An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it's official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
- Browse Titles
NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-.


StatPearls [Internet].
Delivery, face and brow presentation.
Julija Makajeva ; Mohsina Ashraf .
Affiliations
Last Update: January 9, 2023 .
- Continuing Education Activity
Face and brow presentation is a malpresentation during labor when the presenting part is either the face or, in the case of brow presentation, it is the area between the orbital ridge and the anterior fontanelle. This activity reviews the evaluation and management of these two presentations and explains the role of the interprofessional team in managing delivery safely for both the mother and the baby.
- Describe the mechanism of labor in the face and brow presentation.
- Summarize potential maternal and fetal complications during the face and brow presentations.
- Review different management approaches for the face and brow presentation.
- Outline some interprofessional strategies that will improve patient outcomes in delivery cases with face and brow presentation issues.
- Introduction
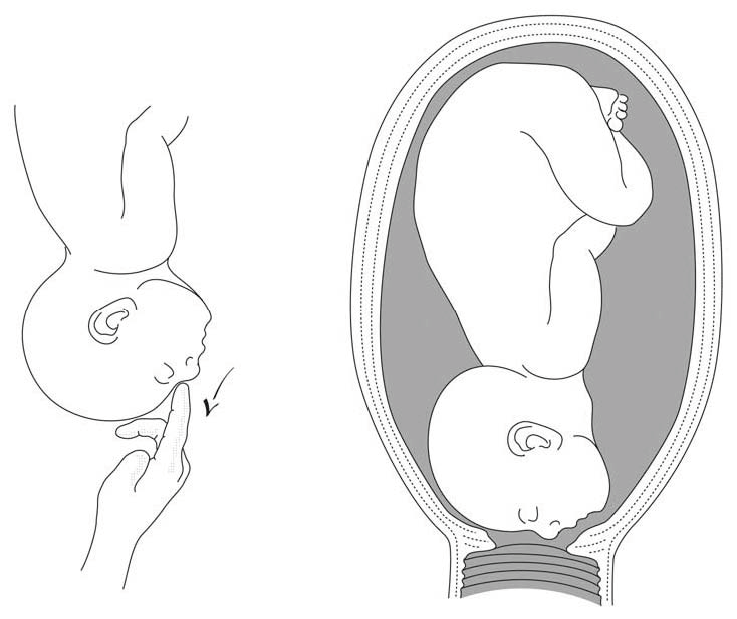
The term presentation describes the leading part of the fetus or the anatomical structure closest to the maternal pelvic inlet during labor. The presentation can roughly be divided into the following classifications: cephalic, breech, shoulder, and compound. Cephalic presentation is the most common and can be further subclassified as vertex, sinciput, brow, face, and chin. The most common presentation in term labor is the vertex, where the fetal neck is flexed to the chin, minimizing the head circumference.
Face presentation – an abnormal form of cephalic presentation where the presenting part is mentum. This typically occurs because of hyperextension of the neck and the occiput touching the fetal back. Incidence of face presentation is rare, accounting for approximately 1 in 600 of all presentations. [1] [2] [3]
In brow presentation, the neck is not extended as much as in face presentation, and the leading part is the area between the anterior fontanelle and the orbital ridges. Brow presentation is considered the rarest of all malpresentation with a prevalence of 1 in 500 to 1 in 4000 deliveries. [3]
Both face and brow presentations occur due to extension of the fetal neck instead of flexion; therefore, conditions that would lead to hyperextension or prevent flexion of the fetal neck can all contribute to face or brow presentation. These risk factors may be related to either the mother or the fetus. Maternal risk factors are preterm delivery, contracted maternal pelvis, platypelloid pelvis, multiparity, previous cesarean section, black race. Fetal risk factors include anencephaly, multiple loops of cord around the neck, masses of the neck, macrosomia, polyhydramnios. [2] [4] [5]
These malpresentations are usually diagnosed during the second stage of labor when performing a digital examination. It is possible to palpate orbital ridges, nose, malar eminences, mentum, mouth, gums, and chin in face presentation. Based on the position of the chin, face presentation can be further divided into mentum anterior, posterior, or transverse. In brow presentation, anterior fontanelle and face can be palpated except for the mouth and the chin. Brow presentation can then be further described based on the position of the anterior fontanelle as frontal anterior, posterior, or transverse.
Diagnosing the exact presentation can be challenging, and face presentation may be misdiagnosed as frank breech. To avoid any confusion, a bedside ultrasound scan can be performed. [6] The ultrasound imaging can show a reduced angle between the occiput and the spine or, the chin is separated from the chest. However, ultrasound does not provide much predicting value in the outcome of the labor. [7]
- Anatomy and Physiology
Before discussing the mechanism of labor in the face or brow presentation, it is crucial to highlight some anatomical landmarks and their measurements.
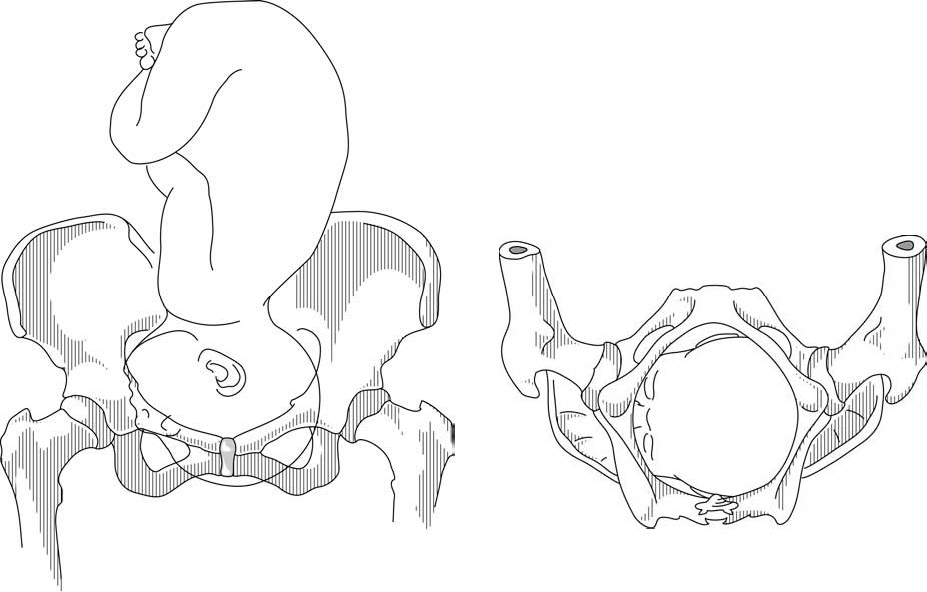
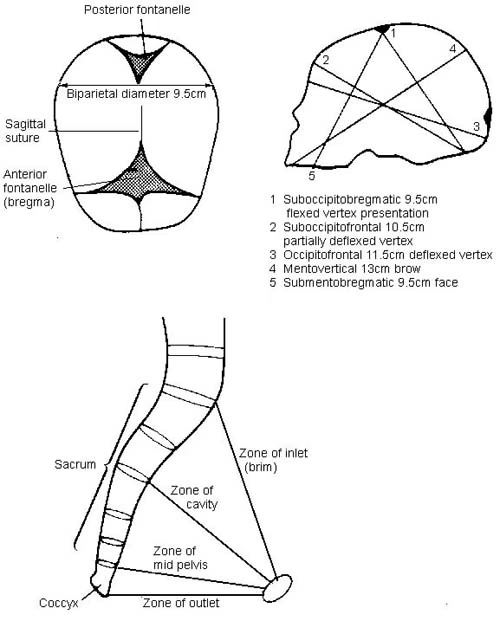
Planes and Diameters of the Pelvis
The three most important planes in the female pelvis are the pelvic inlet, mid pelvis, and pelvic outlet.
Four diameters can describe the pelvic inlet: anteroposterior, transverse, and two obliques. Furthermore, based on the different landmarks on the pelvic inlet, there are three different anteroposterior diameters, named conjugates: true conjugate, obstetrical conjugate, and diagonal conjugate. Only the latter can be measured directly during the obstetric examination. The shortest of these three diameters is obstetrical conjugate, which measures approximately 10.5 cm and is a distance between the sacral promontory and 1 cm below the upper border of the symphysis pubis. This measurement is clinically significant as the fetal head must pass through this diameter during the engagement phase. The transverse diameter measures about 13.5cm and is the widest distance between the innominate line on both sides.
The shortest distance in the mid pelvis is the interspinous diameter and usually is only about 10 cm.
Fetal Skull Diameters
There are six distinguished longitudinal fetal skull diameters:
- Suboccipito-bregmatic: from the center of anterior fontanelle (bregma) to the occipital protuberance, measuring 9.5 cm. This is the presenting diameter in vertex presentation.
- Suboccipito-frontal: from the anterior part of bregma to the occipital protuberance, measuring 10 cm
- Occipito-frontal: from the root of the nose to the most prominent part of the occiput, measuring 11.5cm
- Submento-bregmatic: from the center of the bregma to the angle of the mandible, measuring 9.5 cm. This is the presenting diameter in face presentation where the neck is hyperextended.
- Submento-vertical: from the midpoint between fontanelles and the angle of the mandible, measuring 11.5cm
- Occipito-mental: from the midpoint between fontanelles and the tip of the chin, measuring 13.5 cm. It is the presenting diameter in brow presentation.
Cardinal Movements of Normal Labor
- Neck flexion
- Internal rotation
- Extension (delivers head)
- External rotation (Restitution)
- Expulsion (delivery of anterior and posterior shoulders)
Some of the key movements are not possible in the face or brow presentations.
Based on the information provided above, it is obvious that labor will be arrested in brow presentation unless it spontaneously changes to face or vertex, as the occipito-mental diameter of the fetal head is significantly wider than the smallest diameter of the female pelvis. Face presentation can, however, be delivered vaginally, and further mechanisms of face delivery will be explained in later sections.
- Indications
As mentioned previously, spontaneous vaginal delivery can be successful in face presentation. However, the main indication for vaginal delivery in such circumstances would be a maternal choice. It is crucial to have a thorough conversation with a mother, explaining the risks and benefits of vaginal delivery with face presentation and a cesarean section. Informed consent and creating a rapport with the mother is an essential aspect of safe and successful labor.
- Contraindications
Vaginal delivery of face presentation is contraindicated if the mentum is lying posteriorly or is in a transverse position. In such a scenario, the fetal brow is pressing against the maternal symphysis pubis, and the short fetal neck, which is already maximally extended, cannot span the surface of the maternal sacrum. In this position, the diameter of the head is larger than the maternal pelvis, and it cannot descend through the birth canal. Therefore the cesarean section is recommended as the safest mode of delivery for mentum posterior face presentations.
Attempts to manually convert face presentation to vertex, manual or forceps rotation of the persistent posterior chin to anterior are contraindicated as they can be dangerous.
Persistent brow presentation itself is a contraindication for vaginal delivery unless the fetus is significantly small or the maternal pelvis is large.
Continuous electronic fetal heart rate monitoring is recommended for face and brow presentations, as heart rate abnormalities are common in these scenarios. One study found that only 14% of the cases with face presentation had no abnormal traces on the cardiotocograph. [8] It is advised to use external transducer devices to prevent damage to the eyes. When internal monitoring is inevitable, it is suggested to place monitoring devices on bony parts carefully.
People who are usually involved in the delivery of face/ brow presentation are:
- Experienced midwife, preferably looking after laboring woman 1:1
- Senior obstetrician
- Neonatal team - in case of need for resuscitation
- Anesthetic team - to provide necessary pain control (e.g., epidural)
- Theatre team - in case of failure to progress and an emergency cesarean section will be required.
- Preparation
No specific preparation is required for face or brow presentation. However, it is essential to discuss the labor options with the mother and birthing partner and inform members of the neonatal, anesthetic, and theatre co-ordinating teams.
- Technique or Treatment
Mechanism of Labor in Face Presentation
During contractions, the pressure exerted by the fundus of the uterus on the fetus and pressure of amniotic fluid initiate descent. During this descent, the fetal neck extends instead of flexing. The internal rotation determines the outcome of delivery, if the fetal chin rotates posteriorly, vaginal delivery would not be possible, and cesarean section is permitted. The approach towards mentum-posterior delivery should be individualized, as the cases are rare. Expectant management is acceptable in multiparous women with small fetuses, as a spontaneous mentum-anterior rotation can occur. However, there should be a low threshold for cesarean section in primigravida women or women with large fetuses.
When the fetal chin is rotated towards maternal symphysis pubis as described as mentum-anterior; in these cases further descend through the vaginal canal continues with approximately 73% cases deliver spontaneously. [9] Fetal mentum presses on the maternal symphysis pubis, and the head is delivered by flexion. The occiput is pointing towards the maternal back, and external rotation happens. Shoulders are delivered in the same manner as in vertex delivery.
Mechanism of Labor in Brow Presentation
As this presentation is considered unstable, it is usually converted into a face or an occiput presentation. Due to the cephalic diameter being wider than the maternal pelvis, the fetal head cannot engage; thus, brow delivery cannot take place. Unless the fetus is small or the pelvis is very wide, the prognosis for vaginal delivery is poor. With persistent brow presentation, a cesarean section is required for safe delivery.
- Complications
As the cesarean section is becoming a more accessible mode of delivery in malpresentations, the incidence of maternal and fetal morbidity and mortality during face presentation has dropped significantly. [10]
However, there are still some complications associated with the nature of labor in face presentation. Due to the fetal head position, it is more challenging for the head to engage in the birth canal and descend, resulting in prolonged labor.
Prolonged labor itself can provoke foetal distress and arrhythmias. If the labor arrests or signs of fetal distress appear on CTG, the recommended next step in management is an emergency cesarean section, which in itself carries a myriad of operative and post-operative complications.
Finally, due to the nature of the fetal position and prolonged duration of labor in face presentation, neonates develop significant edema of the skull and face. Swelling of the fetal airway may also be present, resulting in respiratory distress after birth and possible intubation.
- Clinical Significance
During vertex presentation, the fetal head flexes, bringing the chin to the chest, forming the smallest possible fetal head diameter, measuring approximately 9.5cm. With face and brow presentation, the neck hyperextends, resulting in greater cephalic diameters. As a result, the fetal head will engage later, and labor will progress more slowly. Failure to progress in labor is also more common in both presentations compared to vertex presentation.
Furthermore, when the fetal chin is in a posterior position, this prevents further flexion of the fetal neck, as browns are pressing on the symphysis pubis. As a result, descend through the birth canal is impossible. Such presentation is considered undeliverable vaginally and requires an emergency cesarean section.
Manual attempts to change face presentation to vertex, manual or forceps rotation to mentum anterior are considered dangerous and are discouraged.
- Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
A multidisciplinary team of healthcare experts supports the woman and her child during labor and the perinatal period. For a face or brow presentation to be appropriately diagnosed, an experienced midwife and obstetrician must be involved in the vaginal examination and labor monitoring. As fetal anomalies, such as anencephaly or goiter, can contribute to face presentation, sonographers experienced in antenatal scanning should also be involved in the care. It is advised to inform the anesthetic and neonatal teams in advance of the possible need for emergency cesarean section and resuscitation of the neonate. [11] [12]
- Review Questions
- Access free multiple choice questions on this topic.
- Comment on this article.
Disclosure: Julija Makajeva declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies.
Disclosure: Mohsina Ashraf declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies.
This book is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0) ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/ ), which permits others to distribute the work, provided that the article is not altered or used commercially. You are not required to obtain permission to distribute this article, provided that you credit the author and journal.
- Cite this Page Makajeva J, Ashraf M. Delivery, Face and Brow Presentation. [Updated 2023 Jan 9]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-.
In this Page
Bulk download.
- Bulk download StatPearls data from FTP
Related information
- PubMed Links to PubMed
Similar articles in PubMed
- Sonographic diagnosis of fetal head deflexion and the risk of cesarean delivery. [Am J Obstet Gynecol MFM. 2020] Sonographic diagnosis of fetal head deflexion and the risk of cesarean delivery. Bellussi F, Livi A, Cataneo I, Salsi G, Lenzi J, Pilu G. Am J Obstet Gynecol MFM. 2020 Nov; 2(4):100217. Epub 2020 Aug 18.
- Review Sonographic evaluation of the fetal head position and attitude during labor. [Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2022] Review Sonographic evaluation of the fetal head position and attitude during labor. Ghi T, Dall'Asta A. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2022 Jul 6; . Epub 2022 Jul 6.
- Stages of Labor. [StatPearls. 2024] Stages of Labor. Hutchison J, Mahdy H, Hutchison J. StatPearls. 2024 Jan
- Leopold Maneuvers. [StatPearls. 2024] Leopold Maneuvers. Superville SS, Siccardi MA. StatPearls. 2024 Jan
- Review Labor with abnormal presentation and position. [Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am. ...] Review Labor with abnormal presentation and position. Stitely ML, Gherman RB. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am. 2005 Jun; 32(2):165-79.
Recent Activity
- Delivery, Face and Brow Presentation - StatPearls Delivery, Face and Brow Presentation - StatPearls
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
Turn recording back on
Connect with NLM
National Library of Medicine 8600 Rockville Pike Bethesda, MD 20894
Web Policies FOIA HHS Vulnerability Disclosure
Help Accessibility Careers
Learn how UpToDate can help you.
Select the option that best describes you
- Medical Professional
- Resident, Fellow, or Student
- Hospital or Institution
- Group Practice
- Patient or Caregiver
- Find in topic
RELATED TOPICS
INTRODUCTION
Diagnosis and management of face and brow presentations will be reviewed here. Other cephalic malpresentations are discussed separately. (See "Occiput posterior position" and "Occiput transverse position" .)
Prevalence — Face and brow presentation are uncommon. Their prevalences compared with other types of malpresentations are shown below [ 1-9 ]:
● Occiput posterior – 1/19 deliveries
● Breech – 1/33 deliveries
Fetal Presentation, Position, and Lie (Including Breech Presentation)
- Variations in Fetal Position and Presentation |
During pregnancy, the fetus can be positioned in many different ways inside the mother's uterus. The fetus may be head up or down or facing the mother's back or front. At first, the fetus can move around easily or shift position as the mother moves. Toward the end of the pregnancy the fetus is larger, has less room to move, and stays in one position. How the fetus is positioned has an important effect on delivery and, for certain positions, a cesarean delivery is necessary. There are medical terms that describe precisely how the fetus is positioned, and identifying the fetal position helps doctors to anticipate potential difficulties during labor and delivery.
Presentation refers to the part of the fetus’s body that leads the way out through the birth canal (called the presenting part). Usually, the head leads the way, but sometimes the buttocks (breech presentation), shoulder, or face leads the way.
Position refers to whether the fetus is facing backward (occiput anterior) or forward (occiput posterior). The occiput is a bone at the back of the baby's head. Therefore, facing backward is called occiput anterior (facing the mother’s back and facing down when the mother lies on her back). Facing forward is called occiput posterior (facing toward the mother's pubic bone and facing up when the mother lies on her back).
Lie refers to the angle of the fetus in relation to the mother and the uterus. Up-and-down (with the baby's spine parallel to mother's spine, called longitudinal) is normal, but sometimes the lie is sideways (transverse) or at an angle (oblique).
For these aspects of fetal positioning, the combination that is the most common, safest, and easiest for the mother to deliver is the following:
Head first (called vertex or cephalic presentation)
Facing backward (occiput anterior position)
Spine parallel to mother's spine (longitudinal lie)
Neck bent forward with chin tucked
Arms folded across the chest
If the fetus is in a different position, lie, or presentation, labor may be more difficult, and a normal vaginal delivery may not be possible.
Variations in fetal presentation, position, or lie may occur when
The fetus is too large for the mother's pelvis (fetopelvic disproportion).
The uterus is abnormally shaped or contains growths such as fibroids .
The fetus has a birth defect .
There is more than one fetus (multiple gestation).

Position and Presentation of the Fetus
Variations in fetal position and presentation.
Some variations in position and presentation that make delivery difficult occur frequently.
Occiput posterior position
In occiput posterior position (sometimes called sunny-side up), the fetus is head first (vertex presentation) but is facing forward (toward the mother's pubic bone—that is, facing up when the mother lies on her back). This is a very common position that is not abnormal, but it makes delivery more difficult than when the fetus is in the occiput anterior position (facing toward the mother's spine—that is facing down when the mother lies on her back).
When a fetus faces up, the neck is often straightened rather than bent,which requires more room for the head to pass through the birth canal. Delivery assisted by a vacuum device or forceps or cesarean delivery may be necessary.
Breech presentation
In breech presentation, the baby's buttocks or sometimes the feet are positioned to deliver first (before the head).
When delivered vaginally, babies that present buttocks first are more at risk of injury or even death than those that present head first.
The reason for the risks to babies in breech presentation is that the baby's hips and buttocks are not as wide as the head. Therefore, when the hips and buttocks pass through the cervix first, the passageway may not be wide enough for the head to pass through. In addition, when the head follows the buttocks, the neck may be bent slightly backwards. The neck being bent backward increases the width required for delivery as compared to when the head is angled forward with the chin tucked, which is the position that is easiest for delivery. Thus, the baby’s body may be delivered and then the head may get caught and not be able to pass through the birth canal. When the baby’s head is caught, this puts pressure on the umbilical cord in the birth canal, so that very little oxygen can reach the baby. Brain damage due to lack of oxygen is more common among breech babies than among those presenting head first.
In a first delivery, these problems may occur more frequently because a woman’s tissues have not been stretched by previous deliveries. Because of risk of injury or even death to the baby, cesarean delivery is preferred when the fetus is in breech presentation, unless the doctor is very experienced with and skilled at delivering breech babies or there is not an adequate facility or equipment to safely perform a cesarean delivery.
Breech presentation is more likely to occur in the following circumstances:
Labor starts too soon (preterm labor).
The uterus is abnormally shaped or contains abnormal growths such as fibroids .
Other presentations
In face presentation, the baby's neck arches back so that the face presents first rather than the top of the head.
In brow presentation, the neck is moderately arched so that the brow presents first.
Usually, fetuses do not stay in a face or brow presentation. These presentations often change to a vertex (top of the head) presentation before or during labor. If they do not, a cesarean delivery is usually recommended.
In transverse lie, the fetus lies horizontally across the birth canal and presents shoulder first. A cesarean delivery is done, unless the fetus is the second in a set of twins. In such a case, the fetus may be turned to be delivered through the vagina.

- Cookie Preferences

Copyright © 2024 Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA and its affiliates. All rights reserved.

- Physician Physician Board Reviews Physician Associate Board Reviews CME Lifetime CME Free CME
- Student USMLE Step 1 USMLE Step 2 USMLE Step 3 COMLEX Level 1 COMLEX Level 2 COMLEX Level 3 96 Medical School Exams Student Resource Center NCLEX - RN NCLEX - LPN/LVN/PN 24 Nursing Exams
- Nurse Practitioner APRN/NP Board Reviews CNS Certification Reviews CE - Nurse Practitioner FREE CE
- Nurse RN Certification Reviews CE - Nurse FREE CE
- Pharmacist Pharmacy Board Exam Prep CE - Pharmacist
- Allied Allied Health Exam Prep Dentist Exams CE - Social Worker CE - Dentist
- Point of Care
- Free CME/CE
Delivery, Face and Brow Presentation
Introduction.
The term presentation describes the leading part of the fetus or the anatomical structure closest to the maternal pelvic inlet during labor. The presentation can roughly be divided into the following classifications: cephalic, breech, shoulder, and compound. Cephalic presentation is the most common and can be further subclassified as vertex, sinciput, brow, face, and chin. The most common presentation in term labor is the vertex, where the fetal neck is flexed to the chin, minimizing the head circumference.
Face presentation – an abnormal form of cephalic presentation where the presenting part is mentum. This typically occurs because of hyperextension of the neck and the occiput touching the fetal back. Incidence of face presentation is rare, accounting for approximately 1 in 600 of all presentations. [1] [2] [3]
In brow presentation, the neck is not extended as much as in face presentation, and the leading part is the area between the anterior fontanelle and the orbital ridges. Brow presentation is considered the rarest of all malpresentation with a prevalence of 1 in 500 to 1 in 4000 deliveries. [3]
Both face and brow presentations occur due to extension of the fetal neck instead of flexion; therefore, conditions that would lead to hyperextension or prevent flexion of the fetal neck can all contribute to face or brow presentation. These risk factors may be related to either the mother or the fetus. Maternal risk factors are preterm delivery, contracted maternal pelvis, platypelloid pelvis, multiparity, previous cesarean section, black race. Fetal risk factors include anencephaly, multiple loops of cord around the neck, masses of the neck, macrosomia, polyhydramnios. [2] [4] [5]
These malpresentations are usually diagnosed during the second stage of labor when performing a digital examination. It is possible to palpate orbital ridges, nose, malar eminences, mentum, mouth, gums, and chin in face presentation. Based on the position of the chin, face presentation can be further divided into mentum anterior, posterior, or transverse. In brow presentation, anterior fontanelle and face can be palpated except for the mouth and the chin. Brow presentation can then be further described based on the position of the anterior fontanelle as frontal anterior, posterior, or transverse.
Diagnosing the exact presentation can be challenging, and face presentation may be misdiagnosed as frank breech. To avoid any confusion, a bedside ultrasound scan can be performed. [6] The ultrasound imaging can show a reduced angle between the occiput and the spine or, the chin is separated from the chest. However, ultrasound does not provide much predicting value in the outcome of the labor. [7]
Anatomy and Physiology
Register for free and read the full article, learn more about a subscription to statpearls point-of-care.
Before discussing the mechanism of labor in the face or brow presentation, it is crucial to highlight some anatomical landmarks and their measurements.
Planes and Diameters of the Pelvis
The three most important planes in the female pelvis are the pelvic inlet, mid pelvis, and pelvic outlet.
Four diameters can describe the pelvic inlet: anteroposterior, transverse, and two obliques. Furthermore, based on the different landmarks on the pelvic inlet, there are three different anteroposterior diameters, named conjugates: true conjugate, obstetrical conjugate, and diagonal conjugate. Only the latter can be measured directly during the obstetric examination. The shortest of these three diameters is obstetrical conjugate, which measures approximately 10.5 cm and is a distance between the sacral promontory and 1 cm below the upper border of the symphysis pubis. This measurement is clinically significant as the fetal head must pass through this diameter during the engagement phase. The transverse diameter measures about 13.5cm and is the widest distance between the innominate line on both sides.
The shortest distance in the mid pelvis is the interspinous diameter and usually is only about 10 cm.
Fetal Skull Diameters
There are six distinguished longitudinal fetal skull diameters:
- Suboccipito-bregmatic: from the center of anterior fontanelle (bregma) to the occipital protuberance, measuring 9.5 cm. This is the presenting diameter in vertex presentation.
- Suboccipito-frontal: from the anterior part of bregma to the occipital protuberance, measuring 10 cm
- Occipito-frontal: from the root of the nose to the most prominent part of the occiput, measuring 11.5cm
- Submento-bregmatic: from the center of the bregma to the angle of the mandible, measuring 9.5 cm. This is the presenting diameter in face presentation where the neck is hyperextended.
- Submento-vertical: from the midpoint between fontanelles and the angle of the mandible, measuring 11.5cm
- Occipito-mental: from the midpoint between fontanelles and the tip of the chin, measuring 13.5 cm. It is the presenting diameter in brow presentation.
Cardinal Movements of Normal Labor
- Neck flexion
- Internal rotation
- Extension (delivers head)
- External rotation (Restitution)
- Expulsion (delivery of anterior and posterior shoulders)
Some of the key movements are not possible in the face or brow presentations.
Based on the information provided above, it is obvious that labor will be arrested in brow presentation unless it spontaneously changes to face or vertex, as the occipito-mental diameter of the fetal head is significantly wider than the smallest diameter of the female pelvis. Face presentation can, however, be delivered vaginally, and further mechanisms of face delivery will be explained in later sections.
Indications
As mentioned previously, spontaneous vaginal delivery can be successful in face presentation. However, the main indication for vaginal delivery in such circumstances would be a maternal choice. It is crucial to have a thorough conversation with a mother, explaining the risks and benefits of vaginal delivery with face presentation and a cesarean section. Informed consent and creating a rapport with the mother is an essential aspect of safe and successful labor.
Contraindications
Vaginal delivery of face presentation is contraindicated if the mentum is lying posteriorly or is in a transverse position. In such a scenario, the fetal brow is pressing against the maternal symphysis pubis, and the short fetal neck, which is already maximally extended, cannot span the surface of the maternal sacrum. In this position, the diameter of the head is larger than the maternal pelvis, and it cannot descend through the birth canal. Therefore the cesarean section is recommended as the safest mode of delivery for mentum posterior face presentations.
Attempts to manually convert face presentation to vertex, manual or forceps rotation of the persistent posterior chin to anterior are contraindicated as they can be dangerous.
Persistent brow presentation itself is a contraindication for vaginal delivery unless the fetus is significantly small or the maternal pelvis is large.
Continuous electronic fetal heart rate monitoring is recommended for face and brow presentations, as heart rate abnormalities are common in these scenarios. One study found that only 14% of the cases with face presentation had no abnormal traces on the cardiotocograph. [8] It is advised to use external transducer devices to prevent damage to the eyes. When internal monitoring is inevitable, it is suggested to place monitoring devices on bony parts carefully.
People who are usually involved in the delivery of face/ brow presentation are:
- Experienced midwife, preferably looking after laboring woman 1:1
- Senior obstetrician
- Neonatal team - in case of need for resuscitation
- Anesthetic team - to provide necessary pain control (e.g., epidural)
- Theatre team - in case of failure to progress and an emergency cesarean section will be required.
Preparation
No specific preparation is required for face or brow presentation. However, it is essential to discuss the labor options with the mother and birthing partner and inform members of the neonatal, anesthetic, and theatre co-ordinating teams.
Technique or Treatment
Mechanism of Labor in Face Presentation
During contractions, the pressure exerted by the fundus of the uterus on the fetus and pressure of amniotic fluid initiate descent. During this descent, the fetal neck extends instead of flexing. The internal rotation determines the outcome of delivery, if the fetal chin rotates posteriorly, vaginal delivery would not be possible, and cesarean section is permitted. The approach towards mentum-posterior delivery should be individualized, as the cases are rare. Expectant management is acceptable in multiparous women with small fetuses, as a spontaneous mentum-anterior rotation can occur. However, there should be a low threshold for cesarean section in primigravida women or women with large fetuses.
When the fetal chin is rotated towards maternal symphysis pubis as described as mentum-anterior; in these cases further descend through the vaginal canal continues with approximately 73% cases deliver spontaneously. [9] Fetal mentum presses on the maternal symphysis pubis, and the head is delivered by flexion. The occiput is pointing towards the maternal back, and external rotation happens. Shoulders are delivered in the same manner as in vertex delivery.
Mechanism of Labor in Brow Presentation
As this presentation is considered unstable, it is usually converted into a face or an occiput presentation. Due to the cephalic diameter being wider than the maternal pelvis, the fetal head cannot engage; thus, brow delivery cannot take place. Unless the fetus is small or the pelvis is very wide, the prognosis for vaginal delivery is poor. With persistent brow presentation, a cesarean section is required for safe delivery.
Complications
As the cesarean section is becoming a more accessible mode of delivery in malpresentations, the incidence of maternal and fetal morbidity and mortality during face presentation has dropped significantly. [10]
However, there are still some complications associated with the nature of labor in face presentation. Due to the fetal head position, it is more challenging for the head to engage in the birth canal and descend, resulting in prolonged labor.
Prolonged labor itself can provoke foetal distress and arrhythmias. If the labor arrests or signs of fetal distress appear on CTG, the recommended next step in management is an emergency cesarean section, which in itself carries a myriad of operative and post-operative complications.
Finally, due to the nature of the fetal position and prolonged duration of labor in face presentation, neonates develop significant edema of the skull and face. Swelling of the fetal airway may also be present, resulting in respiratory distress after birth and possible intubation.
Clinical Significance
During vertex presentation, the fetal head flexes, bringing the chin to the chest, forming the smallest possible fetal head diameter, measuring approximately 9.5cm. With face and brow presentation, the neck hyperextends, resulting in greater cephalic diameters. As a result, the fetal head will engage later, and labor will progress more slowly. Failure to progress in labor is also more common in both presentations compared to vertex presentation.
Furthermore, when the fetal chin is in a posterior position, this prevents further flexion of the fetal neck, as browns are pressing on the symphysis pubis. As a result, descend through the birth canal is impossible. Such presentation is considered undeliverable vaginally and requires an emergency cesarean section.
Manual attempts to change face presentation to vertex, manual or forceps rotation to mentum anterior are considered dangerous and are discouraged.
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
A multidisciplinary team of healthcare experts supports the woman and her child during labor and the perinatal period. For a face or brow presentation to be appropriately diagnosed, an experienced midwife and obstetrician must be involved in the vaginal examination and labor monitoring. As fetal anomalies, such as anencephaly or goiter, can contribute to face presentation, sonographers experienced in antenatal scanning should also be involved in the care. It is advised to inform the anesthetic and neonatal teams in advance of the possible need for emergency cesarean section and resuscitation of the neonate. [11] [12]
Gardberg M,Leonova Y,Laakkonen E, Malpresentations--impact on mode of delivery. Acta obstetricia et gynecologica Scandinavica. 2011 May; [PubMed PMID: 21501123]
Tapisiz OL,Aytan H,Altinbas SK,Arman F,Tuncay G,Besli M,Mollamahmutoglu L,Danışman N, Face presentation at term: a forgotten issue. The journal of obstetrics and gynaecology research. 2014 Jun; [PubMed PMID: 24888918]
Zayed F,Amarin Z,Obeidat B,Obeidat N,Alchalabi H,Lataifeh I, Face and brow presentation in northern Jordan, over a decade of experience. Archives of gynecology and obstetrics. 2008 Nov; [PubMed PMID: 18283473]
Bashiri A,Burstein E,Bar-David J,Levy A,Mazor M, Face and brow presentation: independent risk factors. The journal of maternal-fetal [PubMed PMID: 18570114]
Shaffer BL,Cheng YW,Vargas JE,Laros RK Jr,Caughey AB, Face presentation: predictors and delivery route. American journal of obstetrics and gynecology. 2006 May; [PubMed PMID: 16647888]
Bellussi F,Ghi T,Youssef A,Salsi G,Giorgetta F,Parma D,Simonazzi G,Pilu G, The use of intrapartum ultrasound to diagnose malpositions and cephalic malpresentations. American journal of obstetrics and gynecology. 2017 Dec; [PubMed PMID: 28743440]
Ghi T,Eggebø T,Lees C,Kalache K,Rozenberg P,Youssef A,Salomon LJ,Tutschek B, ISUOG Practice Guidelines: intrapartum ultrasound. Ultrasound in obstetrics [PubMed PMID: 29974596]
Benedetti TJ,Lowensohn RI,Truscott AM, Face presentation at term. Obstetrics and gynecology. 1980 Feb; [PubMed PMID: 7352081]
Ducarme G,Ceccaldi PF,Chesnoy V,Robinet G,Gabriel R, [Face presentation: retrospective study of 32 cases at term]. Gynecologie, obstetrique [PubMed PMID: 16630740]
Cruikshank DP,Cruikshank JE, Face and brow presentation: a review. Clinical obstetrics and gynecology. 1981 Jun; [PubMed PMID: 7307363]
Domingues AP,Belo A,Moura P,Vieira DN, Medico-legal litigation in Obstetrics: a characterization analysis of a decade in Portugal. Revista brasileira de ginecologia e obstetricia : revista da Federacao Brasileira das Sociedades de Ginecologia e Obstetricia. 2015 May; [PubMed PMID: 26107576]
. Intrapartum care for healthy women and babies. 2022 Dec 14:(): [PubMed PMID: 32212591]
Use the mouse wheel to zoom in and out, click and drag to pan the image
Medical Information

Delivery, Face Presentation, and Brow Presentation: Understanding Fetal Positions and Birth Scenarios
Introduction:.
During childbirth, the position of the baby plays a significant role in the delivery process. While the most common fetal presentation is the head-down position (vertex presentation), variations can occur, such as face presentation and brow presentation. This comprehensive article aims to provide a thorough understanding of delivery, face presentation, and brow presentation, including their definitions, causes, complications, and management approaches.
Delivery Process:
- Normal Vertex Presentation: In a typical delivery, the baby is positioned head-down, with the back of the head (occiput) leading the way through the birth canal.
- Engagement and Descent: Prior to delivery, the baby's head engages in the pelvis and gradually descends, preparing for birth.
- Cardinal Movements: The baby undergoes a series of cardinal movements, including flexion, internal rotation, extension, external rotation, and restitution, which facilitate the passage through the birth canal.
Face Presentation:
- Definition: Face presentation occurs when the baby's face is positioned to lead the way through the birth canal instead of the vertex (head).
- Causes: Face presentation can occur due to factors such as abnormal fetal positioning, multiple pregnancies, uterine abnormalities, or maternal pelvic anatomy.
- Complications: Face presentation is associated with an increased risk of prolonged labor, difficulties in delivery, increased fetal malposition, birth injuries, and the need for instrumental delivery.
- Management: The management of face presentation depends on several factors, including the progression of labor, the size of the baby, and the expertise of the healthcare provider. Options may include closely monitoring the progress of labor, attempting a vaginal delivery with careful maneuvers, or considering a cesarean section if complications arise.
Brow Presentation:
- Definition: Brow presentation occurs when the baby's head is partially extended, causing the brow (forehead) to lead the way through the birth canal.
- Causes: Brow presentation may result from abnormal fetal positioning, poor engagement of the fetal head, or other factors that prevent full flexion or extension.
- Complications: Brow presentation is associated with a higher risk of prolonged labor, difficulty in descent, increased chances of fetal head entrapment, birth injuries, and the potential need for instrumental delivery or cesarean section.
- Management: The management of brow presentation depends on various factors, such as cervical dilation, progress of labor, fetal size, and the presence of complications. Close monitoring, expert assessment, and a multidisciplinary approach may be necessary to determine the safest delivery method, which can include vaginal delivery with careful maneuvers, instrumental assistance, or cesarean section if warranted.
Delivery Techniques and Intervention:
- Obstetric Maneuvers: In certain situations, skilled healthcare providers may use obstetric maneuvers, such as manual rotation or the use of forceps or vacuum extraction, to facilitate delivery, reposition the baby, or prevent complications.
- Cesarean Section: In cases where vaginal delivery is not possible or poses risks to the mother or baby, a cesarean section may be performed to ensure a safe delivery.
Conclusion:
Delivery, face presentation, and brow presentation are important aspects of childbirth that require careful management and consideration. Understanding the definitions, causes, complications, and appropriate management approaches associated with these fetal positions can help healthcare providers ensure safe and successful deliveries. Individualized care, close monitoring, and multidisciplinary collaboration are crucial in optimizing maternal and fetal outcomes during these unique delivery scenarios.
Hashtags: #Delivery #FacePresentation #BrowPresentation #Childbirth #ObstetricDelivery
On the Article

Krish Tangella MD, MBA

Alexander Enabnit

Alexandra Warren
Please log in to post a comment.
Related Articles
Test your knowledge, asked by users, related centers, related specialties, related physicians, related procedures, related resources, join dovehubs.
and connect with fellow professionals
Related Directories
At DoveMed, our utmost priority is your well-being. We are an online medical resource dedicated to providing you with accurate and up-to-date information on a wide range of medical topics. But we're more than just an information hub - we genuinely care about your health journey. That's why we offer a variety of products tailored for both healthcare consumers and professionals, because we believe in empowering everyone involved in the care process. Our mission is to create a user-friendly healthcare technology portal that helps you make better decisions about your overall health and well-being. We understand that navigating the complexities of healthcare can be overwhelming, so we strive to be a reliable and compassionate companion on your path to wellness. As an impartial and trusted online resource, we connect healthcare seekers, physicians, and hospitals in a marketplace that promotes a higher quality, easy-to-use healthcare experience. You can trust that our content is unbiased and impartial, as it is trusted by physicians, researchers, and university professors around the globe. Importantly, we are not influenced or owned by any pharmaceutical, medical, or media companies. At DoveMed, we are a group of passionate individuals who deeply care about improving health and wellness for people everywhere. Your well-being is at the heart of everything we do.
For Patients
For professionals, for partners.
Brow Presentation
- First Online: 02 August 2023
Cite this chapter

- Syeda Batool Mazhar 2 &
- Zahra Ahmed Muslim 2
469 Accesses
Brow presentation is the rarest of all malpresentations. Anencephaly, neck masses in fetus, polyhydramnios, multiple loops of cord around neck are the fetal factors leading to brow presentation. Contracted pelvis, preterm labour, platypelloid pelvis are some of the contributory maternal factors for brow presentation. Diagnosis is usually made during second stage of labour during prevaginal examination when anterior frontanelle and face are palpated. Cesarean section is performed in brow presentation as it is unusual to get conversion in average sized fetus once membranes have ruptured.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.

Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Durable hardcover edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Arulkumaran S, Robson M, editors. Munro Kerr operative obstetrics. 13th ed. Elsevier, Amsterdam; 2019. p. 89–93.
Google Scholar
Malvasi A, Barbera A, Di Vagno G, Gimovsky A, Berghella V, Ghi T, Di Renzo GC, Tinelli A. Asynclitism: a literature review of an often forgotten clinical condition. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2015;28(16):1890–4. https://doi.org/10.3109/14767058.2014.972925 . Epub 2014 Oct 29.PMID: 25283847.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Bellussi F, Ghi T, Youssef A, Salsi G, Giorgetta F, Parma D, Simonazzi G, Gianluigi P. The use of intrapartum ultrasound to diagnose malpositions and cephalic malpresentations. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2017;217(6):633–41.
Lanni SM, Gherman R, Gonik B. Malpresentations. Amsterdam: Elsevier; 2017.
Book Google Scholar
Bashiri A, Burstein E, Bar-David J, et al. Face and brow presentation: independent risk factors. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2008;21(6):357–60.
Hawkins JL, Koffel BL. Chapter 35. In: Chestnut’s obstetric anesthesia: principles and practice: abnormal presentation & multiple gestation. 6th ed; 2020. p. 830.
Meltzer RM, Sactleben MR, Friedman EA. Brow presentation. Obstet Gynecol Surv. 1968;23(6):255–63.
Article Google Scholar
Borell U, Fernstrom I. The mechanism of labour in face and brow presentation: a radiological study. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 1960;39:626–44.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Levy DL. Persistent brow presentation: a new approach to management. South Med J. 1976;69(2):191–2.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
MCH Centre, PIMS, Islamabad, Pakistan
Syeda Batool Mazhar & Zahra Ahmed Muslim
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Sarojini Naidu Medical College, Agra, Uttar Pradesh, India
Ruchika Garg
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Mazhar, S.B., Muslim, Z.A. (2023). Brow Presentation. In: Garg, R. (eds) Labour and Delivery. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-6145-8_8
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-6145-8_8
Published : 02 August 2023
Publisher Name : Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN : 978-981-19-6144-1
Online ISBN : 978-981-19-6145-8
eBook Packages : Medicine Medicine (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
7.10 Brow presentation
Brow presentation constitutes an absolute foeto-pelvic disproportion, and vaginal delivery is impossible (except with preterm birth or extremely low birth weight).
This is an obstetric emergency, because labour is obstructed and there is a risk of uterine rupture and foetal distress.
7.10.1 Diagnosis
- Head is high; as with a face presentation, there is a cleft between the head and back, but it is less marked.
- the chin (it is not a face presentation),
- the posterior fontanelle (it is not a vertex presentation).
Figures 7.9 - Brow presentation
Any mobile presenting part can subsequently flex. The diagnosis of brow presentation is, therefore, not made until after the membranes have ruptured and the head has begun to engage in a fixed presentation. Some brow presentations will spontaneously convert to a vertex or, more rarely, a face presentation.
During delivery, the presenting part is slow to descend: the brow is becoming impacted.
7.10.2 Management
Foetus alive.
- Perform a caesarean section. When performing the caesarean section, an assistant must be ready to free the head by pushing it upward with a hand in the vagina.
- Convert the brow presentation to a face presentation: between contractions, insert the fingers through the cervix and move the head, encouraging extension (Figures 7.10).
- Attempt internal podalic version ( Section 7.9 ).
Both these manoeuvres pose a significant risk of uterine rupture. Vacuum extraction, forceps and symphysiotomy are contra-indicated.
Foetus dead
Perform an embryotomy if the cervix is sufficiently dilated (Chapter 9, Section 9.7 ) otherwise, a caesarean section.
- GP practice services
- Health advice
- Health research
- Medical professionals
Health topics
Advice and clinical information on a wide variety of healthcare topics.
All health topics
Latest features
Allergies, blood & immune system
Bones, joints and muscles
Brain and nerves
Chest and lungs
Children's health
Cosmetic surgery
Digestive health
Ear, nose and throat
General health & lifestyle
Heart health and blood vessels
Kidney & urinary tract
Men's health
Mental health
Oral and dental care
Senior health
Sexual health
Signs and symptoms
Skin, nail and hair health
Travel and vaccinations
Treatment and medication
Women's health
Healthy living
Expert insight and opinion on nutrition, physical and mental health.
Exercise and physical activity
Healthy eating
Healthy relationships
Managing harmful habits
Mental wellbeing
Relaxation and sleep
Managing conditions
From ACE inhibitors for high blood pressure, to steroids for eczema, find out what options are available, how they work and the possible side effects.
Featured conditions
ADHD in children
Crohn's disease
Endometriosis
Fibromyalgia
Gastroenteritis
Irritable bowel syndrome
Polycystic ovary syndrome
Scarlet fever
Tonsillitis
Vaginal thrush
Health conditions A-Z
Medicine information
Information and fact sheets for patients and professionals. Find out side effects, medicine names, dosages and uses.
All medicines A-Z
Allergy medicines
Analgesics and pain medication
Anti-inflammatory medicines
Breathing treatment and respiratory care
Cancer treatment and drugs
Contraceptive medicines
Diabetes medicines
ENT and mouth care
Eye care medicine
Gastrointestinal treatment
Genitourinary medicine
Heart disease treatment and prevention
Hormonal imbalance treatment
Hormone deficiency treatment
Immunosuppressive drugs
Infection treatment medicine
Kidney conditions treatments
Muscle, bone and joint pain treatment
Nausea medicine and vomiting treatment
Nervous system drugs
Reproductive health
Skin conditions treatments
Substance abuse treatment
Vaccines and immunisation
Vitamin and mineral supplements
Tests & investigations
Information and guidance about tests and an easy, fast and accurate symptom checker.
About tests & investigations
Symptom checker
Blood tests
BMI calculator
Pregnancy due date calculator
General signs and symptoms
Patient health questionnaire
Generalised anxiety disorder assessment
Medical professional hub
Information and tools written by clinicians for medical professionals, and training resources provided by FourteenFish.
Content for medical professionals
FourteenFish training
- Professional articles
Evidence-based professional reference pages authored by our clinical team for the use of medical professionals.
View all professional articles A-Z
Actinic keratosis
Bronchiolitis
Molluscum contagiosum
Obesity in adults
Osmolality, osmolarity, and fluid homeostasis
Recurrent abdominal pain in children
Medical tools and resources
Clinical tools for medical professional use.
All medical tools and resources
Malpresentations and malpositions
Peer reviewed by Dr Laurence Knott Last updated by Dr Colin Tidy, MRCGP Last updated 22 Jun 2021
Meets Patient’s editorial guidelines
Medical Professionals
Professional Reference articles are designed for health professionals to use. They are written by UK doctors and based on research evidence, UK and European Guidelines. You may find one of our health articles more useful.
In this article :
Malpresentation, malposition.
Usually the fetal head engages in the occipito-anterior position (more often left occipito-anterior (LOA) rather than right) and then undergoes a short rotation to be directly occipito-anterior in the mid-cavity. Malpositions are abnormal positions of the vertex of the fetal head relative to the maternal pelvis. Malpresentations are all presentations of the fetus other than vertex.
Obstetrics - the pelvis and head
Continue reading below
Predisposing factors to malpresentation include:
Prematurity.
Multiple pregnancy.
Abnormalities of the uterus - eg, fibroids.
Partial septate uterus.
Abnormal fetus.
Placenta praevia.
Primiparity.
Breech presentation
See the separate Breech Presentations article for more detailed discussion.
Breech presentation is the most common malpresentation, with the majority discovered before labour. Breech presentation is much more common in premature labour.
Approximately one third are diagnosed during labour when the fetus can be directly palpated through the cervix.
After 37 weeks, external cephalic version can be attempted whereby an attempt is made to turn the baby manually by manipulating the pregnant mother's abdomen. This reduces the risk of non-cephalic delivery 1 .
Maternal postural techniques have also been tried but there is insufficient evidence to support these 2 .
Many women who have a breech presentation can deliver vaginally. Factors which make this less likely to be successful include 3 :
Hyperextended neck on ultrasound.
High estimated fetal weight (more than 3.8 kg).
Low estimated weight (less than tenth centile).
Footling presentation.
Evidence of antenatal fetal compromise.
Transverse lie 4
When the fetus is positioned with the head on one side of the pelvis and the buttocks in the other (transverse lie), vaginal delivery is impossible.
This requires caesarean section unless it converts or is converted late in pregnancy. The surgeon may be able to rotate the fetus through the wall of the uterus once the abdominal wall has been opened. Otherwise, a transverse uterine incision is needed to gain access to a fetal pole.
Internal podalic version is no longer attempted.
Transverse lie is associated with a risk of cord prolapse of up to 20%.
Occipito-posterior position
This is the most common malposition where the head initially engages normally but then the occiput rotates posteriorly rather than anteriorly. 5.2% of deliveries are persistent occipito-posterior 5 .
The occipito-posterior position results from a poorly flexed vertex. The anterior fontanelle (four radiating sutures) is felt anteriorly. The posterior fontanelle (three radiating sutures) may also be palpable posteriorly.
It may occur because of a flat sacrum, poorly flexed head or weak uterine contractions which may not push the head down into the pelvis with sufficient strength to produce correct rotation.
As occipito-posterior-position pregnancies often result in a long labour, close maternal and fetal monitoring are required. An epidural is often recommended and it is essential that adequate fluids be given to the mother.
The mother may get the urge to push before full dilatation but this must be discouraged. If the head comes into a face-to-pubis position then vaginal delivery is possible as long as there is a reasonable pelvic size. Otherwise, forceps or caesarean section may be required.
Occipito-transverse position
The head initially engages correctly but fails to rotate and remains in a transverse position.
Alternatives for delivery include manual rotation of fetal head using Kielland's forceps, or delivery using vacuum extraction. This is inappropriate if there is any fetal acidosis because of the risk of cerebral haemorrhage.
Therefore, there must be provision for a failure of forceps delivery to be changed immediately to a caesarean. The trial of forceps is therefore often performed in theatre. Some centres prefer to manage by caesarean section without trial of forceps.
Face presentations
Face presents for delivery if there is complete extension of the fetal head.
Face presentation occurs in 1 in 1,000 deliveries 5 .
With adequate pelvic size, and rotation of the head to the mento-anterior position, vaginal delivery should be achieved after a long labour.
Backwards rotation of the head to a mento-posterior position requires a caesarean section.
Brow positions
The fetal head stays between full extension and full flexion so that the biggest diameter (the mento-vertex) presents.
Brow presentation occurs in 0.14% of deliveries 5 .
Brow presentation is usually only diagnosed once labour is well established.
The anterior fontanelle and super orbital ridges are palpable on vaginal examination.
Unless the head flexes, a vaginal delivery is not possible, and a caesarean section is required.
Further reading and references
- Hofmeyr GJ, Kulier R, West HM ; External cephalic version for breech presentation at term. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Apr 1;(4):CD000083. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000083.pub3.
- Hofmeyr GJ, Kulier R ; Cephalic version by postural management for breech presentation. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Oct 17;10:CD000051. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000051.pub2.
- Management of Breech Presentation ; Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists (Mar 2017)
- Szaboova R, Sankaran S, Harding K, et al ; PLD.23 Management of transverse and unstable lie at term. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2014 Jun;99 Suppl 1:A112-3. doi: 10.1136/archdischild-2014-306576.324.
- Gardberg M, Leonova Y, Laakkonen E ; Malpresentations - impact on mode of delivery. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2011 May;90(5):540-2. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0412.2011.01105.x.
Article History
The information on this page is written and peer reviewed by qualified clinicians.
Next review due: 21 Jun 2026
22 jun 2021 | latest version.
Last updated by
Peer reviewed by

Feeling unwell?
Assess your symptoms online for free
Sonographic diagnosis of fetal head deflexion and the risk of cesarean delivery
Affiliations.
- 1 Department of Medical and Surgical Sciences, Sant'Orsola-Malpighi University Hospital, University of Bologna, Bologna, Italy. Electronic address: [email protected].
- 2 Department of Medical and Surgical Sciences, Sant'Orsola-Malpighi University Hospital, University of Bologna, Bologna, Italy.
- 3 Department of Medical and Surgical Sciences, Sant'Orsola-Malpighi University Hospital, University of Bologna, Bologna, Italy; Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Ospedale Maggiore, Bologna, Italy.
- 4 Section of Hygiene, Public Health and Medical Statistics, Department of Biomedical and Neuromotor Sciences, Alma Mater Studiorum - University of Bologna, Bologna, Italy.
- PMID: 33345926
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajogmf.2020.100217
Background: Malpositions and deflexed cephalic malpresentations are well recognized causes of dysfunctional labor, may result in fetal and maternal complications, and are diagnosed more precisely with an ultrasound examination than with a digital examination.
Objective: This study aimed to assess the incidence of malpositions and deflexed cephalic malpresentations at the beginning of the second stage of labor and to evaluate the role of the sonographic diagnosis of deflexion in the prediction of the mode of delivery.
Study design: Women in labor with a singleton pregnancy at term with fetuses in a cephalic presentation at 10 cm of cervical dilatation were prospectively examined. A transabdominal ultrasound was performed to assess the fetal head position by demonstrating the fetal occiput or the eyes. Deflexion was assessed by the measurement of the occiput-spine angle when the occiput was anterior or transverse and by qualitative assessment of the relationship between chin and thorax when the occiput was posterior. Transperineal ultrasound was performed in occiput posterior fetuses to discriminate between sinciput, brow, and face presentation. Maternal, labor, and neonatal parameters including maternal age, induction of labor, use of epidural, birthweight, arterial pH, and neonatal intensive care unit admission were recorded. Patients were divided into 2 groups according to the sonographic diagnosis of head deflexion. Adjusted odds ratios were calculated using multivariate logistic regression to determine the association between cesarean delivery and the 2 groups. In addition, labor and neonatal characteristics were compared between occiput anterior and occiput posterior-occiput transverse fetuses.
Results: Of the 200 women at the beginning of the second stage, the fetus was in occiput anterior position in 156 (78%), transverse in 11 (5.5%), and posterior in 33 (16.5%) cases. Deflexion was diagnosed in 33 of 156 (21.2%) occiput anterior fetuses and 19 of 44 (43.2%) occiput posterior and occiput transverse fetuses. Cesarean deliveries were significantly associated with fetal head deflexion both in occiput anterior (P=.001) and occiput posterior (P<.001) fetuses. Sonographic diagnosis of fetal head deflexion was an independent risk factor for cesarean delivery both in occiput anterior (adjusted odds ratio, 5.37; 95% confidence interval, 1.819-15.869) and occiput posterior (adjusted odds ratio, 13.9; 95% confidence interval, 1.958-98.671) cases, and it was an independent risk factor for cesarean delivery regardless of the occiput position (adjusted odds ratio, 5.83; 95% confidence interval, 2.47-13.73).
Conclusion: The sonographic diagnosis of fetal head deflexion at the beginning of the second stage increases the risk of cesarean delivery.
Keywords: deflexion; intrapartum sonography; labor; malposition; malpresentation; occiput posterior position; ultrasound in labor; ultrasound in labor and delivery.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
- Cesarean Section
- Fetus* / diagnostic imaging
- Head / diagnostic imaging
- Infant, Newborn
- Labor Presentation*
- Ultrasonography, Prenatal
- MSD careers
Fetal Presentation, Position, and Lie (Including Breech Presentation)
- Variations in Fetal Position and Presentation |
During pregnancy, the fetus can be positioned in many different ways inside the mother's uterus. The fetus may be head up or down or facing the mother's back or front. At first, the fetus can move around easily or shift position as the mother moves. Toward the end of the pregnancy the fetus is larger, has less room to move, and stays in one position. How the fetus is positioned has an important effect on delivery and, for certain positions, a cesarean delivery is necessary. There are medical terms that describe precisely how the fetus is positioned, and identifying the fetal position helps doctors to anticipate potential difficulties during labor and delivery.
Presentation refers to the part of the fetus’s body that leads the way out through the birth canal (called the presenting part). Usually, the head leads the way, but sometimes the buttocks (breech presentation), shoulder, or face leads the way.
Position refers to whether the fetus is facing backward (occiput anterior) or forward (occiput posterior). The occiput is a bone at the back of the baby's head. Therefore, facing backward is called occiput anterior (facing the mother’s back and facing down when the mother lies on her back). Facing forward is called occiput posterior (facing toward the mother's pubic bone and facing up when the mother lies on her back).
Lie refers to the angle of the fetus in relation to the mother and the uterus. Up-and-down (with the baby's spine parallel to mother's spine, called longitudinal) is normal, but sometimes the lie is sideways (transverse) or at an angle (oblique).
For these aspects of fetal positioning, the combination that is the most common, safest, and easiest for the mother to deliver is the following:
Head first (called vertex or cephalic presentation)
Facing backward (occiput anterior position)
Spine parallel to mother's spine (longitudinal lie)
Neck bent forward with chin tucked
Arms folded across the chest
If the fetus is in a different position, lie, or presentation, labor may be more difficult, and a normal vaginal delivery may not be possible.
Variations in fetal presentation, position, or lie may occur when
The fetus is too large for the mother's pelvis (fetopelvic disproportion).
The uterus is abnormally shaped or contains growths such as fibroids .
The fetus has a birth defect .
There is more than one fetus (multiple gestation).

Position and Presentation of the Fetus
Variations in fetal position and presentation.
Some variations in position and presentation that make delivery difficult occur frequently.
Occiput posterior position
In occiput posterior position (sometimes called sunny-side up), the fetus is head first (vertex presentation) but is facing forward (toward the mother's pubic bone—that is, facing up when the mother lies on her back). This is a very common position that is not abnormal, but it makes delivery more difficult than when the fetus is in the occiput anterior position (facing toward the mother's spine—that is facing down when the mother lies on her back).
When a fetus faces up, the neck is often straightened rather than bent,which requires more room for the head to pass through the birth canal. Delivery assisted by a vacuum device or forceps or cesarean delivery may be necessary.
Breech presentation
In breech presentation, the baby's buttocks or sometimes the feet are positioned to deliver first (before the head).
When delivered vaginally, babies that present buttocks first are more at risk of injury or even death than those that present head first.
The reason for the risks to babies in breech presentation is that the baby's hips and buttocks are not as wide as the head. Therefore, when the hips and buttocks pass through the cervix first, the passageway may not be wide enough for the head to pass through. In addition, when the head follows the buttocks, the neck may be bent slightly backwards. The neck being bent backward increases the width required for delivery as compared to when the head is angled forward with the chin tucked, which is the position that is easiest for delivery. Thus, the baby’s body may be delivered and then the head may get caught and not be able to pass through the birth canal. When the baby’s head is caught, this puts pressure on the umbilical cord in the birth canal, so that very little oxygen can reach the baby. Brain damage due to lack of oxygen is more common among breech babies than among those presenting head first.
In a first delivery, these problems may occur more frequently because a woman’s tissues have not been stretched by previous deliveries. Because of risk of injury or even death to the baby, cesarean delivery is preferred when the fetus is in breech presentation, unless the doctor is very experienced with and skilled at delivering breech babies or there is not an adequate facility or equipment to safely perform a cesarean delivery.
Breech presentation is more likely to occur in the following circumstances:
Labor starts too soon (preterm labor).
The uterus is abnormally shaped or contains abnormal growths such as fibroids .
Other presentations
In face presentation, the baby's neck arches back so that the face presents first rather than the top of the head.
In brow presentation, the neck is moderately arched so that the brow presents first.
Usually, fetuses do not stay in a face or brow presentation. These presentations often change to a vertex (top of the head) presentation before or during labor. If they do not, a cesarean delivery is usually recommended.
In transverse lie, the fetus lies horizontally across the birth canal and presents shoulder first. A cesarean delivery is done, unless the fetus is the second in a set of twins. In such a case, the fetus may be turned to be delivered through the vagina.

- Cookie Preferences

Copyright © 2024 Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA and its affiliates. All rights reserved.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The term presentation describes the leading part of the fetus or the anatomical structure closest to the maternal pelvic inlet during labor. The presentation can roughly be divided into the following classifications: cephalic, breech, shoulder, and compound. Cephalic presentation is the most common and can be further subclassified as vertex, sinciput, brow, face, and chin. The most common ...
The vast majority of fetuses at term are in cephalic presentation. Approximately 5 percent of these fetuses are in a cephalic malpresentation, such as occiput posterior or transverse, face ( figure 1A-B ), or brow ( figure 2) [ 1 ]. Diagnosis and management of face and brow presentations will be reviewed here.
Diagnosis of a brow presentation can occasionally be made with abdominal palpation by Leopold maneuvers. A prominent occipital prominence is encountered along the fetal back, and the fetal chin is also palpable; however, the diagnosis of a brow presentation is usually confirmed by examination of a dilated cervix.
Fetal lie: Relation of the fetus to the long axis of the uterus; longitudinal, oblique, or transverse. Normal fetal lie is longitudinal, normal presentation is vertex, and occiput anterior is the most common position. Abnormal fetal lie, presentation, or position may occur with. Fetopelvic disproportion (fetus too large for the pelvic inlet)
In face presentation, the baby's neck arches back so that the face presents first rather than the top of the head.. In brow presentation, the neck is moderately arched so that the brow presents first.. Usually, fetuses do not stay in a face or brow presentation. These presentations often change to a vertex (top of the head) presentation before or during labor.
Brow: brow presentation represents deflexion of the fetal head but not to the same degree as the complete extension causing a face presentation, with an incidence of approximately 1 in 2000 births. In a brow presentation, the presenting diameter is mento-vertical, at approximately 13 cm, and is therefore the most unfavourable of cephalic ...
During vertex presentation, the fetal head flexes, bringing the chin to the chest, forming the smallest possible fetal head diameter, measuring approximately 9.5cm. With face and brow presentation, the neck hyperextends, resulting in greater cephalic diameters. As a result, the fetal head will engage later, and labor will progress more slowly.
Causes: Brow presentation may result from abnormal fetal positioning, poor engagement of the fetal head, or other factors that prevent full flexion or extension. Complications: Brow presentation is associated with a higher risk of prolonged labor, difficulty in descent, increased chances of fetal head entrapment, birth injuries, and the ...
Brow Presentation: Brow is a cephalic deflection malpresentation with the partially deflexed fetal head midway between complete flexion (vertex) and full extension (face) (Fig. 2 ). The frontal bone is the designated point for its position in maternal pelvis. On vaginal examination, the brow, orbits, and root of the nose are palpable.
7.10.1 Diagnosis. 7.10.2 Management. Foetus alive. Foetus dead. Brow presentation constitutes an absolute foeto-pelvic disproportion, and vaginal delivery is impossible (except with preterm birth or extremely low birth weight). This is an obstetric emergency, because labour is obstructed and there is a risk of uterine rupture and foetal distress.
The use of intrapartum ultrasound to assess fetal position and presentation, in addi-tion to fetal attitude, to predict and aid in decision making regarding delivery can help in improving management decision making. Cephalic malpresentation and malposition is a unique subset of fetal orientation and can benefit from intrapartum ultrasound ...
The diagnosis of brow presentation is made by vaginal examination. The posterior fontanelle, mouth, and chin cannot be palpated in the brow presentation. Ultrasound to exclude major anomalies or macrosomia should be considered. The position is defined using the anterior fontanelle as the reference point (ie, frontum anterior or frontum posterior).
The presenting part may be the fetal vertex, the anterior fontanelle, the superior orbital ridge, or the mouth, revealing vertex, sinciput, brow, or face presentation. Often, brow and sinciput are not diagnosed or misdiagnosed by palpation, and these may be more accurately identified and characterized on ultrasound.
Brow positions. The fetal head stays between full extension and full flexion so that the biggest diameter (the mento-vertex) presents. Brow presentation occurs in 0.14% of deliveries 5. Brow presentation is usually only diagnosed once labour is well established. The anterior fontanelle and super orbital ridges are palpable on vaginal examination.
The chin is not palpable in brow presentation, but it is with a face presentation and is used to further characterize the fetal position that is described as mentum (chin) anterior, mentum transverse, or mentum posterior. ... Given the considerable perinatal morbidity associated with fetal malpresentation, accurate diagnosis is of considerable ...
Cephalo pelvic disproportion has been associated with brow presentation in from 7.7 to 53.8 per cent of cases,l' 8-12, 15, 19, 20 but the impor-tance of this factor has been doubted by some.21, 22 Leiomyomas of the uterus10, 19 and bicornuate uterus19 have been reported to be associated with the abnormal presentation.
Among head-deflexed OP fetuses, we diagnosed sinciput presentation in all but 1, with caput succedaneum suggestive for brow presentation . Of the head-deflexed fetuses, 10 of 33 (30.3%) OA fetuses and 14 of 19 (77.8%) OP or OT fetuses were delivered by cesarean delivery ( Figure 5 ).
Cesarean deliveries were significantly associated with fetal head deflexion both in occiput anterior (P=.001) and occiput posterior (P<.001) fetuses. Sonographic diagnosis of fetal head deflexion was an independent risk factor for cesarean delivery both in occiput anterior (adjusted odds ratio, 5.37; 95% confidence interval, 1.819-15.869) and ...
Brow presentation may be seen on transperineal ultrasound, demonstrating an orbit just below the pubic symphysis (Figure 7). 33 This is not characteristic of a typical OP position. 33 In addition, the fetal attitude can be measured transabdominally in the OA position using the OSA, which may help diagnose brow presentation, although no specific ...
During pregnancy, the fetus can be positioned in many different ways inside the mother's uterus. The fetus may be head up or down or facing the mother's back or front. At first, the fetus can move around easily or shift position as the mother moves. Toward the end of the pregnancy the fetus is larger, has less room to move, and stays in one ...
Palpation usually confirms the diagnosis, but moulding of the fetal skull and edema can make palpation difficult. Sonography can be used as a diagnostic aid. ... and for breech presentations (3.1%). However, the incidence of brow presentation was higher than expected, and the incidence of face and transverse presentations lower. This variation ...
A cephalic presentation or head presentation or head-first presentation is a situation at childbirth where the fetus is in a longitudinal lie and the head enters the pelvis first; the most common form of cephalic presentation is the vertex presentation, where the occiput is the leading part (the part that first enters the birth canal). All other presentations are abnormal (malpresentations ...
A well-flexed fetal head presents the most favourable diameters to the maternal pelvis. If the fetal neck is deflexed, the leading part of the fetal head lies more anteriorly and a brow presentation can occur while if there is complete extension of the fetal neck, the face then becomes the leading part producing face presentation (Figure 3a-c ).