
- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons

Margin Size
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

6.32: Comparison of Analog and Digital Communication
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 1884

- Don H. Johnson
- Rice University via Connections
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
Learning Objectives
- Digital communication systems offer much more efficiency, better performance, and much greater flexibility.
Analog communication systems, amplitude modulation (AM) radio being a typifying example, can inexpensively communicate a bandlimited analog signal from one location to another (point-to-point communication) or from one point to many (broadcast). Although it is not shown here, the coherent receiver provides the largest possible signal-to-noise ratio for the demodulated message. An analysis of this receiver thus indicates that some residual error will always be present in an analog system's output.
Although analog systems are less expensive in many cases than digital ones for the same application, digital systems offer much more efficiency, better performance, and much greater flexibility.
- Efficiency : The Source Coding Theorem allows quantification of just how complex a given message source is and allows us to exploit that complexity by source coding (compression). In analog communication, the only parameters of interest are message bandwidth and amplitude. We cannot exploit signal structure to achieve a more efficient communication system.
- Performance : Because of the Noisy Channel Coding Theorem, we have a specific criterion by which to formulate error-correcting codes that can bring us as close to error-free transmission as we might want. Even though we may send information by way of a noisy channel, digital schemes are capable of error-free transmission while analog ones cannot overcome channel disturbances; see this problem for a comparison.
- Flexibility : Digital communication systems can transmit real-valued discrete-time signals, which could be analog ones obtained by analog-to-digital conversion, and symbolic-valued ones (computer data, for example). Any signal that can be transmitted by analog means can be sent by digital means, with the only issue being the number of bits used in A/D conversion (how accurately do we need to represent signal amplitude). Images can be sent by analog means (commercial television), but better communication performance occurs when we use digital systems (HDTV). In addition to digital communication's ability to transmit a wider variety of signals than analog systems, point-to-point digital systems can be organized into global (and beyond as well) systems that provide efficient and flexible information transmission. Computer networks , explored in the next section, are what we call such systems today. Even analog-based networks, such as the telephone system, employ modern computer networking ideas rather than the purely analog systems of the past.
Consequently, with the increased speed of digital computers, the development of increasingly efficient algorithms, and the ability to interconnect computers to form a communications infrastructure, digital communication is now the best choice for many situations.
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
Electronics Coach
All About Electronics
Difference Between Analog and Digital Communication
The crucial difference between Analog and Digital Communication is that Analog communication uses analog signals for transmission and reception of data while digital communication uses digital signals for transmitting and receiving data. Analog signals are the continuous time-varying signal while digital signals are those which consist of discrete values.
Digital communication provides various advantages such as it is immune to noise and distortion as it possesses greater signal to noise ratio. The uses of repeaters in case of digital communication improve the SNR (Signal to Noise Ratio) further. Moreover, digital communication requires less power than analog communication.
The other differences between Analog and Digital Communication can be understood with the help of comparison chart and key differences.
Content: Analog and Digital Communication
Comparison Chart
- Key Differences
Definition of Analog Communication
In analog communication, the data is transferred from transmitter and receiver with the help of analog signal. Analog signal possesses continuous varying amplitude with time. Any type of data such as voice, sound etc. can be transferred through an analog signal.

Firstly, the data needs to be converted into electrical form. As voice, sound is non-electric in nature, it can be converted into electric form with the help of transducer. Then this signal is passed through the communication channel.
Analog communication is appropriate for short distance communication. Although, we can also use it for long distance communication with the help of analog modulation technique such as amplitude modulation and angle modulation.
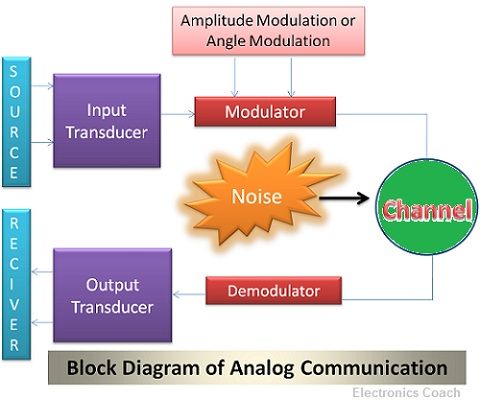
Modulation is the process of multiplying the low-frequency information signal with a high-frequency carrier signal. Then, this signal is transmitted through the channel. Thus, one modulator is required at the transmitter end, and one demodulator is connected at receiving end for retrieving the original signal.
The major drawback of Analog Communication is that the strength of the signal starts diminishing with the increase in the distance travelled. Thus, the signal to noise ratio starts getting degrade. Moreover, noise affects the Analog signal more than digital signal because analog signal is a continuous time-varying signal.
Definition of Digital Communication
Digital Communication is the one which uses digital signals for transmitting information between source and destination. Digital signals are represented by a square wave. This signal consists of discrete values rather than continuous values.

The digital signal is formed by the sampling of the analog signal. The samples of Analog signal are taken, and they are quantized. Digital signals usually consist of signals with two states ON or OFF, i.e. 0 & 1. After the sampling and quantization, the digital signal so obtained is modulated by digital modulation techniques.
PCM (Pulse Coded Modulation) , DPCM are some of the digital modulation techniques. The digital communication system also consists of repeaters to intensify the signal which undergoes attenuation due to travelling a particular distance. The repeaters intensify the information signal and suppress the noise signal. Thus repeaters also maintain the SNR effectively.
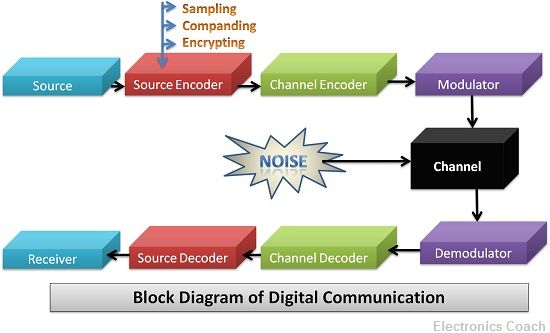
The significant advantage of using Digital Communication is that it is not deteriorated by channel noise. This is because the digital signal is not a continuously varying signal.
Thus, if noise effects mix with the digital signal, the original signal can be retrieved from the distorted signal. This is because if noise effects one of the points of the signal amplitude, we know the range in which that point lies because digital signal consists of discrete values.
Key Differences Between Analog and Digital Communication
- Bandwidth: This factor creates the key difference between Analog and digital communication. Analog signal requires less bandwidth for the transmission while digital signal requires more bandwidth for the transmission.
- Power Requirement: Power requirement in case of digital communication is less a compared to Analog communication. Since the bandwidth requirement in digital systems is more thus, they consume less power. And Analog communication system requires less bandwidth thus more power.
- Fidelity: Fidelity is a factor which creates a crucial difference between Analog and digital communication. Fidelity is the ability of the receiver which receives the output exactly in coherence with that of transmitted input. Digital communication offers more fidelity as compared to Analog Communication.
- Hardware Flexibility: The hardware of analog communication system is not as flexible as digital communication. The equipment used in digital technology are compact in size and consumes less power.
- Error Rate: Error rate is another significant difference which separates Analog and Digital Communication. In Analog instruments, there is an error due to parallax or other kinds of observational method.
- Synchronization: Digital communication system offers to synchronize which is not effective in analog communication. Thus, synchronization also creates a key difference between Analog and Digital Communication.
- Cost: Digital communication equipments are costly and digital signal require more bandwidth for transmission.
Analog communication is entirely the use of continuous time varying signal for the transmission of information from the sender to receiver. On the other hand, digital communication utilizes the usage of digital technology for sending the information over the channel.
Analog communication is becoming obsolete in contemporary times with the advent of digital technology. The drawback of using digital communication is that it requires more bandwidth for transmission which makes it costly. Thus, if cost is not the issue we can use digital communication for our purpose, but if we need an economical system then choose Analog.
Related Terms:
- Digital Electronics
- Difference between Amplitude Modulation and Frequency Modulation
- Difference Between Modulation and Demodulation
- Communication System
Reader Interactions
khan Gach says
October 12, 2021 at 8:43 am
Thanks for your sharing and be blessed always.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Analog vs. Digital

Analog and digital signals are used to transmit information, usually through electric signals. In both these technologies, the information, such as any audio or video, is transformed into electric signals. The difference between analog and digital technologies is that in analog technology, information is translated into electric pulses of varying amplitude. In digital technology, translation of information is into binary format (zero or one) where each bit is representative of two distinct amplitudes.
Comparison chart
Definitions of analog vs. digital signals.
An Analog signal is any continuous signal for which the time varying feature (variable) of the signal is a representation of some other time varying quantity, i.e., analogous to another time varying signal. It differs from a digital signal in terms of small fluctuations in the signal which are meaningful.
A digital signal uses discrete (discontinuous) values. By contrast, non-digital (or analog) systems use a continuous range of values to represent information. Although digital representations are discrete, the information represented can be either discrete, such as numbers or letters, or continuous, such as sounds, images, and other measurements of continuous systems.
Properties of Digital vs Analog signals
Digital information has certain properties that distinguish it from analog communication methods. These include
- Synchronization – digital communication uses specific synchronization sequences for determining synchronization.
- Language – digital communications requires a language which should be possessed by both sender and receiver and should specify meaning of symbol sequences.
- Errors – disturbances in analog communication causes errors in actual intended communication but disturbances in digital communication does not cause errors enabling error free communication. Errors should be able to substitute, insert or delete symbols to be expressed.
- Copying – analog communication copies are quality wise not as good as their originals while due to error free digital communication, copies can be made indefinitely.
- Granularity – for a continuously variable analog value to be represented in digital form there occur quantization error which is difference in actual analog value and digital representation and this property of digital communication is known as granularity.
Digital vs Analog Waveforms

Here are some differences between analog and digital waves:
- Representation : Analog signals are represented by a sine wave, while digital signals are represented by square waves.
- Signal type : Analog signals are continuous signals, so they move in a continuous, fluid movement with infinite values. Digital signals are time-separated signals that travel in discrete patterns.
- How they represent Information : Analog signals send a voltage that represents a value, while digital signals only have two states: on (1) and off (0).
Differences in Usage in Equipment
Many devices come with built in translation facilities from analog to digital. Microphones and speaker are perfect examples of analog devices. Analog technology is cheaper but there is a limitation of size of data that can be transmitted at a given time.
Digital technology has revolutionized the way most of the equipments work. Data is converted into binary code and then reassembled back into original form at reception point. Since these can be easily manipulated, it offers a wider range of options. Digital equipment is more expensive than analog equipment.
Comparison of Analog vs Digital Quality
Digital devices translate and reassemble data and in the process are more prone to loss of quality as compared to analog devices. Computer advancement has enabled use of error detection and error correction techniques to remove disturbances artificially from digital signals and improve quality.
Differences in Applications
Digital technology has been most efficient in cellular phone industry. Analog phones have become redundant even though sound clarity and quality was good.
Analog technology comprises of natural signals like human speech. With digital technology this human speech can be saved and stored in a computer. Thus digital technology opens up the horizon for endless possible uses.
Analog vs Digital Music
This video compares the analog ( vinyl ) and digital versions of Pink Floyd's "Dark Side of the Moon."
- Wikipedia: Analog signal
- Wikipedia: Digital data
About the Author

Related Comparisons

Share this comparison via:
If you read this far, you should follow us:
"Analog vs Digital." Diffen.com. Diffen LLC, n.d. Web. 23 May 2024. < >
Comments: Analog vs Digital
Anonymous comments (5).
April 3, 2014, 9:16pm I prefer digital than analogue. — 82.✗.✗.0
February 7, 2014, 9:17am Analogy signal is a continuous signals which represents physical measurements.......thnx for ur guidance — 41.✗.✗.118
June 3, 2014, 5:07am Good content — 42.✗.✗.247
April 11, 2011, 10:23pm this is good. good — 195.✗.✗.30
May 18, 2014, 9:42am Thnk a lot.......vry nic fr undstanding. — 37.✗.✗.125
- Converter vs Inverter
- AC vs DC current
- HDMI vs VGA
- Current vs Voltage
- Li-ion vs NiCad
Edit or create new comparisons in your area of expertise.
Stay connected
© All rights reserved.
- YouTube Thumbnail Downloader
- Image Compressor
- QR Code Generator
- Environment
- Submit An Article
- Privacy Policy
- Terms and Conditions
Introduction to Analog vs Digital Communication
- by Refresh Science
- January 14, 2022 January 15, 2022
Modern society in communicating does not need to meet face to face. The communication that people have makes it possible to transmit images, sounds, and videos via online. The word communication itself comes from the Latin “communicare”. Communication itself can also be interpreted as a process of sharing or exchanging information that usually connects individuals and systems. In the world of communication, there are also several kinds such as analog and digital communication. You need to know the difference between analog vs digital communication.
What Is Analog Communication?
Based on Physics and radio electronics , analog communication is the process of sending and receiving information that can take various forms. Examples of analog communication are voice, image, and video. The process of distributing information from this type of communication is done through analog signals. In the world of analog communication is also related to analog communication systems. The system consists of several elements that are combined together to build an analog communication bridge between fellow senders and recipients of the information.
What is Digital Communication?
In this analog vs digital article, we will also discuss the definition of digital communication. The definition of digital communication is the process of sending information that can be in the form of sound, images, and others through digital signals. Digital and analog signals are different things. The majority of modern technologies utilize digital communications, such as email, phone calls, SMS, video conferencing, and others.
To know more about Social Media Communication – Click here
Download Analog vs Digital Communication PowerPoint Presentation:
What’s the difference between analog communication and digital communication.
When discussing the difference between digital and analog communication then the answer will be long. You can see some points of difference between the two types of communication as follows:

Why is Digital Communication Better than Analog?
In the future, there will be no more people using analog communication. All will switch to digital communication because it has many advantages. This time we will start discussing the many advantages of digital communication. You can find out the advantages of digital communication below:
1. Digital Communication is only immune from parallax errors because it is not affected by noise.
2. The hardware used to support this communication system is much more concise than analog communication so that the device size can be smaller.
3. Hardware for delivering information via digital communication is not as complex as analog communication.
4. Bandwidth for digital used in the form of high bandwidth.
5. Information can be delivered with less power.
6. Digital communication system is more portable than an analog communication system
Is Digital or Analog More Reliable?
Based on the discussion from the previous point, we can understand that digital is much more reliable. The information sent is also more protected from parallax errors because digital is not affected by noise. In addition, technology is more compact so it is more portable and people can take it to various places. The technology also only requires less power, so it is enough to just use the battery without having to charge it frequently. Even some countries have started to incorporate analog technology into museums and have begun to slowly phase out the production of analog communications.
What Is the Disadvantage of Digital Communication?
Although we already know that digital communication is more reliable than analog communication, this digital technology also has several weaknesses. The disadvantages of digital communication can be found in the following.
1. Still experiencing sampling error
2. Requires high bandwidth to be able to carry out its function as an introduction to information
3. Requires synchronization via synchronous modulation based on information from multiple websites
4. Technology users need to pay a higher price than analog technology users
What Is an Example of Digital Communication?
You are now wondering what is an example of a technology that utilizes digital communication. Some examples of technology are phones, email, social media , websites, apps, television, digital radio, streaming media, online games, digital documents, digital advertising, and so on. Modern human life absolutely cannot be separated from this digital communication.

Which Modulation System Is Digital?
In the world of digital communication, there is also the term Digital Modulation. Digital modulation itself means the process of coding the digital information signal into a certain phase, amplitude, or signal frequency. The encoding process will affect the bandwidth in a larger amount than analog.
Modulation techniques convert several bits of transmitted information into a symbol. The rate of symbols will affect the bandwidth and each symbol consists of a large number of bits. Digital modulation techniques themselves are nonlinear and linear. Linear Modulation has an amplitude that is channeled in the form of a linear line. Linear modulation is used in wireless LANs. While nonlinear is more used on most smartphones and also wireless data systems.
In this discussion of analog vs digital communication, we can conclude that most countries prefer to use digital communication technology. The technology that supports digital communication is also smaller, making it easier to carry anywhere. The application is easier because it is portable, such as on phones, SMS, social media , and others.
Introduction to Analog and Digital Communication
Ieee account.
- Change Username/Password
- Update Address
Purchase Details
- Payment Options
- Order History
- View Purchased Documents
Profile Information
- Communications Preferences
- Profession and Education
- Technical Interests
- US & Canada: +1 800 678 4333
- Worldwide: +1 732 981 0060
- Contact & Support
- About IEEE Xplore
- Accessibility
- Terms of Use
- Nondiscrimination Policy
- Privacy & Opting Out of Cookies
A not-for-profit organization, IEEE is the world's largest technical professional organization dedicated to advancing technology for the benefit of humanity. © Copyright 2024 IEEE - All rights reserved. Use of this web site signifies your agreement to the terms and conditions.
- Fundamentals of Electrical Engineering I
- Ch 6 : Information Communication
Comparison of Analog and Digital Communication
Analog communication systems, amplitude modulation (AM) radio being a typifying example, can inexpensively communicate a bandlimited analog signal from one location to another (point-to-point communication) or from one point to many (broadcast). Although it is not shown here, the coherent receiver provides the largest possible signal-to-noise ratio for the demodulated message. An analysis of this receiver thus indicates that some residual error will always be present in an analog system's output.
Although analog systems are less expensive in many cases than digital ones for the same application, digital systems offer much more efficiency, better performance, and much greater flexibility.
- Efficiency : The Source Coding Theorem allows quantification of just how complex a given message source is and allows us to exploit that complexity by source coding (compression). In analog communication, the only parameters of interest are message bandwidth and amplitude. We cannot exploit signal structure to achieve a more efficient communication system.
- Performance : Because of the Noisy Channel Coding Theorem, we have a specific criterion by which to formulate error-correcting codes that can bring us as close to error-free transmission as we might want. Even though we may send information by way of a noisy channel, digital schemes are capable of error-free transmission while analog ones cannot overcome channel disturbances; see this problem for a comparison.
- Flexibility : Digital communication systems can transmit real-valued discrete-time signals, which could be analog ones obtained by analog-to-digital conversion, and symbolic-valued ones (computer data, for example). Any signal that can be transmitted by analog means can be sent by digital means, with the only issue being the number of bits used in A/D conversion (how accurately do we need to represent signal amplitude). Images can be sent by analog means (commercial television), but better communication performance occurs when we use digital systems (HDTV). In addition to digital communication's ability to transmit a wider variety of signals than analog systems, point-to-point digital systems can be organized into global (and beyond as well) systems that provide efficient and flexible information transmission. Computer networks , explored in the next section, are what we call such systems today. Even analog-based networks, such as the telephone system, employ modern computer networking ideas rather than the purely analog systems of the past.
Consequently, with the increased speed of digital computers, the development of increasingly efficient algorithms, and the ability to interconnect computers to form a communications infrastructure, digital communication is now the best choice for many situations.
This textbook is open source. Download for free at http://cnx.org/contents/[email protected] .
Explore CircuitBread
- 235 Tutorials
- 104 EE FAQs
- 12 Study Guides
- 207 Reference Materials
- 9 Textbooks
- 295 Equations Library
- 91 Glossary of Terms
Friends of CircuitBread

Try OLC's Bill of Materials Tool ›

Free Semiconductor Lifecycle Webinars ›

Power Supply Related Technical Resources + 1 Perk ›

Free Aerodynamics Technical Articles ›
Get the latest tools and tutorials, fresh from the toaster.
What are you looking for?
Message sent.
Thanks for the message, our team will review it shortly.
Log In or Sign Up
Username should have no spaces, underscores and only use lowercase letters.
Thanks for joining CircuitBread!
Please confirm your email address by clicking the link in the email we sent you.
Didn't receive anything? Resend now.

Search form
You are here.

- Comparison of Analog and Digital Communication

Analog communication systems, amplitude modulation (AM) radio being a typifying example, can inexpensively communicate a bandlimited analog signal from one location to another (point-to-point communication) or from one point to many (broadcast). Although it is not shown here, the coherent receiver ( Figure 6.6 ) provides the largest possible signal-to-noise ratio for the demodulated message. An analysis (Section 6.12) of this receiver thus indicates that some residual error will always be present in an analog system's output.
Although analog systems are less expensive in many cases than digital ones for the same application, digital systems offer much more efficiency, better performance, and much greater flexibility.
- Efficiency : The Source Coding Theorem allows quantifcation of just how complex a given message source is and allows us to exploit that complexity by source coding (compression). In analog communication, the only parameters of interest are message bandwidth and amplitude. We cannot exploit signal structure to achieve a more efcient communication system.
- Performance : Because of the Noisy Channel Coding Theorem, we have a specifc criterion by which to formulate error-correcting codes that can bring us as close to error-free transmission as we might want. Even though we may send information by way of a noisy channel, digital schemes are capable of error-free transmission while analog ones cannot overcome channel disturbances; see this problem ( Information Communication Problems ) for a comparison.
- Flexibility : Digital communication systems can transmit real-valued discrete-time signals, which could be analog ones obtained by analog-to-digital conversion, and symbolic-valued ones (computer data, for example). Any signal that can be transmitted by analog means can be sent by digital means, with the only issue being the number of bits used in A/D conversion (how accurately do we need to represent signal amplitude). Images can be sent by analog means (commercial television), but better communication performance occurs when we use digital systems (HDTV). In addition to digital communication's ability to transmit a wider variety of signals than analog systems, point-to-point digital systems can be organized into global (and beyond as well) systems that provide efficient and flexible information transmission. Computer networks , explored in the next section, are what we call such systems today. Even analog-based networks, such as the telephone system, employ modern computer networking ideas rather than the purely analog systems of the past.
Consequently, with the increased speed of digital computers, the development of increasingly efficient algorithms, and the ability to interconnect computers to form a communications infrastructure, digital commu nication is now the best choice for many situations.
- Front Matter
- Analog Signals
- Digital Signals
- Structure of Communication Systems
- The Sinusoid Exercise 1.4.1 Exercise 1.4.2
- Communicating Information with Signals
- Introduction Problems
- Solutions to Exercises in Chapter 1
- Definitions Exercise 2.1.1 Exercise 2.1.2
- Euler's Formula
- Calculating with Complex Numbers Exercise 2.1.3 Example 2.1
- Complex Exponentials
- Real Exponentials
- Square Wave
- Signal Decomposition Example 2.2 Exercise 2.3.1
- Real-and Complex-valued Signals
- Unit Sample
- Symbolic-valued Signals
- Cascade Interconnection
- Parallel Interconnection
- Feedback Interconnection
- Time Reversal Exercise 2.6.1
- Derivative Systems and Integrators
- Linear Systems
- Time-Invariant Systems
- Signals and Systems Problems Problem 2.1: Complex Number Arithmetic Problem 2.2: Discovering Roots Problem 2.3: Cool Exponentials Problem 2.4: Complex-valued Signals Problem 2.5: Problem 2.6: Problem 2.7: Linear, Time-Invariant Systems Problem 2.8: Linear Systems Problem 2.9: Communication Channel Problem 2.10: Analog Computers
- Solutions to Exercises in Chapter 2
- Voltage, Current, and Generic Circuit Elements Exercise 3.1.1
- Ideal and Real-World Circuit Elements
- Kirchhof's Current Law Exercise 3.4.1
- Kirchhof's Voltage Law (KVL) Exercise 3.4.2
- Power Dissipation in Resistor Circuits Exercise 3.5.1 Exercise 3.5.2
- Series and Parallel Circuits Exercise 3.6.1 Exercise 3.6.2 Example 3.1 Exercise 3.6.3
- Equivalent Circuits: Resistors and Sources Exercise 3.7.1 Example 3.2 Exercise 3.7.2
- Circuits with Capacitors and Inductors
- The Impedance Concept
- Time and Frequency Domains Example 3.3 Exercise 3.10.1
- Power in the Frequency Domain Exercise 3.11.1 Exercise 3.11.2
- Equivalent Circuits: Impedances and Sources Example 3.4
- Transfer Functions Exercise 3.13.1
- Designing Transfer Functions Example 3.5
- Formal Circuit Methods: Node Method Example 3.6: Node Method Example Exercise 3.15.1 Exercise 3.15.2
- Power Conservation in Circuits
- Electronics
- Dependent Sources
- Operational Amplifiers
- Inverting Amplifier
- Active Filters Example 3.7 Exercise 3.19.1
- Intuitive Way of Solving Op-Amp Circuits Example 3.8
- Analog Signal Processing Problems Problem 3.1: Simple Circuit Analysis Problem 3.2: Solving Simple Circuits Problem 3.3: Equivalent Resistance Problem 3.4: Superposition Principle Problem 3.5: Current and Voltage Divider Problem 3.6: Thevenin and Mayer-Norton Equivalents Problem 3.7: Detective Work Problem 3.8: Bridge Circuits Problem 3.9: Cartesian to Polar Conversion Problem 3.10: The Complex Plane Problem 3.11: Cool Curves Problem 3.12: Trigonometric Identities and Complex Exponentials Figure 3.61Problem 3.13: Transfer Functions Problem 3.14: Using Impedances Problem 3.15: Measurement Chaos Problem 3.16: Transfer Functions Problem 3.17: A Simple Circuit Problem 3.18: Circuit Design Problem 3.19: Equivalent Circuits and Power Problem 3.20: Power Transmission Problem 3.21: Optimal Power Transmission Problem 3.22: Big is Beautiful Problem 3.23: Sharing a Channel Problem 3.24: Circuit Detective Work Problem 3.25: Mystery Circuit Problem 3.26: More Circuit Detective Work Problem 3.27: Linear, Time-Invariant Systems Problem 3.28: Long and Sleepless Nights Problem 3.29: A Testing Circuit Problem 3.30: Black-Box Circuit Problem 3.31: Solving a Mystery Circuit Problem 3.32: Find the Load Impedance Problem 3.33: Analog "Hum" Rejection Problem3.34: An Interesting Circuit Problem 3.35: A Simple Circuit Problem 3.36: An Interesting and Useful Circuit Problem 3.37: A Circuit Problem Problem 3.38: Analog Computers Problem 3.39: Transfer Functions and Circuits Problem 3.40: Fun in the Lab Problem 3.41: Dependent Sources Problem 3.42: Operational Amplifers Problem 3.43: Op-Amp Circuit Problem 3.44: Why Op-Amps are Useful Problem 3.45: Operational Amplifiers Problem 3.46: Designing a Bandpass Filter Problem 3.47: Pre-emphasis or De-emphasis? Problem 3.48: Active Filter Problem 3.49: This is a filter? Problem 3.50: Optical Receivers Problem 3.51: Reverse Engineering
- Solutions to Exercises in Chapter 3
- Introduction to the Frequency Domain
- Complex Fourier Series Exercise 4.2.1 Example 4.1 Exercise 4.2.2
- Classic Fourier Series Exercise 4.3.1 Exercise 4.3.2 Exercise 4.3.3 Example 4.2
- A Signal's Spectrum Exercise 4.4.1 Exercise 4.4.2
- Fourier Series Approximation of Signals Exercise 4.5.1
- Encoding Information in the Frequency Domain Exercise 4.6.1 Exercise 4.6.2
- Filtering Periodic Signals Example 4.3 Exercise 4.7.1
- Derivation of the Fourier Transform Example 4.4 Exercise 4.8.1 Exercise 4.8.2 Example 4.5 Exercise 4.8.3 Exercise 4.8.4
- Transfer Functions
- Commutative Transfer Functions
- Modeling the Speech Signal Exercise 4.10.1 Exercise 4.10.2 Exercise 4.10.3
- Frequency Domain Problems Problem 4.1: Simple Fourier Series Problem 4.2: Fourier Series Problem 4.3: Phase Distortion Problem 4.4: Approximating Periodic Signals Problem 4.5: Long, Hot Days Problem 4.6: Fourier Transform Pairs Problem 4.7: Duality in Fourier Transforms Problem 4.8: Spectra of Pulse Sequences Problem 4.10: Lowpass Filtering a Square Wave Problem 4.11: Mathematics with Circuits Problem 4.12: Where is that sound coming from? Problem 4.13: Arrangements of Systems Problem 4.14: Filtering Problem 4.15: Circuits Filter! Problem 4.16: Reverberation Problem 4.17: Echoes in Telephone Systems Problem 4.18: Effective Drug Delivery Problem 4.19: Catching Speeders with Radar Problem 4.20: Demodulating an AM Signal Problem 4.21: Unusual Amplitude Modulation Problem 4.22: Sammy Falls Asleep... Problem 4.23: Jamming Problem 4.24: AM Stereo Problem 4.25: Novel AM Stereo Method Problem 4.26: A Radical Radio Idea Problem 4.27: Secret Communication Problem 4.28: Signal Scrambling
- Solutions to Exercises in Chapter 4
- Introduction to Digital Signal Processing
- Computer Architecture
- Representing Numbers Exercise 5.2.1 Exercise 5.2.2
- Computer Arithmetic and Logic Exercise 5.2.3
- Analog-to-Digital Conversion
- The Sampling Theorem Exercise 5.3.1 Exercise 5.3.2 Exercise 5.3.3
- Amplitude Quantization Exercise 5.4.1 Exercise 5.4.2 Exercise 5.4.3 Exercise 5.4.4
- Symbolic Signals
- Discrete-Time Systems
- Discrete-Time Fourier Transform (DTFT)
- Discrete Fourier Transforms (DFT)
- DFT: Computational Complexity
- Fast Fourier Transform (FFT)
- Spectrograms
- Discrete-Time Systems in the Time-Domain
- Filtering in the Frequency Domain
- Efficiency of Frequency-Domain Filtering
- Discrete-Time Filtering of Analog Signals
- Digital Signal Processing Problems
- Solutions to Exercises in Chapter 5
- Information Communication
- Types of Communication Channels
- Wireline Channels
- Wireless Channels
- Line-of-Sight Transmission
- The Ionosphere and Communications
- Communication with Satellites
- Noise and Interference
- Channel Models
- Baseband Communication
- Modulated Communication
- Signal-to-Noise Ratio of an Amplitude-Modulated Signal
- Digital Communication
- Binary Phase Shift Keying
- Frequency Shift Keying
- Digital Communication Receivers
- Digital Communication in the Presence of Noise
- Digital Communication System Properties
- Digital Channels
- Source Coding Theorem
- Compression and the Huffman Code
- Subtlies of Coding
- Channel Coding
- Repetition Codes
- Block Channel Coding
- Error-Correcting Codes: Hamming Distance
- Error-Correcting Codes: Channel Decoding
- Error-Correcting Codes: Hamming Codes
- Noisy Channel Coding Theorem
- Converse to the Noisy Channel Coding Theorem
- Capacity of a Channel
- Communication Networks
- Message Routing
- Network architectures and interconnection
- Communication Protocols
- Information Communication Problems
- Solutions to Exercises in Chapter 6
- Permutations and Combinations
- Frequency Allocations
- Solutions to Exercises in Chapter 7
- Back Matter
This action cannot be undo.
Choose a delete action Empty this page Remove this page and its subpages
Content is out of sync. You must reload the page to continue.
New page type Book Topic Interactive Learning Content
- Config Page
- Add Page Before
- Add Page After
- Delete Page


- Selected Reading
- UPSC IAS Exams Notes
- Developer's Best Practices
- Questions and Answers
- Effective Resume Writing
- HR Interview Questions
- Computer Glossary
Difference between Analog Communication and Digital Communication
In electrical and electronics engineering, the communication is defined as the process of broadcasting, transmitting, storing or viewing the data and information using electronic devices and circuits.
Based on the nature of signals and devices used for processing the information, the electronic communication can be classified into following two types −
Analog Communication
Digital Communication
In this post, we will take a look at the major differences between analog communication and digital communication by considering various parameters such as basic definition, cost, hardware technology, noise, power requirement, need of modulation, applications, etc. Also, a short description of analog communication and digital communication is added for your reference.
What is Analog Communication?
The type of communication in which the data and information is transferred with the help of analog signals in between transmitter and receiver is called the analog communication . Therefore, the analog communication uses continuous time signals for transmission of information.

The process involved in analog communication is illustrated in Figure-1. Where, the information in the form of analog signal is input to a transducer, which supplies it to the modulator. The modulator broadcast the modulated information on a communication channel. At receiver end, a demodulator circuit is employed for extracting the information from the modulated signal to produce the output message.
What is Digital Communication?
The communication in which the information is transferred by using digital signals in between transmitter and receiver is known as digital communication .
Hence, in case of digital communication, discrete time signals are used for carrying the information from one point to another. The block diagram shown in Figure-2 illustrates the digital communication system.

Here, the information is first encoded in digital signals (binary form) and modulated. The modulator then broadcast the information in digital form (in the form of data packets) on the communication channel. On the receiver end, the demodulator recovers the information and supplies it to the decoder, so that output message can be obtained.
The following table highlights the fundamental differences between analog communication and digital communication −
Due to many technical and economic advantages, digital communication has now become the preferred mode of data transmission over analog communication.

Related Articles
- Difference between Horizontal Communication and Diagonal Communication
- Difference between Communication and Transmission
- Difference Between Analog and Digital Computer
- Difference between Analog and Digital Circuits
- Difference between Analog and Digital Multimeter
- Difference between Analog and Digital Signal
- Difference Between Analog and Digital Modulation
- Difference between Social Marketing and Health Communication
- Difference between Analog Electronics and Digital Electronics
- Difference between Analog Instrument and Digital Instrument
- Difference Between Analog Delay and Digital Delay
- Difference Between Analog Tuner and Digital Tuner
- Difference Between Analog TV and Digital TV
- Difference between Point-to-Point and Multi-point Communication
- Differences between Digital and Analog System.
Kickstart Your Career
Get certified by completing the course
To Continue Learning Please Login
Difference Between Analog and Digital Communication
Definition : Analog and digital communications are the two types of data transmission system however several factors generate the difference between the two. The major difference between analog and digital communication lies in the signal being transmitted . In analog communication, the message signal is in analog form i.e., continuous time signal.
As against in digital communication, usually digital data i.e., discrete time signals containing information is transmitted.
In analog communication, the information carrying signal is generally a sine wave. However, in digital communication, the message signal is usually represented by a square wave.
There exist some other crucial differences between the two which we will be going to discuss with the help of comparison chart. But before that have a look at the contents given below that are to be discussed under this article.
Content: Analog Vs Digital Communication
Comparison chart.
- Key Differences
Applications
Definition of analog communication.
A method of transmitting a message in the form of the continuous time signal is known as analog communication. The signal can be an image, audio or video message that must be transmitted from an end to another.
Let’s have a look at the pictorial representation of an analog signal:
The figure below represents the analog communication system:
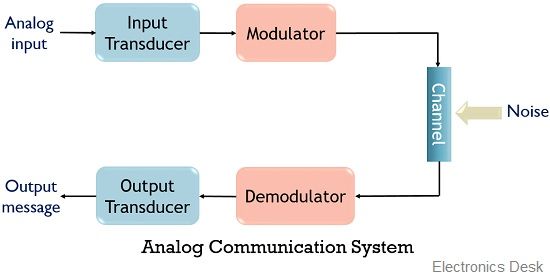
Here, the figure clearly shows that it consists of an input transducer with a modulator and an output transducer with demodulator between a communication channel.
The analog signal containing information is first provided to the input transducer where the analog message signal is first converted into an equivalent electrical signal.
This signal is then provided to the modulator circuit where modulation of the applied signal is performed in order to have long distance and proper signal transmission. The modulated signal is then transmitted through the communication channel where noise components also get added in it.
On reaching the receiver end, the transmitted signal undergoes demodulation by which originally transmitted signal is recovered from the modulated one. This signal is then fed to the output transducer where the actually transmitted analog signal is received.
Definition of Digital Communication
A way of communication in which the message is transmitted in the form of digital pulses or non-continuous form is known as digital communication. Here, the information is sent in digital format.
Let us see the pictorial representation of a digital signal:
The figure below represents the digital communication system:
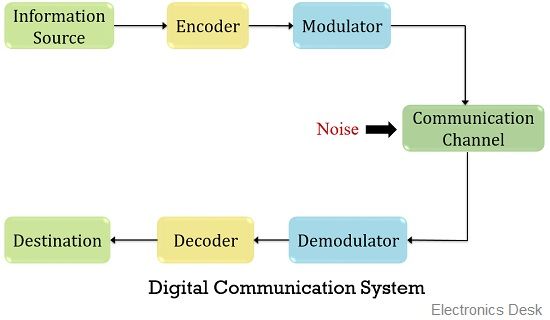
Here, the above figure clearly represents a digital communication system comprising of information source along with source encoder and a modulator. At the other end of the communication channel, a source decoder and demodulator is present.
A discrete information source generates a message signal that does not show continuous variation with time. This signal is provided to the source encoder. This unit provides a digitized message signal i.e., in the form of a binary sequence.
The binary sequence is then fed to the modulator, where the modulation of the digital signal takes place. This modulated digital signal is then sent via communication channel. During communication, the signal undergoes some distortion due to interference caused by additional noise components.
At the receiver, the digital signal is first demodulated in order to get the originally transmitted digital signal. This digitized signal is then fed to the source decoder which converts the digital signal into user understandable format.
Key Difference between Analog and Digital Communication
- During analog communication, a signal that varies constantly with time is transmitted. While in digital communication a signal in the form of pulses carries information and is transmitted.
- Due to analog nature of the signal being transmitted, coding of the signal is not achievable in analog communication. However, due to the discrete nature of the signal being transmitted, the coding of the signal can be easily achieved in digital communication.
- A digital system makes use of repeater circuits between transmitter and receiver that performs regeneration of signal thereby increasing chances of getting actually transmitted signal. While repeaters are not a part of an analog communication system thus they are more prone to signal distortion leading to reception of the distorted signal.
- A digital communication system is comparatively more immune to noise effects at the time of transmission than the analog communication system. This is so because the digital nature of the transmitted signal decreases the interference due to external noise.
- Transmitting information through an analog communication system is quite expensive than the digital communication system.
- The channel bandwidth needed for analog signal transmission is low in case of analog communication system. However, in the digital communication system, the channel bandwidth needed for transmission is comparatively higher.
- As coding is not permissible in analog signal transmission thus data in analog communication system can never be encrypted thus is not secured. On the contrary, it is quite easy to encrypt the digital data hence digital communication is more secure than the analog communication.
- As analog communication does not show better immunity towards noise thus the error probability is high in its case. Whereas, in digital communication, the transmitted signal shows immunity towards noise hence the probability of error is low in its case.
Analog Communication
It finds applications majorly in television broadcasting and radio broadcasting. Also, at the time of telephonic conversion, analog communication is taken into consideration.
Digital Communication
It is used in computers and satellite communication system. As digital communication supports data encryption thus is widely used for military purpose and long-distance communication.
So, from the above discussion, we can conclude that an analog signal is nothing but a composition of continuous values. However, a digital signal is a composition of discrete pulses. Both find applications in different fields according to the properties exhibited by them.
Related Terms:
- Difference Between Amplitude Modulation and Frequency Modulation
- Noise in Communication System
1 thought on “Difference Between Analog and Digital Communication”
Helpful article!
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- New Products
- Top Sellers
- Gift Certificates
- Raspberry Pi
- Single Board Comp.
- Microcontrollers
- Machine Learning
- Prototyping Boards
- all development
- Environment
- all sensors
- 3D Printing
- Instruments
- Arts/Crafts Supplies
- LED & Illumination
- Buttons & Switches
- LCDs & OLEDs
- Cables & Wire
- all components
- Sewable Electronics
- E-Textile Power
- E-Textile Kits
- all e-textiles
- Motors & Drivers
- Robotics Kits
- all robotics
- GPS & GNSS
- Wireless Kits
- all wireless/IoT
- Audio Boards
- Audio Cables
- Audio Chips
Analog vs. Digital
We live in an analog world. There are an infinite amount of colors to paint an object (even if the difference is indiscernible to our eye), there are an infinite number of tones we can hear, and there are an infinite number of smells we can smell. The common theme among all of these analog signals is their infinite possibilities.
Digital signals and objects deal in the realm of the discrete or finite , meaning there is a limited set of values they can be. That could mean just two total possible values, 255, 4,294,967,296, or anything as long as it's not ∞ (infinity).
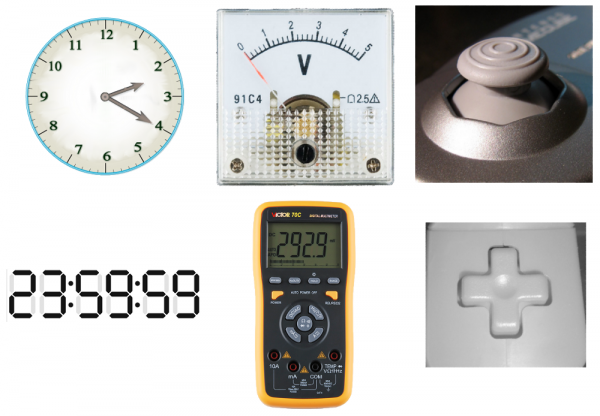

Real-world objects can display data, gather inputs by either analog or digital means. (From left to right): Clocks, multimeters , and joysticks can all take either form (analog above, digital below).
Working with electronics means dealing with both analog and digital signals, inputs and outputs. Our electronics projects have to interact with the real, analog world in some way, but most of our microprocessors, computers, and logic units are purely digital components. These two types of signals are like different electronic languages; some electronics components are bi-lingual, others can only understand and speak one of the two.
In this tutorial, we'll cover the basics of both digital and analog signals, including examples of each. We'll also talk about analog and digital circuits, and components.
Suggested Reading
The concepts of analog and digital stand on their own, and don't require a lot of previous electronics knowledge. That said, if you haven't already, you should peek through some of these tutorials:
- Voltage, Current, Resistance and Ohm's Law
- What is a Circuit
- And some mathematics concepts: reading graphs, and understanding the difference between finite and infinite sets.
Analog Signals
Define: signals.
Before going too much further, we should talk a bit about what a signal actually is, electronic signals specifically (as opposed to traffic signals, albums by the ultimate power-trio , or a general means for communication). The signals we're talking about are time-varying "quantities" which convey some sort of information. In electrical engineering the quantity that's time-varying is usually voltage (if not that, then usually current). So when we talk about signals, just think of them as a voltage that's changing over time.
Signals are passed between devices in order to send and receive information, which might be video, audio, or some sort of encoded data. Usually the signals are transmitted through wires, but they could also pass through the air via radio frequency (RF) waves. Audio signals, for example might be transferred between your computer's audio card and speakers, while data signals might be passed through the air between a tablet and a WiFi router.
Analog Signal Graphs
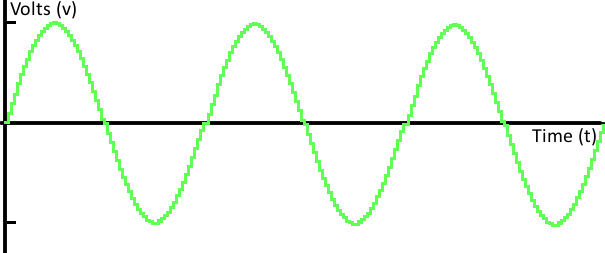
Because a signal varies over time, it's helpful to plot it on a graph where time is plotted on the horizontal, x -axis, and voltage on the vertical, y -axis. Looking at a graph of a signal is usually the easiest way to identify if it's analog or digital; a time-versus-voltage graph of an analog signal should be smooth and continuous .
While these signals may be limited to a range of maximum and minimum values, there are still an infinite number of possible values within that range. For example, the analog voltage coming out of your wall socket might be clamped between -120V and +120V, but, as you increase the resolution more and more, you discover an infinite number of values that the signal can actually be (like 64.4V, 64.42V, 64.424V, and infinite, increasingly precise values).
Example Analog Signals
Video and audio transmissions are often transferred or recorded using analog signals. The composite video coming out of an old RCA jack, for example, is a coded analog signal usually ranging between 0 and 1.073V. Tiny changes in the signal have a huge effect on the color or location of the video.
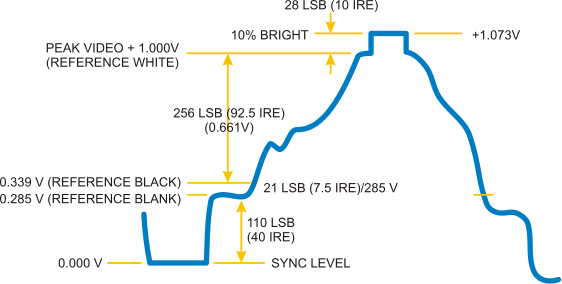
An analog signal representing one line of composite video data.
Pure audio signals are also analog. The signal that comes out of a microphone is full of analog frequencies and harmonics, which combine to make beautiful music.
Digital Signals
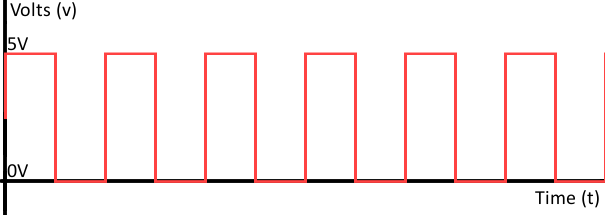
Digital signals must have a finite set of possible values. The number of values in the set can be anywhere between two and a-very-large-number-that's-not-infinity. Most commonly digital signals will be one of two values -- like either 0V or 5V. Timing graphs of these signals look like square waves .
Or a digital signal might be a discrete representation of an analog waveform. Viewed from afar, the wave function below may seem smooth and analog, but when you look closely there are tiny discrete steps as the signal tries to approximate values:
That's the big difference between analog and digital waves. Analog waves are smooth and continuous, digital waves are stepping, square, and discrete.
Example Digital Signals
Not all audio and video signals are analog. Standardized signals like HDMI for video (and audio) and MIDI , I 2 S , or AC'97 for audio are all digitally transmitted.
Most communication between integrated circuits is digital. Interfaces like serial , I 2 C , and SPI all transmit data via a coded sequence of square waves.
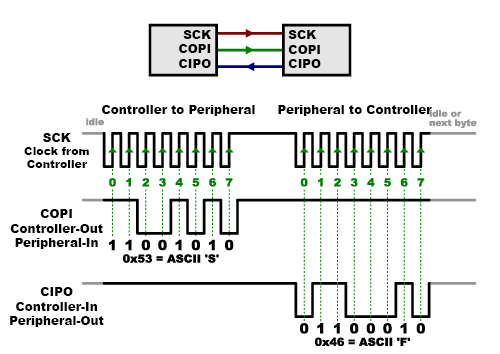
Serial peripheral interface (SPI) uses many digital signals to transmit data between devices.
Analog and Digital Circuits
Analog electronics.
Most of the fundamental electronic components -- resistors , capacitors , inductors, diodes , transistors, and operational amplifiers -- are all inherently analog. Circuits built with a combination of solely these components are usually analog.
Analog circuits are usually complex combinations of op amps, resistors, caps, and other foundational electronic components. This is an example of a class B analog audio amplifier.
Analog circuits can be very elegant designs with many components, or they can be very simple, like two resistors combining to make a voltage divider . In general, though, analog circuits are much more difficult to design than those which accomplish the same task digitally. It takes a special kind of analog circuit wizard to design an analog radio receiver, or an analog battery charger; digital components exist to make those designs much simpler.
Analog circuits are usually much more susceptible to noise (small, undesired variations in voltage). Small changes in the voltage level of an analog signal may produce significant errors when being processed.
Digital Electronics
Digital circuits operate using digital, discrete signals. These circuits are usually made of a combination of transistors and logic gates and, at higher levels, microcontrollers or other computing chips. Most processors, whether they're big beefy processors in your computer, or tiny little microcontrollers, operate in the digital realm.
Digital circuits make use of components like logic gates, or more complicated digital ICs (usually represented by rectangles with labeled pins extending from them).
Digital circuits usually use a binary scheme for digital signaling. These systems assign two different voltages as two different logic levels -- a high voltage (usually 5V, 3.3V, or 1.8V) represents one value and a low voltage (usually 0V) represents the other.
Although digital circuits are generally easier to design, they do tend to be a bit more expensive than an equally tasked analog circuit.
Analog and Digital Combined
It's not rare to see a mixture of analog and digital components in a circuit. Although microcontrollers are usually digital beasts, they often have internal circuitry which enables them to interface with analog circuitry ( analog-to-digital converters , pulse-width modulation , and digital-to-analog converters. An analog-to-digital converter (ADC) allows a microcontroller to connect to an analog sensor (like photocells or temperature sensors), to read in an analog voltage. The less common digital-to-analog converter allows a microcontroller to produce analog voltages, which is handy when it needs to make sound.
Resources and Going Further
Now that you know the difference between analog and digital signals, we'd suggest checking out the Analog to Digital Conversion tutorial. Working with microcontrollers, or really any logic-based electronics, means working in the digital realm most of the time. If you want to sense light, temperature, or interface a microcontroller with a variety of other analog sensors, you'll need to know how to convert the analog voltage they produce into a digital value.
Interested in learning more foundational topics?
See our Engineering Essentials page for a full list of cornerstone topics surrounding electrical engineering.
Take me there!

Also, consider reading our Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) tutorial. PWM is a trick microcontrollers can use to make a digital signal appear to be analog.
Here are some other subjects which deal heavily with digital interfaces:
- Logic Levels
- Serial Communication
- SPI Communication
- I 2 C Communication
- IR Communication
Or, if you'd like to delve further into the analog realm, consider checking out these tutorials:
- Voltage Dividers
- Transistors
- Electrical Engineering
- Creative Commons tutorials are CC BY-SA 4.0
- Your Account
- Analog vs Digital
Understanding the Difference Between Analog and Digital: A Comprehensive Guide
- March 16, 2024

In the world of technology, there are two main types of systems that are used to process information: analog and digital. While both of these systems have their own unique characteristics, they are often confused with one another. In this guide, we will explore the key differences between analog and digital systems, and how they are used in different contexts. We will also examine the advantages and disadvantages of each system, and provide examples of real-world applications. Whether you are a tech enthusiast or just looking to understand the basics, this guide will provide you with a comprehensive overview of the difference between analog and digital systems.

What is Analog?
Definition of analog.
Analog refers to any signal or data that is continuously variable, as opposed to digital signals which are quantized and discrete. Analog signals can take on any value within a range, making them inherently more flexible and adaptable than digital signals.
Examples of Analog Devices
- Audio cassettes and record players
- Film cameras and projectors
- VCRs and Betamax players
- Televisions with analog tuners
- Traditional telephone systems with analog lines
- Analog clocks and watches
- Guitar amplifiers and analog effects pedals
- Microfilm readers and projectors
- Traditional thermostats and temperature gauges
- Paper books and newspapers
Note: The examples listed above are just a few of the many types of analog devices that were commonly used before the widespread adoption of digital technology.
What is Digital?
Definition and examples.
Definition of Digital
Digital refers to the use of numerical or binary data to represent and process information. In simpler terms, digital technology uses a series of ones and zeros to store, process, and transmit information. This is in contrast to analog technology, which uses continuous signals to represent information.
Examples of Digital Devices
Digital devices are everywhere in our modern world. Here are some examples of digital devices that you might use in your daily life:
- Smartphones: These devices use digital technology to send and receive voice and data communications. They also use digital cameras to capture images and videos.
- Laptops and desktop computers: These devices use digital technology to process information and store data on hard drives or solid-state drives.
- Tablets: These devices are similar to smartphones but are larger and more versatile. They use digital technology to access the internet, play games, and run apps.
- Smartwatches: These devices use digital technology to track fitness and health data, send and receive notifications, and control other digital devices.
- Digital cameras: These devices use digital technology to capture and store images and videos. They can also be connected to computers and other devices to transfer and share files.
- E-readers: These devices use digital technology to display and store electronic books. They can also be used to browse the internet and access other digital content.
These are just a few examples of the many digital devices that are available today. As technology continues to advance, we can expect to see even more innovative digital devices in the future.
How are Analog and Digital Different?
Key differences.
- Quantification : Analog signals are continuous and vary in amplitude, while digital signals are quantized and represent data in discrete form.
- Conversion : Analog signals are difficult to process and store, requiring specialized equipment. Digital signals, on the other hand, are converted into binary code, making them easier to process and store in electronic devices.
- Signal Transmission : Analog signals degrade over long distances due to noise and interference, while digital signals can be transmitted over long distances without significant loss of quality.
These differences between analog and digital signals are the result of their underlying technology and the way they represent and transmit information. By understanding these differences, it becomes easier to choose the right signal type for a given application.
Why Understand the Difference Between Analog and Digital?
Importance of understanding the difference.
Understanding the difference between analog and digital is crucial in today’s world as technology continues to advance and evolve. By understanding the difference between these two types of signals, individuals can improve their communication, enhance their technology, and gain a better understanding of electronics.
Improved Communication
Communication is a vital aspect of modern society, and understanding the difference between analog and digital signals can lead to improved communication. Analog signals are continuous signals that can vary in amplitude, frequency, or phase, whereas digital signals are discrete signals that can only take on specific values. Knowing the difference between these two types of signals can help individuals choose the appropriate communication technology for their needs, whether it be analog or digital.
Enhanced Technology
Understanding the difference between analog and digital signals can also lead to enhanced technology. Analog signals are limited in the amount of information they can transmit, whereas digital signals can transmit much more information. This allows for more advanced technology, such as high-definition television and high-speed internet, to be developed. By understanding the difference between these two types of signals, individuals can make informed decisions when it comes to purchasing and using technology.
Better Understanding of Electronics
Understanding the difference between analog and digital signals can also lead to a better understanding of electronics. Analog signals are used in many different types of electronics, including audio and video equipment, while digital signals are used in computers and other digital devices. By understanding the difference between these two types of signals, individuals can gain a better understanding of how electronics work and how to troubleshoot and repair them. This knowledge can be particularly useful for those who work in the field of electronics or who are interested in pursuing a career in this area.
How to Convert Analog to Digital?
Methods of conversion, analog-to-digital conversion techniques.
There are several methods to convert analog signals to digital format . The two most common techniques are:
- Sampling : In this method, the analog signal is sampled at regular intervals to capture its value at that point in time. The sampled values are then converted into digital form using an ADC (Analog-to-Digital Converter).
- Quantization : This method involves converting the continuous analog signal into discrete levels or steps. Each step represents a certain range of the original signal value. The analog signal is then compared to each step, and the closest step is assigned as the digital value.
Conversion Tools and Devices
There are various tools and devices available to convert analog signals to digital format . Some of the commonly used devices are:
- Analog-to-Digital Converters (ADCs) : These are electronic devices that convert analog signals to digital form. They are widely used in audio and video recording, telecommunications, and other fields.
- Digital Multimeters : These are electronic measuring instruments that can measure various parameters such as voltage, current, and resistance. They have an analog-to-digital converter built-in that converts the analog signal to digital form.
- Data Acquisition Systems (DAS) : These are specialized devices that are used to collect and process data from various sensors and instruments. They have multiple input channels and a high-resolution ADC that can convert the analog signals to digital format .
- Signal Processing Software : There are various software programs available that can convert analog signals to digital format . They can be used to process and analyze the digital data, and perform various signal processing operations.
Overall, converting analog signals to digital format is a crucial step in many fields, and there are various techniques and tools available to achieve this conversion accurately and efficiently.
How to Convert Digital to Analog?
Digital-to-analog conversion techniques.
When it comes to converting digital signals to analog, there are several techniques that can be used. One of the most common methods is using a digital-to-analog converter (DAC). A DAC is an electronic device that converts digital signals into analog signals. This is done by taking the binary code that represents the digital signal and using it to control the voltage or current of an analog signal.
Another technique for converting digital signals to analog is using a modulator. A modulator is a device that modulates a digital signal onto an analog carrier wave. This is done by varying the amplitude, frequency, or phase of the carrier wave in accordance with the digital signal. This technique is commonly used in radio and television broadcasting.
There are also several tools and devices that can be used to convert digital signals to analog. One example is an audio interface, which is a device that allows a computer to send and receive audio signals. An audio interface can be used to convert digital audio signals from a computer into analog signals that can be sent to a recording device or amplifier.
Another tool that can be used for digital-to-analog conversion is a sound card. A sound card is a hardware component that is installed in a computer and is used to process and output audio signals. A sound card can be used to convert digital audio signals into analog signals that can be sent to speakers or headphones.
In addition to these tools, there are also software programs that can be used to convert digital signals to analog. These programs can be used to convert digital audio files into analog waveforms that can be played on an analog audio device.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the difference between analog and digital signals? An analog signal is a continuous signal that can take on any value within a range, whereas a digital signal is a discrete signal that can only take on specific values, usually represented by binary digits (bits).
- Can analog and digital signals be converted into each other? Yes, analog signals can be converted into digital signals using an analog-to-digital converter (ADC), and digital signals can be converted into analog signals using a digital-to-analog converter (DAC).
- Which is better, analog or digital? The choice between analog and digital depends on the specific application and requirements. Analog signals are typically better for applications that require continuous signals, such as audio and video, while digital signals are better for applications that require precise and reliable data transmission, such as computer data storage and communication.
- How is analog technology different from digital technology? Analog technology uses continuous signals that can vary over a range of values, while digital technology uses discrete signals that can only take on specific values represented by bits. Analog technology is typically less precise and reliable than digital technology, but it can offer better signal quality for certain applications.
- What are some examples of analog devices? Some examples of analog devices include audio tape players, vinyl record players, and film cameras.
- What are some examples of digital devices? Some examples of digital devices include smartphones, computers, and digital cameras.
1. What is the difference between analog and digital?
Analog refers to signals or data that are continuously varying, while digital refers to signals or data that are represented by discrete values or bits. In simpler terms, analog signals are like waves that can take on any value within a range, while digital signals are like a series of 1s and 0s that represent specific information.
2. How are analog and digital signals transmitted?
Analog signals are transmitted over long distances using analog transmission lines, while digital signals are transmitted using digital transmission lines. Analog transmission lines are typically slower and more susceptible to interference, while digital transmission lines are faster and more reliable.
3. What are some examples of analog signals?
Examples of analog signals include sound waves, radio waves, and television signals. These signals are continuously varying and can take on any value within a range.
4. What are some examples of digital signals?
Examples of digital signals include computer data, digital audio, and digital video. These signals are represented by discrete values or bits and can be transmitted over long distances without losing any information.
5. What are the advantages of analog signals?
Analog signals have the advantage of being able to transmit a continuous range of information, which can be useful in certain applications. They are also relatively simple to transmit and receive, as they do not require complex decoding or processing.
6. What are the advantages of digital signals?
Digital signals have the advantage of being able to transmit a large amount of information in a small amount of space, making them ideal for applications where bandwidth is limited. They are also more reliable and less susceptible to interference than analog signals.
7. What are some disadvantages of analog signals?
One disadvantage of analog signals is that they are susceptible to interference and noise, which can cause degradation in the quality of the signal. They are also more difficult to transmit over long distances and may require more complex transmission and reception equipment.
8. What are some disadvantages of digital signals?
One disadvantage of digital signals is that they require more complex processing and decoding to extract the information they contain. They are also more susceptible to errors caused by bit flips or other types of data corruption.
9. What are some applications of analog signals?
Analog signals are commonly used in applications such as audio and video recording, radio and television broadcasting, and medical monitoring.
10. What are some applications of digital signals?
Digital signals are commonly used in applications such as computer networking, digital audio and video transmission, and wireless communication. They are also used in the internet, where they are used to transmit and receive data over long distances.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Related Articles

Understanding the Differences Between Analog and Digital Electronics

Understanding the Differences Between Analog and Digital Technology

The Superiority of Digital Circuits: A Comprehensive Analysis
- Machine Learning Decision Tree – Solved Problem (ID3 algorithm)
- Poisson Distribution | Probability and Stochastic Process
- Conditional Probability | Joint Probability
- Solved assignment problems in communicaion |online Request
- while Loop in C++
EngineersTutor
Analog versus digital communications.
Analog signal is a continuous signal and takes infinite number of amplitude values. Note that ‘ Majority of signals in the world around us are in analog form ’. Voice is best example of analog signal. Other examples are: heart beat signal, temperature, atmospheric pressure etc. Digital signal is discrete in nature. Discrete means countable (finite). Digital signal has only two levels ( bit 1 and bit 0 ). In electrical engineering bit 1 is represented with 5 V and bit 0 is represented with 0 V.
Communication systems can be: (i) Analog. (ii) Digital.
Analog transmission
The analog signal attenuates (losses power) over distance of the transmission. To overcome the attenuation, amplifiers are used to strengthen the signals. However, noises are also amplified.
Advantages of Analog communications:
- Transmitters and Receivers are simple
- Low bandwidth requirement
- FDM can be used
Disadvantages of analog communication
- Noise affects the signal quality
- It is not possible to separate noise and signal
- Repeaters can‘t be used between transmitters and receivers
- Coding is not possible
- It is not suitable for the transmission of secret information
- Noise affects the signal quality. It is not possible to separate noise and signal
Digital transmission
Digital transmission is the transmission of digital pulses between two or more points/places. The signals can be binary (1010101111) or any other form of discrete-level digital pulses. Digital signals can be transmitted over a limited distance due to the attenuation and noises. Repeater can overcome the attenuation and are used to reconstruct the transmitted bits without amplifying noise signals.
Advantages of Digital communications
Note that today’s tendency is to change an analog signal to digital data.
- It has a better noise immunity. The effect of distortion, noise and interference is less in a digital communication system. i.e., Digital circuits are less subject to distortion and interference than analog circuits
- Low cost, VLSI technologies have made the cost of circuits for digital signals cheaper than that for analog signals Better capacity utilization, the high bandwidth digital links are cheaper than their analog counterparts and it is easier to have high degree multiplexing (a technique which allows multiple users sharing a common link) on digital links
- Combining digital signals using TDM (Time Division Multiplexing) is simpler than combining analog signals using FDM (Frequency Division Multiplexing).
- Better security and privacy, it is easier to encrypt (converting to secret messages) digital signals
- In digital systems transmission errors can be corrected and detected more accurately. So probability of occurring errors is less
Disadvantages of Digital Communication
- Digital communication system requires a larger channel bandwidth. The transmission of digitally encoded analog signals requires significantly more bandwidth. This is due to modulation and other changes made for ease of transmission. Remember that bandwidth is costliest parameter in any communication system.
- Additional encoding (Analog to Digital) and decoding (Digital to analog) circuitry required Digital transmission requires precise time synchronization between transmitter and receiver. But the analog signals generally do not support such requirement.
- ← Analog versus Digital signals
- Frequency, Wavelength and Phase of a signal →
Gopal Krishna
Hey Engineers, welcome to the award-winning blog,Engineers Tutor. I'm Gopal Krishna. a professional engineer & blogger from Andhra Pradesh, India. Notes and Video Materials for Engineering in Electronics, Communications and Computer Science subjects are added. "A blog to support Electronics, Electrical communication and computer students".
You May Also Like
Importance of electronic communications, types of fm | carson’s rule, signal bandwidth vs channel bandwidth, leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- Reflection of Light
- Equations of Motion
- Wave Theory
- Electromagnetic Induction
- Physics Notes Class 8
- Physics Notes Class 9
- Physics Notes Class 10
- Physics Notes Class 11
- Physics Notes Class 12
- Difference between SOP and POS in Digital Logic
- What is the difference between a number and a digit?
- Difference between PPI and DPI
- Difference between Real and Virtual Images
- Difference Between Digital And Analog System
- Difference Between Digital Audio and MIDI
- Difference between Analog Computer and Digital Computer
- Difference between HDMI and VGA
- Difference Between AND Gate and OR Gate
- Difference between Direct and Arbitrated Digital Signature
- Difference between Malware and Adware
- Difference between ADO and ADO.NET
- Difference between FDMA and TDMA
- Difference between Virus and Adware
- Difference between Sensor and Actuator
- Difference between DVR and NVR
- Difference between SONET and DWDM
- Difference between Serial Adder and Parallel Adder
- Difference between PDH and SDH
Difference Between Analog and Digital signal
Analog and digital signals are two fundamental types of electrical signals used to transmit information in various electronic systems. Analog signals are continuous and vary smoothly over time, while digital signals are discrete and represented by a series of discrete values.
Understanding the difference between these signals is important in telecommunications, electronics, and signal processing. In this article, we will go through the difference between analog and digital signals.
Table of Content
What is an Analog Signal?
What is digital signal, difference between analog and digital signal.
Analog signal is a type of signal that represents continuous data using a continuous range of values. In other words, it can take on any value within a certain range. Analog signals are characterized by their smooth and continuous nature.
For example, imagine a sound wave. In analog form, the sound wave is represented by a continuously varying electrical signal that mirrors the fluctuations in air pressure caused by the sound.
Digital signal is a type of signal that represents data as a sequence of discrete values, typically using binary numbers, it also contain different voltage values. Unlike analog signals, which vary continuously over time, digital signals are discrete and quantized, meaning they only take on specific, distinct values.
In digital communication and computing systems, information is encoded into digital signals for transmission, processing, and storage. These signals are commonly used in telecommunications, audio and video processing, computer networks, and many other applications.
The difference between analog signal and digital signal could be understood from the table given below:
Related Articles ,
Analog to Digital Conversion Digital to Analog Conversion Advantages and Disadvantages of Digital Signals Advantages and Disadvantages of Analog signals Different Types of Signals
Analog And Digital signal: FAQs
Give some examples of analog signal..
Some examples of analog signals are: Voltage fluctuations in an audio signal transmitted through a microphone. The varying voltage output from a potentiometer used to control the brightness of a light. The continuous waveforms produced by an analog clock’s minute hand as it moves around the face. The fluctuating voltage levels representing temperature readings from a thermocouple sensor.
Give some examples of digital signal.
Some examples of digital signals are: Binary signals transmitted over computer networks, represented by sequences of 0s and 1s. Digital audio signals encoded as a series of binary numbers in CDs or MP3 files. The square wave output from a digital pulse generator used in electronic testing equipment. The binary code stored in a digital memory chip, representing text, images, or program instructions.
Which is better: analog or digital signal?
It depends on the specific application. Analog signals are continuous and can represent a wide range of values with precision, while digital signals are discrete and offer better resistance to noise and distortion.
What are analog and digital signals used for?
Analog signals are used in older technologies like traditional telephones, vinyl records, and analog cameras. Digital signals are used in modern technologies like smartphones, digital cameras, and computers.
How to convert analog signal into digital signal?
Analog-to-digital conversion (ADC) is used to convert analog signals into digital ones. This process involves sampling the analog signal at regular intervals and measuring its amplitude at each sample point. The sampled values are then quantized and encoded into binary digits (bits) to create a digital representation of the original analog signal.

Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.
- Physics-Difference-Between
- School Learning
- School Physics
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?
Analog and Digital Communications
- Living reference work entry
- First Online: 31 July 2018
- Cite this living reference work entry

- Xin-Lin Huang 4
Analog and digital communications
Definitions
The analog signal can be one of infinite number of values, while the digital signal can only be one of finite number of values. The analog signal transmission from one part to other parts is called analog communications, while the digital signal transmission from one part to other parts is called digital communications.
Historical Background
In practice, most signals that exist in the nature are analog signals, such as voice, image, video, temperature, pressure, and so on. There are infinite numbers of possible values for analog signal, which is continuous with time in most cases. According to the Nyquist theorem, the low-pass and band-pass analog signals can be converted into digital signals through sampling, quantization, and coding processes, which is known as analog-to-digital converting (ADC). During the ADC process, the error called quantization error is caused in the quantization process. After ADC process, the analog signal...
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
Institutional subscriptions
Hui SY, Yeung KH (2003) Challenges in the migration to 4G mobile systems. IEEE Commun Mag 41(12):54–59
Article Google Scholar
Kumar A, Liu Y, Sengupta J, Divya JS (2010) Evolution of mobile wireless communication networks 1G to 4G. Int J Electr Commun Technol 1(1):68–72
Google Scholar
Tachikawa K (2003) A perspective on the evolution of mobile communications. IEEE Commun Mag 41(10):66–73
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Tongji University, Shanghai, China
Xin-Lin Huang
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Xin-Lin Huang .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Waterloo , Waterloo, ON, Canada
Xuemin (Sherman) Shen
Faculty of Business and Information Technology, University of Ontario Institute of Technology, Oshawa, ON, Canada
Xiaodong Lin
Dpt.of Electrical & Computer Engineering, University of Nebraska–Lincoln, Omaha, NE, USA
Section Editor information
No affiliation provided
Hsiao-hwa Chen
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer International Publishing AG, part of Springer Nature
About this entry
Cite this entry.
Huang, XL. (2018). Analog and Digital Communications. In: Shen, X., Lin, X., Zhang, K. (eds) Encyclopedia of Wireless Networks. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-32903-1_82-1
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-32903-1_82-1
Received : 11 March 2018
Accepted : 22 June 2018
Published : 31 July 2018
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-319-32903-1
Online ISBN : 978-3-319-32903-1
eBook Packages : Springer Reference Computer Sciences Reference Module Computer Science and Engineering
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
Tech Differences
Know the Technical Differences
Difference Between Analog and Digital Signal
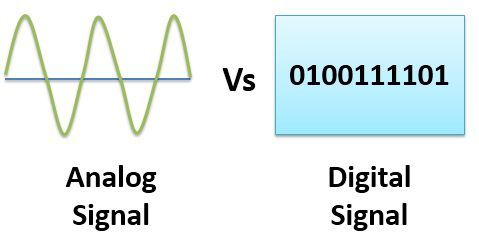
The fundamental difference between analog and digital signal is that analog signal is represented by the sine waves whereas, the digital signal is represented by square waves. Lets us learn some more differences between analog and digital signal with the help of comparison chart shown below.
Content: Analog Vs Digital Signal
Comparison chart.
- Key Differences
Definition of Analog Signal
Analog signal is a kind of continuous wave form that changes over time. An anlaog signal is further classified into simple and composite signals. A simple analog signal is a sine wave that cannot be decomposed further. On the other hand, a composite analog signal can be further decomposed into multiple sine waves.
An analog signal is described using amplitude, period or frequency and phase. Amplitude marks the maximum height of the signal. Frequency marks the rate at which signal is changing. Phase marks the position of the wave with respect to time zero.
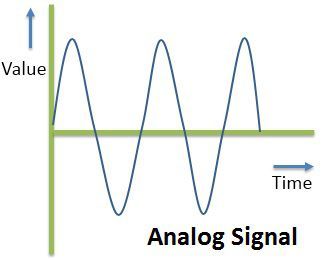
Definition of Digital Signal
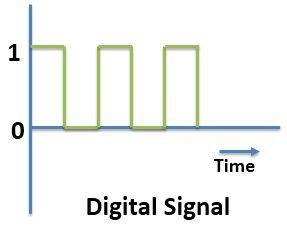
A digital signal is more immune to the noise; hence, it hardly faces any distortion. Digital signals are easier to transmit and are more reliable when compared to analog signals. Digital signal has a finite range of values. The digital signal consists 0s and 1s.
Key Differences Between Analog and Digital Signal
- An analog signal represents a continuous wave that keeps changing over a time period. On the other hand, a digital signal represents a noncontinuous wave that carries information in a binary format and has discrete values.
- An analog signal is always represented by the continuous sine wave whereas, a digital signal is represented by square waves.
- While talking of analog signal we describe the behaviour of the wave in respect of amplitude, period or frequency, and phase of the wave. On the other hand, while talking of discrete signals we describe the behaviour of the wave in respect of bit rate and bit interval.
- The range of an anlaog signal is not fixed whereas the range of the digital signal is finite and which can be 0 or 1.
- An analog signal is more prone to distortion in response to noise, but a digital signal has immunity in response to noise hence it rarely faces any distortion.
- An analog signal transmits data in the form of wave whereas, a digital signal transmits the data in the binary form i.e. in the form of bits.
- The best example of an analog signal is a human voice, and the best example of a digital signal is the transmission of data in a computer.
Digital signal is nowadays replacing the analog signal, but analog signal is still best for audio transmission.
Related Differences:
- Difference Between Modulation and Demodulation
- Difference Between AM and FM
- Difference Between Radio wave and Microwave
- Difference Between Analog and Digital Computer
- Difference Between QAM and QPSK
Shubham says
December 2, 2017 at 4:13 am
April 23, 2018 at 7:35 pm
Should include a venn diagram comparing and contrasting the two
your guy bill nye says
May 3, 2018 at 6:04 pm
this is awesome
Odd Number says
May 18, 2018 at 4:16 pm
That was a great content. Good, keep it up.
May 25, 2018 at 11:19 am
August 25, 2018 at 5:31 am
Wonderful points you have mentioned here, I really liked your article, your article is very petrified me in the learning process and provide additional knowledge to me, maybe I can learn more from you, Thank you
Jonas Mwanapabo says
August 30, 2018 at 6:26 pm
Really helpful information.
Harsh Dudhatra says
September 10, 2018 at 8:43 am
It was really very helpful
Shubham Bhosale says
September 18, 2018 at 12:12 pm
Good information
September 24, 2018 at 4:04 pm
This is so informative guys! Thank you
Wallace103 says
December 19, 2018 at 4:31 pm
it is awesome
Belbo Baigans says
December 31, 2018 at 5:43 am
Nice article dear
Pravin says
February 6, 2019 at 7:02 am
Nice….very informative article
February 15, 2019 at 6:25 pm
Nice information made easy. Hoping for more…
Bilbo Baggins says
February 19, 2019 at 6:57 pm
Very informative thank you, mam.
LeBronxiiii says
March 14, 2019 at 6:25 pm
Really nice!
March 18, 2019 at 11:40 pm
It does make sense……
March 25, 2019 at 4:01 pm
This was a good article.
Caroline says
March 26, 2019 at 7:17 pm
Your information is accurate.
March 26, 2019 at 7:41 pm
March 27, 2019 at 5:09 pm
this information was absolute
Jay McKenzie says
March 27, 2019 at 7:13 pm
wow. this is helpful.
Jannatul Ferdows Mim says
March 29, 2019 at 6:45 am
OH! Really like this 🙂
Jim Dougherty says
April 10, 2019 at 6:29 am
Very well done. The comparison between analog and digital signals was very easy to understand. Mentioning that analog was still the best method for transmitting audio means that we will be able to use radio receivers that were built decades ago well into the future.
Indi Jonk says
April 18, 2019 at 5:43 pm
Good article.
May 1, 2019 at 8:16 pm
Woooow so inspired
Akash rajoria says
May 11, 2019 at 2:13 am
It is very simple to learn. And each point is easy and clear. described in a good way…
May 23, 2019 at 10:44 pm
very useful!
May 29, 2019 at 3:33 pm
Lucid content….
August 7, 2019 at 1:40 pm
Awesome explanation!
August 23, 2019 at 7:31 pm
I finally understand the basics. Thank you.
Geenesh Acharya says
September 25, 2019 at 1:46 pm
Awesome explanation😍😍👌👌👌👌
abdur rahman vendeveluke says
September 25, 2019 at 2:36 pm
great content 🙂
Reyan Glioover says
October 14, 2019 at 8:22 am
Ooh i love this content….
October 14, 2019 at 4:00 pm
This was very helpful.
Damptey, Isaac says
October 22, 2019 at 7:51 pm
That’s really a nice content. I appreciate your efforts.
November 1, 2019 at 2:00 am
Very good information.
December 1, 2019 at 9:46 am
Very helpful information
January 14, 2020 at 9:17 pm
Good info so far but am i the only one from 2020!
Dinesh says
February 8, 2020 at 7:00 am
Nice.. Helpful information ☝️☝️
February 8, 2020 at 7:01 am
Jercy Packson says
February 27, 2020 at 8:44 pm
good article, I know how to use consultation
Thabani says
August 25, 2020 at 8:22 am
useful comment, thank you!
Jayden Burns says
November 11, 2020 at 3:11 pm
November 11, 2020 at 3:12 pm
I mean VERY good.
Mondo Cassie says
January 8, 2021 at 7:40 pm
Yo nice writing you got here! It was very informative
UNKNOWN says
May 17, 2021 at 4:04 pm
dont take down my comments i will find you
Amongus Balls says
November 30, 2021 at 5:53 pm
Tatsumi says
September 9, 2022 at 4:34 pm
sussybakadaddy says
February 24, 2023 at 4:23 pm
great information that i dissident need😐😐😐😐😐😐😐😐😐😐😐😐😐😐😐
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
Differentiate between analog and digital communication.
- COMMUNICATION


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
In digital communication physical transfer of data occurs in the form of digital bit stream i.e 0 or 1 over a point-to-point or point-to-multipoint transmission medium. In digital communication the digital transmission data can be broken into packets as discrete messages which is not allowed in analog communication.
2. Consumes less bandwidth than digital signals to carry the same information. 3. Analog systems are readily in place around the world. 11. 4. Analog signal is less susceptible to noise. Digital Signal:- • A digital signal is a discrete form. • It can have only a limited number of defined values such as 1 and 0.
Learning Objectives. Digital communication systems offer much more efficiency, better performance, and much greater flexibility. Analog communication systems, amplitude modulation (AM) radio being a typifying example, can inexpensively communicate a bandlimited analog signal from one location to another (point-to-point communication) or from ...
The other differences between Analog and Digital Communication can be understood with the help of comparison chart and key differences.
Analog and digital signals are used to transmit information, usually through electric signals. In both these technologies, the information, such as any audio or video, is transformed into electric signals. The difference between analog and digital technologies is that in analog technology, information is translated into electric pulses of varying amplitude. In digital technology, translation ...
In this analog vs digital article, we will also discuss the definition of digital communication. The definition of digital communication is the process of sending information that can be in the form of sound, images, and others through digital signals. Digital and analog signals are different things. The majority of modern technologies utilize digital communications, such as email, phone calls ...
This book primarily focuses on the design of analog and digital communication systems; and has been structured to cater to the second year engineering undergraduate students of Computer Science, Information Technology, Electrical Engineering and Electronics and Communication departments. For better understanding, the basics of analog communication systems are outlined before the digital ...
Analog communication systems, amplitude modulation (AM) radio being a typifying example, can inexpensively communicate a bandlimited analog signal from one location to another (point-to-point communication) or from one point to many (broadcast). Digital communication systems offer much more efficiency, better performance, and much greater flexibility.
In addition to digital communication's ability to transmit a wider variety of signals than analog systems, point-to-point digital systems can be organized into global (and beyond as well) systems that provide efficient and flexible information transmission. Computer networks, explored in the next section, are what we call such systems today.
There are also other approaches to spread-spectrum communications, such as frequency hopping. This used for robustness (resistance to jamming) and security.
In this post, we will take a look at the major differences between analog communication and digital communication by considering various parameters such as basic definition, cost, hardware technology, noise, power requirement, need of modulation, applications, etc. Also, a short description of analog communication and digital communication is added for your reference.
The major difference between analog and digital communication lies in the signal being transmitted. There exist some other crucial differences between the two which we will be going to discuss with the help of comparison chart.
In general, though, analog circuits are much more difficult to design than those which accomplish the same task digitally. It takes a special kind of analog circuit wizard to design an analog radio receiver, or an analog battery charger; digital components exist to make those designs much simpler.
Download Analog vs Digital Communication PowerPoint Presentation: Download PPT - https://refreshscience.com/analog-vs-... ...more
Communication is a vital aspect of modern society, and understanding the difference between analog and digital signals can lead to improved communication. Analog signals are continuous signals that can vary in amplitude, frequency, or phase, whereas digital signals are discrete signals that can only take on specific values.
It has a better noise immunity. The effect of distortion, noise and interference is less in a digital communication system. i.e., Digital circuits are less subject to distortion and interference than analog circuits. Low cost, VLSI technologies have made the cost of circuits for digital signals cheaper than that for analog signals.
Discuss the differences between the analog and digital systems to carry voice and data.
Analog and digital signals are two fundamental types of electrical signals used to transmit information in various electronic systems. Analog signals are continuous and vary smoothly over time, while digital signals are discrete and represented by a series of discrete values. Understanding the difference between these signals is important in ...
The modulation modes adopted in analog communications include amplitude modulation, frequency modulation, and phase modulation. Digital communication system uses digital amplitude modulation, digital phase modulation, digital frequency modulation, and APK modulation. Since the digital signal can only be one of finite number of values, the main difference of demodulations between analog and ...
The fundamental difference between analog and digital signal is that analog signal is represented by the sine waves whereas, the digital signal is represented by square waves. Lets us learn some more differences between analog and digital signal with the help of comparison chart shown below.
In this lecture of analog communication, Analog Signal, Characteristics of Analog signal, Digital Signal, Characteristics of Digital signal alongside analog...
Digital is defined as storing or recording information in binary code, using the numerals 0 and 1 to demonstrate whether the signal is absent or present. If you are responsible for choosing how people in your business communicate, it's helpful to know the differences between analog and digital communication.
Analog communication uses signals that can be represented by sine waves. Digital communication uses signals that can be represented by square waves. Analog communication signals consist of continuous values. Digital communication signals consist of discrete values. Analog communications are affected by noise.