
- Tutoring Coming Soon

5HR02 Assignment Example
- August 16, 2021
- Posted by: Harry King
- Category: CIPD Level 5

Task One – Presentation Pack
The MD has asked you to prepare a presentation to the managers to position them around key contemporary labour market trends and their significance for workforce planning. This will also cover turnover and retention trends and the factors that influence why people choose to leave or remain. The pack needs to include presentation slides and supporting notes.
The presentation must include:
- an explanation on how organisations strategically position themselves in competitive labour markets. (AC 1)
- an explanation of the impact of changing labour market conditions on resourcing decisions. (AC 2)
- a discussion on the role of government, employers and trade unions in ensuring future skills needs are met. (AC 3)
- an examination of turnover and retention trends and the factors that influence why people choose to leave or remain (AC1)
It is essential that you refer to current labour market and turnover and retention trends / conditions to ensure that your work is contemporary and relevant. Please ensure that any references and sources drawn upon are acknowledged correctly and supported by a bibliography.
Task Two – Inhouse Manual
For this task you need to create chapters for an inhouse manual for managers on what is involved in Talent Management and Workforce Planning and how to undertake appropriate actions. As your manual is being prepared for managers, it should be written in a professional format and style.
Your manual should have a title page, contents page and a brief introduction. Your manual should be broken down into chapters covering the following:
Chapter 1 – Workforce Planning
- an analysis of the impact of effective workforce planning. (AC 1)
- an evaluation of the techniques used to support the process of workforce planning
- explain approaches to succession and contingency planning aimed at mitigating workforce risks. (AC 3)
- assess the strengths and weaknesses of different methods of recruitment and selection to build effective workforces (AC 4)
Chapter 2 – Talent Management
- compare different approaches to developing and retaining talent on an individual and group level. (AC 2)
- evaluate approaches that an organisation can take to build and support different talent pools. (AC 3)
- evaluate the benefits of diversity in building and supporting talent pools (AC 4)
- explain the impact associated with dysfunctional employee turnover. (AC 5)
Chapter 3 – Contractual Arrangements and Onboarding
- Assess suitable types of contractual arrangements dependent on specific workforce
- Differentiate between the main types of contractual terms in contracts. (AC 2)
- Explain the components and benefits of effective onboarding. (AC 3)
It is essential that you refer to academic concepts, theories and professional practice for the tasks to ensure that your work is supported by analysis. Please ensure that any references and sources drawn upon are acknowledged correctly and supported by a bibliography.
INTRODUCTION
Talent management and workforce planning are essential elements of people practice that contribute to organisational performance and attainment of organisational goals. Managing talent and workforce are essential for dealing with various organisational challenges and strategising people practice in businesses. While workforce planning is a core business process that aligns people strategy with organisational needs, talent management involves understanding employees potential in a workplace to speed up the process of organisational growth and development. Importantly is to understand that there is an existing relationship between an effective workforce and the development of suitable talent pools in an organisation. Therefore, the two should be structured to favour organisational goals and objectives. This manual gives an insight into contracting, effective onboarding, labour market trends and their significance to an organisation and practical intervention tools required to mitigate risks associated with poor workforce planning and talent management.
Workforce Planning
1.1 ac 2.1 – an analysis of the impact of effective workforce planning..
Workforce planning refers to the process of balancing skills with organisational demand (Weeks, 2020). It is a core business process that involves analysing the current workforce and establishing future labour supply needs, establishing the existing gap between the present and the future and coming up with solutions that can be accomplished in an organisational setting to accomplish the general workforce goals and objectives. Effective workforce planning primarily focuses on getting the right workforce, placed at the right roles, at the right time and for the right cost (Weeks, 2020). Depending on organisational needs, workforce planning can either be long term or short term. However, workforce planning should be linked to organisational goals as part of the strategic business process essential for engaging with the workforce change agenda.
Effective workforce planning has various impacts on an organisation. Objectively, there are more positive impacts of effective workforce planning compared to the negative impacts. The positive impacts manifest as benefits to the organisation, and they include reduced labour costs, enhanced employee retention, improved productivity and quality output, employees’ work-life balance, effective identification and response to changing customer needs and identification for focussed people development.
Enhanced employee retention occurs as a result of a thorough assessment of business needs and the potential of the existing workforce. In addition to hiring a talented workforce as part of effective workforce planning, organisations through the HR office can identify industrial positions that are hard to fill and if the employees left it would damage organisational performance and use workforce planning to establish the cause of turnover and come up with strategies to mitigate the causes and enhance retention (Downs, 2016).
Improved productivity and quality output can be achieved through effective workforce planning through avoidance of delays and labour supply distractions that impact organisational performance. Effective workforce planning allows organisations to meet the set production goals and creates a clear pattern for the supply and demand of the workforce in an organisation. Additionally, it acts as a guidance tool for managers to prioritise recruitment and selection in different business cycles.
1.2 AC 2.2 – an evaluation of the techniques used to support the process of workforce planning
Supporting the workforce planning process is an integral part of people practice that requires effective communication between HR and other stakeholders in an organisation. The workforce planning process should be based on primary organisational strategies that link people management and daily business operations (Weeks, 2020). It is important to note that workforce planning can take many forms, but it can best be described using five ideal stages that are interactive, as illustrated in the figure below.
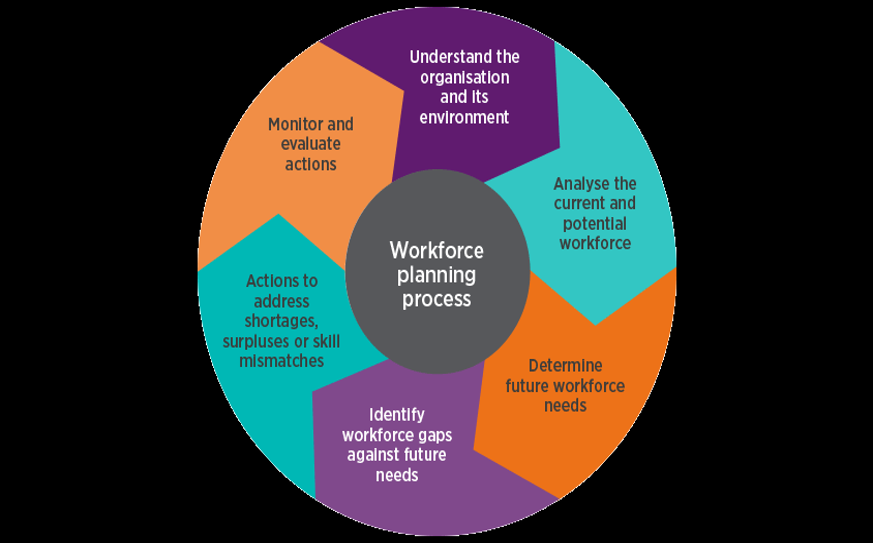
The first step of workforce planning is understanding the business and its operating environment. This step involves the identification of the business structure and changes that can be made to the structure and processes to enhance labour supply. For example, workforce planning can assess if a business is willing to adopt new technology so as to hire a limited number of employees or employees who have adequate skills and knowledge to handle the new technology. The second step involves an analysis of the workforce. It involves identification and analysing skills, talents, abilities and knowledge and other employee views and attributes that comprise the workforce in an organisation. Analysing the workforce is essential for establishing reasons for turnover in different departments as well as causes of understaffing and departments affected.
The third step is determining future work needs through the identification of gaps in workforce skills and knowledge. This stage is achieved by the use of various workforce planning tools such as scenario planning tool. It shows the future industrial needs in terms of skills, capabilities and knowledge. Establishing future workforce needs is essential for business continuity and sustainability as contingency and adaptive plans can be developed to meet future needs. The fourth step is the development of an action plan that has functional, numerical and adaptation flexibility. This is an action plan that can be easily adopted and affect change in an organisation as need it may be needed. Implementation of the action plan requires effective communication to enhance the workforce planning efficiency. The fifth and final step is monitoring and evaluation. It involves regular reviews of outcome to establish effectiveness and areas of weakness (pierce, 2017).
1.3 AC 2.3 – Approaches to succession and contingency planning aimed at mitigating workforce risks.
Succession planning is one of the fundamental people practice functions that mitigate numerous organisational risks. CIPD (2020) defines succession planning as a process of identifying and developing potential future leaders and managers of senior positions. The primary purpose of succession planning is to ensure that the key roles and positions in an organisation are filled in case of a resignation or sudden departure. There are different approaches to succession planning.
The traditional approach to succession planning involves large organisations developing highly structured, confidential top-down succession plans that were designed to identify an internal successor for each of the senior positions. However, changes in organisational structures with most organisations adopting flatter other than hierarchical structures has made the traditional approach obsolete. An example of a hierarchical succession plan is attached in appendix A.
Modern succession planning involves openness and diversity, and it is linked to an organisations talent management practice. This means that the successor is identified based on talent, skills and abilities, and they do not have to come from within the organisation but can also be sourced externally. A good example to illustrate the modern approach is the progressive organisations. These organisations utilise the whole workforce approach in managing and developing talent within the organisation, then identify the critical business roles at all levels of the organisation. The modern approach is most suitable for managing Workforce risks, as it is based on abilities and development at all levels of an organisation.
1.4 AC 2.4 – Strengths and weaknesses of different methods of recruitment and selection to build effective workforces
According to Green (2020), the process of attracting the right workforce at the right time for the right role and cost is known as recruitment. Selection, on the other hand, refers to the process of shortlisting and assessing the recruited candidates. Recruitment is a critical resourcing element as organisations should attract the most talented individuals to perform various organisational roles. People practitioners in an organisation are responsible for recruitment and selection, which may be conducted differently.
Recruitment can be done through an external strategy that may include outsourcing the process to a recruiting agent. Although this approach is used by organisations that don’t have HR departments, such as architects and lawyer, it provides the most talented candidates. The disadvantage of using this method is that it can be very expensive. Other recruitment methods include recruitment using online sources, use of internal referral schemes and local arrangements based on an organisational relationship with the community, learning institutions or jobcentres.
Methods of selection described in the CIPD (2020) website include psychometric testing, selection interviews, and assessment centres. Selection should be made fairly, putting into consideration organisational needs and objectives. The figure below illustrates different recruitment and selection methods with their advantage and disadvantages.
Talent Management
2.1 ac 3.2 – approaches to developing and retaining talent on an individual and group level..
Talent development in an organisational setting is linked to various formal and informal learning interventions. Organisations can adopt different approaches to developing and retaining talent on an individual and team level by adopting various techniques. The common approaches to developing and retaining talent include the use of continuous learning and development program. Internal learning and development programs are essential for developing the talent of the existing workforce through skilling and reskilling of employees. The primary advantage of using learning and development programs for talent development and retention is that it enhances employees’ skills and abilities and prepares them to meet future organisational needs.
Coaching and mentoring is an important informal approach that is designed to meet individual needs in the talent development process. Coaching and mentoring involves the development of programs that enhance talent development. While coaching is an effective way of fostering skills, mentoring involves the preparation of an employee to engage in higher responsibilities. This approach is designed to foster face to face interactions between the coach/mentor and the person undergoing mentorship. It is a suitable approach to talent retention as it enhances the relationship between employees and their managers who interact during mentorship and create an understanding that is essential for improved organisational performance.
2.2 AC 3.3 – Approaches that an organisation can take to build and support different talent pools.
Talent pools are groups of high performing employees who are being developed to assume greater responsibilities in particular business areas. Talent pools are the basis for organisational succession planning. Employees that should be assigned to talent pools are high performing employees, high potential employees and people who embody organisational culture and values. There are various activities that an organisation can undertake to build and support an effective talent pool.
Firstly, organisations need to create a continual assessment process that analyses the current talent needs and forecasts future organisational needs. An effective talent management system is essential for this analysis, and technological means can also be applied. Open communication and collaboration among employers and employees are essential for talent acquisition and retention of an effective talent pool.
Secondly, an organisation should network both internally and externally. An effective talent pool comprises internal employees and outsiders that have the potential to benefit an organisation. Employers can use social media to build their talent pool by attracting and retaining records of the best candidates. With technological advancements, organisations should use the internet to build and support their talent pool.
2.3 AC 3.4 – Benefits of diversity in building and supporting talent pools
A diverse workforce is essential for establishing a diverse talent pool in an organisation. A diverse talent pool means that an organisation can benefit from different capabilities that enhance organisational performance and competitive advantage. Organisations with diverse workforce attract talent from a global scale which is resourceful for the organisation. The second benefit of diversity is that the workforce can deal with a wide range of customers, thus expansion and enhanced productivity.
Another benefit of diversity is that it gives an organisation market competitiveness that enhances organisational developments by creating new opportunities for the business. By supporting and including a diverse workforce organisation brand, employees select the organisations as an employer of choice. Diversity in recruitment and retention is essential for the development of a positive corporate reputation. With enhanced competitive advantage, a business can enjoy enhanced productivity and performance.
2.4 AC 3.5 – Explain the impact associated with dysfunctional employee turnover.
Abnormal rates of employee turnover are known as dysfunctional employee turnover. Usually, this is a higher rate than the usual turnover rate experienced in an organisation—dysfunctional employee turnover costs organisation financial and non-financial costs. Financially, the recruitment and selection process can be costly in terms of resources invested in identifying and selecting a talented workforce. Industries with resource scarcity can also suffer losses as finding skilled personnel might take longer than expected. This means that dysfunctional turnover can cost an employer valuable productivity time and profits that could have been generated.
Dysfunctional turnover results in an increased workload for the remaining employees whose productivity and morale may be affected. In turn, this can be costly for the business as the rate of production and performance will decline. HR practitioners need to develop and implement a strategic workforce plan that ensures effective recruitment and selection and minimises the rate of turnover in an organisation (Peters, 2020).
3. Contractual Arrangements and Onboarding
3.1 ac 4.1 – assess suitable types of contractual arrangements dependent on specific workforce needs.
Employment contracts refer to a legally binding agreement between an employer and employee (Suff, 2020). It is important to note that contractual agreement is based on expressed terms and implied terms as agreed by the employee and employer. According to the Employment Act, there are different types of employment contracts that are acceptable in the UK.
First is the permanent terms employment contract. This contract is indefinite in nature. It involves an agreement of continuous work collaboration between the employee and employer until either party is no longer willing to continue with the contract. In this contractual agreement, the employee is entitled to all forms of benefits as stipulated in the Employment Act. Works that mostly utilise this type of contracts are jobs offered by government institutions or agencies (Suff, 2020).
The second type of contractual agreement is the fixed term or temporal employment contract. This contractual agreement has a start date and an end date. Importantly is to understand that employees under these contracts are entitled to the same privileges and rights as those in permanent employment contracts. At the end of the contract duration, an employer may decide to renew the contract if the employee agrees to the terms or vice versa.
The third type of contractual agreement is the independent contractor. This is also known as a self-employed person. Independent contractors are not bound by employment contracts but by contracts of work. This means that they are responsible for their tax compliance and other statutory deductions and benefits. Consultants such as engineers and lawyers primarily work under independent contracts (Suff, 2020).
3.2 AC 4.2 – Differentiate between the main types of contractual terms in contracts.
The main terms of contractual terms in a contract include the expressed terms and the implied terms. Expressed terms are terms that are actually stated in the contract document or are communicated verbally. Written expressed terms can be contained in the employment contract or in other organisational documents. Express terms should be compliant with relevant laws, and employers should be careful to comply with the minimum legal standards for each express term they use. For example, when employing a new worker, the employment contract contains express terms that detail information on the wages, work hours, and leaves, which are express terms supported by the law.
On the other hand, implied terms refer to contracts that are neither written nor spoken but emerge from circumstances or a mutual understanding. Implied contractual terms can either be implied facts or fundamental law. An example of an implied term could be working overtime. Although the employment contract may not have stated overtime compensation, there is an implied contract that all employees working overtime should be accordingly compensated. The primary differences in expressed and implied contractual terms are summarised in the table below.
3.3 AC 4.3 – Explain the components and benefits of effective onboarding.
Onboarding is the process through which employees adjust to their new roles and work environment. It is important to note that it is not only the new employees who need onboarding but also tailor-made onboarding programs that can be developed for various groups such as newly promoted employees, remote workers and also the transferred staff. A practical onboarding component includes initial orientation, functional training, role clarification sessions, team assimilation, and leadership assessment (Sherwood, 2017).
The initial orientation is the process that involves the introduction of new members to the organisation. After the introduction, the members are then provided with an overview of the organisation’s products, activities, and structure. Role clarification is crucial for guiding employees towards achieving organisational goals. Team assimilation and leadership assessments are the last stages between 60 and 90 days into an organisation.
The primary benefits of an effective onboarding program include:
- Employees settle in quickly
- Employees are easily integrated into their respective work teams or groups.
- The new employees easily understand the organisational values and culture
- Comfort makes it easy for employees to be more productive
- Employees are able to work to their highest potential.
CIPD (2020a). Diversity and Inclusion in the Workplace | Factsheets | CIPD . [online] CIPD. Available at: https://www.cipd.co.uk/knowledge/fundamentals/relations/diversity/factsheet [Accessed 11 May 2021].
CIPD (2020b). Succession Planning | Factsheets . [online] CIPD. Available at: https://www.cipd.co.uk/knowledge/strategy/resourcing/succession-planning-factsheet#gref [Accessed 11 May 2021].
Downs, B. (2016). Benefits of Workforce Planning – Business Benefits Group . [online] Business Benefits Group. Available at: https://www.bbgbroker.com/benefits-of-workforce-planning/ [Accessed 11 May 2021].
Gill, R. (2015). Why the PR strategy of storytelling improves employee engagement and adds value to CSR: An integrated literature review. Public Relations Review , 41(5), pp.662–674.
Green (2020a). Recruitment Process Overview | Factsheets . [online] CIPD. Available at: https://www.cipd.co.uk/knowledge/fundamentals/people/recruitment/factsheet#gref [Accessed 11 May 2021].
Green, M. (2020b). Induction | Factsheets . [online] CIPD. Available at: https://www.cipd.co.uk/knowledge/fundamentals/people/recruitment/induction-factsheet#gref [Accessed 11 May 2021].
Kotelva, D., (2018). Which ERP system is better: Oracle vs SAP vs Dynamics 365? | Infopulse. [online] Infopulse. Available at: https://www.infopulse.com/blog/which-erp-system-is-better-oracle-vs-sap-vs-dynamics-365/
Peters, R. (2020). Employer Branding | Factsheets . [online] CIPD. Available at: https://www.cipd.co.uk/knowledge/fundamentals/people/recruitment/brand-factsheet#gref [Accessed 11 May 2021].
Pierce (2017). 5 Simple Steps to Efficient Workforce Planning | Mitrefinch Inc. [online] Mitrefinch. Available at: https://mitrefinch.com/blog/5-simple-steps-workforce-planning/#:~:text=%20Follow%205%20Simple%20Steps%20to%20Efficient%20Workforce [Accessed 10 May 2021].
Sherwood, K. (2017). 5 Components of Successful and Practical Onboarding . [online] Training Industry. Available at: https://trainingindustry.com/articles/onboarding/5-key-components-of-successful-and-practical-onboarding/ [Accessed 11 May 2021].
Suff, R. (2020). Contracts of Employment | Factsheets . [online] CIPD. Available at: https://www.cipd.co.uk/knowledge/fundamentals/emp-law/terms-conditions/contracts-factsheet#gref [Accessed 11 May 2021].
Taylor, S. and Woodhams, C. (2012). Managing people and organisations . London: Chartered Institute Of Personnel And Development.
Weeks, A. (2020). Workforce Planning | Factsheets . [online] CIPD. Available at: https://www.cipd.co.uk/knowledge/strategy/organisational-development/workforce-planning-factsheet#:~:text=The%20following%20points%20are%20key%20in%20workforce%20planning%3A [Accessed 11 May 2021].
Weeks, A. (2021). Talent Management Overview | Factsheets | CIPD . [online] CIPD. Available at: https://www.cipd.co.uk/knowledge/strategy/resourcing/talent-factsheet [Accessed 11 May 2021].

5HR02 Talent management and workforce planning assignment guideline
Introduction to the unit 5hr02 talent management and workforce planning.
5HR02 is a unit that helps learners understand the labour market trends and their connotation in workforce planning to attract suitable candidates to join an organisation. Learners review employers’ role in positioning their organisation in the labour market. Professionals analyse the labour market before making resourcing decisions to ensure that they have the right people for the available job opportunities in the organisation.
Learners gain insight into the diverse workforce planning processes and techniques and the different recruitment and selection methods. These are significant in ensuring that effective workforces are built to enhance the retention of workers in an organisation. Additionally, the unit provides information on employee turnover trends in organisations and develops strategies effective to enhance employee retention and develop talent pools.
5HR02 Assignment guideline
The assessment introduces a case study of OcMara Industries, a global organisation operating in the energy sector. Students are expected to provide evidence to help understand the labour market trends. As the organisation expands into more sustainable energy sources and environmentally productive processes, the senior managers have developed people practice objectives. The objectives are to recruit staff members with skills and capabilities to serve in the new areas of development and retain them to protect them from being poached by competitors.
As the students prepare to complete the assessment, they must get insight from CIPD factsheets articles. Among the most important factsheets that will guide students in completing the assessments are the resource and talent planning factsheet that explains the talent management strategies and approaches to managing people. The employee and turnover retention factsheet identifies why employees leave the organisation and develop strategies and practices to retain talent. The CIPD Podcast “From surviving to thriving: key changes facing people practice in 2020” provides a discussion of changes that need to be implemented at work, such as work-life balance to build a fair, brave and equal workplace for all employees. 5HR02 assignment is divided into three tasks. The first task is a poster presentation for strategic positioning and the labour market, the workforce planning and recruitment pack, and finally, a proposal presentation pack on talent retention.
Task 1: Strategic positioning and labour market
The students will prepare a poster presentation to the people practice manager on research about the labour market trends in the UK. Students will refer to “SAP”, a company that won the Employer Brand Management Awards in 2019. The presentation will provide answers to the following assessment criteria sections;-
AC 1.1 An explanation of how “SAP” strategically positions itself in the competitive marketplace
Students will review SAP engagement in positioning itself in the labour market. Learners bring evidence by analysing the organisation’s competitive environment and evaluating the strengths and weaknesses of organisation positioning and employee experiences. Other characteristics that the students should look at while answering the question are;-
- SAP as an employer of choice
- Employer branding
- Organisational ethics and reputation
- Organisational image
- Rewarding and SAP culture
AC 1.2 An explanation of the changing labour market conditions and their impact on the UK
Learners explain the differences between the tight and loose market conditions, with examples of the countries with the defined market conditions. For example, the UK has a tight labour market condition while Saudi Arabia has a loose labour market condition. Next, learners explain the trends in labour supply and demand in the energy sector and the reasons for the identified trends considering the external business environment. Essential factors to consider are the political, economic, social, technological, environmental and legal issues that affect resourcing decisions made within organisations in the energy sector. Students also explain how the crises affect employee retention and skills shortage in the energy sector.
AC 1.3 role of the government, employers and trade unions in ensuring future skill needs are met in the UK global energy sector.
Governments ensure that future skills needs are met by funding for numeracy, literacy and IT skills. The government ensures that organisations’ policies are implemented to help analyse the future skills needs of the employees in the energy sector. Governments ensure that employers meet the workforce requirements that enhance the recruitment of skilled people into the job.
Employers provide development opportunities and programmes to improve employees’ skills. Training and development programmes help improve employees’ knowledge and quality of work. The energy sector benefits from employers who provide development opportunities and experiences adequate to support the accomplishment of future skills.
Trade unions develop agendas that support employee learning and development. They strive to keep the agendas real and identify representatives to work with employers in implementing the agendas.
Task 2: Workforce planning and recruitment
The second task in the unit requires students to present a report to the company manager in an HRBPS meeting on the workforce planning and recruitment concept. The section provides answers to the following questions;-
AC 2.1 Analysis of the impact of workforce planning in terms of forecasting demand for labour utilising both internal and external sources of supply
Students explain the gaps between labour demand and supply explain the pros and cons of forecasting in workforce planning when utilising internal and external sources of supply for OcMara Company. In explaining this answer, students will examine the benefits and disadvantages of developing internal talent and how OcMara would benefit from developing talent from within the organisation. In the same case, the advantages and disadvantages of developing external talent at OcMara are explained to answer the question comprehensively.
AC 2.2 evaluation of the effectiveness of promotion/demotion rates, employee turnover rates and critical incident analysis techniques used to support the workforce planning process
Students explain the techniques that managers use in workforce planning processes. Learners explain the importance of promotion and demotion in supporting workforce planning processes. They also explain the value of measuring employee turnover the pros and cons of supporting workforce planning. Learners then define critical incident analysis and its effectiveness in workforce planning. Finally, students explain these techniques by linking them to OcMara.
AC 2.3 an explanation of how the appraisal can be used to identify who is interested in progression, managing contingency and mitigating risks through OcMara developing their talent pools
The learners define appraisal and explain how this can be used to identify employees interested in taking opportunities that will enhance their career progressions. Learners explain how OcMara would use appraisals to manage risks and develop talent pools to meet the organisational goals. Learners also explain how appraisals would be used in managing contingencies and determining the employee skills needs.
AC 2.4 Assessment of the use of social media and advertising to recruit employees. An assessment of interviews and job references as methods of selection.
There are different recruitment methods that learners should consider when identifying talent in the organisation. This question focuses on the social media and advertising recruitment methods specifically. Students explain how they use these methods to attract and recruit the right talent whose values connect to the organisational values.
The unit helps learners gain insight on the different selection methods effective to evaluate the learners’ capability to perform in the available job position. Students explain the reliability and effectiveness of these methods in identifying employees’ capabilities to perform. Interviews connect employers with potential candidates, and they ask questions to allow candidates to explain who they are and their capability to perform. Job references are selection methods where employers engage with candidates’ former employers or colleagues to understand better the candidates’ potential in the new job position.
AC 4.1 Assessment of how OcMara could introduce zero-hours and contractor contracts for the new staff it is hoping to recruit
CIPD provides a factsheet on zero-hours contracts, which offers no work guarantee. Contractor contracts identify the terms and conditions of work that establish the relationships between the employers and new staff in the organisation. When hoping to recruit talent, OcMara should be keen to avoid zero-hours contracts because there are no fluctuations in the energy sector. Contractor contracts
AC 4.2 Discussion on the differences between express and implied terms of contracts and what is meant by custom and practice
The express and implied terms of contracts are the agreements that bind the employers and employees. The terms are defined according to Employment Rights Act 1996. Express terms are relevant to the law and govern the employers to respect employees’ legal rights. They are statements explaining employees’ statutory rights such as parental leave, flexible working hours, minimum wages and part-time working.
Implied terms of a contract are incorporated to develop agreements between employers and employees and create business efficacy. Examples include mutual trust and confidence, duty to provide a safe workplace, right for employees to receive minimum wages and equality between men and women’s pay. Express and implied terms are given to employees before they start working in an organisation and should be in writing.
AC 4.3 Explanation of how role information and socialisation can be included in an effective onboarding programme. Benefits of onboarding in terms of appreciation of the organisation culture and norms and employee effectiveness are also provided.
Role information is an onboarding component where people professionals help new staff members understand the roles they will perform in the organisation. Socialisation is a component that helps employees understand organisational policies and culture. These functions help employees commit to the organisation and function effectively
The benefits of onboarding are that employees become successfully integrated into the new organisation. In addition, with a good understanding of the organisational culture, chances of induction crisis are reduced. Other benefits of induction are employees’ capability to appreciate organisational culture, increased employee retention and reduced turnover.
Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
- CIPD LEVEL 3
- CIPD LEVEL 5
- CIPD Level 5_New Brief
- CIPD LEVEL 7
Latest Posts
Quick links.
Privacy Policy
Refund Policy
Terms of Service
Terms - Privacy Policy & Safety
© 2021 All Rights Reserved
- WordPress.org
- Documentation
- Learn WordPress

- CIPD Level 3 Course
- CIPD Level 5
- CIPD Level 7 Courses
- ILM Assignment Help
- CMI Assignment Help
5HR02 Talent Management and Workforce Planning
- February 23, 2022
- Posted by: admin
- Category: CIPD Level 5

An introduction to the unit 5HR02 Talent management and workforce planning
Learning 5HR02 helps learners understand labour market trends and how they relate to workforce planning to attract the best candidates to join an organisation. Participants examine employers’ role in positioning themselves in the labour market. To ensure that they are resourcing their organisations with the right people, professionals assess the labour market before making resourcing decisions.
Learners will gain insight into diverse workforce planning processes, techniques, and recruitment and selection methods throughout the course. These factors contribute to the retention of workers by improving the quality of the workforce built in an organisation. Additionally, the unit supports employers in improving employee retention and developing talent pools by providing information about employee turnover trends.
Guidelines for 5HR02 Assignments
In this assessment, we present the case study of OcMara Industries, a global company involved in energy. Students are expected to provide evidence to support their understanding of labour market trends. Our senior managers have developed people practice objectives to expand our use of sustainable energy sources and environmentally friendly processes. The objective is to recruit and retain staff with the skills and capabilities necessary to serve in the new development areas and protect them from the competition.
Students must read the CIPD factsheet articles as they prepare to complete the assessment. The resource and talent planning factsheet explains how to manage talent and explains talent management strategies. It is among the essential factsheets students can use when completing assessments. We identify why employees leave the organisation and develop strategies and practices to retain talent in the employee and turnover retention factsheet. CIPD Podcast “From surviving to thriving: key changes facing people practice in 2020” discusses factors that should be implemented at work, such as work-life balance to build a workplace that is fair, brave, and equal for everyone. The 5HR02 assignment is divided into three parts. It begins with a poster presentation on strategic positioning and the labour market, followed by a workplace planning and recruitment package, and finally a proposal presentation on talent retention.
The first task focuses on positioning and labour market issues
To present research on labour market trends in the UK, students will prepare posters to be presented to the people practice manager. This year’s Employer Brand Management Awards were won by SAP, a company students will discuss. Students will provide answers to the following sections of the assessment criteria:-
AC 1.1 An explanation of how SAP strategically positions itself in an increasingly competitive market
The objective of this course is to review SAP’s efforts in positioning itself in the labour market. Students provide evidence by analysing the organisation’s competitive environment and evaluating the strengths and weaknesses of the organisation’s positioning and employee experiences. Students should also consider the following characteristics in answering the question:-
- Choosing SAP as an employer
- Branding for employers
- Ethics and reputation of organisations
- Image of the organisation
- SAP’s culture of rewarding
AC 1.2 Explains how the UK’s labour market is changing and how it affects the country.
In this lesson, learners demonstrate the differences between markets with tight and loose conditions, comparing examples of countries with tight and loose market conditions. Accordingly, the UK labour market is tight, while Saudi Arabia’s labour market is loose. After that, learners explain trends in supply and demand for labour in the energy sector and how the external business environment affects the identified trends. Politics, economics, society, technology, environment, and law all play a role in resourcing decisions by organisations operating in the energy sector. In addition, students discuss the effects of the economic crisis on employee retention and skills shortages in the energy industry.
AC 1.3 Ensure future skill needs of the UK global energy sector are met by the government, employers, and unions.
Governments fund numeracy, literacy, and IT skills to meet future skills needs. However, it is the government’s responsibility to ensure that organisations’ policies are implemented to assess the future skills requirements of employees in the energy industry. In addition, the government ensures that employers are meeting the workforce requirements that enable them to recruit skilled workers.
Employers offer employees development opportunities and training programs to enhance their skills. Development programs improve an employee’s knowledge and work quality. The energy sector benefits from employers who offer opportunities to develop skills and provide experiences that support future skills development.
Unions have agendas that support employees’ learning and development. They work with employers to implement agendas as authentic as possible and identify representatives to implement agendas.
Task 2: Recruitment and planning of the workforce
The second task in the unit requires students to present a report on workforce planning and recruitment to the company manager during an HRBPS meeting. In this section, students answer questions such as;-
AC 2.1 An analysis of workforce planning in terms of predicting labour demand by using internal and external sources of supply
The students explain the gap between labour demand and supply and the pros and cons of forecasting in workforce planning when using internal and external sources of supply for OcMara Company. In addition, students will examine how OcMara can benefit by developing talent from within by examining the advantages and disadvantages of internal talent development. The advantages and disadvantages of developing external talent at OcMara are also discussed to address the question comprehensively.
AC 2.2 Using critical incident analysis and promotion/demotion rates to support the workforce planning process and evaluate their effectiveness .
They explain how managers plan their workforces using various techniques. Participants discuss the importance of promotion and demotion as part of workforce planning. Additionally, they describe the importance of measuring employee turnover and the pros and cons of supporting workforce planning. Finally, they describe the critical incident analysis and its effectiveness in workforce planning. In addition, they describe OcMARA concerning these techniques.
AC 2.3 An explanation of how OcMara can be used to identify candidates interested in progression, manage risk, and mitigate contingency through developing their talent pools
Learning participants define appraisal and explain how this can be used to identify employees interested in taking on opportunities that will advance their careers. In this lesson, learners explain how OcMara would use appraisals to manage risks and develop talent pools to reach its organisation’s goals. Furthermore, learners explain how appraisals can manage contingencies and determine employee skill requirements.
AC 2.4 Examines how social media and advertising are used in recruiting. It evaluates interviews and job references as methods of selection.
When identifying talent in an organisation, learners should consider different recruitment methods. Specifically, this question addresses social media and advertising recruitment methods. This is done by matching a candidate’s values with the organisational values, thus attracting and retaining the right talent.
By completing the unit, learners will gain insight into the different selection methods that evaluate a candidate’s capability to perform well in the position they are applying for. These students describe the effectiveness of these methods in identifying employees’ abilities to perform. First, candidates answer interview questions to explain who they are and their ability to perform—employers interview candidates to determine their suitability for the job. The process of job references refers to how employers gain insight into a candidate’s potential for a new job position by consulting with the candidate’s previous employers or colleagues.
AC 4.1 Evaluation of how OcMara could introduce zero-hours contracts for its new employees
The CIPD offers a factsheet explaining zero-hour contracts, which do not provide work guarantees. Contractor contracts establish the relationship between the employer and new staff in the organisation by establishing the terms and conditions of work. OcMara should avoid zero-hours contracts to recruit talent because the energy sector does not experience fluctuations. Contractor contracts
AC 4.2 A discussion of the differences between express and implied terms of contracts, as well as the meaning and significance of custom and practice
Employers and employees bind themselves to contracts that express implied terms. These terms are defined by the Employment Rights Act 1996. Employers must respect employees’ legal rights by implementing express terms relevant to the law. The statements explain employees’ statutory rights, such as parental leave, flexible working hours, minimum wages, and part-time employment.
To create business efficiency by establishing agreements between employers and employees, implied contract terms are incorporated. Mutual trust and confidence are examples of the duty to provide a safe workplace, the right to a minimum wage for workers, and pay equality for men and women. Generally, employees are given express and implied terms before starting work in an organisation, and the terms should be in writing.
AC 4.3 Describes how role information and socialisation can be incorporated into an effective onboarding program. In addition, onboarding contributes to an understanding of the organisation’s culture and norms and employee effectiveness.
It is part of the onboarding process where people professionals help new staff members understand their roles in the organisation. In addition, the socialisation process helps employees to understand the organisation’s policies and culture. When employees understand these aspects of the organisation, they are more committed and productive.
Employees become successful in integrating into a new organisation through onboarding. The chances of an induction crisis are also reduced when one understands the organisational culture. Induction also benefits employees to appreciate the company’s culture, increase employee retention, and reduce turnover.
Calculate the price of your order


CIPD Level 5HR02 Talent Management & Workforce Planning Assignment Example, UK
Learning talent management skills and workforce planning strategies is an essential aspect of the CIPD Level 5 learners. The study of talent management develops the understanding of the employees at the workplace and identify & retain the right talented employees can help an organization to grow faster. Whereas, workforce planning is a business core process that keeps aligning the people strategy with organizational needs. Both talent management and workforce planning should be structured in the favour of business goals and objectives.
Pay & Get Instant Solution of this Assignment of Essay by UK Writers
Talent management and workforce planning is the way to make a high-performance workplace by managing valuable employees and focusing on the challenges and issues faced by a business. Thus, learners should consider this module the key priorities of their studies. We are going to discuss some relevant assignment examples and topics to enhance your learning even better. Therefore, we have divided the examples according to the learning outcomes of the module mentioned below.
CIPD Level 5HR02 Task 1: Understand key contemporary labour market trends and their significance for workforce planning.
1.1 explain how organisations strategically position themselves in competitive labour markets..
Organisations strategize their position in the labour market based on various elements such as the cost of labour, availability of skilled workers, and regulatory environment. Firms seek to minimize their costs while still being able to access a suitably skilled workforce. At the same time, they also want to be located in an environment that is conducive to doing business.
There are a few ways in which firms can strategize their position in the labour market.
- One way is by locating themselves in areas where the cost of labor is relatively low. This allows them to reduce their overall expenses and remain competitive.
- Another way is by locating themselves near sources of skilled labor. This allows them to have access to a pool of workers with the necessary skills and knowledge to support the organization’s operations.
- Finally, firms can also choose to locate themselves in environments that are supportive of business activity. This includes factors such as the availability of infrastructure and the existence of favorable government policies.
1.2 Explain the impact of changing labour market conditions on resourcing decisions.
Rapidly changing labour market conditions can have a significant impact on an organization’s resourcing decisions. As organizations attempt to navigate an increasingly complex and competitive landscape, they must be adaptive and agile in their planning and execution. In order to make the best possible decisions, organizations need to understand the evolving nature of the labour market and its effect on the business.
There are a number of factors that can contribute to changing labour market conditions, such as globalization, technological advancement, shifts in demographics, and changes in government policy. Each of these factors can have a profound effect on the availability and cost of talent, as well as the skills and expertise required to perform certain roles. As a result, organizations must be constantly monitoring labour market trends in order to stay ahead of the curve and make the most informed decisions possible.
1.3 Discuss the role of government, employers and trade unions in ensuring future skills needs are met.
Governments play a critical role in ensuring that future skills needs are met. Through initiatives such as workforce planning, education and training, and immigration policy, governments can help to ensure that businesses have access to the talent they need to stay competitive.
Employers also have a responsibility to invest in the development of their workforce and to create an environment that attracts and retains top talent.
Finally, trade unions can help to ensure that workers have the skills and training they need to meet the demands of the labour market.
By working together, these three groups can help to ensure that the future needs of the labour market are met.
Buy Non Plagiarized & Properly Structured Assignment Solution
5HR02 Assignment Activity 2: Understand the purpose and importance of workforce planning.
2.1 analyse the impact of effective workforce planning..
Workforce planning is essential for organisations to ensure they have the right number of employees with the right skills to meet the needs of the business. Without effective planning, organisations can experience a number of negative consequences, such as:
- Increased costs due to overtime or hiring temps
- Poor customer service due to lack of staff
- Reduced productivity as a result of staff shortages
- Staff morale problems caused by overworking or feeling undervalued
- Difficulty attracting and retaining the best staff
- Increased risk of legal action due to not having enough staff to comply with health and safety regulations.
2.2 Evaluate the techniques used to support the process of workforce planning.
There are a number of different techniques that can be used to support workforce planning, including:
- Workforce analysis – this involves looking at factors such as the skills mix of the current workforce, projected retirements and resignations, and future business needs to identify any gaps.
- Benchmarking – this involves comparing your organisation’s workforce against others in your industry to identify any areas where you may be falling behind.
- Workforce modelling – this involves using software to create models of different workforce scenarios, which can help to plan for future needs.
- Skills audits – this involves assessing the skills of your current workforce and identifying any training needs.

2.3 Explain approaches to succession and contingency planning aimed at mitigating workforce risks.
When it comes to succession and contingency planning, there are a few different approaches that organizations can take in order to mitigate risks associated with their workforce. Typically, these strategies fall into two main categories: organizational and individual.
Organizational succession and contingency planning generally involve putting systems and processes in place at the company level in order to ensure that critical functions can be adequately fulfilled even in the event of staff turnover or other disruptions. For instance, an organization might develop cross-training programs so that employees are able to fill multiple roles within the company, or create detailed job descriptions and manuals to make it easier for someone new to step into a particular position. Contingency plans might also be developed for specific situations, such as what to do in the event of a natural disaster or pandemic.
Individual succession and contingency planning, on the other hand, generally involve taking steps at the level of the individual employee to ensure that they are prepared to take on new responsibilities or fill critical roles in the event of turnover or other disruptions. This might include providing employees with opportunities to develop new skills, preparing them for specific succession scenarios, or offering mentorship or other forms of support.
2.4 Assess the strengths and weaknesses of different methods of recruitment and selection to build effective workforces.
There are a number of different methods that can be used to recruit and select employees, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Some of the most common methods include:
- Job postings – this is one of the simplest and most common methods of recruitment, but it can be difficult to reach a wide audience, and you may only received applications from people who are actively looking for a job.
- Networking – this involves reaching out to your personal and professional networks to see if anyone is interested in the position or knows someone who might be a good fit. This can be a great way to find qualified candidates, but it can also be time-consuming.
- Referrals – this involves asking current employees if they know anyone who might be interested in the position. Referrals can be a great source of high-quality candidates, but you may only receive a few referrals.
- Recruitment agencies – this involves using a professional agency to help you find candidates. This can be a great way to find qualified candidates, but it can also be expensive.
- Assessment centres – this involves bringing candidates to a central location to participate in a series of activities and tests designed to assess their suitability for the position. This can be a great way to assess multiple candidates at once, but it can also be expensive and time-consuming.
- Interviews – this is one of the most common methods of selection, but it can be difficult to get an accurate sense of a candidate’s suitability for the position from a one-hour conversation.
Each of these methods has its own strengths and weaknesses, and the best approach for your organization will depend on your specific needs and circumstances.
Please Write Fresh Non Plagiarized Assignment on this Topic
Level 5 CIPD 5HR02 Assignment Task 3 : Understand the purpose and impact of effective talent management.
3.1 examine turnover and retention trends and the factors that influence why people choose to leave or remain..
According to recent studies, there are several reasons why employees choose to leave or remain with a company. Here are some of the most common findings:
One of the most significant factors is compensation. If employees feel they are not being paid what they are worth, they will likely look for another job. Considering the cost of living and other financial obligations, this is understandable. Additionally, company culture also plays a role in someone’s decision to stay or go. If an employee feels management is unfair or that their work situation is unfavorable, they will be more likely to seek new opportunities elsewhere.
Retention rates are higher when employees feel enabled and supported by their company. When an individual’s goals align with those of the organization, they are more likely to stay put. Furthermore, if an employee feels their job is secure and that there is room for growth within the company, they will be less inclined to look for other work. Lastly, a positive relationship with one’s immediate supervisor is another key factor in retention. Employees who feel respected and supported by their boss are more likely to stick around.
3.2 Compare different approaches to developing and retaining talent on an individual and group level.
There are a variety of ways companies develop and retain talent. Some organizations focus on individual development, while others take a more group-oriented approach. Here is a comparison of the two:
Individual Development:
With this method, each employee is responsible for their own development. They are given the freedom to choose which areas they want to focus on and are given the resources to do so. This approach can be very motivating for employees as they feel empowered to take control of their own career. Additionally, it allows employees to develop at their own pace and in a way that best suits their learning style. However, this method can be less effective for developing team skills and may not be as aligned with company objectives.
Group Development:
This approach focuses on developing talent within a team or department. It is often used to improve team morale and build cohesion. Additionally, it can be more aligned with company objectives as it allows for better control over the development process. However, this method can be less motivating for employees as they may feel like they are not in control of their own development. Additionally, it can be more difficult to tailor the development process to each individual’s needs.
3.3 Evaluate approaches that an organisation can take to build and support different talent pools.
There are a few different approaches that an organisation can take to build and support different talent pools. Some common ones are:
- Focusing on specific groups or demographics within the workforce that may be underrepresented or have unique skillsets. This could involve things like targeted recruiting, mentorship programs, and development opportunities.
- Encouraging employees to develop their skillsets and knowledge in specific areas through training and development programs. This could help to create a more well-rounded workforce and give employees the chance to grow into new roles.
- Working with external partners or organisations to source talent from different pools. This could involve things like internships, apprenticeships, or even just networking opportunities.
Each organisation will have different needs when it comes to building and supporting their talent pools. It’s important to assess what those needs are and then put together a plan that will best meet those needs. Talent management is an ongoing process, so it’s also important to review and adjust your approach as needed over time.
3.4 Evaluate the benefits of diversity in building and supporting talent pools.
There are many benefits to diversity in building and supporting talent pools.
- First, businesses can draw from a larger pool of qualified candidates, which can lead to more creativity and innovation.
- Second, diversity can help businesses better understand and serve their customers, as well as identify new market opportunities.
- Third, a diverse workforce can help businesses better reflect the community in which they operate.
- And finally, research shows that diverse teams are more effective and productive than homogeneous teams.
3.5 Explain the impact associated with dysfunctional employee turnover.
When an organization experiences dysfunctional employee turnover, it means that employees are leaving the company at a rate that exceeds the rate of attrition. This can have a number of negative impacts on the organization, including:
1) Decreased productivity: When employees leave the company, they take with them institutional knowledge and expertise. This can lead to decreased productivity as new employees need time to get up to speed.
2) Higher costs: It costs money to replace employees, and these costs can add up if you’re losing employees at a high rate. Not only do you have to pay for recruitment and training, but you also lose out on the potential revenue that could be generated by these employees.
3) Lower morale: Dysfunctional employee turnover can lead to lower morale among remaining employees. This is because employees may feel like they are working in a revolving door and that their efforts are not appreciated.
4) Decreased customer satisfaction: When employees leave, it can impact customer satisfaction. This is because customers may have to deal with new employees who are not familiar with the company’s products and services.
5) Damage to the company’s reputation: Dysfunctional employee turnover can damage the company’s reputation, as it may be seen as an indication that the company is not a good place to work. This can make it more difficult to attract and retain top talent.
CIPD Level 5HR02 Learning Outcome 4: Understand the importance of managing contractual arrangements and effective onboarding.
4.1 assess suitable types of contractual arrangements dependent on specific workforce need..
As an HR professional, it is important to be aware of the different types of contractual arrangements that can be used in order to meet the specific workforce needs of an organisation. The most appropriate type of contract will depend on a number of factors, such as the nature of the work to be carried out, the duration of the project, and the geographical location of the workers.
There are four main types of contractual arrangements that are commonly used in the workplace:
1. Permanent contracts – These are the most common type of contract, and usually involve an employee working for an organisation on a long-term basis. The terms and conditions of permanent contracts can vary considerably, but typically include benefits such as holiday entitlement and sick pay.
2. Fixed-term contracts – These are typically used for specific projects or when there is a need for additional staff on a short-term basis. The terms and conditions of fixed-term contracts are generally similar to those of permanent contracts, but they will usually specify an end date for the employment agreement.
3. Casual contracts – These are typically used for workers who are needed on an ad hoc basis, such as in the hospitality industry. Casual contracts do not usually include any employment benefits, and the hours of work can vary considerably from one week to the next.
4. Zero-hours contracts – These are similar to casual contracts, but the employee is not guaranteed any minimum number of hours per week. These types of contracts are becoming increasingly common in the UK, although they have been criticised for providing little security for workers.
When selecting the most appropriate type of contract, it is important to consider the specific needs of the organisation and the workers involved. In some cases, a combination of different types of contracts may be used in order to meet the requirements of both the employer and the employee.
4.2 Differentiate between the main types of contractual terms in contracts.
When it comes to contracts, there are a few different types of terms that you should be aware of. These include express terms, implied terms, conditions, and warranties.
Express terms are those that are explicitly stated in the contract. They are the basis of the agreement between the parties and can be either written or oral. Implied terms are those that are not expressly stated in the contract but are assumed to be part of it. These might include things like a duty of care or good faith.
Conditions are essential terms of the contract that give rise to a contractual obligation. If these aren’t met, then one party may be able to end the contract or sue for damages.
Warranties are less important terms of the contract that simply state certain facts about the subject matter of the contract. If these turn out to be false, then one party may be able to sue for damages.
4.3 Explain the components and benefits of effective onboarding.
Onboarding programs are designed to help new employees transition into their roles successfully. By orienting newbies to the company culture, work expectations and goals, onboarding can accelerate their time to productivity and decrease turnover.
An effective onboarding program will include the following components:
- An Orientation to the Company Culture:
New employees should be given a tour of the office and introduced to everyone on their first day. This will help them feel comfortable in their new surroundings and start to build a network of colleagues. During orientation, they should also be taught about the company culture, values and mission. This will ensure that they understand what is expected of them and help them seamlessly integrate into the workplace.
2. A Review of Job Responsibilities:
On their first day, new employees should sit down with their manager and review their job responsibilities. This will ensure that they understand what is expected of them and help them hit the ground running.
3. Training on Company Policies and Procedures:
New employees should be given a company handbook on their first day and be given time to read through it. They should also be trained on company policies and procedures, such as the attendance policy, dress code, etc. This will ensure that they are familiar with the rules and regulations of the company and avoid any potential issues down the road.
4. Setting Performance Expectations:
New employees should sit down with their manager and set performance expectations. This will help them understand what is expected of them and help them stay on track.
5. A Mentor or Buddy Program:
Pairing new employees with a mentor or buddy can help them transition into their new role. The mentor or buddy can answer any questions they have and help them acclimate to the company culture.
An effective onboarding program will help new employees transition into their roles successfully and decrease turnover. By orienting newbies to the company culture, work expectations and goals, onboarding can accelerate their time to productivity.
Purchase CIPD Level 5 5HR02 Assignment Answers At Cheap Prices in UK
Are you looking for CIPD Level 5 5HR02 Assignment Answers at cheap prices in UK? If yes, then congratulations because you have landed at the right place. Studentsassignmenthelp.co.uk offers the best quality and plagiarism free CIPD Level 5 5HR02 assignment solutions at pocket-friendly prices.
If you want an academic writer to complete an assignment. You might want to get in touch with assignment service providers. There are many writing services online that claim they can provide online assignment writing help , but the question is which one you should choose.
Make your writing dreams come true with CIPD assignment help ! We are experts in all kinds of essays, homework, and coursework. Our writers are here to help you in writing your paper. You can also get the “ do my assignment for me ” service at a low cost.
CIPD assignment writing help for students is now at their doorstep. Students Assignment Help the UK provides high-quality management assignment help . We work day and night to offer you plagiarism-free CIPD Level 5 assignments within the deadline. So, just order now!
Related Answers
- Kotter’s 8-Step Model of Change Management: CIPD Assignment Sample, UK
- CIPD Level 7OS06 Well-Being At Work Assignment Example UK
- CIPD Level 7OS05 Managing People In An International Context Assignment Example UK
- CIPD Level 7OS04 Advance Diversity And Inclusion Assignment Example UK
- CIPD Level 7OS03 Technology-Enhanced Learning Assignment Example, UK
- CIPD Level 7OS02 Learning And Development Practice Assignment Example UK
- CIPD Level 7OS01 Advanced Employment Law In Practice Assignment Example UK
- CIPD Level 7LD01 Organizational Design Development Assignment Example UK
- CIPD Level 7HR03 Strategic Reward Management Assignment Example UK
- CIPD Level 7HR02 Resource And Talent Management To Sustain Success Assignment Example UK
- CIPD Level 7HR01 Strategic Employment Relations Assignment Example UK
- CIPD Level 7CO04 Business Research In People Practice Assignment Example UK
- CIPD Level 7CO03 Personal Effectiveness, Ethics & Business Acumen Assignment Example UK
- CIPD Level 7CO02 People Management & Development Strategies For Performance Assignment Example, UK
- CIPD Level 7CO01 Work And Working Lives In A Changing Business Environment Assignment Example, UK
- CIPD Level 5OS07 Well-Being At Work Assignment Example, UK
- CIPD Level 5OS06 Leadership And Management Development Assignment Example UK
- CIPD Level 5OS05 Diversity And Inclusion Assignment Example, UK
- CIPD Level 5OS04 People Management In An International Context Assignment Example, UK
- CIPD Level 5OS03 Learning And Development Essentials Assignment Example, UK

Get Free Assignment Quote
Enter Discount Code If You Have, Else Leave Blank

do you want plagiarism free & researched assignment solution!
UPTO 15 % DISCOUNT
Get Your Assignment Completed At Lower Prices
- +44 2871140060

- Terms of Service
5HR02 Assignment Example
- April 10, 2023
- Posted by: Fletcher Samuel

TALENT MANAGEMENT AND WORKFORCE PLANNING
Ac 1.1 how can organisations strategically position themselves in competitive labour markets.
The labour market can be defined as the state whereby employers look for skills to enhance the performance of duties in an organisation. In contrast, employees look for employers to provide them with job opportunities ( Graham and Anwar, 2019) . On the other hand, employer branding is the technique through which an organisation strategically positions itself through the display of their various virtues, such as positive orgaisational culture, to attract skills and talents from the public by showcasing unique attributes. People management professionals in organisations play a significant role in ensuring that the organisation attains desired skills, and this is implemented through evaluating the skills needs of the organisation. After evaluation, people professionals determined the recruitment criteria to be applied so that the organisation can attain those skills. In some cases, the organisation designs a development programme that is implemented in the onboarding process whereby employees are educated on various aspects, such as training on the use of modern technology to perform duties.
Employer branding has a major benefit as it enhances the development of a positive corporate image which impacts an organisation’s revenue and continued success ( Saini and Jawahar, 2019) . Through employer branding, prospective employees are attracted by the values and thus work exemplary to meet the targets and needs of the organisation, which leads to orgaisational development. For example, in my organisation in the Real Estate and Investment Company, we ensured that employer branding has been attained, and this attracted effective marketing skills from the public, and those individuals contributed to increased sales and this orgaisational development. We adopted the use of modern technology as an orgaisational culture, and this led to the realization of the desired skills and the impact of modern technology to orgaisational development.
AC 1.2 What is the impact of changing labour market conditions on resourcing decisions?
Resourcing is the process through which an organisation effectively recruits and selects employees to fill specific positions in the organisation by evaluating their skills. Changing labour markets impacts on resourcing decisions in various ways as labour markets create an orgaisational image which helps in attracting skills ( Sabel, 2019) . There are two main labour market trends which include tight and loose labour markets. A tight labour market can be defined as a situation where few potential employees meet an organization’s demand. This impacts resourcing as an organisation is not in a position to attain all the required skills to enhance the continued performance of duties in the organisation. Loose labour markets, on the other side, can be defined as the situation where there is a large number of skilled employees while the opportunities in the organisation are few. This also affects resourcing decisions as people professionals may not effectively evaluate all the available personalities during the recruitment process.
Changing labour markets, such as development in technology, impacts resourcing decisions such as recruitment methods, development decisions, and retention strategies. This can be analysed through the evaluation of the PESTEL analysis, which entails political, economic, social, technological, environmental, and legal aspects. Development in technology is a modern development that highly impacts resourcing decisions ( Blut and Wang, 2020) . For example, in our organisation, people management professionals have adopted employee development as an effective resourcing strategy which involves training of employees on the use of modern technology to enhance effective communication and performance of duties. Through this implementation, the turnover rate of the organisation has highly reduced, and thus identified that changing labour markets impact on resourcing decisions.
AC 1.3 What is the role of government, employers and trade unions in ensuring future skills needs are met?
Role of the government.
The government plays a significant role in ensuring that future skills needs are met through the setting of policies that are aimed at guiding employers in implementing employee development and offering financial support to enhance the implementations ( Hackitt, 2018) . Due to the continued developments, the government evaluates various aspects, such as the development of technology, and sets policies that necessitate employers to enhance employee skills development. Additionally, the government supports changes in workforce requirements in organisations and sets various standards that employees should attain in order to perform various duties. This leads to the development of skills to meet the future skills needs and it entails evaluation of various countries and their developments and this guides in the effective implementation of the policies.
Role of employers
Employers play an important role in ensuring that future skills needs are met through conducting an evaluation of employees’ skills in the organisation. This is done by people management professionals whereby they evaluate employees’ skills against the organisation’s future needs ( Tan and Laswad, 2018) . This guides in the implementation of effective training and development programmes in the organisation for employees. For example, in our organisation at Real Estate and Investment Company, people professionals evaluated employees’ skills and determined that effective communication is a key skill that is required. This led to the implementation of a training programme aimed at enhancing employees’ skills on effective communication strategies, such as through the use of modern technology, active listening, and enhancement of professionalism while communicating with customers.
Role of trade unions
Trade unions also play a role in ensuring that future skills are met through the development of union-led agendas that focus on the implementation of training programmes for employees. Trade unions act as a representation of employee needs, and thus they evaluate the skills and needs for employees and present them to their employers ( Stone et al., 2020) . Additionally, trade unions play a role in ensuring that future skills needs are met through representing employees to employers in the case of a conflict. For example, employees may demand the implementation of a training programme that may not be welcomed by their employers. In this case, trade unions evaluate the case to determine the impact of the employee desires, and in the case where this is aimed at enhancing their skills, trade unions represent the complaint to the employer and seek for a solution.
AC 2.1 Impact of effective workforce planning?
Effective workforce planning impacts on effective forecasting of demand and supply of labour, both internal and external, and effective ways to address the issues ( Stewart and Brown, 2019) . For example, people professionals in an organisation evaluate employees’ needs which are essential in enhancing orgaisational development ( Hackitt, 2018) . After evaluation, a comparison is conducted on the availability of the skills and the possible supply. In the case of internal supply of labour, people professionals use existing employees in the organisation to perform various duties. Employee training and development can be adopted to enhance the employees’ skills to meet the needs of the organisation. External supply of labour, however, entails the recruitment of new employees in the organisation to meet the various needs.
Additionally, effective workforce planning improves on the recruitment process and thus reduces the hiring cost. People professionals in an organisation recruit employees through adopting various procedures. Through workforce planning, people professionals enhance the recruitment process as it focuses on the selection of a specific talent and thus narrows down the selection criteria ( Stewart and Brown, 2019) . The organisation is in a position to attain effective skills as employees are evaluated following the selection criteria. Moreover, the cost of hiring is significantly reduced as the organisation does not have to implement employee training programmes after the recruitment procedure since the selected employees meet the desired criteria and thus save on the cost of hiring.
AC 2.2 Could you evaluate the techniques used to support the process of workforce planning?
Orgaisational strategy is a technique that can be used to support workforce planning as it entails techniques used to forecast demand and supply for labour. Techniques used to forecast demand for labour support workforce planning through implementing managerial judgment. People professionals make management judgments focused on the demand for labour through conducting an evaluation of the existing staff in comparison with the needs of the organisation. Additionally, organisations works back from cost as a technique to evaluate the demand of labour. This includes the costs incurred from the recruitment and development of employees to attain the desired skills.
Techniques used to forecast on supply of labour can also be used to support the process of workforce planning through the evaluation of promotion and demotion rates in the organisation. People professionals play a significant role in ensuring that employees are promoted or demoted in the organisation based on various aspects ( Graham and Anwar, 2019) . Moreover, employee turnover rate is an aspect used to evaluate the supply of labour in organisations. Some of the major causes of turnover is lack of employee well-being or poor orgaisational culture. These aspects support the process of workforce planning as orgaisational managers focus on the key aspect and implement effective response actions. For example, people professionals can implement employee involvement in decision-making to help identify various challenges that affect effective workforce planning.
AC 2.3 Could you explain two approaches to succession and contingency planning aimed at mitigating workforce risks?
Succession planning can be defined as the process through which an organisation evaluates key positions in the organisation and identifies unique individuals who can fill up those positions. Contingency planning involves an organisation effectively preparing for various occurrences which have been predicted, and this involves getting the desired skills to deal with the challenges. Developing talent pools is one of the approaches to succession and contingency planning aimed at mitigating workforce risks. Talent pools involve people professionals evaluating various skills that can be adopted in the organisation to enhance employees’ knowledge on the effective performance of duties ( Smith et al., 2022) . People professionals thus implement training and development programmes aimed at enhancing employees’ skills. For example, current developments in technology have created the need for organisations to digitize their operations. People professionals thus train employees on the effective use of technology in various aspects of the organisation, such as communication and marketing, and this helps in mitigating workforce risks such as digital marketing and feedback collection from orgaisational customers.
Appraisal is an approach to contingency and workforce planning as it helps determine those interested in progression in the organisation. People professionals can conduct appraisals by evaluating employees’ performance in the organisation. This guides in identifying employees who perform effectively on their roles and thus can be determined as those interested in progression. Additionally, people management professionals can collect feedback from employees to get their views on progression. For example, at Real Estate and Investment Company, we implemented surveys to collect employee feedback on their views. These guides people professionals in selecting the employees interested in progression and enhancing their skills, and this helps in mitigating workforce risks such as turnover.
AC 2.4 Could you briefly assess the strengths and weaknesses of these methods as well as another recruitment method and another selection method?
Recruitment method.
The use of social media platforms is a recruitment method that involves orgaisational managers using various social media platforms such as Facebook, Twitter, or Instagram to advertise vacant positions. The main advantage of using these social media platforms is that the advertisements reach a wide variety of potential employees, and thus people professionals can attain diverse skills ( McRobert et al., 2018) . Additionally, through social media advertisement, the organisation gains publicity, and this enhances the continued growth of clientele and the development of a positive orgaisational impact. However, this method leads to the attraction of a large number of people, which creates a challenge for people professionals to evaluate all the applications and thus becomes time-consuming.
Selection method
Interviews are a selection method that can be adopted in an organisation to attain the desired skills and personalities for vacant positions. Through interviews, people professionals in an organisation conduct physical or virtual interviews with the applicants. The main benefit of interviews as a lection method is that people professionals are in a position to evaluate an individual’s code of conduct which is determined through their facial expressions and physical conduct. This helps the organisation select the individuals who possess the right attributes to perform duties effectively. However, interviews are costly and thus create a negative impact on the organisation’s finances. Moreover, interviews take a long time as all employees have to communicate directly with the recruitment team, which slows down the organisation’s development.
AC 3.1 Turnover and retention trends, and factors influence why people choose to leave or remain?
Management issues.
Management strategies adopted by people professionals in an organisation contribute to turnover trends. For example, an organisation could adopt a hierarchical management structure that entails decisions being made by senior orgaisational managers. This creates an increased rate of turnover as employees do not feel included in the orgaisational development. Through this, employees might choose to leave the organisation due to poor management strategy ( Belete, 2018) . To deal with this, people management professionals could implement employee involvement in decision-making. This allows employees to give their feedback on various aspects and thus people professionals can determine various challenges and implement effective decisions aimed at dealing with the challenges hence reducing turnover.
Recognition and reward
Recognition and reward is a retention trend that exists in an organisation, and this is one of the main reasons why individuals choose to remain in the organisation. Recognition and reward is a motivational approach that can be adopted by people professionals in an organisation with the aim of enhancing employee well-being (Belete, 2018) . There are various forms of rewards that can be adopted which can be tangible or intangible. Intangible rewards include recognition whereby employees are recognized for their actions and this enhances their motivation. In contrast, tangible rewards involve monetary incentives whereby employees receive rewards such as bonuses or pay increase for their achievements. This creates a reason why employees choose to stay in an organisation.
AC 3. 2 I want to compare different approaches to developing and retaining talent on an individual and group level. Could you give me some pointers?
Talents are unique skills that are possessed by individuals in an organisation and which people professionals focus on to retain and develop at an individual and group level. One of the major approaches that can be adopted involves the training and development of employees. This focuses on the development of talent on both individual and group level ( Stone et al., 2020) . To effectively implement a training programme, people professionals in an organisation evaluate employees’ skills through various procedures such as observation or evaluation of performance reports. For example, people professionals in an organisation can implement a training programme aimed at educating employees on problem-solving skills. This guides in the development of professionalism and develops skills and thus guides in developing and retaining talent at both individual and group levels.
Implementing fair and an equitable reward is an approach that can be adopted by people professionals in an organisation to develop and retain talent within a group and individual level. Reward is an essential aspect of enhancing employee motivation ( Stone et al., 2020) . People professionals can adopt monetary rewards, which include bonuses or pay increases, to act as a motivation for employees. Through this, the rate at which employees leave an organisation is reduced, and employees are motivated to perform their duties effectively and thus attaining the organisation’s strategic goals. Through this, talents are effectively retained at an individual and group level in the organisation.
AC 3.3 Could you evaluate approaches that an organisation can take to build and support different talent pools?
Role performance reviews.
Talent pools in an organisation can be defined as a group of employees who are effectively prepared to take up various roles in the organisation by enhancing their skills. Role performance reviews is an approach that can be taken to support different talent pools ( King and Vaiman, 2019) . For example, people professionals in an organisation can allocate employee management roles to role pay. This helps in the identification of key skills among the employees that can be developed to create the development of talent pools. Through role play, people professionals also identify gaps and possible developments that can be enhanced, and this supports the development of various talent pools in the organisation.
Learning and development initiatives
Learning and development initiatives such as coaching and mentoring is an approach that an organisation can take to support different talent pools. Through coaching, people professionals in an organisation evaluate employees’ skills and create a comparison with the desired skills and knowledge to meet orgaisational needs. This guides in the effective implementation of a coaching programme to enhance employees’ skills ( King and Vaiman, 2019) . For example, on our organisation at Real Estate and Investment Company, talent pools are built to enhance the digitization of sales and access to international markets. This led to the implementation of a coaching programme that focused on enhancing employees’ marketing and management skills as this led to the effective performance of management roles. Additionally, employees received support of the adoption of modern technology to enhance efficiency of performance.
AC 3.4 Could you evaluate two benefits of diversity in building and supporting talent pools?.
Increased creativity leading to low employee turnover.
Diversity in supporting talent pools leads to increased creativity leading to low employee turnover rate in the organisation. For example, during the development of talent pools, employees are involved in the decision-making process and thus implement creativity in identifying various aspects that can be adopted in the organisation ( Belete, 2018) . Moreover, through the development of creativity, employees attain essential skills that guide them in dealing with various orgaisational challenges, and this contributed to reduce turnover. A reduction in the turnover rate in an organisation impacts positively on the continued success and attainment of the main orgaisational objectives.
Positive impact on employer brand
Diversity in building and supporting talent pools leads to the development of a positive impact to the employer brand. This is an important aspect as it leads to the development of a positive orgaisational culture that attracts talents. Additionally, through the employer brand, the organisation is in a position to attain its strategic objectives as employees work towards the attainment of their individual targets. This leads to orgaisational development and success. Additionally, through the positive impact on the employer brand, there is a reduced risk of discrimination among employees as they are all involved in various orgaisational developments.
AC 3.5 Impact associated with dysfunctional employee turnover?
Dysfunctional employee turnover can be described as the rate at which employees voluntarily leave the organisation, and these are the skilled employees leaving the unskilled ( Dwesini, 2019) . Dysfunctional employee turnover leads to both direct and indirect costs in the organisation, such as in the recruitment and selection of employees. In an organisation, people professionals use various resources to enhance the effective recruitment process. Moreover, employee development during the onboarding process involves training programmes that are costly to implement. These costs affect the organisation’s financial status and lead to reduced income this, affecting orgaisational development.
Additionally, dysfunctional employee turnover leads to the loss of essential skills in the organisation as skilled employees leave. This affects the organisation’s productivity and future developments. For example, in the case where an organisation losses all skilled employees through turnover, there will be no individuals to take up management positions which may arise within the organisation and thus slowing down orgaisational development. Additionally, through losing skills through dysfunctional turnover, the organisation might face competition from other organisations in the case these employees are absorbed in these organisations. This affects orgaisational development, and thus people professionals should implement effective response actions to deal with dysfunctional turnover, such as adopting employee involvement in decision-making.
AC 4.1 Could you assess suitable types of contractual arrangements dependent on specific workforce need.
Contractual arrangements are agreements that are made between two parties and are bid by the law and these create a restriction on the various actions that should be taken by the parties involved. Some of the main contractual arrangements in organisations include permanent contracts, temporary contracts, and pay per hour ( Datta et al., 2019) . The gig economy is an example of a factor that impacts the adoption of contractor contracts in an organisation. The gig economy entails labour markets that rely on employees that are hired on a part-time basis or contracts. Through contracts, the organisation is in apposition to save on cost of paying full-time employees, especially in the case where the duties performed are not long-lived. Additionally, through contracts, people professionals in an organisation are in a position to attain professional skills as individuals hired specialize on a given aspect of duty performance and this enhances orgaisational development.
Permanent contracts are contractual arrangements that involve organisation hiring employees permanently in the organisation and setting effective salary scales. This type of contractual arrangement has a major benefit as it enhances the continued development of the organisation as people professionals can implement development programmes for employees to enhance their skills. Additionally, through permanent contracts, the organisation develops a positive orgaisational culture help in setting the direction of the organisation. Permanent contracts can be used in work practice terms as people professionals can set an evaluation criterion that guides in the identification of various challenges or opportunities in the organisation.
AC 4.2 Difference between express terms and implied terms?
Expressed terms.
Expressed terms of contracts are legal agreements between two parties that involve employees and their employer, and they might be oral or in the form of writing. These terms guide organisations in the performance of duties through highlighting various laws and procedures that should be followed ( Kot-Radojewska and Timenko, 2018) . Orgaisational managers ensure that expressed terms adopted in the organisation are in line with the legal requirements of the country as stated in the Employment Rights Act 1996. Expressed terms ensures that employees attain the full benefits in their organisation, such as working for 40 hours a week, getting off days, enjoying holiday day off, and gaining development benefits such as skills development through training. Employees have to evaluate all the expressed terms before agreeing to them, and this enhances effective orgaisational performance and development.
Implied terms
Implied terms of contracts entail a written agreement between two parties involved, which include employer and employees. Implied terms focus on collective agreements, such as ensuring that the employer and the employee agree on the involvement of trade unions. This is an essential aspect as trade unions play a major role in the continued performance of an organisation as they represent employees’ needs to the employers. Additionally, implied terms incorporate individual employee contracts, which entails the details of terms of contract over a given period. Employees should effectively evaluate these contracts and ensure that the terms are favorable before signing them. An implied terms of contract is made legal through signing by the two involved parties.
AC 4.3 Could you explain the components and two benefits of effective onboarding?
Onboarding can be defined as the process through which newly hired employees are incorporated into the organisation through the adoption of various aspects such as training. The main components of effective onboarding include orgaisational and departmental information and clarification of expectations.
Components of effective onboarding
Clarification of expectations is a main component of effective onboarding and this involves people professionals offering guidance on the expectations from employees ( Smith et al., 2022) . Through this, employees are in a position to understand their role and perform duties in line with the organisation’s expectations hence effective performance. Additionally, to enhance effective onboarding, organisations should provide organisation and departmental information. This offers guidance to employees in understanding the structure and needs of the organisation.
Benefits of effective onboarding
Effective onboarding leads to the effective integration of employees in to the organisation by making them understand the orgaisational structure effectively (Smith et al., 2022). The integration process allows new hires to understand the effective performance of duties in the organisation. This leads to continued orgaisational development and thus leads to low risk of employee turnover. Additionally, effective onboarding leads to the development of a positive orgaisational culture which impacts positively on the organisation.
Did you enjoy our articles?
Click the order button below to get a high-quality paper.
You can talk to the writer using our messaging system and keep track of how your assignment is going.
Ali, Z., Mahmood, B. and Mehreen, A., 2019. Linking succession planning to employee performance: The mediating roles of career development and performance appraisal. Australian Journal of Career Development , 28 (2), pp.112-121. https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/abs/10.1177/1038416219830419 [accessed on December 13, 2022]
Belete, A.K., 2018. Turnover intention influencing factors of employees: an empirical work review. Journal of Entrepreneurship & Organization Management , 7 (3), pp.1-7. https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/c3a2/6253e522d8b3a4cfc15b24c86f841d4e837c.pdf accessed on December 13, 2022]
Blut, M. and Wang, C., 2020. Technology readiness: a meta-analysis of conceptualizations of the construct and its impact on technology usage. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science , 48 (4), pp.649-669. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11747-019-00680-8 [accessed on December 13, 2022]
Datta, N., Giupponi, G. and Machin, S., 2019. Zero-hours contracts and labour market policy. Economic Policy , 34 (99), pp.369-427. https://academic.oup.com/economicpolicy/article-abstract/34/99/369/5524663 [accessed on December 13, 2022]
Dwesini, N.F., 2019. Causes and prevention of high employee turnover within the hospitality industry: A literature review. African Journal of Hospitality, Tourism and Leisure , 8 (3), pp.1-15. https://www.ajhtl.com/uploads/7/1/6/3/7163688/article_38_vol_8_3__2019.pdf [accessed on December 13, 2022]
Graham, M. and Anwar, M., 2019. The global gig economy: Towards a planetary labour market?. First Monday , 24 (4). https://ora.ox.ac.uk/objects/uuid:f3bf8e6a-9f42-4b16-8f81-73f0ae8aad4f/files/md7cbec0c3cd81bdc3c3965a0881f33fe [accessed on December 13, 2022]
Hackitt, J., 2018. Building a safer future. Independent Review of building regulations and fire safety: Final report . https://www.longworth-uk.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/07/Building-a-Safer-Future-Overview.pdf [accessed on December 13, 2022]
King, K.A. and Vaiman, V., 2019. Enabling effective talent management through a macro-contingent approach: A framework for research and practice. BRQ Business Research Quarterly , 22 (3), pp.194-206. https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/abs/10.1016/j.brq.2019.04.005 [accessed on December 13, 2022]
Kot-Radojewska, M. and Timenko, I.V., 2018. Employee loyalty to the organization in the context of the form of employment. Oeconomia Copernicana , 9 (3), pp.511-527. http://economic-research.pl/Journals/index.php/oc/article/view/1053 [accessed on December 13, 2022]
McRobert, C.J., Hill, J.C., Smale, T., Hay, E.M. and Van der Windt, D.A., 2018. A multi-modal recruitment strategy using social media and internet-mediated methods to recruit a multidisciplinary, international sample of clinicians to an online research study. PLoS One , 13 (7), p.e0200184. https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0200184 [accessed on December 13, 2022]
Sabel, C., 2019. Moebius-strip organizations and open labor markets: some consequences of the reintegration of conception and execution in a volatile economy. In Social theory for a changing society (pp. 23-61). Routledge. https://www.taylorfrancis.com/chapters/edit/10.4324/9780429306440-2/moebius-strip-organizations-open-labor-markets-consequences-reintegration-conception-execution-volatile-economy-charles-sabel [accessed on December 13, 2022]
Saini, G.K. and Jawahar, I.M., 2019. The influence of employer rankings, employment experience, and employee characteristics on employer branding as an employer of choice. Career Development International . https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Avinash-Pawar-6/publication/340081711_Study_on_Employer_Branding_in_IT_Companies_The_Indian_Scenario/links/5e76165ca6fdcccd6213d06f/Study-on-Employer-Branding-in-IT-Companies-The-Indian-Scenario.pdf [accessed on December 13, 2022]
Smith, C.E., Matthews, R.A., Mills, M.J., Hong, Y.H. and Sim, S., 2022. Organizational Benefits of Onboarding Contingent Workers: an Anchoring Model Approach. Journal of Business and Psychology , 37 (3), pp.525-541. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10869-021-09757-0 [accessed on December 13, 2022]
Stone, R.J., Cox, A. and Gavin, M., 2020. Human resource management . John Wiley & Sons. https://books.google.com/books?hl=en&lr=&id=uCIgEAAAQBAJ&oi=fnd&pg=PR13&dq=Role+of+trade+unions+in+ensuring+future+skills+needs+are+met&ots=PJMJRx4PE8&sig=sKajQPsVhPMIaxm748rLWQNxFME [accessed on December 13, 2022]
Stewart, G.L. and Brown, K.G., 2019. Human resource management . John Wiley & Sons. https://books.google.com/books?hl=en&lr=&id=53eYDwAAQBAJ&oi=fnd&pg=PA2&dq=the+impact+of+effective+workforce+planning&ots=XFzEkescan&sig=pGzJ7iu1I9_MVGpArTDuVe61QBA [accessed on December 13, 2022]
Tan, L.M. and Laswad, F., 2018. Professional skills required of accountants: what do job advertisements tell us? Accounting Education , 27 (4), pp.403-432. https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/09639284.2018.1490189 [accessed on December 13, 2022]
Related Articles:
- CIPD Level 5
Cite This Paper
Our writing service is available in the UK, USA, Ireland, Canada, Australia, Saudi Arabia, Singapore, and other countries around the world.


5HR01 Assignment Example
Anon, Collective employment law. Oxford Reference. Available at:
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
Or copy link
www.cipdforum.co.uk


- Username or email *
- Password *
Remember me
Lost your password?
- Email address *
- Username *
- Confirm Password *
Want to become an instructor?
- 5co02 Assignment Example Task One
- CIPD Level 5

Table of Contents
Evidence-based practice is a systematic decision-making model that emphasises informed decisions on a robust evidence-based basis alongside effective reasoning (Young, 2022). It involves employing skills encompassing critical thinking alongside analysis for evaluating available data to ensure that the results are defendable to others and have proper justifications. This approach encourages individuals to incorporate the best data available with professional know-how (Young, 2022). It enhanced the choices’ credibility and quality by emphasising evidence-based judgments and applying critical thinking, leading to more responsible and effective decision-making procedures.
Decision-making models
The rational model
This entails a systematic procedure in which decisions are made based on rigorous examination of the available information to optimise the results. Nevertheless, the concept’s drawbacks become apparent in a complicated work atmosphere (Indeed Editorial Team, 2023). For instance, a people professional picking a new training program might face restrictions, including inadequate knowledge of employee learning preferences, diverse skill levels and time limits. The rational approach assumes that ideal conditions seldom exist, leading to judgments that may ignore complicated elements impacting learning efficacy and employee engagement. In such situations, a more adaptable approach, including limited rationality, could be more appropriate for the evolving workplace realities.
Bounded rationality
This is a decision-making approach that considers cognitive limits besides environmental restrictions. Following cognitive constraints, time and information, judgments under the approach strive for adequate instead of optimum outcomes (The Decision Lab). For instance, a people professional applying evidence-based practice could be entrusted with rising employee engagement. Bounded rationality could encompass reviewing the current research on engagement approaches while maintaining time restrictions alongside resource availability. Even if it fails to meet the threshold of being the best answer, the people professional could adopt an evidence-based initiative corresponding with the entity’s restrictions and context.
Application of evidence-based practice
The following are ways in which evidence-based practice can be applied
Recruiting and talent acquisition
People professionals could utilise evidence-based practice in identifying and understanding evidence on various recruiting tactics (Boatman, 2021). For instance, businesses could use data regarding the success rates of different sourcing avenues, including social media, referrals and job boards, in making informed judgments concerning areas to invest resources for an optimal efficacy.
Performance appraisals
People professionals could use evidence-based practice to conduct performance assessments by studying the research on performance evaluation approaches (Boatman, 2021). They could assess the effectiveness of various approaches, such as goal setting and 360-degree feedback, and customise their assessment procedure based on evidence-based information.
Development and training
Decisions on training programs could be guided by evidence-based practice. People professionals could research to determine the training approaches that produce the greatest outcome, considering factors including skill transfer and learning retention (Boatman, 2021). For instance, they may research the best balance of in-person training and e-learning for a particular skill set.
Porters Five forces
This is a popular analysis tool which assesses an industry’s competitive dynamics. It assesses five vital impacts on an entity: competitive rivalry, suppliers, new entrants, substitutes and buyers (Vaidya, 2022). It offers insights into the industry’s attractiveness alongside potential hindrances by thoroughly assessing the elements. It could detect threats, including replacement products or new entrants, chances, buyer or supplier power and competition intensity for entity diagnosis. The approach gives a comprehensive perspective regarding an entity’s competitive atmosphere. The various aspects it considers help firms comprehend the dynamics determining their sector’s attractiveness. Besides, the framework assists strategic decision-making by identifying critical elements that impact an entity’s sustainability and profitability (The Investopedia Team, 2023). Nevertheless, the model oversimplifies particular circumstances or sectors. Not all the sectors fall into these categories, and the model might not adequately depict the complexity of fast technological growth, globalisation and new disruptive breakthroughs.
These qualitative analysis tools encompass direct contact with people to get information and insights. They offer deeper comprehension, context-rich facts, and the ability to ask follow-up queries to elicit details. Interviews are advantageous for diagnosing organisational opportunities, difficulties and challenges since they allow stakeholders, workers or consumers to express their issues, share their encounters and recommend improvements (Obsidian HR, 2021). They offer contextual information that could reveal underlying perspectives or issues that quantitative data could overlook. Besides, the interviewers could adjust queries based on interviewee feedback, allowing for deeper investigations on particular subjects (Prasanna, 2023). However, they can be subjective and biased. Biases from the interviewee and interviewer could impact interviews, leading to incomplete or distorted information. Besides, interviews are cost and time-intensive to prepare, implement and analyse, which makes them unfeasible for large-scale data gathering.
Critical thinking is the objective assessment, evaluation and synthesis of information, circumstances and ideas to reach reasoned conclusions and judgments (CIPD, 2019). It encompasses the capacity to challenge assumptions, explore optional perspectives and apply facts and reasoning to produce well-reasoned and educated answers or judgments
Principles of critical thinking
The validity of evidence
This core principle deals with the validity, usefulness and dependability of data or information applied in support of conclusions and arguments. Critical thinkers assess proofs’ context, approaches and sources to ensure their reliability and correctness. Valid proof strengthens thinking, permitting informed decision-making alongside the development of well-reasoned and logical perspectives (O’Reilly, n.d.). Critical thinkers encourage intellectual integrity while pursuing reasonable conclusions based on trustworthy and objective information by respecting evidential validity.
I applied the principle when suggesting a new employee wellness program to decrease stress levels. Using the principle, I collected data on productivity measures, absence rates and employee surveys to support the program’s necessity and ensured all my sources were updated and peer-reviewed. By presenting this credible evidence, I increased the credibility of my proposition by emphasising the program’s possible influence on employee well-being and corporate success. The method exhibited critical thinking by ensuring that my plan was based on credible evidence, raising the chance of garnering support and implementing an efficient solution.
Awareness of bias
The principle encompasses the identification of personal biases that could affect judgements and having alertness to potential biases on other individuals’ information sources and viewpoints (Masterclass, 2021). Critical thinkers admit that biases could affect decision-making and thinking. They actively seek various perspectives, scrutinise potential bias sources, and constantly check their cognitive preferences. The concept encourages open-mindedness, objectivity and dedication to base the conclusions on unbiased and trustworthy data, leading to more reasoned and well-rounded outcomes in critical thinking (Masterclass, 2021).
Application of others’ ideas
I applied the principle when a coworker considered creating a new performance assessment strategy during a people professional meeting. I attentively listened to their idea and examined any biases that could impact my opinion against them before objectively assessing the proposal. I promoted an open debate by encouraging the team members to critically explore any biases in the proposed system, which led to a well-rounded assessment. The approach indicated my dedication to spotting biases in other individuals’ ideas, promoting a more objective and inclusive decision-making procedure that considers various points of view and adds to the general success of the team’s aims.
De-bono six thinking hats
This is a decision-making approach which facilitates the methodical considerations of various perspectives. It has six hats, each of which symbolises a particular thinking way. The white hat symbolises facts; black is negative/cautious, green is creative, red is emotions, blue is management/overview and yellow is positive (Bhasin, 2020). By wearing every hat consecutively, decision-makers could rigorously investigate a subject, enhancing critical thinking and reducing cognitive biases. This approach guarantees that diverse perspectives are considered, leading to more successful and balanced conclusions. For instance, applying the red hat could expose emotional concerns, but the green hat generates imaginative solutions. The approach helps in making informed, well-rounded judgments by combining several perspectives.
Pros and cons
The six thinking hats model is a structured approach that drives talks, ensuring that several views undergo a thorough examination, which could lead to a more complete judgment. In addition, it decreases bias. By encouraging various thought modes, the model assists the participants in recognising and separating personal biases, leading to more objective decision-making and analysis (Bhasin, 2020). However, the model’s simplicity could oversimplify complicated subjects, which leaves out deeper details. Besides, following a predefined hat sequence could stifle free-flowing talk alongside the natural ideas movement.
Action learning approaches
This is a decision-making framework emphasising learning through action and reflection. It encompasses a group of individuals operating together in solving complicated concerns or making choices (Indeed Editorial Team, 2023). The participants act and reflect on the results before adjusting their methodologies to respond to the new insights. The framework encourages continued growth besides hands-on learning. Entities could apply it to ensure results by fostering experimentation, learning from errors and adapting to actual adaptation. The approach enables the teams to apply various abilities, assess challenges holistically, and collaborate to find successful solutions and promote collective and individual growth (Indeed Editorial Team, 2023).
Action learning encourages the participants to acquire knowledge by permitting them to acquire practical insights through actual world experimentation, which enhances decision-making abilities and problem-solving skills (Indeed Editorial Team, 2023). However, it is time-consuming following its iterative nature, which makes it inappropriate for time-sensitive judgments.
Best-fit model
This approach posits that decisions should be made according to a circumstance’s outstanding goals, restrictions and context. It argues for judgments that are tailored to the particular situations. It considers elements including external atmosphere, resources and culture. The approach involves conducting a comprehensive study on the challenge, assessing optional possibilities besides choosing one that best satisfies the outstanding requirements (MBA Knowledge Base, 2021). The model enhances the chances to succeed and acquire optimal outcomes by aligning decisions with the situation, recognising that efficient decision-making deals with appropriateness instead of universality.
The approach guarantees that the decisions have contextual relevance, which enhances the opportunity to succeed and adapt to particular circumstances (MBA Knowledge Base, 2021). However, it is subjective, which calls for objectivity maintenance and inclusion in the decision-making procedure.
This refers to an unselfish care for others’ well-being, even if it insinuates foregoing personal gain. It embodies a noble part of human nature and is critical to moulding moral decision-making (Waters, 2021). Understanding the theory encourages individuals to recognise the value of social responsibility, compassion and empathy in their ethical decisions. It can encourage individuals to favour the greater benefit over their selfish interests, which impacts actions benefiting society. People embracing altruism are more likely to make ethically right decisions that benefit others, developing collaboration and building a just and peaceful community (Waters, 2021). This altruistic consciousness is a guiding principle supporting ethical behaviours and builds a more thoughtful and caring society.
Altruism encourages individuals to comprehend others’ well-being. This fosters a sense of interconnectivity alongside empathy, which could lead to increased support and collaboration alongside community bonding (Waters, 2021). Organisations or people with ill motives could take advantage of the model. This can encompass taking advantage of others’ kindness for their benefit.
Communitarianism
This political and moral framework stresses the community’s responsibility alongside shared ideals in impacting ethical judgments. It stresses the interconnection of individuals within a society and implies that moral judgments should consider the general community’s well-being. Understanding the model assists individuals in making better decisions since it teaches them ways of balancing their interests with the overall good. It encourages comprehension of ways a person’s activities impact the community and fosters responsibility towards others. People could make ethical choices that emphasise community benefit above personal interests through adapting communitarian ideas, building social cohesiveness, and contributing to a more just and peaceful society that values mutual assistance and collaboration (Gotelli, 2015).
Communitarianism stressed the significance of communal links and shared values, which could enhance collaboration and social ties, generating a sense of belonging and togetherness (Gotelli, 2015). However, balancing social needs and individual desires could be challenging, resulting in ethical difficulties and moral dilemmas.
This refers to an ethical framework emphasising the value of adhering to moral standards and principles during decision-making, regardless of the results. It has the implication that behaviours are acceptable on the basis of their adherence to ethical rules instead of the results they establish (Regoli, 2019). Understanding the approach could assist one in making moral decisions by emphasising moral principles’ universality, honesty and obligation. It encourages individuals to assess their acts’ ethical consequences, regardless of prospective downsides or rewards (Regoli, 2019). People embracing deontological concepts could make morally sound judgments and act according to widely recognised ideals. The strategy promotes ethical conduct, builds trust and contributes to a principled and just society.
Deontology provides a clear approach for judgment-making on a universal principle basis, enhancing moral consistency and eliminating ethical relativism. Nevertheless, deontology’s thorough commitment to principles and norms might only sometimes accommodate the complicated real-world activities needing trade-offs, resulting in morally challenging conclusions (Regoli, 2019).
Financial performance
This refers to examining an entity’s general monetary effectiveness and health in utilising its resources to establish profits and attain its aims (CFI Team, 2021). It entails various measurements alongside indicators that reveal an entity’s ability to produce income, manage stress, reduce expenses, and establish stakeholder value. It can be measured by return on investment and cash flow.
Return on Investment (ROI)
This popular monetary statistic measures an investment’s profitability in relation to its cost. It calculates the percentage of ROI in relation to the initial investment. It is calculated as net profit divided by initial investment multiplied by one hundred (Net profit/initial investment *100). A higher ROI shows superior monetary success since it represents efficient resource allocation to establish profits (CFI Team, 2021).
This denotes the money movement out of and into a corporation over time. It represents an entity’s capacity to earn cash from operations and its liquidity to satisfy financial commitments. Positive cash flow shows more money coming in than going out, showing a powerful financial condition (CFI Team, 2021). An entity’s cash flow could be calculated through tracking its financing, investing and operating operations.
Non-financial performance
This measures an entity’s accomplishments and efficiency in areas without financial relations (Indeed Editorial Team, 2023). It involves assessing customer satisfaction, social responsibility, operational efficiency and environmental impact to measure its general performance and contribution to its stakeholders.
Customer satisfaction
This vital non-financial performance assesses how efficiently an entity satisfies its customers’ demands and expectations (Indeed Editorial Team, 2023). It can be done through surveys, customer assessments, and comments. Businesses evaluate customer sentiment by utilising tools including NPS, net promoter score, or CSAT, and customer satisfaction score (Indeed Editorial Team, 2023). For instance, a corporation could conduct post-purchase surveys to gauge consumers’ satisfaction with its services or products. Greater customer satisfaction shows that the entity offers value and effectively addresses customer requests. Positive customer encounters could enhance brand reputation, customer loyalty and repeat business. Besides, companies could get insights into their non-financial performance and make needed adjustments to enhance customer associations and general success by evaluating customer happiness.
Value refers to the advantages, benefits and worth that an entity’s projects, services and goods bring to its stakeholders (DecisionWise, 2018). It could encompass factors such as satisfaction, utility and quality, contributing to financial gains, market competitiveness and client loyalty.
Contrarily, impact refers to the repercussions, outcomes and effects of an entity’s decisions, activities or initiatives regarding several factors, including stakeholder interactions, environmental sustainability and social responsibility (Waters, 2021).
Ways people practice create value.
Enhanced productivity and performance
Efficient people practices encompass employee engagement programs, skill growth, and adequate training that contribute to enhanced entity productivity and performance. Employees with the requisite expertise and skills may conduct their roles more efficiently, leading to better work quality and increased productivity. Besides, strategies that promote employee recognition, involvement and a favourable work atmosphere assist in boosting motivation and morale (Komm et al., 2021). The enhanced motivation results in better role devotion, enhanced teamwork, and a willingness to go the extra mile in achieving corporate goals.
Acquiring and attracting talent
Investment in excellent people practices, including a supportive work tradition, career growth chances and competitive salary, result in excellent recruitment and retention. Employees are more likely to stay with a firm that acknowledges their contributions and offers chances for growth. This decreased turnover expenses (Komm et al., 2021). Furthermore, excellent comments from pleased employees could assist the firm in attracting new talent. Engaged and skilled employees contribute to knowledge exchange, innovation and an excellent work atmosphere, which establish value through strengthening organisational capabilities and presenting the firm as an employer of choice in a competitive labour market.
Checking and ensuring that goals are attained
Value measurement helps entities determine if their defined goals and objectives are being achieved. Companies could establish whether their plans produce the expected outcomes by reviewing KPIs (key performance indicators) and comparing them to predetermined goals. This process encourages informed decision-making and permits modifications if the objectives must be fulfilled. Besides, it guarantees that resources are effectively allocated to the events that contribute the most to business success, enhancing effectiveness and efficiency (Komm et al., 2021).
Ensuring a people practice contribution
Evaluating the effect of people’s practice efforts on employee performance, happiness, and entity outcomes forms part of value measurement. Entities could assess the effect of people practice strategies on general entity success through quantifying elements, including training efficacy, retention rates and employee engagement (Komm et al., 2021). This data-driven initiative offers insights into the efficacy of various people-focused initiatives, permitting the people professionals to modify their approaches to positively impact the workforce, consequently raising entity performance, employee morale and productivity.
Methods of measuring value
Cost-benefit analysis
This refers to a systematic approach that involves weighing the potential costs and advantages of an action, project and decision (Hayes, 2023). It measures particular actions’ benefits, goods, costs, and adverse effects. Entities could analyse the total costs against the benefits by giving monetary values to such aspects to recognise if the activity has financial sustainability. This analysis enhances decision-making by providing an official approach for determining if the prospective benefits outweigh the expenses, permitting businesses to prioritise strategies that offer the greatest return on investment.
This is validating a system’s efficacy, dependability and correctness. It entails acquiring evidence, information or data to show that a given outcome or strategy attains the desired requirements or goals (Drouin-Rousseau et al., 2023). Validation guarantees that a process or system consistently generates the needed outcomes and adheres to the applicable standards. It is vital in several industries since it raises the general work’s credibility, minimises risks and prevents errors.
Reference list
Bhasin, H. (2020). Six Thinking Hats: Definition, Benefits & Framework Explained . [online] Marketing91. Available at: https://www.marketing91.com/six-thinking-hats/ [Accessed 24 Aug. 2023].
Boatman, A. (2021). What is Evidence-Based HR? Examples, Benefits, and Process . [online] AIHR. Available at: https://www.aihr.com/blog/evidence-based-hr/#:~:text=Evidence%2Dbased%20HR%20is%20the [Accessed 24 Aug. 2023].
CFI Team (2022). Financial Performance . [online] Corporate Finance Institute. Available at: https://corporatefinanceinstitute.com/resources/accounting/financial-performance/ [Accessed 24 Aug. 2023].
CIPD (2019). CIPD | Critical thinking | Podcast . [online] CIPD. Available at: https://www.cipd.org/en/knowledge/podcasts/critical-thinking/#:~:text=Warren%20Howlett%3A%20Critical%20thinking%20is [Accessed 24 Aug. 2023].
DecisionWise (2018). Impact: Seeing Positive and Worthwhile Outcomes and Results for Your Work . [online] DecisionWise. Available at: https://decision-wise.com/resources/articles/impact-seeing-positive-and-worthwhile-outcomes-and-results-for-your-work/ [Accessed 24 Aug. 2023].
Drouin-Rousseau, S., Fernet, C., Austin, S., Fabi, B. and Morin, A., J.S. (2023). Employee human resource management values: validation of a new concept and scale . [online] Available at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1049657/full [Accessed 24 Aug. 2023].
Gotelli, E. (2015). Communitarianism: Pros and cons . [online] prezi.com. Available at: https://prezi.com/caz-qeuri3he/communitarianism-pros-and-cons/ [Accessed 24 Aug. 2023].
Hayes, A. (2023). What Is Cost-Benefit Analysis, How Is it Used, What Are its Pros and Cons? [online] Investopedia. Available at: https://www.investopedia.com/terms/c/cost-benefitanalysis.asp#:~:text=A%20cost%2Dbenefit%20analysis%20is%20the%20process%20used%20to%20measure [Accessed 24 Aug. 2023].
Indeed Editorial Team (2023a). 6 examples of non-financial measures of performance . [online] Available at: https://uk.indeed.com/career-advice/career-development/non-financial-measures-of-performance [Accessed 24 Aug. 2023].
Indeed Editorial Team (2023b). What Is Action Learning? (And How To Use It at Work) . [online] Available at: https://www.indeed.com/career-advice/career-development/action-learning#:~:text=Action%20learning%20is%20the%20process,to%20reflect%20on%20each%20solution. [Accessed 24 Aug. 2023].
Indeed Editorial Team (2023c). What Is the Rational Model of Decision-Making? (With Steps) . [online] Indeed Career Guide. Available at: https://ca.indeed.com/career-advice/career-development/rational-model-of-decision-making#:~:text=The%20rational%20model%20of%20decision%2Dmaking%20uses%20logical%20steps%20to [Accessed 24 Aug. 2023].
Jean, J. (2023). Weighing The Pros And Cons Of Remote Work . [online] eLearning Industry. Available at: https://elearningindustry.com/weighing-the-pros-and-cons-of-remote-work [Accessed 24 Aug. 2023].
Komm, A., Pollner, F., Schaninger, B. and Sikka, S. (2021). The new possible: How HR can help build the organization of the future | McKinsey . [online] McKinsey & Company. Available at: https://www.mckinsey.com/capabilities/people-and-organizational-performance/our-insights/the-new-possible-how-hr-can-help-build-the-organization-of-the-future [Accessed 24 Aug. 2023].
MasterClass (2021). How to Identify Cognitive Bias: 12 Examples of Cognitive Bias . [online] Available at: https://www.masterclass.com/articles/how-to-identify-cognitive-bias [Accessed 24 Aug. 2023].
MBA Knowledge Base (2021). Best Fit and Best Practice Approaches in Strategic HRM . [online] MBA Knowledge Base. Available at: https://www.mbaknol.com/human-resource-management/best-fit-and-best-practice-approaches-in-strategic-hrm/#:~:text=Best%20Fit%20Approach&text=Strategy%20involves%20planning%20future%20activities [Accessed 24 Aug. 2023].
Obsidian HR (2021). Pros & Cons of 6 Different Types of Interviews . [online] Obsidian HR. Available at: https://www.obsidianhr.com/pros-cons-of-6-different-types-of-interviews/ [Accessed 24 Aug. 2023].
O’Reilly (n.d.). Chapter 9: Valid and Sound Arguments – An Introduction to Critical Thinking and Creativity: Think More, Think Better [Book] . [online] www.oreilly.com. Available at: https://www.oreilly.com/library/view/an-introduction-to/9780470195093/OEBPS/c09.htm#:~:text=A%20valid%20argument%20is%20one [Accessed 24 Aug. 2023].
Prasanna (2022). Interviews Advantages And Disadvantages | What is an Interview? 6 Merits and Demerits of Interview . [online] A Plus Topper. Available at: https://www.aplustopper.com/interviews-advantages-and-disadvantages/ [Accessed 24 Aug. 2023].
Regoli, N. (2019). 12 Pros and Cons of Deontological Ethics . [online] ConnectUS. Available at: https://connectusfund.org/12-pros-and-cons-of-deontological-ethics [Accessed 24 Aug. 2023].
The Decision Lab (2022). Bounded Rationality – Biases & Heuristics | The Decision Lab . [online] The Decision Lab. Available at: https://thedecisionlab.com/biases/bounded-rationality [Accessed 24 Aug. 2023].
The Investopedia Team (2023). Porter’s 5 Forces Explained and How to Use the Model . [online] Investopedia. Available at: https://www.investopedia.com/terms/p/porter.asp [Accessed 24 Aug. 2023].
Vaidya, D. (2022). Porter’s Five Forces . [online] WallStreetMojo. Available at: https://www.wallstreetmojo.com/porters-five-forces/ [Accessed 24 Aug. 2023].
Waters, S. (2021). What is altruism (and is it important for work)? | BetterUp . [online] www.betterup.com. Available at: https://www.betterup.com/blog/altruism [Accessed 24 Aug. 2023].
Young, J. (2022). CIPD | Evidence-based practice for effective decision-making | Factsheets . [online] CIPD. Available at: https://www.cipd.org/en/knowledge/factsheets/evidence-based-practice-factsheet/ [Accessed 24 Aug. 2023].
- 5CO02 Assignment Example

- CIPD Level 3
- CIPD Level 7
+44 2871140060
Image Disclaimer:
The images used on this website are not our own and are solely utilised for research purposes. Any credit for these images belongs to their rightful copyright owners. We do not claim ownership or authorship of any images displayed on this website. If you believe that any image used here infringes upon your copyright, please contact us immediately, and we will promptly remove it or provide proper attribution as per your request.
Content Disclaimer:
The papers shared on this platform are provided for reference purposes only. Users are strictly advised against submitting these papers to any educational institution or academic platform for grading or assessment purposes.
© 2024 CIPD Modules. All rights Reserved.
- Privacy policy
- Refund and Returns Policy

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
5HR02 Assignment Example , Talent Management and Workforce Planning will guide you on how to handle the assignment and course. ... Disclaimer: CIPD Assignment Help is a custom writing service that provides online on-demand written work for assistance purposes. All the work should be used in accordance with the appropriate policies and ...
An introduction to the unit 5HR02 Talent management and workforce planning. 5HR02 is a unit that teaches students about labour market trends and their implications for workforce planning to attract qualified candidates to join an organization. Learners examine the role of employers in positioning their organizations in the labour market.
The CIPD Podcast "From surviving to thriving: key changes facing people practice in 2020" provides a discussion of changes that need to be implemented at work, such as work-life balance to build a fair, brave and equal workplace for all employees. 5HR02 assignment is divided into three tasks.
Workforce Planning and Recruitment Pack. AC 2.1 Analysis of the impact of workforce planning in terms of forecasting demand for labour utilising both internal and external sources of supply. AC 2.2 An evaluation of the effectiveness of promotion/demotion rates, employee turnover rates, and critical incident analysis techniques used to support ...
The 5HR02 assignment is compartmentalized into three distinct tasks. The inaugural task mandates the creation of a poster presentation that explores strategic alignment with the labour market, followed by the formulation of a workforce planning and recruitment dossier. Lastly, students are required to assemble a proposal presentation package ...
5HR02 Assignment Examples. Workforce Planning and Recruitment Pack. ... For example, some of the key factors affecting the external supply of human resources include the literacy level of a nation, population rate, technological advancement, and compensation system. ... CIPD Level 3 Past Papers; CIPD Level 5 Past Papers; CIPD Level 7 Past Papers;
Learning 5HR02 helps learners understand labour market trends and how they relate to workforce planning to attract the best candidates to join an organisation. Participants examine employers' role in positioning themselves in the labour market. To ensure that they are resourcing their organisations with the right people, professionals assess ...
5HR02 Assignment Examples. Workforce Planning and Recruitment Pack. AC 2.2 An evaluation of the effectiveness of promotion/demotion rates, employee turnover rates, and critical incident analysis techniques used to support workforce planning. ... CIPD Level 3 Past Papers; CIPD Level 5 Past Papers; CIPD Level 7 Past Papers; Contact via iMessage ...
5HR02 Assignment Examples. Estimated reading: 0 minutes 1243 views. Workforce Planning and Recruitment Pack. 5HR02 Assignment Examples - Previous 5HR01 Assignment Example Next - 5HR02 Assignment Examples 5HR03 Assignment Examples.
CIPD Level 5. /. 5HR02 Assignment Example. Admin May 13, 2024 CIPD Level 5.
CIPD 5HR02 Assignment Example | Talent management and WorkforcePplanning . Get Custom CIPD Assignment from Reliable Writers that Offer CIPD Assignment Help. Money Back Guarantee. Save Time. 24/7 Customer support. Guaranteed A or B Grade. Achieve more in less time. GET A FREE QUOTE.
Introduction. This segment is a workforce planning and recruitment pack for the management, enhancing awareness about forecasting demand and supply of labour, utilising internal and external sources, promoting and demotion rates, critical incident analysis techniques among others. The pack also consists of information on performance appraisals ...
3 Level 5 CIPD 5HR02 Assignment Task 3 : Understand the purpose and impact of effective talent management. 3.1 3.1 Examine turnover and retention trends and the factors that influence why people choose to leave or remain. 3.2 3.2 Compare different approaches to developing and retaining talent on an individual and group level.
5HR02 Assignment Examples. Workforce Planning and Recruitment Pack. Introduction; Updated on April 11, 2023 . Introduction ... (CIPD 2018; Kapur 2022; Pahlanie et al. 2020). Workforce planning has emerged as a key HR subject in the contemporary global market. In specific, with a clear understanding of the existing workforce and future goals, HR ...
5HR02 Talent Management and Workforce Planning May21 CIPD Candidate Assessment Activity Title of unit/s Talent Management and Workforce Planning Unit No/s 5HR02 Level 5 Credit value 6 Assessment method(s) Written answers to questions Review date September 2022 Understand labour market trends and their significance for workforce planning. 1. Be able to explain how organisations position ...
Our meticulously crafted sample paper for the 5HR02 assignment is the key to your academic success. Here's why our sample paper is a must-have for you: Expert Guidance: Our experienced writers have created a sample paper that showcases the highest standards of quality and professionalism. You can learn from the best.
5HR02. Talent management and workforce planning . 5 . 6 : 60 . 25 : 5HR03. Reward for performance and contribution . 5 : 6 . 60 : 25 . Ref RQFUnit title . ... The CIPD will set assignments for all core units. For the specialist and optional units, centres will be required to set their own assignments, based on guidance provided by the CIPD. ...
For example, in our organisation, people management professionals have adopted employee development as an effective resourcing strategy which involves training of employees on the use of modern technology to enhance effective communication and performance of duties. Through this implementation, the turnover rate of the organisation has highly ...
Compare the types of employee bodies, union and non-union forms of employee representation. (AC 4.2) Evaluate the purpose of collective bargaining and how it works. (AC 4.3) Must Read: 5HR01 Employment Relationship Management. Review emerging developments to inform approaches to employee voice and engagement. (AC 1.1)
3) Explain how people and organisational performance can impact on the approach to reward. (AC 1.3) 4) Compare two different types of benefits offered by organisations and the merits of each. (AC 1.4) 5) Assess the contribution of extrinsic and intrinsic rewards to improving employee contribution and sustained organisational performance.
5HR01 Assignment Example. Estimated reading: 0 minutes 2044 views. Section 1. Section 2. Reference. Anon, Collective employment law. Oxford Reference. Available at: 5HR01 Assignment Example - Previous 5CO03 Assignment Examples Next - 5HR01 Assignment Example 5HR02 Assignment Examples.
According to CIPD (2021a), rewards may also include fixed pay, which is the guaranteed income or salary paid to employees as recompense for the work they have performed for a set term. Other compensations that includes bonuses, pension, incentives, and overtime that is advanced to the employees, may also constitute the reward.
AC 1.1. Evidence-based practice is a systematic decision-making model that emphasises informed decisions on a robust evidence-based basis alongside effective reasoning (Young, 2022). It involves employing skills encompassing critical thinking alongside analysis for evaluating available data to ensure that the results are defendable to others ...