement Scales
We have divided this instrument into two portions. In the first section, there is demographic information of respondents. The second section includes 14 items based on family stress, academic stress, students' depression levels, and students' academic performance. Academic and family stress were measured by 3 item scale for each construct, and students' depression level and academic performance were measured by 4 item scale for each separate construct. The five-point Likert scale is used to measure the items, in which one signifies strongly disagree (S.D), second signifies disagree (D.A), third signifies neither agree nor disagree (N), fourth signifies agree (A.G), and the fifth signifies strongly agree (S.A). The questionnaire has been taken from Gold Berg ( 87 ), which is modified and used in the given questionnaire.
Data Analysis and Results
The researchers used the SEM technique to determine the correlation between stress, depression, and academic performance. According to Prajogo and Cooper ( 88 ), it can remove biased effects triggered by the measurement faults and shape a hierarchy of latent constructs. SPSS v.23 and AMOS v.23 have been used to analyze the collected data. Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin test is used to test the competence of the sample. The value obtained is 0.868, which fulfills the Kaiser et al. ( 89 ), a minimum requirement of 0.6. The multicollinearity factor was analyzed through the variance inflation factor (VIF). It shows the value of 3.648 and meets the requirement of Hair et al. ( 90 ), which is < 4. It also indicates the absence of multicollinearity. According to Schwarz et al. ( 91 ), common method bias (CMB) is quite complex in quantitative studies. Harman's test of a single factor has been used to analyze CMB. The result obtained for the single factor is 38.63%. As stated by Podsakoff et al. ( 92 ), if any of the factors gives value < 50% of the total variance, it is adequate and does not influence the CMB. Therefore, we can say that there is no issue with CMB. Considering the above results are adequate among the measurement and structural model, we ensure that the data is valued enough to analyze the relation.
Assessment of the Measurement and Structural Model
The association between the manifest factors and their elements is examined by measuring model and verified by the Confirmatory Factor Analysis (CFA). CFA guarantees legitimacy and the unidimensional of the measurement model ( 93 ). Peterson ( 94 ) stated that the least required, i.e., 0.8 for the measurement model, fully complies with its Cronbach's alpha value, i.e., 0.802. Therefore, it can confidently be deduced that this measurement model holds satisfactory reliability. As for the psychological legitimacy can be analyzed through factor loading, where the ideal loading is above 0.6 for already established items ( 95 ). Also, according to the recommendation of Molina et al. ( 96 ), the minimum value of the average variance extracted (AVE) for all results is supposed to be >0.5. Table 2 gives detail of the variables and their quantity of things, factor loading, merged consistency, and AVE values.
Instrument reliability and validity.
A discriminant validity test was performed to ensure the empirical difference of all constructs. For this, it was proposed by Fornell and Larcker ( 97 ) that the variance of the results is supposed to be greater than other constructs. The second indicator of discriminant validity is that the square root values of AVE have a greater correlation between the two indicators. Hair et al. ( 90 ) suggested that the correlation between the pair of predictor variables should not be higher than 0.9. Table 3 shows that discriminant validity recommended by Hair et al. ( 90 ) and Fornell and Larcker ( 97 ) was proved clearly that both conditions are fulfilled and indicates that the constructs have adequate discriminant validity.
Discriminant validity analysis.
Acd. Strs, Academic Stress; Fam. Strs, Family Stress; Std. Dep. Lev, Student's Depression Level; Std. Acd. Perf, Student's Academic Performance .
Kaynak ( 98 ) described seven indicators that ensure that the measurement model fits correctly. These indicators include standardized root mean squared residual (SRMR), root means a square error of approximation (RMSEA), comparative fit index (CFI), normative fit index (NFI), adjusted goodness of fit index (AGFI), the goodness of fit index (GFI) and chi-square to a degree of freedom (x 2 /DF). Tucker-Lewis's index (TLI) is also included to ensure the measurement and structural model's fitness. In the measurement model, the obtained result shows that the value of x 2 /DF is 1.898, which should be lower than 2 suggested by Byrne ( 99 ), and this value also meets the requirement of Bagozzi and Yi ( 100 ), i.e., <3. The RMSEA has the value 0.049, which fully meets the requirement of 0.08, as stated by Browne and Cudeck ( 101 ). Furthermore, the SRMR acquired value is 0.0596, which assemble with the required need of < 0.1 by Hu and Bentler ( 102 ). Moreover, according to Bentler and Bonett ( 103 ), McDonald and Marsh ( 104 ), and Bagozzi and Yi ( 100 ), the ideal value is 0.9, and the values obtained from NFI, GFI, AGFI, CFI, and TLI are above the ideal value.
Afterward, the structural model was analyzed and achieved the findings, which give the value of x 2 /DF 1.986. According to Browne and Cudeck ( 101 ), the RMSEA value should not be greater than 0.08, and the obtained value of RMSEA is 0.052, which meets the requirement perfectly. The minimum requirement of Hu and Bentler ( 102 ) should be <0.1, for the structural model fully complies with the SRMR value 0.0616. According to a recommendation of McDonald and Marsh ( 104 ) and Bagozzi and Yi ( 100 ), the ideal value must be up to 0.9, and Table 4 also shows that the values of NFI, GFI, AGFI, CFI, and TLI, which are above than the ideal value and meets the requirement. The above results show that both the measurement and structural models are ideally satisfied with the requirements and the collected data fits correctly.
Analysis of measurement and structural model.
Testing of Hypotheses
The SEM technique is used to examine the hypotheses. Each structural parameter goes along with the hypothesis. The academic stress (Acd. Strs) with the value β = 0.293 while the p -value is 0.003. These outcomes show a significant positive relationship between academic stress (Acd. Strs) and students' depression levels (Std. Dep. Lev). With the β = 0.358 and p = 0.001 values, the data analysis discloses that the family stress (Fam. Strs) has a significant positive effect on the students' depression level (Std. Dep. Lev). However, the student's depression level (Std. Dep. Lev) also has a significant negative effect on their academic performance (Std. Acd. Perf) with the values of β = −0.319 and p = 0.001. Therefore, the results supported the following hypotheses H 1 , H 2 , and H 3 . The sub-hypotheses analysis shows that the results are statistically significant and accepted. In Table 5 , the details of the sub-hypotheses and the principals are explained precisely. Please see Table 6 to review items with their mean and standard deviation values. Moreover, Figure 2 represents the structural model.
Examining the hypotheses.
Description of items, mean, and standard deviation.

Structural model.
Discussion and Conclusion
These findings add to our knowledge of how teenage depression is predicted by academic and familial stress, leading to poor academic performance, and they have practical implications for preventative and intervention programs to safeguard adolescents' mental health in the school context. The outcomes imply that extended academic stress positively impacts students' depression levels with a β of 0.293 and a p -value sof 0.003. However, according to Wang et al. ( 5 ), a higher level of academic stress is linked to a larger level of school burnout, which leads to a higher degree of depression. Satinsky et al. ( 105 ) also claimed that university officials and mental health specialists have expressed worry about depression and anxiety among Ph.D. students, and that his research indicated that depression and anxiety are quite common among Ph.D. students. Deb et al. ( 106 ) found the same results and concluded that depression, anxiety, behavioral difficulties, irritability, and other issues are common among students who are under a lot of academic stress. Similarly, Kokou-Kpolou et al. ( 107 ) revealed that depressive symptoms are common among university students in France. They also demonstrate that socioeconomic and demographic characteristics have a role.
However, Wang et al. ( 5 ) asserted that a higher level of academic stress is associated with a higher level of school burnout, which in return, leads to a higher level of depression. Furthermore, Satinsky et al. ( 105 ) also reported that university administrators and mental health clinicians have raised concerns about depression and anxiety and concluded in his research that depression and anxiety are highly prevalent among Ph.D. students. Deb et al. ( 106 ) also reported the same results and concluded that Depression, anxiety, behavioral problems, irritability, etc. are few of the many problems reported in students with high academic stress. Similary, Kokou-Kpolou et al. ( 107 ) confirmed that university students in France have a high prevalence of depressive symptoms. They also confirm that socio-demographic factors and perceived stress play a predictive role in depressive symptoms among university students. As a result, academic stress has spread across all countries, civilizations, and ethnic groups. Academic stress continues to be a serious problem impacting a student's mental health and well-being, according to the findings of this study.
With the β= 0.358 and p = 0.001 values, the data analysis discloses that the family stress (Fam. Strs) has a significant positive effect on the students' depression level (Std. Dep. Lev). Aleksic ( 108 ) observed similar findings and concluded that many and complicated concerns of personal traits, as well as both home and school contexts, are risk factors for teenage depression. Similarly, Wang et al. ( 109 ) indicated that, among the possible risk factors for depression, family relationships need special consideration since elements like parenting styles and family dynamics influence how children grow. Family variables influence the onset, maintenance, and course of juvenile depression, according to another study ( 110 ). Depressed adolescents are more likely than normal teenagers to have bad family and parent–child connections.
Conversely, students' depression level has a significantly negative impact on their academic performance with β and p -values of −0.319 and 0.001. According ( 111 ), anxiety and melancholy have a negative influence on a student's academic performance. Adolescents and young adults suffer from depression, which is a common and dangerous mental illness. It's linked to an increase in family issues, school failure, especially among teenagers, suicide, drug addiction, and absenteeism. While the transition to adulthood is a high-risk period for depression in general ( 5 ), young people starting college may face extra social and intellectual challenges that increase their risk of melancholy, anxiety, and stress ( 112 ). Students' high rates of depression, anxiety, and stress have serious consequences. Not only may psychological morbidity have a negative impact on a student's academic performance and quality of life, but it may also disturb family and institutional life ( 107 ). Therefore, long-term untreated depression, anxiety, or stress can have a negative influence on people's ability to operate and produce, posing a public health risk ( 113 ).
Theoretical Implications
The current study makes various contributions to the existing literature on servant leadership. Firstly, it enriches the limited literature on the role of family and academic stress and their impact on students' depression levels. Although, a few studies have investigated stress and depression and its impact on Students' academic performance ( 14 , 114 ), however, their background i.e., family and institutions are largely ignored.
Secondly, it explains how the depression level impacts students' academic learning, specifically in the Asian developing countries region. Though a substantial body of empirical research has been produced in the last decade on the relationship between students' depression levels and its impact on their academic achievements, however, the studies conducted in the Pakistani context are scarce ( 111 , 115 ). Thus, this study adds further evidence to prior studies conducted in different cultural contexts and validates the assumption that family and academic stress are key sources depression and anxiety among students which can lead toward their low academic grades and their overall performance.
This argument is in line with our proposed theory in the current research i.e., cognitive appraisal theory which was presented in 1966 by psychologist Richard Lazarus. Lazarus's theory is called the appraisal theory of stress, or the transactional theory of stress because the way a person appraises the situation affects how they feel about it and consequently it's going to affect his overall quality of life. In line with the theory, it suggests that events are not good or bad, but the way we think about them is positive or negative, and therefore has an impact on our stress levels.
Practical Implications
According to the findings of this study, high levels of depressive symptoms among college students should be brought to the attention of relevant departments. To prevent college student depression, relevant departments should improve the study and life environment for students, try to reduce the generation of negative life events, provide adequate social support for students, and improve their cognitive and coping capacities to improve their mental qualities.
Stress and depression, on the other hand, may be managed with good therapy, teacher direction, and family support. The outcomes of this study provide an opportunity for academic institutions to address students' psychological well-being and requirements. Emotional well-being support services for students at Pakistan's higher education institutions are lacking in many of these institutions, which place a low priority on the psychological requirements of these students. As a result, initiatives that consistently monitor and enhance kids' mental health are critical. Furthermore, stress-reduction treatments such as biofeedback, yoga, life-skills training, mindfulness meditation, and psychotherapy have been demonstrated to be useful among students. Professionals in the sector would be able to adapt interventions for pupils by understanding the sources from many spheres.
Counseling clinics should be established at colleges to teach students about stress and sadness. Counselors should instill in pupils the importance of positive conduct and decision-making. The administration of the school should work to create a good and safe atmosphere. Furthermore, teachers should assume responsibility for assisting and guiding sad pupils, since this will aid in their learning and performance. Support from family members might also help you get through difficult times.
Furthermore, these findings support the importance of the home environment as a source of depression risk factors among university students, implying that family-based treatments and improvements are critical in reducing depression among university students.
Limitations and Future Research Implications
The current study has a few limitations. The researcher gathered data from the higher education level of university students studying in Islamabad and Rawalpindi institutions. In the future, researchers are required to widen their region and gather information from other cities of Pakistan, for instance, Lahore, Karachi, etc. Another weakness of the study is that it is cross-sectional in nature. We need to do longitudinal research in the future to authoritatively assert the cause-and-effect link between academic and familial stress and their effects on students' academic performance since cross-sectional studies cannot establish significant cause and effect relationships. Finally, the study's relatively small sample size is a significant weakness. Due to time and budget constraints, it appears that the capacity to perform in-depth research of all firms in Pakistan's pharmaceutical business has been limited. Even though the findings are substantial and meaningful, the small sample size is predicted to limit generalizability and statistical power. This problem can be properly solved by increasing the size of the sample by the researchers, in future researches.
Data Availability Statement
Ethics statement.
Ethical review and approval was not required for the study on human participants in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation was not required for this study in accordance with the national legislation and the institutional requirements.
Author Contributions
All authors contributed to conceptualization, formal analysis, investigation, methodology, writing and editing of the original draft, and read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
This work was funded by the 2020 Heilongjiang Province Philosophy and Social Science Research Planning Project on Civic and Political Science in Universities (Grant No. 20SZB01). This work is supported by the Scientific Grant Agency of the Ministry of Education, Science, Research, and Sport of the Slovak Republic and the Slovak Academy Sciences as part of the research project VEGA 1/0797/20: Quantification of Environmental Burden Impacts of the Slovak Regions on Health, Social and Economic System of the Slovak Republic.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher's Note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Acknowledgments
Authors would like to thank all persons who directly or indirectly participated in the completion of this manuscript.
Anxiety and Depression Among College Students Essay
- To find inspiration for your paper and overcome writer’s block
- As a source of information (ensure proper referencing)
- As a template for you assignment
Introduction
Methods section.
Education is expected to have appositive importance on the student’s life by enhancing their capability to think and improving their competency. However, it often acts as a source of stress that affects students’ mental health adversely. This causation of academic stress often emanates from the need to have high grades, the requirement to change attitude for success, and even pressures put by various school assignments. These pressures introduced by education can make the student undergo a series of anxiety, depression, and stress trying to conform to the forces. The causes of academic stress are well-researched but there is still no explanation why the rate of strain increases despite some measures being implemented to curb student stress. This research explores this niche by using 100 participants who study at my college.
Nowadays there are many reasons that cause stress among growing number of students who might not know they are going through the condition most of the time. Hence, undiscovered discouragement or uneasiness can cause understudies to feel that they are continually passing up unique open doors. It prompts substance misuse; self-destruction is the second most typical reason for death among undergrads. The main hypothesis of this article is that college and university students have higher depression rates.
Problem Statement
This proposal undercovers how the problem of anxiety and depression is progressing if not addressed. With such countless youngsters experiencing undiscovered tension, it may be challenging for them to appreciate school. Understudies’ emotional well-being is risked when pressure and trouble go unnoticed, which can prompt social and educational issues (Nelson & Liebel, 2018). Educators might battle to perceive uneasiness since these circumstances manifest themselves contrastingly in different people.
Anxiety and depression are complicated disorders with numerous elements that impact people differently. Teachers and staff must be well trained to deal with these unforeseen events. Understudies coming to college come from various financial foundations, which can prompt an assortment of psychological wellness chances (Li et al., 2021). Additionally, current works will be evaluated to differentiate the risk factors associated with stress among university undergraduates worldwide.
There are various reasons which might cause the onset of anxiety and depression. It can be absence of rest, terrible dietary patterns, and lack of activity add to the gloom in undergrads (Ghrouz et al., 2019). Scholarly pressure, which incorporates monetary worries, strain to track down a decent profession after graduation, and bombed connections, is sufficient to drive a few understudies to exit school or more awful.
Numerous parts of school life add to despondency risk factors. For example, understudies today are owing debtors while having fewer work prospects than prior. Discouraged kids are bound to foster the problems like substance misuse (Lattie et al., 2019). For adaptation to close-to-home trouble, discouraged understudies are more inclined than their non-discouraged companions to knock back the firewater, drink pot, and participate in unsafe sexual practices.
Hypothesis on the Topic
The central hypothesis for this study is that college students have a higher rate of anxiety and depression. The study will integrate various methodologies to prove the hypothesis of nullifying it. High rates of anxiety and depression can lead to substance misuse, behavioral challenges, and suicide (Lipson et al., 2018). Anxiety is one of the most critical indicators of academic success, it shows how students’ attitudes change, reflecting on their overall performance.
Participants
The study will use college students who are joining and those already in college. The research period is planned to last six months; college students are between the ages of 18 and 21 and life is changing rapidly at this age (Spillebout et al., 2019). This demography will come from the college where I study. The participants will be chosen randomly, the total number will be 100, both female and male, and from all races.
Apparatus/ Materials/ Instruments
Some of the materials to be used in the study will include pencils, papers, and tests. Paper and pencil are typical supplies that students are familiar with, so using them will not cause additional stress. It will be used during the interview with the students and throughout the study will be in effect (Huang et al., 2018). These have been applied in various studies before, and, hence, they will be instrumental in this study.
The study will follow a step-wise procedure to get the required results. First, the students’ pre-depression testing results would be researched and recorded. Second, the students would undergo standardized testing in the same groups. Scholarly accomplishment is impacted by past intellectual performance and standardized testing (Chang et al., 2020). Third, the students’ levels of depression and anxiety would be monitored along with their test results.
The study will use a descriptive, cross-sectional design with categorical and continuous data. The sample demographic characteristics were described using descriptive statistics. Pearson’s proportion of skewness values and common mistake of skewness was utilized to test the ordinariness of the persistent factors. The distinctions in mean scores between sociodemographic variables and stress will be examined using Tests (Lipson et al., 2018). The independent variable will be essential because it will provide the basis of measurement.
The 100 participants had different anxiety levels, as seen from the Test taken and the various evaluations. Forty-five of the participants had high levels, 23 had medium levels, while the remaining 32 had low levels (Lipson et al., 2018). The correlation and ANOVA, which had a degree of era margin of 0.05, were allowed (Lipson et al., 2018). This finding aligns intending to have clear and comprehensive outcomes.
Significance of the Study
If the results would be not significant, it means that students are not subjected to more pressure on average. If the study results in significant outcomes, this would mean that there is much that needs to be done to reduce student’s anxiety. The idea that scholarly accomplishment is indispensable to progress is built up in higher instructive conditions (Nelson & Liebel, 2018). Many colleges devote money to tutoring, extra instruction, and other support services to help students succeed.
APA Ethical Guidelines
The study will have to follow the APA ethical guidelines because it involves experimenting with humans. Some of the policies include having consent from the participant, debriefing the participant on the study’s nature, and getting IRB permission (Nelson & Liebel, 2018). Ethical guidelines should comply with proficient, institutional, and government rules. They habitually administer understudies whom they likewise instruct to give some examples of obligations.
Limitations
The study also had some limitations, making it hard to get the desired outcomes. It was not easy to detect the population-level connections, but not causality. This case hardened the aspect of confounding and getting the relevant random assignment needed for the study had to access (Nelson & Liebel, 2018). For the right individuals for the investigation to be identified, the sampling was not easy.
This study would be essential as it will create a platform for future studies. The result that was gotten shows that many college students are undergoing the problem of anxiety and depression without knowing that it is happening. Educators will have awareness on what aspects of academics they need to modify to ensure their students are not experiencing mental health challenges. Hence, it makes it possible for future researchers to conduct studies to provide possible solutions.
Chang, J., Yuan, Y., & Wang, D. (2020). Mental health status and its influencing factors among college students during the epidemic of COVID-19. Journal of Southern Medical University , 40(2), 171-176.
Ghrouz, A. K., Noohu, M. M., Manzar, D., Warren Spence, D., BaHammam, A. S., & Pandi-Perumal, S. R. (2019). Physical activity and sleep quality in relation to mental health among college students. Sleep and Breathing Journal , 23(2), 627-634.
Huang, J., Nigatu, Y. T., Smail-Crevier, R., Zhang, X., & Wang, J. (2018). Interventions for common mental health problems among university and college students: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Journal of Psychiatric Research , 107, 1-10.
Lattie, E. G., Adkins, E. C., Winquist, N., Stiles-Shields, C., Wafford, Q. E., & Graham, A. K. (2019). Digital mental health interventions for depression, anxiety, and enhancement of psychological well-being among college students: A systematic review. Journal of Medical Internet Research , 21(7), e12869.
Li, Y., Zhao, J., Ma, Z., McReynolds, L. S., Lin, D., Chen, Z.,… & Liu, X. (2021). Mental health among college students during the COVID-19 pandemic in China: A 2-wave longitudinal survey. Journal of Affective Disorders , 281, 597-604.
Lipson, S. K., Kern, A., Eisenberg, D., & Breland-Noble, A. M. (2018). Mental health disparities among college students of color. Journal of Adolescent Health , 63(3), 348-356.
Nelson, J. M., & Liebel, S. W. (2018). Anxiety and depression among college students with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD): Cross-informant, sex, and subtype differences. Journal of American College Health , 66(2), 123-132.
Spillebout, A., Dechelotte, P., Ladner, J., & Tavolacci, M. P. (2019). Mental health among university students with eating disorders and irritable bowel syndrome in France. Journal of Affective Disorders , 67(5), 295-301.
The following table shows the significant issues that affect the mental health state of most college students. Based on Huang et al.’s research, the biggest concern for most students included stress about their loved ones. Additionally, the authors found that worrying about one’s academics and schooling was the second depressing experience among most college students.
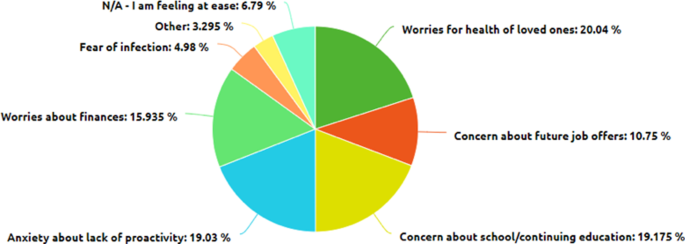
The following figure shows how on top of the current stressors for students, COVID-19 affects their mental health. Li et al.’s research demonstrates that COVID-19 placed more financial burden than before, especially on students with part-time jobs who often face anxiety and stress due to lack of tuition fees (Li et al., 2021). Generally, the research shows that the financial consequences of coronavirus affect the mental state of most college students.
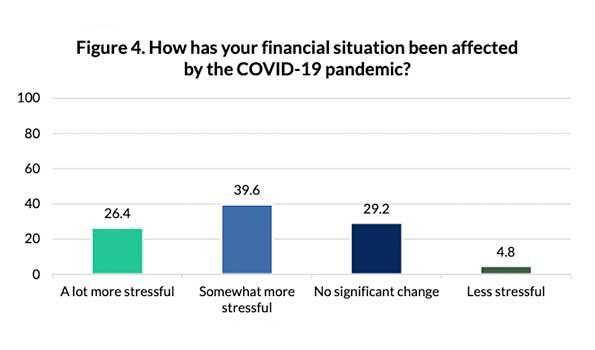
- Medication and Preventive Systems
- How Cognitive Behavioral Therapy Benefits Children
- The Methods to Reduce Preoperational Anxiety
- Defense Mechanisms and Brain Structure
- Coping with Stress and Physical Health Problems
- Quality of Life With Schizophrenia
- Schizophrenia: The Etiology Analysis
- Schizophrenia as a Chronic Mental Disorder
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2023, April 10). Anxiety and Depression Among College Students. https://ivypanda.com/essays/anxiety-and-depression-among-college-students/
"Anxiety and Depression Among College Students." IvyPanda , 10 Apr. 2023, ivypanda.com/essays/anxiety-and-depression-among-college-students/.
IvyPanda . (2023) 'Anxiety and Depression Among College Students'. 10 April.
IvyPanda . 2023. "Anxiety and Depression Among College Students." April 10, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/anxiety-and-depression-among-college-students/.
1. IvyPanda . "Anxiety and Depression Among College Students." April 10, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/anxiety-and-depression-among-college-students/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Anxiety and Depression Among College Students." April 10, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/anxiety-and-depression-among-college-students/.

Essays About Depression: Top 8 Examples Plus Prompts
Many people deal with mental health issues throughout their lives; if you are writing essays about depression, you can read essay examples to get started.
An occasional feeling of sadness is something that everyone experiences from time to time. Still, a persistent loss of interest, depressed mood, changes in energy levels, and sleeping problems can indicate mental illness. Thankfully, antidepressant medications, therapy, and other types of treatment can be largely helpful for people living with depression.
People suffering from depression or other mood disorders must work closely with a mental health professional to get the support they need to recover. While family members and other loved ones can help move forward after a depressive episode, it’s also important that people who have suffered from major depressive disorder work with a medical professional to get treatment for both the mental and physical problems that can accompany depression.
If you are writing an essay about depression, here are 8 essay examples to help you write an insightful essay. For help with your essays, check out our round-up of the best essay checkers .
- 1. My Best Friend Saved Me When I Attempted Suicide, But I Didn’t Save Her by Drusilla Moorhouse
- 2. How can I complain? by James Blake
- 3. What it’s like living with depression: A personal essay by Nadine Dirks
- 4. I Have Depression, and I’m Proof that You Never Know the Battle Someone is Waging Inside by Jac Gochoco
- 5. Essay: How I Survived Depression by Cameron Stout
- 6. I Can’t Get Out of My Sweat Pants: An Essay on Depression by Marisa McPeck-Stringham
- 7. This is what depression feels like by Courtenay Harris Bond
8. Opening Up About My Struggle with Recurring Depression by Nora Super
1. what is depression, 2. how is depression diagnosed, 3. causes of depression, 4. different types of depression, 5. who is at risk of depression, 6. can social media cause depression, 7. can anyone experience depression, the final word on essays about depression, is depression common, what are the most effective treatments for depression, top 8 examples, 1. my best friend saved me when i attempted suicide, but i didn’t save her by drusilla moorhouse.
“Just three months earlier, I had been a patient in another medical facility: a mental hospital. My best friend, Denise, had killed herself on Christmas, and days after the funeral, I told my mom that I wanted to die. I couldn’t forgive myself for the role I’d played in Denise’s death: Not only did I fail to save her, but I’m fairly certain I gave her the idea.”
Moorhouse makes painstaking personal confessions throughout this essay on depression, taking the reader along on the roller coaster of ups and downs that come with suicide attempts, dealing with the death of a loved one, and the difficulty of making it through major depressive disorder.
2. How can I complain? by James Blake
“I wanted people to know how I felt, but I didn’t have the vocabulary to tell them. I have gone into a bit of detail here not to make anyone feel sorry for me but to show how a privileged, relatively rich-and-famous-enough-for-zero-pity white man could become depressed against all societal expectations and allowances. If I can be writing this, clearly it isn’t only oppression that causes depression; for me it was largely repression.”
Musician James Blake shares his experience with depression and talks about his struggles with trying to grow up while dealing with existential crises just as he began to hit the peak of his fame. Blake talks about how he experienced guilt and shame around the idea that he had it all on the outside—and so many people deal with issues that he felt were larger than his.
3. What it’s like living with depression: A personal essay by Nadine Dirks
“In my early adulthood, I started to feel withdrawn, down, unmotivated, and constantly sad. What initially seemed like an off-day turned into weeks of painful feelings that seemed they would never let up. It was difficult to enjoy life with other people my age. Depression made typical, everyday tasks—like brushing my teeth—seem monumental. It felt like an invisible chain, keeping me in bed.”
Dirks shares her experience with depression and the struggle she faced to find treatment for mental health issues as a Black woman. Dirks discusses how even though she knew something about her mental health wasn’t quite right, she still struggled to get the diagnosis she needed to move forward and receive proper medical and psychological care.
4. I Have Depression, and I’m Proof that You Never Know the Battle Someone is Waging Inside by Jac Gochoco
“A few years later, at the age of 20, my smile had fallen, and I had given up. The thought of waking up the next morning was too much for me to handle. I was no longer anxious or sad; instead, I felt numb, and that’s when things took a turn for the worse. I called my dad, who lived across the country, and for the first time in my life, I told him everything. It was too late, though. I was not calling for help. I was calling to say goodbye.”
Gochoco describes the war that so many people with depression go through—trying to put on a brave face and a positive public persona while battling demons on the inside. The Olympic weightlifting coach and yoga instructor now work to share the importance of mental health with others.
5. Essay: How I Survived Depression by Cameron Stout
“In 1993, I saw a psychiatrist who prescribed an antidepressant. Within two months, the medication slowly gained traction. As the gray sludge of sadness and apathy washed away, I emerged from a spiral of impending tragedy. I helped raise two wonderful children, built a successful securities-litigation practice, and became an accomplished cyclist. I began to take my mental wellness for granted. “
Princeton alum Cameron Stout shared his experience with depression with his fellow Tigers in Princeton’s alumni magazine, proving that even the most brilliant and successful among us can be rendered powerless by a chemical imbalance. Stout shares his experience with treatment and how working with mental health professionals helped him to come out on the other side of depression.
6. I Can’t Get Out of My Sweat Pants: An Essay on Depression by Marisa McPeck-Stringham
“Sometimes, when the depression got really bad in junior high, I would come straight home from school and change into my pajamas. My dad caught on, and he said something to me at dinner time about being in my pajamas several days in a row way before bedtime. I learned it was better not to change into my pajamas until bedtime. People who are depressed like to hide their problematic behaviors because they are so ashamed of the way they feel. I was very ashamed and yet I didn’t have the words or life experience to voice what I was going through.”
McPeck-Stringham discusses her experience with depression and an eating disorder at a young age; both brought on by struggles to adjust to major life changes. The author experienced depression again in her adult life, and thankfully, she was able to fight through the illness using tried-and-true methods until she regained her mental health.
7. This is what depression feels like by Courtenay Harris Bond
“The smallest tasks seem insurmountable: paying a cell phone bill, lining up a household repair. Sometimes just taking a shower or arranging a play date feels like more than I can manage. My children’s squabbles make me want to scratch the walls. I want to claw out of my own skin. I feel like the light at the end of the tunnel is a solitary candle about to blow out at any moment. At the same time, I feel like the pain will never end.”
Bond does an excellent job of helping readers understand just how difficult depression can be, even for people who have never been through the difficulty of mental illness. Bond states that no matter what people believe the cause to be—chemical imbalance, childhood issues, a combination of the two—depression can make it nearly impossible to function.
“Once again, I spiraled downward. I couldn’t get out of bed. I couldn’t work. I had thoughts of harming myself. This time, my husband urged me to start ECT much sooner in the cycle, and once again, it worked. Within a matter of weeks I was back at work, pretending nothing had happened. I kept pushing myself harder to show everyone that I was “normal.” I thought I had a pattern: I would function at a high level for many years, and then my depression would be triggered by a significant event. I thought I’d be healthy for another ten years.”
Super shares her experience with electroconvulsive therapy and how her depression recurred with a major life event despite several years of solid mental health. Thankfully, Super was able to recognize her symptoms and get help sooner rather than later.
7 Writing Prompts on Essays About Depression
When writing essays on depression, it can be challenging to think of essay ideas and questions. Here are six essay topics about depression that you can use in your essay.

Depression can be difficult to define and understand. Discuss the definition of depression, and delve into the signs, symptoms, and possible causes of this mental illness. Depression can result from trauma or personal circumstances, but it can also be a health condition due to genetics. In your essay, look at how depression can be spotted and how it can affect your day-to-day life.
Depression diagnosis can be complicated; this essay topic will be interesting as you can look at the different aspects considered in a diagnosis. While a certain lab test can be conducted, depression can also be diagnosed by a psychiatrist. Research the different ways depression can be diagnosed and discuss the benefits of receiving a diagnosis in this essay.
There are many possible causes of depression; this essay discusses how depression can occur. Possible causes of depression can include trauma, grief, anxiety disorders, and some physical health conditions. Look at each cause and discuss how they can manifest as depression.

There are many different types of depression. This essay topic will investigate each type of depression and its symptoms and causes. Depression symptoms can vary in severity, depending on what is causing it. For example, depression can be linked to medical conditions such as bipolar disorder. This is a different type of depression than depression caused by grief. Discuss the details of the different types of depression and draw comparisons and similarities between them.
Certain genetic traits, socio-economic circumstances, or age can make people more prone to experiencing symptoms of depression. Depression is becoming more and more common amongst young adults and teenagers. Discuss the different groups at risk of experiencing depression and how their circumstances contribute to this risk.
Social media poses many challenges to today’s youth, such as unrealistic beauty standards, cyber-bullying, and only seeing the “highlights” of someone’s life. Can social media cause depression in teens? Delve into the negative impacts of social media when writing this essay. You could compare the positive and negative sides of social media and discuss whether social media causes mental health issues amongst young adults and teenagers.
This essay question poses the question, “can anyone experience depression?” Although those in lower-income households may be prone to experiencing depression, can the rich and famous also experience depression? This essay discusses whether the privileged and wealthy can experience their possible causes. This is a great argumentative essay topic, discuss both sides of this question and draw a conclusion with your final thoughts.
When writing about depression, it is important to study examples of essays to make a compelling essay. You can also use your own research by conducting interviews or pulling information from other sources. As this is a sensitive topic, it is important to approach it with care; you can also write about your own experiences with mental health issues.
Tip: If writing an essay sounds like a lot of work, simplify it. Write a simple 5 paragraph essay instead.
FAQs On Essays About Depression
According to the World Health Organization, about 5% of people under 60 live with depression. The rate is slightly higher—around 6%—for people over 60. Depression can strike at any age, and it’s important that people who are experiencing symptoms of depression receive treatment, no matter their age.
Suppose you’re living with depression or are experiencing some of the symptoms of depression. In that case, it’s important to work closely with your doctor or another healthcare professional to develop a treatment plan that works for you. A combination of antidepressant medication and cognitive behavioral therapy is a good fit for many people, but this isn’t necessarily the case for everyone who suffers from depression. Be sure to check in with your doctor regularly to ensure that you’re making progress toward improving your mental health.
If you’re still stuck, check out our general resource of essay writing topics .

Amanda has an M.S.Ed degree from the University of Pennsylvania in School and Mental Health Counseling and is a National Academy of Sports Medicine Certified Personal Trainer. She has experience writing magazine articles, newspaper articles, SEO-friendly web copy, and blog posts.
View all posts

Personalize Your Experience
Log in or create an account for a personalized experience based on your selected interests.
Already have an account? Log In
Free standard shipping is valid on orders of $45 or more (after promotions and discounts are applied, regular shipping rates do not qualify as part of the $45 or more) shipped to US addresses only. Not valid on previous purchases or when combined with any other promotional offers.
Register for an enhanced, personalized experience.
Receive free access to exclusive content, a personalized homepage based on your interests, and a weekly newsletter with topics of your choice.
Home / Parenting, Kids & Teens / Depression in college students: How to help students manage their mental health
Depression in college students: How to help students manage their mental health
Please login to bookmark.

Parents hope college will be a time for their kids to spread their wings and fly. Yet college students are now experiencing record high rates of depression and anxiety. During the 2022-2023 academic year, 41% of students reported experiencing symptoms of depression and 36% said they experienced anxiety, according to the latest Healthy Minds Study . Understandably, parents want to know what they can do to help their college age kids manage their mental health so depression doesn’t dock their wings.
Any single case of depression can have multiple causes involving a mix of biological, genetic or social factors. However, one common cause of depression in college students is the sheer scope of change that comes with moving on from the familiar world of home and high school, according to Paige I. Partain, M.D., a pediatrician at the Mayo Clinic Children’s Center in Rochester, Minnesota, with expertise in child and adolescent mental health.
In addition to changes in housing and social connections, going to college typically accelerates academic expectations. It also scrambles students’ sleep, diet and exercise patterns. For some college students — even those with no history of depression — having so many facets of their lives suddenly challenged and changed can create enough stress to trigger depression, says Dr. Partain
She adds, however, that it’s important “for parents and students alike to recognize that depression can be totally untriggered.” Sometimes students can be on top of their coursework, getting along with new friends and otherwise outwardly crushing college when they sense that their moods have dipped.
If students are baffled about why they’re feeling down, helping them understand that sometimes depression occurs without an identifiable cause is important. It can help relieve the added burden of wondering what’s wrong with them — or blaming themselves — for feeling depressed.
Says Dr. Partain, “I can’t express enough what a difference it makes when I’m talking to teenagers or young adults in their early twenties and I can explain that sometimes it just happens. It can be even more frustrating when you don’t know why depression happens. But I can see the relief in their eyes. They’re like, ‘Yes, you get it.’ To be able to just empathize and label the phenomena can be incredibly powerful.”
Spotting signs of depression in college students
Along with feeling sad and down, common signs of depression in college kids include:
- Changes in appetite such as eating more or less than usual.
- Sleep disturbances, such as insomnia or sleeping too much.
- Losing in interest in favorite pastimes including playing sports, making art or hanging out with friends. “Isolation is a really key symptom, particularly for teens and young adults,” says Dr. Partain.
People often experience depression and anxiety at the same time , and college kids are no exception. Determining which one came first can be a “chicken or the egg” question, says Dr. Partain. But big shifts in a student’s mood and behavior may indicate underlying depression.
“If your kid is not one who tends to be anxious, and all of a sudden, there’s worry about everything, that might be an indicator of a problem with mood.” On the flip side, she says, if your kid is usually “a type-A go-getter, and normally a little more anxious, and all of a sudden the work isn’t getting done and grades are slipping, that can also be an indicator that there’s a problem with mood.”
Irritability is another common symptom of depression. “We think a lot about feeling sad or down, and that can certainly be the case for a teenager or a young adult. But there is good medical research to suggest that irritability might be an even better indicator of underlying mood problems,” says Dr. Partain. “It’s another textbook symptom to be aware of.”
What to say if your child seems depressed
Sometimes, parents who think their kids might be depressed are wary of butting into their business. Or they may keep quiet because they’re just not sure how to talk about depression. If parents ask Dr. Partain if they should try talking to their child’s friends or professors about their concerns, she advises them not to go around their child’s back.
Rather, Dr. Partain recommends that parents raise their concerns with their kids in a straightforward way. “As you’re trying to help children develop independence and capability — regardless of the dynamic that you have with your child — I advocate for talking with kids directly.”
To get a better sense of how children are feeling, Dr. Partain says it’s fine to initiate the conversation by text with a simple message like this: Just checking in to say I love you. How are you doing? I want to make sure you’re doing okay.
Let them know that you’re concerned and let them respond in their own time.
If your child shares feelings of being depressed or anxious, make it clear that you’re available to help in whatever way works. “You can ask, ‘Do you want my help, or is this something you want to take care of on your own?’ The biggest thing to avoid is invalidating language: ‘You’ll get over it.’ ‘Going to college is just hard,’ ” says Dr. Partain. “Parents might find a slightly different approach for every kid, but they should feel empowered to speak up because parents can play a powerful role in helping children understand what they’re experiencing.”
Help your college kid develop strategies to cope with depression
With college students experiencing depression or anxiety for the first time, parents can share self-care strategies that have been proved to ease symptoms of depression, including:
- Exercising .
- Connecting with friends.
- Eating healthy foods.
- Spending time in nature.
- Getting adequate sleep, as young adults need between seven and nine hours a night
- Finding a community on campus, whether it be with a group of fellow ultimate Frisbee fans or a religious or political organization.
If students are experiencing any kind of acute or prolonged dip in mood, their parents can also encourage them to seek treatment and help them navigate campus mental health resources. As students’ mental health becomes a central part of the conversation on college and university campuses, Dr. Partain says that more schools are preemptively providing students and parents with information about counseling and medical services.
“I encourage all parents to keep that information handy,” she says. “Even if you have a kid who’s done great and never had difficulty with mental health, it’s helpful to know about available resources, so if your child reaches the point of saying, ‘Mom, Dad, what do I do?’ you can help provide answers.”
Parents can also provide important support to students who have a history of depression, Dr. Partain says. If your child is taking an antidepressant, you can ask the healthcare professional to dispense the prescription in a 90-day supply, with refills that can be obtained at a pharmacy near campus.
As students in Dr. Partain’s care are preparing to transition to college, she has a conversation with them about their specific symptoms of depression. She also reviews the self-care strategies that have helped them feel better in the past. “Depression looks different for everyone, and it’s important for students to do the mental exercise of saying, What does it look like for me? Is it that I’m isolating myself? Is it that I’m less talkative? Is it that I’m more irritable? Is it that I don’t enjoy reading anymore?” says Dr. Partain.
The point of the conversation is to help students become more self-aware about what depression looks like for them, and spot early warning signs so they can act quickly to protect their emotional health. She encourages parents and children to have a version of this conversation together, too, and to develop a shared relapse prevention plan.
Then, if students begin to feel depression coming back while they’re away at college, their parents can reinforce whatever self-care strategies have helped get through rough patches before. For students already seeing therapists, noticing an uptick in symptoms can prompt them to reach out to ask for some extra sessions, with help from parents if needed.
“Almost all therapy providers have the ability to treat people who are in crisis or who feel like they’re significantly worsening. The same goes for healthcare professionals if students are on a medication. If I get a message from a college kid saying, ‘My mood is getting a lot worse,’ I’m going to get them seen within a week, and many other healthcare professionals will too,” says Dr. Partain.
Create a crisis plan
If students have had inpatient treatment or thoughts of suicide in any context in the past, it’s also critically important for them and their parents to have shared emergency safety plans. This can be activated if students ever becomes severely distressed again.
“Sometimes, depending on the family dynamic, the safety plan may not include having the child call the parent. The plan for the child may be calling Aunt Jane, or calling Grandma. But it’s really powerful for the parents to be able to reinforce that and say, ‘That’s OK. I want you to be safe,’ ” says Dr. Partain.
A common worry she hears from parents is that discussing suicide may make it more likely that their child will contemplate or attempt suicide. But, she says, there’s no data showing that talking about suicide makes people more likely to attempt it. In fact, it does the opposite : “Talking about it makes it easier for them to seek help in the moment. The way I phrase it to my patients is, ‘I’m really glad that you’re not having those kinds of thoughts. But I know things can change quickly, and this safety plan is just something we want to have in our back pocket.” Parents don’t have to hammer on the subject,” she adds, “but it’s an important conversation to have, and I wouldn’t avoid it.”

Relevant reading
I'm a Psychologist
What does a therapist do every day? What character traits are essential for therapists to have? Follow therapists as they work to keep people happy and healthy. These health heroes do the important work of helping patients care for their mental health. Discover how they work with other healthcare providers…

Discover more Parenting, Kids & Teens content from articles, podcasts, to videos.
Want more children’s health and parenting information? Sign up for free to our email list.
Children’s health information and parenting tips to your inbox.
Sign-up to get Mayo Clinic’s trusted health content sent to your email. Receive a bonus guide on ways to manage your child’s health just for subscribing.
You May Also Enjoy

by Guillaume Federighi AKA Hey Gee

by Pat McCaw, M.D.

Privacy Policy
We've made some updates to our Privacy Policy. Please take a moment to review.

How to Discuss Your Mental Health on College Applications
Should you write about depression in your personal statement? Should you disclose mental health challenges elsewhere on your college application? Here’s what experts say.
Within the next few months, many rising high school seniors will be staring at a blank computer screen with the same question on their minds: What should I write about in my college application essay? This question can feel heavy. After all, by the time students approach the end of their junior year, they’ve surely heard lots about “THE” college essay. The concept can feel overwhelming so it’s no surprise that many students struggle when it comes to choosing the perfect topic.
For students who experienced a mental health challenge while in high school, this question takes on another dimension. Should they talk about how they coped with say, depression, or any other mental health condition? Should they refer to it only in passing? Should they avoid mentioning it at all? What is the best way to handle such an important topic?
While this is a very complicated topic, the college planning experts I talked with all offered similar advice.
The Purpose of a College Application Essay
Before thinking about whether or not you should write about mental health in your college essay, you should remember what the essay — or the “personal statement”— is all about in the first place. What is the purpose of the essay?
No matter which prompt students select, and for all college applicants, those with or without mental health challenges, the essay is the only part of the application in which college admissions officers have the opportunity to hear the voices of the student. The rest of the application contains numbers, statistics, and comments from teachers and counselors.
This is why the personal statement, as college planning experts concur, is where you should share part of your true self in the most positive light. Think about what a college wants to know about you as a person, or what a university would gain by having you become a part of the campus community. Dig deep to figure out what makes you, you.
Use your essay as an opportunity to bring your college application to life. Try to strive for it to represent you in an authentic yet optimistic way. One former reader of applications at a top university’s admission office shared a fun way to see if your essay checks out. She asked me, “Does the essay pass the midnight test”?
Picture an exhausted admissions officer with a stack of unread application files on her desk. She is reading yours at midnight at the end of a 16-hour day. Does your essay draw the officer in and make her eager to read until the end of your essay to learn more about you? Will she be eager enough for her to conclude that, yes, we want this student on our campus next fall? Or does your essay sound far too similar to some of the others she’s read that day?
The purpose of your essay is to take the reader beyond the numbers (test scores and GPA) and into who you are as a real live human being.
Experts on Writing About Mental Health
All counselors interviewed for this piece agreed that students’ college essays should not be about their struggles with mental health. Wendy Kahn , a Chicago-based college planner, and Anna Seltz, of Higher Ed U , a college consulting organization in Philadelphia, both spoke about how students should try to talk about themselves in a positive light, taking the opportunity to showcase one of their many outstanding qualities, like intellectual curiosity, personal growth, or maturity.
A couple of the counselors — Bruce Vinik of Vinik Educational Services and Marsha Shaines of College Strategies in Kensington, Maryland — said that the only case in which a student should consider writing about her mental health challenges is if the struggle truly defines her as a person. Even then, both counselors saw this as the rare exception, and suggest that instead, most students should take advantage of the opportunity to explore one of the many other attributes that makes them unique. Vinik says that mental health problems should only be shared in the essay if the college would not be able to understand the applicant without knowing about this part of her. Generally, he discourages selecting this as a primary topic.
The Additional Information Section
All of the college planners mentioned above agree that if your mental health struggle in high school clearly impacted your performance, then you should mention it in the “Additional Information” portion of the Common Application — but only in a factual manner. If you missed three months of your sophomore year to deal with a mental health condition, you should explain that you spent those months dealing with a “health challenge,” overcame it, and are now back on track, advises Vinik.
The three other college counselors generally agreed with this sentiment. All expressed that if the mental health challenges have made an impact on your grades, involvement in class, attendance, or ability to participate in school activities, you should provide a short, factual summary (no more than two paragraphs) for background purposes, always emphasizing your recovery after these difficult moments and your preparedness for a college environment.
Seltz suggests that talking about this in your admissions interview may be another route that applicants can explore. Seltz recommends taking an approach like the one outlined for personal statements above: Briefly explain how the challenge affected your grades and focus mostly on the fact that those problems are now under control. Making sure to emphasize the way/s that the challenge helped you to grow as a person is also important.
All of the college planners suggest that you talk with your high school counselor to ensure that what you are saying about mental illness in the college application is consistent with what the counselor may or may not say in her own counselor recommendation. Or, if you’d prefer that the counselor not address your mental health issues, request that as well. School counselors are almost always open to any guidance you may have for what you’d like them to include in or leave out of your letter of recommendation.
Dealing With Mental Health Challenges Past the Application
Being told that you cannot share a part of yourself that may have had a large impact on your life can be difficult to hear. Unfortunately, mental health is a stigmatized topic, and it’s difficult to explore its nuances and complexities in the short and streamlined format of a college application. It is also extremely important to remember that with or without mental health challenges, you are far more complex than a 650-word personal statement.
The fact that you are not writing about it on your application doesn’t mean that colleges don’t want the “real” you, or that you will be unable to succeed. A mental health condition does not disqualify you from having an excellent collegiate experience by any means, the same way that a physical limitation would not interfere with your success as a student. As you explore your college options, be sure to look for campuses that are particularly mental-health friendly, and focus on finding resources you can rely on as a student. From counseling services to wellness organizations, many campuses make student mental health a priority, and selecting this kind of college will help you embrace your challenges and thrive in a new environment.
If you are worried that your problems are not yet under control — and that college may exacerbate them — you may want to consider taking a gap year and working with a local counselor to prepare for the big transition. There are lots of really wonderful gap year programs for students in this exact position. If you think you might be interested in this option, talk with your school counselor about exploring what programs are available to you.
Be personal in your college application essay — but do so in an optimistic and positive way. The purpose of the essay is to convince the reader that you belong on their campus next fall. Don’t leave the reader with any unanswered questions or red flags about you. Be clear about who you are and your will to enhance whatever campus you find yourself on. This is the best way to tell the story of who you are.
If there are circumstances that need to be explained — such as time off, a drop in grades, or diminished participation in extracurricular activities, do so in a factual and concise manner in the “Additional Information” section.
Yes, you may have experienced a mental health challenge, and/or you may be going to college with mental illness. But don’t let that singularly define you as a person. You have the propensity to offer much more to a college than your diagnosis. And the personal statement essay is the place to show the college who you are as an individual, why you are ready for college, and what strong and special qualities you will bring to the campus community if accepted.
If you’re currently applying for colleges and are planning on taking the SAT or the ACT, our tutors are here to help. Connect with them for your respective test below:
Related Highschool & College Admissions Resources:
- 2023 ACT Test Dates: Upcoming ACT Test Dates for 2023
- Everything You Need To Know About AP Scholar Awards & Recognitions
- 2023 SAT Test Dates: All Upcoming SAT Dates for 2023
- How To Determine If I Should Take the ACT or the SAT
- How Much Do Extracurriculars Matter For College Applications?
RECENT POSTS

ACT and SAT Score Comparison: Score Conversions and Chart

ACT Test Dates 2024: Upcoming Test Dates & Deadlines for the ACT Exam

How To Check Your SAT Score: A Step-By-Step Guide

Sign Up For the Latest News
- 60 Chelsea Piers Ste 6020, New York, NY 10011
- [email protected]
- 844 663 9484

Depression: Should I Talk about My Mental Illness in My Application?

Written by Mary Sue Youn on September 2nd, 2017
- college admissions advice ,
- college applications ,
- First of all, know that you are not alone. According to recent studies by the Center for Collegiate Mental Health anxiety and depression are the most common mental illnesses seen by college counseling centers. In fact, there has been a 30% increase in counseling center utilization on campus over the last five years. Please know that many students struggle with similar issues and colleges are accustomed to these inquiries.
- Don’t be afraid to talk about your struggles in your application. Students dealing with mental illness in high school have often demonstrated tremendous fortitude in overcoming their challenges and carrying on with their schooling. However, frequent absences or substantial dips in grades are noticed during an application review. As an admissions officer, I strongly preferred to hear the reasons behind these anomalies directly from the student, rather than their teacher or guidance counselor. In fact, our counseling center showed us that students who could openly talk about their mental illness and advocate for themselves and what they needed were much more likely to have positive outcomes in the college setting. I particularly advise students to write about their depression if there was a significant change in grades or time away from school while undergoing treatment. Contrary to popular belief, mental illness was not seen in the admission office as a reason to deny the student, but provided necessary context for the admission reader about that student’s high school experience.
- Do realize that you are more than your mental illness—and your main essay should reflect that. The main personal statement of your application should be an expression of your unique personality and interests. Are you a scientist, a writer, an artist? Are you funny, do you love to debate, or are you a meticulous researcher? Your main essay should reflect the wonderful qualities that you bring to any college campus, not only your depression. A statement about your treatment for depression is usually most appropriate for the Additional Information section on the Common Application , or for a supplemental essay in a college’s own portion of the application. Keep the statement short (1-2 paragraphs at most), and focus on the coping skills you’ve developed from treatment that will serve you well in college.
- Be aware of campus resources before you head off to college officially. Ask questions about counseling centers when you visit campus, or give them a call if you are unable to visit. Many campuses provide individual or group therapy on campus, while others refer students to work with therapists local to the area. Even if you are not currently experiencing depressive symptoms, it is important to know what’s available should your depression reoccur during the stresses of college life. The National Alliance for Mental Illness (NAMI) has a wonderful college guide resource to get you started .

amet, adipisicing elit sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt?
Follow these pre-application steps to help your student stay on track for admissions success., related resources.

Read | Posted on May 17th, 2024
The Top 3 FAQs about Pre-Law

Read | Posted on May 15th, 2024
Pros and Cons of Studying Abroad; Listener Q&A
Read | Posted on May 8th, 2024
All about Working with College Admissions and Finance Counselors
Browse categories.
- Applying For Financial Aid
- Choosing The Right College
- College Admissions Consulting
- College Applications
- College Coach Mentionables: News & Events
- College Entrance Exams
- College Essays
- College Loan Advice
- College Visits
- Finding Scholarships
- How To Pay For College
- Meet a College Finance Expert
- Meet An Admissions Counselor
- Uncategorized
Interested?
Call 877-402-6224 or complete the form for information on getting your student started with one of our experts.


Clinical psychology
- Anxiety disorders
- Feeding and eating disorders
- Mood disorders
- Neuro-developmental disorders
- Personality disorders
- Affirmations
- Cover Letters
- Relationships
- Resignation & Leave letters
Psychotherapy
Personality.
Table of Contents
Mention depression in your college essay? (yes or no)
As a BetterHelp affiliate, we may receive compensation from BetterHelp if you purchase products or services through the links provided.
The Optimistminds editorial team is made up of psychologists, psychiatrists and mental health professionals. Each article is written by a team member with exposure to and experience in the subject matter. The article then gets reviewed by a more senior editorial member. This is someone with extensive knowledge of the subject matter and highly cited published material.
In this article, we will explain if you should mention depression in your college essay or not, and other important points to remember while writing your college essay.
Mention depression in a college essay?
College essays are meant to provide an insight into your personality that your academic transcripts and certificates do not. They are a way for you to introduce yourself to the college committee. That is why it is important to mention what is your core personality and who you are as a person. If you feel that depression is now a part of you, something that has changed you and has helped you to grow then you should mention it. College administrators and individuals who will review your college essays know that a lot of students these days experience depression and therefore are accepting of it rather than seeing it as an undesirable trait.
In addition, they accept the possibility that students may sometimes use the services of professional essay writing services if they are experiencing psychological problems.
Reasons to mention depression in your college essay
In case you wish to mention depression in your college essay here are some reasons why you should:
It impacted your high school experience
Your academic performance suffered, to explain a gap year or period, you wish to highlight how you overcame it, to show how you turned your weakness into your strength, it defines you as a person, to highlight how you handle your mental health now.
You shouldn’t just mention your depression in your college essay unless it impacted your high school experience. In case because of depression, you felt that you were unable to participate in the school extracurricular activities or were not able to enjoy it as much as others. Then you can mention it, but ensure that its impact was quite significant in nature. Another reason to mention your depression in your college is to highlight how high school can be a little difficult for some individuals and how it affects one’s mental health negatively. But ensure that you are not blaming the education system but providing a viewpoint.
In case you were unable to perform well academically due to depression, then you can mention it in your college essay. You can provide an explanation as to why your academy performance suffered so much while reassuring the committee that you have bounced back from it and won’t let it affect your college grades now. Especially if you were a student who used to score very high marks and in a particular year were not able to score as much. In case there are inconsistencies between your grades you can use your college essay and an explanation platform for it.
In case you took a gap year or period during your school or after your high school ended you can mention your depression in your college essay. Be sure to explain how and why it was necessary for you to take this year, build upon your mental health and how you were able to successfully overcome depression after taking this gap year. Mention how you felt during this time of period and how other people like your family members, friends and classmates help you with it. Mention how your experience during the gap years was, what other activities did you learn or do during this time period, be sure to mention any internship or course that you did.
A reason to mention depression in your college is it could be to illustrate your journey on how you overcame depression. You could mention the feelings and the emotions that you went through during this time, how your family and friends helped you, and what different activities did you engage in to help with depression. You could also mention your journey of self-realization during the therapy sessions or how going through depression changed your outlook on life and the world in general.
You can mention depression in your college essay to show them how you turned your weakness into your strength, that is how you overcame depression, and rather than seeing it as a mistake turned it into a learning experience. Mention what you learned during this time of yours and how your outlook towards life is no different from before.
If you feel that you are a different person because of depression you can mention it in your college essay explaining what changes it brought in you. In the essay explain what type of a person you were before and how depression changed things about you that you are now proud of. Be sure to only mention in your college essay if you feel that it has changed you and the definition of who you are. Explain your journey from your older self to new you and highlight what realizations you mean about yourself.
If you feel that you are more and better equipped at handling your mental health and actively taking steps to improve it even now, mention your depression in your college essay. In case you have started ensuring that you do yoga or practice mindfulness, take out time to explore your hobbies then it is a good idea to mention these things in your college essay.
Points to remember when you want to mention depression in your college essay
Here are a few points that you must remember while writing and mentioning depression in your college essay:
You are not alone
It is okay to talk about your struggles, you are more than just being depressed, focus on your coping skills, research about your college’s counseling services.
Remember that you’re not alone and that many students just like you have also struggled through depression and gotten into college. College administrators know that and know how tough it can be to deal with and overcome depression. Knowing that you have gone through something as life-changing as depression and come and be able to come out of it. It takes a lot of courage and strength to be able to do that. You are understood and wanted by colleges based on who you are now.
Depression is not an easy thing to go through and it is even harder to overcome it and begin to rebuild your life. It is okay to talk about your struggles, you’re weak moments and times when it was tough for you. Be confident about your life journey and the obstacles that you have faced. There is nothing for you to hide or be ashamed of. Be comfortable in talking and expressing about depression as it will show your maturity and how well you can handle adversities in life.
Remember that depression is something that happened to you and that it does not define who you are. You’re more than just being depressed you’re also all your other personalities and traits. Just like if a person has a cough we do not say that they are “cough”, similarly you had or have depression but you are not “depression”. Do not let depression be the only thing that defines you as you are much more than that.
While writing the college essay be sure to mention what different coping skills and mechanisms did you use to overcome depression. Don’t let the college essay just be about your struggles and the problems that you faced. Mention how you tackled them and overcame them. The faculty is more interested in knowing how you deal with difficulties and problems in life rather than which problem you faced. So let your essay be more about the coping skills that you have used and the new ones that you developed because of depression rather than talking just about the downfalls that depression caused.
While applying to a college ensure that you go through the website properly and research as to what counseling services your college provides in case you have difficulty keeping up with the curriculum and college life. This will also help you have an understanding of what your college’s approach to mental health is. If the college has a proper counseling center where 24*7 help is available. It indicates that the college is aware of the importance of mental health and is working actively to ensure that the students are given the proper treatment and care they wish for.
In this article, we explained if you should mention depression in your college essay or not, and other important points to remember while writing your college essay.
BetterHelp: A Better Alternative
Those who are seeking therapy online may also be interested in BetterHelp . BetterHelp offers plenty of formats of therapy, ranging from live chats, live audio sessions and live video sessions. In addition, unlimited messaging through texting, audio messages and even video messages are available here.
BetterHelp also offers couples therapy and therapy for teenagers in its platform. Furthermore, group sessions can also be found in this platform, covering more than twenty different topics related to mental health and mental illness. The pricing of BetterHelp is also pretty cost-effective, especially considering the fact that the platform offers financial aid to most users.
FAQs: Mention depression in a college essay?
Is it okay to write about depression in a college essay.
It is okay to write about depression in a college essay when you are mentioning it to explain an inconsistency in your academic records. For example, explaining a gap year or drop in grades.
Is it OK to write about mental health in college essays?
It is ok to write about mental health in college essays, but avoid making it the main essay. You can mention it if you deem it to be very important. It is preferable if you do not write your main essay about your mental health.
What should you not write your college essay on?
You should not be bragging about your accomplishments and achievements in your college essay. Your transcripts and other certificates will do that for you. Avoid writing about highly sensitive topics and illegal or illicit behaviors you might have been a part of in the past. Also do not write about how lucky you are to be able to apply there.
Is it bad to swear in a college essay?
Yes, it is a terrible idea to swear in a college essay as many articles by college admission boards have mentioned that using profanities in college essays leads to people losing their seats. They consider using swear words a significant mistake that every student must avoid.
What are the best college essay topics?
The best college essay topics are where one shares their life story, how they learned from difficulties in life, when they challenged a long-held belief of theirs or how they grew as an individual. It can mention things that captivate you, people you admire, or any other topic of your choice.
Do colleges look at mental health records?
It is actually illegal for college to specifically ask for details regarding your mental or physical health. As it is considered discrimination, they can not look at your mental health records.
References
https://www.collegetransitions.com/blog/tackling-depression-anxiety-on-your-college-application-and-beyond
https://www.noodle.com/articles/how-to-discuss-your-mental-health-on-college-applications
https://blog.getintocollege.com/depression-should-i-talk-about-my-mental-illness-in-my-application/
Was this helpful?
Overcome depression and find joy in life again with betterhelp.

Living with depression can feel like an uphill battle, but you don’t have to face it alone.
BetterHelp offers accessible, affordable, and convenient online therapy that can help you manage your symptoms and improve your quality of life. Our licensed therapists specialize in treating depression and can provide you with the personalized support and guidance you need to overcome your challenges.
Whether you’re struggling with feelings of sadness, hopelessness, or fatigue, BetterHelp can help you develop coping strategies, build resilience, and find joy in life again.
Don’t wait to start feeling better – sign up for BetterHelp today and take the first step towards a brighter tomorrow.
Related Posts
How not to gain weight on mirtazapine (9+ amazing tips), why is my postdoc making me depressed, can work on a 3-11 shift lead to depression (+how to cope).

- Campus Culture
- High School
- Top Schools
Addressing Depression in Your Personal Statement
- college application essays
- essay topic
Did you know 20% of teenagers experience depression before reaching adulthood? It is also during this time that college applicants have to answer the most intimate question in order to gain acceptance at their dream school. What defines you?

While it may feel extremely vulnerable to talk about your experience with depression, don’t let that immediately deter you from choosing it as your personal statement essay topic. Here are 5 examples that may help you approach the topic in an essay:
UC Irvine ‘17
Throughout the past few years, I have gone through depression. The inability to focus not only in school, but also in life, is something I have struggled to overcome. The majority of the time, I am able to successfully distinguish my emotions from my academics because of my overly organized tendencies. At other times, the feelings that come with depression are inevitable. Depression, for me, is hopelessness. My biggest struggle with depression is not being able to see the light at the end of the tunnel; therefore, this way of thinking has caused me to feel unmotivated, alone, and frightened. Because of this, I have spent endless nights contemplating my life till 4 or 5 in the morning, I have no motivation to wake up in the mornings, and I feel pain and grief on a daily basis. Keep reading.
Brittanybea
Uc berkeley ‘19.
On a warm August morning I sat shivering and shaking in the waiting room to my doctor’s office. I had my mother make the appointment but didn’t give her the reason; I’m not even sure I really knew the reason. I just knew something was wrong. The past five years had been all uphill - outwardly, at least. I was doing increasingly well in school, growing more independent, and had greater opportunities at my feet. Inwardly, however, was an entirely different story. Those five years felt like an upbeat movie I was watching while in my own personal prison. I was happy for the characters, even excited for their accomplishments. The problem was that my outward self was a character entirely distinct from the internal me. View full essay.
869749923096609FB
Williams college ‘19.
Perhaps the greatest blessing my parents have ever granted me was the move from our apartment in the Bronx to a two-family home in Queens, two blocks away from a public library. The library had all the boons my young heart could desire: bounties of books, air conditioning in the summer, and sweet solace from a dwelling teeming with the cries of an infant sister, a concept I couldn’t yet fathom. Read more.
When I was younger, people chided me for being pessimistic. It was my sincere belief that there were no rewards to be reaped from a life here on earth. I was bored, unhappy, and apathetic. War, injustice, environmental collapse, the mean thing X said to me the other day-it all made me see the world as a tumultuous and unpleasant place. Continue reading.
879216135461584FB
Dish soap, pepper, a toothpick, and an empty pie tin. The first materials I ever used to perform a simple experiment in grade school. Looking back that would be the moment I fell in love with science. I can still feel the excitement I felt as I watched as the pepper dart off to the edges of the pie tin as I touched the water with the end of a soap coated toothpick. Though I didn’t have to question how or why the reaction happened, I never stopped wondering. It was then that a passion for science ignited in me. It was a fire in my soul that could never die out. However, I couldn’t have been more wrong. As I grew older, the fire within me began to dim and in the year 2012, it became extinguished; the world as I knew it had ended. View full profile.
While this essay topic helped these students gain acceptances to UC Irvine , UC Berkeley , Williams , Vassar and NYU , it doesn’t mean it will work in the exact same way for you. Brainstorm and think carefully about what you want to write in your personal statement and how you want to share your own, unique story. For more inspiration, AdmitSee has a database of 60,000+ successful college applications files waiting for you!
About The Author

Frances was born in Hong Kong and received her bachelor’s degree from Georgetown University. She loves super sad drama television, cooking, and reading. Her favorite person on Earth isn’t actually a member of the AdmitSee team - it’s her dog Cooper.
Browse Successful Application Files

Last week, Prompt's CEO shared what mistakes to avoid in your college essay. In Part 2 of this two-part blog series, learn how to pick an essay topic. The key: focus on an admissions officer’s...

With an otherwise great college application, how important can college essays really be? When only 1 in 5 students applying to selective colleges have compelling essays, make sure you avoid this essay mistake....

In this second part of his two-part series, college admissions coach Justin Taylor explains key admissions lessons from 2020, an unprecedented year of firsts, that can help you strategize as we enter into this next application...

In Part one of this two-part series, college admissions coach Justin Taylor explains key lessons about 2020, “a year like no other,” that could seriously boost your chances in 2021, including smarter list building and transcript GPA...
We are so excited to announce that for this year’s scholarship, we selected five scholarship winners to maximize the impact of our $5,000 college scholarship prize money....

- 1. Webinar Series: College Application Prep for High School Juniors
- 2. College Application Lessons from 2020-2021: Strategizing through Covid Changes (Part 2)
- 3. College Admissions Lessons from 2020-2021: Strategizing through Covid Changes (Part 1)

- 5. COVID-19 and Your College Essay: Should You Write About It?
- 6. College Search: How to Find Your Best College Fit
- 7. College Tours 101: Everything You Need to Know
- 8. Waitlisted? 5 Ways to Move from the College Waitlist to Acceptance
- 9. When (and why) should you send additional materials to colleges you’re interested in?
- 10. How to Make Your College Essay Stand Out
- 1. How to Write College Essays to Boost your Chances Part 2: Focusing the Priority
- 2. How to Write College Essays to Boost your Chances Part 1: Biggest Essay Mistakes
- 3. College Application Lessons from 2020-2021: Strategizing through Covid Changes (Part 2)
- 5. Winners of the AdmitSee 2020 College Scholarship
- 6. COVID-19 and Your College Essay: Should You Write About It?
- 7. Education, Access and Systemic Racism
- 8. Applying to BS/MD Direct Medical Programs: Why Early Med School Admission Might be Right for You
- 9. How to Get Off the College Waitlist (5 Go-To Strategies)
- 10. College admissions prep during the Coronavirus

Should I Mention Depression on My College Application?
Colleges scrutinize applications from troubled students more closely.
Should I Put Depression on My College Apps?

Phil Bliss | TheiSpot.com for USN&WR
Growing up in New York City, Emily Isaac studied Hebrew, performed in school musicals, and played soccer. She fantasized about going to a prestigious university like Harvard and becoming a lawyer for Hollywood celebrities. But her drive and ambition faded when she reached high school. She ignored homework assignments and argued with teachers. Her grades dropped to mostly C's and D's. She was so difficult that she was asked to leave three private schools in two years. Emily says she was angry and depressed over a family member's drug use. At age 17 last fall, she was applying to colleges and had a tough decision to make: How to present herself to admissions officers increasingly wary of troubled students?
Concerned about liability and campus safety in the wake of shootings at Northern Illinois University and Virginia Tech, more colleges and universities are scrutinizing the character of applicants. They want to know about students' past behavior, and, if there is any doubt, they will call high school counselors for answers. Admissions officers say "youthful indiscretions" like a schoolyard brawl or an unpaid traffic ticket aren't likely to result in denial letters. But a pattern of troubling behavior could cost someone an admission.
"We're not only admitting students for intellectual reasons but for community reasons," says Debra Shaver, director of admissions at Smith College, a private women's liberal arts school in Massachusetts. "We want to make sure they will be good community members." Smith and other schools acknowledge that making judgments about character is sometimes a messy process. It doesn't involve precise measures like SAT scores or grade-point average. "In some cases, you say, 'This makes me nervous,' and maybe it is an intuition and some reasonable people would disagree, but it goes with the territory," says Bruce Poch, dean of admissions at Pomona College in Claremont, Calif.
Full disclosure. It's not surprising, then, that students like Emily agonize over the decision to disclose personal and academic problems. "We finally hired an independent counselor," says Lisa Kaufman, Emily's mother.
Not all counselors agree on what advice to give families. Some discourage students from bringing up mental illnesses and emotional problems altogether. Others say full disclosure helps when a student's records show poor grades or other inconsistencies that are likely to make colleges suspicious. Shirley Bloomquist, an independent college counselor in Great Falls, Va., says she once called a liberal arts college in Massachusetts to say she was disappointed by its decision to reject an applicant who had written about overcoming a drug addiction. The student had completed a drug rehabilitation program and had been clean for a year. "Colleges are more concerned than ever about student emotional stability," Bloomquist says. "I think it is imperative that the student, the parent, and the high school counselor discuss the situation and decide what should or should not be revealed."
Sally Rubenstone, senior counselor with CollegeConfidential.com and coauthor of Panicked Parents' Guide to College Admission, says being forthright about past behavior or mental health problems doesn't mean "The Jerry Springerization of the College Admissions Essay." "Sometimes I have to implore [students] to stay mum," she says. "There are clearly times when personal problems are too personal—or inappropriate—to include in a college essay."
Emily's problems, however, needed airing—but not all of them. For example, she didn't disclose her troubles in middle school because colleges asked only (via the Common Application) about academic and behavioral misconduct in high school. She says she was asked to leave one high school after a confrontation with another student, but the offense was never recorded in her file, so she didn't volunteer that information either. On the advice of her counselor, Emily wrote cover letters and an essay focusing instead on the reasons for her documented troubles in school and how she had grown from those experiences.
Although colleges would know from her transcripts that she had been at a boarding school for troubled teens, Emily didn't explicitly mention depression in her essay. Rubenstone, who served as Emily's counselor in the admissions process, says, "Colleges can run scared when they hear the word depression. " Emily, who got treatment, hoped colleges would pay attention to her improvement instead. "I thought I was taking a risk, but I had faith that people would understand," she says. In one of her cover letters, Emily wrote: "What I am trying to say is that my past no longer dictates my future and that I am a far more capable, hard-working, mature student than depicted in my forms."
Colleges cannot legally deny admission specifically on the basis of mental illness, but it's hard to account for how that characteristic figures into the calculus of who gets in and who doesn't. Admissions officers undoubtedly are aware that the shooters at Virginia Tech and Northern Illinois had troubled histories before they applied to school: Indeed, the graduate student responsible for the NIU attack had written about his emotional struggles in adolescence in his admission application. Admissions officers, ever mindful of the diversity on campus, also are aware that reports of depressed college students are on the rise.
Not all colleges offer students a second chance. One high school senior in Tucson, Ariz., with an impressive academic record was rejected by a selective liberal arts college after his counselor says he told the school that the student had been disciplined for smoking marijuana on a field trip. The counselor says he helped the student with his essay, believing that if it struck the right tone and offered a sincere apology and a pledge from the student that he would not make the same mistake again, the essay would persuade the college to admit him. It didn't. "This particular school was trying very hard to diminish its reputation as being 'kind of tolerant of druggies'—the very words used by the college representative," the counselor says.
Barmak Nassirian of the American Association of Collegiate Registrars and Admissions Officers says too much pressure is being put on college admission officers who lack the expertise to evaluate the seriousness of an offense or an applicant's emotional well-being. In the absence of clear guidelines, Nassirian says, colleges should stop asking about past behavior altogether. "It's very tempting for colleges to say we're excluding the next Jack the Ripper from sitting next to your son or daughter," he says. "But it's really your son or daughter who is getting nabbed and getting nabbed for having done something stupid in high school."
Common Application. That may be the reason that many high schools don't disclose information about a student's disciplinary history. A recent survey of 2,306 public and private high schools found that only 23 percent of schools said they allowed for the disclosure of such information to colleges, 39 percent said they disclose sometimes, and 38 percent said they never do. The results refer to questions asked by about 340 colleges that use the Common Application, which inquires if students have ever been convicted of a crime or been severely disciplined in high school. This year, 347,837 high school students used the Common Application. Of those, only 2 percent said they had a serious discipline problem in high school, and 0.22 percent said they were convicted of a misdemeanor or felony.
It's not clear how many students refuse to answer the questions or conceal their past troubles. In what one admissions counselor sees as a separate, disturbing trend, high schools that once suspended or expelled students for offenses such as academic dishonesty now strike deals with parents and students that result in less severe consequences and no record of the student's indiscretion. One New York student who has been accepted to several competitive schools says he caught a lucky break when the private high school he attended his freshman year decided that rather than expel him, it would let him quietly transfer to another school after he was caught stealing a biology exam. The school told him it would not notify colleges about the incident. At his new high school, the student was suspended for insulting another student. And again he was able to cut a deal with the principal at that school. The student, who requested anonymity, says he was able to "work off" the suspension from his record by performing community service. He says his guidance counselor discouraged him from bringing up either incident on his college applications. "It's not that I wanted to lie," he says. "I just didn't want to lose everything that I've worked so hard for."
If an applicant's school records raise suspicion, colleges say they will make every effort to verify the information. Some, for instance, will turn to Google, Facebook, or another source on the Internet. But it's not clear how thorough most colleges are when high schools don't cooperate. It is often the case, some say, that an anonymous tipster or an upset parent of a child who was not admitted to the school will come forward. Colleges say a high school's refusal to share information could damage the school's relationship with the college, especially in the event that the applicant is admitted and later commits a crime.
Marlyn McGrath Lewis, director of admissions at Harvard, says high schools that knowingly withhold troubling information about applicants will be held responsible. "We're not a detective agency," she says. "We operate on the assumption that schools are behaving honorably." If administrators learn that an applicant has lied, colleges can rescind offers of admission. That's what happened in 1995 when Harvard administrators found out that an admitted applicant had killed her mother when she was 14. The applicant, a straight-A student, had not disclosed the incident in her Harvard application on the advice of her lawyer.
Seth Allen, dean of admissions at Grinnell College, a liberal arts school in Iowa, says colleges expect that students will answer questions about their past behavior truthfully and completely. "We want to understand if you slipped up why it happened," he says. "If we understand that there is a death in the family or a personal crisis that would help us say, 'This is not a normal pattern of behavior,' we can forgive you." Sometimes, he adds, an honest and thoughtful response can make a candidate more appealing.
Earlier this year, Emily was offered admission to six schools; she has decided to attend Simmons College in Boston. She was turned down by four other schools. "I'm grateful because I feel people are willing to take a chance on me," she says. "It just makes me hopeful that the world is moving away from fear and towards acceptance of those of us who haven't had the easiest times."
Tags: college admissions , mental health , depression
Popular Stories
The Short List: Grad School

Best Colleges

Law Admissions Lowdown

Best Graduate Schools

2024 Best Online Programs

Compare online degree programs using the new U.S. News rankings and data.
Are you seeking one-on-one college counseling and/or essay support? Limited spots are now available. Click here to learn more.
Mental Health in College Students – From Application to Enrollment
August 16, 2022
Sometimes it takes unspeakably tragic events to bring the existence of a widespread problem into the national conversation. In the past decade, highly-publicized suicides at Penn, Hamilton College, MIT, NYU, and Cornell, among others, have moved the discussion of mental health in college students right to the forefront of the higher education discourse.
Thankfully, these are, of course, extreme cases of mental health challenges. However, the shift in focus could benefit the massive numbers of students who enter college each year with depression/anxiety. According to a survey by the CDC in 2022, 44% of American adolescents report feeling persistent feelings of sadness and hopelessness; 28% said that they had thoughts of self-harm at some point in their lives. Perhaps even more startling is the fact that only an estimated 40% of those suffering actually receive any form of treatment (the National Institute of Mental Health). According to just about every survey in the world conducted after March 2020, the pandemic has had a profoundly determinantal impact on teens’ (and everybody’s) mental health.
In this piece, we will offer recommendations for dealing with depression/anxiety on your college application. But perhaps more importantly, we will share what mental health experts and current research says are important considerations for managing your illness on campus.
*Disclaimer: Mind you, we are college planning experts, not mental health experts. We are merely summarizing mental health considerations as related to college admissions and attendance. Your mental health provider may offer additional advice based on the specifics of your situation .
Impact on your high school career
For many, dealing with a mental health condition will negatively impact their high school career in some way, potentially impacting areas such as academic performance, school attendance, teacher relationships, and extracurricular involvement. There is ample statistical evidence to support this. For example, students with social phobia are twice as likely to fail a grade as those without. Students with a depression diagnosis have been found to earn significantly lower grades than their similarly-abled peers.
Given the impact of mental illness on a teen’s academics, a significant number of high school seniors are faced with a difficult choice each year—do I reveal my condition on my college application? There is no blanket answer that will guide every applicant. Ultimately, the decision to reveal your condition is an entirely personal one.
Did your academic performance suffer?
Perhaps your mental health issues were managed successfully and never impacted your grades. If this is the case, we advise that there is no reason to reveal your condition on an application. You should, however, still check out our recommendations on how to check out a college’s mental health services (below).
If your academic performance did suffer as a result of your condition and you do choose to share your challenges with prospective colleges in an essay and/or interview, we recommend that you consider framing your experience in one of the following ways:
The “overcoming obstacles” angle
Overcoming challenges and citing evidence of personal growth can be a winning story arc. If a bout of depression during your sophomore year contributed toward failing grades but you received treatment and rebounded academically the following year, then revealing that journey may be extremely helpful to your admissions chances. Knowing that you faced a significant challenge in your life and successfully emerged from it speaks volumes about your resilience, maturity, and grit, traits that are greatly valued by admissions officers.
Weakness as strength
Another approach is highlighting the strength that you draw from what others call an “illness.” An associate of Abraham Lincoln said of our 16th president that the “melancholy dripped from him as he walked.” Yet, many historians feel that Lincoln’s lifelong depression helped sparked his legendary wisdom, insight, and brilliant strategic thinking. Lincoln was hardly alone. Many of the greatest, most creative minds throughout history were, at least in part, driven by mental conditions. Darwin, Michelangelo, and Einstein were all likely sufferers of Obsessive Compulsive Disorder. If we were to list all of all the great writers, artists, comedians, actors, and directors who were influenced by depression and anxiety, this blog post would be longer than the 1,017 page novel, Bleak House, penned by Charles Dickens, who was himself a lifelong victim of severe depression.
The semantic shift
Cautious applicants might consider simply substituting the term “medical condition” for “mental illness.” After all, mental health issues are treatable medical conditions in the same vein as mono or a broken bone. Simply stating that you were afflicted by a “serious medical condition” which caused a temporary academic decline and led to you quitting the school newspaper and the baseball team will suffice.
Check out a college’s services ahead of time
In a recent survey of college students with a diagnosed mental health condition, 45% rated their respective college as being somewhere between supportive and very supportive. The other 55% felt that mental health care on campus was less than ideal. Factors that were rated as being most important by students included: access to a psychiatrist for medication management, a 24-hour crisis hotline, community connections to additional mental healthcare, and the school’s overall culture of understanding that college can be stress-inducing and that mental health is paramount.
It is essential that parents and students research the mental health services on campus ahead of time. Check out each prospective college’s counseling office online to get a sense of what is available to students. If a college does not offer long-term therapy on campus, then parents should take the reins and find a good private therapist located near campus who accepts their insurance. Do this well before school starts.
Colleges are expanding mental health services
Many state universities, despite budget crunches, are recognizing the need to expand their mental health offerings. For example, in the fall of 2017, UCLA began offering free online screenings for depression; 2,700 students took advantage. Ohio State opened a dozen new mental health clinics in 2016. Penn State has increased their spending on mental health significantly in the last few years. The University of Michigan and Virginia Tech, in an attempt to make mental health more accessible, have embedded counselors in buildings around campus, rather than at one centralized location. Many schools operate prevention/wellness programs that assist students before they enter a crisis. These schools include Harvard, Georgia Tech, UVA, and Bowdoin College.
Amherst, Skidmore, Princeton, Drexel, and Carnegie Mellon are just a handful of schools that now offer access to 24-hour crisis hotlines manned by either peers or professional counselors. Unfortunately, excessively long wait times for a counseling appointment at many schools persist. At schools like Northwestern, Carleton College, and WashU, wait times to see a counselor range from one-to-three weeks.
Relevant statistics on mental health at college
Just to highlight some other meaningful stats on the subject:
- Only 50% of college students report disclosing their mental health issue to their school
- Of those with a diagnosed mental illness who dropped out of college, 64% directly attribute this event to their condition/disorder.
- Only 36% of college students with a mental illness are sure that their university includes mental health information on their website.
- 39% of students reported a wait time of 5+ to obtain an appointment for clinical services and supports.
- 73% of those entering college with previous mental health concerns have experienced a “mental health crisis” while on campus.
- Half of students believe that their peers will think less of anyone receiving treatment for mental health.
- The percentage of college students seriously considering suicide has doubled in the last decade.
- More than 1,000 suicides occur on college campuses each year.
College Transitions bottom line
If you are going to discuss your depression, anxiety, or other mental condition in your application, do so in a strategic manner for the purpose of illuminating otherwise unexplained inconsistencies in your academic record. A well-conceived and well-delivered narrative about your struggles with mental illness can be beneficial to your admissions chances. Contrarily, a poorly crafted disclosure may have the opposite effect.
Of even greater importance is that you do your research on the mental health services offered at each prospective college. Ensuring that the necessary supports at your disposal is critical to your overall well-being. It is also likely critical to your academic performance over the next four years.
To view hundreds of free and easy-to-sort tables of higher education data, visit our DATAVERSE .
- Application Strategies
Andrew Belasco
A licensed counselor and published researcher, Andrew's experience in the field of college admissions and transition spans two decades. He has previously served as a high school counselor, consultant and author for Kaplan Test Prep, and advisor to U.S. Congress, reporting on issues related to college admissions and financial aid.
- 2-Year Colleges
- Best Colleges by Major
- Best Colleges by State
- Big Picture
- Career & Personality Assessment
- College Essay
- College Search/Knowledge
- College Success
- Costs & Financial Aid
- Data Visualizations
- Dental School Admissions
- Extracurricular Activities
- Graduate School Admissions
- High School Success
- High Schools
- Homeschool Resources
- Law School Admissions
- Medical School Admissions
- Navigating the Admissions Process
- Online Learning
- Outdoor Adventure
- Private High School Spotlight
- Research Programs
- Summer Program Spotlight
- Summer Programs
- Teacher Tools
- Test Prep Provider Spotlight
“Innovative and invaluable…use this book as your college lifeline.”
— Lynn O'Shaughnessy
Nationally Recognized College Expert
College Planning in Your Inbox
Join our information-packed monthly newsletter.

COMMENTS
Core Tip: This study reviewed the extant literature by identifying nonpathological factors related to college students' depression, investigating the methods of predicting depression, and exploring nonpharmaceutical interventions for depression among college students.The influencing factors can be categorized into students' demographic characteristics, college experience, lifestyle, and ...
The author argues that it is not advisable to write about mental health issues such as ADD or anxiety in your college application essay, as it may raise doubts about your ability to cope with college. She suggests focusing on other topics that showcase your strengths and interests, and seeking help if you need it.
COVID-19 and Student Mental Health. Empirical studies reported a high prevalence of college mental health issues during the early phase of COVID-19 around the world (Cao et al., 2020; Chang et al., 2020; Liu et al., 2020, Rajkumar, 2020; Saddik et al., 2020).In the U.S. a few, but a growing number of empirical surveys and studies were conducted to assess college students' mental health ...
This web page features 10 students who speak candidly about their mental health issues, such as depression, anxiety, and stress, and how they affect their college experience. They also offer suggestions for how professors and schools can better support them.
The article explores how colleges and universities are responding to the rising demand for mental health care amid the pandemic and other challenges. It discusses the creative solutions, such as group therapy, peer counseling, and telehealth, as well as the role of faculty and staff in supporting students.
Depression can take a toll on many aspects of a young person's life, including academic performance, social life, and physical health. It can also increase their risk of substance abuse and co-occurring mental health conditions. For this reason, it is crucial to recognize the signs of depression in college students and provide tools, resources ...
Learn how to talk about mental health or disability in your college applications without compromising your chances of admission. Find out what to focus on, what to avoid, and what resources are available for your well-being in college.
Learn how to approach the topic of depression in your college essay thoughtfully and sensitively. Find out how to focus on growth, self-awareness, relevance, and feedback, and how to avoid oversharing.
The distress that comes with anxiety and depression can impact many aspects of a student's life. Research from 2021 revealed that untreated mental health is linked to alcohol and substance ...
Learn how depression affects college students and what you can do to cope with it. Find out the common causes, signs, and treatment options for depression, and how to get help from your college health center or other resources.
In their essay, they wrote frankly about depression, anxiety and shame after their mom's cancer diagnosis and eventual death — providing context for why they "did not look like what was ...
Depression negatively affects a student's motivation to learn. 3.37: 1.405: Unfair treatment by teachers causes academic depression in students. 3.12: 1.620: Depression has negatively affected my learning capabilities. 2.99: 1.280: Depression has negatively affected my academic grades. 3.19: 1.201: Sometimes I don't see value in my life. I feel ...
The central hypothesis for this study is that college students have a higher rate of anxiety and depression. The study will integrate various methodologies to prove the hypothesis of nullifying it. High rates of anxiety and depression can lead to substance misuse, behavioral challenges, and suicide (Lipson et al., 2018).
Learn how to write an essay about depression from personal stories and insights. Find out the causes, types, and treatments of depression and how it affects people's lives.
Learn how to recognize and support your child's mental health if they are struggling with depression or anxiety in college. Find out the common causes, signs and strategies to cope with depression and access campus resources.
Learn when and how to mention your mental health challenges in your college essay or additional information section. Get expert advice on how to showcase your strengths and resilience in a positive light.
Learn how to handle the topic of depression in your college application process from a former admissions officer. Find out when and how to write about your treatment, and what resources are available on campus.
Learn why and how to talk about your depression in your college essay, and what benefits and challenges it can bring. Find out the reasons, tips and points to remember while writing about your mental health journey.
Learn from real examples of college applicants who shared their personal stories of depression and how it shaped their identity and goals. Find out how to approach this sensitive topic in your personal statement and stand out from other candidates.
Rubenstone, who served as Emily's counselor in the admissions process, says, "Colleges can run scared when they hear the word depression. " Emily, who got treatment, hoped colleges would pay ...
Thankfully, these are, of course, extreme cases of mental health challenges. However, the shift in focus could benefit the massive numbers of students who enter college each year with depression/anxiety. According to a survey by the CDC in 2022, 44% of American adolescents report feeling persistent feelings of sadness and hopelessness; 28% said ...
r/ApplyingToCollege is the premier forum for college admissions questions, advice, and discussions, from college essays and scholarships to college list help and application advice, career guidance, and more.
Unless you can say you've overcome it, it's not a good idea. The reasoning is pretty callous, but colleges don't like depressed people or those prone to panic attacks on campus. Especially with eating disorders, because people with eating disorders tend to die, and having a death on campus looks really bad for the college. 3.