
- Options Income Mastery
- Accelerator Program

Option Assignment Process
Options trading 101 - the ultimate beginners guide to options.
Download The 12,000 Word Guide

One of the biggest fears that new options traders have is that they may get assigned. The option assignment process means that the option writer is obligated to deliver on the terms specified in a contract.
For example, if a put option is assigned, the options writer would need to buy the underlying security at the strike price dictated in the contract.
Likewise for a call option, the options write would need to sell the underlying security at the strike price dictated in the contract.
As an options trader you’re usually seeking to make a profit from directional bets or to hedge your portfolio.
You’re rarely, if ever, looking to actually buy or sell the underlying security so being assigned can sound like a scary prospect.
This article will explore the option assignment process so you can understand how it works and how you can prevent yourself getting stuck with buying or selling an underlying security.
When Assignment Occurs
Assignment occurs when an option holder exercises an option. Exercising an option simply means that the option holder executes the terms in the options contract.
So for example if you are holding a call option, you have the right, but not the obligation to buy the underlying security at the agreed strike price.
When you exercise the option, the option holder will need to sell the underlying security at the agreed strike price and for the agreed quantity.
If you’re dealing with European style options, you will know when expiration is possible because they can only be exercised on the expiration date itself.

For American style options, which is what most people trade, options can be exercised at any time before the expiration date.
This means that if you are an options writer of American style options, you could theoretically be asked at any time to comply with the terms of the contract.
Unfortunately, there is no knowing when an assignment will take place.
However, generally options are not exercised prior to expiration as it is usually much more profitable to sell the option instead.
It’s worth noting that this will only happen to you if you’re an options seller. Option buyers can never be assigned.
There are two key steps to assignment and to make it fair, the process of selecting who is assigned is random.
In the first step, the Options Clearing Corporation (OCC) will issue an exercise notice to a randomly selected Clearing Member who maintains an account with the OCC.
In the second step, the Clearing Member then assigns the exercise notice to an individual account.
When You Are Most At Risk
There are several situations that can dramatically increase the risk that you will be assigned:
Situation 1: Your option is In The Money (ITM)
When an option is ITM, an option holder would stand to profit if they exercised the option.
The deeper the option is ITM, the greater the profit for the option holder and therefore the higher risk they may exercise the option and you will be assigned.
Situation 2: The option has an upcoming dividend
An ITM call buyer can profit from exercising an option before its ex-dividend date if the extrinsic value of the call is less than the amount of the dividend.
Situation 3: There is no extrinsic value left
If there is no extrinsic value left, an option buyer could be tempted to exercise the option.
If there is extrinsic value, an option buyer would typically make a bigger profit by selling the option and buying/selling shares of the underlying asset.
How You Can Avoid The Risk Of Being Assigned
There are several steps you can take to avoid, or at the very least minimise, your risk of being assigned.
The first step to consider is avoiding selling any options that have an upcoming dividend.
Before selling any option, first check that the underlying security doesn’t have an upcoming dividend and if it does, consider waiting until after the dividend has occurred (i.e. the stock has gone ex-dividend).
If you do end up selling an option with an upcoming dividend, then the second step to protecting yourself is to close your position early as your risk begins to increase.
For example, if you are short an option with an extrinsic value less than the dividend amount and the ex-dividend of the underlying security is not too far away, close your position.
Otherwise you risk being assigned and being forced to pay the dividend as well!
To completely avoid early assignment risk, you could always sell only European style options which are cash settled at expiration. You can read more that here and here .
The final way to manage your risk is to close positions well before expiration date approaches.
As the time left to expiration decreases, so too does the extrinsic value. For option buyers, it means they could stand to benefit and so there is a risk they may exercise the option.
While this article deals with the process and risks behind being assigned, there will be times when this isn’t an issue for you.
Provided you have enough capital to meet the assignment, you may be fine with being assigned.
If this is the case, you would simply have a new stock position added which you could hold onto or immediately liquidate.
In the event that you don’t have enough capital, your broker will issue you with a margin call and the position should be automatically closed.
As the process of assignment can differ between brokers, its best you contact your broker to check the specific process they use when issuing assignments to individual accounts.
In general, provided you take a few key steps to mitigate your risks, particularly around dividend issuing securities, the chances of assignment are very low.
Trade safe!
Disclaimer: The information above is for educational purposes only and should not be treated as investment advice . The strategy presented would not be suitable for investors who are not familiar with exchange traded options. Any readers interested in this strategy should do their own research and seek advice from a licensed financial adviser.

Like it? Share it!
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Closed my Oct BB (a few moments ago) for 34% profit…that is the best of the 3 BBs I traded since Gav taught us the strategy…so, the next coffee or beer on me, Gav 🙂
FEATURED ARTICLES

Small Account Option Strategies

The Ultimate Guide To Implied Volatility

What Is A Calendar Spread?
3,500 word guide.

Everything You Need To Know About Butterfly Spreads

Iron Condors: The Complete Guide With Examples and Strategies

How Does Stock Option Assignment Work?
Stock option assignment.
By strict definition, this term basically means the transfer of a person’s rights to another person or business. In terms of stock options, it refers to a notice given to an option writer that states the option (that was sold to a buyer) has officially been exercised. Exercised as in executed, not exorcised, which would have an entirely different meaning. Whenever a seller has been assigned then he or she is obligated to finish the requirements as stated in the option. For instance, if the option was a call then the writer/seller of the option would have to sell the security at the agreed upon price.
The OCC and the stock option assignment process
When the holder of an option wants to exercise the option he/she notifies his/her broker. The broker will notify the Options Clearing Corporation (OCC) of the event. After this, OCC fulfills the rest of the contract and then selects a firm that happened to be short the same contract. After notifying the firm, this group will then carry out the obligation as specified by contract.
They will choose a customer who was short the option for the official assignment. (The customer can be anyone from a random person, to a first-come or even first out basis) The customer is then assigned the exercise, which requires that he or she complete the obligation. Remember that the person is not actually buying the call—on the contrary he is buying the stock at the stated strike price.
Take a moment to consider who the OCC really is. The Options Clearing Corporation (OCC) was first opened in 1973 and is currently the largest equity derivative clearing organization worldwide. It is a clearing firm that works with commodities, commodity options and security futures. They play the part as guarantor to each of these contracts, and try and make sure that all contractual obligations are completely fulfilled, as they are essentially clearing these deals and taking responsibility.
This organization operates under the watchful eye of the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) as well as the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC). The OCC clears put and call options on regular stocks, stock indexes, foreign currencies, interest rate composites and single-stock futures, as well as other types of equities. It also works with futures contracts. This organization is controlled by a board of directors. Most of the revenue is made from clearing fees that come straight from its members. The OCC cooperates with all of the top exchanges in the United States, including the American Stock Exchange, International Securities Exchange, NYSE Arca, Chicago Board Options Exchange, the Boston Stock Exchange and the Philadelphia Stock Exchange.
American Options Trading
With American style options, assignment can happen at anytime. With European style options, assignment can only take place when the option is about to expire. Many traders, especially newer ones are afraid of getting assigned stock when they sell options.
Unless the option is in the money and there are only a few days left to expiration assignment is not something to worry about. Even if a trader is assigned stock, either long or short, the trader can turn around and exit that position in the market.
If you sell a covered call, you own the stock and sell a call against it. In this case, you want your stock to be called away (sold at the stock price) since that results in the highest percentage profit.
On the other hand if you are interested in buying stock at a certain price, you can sell a naked put option at the price you would be happy buying the stock and if the stock gets to your price, you will be “put’ the stock – which means you will have to buy it at that price. You also get a credit in the amount you sold the option for. So you get a discount on the stock as well.
Index option trading
When trading index options, it is good to know that these are cash based and so there is no stock involved. If you are “assigned” your broker will just take the money out of your account.
What I understand then is that if I get assigned I have to have enough money in my account(s) for the stock purchase or sale if I’m trading option spreads (either calls or puts). I can’t use margin. Is this correct?
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- Assets & Markets
What Is an Option Assignment?
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/image0-MichaelBoyle-30f78c37d3174fe298f9407f0b5413e2.jpeg)
Definition and Examples of Assignment
How does assignment work, what it means for individual investors.
Morsa Images / Getty Images
An option assignment represents the seller of an option’s obligation to fulfill the terms of the contract by either selling or purchasing the underlying security at the exercise price. Let’s explain what that means in more detail.
Key Takeaways
- An assignment represents the seller of an option’s obligation to fulfill the terms of the contract by either selling or purchasing the underlying security at the exercise price.
- If you sell an option and get assigned, you have to fulfill the transaction outlined in the option.
- You can only get assigned if you sell options, not if you buy them.
- Assignment is relatively rare, with only 7% of options ultimately getting assigned.
An assignment represents the seller of an option’s obligation to fulfill the terms of the contract by either selling or purchasing the underlying security at the exercise price. Let’s explain what that means in more detail.
When you sell an option to someone, you’re selling them the right to make you engage in a future transaction. For example, if you sell someone a put option , you’re promising to buy a stock at a set price any time between when the transaction happens and the expiration date of the option.
If the holder of the option doesn’t do anything with the option by the expiration date, the option expires. However, if they decide that they want to go through with the transaction, they will exercise the option.
If the holder of an option chooses to exercise it, the seller will receive a notification, called an assignment, letting them know that the option holder is exercising their right to complete the transaction. The seller is legally obligated to fulfill the terms of the options contract.
For example, if you sell a call option on XYZ with a strike price of $40 and the buyer chooses to exercise the option, you’ll be assigned the obligation to fulfill that contract. You’ll have to buy 100 shares of XYZ at whatever the market price is, or take the shares from your own portfolio and sell them to the option holder for $40 each.
Options traders only have to worry about assignment if they sell options contracts. Those who buy options don’t have to worry about assignment because in this case, they have the power to exercise a contract, or choose not to.
The options market is huge, in that options are traded on large exchanges and you likely do not know who you’re buying contracts from or selling them to. It’s not like you sell an option to someone you know and they send you an email if they choose to exercise the contract, rather it is an organized process.
In the U.S., the Options Clearing Corporation (OCC), which is considered the options industry clearinghouse, helps to facilitate the exchange of options contracts. It guarantees a fair process of option assignments, ensuring that the obligations in the contract are fulfilled.
When an investor chooses to exercise a contract, the OCC randomly assigns the obligation to someone who sold the option being exercised. For example, if 100 people sold XYZ calls with a strike of $40, and one of those options gets exercised, the OCC will randomly assign that obligation to one of the 100 sellers.
In general, assignments are uncommon. About 7% of options get exercised, with the remaining 93% expiring. Assignment also tends to grow more common as the expiration date nears.
If you are assigned the obligation to fulfill an options contract you sold, it means you have to accept the related loss and fulfill the contract. Usually, your broker will handle the transaction on your behalf automatically.
If you’re an individual investor, you only have to worry about assignment if you’re involved in selling options. Even then, assignments aren't incredibly common. Less than 7% of options get assigned and they tend to get assigned as the option’s expiration date gets closer.
Having an option assigned does mean that you are forced to lock in a loss on an option, which can hurt. However, if you’re truly worried about assignment, you can plan to close your position at some point before the expiration date or use options strategies that don’t involve selling options that could get exercised.
The Options Industry Council. " Options Assignment FAQ: How Can I Tell When I Will Be Assigned? " Accessed Oct. 18, 2021.
We couldn’t find any results matching your search.
Please try using other words for your search or explore other sections of the website for relevant information.
We’re sorry, we are currently experiencing some issues, please try again later.
Our team is working diligently to resolve the issue. Thank you for your patience and understanding.
News & Insights

Trading Options: Understanding Assignment
December 14, 2020 — 06:00 am EST
Written by FINRA & OCC Staff ([email protected]) for Finra ->

financial chart on lcd display picture
When someone buys options to open a new position (“Buy to Open”), they are buying a right —either the right to buy the underlying security at a specified price (the strike price) in the case of a call option, or the right to sell the underlying security in the case of a put option.
On the flip side, when an individual sells, or writes, an option to open a new position (“Sell to Open”), they are accepting an obligation —either an obligation to sell the underlying security at the strike price in the case of a call option or the obligation to buy that security in the case of a put option. When an individual sells options to open a new position, they are said to be “short” those options. The seller does this in exchange for receiving the option’s premium from the buyer.
American-style options allow the buyer of a contract to exercise at any time during the life of the contract, whereas European-style options can be exercised only during a specified period just prior to expiration. For an investor selling American-style options, one of the risks is that the investor may be called upon at any time during the contract’s term to fulfill its obligations. That is, as long as a short options position remains open, the seller may be subject to “assignment” on any day equity markets are open.

What is assignment?
An option assignment represents the seller’s obligation to fulfill the terms of the contract by either selling or buying the underlying security at the exercise price. This obligation is triggered when the buyer of an option contract exercises their right to buy or sell the underlying security.
To ensure fairness in the distribution of American-style and European-style option assignments, the Options Clearing Corporation (OCC), which is the options industry clearing house, has an established process to randomly assign exercise notices to firms with an account that has a short option position. Once a firm receives an assignment, it then assigns this notice to one of its customers who has a short option contract of the same series. This short option contract is selected from a pool of such customers, either at random or by some other procedure specific to the brokerage firm.
How does an investor know if an option position will be assigned?
While an option seller will always have some level of uncertainty, being assigned may be a somewhat predictable event. Only about 7% of options positions are typically exercised, but that does not imply that investors can expect to be assigned on only 7% of their short positions. Investors may have some, all or none of their short positions assigned.
And while the majority of American-style options exercises (and assignments) happen on or near the contract’s expiration, a long options holder can exercise their right at any time, even if the underlying security is halted for trading. Someone may exercise their options early based upon a significant price movement in the underlying security or if shares become difficult to borrow as the result of a pending corporate action such as a buyout or takeover.
Note: European-style options can only be exercised during a specified period just prior to expiration. In U.S. markets, the majority of options on commodity and index futures are European-style, while options on stocks and exchange-traded funds (ETF) are American-style. So, while SPDR S&P 500, or SPY options, which are options tied to an ETF that tracks the S&P 500, are American-style options, S&P 500 Index options, or SPX options, which are tied to S&P 500 futures contracts, are European-style options.
What happens after an option is assigned?
An investor who is assigned on a short option position is required to meet the terms of the written option contract upon receiving notification of the assignment. In the case of a short equity call, the seller of the option must deliver stock at the strike price and in return receives cash. An investor who doesn’t already own the shares will need to acquire and deliver shares in return for cash in the amount of the strike price, multiplied by 100, since each contract represents 100 shares. In the case of a short equity put, the seller of the option is required to purchase the stock at the strike price.
How might an investor’s account balance fluctuate after opening a short options position?
It is normal to see an account balance fluctuate after opening a short option position. Investors who have questions or concerns or who do not understand reported trade balances and assets valuations should contact their brokerage firm immediately for an explanation. Please keep in mind that short option positions can incur substantial risk in certain situations.
For example, say XYZ stock is trading at $40 and an investor sells 10 contracts for XYZ July 50 calls at $1.00, collecting a premium of $1,000, since each contract represents 100 shares ($1.00 premium x 10 contracts x 100 shares). Consider what happens if XYZ stock increases to $60, the call is exercised by the option holder and the investor is assigned. Should the investor not own the stock, they must now acquire and deliver 1,000 shares of XYZ at a price of $50 per share. Given the current stock price of $60, the investor’s short stock position would result in an unrealized loss of $9,000 (a $10,000 loss from delivering shares $10 below current stock price minus the $1,000 premium collected earlier).
Note: Even if the investor’s short call position had not been assigned, the investor’s account balance in this example would still be negatively affected—at least until the options expire if they are not exercised. The investor’s account position would be updated to reflect the investor’s unrealized loss—what they could lose if an option is exercised (and they are assigned) at the current market price. This update does not represent an actual loss (or gain) until the option is actually exercised and the investor is assigned.
What happens if an investor opened a multi-leg strategy, but one leg is assigned?
American-style option holders have the right to exercise their options position prior to expiration regardless of whether the options are in-, at- or out-of-the-money. Investors can be assigned if any market participant holding calls or puts of the same series submits an exercise notice to their brokerage firm. When one leg is assigned, subsequent action may be required, which could include closing or adjusting the remaining position to avoid potential capital or margin implications resulting from the assignment. These actions may not be attractive and may result in a loss or a less-than-ideal gain.
If an investor’s short option is assigned, the investor will be required to perform in accordance with their obligation to purchase or deliver the underlying security, regardless of the overall risk of their position when taking into account other options that may be owned as part of the overall multi-leg strategy. If the investor owns an option that serves to limit the risk of the overall spread position, it is up to the investor to exercise that option or to take other action to limit risk.
Below are a couple of examples that underscore how important it is for every investor to understand the risks associated with potential assignment during market hours and potentially adverse price movements in afterhours trading.
Example #1: An investor is short March 50 XYZ puts and long March 55 XYZ puts. At the close of business on March expiration, XYZ is priced at $56 per share, and both puts are out of the money, which means they have no intrinsic value. However, due to an unexpected news announcement shortly after the closing bell, the price of XYZ drops to $40 in after-hours trading. This could result in an assignment of the short March 50 puts, requiring the investor to purchase shares of XYZ at $50 per share. The investor would have needed to exercise the long March 55 puts in order to realize the gain on the initial multi-leg position. If the investor did not exercise the March 55 puts, those puts may expire and the investor may be exposed to the loss on the XYZ purchase at $50, a $10 per share loss with XYZ now trading at $40 per share, without receiving the benefit of selling XYZ at $55. Example #2: An investor is short March 50 XYZ puts and long April 50 XYZ puts. At the close of business on March expiration, XYZ is priced at $45 per share, and the investor is assigned XYZ stock at $50. The investor will now own shares of XYZ at $50, along with the April 50 XYZ puts, which may be exercised at the investor’s discretion. If the investor chooses not to exercise the April 50 puts, they will be required to pay for the shares that were assigned to them on the short March 50 XYZ puts until the April 50 puts are exercised or shares are otherwise disposed of.
Note: In either example, the short put position may be assigned prior to expiration at the discretion of the option holder. Investors can check with their brokerage firm regarding their option exercise procedures and cut-off times.
For options-specific questions, you may contact OCC’s Investor Education team at [email protected] , via chat on OptionsEducation.org or subscribe to the OIC newsletter . If you have questions about options trading in your brokerage account, we encourage you to contact your brokerage firm. If after doing so you have not resolved the issue or have additional concerns, you can contact FINRA . Subscribe to FINRA's newsletter for more information about saving and investing.
FINRA is dedicated to investor protection and market integrity. It regulates one critical part of the securities industry – brokerage firms doing business with the public in the United States. FINRA, overseen by the SEC, writes rules, examines for and enforces compliance with FINRA rules and federal securities laws, registers broker-dealer personnel and offers them education and training, and informs the investing public. In addition, FINRA provides surveillance and other regulatory services for equities and options markets, as well as trade reporting and other industry utilities. FINRA also administers a dispute resolution forum for investors and brokerage firms and their registered employees. For more information, visit www.finra.org .
Photo Credit: ©iStockphoto.com/da-kuk
The views and opinions expressed herein are the views and opinions of the author and do not necessarily reflect those of Nasdaq, Inc.

More Related Articles
This data feed is not available at this time.
Sign up for the TradeTalks newsletter to receive your weekly dose of trading news, trends and education. Delivered Wednesdays.
To add symbols:
- Type a symbol or company name. When the symbol you want to add appears, add it to My Quotes by selecting it and pressing Enter/Return.
- Copy and paste multiple symbols separated by spaces.
These symbols will be available throughout the site during your session.
Your symbols have been updated
Edit watchlist.
- Type a symbol or company name. When the symbol you want to add appears, add it to Watchlist by selecting it and pressing Enter/Return.
Opt in to Smart Portfolio
Smart Portfolio is supported by our partner TipRanks. By connecting my portfolio to TipRanks Smart Portfolio I agree to their Terms of Use .
The Mechanics of Option Trading, Exercise, and Assignment
Options were originally traded in the over-the-counter ( OTC ) market , where the terms of the contract were negotiated. The advantage of the OTC market over the exchanges is that the option contracts can be tailored: strike prices, expiration dates, and the number of shares can be specified to meet the needs of the option buyer. However, transaction costs are greater and liquidity is less.
Option trading really took off when the first listed option exchange — the Chicago Board Options Exchange ( CBOE )— was organized in 1973 to trade standardized contracts, greatly increasing the market and liquidity of options. The CBOE was the original exchange for options, but, by 2003, it has been superseded in size by the electronic Nasdaq International Securities Exchange (ISE), based in New York. Most options sold in Europe are traded through electronic exchanges. Other exchanges for options in the United States include: New York Stock Exchange , and the NASDAQtrader.com .
Option exchanges are central to the trading of options:
- they establish the terms of the standardized contracts
- they provide the infrastructure — both hardware and software — to facilitate trading, which is increasingly computerized
- they link together investors, brokers, and dealers on a centralized system, so that traders can from the best bid and ask prices
- they guarantee trades by taking the opposite side of each transaction
- they establish the trading rules and procedures
Options are traded just like stocks — the buyer buys at the ask price and the seller sells at the bid price . The settlement time for option trades is 1 business day ( T+1 ). However, to trade options, an investor must have a brokerage account and be approved for trading options and must also receive a copy of the booklet Characteristics and Risks of Standardized Options .
The option holder, unlike the holder of the underlying stock, has no voting rights in the corporation, and is not entitled to any dividends. Brokerage commissions are still charged for options even though the commissions for stocks have been free for a while. Prices for most options range from $0.65 to $1 per contract .
The Options Clearing Corporation (OCC)
The Options Clearing Corporation ( OCC ) is the counterparty to all option trades. The OCC issues, guarantees, and clears all option trades involving its member firms, including all U.S. option exchanges, and ensures that sales are transacted according to the current rules. The OCC is jointly owned by its member firms — the exchanges that trade options — and issues all listed options, and controls and effects all exercises and assignments. To provide a liquid market, the OCC guarantees all trades by acting as the other party to all purchases and sales of options.
The OCC, like other clearing companies, is the direct participant in every purchase and sale of an option contract. When an option writer or holder sells his contracts to someone else, the OCC serves as an intermediary in the transaction. The option writer sells his contract to the OCC and the option buyer buys it from the OCC.
The OCC publishes statistics, news on options, and any notifications about changes in the trading rules, or the adjustment of certain option contracts because of a stock split or that were subjected to unusual circumstances, such as a merger of companies whose stock was the underlying security to the option contracts.
The OCC operates under the jurisdiction of both the Securities and Exchange Commission ( SEC ) and the Commodities Futures Trading Commission ( CFTC ). Under its SEC jurisdiction, OCC clears transactions for put and call options on common stocks and other equity issues, stock indexes, foreign currencies, interest rate composites and single-stock futures . As a registered Derivatives Clearing Organization ( DCO ) under CFTC jurisdiction, the OCC clears and settles transactions in futures and options on futures .
The Exercise of Options by Option Holders and the Assignment to Fulfill the Contract to Option Writers
When an option holder wants to exercise his option, he must notify his broker of the exercise, and if it is the last trading day for the option, the broker must be notified before the exercise cut-off time , which will probably be earlier than on trading days before the last day, and the cut-off time may differ for different option classes or for index options. Although policies differ among brokerages, it is the duty of the option holder to notify his broker to exercise the option before the cut-off time.
When the broker is notified, then the exercise instructions are sent to the OCC, which then assigns the exercise to one of its Clearing Members who are short in the same option series as is being exercised. The Clearing Member will then assign the exercise to one of its customers who is short in the option. The customer is selected by a specific procedure, usually on a first-in, first-out basis, or some other fair procedure approved by the exchanges. Thus, there is no direct connection between an option writer and a buyer.
To ensure contract performance, option writers are required to post margin, the amount depending on how much the option is in the money. If the margin is deemed insufficient, then the option writer will be subjected to a margin call. Option holders don't need to post margin because they will only exercise the option if it is in the money. Options, unlike stocks, cannot be bought on margin.
Because the OCC is always a party to an option transaction, an option writer can close out his position by buying the same contract back, even while the contract buyer retains his position, because the OCC draws from a pool of contracts with no connection to the original contract writer and buyer.
A diagram outlining the exercise and assignment of a call.
Example: No Direct Connection between Investors Who Write Options and those Who Buy Them
John Call-Writer writes an option that legally obligates him to provide 100 shares of JXYZ for the price of $30 until April. The OCC buys the contract, adding it to the millions of other option contracts in its pool. Sarah Call-Buyer buys a contract that has the same terms that John Call-Writer wrote — in other words, it belongs to the same option series . However, option contracts have no name on them. Sarah buys from the OCC, just as John sold to the OCC, and she just gets a contract giving her the right to buy 100 shares of JXYZ for $30 per share until April.
Scenario 1 — Exercises of Options are Assigned According to Specific Procedures
In February, the price of JXYZ rises to $35, and Sarah thinks it might go higher in the long run, but since March and April generally are volatile times for most stocks, she decides to exercise her call (sometimes called calling the stock ) to buy JXYZ stock at $30 per share to be able to hold the stock indefinitely. She instructs her broker to exercise her call; her broker forwards the instructions to the OCC, which then assigns the exercise to one of its participating members who provided the call for sale; the participating member, in turn, assigns it to an investor who wrote such a call; in this case, it happened to be John's brother, Sam Call-Writer. John got lucky this time. Sam, unfortunately, either must turn over his appreciated shares of JXYZ, or he'll have to buy them in the open market to provide them. This is the risk that an option writer must take — an option writer never knows when he'll be assigned an exercise when the option is in the money.
Scenario 2 — Closing Out an Option Position by Buying Back the Contract
John Call-Writer decides that JXYZ might climb higher in the coming months, and so decides to close out his short position by buying a call contract with the same terms that he wrote — one that is in the same option series. Sarah, on the other hand, decides to maintain her long position by keeping her call contract until April. This can happen because there are no names on the option contracts. John closes his short position by buying the call back from the OCC at the current market price, which may be higher or lower than what he paid, resulting in either a profit or a loss. Sarah can keep her contract because when she sells or exercises her contract, it will be with the OCC, not with John, and Sarah can be sure that the OCC will fulfill the terms of the contract if she should decide to exercise it later on.
Thus, the OCC allows each investor to act independently of the other .
When the assigned option writer must deliver stock, she can deliver stock already owned, buy it on the market for delivery, or ask her broker to go short on the stock and deliver the borrowed shares. However, finding borrowed shares to short may not always be possible, so this method may not be available.
If the assigned call writer buys the stock in the market for delivery, the writer only needs the cash in his brokerage account to pay for the difference between what the stock cost and the strike price of the call, since the writer will immediately receive cash from the call holder for the strike price. Similarly, if the writer is using margin, then the margin requirements apply only to the difference between the purchase price and the strike price of the option. Full margin requirements, however, apply to shorted stock.
An assigned put writer will need either the cash or the margin to buy the stock at the strike price, even if he intends to sell the stock immediately after the exercise of the put. When the call holder exercises, he can keep the stock or immediately sell it. However, he must have the margin, if he has a margin account, or cash, for a cash account, to pay for the stock, even if he sells it immediately. He can also use the delivered stock to cover a short in the stock. (Note: equity requirements differ because an assigned call writer immediately receives the cash upon delivery of the shares, whereas a put writer or a call holder who purchased the shares may decide to keep the stock.)
Example: Fulfilling a Naked Call Exercise
A call writer receives an exercise notice on 10 call contracts with a strike of $30 per share on JXYZ stock on which she is still short. The stock currently trades at $35 per share. She does not own the stock, so, to fulfill her contract, she must buy 1,000 shares of stock in the market for $35,000 then sell it for $30,000, resulting in an immediate loss of $5,000 minus the commissions of the stock purchase and assignment.
Both the exercise and assignment incur brokerage commissions for both holder and assigned writer. Generally, the commission is smaller to sell the option than it is to exercise it. However, there may be no choice if it is the last day of trading before expiration. Although the buying and selling of options is settled in 1 business day after the trade, settlement for an exercise or assignment occurs on the 2 nd business day after the exercise or assignment ( T+2 ), since it involves the purchase of the underlying stock.
Often, a writer will want to cover his short by buying the written option back on the open market. However, once he receives an assignment, then it is too late to cover his short position by closing the position with a purchase. Assignment is usually selected from writers still short at the end of the trading day. A possible assignment can be anticipated if the option is in the money at expiration, the option is trading at a discount, or the underlying stock is about to pay a large dividend.
The OCC automatically exercises any option that is in the money by at least $0.01 ( automatic exercise , Exercise-by-Exception , Ex-by-Ex ), unless notified by the broker not to. A customer may not want to exercise an option that is only slightly in the money if the transaction costs would exceed the net profit from the exercise. In spite of the automatic exercise by the OCC, the option holder should notify his broker by the exercise cut-off time , which may be before the end of the trading day, of an intention to exercise. Exact procedures will depend on the broker.
Any option that is sold on the last trading day before expiration would likely be bought by a market maker. Because a market maker's transaction costs are lower than for retail customers, a market maker may exercise an option even if it is only a few cents in the money. Thus, any option writer who does not want to be assigned should close out his position before expiration day if there is any chance that it will be in the money even by a few pennies.
Early Exercise
Sometimes, an option will be exercised before its expiration day — called early exercise , or premature exercise . Because options have a time value in addition to intrinsic value, most options are not exercised early. However, there is nothing to prevent someone from exercising an option, even if it is not profitable to do so, and sometimes it does occur, which is why anyone who is short an option should expect the possibility of being assigned early.
When an option is trading below parity (below its intrinsic value), then arbitrageurs can take advantage of the discount to profit from the difference, because their transaction costs are very low. An option with a high intrinsic value will have little time value, and so, because of the difference between supply and demand in the market at any given moment, the option could be trading for less than its true worth. An arbitrageur will almost certainly take advantage of the price discrepancy for an instant profit. Anyone who is short an option with a high intrinsic value should expect a good possibility of being assigned an exercise.
Example: Early Exercise by Arbitrageurs Profiting from an Option Discount
JXYZ stock is currently at $40 per share. Calls on the stock with a strike of $30 are selling for $9.80. This is a difference of $0.20 per share, enough of a difference for an arbitrageur, whose transaction costs are typically much lower than for a retail customer, to profit immediately by selling short the stock at $40 per share, then covering his short by exercising the call for a net of $0.20 per share minus the arbitrageur's small transaction costs.
Option discounts will only occur when the time value of the option is small, because either it is deep in the money or the option will soon expire.
Option Discounts Arising from an Imminent Dividend Payment on the Underlying Stock
When a large dividend is paid by the underlying stock, its price drops on the ex-dividend date, resulting in a lower value for the calls. The stock price may remain lower after the payment, because the dividend payment lowers the book value of the company. This causes many call holders to either exercise early to collect the dividend, or to sell the call before the drop in stock price. When many call holders sell at the same time, it causes the call to sell at a discount to the underlying, thereby creating opportunities for arbitrageurs to profit from the price difference. However, there is some risk that the transaction will lose money, because the dividend payment and drop in stock price may not equal the premium paid for the call, even if the dividend is more than the time value of the call.
Example: Arbitrage Profit/Loss Scenario for a Dividend-Paying Stock
JXYZ stock is currently trading at $40 per share and will pay a dividend of $1 the next day. A call with a $30 strike is selling for $10.20, the $0.20 being the time value of the premium. So an arbitrageur decides to buy the call and exercise it to collect the dividend. Since the dividend is $1, but the time value is only $0.20, this could lead to a profit of $0.80 per share, but on the ex-dividend date, the stock drops to $39. Adding the $1 dividend to the share price yields $40, which is still less than buying the stock for $30 + $10.20 for the call. It might be profitable if the stock does not drop as much on the ex-date or it recovers after the ex-date sufficiently to make it profitable. But this is a risk for the arbitrageur, and this transaction is, thus, known as risk arbitrage , because the profit is not guaranteed.
2019 Statistics for the Fate of Options
Data Source: https://www.optionseducation.org/referencelibrary/faq/options-exercise
All option writers who didn't close out their position earlier by buying an offsetting contract made the maximum profit — the premium — on those contracts that expired. Option writers have lost at least something when the option is exercised, because the option holder wouldn't exercise it unless it was in the money. The more the exercised option was in the money, the greater the loss is for the assigned option writer and the greater the profits for the option holder. A closed out transaction could be at a profit or a loss for both holders and writers of options, but closing out a transaction is usually done either to maximize profits or to minimize losses, based on expected changes in the price of the underlying security until expiration.
Understanding the Life Cycle of an Option Trade
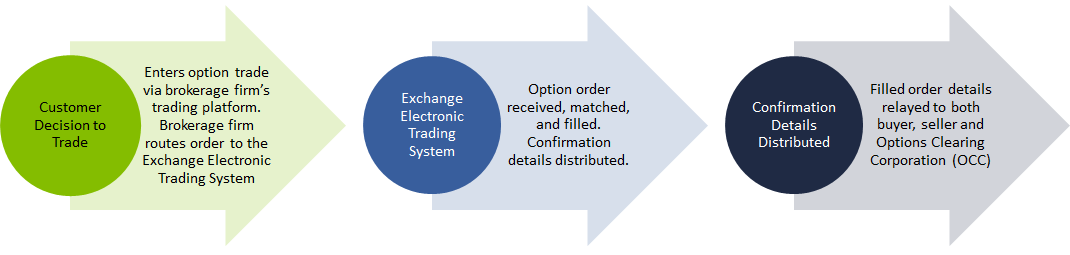
Exercise and Assignment
- Before expiration : An American style option holder has the right to exercise an option before its expiration. Should they choose to do so, an option holder must submit an exercise notice to their brokerage firm along with instructions. These instructions are then relayed to OCC which in turn triggers the assignment process.
- On expiration : OCC administers the automatic exercise process, which occurs when an option contract is a penny or more in-the-money. This procedure is also known as exercise-by-exception, or ex-by-ex. Even when expiring options meet these criteria, the options will not be automatically exercised if contrary instructions are received by OCC.
- Contrary Exercise Advice : A long options holder has the right to exercise as well as the right to not exercise an options contract. This is especially important on an option’s expiration date when the ex-by-ex process is applied. The holder of a long in-the-money (ITM) option at expiration may decide not to exercise whereas the long out-of-the-money (OTM) option holder may decide to exercise their option contract. In either circumstance, a ‘contrary exercise’ notice instructing OCC that the option holder elects not to follow the Ex-by-Ex procedure must be submitted to the OCC by the defined time deadline.
Exercises Notices Generate Assignments


COMMENTS
OCC's standard assignment process operates as follows. An assignment "wheel". is created for each option series for which there is an exercise and all short positions of. that series are placed on the wheel. Positions are placed on the wheel in sequential order. based on a unique data base identification code given to a position account ...
The assignment process is done at random by the Options Clearing Corporation (OCC). A trader will become more acquainted with the operations of the OCC as he or she learns to trade options. When a ...
To ensure fairness in the distribution of American-style and European-style option assignments, the Options Clearing Corporation (OCC), which is the options industry clearing house, has an established process to randomly assign exercise notices to firms with an account that has a short option position.
To ensure fairness in the distribution of equity and index option assignments, OCC utilizes a random procedure to assign exercise notices to clearing member accounts maintained with OCC. The assigned firm must then use an exchange-approved method (usually a random process or the first-in, first-out method) to allocate notices to its accounts ...
same instructions to OCC. After accepting exercise instructions, OCC then randomly assigns the short position of the exercised option contract and notifies the OCC Clearing Member associated with the short position of the assignment. Then, the assigned Clearing Member firm completes their own method of assignment and notifies one of their
The OCC facilitates the assignment process. Assume the put option holder sends a request to exercise their put option. The broker then sends a notice of exercise to the Options Clearing Corporation (OCC). The OCC randomly selects a clearing member firm that is short the exercised contract and assigns the firm the exercised option.
The entity in charge of facilitating exercises and assignments in the U.S. is the Options Clearing Corporation (OCC). Option assignment rules are followed, and the OCC ensures a fair process. An options assignment happens when the holder exercises a contract. The OCC then randomly allocates this assignment to brokerage firms that have account ...
There are two key steps to assignment and to make it fair, the process of selecting who is assigned is random. Access 9 Free Option Books. In the first step, the Options Clearing Corporation (OCC) will issue an exercise notice to a randomly selected Clearing Member who maintains an account with the OCC.
Your first assignment: decoding this important options term before you start trading. ... (OCC), which is the options industry clearing house, has an established process to randomly assign ...
Assignment. The holder of an American-style option contract can exercise the option at any time before expiration. Therefore, an option writer may be assigned an exercise notice on a short option position at any time before expiration. If an option writer is short an option that expires in-the-money, they should expect assignment on that ...
Learn about the options expiration and assignment process and what it means for you as an options trader. Options contracts have finite expiration dates and are regulated by the Options Clearing Corporation. In this video, we'll cover the entire options expiration and assignment process so that you have a clear understanding of what happens ...
The OCC and the stock option assignment process. When the holder of an option wants to exercise the option he/she notifies his/her broker. The broker will notify the Options Clearing Corporation (OCC) of the event. After this, OCC fulfills the rest of the contract and then selects a firm that happened to be short the same contract.
The OCC uses a random assignment process to ensure fairness in the distribution of options assignments. The OCC randomly selects a clearing member account maintained with the OCC for the assignment. The assigned brokerage firm must then use one of two methods to notify its accounts of the assignment.
It guarantees a fair process of option assignments, ensuring that the obligations in the contract are fulfilled. When an investor chooses to exercise a contract, the OCC randomly assigns the obligation to someone who sold the option being exercised. For example, if 100 people sold XYZ calls with a strike of $40, and one of those options gets ...
12 CFR 8: the OCC's current assessment policy as published in the U.S. Code of Federal Regulations. For additional information, please contact Bank Assessment Customer Service at (202) 649‑7946. The following are examples of questions frequently asked by banking industry personnel. The corresponding answers may clarify issues regarding the ...
The Options Clearing Corporation (OCC) is responsible for listing all options and controls the exercise and assignment process. The OCC provides a liquid market for traders and guarantees all options transactions. View risk disclosures. The Options Clearing Corporation (OCC) is jointly owned by the exchanges that trade options.
The Clearing Member Trade Assignment ("CMTA") process facilitates the transfer of option trades/positions from one OCC Clearing Member to another in an automated, seamless fashion. Under this process, an Executing Clearing Member and a Carrying Clearing Member can agree to have trades executed by the Executing Clearing Member sent directly to the Carrying Clearing Member's accounts for ...
To ensure fairness in the distribution of American-style and European-style option assignments, The Options Clearing Corporation (OCC), which is the options industry clearing house, has an established process to randomly assign exercise notices to firms with an account that has a short option position.
What is assignment? ... (OCC), which is the options industry clearing house, has an established process to randomly assign exercise notices to firms with an account that has a short option ...
and European-style option assignments, The Options Clearing Corporation (OCC), which is the options industry clearing house, has an established process to randomly assign exercise notices to firms with an account that has a short option position. Once a firm receives an assignment, it then assigns this notice to
The OCC, like other clearing companies, is the direct participant in every purchase and sale of an option contract. When an option writer or holder sells his contracts to someone else, the OCC serves as an intermediary in the transaction. The option writer sells his contract to the OCC and the option buyer buys it from the OCC.
These instructions are then relayed to OCC which in turn triggers the assignment process. On expiration: OCC administers the automatic exercise process, which occurs when an option contract is a penny or more in-the-money. This procedure is also known as exercise-by-exception, or ex-by-ex. Even when expiring options meet these criteria, the ...
This video helps you understand the options assignment process and how it impacts you as a trader. A more advanced tutorial on the exact process that happens behind the scenes when an option contract gets assigned. From the exercise request to your broker and the OCC's handling of the assignment to the ultimate party who is given shares or stock.
Exercise or assignment of equity options results in acquisition or delivery of the underlying shares. Unit of Trade: Each standard contract represents 100 shares of the underlying equity. Corporate actions, such as rights offerings, stock dividends, and mergers can result in adjusted contracts representing something other than 100 shares of stock.