

How to Master at Literature Mapping: 5 Most Recommended Tools to Use
This article is also available in: Turkish , Spanish, Russian , and Portuguese
After putting in a lot of thought, time, and effort, you’ve finally selected a research topic . As the first step towards conducting a successful and impactful research is completed, what follows it is the gruesome process of literature review . Despite the brainstorming, the struggle of understanding how much literature is enough for your research paper or thesis is very much real. Unlike the old days of flipping through pages for hours in a library, literature has come easy to us due to its availability on the internet through Open Access journals and other publishing platforms. This ubiquity has made it even more difficult to cover only significant data! Nevertheless, an ultimate solution to this problem of conglomerating relevant data is literature mapping .

Table of Contents
What is Literature Mapping?
Literature mapping is one of the key strategies when searching literature for your research. Since writing a literature review requires following a systematic method to identify, evaluate, and interpret the work of other researchers, academics, and practitioners from the same research field, creating a literature map proves beneficial. Mapping ideas, arguments, and concepts in a literature is an imperative part of literature review. Additionally, it is stated as an established method for externalizing knowledge and thinking processes. A map of literature is a “graphical plan”, “diagrammatic representation”, or a “geographical metaphor” of the research topic.
Researchers are often overwhelmed by the large amount of information they encounter and have difficulty identifying and organizing information in the context of their research. It is recommended that experts in their fields develop knowledge structures that are richer not only in terms of knowledge, but also in terms of the links between this knowledge. This knowledge linking process is termed as literature mapping .
How Literature Mapping Helps Researchers?
Literature mapping helps researchers in following ways:
- It provides concrete evidence of a student’s understanding and interpretation of the research field to share with both peers and professors.
- Switching to another modality helps researchers form patterns to see what might otherwise be hidden in the research area.
- Furthermore, it helps in identifying gaps in pertinent research.
- Finally, t lets researchers identify potential original areas of study and parameters of their work.
How to Make a Literature Map?
Literature mapping is not only an organizational tool, but also a reflexive tool. Furthermore, it distinguishes between declarative knowledge shown by identifying key concepts, ideas and methods, and procedural knowledge shown through classifying these key concepts and establishing links or relationships between them. The literature review conceptualizes research structures as a “knowledge production domain” that defines a productive and ongoing constructive element. Thus, the approaches emphasize the identity of different scientific institutions from different fields, which can be mapped theoretically, methodologically, or fundamentally.
The two literature mapping approaches are:
- Mapping with key ideas or descriptors: This is developed from keywords in research topics.
- Author mapping: This is also termed as citation matching that identifies key experts in the field and may include the use of citations to interlink them.
Generally, literature maps can be subdivided by categorization processes based on theories, definitions, or chronology, and cross-reference between the two types of mapping. Furthermore, researchers use mind maps as a deductive process, general concept-specific mapping (results in a right triangle), or an inductive process mapping to specific concepts (results in an inverted triangle).
What are Different Literature Mapping Methods?
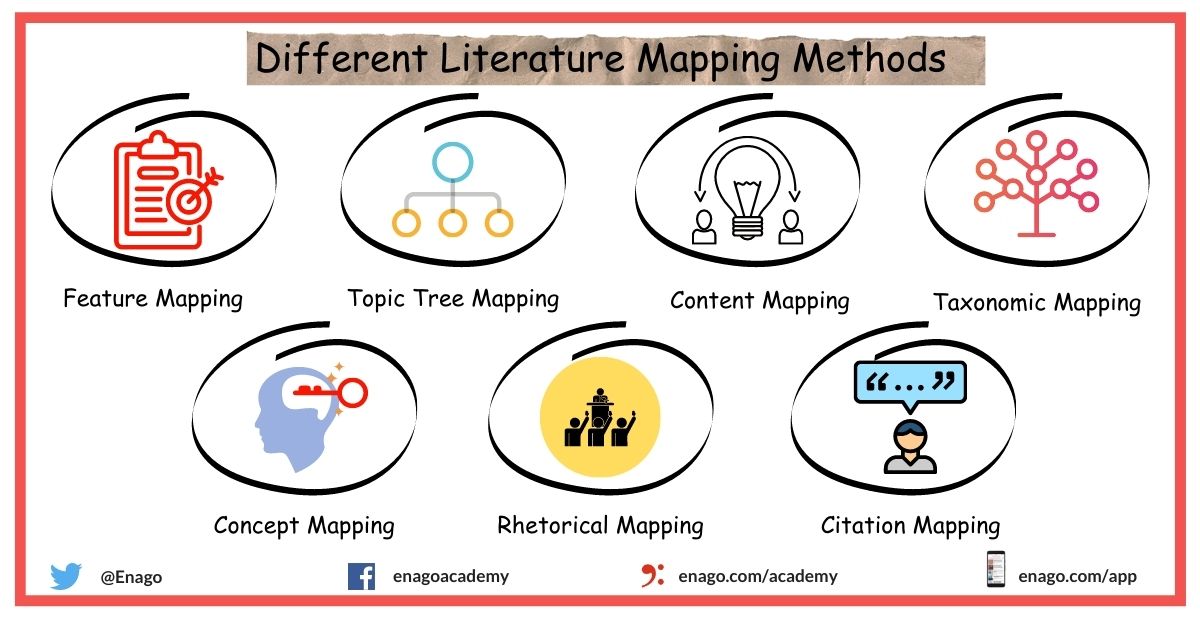
The different types of literature mapping and representations are as follows:
1. Feature Mapping:
Argument structures developed from summary registration pages.
2. Topic Tree Mapping:
Summary maps showing the development of the topic in sub-themes up to any number of levels.
3. Content Mapping:
Linear structure of organization of content through hierarchical classification.
4. Taxonomic Mapping:
Classification through standardized taxonomies.
5. Concept Mapping:
Linking concepts and processes allows procedural knowledge from declarative information. With a basic principle of cause and effect and problem solving, concept maps can show the relationship between theory and practice.
6. Rhetorical Mapping:
The use of rhetoric communication to discuss, influence, or persuade is particularly important in social policy and political science and can be considered a linking strategy. A number of rhetorical tools have been identified that can be used to present a case, including ethos, metaphor, trope, and irony.
7. Citation Mapping:
Citation mapping or matching is a research process established to specifically establish links between authors by citing their articles. Traditional manual citation indexes have been replaced by automated databases that allow visual mapping methods (e.g. ISI Web of Science). In conclusion, citation matching in a subject area can be effective in determining the frequency of authors and specific articles.
5 Most Useful Literature Mapping Tools
Technology has made the literature mapping process easier now. However, with numerous options available online, it does get difficult for researchers to select one tool that is efficient. These tools are built behind explicit metadata and citations when coupled with some new machine learning techniques. Here are the most recommended literature mapping tools to choose from:
1. Connected Papers
a. Connected Papers is a simple, yet powerful, one-stop visualization tool that uses a single starter article.
b. It is easy to use tool that quickly identifies similar papers with just one “Seed paper” (a relevant paper).
c. Furthermore, it helps to detect seminal papers as well as review papers.
d. It creates a similarity graph not a citation graph and connecting lines (based on the similarity metric).
e. Does not necessarily show direct citation relationships.
f. The identified papers can then be exported into most reference managers like Zotero, EndNote, Mendeley, etc.
2. Inciteful
a. Inciteful is a customizable tool that can be used with multiple starter articles in an iterative process.
b. Results from multiple seed papers can be imported in a batch with a BibTex file.
c. Inciteful produces the following lists of papers by default:
- Similar papers (uses Adamic/Adar index)
- “Most Important Papers in the Graph” (based on PageRank)
- Recent Papers by the Top 100 Authors
- The Most Important Recent Papers
d. It allows filtration of results by keywords.
e. Importantly, seed papers can also be directly added by title or DOI.
a. Litmaps follows an iterative process and creates visualizations for found papers.
b. It allows importing of papers using BibTex format which can be exported from most reference managers like Zotero, EndNote, Mendeley. In addition, it allows paper imports from an ORCID profile.
c. Keywords search method is used to find Litmaps indexed papers.
d. Additionally, it allows setting up email updates of “emergent literature”.
e. Its unique feature that allows overlay of different maps helps to look for overlaps of papers.
f. Lastly, its explore function allows finding related papers to add to the map.
4. Citation-based Sites
a. CoCites is a citation-based method for researching scientific literature.
b. Citation Gecko is a tool for visualizing links between articles.
c. VOSviewer is a software tool for creating and visualizing bibliometric networks. These networks are for example journals, may include researchers or individual publications, which can be generated based on citation, bibliographic matching , co-citation, or co-authorship relationships. VOSviewer also offers text mining functionality that can be used to create and visualize networks of important terms extracted from a scientific literature.
5. Citation Context Tools
a. Scite allow users to see how a publication has been cited by providing the context of the citation and a classification describing whether it provides supporting or contrasting evidence for the cited claim.
b. Semantic Scholar is a freely available, AI-powered research tool for scientific literature.
Have you ever mapped your literature? Did you use any of these tools before? Lastly, what are the strategies and methods you use for literature mapping ? Let us know how this article helped you in creating a hassle-free and comprehensive literature map.
It’s very good and detailed.
It’s very good and clearly . It teaches me how to write literature mapping.
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles

- Promoting Research
- Thought Leadership
- Trending Now
How Enago Academy Contributes to Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) Through Empowering Researchers
The United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) are a universal call to action to end…

- Reporting Research
AI Assistance in Academia for Searching Credible Scholarly Sources
The journey of academia is a grand quest for knowledge, more specifically an adventure to…
- Language & Grammar
Best Plagiarism Checker Tool for Researchers — Top 4 to choose from!
While common writing issues like language enhancement, punctuation errors, grammatical errors, etc. can be dealt…

- Industry News
- Publishing News
2022 in a Nutshell — Reminiscing the year when opportunities were seized and feats were achieved!
It’s beginning to look a lot like success! Some of the greatest opportunities to research…

- Manuscripts & Grants
Writing a Research Literature Review? — Here are tips to guide you through!
Literature review is both a process and a product. It involves searching within a defined…
2022 in a Nutshell — Reminiscing the year when opportunities were seized and feats…

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

As a researcher, what do you consider most when choosing an image manipulation detector?

Search form
You are here, structuring your ideas: creating a literature map.
It is important to have a plan of the areas to be discussed, using this to indicated how these will link together. In the overall structure of the literature review, there should be a logical flow of ideas and within each paragraph there should be a clear theme, around which related ideas are explored and developed. A literature map can be useful for this purpose as it enables you to create a visual representation of the themes and how they could relate to one another.
A literature map (Cresswell, 2011) is a two dimensional diagrammatic representation of information where links are made between concepts by drawing arrows (which could be annotated to define the nature of these links). Constructing a literature map helps you to:
- develop your understanding of the key issues and research findings in the literature
- to organise ideas in your mind
- to see more clearly how different research studies relate to one another and to group those with similar findings.
Your map can then be used as a plan for your literature review.
As well has helping you to organise the literature for your review, a literature map can be used to help you analyse the information in a particular journal article, supporting the exploration of strengths and weaknesses of the methodology and the resultant findings and enabling you to explore how key themes and concepts in the article link together.
It is important to represent the different views and any conflicting research findings that exist in the literature (Newby, 2014). There is a danger of selective referencing, only including literature that supports your own beliefs and findings, disregarding alternative views. This should be avoided as it is based on the assumption that your views are the correct ones, and it is possible that you could miss key ideas and findings that could take your research in new and exciting directions.
- research methods
- literature reviews
Creative Commons
Press ESC to close
Creating a Comprehensive Literature Review Map: A Step-by-Step Example
- backlinkworks
- Writing Articles & Reviews
- October 16, 2023

A literature review is an essential component of any academic research paper or thesis. IT involves examining existing literature, scholarly articles, books, and other sources related to your research topic. A literature review map acts as a visual representation of the concepts, studies, and theories that have been covered in the literature. In this article, we will guide you through the process of creating a comprehensive literature review map, step-by-step, to help you structure and organize your literature review effectively.
Step 1: Define Your Research Topic
The first step in creating a literature review map is to clearly define your research topic. Be specific and narrow down your focus to ensure that you have a manageable scope for your literature review. Take into consideration the research objectives or guiding questions that will shape your review.
Step 2: Identify Relevant Keywords
Once you have defined your research topic, identify the keywords and search terms that are most relevant to your study. Brainstorm a list of potential keywords that are commonly used in the literature related to your topic. These keywords will help you locate relevant sources during your literature search.
Step 3: Conduct a Thorough Literature Search
Using databases and search engines specific to your field of study, begin conducting a thorough literature search using the identified keywords. Take note of the key articles, books, and studies that are relevant to your research topic. In this step, IT is important to evaluate the credibility and quality of the sources to ensure that you are referring to reputable and reliable information.
Step 4: Read and Analyze the Literature
After collecting a substantial number of sources, carefully read and analyze each one. Highlight key concepts, methodologies, and findings that are relevant to your research. As you progress, make notes or annotations to help you remember important details and connections between different sources.
Step 5: Organize the Literature
Now that you have read and analyzed the literature, IT ‘s time to organize the information into a coherent structure. One effective way to do this is by using a literature review map. Start by creating categories or themes based on the concepts or theories that emerge from the literature. Group together similar ideas or findings to create a visual representation of the interconnectedness of the sources.
Step 6: Create the Literature Review Map
With your categorized information, you can now create the literature review map. This can be done using software such as Microsoft Word, PowerPoint, or dedicated mind mapping tools. Start with your main research topic in the center and branch out with subcategories based on the themes or concepts identified earlier. Connect relevant sources to each subcategory, illustrating how they contribute to the overall understanding of your research topic.
Step 7: Revise and Refine
Review your literature review map for coherence and completeness. Ensure that all the key sources are accurately placed within the appropriate category or subcategory. Check for any gaps in your coverage and make sure that the map represents a comprehensive overview of the literature on your research topic.
Q: How many sources should I include in my literature review map?
A: The number of sources you include will depend on the requirements of your research and the depth of analysis you aim to achieve. However, IT is generally recommended to thoroughly examine a range of sources, including both seminal texts and recent publications, to ensure a well-rounded and comprehensive literature review.
Q: How do I determine the credibility of the sources for my literature review?
A: Evaluating the credibility of your sources is crucial to ensure that you are basing your review on reputable information. Consider the author’s qualifications, the credibility and reputation of the publishing outlet, the presence of citations within the article, and the overall coherence and consistency of the research findings.
Q: Can I use a literature review map for disciplines outside of the humanities and social sciences?
A: Absolutely! While literature reviews are commonly associated with humanities and social sciences, they are applicable to any academic field. Whether you are conducting research in the sciences, engineering, or any other discipline, a literature review map will help you organize and present the relevant scholarly literature specific to your research topic.
By following these step-by-step guidelines, you can create a comprehensive literature review map that will serve as a valuable tool throughout your research. Remember to regularly update and refine your map as you progress in your studies. A well-organized literature review will not only demonstrate your knowledge and understanding of the field, but also provide a solid foundation for your own research and contribute to the wider scholarly conversation.
Understanding the Advantages of SATA Hard Drives
3) top 10 wordpress website packages for beginners.

Recent Posts
- Driving Organic Growth: How a Digital SEO Agency Can Drive Traffic to Your Website
- Mastering Local SEO for Web Agencies: Reaching Your Target Market
- The Ultimate Guide to Unlocking Powerful Backlinks for Your Website
- SEO vs. Paid Advertising: Finding the Right Balance for Your Web Marketing Strategy
- Discover the Secret Weapon for Local SEO Success: Local Link Building Services
Popular Posts

Shocking Secret Revealed: How Article PHP ID Can Transform Your Website!

Unlocking the Secrets to Boosting Your Alexa Rank, Google Pagerank, and Domain Age – See How You Can Dominate the Web!

Uncovering the Top Secret Tricks for Mastering SPIP PHP – You Won’t Believe What You’re Missing Out On!

The Ultimate Collection of Free Themes for Google Sites

Discover the Shocking Truth About Your Website’s Ranking – You Won’t Believe What This Checker Reveals!
Explore topics.
- Backlinks (2,425)
- Blog (2,744)
- Computers (5,318)
- Digital Marketing (7,741)
- Internet (6,340)
- Website (4,705)
- Wordpress (4,705)
- Writing Articles & Reviews (4,208)
Literature Mapping Tools
- Research Rabbit
- Connected Papers
- Library Subscriptions
- A.I. Glossary
- Need Assistance?
Head, Research and Engagement

Literature Reviews: A Working Definition
A literature review is a methodical or organized review of the published literature on a specific topic or research question designed to analyze--not just summarize--scholarly writings that are related directly to your research question. That is, it represents the literature that provides the context for your research and shows a correspondence between those writings and your own work.
Before you get started...
The past few years have seen an explosion of online tools designed to automate the process of doing literature reviews. These tools generally work by asking you to identify a relevant article (often called a "seed article") and use the metadata attached to articles (such as authors and keywords), or citations and reference lists to find related articles. Most tools offer some type of visualization feature to trace the connections between papers, and increasingly, tools offer summaries of the research content. These tools provide researchers with an option to at least partially automate some of their literature review work which can save a lot of time.
Things to keep in mind:
- Very little independent research has been done to test the reliability, scope, and accuracy of these tools
- In our own testing of tools that provide summaries of articles, we have sometimes found that summaries do not reflect the same key take-aways that we have identified
- Reproducibility of searches is questionable so they may not be the best choice for things like systematic reviews
- Because of the reliance on citation chaining, there is a built in bias towards heavily cited works which ends up creating a feedback loop that may cause you to miss relevant and/or newer materials
- Not everything is indexed in the data sets used by a given tool; this is particularly the case in the arts and humanities which are more oriented towards books
- Both the tools themselves, many of which are open access projects, and the indices they rely on may stop being updated/maintained, or go offline for a variety of reasons
- You still need to use a library to access full text in a majority of cases
NOTE: This is a rapidly evolving field and we will be updating this guide on a regular basis.
- Next: Elicit >>
- Last Updated: Feb 23, 2024 1:40 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.udel.edu/litmap
- Regional and Online Students
- Interlibrary Loan Login
- Support Your Library
- Academic Coaching
- Course Guides
- Course Reserves
- Guides and Tutorials
- Study Spaces
- Tutor Appointments
- Writing Help/Support
- Librarian Appointments
- Chat with Librarian
- Citing Sources
- Technology Request Form
- Technology Support
- Compute, Scan, Print, Copy
- Zoom/Webex Help
- Blackboard Help
- Qualtrics Help
- 3D Printing and Scanning
- Poster Printing
- Arhives and Special Collections
- Borrowing from Other Libraries
- Library Account
- Reserve a Room
- ROC Students
- Open Education Resources
- Promotion and Tenure
- Request Library Instruction
- Request Student Learning Assistants
- Research and Publication
- Suggest a Purchase
- Zoom/Webex help
- A-Z Site Index
- Hours of Operation
- Libraries and Learning Commons
- Library Use Policies
- Newsletters
- Staff and Department Directory
- Renew Books
Learning Commons at the
Wilson Library
- University of La Verne
- Subject Guides
- Wilson Library Subguides
How to Construct Literature Maps
Chat with a librarian, subject librarian.

This LibGuide will help you
This LibGuide will help you locate resources for constructing a literature map. If you need more assistance please click on the 24/7 Chat service or contact me using the links on the left hand side of the page.
Resources for Creating Literature Maps
- Owl English's Resource for Literature Mapping This resource provides an overview of stasis theory and what you can do with it to help you conduct research, compose documents, and work in teams.
- Wilson Library's "Sage Research Methods" Resources on Literature Mapping This resource provides suggestions for books, articles, videos and more for designing literature maps.
Visual of How to Create a Literature Map
- Sample Look at a Literature Map (scroll to bottom of page) This is an example of the literature review process, and in particular, literature mapping (scroll to the bottom of the page).
Sample Charts for Designing Literature Review
- Sample Designs for Literature Mapping
- Last Updated: Oct 27, 2021 11:04 AM
- URL: https://laverne.libguides.com/c.php?g=846275
- Article Databases
- Google Scholar
- Interlibrary Services
- Research Guides
- Staff Directory
- Study Rooms
- Citation Linker
- Digital Collections
- Digital Commons
- Reference Tools
- Special Collections
- All Resources
- Ask-A-Librarian
- Borrowing & Renewals
- Computing & Printing
- Copyright@Wayne
- Course Reserves
- Equipment Checkout
- Instruction
- Research Support
- Rooms & Spaces
- The Publishing House
- Technology Support
- All Services
- Arthur Neef Law Library
- Purdy/Kresge Library
- Reuther Library
- Shiffman Medical Library
- Undergraduate Library
- Accessibility
- Desktop Advertising
- Maps & Directions
- All Information
- Appointments
- WSU Login Academica, Canvas, Email, etc.
- My Library Account Renew Books, Request Material, etc.
- Make a Gift
- back to Wayne.edu
- Skip to Quicklinks
- Skip to Sitemap
- Skip to Main Navigation
- Skip to News
- Interlibrary Loan
Information
- {{guide_title}}
Academic & Research Focused Artificial Intelligence Tools
- Thoughts on Using AI Tools
- Ethics of Using AI in Research
- AI Generated Content and Copyright
- Citing ChatGPT and Other AI Tools in APA Style
- Citing ChatGPT and Other AI Tools In MLA Style
- Citing ChatGPT and Other AI Tools in Chicago Style/Turabian
- Generative AI Programs
- Grammar & Writing AIs
Using Literature Mappers in Your Research
Literature mapping tools, suggest a new ai tool.
- Last updated
Literature mapping is a way of discovering scholarly articles by exploring connections between publications. Similar articles are often linked by citations, authors, funders, keywords, and other metadata. You can use these tools to increase the scale and scope of the literature for your projects. Many provide stunning graphical displays of search results
Use of these tools should supplement not replace the use of the databases provided by the Wayne State University Libraries
- Research Rabbit Excellent research tool for locating and managing articles. Very powerful with lots of great features.
- Inciteful Well rounded research tool with some unique functions.
- Open Knowledge Maps Unlike most of the other tools on this list, this tool bases it search on keyword terms rather than a key article or author.
- Connected Papers lets you explore connected papers in a visual graph, beginning with a starter paper you select. You can start with a DOI, URL, or paper title. Purposes: (1) Get a visual overview of a new academic field; (2) Make sure you haven’t missed an important paper; (3) Create the bibliography to your thesis; and (4) Discover the most relevant prior and derivative works.
- Pure Suggest Good basic lit mapping tool that keeps things simple and direct.
- Suggest a Resource Know of a great AI-based tool for academic or research use? Click the link to make a suggestion. The WSU Libraries will evaluate suggestions twice a year for inclusion on this Guide
This list was last updated on: January 17, 2024
- << Previous: Grammar & Writing AIs
- Last Updated: May 24, 2024 2:13 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.wayne.edu/ResearchAI
- Borrowing & Renewals
- Computing & Printing
- Rooms & Spaces
- Maps & Directions
- Make Appointment


Brand new to Litmaps? Start here for a quick overview of what we're all about.
Welcome! Litmaps is a website that can help with academic literature discovery, collection, and comprehension.
Use Litmaps to
Find articles for your research
Finish your literature review faster
Stay up-to-date on the latest research , automatically
How is Litmaps Different?
Litmaps is different from search databases you may be familiar with. Instead of searching using keywords, Litmaps searches the citation network .
What’s the Citation Network?
When a paper references another paper, it indicates a link between the content of the two papers: There must be something in common between them for the reference to have been made.
We can represent this link using a line. Here, paper A cites paper B:

Other papers may have also cited paper B:

Indeed, B will have cited other papers itself!

These citation links continue on and on, create a huge “citation network”. Litmaps uses this network to:
Visualize how papers relate to one another
Analyze trends to discover new papers
Discover unexpected connections between topics
How do I get started with Litmaps?
Check out this guide for step-by-step instructions on how to do your first search with Litmaps.
Search for a single paper in Litmaps, and use it as a starting point to generate a literature map. Litmaps traverses the citation network to find the most relevant papers based on one or more inputted paper(s). It quick compiles and visualizes a relevant list of reading material based on your input paper.
As you explore relevant papers using the Map, you can keep track of what you find using Tags . Litmaps Tags are a way to organize and keep track of your literature library.
Litmaps aims to enhance the research discovery process by helping you find relevant papers faster, build collections, and discover previously overlooked links between subjects.
Check out these resources to learn how to use Litmaps to serve your research needs:
Litmaps YouTube
Litmaps LinkedIn
Litmaps Twitter
Litmaps Guides
Literature Review Course with Litmaps
Something went wrong when searching for seed articles. Please try again soon.
No articles were found for that search term.
Author, year The title of the article goes here
Upcoming Litmaps Webinar
LITERATURE REVIEW SOFTWARE FOR BETTER RESEARCH
“Litmaps is a game changer for finding novel literature... it has been invaluable for my productivity.... I also got my PhD student to use it and they also found it invaluable, finding several gaps they missed”
Varun Venkatesh
Austin Health, Australia

As a full-time researcher, Litmaps has become an indispensable tool in my arsenal. The Seed Maps and Discover features of Litmaps have transformed my literature review process, streamlining the identification of key citations while revealing previously overlooked relevant literature, ensuring no crucial connection goes unnoticed. A true game-changer indeed!
Ritwik Pandey
Doctoral Research Scholar – Sri Sathya Sai Institute of Higher Learning

Using Litmaps for my research papers has significantly improved my workflow. Typically, I start with a single paper related to my topic. Whenever I find an interesting work, I add it to my search. From there, I can quickly cover my entire Related Work section.
David Fischer
Research Associate – University of Applied Sciences Kempten
“It's nice to get a quick overview of related literature. Really easy to use, and it helps getting on top of the often complicated structures of referencing”
Christoph Ludwig
Technische Universität Dresden, Germany
“This has helped me so much in researching the literature. Currently, I am beginning to investigate new fields and this has helped me hugely”
Aran Warren
Canterbury University, NZ
“I can’t live without you anymore! I also recommend you to my students.”
Professor at The Chinese University of Hong Kong
“Seeing my literature list as a network enhances my thinking process!”
Katholieke Universiteit Leuven, Belgium
“Incredibly useful tool to get to know more literature, and to gain insight in existing research”
KU Leuven, Belgium
“As a student just venturing into the world of lit reviews, this is a tool that is outstanding and helping me find deeper results for my work.”
Franklin Jeffers
South Oregon University, USA
“Any researcher could use it! The paper recommendations are great for anyone and everyone”
Swansea University, Wales
“This tool really helped me to create good bibtex references for my research papers”
Ali Mohammed-Djafari
Director of Research at LSS-CNRS, France
“Litmaps is extremely helpful with my research. It helps me organize each one of my projects and see how they relate to each other, as well as to keep up to date on publications done in my field”
Daniel Fuller
Clarkson University, USA
As a person who is an early researcher and identifies as dyslexic, I can say that having research articles laid out in the date vs cite graph format is much more approachable than looking at a standard database interface. I feel that the maps Litmaps offers lower the barrier of entry for researchers by giving them the connections between articles spaced out visually. This helps me orientate where a paper is in the history of a field. Thus, new researchers can look at one of Litmap's "seed maps" and have the same information as hours of digging through a database.
Baylor Fain
Postdoctoral Associate – University of Florida

Howard Aldrich
Kenan professor of sociology, dept of sociology @ unc chapel hill.

Powerful Tools for Mapping a Research Literature

Professor Courtney Page Tan , Assistant Professor of Human Resilience in the Department of Security and Emergency Services at Embry-Riddle Aeronautical University, has compiled a list of powerful literature mapping tools. You can use these tools to increase the scale and scope of the literature for your projects. Many provide stunning graphical displays of search results (Edward Tufte would approve).
Connected Papers lets you explore connected papers in a visual graph, beginning with a starter paper you select. You can start with a DOI, URL, or paper title. Purposes: (1) Get a visual overview of a new academic field; (2) Make sure you haven’t missed an important paper; (3) Create the bibliography to your thesis; and (4) Discover the most relevant prior and derivative works.
scite_ Smart Citations for Intelligent Research . Smart Citations allow users to see how a scientific paper has been cited by providing the context of the citation and a classification describing whether it provides supporting or disputing evidence for the cited claim. They claim a database of over 23 million full-text articles.
Open Knowledge Maps . Calling themselves a “visual interface to the world’s scientific community,” their tool allows you to start with a few keywords to search for literature on a topic. Results display the main areas at a glance, and papers related to each area. In addition to giving you an overview of the area, it helps you identify important concepts. They highlight open access papers in their search results.
Local Citation Network . You input an article using its DOI or a scanned copy containing DOIs and the program shows you suggested articles for you to follow up.
They explain that “This web app aims to help scientists with their literature review using metadata from Microsoft Academic and Crossref . Academic papers cite one another, thus creating a citation network (= graph) . Each node (= vertex) represents an article and each edge (= link / arrow) represents a reference / citation. Citation graphs are a topic of bibliometrics, for which other great software exists as well .
This web app visualizes subsets of the global citation network that I call “local citation networks,” defined by the references of a given set of input articles. In addition, the most cited references missing in the set of input articles are suggested for further review.”
Citation Gecko Gecko is designed to help you find the most relevant papers to your research and give you a more complete sense of the research landscape. Users start from a small set of ‘seed papers’ that define an area you are interested. Gecko will search the citation network for connected papers allowing you to quickly identify important papers you may have missed.
PRISMA Flow Diagram Generator . This is the most complex of the tools. It generates a graphical representation of the flow of citations reviewed in the course of a Systematic Review. Click here for an example.
Share this:
- Mon. May 27th, 2024
The City Whisperer
How to bring dead city areas to life

How to Create a Literature Map

How to create a literature map. The Literature Map helps researchers review literature for gaps and points of impact. They are useful in both academic and industry related research projects to help gain traction and market interest.
Book a seat for our upcoming Literature Mapping Webinar Workshop
Learn More about Literature Mapping
Research projects usually start with a Literature Review which involves using tools such as search engines ( e.g. google scholar) and document management and reference systems (e.g. Endnote and Mandalay).
The literature review will attempt to create a space for the research project that has not been covered or is yet to be developed.
Literature Mapping uses graphical methods to plot your literature in a graphical format. There are many types of graphical method from mind mapping to infographic formats.
See our Research Gate Forum where leading experts have discussed the various graphical literature tools from Mind Maps through to Quiqqa and other methods.
Dr Jonathan Drane has developed a unique but simple literature mapping method which streamlines your literature review and helps you refine your topic and its place in the literature universe.
‘In our method we prefer to use a ‘cards on desktop’ graphical logic. It uses cards (like the icons on your desktop) and allocates identifiers to the cards including different colours as well as other key information points. Think of each card as if it was a library card which is also linked back to the actual publication it refers to’. Dr Jonathan Drane
In the method there is also an X-Y axis to allow for key concept themes to be pinned to the axis. From there each card is positioned based on its alignment to the theme. In the chart below this method is applied to City Growth Dynamics themes from Dr Drane’s doctorate.
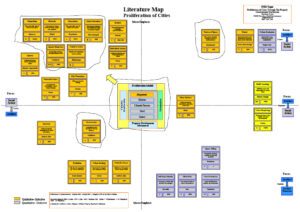
‘ As I spent weeks in the literature mapping phase of my doctorate I realised that it was made clearer by using graphical representation of the various themes and concepts.’ Dr Jonathan Drane
An example of his literature map system is shown above which is extracted from Dr Drane’s Doctorate .
Impact and Strategic Importance
Research occurs in a huge range of endeavours from academic research to competitive analysis, market and corporate strategy. A central activity in these is to make sure you know what the current literature, articles and books are in the relevant strategic arena.
The use of literature review is essential to maintaining a strategic advantage and identifying the gaps in the theory or in corporate offerings.
We recommed that you take some time out and attend our upcoming webinar on this topic . Whether you are an academic or a business person or government researcher, this is important.
We look forward to seeing you at this webinar.

Dr Jonathan Drane
Download this article and other related resources (free).

Fill in this form to receive free downloads:
Your message (optional)
Other readings and links:
Link to Jonathan’s Research Gate page page on Literature Mapping
Link to Jonathan’s Doctorate
JDNEST Ep5- Special Interview with Ryan Muir- Echidna Strip- Startup Journey and Stories
Jdnest ep4- curiosity and professor julius sumner miller- startup journey and stories, jdnest ep3- special interview with leonie cutts- ccs corporation- startup journey and stories, jdnest ep 2: pathways and circularity- startup journey and stories.

3 Innovative Literature Mapping Tools for Citation Maps
In the ever-evolving landscape of academic research, navigating through vast amounts of literature can be daunting. Enter innovative literature mapping tools, packed with unique features.
They simplify and revolutionise the way researchers interact with scientific literature, enhancing the efficiency and depth of literature reviews.
Let’s dive into how these tools are reshaping the approach to academic research.
Innovative Literature Mapping Tools
What is a literature mapping tool.
A citation mapping tool is a game-changer. Think of it as a detective tool that uncovers the intricate web of connections within scientific literature.

These tools visualise citation relationships, creating a citation map or literature map that guides you through the complex maze of scholarly papers.
One popular example is Inciteful, offering innovative literature mapping tools that not only track citation links but also analyse the context of the citation, revealing direct citation relationships and co-citation networks.
Imagine you have a ‘seed paper,’ a starting point in your literature review. A literature mapping tool then take this seed paper and branch out, finding papers:
- That cite it (direct citation relationships) or
- Those that share a thematic connection (co-citation).
This forms a citation tree or network, showing you not just one paper but a cluster of similar papers, interconnected by their citation relationships.
More modern citation mapping tool also integrated AI. They not only map out citation relationships but also delve into the citation context or sentiment, offering a richer, more nuanced understanding of how papers are interconnected.
Litmaps is a cutting-edge citation mapping tool that offers a unique approach to visualising the connections in scientific literature.
It’s designed to simplify and enhance the process of conducting a literature review, especially for researchers looking to map out the citation landscape of a specific topic.
At its core, Litmaps lets you visualise citation relationships in a dynamic, interactive manner. It works by creating a literature map that shows how different papers are connected through citations.

You start with a ‘seed paper,’ and Litmaps builds a citation network around it, by:
- Identifying seminal papers,
- similar papers, and
- Other papers that cite your chosen article.
This is particularly helpful for understanding the context and development of research in a given field.
One of the key features of Litmaps is its ability to create a citation tree. This tree not only shows direct citation relationships but also highlights co-citations. This gives you a deeper insight into how ideas and research are interconnected.
In terms of visualisation, Litmaps excels. It uses a similarity graph, not just a standard citation graph, to display connections.
This means you’re seeing a more nuanced representation of the literature, based on the similarity metric of papers, rather than just citation counts.
Litmaps also allows for a high level of customisation. You can filter papers based on:
- The number of citations,
- Publication date, and even
- Specific keywords.
This makes it a highly flexible tool for conducting systematic reviews and meta-analysis.
Litmaps also have a more user-friendly interface, and additional features like tracking the latest papers on a specific topic or a random set of systematic reviews.
Inciteful is an innovative literature mapping tool that stands out in the field of academic research for its unique approach to visualizing citation networks.

This tool is designed to make the process of literature review more intuitive and insightful, especially for researchers and scholars delving into new or complex fields.
When you use Inciteful, you start by selecting a ‘seed paper’. From this single paper, Inciteful creates a citation network, branching out to reveal not only papers that cite your chosen article but also those that are contextually related through co-citation and citation relationships.
This forms a comprehensive citation map, allowing you to see how various research pieces interconnect.
A standout feature of Inciteful is its visualization capabilities. The tool presents a citation graph, where each node represents a paper, and connecting lines indicate citation links.
This visualization helps you grasp the structure of scientific discourse in a field, revealing seminal papers, emerging trends, and key authors. You can then filter and sort papers based on keywords, number of citations, or publication date.
Inciteful isn’t just about numbers of citations; it delves deeper. The tool analyzes the context of citations, bringing to light the sentiment and relevance of each citation relationship.
This adds an extra layer of depth to your literature review, offering insights that go beyond traditional citation counting. Inciteful Incorporates metadata from various sources like:
- Google Scholar,
- Web of Science, and
- Microsoft Academic
Inciteful also ensures that its citation network is rich and current. The tool also supports importing bibliographic data in BibTeX format, making it flexible and adaptable to various research needs.
This makes Inciteful not just a powerful research tool but also a highly customizable one, suited for everything from quick overviews to in-depth systematic reviews.
Connected Papers
Connected Papers is a cool literature mapping tool that offers researchers and scholars an intuitive way to explore the citation network of a specific paper or topic.
It stands out compared to the other mapping tools for its user-friendly design and effective visualisation techniques.

Connected Papers takes a ‘seed paper’ of your choice, then generates a citation graph based on the seed paper, producing a visual network that displays how this paper is connected to others through direct citations and co-citations.
This network reveals the most relevant papers, showing you the ‘big picture’ of research trends and developments related to your topic.
The citation graph in Connected Papers isn’t just a simple map; it’s a detailed visualisation tool. Each node represents a paper, and the lines between them indicate citation relationships.
This visualisation allows you to easily identify:
- Research papers,
- Citations, and even
- Emerging trends in the field.
You can see at a glance which papers are most cited and how they interlink, providing a comprehensive overview of the scientific landscape.
Connected Papers uses metadata and bibliographic information from databases like Google Scholar, Web of Science, and Microsoft Academic. This ensures that the citation network you’re exploring is both extensive and up-to-date.
It also supports importing data in BibTeX format, making it versatile for different research needs.
This tool is particularly valuable for researchers who are looking to map out the landscape of a new or complex field. It helps in identifying related papers that might not be immediately obvious, providing a deeper understanding of the subject matter.
Literature Review Made Easy, With Citation Map Tools
Litmaps, Inciteful, and Connected Papers represent the forefront of academic research tools, each bringing a unique approach to literature mapping.
They empower researchers with advanced visualisation, comprehensive citation networks, and user-friendly interfaces, making literature reviews more efficient and insightful.
As the landscape of scientific research continues to grow, these tools are invaluable allies in navigating and understanding the complex web of academic knowledge.

Dr Andrew Stapleton has a Masters and PhD in Chemistry from the UK and Australia. He has many years of research experience and has worked as a Postdoctoral Fellow and Associate at a number of Universities. Although having secured funding for his own research, he left academia to help others with his YouTube channel all about the inner workings of academia and how to make it work for you.
Thank you for visiting Academia Insider.
We are here to help you navigate Academia as painlessly as possible. We are supported by our readers and by visiting you are helping us earn a small amount through ads and affiliate revenue - Thank you!

2024 © Academia Insider


Literature Reviews
- Getting started
What is a literature review?
Why conduct a literature review, stages of a literature review, lit reviews: an overview (video), check out these books.
- Types of reviews
- 1. Define your research question
- 2. Plan your search
- 3. Search the literature
- 4. Organize your results
- 5. Synthesize your findings
- 6. Write the review
- Artificial intelligence (AI) tools
- Thompson Writing Studio This link opens in a new window
- Need to write a systematic review? This link opens in a new window

Contact a Librarian
Ask a Librarian
Definition: A literature review is a systematic examination and synthesis of existing scholarly research on a specific topic or subject.
Purpose: It serves to provide a comprehensive overview of the current state of knowledge within a particular field.
Analysis: Involves critically evaluating and summarizing key findings, methodologies, and debates found in academic literature.
Identifying Gaps: Aims to pinpoint areas where there is a lack of research or unresolved questions, highlighting opportunities for further investigation.
Contextualization: Enables researchers to understand how their work fits into the broader academic conversation and contributes to the existing body of knowledge.

tl;dr A literature review critically examines and synthesizes existing scholarly research and publications on a specific topic to provide a comprehensive understanding of the current state of knowledge in the field.
What is a literature review NOT?
❌ An annotated bibliography
❌ Original research
❌ A summary
❌ Something to be conducted at the end of your research
❌ An opinion piece
❌ A chronological compilation of studies
The reason for conducting a literature review is to:

Literature Reviews: An Overview for Graduate Students
While this 9-minute video from NCSU is geared toward graduate students, it is useful for anyone conducting a literature review.

Writing the literature review: A practical guide
Available 3rd floor of Perkins

Writing literature reviews: A guide for students of the social and behavioral sciences
Available online!

So, you have to write a literature review: A guided workbook for engineers

Telling a research story: Writing a literature review

The literature review: Six steps to success

Systematic approaches to a successful literature review
Request from Duke Medical Center Library

Doing a systematic review: A student's guide
- Next: Types of reviews >>
- Last Updated: May 17, 2024 8:42 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.duke.edu/litreviews

Services for...
- Faculty & Instructors
- Graduate Students
- Undergraduate Students
- International Students
- Patrons with Disabilities
- Harmful Language Statement
- Re-use & Attribution / Privacy
- Support the Libraries

Chaos to Clarity: Structuring Your Literature Review Format
Master literature review format! Learn key sections, effective citation & analysis tips to write a strong academic review.
Ever wondered how to dive into a mountain of books and articles and come up with something that not just makes sense but shines new light on a topic? What if there was a way to neatly tie together all that information, spot what’s missing, and maybe even pave the way for discoveries?
That’s what you are going to learn in this article, literature reviews—a place where chaos meets order, and where your insights could set the stage for the next big thing. Let’s break down the literature review format , your essential guide to properly writing a literature review.
Dissecting Literature Review Format
There are 6 main sections to make a note of while writing a literature review. Those are:
The Introduction Section
Topic background, conceptual framework.
- Synthesis and Evaluation in Literature Reviews
- Conclusion for Your Literature Review
- Reference List in Your Literature Review
Also Read: Essential Components of a Literature Review
The introduction of your literature review is where you set the stage for the entire document. It’s your first opportunity to engage your readers and provide a clear blueprint of what your review will cover and why it matters. This section does more than merely introduce the topic; it establishes the context, defines the scope, and outlines the purpose and objectives of your literature review.
Things to keep in mind while writing an introduction:
- Craft a compelling opening
- Establish the Context and Justification
- Define the Scope and Objectives
- Lay out the Structure
- Give an overview of the Structure
The “Topic Background” section of a literature review serves as the cornerstone for understanding the evolution and current state of the subject matter. It is divided into two crucial sub-sections: Historical Context and Current State of the Topic .
Delving into these areas provides you with a comprehensive backdrop against which the literature review is framed, enriching the reader’s understanding of why the topic is of interest and what has influenced its development to the current state.
Historical Context

The Historical Context is fundamental in setting the stage for the entire literature review. This section is not just a chronology of events or developments; it’s a curated narrative that highlights the key milestones and turning points that have significantly impacted the topic.
By examining the historical evolution, the review establishes a timeline of how understanding and perspectives have shifted over the years.
Summary Of Key Historical Developments
This involves identifying and summarizing the major breakthroughs, shifts in thinking, or seminal works that have shaped the topic. It’s important to focus on developments that have a direct relevance to the current understanding and state of the subject. For example, if the topic is about the evolution of renewable energy technologies, this part would outline the initial discovery and use of renewable sources, significant technological innovations, and pivotal policy decisions that have influenced the field.
Relevance Of Historical Context To The Topic
After outlining the key historical developments, it’s crucial to connect these events to the present topic. This means discussing how past events have laid the groundwork for current theories, practices, or debates within the field. It involves analyzing the impact of historical milestones on the subject matter, and explaining how they have contributed to current knowledge, challenges, and research questions. This section makes it clear why understanding history is essential for anyone researching or studying the topic today.
Current State Of The Topic
Moving from the historical context, the review transitions to the present with the Current State of the Topic. This part assesses the latest research, trends, debates, and technological advancements that define the subject area at the moment.
Current Trends Or Updates
Here, the focus shifts to what is happening in the field right now. This could include recent research findings, emerging theories, new methodologies, or the latest technological innovations. The aim is to provide a snapshot of the current research landscape, identifying what themes, questions, or problems are being actively explored. For instance, in the context of digital marketing, this might involve discussing the rise of artificial intelligence in customer relationship management or the impact of social media trends on marketing strategies.
Impact Of These Trends On The Subject Matter
The final step is to assess the implications of these current trends for the topic. This includes considering how recent developments have advanced the field, the challenges they present, and the opportunities they open up for future research. It’s about connecting the dots between what’s happening now and what it means for the subject area moving forward. This not only helps to frame the research questions that the literature review will address but also sets the stage for identifying gaps in the current knowledge, thereby guiding the direction of future studies.
Also Read: What is a literature review? Get the concept and start using it
When doing a literature review, it’s essential to lay a solid foundation for your exploration through a well-defined conceptual framework. This framework acts as a compass, guiding your review’s direction by establishing the key concepts, theories, and perspectives that underpin your topic.
Definitions And Descriptions
Before diving into the depths of your literature review, it’s crucial to start with the basics. This means clearly identifying and defining the key concepts related to your topic. Think of this as setting the stage for your readers, ensuring they have a clear understanding of the fundamental terms and ideas you will be exploring.
Key Concepts Related To The Topic
Begin by listing the essential concepts central to your review. These are the building blocks of your topic, the terms that will repeatedly appear throughout your exploration.
Detailed Definitions And Their Relevance
Once you’ve identified these concepts, provide precise and comprehensive definitions for each. Don’t hesitate to explore different dimensions or interpretations of these terms, as this can enrich your readers’ understanding. More importantly, discuss why these concepts are crucial to your review. How do they shape the scope of your exploration? How do they relate to each other and to the broader topic? This step ensures that your readers are not just familiar with the terms but also understand their significance within your review’s context.

Theoretical Perspectives
With the key concepts clearly defined, it’s time to frame your literature review within relevant theoretical perspectives. This is where you align your exploration with existing theories, models, or frameworks that provide insights into your topic.
Important Theories Related To The Topic
Identify the theories that are foundational to your topic. These could range from well-established theories that have long guided research in your field to more contemporary models that offer new insights. For example, a review of organizational behavior might draw on theories of motivation, leadership styles, and organizational culture.
Evaluation Of These Theories And Their Influence On The Topic
After pinpointing the relevant theories, critically assess their contributions to the topic. Consider questions like: How have these theories shaped understanding of the topic? What insights do they offer, and where do they fall short? Are there controversies or debates surrounding these theories? This evaluation not only deepens your review’s analytical depth but also positions your work within the larger academic conversation.
Synthesis And Evaluation In Literature Reviews

The “Synthesis and Evaluation” section is where your literature review truly comes to life. Here, you’re not just summarizing what others have said; you’re weaving together diverse strands of research to present a cohesive picture of the topic at hand.
Comparison And Contrast Of Sources
Synthesizing the literature involves more than listing findings from various studies; it’s about drawing connections between them, highlighting areas of agreement and dispute, and weaving these into a narrative that adds depth and breadth to your understanding of the topic.
Comparative Analysis
Start by grouping your sources based on similarities in their findings, methodologies, or theoretical approaches. This clustering will help you identify trends and common themes across the literature. For example, if several studies have found similar outcomes under comparable conditions, these findings can be grouped to strengthen a particular argument or observation about the topic.
Contrasts Or Conflicts Among Sources
Equally important is the identification of discrepancies in the literature. Do some studies present findings that directly contradict others? Are there differences in how researchers have interpreted similar data? Highlighting these conflicts is crucial, as it can indicate areas where the topic is still evolving or where further research is needed. It also shows your ability to critically engage with the material, a hallmark of scholarly rigor.
Analysis Of Gaps In Literature
One of your primary tasks in the synthesis and evaluation section is to identify what’s missing in the current body of research. This requires a critical eye and a deep understanding of both your topic and the broader field in which it resides.
Identification Of Research Gaps
As you comb through the literature, ask yourself: What questions remain unanswered? Are there underexplored areas or populations? Perhaps certain methodologies have been overlooked, or theoretical perspectives have not been considered. Pinpointing these gaps is not a mere exercise in academic critique; it’s a vital step in advancing knowledge within the field.
Implications Of These Gaps For Future Research
Highlighting gaps in the literature sets the stage for future studies. It’s where you, as the reviewer, can suggest new research directions that could fill these voids or further explore the topic. Discussing the implications of these gaps not only enriches your review but also contributes to the ongoing scholarly conversation.
Conclusion For Your Literature Review
The conclusion of your literature review is where you bring together all the strands of your argument, synthesizing the insights gained and highlighting the significance of your findings. It’s not just a summary of what has been discussed; it’s an opportunity to underscore the relevance of the review, reflect on the broader implications of your synthesis and evaluation, and suggest directions for future research.
Summary Of Key Points
Start your conclusion by succinctly summarizing the main points and findings of your review. This isn’t about rehashing every detail but rather about distilling the essence of your exploration. Highlight the critical trends, themes, and conflicts you’ve uncovered, and remind your readers of the significance of these discoveries.
Relevance And Implications Of The Literature For The Topic
Next, focus on the relevance and implications of your findings. This involves stepping back to consider the bigger picture—how does your literature review contribute to the understanding of your topic? Discuss the impact of the trends and gaps you’ve identified on the field, and elaborate on how your synthesis of the literature advances or enriches existing knowledge.
Reflection On The Research Process
Reflecting on the research process itself can provide valuable insights. Consider discussing the challenges you encountered in navigating the literature, such as dealing with conflicting findings or the scarcity of research on certain aspects of your topic.
Directions For Future Research
One of the most critical aspects of your conclusion is to suggest directions for future research. Be as precise as possible, whether suggesting new methodologies, theoretical frameworks, or specific topics that warrant deeper investigation.
Final Thoughts
End your conclusion with a strong closing statement that reiterates the value of your literature review. Emphasize the importance of continued research on your topic and the potential it holds for advanced understanding within your field. A compelling conclusion reaffirms the significance of your work, leaving your readers with a clear sense of its contribution and the urgent need for further exploration.
Reference List In Your Literature Review
The Reference List is the backbone of your literature review, providing a comprehensive compilation of all the sources you’ve cited throughout your exploration. It’s not merely a formality but a crucial component that lends credibility and rigor to your work.
Importance Of Accuracy And Consistency
The cornerstone of a reliable Reference List is accuracy and consistency in citation style. Whether you’re adhering to APA , MLA , Chicago , or another academic citation format, it’s vital to apply the rules with precision. This includes correctly formatting author names, publication dates, titles, and publication details.
Organizing Your References
While different citation styles have their own rules for listing references, organizing them in a way that enhances readability and accessibility is universally beneficial. Alphabetical order by the author’s last name is the most common method, as it allows readers to easily locate sources.
Comprehensive Coverage
Your Reference List should be exhaustive, including every work you’ve cited in your review. This extends beyond journal articles and books to encompass reports, conference papers, online resources, and any other materials that have informed your analysis.
The Value Of Annotations
While not always required, providing brief annotations for key sources can add tremendous value to your Reference List. An annotated bibliography offers a succinct summary of each source’s main arguments, methodologies, and findings, as well as its relevance to your literature review.
Digital Accessibility
In today’s digital age, considering the accessibility of your referenced works can greatly enhance the utility of your Reference List. Whenever possible, include Digital Object Identifiers (DOIs) or stable URLs for online sources, ensuring readers can directly access the materials.
Also read: What Is A DOI? Exploring The Purpose And Importance
Reflecting On Ethical Scholarship
Finally, your Reference List is a reflection of ethical scholarship. By accurately citing all the sources that have informed your work, you’re honoring the intellectual property of other researchers and upholding the academic community’s standards of integrity and respect.
Crafting a meticulous Reference List is an essential aspect of your literature review that underscores the credibility, depth, and ethical foundation of your research. By adhering to the principles of accuracy, comprehensiveness, and accessibility, you not only facilitate further inquiry but also pay homage to the collective endeavor of knowledge advancement in your field.
Related Article: Navigating the AMA Citation Format: Best Tips for Referencing
In conclusion, writing a literature review involves meticulous structuring, beginning with an engaging introduction that sets the stage, followed by a detailed exploration of the topic’s background, including its historical context and current state.
A robust conceptual framework lays the groundwork for analysis, leading to a critical synthesis and evaluation of relevant literature.
The conclusion ties together the review’s key findings and implications, while the reference list meticulously catalogs all cited works. Mastering each section ensures a comprehensive and insightful review, essential for advancing academic understanding and contributing to scholarly discussions.
Related Article: Preliminary Literature Review: A Guide for Effective Research
Science Figures, Graphical Abstracts, And Infographics For Your Research
Revolutionize your research with infographics from Mind the Graph . From science figures, graphical abstracts to infographics, you can unleash the power of creative visuals with this user-friendly platform and make your research captivating.

Subscribe to our newsletter
Exclusive high quality content about effective visual communication in science.
Unlock Your Creativity
Create infographics, presentations and other scientifically-accurate designs without hassle — absolutely free for 7 days!
About Sowjanya Pedada
Sowjanya is a passionate writer and an avid reader. She holds MBA in Agribusiness Management and now is working as a content writer. She loves to play with words and hopes to make a difference in the world through her writings. Apart from writing, she is interested in reading fiction novels and doing craftwork. She also loves to travel and explore different cuisines and spend time with her family and friends.
Content tags
A systematic exploration of scoping and mapping literature reviews
- Brief Report
- Open access
- Published: 23 May 2024
Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article

- Eirini Christou ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-6928-1013 1 ,
- Antigoni Parmaxi ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-0687-0176 1 &
- Panayiotis Zaphiris ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-8112-5099 1
178 Accesses
Explore all metrics
Systematic literature mapping can help researchers identify gaps in the research and provide a comprehensive overview of the available evidence. Despite the importance and benefits of conducting systematic scoping and mapping reviews, many researchers may not be familiar with the methods and best practices for conducting these types of reviews. This paper aims to address this gap by providing a step-by-step guide to conducting a systematic scoping or mapping review, drawing on examples from different fields. This study adopts a systematic literature review approach aiming to identify and present the steps of conducting scoping and mapping literature reviews and serves as a guide on conducting scoping or mapping systematic literature reviews. A number of 90 studies were included in this study. The findings describe the steps to follow when conducting scoping and mapping reviews and suggest the integration of the card sorting method as part of the process. The proposed steps for undertaking scoping and mapping reviews presented in this manuscript, highlight the importance of following a rigorous approach for conducting scoping or mapping reviews.
Similar content being viewed by others
A scoping review on the conduct and reporting of scoping reviews.
How methodological frameworks are being developed: evidence from a scoping review

Literature Reviews: An Overview of Systematic, Integrated, and Scoping Reviews
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
1 Introduction
An essential component of academic research is literature review. A systematic literature review, also known as a systematic review, is a method for locating, assessing, and interpreting all research related to a specific research question, topic, or phenomenon of interest [ 1 ].
Scoping and mapping reviews are variations of systematic literature mapping [ 2 ]. Both mapping and scoping reviews can help researchers to understand the scope and breadth of the literature in a given field, identify gaps in the research, and provide a comprehensive overview of the available evidence. Systematic literature mapping purposely focuses on a narrower but more general academic or policy issue and does not try to synthesize the results of research to address a particular subject. The scoping review is exploratory in nature, whereas the mapping review can be conclusive in describing the available evidence and identifying gaps. Mapping review includes a thorough, systematic search of a wide field. It identifies the body of literature that is currently available on a subject and points out any glaring gaps in the evidence [ 3 ].
1.1 Rationale
Despite the importance and benefits of conducting systematic scoping and mapping reviews, many researchers may not be familiar with the methods and best practices for conducting these types of reviews. This paper aims to address this gap by providing a step-by-step guide to conducting a systematic scoping or mapping review, drawing on examples from different fields.
This study adopts a systematic literature review approach aiming to identify and present the differences and the steps of conducting scoping and mapping literature review. The paper provides practical guidance on how to address common challenges in conducting systematic scoping or mapping reviews, such as dealing with the volume of studies identified, managing the data extraction and synthesis process, and ensuring rigor and reproducibility in the review methodology. The main research questions that guide this study are:
RQ1: What is a systematic scoping review and how is it conducted?
RQ2: What is a systematic mapping review and how is it conducted?
RQ3: What are the main differences between systematic scoping and systematic mapping reviews?
Overall, this paper will be a valuable resource for researchers who are interested in conducting a systematic scoping or mapping review. By providing clear guidance and practical examples, the paper aims to promote best practices in systematic scoping and mapping review methodology. The study is organized as follows: The following section presents the methodology of the study, followed by the results showing the process of the scoping and mapping literature review and presenting some examples. Finally, suggestions on how to plan and perform a quality scoping and mapping review are presented.
2 Methodology
The methodology of this paper was adopted by Xiao and Watson [ 4 ].
2.1 Literature search
The search was conducted in two well-known online databases, Web of Science and EBSCOHost, across various disciplines. The searched terms combined keywords related to the performance of scoping and mapping literature review, such as “systematic literature review”, “methodology”, “map”, “mapping” and “scoping”. The title of each manuscript was used to determine its initial relevance. If the content of the title suggested that it would explain the method of the literature review process, we obtained the full reference, which included the author, year, title, and abstract, for additional analysis.
2.2 Initial search results
The query string used for the database search is the following: systematic literature review AND methodology AND (“map” OR “mapping” OR “scoping”). Abstract search was conducted in both databases for the last 10 years (2013–2022). A search on EBSCOHost revealed 643 results of which 291 were duplicated and automatically removed. After applying the database filters to limit the articles to peer-reviewed academic journal articles written in English, a number of 102 papers were excluded. Additional 109 papers were duplicated and removed manually. After an initial screening of the titles, a total of 13 studies were identified as relevant to the methodology of the scoping and mapping literature review. A search on Web of Science, revealed 888 results of which 9 were duplicate and removed, and 157 were found to be related to the methodology of scoping or mapping literature reviews after the first title screening. Last search was conducted on the 2nd of November 2022. Both sources revealed 161 related studies, excluding 9 duplicates that were removed.
2.3 Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Only studies that provide instructions on how to perform a scoping or mapping review were included in this paper. Reviews of the literature on certain subjects and in languages other than English were excluded. The study is limited to papers published within the last 10 years, aiming to collect recent information for performing scoping or mapping reviews. Inclusion and exclusion criteria can be found in Table 1 .
2.4 Screening
To further assess the 161 studies’ applicability to the study topic, their abstracts were reviewed. The manuscripts were evaluated independently and in parallel by two researchers. The researchers’ differing opinions were discussed and settled. Then the full-text of a total of 20 studies was acquired for quality evaluation.
2.5 Eligibility and quality evaluation
To further assess the quality and relevance of the studies, the full-text papers were reviewed. Journal articles and books published by prominent publishers were included in the review as they contained high-quality research. Because there is no peer review procedure, the majority of technical reports and online presentations were excluded.
Two researchers worked independently and simultaneously on evaluating eligibility and quality. Any disagreements between them were discussed and resolved. A total of ten (10) studies were excluded after careful review: one study was excluded because it lacked instructions on how the scoping or mapping review methodology was conducted, three studies were excluded because the methodology was not related to scoping or mapping review, while five studies were disregarded because they focused on a particular subject. One of the studies’ full text couldn’t be accessed. This resulted in ten (10) eligible for full-text analysis.
2.6 Iterations
Through backward and forward searching, additional 18 studies were discovered, from which only 10 met the inclusion criteria. The forward and backward search was also used to find manuscripts that applied scoping or mapping literature review methodology. After finding the article that established the scoping or mapping review methodology, articles that had cited the methodology paper to find instances of best practices in different fields were searched. Following consideration of examples’ adherence to the methodology, preference was given to planning-related articles. In total, 90 studies were analyzed in this study, i.e. 10 methodological papers that describe the application of scoping or mapping review, as well as 80 papers that demonstrate the application of the scoping and mapping methodology in different fields, that are used as examples. The PRISMA flow diagram (see Fig. 1 ) depicts the process of the search strategy [ 5 ].
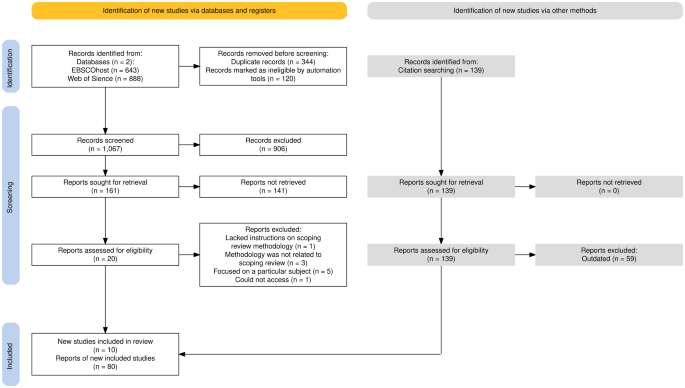
PRISMA flow diagram
2.7 Extraction and analysis of data
Data were extracted in the process of scoping literature reviews, including information with regards to formulating the problem, establishing and validating the review procedure, searching the literature, screening for inclusion, evaluating quality, extracting data, analyzing and synthesizing data, and reporting the findings (Xiao & Watson, 2019). NVivo software was used for all data extraction and coding procedures. Initially, two researchers each took information from articles for cross-checking. The two researchers reached an agreement on what to extract from the publications after reviewing a few articles together. Then the first author classified the data based on the research questions.
In this section we present the findings of our review.
3.1 Defining “Scoping” and “mapping” review
According to [ 2 ], scoping and mapping reviews are variations of systematic literature mapping that focus on narrower but more general academic or policy issues. A scoping review is exploratory in nature, seeking to identify the nature and extent of research on a particular topic, and can be used to identify gaps in the literature. An example of a research question suitable for a scoping review is “What engagement strategies do educators use in classroom settings to facilitate teaching and learning of diverse students in undergraduate nursing programs?“ [ 6 ]. A mapping review, on the other hand, is a thorough and systematic search of a wide field of literature that aims to identify the body of literature currently available on a subject and point out any glaring gaps in the evidence. An example of a research question suitable for a mapping review is “What are the currently available animal models for cystic fibrosis” [ 3 ]. Overall, each type of review has its own specific aims and can be useful for different types of research questions.
3.1.1 Defining scoping review
There is no single definition for scoping reviews in the literature. According to [ 7 ], scoping review is a type of knowledge synthesis that uses a systematic process to map the evidence on a subject and identify key ideas, theories, sources, and knowledge gaps. The goal of a scoping review is to include all relevant information that is available, including ‘grey’ literature, which includes unpublished research findings, therefore including all available literature and evidence, but the reviewers can decide what type of publications they would like to include [ 8 , 9 , 10 , 11 ].
Scoping review process is sometimes used as a preliminary step before a systematic literature review, in cases where the topic or research area in focus has not yet been extensively reviewed or is complicated or heterogeneous in nature and the types of evidence available remain unclear [ 3 ]. For example, while a scoping review might serve as the foundation for a full systematic review, it does not aim to evaluate the quality of the evidence like systematic reviews do [ 8 ]. Moreover, scoping review is also referred to as a “pilot study” [ 12 ], that can be used as a “trial run” of the entire systematic map; it helps to mold the intended approach for the review and inform the protocol development.
Rapid and scoping meta-reviews were also referred as types of scoping reviews. A “rapid review” is a particular kind of scoping review, which aims to provide an answer to a particular query and can shorten the process compared to a full systematic review [ 3 ]. The “scoping meta-review” (SMR) is a scoping evaluation of systematic reviews that offers researchers a flexible framework for field mapping and a way to condense pertinent research activities and findings, similar to a scoping review [ 13 ].
Almost all of the scoping studies identified in the corpus, draw from previews scoping review frameworks, such as the one proposed by [ 14 , 15 ] and the authors’ manual provided by the Joanna Briggs Institute [ 11 , 16 , 17 , 18 ].
3.1.2 Defining mapping review
A mapping review, also referred to as a “systematic map”, is “a high-level review with a broad research question” [ 3 ](p.133). The mapping review includes a thorough, systematic search of a wide field. It identifies the body of literature that is currently available on a subject and points out any gaps in the evidence. The mapping review can be conclusive in describing the available evidence and identifying gaps, whereas the scoping review is exploratory in nature [ 3 ].
The term “mapping” is used to describe the process of synthesizing and representing the literature numerically and thematically in tables, figures, or graphical representations, which can be thought of as the review output. Mapping enables researchers to pinpoint potential areas for further study as well as gaps in the literature [ 19 ].
Systematic mapping uses the same strict procedures as systematic reviews do. However, systematic mapping can be used to address open or closed-framed questions on broad or specific topics, because it is not constrained by the requirement to include fully specified and defined key elements [ 12 ]. Systematic mapping is especially useful for broad, multifaceted questions about an interesting topic that might not be appropriate for systematic review because they involve a variety of interventions, populations, or outcomes, or because they draw on evidence that is not just from primary research [ 12 ].
3.2 Process of conducting mapping and scoping reviews
As noted in the previous sections, mapping reviews and scoping reviews both aim to provide a broad overview of the literature, but the former focuses on the scope of the literature while the latter focuses on the nature and extent of available evidence on a specific research question or topic. In understanding the process for conducting mapping and scoping reviews, we adopted the eight steps proposed by Xiao and Watson [ 4 ] that are common for all types of reviews: (1) Formulate the problem; (2) Establishing and validating the review procedure; (3) Searching the literature; (4) Screening for inclusion; (5) Evaluating quality; (6) Extracting data; (7) Analyzing and synthesizing data; (8) Reporting the findings. The steps are explained in detail below and describe the methodology for both scoping and mapping reviews, distinguishing their differences where applicable. A summary of the review types along with their characteristics and steps as identified from the literature are presented in Table 2 .
3.2.1 Step 1 formulate the problem
The first step for undertaking a mapping or a scoping review is to formulate the problem by setting the research question that should be investigated, taking into account the topic’s scope [ 12 ]. It is important to clearly state the review objectives and specific review questions for the scoping review. The objectives should indicate what the scoping review is trying to achieve [ 10 , 20 ].
In mapping reviews, it can be helpful to create a conceptual framework or model (visual or textual) to describe what will be explored by the map when determining the mapping review’s scope. It should also be determined whether the topic’s scope is broad, specific, or likely to be supported by a substantial body of evidence [ 12 ].
3.2.1.1 Defining the research question(s)
Prior to beginning their search and paper selection process, the authors should typically define their research question(s) [ 3 ]. There are specific formats that are recommended for structuring the research question(s), as well as the exclusion and inclusion criteria of mapping and scoping reviews [ 21 ] (see Table 3 ).
PCC (Population, Concept, and Context) and PICO format (Population, Intervention, Comparator and Outcome) are often used in scoping and mapping reviews. It is recommended that research questions for scoping reviews follow the PCC format and include all of its components [ 17 , 18 , 21 ]. Information about the participants (e.g. age), the principal idea or “concept,” and the setting of the review, should all be included in the research question. The context should be made explicit and may take into account geographical or locational considerations, cultural considerations, and particular racial or gender-based concerns [ 10 ].
Researchers use the PCC format in order to determine the eligibility of their research questions, as well as to define their inclusion criteria (e.g [ 22 , 23 , 24 , 25 , 26 ]). Most scoping reviews have a single main question, but some of them are better served by one or more sub-questions that focus on specific PCC characteristics [ 8 , 18 ].
3.2.2 Step 2. Establishing and validating the review procedure
A protocol is crucial for scoping and mapping reviews because it pre-defines the scoping review’s goals and procedures [ 11 , 17 , 18 , 20 ], it clearly states all methodological decisions since the very beginning [ 2 ], and it also specifies the strategy to be used at each stage of the review process [ 12 ]. Similar to all systematic reviews, scoping reviews start with the creation of an a-priori protocol that includes inclusion and exclusion criteria that are directly related to the review’s objectives and questions [ 7 , 11 , 17 , 18 , 20 ]. In order to decrease study duplication and improve data reporting transparency, the use of formalized, registered protocols is suggested [ 18 , 19 ]. The international prospective register of systematic reviews, known as PROSPERO, states that scoping reviews (and literature reviews) are currently ineligible for registration in the database. While this could change in the future, scoping reviews can currently be registered with the Open Science Framework ( https://osf.io/ ) or Figshare ( https://figshare.com/ ), and their protocols can be published in select publications, including the JBI Evidence Synthesis [ 18 ].
Scoping and mapping reviews should require at least two reviewers in order to minimize reporting bias, as well as to ensure consistency and clarity [ 3 , 16 , 17 , 18 ]. The reviewers should include a plan for the results presentation during the protocol development, such as a draft chart or table that could be improved at the end when the reviewers become more familiar with the information they have included in the review [ 17 , 18 ].
3.2.3 Step 3. Searching the literature
Searching the literature requires to prepare a search strategy, decide on search terms, search databases or journals, and perform a manual search [ 27 ]. For example, deciding on search terms, can follow an iterative process that is further explained in the sub-section below. Thinking about searching in terms of broader to narrower strategies is helpful. Fewer databases and/or journals will be checked out in narrower searches (search only in the title, keywords, and abstract fields), which are frequently used in scoping reviews, while multiple databases can be checked for mapping reviews [ 2 ].
Search strategy
Mapping and scoping review search should aim to be as thorough as possible [ 12 ] to find both published and unpublished evidence. An inclusive approach is frequently preferred for scoping reviews to prevent potential omission of crucial information [ 10 , 17 , 18 ].
According to JBI, there should be a three-step search process for scoping reviews [ 10 , 17 , 18 ]. The first step is a quick search of at least two databases followed by a text word check of the article’s title, abstract, and body of text that are then analyzed. All determined index terms and keywords are used in the second stage across all included databases. In the third stage, additional studies should be looked up in the identified reports and articles’ reference lists [ 10 , 11 , 18 ]. The reviewers may look solely at the reference lists of the studies that were chosen from the full-text and/or included in the review, or they may look at the reference lists of all identified studies. In any case, it needs to be made very clear which group of studies will be looked at [ 8 , 11 , 18 ]. As reviewers gain more familiarity with the body of available evidence, new keywords, sources, and possibly helpful search terms may be found and incorporated into the search strategy, hence the search for a scoping review may be quite iterative. If so, it is crucial that the entire search process and the outcomes are open to scrutiny and audit [ 11 , 18 ].
In the same line, it is recommended for mapping reviews to search multiple databases [ 2 ] in all pertinent searchable fields (e.g., title, abstract, keywords, etc.) [ 3 ]. Thematic keywords, along with all of their synonyms and regional/temporal variations, are joined together to form Boolean strings using Boolean signs. Building looser, multiple Boolean strings instead of well-targeted ones (for example, using OR instead of AND, NOT, and exact phrases, respectively) is preferable. The latter runs the risk of omitting crucial references, whereas the former may return a sizable sample of sparsely relevant references [ 2 ]. Focusing the search on a specific component and then filtering all the results can be more effective for mapping reviews [ 3 ].
3.2.4 Step 4. Screening for inclusion
Screening and choosing the studies to be included in a review are the main objectives of this phase. According to [ 27 ], there are two levels of screening. Titles and abstracts are scanned in the first level to limit the range of the studies to be included, while full texts are scanned in the second level to re-examine the relevance of the studies and to settle disagreements between reviewers regarding the study selection. Discussions, meetings, consulting a third reviewer, and determining inter-rater reliability/agreement (using Cohen’s kappa coefficient or intraclass correlation coefficient) are the most typical ways to resolve disagreements. Soaita et al. (2020) [ 2 ] also support that the sample of retrieved references should be ‘cleaned-up’ once it has been finalized and duplicates have been automatically removed.
Different methodological approaches, including primary research articles, summary articles, opinion pieces, and grey literature, can all be included in the literature that scoping reviews identify and analyze [ 7 , 18 , 19 ], but they may also serve as an exclusion criterion [ 2 ]. Peters, Godfrey, et al. (2020) [ 18 ] advice against limiting source inclusion based on language unless there are compelling justifications for doing so (such as practical considerations).
According to the PRISMA extension for scoping reviews (PRISMA-ScR), a description of the study selection process must be provided in both a narrative and flow diagram format. Including the date of the most recent literature search, enables the reader to assess how current the scoping review is [ 7 ].
3.2.4.1 Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Inclusion criteria offer a framework on which the reviewers can decide which sources to include in the scoping review. To ensure transparency and replicability, the exclusion and inclusion criteria need to be documented [ 7 , 8 , 10 , 11 , 17 ]. Authors should specify any limitations by year, language, publication status, or other factors, and explain why each one was put in place [ 7 ].
When it comes to mapping reviews, criteria should be created whenever possible with participation from stakeholders. Depending on the type of research questions, stakeholders may include practitioners, designers, policy makers, scientists and research funding bodies, but attention should be paid to avoid bias [ 12 ].
3.2.5 Step 5. Evaluating quality
Scoping and mapping reviews are not concerned with quality assessment as a criterion for inclusion [ 2 ]. Assessments of reporting quality and bias risk are typically outside the scope. Although it is possible to extract study characteristics that reflect study and reporting quality, bias cannot be assessed against a specific hypothesis if a mapping review is exploratory [ 3 ].
3.2.6 Step 6. Extracting data
The process of data extraction for a scoping review is also known as “charting the results”. A draft charting table or form needs to be created to capture the key details about the relevance of the included studies to the review question, as well as the characteristics of the included studies. The data extraction process can be iterative, with the charting table being constantly updated.
The reviewers should become familiar with the source results and test the extraction form on two or three studies to ensure that all relevant results are extracted [ 7 , 8 , 10 , 11 , 17 , 18 , 28 ]. In order to increase reporting transparency, authors should explain the main revisions with a justification if the charting process was iterative (i.e., the form was continuously updated). If appropriate, details about the procedures used to collect and verify information from the researchers of the included sources of evidence should be provided [ 7 ]. Author(s), year of publication, source origin, country of origin, objectives, purpose, study population, sample size, methodology, intervention type and comparator, concept, duration of the intervention, how outcomes are measured, and key findings that are related to the review question are all types of information that may be extracted [ 7 , 8 , 10 , 11 , 17 ].
When it comes to data extraction for mapping reviews, it is restricted to important study characteristics and outcomes due to the size of a mapping review [ 3 ]. The process of mapping is intended to produce a practical and organized resource that provides enough detail about studies to be helpful in further work [ 12 ].
To move beyond a straightforward list of citations, it is crucial to maintain a high level of clarity throughout any databases that are created. Studies that are discussed in several papers or that seem to be connected should be marked in the database. In the future, this helps prevent the double counting of research findings in syntheses that might overlook connections between study lines in the databases [ 12 ].
Aiming to capture the key characteristics of the included studies in the scoping and mapping reviews, we suggest the use of a guiding table for extracting data (see Supplementary_Material_1_Guiding_Table).
3.2.7 Step 7. Analyzing and synthesizing data
Authors may extract results and map descriptively. Simple frequency counts of concepts, populations, characteristics, or other fields of data will suffice for many scoping reviews [ 17 , 18 ]. In-depth analysis of quantitative data is not typically required in scoping reviews, although in some cases the authors may take into consideration a more advanced analysis depending on the nature and purpose of their review. A meta-analysis or interpretive qualitative analysis is probably not necessary in scoping reviews [ 17 , 18 ].
When it comes to mapping reviews, no results synthesis is carried out [ 12 ]. Different analytical approaches can be used to map chronological, geographical, conceptual, and thematic trends, which include some form of coding, once the sample has been limited to the pertinent references [ 2 ]. It is possible to identify correlations, trends, gaps, and clusters using simple numerical accounts of frequencies in each category (for example, the number of studies looking at a specific species) and more complex cross-tabulations (for instance, the number of studies looking at the effectiveness of a specific intervention, in a particular farming system, for a named species). Users have access to the map and can query it to find information pertaining to any chosen combinations of the subsets of the meta-data [ 12 ].
3.2.8 Step 8. Reporting the findings
Authors should specify exactly how the evidence will be presented, whether it be in a narrative format, table, or visual representation, such as a map or diagram [ 7 ].
In scoping reviews, a summary of all the relevant information gathered can be presented [ 8 ] using a logical and descriptive summary of the findings based on the research questions [ 10 , 11 , 17 ]. The distribution of studies by year or period of publication, countries of origin, field of intervention, and research methodologies, may be displayed in the tables and charts accompanied with a narrative summary that explains how the results relate to the review’s objectives [ 7 , 11 , 17 , 18 ].
The conclusions should be consistent with the review objective or question based on the findings of the scoping review [ 10 ]. Following the conclusions, specific recommendations for future research based on gaps in knowledge identified by the review results can be presented. Because of the lack of a methodological quality appraisal, recommendations for practice may be unable to be developed; however, suggestions based on the conclusions may be made [ 10 ].
A scoping review’s results section should include a PRISMA flow diagram and details the outcomes of the search strategy and selection procedure [ 7 , 17 ] outlining the grounds for exclusion at the full-text level of screening [ 7 ]. For example, a study [ 29 ] used the PRISMA-ScR extension for scoping reviews to ensure all important sections have been covered in their review.
Mapping reviews may place more emphasis on describing the evidence. The use of pivot tables and pivot charts is helpful for quickly visualizing the amount (and quality, if it is measured) of evidence across a variety of meta-data variables [ 12 ]. Such visualizations can display the quantity of research, the conclusions of a critical appraisal, the sample size across nations, outcomes, populations, or variables. These visualizations can contain categorical variables as additional dimensions. The geographic distribution of study effort and type may be particularly important in mapping reviews with a global or large-scale reach [ 12 ].
4 Discussion
This systematic literature review aimed to describe the process of conducting mapping and scoping literature reviews. In summary, the main difference between the two types of reviews is in their focus and scope. Mapping reviews provide a comprehensive overview of the literature while scoping reviews identify gaps and inconsistencies in the literature and outline potential areas for future research.
A lot of the methodological papers included in this systematic literature review (e.g [ 10 , 19 , 28 ]), referred to the “consultation process” as an additional, optional step that has been suggested by [ 14 ]. In this stage, subject experts or potential review users like practitioners, consumers, and policymakers may be consulted [ 8 ]. Researchers argue that this step should be mandatory [ 15 , 28 ]. In agreement with Levac et al.’s [ 15 ] choice, Daudt et al. [ 28 ] encourage the use of the consultation stage whenever it is practical because it adds richness to the entire research process and, consequently, the findings. Despite the fact that stakeholder consultations can make scoping review planning and execution more difficult, they guarantee that the findings are pertinent to educational practice and/or policies [ 19 ].
Scoping and mapping reviews should require more than one author to eliminate bias and ensure their quality. The card-sorting technique is suggested to be employed within the review process as a means for resolving discrepancies between the stakeholders and come to an agreement on the categorization and evaluation of the data to be included. Other studies (e.g [ 30 , 31 , 32 , 33 ]), propose the card-sorting technique as a method for resolving disagreements between people’s disparities, as well as to evaluate and verify extracted themes from datasets. Card sorting is a quick and reliable sorting method that finds patterns in how users would expect to find content or functionality. Due to the patterns and insights it exposes about how people organize and categorize content, card sorting is a successful approach for resolving categorization disagreements [ 34 ]. According to Wood and Wood [ 35 ], the majority of card sorting projects involve an open sort, where participants receive a list of items and are asked to organize them in the most appropriate way. However, in some cases, a pre-existing set of categories is given to the participants, the so-called closed card sorting project. This assumes that the existing categories are already well-organized, and the goal is to make minor adjustments. Wood and Wood [ 35 ], suggest that it’s best to start with an open sort and analyze the data before conducting a closed sort for validation. If a closed sort is necessary, it should be kept simple, and the results may not be optimal. For example, in a study [ 30 ] that aimed to review the use of makerspaces for educational purposes, the card sorting technique was used for the development of the coding scheme. A three-member academic committee, consisting of three professors took part in the card sorting exercise where they went through the abstracts of the relevant papers and were asked to categorize each manuscript after discussion. They then categorized the manuscripts in the three major themes and 11 subcategories that emerged during the card sorting exercise [ 30 ]. Similarly, the authors of [ 31 ] employed the card sorting technique in their research in order to agree on the main categorization and sub-categorization of the articles identified for inclusion in their review. Card sorting can be integrated as an additional step when conducting scoping and mapping reviews, as it provides useful insights from the experts’ perspective and makes the mapping process more inclusive (see Fig. 2 ).

Proposed steps for conducting scoping and mapping reviews
5 Conclusion
Scoping and mapping reviews need a methodological framework that is rigorous, consistent, and transparent, so that the results can be trusted and the review replicated. This provides enough information for the readers to evaluate the review’s accuracy, relevance, and thoroughness [ 8 ]. Scoping reviews should be carried out in accordance with established methodological guidance and reported using reporting standards (like PRISMA-ScR) guidelines [ 36 ]. The proposed steps for undertaking scoping and mapping reviews presented in this manuscript, highlight the importance of following a rigorous approach for conducting scoping or mapping reviews. Overall, this paper is a valuable resource for researchers who are interested in conducting a systematic scoping or mapping review in different fields and are looking to apply these review methods to their own research questions.
5.1 Limitations and future work
This study does not lack limitations. As specific keywords and specific databases were searched, not all relevant work is included. The study was also limited to the past 10 years, letting out methodologies and frameworks for scoping and mapping literature reviews that were not published within the specific timeframe. The fact that the number of methodological papers identified for inclusion are limited to ten, makes it difficult to clarify the differences between mapping and scoping reviews. Therefore, further research is encouraged in order to clarify and verify the differences and similarities between the two. The application of the proposed process for conducting systematic scoping and mapping reviews on specific topics will verify the process.
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author, [EC], upon reasonable request.
Kitchenham, B., Charters, S.: Guidelines for performing Systematic Literature Reviews in Software Engineering, (2007). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2016.2603219
Soaita, A.M., Serin, B., Preece, J.: A methodological quest for systematic literature mapping. Int. J. Hous. Policy. 20 , 320–343 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1080/19491247.2019.1649040
Article Google Scholar
Leenaars, C., Tsaioun, K., Stafleu, F., Rooney, K., Meijboom, F., Ritskes-Hoitinga, M., Bleich, A.: Reviewing the animal literature: How to describe and choose between different types of literature reviews. Lab. Anim. 55 , 129–141 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1177/0023677220968599
Xiao, Y., Watson, M.: Guidance on conducting a systematic literature review. J. Plan. Educ. Res. 39 , 93–112 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1177/0739456X17723971
Haddaway, N.R., Page, M.J., Pritchard, C.C., McGuinness, L.A.: PRISMA: An R package and Shiny app for producing PRISMA 2020-compliant flow diagrams, with interactivity for optimised digital transparency and Open Synthesis, Campbell Syst. Rev. 18 (2022). (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/CL2.1230
Iduye, D., Vukic, A., Waldron, I., Price, S., Sheffer, C., McKibbon, S., Dorey, R., Yu, Z.: Educators’ strategies for engaging diverse students in undergraduate nursing education programs: A scoping review protocol. JBI Evid. Synth. 19 , 1178–1185 (2021). https://doi.org/10.11124/JBIES-20-00039
Tricco, A.C., Lillie, E., Zarin, W., O’Brien, K.K., Colquhoun, H., Levac, D., Moher, D., Peters, M.D.J., Horsley, T., Weeks, L., Hempel, S., Akl, E.A., Chang, C., McGowan, J., Stewart, L., Hartling, L., Aldcroft, A., Wilson, M.G., Garritty, C., Lewin, S., Godfrey, C.M., MacDonald, M.T., Langlois, E.V., Soares-Weiser, K., Moriarty, J., Clifford, T., Tunçalp, Ö., Straus, S.E.: PRISMA extension for scoping reviews (PRISMA-ScR): Checklist and explanation. Ann. Intern. Med. 169 , 467–473 (2018). https://doi.org/10.7326/M18-0850/SUPPL_FILE/M18-0850_SUPPLEMENT.PDF
McKinstry, C., Brown, T., Gustafsson, L.: Scoping reviews in occupational therapy: The what, why, and how to. Aust Occup. Ther. J. 61 , 58–66 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1111/1440-1630.12080 WE - Science Citation Index Expanded (SCI-EXPANDED)
Peterson, J., Pearce, P.F., Ferguson, L.A., Langford, C.A.: Understanding scoping reviews: Definition, purpose, and process. J. Am. Assoc. Nurse Pract. 29 , 12–16 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1002/2327-6924.12380
Khalil, H., Peters, M., Godfrey, C.M., McInerney, P., Soares, C.B., Parker, D.: An evidence-based Approach to Scoping Reviews. Worldviews Evidence-Based Nurs. 13 , 118–123 (2016)
Peters, M.D.J., Godfrey, C., McInerney, P., Munn, Z., Trico, A., Khalil, H.: Chap. 11: Scoping reviews, in: JBI Man. Evid. Synth. JBI. (2017). https://doi.org/10.46658/JBIMES-20-12
James, K.L., Randall, N.P., Haddaway, N.R.: A methodology for systematic mapping in environmental sciences. Environ. Evid. 5 , 1–13 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13750-016-0059-6
Sarrami-Foroushani, P., Travaglia, J., Debono, D., Clay-Williams, R., Braithwaite, J.: Scoping Meta-review: Introducing a New Methodology. Clin. Transl Sci. 8 , 77–81 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1111/CTS.12188
Arksey, H., O’malley, L.: Scoping studies: Towards a methodological framework. Int. J. Soc. Res. Methodol. 8 , 19–32 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1080/1364557032000119616
Levac, D., Colquhoun, H., O’Brien, K.K.: Scoping studies: Advancing the methodology. Implement. Sci. 5 , 1–9 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1017/cbo9780511814563.003
Peters, M., Godfrey, C., McInerney, P., Soares, C., Parker, K.H.D.: Chap. 11: Scoping reviews. In: Aromataris, E., Munn, Z. (eds.) JBI Rev. Man. JBI, Adelaide (2015)
Google Scholar
Peters, M.D.J., Marnie, C., Tricco, A.C., Pollock, D., Munn, Z., Alexander, L., McInerney, P., Godfrey, C.M., Khalil, H.: Updated methodological guidance for the conduct of scoping reviews. JBI Evid. Synth. 18 , 2119–2126 (2020). https://doi.org/10.11124/JBIES-20-00167 WE - Emerging Sources Citation Index (ESCI)
Peters, M.D.J., Godfrey, C., McInerney, P., Munn, Z., Trico, A., Khalil, H.: Chap. 11: Scoping Reviews, JBI Man. Evid. Synth. (2020). https://doi.org/10.46658/JBIMES-20-12
Thomas, A., Lubarsky, S., Durning, S.J., Young, M.E.: Knowledge syntheses in medical education: Demystifying scoping reviews. Acad. Med. 92 , 161–166 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1097/ACM.0000000000001452
Peters, M.D.J., Godfrey, C.M., Khalil, H., McInerney, P., Parker, D., Soares, C.B.: Guidance for conducting systematic scoping reviews. Int. J. Evid. Based Healthc. 13 , 141–146 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1097/XEB.0000000000000050
Sager, M., Pistone, I.: Mismatches in the production of a scoping review: Highlighting the interplay of (in)formalities. J. Eval Clin. Pract. 25 , 930–937 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1111/jep.13251
Balsiger, F., Wagner, B., Jende, J.M.E., Marty, B., Bendszus, M., Scheidegger, O., Kurz, F.T.: Methodologies and MR parameters in quantitative magnetic resonance neurography: A scoping review protocol. METHODS Protoc. 5 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/mps5030039 WE - Emerging Sources Citation Index (ESCI)
Kesztyus, D., Brucher, S., Kesztyus, T.: Use of infrared thermography in medical diagnostics: A scoping review protocol. BMJ Open. 12 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2021-059833 WE - Science Citation Index Expanded (SCI-EXPANDED)
Olaniyi, A.A., Ncama, B.P., Amod, H.: Mapping evidence of neonatal resuscitation training on the practices of Unskilled Birth attendants in Low-Resource Countries: Protocol for a scoping review. JMIR Res. Protoc. 10 (2021). https://doi.org/10.2196/18935 WE - Emerging Sources Citation Index (ESCI)
Rosca, E.C., Tudor, R., Cornea, A., Simu, M.: Parkinson’s Disease in Romania: A scoping review protocol. BRAIN Sci. 11 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11020251 WE - Science Citation Index Expanded (SCI-EXPANDED)
Walker, K., Asoodar, M., Rudolph, J., Meguerdichian, M., Yusaf, T., Campbell-Taylor, K., van Merrienboer, J.: Optimising expert dyad performance in acute care settings: A scoping review protocol. BMJ Open. 11 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2020-047260 WE - Science Citation Index Expanded (SCI-EXPANDED)
Chong, S.W., Lin, T.J., Chen, Y.: A methodological review of systematic literature reviews in higher education: Heterogeneity and homogeneity. Educ. Res. Rev. 35 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.edurev.2021.100426
Daudt, H.M.L., Van Mossel, C., Scott, S.J.: Enhancing the scoping study methodology: A large, inter-professional team’s experience with Arksey and O’Malley’s framework. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 13 , 1–9 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2288-13-48
Qiu, Y.J., Osadnik, C.R., Team, V., Weller, C.D.: Physical activity as an Adjunct to Compression Therapy on Healing outcomes and recurrence in patients with venous Leg ulcers: A scoping review protocol. Front. Med. 8 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2021.614059 WE - Science Citation Index Expanded (SCI-EXPANDED)
Konstantinou, D., Parmaxi, A., Zaphiris, P.: Mapping research directions on makerspaces in education, EMI. Educ. Media Int. 58 , 223–247 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1080/09523987.2021.1976826
Pallaris, G., Zaphiris, P., Parmaxi, A.: Mapping the landscape of Makerspaces in higher education: An inventory of research findings. Interact. Technol. Smart Educ. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1108/ITSE-01-2022-0013
Parmaxi, A., Zaphiris, P., Papadima-Sophocleous, S., Ioannou, A.: Mapping the landscape of computer-assisted language learning: An inventory of research. Interact. Technol. Smart Educ. 10 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1108/ITSE-02-2013-0004
Parmaxi, A., Zaphiris, P.: Computer-mediated communication in computer-assisted language learning: Implications for culture-centered design. Univers. Access. Inf. Soc. 15 , 169–177 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/S10209-015-0405-4/TABLES/3
Morville, P., Rosenfeld, L.: Information architecture for the World Wide Web: Designing large-scale web sites, (2006). https://books.google.com/books?hl=en&lr=&id=2d2Ry2hZc2MC&oi=fnd&pg=PR5&dq=Morville+%26+Rosenfeld,+2007&ots=opbfyu0ODb&sig=cAyUSw0mmdVRYf5ARSNp6DaYYLA (accessed January 17, 2024)
Wood, J.R., Wood, L.E.: Card sorting: Current practices and beyond. J. Usability Stud. 4 , 1–6 (2008). http://usabilityprofessionals.org/upa_publications/jus/2008november/JUS_Wood_Nov2008.pdf
Munn, Z., Pollock, D., Khalil, H., Alexander, L., Mclnerney, P., Godfrey, C.M., Peters, M., Tricco, A.C.: What are scoping reviews? Providing a formal definition of scoping reviews as a type of evidence synthesis. JBI Evid. Synth. 20 , 950–952 (2022). https://doi.org/10.11124/JBIES-21-00483 WE - Emerging Sources Citation Index (ESCI)
Download references
Acknowledgements
This work has been supported through funding from the Cyprus University of Technology.
Open access funding provided by the Cyprus Libraries Consortium (CLC).
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Cyprus University of Technology, Limassol, Cyprus
Eirini Christou, Antigoni Parmaxi & Panayiotis Zaphiris
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
E.C. and A.P. wrote the main manuscript text. All authors contributed and agreed on the methodology to be followed. A.P. and E.C. screened and decided on the papers to be included in the study. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Eirini Christou .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Material 1
Rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Christou, E., Parmaxi, A. & Zaphiris, P. A systematic exploration of scoping and mapping literature reviews. Univ Access Inf Soc (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10209-024-01120-3
Download citation
Accepted : 15 May 2024
Published : 23 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s10209-024-01120-3
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Scoping review
- Mapping review
- Review methodology
- Systematic literature mapping
- Card sorting
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
Literature Reviews
- What is a Literature Review?
- Concept Mapping
- Writing a Proposal
- For Faculty
Need help? Ask a librarian

Concept map example: Chocolate Purchasing Factors
What is concept mapping.
Concept Maps are a way to graphically represent ideas and how they relate to each other.
Concept maps may be simple designs illustrating a central theme and a few associated topics or complex structures that delineate hierarchical or multiple relationships.
J.D. Novak developed concept maps in the 1970's to help facilitate the research process for his students. Novak found that visually representing thoughts helped students freely associate ideas without being blocked or intimidated by recording them in a traditional written format.
Concept mapping involves defining a topic; adding related topics; and linking related ideas
Use Bubbl.us or search for more free mind-mapping tools on the web.
More Examples of Concept Maps
- Govt Factors in Consumer Choice
- Mental Health
- Social Psychology
- << Previous: Examples
- Next: Writing a Proposal >>
- Last Updated: Apr 29, 2024 4:24 PM
- URL: https://researchguides.njit.edu/literaturereview

- Research Guides
Literature Review: A Self-Guided Tutorial
Using concept maps.
- Literature Reviews: A Recap
- Peer Review
- Reading the Literature
- Developing Research Questions
- Considering Strong Opinions
- 2. Review discipline styles
- Super Searching
- Finding the Full Text
- Citation Searching This link opens in a new window
- When to stop searching
- Citation Management
- Annotating Articles Tip
- 5. Critically analyze and evaluate
- How to Review the Literature
- Using a Synthesis Matrix
- 7. Write literature review
Concept maps or mind maps visually represent relationships of different concepts. In research, they can help you make connections between ideas. You can use them as you are formulating your research question, as you are reading a complex text, and when you are creating a literature review. See the video and examples below.
How to Create a Concept Map
Credit: Penn State Libraries ( CC-BY ) Run Time: 3:13
- Bubbl.us Free version allows 3 mind maps, image export, and sharing.
- MindMeister Free version allows 3 mind maps, sharing, collaborating, and importing. No image-based exporting.
Mind Map of a Text Example

Credit: Austin Kleon. A map I drew of John Berger’s Ways of Seeing in 2008. Tumblr post. April 14, 2016. http://tumblr.austinkleon.com/post/142802684061#notes
Literature Review Mind Map Example
This example shows the different aspects of the author's literature review with citations to scholars who have written about those aspects.

Credit: Clancy Ratliff, Dissertation: Literature Review. Culturecat: Rhetoric and Feminism [blog]. 2 October 2005. http://culturecat.net/node/955 .
- << Previous: Reading the Literature
- Next: 1. Identify the question >>
- Last Updated: Feb 22, 2024 10:53 AM
- URL: https://libguides.williams.edu/literature-review
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- J Mark Access Health Policy
- v.11(1); 2023
- PMC10392303

Rapid literature review: definition and methodology
Beata smela.
a Assignity, Cracow, Poland
Mondher Toumi
b Public Health Department, Aix-Marseille University, Marseille, France
Karolina Świerk
Clement francois, małgorzata biernikiewicz.
c Studio Slowa, Wroclaw, Poland
Emilie Clay
d Clever-Access, Paris, France
Laurent Boyer
Introduction: A rapid literature review (RLR) is an alternative to systematic literature review (SLR) that can speed up the analysis of newly published data. The objective was to identify and summarize available information regarding different approaches to defining RLR and the methodology applied to the conduct of such reviews.
Methods: The Medline and EMBASE databases, as well as the grey literature, were searched using the set of keywords and their combination related to the targeted and rapid review, as well as design, approach, and methodology. Of the 3,898 records retrieved, 12 articles were included.
Results: Specific definition of RLRs has only been developed in 2021. In terms of methodology, the RLR should be completed within shorter timeframes using simplified procedures in comparison to SLRs, while maintaining a similar level of transparency and minimizing bias. Inherent components of the RLR process should be a clear research question, search protocol, simplified process of study selection, data extraction, and quality assurance.
Conclusions: There is a lack of consensus on the formal definition of the RLR and the best approaches to perform it. The evidence-based supporting methods are evolving, and more work is needed to define the most robust approaches.
Introduction
A systematic literature review (SLR) summarizes the results of all available studies on a specific topic and provides a high level of evidence. Authors of the SLR have to follow an advanced plan that covers defining a priori information regarding the research question, sources they are going to search, inclusion criteria applied to choose studies answering the research question, and information regarding how they are going to summarize findings [ 1 ].
The rigor and transparency of SLRs make them the most reliable form of literature review [ 2 ], providing a comprehensive, objective summary of the evidence for a given topic [ 3 , 4 ]. On the other hand, the SLR process is usually very time-consuming and requires a lot of human resources. Taking into account a high increase of newly published data and a growing need to analyze information in the fastest possible way, rapid literature reviews (RLRs) often replace standard SLRs.
There are several guidelines on the methodology of RLRs [ 5–11 ]; however, only recently, one publication from 2021 attempted to construct a unified definition [ 11 ]. Generally, by RLRs, researchers understand evidence synthesis during which some of the components of the systematic approach are being used to facilitate answering a focused research question; however, scope restrictions and a narrower search strategy help to make the project manageable in a shorter time and to get the key conclusions faster [ 4 ].
The objective of this research was to collect and summarize available information on different approaches to the definition and methodology of RLRs. An RLR has been run to capture publications providing data that fit the project objective.
To find publications reporting information on the methodology of RLRs, searches were run in the Medline and EMBASE databases in November 2022. The following keywords were searched for in titles and abstracts: ‘targeted adj2 review’ OR ‘focused adj2 review’ OR ‘rapid adj2 review’, and ‘methodology’ OR ‘design’ OR ‘scheme’ OR ‘approach’. The grey literature was identified using Google Scholar with keywords including ‘targeted review methodology’ OR ‘focused review methodology’ OR ‘rapid review methodology’. Only publications in English were included, and the date of publication was restricted to year 2016 onward in order to identify the most up-to-date literature. The reference lists of each included article were searched manually to obtain the potentially eligible articles. Titles and abstracts of the retrieved records were first screened to exclude articles that were evidently irrelevant. The full texts of potentially relevant papers were further reviewed to examine their eligibility.
A pre-defined Excel grid was developed to extract the following information related to the methodology of RLR from guidelines:
- Definition,
- Research question and searches,
- Studies selection,
- Data extraction and quality assessment,
- Additional information.
There was no restriction on the study types to be analyzed; any study reporting on the methodology of RLRs could be included: reviews, practice guidelines, commentaries, and expert opinions on RLR relevant to healthcare policymakers or practitioners. The data extraction and evidence summary were conducted by one analyst and further examined by a senior analyst to ensure that relevant information was not omitted. Disagreements were resolved by discussion and consensus.
Studies selection
A total of 3,898 records (3,864 articles from a database search and 34 grey literature from Google Scholar) were retrieved. After removing duplicates, titles and abstracts of 3,813 articles were uploaded and screened. The full texts of 43 articles were analyzed resulting in 12 articles selected for this review, including 7 guidelines [ 5–11 ] on the methodology of RLRs, together with 2 papers summarizing the results of the Delphi consensus on the topic [ 12 , 13 ], and 3 publications analyzing and assessing different approaches to RLRs [ 4 , 14 , 15 ].
Overall, seven guidelines were identified: from the World Health Organization (WHO) [ 5 ], National Collaborating Centre for Methods and Tools (NCCMT) [ 7 ], the UK government [ 8 ], the Oxford Centre for Evidence Based Medicine [ 9 ], the Cochrane group [ 6 , 11 ], and one multi-national review [ 10 ]. Among the papers that did not describe the guidelines, Gordon et al. [ 4 ] proposed 12 tips for conducting a rapid review in the right settings and discussed why these reviews may be more beneficial in some circumstances. The objective of work conducted by Tricco et al. [ 13 ] and Pandor et al. [ 12 ] was to collect and compare perceptions of rapid reviews from stakeholders, including researchers, policymakers, industry, journal editors, and healthcare providers, and to reach a consensus outlining the domains to consider when deciding on approaches for RLRs. Haby et al. [ 14 ] run a rapid review of systematic reviews and primary studies to find out the best way to conduct an RLR in health policy and practice. In Tricco et al. (2022) [ 15 ], JBI position statement for RLRs is presented.
From all the seven identified guidelines information regarding definitions the authors used for RLRs, approach to the PICOS criteria and search strategy development, studies selection, data extractions, quality assessment, and reporting were extracted.
Cochrane Rapid Reviews Methods Group developed methods guidance based on scoping review of the underlying evidence, primary methods studies conducted, as well as surveys sent to Cochrane representative and discussion among those with expertise [ 11 ]. They analyzed over 300 RLRs or RLR method papers and based on the methodology of those studies, constructed a broad definition RLR, one that meets a minimum set of requirements identified in the thematic analysis: ‘ A rapid review is a form of knowledge synthesis that accelerates the process of conducting a traditional systematic review through streamlining or omitting a variety of methods to produce evidence in a resource-efficient manner .’ This interpretation aligns with more than 50% of RLRs identified in this study. The authors additionally provided several other definitions, depending on specific situations or requirements (e.g., when RLR is produced on stakeholder’s request). It was additionally underlined that RLRs should be driven by the need of timely evidence for decision-making purposes [ 11 ].
Rapid reviews vary in their objective, format, and methods used for evidence synthesis. This is a quite new area, and still no agreement on optimal methods can be found [ 5 ]. All of the definitions are highlighting that RLRs are completed within shorter timeframes than SLRs, and also lack of time is one of the main reasons they are conducted. It has been suggested that most rapid reviews are conducted within 12 weeks; however, some of the resources suggest time between a few weeks to no more than 6 months [ 5 , 6 ]. Some of the definitions are highlighting that RLRs follow the SLR process, but certain phases of the process are simplified or omitted to retrieve information in a time-saving way [ 6 , 7 ]. Different mechanisms are used to enhance the timeliness of reviews. They can be used independently or concurrently: increasing the intensity of work by intensifying the efforts of multiple analysts by parallelization of tasks, using review shortcuts whereby one or more systematic review steps may be reduced, automatizing review steps by using new technologies [ 5 ]. The UK government report [ 8 ] referred to two different RLRs: in the form of quick scoping reviews (QSR) or rapid evidence assessments (REA). While being less resource and time-consuming compared to standard SLRs, QSRs and REAs are designed to be similarly transparent and to minimize bias. QSRs can be applied to rather open-ended questions, e.g., ‘what do we know about something’ but both, QSRs and REAs, provide an understanding of the volume and characteristics of evidence on a specific topic, allowing answering questions by maximizing the use of existing data, and providing a clear picture of the adequacy of existing evidence [ 8 ].
Research questions and searches
The guidelines suggest creating a clear research question and search protocol at the beginning of the project. Additionally, to not duplicate RLRs, the Cochrane Rapid Reviews Methods Group encourages all people working on RLRs to consider registering their search protocol with PROSPERO, the international prospective register of reviews; however, so far they are not formally registered in most cases [ 5 , 6 ]. They also recommend involving key stakeholders (review users) to set and refine the review question, criteria, and outcomes, as well as consulting them through the entire process [ 11 ].
Regarding research questions, it is better to structure them in a neutral way rather than focus on a specific direction for the outcome. By doing so, the researcher is in a better position to identify all the relevant evidence [ 7 ]. Authors can add a second, supportive research question when needed [ 8 ]. It is encouraged to limit the number of interventions, comparators and outcomes, to focus on the ones that are most important for decision-making [ 11 ]. Useful could be also reviewing additional materials, e.g., SLRs on the topic, as well as conducting a quick literature search to better understand the topic before starting with RLRs [ 7 ]. In SLRs researchers usually do not need to care a lot about time spent on creating PICOS, they need to make sure that the scope is broad enough, and they cannot use many restrictions. When working on RLRs, a reviewer may spend more or less time defining each of the components of the study question, and the main step is making sure that PICOS addresses the needs of those who requested the rapid review, and at the same time, it is feasible within the required time frame [ 7 ]. Search protocol should contain an outline of how the following review steps are to be carried out, including selected search keywords and a full strategy, a list of data sources, precise inclusion and exclusion criteria, a strategy for data extraction and critical appraisal, and a plan of how the information will be synthesized [ 8 ].
In terms of searches running, in most cases, an exhaustive process will not be feasible. Researchers should make sure that the search is effective and efficient to produce results in a timely manner. Cochrane Rapid Reviews Methods Group recommends involving an information specialist and conducting peer review of at least one search strategy [ 11 ]. According to the rapid review guidebook by McMaster University [ 7 ], it is important that RLRs, especially those that support policy and program decisions, are being fed by the results of a body of literature, rather than single studies, when possible. It would result in more generalizable findings applied at the level of a population and serve more realistic findings for program decisions [ 7 ]. It is important to document the search strategy, together with a record of the date and any date limits of the search, so that it can easily be run again, modified, or updated. Furthermore, the information on the individual databases included in platform services should always be reported, as this depends on organizations’ subscriptions and must be included for transparency and repeatability [ 7 , 8 ]. Good solution for RLRs is narrowing the scope or searching a limited number of databases and other sources [ 7 ]. Often, the authors use the PubMed/MEDLINE, Cochrane Library, and Embase databases. In most reviews, two or more databases are searched, and common limits are language (usually restricted to English), date, study design, and geographical area. Some RLRs include searching of grey literature; however, contact with authors is rather uncommon [ 5 , 8 ]. According to the flexible framework for restricted systematic review published by the University of Oxford, the search should be run in at least one major scientific database such as PubMed, and one other source, e.g., Google Scholar [ 9 ]. Grey literature and unpublished evidence may be particularly needed and important for intervention questions. It is related to the fact that studies that do not report the effects of interventions are less likely to be published [ 8 ]. If there is any type of evidence that will not be considered by the RLRs, e.g., reviews or theoretical and conceptual studies, it should also be stated in the protocol together with justification [ 8 ]. Additionally, authors of a practical guide published by WHO suggest using a staged search to identify existing SLRs at the beginning, and then focusing on studies with other designs [ 5 ]. If a low number of citations have been retrieved, it is acceptable to expand searches, remove some of the limits, and add additional databases and sources [ 7 ].
Searching for RLRs is an iterative process, and revising the approach is usually needed [ 7 ]. Changes should be confirmed with stakeholders and should be tracked and reflected in the final report [ 5 ].
The next step in the rapid review is the selection of studies consisting of two phases: screening of titles and abstracts, and analysis of full texts. Prior to screening initiation, it is recommended to conduct a pilot exercise using the same 30–50 abstracts and 5–10 full-texts for the entire screening team in order to calibrate and test the review form [ 11 ]. In contrast to SLRs, it can be done by one reviewer with or without verification by a second one. If verification is performed, usually the second reviewer checks only a subset of records and compares them. Cochrane Group, in contrast, recommends a stricter approach: at least 20% of references should be double-screened at titles and abstracts stage, and while the rest of the references may be screened by one reviewer, the excluded items need to be re-examined by second reviewer; similar approach is used in full-text screening [ 11 ]. This helps to ensure that bias was reduced and that the PICOS criteria are applied in a relevant way [ 5 , 8 , 9 , 11 ]. During the analysis of titles and abstracts, there is no need to report reasons for exclusion; however, they should be tracked for all excluded full texts [ 7 ].
Data extraction and quality assessment
According to the WHO guide, the most common method for data extraction in RLRs is extraction done by a single reviewer with or without partial verification. The authors point out that a reasonable approach is to use a second reviewer to check a random sample of at least 10% of the extractions for accuracy. Dual performance is more necessary for the extraction of quantitative results than for descriptive study information. In contrast, Cochrane group recommends that second reviewer should check the correctness and completeness of all data [ 11 ]. When possible, extractions should be limited to key characteristics and outcomes of the study. The same approach to data extraction is also suggested for a quality assessment process within rapid reviews [ 5 , 9 , 11 ]. Authors of the guidebook from McMaster University highlight that data extraction should be done ideally by two reviewers independently and consensus on the discrepancies should always be reached [ 7 ]. The final decision on the approach to this important step of review should depend on the available time and should also reflect the complexity of the research question [ 9 ].
For screening, analysis of full texts, extractions, and quality assessments, researchers can use information technologies to support them by making these review steps more efficient [ 5 ].
Before data reporting, a reviewer should prepare a document with key message headings, executive summary, background related to the topic and status of the current knowledge, project question, synthesis of findings, conclusions, and recommendations. According to the McMaster University guidebook, a report should be structured in a 1:2:20 format, that is, one page for key messages, two pages for an executive summary, and a full report of up to 20 pages [ 7 ]. All the limitations of the RLRs should be analyzed, and conclusions should be drawn with caution [ 5 ]. The quality of the accumulated evidence and the strength of recommendations can be assessed using, e.g., the GRADE system [ 5 ]. When working on references quoting, researchers should remember to use a primary source, not secondary references [ 7 ]. It would be worth considering the support of some software tools to automate reporting steps. Additionally, any standardization of the process and the usage of templates can support report development and enhance the transparency of the review [ 5 ].
Ideally, all the review steps should be completed during RLRs; however, often some steps may need skipping or will not be completed as thoroughly as should because of time constraints. It is always crucial to decide which steps may be skipped, and which are the key ones, depending on the project [ 7 ]. Guidelines suggest that it may be helpful to invite researchers with experience in the operations of SLRs to participate in the rapid review development [ 5 , 9 ]. As some of the steps will be completed by one reviewer only, it is important to provide them with relevant training at the beginning of the process, as well as during the review, to minimize the risk of mistakes [ 5 ].
Additional information
Depending on the policy goal and available resources and deadlines, methodology of the RLRs may be modified. Wilson et al. [ 10 ] provided extensive guidelines for performing RLR within days (e.g., to inform urgent internal policy discussions and/or management decisions), weeks (e.g., to inform public debates), or months (e.g., to inform policy development cycles that have a longer timeline, but that cannot wait for a traditional full systematic review). These approaches vary in terms of data synthesis, types of considered evidence and project management considerations.
In shortest timeframes, focused questions and subquestions should be formulated, typically to conduct a policy analysis; the report should consist of tables along with a brief narrative summary. Evidence from SLRs is often considered, as well as key informant interviews may be conducted to identify additional literature and insights about the topic, while primary studies and other types of evidence are not typically feasible due to time restrictions. The review would be best conducted with 1–2 reviewers sharing the work, enabling rapid iterations of the review. As for RLRs with longer timeline (weeks), these may use a mix of policy, systems and political analysis. Structure of the review would be similar to shorter RLRs – tabular with short narrative summary, as the timeline does not allow for comprehensive synthesis of data. Besides SLRs, primary studies and other evidence may be feasible in this timeframe, if obtained using the targeted searches in the most relevant databases. The review team should be larger, and standardized procedures for reviewing of the results and data extraction should be applied. In contrast to previous timeframe, merit review process may be feasible. For both timeframes, brief consultations with small transdisciplinary team should be conducted at the beginning and in the final stage of the review to discuss important matters.
For RLRs spanning several months, more comprehensive methodology may be adapted in terms of data synthesis and types of evidence. However, authors advise that review may be best conducted with a small review team in order to allow for more in-depth interpretation and iteration.
Studies analyzing methodology
There have been two interesting publications summarizing the results of Delphi consensus on the RLR methodology identified and included in this review [ 12 , 13 ].
Tricco et al. [ 13 ] first conducted an international survey and scoping review to collect information on the possible approaches to the running of rapid reviews, based on which, they employed a modified Delphi method that included inputs from 113 stakeholders to explore the most optimized approach. Among the six most frequent rapid review approaches (not all detailed here) being evaluated, the approach that combines inclusion of published literature only, a search of more than one database and limitations by date and language, study selection by one analyst, data extraction, and quality assessment by one analyst and one verifier, was perceived as the most feasible approach (72%, 81/113 responses) with the potentially lowest risk of bias (12%, 12/103). The approach ranked as the first one when considering timelines assumes updating of the search from a previously published review, no additional limits on search, studies selection and data extraction done by one reviewer, and no quality assessment. Finally, based on the publication, the most comprehensive RLRs can be made by moving on with the following rules: searching more than one database and grey literature and using date restriction, and assigning one reviewer working on screening, data extraction, and risk of bias assessment ( Table 1 ). Pandor et al. [ 12 ] introduced a decision tool for SelecTing Approaches for Rapid Reviews (STARR) that were produced through the Delphi consensus of international experts through an iterative and rigorous process. Participants were asked to assess the importance of predefined items in four domains related to the rapid review process: interaction with commissioners, understanding the evidence base, data extraction and synthesis methods, and reporting of rapid review methods. All items assigned to four domains achieved > 70% of consensus, and in that way, the first consensus-driven tool has been created that supports authors of RLRs in planning and deciding on approaches.
Six most frequent approaches to RLRs (adapted from Tricco et al. [ 13 ]).
Haby et al. [ 14 ] run searches of 11 databases and two websites and developed a comprehensive overview of the methodology of RLRs. With five SLRs and one RCT being finally included, they identified the following approaches used in RLRs to make them faster than full SLRs: limiting the number and scope of questions, searching fewer databases, limited searching of grey literature, restrictions on language and date (e.g., English only, most recent publications), updating the existing SLRs, eliminating or limiting hand searches of reference lists, noniterative search strategies, eliminating consultation with experts, limiting dual study selection, data extraction and quality assessment, minimal data synthesis with short concise conclusions or recommendations. All the SLRs included in this review were consistent in stating that no agreed definition of rapid reviews is available, and there is still no final agreement on the best methodological rules to be followed.
Gordon et al. [ 4 ] explained the advantages of performing a focused review and provided 12 tips for its conduction. They define focused reviews as ‘a form of knowledge synthesis in which the components of the systematic process are applied to facilitate the analysis of a focused research question’. The first tip presented by the authors is related to deciding if a focused review is a right solution for the considered project. RLRs will suit emerging topics, approaches, or assessments where early synthesis can support doctors, policymakers, etc., but also can direct future research. The second, third, and fourth tips highlight the importance of running preliminary searches and considering narrowing the results by using reasonable constraints taking into account the local context, problems, efficiency perspectives, and available time. Further tips include creating a team of experienced reviewers working on the RLRs, thinking about the target journal from the beginning of work on the rapid review, registering the search protocol on the PROSPERO registry, and the need for contacting authors of papers when data available in publications are missing or incongruent. The last three tips are related to the choice of evidence synthesis method, using the visual presentation of data, and considering and describing all the limitations of the focused review.
Finally, a new publication by Tricco et al. from 2022, describing JBI position statement [ 15 ] underlined that for the time being, there is no specific tool for critical appraisal of the RLR’s methodological quality. Instead, reviewers may use available tools to assess the risk of bias or quality of SLRs, like ROBIS, the JBI critical appraisal tools, or the assessment of multiple systematic reviews (AMSTAR).
Inconsistency in the definitions and methodologies of RLR
Although RLR was broadly perceived as an approach to quicken the conduct of conventional SLR, there is a lack of consensus on the formal definition of the RLR, so as to the best approaches to perform it. Only in 2021, a study proposing unified definition was published; however, it is important to note that the most accurate definition was only matching slightly over 50% of papers analysed by the authors, which underlines the lack of homogeneity in the field [ 11 ]. The evidence-based supporting methods are evolving, and more evidence is needed to define the most robust approaches [ 5 ].
Diverse terms are used to describe the RLR, including ‘rapid review’, focused systematic review’, ‘quick scoping reviews’, and ‘rapid evidence assessments’. Although the general principles of conducting RLR are to accelerate the whole process, complexity was seen in the methodologies used for RLRs, as reflected in this study. Also, inconsistencies related to the scope of the questions, search strategies, inclusion criteria, study screening, full-text review, quality assessment, and evidence presentation were implied. All these factors may hamper decision-making about optimal methodologies for conducting rapid reviews, and as a result, the efficiency of RLR might be decreased. Additionally, researchers may tend to report the methodology of their reviews without a sufficient level of detail, making it difficult to appraise the quality and robustness of their work.
Advantages and weaknesses of RLR
Although RLR used simplified approaches for evidence synthesis compared with SLR, the methodologies for RLR should be replicable, rigorous, and transparent to the greatest extent [ 16 ]. When time and resources are limited, RLR could be a practical and efficient tool to provide the summary of evidence that is critical for making rapid clinical or policy-related decisions [ 5 ]. Focusing on specific questions that are of controversy or special interest could be powerful in reaffirming whether the existing recommendation statements are still appropriate [ 17 ].
The weakness of RLR should also be borne in mind, and the trade-off of using RLR should be carefully considered regarding the thoroughness of the search, breadth of a research question, and depth of analysis [ 18 ]. If allowed, SLR is preferred over RLR considering that some relevant studies might be omitted with narrowed search strategies and simplified screening process [ 14 ]. Additionally, omitting the quality assessment of included studies could result in an increased risk of bias, making the comprehensiveness of RLR compromised [ 13 ]. Furthermore, in situations that require high accuracy, for example, where a small relative difference in an intervention has great impacts, for the purpose of drafting clinical guidelines, or making licensing decisions, a comprehensive SLR may remain the priority [ 19 ]. Therefore, clear communications with policymakers are recommended to reach an agreement on whether an RLR is justified and whether the methodologies of RLR are acceptable to address the unanswered questions [ 18 ].
Disclosure statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
- Skip to search box
- Skip to main content
Princeton University Library
Literature mapping.
- Manual Mapping
- Connected Papers
- Open Knowledge Maps
Research Rabbit
Research Rabbit creates citation maps as well as networks of recommended articles based on user provided collections of articles. You can get article and collaborator recommendations, set alerts, and share collections. User account required for use, but always free.
- Import collection from Zotero or build a new collection using Pubmed ID, DOI, or keyword search.
- Literature maps include network view and timeline view.
- << Previous: Open Knowledge Maps
- Last Updated: Dec 15, 2023 3:29 PM
- URL: https://libguides.princeton.edu/litmapping

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Here are the most recommended literature mapping tools to choose from: 1. Connected Papers. a. Connected Papers is a simple, yet powerful, one-stop visualization tool that uses a single starter article. b. It is easy to use tool that quickly identifies similar papers with just one "Seed paper" (a relevant paper). c.
Literature mapping is a way of discovering scholarly articles by exploring connections between publications.. Similar articles are often linked by citations, authors, funders, keywords, and other metadata. These connections can be explored manually in a database such as Scopus or by the use of free browser-based tools such as Connected Papers, L itMaps, and Open Knowledge Maps.
A literature map (Cresswell, 2011) is a two dimensional diagrammatic representation of information where links are made between concepts by drawing arrows (which could be annotated to define the nature of these links). Constructing a literature map helps you to: develop your understanding of the key issues and research findings in the literature
06/06/2023. Literature mapping is a process that involves analyzing and visualizing the scientific literature on a particular topic to identify research gaps, improve collaboration, and inform decision-making. In this article, we list five benefits of literature mapping for scientists and researchers and show you types and tools to save your ...
Step 1: Define Your Research Topic. The first step in creating a literature review map is to clearly define your research topic. Be specific and narrow down your focus to ensure that you have a manageable scope for your literature review. Take into consideration the research objectives or guiding questions that will shape your review.
A literature review is a methodical or organized review of the published literature on a specific topic or research question designed to analyze--not just summarize--scholarly writings that are related directly to your research question. That is, it represents the literature that provides the context for your research and shows a correspondence ...
Examples of literature reviews. Step 1 - Search for relevant literature. Step 2 - Evaluate and select sources. Step 3 - Identify themes, debates, and gaps. Step 4 - Outline your literature review's structure. Step 5 - Write your literature review.
Resources for Creating Literature Maps. This resource provides an overview of stasis theory and what you can do with it to help you conduct research, compose documents, and work in teams. This resource provides suggestions for books, articles, videos and more for designing literature maps.
Literature mapping is a way of discovering scholarly articles by exploring connections between publications. Similar articles are often linked by citations, authors, funders, keywords, and other metadata. You can use these tools to increase the scale and scope of the literature for your projects.
Check out this guide for step-by-step instructions on how to do your first search with Litmaps. Search for a single paper in Litmaps, and use it as a starting point to generate a literature map. Litmaps traverses the citation network to find the most relevant papers based on one or more inputted paper (s). It quick compiles and visualizes a ...
I feel that the maps Litmaps offers lower the barrier of entry for researchers by giving them the connections between articles spaced out visually. This helps me orientate where a paper is in the history of a field. Thus, new researchers can look at one of Litmap's "seed maps" and have the same information as hours of digging through a database.
Consideration of prior, relevant literature is essential for all research disciplines and all research projects. When reading an article, independent of discipline, the author begins by describing previous research to map and assess the research area to motivate the aim of the study and justify the research question and hypotheses.
Open Knowledge Maps. Calling themselves a "visual interface to the world's scientific community," their tool allows you to start with a few keywords to search for literature on a topic. Results display the main areas at a glance, and papers related to each area. In addition to giving you an overview of the area, it helps you identify ...
Literature maps use graphic techniques of shaping and grouping written information into categories for a research project, presentation or learning exercise. The process of mapping **helps the mind visualize** relationships and connections from any type of literature such as works with artistic merit or a body of ...
This article develops an approach to systematic literature mapping that can contribute to advancing housing knowledge and theory in three ways. At a basic level, it informs more systematic, balanced and transparent literature reviews than currently performed in housing studies. As a self-contained project, it unravels research gaps, highlights ...
LitMaps. Litmaps creates interactive literature maps: collections of articles that make up your different research topics. Create maps for your research by searching our literature database; linking your reference manager; or through automatic generation from seed articles.
I am explaining process of doing #LiteratureReview in research, particularly in #QualitativeResearch, further I will speak about synthesizing literature and ...
How to create a literature map. The Literature Map helps researchers review literature for gaps and points of impact. They are useful in both academic and industry related research projects to help gain traction and market interest. Book a seat for our upcoming Literature Mapping Webinar Workshop. Learn More about Literature Mapping
Inciteful. Inciteful is an innovative literature mapping tool that stands out in the field of academic research for its unique approach to visualizing citation networks. This tool is designed to make the process of literature review more intuitive and insightful, especially for researchers and scholars delving into new or complex fields.
When multiple maps are visible, give papers from the same map similar y values. If one paper cites another, give them both similar y values. In particular, try to minimise the total length of all ...
Definition: A literature review is a systematic examination and synthesis of existing scholarly research on a specific topic or subject. Purpose: It serves to provide a comprehensive overview of the current state of knowledge within a particular field. Analysis: Involves critically evaluating and summarizing key findings, methodologies, and ...
Dissecting Literature Review Format. There are 6 main sections to make a note of while writing a literature review. Those are: The Introduction Section. Topic Background. Conceptual Framework. Synthesis and Evaluation in Literature Reviews. Conclusion for Your Literature Review. Reference List in Your Literature Review.
An essential component of academic research is literature review. A systematic literature review, also known as a systematic review, is a method for locating, assessing, and interpreting all research related to a specific research question, topic, or phenomenon of interest [].Scoping and mapping reviews are variations of systematic literature mapping [].
Manual literature mapping is a method of locating an article that is highly relevant to your topic and using it as a starting point to connect you to other relevant literature. Below are the steps for manually mapping literature in the multidisciplinary database Scopus . Step 1: Find a highly relevant article on your topic.
Concept maps may be simple designs illustrating a central theme and a few associated topics or complex structures that delineate hierarchical or multiple relationships. J.D. Novak developed concept maps in the 1970's to help facilitate the research process for his students. Novak found that visually representing thoughts helped students freely ...
Concept maps or mind maps visually represent relationships of different concepts. In research, they can help you make connections between ideas. You can use them as you are formulating your research question, as you are reading a complex text, and when you are creating a literature review. See the video and examples below.
Literature Review In Research. A literature review provides a detailed description, summary, and evaluation of prior research on a specific subject or theory. It helps place each work within the context of understanding the research problem, identify new ways to interpret prior research and reveal any gaps in the literature.
Introduction: A rapid literature review (RLR) is an alternative to systematic literature review (SLR) that can speed up the analysis of newly published data. The objective was to identify and summarize available information regarding different approaches to defining RLR and the methodology applied to the conduct of such reviews.
Research Rabbit. Research Rabbit creates citation maps as well as networks of recommended articles based on user provided collections of articles. You can get article and collaborator recommendations, set alerts, and share collections. User account required for use, but always free. Import collection from Zotero or build a new collection using ...