
Thursday, February 23: The Clark Library is closed today.

MLA Style (9th Edition) Citation Guide: Journal Articles
- Introduction to MLA Style
- Journal Articles
- Magazine/Newspaper Articles
- Books & Ebooks
- Government & Legal Documents
- Biblical Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Videos/DVDs/TV Shows
- How to Cite: Other
- 9th Edition Updates
- Additional Help
Table of Contents
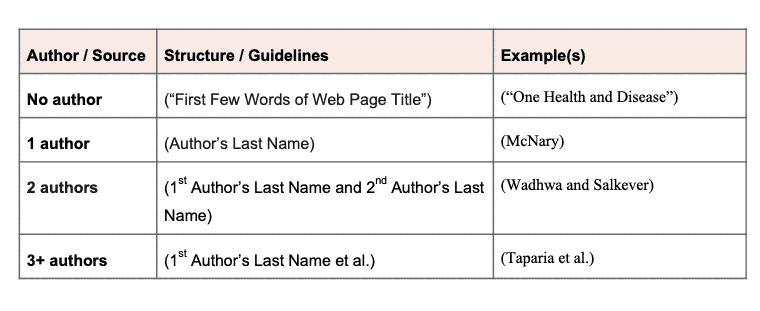
Basic style for citations of electronic sources (including online databases), journal article from library database with doi or a url, journal article in print.
Note: For your Works Cited list, all citations should be double spaced and have a hanging indent.
A "hanging indent" means that each subsequent line after the first line of your citation should be indented by 0.5 inches.
If there is no known author, start the citation with the title of the article instead.
Access Date
Date of access is optional in MLA 8th/9th edition; it is recommended for pages that may change frequently or that do not have a copyright/publication date.
In your works cited list, abbreviate months as follows:
January = Jan. February = Feb. March = Mar. April = Apr. May = May June = June July = July August = Aug. September = Sept. October = Oct. November = Nov. December = Dec.
Spell out months fully in the body of your paper.
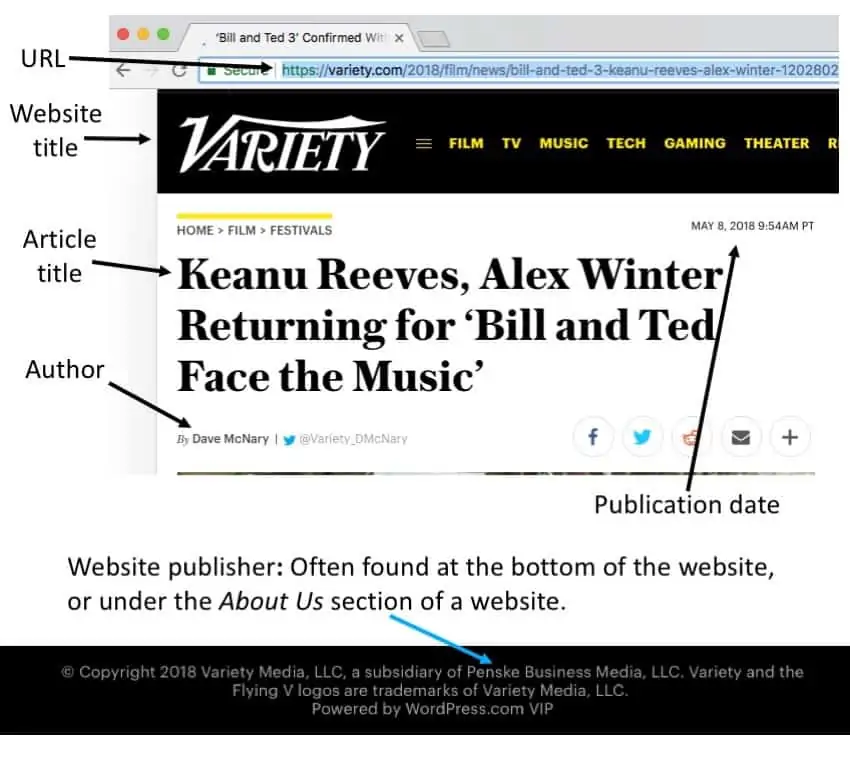
Here are some common features you should try to find before citing electronic sources in MLA style. Not every Web page will provide all of the following information. However, collect as much of the following information as possible both for your citations and for your research notes:
- Author and/or editor names (if available); last names first.
- "Article name in quotation marks."
- Title of the website, project, or book in italics.
- Any version numbers available, including editions (ed.), revisions, posting dates, volumes (vol.), or issue numbers (no.).
- Publisher information, including the publisher name and publishing date.
- Take note of any page numbers (p. or pp.) or paragraph numbers (par. or pars.).
- Many scholarly journal articles found in databases include a DOI (digital object identifier). If a DOI is available, cite the DOI number instead of the URL.
- “permalink,” which is a shortened, stable version of a URL. Look for a “share” or “cite this” button to see if a source includes a permalink. If you can find a permalink, use that instead of a URL.
- Date you accessed the material (Date Accessed)—While not required, it is highly recommended, especially when dealing with pages that change frequently or do not have a visible copyright date.
- Remember to cite containers after your regular citation. Examples of containers are collections of short stories or poems, a television series, or even a website. A container is anything that is a part of a larger body of works.
Cite online databases (e.g. LexisNexis, ProQuest, JSTOR, ScienceDirect) and other subscription services as containers. Thus, provide the title of the database (italicized) before the DOI or URL. If a DOI is not provided, use the URL instead. Provide the date of access if you wish.
The eighth edition of the MLA Handbook does not require that you include a date of access—the date on which you consulted a work—when you cite an online work from a reliable, stable source. However, you may include an access date as an optional element if it will be useful to others. (See the MLA Handbook, eighth edition, pp. 50–53, for more on optional elements.)
Including an access date for an online work may be especially useful if the work lacks a publication date or if you suspect that the work may be altered or removed, which is more common with informal or self-published works. Place the access date at the end of the entry.
Author's Last Name, First Name. "Title of Article: Subtitle if Any." Name of Journal , vol. Volume Number, no. Issue Number, Date of Publication, pp. First Page Number-Last Page Number. N ame of Database, doi:DOI number/URL/ Permalink .
Works Cited List Example:
Cardanay, Audrey. “Illustrating Motion, Music, and Story.” General Music Today, vol. 29, no. 3, 2016, pp. 25-29. Academic Search Premier , doi:10.1177/1048371315626498.
In-Text Citation Example:
(Author's Last Name Page Number)
Example: ( Cardanay 444)
Two Authors
First Author's Last Name, First Name, and Second Author's First Name Last Name. "Title of Article: Subtitle if Any." Name of Journal , vol. Volume Number, no. Issue Number, Date of Publication, pp. First Page Number-Last Page Number. Name of Database , doi:DOI number/URL/Permalink.
Best, David, and Sharon Marcus. “Surface Reading: An Introduction.” Representations , vol. 108, no. 1, Fall 2009, pp. 1-21. JSTOR , doi:10.1525/rep.2009.108.1.1.
(First Author's Last Name and Second Author's Last Name Page Number)
Example: (Best and Marcus 18)
Three or More Authors
For sources with three or more authors, list only the first author’s name followed by the phrase et al. (Latin for “and others”)
First Author's Last Name, First Name et al. "Title of Article: Subtitle if Any." Name of Journal, vol. Volume Number, no. Issue Number, Date of Publication, pp. First Page Number-Last Page Number. Name of Database, doi:DOI number/URL/Permalink.
Isaac, Kathleen et al. "Incorporating Spirituality in Primary Care." Journal of Religion and Health , vol. 55, no. 3, 2016, pp. 1065-77. ATLA Religion Database , login.uportland.idm.oclc.org/login?url=https://search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&db=aph&AN=114118885&site=ehost-live&scope=site.
(First Author's Last Name et al. Page Number)
Example: (Isaac et al. 1067)
Author's Last Name, First Name. "Title of Article: Subtitle if Any." Name of Journal , vol. Volume Number, no. Issue Number, Date of Publication, pp. First Page Number-Last Page Number.
Poythress, Vern S. "Rain Water Versus a Heavenly Sea in Genesis 1:6-8." The Westminster Theological Journal, vol. 77, no. 2, 2015, pp. 181-91.
Example: (Poythress 183)
- << Previous: How to Cite: Common Sources
- Next: Magazine/Newspaper Articles >>
- Last Updated: Apr 11, 2024 1:28 PM
- URL: https://libguides.up.edu/mla
Works-Cited-List Entries
How to cite an online work.
To create a basic works-cited-list entry for an online work, list the author, the title of the work, the title of the website as the title of the container, and the publication details. You may need to include other elements depending on the type of work (e.g., book, scholarly article, blog post) and how you accessed it (e.g., from a journal website, from a database). Below are sample entries for online works along with links to posts containing many other examples.
Article on a website
Deresiewicz, William. “The Death of the Artist—and the Birth of the Creative Entrepreneur.” The Atlantic , 28 Dec. 2014, theatlantic.com/magazine/archive/2015/01/ the-death-of-the-artist-and-the-birth-of-thecreative-entrepreneur/383497/.
Book on a website
Poe, Edgar Allan. “The Masque of the Red Death.” The Complete Works of Edgar Allan Poe , edited by James A. Harrison, vol. 4, Thomas Y. Crowell, 1902, pp. 250-58. HathiTrust Digital Library , hdl.handle.net/2027/coo.31924079574368.
Journal Article in a Database
Goldman, Anne. “Questions of Transport: Reading Primo Levi Reading Dante.” The Georgia Review , vol. 64, no. 1, spring 2010, pp. 69-88. JSTOR , www.jstor.org/stable/41403188.
More Examples
Digital Sources
Government Publications
Journal Articles
Reference Works
Social Media
- Previous Example
- Next Example
MLA Citation Guide: Citing in the body of your paper
- "Works Cited" List Outlined
- Books and book chapters
- Periodicals
- Citing in the body of your paper
- MLA Online Tutorials
In-Text Citations (see pages 54 - 58, 116 - 128 of the MLA Handbook, 8th Edition)
In the body of your paper, use parenthetical documentation (Chapter 5 of MLA Handbook ). The purpose of your documentation is for your readers to be able to locate the sources which you cite in your text when they look at your bibliography ("Works Cited") located at the end of your paper. You give the minimum of information necessary for your readers to do this, such as just the author's last name and the page(s) to which you refer.
- When you omit the author's name in your sentence:
This point has already been argued (Tannen 178-85).
- When you include the author's name in your sentence:
Tannen has argued this point (178-85).
- When you cite more than one work by the same author (shortened version of title is acceptable, using first words:
Shakespeare's King Lear has been called a "comedy of the grotesque" (Frye, Anatomy 237).
- When the work has more than one author:
Others hold the opposite point of view (e.g., Kerrigan and Braden 210-15).
- When the work has no author, use title (shortened form is ok) of article or book:
A New York Times editorial called Ralph Ellison "a writer of universal reach" ("Death").
- If your source uses explicit paragraph numbers rather than page numbers -- as some publications on the web do -- give the relevant number or numbers, preceded by the label par. or pars . Change the label appropriately if another kind of part is numbered in the source instead of pages, such as sections ( sec., secs .) or chapters ( ch., chs .). If the author's name begins such a citation, place a comma after the name.
There is little evidence here for the claim that "Eagleton has belittled the gains of postmodernism" (Chan, par.41).
- When a source has no page numbers or any other kind of part number, no number should be given in a parenthetical citation. Do not count unnumbered paragraphs or other parts.
"As we read we . . . construct the terrain of a book" (Hollmichel), something that is more difficult when the text reflows on a screen.
- In parenthetical citations of a literary work available in multiple editions, such as commonly studied novel, play, or poem, it is often helpful to provide division numbers in addition to, or instead of, page numbers, so that readers can find references in any edition of the work.
Austen begins the final chapter of Mansfield Park with a dismissive "Let other pens dwell," thereby announcing her decision to avoid dwelling on the professions of love made by Fanny and Edmund (533; vol.3, ch.17).
- For works in time-based media, such as audio and video recordings, cite relevant time or range of times. Give the numbers of the hours, minutes and seconds as displayed on your media player, separating the numbers with colons.
Buffy's promise that "there's not going to be incidents like at my old school" is obviously not one on which she can follow through ("Buffy" 00:03:16-17).
Subject Guide

- << Previous: Periodicals
- Next: MLA Online Tutorials >>
- Last Updated: Apr 1, 2024 11:55 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/MLA
Home / Guides / Citation Guides / MLA Format / MLA Website Citation
How to Cite a Website in MLA
If you are a student faced with creating an MLA website citation for the first time, you may be confused about where to begin. This guide is here to answer all of your questions and take the guesswork out of creating an MLA citation for websites.
All academic fields require students and researchers to document their sources. Those studying the humanities, including fields in language literature, will typically follow MLA format when structuring their papers as well as when documenting sources.
Citing your sources is a necessary part of any research paper or project. This element serves both to give credit to the researchers and authors whose work informed yours, as well as to preserve academic integrity. Any source that provided you with ideas or information that you have included in your work and which are not considered common knowledge must be included, including websites.
The Modern Language Association is not associated with this guide. All of the information, however, is based on the MLA Handbook, Ninth Edition as well as the MLA website, and is presented as guidance for students writing in this style.
If you are looking for help with APA format , our reference library can provide you with guidance for this and more styles .
What You Need
To cite a website, you should have the following information:
- Title of source.
- Title of the container ,
- Other contributors (names and roles),
- Publication date,
- Location of the source (such as DOI, URL, or page range).
The Modern Language Association refers to these guidelines as “core elements” on page 105 of the Handbook. If your teacher has asked you to cite your sources in this format, these elements will form the foundation for each MLA website citation included in your MLA Works Cited list, as well as the entries for sources in any other format.
If one of the elements does not apply, students may omit it. Supplemental items may also be included when necessary. In addition to the supplemental details discussed below, a list of additional supplemental components can be found on the MLA website.
If it’s an APA citation website page or an APA reference page you need help with, we have many other resources available for you!
Table of Contents
This guide includes the following sections:
- MLA9 Changes
- Citing websites with an author
- Citing websites with no author
- Citing websites with no formal title
- Citing social media websites
- In-text citations
Changes to MLA Citation for Websites in Ninth Edition
In previous editions, students and researchers creating an MLA website citation were not required to include the URL. However, beginning with MLA 8, it is recommended that you include the URL when creating a citation for a website unless your teacher instructs you otherwise. Even though web pages and URLs can be taken down or changed, it is still possible to learn about the source from the information seen in the URL.
When including URLs in a citation, http:// and https:// should be omitted from the website’s address ( Handbook 195). Additionally, If you are creating a citation that will be read on a digital device, it is helpful to make the URL clickable so that readers can directly access the source themselves.
If the website’s publisher includes a permalink or DOI (Digital Object Identifier), these are preferable as they are not changeable in the same manner as URLs. Whether you include a URL, permalink, or DOI, this information should be included in the location portion of your citation.
Another change that occurred with the eighth edition that impacts how to cite a website in MLA is the removal of the date the website was accessed. While you may still find it useful to include this information or your teacher may request it, it is no longer a mandatory piece of your citation. Should you choose to add this optional information, you may list it after the URL in the following manner:
- Accessed Day Month Year.
- Accessed 2 May 1998.
- Accessed 31 Apr. 2001.
- Accessed 17 Sept. 2010.
For an overview of additional formatting changes in the ninth edition, including resources to help with writing an annotated bibliography , check out the rest of EasyBib.com’s writing and citation guides, and try out our plagiarism checker for help with grammar and to avoid unintentional plagiarism.
MLA 9: Citing Websites With an Author
To make an MLA 9 citation for a website, you will need the following pieces of information:
- author’s name
- title of the article or page
- title of the website
- name of the publisher (Note: Only include the name of the publisher when it differs from the name of the website.)
- date the page or site was published (if available)
Citing a Website in MLA
Place the author’s name in reverse order, the last name first, followed by a comma, and then the first name followed by a period. The title of the web page or article is placed in quotation marks, with a period before the end quotation. The title of the website is written in italics followed by a comma. If the name of the publisher differs from the name of the website, include it after the title. Immediately following the publisher is the date that the page or article was published or posted. Finally, end with the URL, permalink, or DOI, followed by a period.
View Screenshot | Cite your source
In-text website citation with one author
The in-text citation for a website with an author is reflected as the author’s last name in parentheses, followed by a period. Unless the website includes numbered paragraphs or sections, you should not include any additional information. For the website used in the example above, the in-text citation would be written as follows:
Cite your source
An APA parenthetical citation is similar, except it also includes the year the source was published.
To learn more about formatting MLA in-text & parenthetical citations , be sure to check out the rest of EasyBib.com’s resources and citation guides.
How to cite a website with two authors in MLA 9
According to Section 5.7 of the Handbook , for a website with two authors, place the authors’ names in the same order as the source (similar to an APA citation ). The first name should be formatted in reverse order as was done for a single author. The second name, however, is written as First Name Last Name and is followed by a period, as demonstrated in the template that follows:
In-text website citation with two authors
The in-text citation for a website with two authors should include both authors’ last names, in the order in which they are listed in the source and your works cited:
How to cite a website with three or more authors in MLA 9
For a source with three or more authors, you should place the authors’ names in the same order as the source. The first name is listed in reverse order and is followed by a comma and et al. Et al is the abbreviation for et alia, a gender-neutral Latin phrase meaning “and others.”
In-text website citation with 3+ authors
The in-text citation for a website with three or more authors should contain only the first author’s last name, followed by et al. ( Handbook 232):
Click on this page if you’re looking for information on how to create an APA in-text citation .
MLA 9 Citation for Websites with No Author
Sometimes, websites do not state who wrote the information on the page. When no author is listed, you may omit the author information from the MLA citation for the website and begin, instead, with the title ( Handbook 108).
Note about web pages by organizations/corporations: Often, web pages are published by organizations or corporations with no author indicated. In these cases, you can assume that the publisher also authored the web page (like the example above). Since the author and publisher are the same in these cases, you can skip showing an author and just indicate the organization /corporation as the publisher ( Handbook 119 ).
In-text website citation with no author
The in-text citation for a website without an author is noted with the first noun phrase or words in the title in quotations and parenthesis, followed by a period. Unless the website includes numbered paragraphs or sections, you should not include any additional information. For the website used in the example above, the in-text citation would be written as follows:
MLA 9 Citation for Websites Without a Formal Title
When citing a web page that does not include a formal title, it is acceptable to include a description of the page. Do not place the description in italics or quotation marks. Follow the description with the name of the website.
In-text website citation without a title
The in-text citation for a website without a formal title uses a shortened version of the webpage description for the in-text citation. Use the first noun phrase of the description from your Works Cited citation in parenthesis, followed by a period. For the website used in the example above, the in-text citation would be written as follows:
MLA 9 Citation for Social Media Websites
In an increasingly digital world, social media platforms have become one of the most popular sources students turn to when writing a research paper. From Black history facts , to quotes from notable people, such as Martin Luther King and Winston Churchill , social media has become a mega influence in our world.
When citing social media in your work, follow the same format as an MLA citation for a website. Here are some examples of ways you can cite various social media platforms in your work:
How to cite Twitter in MLA 9
Many notable individuals use Twitter as a platform to share intriguing ideas. It’s a shame Twitter was unavailable to long-gone scientists, authors, and presidents such as Albert Einstein , Mark Twain , and Abraham Lincoln . Luckily, we have the Twitter profiles of today’s great minds at our fingertips!
To cite a tweet, you will begin with the account holder’s name and their Twitter handle in square brackets, followed by a period ( Handbook 118). After this, in quotations, you should enter the full text of the tweet, including any hashtags. The publisher, Twitter, is then listed in italics, followed by the date the tweet was posted in day, month, year format. Finally, include a URL to the tweet followed by a period.
Note: When the account name and username are similar, the username can be excluded from the citation. For example, if the account’s username was @FirstNameLastName or @OrganizationName.
In-text website citation of a Twitter post
The in-text citation for a Twitter post is reflected as the author’s last name in parentheses, followed by a period. For the tweet used in the example above, the in-text citation would be written as follows:
How to cite Instagram in MLA 9
To cite an Instagram post, begin with the account holder’s name and their username in square brackets. In quotations, list the title of the photo, if it is given. If there is no title, write a brief description of the picture but do not place it in italics or quotation marks. The publisher, Instagram, is then listed in italics. Any other contributors (such as the photographer, if it is not the same as the account holder) are then listed, after which you will add the date the photo was published and the URL.
In-text website citation of an Instagram post
The in-text citation for an Instagram post is reflected as the author’s last name or the name of the account in parentheses, followed by a period. For the Instagram post used in the example above, the in-text citation would be written as follows:
How to cite Facebook in MLA 9
To cite a Facebook post, begin with the account holder’s name or username. In quotations, list the title or caption of the post, if it is given. If there is no title or caption, write a brief description of the post, but do not place it in italics or quotation marks. Examples: Image of Malcolm X, or, Muhammed Ali headshot.
The publisher, Facebook, is then listed in italics, after which you will add the date posted and URL.
In-text website citation of a Facebook post
The in-text citation for a Facebook post is reflected as the author’s last name or the name of the account in parentheses, followed by a period. For the Facebook post used in the example above, the in-text citation would be written as follows:
Social media and website comments
Citing the comments left on social media or a website begins with the commenter’s name or username. To indicate that you are citing a comment, follow the name with a period and then the words Comment on , followed by the title of the source (for example, the name of the article) in quotation marks. This is then followed by the title of the website in italics, and the publisher, if applicable. The date is then listed, followed by the URL, permalink, or DOI.
In-text citation of a social media comment
The in-text citation for a social media comment is reflected as the author’s last name in parentheses, followed by a period. For the post used in the example above, the in-text citation would be written as follows:
In-text Citations for Websites
In-text citations generally consist of parentheses and the last names of the authors or the first few words of the web page title.
Since there are no page numbers, unless the web page includes numbered paragraphs or sections, you don’t need to include any additional information.
When you have multiple authors, place them in the same order they are listed in the source.
If what you really need is an APA book citation or a reference for an APA journal , there are more guides on EasyBib.com for you to explore.
Visit our EasyBib Twitter feed to discover more citing tips, fun grammar facts, and the latest product updates.
Troubleshooting
Solution #1: when and how to reference entire websites versus specific pages in mla.
Reference an entire website when your information comes from multiple pages or if you are describing the entirety of the website. If your information is only from one page, only cite the singular page.
Whole website, author known
- Write the author’s name in last name, first name format with a period following.
- Next, write the name of the website in italics.
- Write the contributing organization’s name with a comma following.
- List the date in day, month, year format with a comma following.
- Lastly, write the URL with a period following.
Works cited example:
Night, Samuel. Food Creations , International Hypothetical Chefs’ Club, 21 May 2021, www.foodcreationshypotheticalwebsite.com/best_macaroni_recipe.
In-text example:
Whole website, author unknown
- If there is no specific author, begin the citation by writing the website name in italics.
Food Creations , International Hypothetical Chefs’ Club, 21 May 2021, www.foodcreationshypotheticalwebsite.com/best_macaroni_recipe.
( Food Creations )
Webpage, author known
If information is from only a few pages or the pages cover multiple topics, reference each page
- If an author is named, write the author’s name in last name, first name format.
- If a title is not provided, create your own description of the page.
- List the title of the website in italics with a comma following.
- Write the date that the page was created followed by a comma.
- Lastly, list the URL followed by a period.
Blake, Evan. “Best Southern Macaroni Recipe.” Food Creations , International Hypothetical Chefs’ Club, 21 May 2021, www.foodcreationshypotheticalwebsite.com/best_macaroni_recipe.
Webpage, author unknown
If an author is not named, write the name of the page in quotation marks with a period following.
“Best Southern Macaroni Recipe.” Food Creations , International Hypothetical Chefs’ Club, 21 May 2021, www.foodcreationshypotheticalwebsite.com/best_macaroni_recipe.
(“Best Southern Macaroni Recipe”)
Solution #2: Referencing a conversation on social media in MLA
The in-text citation should identify the author and talk about the format (e.g., video, post, image, etc.) in prose.
Lilly West’s photo of traditional Japanese sweets shows an example of nature influencing Japanese design.
The basic structure of a works-cited reference for social media stays the same no matter the format or the social media service (e.g., Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, etc.). Here are works- cited-list entry guidelines:
- The name is listed in last name, first name format with a period following. If an organization, just write the organization’s name as it’s usually presented.
- If the username is very different from the author’s real name, include it in brackets after the user’s real name but before the period.
- Write the title, post text, or description of the post in quotation marks. End it with a period.
- Write the website name in italics with a comma afterward.
- List the day, month, and year that the post was created followed by a comma.
- List the URL followed by a period. Leave out “https://” and “http://”.
Facebook example:
West, Lily. “Kyoto Japanese sweets.” Facebook , 30 May 2021, www.facebook.com/hypotheticalexample/thispostisnotreal.
Twitter reference example:
West, Lily [@lilianhypotheticalwestbest]. “Kyoto Japanese sweets.” Twitter, 30 May 2021, www.twitter.com/hypotheticalexample/thispostisnotreal.
Instagram reference example:
West, Lily [@lilianhypotheticalwestbest]. “Kyoto Japanese sweets.” Instagram , 30 May 2021, www.instagram.com/hypotheticalexample/thisphotoisnotreal.
Solution #3: How to cite a social media post without a title or text
If there is no text or title where the title element usually goes, instead describe the post without quotation marks. Example:
West, Lily [@lilianhypotheticalwestbest]. Photo of traditional Japanese sweets on a green plate. Instagram , photographed by Bethany Lynn, 30 May 2021, www.instagram.com/hypotheticalexample/thisphotoisnotreal.
Solution #4: How to cite a social media post with a long title or text
If the text is very long, you can shorten it by adding ellipsis at the end of the text. Example:
West, Lily [@lilianhypotheticalwestbest]. “Nothing is better in life than feeling like all of the effort you’ve invested has finally. . . .” Twitter, 17 Feb. 2021, www.twitter.com/hypotheticalexample/thispostisnotreal.
- Works Cited
MLA Handbook . 9th ed., Modern Language Association of America, 2021.
Published October 31, 2011. Updated June 5, 2021.
Written and edited by Michele Kirschenbaum and Elise Barbeau. Michele Kirschenbaum is a school library media specialist and the in-house librarian at EasyBib.com. Elise Barbeau is the Citation Specialist at Chegg. She has worked in digital marketing, libraries, and publishing.
MLA Formatting Guide
MLA Formatting
- Annotated Bibliography
- Bibliography
- Block Quotes
- et al Usage
- In-text Citations
- Paraphrasing
- Page Numbers
- Sample Paper
- MLA 8 Updates
- MLA 9 Updates
- View MLA Guide
Citation Examples
- Book Chapter
- Journal Article
- Magazine Article
- Newspaper Article
- Website (no author)
- View all MLA Examples
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
It’s 100% free to create MLA citations. The EasyBib Citation Generator also supports 7,000+ other citation styles. These other styles—including APA, Chicago, and Harvard—are accessible for anyone with an EasyBib Plus subscription.
No matter what citation style you’re using (APA, MLA, Chicago, etc.), the EasyBib Citation Generator can help you create the right bibliography quickly.
Yes, there’s an option to download source citations as a Word Doc or a Google Doc. You may also copy citations from the EasyBib Citation Generator and paste them into your paper.
Creating an account is not a requirement for generating MLA citations. However, registering for an EasyBib account is free, and an account is how you can save all the citations you create. This can help make it easier to manage your citations and bibliographies.
Yes! Whether you’d like to learn how to construct citations on your own, our Autocite tool isn’t able to gather the metadata you need, or anything in between, manual citations are always an option. Click here for directions on using creating manual citations.
If any important information is missing (e.g., author’s name, title, publishing date, URL, etc.), first see if you can find it in the source yourself. If you cannot, leave the information blank and continue creating your citation.
It supports MLA, APA, Chicago, Harvard, and over 7,000 total citation styles.
If there is no author, the title becomes the website page’s identifier.
In-text example (no author): ( Honey Bee Medley )
Works cited example (no author): Honey Bee Medley . Hivemind Press, 2018, www.hivebees.com/honey-bees.
If there is no publication date, include an accessed date instead.
Works cited example (no author, no date): Honey Bee Medley . Hivemind Press, www.hivebees.com/honey-bees. Accessed 17 Nov. 2020.
If there is no title, briefly describe the source.
Works cited example (no author, no date, no title): Collage of honey bees. Hivemind Press, www.hivebees.com/honey-bees. Accessed 17 Nov. 2020.
To cite a website that has no page number in MLA, it is important that you know the name of the author, title of the webpage, website, and URL. The templates for an in-text citation and works-cited-list entry of a website that has no page number, along with examples, are given below:
In-text citation template and example:
You can use a time stamp if you are referring to an audio or video. Otherwise, use only the author’s surname.
(Author Surname)
Works-cited-list entry template and example:
Author or Organization Name. “Title of the Webpage.” Website Name . Publication Date, URL.
Dutta, Smita S. “What is Extra Sensory Perception?” Medindia . 16 Nov. 2019, www.medindia.net/patients/patientinfo/extra-sensory-perception.htm#3 .
Abbreviate the month in the date field.
MLA Citation Examples
Writing Tools
Citation Generators
Other Citation Styles
Plagiarism Checker
Upload a paper to check for plagiarism against billions of sources and get advanced writing suggestions for clarity and style.
Get Started
Lemieux Library and McGoldrick Learning Commons
Catalog search, site search.
- Seattle University
- Lemieux Library
Citing Your Sources Guide
Introduction to citations.
- APA In-text Citations - The Basics
- APA Reference List - The Basics
- APA Reference List - Examples
- APA Handouts
- Citing AI in APA Style
- House and Senate Reports and Documents
- Congressional Record
- Congressional Bills and Resolutions
- Federal Laws/Statutes
- Executive Documents - Presidential papers, Proclamations, and Executive Orders
- Rules/Regulations - Code of Federal Regulations (C.F.R.) and the Federal Register
- Foreign Relations of the United States
- State Legislative Documents
- State Statutes (Laws)
- Court Cases (decisions/opinions)
- Government Agencies
- MLA In-Text Citations - The Basics
- MLA Works Cited List - The Basics
- MLA Works Cited - Examples
- Chicago/Turabian - The Basics
- Chicago/Turabian in-text citations
- Chicago/Turabian Bibliography - Examples
- APA Art Citations
- MLA Art Citations
- Chicago Art Citations
- ArtSTOR Citations
- AMA reference list
- Citing Business Resources This link opens in a new window
- Citation Managers
Get Research Help
Student engagement librarian.

This guide covers the three main citation styles you may be asked to use while attending Seattle University. Please review the examples and information, and if you need more support, see the Style Manuals provided by the library, either in print or ebook form.
if you are looking for instructions on citing artworks, photographs, or visual media, check the Citing Artworks or Images Section, sorted by citation style.
- Purdue Online Writing Lab (OWL) Citation guides A somewhat out of date, but detailed guide to citations in all three major styles.
Manual of Style: This refers to a detailed guide to a particular citation style, such as the Chicago Manual of Style. These get updated regularly, so be sure to check with your professor which edition they want you to use for your assignments.
DOI: Digital object identifier, which is a specific code that corresponds to a digital object like an article or ebook.
ORCID ID: Similar to a DOI, the ORCID ID is a specific code that corresponds to a specific author/researcher.
et al: Means "and others" in latin. This is sometimes used in citations when there are more than a certain number of authors.
Citation: A citation is a collection of information that tells your reader that certain material in your work came from another source. It also gives your reader all the information necessary to find the location of any source included in your reference list/bibliography/works cited.
Useful Differences between Citation Styles
Differences between APA, MLA, and Chicago:
APA: The list of citations at the end is called a Reference List.
MLA : The list of citations at the end is called a Works Cited.
Chicago/Turabian: The list of citations at the end is called a Bibliography.
- Next: APA - 7th ed. >>
- Last Updated: Jan 5, 2024 3:46 PM
- URL: https://library.seattleu.edu/guides/citation
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
MLA Works Cited: Electronic Sources (Web Publications)

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
The MLA Handbook highlights principles over prescriptive practices. Essentially, a writer will need to take note of primary elements in every source, such as author, title, etc. and then assort them in a general format. Thus, by using this methodology, a writer will be able to cite any source regardless of whether it’s included in this list.
However, this guide will highlight a few concerns when citing digital sources in MLA style.
Best Practices for Managing Online Sources
Because online information can change or disappear, it is always a good idea to keep personal copies of important electronic information whenever possible. Downloading or even printing key documents ensures you have a stable backup. You can also use the Bookmark function in your web browser in order to build an easy-to-access reference for all of your project's sources (though this will not help you if the information is changed or deleted).
It is also wise to keep a record of when you first consult with each online source. MLA uses the phrase, “Accessed” to denote which date you accessed the web page when available or necessary. It is not required to do so, but it is encouraged (especially when there is no copyright date listed on a website).
Important Note on the Use of URLs in MLA
Include a URL or web address to help readers locate your sources. Because web addresses are not static (i.e., they change often) and because documents sometimes appear in multiple places on the web (e.g., on multiple databases), MLA encourages the use of citing containers such as Youtube, JSTOR, Spotify, or Netflix in order to easily access and verify sources. However, MLA only requires the www. address, so eliminate all https:// when citing URLs.
Many scholarly journal articles found in databases include a DOI (digital object identifier). If a DOI is available, cite the DOI number instead of the URL.
Online newspapers and magazines sometimes include a “permalink,” which is a shortened, stable version of a URL. Look for a “share” or “cite this” button to see if a source includes a permalink. If you can find a permalink, use that instead of a URL.
Abbreviations Commonly Used with Electronic Sources
If page numbers are not available, use par. or pars. to denote paragraph numbers. Use these in place of the p. or pp. abbreviation. Par. would be used for a single paragraph, while pars. would be used for a span of two or more paragraphs.

Basic Style for Citations of Electronic Sources (Including Online Databases)
Here are some common features you should try to find before citing electronic sources in MLA style. Not every web page will provide all of the following information. However, collect as much of the following information as possible:
- Author and/or editor names (if available); last names first.
- "Article name in quotation marks."
- Title of the website, project, or book in italics.
- Any version numbers available, including editions (ed.), revisions, posting dates, volumes (vol.), or issue numbers (no.).
- Publisher information, including the publisher name and publishing date.
- Take note of any page numbers (p. or pp.) or paragraph numbers (par. or pars.).
- DOI (if available, precede it with "https://doi.org/"), otherwise a URL (without the https://) or permalink.
- Date you accessed the material (Date Accessed). While not required, saving this information it is highly recommended, especially when dealing with pages that change frequently or do not have a visible copyright date.
Use the following format:
Author. "Title." Title of container (self contained if book) , Other contributors (translators or editors), Version (edition), Number (vol. and/or no.), Publisher, Publication Date, Location (pages, paragraphs and/or URL, DOI or permalink). 2 nd container’s title , Other contributors, Version, Number, Publisher, Publication date, Location, Date of Access (if applicable).
Citing an Entire Web Site
When citing an entire website, follow the same format as listed above, but include a compiler name if no single author is available.
Author, or compiler name (if available). Name of Site. Version number (if available), Name of institution/organization affiliated with the site (sponsor or publisher), date of resource creation (if available), DOI (preferred), otherwise include a URL or permalink. Date of access (if applicable).
Editor, author, or compiler name (if available). Name of Site . Version number, Name of institution/organization affiliated with the site (sponsor or publisher), date of resource creation (if available), URL, DOI or permalink. Date of access (if applicable).
The Purdue OWL Family of Sites . The Writing Lab and OWL at Purdue and Purdue U, 2008, owl.english.purdue.edu/owl. Accessed 23 Apr. 2008.
Felluga, Dino. Guide to Literary and Critical Theory . Purdue U, 28 Nov. 2003, www.cla.purdue.edu/english/theory/. Accessed 10 May 2006.
Course or Department Websites
Give the instructor name. Then list the title of the course (or the school catalog designation for the course) in italics. Give appropriate department and school names as well, following the course title.
Felluga, Dino. Survey of the Literature of England . Purdue U, Aug. 2006, web.ics.purdue.edu/~felluga/241/241/Home.html. Accessed 31 May 2007.
English Department . Purdue U, 20 Apr. 2009, www.cla.purdue.edu/english/. Accessed 31 May 2015.
A Page on a Web Site
For an individual page on a Web site, list the author or alias if known, followed by an indication of the specific page or article being referenced. Usually, the title of the page or article appears in a header at the top of the page. Follow this with the information covered above for entire Web sites. If the publisher is the same as the website name, only list it once.
Lundman, Susan. “How to Make Vegetarian Chili.” eHow , www.ehow.com/how_10727_make-vegetarian-chili.html. Accessed 6 July 2015.
“ Athlete's Foot - Topic Overview. ” WebMD , 25 Sept. 2014, www.webmd.com/skin-problems-and-treatments/tc/athletes-foot-topic-overview.
Citations for e-books closely resemble those for physical books. Simply indicate that the book in question is an e-book by putting the term "e-book" in the "version" slot of the MLA template (i.e., after the author, the title of the source, the title of the container, and the names of any other contributors).
Silva, Paul J. How to Write a Lot: A Practical Guide to Productive Academic Writing. E-book, American Psychological Association, 2007.
If the e-book is formatted for a specific reader device or service, you can indicate this by treating this information the same way you would treat a physical book's edition number. Often, this will mean replacing "e-book" with "[App/Service] ed."
Machiavelli, Niccolo. The Prince , translated by W. K. Marriott, Kindle ed., Library of Alexandria, 2018.
Note: The MLA considers the term "e-book" to refer to publications formatted specifically for reading with an e-book reader device (e.g., a Kindle) or a corresponding web application. These e-books will not have URLs or DOIs. If you are citing book content from an ordinary webpage with a URL, use the "A Page on a Web Site" format above.
An Image (Including a Painting, Sculpture, or Photograph)
Provide the artist's name, the work of art italicized, the date of creation, the institution and city where the work is housed. Follow this initial entry with the name of the Website in italics, and the date of access.
Goya, Francisco. The Family of Charles IV . 1800. Museo Nacional del Prado, Madrid. Museo Nacional del Prado , www.museodelprado.es/en/the-collection/art-work/the-family-of-carlos-iv/f47898fc-aa1c-48f6-a779-71759e417e74. Accessed 22 May 2006.
Klee, Paul. Twittering Machine . 1922. Museum of Modern Art, New York. The Artchive , www.artchive.com/artchive/K/klee/twittering_machine.jpg.html. Accessed May 2006.
If the work cited is available on the web only, then provide the name of the artist, the title of the work, and then follow the citation format for a website. If the work is posted via a username, use that username for the author.
Adams, Clifton R. “People Relax Beside a Swimming Pool at a Country Estate Near Phoenix, Arizona, 1928.” Found, National Geographic Creative, 2 June 2016, natgeofound.tumblr.com/.
An Article in a Web Magazine
Provide the author name, article name in quotation marks, title of the web magazine in italics, publisher name, publication date, URL, and the date of access.
Bernstein, Mark. “ 10 Tips on Writing the Living Web. ” A List Apart: For People Who Make Websites , 16 Aug. 2002, alistapart.com/article/writeliving. Accessed 4 May 2009.
An Article in an Online Scholarly Journal
For all online scholarly journals, provide the author(s) name(s), the name of the article in quotation marks, the title of the publication in italics, all volume and issue numbers, and the year of publication. Include a DOI if available, otherwise provide a URL or permalink to help readers locate the source.
Article in an Online-only Scholarly Journal
MLA requires a page range for articles that appear in Scholarly Journals. If the journal you are citing appears exclusively in an online format (i.e. there is no corresponding print publication) that does not make use of page numbers, indicate the URL or other location information.
Dolby, Nadine. “Research in Youth Culture and Policy: Current Conditions and Future Directions.” Social Work and Society: The International Online-Only Journal, vol. 6, no. 2, 2008, www.socwork.net/sws/article/view/60/362. Accessed 20 May 2009.
Article in an Online Scholarly Journal That Also Appears in Print
Cite articles in online scholarly journals that also appear in print as you would a scholarly journal in print, including the page range of the article . Provide the URL and the date of access.
Wheelis, Mark. “ Investigating Disease Outbreaks Under a Protocol to the Biological and Toxin Weapons Convention. ” Emerging Infectious Diseases , vol. 6, no. 6, 2000, pp. 595-600, wwwnc.cdc.gov/eid/article/6/6/00-0607_article. Accessed 8 Feb. 2009.
An Article from an Online Database (or Other Electronic Subscription Service)
Cite online databases (e.g. LexisNexis, ProQuest, JSTOR, ScienceDirect) and other subscription services as containers. Thus, provide the title of the database italicized before the DOI or URL. If a DOI is not provided, use the URL instead. Provide the date of access if you wish.
Alonso, Alvaro, and Julio A. Camargo. “ Toxicity of Nitrite to Three Species of Freshwater Invertebrates. ” Environmental Toxicology, vol. 21, no. 1, 3 Feb. 2006, pp. 90-94. Wiley Online Library , https://doi.org/10.1002/tox.20155. Accessed 26 May 2009.
Langhamer, Claire. “Love and Courtship in Mid-Twentieth-Century England.” Historical Journal, vol. 50, no. 1, 2007, pp. 173-96. ProQuest , https://doi.org/10.1017/S0018246X06005966. Accessed 27 May 2009.
E-mail (including E-mail Interviews)
Give the author of the message, followed by the subject line in quotation marks. State to whom the message was sent with the phrase, “Received by” and the recipient’s name. Include the date the message was sent. Use standard capitalization.
Kunka, Andrew. “ Re: Modernist Literature. ” Received by John Watts, 15 Nov. 2000.
Neyhart, David. “ Re: Online Tutoring. ” Received by Joe Barbato, 1 Dec. 2016.
A Listserv, Discussion Group, or Blog Posting
Cite web postings as you would a standard web entry. Provide the author of the work, the title of the posting in quotation marks, the web site name in italics, the publisher, and the posting date. Follow with the date of access. Include screen names as author names when author name is not known. If both names are known, place the author’s name in brackets.
Author or compiler name (if available). “Posting Title.” Name of Site , Version number (if available), Name of institution/organization affiliated with the site (sponsor or publisher), URL. Date of access.
Salmar1515 [Sal Hernandez]. “Re: Best Strategy: Fenced Pastures vs. Max Number of Rooms?” BoardGameGeek , 29 Sept. 2008, boardgamegeek.com/thread/343929/best-strategy-fenced-pastures-vs-max-number-rooms. Accessed 5 Apr. 2009.
Begin with the user's Twitter handle in place of the author’s name. Next, place the tweet in its entirety in quotations, inserting a period after the tweet within the quotations. Include the date and time of posting, using the reader's time zone; separate the date and time with a comma and end with a period. Include the date accessed if you deem necessary.
@tombrokaw. “ SC demonstrated why all the debates are the engines of this campaign. ” Twitter, 22 Jan. 2012, 3:06 a.m., twitter.com/tombrokaw/status/160996868971704320.
@PurdueWLab. “ Spring break is around the corner, and all our locations will be open next week. ” Twitter , 5 Mar. 2012, 12:58 p.m., twitter.com/PurdueWLab/status/176728308736737282.
A YouTube Video
Video and audio sources need to be documented using the same basic guidelines for citing print sources in MLA style. Include as much descriptive information as necessary to help readers understand the type and nature of the source you are citing. If the author’s name is the same as the uploader, only cite the author once. If the author is different from the uploader, cite the author’s name before the title.
McGonigal, Jane. “Gaming and Productivity.” YouTube , uploaded by Big Think, 3 July 2012, www.youtube.com/watch?v=mkdzy9bWW3E.
“8 Hot Dog Gadgets put to the Test.” YouTube, uploaded by Crazy Russian Hacker, 6 June 2016, www.youtube.com/watch?v=WBlpjSEtELs.
A Comment on a Website or Article
List the username as the author. Use the phrase, Comment on, before the title. Use quotation marks around the article title. Name the publisher, date, time (listed on near the comment), and the URL.
Not Omniscient Enough. Comment on “ Flight Attendant Tells Passenger to ‘Shut Up’ After Argument Over Pasta. ” ABC News, 9 Jun 2016, 4:00 p.m., abcnews.go.com/US/flight-attendant-tells-passenger-shut-argument-pasta/story?id=39704050.
How To Properly Reference A Book In An Essay – (2024 Style Guide)
May 18, 2024 | 0 comments

May 18, 2024 | Blog | 0 comments
Referencing a book in an essay is a crucial skill in academic writing.
It not only supports your arguments but also helps avoid plagiarism.
Yet, the process can be complex, considering various styles and formats.
This article aims to simplify that process.
We’ll explore common referencing styles like APA, MLA, Chicago, Harvard, and OSCOLA.
By the end, you will understand how to reference a book in an essay, regardless of your style guide.
Read Also : Research Paper Format: How to Cite a Research Paper in APA, MLA, Chicago, Harvard, ASA Styles
Understanding the Importance of Book Referencing
Book referencing is more than just a formality in academic writing. It’s a way to credit the authors whose work has informed your research and show respect for their intellectual property.
Moreover, it allows your readers to track down your sources if they wish to explore the topic further. This transparency enhances your work’s credibility and allows the academic dialogue to continue beyond your essay.
School Application Essay Writing Help
Feeling overwhelmed by the task of writing a standout school application essay that highlights your leadership abilities? Our proven step-by-step guide and personalized essay writing assistance will help you craft a compelling narrative that leaves a lasting impression on admissions committees.
Common Referencing Styles Overview
Several referencing styles are used in academic writing. Each style has its own set of rules for formatting citations and reference lists.
The choice of style often depends on the academic discipline. For instance, humanities often use MLA, while social sciences prefer APA.
Here are the most common styles:
APA (American Psychological Association)
Mla (modern language association), chicago manual of style, harvard referencing style, oscola (oxford university standard for citation of legal authorities).
APA style is commonly used in social sciences. It emphasizes the author and the date of publication in its in-text citations.
The reference list entries start with the author’s last name, followed by the initials of the first and middle names. The year of publication comes next, followed by the title of book and the publisher.
MLA style is popular in humanities, especially in literature and language studies. It focuses on the author’s name and the page number in its in-text citations.
The reference list entries start with the author’s name, the book’s title, the publisher, and the year of publication.
The Chicago Manual of Style is versatile and used in various academic disciplines. It offers two citation systems: notes, bibliography, and author-date.
The notes and bibliography system is preferred in literature, history, and the arts, while the author-date system is more common in the physical, natural, and social sciences.
Harvard style is widely used in many universities worldwide. It uses an author-date system for in-text citations.
The reference list entries start with the author’s last name and initials, year of publication, title of the book, city of publication, and publisher.
OSCOLA is a referencing style used specifically for legal documents . It uses footnotes for citations and does not require a bibliography.
The first citation of a book includes the author’s name, the title, the edition, and the publisher’s details. Subsequent citations include the author’s name, the abbreviated title, and the relevant page number(s).
Read Also : Step-By-Step Guide on How To Write A Process Essay (W/ Essay Example)
Step-by-Step Guide to Referencing a Book
Referencing a book in an essay involves the in-text citation and the reference list entry. The in-text citation is a brief reference within your text that indicates the source you consulted.
It should direct readers to the entry in your reference list, which contains detailed information about the book you cited.
Here’s a general guide:
- Start by listing the author’s last name, followed by a comma and the first name.
- After the author’s name, write the title of the book.
- Then, list the place of publication or the city of publication, followed by a colon and the publisher’s name.
- Finally, include the year of publication.
MLA Style Referencing
In MLA style, the author’s name is inverted (last name first). The title of the book is should be in italics.
The city of publication is not required unless the book was published before 1900. The publisher’s name is followed by the year of publication.
For example: Smith, John. The Great Book . Penguin, 2005.
Read Also: IEEE Format: Writing Guide With IEEE Citation Style Examples
APA Style Referencing
In APA style, the author’s name is also inverted. The year of publication comes after the author’s name.
The book title is in sentence case and italicized, meaning only the first word of the title, the first word after a colon or a dash, and any proper nouns are capitalized.
For example: Smith, J. (2005). The great book . Penguin.
Chicago Style Referencing
The author’s name is not inverted in the bibliography entry in the Chicago Manual of Style. The book title is in title case and italicized.
The city of publication, publisher’s name, and year of publication follow the title.
College Application Essay Writing Help
Are you struggling to craft a leadership essay that truly captures your unique experiences and qualifications? Our step-by-step guide and expert college application essay writing help will transform your leadership narrative and propel you towards your dreams!
APA Style: How to Write Book Titles in Essays
In APA style, you must italicize the title of the book when referring to the book in your essay. Here’s how you do it:
- Write the name of the author, e.g. , “According to Smith (2020),…”
- Italicize the title : The Great Gatsby.
- Include the publication and page numbers if you are quoting directly: (Smith, 2020, p. 23).
Questions? You might be wondering if there are exceptions. Yes, if you are writing the book title within the text, always use italics .
MLA Style Essay: Citing a Book Title
In MLA style, the process is slightly different. Here’s what you need to know:
- Italicize the title of the book.
- List the author’s name : First name Last name, followed by the title in italics , e.g. , Fitzgerald, F. Scott, The Great Gatsby .
- Ensure you include the name of the publisher and the year of publication on the works cited page : Charles Scribner’s Sons, 1925.
If you have two authors , list them both: Smith, John, and Jane Doe, Book Title .
For three or more authors , list the first author’s last name followed by “et al.”: Brown, et al.
Read Also: Bibliography vs Works Cited: How To Succeed Writing It
Chicago Style Essay: Writing the Book Title
In Chicago style, you also italicize the title of the book. Here’s how:
- List the author’s name first: Last name, First name.
- Title in italics : The Great Gatsby .
- Include the publisher, publication year , and page number if needed: (New York: Scribner, 1925).
When citing in-text, you might ask, “Do I need to include the publication details every time?” No, just the author’s last name and the page number are fine for subsequent citations.
Should We Underline or Italicize Book Titles?
A common question: Should book titles be underlined or italicized ? In modern writing styles, italicizing is the standard. However, in older documents, you might find books underlined . For clarity:
- Titles of stories, essays, and poems should be placed in quotation marks .
- Longer works like books should always be italicized.
Narrative Essay Writing Help
If you\'re looking to take your storytelling abilities to new heights, be sure to check out our comprehensive Narrative Essay Writing help – your ultimate guide to crafting captivating tales that will leave readers hungering for more!
How to Cite a Book (entire book)- In-Text Citations vs. Reference List Entries
In-text citations and reference list entries are two sides of the same coin. They work together to provide complete information about the sources you’ve used.
As the name suggests, in-text citations appear within the body of your essay. They briefly signal the source of your information, usually by including the author’s last name and the year of publication.
On the other hand, reference list entries appear at the end of your essay. They provide full details about each source, allowing readers to locate and consult them if desired.
In-Text Citation Examples
In MLA style, an in-text citation might read: (Smith 45). This indicates that the information comes from page 45 of a work by Smith.
In APA style, the citation would include the year of publication (Smith, 2005, p.45). This shows that the information comes from page 45 of a work published by Smith in 2005.
Reference List Entry Examples
A reference list entry in MLA style, usually placed under the works cited section, might read: Smith, John. The Great Book . Penguin, 2005.
In APA style, the entry would look slightly different: Smith, J. (2005). The great book . Penguin.
These entries provide all the information needed to locate the source: the author’s name, the title of the work, and the publisher’s name and year of publication.
Descriptive Essay Writing Help
\"Unlock the power of vivid imagery and captivate your readers with our Descriptive Essay Writing Help—guaranteed to elevate your writing to new heights!\"
Citing a Chapter or Essay from a Book
When citing a chapter or essay from a book, you need to acknowledge the specific part of the work you’re referring to. This is important because it allows your readers to locate the exact source of your information.
In MLA style, you might write: Smith, John. “Chapter 1.” The Great Book , Penguin, 2005, pp. 1-20.
The format would be slightly different in APA style: Smith, J. (2005). Chapter 1. In The Great Book (pp. 1-20). Penguin.
These formats indicate that the information comes from the book’s first chapter, which spans pages 1 to 20.
Citing Books with Multiple Authors
When a book has multiple authors, you need to include all their names in the citation. The order of the names should match the order on the book’s title page.
In APA style, you would write: Smith, J., & Johnson, M. (2005). The Great Book . Penguin.
In MLA style, the format would be: Smith, John, and Mary Johnson. The Great Book . Penguin, 2005.
These formats show that the book was co-authored by John Smith and Mary Johnson.
Special Cases in Book Referencing
Special cases in book referencing require a different approach. These include edited books, translations, books without authors, and e-books or online sources.
Edited Books and Translations
You should include the editor’s name in the citation for edited books.
For example, in APA style: Smith, J. (Ed.). (2005). The Great Book . Penguin. For translations, include the translator’s name: Smith, J. (Trans.). (2005). The Great Book . Penguin.
Books Without Authors
Books without authors should be cited by their titles.
For example, in MLA style, the format would be: The Great Book . Penguin, 2005. In APA style, the format would be: The Great Book . (2005). Penguin.
E-Books and Online Sources
E-books and online sources should include the URL or DOI at the end of the citation.
For example, in APA style: Smith, J. (2005). The Great Book . Penguin. https://doi.org/10.1234/abcd.
Other Types of Print Books
There are different ways to cite a book title depending on the type of book:
- For a chapter of a book , list the chapter title in double quotation marks , followed by the book title in italics.
- When using a book with three or more authors , list the first author and add “et al.”
- For a single author: Smith, John. Understanding Psychology .
- For a chapter: Smith, John. “Cognitive Development,” in Understanding Psychology .
Remember to list at the end all the works cited in a works cited list or bibliography, depending on your citation style.
Cheap Essay Writing Services
Discover the secret to top grades without breaking the bank – try our Affordable Essay Writing Services today for unbeatable quality at an unbeatable price!
Final Tips and Best Practices
Consistency is key when referencing a book in an essay. Ensure that you use the same citation style throughout your work. This will make your work look professional and make it easier for your readers to follow your references.
Remember to always check your citations for accuracy. A small mistake in the author’s name, title, or publication year can lead to confusion, so keeping a running list of sources as you research is also a good idea. This will make the referencing process much easier when writing your essay.
In conclusion, referencing a book in an essay is a crucial skill in academic writing. It not only helps avoid plagiarism but also adds credibility to your work.
By understanding and applying the correct referencing styles, you can ensure your work is professional, accurate, and respected in the academic community.
How to Reference a Book in an Essay- FAQs
How do you write a reference for a book in an essay .
When referencing a book in an essay , you should include the author ‘s last name and the page number in parenthesis after the quotation marks or paraphrased text . For example: (Doe 45).
How do you reference a book in a sentence ?
To reference a book in a sentence , you can mention the author’s name within the text and include the page number in parenthesis at the end of the sentence. For example: According to Doe (45)…
How do you Harvard reference a book in an essay ?
When using the Harvard referencing style for a book in an essay , include the author’s name and the year of publication in parenthesis after the cited text. For example: (Doe 2010).
How to write a reference of a book example ?
An example of referencing a book would be: Author’s Last Name, First Initial. (Year of Publication). Title of Book. Publisher.

Experienced writer and dedicated professor with a passion for crafting compelling narratives and nurturing the next generation of critical thinkers
People Also Read
- Essay Writing Help: The Chicago Reference Style
- A Short Guide to Academic Writing Style
- How to Structure an Informative Essay: A Step-by-Step Guide

Most Popular Articles
Racism thesis statement example, how to rephrase a thesis statement, capstone project topic suggestions, how to write an abortion essay, should students wear school uniforms essay, list causal essay topics write, respect essay, signal words, great synonyms, informative speech examples, essay writing guide, introduction paragraph for an essay, argumentative essay writing, essay outline templates, write an autobiographical essay, personal narrative essay ideas, descriptive essay writing, how to write a reflective-essay, how to write a lab report abstract, how to write a grant proposal, point of view in an essay, debate topics for youth at church, theatre research paper topics, privacy overview.
- Free Tools for Students
- Harvard Referencing Generator
Free Harvard Referencing Generator
Generate accurate Harvard reference lists quickly and for FREE, with MyBib!
🤔 What is a Harvard Referencing Generator?
A Harvard Referencing Generator is a tool that automatically generates formatted academic references in the Harvard style.
It takes in relevant details about a source -- usually critical information like author names, article titles, publish dates, and URLs -- and adds the correct punctuation and formatting required by the Harvard referencing style.
The generated references can be copied into a reference list or bibliography, and then collectively appended to the end of an academic assignment. This is the standard way to give credit to sources used in the main body of an assignment.
👩🎓 Who uses a Harvard Referencing Generator?
Harvard is the main referencing style at colleges and universities in the United Kingdom and Australia. It is also very popular in other English-speaking countries such as South Africa, Hong Kong, and New Zealand. University-level students in these countries are most likely to use a Harvard generator to aid them with their undergraduate assignments (and often post-graduate too).
🙌 Why should I use a Harvard Referencing Generator?
A Harvard Referencing Generator solves two problems:
- It provides a way to organise and keep track of the sources referenced in the content of an academic paper.
- It ensures that references are formatted correctly -- inline with the Harvard referencing style -- and it does so considerably faster than writing them out manually.
A well-formatted and broad bibliography can account for up to 20% of the total grade for an undergraduate-level project, and using a generator tool can contribute significantly towards earning them.
⚙️ How do I use MyBib's Harvard Referencing Generator?
Here's how to use our reference generator:
- If citing a book, website, journal, or video: enter the URL or title into the search bar at the top of the page and press the search button.
- Choose the most relevant results from the list of search results.
- Our generator will automatically locate the source details and format them in the correct Harvard format. You can make further changes if required.
- Then either copy the formatted reference directly into your reference list by clicking the 'copy' button, or save it to your MyBib account for later.
MyBib supports the following for Harvard style:
🍏 What other versions of Harvard referencing exist?
There isn't "one true way" to do Harvard referencing, and many universities have their own slightly different guidelines for the style. Our generator can adapt to handle the following list of different Harvard styles:
- Cite Them Right
- Manchester Metropolitan University (MMU)
- University of the West of England (UWE)

Daniel is a qualified librarian, former teacher, and citation expert. He has been contributing to MyBib since 2018.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
In-text citations: Author-page style. MLA format follows the author-page method of in-text citation. This means that the author's last name and the page number (s) from which the quotation or paraphrase is taken must appear in the text, and a complete reference should appear on your Works Cited page. The author's name may appear either in the ...
Create manual citation. The guidelines for citing an essay in MLA format are similar to those for citing a chapter in a book. Include the author of the essay, the title of the essay, the name of the collection if the essay belongs to one, the editor of the collection or other contributors, the publication information, and the page number (s).
Revised on March 5, 2024. An MLA in-text citation provides the author's last name and a page number in parentheses. If a source has two authors, name both. If a source has more than two authors, name only the first author, followed by " et al. ". If the part you're citing spans multiple pages, include the full page range.
If an article has three or more authors, include only the first author's name, followed by " et al. ". MLA journal citation: 3+ authors. MLA format. Author last name, First name, et al. " Article Title .". Journal Name, vol. Volume, no. Issue, Month Year, Page range. DOI or URL. MLA Works Cited entry.
The nine core elements of MLA citations. 1. Author. Begin each source entry with the name of the author (s) or creator (s). The name of the first author is always inverted (Last name, First name). When a source has two authors, the second author's name is shown in the normal order (First name Last name).
An in-text citation can be included in one of two ways as shown below: 1. Put all the citation information at the end of the sentence: 2. Include author name as part of the sentence (if author name unavailable, include title of work): Each source cited in-text must also be listed on your Works Cited page. RefWorks includes a citation builder ...
In-Text Citations: An Overview. In-text citations are brief, unobtrusive references that direct readers to the works-cited-list entries for the sources you consulted and, where relevant, to the location in the source being cited. An in-text citation begins with the shortest piece of information that directs your reader to the entry in the ...
Many scholarly journal articles found in databases include a DOI (digital object identifier). If a DOI is available, cite the DOI number instead of the URL. "permalink," which is a shortened, stable version of a URL. Look for a "share" or "cite this" button to see if a source includes a permalink. If you can find a permalink, use ...
In the case of a group project, list all names of the contributors, giving each name its own line in the header, followed by the remaining MLA header requirements as described below. Format the remainder of the page as requested by the instructor. In the upper left-hand corner of the first page, list your name, your instructor's name, the ...
For a print source, you need the following information: The name of the author or authors for articles with one or two authors. For articles with three or more authors, only the first author's name is used followed by et al. The name of the article in quotation marks. The name of the journal in italics.
How to Cite an Online Work. To create a basic works-cited-list entry for an online work, list the author, the title of the work, the title of the website as the title of the container, and the publication details. You may need to include other elements depending on the type of work (e.g., book, scholarly article, blog post) and how you accessed ...
In-Text Citations (see pages 54 - 58, 116 - 128 of the MLA Handbook, 8th Edition) In the body of your paper, use parenthetical documentation (Chapter 5 of MLA Handbook).The purpose of your documentation is for your readers to be able to locate the sources which you cite in your text when they look at your bibliography ("Works Cited") located at the end of your paper.
The author's name might be unknown. If it's the case, use the first several words from the article's title but omit "A," "An," or "The" at the beginning. It can be written in quotes or italics, depending on how it's written in your list of references. The number of words you pick to use depends on the title.
Cite your MLA source. Start by applying these MLA format guidelines to your document: Use an easily readable font like 12 pt Times New Roman. Set 1 inch page margins. Use double line spacing. Include a ½" indent for new paragraphs. Include a four-line MLA heading on the first page. Center the paper's title.
Write the author's name in last name, first name format with a period following. Next, write the name of the website in italics. Write the contributing organization's name with a comma following. List the date in day, month, year format with a comma following. Lastly, write the URL with a period following.
The new, ninth edition builds on the MLA's unique approach to documenting sources using a template of core elements--facts, common to most sources, like author, title, and publication date--that allows writers to cite any type of work, from books, e-books, and journal articles in databases to song lyrics, online images, social media posts ...
Note: The MLA considers the term "e-book" to refer to publications formatted specifically for reading with an e-book reader device (e.g., a Kindle) or a corresponding web application.These e-books will not have URLs or DOIs. If you are citing book content from an ordinary webpage with a URL, use the "A Page on a Web Site" format above.
In an MLA Works Cited entry for a journal article, the article title appears in quotation marks, the name of the journal in italics—both in title case. List up to two authors in both the in-text citation and the Works Cited entry. For three or more, use "et al.". MLA format. Author last name, First name.
The most basic type of APA in-text citation includes the author name followed by a comma and the resource publication date. If you are citing a specific part of the text (e.g., a quotation), include the page number ("p.") or page range ("pp."). When citing a page range, an en dash (-) should be used (e.g., "pp. 14-19).
Citing a Chapter or Essay from a Book. When citing a chapter or essay from a book, you need to acknowledge the specific part of the work you're referring to. This is important because it allows your readers to locate the exact source of your information. In MLA style, you might write: Smith, John. "Chapter 1."
Here's how to use our reference generator: If citing a book, website, journal, or video: enter the URL or title into the search bar at the top of the page and press the search button. Choose the most relevant results from the list of search results.
Revised on March 5, 2024. An MLA website citation includes the author's name, the title of the page (in quotation marks), the name of the website (in italics), the publication date, and the URL (without "https://"). If the author is unknown, start with the title of the page instead. If the publication date is unknown, or if the content is ...
If the book cover or title page specifies an edition, add the edition number or name, followed by the abbreviation "ed.", after the title. Note that versions of the Bible are treated slightly differently. MLA format. Author last name, First name. Book Title. Edition ed., Publisher, Year. MLA Works Cited entry.