- Privacy Policy

Home » Research Paper Introduction – Writing Guide and Examples

Research Paper Introduction – Writing Guide and Examples
Table of Contents

Research Paper Introduction
Research paper introduction is the first section of a research paper that provides an overview of the study, its purpose, and the research question (s) or hypothesis (es) being investigated. It typically includes background information about the topic, a review of previous research in the field, and a statement of the research objectives. The introduction is intended to provide the reader with a clear understanding of the research problem, why it is important, and how the study will contribute to existing knowledge in the field. It also sets the tone for the rest of the paper and helps to establish the author’s credibility and expertise on the subject.
How to Write Research Paper Introduction
Writing an introduction for a research paper can be challenging because it sets the tone for the entire paper. Here are some steps to follow to help you write an effective research paper introduction:
- Start with a hook : Begin your introduction with an attention-grabbing statement, a question, or a surprising fact that will make the reader interested in reading further.
- Provide background information: After the hook, provide background information on the topic. This information should give the reader a general idea of what the topic is about and why it is important.
- State the research problem: Clearly state the research problem or question that the paper addresses. This should be done in a concise and straightforward manner.
- State the research objectives: After stating the research problem, clearly state the research objectives. This will give the reader an idea of what the paper aims to achieve.
- Provide a brief overview of the paper: At the end of the introduction, provide a brief overview of the paper. This should include a summary of the main points that will be discussed in the paper.
- Revise and refine: Finally, revise and refine your introduction to ensure that it is clear, concise, and engaging.
Structure of Research Paper Introduction
The following is a typical structure for a research paper introduction:
- Background Information: This section provides an overview of the topic of the research paper, including relevant background information and any previous research that has been done on the topic. It helps to give the reader a sense of the context for the study.
- Problem Statement: This section identifies the specific problem or issue that the research paper is addressing. It should be clear and concise, and it should articulate the gap in knowledge that the study aims to fill.
- Research Question/Hypothesis : This section states the research question or hypothesis that the study aims to answer. It should be specific and focused, and it should clearly connect to the problem statement.
- Significance of the Study: This section explains why the research is important and what the potential implications of the study are. It should highlight the contribution that the research makes to the field.
- Methodology: This section describes the research methods that were used to conduct the study. It should be detailed enough to allow the reader to understand how the study was conducted and to evaluate the validity of the results.
- Organization of the Paper : This section provides a brief overview of the structure of the research paper. It should give the reader a sense of what to expect in each section of the paper.
Research Paper Introduction Examples
Research Paper Introduction Examples could be:
Example 1: In recent years, the use of artificial intelligence (AI) has become increasingly prevalent in various industries, including healthcare. AI algorithms are being developed to assist with medical diagnoses, treatment recommendations, and patient monitoring. However, as the use of AI in healthcare grows, ethical concerns regarding privacy, bias, and accountability have emerged. This paper aims to explore the ethical implications of AI in healthcare and propose recommendations for addressing these concerns.
Example 2: Climate change is one of the most pressing issues facing our planet today. The increasing concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere has resulted in rising temperatures, changing weather patterns, and other environmental impacts. In this paper, we will review the scientific evidence on climate change, discuss the potential consequences of inaction, and propose solutions for mitigating its effects.
Example 3: The rise of social media has transformed the way we communicate and interact with each other. While social media platforms offer many benefits, including increased connectivity and access to information, they also present numerous challenges. In this paper, we will examine the impact of social media on mental health, privacy, and democracy, and propose solutions for addressing these issues.
Example 4: The use of renewable energy sources has become increasingly important in the face of climate change and environmental degradation. While renewable energy technologies offer many benefits, including reduced greenhouse gas emissions and energy independence, they also present numerous challenges. In this paper, we will assess the current state of renewable energy technology, discuss the economic and political barriers to its adoption, and propose solutions for promoting the widespread use of renewable energy.
Purpose of Research Paper Introduction
The introduction section of a research paper serves several important purposes, including:
- Providing context: The introduction should give readers a general understanding of the topic, including its background, significance, and relevance to the field.
- Presenting the research question or problem: The introduction should clearly state the research question or problem that the paper aims to address. This helps readers understand the purpose of the study and what the author hopes to accomplish.
- Reviewing the literature: The introduction should summarize the current state of knowledge on the topic, highlighting the gaps and limitations in existing research. This shows readers why the study is important and necessary.
- Outlining the scope and objectives of the study: The introduction should describe the scope and objectives of the study, including what aspects of the topic will be covered, what data will be collected, and what methods will be used.
- Previewing the main findings and conclusions : The introduction should provide a brief overview of the main findings and conclusions that the study will present. This helps readers anticipate what they can expect to learn from the paper.
When to Write Research Paper Introduction
The introduction of a research paper is typically written after the research has been conducted and the data has been analyzed. This is because the introduction should provide an overview of the research problem, the purpose of the study, and the research questions or hypotheses that will be investigated.
Once you have a clear understanding of the research problem and the questions that you want to explore, you can begin to write the introduction. It’s important to keep in mind that the introduction should be written in a way that engages the reader and provides a clear rationale for the study. It should also provide context for the research by reviewing relevant literature and explaining how the study fits into the larger field of research.
Advantages of Research Paper Introduction
The introduction of a research paper has several advantages, including:
- Establishing the purpose of the research: The introduction provides an overview of the research problem, question, or hypothesis, and the objectives of the study. This helps to clarify the purpose of the research and provide a roadmap for the reader to follow.
- Providing background information: The introduction also provides background information on the topic, including a review of relevant literature and research. This helps the reader understand the context of the study and how it fits into the broader field of research.
- Demonstrating the significance of the research: The introduction also explains why the research is important and relevant. This helps the reader understand the value of the study and why it is worth reading.
- Setting expectations: The introduction sets the tone for the rest of the paper and prepares the reader for what is to come. This helps the reader understand what to expect and how to approach the paper.
- Grabbing the reader’s attention: A well-written introduction can grab the reader’s attention and make them interested in reading further. This is important because it can help to keep the reader engaged and motivated to read the rest of the paper.
- Creating a strong first impression: The introduction is the first part of the research paper that the reader will see, and it can create a strong first impression. A well-written introduction can make the reader more likely to take the research seriously and view it as credible.
- Establishing the author’s credibility: The introduction can also establish the author’s credibility as a researcher. By providing a clear and thorough overview of the research problem and relevant literature, the author can demonstrate their expertise and knowledge in the field.
- Providing a structure for the paper: The introduction can also provide a structure for the rest of the paper. By outlining the main sections and sub-sections of the paper, the introduction can help the reader navigate the paper and find the information they are looking for.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Paper Title – Writing Guide and Example

Research Paper – Structure, Examples and Writing...

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples

Future Research – Thesis Guide

Research Methodology – Types, Examples and...

Get science-backed answers as you write with Paperpal's Research feature
How to Write a Research Question: Types and Examples

The first step in any research project is framing the research question. It can be considered the core of any systematic investigation as the research outcomes are tied to asking the right questions. Thus, this primary interrogation point sets the pace for your research as it helps collect relevant and insightful information that ultimately influences your work.
Typically, the research question guides the stages of inquiry, analysis, and reporting. Depending on the use of quantifiable or quantitative data, research questions are broadly categorized into quantitative or qualitative research questions. Both types of research questions can be used independently or together, considering the overall focus and objectives of your research.
What is a research question?
A research question is a clear, focused, concise, and arguable question on which your research and writing are centered. 1 It states various aspects of the study, including the population and variables to be studied and the problem the study addresses. These questions also set the boundaries of the study, ensuring cohesion.
Designing the research question is a dynamic process where the researcher can change or refine the research question as they review related literature and develop a framework for the study. Depending on the scale of your research, the study can include single or multiple research questions.
A good research question has the following features:
- It is relevant to the chosen field of study.
- The question posed is arguable and open for debate, requiring synthesizing and analysis of ideas.
- It is focused and concisely framed.
- A feasible solution is possible within the given practical constraint and timeframe.
A poorly formulated research question poses several risks. 1
- Researchers can adopt an erroneous design.
- It can create confusion and hinder the thought process, including developing a clear protocol.
- It can jeopardize publication efforts.
- It causes difficulty in determining the relevance of the study findings.
- It causes difficulty in whether the study fulfils the inclusion criteria for systematic review and meta-analysis. This creates challenges in determining whether additional studies or data collection is needed to answer the question.
- Readers may fail to understand the objective of the study. This reduces the likelihood of the study being cited by others.
Now that you know “What is a research question?”, let’s look at the different types of research questions.
Types of research questions
Depending on the type of research to be done, research questions can be classified broadly into quantitative, qualitative, or mixed-methods studies. Knowing the type of research helps determine the best type of research question that reflects the direction and epistemological underpinnings of your research.
The structure and wording of quantitative 2 and qualitative research 3 questions differ significantly. The quantitative study looks at causal relationships, whereas the qualitative study aims at exploring a phenomenon.
- Quantitative research questions:
- Seeks to investigate social, familial, or educational experiences or processes in a particular context and/or location.
- Answers ‘how,’ ‘what,’ or ‘why’ questions.
- Investigates connections, relations, or comparisons between independent and dependent variables.
Quantitative research questions can be further categorized into descriptive, comparative, and relationship, as explained in the Table below.
| Descriptive research questions | These measure the responses of a study’s population toward a particular question or variable. Common descriptive research questions will begin with “How much?”, “How regularly?”, “What percentage?”, “What time?”, “What is?” Research question example: How often do you buy mobile apps for learning purposes? |
| Comparative research questions | These investigate differences between two or more groups for an outcome variable. For instance, the researcher may compare groups with and without a certain variable. Research question example: What are the differences in attitudes towards online learning between visual and Kinaesthetic learners? |
| Relationship research questions | These explore and define trends and interactions between two or more variables. These investigate relationships between dependent and independent variables and use words such as “association” or “trends. Research question example: What is the relationship between disposable income and job satisfaction amongst US residents? |
- Qualitative research questions
Qualitative research questions are adaptable, non-directional, and more flexible. It concerns broad areas of research or more specific areas of study to discover, explain, or explore a phenomenon. These are further classified as follows:
| Exploratory Questions | These question looks to understand something without influencing the results. The aim is to learn more about a topic without attributing bias or preconceived notions. Research question example: What are people’s thoughts on the new government? |
| Experiential questions | These questions focus on understanding individuals’ experiences, perspectives, and subjective meanings related to a particular phenomenon. They aim to capture personal experiences and emotions. Research question example: What are the challenges students face during their transition from school to college? |
| Interpretive Questions | These questions investigate people in their natural settings to help understand how a group makes sense of shared experiences of a phenomenon. Research question example: How do you feel about ChatGPT assisting student learning? |
- Mixed-methods studies
Mixed-methods studies use both quantitative and qualitative research questions to answer your research question. Mixed methods provide a complete picture than standalone quantitative or qualitative research, as it integrates the benefits of both methods. Mixed methods research is often used in multidisciplinary settings and complex situational or societal research, especially in the behavioral, health, and social science fields.
What makes a good research question
A good research question should be clear and focused to guide your research. It should synthesize multiple sources to present your unique argument, and should ideally be something that you are interested in. But avoid questions that can be answered in a few factual statements. The following are the main attributes of a good research question.
- Specific: The research question should not be a fishing expedition performed in the hopes that some new information will be found that will benefit the researcher. The central research question should work with your research problem to keep your work focused. If using multiple questions, they should all tie back to the central aim.
- Measurable: The research question must be answerable using quantitative and/or qualitative data or from scholarly sources to develop your research question. If such data is impossible to access, it is better to rethink your question.
- Attainable: Ensure you have enough time and resources to do all research required to answer your question. If it seems you will not be able to gain access to the data you need, consider narrowing down your question to be more specific.
- You have the expertise
- You have the equipment and resources
- Realistic: Developing your research question should be based on initial reading about your topic. It should focus on addressing a problem or gap in the existing knowledge in your field or discipline.
- Based on some sort of rational physics
- Can be done in a reasonable time frame
- Timely: The research question should contribute to an existing and current debate in your field or in society at large. It should produce knowledge that future researchers or practitioners can later build on.
- Novel
- Based on current technologies.
- Important to answer current problems or concerns.
- Lead to new directions.
- Important: Your question should have some aspect of originality. Incremental research is as important as exploring disruptive technologies. For example, you can focus on a specific location or explore a new angle.
- Meaningful whether the answer is “Yes” or “No.” Closed-ended, yes/no questions are too simple to work as good research questions. Such questions do not provide enough scope for robust investigation and discussion. A good research question requires original data, synthesis of multiple sources, and original interpretation and argumentation before providing an answer.
Steps for developing a good research question
The importance of research questions cannot be understated. When drafting a research question, use the following frameworks to guide the components of your question to ease the process. 4
- Determine the requirements: Before constructing a good research question, set your research requirements. What is the purpose? Is it descriptive, comparative, or explorative research? Determining the research aim will help you choose the most appropriate topic and word your question appropriately.
- Select a broad research topic: Identify a broader subject area of interest that requires investigation. Techniques such as brainstorming or concept mapping can help identify relevant connections and themes within a broad research topic. For example, how to learn and help students learn.
- Perform preliminary investigation: Preliminary research is needed to obtain up-to-date and relevant knowledge on your topic. It also helps identify issues currently being discussed from which information gaps can be identified.
- Narrow your focus: Narrow the scope and focus of your research to a specific niche. This involves focusing on gaps in existing knowledge or recent literature or extending or complementing the findings of existing literature. Another approach involves constructing strong research questions that challenge your views or knowledge of the area of study (Example: Is learning consistent with the existing learning theory and research).
- Identify the research problem: Once the research question has been framed, one should evaluate it. This is to realize the importance of the research questions and if there is a need for more revising (Example: How do your beliefs on learning theory and research impact your instructional practices).
How to write a research question
Those struggling to understand how to write a research question, these simple steps can help you simplify the process of writing a research question.
| Topic selection | Choose a broad topic, such as “learner support” or “social media influence” for your study. Select topics of interest to make research more enjoyable and stay motivated. |
| Preliminary research | The goal is to refine and focus your research question. The following strategies can help: Skim various scholarly articles. List subtopics under the main topic. List possible research questions for each subtopic. Consider the scope of research for each of the research questions. Select research questions that are answerable within a specific time and with available resources. If the scope is too large, repeat looking for sub-subtopics. |
| Audience | When choosing what to base your research on, consider your readers. For college papers, the audience is academic. Ask yourself if your audience may be interested in the topic you are thinking about pursuing. Determining your audience can also help refine the importance of your research question and focus on items related to your defined group. |
| Generate potential questions | Ask open-ended “how?” and “why?” questions to find a more specific research question. Gap-spotting to identify research limitations, problematization to challenge assumptions made by others, or using personal experiences to draw on issues in your industry can be used to generate questions. |
| Review brainstormed questions | Evaluate each question to check their effectiveness. Use the FINER model to see if the question meets all the research question criteria. |
| Construct the research question | Multiple frameworks, such as PICOT and PEA, are available to help structure your research question. The frameworks listed below can help you with the necessary information for generating your research question. |
| Framework | Attributes of each framework |
| FINER | Feasible Interesting Novel Ethical Relevant |
| PICOT | Population or problem Intervention or indicator being studied Comparison group Outcome of interest Time frame of the study |
| PEO | Population being studied Exposure to preexisting conditions Outcome of interest |
Sample Research Questions
The following are some bad and good research question examples
- Example 1
| Unclear: How does social media affect student growth? |
| Clear: What effect does the daily use of Twitter and Facebook have on the career development goals of students? |
| Explanation: The first research question is unclear because of the vagueness of “social media” as a concept and the lack of specificity. The second question is specific and focused, and its answer can be discovered through data collection and analysis. |
- Example 2
| Simple: Has there been an increase in the number of gifted children identified? |
| Complex: What practical techniques can teachers use to identify and guide gifted children better? |
| Explanation: A simple “yes” or “no” statement easily answers the first research question. The second research question is more complicated and requires the researcher to collect data, perform in-depth data analysis, and form an argument that leads to further discussion. |
References:
- Thabane, L., Thomas, T., Ye, C., & Paul, J. (2009). Posing the research question: not so simple. Canadian Journal of Anesthesia/Journal canadien d’anesthésie , 56 (1), 71-79.
- Rutberg, S., & Bouikidis, C. D. (2018). Focusing on the fundamentals: A simplistic differentiation between qualitative and quantitative research. Nephrology Nursing Journal , 45 (2), 209-213.
- Kyngäs, H. (2020). Qualitative research and content analysis. The application of content analysis in nursing science research , 3-11.
- Mattick, K., Johnston, J., & de la Croix, A. (2018). How to… write a good research question. The clinical teacher , 15 (2), 104-108.
- Fandino, W. (2019). Formulating a good research question: Pearls and pitfalls. Indian Journal of Anaesthesia , 63 (8), 611.
- Richardson, W. S., Wilson, M. C., Nishikawa, J., & Hayward, R. S. (1995). The well-built clinical question: a key to evidence-based decisions. ACP journal club , 123 (3), A12-A13
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
- Scientific Writing Style Guides Explained
- Ethical Research Practices For Research with Human Subjects
- 8 Most Effective Ways to Increase Motivation for Thesis Writing
- 6 Tips for Post-Doc Researchers to Take Their Career to the Next Level
Transitive and Intransitive Verbs in the World of Research
Language and grammar rules for academic writing, you may also like, how to write the first draft of a..., mla works cited page: format, template & examples, academic editing: how to self-edit academic text with..., measuring academic success: definition & strategies for excellence, phd qualifying exam: tips for success , quillbot review: features, pricing, and free alternatives, what is an academic paper types and elements , 9 steps to publish a research paper, what are the different types of research papers, how to make translating academic papers less challenging.
Research: From selecting a topic to writing the bibliography
- Selecting a Topic
- Developing a Research Question
- What Type of Source Do I Need?
- Selecting the Best Place to Search
- Search Like a Pro
- Evaluating Information
Research Questions Worth Asking
This video from the UMD, Global Campus gives a good introduction to research questions.
What is a research question?
Once you have selected a topic, you need to develop a research question. You may be used to working with a thesis statement, but a thesis statement is an answer. If you start your research with an answer, you might miss something important or your paper might be too one-sided. Starting with a question allows you to explore your topic while still having it clearly defined.
A good research question is specific and focused.
Topic : Netflix
Research Question : How has the rise of streaming television changed the nature of advertising during television shows?
Topic : the environmental impact of fracking
Research Question : What are some of the most effective ways of protecting local ground water from the waste water produced by fracking?
Tip: Beware of research questions that are too broad or too narrow.
Too Broad: Why is reality television so popular?
Too Narrow: What are the economic and social consequences of the popularity of Jersey Shore on the lives of teenagers living in Omaha, Nebraska?
Tip: be willing to tweak your research question as you go.
Research Question: How has the rise of streaming television changed the nature of advertising during television shows?
Potential Research Finding: Advertising during television hasn't changed much recently.
New Research Question: Why has advertising on television been able to remain the same when how we watch television has changed so much?
Examples of Research Questions
The assignment is a 10-15 page paper relying primarily on scholarly resources.
- How is malaria treated?
- Will tablet computing replace the need for laptops?
- How much has the popularity of Harry Potter improved the reading scores of second graders in Missouri?
- At what point in time will the need for nurses in pedatric wards outpace the graduation rates from nursing schools?
- In what ways have online communities changed the nature of support systems available for people with Attention Deficit Disorder?
- How has mountaintop removal mining in western Kentucky impacted the migratory habits of the local bird population?
- << Previous: Selecting a Topic
- Next: What Type of Source Do I Need? >>
- Last Updated: May 28, 2024 5:06 PM
- URL: https://libguides.gwu.edu/research
Research Aims, Objectives & Questions
The “Golden Thread” Explained Simply (+ Examples)
By: David Phair (PhD) and Alexandra Shaeffer (PhD) | June 2022
The research aims , objectives and research questions (collectively called the “golden thread”) are arguably the most important thing you need to get right when you’re crafting a research proposal , dissertation or thesis . We receive questions almost every day about this “holy trinity” of research and there’s certainly a lot of confusion out there, so we’ve crafted this post to help you navigate your way through the fog.
Overview: The Golden Thread
- What is the golden thread
- What are research aims ( examples )
- What are research objectives ( examples )
- What are research questions ( examples )
- The importance of alignment in the golden thread
What is the “golden thread”?
The golden thread simply refers to the collective research aims , research objectives , and research questions for any given project (i.e., a dissertation, thesis, or research paper ). These three elements are bundled together because it’s extremely important that they align with each other, and that the entire research project aligns with them.
Importantly, the golden thread needs to weave its way through the entirety of any research project , from start to end. In other words, it needs to be very clearly defined right at the beginning of the project (the topic ideation and proposal stage) and it needs to inform almost every decision throughout the rest of the project. For example, your research design and methodology will be heavily influenced by the golden thread (we’ll explain this in more detail later), as well as your literature review.
The research aims, objectives and research questions (the golden thread) define the focus and scope ( the delimitations ) of your research project. In other words, they help ringfence your dissertation or thesis to a relatively narrow domain, so that you can “go deep” and really dig into a specific problem or opportunity. They also help keep you on track , as they act as a litmus test for relevance. In other words, if you’re ever unsure whether to include something in your document, simply ask yourself the question, “does this contribute toward my research aims, objectives or questions?”. If it doesn’t, chances are you can drop it.
Alright, enough of the fluffy, conceptual stuff. Let’s get down to business and look at what exactly the research aims, objectives and questions are and outline a few examples to bring these concepts to life.

Research Aims: What are they?
Simply put, the research aim(s) is a statement that reflects the broad overarching goal (s) of the research project. Research aims are fairly high-level (low resolution) as they outline the general direction of the research and what it’s trying to achieve .
Research Aims: Examples
True to the name, research aims usually start with the wording “this research aims to…”, “this research seeks to…”, and so on. For example:
“This research aims to explore employee experiences of digital transformation in retail HR.” “This study sets out to assess the interaction between student support and self-care on well-being in engineering graduate students”
As you can see, these research aims provide a high-level description of what the study is about and what it seeks to achieve. They’re not hyper-specific or action-oriented, but they’re clear about what the study’s focus is and what is being investigated.
Need a helping hand?
Research Objectives: What are they?
The research objectives take the research aims and make them more practical and actionable . In other words, the research objectives showcase the steps that the researcher will take to achieve the research aims.
The research objectives need to be far more specific (higher resolution) and actionable than the research aims. In fact, it’s always a good idea to craft your research objectives using the “SMART” criteria. In other words, they should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant and time-bound”.
Research Objectives: Examples
Let’s look at two examples of research objectives. We’ll stick with the topic and research aims we mentioned previously.
For the digital transformation topic:
To observe the retail HR employees throughout the digital transformation. To assess employee perceptions of digital transformation in retail HR. To identify the barriers and facilitators of digital transformation in retail HR.
And for the student wellness topic:
To determine whether student self-care predicts the well-being score of engineering graduate students. To determine whether student support predicts the well-being score of engineering students. To assess the interaction between student self-care and student support when predicting well-being in engineering graduate students.
As you can see, these research objectives clearly align with the previously mentioned research aims and effectively translate the low-resolution aims into (comparatively) higher-resolution objectives and action points . They give the research project a clear focus and present something that resembles a research-based “to-do” list.

Research Questions: What are they?
Finally, we arrive at the all-important research questions. The research questions are, as the name suggests, the key questions that your study will seek to answer . Simply put, they are the core purpose of your dissertation, thesis, or research project. You’ll present them at the beginning of your document (either in the introduction chapter or literature review chapter) and you’ll answer them at the end of your document (typically in the discussion and conclusion chapters).
The research questions will be the driving force throughout the research process. For example, in the literature review chapter, you’ll assess the relevance of any given resource based on whether it helps you move towards answering your research questions. Similarly, your methodology and research design will be heavily influenced by the nature of your research questions. For instance, research questions that are exploratory in nature will usually make use of a qualitative approach, whereas questions that relate to measurement or relationship testing will make use of a quantitative approach.
Let’s look at some examples of research questions to make this more tangible.
Research Questions: Examples
Again, we’ll stick with the research aims and research objectives we mentioned previously.
For the digital transformation topic (which would be qualitative in nature):
How do employees perceive digital transformation in retail HR? What are the barriers and facilitators of digital transformation in retail HR?
And for the student wellness topic (which would be quantitative in nature):
Does student self-care predict the well-being scores of engineering graduate students? Does student support predict the well-being scores of engineering students? Do student self-care and student support interact when predicting well-being in engineering graduate students?
You’ll probably notice that there’s quite a formulaic approach to this. In other words, the research questions are basically the research objectives “converted” into question format. While that is true most of the time, it’s not always the case. For example, the first research objective for the digital transformation topic was more or less a step on the path toward the other objectives, and as such, it didn’t warrant its own research question.
So, don’t rush your research questions and sloppily reword your objectives as questions. Carefully think about what exactly you’re trying to achieve (i.e. your research aim) and the objectives you’ve set out, then craft a set of well-aligned research questions . Also, keep in mind that this can be a somewhat iterative process , where you go back and tweak research objectives and aims to ensure tight alignment throughout the golden thread.
The importance of strong alignment
Alignment is the keyword here and we have to stress its importance . Simply put, you need to make sure that there is a very tight alignment between all three pieces of the golden thread. If your research aims and research questions don’t align, for example, your project will be pulling in different directions and will lack focus . This is a common problem students face and can cause many headaches (and tears), so be warned.
Take the time to carefully craft your research aims, objectives and research questions before you run off down the research path. Ideally, get your research supervisor/advisor to review and comment on your golden thread before you invest significant time into your project, and certainly before you start collecting data .
Recap: The golden thread
In this post, we unpacked the golden thread of research, consisting of the research aims , research objectives and research questions . You can jump back to any section using the links below.
As always, feel free to leave a comment below – we always love to hear from you. Also, if you’re interested in 1-on-1 support, take a look at our private coaching service here.

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
You Might Also Like:

39 Comments
Thank you very much for your great effort put. As an Undergraduate taking Demographic Research & Methodology, I’ve been trying so hard to understand clearly what is a Research Question, Research Aim and the Objectives in a research and the relationship between them etc. But as for now I’m thankful that you’ve solved my problem.
Well appreciated. This has helped me greatly in doing my dissertation.
An so delighted with this wonderful information thank you a lot.
so impressive i have benefited a lot looking forward to learn more on research.
I am very happy to have carefully gone through this well researched article.
Infact,I used to be phobia about anything research, because of my poor understanding of the concepts.
Now,I get to know that my research question is the same as my research objective(s) rephrased in question format.
I please I would need a follow up on the subject,as I intends to join the team of researchers. Thanks once again.
Thanks so much. This was really helpful.
I know you pepole have tried to break things into more understandable and easy format. And God bless you. Keep it up
i found this document so useful towards my study in research methods. thanks so much.
This is my 2nd read topic in your course and I should commend the simplified explanations of each part. I’m beginning to understand and absorb the use of each part of a dissertation/thesis. I’ll keep on reading your free course and might be able to avail the training course! Kudos!
Thank you! Better put that my lecture and helped to easily understand the basics which I feel often get brushed over when beginning dissertation work.
This is quite helpful. I like how the Golden thread has been explained and the needed alignment.
This is quite helpful. I really appreciate!
The article made it simple for researcher students to differentiate between three concepts.
Very innovative and educational in approach to conducting research.
I am very impressed with all these terminology, as I am a fresh student for post graduate, I am highly guided and I promised to continue making consultation when the need arise. Thanks a lot.
A very helpful piece. thanks, I really appreciate it .
Very well explained, and it might be helpful to many people like me.
Wish i had found this (and other) resource(s) at the beginning of my PhD journey… not in my writing up year… 😩 Anyways… just a quick question as i’m having some issues ordering my “golden thread”…. does it matter in what order you mention them? i.e., is it always first aims, then objectives, and finally the questions? or can you first mention the research questions and then the aims and objectives?
Thank you for a very simple explanation that builds upon the concepts in a very logical manner. Just prior to this, I read the research hypothesis article, which was equally very good. This met my primary objective.
My secondary objective was to understand the difference between research questions and research hypothesis, and in which context to use which one. However, I am still not clear on this. Can you kindly please guide?
In research, a research question is a clear and specific inquiry that the researcher wants to answer, while a research hypothesis is a tentative statement or prediction about the relationship between variables or the expected outcome of the study. Research questions are broader and guide the overall study, while hypotheses are specific and testable statements used in quantitative research. Research questions identify the problem, while hypotheses provide a focus for testing in the study.
Exactly what I need in this research journey, I look forward to more of your coaching videos.
This helped a lot. Thanks so much for the effort put into explaining it.
What data source in writing dissertation/Thesis requires?
What is data source covers when writing dessertation/thesis
This is quite useful thanks
I’m excited and thankful. I got so much value which will help me progress in my thesis.
where are the locations of the reserch statement, research objective and research question in a reserach paper? Can you write an ouline that defines their places in the researh paper?
Very helpful and important tips on Aims, Objectives and Questions.
Thank you so much for making research aim, research objectives and research question so clear. This will be helpful to me as i continue with my thesis.
Thanks much for this content. I learned a lot. And I am inspired to learn more. I am still struggling with my preparation for dissertation outline/proposal. But I consistently follow contents and tutorials and the new FB of GRAD Coach. Hope to really become confident in writing my dissertation and successfully defend it.
As a researcher and lecturer, I find splitting research goals into research aims, objectives, and questions is unnecessarily bureaucratic and confusing for students. For most biomedical research projects, including ‘real research’, 1-3 research questions will suffice (numbers may differ by discipline).
Awesome! Very important resources and presented in an informative way to easily understand the golden thread. Indeed, thank you so much.
Well explained
The blog article on research aims, objectives, and questions by Grad Coach is a clear and insightful guide that aligns with my experiences in academic research. The article effectively breaks down the often complex concepts of research aims and objectives, providing a straightforward and accessible explanation. Drawing from my own research endeavors, I appreciate the practical tips offered, such as the need for specificity and clarity when formulating research questions. The article serves as a valuable resource for students and researchers, offering a concise roadmap for crafting well-defined research goals and objectives. Whether you’re a novice or an experienced researcher, this article provides practical insights that contribute to the foundational aspects of a successful research endeavor.
A great thanks for you. it is really amazing explanation. I grasp a lot and one step up to research knowledge.
I really found these tips helpful. Thank you very much Grad Coach.
I found this article helpful. Thanks for sharing this.
thank you so much, the explanation and examples are really helpful
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
- Research Papers
How to Write a Research Introduction
Last Updated: December 6, 2023 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Megan Morgan, PhD . Megan Morgan is a Graduate Program Academic Advisor in the School of Public & International Affairs at the University of Georgia. She earned her PhD in English from the University of Georgia in 2015. There are 7 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 2,654,044 times.
The introduction to a research paper can be the most challenging part of the paper to write. The length of the introduction will vary depending on the type of research paper you are writing. An introduction should announce your topic, provide context and a rationale for your work, before stating your research questions and hypothesis. Well-written introductions set the tone for the paper, catch the reader's interest, and communicate the hypothesis or thesis statement.
Introducing the Topic of the Paper

- In scientific papers this is sometimes known as an "inverted triangle", where you start with the broadest material at the start, before zooming in on the specifics. [2] X Research source
- The sentence "Throughout the 20th century, our views of life on other planets have drastically changed" introduces a topic, but does so in broad terms.
- It provides the reader with an indication of the content of the essay and encourages them to read on.

- For example, if you were writing a paper about the behaviour of mice when exposed to a particular substance, you would include the word "mice", and the scientific name of the relevant compound in the first sentences.
- If you were writing a history paper about the impact of the First World War on gender relations in Britain, you should mention those key words in your first few lines.

- This is especially important if you are attempting to develop a new conceptualization that uses language and terminology your readers may be unfamiliar with.

- If you use an anecdote ensure that is short and highly relevant for your research. It has to function in the same way as an alternative opening, namely to announce the topic of your research paper to your reader.
- For example, if you were writing a sociology paper about re-offending rates among young offenders, you could include a brief story of one person whose story reflects and introduces your topic.
- This kind of approach is generally not appropriate for the introduction to a natural or physical sciences research paper where the writing conventions are different.
Establishing the Context for Your Paper

- It is important to be concise in the introduction, so provide an overview on recent developments in the primary research rather than a lengthy discussion.
- You can follow the "inverted triangle" principle to focus in from the broader themes to those to which you are making a direct contribution with your paper.
- A strong literature review presents important background information to your own research and indicates the importance of the field.

- By making clear reference to existing work you can demonstrate explicitly the specific contribution you are making to move the field forward.
- You can identify a gap in the existing scholarship and explain how you are addressing it and moving understanding forward.

- For example, if you are writing a scientific paper you could stress the merits of the experimental approach or models you have used.
- Stress what is novel in your research and the significance of your new approach, but don't give too much detail in the introduction.
- A stated rationale could be something like: "the study evaluates the previously unknown anti-inflammatory effects of a topical compound in order to evaluate its potential clinical uses".
Specifying Your Research Questions and Hypothesis

- The research question or questions generally come towards the end of the introduction, and should be concise and closely focused.
- The research question might recall some of the key words established in the first few sentences and the title of your paper.
- An example of a research question could be "what were the consequences of the North American Free Trade Agreement on the Mexican export economy?"
- This could be honed further to be specific by referring to a particular element of the Free Trade Agreement and the impact on a particular industry in Mexico, such as clothing manufacture.
- A good research question should shape a problem into a testable hypothesis.

- If possible try to avoid using the word "hypothesis" and rather make this implicit in your writing. This can make your writing appear less formulaic.
- In a scientific paper, giving a clear one-sentence overview of your results and their relation to your hypothesis makes the information clear and accessible. [10] X Trustworthy Source PubMed Central Journal archive from the U.S. National Institutes of Health Go to source
- An example of a hypothesis could be "mice deprived of food for the duration of the study were expected to become more lethargic than those fed normally".

- This is not always necessary and you should pay attention to the writing conventions in your discipline.
- In a natural sciences paper, for example, there is a fairly rigid structure which you will be following.
- A humanities or social science paper will most likely present more opportunities to deviate in how you structure your paper.
Research Introduction Help

Community Q&A
- Use your research papers' outline to help you decide what information to include when writing an introduction. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 1
- Consider drafting your introduction after you have already completed the rest of your research paper. Writing introductions last can help ensure that you don't leave out any major points. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0

- Avoid emotional or sensational introductions; these can create distrust in the reader. Thanks Helpful 50 Not Helpful 12
- Generally avoid using personal pronouns in your introduction, such as "I," "me," "we," "us," "my," "mine," or "our." Thanks Helpful 31 Not Helpful 7
- Don't overwhelm the reader with an over-abundance of information. Keep the introduction as concise as possible by saving specific details for the body of your paper. Thanks Helpful 24 Not Helpful 14
You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://library.sacredheart.edu/c.php?g=29803&p=185916
- ↑ https://www.aresearchguide.com/inverted-pyramid-structure-in-writing.html
- ↑ https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide/introduction
- ↑ https://writing.wisc.edu/Handbook/PlanResearchPaper.html
- ↑ https://dept.writing.wisc.edu/wac/writing-an-introduction-for-a-scientific-paper/
- ↑ https://writing.wisc.edu/handbook/assignments/planresearchpaper/
- ↑ http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3178846/
About This Article

To introduce your research paper, use the first 1-2 sentences to describe your general topic, such as “women in World War I.” Include and define keywords, such as “gender relations,” to show your reader where you’re going. Mention previous research into the topic with a phrase like, “Others have studied…”, then transition into what your contribution will be and why it’s necessary. Finally, state the questions that your paper will address and propose your “answer” to them as your thesis statement. For more information from our English Ph.D. co-author about how to craft a strong hypothesis and thesis, keep reading! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Abdulrahman Omar
Oct 5, 2018
Did this article help you?
May 9, 2021
Lavanya Gopakumar
Oct 1, 2016
Dengkai Zhang
May 14, 2018
Leslie Mae Cansana
Sep 22, 2016

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Don’t miss out! Sign up for
wikiHow’s newsletter
- Affiliate Program

- UNITED STATES
- 台灣 (TAIWAN)
- TÜRKIYE (TURKEY)
- Academic Editing Services
- - Research Paper
- - Journal Manuscript
- - Dissertation
- - College & University Assignments
- Admissions Editing Services
- - Application Essay
- - Personal Statement
- - Recommendation Letter
- - Cover Letter
- - CV/Resume
- Business Editing Services
- - Business Documents
- - Report & Brochure
- - Website & Blog
- Writer Editing Services
- - Script & Screenplay
- Our Editors
- Client Reviews
- Editing & Proofreading Prices
- Wordvice Points
- Partner Discount
- Plagiarism Checker
- APA Citation Generator
- MLA Citation Generator
- Chicago Citation Generator
- Vancouver Citation Generator
- - APA Style
- - MLA Style
- - Chicago Style
- - Vancouver Style
- Writing & Editing Guide
- Academic Resources
- Admissions Resources
Where to Put the Research Question in a Paper
Silke Haidekker has a PhD in Pharmacology from the University of Hannover. She is a Clinical Research Associate in multiple pharmaceutical companies in Germany and the USA. She now works as a full-time medical translator and writer in a small town in Georgia.
Of Rats and Panic Attacks: A Doctoral Student’s Tale
You would probably agree that the time spent writing your PhD dissertation or thesis is not only a time of taking pride or even joy in what you do, but also a time riddled with panic attacks of different varieties and lengths. When I worked on my PhD thesis in pharmacology in Germany many years back, I had my first panic attack as I first learned how to kill rats for my experiments with a very ugly tool called a guillotine! After that part of the procedure, I was to remove and mash their livers, spike them with Ciclosporin A (an immunosuppressive agent), and then present the metabolites by high-pressure liquid chromatography.
Many rats later, I had another serious panic attack. It occurred at the moment my doctoral adviser told me to write my first research paper on the Ciclosporin A metabolites I had detected in hundreds of slimy mashes of rat liver. Sadly, this second panic attack led to a third one that was caused by living in the pre-internet era, when it was not as easy to access information about how to write research papers .
How I got over writing my first research paper is now ancient history. But it was only years later, living in the USA and finally being immersed in the language of most scientific research papers, that my interest in the art of writing “good” research papers was sparked during conferences held by the American Medical Writers Association , as well as by getting involved in different writing programs and academic self-study courses.
How to State the Research Question in the Introduction Section
Good writing begins with clearly stating your research question (or hypothesis) in the Introduction section —the focal point on which your entire paper builds and unfolds in the subsequent Methods, Results, and Discussion sections . This research question or hypothesis that goes into the first section of your research manuscript, the Introduction, explains at least three major elements:
a) What is known or believed about the research topic?
B) what is still unknown (or problematic), c) what is the question or hypothesis of your investigation.
Some medical writers refer to this organizational structure of the Introduction as a “funnel shape” because it starts broadly, with the bigger picture, and then follows one scientifically logical step after the other until finally narrowing down the story to the focal point of your research at the end of the funnel.
Let’s now look in greater detail at a research question example and how you can logically embed it into the Introduction to make it a powerful focal point and ignite the reader’s interest about the importance of your research:
a) The Known
You should start by giving your reader a brief overview of knowledge or previous studies already performed in the context of your research topic.
The topic of one of my research papers was “investigating the value of diabetes as an independent predictor of death in people with end-stage renal disease (ESRD).” So in the Introduction, I first presented the basic knowledge that diabetes is the leading cause of end-stage renal disease (ESRD) and thus made the reader better understand our interest in this specific study population. I then presented previous studies already showing that diabetes indeed seems to represent an independent risk factor for death in the general population. However, very few studies had been performed in the ESRD population and those only yielded controversial results.
Example : “It seems well established that there is a link between diabetic nephropathy and hypertensive nephropathy and end-stage renal disease (ESRD) in Western countries. In 2014, 73% of patients in US hospitals had comorbid ESRD and type 2 diabetes (1, 2, 3)…”
b) The Unknown
In our example, this “controversy” flags the “unknown” or “problematic” and therefore provides strong reasons for why further research is justified. The unknown should be clearly stated or implied by using phrases such as “were controversial” (as in our example), “…has not been determined,” or “…is unclear.” By clearly stating what is “unknown,” you indicate that your research is new. This creates a smooth transition into your research question.
Example : “However, previous studies have failed to isolate diabetes as an independent factor, and thus much remains unknown about specific risk factors associated with both diabetes and ESRD .”
c) The Research Question (Hypothesis)
Your research question is the question that inevitably evolves from the deficits or problems revealed in the “Unknown” and clearly states the goal of your research. It is important to describe your research question in just one or two short sentences, but very precisely and including all variables studied, if applicable. A transition should be used to mark the transition from the unknown to the research question using one word such as “therefore” or “accordingly,” or short phrases like “for this reason” or “considering this lack of crucial information.”
In our example, we stated the research question as follows:
Example : “Therefore, the primary goal of our study was to perform a Kaplan-Meier survival study and to investigate, by means of the Cox proportional hazard model, the value of diabetes as an independent predictor of death in diabetic patients with ESRD.”
Note that the research question may include the experimental approach of the study used to answer the research question.
Another powerful way to introduce the research question is to state the research question as a hypothesis so that the reader can more easily anticipate the answer. In our case, the question could be put as follows:
Example : “To test the hypothesis that diabetes is an independent predictor of death in people with ESRD, we performed a Kaplan-Survival study and investigated the value of diabetes by means of the Cox proportional hazard model.”
Note that this sentence leads with an introductory clause that indicates the hypothesis itself, transitioning well into a synopsis of the approach in the second half of the sentence.
The generic framework of the Introduction can be modified to include, for example, two research questions instead of just one. In such a case, both questions must follow inevitably from the previous statements, meaning that the background information leading to the second question cannot be omitted. Otherwise, the Introduction will get confusing, with the reader not knowing where that question comes from.
Begin with your research purpose in mind
To conclude, here is my simple but most important advice for you as a researcher preparing to write a scientific paper (or just the Introduction of a research paper) for the first time: Think your research question through precisely before trying to write it down; have in mind the reasons for exactly why you wanted to do this specific research, what exactly you wanted to find out, and how (by which methods) you did your investigation. If you have the answers to these questions in mind (or even better, create a comprehensive outline ) before starting the paper, the actual writing process will be a piece of cake and you will finish it “like a rat up a drainpipe”! And hopefully with no panic attacks.
Wordvice Resources
Before submitting your master’s thesis or PhD dissertation to academic journals for publication, be sure to receive proofreading services (including research paper editing , manuscript editing , thesis editing , and dissertation editing ) to ensure that your research writing is error-free. Impress your journal editor and get into the academic journal of your choice.
- Tel: +81-3-5541-4400 (Monday–Friday, 09:30–18:00)

10 tips for writing an effective introduction to original research papers

After the title and abstract, the introduction is the next thing your audience will read, so it's vital to begin strongly. The introduction is your opportunity to show readers and reviewers why your research topic is worth reading about and why your paper warrants their attention.
The introduction serves multiple purposes. It presents the background to your study, introduces your topic and aims, and gives an overview of the paper. A good introduction will provide a solid foundation and encourage readers to continue on to the main parts of your paper—the methods, results, and discussion.
In this article, we present 10 tips for writing an effective introduction. These tips apply primarily to full papers and letters reporting original research results. Although some tips will be more suited to papers in certain fields, the points are broadly applicable.
1. Start broadly and then narrow down
In the first paragraph, briefly describe the broad research area and then narrow down to your particular focus. This will help position your research topic within the broader field, making the work accessible to a broader audience, not just to specialists in your field.
2. State the aims and importance
Papers rejected for "not showing the importance of the topic" or "lacking clear motivation" usually neglect this point. Say what you want to achieve and why your reader should be interested in finding out whether you achieve it. The basic structure can be as simple as "We aim to do X, which is important because it will lead to Y."
3. Cite thoroughly but not excessively
Instead of simply saying that the topic is important, show why the topic is important .
Once you've narrowed your focus to the specific topic of your study, you should thoroughly cover the most recent and most relevant literature pertaining to your study. Your review of the literature should be complete, but not overly long— remember, you're not writing a review article . If you find that your introduction is too long or overflowing with citations, one possible solution is to cite review articles, rather than all the individual articles that have already been summarized in the review.
4. Avoid giving too many citations for one point
Consider the following sentence: "Many studies have found a significant association between X and Y [4-15]." This sentence cites too many studies at once. Although references [4-15] might provide a good overview of the topic, this sentence doesn't provide enough context or explanation for these past studies. If all of these references are worth citing, they should be discussed in greater specificity. For example, "A significant association has been found between X and Y in men [4-7], women [8-11], and children [12-15]."
Get featured articles and other author resources sent to you in English, Japanese, or both languages via our monthly newsletter.
5. Clearly state either your hypothesis or research question
For research in empirical sciences, stating a hypothesis can be an effective way of framing the research. For example, instead of stating "In this study, we show that X is related to Y by method A," you could say, "In this study, we hypothesize that X is related to Y, and we use method A to test this hypothesis." For research in formal sciences or exploratory research, you could consider stating a research question instead: "In this study, we examine the following research question: Is X related to Y?" Note that the research question doesn't always have to be stated in the interrogative form (with a question mark); instead, you can put the question into a declarative sentence: "In this study, we investigate whether X is related to Y." Hypotheses and research questions are effective because they help give shape to the paper and serve as "signpost phrases" that guide readers through your paper smoothly.
6. Consider giving an overview of the paper
Example structure of an introduction
Introductory paragraph:
- Give a general introduction to the topic for broad audience
- Narrow the focus to your particular topic
- State your research problem and aims
Literature review (usually several paragraphs):
- Summarize the relevant literature on your topic
- Describe the current state of the art
- Note any gaps in the literature that your study will address
Research targets (usually one paragraph):
- State your hypothesis or research question
- Briefly describe how you will accomplish your aims
- Give a preview of your main results and state the contribution of the work (optional)
Paper overview (optional; one paragraph):
- Give a section-by-section overview of the paper's contents
An organizational overview is more common in some fields than others. It is particularly common in technology, but less so in medicine. In the last paragraph of your introduction, consider giving a section-by-section overview of your paper if it is appropriate for your field. For example, "In Section II, we describe our analysis methods and the datasets we used. In Section III we present the results. In Section IV, we discuss the results and compare our findings with those in the literature. In Section V, we state our conclusions and suggest possible topics for future research."
7. Keep it short
Try to avoid an overly long introduction. A good target is 500 to 1000 words, although checking the journal's guidelines and past issues will provide the clearest guidance.
8. Show, don't tell
One goal of the introduction is explaining why your research topic is worthy of study. One of the most common pitfalls is to simply say, "Subject X is important." Instead of simply saying that the topic is important, show why the topic is important . For example, instead of writing "The development of new materials is important for the automotive industry," you could write, "The development of new materials is necessary for the automotive industry to produce stronger, lighter vehicles, which will improve safety and fuel economy ."
9. Don't bury your readers in detail
In the introduction, if your paper is in a field that commonly summarizes the study's main results before starting the methods, you should avoid stating too many detailed results because these results need the development in the other sections of your paper to be properly understood. Instead of saying "We find that our algorithm requires 55% of the memory and 45% of the computation time of the conventional algorithm," it is usually better to give a general overview of the findings in the introduction: "Here we compare the proposed algorithm with a conventional algorithm in terms of memory use and computational speed, showing that the proposed algorithm is both smaller and faster ." Some older style guides suggest holding back the main result to build suspense, but now journals in many fields— medicine being a notable exception —encourage giving a preview of your main results in the introduction.
10. Check the journal requirements
Many journals have specific requirements for the introduction in their guidelines for authors. For example, there might be a maximum word count stated or the guidelines might require specific content, such as a hypothesis statement or a summary of your main results.
Concluding remarks
I would like to close with one last piece of advice: When you begin drafting a paper, the introduction should be one of the first things you plan . The introduction serves as the roadmap for your paper; by clearly stating the study's background, aims, and hypothesis/research question, the introduction can guide you as you write the rest of the paper. It's such an important section—setting the scene for everything that follows—that many authors write the methods, results, and discussion sections in full before completing the introduction.
I hope these tips help you to write effective introductions that capture the attention of readers and reviewers. If you're interested in more writing tips, check out our 10 Tips for Writing an Effective Abstract . Also, through our EditingPLUS service , you can get writing tips and advice about your specific manuscript from a specialist editor.
Stay up to date
Our monthly newsletter offers valuable tips on writing and presenting your research most effectively, as well as advice on avoiding or resolving common problems that authors face.

Looking for subject-specialists?
Your research represents you, and your career reflects thousands of hours of your time.
Here at ThinkSCIENCE, our translation and editing represent us, and our reputation reflects thousands of published papers and millions of corrections and improvements.
- How it works

How to Write the Research Questions – Tips & Examples
Published by Owen Ingram at August 13th, 2021 , Revised On October 3, 2023
Conducting research and writing an academic paper requires a clear direction and focus.
A good research question provides purpose to your research and clarifies the direction. It further helps your readers to understand what issue your research aims to explore and address.
If you are unsure about how to write research questions, here is a list of the attributes of a good research question;
- The research question should contain only a single problem
- You should be able to find the answer to it using primary and secondary data sources
- You should be able to address it within the time limit and other constraints
- Can attain in-depth and detailed results
- Relevant and applicable
- Should relate to your chosen field of research
Whenever you want to discover something new about a topic , you will ask a question about it. Therefore, the research question is important in the overall research process and provides the author with the reading and writing guidelines.
In a research paper or an essay, you will need to create a single research question that highlights just one problem or issue. The thesis statement should include the specific problem you aim to investigate to establish your argument’s central position or claim.
A larger project such as a dissertation or thesis , on the other hand, can have multiple research questions, but every question should focus on your main research problem . Different types of research will help you answer different research questions, but they should all be relevant to the research scope.
How to Write a Research Question
Steps to develop your research question.
- Choose a topic with a wide range of published literature
- Read and skim relevant articles to find out different problems and issues
- Specify a theoretical or practical research problem that your research question will address
- Narrow down the focus of your selected core niche

Example Research Question (s)
Here are examples of research problems and research questions to help you understand how to create a research question for a given research problem.
| Example Research Problem | Example Research Question (s) |
|---|---|
| A small-scale company, ‘A’ in the UK, cannot allocate a marketing budget for next year due to their poor revenue collection in the running year. | What practical steps can the company take to improve its revenue? |
| Many fresh graduates in the UK are working as freelancers despite having attained degrees well known academic institutes, but what is causing these youngsters to engage in this type of work? | What is the cause of fresh graduates engaging in freelance activities rather than going for full-time employment? What are the advantages and disadvantages of the gig economy for young people? How do age, gender, and academic qualification relate to people’s perception of freelancing? |
Types of Research Questions
There are two main types of research; quantitative and qualitative research . Both types of research require research questions. What research question you will answer is dependent on the type of research you wish to employ.
The first part of designing research is to find a gap and create a fully focused research question.
The following table shows common research questions for a dissertation project. However, it is important to note that these examples of dissertation research questions are straightforward, and the actual research questions may be more complicated than these examples.
| Research question type | Formulation |
|---|---|
| Descriptive approach | What will be the properties of A? |
| Comparative approach | What are the similarities and differences between A and B? |
| Correlational approach | How can you correlate variables A and B? |
| Exploratory approach | Factors affecting the rate of C? Does A and B also influence C? |
| Explanatory approach | What are the causes of C? How does B impact A? What is causing D? |
| Evaluation approach | How useful and influential is C? What role does B play? What are the advantages and disadvantages of A? |
| Action research | How can you improve X with different interventions? |
What data collection method best suits your research?
- Find out by hiring an expert from ResearchProspect today!
- Despite how challenging the subject may be, we are here to help you.
Steps to Write Research Questions
The research question provides you with a path and focuses on the real problem and the research gap you aim to fill. These are steps you need to take if you are unsure about how to write a research question:
Choose an Interesting Topic
Choose a topic of research according to your interest. The selected topic should be neither too broad nor too narrow.
Do Preliminary Research on the Topic
Find articles, books, journals, and theses relevant to your chosen topic. Understand what research problem each scholar addressed as part of their research project.
Consider your Audience
It is necessary to know your audience to develop focused research questions for your essay or dissertation. You can find aspects of your topic that could be interesting to your audience when narrowing your topic.
Start Asking Questions
What, why, when, how, and other open-ended questions will provide in-depth knowledge about the topic.
Evaluate your Question
After formulating a research question, evaluate to check its effectiveness and how it can serve the purpose. Revise and refine the dissertation research question.
- Do you have a clear research question?
It would help if you formed the research question after finding a research gap. This approach will enable the research to solve part of the problem.
- Do you have a focused research question?
It is necessary that the research question is specific and relating to the central aim of your research.
- Do you have a complex research question?
The research question cannot be answered by yes or no but requires in-depth analysis. It often begins with “How” or “Why.”
Begin your Research
After you have prepared dissertation research questions, you should research the existing literature on similar topics to find various perspectives.
Also See: Formulation of Research Question
If you have been struggling to devise research questions for your dissertation or are unsure about which topic would be suitable for your needs, then you might be interested in taking advantage of our dissertation topic and outline service, which includes several topic ideas in your preferred area of study and a 500/1000 words plan on your chosen topic. Our topic and outline service will help you jump-start your dissertation project.
Find out How Our Topics & Outline Service Can Help You!
Tips on How to Write a Strong Research Question
A research question is the foundation of the entire research. Therefore, you should spend as much time as required to refine the research question.
If you have good research questions for the dissertation, research paper , or essay, you can perform the research and analyse your results more effectively. You can evaluate the strength of the research question with the help of the following criteria. Your research question should be;
Intensive and Researchable
- It should cover a single issue
- The question shouldn’t include a subjective judgment
- It can be answerable with the data analysis or research=
Practical and Specific
- It should not include a course of action, policy, or solution
- It should be well-defined
- Answerable within research limits
Complicated and Arguable
- It should not be simple to answer
- Need in-depth knowledge to find facts
- Provides scope for debate and deliberation
Unique and Relevant
- It should lie in your field of study
- Its results should be contributable
- It should be unique
Conclusion – How to Write Research Questions
A research question provides a clear direction for research work. A bigger project, such as a dissertation, may have more than one research question, but every question should focus on one issue only.
Your research questions should be researchable, feasible to answer, specific to find results, complex (for Masters and PhD projects), and relevant to your field of study. Dissertation research questions depend upon the research type you are basing your paper on.
Start creating a research question by choosing an interesting topic, do some preliminary research, consider your audience, start asking questions, evaluating your question, and begin your research.
At ResearchProspect, we have dissertation experts for all academic subjects. Whether you need help with the individual chapters or the whole dissertation paper, you can be confident that your paper competed to the highest academic standard. There is a reason why our clients keep returning to us over and over. You can also look at our essay services if you are struggling to draft a first-class academic paper.
At ResearchProspect, we have dissertation experts for all academic subjects. Whether you need help with the individual chapters or the whole dissertation paper, you can be confident that your paper competed to the highest academic standard. There is a reason why our clients keep returning to us over and over.
You can also look at our essay services if you are struggling to draft a first-class academic paper.
Place Order
Frequently Asked Questions
How are research questions written.
Research questions are written by:
- Identifying your topic.
- Considering what you want to explore.
- Making questions clear and concise.
- Ensuring they’re researchable.
- Avoiding bias or leading language.
- Focusing on one main idea per question.
What are examples of research questions?
- Does regular exercise improve mental well-being in adults over 50?
- How do online courses impact student engagement compared to traditional classes?
- What are the economic effects of prolonged pandemic lockdowns?
- How does early childhood nutrition influence academic performance in later life?
- Does urban green space reduce stress levels?
How to write a research question?
- Identify a specific topic or issue of interest.
- Conduct preliminary research to understand existing knowledge.
- Narrow the focus to address gaps or unresolved issues.
- Phrase the question to be clear, concise, and researchable.
- Ensure it is specific enough for systematic investigation.
How to formulate my research questions for my geography dissertation?
- Identify a geographical topic or phenomenon of interest.
- Review existing literature to find gaps.
- Consider spatial, temporal, environmental, or societal aspects.
- Ensure questions are specific, feasible, and significant.
- Frame questions to guide methodology: quantitative, qualitative, or mixed.
- Seek feedback from peers/advisors.
You May Also Like
This article is a step-by-step guide to how to write statement of a problem in research. The research problem will be half-solved by defining it correctly.
Struggling to find relevant and up-to-date topics for your dissertation? Here is all you need to know if unsure about how to choose dissertation topic.
Make sure that your selected topic is intriguing, manageable, and relevant. Here are some guidelines to help understand how to find a good dissertation topic.
USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

- How It Works
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- The Research Problem/Question
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Applying Critical Thinking
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
A research problem is a definite or clear expression [statement] about an area of concern, a condition to be improved upon, a difficulty to be eliminated, or a troubling question that exists in scholarly literature, in theory, or within existing practice that points to a need for meaningful understanding and deliberate investigation. A research problem does not state how to do something, offer a vague or broad proposition, or present a value question. In the social and behavioral sciences, studies are most often framed around examining a problem that needs to be understood and resolved in order to improve society and the human condition.
Bryman, Alan. “The Research Question in Social Research: What is its Role?” International Journal of Social Research Methodology 10 (2007): 5-20; Guba, Egon G., and Yvonna S. Lincoln. “Competing Paradigms in Qualitative Research.” In Handbook of Qualitative Research . Norman K. Denzin and Yvonna S. Lincoln, editors. (Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 1994), pp. 105-117; Pardede, Parlindungan. “Identifying and Formulating the Research Problem." Research in ELT: Module 4 (October 2018): 1-13; Li, Yanmei, and Sumei Zhang. "Identifying the Research Problem." In Applied Research Methods in Urban and Regional Planning . (Cham, Switzerland: Springer International Publishing, 2022), pp. 13-21.
Importance of...
The purpose of a problem statement is to:
- Introduce the reader to the importance of the topic being studied . The reader is oriented to the significance of the study.
- Anchors the research questions, hypotheses, or assumptions to follow . It offers a concise statement about the purpose of your paper.
- Place the topic into a particular context that defines the parameters of what is to be investigated.
- Provide the framework for reporting the results and indicates what is probably necessary to conduct the study and explain how the findings will present this information.
In the social sciences, the research problem establishes the means by which you must answer the "So What?" question. This declarative question refers to a research problem surviving the relevancy test [the quality of a measurement procedure that provides repeatability and accuracy]. Note that answering the "So What?" question requires a commitment on your part to not only show that you have reviewed the literature, but that you have thoroughly considered the significance of the research problem and its implications applied to creating new knowledge and understanding or informing practice.
To survive the "So What" question, problem statements should possess the following attributes:
- Clarity and precision [a well-written statement does not make sweeping generalizations and irresponsible pronouncements; it also does include unspecific determinates like "very" or "giant"],
- Demonstrate a researchable topic or issue [i.e., feasibility of conducting the study is based upon access to information that can be effectively acquired, gathered, interpreted, synthesized, and understood],
- Identification of what would be studied, while avoiding the use of value-laden words and terms,
- Identification of an overarching question or small set of questions accompanied by key factors or variables,
- Identification of key concepts and terms,
- Articulation of the study's conceptual boundaries or parameters or limitations,
- Some generalizability in regards to applicability and bringing results into general use,
- Conveyance of the study's importance, benefits, and justification [i.e., regardless of the type of research, it is important to demonstrate that the research is not trivial],
- Does not have unnecessary jargon or overly complex sentence constructions; and,
- Conveyance of more than the mere gathering of descriptive data providing only a snapshot of the issue or phenomenon under investigation.
Bryman, Alan. “The Research Question in Social Research: What is its Role?” International Journal of Social Research Methodology 10 (2007): 5-20; Brown, Perry J., Allen Dyer, and Ross S. Whaley. "Recreation Research—So What?" Journal of Leisure Research 5 (1973): 16-24; Castellanos, Susie. Critical Writing and Thinking. The Writing Center. Dean of the College. Brown University; Ellis, Timothy J. and Yair Levy Nova. "Framework of Problem-Based Research: A Guide for Novice Researchers on the Development of a Research-Worthy Problem." Informing Science: the International Journal of an Emerging Transdiscipline 11 (2008); Thesis and Purpose Statements. The Writer’s Handbook. Writing Center. University of Wisconsin, Madison; Thesis Statements. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Tips and Examples for Writing Thesis Statements. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Selwyn, Neil. "‘So What?’…A Question that Every Journal Article Needs to Answer." Learning, Media, and Technology 39 (2014): 1-5; Shoket, Mohd. "Research Problem: Identification and Formulation." International Journal of Research 1 (May 2014): 512-518.
Structure and Writing Style
I. Types and Content
There are four general conceptualizations of a research problem in the social sciences:
- Casuist Research Problem -- this type of problem relates to the determination of right and wrong in questions of conduct or conscience by analyzing moral dilemmas through the application of general rules and the careful distinction of special cases.
- Difference Research Problem -- typically asks the question, “Is there a difference between two or more groups or treatments?” This type of problem statement is used when the researcher compares or contrasts two or more phenomena. This a common approach to defining a problem in the clinical social sciences or behavioral sciences.
- Descriptive Research Problem -- typically asks the question, "what is...?" with the underlying purpose to describe the significance of a situation, state, or existence of a specific phenomenon. This problem is often associated with revealing hidden or understudied issues.
- Relational Research Problem -- suggests a relationship of some sort between two or more variables to be investigated. The underlying purpose is to investigate specific qualities or characteristics that may be connected in some way.
A problem statement in the social sciences should contain :
- A lead-in that helps ensure the reader will maintain interest over the study,
- A declaration of originality [e.g., mentioning a knowledge void or a lack of clarity about a topic that will be revealed in the literature review of prior research],
- An indication of the central focus of the study [establishing the boundaries of analysis], and
- An explanation of the study's significance or the benefits to be derived from investigating the research problem.
NOTE: A statement describing the research problem of your paper should not be viewed as a thesis statement that you may be familiar with from high school. Given the content listed above, a description of the research problem is usually a short paragraph in length.
II. Sources of Problems for Investigation
The identification of a problem to study can be challenging, not because there's a lack of issues that could be investigated, but due to the challenge of formulating an academically relevant and researchable problem which is unique and does not simply duplicate the work of others. To facilitate how you might select a problem from which to build a research study, consider these sources of inspiration:
Deductions from Theory This relates to deductions made from social philosophy or generalizations embodied in life and in society that the researcher is familiar with. These deductions from human behavior are then placed within an empirical frame of reference through research. From a theory, the researcher can formulate a research problem or hypothesis stating the expected findings in certain empirical situations. The research asks the question: “What relationship between variables will be observed if theory aptly summarizes the state of affairs?” One can then design and carry out a systematic investigation to assess whether empirical data confirm or reject the hypothesis, and hence, the theory.
Interdisciplinary Perspectives Identifying a problem that forms the basis for a research study can come from academic movements and scholarship originating in disciplines outside of your primary area of study. This can be an intellectually stimulating exercise. A review of pertinent literature should include examining research from related disciplines that can reveal new avenues of exploration and analysis. An interdisciplinary approach to selecting a research problem offers an opportunity to construct a more comprehensive understanding of a very complex issue that any single discipline may be able to provide.
Interviewing Practitioners The identification of research problems about particular topics can arise from formal interviews or informal discussions with practitioners who provide insight into new directions for future research and how to make research findings more relevant to practice. Discussions with experts in the field, such as, teachers, social workers, health care providers, lawyers, business leaders, etc., offers the chance to identify practical, “real world” problems that may be understudied or ignored within academic circles. This approach also provides some practical knowledge which may help in the process of designing and conducting your study.
Personal Experience Don't undervalue your everyday experiences or encounters as worthwhile problems for investigation. Think critically about your own experiences and/or frustrations with an issue facing society or related to your community, your neighborhood, your family, or your personal life. This can be derived, for example, from deliberate observations of certain relationships for which there is no clear explanation or witnessing an event that appears harmful to a person or group or that is out of the ordinary.
Relevant Literature The selection of a research problem can be derived from a thorough review of pertinent research associated with your overall area of interest. This may reveal where gaps exist in understanding a topic or where an issue has been understudied. Research may be conducted to: 1) fill such gaps in knowledge; 2) evaluate if the methodologies employed in prior studies can be adapted to solve other problems; or, 3) determine if a similar study could be conducted in a different subject area or applied in a different context or to different study sample [i.e., different setting or different group of people]. Also, authors frequently conclude their studies by noting implications for further research; read the conclusion of pertinent studies because statements about further research can be a valuable source for identifying new problems to investigate. The fact that a researcher has identified a topic worthy of further exploration validates the fact it is worth pursuing.
III. What Makes a Good Research Statement?
A good problem statement begins by introducing the broad area in which your research is centered, gradually leading the reader to the more specific issues you are investigating. The statement need not be lengthy, but a good research problem should incorporate the following features:
1. Compelling Topic The problem chosen should be one that motivates you to address it but simple curiosity is not a good enough reason to pursue a research study because this does not indicate significance. The problem that you choose to explore must be important to you, but it must also be viewed as important by your readers and to a the larger academic and/or social community that could be impacted by the results of your study. 2. Supports Multiple Perspectives The problem must be phrased in a way that avoids dichotomies and instead supports the generation and exploration of multiple perspectives. A general rule of thumb in the social sciences is that a good research problem is one that would generate a variety of viewpoints from a composite audience made up of reasonable people. 3. Researchability This isn't a real word but it represents an important aspect of creating a good research statement. It seems a bit obvious, but you don't want to find yourself in the midst of investigating a complex research project and realize that you don't have enough prior research to draw from for your analysis. There's nothing inherently wrong with original research, but you must choose research problems that can be supported, in some way, by the resources available to you. If you are not sure if something is researchable, don't assume that it isn't if you don't find information right away--seek help from a librarian !
NOTE: Do not confuse a research problem with a research topic. A topic is something to read and obtain information about, whereas a problem is something to be solved or framed as a question raised for inquiry, consideration, or solution, or explained as a source of perplexity, distress, or vexation. In short, a research topic is something to be understood; a research problem is something that needs to be investigated.
IV. Asking Analytical Questions about the Research Problem
Research problems in the social and behavioral sciences are often analyzed around critical questions that must be investigated. These questions can be explicitly listed in the introduction [i.e., "This study addresses three research questions about women's psychological recovery from domestic abuse in multi-generational home settings..."], or, the questions are implied in the text as specific areas of study related to the research problem. Explicitly listing your research questions at the end of your introduction can help in designing a clear roadmap of what you plan to address in your study, whereas, implicitly integrating them into the text of the introduction allows you to create a more compelling narrative around the key issues under investigation. Either approach is appropriate.
The number of questions you attempt to address should be based on the complexity of the problem you are investigating and what areas of inquiry you find most critical to study. Practical considerations, such as, the length of the paper you are writing or the availability of resources to analyze the issue can also factor in how many questions to ask. In general, however, there should be no more than four research questions underpinning a single research problem.
Given this, well-developed analytical questions can focus on any of the following:
- Highlights a genuine dilemma, area of ambiguity, or point of confusion about a topic open to interpretation by your readers;
- Yields an answer that is unexpected and not obvious rather than inevitable and self-evident;
- Provokes meaningful thought or discussion;
- Raises the visibility of the key ideas or concepts that may be understudied or hidden;
- Suggests the need for complex analysis or argument rather than a basic description or summary; and,
- Offers a specific path of inquiry that avoids eliciting generalizations about the problem.
NOTE: Questions of how and why concerning a research problem often require more analysis than questions about who, what, where, and when. You should still ask yourself these latter questions, however. Thinking introspectively about the who, what, where, and when of a research problem can help ensure that you have thoroughly considered all aspects of the problem under investigation and helps define the scope of the study in relation to the problem.
V. Mistakes to Avoid
Beware of circular reasoning! Do not state the research problem as simply the absence of the thing you are suggesting. For example, if you propose the following, "The problem in this community is that there is no hospital," this only leads to a research problem where:
- The need is for a hospital
- The objective is to create a hospital
- The method is to plan for building a hospital, and
- The evaluation is to measure if there is a hospital or not.
This is an example of a research problem that fails the "So What?" test . In this example, the problem does not reveal the relevance of why you are investigating the fact there is no hospital in the community [e.g., perhaps there's a hospital in the community ten miles away]; it does not elucidate the significance of why one should study the fact there is no hospital in the community [e.g., that hospital in the community ten miles away has no emergency room]; the research problem does not offer an intellectual pathway towards adding new knowledge or clarifying prior knowledge [e.g., the county in which there is no hospital already conducted a study about the need for a hospital, but it was conducted ten years ago]; and, the problem does not offer meaningful outcomes that lead to recommendations that can be generalized for other situations or that could suggest areas for further research [e.g., the challenges of building a new hospital serves as a case study for other communities].
Alvesson, Mats and Jörgen Sandberg. “Generating Research Questions Through Problematization.” Academy of Management Review 36 (April 2011): 247-271 ; Choosing and Refining Topics. Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; D'Souza, Victor S. "Use of Induction and Deduction in Research in Social Sciences: An Illustration." Journal of the Indian Law Institute 24 (1982): 655-661; Ellis, Timothy J. and Yair Levy Nova. "Framework of Problem-Based Research: A Guide for Novice Researchers on the Development of a Research-Worthy Problem." Informing Science: the International Journal of an Emerging Transdiscipline 11 (2008); How to Write a Research Question. The Writing Center. George Mason University; Invention: Developing a Thesis Statement. The Reading/Writing Center. Hunter College; Problem Statements PowerPoint Presentation. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Procter, Margaret. Using Thesis Statements. University College Writing Centre. University of Toronto; Shoket, Mohd. "Research Problem: Identification and Formulation." International Journal of Research 1 (May 2014): 512-518; Trochim, William M.K. Problem Formulation. Research Methods Knowledge Base. 2006; Thesis and Purpose Statements. The Writer’s Handbook. Writing Center. University of Wisconsin, Madison; Thesis Statements. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Tips and Examples for Writing Thesis Statements. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Pardede, Parlindungan. “Identifying and Formulating the Research Problem." Research in ELT: Module 4 (October 2018): 1-13; Walk, Kerry. Asking an Analytical Question. [Class handout or worksheet]. Princeton University; White, Patrick. Developing Research Questions: A Guide for Social Scientists . New York: Palgrave McMillan, 2009; Li, Yanmei, and Sumei Zhang. "Identifying the Research Problem." In Applied Research Methods in Urban and Regional Planning . (Cham, Switzerland: Springer International Publishing, 2022), pp. 13-21.
- << Previous: Background Information
- Next: Theoretical Framework >>
- Last Updated: May 30, 2024 9:38 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide

The Plagiarism Checker Online For Your Academic Work
Start Plagiarism Check
Editing & Proofreading for Your Research Paper
Get it proofread now
Online Printing & Binding with Free Express Delivery
Configure binding now
- Academic essay overview
- The writing process
- Structuring academic essays
- Types of academic essays
- Academic writing overview
- Sentence structure
- Academic writing process
- Improving your academic writing
- Titles and headings
- APA style overview
- APA citation & referencing
- APA structure & sections
- Citation & referencing
- Structure and sections
- APA examples overview
- Commonly used citations
- Other examples
- British English vs. American English
- Chicago style overview
- Chicago citation & referencing
- Chicago structure & sections
- Chicago style examples
- Citing sources overview
- Citation format
- Citation examples
- College essay overview
- Application
- How to write a college essay
- Types of college essays
- Commonly confused words
- Definitions
- Dissertation overview
- Dissertation structure & sections
- Dissertation writing process
- Graduate school overview
- Application & admission
- Study abroad
- Master degree
- Harvard referencing overview
- Language rules overview
- Grammatical rules & structures
- Parts of speech
- Punctuation
- Methodology overview
- Analyzing data
- Experiments
- Observations
- Inductive vs. Deductive
- Qualitative vs. Quantitative
- Types of validity
- Types of reliability
- Sampling methods
- Theories & Concepts
- Types of research studies
- Types of variables
- MLA style overview
- MLA examples
- MLA citation & referencing
- MLA structure & sections
- Plagiarism overview
- Plagiarism checker
- Types of plagiarism
- Printing production overview
- Research bias overview
- Types of research bias
- Example sections
- Types of research papers
- Research process overview
- Problem statement
- Research proposal
- Research topic
- Statistics overview
- Levels of measurment
- Frequency distribution
- Measures of central tendency
- Measures of variability
- Hypothesis testing
- Parameters & test statistics
- Types of distributions
- Correlation
- Effect size
- Hypothesis testing assumptions
- Types of ANOVAs
- Types of chi-square
- Statistical data
- Statistical models
- Spelling mistakes
- Tips overview
- Academic writing tips
- Dissertation tips
- Sources tips
- Working with sources overview
- Evaluating sources
- Finding sources
- Including sources
- Types of sources
Your Step to Success
Plagiarism Check within 10min
Printing & Binding with 3D Live Preview
Research Questions – Definition, Examples & Tips
How do you like this article cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

At the heart of every research endeavor lies a fundamental driving force: the research question. It not only defines the scope and direction of inquiry, it also inspires people to seek knowledge. In the complex journey of the research process , key questions act as guiding stars. In this article, we’ll cover everything you need to know about research questions and provide various examples.
Inhaltsverzeichnis
- 1 Research Questions in a nutshell
- 2 Definition: Research Question
- 3 Characteristics of a Research Question
- 4 How to Create a Research Question
- 5 Types of Research Questions
- 6 Example Questions
- 7 Research Frameworks
- 8 Dos & Donts
- 9 Sub-Questions
- 10 Tips for a Good Research Question
Research Questions in a nutshell
A research question is a clear and concise inquiry around which you center a research study. It helps to define the scope of the study and provides a basis for gathering and analyzing a variety of data.
Definition: Research Question
A research question is a concise inquiry that guides the direction of a research study or investigation. It articulates the specific type of subject that the researcher aims to explore, often framed in a way that suggests investigation or analysis . It serves as a fundamental element in the research process, guiding the selection of appropriate methodologies, the collection of evidence, and the interpretation of results. In essence, a research question serves as the starting point for scholarly inquiry, driving the pursuit of knowledge and understanding within a particular field.
Characteristics of a Research Question
The characteristics of a research question play a pivotal role in shaping the direction and success of a research study. The inquiry not only guides the research process, but also ensures its effectiveness in addressing key issues within the field of study.
It should serve three key purposes:
- Interesting : It should stimulate curiosity and appeal from both the researcher and the audience, motivating researchers to explore the topic further. It also increases the likelihood of commitment from both sides, fostering a deeper understanding and appreciation of the research topic.
- Well-defined : A well-defined research question provides clarity and focus, ensuring that the research study addresses a specific aspect of the topic. This helps avoid ambiguity and ensures that the research process is coherent and purposeful.
- Tractable : By ensuring tractability, researchers can conduct the study effectively, maximizing the likelihood of achieving meaningful results. Tractable research questions are also more likely to lead to successful completion of the study, avoiding setbacks due to unattainable goals.
Furthermore, a good research topic should answer three questions:
- Why is this question significant within the context of the field?
- How does your research build upon and enhance the current body of literature?
- What tangible outcomes can be expected if the question is thoroughly investigated and answered?
By answering these questions and ensuring that your research question is interesting, well-defined, and tractable, you can establish the relevance and significance of your research within the field.
How to Create a Research Question
Formulating an impactful research inquiry can be quite difficult. Nevertheless, by employing a comprehensive multistep approach, this task may turn out to be more manageable for you.

1. Identify a broad topic
Begin by identifying a broad area of interest within your field of study and generate questions based on curiosity and knowledge gaps. This could be based on current trends in the field or gaps in existing literature.
2. Conduct background research
Explore existing literature related to your topic to understand what has already been studied and what questions remain unanswered. This will help you identify potential gaps or areas for further exploration, and narrow your focus . Consider the characteristics mentioned earlier.
3. Consider your audience
Reflect on who your specific target audience is — whether it’s academic researchers or the general public. Tailor your research question to be relevant and accessible for your primary audience, considering their interests and level of expertise.
4. Narrow down the focus
Gradually narrow down your topic to a specific research question or a couple of questions based on the gaps found in existing research.
5. Define your questions
Now that you have found your niche, consider all the steps above and start asking open-ended “how” and “why” questions about your topic. A framework such as SMART Goals , PICOT , or FINER , which we will elaborate on in a later section more thoroughly, might be helpful when generating your key questions.
6. Evaluate your question
Now that you have written down your questions, evaluate them to establish if they are effective or if they need further refinement . For this step, look at the characteristics above again, and determine if they answer all the questions and check all the boxes. Is the research question well-defined and interesting to you and your audience? Think about the possible paths your research could take, which is the question, that effectively captures the essence of your research and aligns with your overarching objectives? It shouldn’t be too broad and also not easily answerable with quick searches.
Types of Research Questions
Research questions can be classified into various types, depending on the types of studies to be undertaken. Below, we will discuss each one of them, and their specifics.
Qualitative
Quantitative, mixed-methods.
A qualitative question is concerned with comprehending a phenomenon , and focuses on finding , explaining , and exploring . Qualitative research is primarily used in social sciences and uses open-ended research questions, and seeks to uncover rich and descriptive data .
The most common types of qualitative questions include:
- Exploratory questions , which seek to understand without influencing the results. The objective is to investigate an issue that has limited existing knowledge, and is typically conducted at the preliminary stages of a research process without research bias .
- Predictive questions , which seek to understand the intent or future outcome around a topic. The objective here it to use past information to predict reactions to hypothetical events.
- Interpretive questions , which aim to understand people’s behavior in a natural setting. The objective is to gather feedback on a group’s behavior without affecting the outcome.
A quantitative question is used to prove or disprove a researcher’s hypothesis through descriptions , comparisons , and relationships . It typically involves the population to be studied, identifying independent vs. dependent variables , and the research design. Quantitative questions are created to express the causality between variables and whether this relationship is relevant.
The most common types of quantitative questions include:
- Descriptive questions , which aim to explain when, where, why, or how something occurred, are the most basic type of quantitative research. They use numerical data and statistical analysis to describe a phenomenon, and their objective is to provide a clear and detailed description of a particular phenomenon.
- Comparative questions are used to compare groups or dependent variables to identify similarities, differences, or relationships between them. Their objective is to uncover the “how” or “why” of a topic by examining variations or relationships.
- Relationship-based questions , such as causal and correlational questions, try to answer whether one variable influences another. These types of questions are used in experimental or in quasi-experimental design studies, to focus on understanding how they are connected or influence each other.
Mixed methods research involves the integration of both qualitative and quantitative approaches within a single study, and for this reason, it’s a popular research method for researching nowadays. Mixed methods research combines both quantitative and qualitative data to explore a research question more thoroughly, and is often used in the behavioral, health, and social sciences.
Mixed methods research questions can help you achieve a more comprehensive picture than a standalone quantitative or qualitative question. However, they can be difficult to implement and come with the same risk of research bias as standalone studies.
Example Questions
In this section, we will provide you with numerous research question examples for each type of quantitative, qualitative, and mixed-method question.
Exploratory Question
- What are the factors influencing employee satisfaction in a new startup company?
Predictive Question
- How much can high schoolers’ GPA and grades predict their academic college performance?
Interpretive Question
- How do cultural beliefs shape peoples view of mental health and help-seeking behaviors?
Descriptive Question
- What are the demographics of students enrolled in online courses at a university?
Comparative Question
- How does lecture-style teaching compare to interactive learning in math comprehension?
Relationship-based Question
- What’s the correlation between social media use and young adults’ feelings of loneliness?
Mixed-Methods Questions
- How does the implementation of a new online learning platform (quantitative) impact student engagement and satisfaction (qualitative) in undergraduate courses?
- How do the perceptions of teachers (qualitative) and the academic performance of students (quantitative) vary across different teaching methodologies?
- How do cultural beliefs and values (qualitative) influence consumer purchasing behavior (quantitative) in the cosmetics industry?
Sample Format
Crafting effective research inquiries is most important for guiding your study and achieving your research goals. Below, you’ll find various question formats, designed to inspire and guide your inquiry. Refer to the accompanying picture for a comprehensive range of question formats suitable for a variety of research purposes and contexts.

Research Frameworks
There are three types of frameworks you can use as foundational elements to ensure that your research question is succinct.
- The PICO framework, which stands for P opulation, I ntervention, C omparison, and O utcome, is commonly used in healthcare research to structure clinical questions. It helps researchers define the key elements of a research question, including the population of interest, the intervention, or exposure being studied, the comparison group, and the outcome of interest.
- The SMART framework, which stands for S pecific, M easurable, A chievable, R elevant, and T ime-bound, is widely used and helps ensure that the question is clear, quantifiable, feasible, aligned with the research objectives, and has a defined time frame for completion.
- The FINER framework, which stands for F easible, I nteresting, N ovel, E thical, and R elevant, provides criteria for evaluating the quality and appropriateness of research questions. It ensures that the question is feasible to address, interesting and relevant to the field, innovative, ethically sound, and directly related tot the research objectives.
Below, we have illustrated each framework with appropriate questions you can ask yourself in order to find out if your research question can be improved.
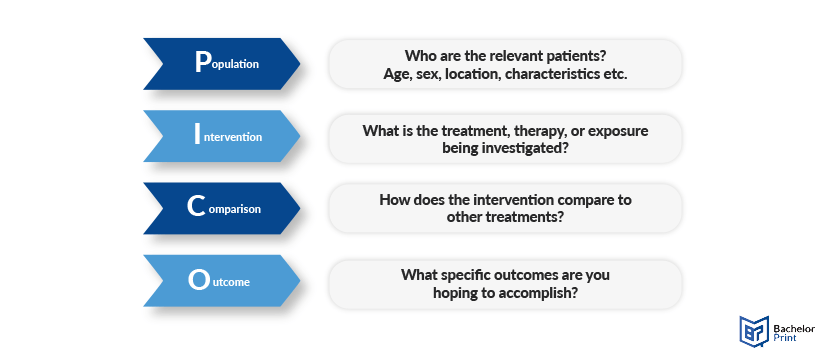
Dos & Donts
Below you’ll find an illustration depicting what you should do and what you should not do when it comes to research questions.
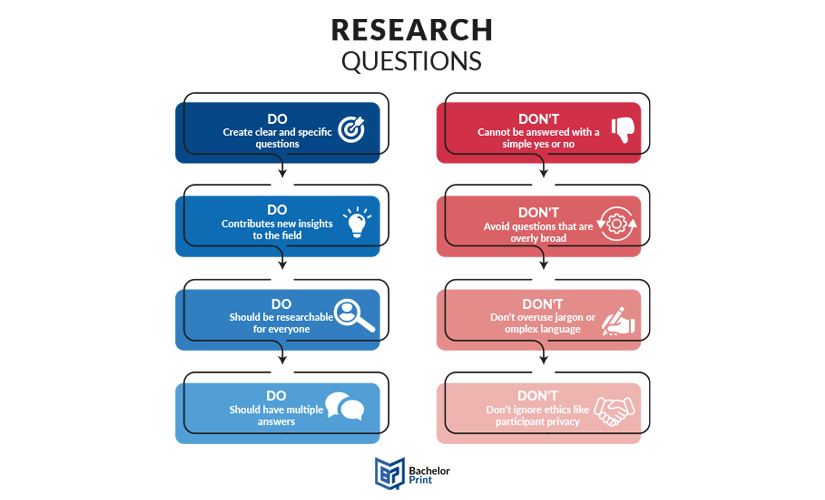
Below you’ll find a table with numerous good and bad examples of research questions together with explanations for each of them.
| Too narrow. Avoid questions that can be answered with a simple statistic or a mere “yes” or “no.” | A proper amount of specificity. Results could serve as grounds for constructing an argument. |
| This question is extremely broad, which would make research methodology fairly difficult. | This question has a very clear focus for which data can be obtained, analyzed, and discussed. |
| This question allows the collection of data, but it can't be used to create a valid argument given that the data is just factual information. | This is a more subjective question that may lead to the formation of an argument based on the results and analysis of the data. |
| This information can be obtained without the need to collect unique data. The question could be answered with a simple search and does not allow for analysis. | This question is more complex and requires both investigation and evaluation, which will lead the research to form a compelling argument. |
Sub-Questions
Sub-questions can be essential in research for clarifying complex topics and providing depth to the analysis when your main research question can’t be answered all at once. They are optional and should be used only if necessary to address the main question. If the main question is straightforward, sub-questions can be omitted. Let’s say that the main research question is “How has the transition to online schooling during COVID-19 pandemic affected sophomore and junior students’ academic performance and engagement?”. Some potential sub-questions could be:
- What impact has online schooling had on grades and test scores during the pandemic?
- How has student participation in classes changed with online schooling?
- How effectively have teachers adapted their instruction methods for online teaching?
Tips for a Good Research Question
Crafting a good research inquiry is a critical step in conducting a successful research project, as we have learned. The selection of successful research topics is crucial for guiding the direction of a study and ensuring that the research addresses relevant issues within the field. Here are some general tips to help you develop a strong research question.
- Be specific and clear : A good question should allow for focused study and straightforward answers. Avoid being broad or vague since this could lead to a sprawling investigation.
- Make it measurable : Your research question should be framed in a way that allows for gathering and analyzing data. It should be possible to measure the aspects of the question through available methods.
- Ensure relevance : The question should be relevant to current issues or contribute to a field of study that interests you. It should address a gap in knowledge or add a new perspective to existing studies.
- Test your question : Before finalizing your research question, test it. Discuss it with peers, mentors, or through preliminary literature reviews to ensure it is focused and engaging.
The most important thing is that whatever subject you focus on, it should be interesting to you and your field. Because that way, the writing and analyzing process will be much more enjoyable and rewarding.
Note: Do not figure out your research question after you have finished your research paper.

What are 5 good research questions?
- What impact does incorporating technology into classroom instruction have on student engagement and academic performance in elementary schools?
- How does mindfulness-based stress reduction therapy compare to cognitive-behavioral therapy in reducing symptoms of anxiety and depression among young adults?
- What are the long-term effects of microplastic pollution on marine biodiversity in coastal ecosystems, and how can we mitigate these effects?
- To what extent do socioeconomic factors influence access to healthcare services among marginalized communities, and what policy interventions could address these disparities?
- How do leadership styles and organizational culture impact employee job satisfaction rates in remote work settings?
What is a research question?
A well-developed research question identifies the main issue that the researchers want to investigate and provides a framework for gathering data to address that issue and also proposes a conclusive solution depending on the research type. It serves as a foundation for the writing process and guides the research project.
What types of research questions are there?
Research questions can be classified into three types:
- Descriptive research questions
- Quantitative research questions
- Mixed-methods research questions
What are 6 research questions?
- Descriptive questions
- Comparative questions
- Relationship-based questions
- Exploratory questions
- Predictive questions
- Interpretive questions
We use cookies on our website. Some of them are essential, while others help us to improve this website and your experience.
- External Media
Individual Privacy Preferences
Cookie Details Privacy Policy Imprint
Here you will find an overview of all cookies used. You can give your consent to whole categories or display further information and select certain cookies.
Accept all Save
Essential cookies enable basic functions and are necessary for the proper function of the website.
Show Cookie Information Hide Cookie Information
| Name | |
|---|---|
| Anbieter | Eigentümer dieser Website, |
| Zweck | Speichert die Einstellungen der Besucher, die in der Cookie Box von Borlabs Cookie ausgewählt wurden. |
| Cookie Name | borlabs-cookie |
| Cookie Laufzeit | 1 Jahr |
| Name | |
|---|---|
| Anbieter | Bachelorprint |
| Zweck | Erkennt das Herkunftsland und leitet zur entsprechenden Sprachversion um. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | ip-api.com |
| Cookie Name | georedirect |
| Cookie Laufzeit | 1 Jahr |
Statistics cookies collect information anonymously. This information helps us to understand how our visitors use our website.
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Google Ireland Limited, Gordon House, Barrow Street, Dublin 4, Ireland |
| Zweck | Cookie von Google zur Steuerung der erweiterten Script- und Ereignisbehandlung. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Cookie Name | _ga,_gat,_gid |
| Cookie Laufzeit | 2 Jahre |
Content from video platforms and social media platforms is blocked by default. If External Media cookies are accepted, access to those contents no longer requires manual consent.
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Meta Platforms Ireland Limited, 4 Grand Canal Square, Dublin 2, Ireland |
| Zweck | Wird verwendet, um Facebook-Inhalte zu entsperren. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | .facebook.com |
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Google Ireland Limited, Gordon House, Barrow Street, Dublin 4, Ireland |
| Zweck | Wird zum Entsperren von Google Maps-Inhalten verwendet. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | .google.com |
| Cookie Name | NID |
| Cookie Laufzeit | 6 Monate |
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Meta Platforms Ireland Limited, 4 Grand Canal Square, Dublin 2, Ireland |
| Zweck | Wird verwendet, um Instagram-Inhalte zu entsperren. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | .instagram.com |
| Cookie Name | pigeon_state |
| Cookie Laufzeit | Sitzung |
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Openstreetmap Foundation, St John’s Innovation Centre, Cowley Road, Cambridge CB4 0WS, United Kingdom |
| Zweck | Wird verwendet, um OpenStreetMap-Inhalte zu entsperren. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | .openstreetmap.org |
| Cookie Name | _osm_location, _osm_session, _osm_totp_token, _osm_welcome, _pk_id., _pk_ref., _pk_ses., qos_token |
| Cookie Laufzeit | 1-10 Jahre |
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Twitter International Company, One Cumberland Place, Fenian Street, Dublin 2, D02 AX07, Ireland |
| Zweck | Wird verwendet, um Twitter-Inhalte zu entsperren. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | .twimg.com, .twitter.com |
| Cookie Name | __widgetsettings, local_storage_support_test |
| Cookie Laufzeit | Unbegrenzt |
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Vimeo Inc., 555 West 18th Street, New York, New York 10011, USA |
| Zweck | Wird verwendet, um Vimeo-Inhalte zu entsperren. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | player.vimeo.com |
| Cookie Name | vuid |
| Cookie Laufzeit | 2 Jahre |
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Google Ireland Limited, Gordon House, Barrow Street, Dublin 4, Ireland |
| Zweck | Wird verwendet, um YouTube-Inhalte zu entsperren. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | google.com |
| Cookie Name | NID |
| Cookie Laufzeit | 6 Monate |
Privacy Policy Imprint
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Starting the research process
- How to Define a Research Problem | Ideas & Examples
How to Define a Research Problem | Ideas & Examples
Published on November 2, 2022 by Shona McCombes and Tegan George. Revised on May 31, 2023.
A research problem is a specific issue or gap in existing knowledge that you aim to address in your research. You may choose to look for practical problems aimed at contributing to change, or theoretical problems aimed at expanding knowledge.
Some research will do both of these things, but usually the research problem focuses on one or the other. The type of research problem you choose depends on your broad topic of interest and the type of research you think will fit best.
This article helps you identify and refine a research problem. When writing your research proposal or introduction , formulate it as a problem statement and/or research questions .
Table of contents
Why is the research problem important, step 1: identify a broad problem area, step 2: learn more about the problem, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about research problems.
Having an interesting topic isn’t a strong enough basis for academic research. Without a well-defined research problem, you are likely to end up with an unfocused and unmanageable project.
You might end up repeating what other people have already said, trying to say too much, or doing research without a clear purpose and justification. You need a clear problem in order to do research that contributes new and relevant insights.
Whether you’re planning your thesis , starting a research paper , or writing a research proposal , the research problem is the first step towards knowing exactly what you’ll do and why.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

As you read about your topic, look for under-explored aspects or areas of concern, conflict, or controversy. Your goal is to find a gap that your research project can fill.
Practical research problems
If you are doing practical research, you can identify a problem by reading reports, following up on previous research, or talking to people who work in the relevant field or organization. You might look for:
- Issues with performance or efficiency
- Processes that could be improved
- Areas of concern among practitioners
- Difficulties faced by specific groups of people
Examples of practical research problems
Voter turnout in New England has been decreasing, in contrast to the rest of the country.
The HR department of a local chain of restaurants has a high staff turnover rate.
A non-profit organization faces a funding gap that means some of its programs will have to be cut.
Theoretical research problems
If you are doing theoretical research, you can identify a research problem by reading existing research, theory, and debates on your topic to find a gap in what is currently known about it. You might look for:
- A phenomenon or context that has not been closely studied
- A contradiction between two or more perspectives
- A situation or relationship that is not well understood
- A troubling question that has yet to be resolved
Examples of theoretical research problems
The effects of long-term Vitamin D deficiency on cardiovascular health are not well understood.
The relationship between gender, race, and income inequality has yet to be closely studied in the context of the millennial gig economy.
Historians of Scottish nationalism disagree about the role of the British Empire in the development of Scotland’s national identity.
Next, you have to find out what is already known about the problem, and pinpoint the exact aspect that your research will address.
Context and background
- Who does the problem affect?
- Is it a newly-discovered problem, or a well-established one?
- What research has already been done?
- What, if any, solutions have been proposed?
- What are the current debates about the problem? What is missing from these debates?
Specificity and relevance
- What particular place, time, and/or group of people will you focus on?
- What aspects will you not be able to tackle?
- What will the consequences be if the problem is not resolved?
Example of a specific research problem
A local non-profit organization focused on alleviating food insecurity has always fundraised from its existing support base. It lacks understanding of how best to target potential new donors. To be able to continue its work, the organization requires research into more effective fundraising strategies.
Once you have narrowed down your research problem, the next step is to formulate a problem statement , as well as your research questions or hypotheses .
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
Methodology
- Sampling methods
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
All research questions should be:
- Focused on a single problem or issue
- Researchable using primary and/or secondary sources
- Feasible to answer within the timeframe and practical constraints
- Specific enough to answer thoroughly
- Complex enough to develop the answer over the space of a paper or thesis
- Relevant to your field of study and/or society more broadly

Research questions anchor your whole project, so it’s important to spend some time refining them.
In general, they should be:
- Focused and researchable
- Answerable using credible sources
- Complex and arguable
- Feasible and specific
- Relevant and original
Your research objectives indicate how you’ll try to address your research problem and should be specific:
A research aim is a broad statement indicating the general purpose of your research project. It should appear in your introduction at the end of your problem statement , before your research objectives.
Research objectives are more specific than your research aim. They indicate the specific ways you’ll address the overarching aim.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. & George, T. (2023, May 31). How to Define a Research Problem | Ideas & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved June 9, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/research-process/research-problem/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write a problem statement | guide & examples, writing strong research questions | criteria & examples, how to write a strong hypothesis | steps & examples, what is your plagiarism score.

Chapter 4. Finding a Research Question and Approaches to Qualitative Research
We’ve discussed the research design process in general and ways of knowing favored by qualitative researchers. In chapter 2, I asked you to think about what interests you in terms of a focus of study, including your motivations and research purpose. It might be helpful to start this chapter with those short paragraphs you wrote about motivations and purpose in front of you. We are now going to try to develop those interests into actual research questions (first part of this chapter) and then choose among various “traditions of inquiry” that will be best suited to answering those questions. You’ve already been introduced to some of this (in chapter 1), but we will go further here.

Developing a Research Question
Research questions are different from general questions people have about the social world. They are narrowly tailored to fit a very specific issue, complete with context and time boundaries. Because we are engaged in empirical science and thus use “data” to answer our questions, the questions we ask must be answerable by data. A question is not the same as stating a problem. The point of the entire research project is to answer a particular question or set of questions. The question(s) should be interesting, relevant, practical, and ethical. Let’s say I am generally interested in the problem of student loan debt. That’s a good place to start, but we can’t simply ask,
General question: Is student loan debt really a problem today?
How could we possibly answer that question? What data could we use? Isn’t this really an axiological (values-based) question? There are no clues in the question as to what data would be appropriate here to help us get started. Students often begin with these large unanswerable questions. They are not research questions. Instead, we could ask,
Poor research question: How many people have debt?
This is still not a very good research question. Why not? It is answerable, although we would probably want to clarify the context. We could add some context to improve it so that the question now reads,
Mediocre research question: How many people in the US have debt today? And does this amount vary by age and location?
Now we have added some context, so we have a better idea of where to look and who to look at. But this is still a pretty poor or mediocre research question. Why is that? Let’s say we did answer it. What would we really know? Maybe we would find out that student loan debt has increased over time and that young people today have more of it. We probably already know this. We don’t really want to go through a lot of trouble answering a question whose answer we already have. In fact, part of the reason we are even asking this question is that we know (or think) it is a problem. Instead of asking what you already know, ask a question to which you really do not know the answer. I can’t stress this enough, so I will say it again: Ask a question to which you do not already know the answer . The point of research is not to prove or make a point but to find out something unknown. What about student loan debt is still a mystery to you? Reviewing the literature could help (see chapter 9). By reviewing the literature, you can get a good sense of what is still mysterious or unknown about student loan debt, and you won’t be reinventing the wheel when you conduct your research. Let’s say you review the literature, and you are struck by the fact that we still don’t understand the true impact of debt on how people are living their lives. A possible research question might be,
Fair research question: What impact does student debt have on the lives of debtors?
Good start, but we still need some context to help guide the project. It is not nearly specific enough.
Better research question: What impact does student debt have on young adults (ages twenty-five to thirty-five) living in the US today?
Now we’ve added context, but we can still do a little bit better in narrowing our research question so that it is both clear and doable; in other words, we want to frame it in a way that provides a very clear research program:
Optimal research question: How do young adults (ages twenty-five to thirty-five) living in the US today who have taken on $30,000 or more in student debt describe the impact of their debt on their lives in terms of finding/choosing a job, buying a house, getting married, and other major life events?
Now you have a research question that can be answered and a clear plan of how to answer it. You will talk to young adults living in the US today who have high debt loads and ask them to describe the impacts of debt on their lives. That is all now in the research question. Note how different this very specific question is from where we started with the “problem” of student debt.
Take some time practicing turning the following general questions into research questions:
- What can be done about the excessive use of force by police officers?
- Why haven’t societies taken firmer steps to address climate change?
- How do communities react to / deal with the opioid epidemic?
- Who has been the most adversely affected by COVID?
- When did political polarization get so bad?
Hint: Step back from each of the questions and try to articulate a possible underlying motivation, then formulate a research question that is specific and answerable.
It is important to take the time to come up with a research question, even if this research question changes a bit as you conduct your research (yes, research questions can change!). If you don’t have a clear question to start your research, you are likely to get very confused when designing your study because you will not be able to make coherent decisions about things like samples, sites, methods of data collection, and so on. Your research question is your anchor: “If we don’t have a question, we risk the possibility of going out into the field thinking we know what we’ll find and looking only for proof of what we expect to be there. That’s not empirical research (it’s not systematic)” ( Rubin 2021:37 ).
Researcher Note
How do you come up with ideas for what to study?
I study what surprises me. Usually, I come across a statistic that suggests something is common that I thought was rare. I tend to think it’s rare because the theories I read suggest it should be, and there’s not a lot of work in that area that helps me understand how the statistic came to be. So, for example, I learned that it’s common for Americans to marry partners who grew up in a different class than them and that about half of White kids born into the upper-middle class are downwardly mobile. I was so shocked by these facts that they naturally led to research questions. How do people come to marry someone who grew up in a different class? How do White kids born near the top of the class structure fall?
—Jessi Streib, author of The Power of the Past and Privilege Lost
What if you have literally no idea what the research question should be? How do you find a research question? Even if you have an interest in a topic before you get started, you see the problem now: topics and issues are not research questions! A research question doesn’t easily emerge; it takes a lot of time to hone one, as the practice above should demonstrate. In some research designs, the research question doesn’t even get clearly articulated until the end of data collection . More on that later. But you must start somewhere, of course. Start with your chosen discipline. This might seem obvious, but it is often overlooked. There is a reason it is called a discipline. We tend to think of “sociology,” “public health,” and “physics” as so many clusters of courses that are linked together by subject matter, but they are also disciplines in the sense that the study of each focuses the mind in a particular way and for particular ends. For example, in my own field, sociology, there is a loosely shared commitment to social justice and a general “sociological imagination” that enables its practitioners to connect personal experiences to society at large and to historical forces. It is helpful to think of issues and questions that are germane to your discipline. Within that overall field, there may be a particular course or unit of study you found most interesting. Within that course or unit of study, there may be an issue that intrigued you. And finally, within that issue, there may be an aspect or topic that you want to know more about.
When I was pursuing my dissertation research, I was asked often, “Why did you choose to study intimate partner violence among Native American women?” This question is necessary, and each time I answered, it helped shape me into a better researcher. I was interested in intimate partner violence because I am a survivor. I didn’t have intentions to work with a particular population or demographic—that came from my own deep introspection on my role as a researcher. I always questioned my positionality: What privileges do I hold as an academic? How has public health extracted information from institutionally marginalized populations? How can I build bridges between communities using my position, knowledge, and power? Public health as a field would not exist without the contributions of Indigenous people. So I started hanging out with them at community events, making friends, and engaging in self-education. Through these organic relationships built with Native women in the community, I saw that intimate partner violence was a huge issue. This led me to partner with Indigenous organizations to pursue a better understanding of how Native survivors of intimate partner violence seek support.
—Susanna Y. Park, PhD, mixed-methods researcher in public health and author of “How Native Women Seek Support as Survivors of Intimate Partner Violence: A Mixed-Methods Study”
One of the most exciting and satisfying things about doing academic research is that whatever you end up researching can become part of the body of knowledge that we have collectively created. Don’t make the mistake of thinking that you are doing this all on your own from scratch. Without even being aware of it, no matter if you are a first-year undergraduate student or a fourth-year graduate student, you have been trained to think certain questions are interesting. The very fact that you are majoring in a particular field or have signed up for years of graduate study in a program testifies to some level of commitment to a discipline. What we are looking for, ideally, is that your research builds on in some way (as extension, as critique, as lateral move) previous research and so adds to what we, collectively, understand about the social world. It is helpful to keep this in mind, as it may inspire you and also help guide you through the process. The point is, you are not meant to be doing something no one has ever thought of before, even if you are trying to find something that does not exactly duplicate previous research: “You may be trying to be too clever—aiming to come up with a topic unique in the history of the universe, something that will have people swooning with admiration at your originality and intellectual precociousness. Don’t do it. It’s safer…to settle on an ordinary, middle-of-the-road topic that will lend itself to a nicely organized process of project management. That’s the clever way of proceeding.… You can always let your cleverness shine through during the stages of design, analysis, and write-up. Don’t make things more difficult for yourself than you need to do” ( Davies 2007:20 ).
Rubin ( 2021 ) suggests four possible ways to develop a research question (there are many more, of course, but this can get you started). One way is to start with a theory that interests you and then select a topic where you can apply that theory. For example, you took a class on gender and society and learned about the “glass ceiling.” You could develop a study that tests that theory in a setting that has not yet been explored—maybe leadership at the Oregon Country Fair. The second way is to start with a topic that interests you and then go back to the books to find a theory that might explain it. This is arguably more difficult but often much more satisfying. Ask your professors for help—they might have ideas of theories or concepts that could be relevant or at least give you an idea of what books to read. The third way is to be very clever and select a question that already combines the topic and the theory. Rubin gives as one example sentencing disparities in criminology—this is both a topic and a theory or set of theories. You then just have to figure out particulars like setting and sample. I don’t know if I find this third way terribly helpful, but it might help you think through the possibilities. The fourth way involves identifying a puzzle or a problem, which can be either theoretical (something in the literature just doesn’t seem to make sense and you want to tackle addressing it) or empirical (something happened or is happening, and no one really understands why—think, for example, of mass school shootings).
Once you think you have an issue or topic that is worth exploring, you will need to (eventually) turn that into a good research question. A good research question is specific, clear, and feasible .
Specific . How specific a research question needs to be is somewhat related to the disciplinary conventions and whether the study is conceived inductively or deductively. In deductive research, one begins with a specific research question developed from the literature. You then collect data to test the theory or hypotheses accompanying your research question. In inductive research, however, one begins with data collection and analysis and builds theory from there. So naturally, the research question is a bit vaguer. In general, the more closely aligned to the natural sciences (and thus the deductive approach), the more a very tight and specific research question (along with specific, focused hypotheses) is required. This includes disciplines like psychology, geography, public health, environmental science, and marine resources management. The more one moves toward the humanities pole (and the inductive approach), the more looseness is permitted, as there is a general belief that we go into the field to find what is there, not necessarily what we imagine we are looking for (see figure 4.2). Disciplines such as sociology, anthropology, and gender and sexuality studies and some subdisciplines of public policy/public administration are closer to the humanities pole in this sense.
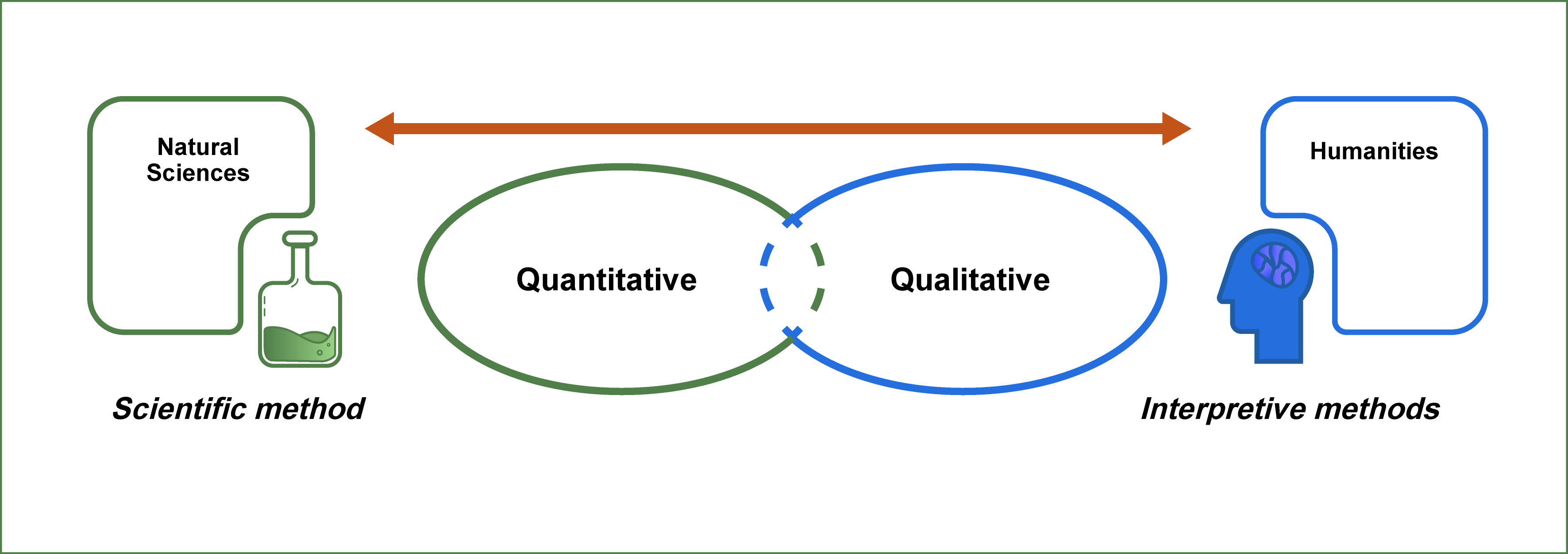
Regardless of discipline and approach, however, it is a good idea for beginning researchers to create a research question as specific as possible, as this will serve as your guide throughout the process. You can tweak it later if needed, but start with something specific enough that you know what it is you are doing and why. It is more difficult to deal with ambiguity when you are starting out than later in your career, when you have a better handle on what you are doing. Being under a time constraint means the more specific the question, the better. Questions should always specify contexts, geographical locations, and time frames. Go back to your practice research questions and make sure that these are included.
Clear . A clear research question doesn’t only need to be intelligible to any reader (which, of course, it should); it needs to clarify any meanings of particular words or concepts (e.g., What is excessive force?). Check all your concepts to see if there are ways you can clarify them further—for example, note that we shifted from impact of debt to impact of high debt load and specified this as beginning at $30,000. Ideally, we would use the literature to help us clarify what a high debt load is or how to define “excessive” force.
Feasible . In order to know if your question is feasible, you are going to have to think a little bit about your entire research design. For example, a question that asks about the real-time impact of COVID restrictions on learning outcomes would require a time machine. You could tweak the question to ask instead about the long-term impacts of COVID restrictions, as measured two years after their end. Or let’s say you are interested in assessing the damage of opioid abuse on small-town communities across the United States. Is it feasible to cover the entire US? You might need a team of researchers to do this if you are planning on on-the-ground observations. Perhaps a case study of one particular community might be best. Then your research question needs to be changed accordingly.
Here are some things to consider in terms of feasibility:
- Is the question too general for what you actually intend to do or examine? (Are you specifying the world when you only have time to explore a sliver of that world?)
- Is the question suitable for the time you have available? (You will need different research questions for a study that can be completed in a term than one where you have one to two years, as in a master’s program, or even three to eight years, as in a doctoral program.)
- Is the focus specific enough that you know where and how to begin?
- What are the costs involved in doing this study, including time? Will you need to travel somewhere, and if so, how will you pay for it?
- Will there be problems with “access”? (More on this in later chapters, but for now, consider how you might actually find people to interview or places to observe and whether gatekeepers exist who might keep you out.)
- Will you need to submit an application proposal for your university’s IRB (institutional review board)? If you are doing any research with live human subjects, you probably need to factor in the time and potential hassle of an IRB review (see chapter 8). If you are under severe time constraints, you might need to consider developing a research question that can be addressed with secondary sources, online content, or historical archives (see chapters 16 and 17).
In addition to these practicalities, you will also want to consider the research question in terms of what is best for you now. Are you engaged in research because you are required to be—jumping a hurdle for a course or for your degree? If so, you really do want to think about your project as training and develop a question that will allow you to practice whatever data collection and analysis techniques you want to develop. For example, if you are a grad student in a public health program who is interested in eventually doing work that requires conducting interviews with patients, develop a research question and research design that is interview based. Focus on the practicality (and practice) of the study more than the theoretical impact or academic contribution, in other words. On the other hand, if you are a PhD candidate who is seeking an academic position in the future, your research question should be pitched in a way to build theoretical knowledge as well (the phrasing is typically “original contribution to scholarship”).
The more time you have to devote to the study and the larger the project, the more important it is to reflect on your own motivations and goals when crafting a research question (remember chapter 2?). By “your own motivations and goals,” I mean what interests you about the social world and what impact you want your research to have, both academically and practically speaking. Many students have secret (or not-so-secret) plans to make the world a better place by helping address climate change, pointing out pressure points to fight inequities, or bringing awareness to an overlooked area of concern. My own work in graduate school was motivated by the last of these three—the not-so-secret goal of my research was to raise awareness about obstacles to success for first-generation and working-class college students. This underlying goal motivated me to complete my dissertation in a timely manner and then to further continue work in this area and see my research get published. I cared enough about the topic that I was not ready to put it away. I am still not ready to put it away. I encourage you to find topics that you can’t put away, ever. That will keep you going whenever things get difficult in the research process, as they inevitably will.
On the other hand, if you are an undergraduate and you really have very little time, some of the best advice I have heard is to find a study you really like and adapt it to a new context. Perhaps you read a study about how students select majors and how this differs by class ( Hurst 2019 ). You can try to replicate the study on a small scale among your classmates. Use the same research question, but revise for your context. You can probably even find the exact questions I used and ask them in the new sample. Then when you get to the analysis and write-up, you have a comparison study to guide you, and you can say interesting things about the new context and whether the original findings were confirmed (similar) or not. You can even propose reasons why you might have found differences between one and the other.
Another way of thinking about research questions is to explicitly tie them to the type of purpose of your study. Of course, this means being very clear about what your ultimate purpose is! Marshall and Rossman ( 2016 ) break down the purpose of a study into four categories: exploratory, explanatory, descriptive, and emancipatory ( 78 ). Exploratory purpose types include wanting to investigate little-understood phenomena, or identifying or discovering important new categories of meaning, or generating hypotheses for further research. For these, research questions might be fairly loose: What is going on here? How are people interacting on this site? What do people talk about when you ask them about the state of the world? You are almost (but never entirely) starting from scratch. Be careful though—just because a topic is new to you does not mean it is really new. Someone else (or many other someones) may already have done this exploratory research. Part of your job is to find this out (more on this in “What Is a ‘Literature Review’?” in chapter 9). Descriptive purposes (documenting and describing a phenomenon) are similar to exploratory purposes but with a much clearer goal (description). A good research question for a descriptive study would specify the actions, events, beliefs, attitudes, structures, and/or processes that will be described.
Most researchers find that their topic has already been explored and described, so they move to trying to explain a relationship or phenomenon. For these, you will want research questions that capture the relationships of interest. For example, how does gender influence one’s understanding of police brutality (because we already know from the literature that it does, so now we are interested in understanding how and why)? Or what is the relationship between education and climate change denialism? If you find that prior research has already provided a lot of evidence about those relationships as well as explanations for how they work, and you want to move the needle past explanation into action, you might find yourself trying to conduct an emancipatory study. You want to be even more clear in acknowledging past research if you find yourself here. Then create a research question that will allow you to “create opportunities and the will to engage in social action” ( Marshall and Rossman 2016:78 ). Research questions might ask, “How do participants problematize their circumstances and take positive social action?” If we know that some students have come together to fight against student debt, how are they doing this, and with what success? Your purpose would be to help evaluate possibilities for social change and to use your research to make recommendations for more successful emancipatory actions.
Recap: Be specific. Be clear. Be practical. And do what you love.
Choosing an Approach or Tradition
Qualitative researchers may be defined as those who are working with data that is not in numerical form, but there are actually multiple traditions or approaches that fall under this broad category. I find it useful to know a little bit about the history and development of qualitative research to better understand the differences in these approaches. The following chart provides an overview of the six phases of development identified by Denzin and Lincoln ( 2005 ):
Table 4.1. Six Phases of Development
| Year/Period | Phase | Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Pre-1945 | Traditional | Influence of positivism; anthropologists and ethnographers strive for objectivity when reporting observations in the field |
| 1945-1970 | Modernist | Emphasis of methodological rigor and procedural formalism as a way of gaining acceptance |
| 1970-1986 | Blurred genres | Large number of alternative approaches emerge, all competing with and contesting positivist and formalist approaches; e.g., structuralism, symbolic interactionism, ethnomethodology, constructionism |
| 1980s-1990s | Crisis of representation | Attention turns to issues of power and privilege and the necessity of reflexivity around race, class, gender positions and identities; traditional notions of validity and neutrality were undermined |
| 1990s-2000 | Triple crisis | Moving beyond issues of representation, questions raised about evaluation of qualitative research and the writing/presentation of it as well; more political and participatory forms emerge; qualitative research to advance social justice advocated |
| 2000s... | Postexperimental | Boundaries expanded to include creative nonfiction, autobiographical ethnography, poetic representation, and other creative approaches |
There are other ways one could present the history as well. Feminist theory and methodologies came to the fore in the 1970s and 1980s and had a lot to do with the internal critique of more positivist approaches. Feminists were quite aware that standpoint matters—that the identity of the researcher plays a role in the research, and they were ardent supporters of dismantling unjust power systems and using qualitative methods to help advance this mission. You might note, too, that many of the internal disputes were basically epistemological disputes about how we know what we know and whether one’s social location/position delimits that knowledge. Today, we are in a bountiful world of qualitative research, one that embraces multiple forms of knowing and knowledge. This is good, but it means that you, the student, have more choice when it comes to situating your study and framing your research question, and some will expect you to signal the choices you have made in any research protocols you write or publications and presentations.
Creswell’s ( 1998 ) definition of qualitative research includes the notion of distinct traditions of inquiry: “Qualitative research is an inquiry process of understanding based on distinct methodological traditions of inquiry that explore a social or human problem. The research builds complex, holistic pictures, analyzes words, reports detailed views of informants , and conducted the study in a natural setting” (15; emphases added). I usually caution my students against taking shelter under one of these approaches, as, practically speaking, there is a lot of mixing of traditions among researchers. And yet it is useful to know something about the various histories and approaches, particularly as you are first starting out. Each tradition tends to favor a particular epistemological perspective (see chapter 3), a way of reasoning (see “ Advanced: Inductive versus Deductive Reasoning ”), and a data-collection technique.
There are anywhere from ten to twenty “traditions of inquiry,” depending on how one draws the boundaries. In my accounting, there are twelve, but three approaches tend to dominate the field.
Ethnography
Ethnography was developed from the discipline of anthropology, as the study of (other) culture(s). From a relatively positivist/objective approach to writing down the “truth” of what is observed during the colonial era (where this “truth” was then often used to help colonial administrators maintain order and exploit people and extract resources more effectively), ethnography was adopted by all kinds of social science researchers to get a better understanding of how groups of people (various subcultures and cultures) live their lives. Today, ethnographers are more likely to be seeking to dismantle power relations than to support them. They often study groups of people that are overlooked and marginalized, and sometimes they do the obverse by demonstrating how truly strange the familiar practices of the dominant group are. Ethnography is also central to organizational studies (e.g., How does this institution actually work?) and studies of education (e.g., What is it like to be a student during the COVID era?).
Ethnographers use methods of participant observation and intensive fieldwork in their studies, often living or working among the group under study for months at a time (and, in some cases, years). I’ve called this “deep ethnography,” and it is the subject of chapter 14. The data ethnographers analyze are copious “field notes” written while in the field, often supplemented by in-depth interviews and many more casual conversations. The final product of ethnographers is a “thick” description of the culture. This makes reading ethnographies enjoyable, as the goal is to write in such a way that the reader feels immersed in the culture.
There are variations on the ethnography, such as the autoethnography , where the researcher uses a systematic and rigorous study of themselves to better understand the culture in which they find themselves. Autoethnography is a relatively new approach, even though it is derived from one of the oldest approaches. One can say that it takes to heart the feminist directive to “make the personal political,” to underscore the connections between personal experiences and larger social and political structures. Introspection becomes the primary data source.
Grounded Theory
Grounded Theory holds a special place in qualitative research for a few reasons, not least of which is that nonqualitative researchers often mistakenly believe that Grounded Theory is the only qualitative research methodology . Sometimes, it is easier for students to explain what they are doing as “Grounded Theory” because it sounds “more scientific” than the alternative descriptions of qualitative research. This is definitely part of its appeal. Grounded Theory is the name given to the systematic inductive approach first developed by Glaser and Strauss in 1967, The Discovery of Grounded Theory: Strategies for Qualitative Research . Too few people actually read Glaser and Strauss’s book. It is both groundbreaking and fairly unremarkable at the same time. As a historical intervention into research methods generally, it is both a sharp critique of positivist methods in the social sciences (theory testing) and a rejection of purely descriptive accounts-building qualitative research. Glaser and Strauss argued for an approach whose goal was to construct (middle-level) theories from recursive data analysis of nonnumerical data (interviews and observations). They advocated a “constant comparative method” in which coding and analysis take place simultaneously and recursively. The demands are fairly strenuous. If done correctly, the result is the development of a new theory about the social world.
So why do I call this “fairly unremarkable”? To some extent, all qualitative research already does what Glaser and Strauss ( 1967 ) recommend, albeit without denoting the processes quite so specifically. As will be seen throughout the rest of this textbook, all qualitative research employs some “constant comparisons” through recursive data analyses. Where Grounded Theory sets itself apart from a significant number of qualitative research projects, however, is in its dedication to inductively building theory. Personally, I think it is important to understand that Glaser and Strauss were rejecting deductive theory testing in sociology when they first wrote their book. They were part of a rising cohort who rejected the positivist mathematical approaches that were taking over sociology journals in the 1950s and 1960s. Here are some of the comments and points they make against this kind of work:
Accurate description and verification are not so crucial when one’s purpose is to generate theory. ( 28 ; further arguing that sampling strategies are different when one is not trying to test a theory or generalize results)
Illuminating perspectives are too often suppressed when the main emphasis is verifying theory. ( 40 )
Testing for statistical significance can obscure from theoretical relevance. ( 201 )
Instead, they argued, sociologists should be building theories about the social world. They are not physicists who spend time testing and refining theories. And they are not journalists who report descriptions. What makes sociologists better than journalists and other professionals is that they develop theory from their work “In their driving efforts to get the facts [research sociologists] tend to forget that the distinctive offering of sociology to our society is sociological theory, not research description” ( 30–31 ).
Grounded Theory’s inductive approach can be off-putting to students who have a general research question in mind and a working hypothesis. The true Grounded Theory approach is often used in exploratory studies where there are no extant theories. After all, the promise of this approach is theory generation, not theory testing. Flying totally free at the start can be terrifying. It can also be a little disingenuous, as there are very few things under the sun that have not been considered before. Barbour ( 2008:197 ) laments that this approach is sometimes used because the researcher is too lazy to read the relevant literature.
To summarize, Glaser and Strauss justified the qualitative research project in a way that gave it standing among the social sciences, especially vis-à-vis quantitative researchers. By distinguishing the constant comparative method from journalism, Glaser and Strauss enabled qualitative research to gain legitimacy.
So what is it exactly, and how does one do it? The following stages provide a succinct and basic overview, differentiating the portions that are similar to/in accordance with qualitative research methods generally and those that are distinct from the Grounded Theory approach:
Step 1. Select a case, sample, and setting (similar—unless you begin with a theory to test!).
Step 2. Begin data collection (similar).
Step 3. Engage data analysis (similar in general but specificity of details somewhat unique to Grounded Theory): (1) emergent coding (initial followed by focused), (2) axial (a priori) coding , (3) theoretical coding , (4) creation of theoretical categories; analysis ends when “theoretical saturation ” has been achieved.
Grounded Theory’s prescriptive (i.e., it has a set of rules) framework can appeal to beginning students, but it is unnecessary to adopt the entire approach in order to make use of some of its suggestions. And if one does not exactly follow the Grounded Theory rulebook, it can mislead others if you tend to call what you are doing Grounded Theory when you are not:
Grounded theory continues to be a misunderstood method, although many researchers purport to use it. Qualitative researchers often claim to conduct grounded theory studies without fully understanding or adopting its distinctive guidelines. They may employ one or two of the strategies or mistake qualitative analysis for grounded theory. Conversely, other researchers employ grounded theory methods in reductionist, mechanistic ways. Neither approach embodies the flexible yet systematic mode of inquiry, directed but open-ended analysis, and imaginative theorizing from empirical data that grounded theory methods can foster. Subsequently, the potential of grounded theory methods for generating middle-range theory has not been fully realized ( Charmaz 2014 ).
Phenomenology
Where Grounded Theory sets itself apart for its inductive systematic approach to data analysis, phenomenologies are distinct for their focus on what is studied—in this case, the meanings of “lived experiences” of a group of persons sharing a particular event or circumstance. There are phenomenologies of being working class ( Charlesworth 2000 ), of the tourist experience ( Cohen 1979 ), of Whiteness ( Ahmed 2007 ). The phenomenon of interest may also be an emotion or circumstance. One can study the phenomenon of “White rage,” for example, or the phenomenon of arranged marriage.
The roots of phenomenology lie in philosophy (Husserl, Heidegger, Merleau-Ponty, Sartre) but have been adapted by sociologists in particular. Phenomenologists explore “how human beings make sense of experience and transform experience into consciousness, both individually and as shared meaning” ( Patton 2002:104 ).
One of the most important aspects of conducting a good phenomenological study is getting the sample exactly right so that each person can speak to the phenomenon in question. Because the researcher is interested in the meanings of an experience, in-depth interviews are the preferred method of data collection. Observations are not nearly as helpful here because people may do a great number of things without meaning to or without being conscious of their implications. This is important to note because phenomenologists are studying not “the reality” of what happens at all but an articulated understanding of a lived experience. When reading a phenomenological study, it is important to keep this straight—too often I have heard students critique a study because the interviewer didn’t actually see how people’s behavior might conflict with what they say (which is, at heart, an epistemological issue!).
In addition to the “big three,” there are many other approaches; some are variations, and some are distinct approaches in their own right. Case studies focus explicitly on context and dynamic interactions over time and can be accomplished with quantitative or qualitative methods or a mixture of both (for this reason, I am not considering it as one of the big three qualitative methods, even though it is a very common approach). Whatever methods are used, a contextualized deep understanding of the case (or cases) is central.
Critical inquiry is a loose collection of techniques held together by a core argument that understanding issues of power should be the focus of much social science research or, to put this another way, that it is impossible to understand society (its people and institutions) without paying attention to the ways that power relations and power dynamics inform and deform those people and institutions. This attention to power dynamics includes how research is conducted too. All research fundamentally involves issues of power. For this reason, many critical inquiry traditions include a place for collaboration between researcher and researched. Examples include (1) critical narrative analysis, which seeks to describe the meaning of experience for marginalized or oppressed persons or groups through storytelling; (2) participatory action research, which requires collaboration between the researcher and the research subjects or community of interest; and (3) critical race analysis, a methodological application of Critical Race Theory (CRT), which posits that racial oppression is endemic (if not always throughout time and place, at least now and here).
Do you follow a particular tradition of inquiry? Why?
Shawn Wilson’s book, Research Is Ceremony: Indigenous Research Methods , is my holy grail. It really flipped my understanding of research and relationships. Rather than thinking linearly and approaching research in a more canonical sense, Wilson shook my world view by drawing me into a pattern of inquiry that emphasized transparency and relational accountability. The Indigenous research paradigm is applicable in all research settings, and I follow it because it pushes me to constantly evaluate my position as a knowledge seeker and knowledge sharer.
Autoethnography takes the researcher as the subject. This is one approach that is difficult to explain to more quantitatively minded researchers, as it seems to violate many of the norms of “scientific research” as understood by them. First, the sample size is quite small—the n is 1, the researcher. Two, the researcher is not a neutral observer—indeed, the subjectivity of the researcher is the main strength of this approach. Autoethnographies can be extremely powerful for their depth of understanding and reflexivity, but they need to be conducted in their own version of rigor to stand up to scrutiny by skeptics. If you are skeptical, read one of the excellent published examples out there—I bet you will be impressed with what you take away. As they say, the proof is in the pudding on this approach.
Advanced: Inductive versus Deductive Reasoning
There has been a great deal of ink shed in the discussion of inductive versus deductive approaches, not all of it very instructive. Although there is a huge conceptual difference between them, in practical terms, most researchers cycle between the two, even within the same research project. The simplest way to explain the difference between the two is that we are using deductive reasoning when we test an existing theory (move from general to particular), and we are using inductive reasoning when we are generating theory (move from particular to general). Figure 4.2 provides a schematic of the deductive approach. From the literature, we select a theory about the impact of student loan debt: student loan debt will delay homeownership among young adults. We then formulate a hypothesis based on this theory: adults in their thirties with high debt loads will be less likely to own homes than their peers who do not have high debt loads. We then collect data to test the hypothesis and analyze the results. We find that homeownership is substantially lower among persons of color and those who were the first in their families to graduate from college. Notably, high debt loads did not affect homeownership among White adults whose parents held college degrees. We thus refine the theory to match the new findings: student debt loads delay homeownership among some young adults, thereby increasing inequalities in this generation. We have now contributed new knowledge to our collective corpus.
The inductive approach is contrasted in figure 4.3. Here, we did not begin with a preexisting theory or previous literature but instead began with an observation. Perhaps we were conducting interviews with young adults who held high amounts of debt and stumbled across this observation, struck by how many were renting apartments or small houses. We then noted a pattern—not all the young adults we were talking to were renting; race and class seemed to play a role here. We would then probably expand our study in a way to be able to further test this developing theory, ensuring that we were not seeing anomalous patterns. Once we were confident about our observations and analyses, we would then develop a theory, coming to the same place as our deductive approach, but in reverse.
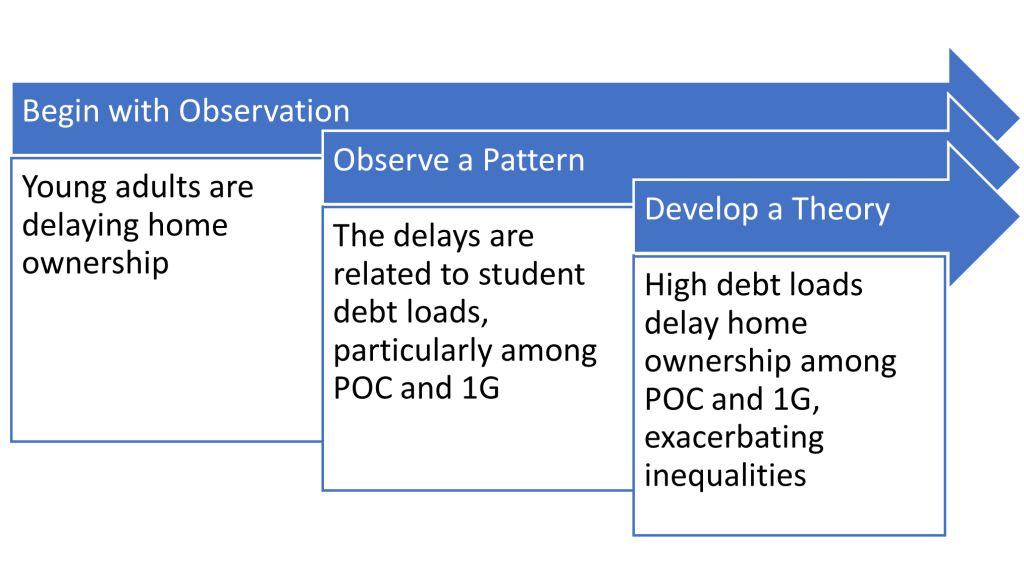
A third form of reasoning, abductive (sometimes referred to as probabilistic reasoning) was developed in the late nineteenth century by American philosopher Charles Sanders Peirce. I have included some articles for further reading for those interested.
Among social scientists, the deductive approach is often relaxed so that a research question is set based on the existing literature rather than creating a hypothesis or set of hypotheses to test. Some journals still require researchers to articulate hypotheses, however. If you have in mind a publication, it is probably a good idea to take a look at how most articles are organized and whether specific hypotheses statements are included.
Table 4.2. Twelve Approaches. Adapted from Patton 2002:132-133.
| Approach | Home discipline | /Data Collection Techniques |
|---|---|---|
| Ethnography | Anthropology | Fieldwork/Observations + supplemental interviews |
| Grounded theory | Sociology | Fieldwork/Observations + Interviews |
| Phenomenology | Philosophy | In-depth interviews |
| Constructivism | Sociology | Focus Groups; Interviews |
| Heuristic inquiry | Psychology | Self-reflections and fieldnotes + interviews |
| Ethnomethodology | Sociology | In-depth interviews + Fieldwork, including social experiments |
| Symbolic interaction | Social psychology | Focus Groups + Interviews |
| Semiotics | Linguistics | Textual analyses + interviews/focus groups |
| Hermeneutics | Theology | Textual analyses |
| Narrative analysis | Literary criticism | Interviews, Oral Histories, Textual Analyses, Historical Artefacts, Content Analyses |
| Ecological psychology | Ecology | Observation |
| Orientational/Standpoint approaches (critical theory, feminist theory) | Law; Sociology | PAR, Interviews, Focus Groups |
Further Readings
The following readings have been examples of various approaches or traditions of inquiry:
Ahmed, Sara. 2007. “A Phenomenology of Whiteness.” Feminist Theory 8(2):149–168.
Charlesworth, Simon. 2000. A Phenomenology of Working-Class Experience . Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.*
Clandinin, D. Jean, and F. Michael Connelly. 2000. Narrative Inquiry: Experience and Story in Qualitative Research . San Francisco: Jossey-Bass.
Cohen, E. 1979. “A Phenomenology of Tourist Experiences.” Sociology 13(2):179–201.
Cooke, Bill, and Uma Kothari, eds. 2001. Participation: The New Tyranny? London: Zed Books. A critique of participatory action.
Corbin, Juliet, and Anselm Strauss. 2008. Basics of Qualitative Research: Techniques and Procedures for Developing Grounded Theory . 3rd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE.
Crabtree, B. F., and W. L. Miller, eds. 1999. Doing Qualitative Research: Multiple Strategies . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE.
Creswell, John W. 1997. Qualitative Inquiry and Research Design: Choosing among Five Approaches. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE.
Glaser, Barney G., and Anselm Strauss. 1967. The Discovery of Grounded Theory: Strategies for Qualitative Research . New York: Aldine.
Gobo, Giampetro, and Andrea Molle. 2008. Doing Ethnography . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE.
Hancock, Dawson B., and Bob Algozzine. 2016. Doing Case Study Research: A Practical Guide for Beginning Research . 3rd ed. New York: Teachers College Press.
Harding, Sandra. 1987. Feminism and Methodology . Bloomington: Indiana University Press.
Husserl, Edmund. (1913) 2017. Ideas: Introduction to Pure Phenomenology . Eastford, CT: Martino Fine Books.
Rose, Gillian. 2012. Visual Methodologies . 3rd ed. London: SAGE.
Van der Riet, M. 2009. “Participatory Research and the Philosophy of Social Science: Beyond the Moral Imperative.” Qualitative Inquiry 14(4):546–565.
Van Manen, Max. 1990. Researching Lived Experience: Human Science for an Action Sensitive Pedagogy . Albany: State University of New York.
Wortham, Stanton. 2001. Narratives in Action: A Strategy for Research and Analysis . New York: Teachers College Press.
Inductive, Deductive, and Abductive Reasoning and Nomothetic Science in General
Aliseda, Atocha. 2003. “Mathematical Reasoning vs. Abductive Reasoning: A Structural Approach.” Synthese 134(1/2):25–44.
Bonk, Thomas. 1997. “Newtonian Gravity, Quantum Discontinuity and the Determination of Theory by Evidence.” Synthese 112(1):53–73. A (natural) scientific discussion of inductive reasoning.
Bonnell, Victoria E. 1980. “The Uses of Theory, Concepts and Comparison in Historical Sociology.” C omparative Studies in Society and History 22(2):156–173.
Crane, Mark, and Michael C. Newman. 1996. “Scientific Method in Environmental Toxicology.” Environmental Reviews 4(2):112–122.
Huang, Philip C. C., and Yuan Gao. 2015. “Should Social Science and Jurisprudence Imitate Natural Science?” Modern China 41(2):131–167.
Mingers, J. 2012. “Abduction: The Missing Link between Deduction and Induction. A Comment on Ormerod’s ‘Rational Inference: Deductive, Inductive and Probabilistic Thinking.’” Journal of the Operational Research Society 63(6):860–861.
Ormerod, Richard J. 2010. “Rational Inference: Deductive, Inductive and Probabilistic Thinking.” Journal of the Operational Research Society 61(8):1207–1223.
Perry, Charner P. 1927. “Inductive vs. Deductive Method in Social Science Research.” Southwestern Political and Social Science Quarterly 8(1):66–74.
Plutynski, Anya. 2011. “Four Problems of Abduction: A Brief History.” HOPOS: The Journal of the International Society for the History of Philosophy of Science 1(2):227–248.
Thompson, Bruce, and Gloria M. Borrello. 1992. “Different Views of Love: Deductive and Inductive Lines of Inquiry.” Current Directions in Psychological Science 1(5):154–156.
Tracy, Sarah J. 2012. “The Toxic and Mythical Combination of a Deductive Writing Logic for Inductive Qualitative Research.” Qualitative Communication Research 1(1):109–141.
A place or collection containing records, documents, or other materials of historical interest; most universities have an archive of material related to the university’s history, as well as other “special collections” that may be of interest to members of the community.
A person who introduces the researcher to a field site’s culture and population. Also referred to as guides. Used in ethnography .
A form of research and a methodological tradition of inquiry in which the researcher uses self-reflection and writing to explore personal experiences and connect this autobiographical story to wider cultural, political, and social meanings and understandings. “Autoethnography is a research method that uses a researcher's personal experience to describe and critique cultural beliefs, practices, and experiences” ( Adams, Jones, and Ellis 2015 ).
The philosophical framework in which research is conducted; the approach to “research” (what practices this entails, etc.). Inevitably, one’s epistemological perspective will also guide one’s methodological choices, as in the case of a constructivist who employs a Grounded Theory approach to observations and interviews, or an objectivist who surveys key figures in an organization to find out how that organization is run. One of the key methodological distinctions in social science research is that between quantitative and qualitative research.
The process of labeling and organizing qualitative data to identify different themes and the relationships between them; a way of simplifying data to allow better management and retrieval of key themes and illustrative passages. See coding frame and codebook.
A later stage coding process used in Grounded Theory in which data is reassembled around a category, or axis.
A later stage-coding process used in Grounded Theory in which key words or key phrases capture the emergent theory.
The point at which you can conclude data collection because every person you are interviewing, the interaction you are observing, or content you are analyzing merely confirms what you have already noted. Achieving saturation is often used as the justification for the final sample size.
A methodological tradition of inquiry that focuses on the meanings held by individuals and/or groups about a particular phenomenon (e.g., a “phenomenology of whiteness” or a “phenomenology of first-generation college students”). Sometimes this is referred to as understanding “the lived experience” of a particular group or culture. Interviews form the primary tool of data collection for phenomenological studies. Derived from the German philosophy of phenomenology (Husserl 1913; 2017).
The number of individuals (or units) included in your sample
A form of reasoning which employs a “top-down” approach to drawing conclusions: it begins with a premise or hypothesis and seeks to verify it (or disconfirm it) with newly collected data. Inferences are made based on widely accepted facts or premises. Deduction is idea-first, followed by observations and a conclusion. This form of reasoning is often used in quantitative research and less often in qualitative research. Compare to inductive reasoning . See also abductive reasoning .
A form of reasoning that employs a “bottom-up” approach to drawing conclusions: it begins with the collection of data relevant to a particular question and then seeks to build an argument or theory based on an analysis of that data. Induction is observation first, followed by an idea that could explain what has been observed. This form of reasoning is often used in qualitative research and seldom used in qualitative research. Compare to deductive reasoning . See also abductive reasoning .
An “interpretivist” form of reasoning in which “most likely” conclusions are drawn, based on inference. This approach is often used by qualitative researchers who stress the recursive nature of qualitative data analysis. Compare with deductive reasoning and inductive reasoning .
A form of social science research that generally follows the scientific method as established in the natural sciences. In contrast to idiographic research , the nomothetic researcher looks for general patterns and “laws” of human behavior and social relationships. Once discovered, these patterns and laws will be expected to be widely applicable. Quantitative social science research is nomothetic because it seeks to generalize findings from samples to larger populations. Most qualitative social science research is also nomothetic, although generalizability is here understood to be theoretical in nature rather than statistical . Some qualitative researchers, however, espouse the idiographic research paradigm instead.
Introduction to Qualitative Research Methods Copyright © 2023 by Allison Hurst is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Introducing Research Questions & Hypotheses in a Proposal or Thesis
Introducing Research Questions & Hypotheses in a Proposal or Thesis Not all proposals (or theses) introduce explicit research questions and hypotheses, but most doctoral research is based on questions and hypotheses whether they are openly stated or not. Research questions are the questions you ask about the topic, problem or phenomenon you are exploring in order to guide and shape your research, while hypotheses are the tentative working answers you develop based on previous scholarship, predominant theories, natural laws and tendencies, and your own assumptions and expectations. Determining exactly what your research questions and hypotheses are can help you define and understand your research more clearly, and including them in your introduction not only allows you to focus on the exact wording and content of those questions and hypotheses, but also opens the door to commentary and assistance from your supervisor and other members of your thesis committee. Your research questions and hypotheses will undoubtedly be closely related to the aims and objectives of your research, and, like those aims and objectives, they can be effectively included in your introduction by displaying them in a list and/or numbering them in order of importance or in relation to your methodology. Finally, outlining the contents of the proposal (or thesis) as a whole is traditional in an introduction, so a brief summary of the chapters and other sections that follow the introduction usually closes an introduction. In a proposal introduction, this may cover only what you include in the proposal itself or it may also include chapters and sections that have not yet been written, but will ultimately appear in the final thesis. Your supervisor will be able to tell you which approach is most appropriate for the proposal stage of a thesis in your discipline and department. In the introduction for the thesis itself, however, the contents of the entire thesis should, of course, be considered in the summary. PhD Thesis Editing Services Not all of the elements I have mentioned in this and previous postings on the proposal process will necessarily be required in any given proposal (or thesis) introduction, and in some introductions, further elements may be needed. University or department guidelines or the advice you receive from your thesis committee may necessitate presenting the elements of your introduction in separate sections, which are always a good idea because they make your text more accessible and digestible for readers. You may also need to present these sections in a specific order, or you may be able to arrange them in whatever order seems most appropriate for providing the introductory material your proposal (and thesis) requires. If you are in doubt about how to organise your introduction (which can be a notoriously difficult chapter to organise in an effective manner), remember that your supervisor and the other members of your thesis committee may be able to offer practical advice regarding what might be effectively rearranged, added, deleted, shortened, clarified or expanded, so do address the problem with them as you work on your chapter and again in the proposal meeting if necessary.
Why Our Editing and Proofreading Services? At Proof-Reading-Service.com we offer the highest quality journal article editing , phd thesis editing and proofreading services via our large and extremely dedicated team of academic and scientific professionals. All of our proofreaders are native speakers of English who have earned their own postgraduate degrees, and their areas of specialisation cover such a wide range of disciplines that we are able to help our international clientele with research editing to improve and perfect all kinds of academic manuscripts for successful publication. Many of the carefully trained members of our expert editing and proofreading team work predominantly on articles intended for publication in scholarly journals, applying painstaking journal editing standards to ensure that the references and formatting used in each paper are in conformity with the journal’s instructions for authors and to correct any grammar, spelling, punctuation or simple typing errors. In this way, we enable our clients to report their research in the clear and accurate ways required to impress acquisitions proofreaders and achieve publication.
Our scientific proofreading services for the authors of a wide variety of scientific journal papers are especially popular, but we also offer manuscript proofreading services and have the experience and expertise to proofread and edit manuscripts in all scholarly disciplines, as well as beyond them. We have team members who specialise in medical proofreading services , and some of our experts dedicate their time exclusively to PhD proofreading and master’s proofreading , offering research students the opportunity to improve their use of formatting and language through the most exacting PhD thesis editing and dissertation proofreading practices. Whether you are preparing a conference paper for presentation, polishing a progress report to share with colleagues, or facing the daunting task of editing and perfecting any kind of scholarly document for publication, a qualified member of our professional team can provide invaluable assistance and give you greater confidence in your written work.
If you are in the process of preparing an article for an academic or scientific journal, or planning one for the near future, you may well be interested in a new book, Guide to Journal Publication , which is available on our Tips and Advice on Publishing Research in Journals website.
Guide to Academic and Scientific Publication
How to get your writing published in scholarly journals.
It provides practical advice on planning, preparing and submitting articles for publication in scholarly journals.
PhD Success
How to write a doctoral thesis.
If you are in the process of preparing a PhD thesis for submission, or planning one for the near future, you may well be interested in the book, How to Write a Doctoral Thesis , which is available on our thesis proofreading website.
PhD Success: How to Write a Doctoral Thesis provides guidance for students familiar with English and the procedures of English universities, but it also acknowledges that many theses in the English language are now written by candidates whose first language is not English, so it carefully explains the scholarly styles, conventions and standards expected of a successful doctoral thesis in the English language.
Why Is Proofreading Important?
To improve the quality of papers.
Effective proofreading is absolutely vital to the production of high-quality scholarly and professional documents. When done carefully, correctly and thoroughly, proofreading can make the difference between writing that communicates successfully with its intended readers and writing that does not. No author creates a perfect text without reviewing, reflecting on and revising what he or she has written, and proofreading is an extremely important part of this process.

Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Welcome to the Purdue Online Writing Lab

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
The Online Writing Lab at Purdue University houses writing resources and instructional material, and we provide these as a free service of the Writing Lab at Purdue. Students, members of the community, and users worldwide will find information to assist with many writing projects. Teachers and trainers may use this material for in-class and out-of-class instruction.
The Purdue On-Campus Writing Lab and Purdue Online Writing Lab assist clients in their development as writers—no matter what their skill level—with on-campus consultations, online participation, and community engagement. The Purdue Writing Lab serves the Purdue, West Lafayette, campus and coordinates with local literacy initiatives. The Purdue OWL offers global support through online reference materials and services.
A Message From the Assistant Director of Content Development
The Purdue OWL® is committed to supporting students, instructors, and writers by offering a wide range of resources that are developed and revised with them in mind. To do this, the OWL team is always exploring possibilties for a better design, allowing accessibility and user experience to guide our process. As the OWL undergoes some changes, we welcome your feedback and suggestions by email at any time.
Please don't hesitate to contact us via our contact page if you have any questions or comments.
All the best,
Social Media
Facebook twitter.
Academic Experience
Great survey questions: How to write them & avoid common mistakes
Learning how to write survey questions is both art and science. The wording you choose can make the difference between accurate, useful data and just the opposite. Fortunately, we’ve got a raft of tips to help.
Figuring out how to make a good survey that yields actionable insights is all about sweating the details. And writing effective questionnaire questions is the first step.
Essential for success is understanding the different types of survey questions and how they work. Each format needs a slightly different approach to question-writing.
In this article, we’ll share how to write survey questionnaires and list some common errors to avoid so you can improve your surveys and the data they provide.
Free eBook: The Qualtrics survey template guide
Survey question types
Did you know that Qualtrics provides 23 question types you can use in your surveys ? Some are very popular and used frequently by a wide range of people from students to market researchers, while others are more specialist and used to explore complex topics. Here’s an introduction to some basic survey question formats, and how to write them well.
Multiple choice
Familiar to many, multiple choice questions ask a respondent to pick from a range of options. You can set up the question so that only one selection is possible, or allow more than one to be ticked.
When writing a multiple choice question…
- Be clear about whether the survey taker should choose one (“pick only one”) or several (“select all that apply”).
- Think carefully about the options you provide, since these will shape your results data.
- The phrase “of the following” can be helpful for setting expectations. For example, if you ask “What is your favorite meal” and provide the options “hamburger and fries”, “spaghetti and meatballs”, there’s a good chance your respondent’s true favorite won’t be included. If you add “of the following” the question makes more sense.
Asking participants to rank things in order, whether it’s order of preference, frequency or perceived value, is done using a rank structure. There can be a variety of interfaces, including drag-and-drop, radio buttons, text boxes and more.
When writing a rank order question…
- Explain how the interface works and what the respondent should do to indicate their choice. For example “drag and drop the items in this list to show your order of preference.”
- Be clear about which end of the scale is which. For example, “With the best at the top, rank these items from best to worst”
- Be as specific as you can about how the respondent should consider the options and how to rank them. For example, “thinking about the last 3 months’ viewing, rank these TV streaming services in order of quality, starting with the best”
Slider structures ask the respondent to move a pointer or button along a scale, usually a numerical one, to indicate their answers.
When writing a slider question…
- Consider whether the question format will be intuitive to your respondents, and whether you should add help text such as “click/tap and drag on the bar to select your answer”
- Qualtrics includes the option for an open field where your respondent can type their answer instead of using a slider. If you offer this, make sure to reference it in the survey question so the respondent understands its purpose.
Also known as an open field question, this format allows survey-takers to answer in their own words by typing into the comments box.
When writing a text entry question…
- Use open-ended question structures like “How do you feel about…” “If you said x, why?” or “What makes a good x?”
- Open-ended questions take more effort to answer, so use these types of questions sparingly.
- Be as clear and specific as possible in how you frame the question. Give them as much context as you can to help make answering easier. For example, rather than “How is our customer service?”, write “Thinking about your experience with us today, in what areas could we do better?”
Matrix table
Matrix structures allow you to address several topics using the same rating system, for example a Likert scale (Very satisfied / satisfied / neither satisfied nor dissatisfied / dissatisfied / very dissatisfied).
When writing a matrix table question…
- Make sure the topics are clearly differentiated from each other, so that participants don’t get confused by similar questions placed side by side and answer the wrong one.
- Keep text brief and focused. A matrix includes a lot of information already, so make it easier for your survey-taker by using plain language and short, clear phrases in your matrix text.
- Add detail to the introductory static text if necessary to help keep the labels short. For example, if your introductory text says “In the Philadelphia store, how satisfied were you with the…” you can make the topic labels very brief, for example “staff friendliness” “signage” “price labeling” etc.
Now that you know your rating scales from your open fields, here are the 7 most common mistakes to avoid when you write questions. We’ve also added plenty of survey question examples to help illustrate the points.
Likert Scale Questions
Likert scales are commonly used in market research when dealing with single topic survyes. They're simple and most reliable when combatting survey bias . For each question or statement, subjects choose from a range of possible responses. The responses, for example, typically include:
- Strongly agree
- Strongly disagree
7 survey question examples to avoid.
There are countless great examples of writing survey questions but how do you know if your types of survey questions will perform well? We've highlighted the 7 most common mistakes when attempting to get customer feedback with online surveys.
Survey question mistake #1: Failing to avoid leading words / questions
Subtle wording differences can produce great differences in results. For example, non-specific words and ideas can cause a certain level of confusing ambiguity in your survey. “Could,” “should,” and “might” all sound about the same, but may produce a 20% difference in agreement to a question.
In addition, strong words such as “force” and “prohibit” represent control or action and can bias your results.
Example: The government should force you to pay higher taxes.
No one likes to be forced, and no one likes higher taxes. This agreement scale question makes it sound doubly bad to raise taxes. When survey questions read more like normative statements than questions looking for objective feedback, any ability to measure that feedback becomes difficult.
Wording alternatives can be developed. How about simple statements such as: The government should increase taxes, or the government needs to increase taxes.
Example: How would you rate the career of legendary outfielder Joe Dimaggio?
This survey question tells you Joe Dimaggio is a legendary outfielder. This type of wording can bias respondents.
How about replacing the word “legendary” with “baseball” as in: How would you rate the career of baseball outfielder Joe Dimaggio? A rating scale question like this gets more accurate answers from the start.
Survey question mistake #2: Failing to give mutually exclusive choices
Multiple choice response options should be mutually exclusive so that respondents can make clear choices. Don’t create ambiguity for respondents.
Review your survey and identify ways respondents could get stuck with either too many or no single, correct answers to choose from.
Example: What is your age group?
What answer would you select if you were 10, 20, or 30? Survey questions like this will frustrate a respondent and invalidate your results.
Example: What type of vehicle do you own?
This question has the same problem. What if the respondent owns a truck, hybrid, convertible, cross-over, motorcycle, or no vehicle at all?
Survey question mistake #3: Not asking direct questions
Questions that are vague and do not communicate your intent can limit the usefulness of your results. Make sure respondents know what you’re asking.
Example: What suggestions do you have for improving Tom’s Tomato Juice?
This question may be intended to obtain suggestions about improving taste, but respondents will offer suggestions about texture, the type of can or bottle, about mixing juices, or even suggestions relating to using tomato juice as a mixer or in recipes.
Example: What do you like to do for fun?
Finding out that respondents like to play Scrabble isn’t what the researcher is looking for, but it may be the response received. It is unclear that the researcher is asking about movies vs. other forms of paid entertainment. A respondent could take this question in many directions.
Survey question mistake #4: Forgetting to add a “prefer not to answer” option
Sometimes respondents may not want you to collect certain types of information or may not want to provide you with the types of information requested.
Questions about income, occupation, personal health, finances, family life, personal hygiene, and personal, political, or religious beliefs can be too intrusive and be rejected by the respondent.
Privacy is an important issue to most people. Incentives and assurances of confidentiality can make it easier to obtain private information.
While current research does not support that PNA (Prefer Not to Answer) options increase data quality or response rates, many respondents appreciate this non-disclosure option.
Furthermore, different cultural groups may respond differently. One recent study found that while U.S. respondents skip sensitive questions, Asian respondents often discontinue the survey entirely.
- What is your race?
- What is your age?
- Did you vote in the last election?
- What are your religious beliefs?
- What are your political beliefs?
- What is your annual household income?
These types of questions should be asked only when absolutely necessary. In addition, they should always include an option to not answer. (e.g. “Prefer Not to Answer”).
Survey question mistake #5: Failing to cover all possible answer choices
Do you have all of the options covered? If you are unsure, conduct a pretest version of your survey using “Other (please specify)” as an option.
If more than 10% of respondents (in a pretest or otherwise) select “other,” you are probably missing an answer. Review the “Other” text your test respondents have provided and add the most frequently mentioned new options to the list.
Example: You indicated that you eat at Joe's fast food once every 3 months. Why don't you eat at Joe's more often?
There isn't a location near my house
I don't like the taste of the food
Never heard of it
This question doesn’t include other options, such as healthiness of the food, price/value or some “other” reason. Over 10% of respondents would probably have a problem answering this question.
Survey question mistake #6: Not using unbalanced scales carefully
Unbalanced scales may be appropriate for some situations and promote bias in others.
For instance, a hospital might use an Excellent - Very Good - Good - Fair scale where “Fair” is the lowest customer satisfaction point because they believe “Fair” is absolutely unacceptable and requires correction.
The key is to correctly interpret your analysis of the scale. If “Fair” is the lowest point on a scale, then a result slightly better than fair is probably not a good one.
Additionally, scale points should represent equi-distant points on a scale. That is, they should have the same equal conceptual distance from one point to the next.
For example, researchers have shown the points to be nearly equi-distant on the strongly disagree–disagree–neutral–agree–strongly agree scale.
Set your bottom point as the worst possible situation and top point as the best possible, then evenly spread the labels for your scale points in-between.
Example: What is your opinion of Crazy Justin's auto-repair?
Pretty good
The Best Ever
This question puts the center of the scale at fantastic, and the lowest possible rating as “Pretty Good.” This question is not capable of collecting true opinions of respondents.
Survey question mistake #7: Not asking only one question at a time
There is often a temptation to ask multiple questions at once. This can cause problems for respondents and influence their responses.
Review each question and make sure it asks only one clear question.
Example: What is the fastest and most economical internet service for you?
This is really asking two questions. The fastest is often not the most economical.
Example: How likely are you to go out for dinner and a movie this weekend?
Dinner and Movie
Dinner Only
Even though “dinner and a movie” is a common term, this is two questions as well. It is best to separate activities into different questions or give respondents these options:
5 more tips on how to write a survey
Here are 5 easy ways to help ensure your survey results are unbiased and actionable.
1. Use the Funnel Technique
Structure your questionnaire using the “funnel” technique. Start with broad, general interest questions that are easy for the respondent to answer. These questions serve to warm up the respondent and get them involved in the survey before giving them a challenge. The most difficult questions are placed in the middle – those that take time to think about and those that are of less general interest. At the end, we again place general questions that are easier to answer and of broad interest and application. Typically, these last questions include demographic and other classification questions.
2. Use “Ringer” questions
In social settings, are you more introverted or more extroverted?
That was a ringer question and its purpose was to recapture your attention if you happened to lose focus earlier in this article.
Questionnaires often include “ringer” or “throw away” questions to increase interest and willingness to respond to a survey. These questions are about hot topics of the day and often have little to do with the survey. While these questions will definitely spice up a boring survey, they require valuable space that could be devoted to the main topic of interest. Use this type of question sparingly.
3. Keep your questionnaire short
Questionnaires should be kept short and to the point. Most long surveys are not completed, and the ones that are completed are often answered hastily. A quick look at a survey containing page after page of boring questions produces a response of, “there is no way I’m going to complete this thing”. If a questionnaire is long, the person must either be very interested in the topic, an employee, or paid for their time. Web surveys have some advantages because the respondent often can't view all of the survey questions at once. However, if your survey's navigation sends them page after page of questions, your response rate will drop off dramatically.
How long is too long? The sweet spot is to keep the survey to less than five minutes. This translates into about 15 questions. The average respondent is able to complete about 3 multiple choice questions per minute. An open-ended text response question counts for about three multiple choice questions depending, of course, on the difficulty of the question. While only a rule of thumb, this formula will accurately predict the limits of your survey.
4. Watch your writing style
The best survey questions are always easy to read and understand. As a rule of thumb, the level of sophistication in your survey writing should be at the 9th to 11th grade level. Don’t use big words. Use simple sentences and simple choices for the answers. Simplicity is always best.
5. Use randomization
We know that being the first on the list in elections increases the chance of being elected. Similar bias occurs in all questionnaires when the same answer appears at the top of the list for each respondent. Randomization corrects this bias by randomly rotating the order of the multiple choice matrix questions for each respondent.
Free Templates: Get free access to 30+ of Qualtrics' best survey templates
While not totally inclusive, these seven survey question tips are common offenders in building good survey questions. And the five tips above should steer you in the right direction.
Focus on creating clear questions and having an understandable, appropriate, and complete set of answer choices. Great questions and great answer choices lead to great research success. To learn more about survey question design, download our eBook, The Qualtrics survey template guide or get started with a free survey account with our world-class survey software .
Sarah Fisher
Related Articles
February 8, 2023
Smoothing the transition from school to work with work-based learning
December 6, 2022
How customer experience helps bring Open Universities Australia’s brand promise to life
August 18, 2022
School safety, learning gaps top of mind for parents this back-to-school season
August 9, 2022
3 things that will improve your teachers’ school experience
August 2, 2022
Why a sense of belonging at school matters for K-12 students
July 14, 2022
Improve the student experience with simplified course evaluations
March 17, 2022
Understanding what’s important to college students
February 18, 2022
Malala: ‘Education transforms lives, communities, and countries’
Stay up to date with the latest xm thought leadership, tips and news., request demo.
Ready to learn more about Qualtrics?

How to Answer the Interview Question: “Tell Me About Yourself”

- Share article on Twitter
- Share article on Facebook
- Share article on LinkedIn
It sounds like the easiest question you can get in an interview, but it’s often the hardest to answer: “Tell me about yourself.” It can be overwhelming to summarize your entire life in a few sentences, but luckily that’s not what you actually need to do. We’ve gathered perspectives from a recruiter and hiring managers so you can confidently introduce yourself in a job interview.
What are they really asking?
This interview question is usually one of the first, and while it’s just an icebreaker on the surface, “the fact that it’s such a broad question is actually a test in itself,” says Jean du Plessis , Senior Engineering Manager at cloud platform Upbound . “They will be looking to see how you respond to an open-ended question and if you can be articulate.”
Learn something new for free
- Intro to ChatGPT
Interviewers are also likely to be assessing how well you understand the industry, role, and company you’re applying to, based on what skills, experience, or anecdotes you choose to highlight in your answer. This is your chance to surface anything that you feel aligns your profile to the opportunity, says Lucy Jones, Headhunter and Director of the Executive Search firm Lawson Brooke . “Number one, before you join the interview: Do your research .”
By the time you meet with a hiring manager, you will have seen a job description and may even have had an initial screening call with someone from the company. “So, you’ve already got a load of intel to help decide which key things from your experience to surface when asked that question,” says Lucy.
Be succinct and curate your story
Remember: You don’t need to regurgitate what’s on your resume — the interviewer might even have your resume on-hand to reference during your conversation. “You can set the expectation with the interviewer around what you’re going to constrain your answer to,” Jean says.
For example, you might choose to focus on roles or aspects of your experience that are transferrable to the position or the type of customer the company serves. “The interviewer can always ask follow-up questions, but having a clear point of view of what you want to share about helps you keep your answer brief and easy to follow,” Jean says.
Curating the story you want to tell about your career ahead of time helps you start the interview on the right foot. You don’t want to go into the rest of the interview feeling flustered because you rambled. Giving a concise, confident answer is like giving a firm handshake, says Jean. “This is the virtual equivalent.”

How to answer “Tell me about yourself” if you’re changing careers
If your background isn’t an obvious fit for the role, this question gives you an opportunity to explain what led you to this point. “I like to see that there’s a narrative thread throughout your work,” says Lisa Tagliaferri , Senior Director of Developer Enablement at the cybersecurity company Chainguard . In addition to her full-time role, Lisa is an interdisciplinary researcher across the humanities and technology and has interviewed many candidates making career changes.
“Think about your personal mission or the themes of your work that have stayed consistent from previous roles,” Lisa says. “You can go through multiple career shifts throughout your life, but there’s usually a common thread you can bring to light.”
For instance, transitioning from teaching to software development might stem from a shared desire to help people, Lisa says. ( Codecademy learner Pj Metz was a high school English teacher when he landed a developer relations job focusing on students and teachers at GitLab.)
Highlighting your passion for teamwork and mentoring or showcasing technology-focused creative projects can add depth to your story, Lisa suggests. “Giving that color and showing your broader interests is a positive thing,” she says.
Sample answer for a career changer
“My name is Adriana, and I currently work as an English teacher. My professional background has primarily been in education, but I’ve always had an interest in technology and its potential to transform learning experiences. I’ve actively incorporated technology educational software and online platforms into my teaching methods to boost student engagement. Through my experience in education, I’ve developed strong communication skills, a knack for problem-solving, and a passion for continuous learning — qualities I believe are highly transferable to the technology field. Recently, I’ve been exploring coding through online courses and have completed several projects that my students and I use in the classroom. I’m drawn to the technology field because of its dynamic nature and its potential to drive innovation and change. I’m particularly excited about the opportunity to leverage my skills and experiences in a new context and to contribute to technological advancements that positively impact society.”
How to answer “Tell me about yourself” if you’re early in your career
You might be light on work experience, but have a wealth of relevant life experience to draw from, Lisa says. “Before you go on the job market, there are ways to do meaningful development projects that showcase your work — from a technical perspective but also from a mission-driven perspective,” she says.
Lisa worked with Computer Science undergraduate students at MIT who were doing Python projects for the digital humanities, ranging from literature and history to music . Some students conducted data analysis on online public archives. “Those students could talk about how history [for example] was important to them in the context of a group development project,” says Lisa. “Those examples are great signal to interviewers that you see how the software you make can be useful in different contexts, and you’re excited about the application of what you build.”
Contributing to open-source code or documentation, or even participating in communities related to your areas of interest are also good examples to highlight. That time spent interacting with your course mates in the Codecademy Forums and contributing to Docs will be worth it!
Sample answer for an entry-level job seeker
“I’m Amrit, a visual art student passionate about leveraging creativity in functional design. While my background is in visual arts, I’ve honed skills in UI/UX design through personal projects. I’ve explored design principles, prototyping, and user research, aiming to create intuitive and visually appealing digital experiences. Last semester I volunteered to re-design a mobile app for our local food co-op. I’m eager to apply my artistic sensibility and design expertise to make digital interfaces more accessible.”
Be authentic and show your personality
You already made it to the interview, which is a strong signal that you meet the minimum hard skills requirements. Now you get to show them what you’re like to work with as a human and set the tone for the rest of your interview.
“The best interviewees, the ones that leave a lasting impression, are the ones that I enjoyed a conversation with,” Jean says. It’s normal to feel nervous, but use that energy to showcase yourself authentically.
Be yourself and inject personal anecdotes to paint a fuller picture of who you are. “This is your one opportunity to make an impression outside of the role-specific requirements, so make an effort to share something interesting about you,” Jean says. And while you do want to be prepared, avoid sounding rehearsed by preparing some bullet points of what you want to share.
Want to practice introducing yourself in an interview? Try out our new beta Interview Simulator : Build a mock interview based on the job title, level, type of interview and company and your own experience, then practice giving written or spoken responses. The AI interviewer is trained to ask intelligent follow-up questions like a recruiter and will provide you with feedback after the session.
Related courses
Front-end engineer, pass the technical interview with python, back-end engineer, technical interview practice with python, full-stack engineer, subscribe for news, tips, and more, related articles.

How I Went from Translator to Engineering Apprentice in 7 Months
Today’s story is from Lizzie Gardiner, a 29-year-old Engineering Apprentice, living in West Yorkshire, England.

9 Tech Organizations that Support the LGBTQ+ Community
Get involved with these organizations during Pride Month and beyond.

How To Tell If You’re “Proficient In Excel” & How To Get Better
Plus, common Excel interview questions and how to answer them.

How I Went from Pharmaceutical Research to Data Analysis in 3 Years
Today’s story is from Mathijs Gaastra, a 34-year-old Web Developer and Data Analyst at a startup in Leiden, Netherlands.

How to Communicate Entry-Level Salary Expectations
You don’t have to show your cards. Here’s how to answer the salary expectations question.

Why Talking About Your Weaknesses Helps You in a Job Interview
Everyone has a weakness — here’s how to use yours to your advantage.

What Does an AI Engineer Do?
What does an AI Engineer do? Learn what AI is, what skills you need to be an AI Engineer, and how to become one.
- Trustworthy AI
Our trust in technology relies on understanding how it works. It’s important to understand why AI makes the decisions it does. We’re developing tools to make AI more explainable, fair, robust, private, and transparent.
Tiny benchmarks for large language models
- Foundation Models
IBM’s Granite model is one of the most transparent LLMs in the world

- AI Transparency
- Open Source
What is red teaming for generative AI?
- Adversarial Robustness and Privacy
- Fairness, Accountability, Transparency
- Natural Language Processing
An AI model trained on data that looks real but won’t leak personal information
- Data and AI Security
The latest AI safety method is a throwback to our maritime past

- Explainable AI
- Generative AI
What is AI alignment?
- Automated AI
- See more of our work on Trustworthy AI
- AI Testing We’re designing tools to help ensure that AI systems are trustworthy, reliable and can optimize business processes.
- Adversarial Robustness and Privacy We’re making tools to protect AI and certify its robustness, and helping AI systems adhere to privacy requirements.
- Explainable AI We’re creating tools to help AI systems explain why they made the decisions they did.
- Fairness, Accountability, Transparency We’re developing technologies to increase the end-to-end transparency and fairness of AI systems.
- Trustworthy Generation We’re developing theoretical and algorithmic frameworks for generative AI to accelerate future scientific discoveries.
- Uncertainty Quantification We’re developing ways for AI to communicate when it's unsure of a decision across the AI application development lifecycle.

Science for Social Good
IBM Science for Social Good partners IBM Research scientists and engineers with academic fellows, subject matter experts from NGOs, public sector agencies, and social enterprises to tackle emerging societal challenges using science and technology.
Publications
- Cynthia Dwork
- Kristjan Greenewald
- Frank Libsch
- Steve Bedell
- Assala Benmalek
- Celia Cintas
- Leshem Choshen
- LREC-COLING 2024
- Brian W. Bauer
- JMIR Mental Health
Building trustworthy AI with Watson
Our research is regularly integrated into Watson solutions to make IBM’s AI for business more transparent, explainable, robust, private, and fair.
What is digital-twin technology?

What would you do if you had a copy of yourself? A digital doppelgänger, identical to you in every way, in an accurate digital rendering of your home, workplace, neighborhood, or city? Even better: What if the digital version of you—your digital twin—was impervious to injury, pain, or embarrassment? The mind boggles at the possibilities. Suffice it to say, you’d probably be able to make decisions for yourself with a lot more certainty of the outcome.
Get to know and directly engage with senior McKinsey experts on digital-twin technology.
Kimberly Borden is a senior partner in McKinsey’s Chicago office. Anna Herlt is a senior partner in the Munich office. Tomás Lajous , Kayvaun Rowshankish , and Rodney W. Zemmel are senior partners in the New York office.
In business, this heightened degree of certainty is extremely valuable—and emerging digital twins may help deliver it.
Put simply, a digital twin is a virtual replica of a physical object, person, or process that can be used to simulate its behavior to better understand how it works in real life. Digital twins are linked to real data sources from the environment, which means that the twin updates in real time to reflect the original version. Digital twins also comprise a layer of behavioral insights and visualizations derived from data. When interconnected within one system, digital twins can form what’s known as an enterprise metaverse : a digital and often immersive environment that replicates and connects every aspect of an organization to optimize simulations, scenario planning, and decision making .
There are a few different types of digital twins. First, there’s a product twin, which is a representation of a product . This digital twin can include products at various stages of the life cycle, from initial concept design and engineering through to full functionality—meaning you get live, real-time data on a product as if it’s in service. One great example of a product twin is something you probably already have in your pocket: Google Maps is a digital twin of the Earth’s surface. It links real-time data on traffic to help optimize your commute.

Introducing McKinsey Explainers : Direct answers to complex questions
Other types of twins include production plant twins, which represent an entire manufacturing facility, or procurement and supply chain twins, also called network twins. And finally, infrastructure twins represent physical infrastructure such as a highway, a building, or even a stadium.
Digital twins have the potential to deliver more agile and resilient operations. And their potential isn’t lost on CEOs: McKinsey research indicates that 70 percent of C-suite technology executives at large enterprises are already exploring and investing in digital twins.
Read on to learn more about the value of digital twins and how to put them to use.
Learn more about McKinsey Digital and McKinsey’s Operations Practice .
What kind of value can digital twins bring to an organization?
One of the areas where digital twins can bring the most value is the reduction in time to market. Digital twins can allow for rapid iterations and optimizations of product designs—far faster than physically testing every single prototype. What’s more, digital twins can result in significant improvements in product quality. By simulating the product throughout the manufacturing process, it’s possible to identify flaws in the design much earlier. (“The companies that harness this first,” says McKinsey senior adviser Will Roper, referring to digital-manufacturing twins, “will really shake up the markets they’re in.”) And finally, by mirroring a product in service, it’s possible to create a single source of truth for how the design is functioning, allowing for real-time adjustment or redesign.
McKinsey has seen organizations post revenue increases of as much as 10 percent by developing digital twins of their customers, allowing those customers to fully interact and immerse themselves within a company’s product. Daimler, for example, has developed customer twins that allow customers to “test drive” a vehicle without ever getting behind the wheel.
How can digital twins affect an organization’s environmental sustainability?
Product digital twins can be particularly helpful in improving sustainability efforts. These digital twins can help organizations reduce the material used in a product’s design, as well as improve the traceability of a product to reduce environmental waste. Consumer electronics manufacturers have made significant improvements to sustainability by using digital twins, reducing scrap waste by roughly 20 percent .
Learn more about McKinsey’s Operations Practice .
How can an organization get started on building its first digital twin?
A key element an organization needs for implementing digital twins is digital maturity . This essentially means data: a high-quality data infrastructure that delivers reliable data from both testing and live environments, as well as the talent needed to build and maintain that infrastructure.
But that doesn’t have to mean that organizations need a complex or dynamic environment to benefit from a digital twin. Some companies are seeing success twinning products as simple as toothbrushes to gain real-time customer feedback. Then, once the initial use case is established, organizations can add more layers of information and real-time feedback to further improve the twin.
Building and scaling a digital twin requires a three-step approach:
- Create a blueprint . A blueprint should define the types of twins an organization will pursue, the order for building them to maximize value and reusability, the way their capabilities will evolve, and their ownership and governance structures.
- Build the base digital twin . A project team then builds the base digital twin over the next three to six months. This phase begins with assembling the core data product, which enables the development of visualizations and allows data science professionals to build out one or two initial use cases.
- Boost capabilities . Once a digital twin is running, an organization can expand its capabilities by adding more data layers and analytics to support new use cases. At this stage, organizations frequently advance their twins from simply representing assets, people, or processes to providing simulations and prescriptions through the use of AI and advanced modeling techniques.
What does the journey from digital twin to enterprise metaverse look like?
Companies can start their journey to an enterprise metaverse with one digital twin, modeled after one data product. A data product delivers a high-quality, ready-to-use data set that people across an organization can easily access and apply. It should be a single, reusable source of truth, enhanced over time, that can serve as the basis for future use cases. Eventually, a first digital twin can evolve based on learnings from behavioral data, ultimately providing increasingly powerful predictive capabilities.
From there, an organization can create multiple interconnected digital twins to simulate the complex relationships between different entities. This can generate richer behavior insights for even more sophisticated use cases—and greater value. For example, an organization might connect a digital twin of its customers with retail stores, inventory, sales, and customer process flows. In doing this, the organization could carry out the following:
- simulate end-to-end impact of business and market changes on retail stores
- create a true omnichannel experience that provides for seamless pause-and-resume customer journeys across channels
- optimize store layouts by responding to shifts in customer preferences
- assess different compensation and staffing models by sales, employee performance, and the characteristics of local stores
Finally, an organization with a healthy digital-twin network can layer on additional technologies required to create an enterprise metaverse. A retailer could, for instance, connect the digital twin of its retail store to digital twins of its warehouses, supply chain, call center, and more until every part of the organization has been replicated.
How are some companies already using digital twins?
Interest in digital twins, combined with rapidly advancing supportive technologies, is spurring market estimates for digital-twin investments of more than $48 billion by 2026 . We’re already seeing some advanced implementations:
- Emirates Team New Zealand. A digital twin of sailing environments, boats, and crew members enables Emirates Team New Zealand to test boat designs without actually building them. This has allowed the champion sailing team to evaluate thousands—rather than just hundreds—of hydrofoil designs.
- Anheuser-Busch InBev. A brewing and supply chain digital twin enables brewers to adjust inputs based on active conditions and can automatically compensate for production bottlenecks (for instance, when vats are full).
- SoFi Stadium. To help optimize stadium management and operations, a digital twin aggregates multiple data sources including information about the stadium’s structure and real-time football data.
- Space Force. This branch of the US Armed Forces is creating a digital twin of space, including replicas of extraterrestrial bodies and satellites.
- SpaceX. A digital twin of the SpaceX’s Dragon capsule spacecraft enables operators to monitor and adjust trajectories, loads, and propulsion systems with the goal of maximizing safety and reliability during transport.
Learn more about McKinsey Digital and McKinsey’s Operations Practice , and explore digital-operations-related job opportunities if you’re interested in working at McKinsey.
Articles referenced:
- “ Digital twins: Flying high, flexing fast ,” November 16, 2022, Kimberly Borden
- “ Digital twins: What could they do for your business? ,” October 3, 2022, Kimberly Borden and Anna Herlt
- “ Digital twins: The foundation of the enterprise metaverse ,” October 2022, Joshan Abraham, Guilherme Cruz, Sebastian Cubela, Tomás Lajous , Kayvaun Rowshankish , Sanchit Tiwari, and Rodney Zemmel
- “ Digital twins: The art of the possible in product development and beyond ,” April 28, 2022, Mickael Brossard , Sebastien Chaigne, Jacomo Corbo, Bernhard Mühlreiter , and Jan Paul Stein
- “ Flying across the sea, propelled by AI ,” March 17, 2021

Want to know more about digital-twin technology?
Related articles.

What is the metaverse?

Digital twins: The foundation of the enterprise metaverse

Digital twins: Flying high, flexing fast

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The first question asks for a ready-made solution, and is not focused or researchable. The second question is a clearer comparative question, but note that it may not be practically feasible. For a smaller research project or thesis, it could be narrowed down further to focus on the effectiveness of drunk driving laws in just one or two countries.
Define your specific research problem and problem statement. Highlight the novelty and contributions of the study. Give an overview of the paper's structure. The research paper introduction can vary in size and structure depending on whether your paper presents the results of original empirical research or is a review paper.
Research paper introduction is the first section of a research paper that provides an overview of the study, its purpose, and the research question (s) or hypothesis (es) being investigated. It typically includes background information about the topic, a review of previous research in the field, and a statement of the research objectives.
Types of research questions. Now that we've defined what a research question is, let's look at the different types of research questions that you might come across. Broadly speaking, there are (at least) four different types of research questions - descriptive, comparative, relational, and explanatory. Descriptive questions ask what is happening. In other words, they seek to describe a ...
1. Start with a broad topic. A broad topic provides writers with plenty of avenues to explore in their search for a viable research question. Techniques to help you develop a topic into subtopics and potential research questions include brainstorming and concept mapping.
Choose a broad topic, such as "learner support" or "social media influence" for your study. Select topics of interest to make research more enjoyable and stay motivated. Preliminary research. The goal is to refine and focus your research question. The following strategies can help: Skim various scholarly articles.
This video from the UMD, Global Campus gives a good introduction to research questions. What is a research question? Once you have selected a topic, you need to develop a research question. You may be used to working with a thesis statement, but a thesis statement is an answer. If you start your research with an answer, you might miss something ...
Most professional researchers focus on topics they are genuinely interested in studying. Writers should choose a broad topic about which they genuinely would like to know more. An example of a general topic might be "Slavery in the American South" or "Films of the 1930s.". Do some preliminary research on your general topic.
The introduction leads the reader from a general subject area to a particular topic of inquiry. It establishes the scope, context, and significance of the research being conducted by summarizing current understanding and background information about the topic, stating the purpose of the work in the form of the research problem supported by a hypothesis or a set of questions, explaining briefly ...
Research Aims: Examples. True to the name, research aims usually start with the wording "this research aims to…", "this research seeks to…", and so on. For example: "This research aims to explore employee experiences of digital transformation in retail HR.". "This study sets out to assess the interaction between student ...
Download Article. 1. Announce your research topic. You can start your introduction with a few sentences which announce the topic of your paper and give an indication of the kind of research questions you will be asking. This is a good way to introduce your readers to your topic and pique their interest.
Good writing begins with clearly stating your research question (or hypothesis) in the Introduction section —the focal point on which your entire paper builds and unfolds in the subsequent Methods, Results, and Discussion sections. This research question or hypothesis that goes into the first section of your research manuscript, the ...
Try to avoid an overly long introduction. A good target is 500 to 1000 words, although checking the journal's guidelines and past issues will provide the clearest guidance. 8. Show, don't tell. One goal of the introduction is explaining why your research topic is worthy of study.
Example Research Question (s) Here are examples of research problems and research questions to help you understand how to create a research question for a given research problem. Example Research Problem. Example Research Question (s) A small-scale company, 'A' in the UK, cannot allocate a marketing budget for next year due to their poor ...
Provide a background of the problem you wish to study. Explain why you have undertaken the study. Describes your research problem. Summarizes the existing knowledge related to your topic. Highlights the contribution that your research will make to your field. States your research question clearly. You can look up these resources to have a clear ...
A good research question is manageable in scope - not too broad, but not too narrow. If your topic is too broad, you may become overwhelmed with the amount of information and find it difficult to organize your ideas. If your topic is too narrow, you may not be able to find enough information to include in your literature review.
A research problem is a definite or clear expression [statement] about an area of concern, a condition to be improved upon, a difficulty to be eliminated, or a troubling question that exists in scholarly literature, in theory, or within existing practice that points to a need for meaningful understanding and deliberate investigation.
Definition: Research Question. A research question is a concise inquiry that guides the direction of a research study or investigation. It articulates the specific type of subject that the researcher aims to explore, often framed in a way that suggests investigation or analysis.It serves as a fundamental element in the research process, guiding the selection of appropriate methodologies, the ...
The type of research problem you choose depends on your broad topic of interest and the type of research you think will fit best. This article helps you identify and refine a research problem. When writing your research proposal or introduction, formulate it as a problem statement and/or research questions.
A good research question is specific, clear, and feasible. Specific. How specific a research question needs to be is somewhat related to the disciplinary conventions and whether the study is conceived inductively or deductively. In deductive research, one begins with a specific research question developed from the literature.
Introducing Research Questions & Hypotheses in a Proposal or Thesis Not all proposals (or theses) introduce explicit research questions and hypotheses, but most doctoral research is based on questions and hypotheses whether they are openly stated or not. Research questions are the questions you ask about the topic, problem or phenomenon you are ...
Mission. The Purdue On-Campus Writing Lab and Purdue Online Writing Lab assist clients in their development as writers—no matter what their skill level—with on-campus consultations, online participation, and community engagement. The Purdue Writing Lab serves the Purdue, West Lafayette, campus and coordinates with local literacy initiatives.
Here's an introduction to some basic survey question formats, and how to write them well. Multiple choice. Familiar to many, multiple choice questions ask a respondent to pick from a range of options. ... Great questions and great answer choices lead to great research success. To learn more about survey question design, download our eBook, ...
Question 1: Is the seller licensed? Research shows that con-artists are experts at the art of persuasion, often using a variety of influence tactics tailored to the vulnerabilities of their victims. Smart investors check the background of anyone promoting an investment opportunity, even before learning about opportunity itself. website.
Sample answer for an entry-level job seeker. "I'm Amrit, a visual art student passionate about leveraging creativity in functional design. While my background is in visual arts, I've honed skills in UI/UX design through personal projects. I've explored design principles, prototyping, and user research, aiming to create intuitive and ...
At IBM Research, we're working on a range of approaches to ensure that AI systems built in the future are fair, robust, explainable, account, and align with the values of the society they're designed for. We're ensuring that in the future, AI applications are as fair as they are efficient across their entire lifecycle.
Put simply, a digital twin is a virtual replica of a physical object, person, or process that can be used to simulate its behavior to better understand how it works in real life. Digital twins are linked to real data sources from the environment, which means that the twin updates in real time to reflect the original version.