- Magnetic & Mechanical Flow Meters & Environmental Sensors
- Flow Meters
- Smart Sensors
- Environmental
- Support & Resources
- Partner Login

Flow Meters and Environmental Sensors for Precision Fluid Measurement

100 Amazing Water Facts You Should Know
- Announcements
- Case Studies
- Customer Testimonials
- New Products
- Press Releases
- Uncategorized
Recent Posts
- It’s Spring Deployment Time
- Understanding 4-20mA Water Level Sensors
- A Winter Weather Guide to Protecting Equipment
- Efficient Irrigation Starts with the Flow Meter
- Enhancing Flood Monitoring with Advanced Sensor Technology

30% of fresh water is in the ground. 1
1.7% of the world’s water is frozen and therefore unusable. 1
Approximately 400 billion gallons of water are used in the United States per day. 1
Nearly one-half of the water used by Americans is used for thermoelectric power generation. 1
In one year, the average American residence uses over 100,000 gallons (indoors and outside). 1
Water can dissolve more substances than any other liquid including sulfuric acid. 1
The freezing point of water lowers as the amount of salt dissolved in at increases. With average levels of salt, seawater freezes at -2 °C (28.4 °F). 2
To create one pint of beer it takes 20 gallons of water. 3
780 million people lack access to an improved water source. 4
In just one day, 200 million work hours are consumed by women collecting water for their families. 4
1/3 what the world spends on bottled water in one year could pay for projects providing water to everyone in need. 4
Unsafe water kills 200 children every hour. 4
Water weighs about 8 pounds a gallon. 5
It takes 120 gallons of water for one egg. 5
A jellyfish and a cucumber are each 95% water. 5
80% of all illness in the developing world is water related. 6
Up to 50% of water is lost through leaks in cities in the developing world. 6
In Nairobi urban poor pay 10 times more for water than in New York. 6
In some countries, less than half the population has access to clean water. 7
$260 billion is the estimated annual economic loss from poor water and sanitation in developing countries. 7
40 billion hours are spent collecting water in Africa alone. 7
The average cost for water supplied to a home in the U.S. is about $2.00 for 1,000 gallons, which equals about 5 gallons for a penny. 8
A person can live about a month without food, but only about a week without water. 8
Water expands by 9% when it freezes. 8
There is about the same amount of water on Earth now as there was millions of years ago. 9
The length of the side of a cube which could hold the Earth’s estimated total volume of water in km = 1150. 10
Americans drink more than one billion glasses of tap water per day. 11
The United States draws more than 40 billion gallons (151 million liters) of water from the Great Lakes every day—half of which is used for electrical power production. 12
85% of the world population lives in the driest half of the planet. 13
Agriculture accounts for ~70% of global freshwater withdrawals (up to 90% in some fast-growing economies). 13
Various estimates indicate that, based on business as usual, ~3.5 planets Earth would be needed to sustain a global population achieving the current lifestyle of the average European or North American. 13
Thirty-six states are anticipating water shortages by 2016. 14
300 tons of water are required to manufacture 1 ton of steel. 15
1 in 6 gallons of water leak from utility pipes before reaching customers in the US. 15
American use 5.7 billion gallons per day from toilet flushes. 15
Refilling a half-liter water bottle 1,740 times with tap water is the equivalent cost of a 99 cent water bottle at a convenience store. 15
It takes about 12 gallons per day to sustain a human (this figure takes into account all uses for water, like drinking, sanitation and food production). 16
By 2025, water withdrawals are predicted to increase by 50 percent in developing countries and 18 percent in developed countries. 18
By 2025 half the world’s people will live in countries with high water stress. 19
A water-efficient dishwasher uses as little as 4 gallons per cycle but hand washing dishes uses 20 gallons of water. 20
The average family of four uses 180 gallons of water per day outdoors. It is estimated that over 50% is wasted from evaporation, wind, or overwatering. 20
It takes more than twice the amount of water to produce coffee than it does tea. 21
Chicken and goat are the least water intensive meats to consume. 21
There have been 265 recorded incidences of water conflicts from 3000 BC to 2012. 21
If the entire world’s water were fit into a 4 liter jug, the fresh water available for us would equal only about one tablespoon. 23
Over 90% of the world’s supply of fresh water is located in Antarctica. 23
Water regulates the Earth’s temperature. 23
On average, 10 gallons per day of your water footprint (or 14% of your indoor use) is lost to leaks. 24
The average pool takes 22,000 gallons of water to fill. 24
It takes about 70 gallons of water to fill a bathtub. 25
Flying from Los Angeles to San Francisco, about 700 miles round-trip, could cost you more than 9,000 gallons of water. 25
Water use has grown at more than twice the rate of population increase in the last century. 26
Only 0.007 percent of the planet’s water is available to fuel and feed its 6.8 billion people. 26
Three quarters of all Americans live within 10 miles of polluted water. 27
Producing a gallon (3.79 liters) of corn ethanol consumes 170 gallons (644 liters) of water in total, from irrigation to final processing. On the other hand, the water requirement to make a gallon of regular gasoline is just five gallons (19 liters). 28
40% of freshwater withdrawals in the United States are used for agriculture. 29
65% of freshwater withdrawals in China are used for agriculture. 29
Freshwater withdrawals for agriculture exceed 90% in many countries: Cambodia 94%, Pakistan 94%, Vietnam 95%, Madagascar 97%, Iran 92%, Ecuador 92%. 29
If everyone in the US flushed the toilet just one less time per day, we could save a lake full of water about one mile long, one mile wide and four feet deep. 30
If everyone in the US used just one less gallon of water per shower every day, we could save some 85 billion gallons of water per year. 30
Over 42,000 gallons of water (enough to fill a 30×50 foot swimming pool) are needed to grow and prepare food for a typical Thanksgiving dinner for eight. 31
An acre of corn will give off 4,000 gallons of water per day in evaporation. 31
In a 100-year period, a water molecule spends 98 years in the ocean, 20 months as ice, about 2 weeks in lakes and rivers, and less than a week in the atmosphere. 31
Water is the most common substance found on earth. 31
Water makes up about 66 percent of the human body. 33
There are no scientific studies that support the recommendation to drink 8 glasses of water per day. 33
Drinking too much water can be fatal (known as water intoxication). 33
There is more fresh water in the atmosphere than in all of the rivers on the planet combined. 34
If all of the water vapor in the Earth’s atmosphere fell at once, distributed evenly, it would only cover the earth with about an inch of water. 34
It takes seven and a half years for the average American residence to use the same amount of water that flows over the Niagara Falls in one second (750,000 gallons). 34
263 rivers either cross or demarcate international political boundaries. 35
Of the estimated 1.4 billion hectares of crop land worldwide, around 80 percent is rainfed and accounts for about 60 percent of global agricultural output (the other 40% of output is from irrigated crop land). 36
Ten percent of homes have leaks that waste 90 gallons or more per day. 37
A leaky faucet that drips at the rate of one drip per second can waste more than 3,000 gallons per year. 37
Each cubic foot of Martian soil contains around two pints of liquid water, though the molecules are not freely accessible, but rather bound to other minerals in the soil. 38
There is an estimated 326 million trillion gallons of water on earth. 39
NASA has discovered water in the form of ice on the moon. 40
A 2.6 billion year old pocket of water was discovered in a mine, 2 miles below the earth’s surface. 41
1 pound of beef requires 1,799 gallons of water. 43
1 gallon of wine requires 1,008 gallons of water. 43
A 0.3 pound burger requires 660 gallons of water. 43
1 slice of bread requires 11 gallons of water. 43
1 apple requires 18 gallons of water. 43
1 pound of chocolate requires 3,170 gallons of water. 43
500 sheets of paper requires 1,321 gallons of water. 43
Ground water occurs almost everywhere beneath the land surface. The widespread occurrence of potable ground water is the reason that it is used as a source of water supply by about one-half the population of the United States. 44
Hydrologists estimate, according to the National Geographic Society, U.S. groundwater reserves to be at least 33,000 trillion gallons — equal to the amount discharged into the Gulf of Mexico by the Mississippi River in the past 200 years. 45
At any given moment, groundwater is 20 to 30 times greater than the amount in all the lakes, streams, and rivers of the United States. 45
About 27 trillion gallons of groundwater are withdrawn for use in the U.S. each year. 46
References: 1. http://water.epa.gov/learn/kids/drinkingwater/water_trivia_facts.cfm 2. http://www.sciencekids.co.nz/sciencefacts/water.html 3. http://www.water.siemens.com/en/about_us/Pages/Water_Footprint.aspx 4. http://blueplanetnetwork.org/water/ 5. http://www.fs.usda.gov/Internet/FSE_DOCUMENTS/stelprdb5303137.doc 6. http://www.cnn.com/SPECIALS/road-to-rio/secret-life-drinking-water 7. http://fieldnotes.unicefusa.org/infographic-world-water-crisis 8. http://water.epa.gov/learn/kids/drinkingwater/waterfactsoflife.cfm 9. http://dnr.wi.gov/org/caer/ce/eek/earth/conserve.htm 10. http://www.brita.net/blue_wonder.html 11. http://www.baycountyfl.gov/water/facts.php 12. http://aqua.wisc.edu/waterlibrary/Default.aspx?tabid=74 13. http://www.unwater.org/water-cooperation-2013/water-cooperation/facts-and-figures/en/ 14. http://www.campusrec.illinois.edu/goGreen/facts.html 15. http://images.fastcompany.com/magazine/154/infographic/water-world.html 16. http://science.howstuffworks.com/environmental/earth/geophysics/run-out-of-water.htm 17. http://science.howstuffworks.com/environmental/earth/geophysics/h2o.htm 18. http://www.ifad.org/english/water/key.htm 19. http://www.worldwatercouncil.org/fileadmin/world_water_council/documents_old/Library/WWVision/Chapter3.pdf 20. http://awesome.good.is/transparency/web/1204/your-daily-dose-of-water/flash.html 21. http://pacinst.org/publication/10-shocking-facts-about-worlds-water/ 22. http://math.ucr.edu/home/baez/physics/General/hot_water.html 23. http://www.waterwise.org.uk/pages/fun-facts.html 24. http://environment.nationalgeographic.com/environment/freshwater/water-conservation-tips/?rptregcta=reg_free_np&rptregcampaign=20131016_rw_membership_r1p_us_se_w# 25. http://environment.nationalgeographic.com/environment/freshwater/water-conservation-tips/?rptregcta=reg_free_np&rptregcampaign=20131016_rw_membership_r1p_us_se_w# 26. http://environment.nationalgeographic.com/environment/freshwater/freshwater-crisis/ 27. https://donate.nationalgeographic.org/SSLPage.aspx?pid=1071 28. http://www.scientificamerican.com/article/top-10-water-wasters/ 29. http://data.worldbank.org/indicator/ER.H2O.FWAG.ZS 30. http://www.sandiego.gov/water/conservation/kids/funfacts.shtml 31. http://www.cleanwaterways.org/kids/fun_facts.html 32. http://nsidc.org/cryosphere/glaciers/quickfacts.html 33. http://www.scientificamerican.com/article/strange-but-true-drinking-too-much-water-can-kill/ 34. http://www.afcec.af.mil/shared/media/document/AFD-130322-056.pdf 35. http://www.transboundarywaters.orst.edu/publications/atlas/atlas_html/interagree.html 36. http://www.fao.org/ag/save-and-grow/en/5/index.html 37. http://www.epa.gov/WaterSense/pubs/fixleak.html 38. http://www.theguardian.com/science/2013/sep/26/nasa-curiosity-rover-mars-soil-water 39. http://science.howstuffworks.com/environmental/earth/geophysics/question157.htm 40. http://www.cnn.com/2009/TECH/space/11/13/water.moon.nasa/index.html?iref=24hours 41. http://www.livescience.com/32028-oldest-water-found-underground.html 42. http://online.wsj.com/news/articles/SB123483638138996305 43. http://environment.nationalgeographic.com/environment/freshwater/embedded-water/ 44. http://pubs.usgs.gov/circ/circ1186/html/gen_facts.html 45. http://www.ngwa.org/Fundamentals/use/Pages/Groundwater-facts.aspx 46. http://www.groundwater.org/get-informed/facts.html
Update: Five facts have been removed as they were pointed out to be inaccurate or redundant. Thanks to the following people who helped us improve this page:
@seametricsinc @MGhydro Wrong: 50% of FW is in Canada and 20% of 'available' FW is in Great Lakes. Also half water supply in 9 countries — Michael E. Campana (@WaterWired) April 28, 2014
@cbdawson glaciers have 68.7% of global freshwater (listed twice) or 75% (listed once) … (1/n) @WaterWired @seametricsinc — Anas Matthæus (@MGhydro) April 28, 2014
@MGhydro @WaterWired @seametricsinc I think that happens a lot. I looked, and it's a quote from a USDA & NPS source, sadly wrong. — Cian Dawson (@cbdawson) April 28, 2014
Have feedback or suggestion of an interesting water fact? Leave it below in the comments.

10 Interesting Things About Water
Water could be the key to finding life.
There aren’t many qualities that are true of all life on Earth, but the need for water is one of them. It’s in all living things, whether they live at the bottom of the ocean or the driest desert. Water made life possible on Earth. Because of this, astrobiologists (scientists who search for life on other planets) think our best bet for finding life is to search for water.
Almost all Earth’s water is in the oceans.
A whopping 96.5 percent of water on Earth is in our oceans, covering 71 percent of the surface of our planet. And at any given time, about 0.001 percent is floating above us in the atmosphere. If all of that water fell as rain at once, the whole planet would get about 1 inch of rain.
Most freshwater is in ice.
Just 3.5 percent of Earth’s water is fresh—that is, with few salts in it. You can find Earth’s freshwater in our lakes, rivers, and streams, but don’t forget groundwater and glaciers. Over 68 percent of Earth’s freshwater is locked up in ice and glaciers. And another 30 percent is in groundwater.
The amount of salt in salt water varies.
In a gallon of average ocean water, there is about 1 cup of salt. But it does vary. The Atlantic Ocean is saltier than the Pacific Ocean, for instance. Most of the salt in the ocean is the same kind of salt we put on our food: sodium chloride. The saltiest water in the world is found in Antarctica in a small lake named Don Juan Pond.
A lot can live in one drop of water.
There can be a lot going on in a single drop of ocean water. It will most likely have millions (yes, millions!) of bacteria and viruses. And it could also have fish eggs, baby crabs, plankton, or even small worms.
Some water may have come from comets.
The rocky material that formed Earth contained some water. But that probably doesn't account for all the water we see today. Comets are mostly water ice. It’s possible that comets made regular water deliveries to Earth. It would take a lot of comets to fill the ocean, but comets could well have made a big contribution.
It’s really great that ice floats.
Usually when solids form, atoms get closer together to form something denser. This is why most solids sink in water. But solid water, or ice, is actually less dense. This is unusual. The water molecules form rings when water freezes. All that space makes ice less dense. This is why it floats. This is great because ice floating on top of a body of water lets the rest of it stay liquid. If ice sank, whole oceans could freeze solid!
Our bodies are mostly water.
A newborn baby is 78 percent water. Adults are 55-60 percent water. Water is involved in just about everything our body does. It’s a big part of the blood that brings nutrients to all our cells. We use it to get rid of wastes. It helps us regulate our body temperature. It acts as a shock absorber for our brain and spinal cord. We are very dependent on water.
In plants, water defies gravity.
Water has an interesting characteristic. It’s sort of “sticky.” It likes to stick to itself and other things. That’s why water forms round droplets. Not all liquids do that. This “stickiness” helps get water from the roots of plants up to the leaves. Water molecules travel up thin straws called xylem in the plant by holding onto each other and the walls of the tube. They’re pulled upwards as water evaporates from the leaves at the top.
We get to see water in three different states, and that’s odd.
We experience water in all three states: solid ice, liquid water, and gas water vapor. That’s actually pretty unusual. While all substances can be solid, liquid, or gas, a lot of them only change states at extreme temperatures. You probably don’t see liquid silver or solid oxygen very much because their melting points and freezing points are at temperatures that would kill us.
Next: 10 Interesting Things About Earth

34 Eye-Opening Facts About Water
Melissa Breyer is Treehugger’s former senior editorial director. Her writing and photography have been featured in The New York Times, The Guardian, National Geographic, Audubon Magazine, and elsewhere.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/mb-head-8efe594c4cb4485b8a5605a4fe1d015d.jpg)
- Hunter College
- F.I.T., State University of New York
- Cornell University
Treehugger / Kristine Klaire Hojilla
- Conservation
In 1993, the United Nations General Assembly designated March 22 as the first World Water Day. And with good reason – without water, we’d be nothing. Just dust. Water is one of the most common substances on earth, and one of the most vital; it’s a tremendously valuable resource, yet one we squander and pollute prodigiously .
So Much Water, So Little Usable
Water is deceptive. For while it pours freely from the heavens and seems to flow endlessly in rivers, it’s a finite resource; we only have what we have. And although there is about 332,500,000 cubic miles of it on earth – only one-hundredth of one percent of the world's water is readily available for human use. We really need to learn how to show it some respect. Which is where World Water Day comes in. Even though water deserves celebration every day, we’ll take this occasion to give a shout-out to this incredible compound that gives us life and sustains the planet around us. So with that in mind, consider the following facts – some wondrous, some disconcerting, all eye-opening.
Facts About Water
1. The average human body is made of 55 to 65 percent water.
2. Newborn babies have even more, ringing in at 78 percent water.
3. A gallon of water weighs 8.34 pounds; a cubic foot of water weighs 62.4 pounds.
4. A liter of water weighs 1 kilo; a cubic meter of water weighs 1 metric ton. (The rest of the statistics are in imperial units since they are U.S.-based and so is this site; but the original metric system was created with base units that could be derived from the weight of a specified volume of pure water ... hence the nice round numbers.)
5. An inch of water covering one acre (27,154 gallons) weighs 113 tons.
6. Water covers 70.9 percent of the planet’s surface.
7. 97 percent of the water on Earth is found in the ocean; 2.5 percent is unavailable fresh water (trapped in glaciers, underground, etc); and 0.5 percent is available freshwater.
8. There is more water in the atmosphere than in all of our rivers combined.
9. If all of the water vapor in our planet’s atmosphere fell as water at once and spread out evenly, it would only cover the globe with about an inch of water.
10. More than one-quarter of all bottled water comes from a municipal water supply – the same place that tap water comes from.
11. Approximately 322 billion gallons of water were used each day in the United States in 2015.
12. In a year, the average American residence uses over 100,000 gallons.
13. Since the average faucet releases 2 gallons of water per minute, you can save up to four gallons of water every morning by turning off the tap while you brush your teeth.
14. A running toilet can waste up to 200 gallons of water each day.
15. At one drip per second, a faucet can leak 3,000 gallons in a year.
16. A bath uses up to 70 gallons of water; a five-minute shower uses 10 to 25 gallons.
17. The first water pipes in the U.S. were made from hollowed logs.
18. Leaks in the New York City water supply system account for 33 to 37 million gallons of wasted water per day.
19. There are around one million miles of water pipeline and aqueducts in the U.S. and Canada, enough to circle the globe 40 times.
20. 748 million people in the world do not have access to an improved source of drinking water.
21. And 2.0 billion people do not have use of an improved sanitation facility.
22. Some 1.8 billion people worldwide drink water that is contaminated with feces.
23. The World Health Organization recommends 2 gallons per person daily to meet the requirements of most people under most conditions; and around 5 gallons per person daily to cover basic hygiene and food hygiene needs.
24. On average, an American resident uses about 100 gallons of water per day.
25. On average, a European resident uses about 50 gallons of water per day.
26. It takes .26 gallons of water to irrigate one calorie of food.
27. (Yet it takes 26 gallons for one calorie of food when water is used inefficiently.)
28. It takes 2.6 gallons of water to make a sheet of paper.
29. It takes 6.3 gallons of water to make 17 ounces of plastic.
30. It takes 924 gallons of water to produce 2.2 pounds of rice.
31. It takes 2,641 gallons of water to make a pair of jeans.
32. It takes 3,962 gallons of water to produce 2.2 pounds of beef.
33. It takes 39,090 gallons of water to manufacture a new car.
34. Collectively, South African women and children walk a daily distance equivalent to 16 trips to the moon and back to fetch water.
“ How Much Water is There on Earth? .” U.S. Geological Survey.
“ Water: A Finite Resource .” Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations .
“ The Water in You: Water and the Human Body .” U.S. Geological Survey .
W. David Yates. Safety Professional's Reference and Study Guide, Third Edition . Taylor & Francis Group, 2020.
“ Weights and Measures .” Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations .
“ Rain and Precipitation .” U.S. Geological Survey .
“ Volumes of the World's Oceans from ETOPO1 .” National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration .
“ Water Facts - Worldwide Water Supply .” Bureau of Reclamation California-Great Basin.
National Wildlife Volume 2 . University of Chicago, 1963
“ The Atmosphere and the Water Cycle .” U.S. Geological Survey .
“ Do you still drink bottled water? .” Columbia University .
“ Total Water Use in the United States .” U.S. Geological Survey.
“ Water Trivia Facts .” United States Environmental Protection Agency.
“ Indoor Water Use in the USA .” Environmental Protection Agency .
“ Fix a Leak Week .” United States Environmental Protection Agency.
“ The WaterSense Current: Summer 2017 .” United States Environmental Protection Agency.
“ Delaware Aqueduct Leak .” Riverkeeper.
“ International Decade for Action: Water for Life .” United Nations .
“ Sanitation .” World Health Organization.
" Water .” World Health Organization .
“ What is the minimum quantity of water needed? .” World Health Organization .
“ Facts and Figures About Water .” World Water Council .
“ Water Equivalency Facts .” TMI Sustainable Aquatics .
“ Drinking Water Facts and Figures .” United States Environmental Protection Agency .
Murray, Anne Firth. From Outrage to Courage: The Unjust and Unhealthy Situation of Women in Poorer Countries and What They are Doing About It . Common Courage Press, 2013.
- 11 Clever Ways to Conserve Water at Home
- Earth Month Challenge: 30 Easy Actions for Every Day of April
- 5 Easy Ways to Save a Lot of Water
- Eco-Friendly Laundry: 11 Low-Tech and Simple Methods for Washing Clothes More Sustainably
- 10 of the Largest Living Things on the Planet
- 10 Ways to Stop Being a Water Waster
- How Much Air Pollution Comes From Cars?
- How to Go Green: In the Bathroom
- Cape Town *May* Not Run Out of Water After All
- 10 Tips for Making Your Dishwasher More Efficient
- Maple Sap and Syrup Production
- 15 Astounding Facts About Trees
- What's the Greenest Way to Get Around Town?
- These Countries Are the World's Biggest Water Wasters
- 5 Satisfying Food Swaps to Help the Planet
- Shower Less to Help Save the Planet

- High contrast
- Press Centre
Search UNICEF
10 things you didn't know about water, how unsafe water, sanitation and hygiene puts children at risk..
- Available in:
Most people know that you can’t survive without water. But the truth is slightly more nuanced. You need more than just water – you need SAFE water.
You also need safe toilets to keep the environment clean, and as well as soap and water to stop the spread of disease.
Find out more about why safe water, sanitation and hygiene are so important:
1. There is a water crisis and it’s happening now. 2.2 billion people still do not have access to safely managed drinking water.
2. Water needs to be more than clean, it must be “safely managed” . Safely managed water means having water at home (on premises), whenever needed, and free from contamination.
3. Without safely managed sanitation, diseases spread rapidly. 3.6 billion people – nearly half of the world – do not have access to safely managed sanitation, meaning a toilet that separates human waste from contact, and a system to ensure that the waste is safely disposed of.
4. Open defecation is one of the clearest signs of inequality. 494 million people practice open defecation, meaning they go out on the side of the road, in fields or bushes.
5. Children are most at risk . Every day, over 1000 children under 5 die from diseases linked to unsafe water, sanitation and hygiene, which also kills 1.4 million people every year.

6. Babies are being born in dirty conditions. In the world’s least developed countries, 16.6 million women give birth in health centres with inadequate water, sanitation and hygiene – putting them at risk of infection, disease and death.
7. Preventing diseases isn’t as easy as it should be. Handwashing with soap and water is one of the simplest and most effective ways to prevent the spread of disease. But 2.3 billion people still don’t have basic handwashing facilities with soap and water at home. That’s nearly a third of the world’s population.
8. Climate change is making it worse. The changing climate is destroying, drying up and contaminating water sources. In 2022, 436 million children were living in areas with high or extremely high water vulnerability, which is being exacerbated by climate change.
9. Rural populations are the most disadvantaged. 8 out of 10 people who lack even basic drinking water live in rural areas. Two-thirds of people who lack even basic sanitation live in rural areas. 9 out of 10 people who practice open defecation live in rural areas.
10. We must do more. The world is not on track to meet the Sustainable Development Goal 6: access to safe water, sanitation and hygiene for all. UNICEF calls for greater political prioritization and increased funding to improve household access to water, sanitation and hygiene, targeting communities most at risk.
Related topics
More to explore, data analysis.
Joint UNICEF-WHO report reveals latest data and gaps in access to basic water, sanitation and hygiene services
1 in 3 people globally do not have access to safe drinking water – UNICEF, WHO
New guidelines launched to protect children and pregnant women from heat stress in Bangladesh
Kingdom of Saudi Arabia pledges US $500 million to protect children around the world from polio and end the disease for good
Essay on Water for Students and Children
500+ words essay on water.
Water is one of the most important substances for life on earth to function. It is equally important for humans as well as animals. Water does not merely help us survive, but it is significant for our day to day functioning. It has numerous uses when we come to think about it. Majority of our earth is covered with water itself, but, not all of it is safe for consumption. Therefore, it makes it essential for us to utilize this transparent substance chemical wisely. Moreover, if we look at the shortage of water happening in our country, it makes it all the more important to conserve it immediately.

Uses of Water
As we have already said that water has numerous uses, we will see where it is used. This part will most importantly help us realize the importance of water . It will make humans aware of what absence of water in the following areas can do to human life. As India’s main occupation is agriculture, water is exhaustively used here. Irrigation and cattle rearing requires a lot of water. Thus, a lot of farmers’ livelihood depends on it.
Further, industries use water for various purposes. It comes in handy when cooling, manufacturing and transporting several goods. For instance, thermal power plants consume quite a substantial amount of water for their running.
Furthermore, the domestic use of water cannot be left behind. In the day to day life of the common man, water plays a vital role. That is to say, from drinking water to washing utensils, we need water every step of the way.
After that, plants need water to survive and make food. It is one of the main elements which help them grow. Hence, water is extremely important for humans, animals, and plants to survive .
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
Do not Waste Water
While water is quite essential and yet so scarce, however, people fail to realize this fact. They waste water with little or no care for the results of this activity. There are various ways in which one can avoid wasting water . To begin with, all households must get their leaking taps checked. They should fix them immediately as every drop is precious.
Similarly, we must choose buckets instead of showers for bathing. This is a very debatable topic and it needs to be settled. Showers waste a lot of water, so people must prefer buckets. This particular habit is quite commonly found in most of the households. People do not turn off their taps while brushing their teeth and washing utensils. Always remember to keep the tap off when doing so.
In addition, encourage rainwater harvesting system in all homes. This can help conserve water like never before.
In short, water is essential for the survival of mankind. But, it is, unfortunately, being waster rapidly. Every citizen and government must come together to tackle this issue. Governments must ensure all areas get water equally. On the other hand, citizens must keep in mind to use it wisely and not waste it unnecessarily.
FAQs on Water
Q.1 State the importance of water.
A.1 Water is of the utmost importance for human and animal life. It gives us water to drink. It also comes in great use for farmers and industries. Even common man requires water for various purposes like drinking, cleaning, bathing and more.
Q.2 List the ways to avoid wastage of water.
A.2 Everyone must avoid wasting water. We can do so by fixing our leaking taps, avoiding showers for bathing, and turning off taps when brushing. Furthermore, we can adopt rainwater harvesting system to conserve water.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App


News | August 15, 2016
10 interesting things about water, water could be the key to finding life.
There aren't many qualities that are true of all life on Earth, but the need for water is one of them. It's in all living things, whether they live at the bottom of the ocean or the driest desert. Water's properties and abundance made life possible on Earth. Because of this, astrobiologists think our best bet for finding life on other planets is to search for water.
Almost all Earth's water is in the oceans
A whopping 96.5 percent of water on Earth is in our oceans, covering 71 percent of the surface of our planet. And at any given time, about 0.001 percent is floating above us in the atmosphere. If all of that water fell as rain at once, the whole planet would get about 1 inch of rain.
Most freshwater is in ice
Just 3.5 percent of Earth's water is fresh - that is, with few dissolved salts. You can find Earth's freshwater in our lakes, rivers, and streams, but don't forget groundwater and glaciers. Over 68 percent of Earth's freshwater is locked up in ice and glaciers. And another 30 percent is in groundwater.
The amount of salt in salt water varies
In a gallon of average ocean water, there is about 1 cup of salt. But it does vary. The Atlantic Ocean is saltier than the Pacific Ocean, for instance. Most of the salt in the ocean is the same kind of salt we put on our food: sodium chloride. The saltiest water in the world is found in Antarctica in a small lake named Don Juan Pond.
A lot can live in one drop of water
There can be a lot going on in a single drop of ocean water. It will most likely have millions (yes, millions!) of bacteria and viruses. And it could also have fish eggs, baby crabs, plankton, or even small worms.
Some water may have come from comets
The rocky material that formed Earth contained some water, but that probably doesn't account for all the water we see today. Comets are mostly water ice, and it's possible that comets made regular water deliveries to Earth. It would take a lot of comets to fill the ocean, but comets could well have made a big contribution.
It's really great that ice floats
Usually when solids form, atoms get closer together to form a material that is denser. This is why most solids sink. But solid water, or ice, is actually less dense, which is unusual. The water molecules form rings when water freezes, and all that space makes ice less dense. That's why it floats. This is great because ice floating on top of a body of water lets the rest of it stay liquid. If ice sank, whole oceans could freeze solid!
Our bodies are mostly water
A newborn baby is 78 percent water. Adults are 55-60 percent water. Water is involved in just about everything our body does. It's a big part of the blood that brings nutrients to all our cells. We use it to get rid of wastes. It helps us regulate our body temperature. It acts as a shock absorber for our brain and spinal cord. We are very dependent on water.
In plants, water defies gravity
An interesting property of water is that it's sort of "sticky." It likes to stick to itself and other things. That's why water forms round droplets. Not all liquids do that. This "stickiness" helps get water from the roots of plants up to the leaves. Water molecules travel up thin straws called xylem in the plant by holding onto each other and the walls of the tube. They're pulled upwards as water evaporates from the leaves at the top.
We get to see water in three different states, and that's odd
We experience water in all three states: solid ice, liquid water, and gas water vapor. That's actually pretty unusual. While all substances can be solid, liquid, or gas, a lot of them only change states at extreme temperatures. You probably don't see liquid silver or solid oxygen very much because their melting points and freezing points are at temperatures that would kill us.
Related Stories

All About the Ocean
The ocean covers 70 percent of Earth's surface.
Biology, Earth Science, Oceanography, Geography, Physical Geography
Loading ...
This article is also available in Spanish .
The ocean covers 70 percent of Earth 's surface. It contains about 1.35 billion cubic kilometers (324 million cubic miles) of water, which is about 97 percent of all the water on Earth. The ocean makes all life on Earth possible, and makes the planet appear blue when viewed from space. Earth is the only planet in our solar system that is definitely known to contain liquid water. Although the ocean is one continuous body of water, oceanographers have divided it into five principal areas: the Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, Arctic, and Southern Oceans. The Atlantic, Indian, and Pacific Oceans merge into icy waters around Antarctica. Climate The ocean plays a vital role in climate and weather . The sun’s heat causes water to evaporate , adding moisture to the air. The oceans provide most of this evaporated water. The water vapor condenses to form clouds, which release their moisture as rain or other kinds of precipitation . All life on Earth depends on this process, called the water cycle . The atmosphere receives much of its heat from the ocean. As the sun warms the water, the ocean transfers heat to the atmosphere. In turn, the atmosphere distributes the heat around the globe. Because water absorbs and loses heat more slowly than land masses, the ocean helps balance global temperatures by absorbing heat in the summer and releasing it in the winter. Without the ocean to help regulate global temperatures, Earth’s climate would be bitterly cold. Ocean Formation After Earth began to form about 4.6 billion years ago, it gradually separated into layers of lighter and heavier rock. The lighter rock rose and formed Earth’s crust . The heavier rock sank and formed Earth’s core and mantle . The ocean’s water came from rocks inside the newly forming Earth. As the molten rocks cooled, they released water vapor and other gases. Eventually, the water vapor condensed and covered the crust with a primitive ocean. Today, hot gases from the Earth’s interior continue to produce new water at the bottom of the ocean. Ocean Floor Scientists began mapping the ocean floor in the 1920s. They used instruments called echo sounders , which measure water depths using sound waves . Echo sounders use sonar technology. Sonar is an acronym for SOund Navigation And Ranging. The sonar showed that the ocean floor has dramatic physical features, including huge mountains, deep canyons , steep cliffs , and wide plains . The ocean’s crust is a thin layer of volcanic rock called basalt . The ocean floor is divided into several different areas. The first is the continental shelf , the nearly flat, underwater extension of a continent. Continental shelves vary in width. They are usually wide along low-lying land, and narrow along mountainous coasts. A shelf is covered in sediment from the nearby continent. Some of the sediment is deposited by rivers and trapped by features such as natural dams. Most sediment comes from the last glacial period , or Ice Age, when the oceans receded and exposed the continental shelf. This sediment is called relict sediment . At the outer edge of the continental shelf, the land drops off sharply in what is called the continental slope . The slope descends almost to the bottom of the ocean. Then it tapers off into a gentler slope known as the continental rise. The continental rise descends to the deep ocean floor, which is called the abyssal plain . Abyssal plains are broad, flat areas that lie at depths of about 4,000 to 6,000 meters (13,123 to 19,680 feet). Abyssal plains cover 30 percent of the ocean floor and are the flattest feature on Earth. They are covered by fine-grained sediment like clay and silt. Pelagic sediments, the remains of small ocean organisms, also drift down from upper layers of the ocean. Scattered across abyssal plains are abyssal hills and underwater volcanic peaks called seamounts. Rising from the abyssal plains in each major ocean is a huge chain of mostly undersea mountains. Called the mid-ocean ridge , the chain circles Earth, stretching more than 64,000 kilometers (40,000 miles). Much of the mid-ocean ridge is split by a deep central rift, or crack. Mid-ocean ridges mark the boundaries between tectonic plates . Molten rock from Earth’s interior wells up from the rift, building new seafloor in a process called seafloor spreading . A major portion of the ridge runs down the middle of the Atlantic Ocean and is known as the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. It was not directly seen or explored until 1973. Some areas of the ocean floor have deep, narrow depressions called ocean trenches . They are the deepest parts of the ocean. The deepest spot of all is the Challenger Deep , which lies in the Mariana Trench in the Pacific Ocean near the island of Guam. Its true depth is not known, but the most accurate measurements put the Challenger Deep at 11,000 meters (36,198 feet) below the ocean’s surface—that’s more than 2,000 meters (6,000 feet) taller than Mount Everest, Earth’s highest point. The pressure in the Challenger Deep is about eight tons per square inch.
Ocean Life Zones From the shoreline to the deepest seafloor, the ocean teems with life. The hundreds of thousands of marine species range from microscopic algae to the largest creature to have ever lived on Earth, the blue whale. The ocean has five major life zones, each with organisms uniquely adapted to their specific marine ecosystem . The epipelagic zone (1) is the sunlit upper layer of the ocean. It reaches from the surface to about 200 meters (660 feet) deep. The epipelagic zone is also known as the photic or euphotic zone, and can exist in lakes as well as the ocean. The sunlight in the epipelagic zone allows photosynthesis to occur. Photosynthesis is the process by which some organisms convert sunlight and carbon dioxide into energy and oxygen . In the ocean, photosynthesis takes place in plants and algae. Plants such as seagrass are similar to land plants—they have roots, stems, and leaves. Algae is a type of aquatic organism that can photosynthesize sunlight. Large algae such as kelp are called seaweed . Phytoplankton also live in the epipelagic zone. Phytoplankton are microscopic organisms that include plants, algae, and bacteria. They are only visible when billions of them form algal blooms , and appear as green or blue splotches in the ocean. Phytoplankton are a basis of the ocean food web . Through photosynthesis, phytoplankton are responsible for almost half the oxygen released into Earth’s atmosphere. Animals such as krill (a type of shrimp), fish, and microscopic organisms called zooplankton all eat phytoplankton. In turn, these animals are eaten by whales, bigger fish, ocean birds, and human beings. The next zone down, stretching to about 1,000 meters (3,300 feet) deep, is the mesopelagic zone (2). This zone is also known as the twilight zone because the light there is very dim. The lack of sunlight means there are no plants in the mesopelagic zone, but large fish and whales dive there to hunt prey . Fish in this zone are small and luminous . One of the most common is the lanternfish, which has organs along its side that produce light. Sometimes, animals from the mesopelagic zone (such as sperm whales ( Physeter macrocephalus ) and squid) dive into the bathypelagic zone (3), which reaches to about 4,000 meters (13,100 feet) deep. The bathypelagic zone is also known as the midnight zone because no light reaches it. Animals that live in the bathypelagic zone are small, but they often have huge mouths, sharp teeth, and expandable stomachs that let them eat any food that comes along. Most of this food comes from the remains of plants and animals drifting down from upper pelagic zones. Many bathypelagic animals do not have eyes because they are unneeded in the dark. Because the pressure is so great and it is so difficult to find nutrients , fish in the bathypelagic zone move slowly and have strong gills to extract oxygen from the water. The water at the bottom of the ocean, the abyssopelagic zone (4), is very salty and cold (2 degrees Celsius, or 35 degrees Fahrenheit). At depths up to 6,000 meters (19,700 feet), the pressure is very strong—11,000 pounds per square inch. This makes it impossible for most animals to live. Animals in this zone have bizarre adaptations to cope with their ecosystem. Many fish have jaws that look unhinged. The jaws allow them to drag their open mouth along the seafloor to find food, such as mussels, shrimp, and microscopic organisms. Many of the animals in this zone, including squid and fish, are bioluminescent. Bioluminescent organisms produce light through chemical reactions in their bodies. A type of angler fish, for example, has a glowing growth extending in front of its huge, toothy mouth. When smaller fish are attracted to the light, the angler fish simply snaps its jaws to eat its prey. The deepest ocean zone, found in trenches and canyons, is called the hadalpelagic zone (5). Few organisms live here. They include tiny isopods , a type of crustacean related to crabs and shrimp. Invertebrates such as sponges and sea cucumbers thrive in the abyssopelagic and hadalpelagic zones. Like many sea stars and jellyfish, these animals are almost entirely dependent on falling parts of dead or decaying plants and animals, called marine detritus . Not all bottom dwellers, however, depend on marine detritus. In 1977, oceanographers discovered a community of creatures on the ocean floor that feed on bacteria around openings called hydrothermal vents. These vents discharge superheated water enriched with minerals from Earth’s interior. The minerals nourish unique bacteria, which in turn nourish creatures such as crabs, clams, and tube worms. Ocean Currents Currents are streams of water running through a larger body of water. Oceans, rivers, and streams have currents. The ocean’s salinity and temperature and the coast’s geographic features determine an ocean current’s behavior. Earth’s rotation and wind also influence ocean currents. Currents flowing near the surface transport heat from the tropics to the poles and move cooler water back toward the Equator . This keeps the ocean from becoming extremely hot or cold. Deep, cold currents transport oxygen to organisms throughout the ocean. They also carry rich supplies of nutrients that all living things need. The nutrients come from plankton and the remains of other organisms that drift down and decay on the ocean floor. Along some coasts, winds and currents produce a phenomenon called upwelling . As winds push surface water away from shore, deep currents of cold water rise to take its place. This upwelling of deep water brings up nutrients that nourish new growth of plankton, providing food for fish. Ocean food chains constantly recycle food and energy this way.
Some ocean currents are enormous and extremely powerful. One of the most powerful is the Gulf Stream , a warm surface current that originates in the tropical Caribbean Sea and flows northeast along the eastern coast of the United States. The Gulf Stream measures up to 80 kilometers (50 miles) wide and is more than a kilometer (3,281 feet) deep. Like other ocean currents, the Gulf Stream plays a major role in climate. As the current travels north, it transfers moisture from its warm tropical waters to the air above. Westerly, or prevailing, winds carry the warm, moist air to the British Isles and to Scandinavia , causing them to have milder winters than they otherwise would experience at their northern latitudes . Northern parts of Norway are near the Arctic Circle but remain ice-free for most of the year because of the Gulf Stream. The weather pattern known as El Niño includes a change to the Humboldt Current (also called the Peru Current) off the western coast of South America. In El Niño conditions, a current of warm surface water travels east along the Equator and prevents the normal upwelling of the cold, nutrient-rich Humboldt Current. El Niño, which can devastate the fisheries of Peru and Ecuador, occurs every two to seven years, usually in December. The paths of ocean currents are partially determined by Earth’s rotation. This is known as the Coriolis effect . It causes large systems, such as winds and ocean currents that would normally move in a straight line, to veer to the right in the northern hemisphere and to the left in the southern hemisphere . People and the Ocean For thousands of years, people have depended on the ocean as a source of food and as a route for trade and exploration . Today, people continue to travel on the ocean and rely on the resources it contains. Nations continue to negotiate how to determine the extent of their territory beyond the coast. The United Nations’ Law of the Sea treaty established exclusive economic zones (EEZs), extending 200 nautical miles (230 miles) beyond a nation’s coastline. Even though some countries have not signed or ratified the treaty (including the U.S.), it is regarded as standard. Russia has proposed extending its EEZ beyond 200 nautical miles because two mid-ocean ridges, the Lomonosov and Medeleev Ridges, are extensions of the continental shelf belonging to Russia. This territory includes the North Pole. Russian explorers in a submersible vehicle planted a metal Russian flag on the disputed territory in 2007. Through the centuries, people have sailed the ocean on trade routes . Today, ships still carry most of the world’s freight , particularly bulky goods such as machinery, grain, and oil . Ocean ports are areas of commerce and culture. Water and land transportation meet there, and so do people of different professions: businesspeople who import and export goods and services; dockworkers who load and unload cargo ; and ships’ crews. Ports also have a high concentration of migrants and immigrants with a wide variety of ethnicities, nationalities, languages, and religions. Important ports in the U.S. are New York/ New Jersey and New Orleans. The busiest ports around the world include the Port of Shanghai in China and the Port of Rotterdam in the Netherlands. Ocean ports are also important for a nation’s armed forces. Some ports are used exclusively for military purposes, although most share space with commercial businesses. “The sun never sets on the British Empire” is a phrase used to explain the scope of the empire of Great Britain , mostly in the 19th century. Although based on the small European island nation of Great Britain, British military sea power extended its empire from Africa to the Americas, Asia, and Australia. Scientists and other experts hope the ocean will be used more widely as a source of renewable energy . Some countries have already harnessed the energy of ocean waves, temperature, currents, or tides to power turbines and generate electricity. One source of renewable energy are generators that are powered by tidal streams or ocean currents. They convert the movement of currents into energy. Ocean current generators have not been developed on a large scale, but are working in some places in Ireland and Norway. Some conservationists criticize the impact the large constructions have on the marine environment. Another source of renewable energy is ocean thermal energy conversion (OTEC). It uses the difference in temperature between the warm, surface water and cold, deep water to run an engine. OTEC facilities exist in places with significant differences in ocean depth: Japan, India and the U.S. state of Hawai'i, for instance. An emerging source of renewable energy is salinity gradient power , also known as osmotic power. It is an energy source that uses the power of freshwater entering into saltwater. This technology is still being developed, but it has potential in delta areas where fresh river water is constantly interacting with the ocean. Fishing Fishers catch more than 90 million tons of seafood each year, including more than 100 species of fish and shellfish . Millions of people, from professional fishers to business owners like restaurant owners and boat builders, depend on fisheries for their livelihood . Fishing can be classified in two ways. In subsistence fishing, fishers use their catch to help meet the nutritional needs of their families or communities. In commercial fishing , fishers sell their catch for money, goods or services. Popular subsistence and commercial fish are tuna, cod, and shrimp. Ocean fishing is also a popular recreational sport. Sport fishing can be competitive or noncompetitive. In sport fishing tournaments, individuals or teams compete for prizes based on the size of a particular species caught in a specific time period. Both competitive and noncompetitive sport fishers need licenses to fish, and may or may not keep the caught fish. Increasingly, sport fishers practice catch-and-release fishing, where a fish is caught, measured, weighed, and often recorded on film before being released back to the ocean. Popular game fish (fish caught for sport) are tuna and marlin. Whaling is a type of fishing that involves the harvesting of whales and dolphins. It has declined in popularity since the 19th century but is still a way of life for many cultures, such as those in Scandinavia, Japan, Canada, and the Caribbean. The ocean offers a wealth of fishing and whaling resources, but these resources are threatened. People have harvested so much fish and marine life for food and other products that some species have disappeared. During the 1800s and early 1900s, whalers killed thousands of whales for whale oil (wax made from boiled blubber ) and ivory (whales’ teeth). Some species, including the blue whale ( Balaenoptera musculus ) and the right whale, were hunted nearly to extinction . Many species are still endangered today. In the 1960s and 1970s, catches of important food fish, such as herring in the North Sea and anchovies in the Pacific, began to drop off dramatically. Governments took notice of overfishing —harvesting more fish than the ecosystem can replenish . Fishers were forced to go farther out to sea to find fish, putting them at risk. (Deep-sea fishing is one of the most dangerous jobs in the world.) Now, they use advanced equipment, such as electronic fish finders and large gill nets or trawling nets, to catch more fish. This means there are far fewer fish to reproduce and replenish the supply. In 1992, the collapse, or disappearance, of cod in Canada’s Newfoundland Grand Banks put 40,000 fishers out of work. A ban was placed on cod fishing, and to this day, neither the cod nor the fisheries have recovered. To catch the dwindling numbers of fish, most fishers use trawl nets. They drag the nets along the seabed and across acres of ocean. These nets accidentally catch many small, young fish and mammals. Animals caught in fishing nets meant for other species are called bycatch . The fishing industry and fisheries management agencies argue about how to address the problem of bycatch and overfishing. Those involved in the fishing industry do not want to lose their jobs, while conservationists want to maintain healthy levels of fish in the ocean. A number of consumers are choosing to purchase sustainable seafood . Sustainable seafood is harvested from sources (either wild or farmed) that do not deplete the natural ecosystem. Mining and Drilling Many minerals come from the ocean. Sea salt is a mineral that has been used as a flavoring and preservative since ancient times. Sea salt has many additional minerals, such as calcium, that ordinary table salt lacks. Hydrothermal vents often form seafloor massive sulfide (SMS) deposits , which contain precious metals. These SMS deposits sit on the ocean floor, sometimes in the deep ocean and sometimes closer to the surface. New techniques are being developed to mine the seafloor for valuable minerals such as copper, lead, nickel, gold, and silver. Mining companies employ thousands of people and provide goods and services for millions more. Critics of undersea mining maintain that it disrupts the local ecology . Organisms—corals, shrimp, mussels—that live on the seabed have their habitat disturbed, upsetting the food chain. In addition, destruction of habitat threatens the viability of species that have a narrow niche . Maui’s dolphin ( Cephalorhynchus hectori maui ), for instance, is a critically endangered species native to the waters of New Zealand’s North Island. The numbers of Maui’s dolphin are already reduced because of bycatch. Seabed mining threatens its habitat, putting it at further risk of extinction. Oil is one of the most valuable resources taken from the ocean today. Offshore oil rigs pump petroleum from wells drilled into the continental shelf. About one-quarter of all oil and natural gas supplies now comes from offshore oil deposits around the world. Offshore drilling requires complex engineering . An oil platform can be constructed directly onto the ocean floor, or it can “float” above an anchor. Depending on how far out on the continental shelf an oil platform is located, workers may have to be flown in. Underwater, or subsea, facilities are complicated groups of drilling equipment connected to each other and a single oil rig. Subsea production often requires remotely operated underwater vehicles (ROVs). Some countries invest in offshore drilling for profit and to prevent reliance on oil from other regions. The Gulf of Mexico near the U.S. states of Texas and Louisiana is heavily drilled. Several European countries, including the United Kingdom, Denmark, and the Netherlands, drill in the North Sea. Offshore drilling is a complicated and expensive program, however. There are a limited number of companies that have the knowledge and resources to work with local governments to set up offshore oil rigs. Most of these companies are based in Europe and North America, although they do business all over the world. Some governments have banned offshore oil drilling. They cite safety and environmental concerns. There have been several accidents where the platform itself has exploded, at the cost of many lives. Offshore drilling also poses threats to the ocean ecosystem. Spills and leaks from oil rigs and oil tankers that transport the material seriously harm marine mammals and birds. Oil coats feathers, impairing birds’ ability to maintain their body temperature and remain buoyant in the water. The fur of otters and seals are also coated, and oil entering the digestive tract of animals may damage their organs. Offshore oil rigs also release metal cuttings, minute amounts of oil, and drilling fluid into the ocean every day. Drilling fluid is the liquid used with machinery to drill holes deep in the planet. This liquid can contain pollutants such as toxic chemicals and heavy metals . Pollution Most oil pollution does not come from oil spills, however. It comes from the runoff of pollutants into streams and rivers that flow into the ocean. Most runoff comes from individual consumers. Cars, buses, motorcycles, and even lawn mowers spill oil and grease on roads, streets, and highways. (Runoff is what makes busy roads shiny and sometimes slippery.) Storm drains or creeks wash the runoff into local waterways, which eventually flow into the ocean. The largest U.S. oil spill in the ocean took place in Alaska in 1989, by the tanker Exxon Valdez . The Exxon Valdez spilled at least 10 million gallons of oil into Prince William Sound. In comparison, American and Canadian consumers spill about 16 million gallons of oil runoff into the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans every year. For centuries, people have used the ocean as a dumping ground for sewage and other wastes. In the 21st century, the wastes include not only oil, but also chemical runoff from factories and agriculture . These chemicals include nitrates and phosphates , which are often used as fertilizers . These chemicals encourage algae blooms. An algae bloom is an increase in algae and bacteria that threatens plants and other marine life. Algae blooms limit the amount of oxygen in a marine environment, leading to what are known as dead zones , where little life exists beneath the ocean’s surface. Algae blooms can spread across hundreds or even thousands of miles. Another source of pollution is plastics . Most ocean debris, or garbage, is plastic thrown out by consumers. Plastics such as water bottles, bags, six-pack rings, and packing material put marine life at risk. Sea animals are harmed by the plastic either by getting tangled in it or by eating it. An example of marine pollution consisting mainly of plastics is the Great Pacific Garbage Patch . The Great Pacific Garbage Patch is a floating dump in the North Pacific. It’s about twice the size of Texas and probably contains about 100 million tons of debris. Most of this debris comes from the western coast of North America (the U.S. and Canada) and the eastern coast of Asia (Japan, China, Russia, North Korea, and South Korea). Because of ocean currents and weather patterns, the patch is a relatively stable formation and contains new and disintegrating debris. The smaller pieces of plastic debris are eaten by jellyfish or other organisms, and are then consumed by larger predators in the food web. These plastic chemicals may then enter a human’s diet through fish or shellfish. Another source of pollution is carbon dioxide. The ocean absorbs most carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. Carbon dioxide, which is necessary for life, is known as a greenhouse gas and traps radiation in Earth’s atmosphere. Carbon dioxide forms many acids, called carbonic acids , in the ocean. Ocean ecosystems have adapted to the presence of certain levels of carbonic acids, but the increase in carbon dioxide has led to an increase in ocean acids. This ocean acidification erodes the shells of animals such as clams, crabs, and corals. Global Warming Global warming contributes to rising ocean temperatures and sea levels . Warmer oceans radically alter the ecosystem. Global warming causes cold-water habitats to shrink, meaning there is less room for animals such as penguins, seals, or whales. Plankton, the base of the ocean food chain, thrives in cold water. Warming water means there will be less plankton available for marine life to eat. Melting glaciers and ice sheets contribute to sea level rise . Rising sea levels threaten coastal ecosystems and property. River deltas and estuaries are put at risk for flooding. Coasts are more likely to suffer erosion . Seawater more often contaminates sources of fresh water. All these consequences—flooding, erosion, water contamination—put low-lying island nations, such as the Maldives in the Indian Ocean, at high risk for disaster. To find ways to protect the ocean from pollution and the effects of climate change, scientists from all over the world are cooperating in studies of ocean waters and marine life. They are also working together to control pollution and limit global warming. Many countries are working to reach agreements on how to manage and harvest ocean resources. Although the ocean is vast, it is more easily polluted and damaged than people once thought. It requires care and protection as well as expert management. Only then can it continue to provide the many resources that living things—including people—need.
The Most Coast . . . Canada has 202,080 kilometers (125,567 miles) of coastline. Short But Sweet . . . Monaco has four kilometers (2.5 miles) of coastline.
No, the Toilet Doesn't Flush Backward in Australia The Coriolis effect, which can be seen in large-scale phenomena like trade winds and ocean currents, cannot be duplicated in small basins like sinks.
Extraterrestrial Oceans Mars probably had oceans billions of years ago, but ice and dry seabeds are all that remain today. Europa, one of Jupiter's moons, is probably covered by an ocean of water more than 96 kilometers (60 miles) deep, but it is trapped beneath a layer of ice, which the warmer water below frequently cracks. One of Saturn's moons, Enceladus, has cryovolcanism, or ice volcanoes. Instead of erupting with lava, ice volcanoes erupt with water, ammonia, or methane. Ice volcanoes may indicate oceanic activity.
International Oil Spill The largest oil spill in history, the Gulf War oil spill, released at least 40 million gallons of oil into the Persian Gulf. Valves at the Sea Island oil terminal in Kuwait were opened on purpose after Iraq invaded Kuwait in 1991. The oil was intended to stop a landing by U.S. Marines, but the oil drifted south to the shores of Saudi Arabia. A study of the Gulf War oil spill (conducted by the United Nations, several countries in the Middle East and the United States) found that most of the spilled oil evaporated and caused little damage to the environment.
Ocean Seas The floors of the Caspian Sea and the Black Sea are more like the ocean than other seas they do not rest on a continent, but directly on the ocean's basalt crust.
Early Ocean Explorers Polynesian people navigated a region of the Pacific Ocean now known as the Polynesian Triangle by 700 C.E. The corners of the Polynesian Triangle are islands: the American state of Hawai'i, the country of New Zealand, and the Chilean territory of Easter Island (also known as Rapa Nui). The distance between Easter Island and New Zealand, the longest length of the Polynesian Triangle, is one-quarter of Earth's circumference, more than 10,000 kilometers (6,200 miles). Polynesians successfully traveled these distances in canoes. It would be hundreds of years before another culture explored the ocean to this extent.
Media Credits
The audio, illustrations, photos, and videos are credited beneath the media asset, except for promotional images, which generally link to another page that contains the media credit. The Rights Holder for media is the person or group credited.
Illustrators
Educator reviewer, expert reviewer, last updated.
March 5, 2024
User Permissions
For information on user permissions, please read our Terms of Service. If you have questions about how to cite anything on our website in your project or classroom presentation, please contact your teacher. They will best know the preferred format. When you reach out to them, you will need the page title, URL, and the date you accessed the resource.
If a media asset is downloadable, a download button appears in the corner of the media viewer. If no button appears, you cannot download or save the media.
Text on this page is printable and can be used according to our Terms of Service .
Interactives
Any interactives on this page can only be played while you are visiting our website. You cannot download interactives.
Related Resources
- Facts About Water
Intriguing Facts About Water
Water has been around on earth for more than 3.5 billion years. Furthermore, it is the only known planet in the solar system where water is present as a liquid on the planet’s surface. In fact, probably would not have evolved if the earth did not have water. Consequently, one of the most important criteria for finding extraterrestrial life on distant planets outside our solar system is water. Hence, water is the earth’s most precious resource for sustaining life. Moreover, nearly 71% of the earth’s surface is covered with water. However, less than a fraction of this percentage is easily accessible freshwater, and this brings us to our first fact:
0.5% of the Earth’s Water is Freshwater
Technically, 3% of the total water on earth is freshwater. However, more than 2.5% of the same is locked up glaciers, soil, atmosphere and the polar ice caps. That leaves just 0.5% as easily accessible freshwater. A significant amount of freshwater is also found deep underground, but it may not be economically feasible for extraction. Unfortunately, anthropogenic activities also have started polluting bodies of freshwater, thereby rendering them unfit for human consumption. Hence, the actual available amount of freshwater is minuscule.
Plastics in the Ocean
We currently have to deal with millions of tons of wastes – and out of these, plastics are the most detrimental to our environment. The issue with plastics is that it is not biodegradable. This means things made from plastics take a very long time to decompose. Every year, an estimated 8 million tons of plastics end up in our oceans. And when these plastics break down, they form minuscule particles called microplastics. These pieces of plastics, which are usually less than 5 millimetres in length, are small enough for plankton and other microscopic organisms to ingest them. As a result, plastics particles enter the food chain, where larger organisms consume plankton, which is in turn consumed by even larger organisms. Eventually, these microplastics make their way into humans, where they can bring out dire repercussions.
Also Read: Types of Pollution – Effects of Various Types of Pollution
Water in Space
Earth might be the only known planet with water in our liquid solar system, however, it is not the only one in the universe. 12 billion light-years away lies a blackhole with a gargantuan cloud of water vapour – and the amount of water present in that cloud is unimaginably large. NASA officially describes the amount as “140 trillion times all the water in the world’s oceans.” Granted, when we look at the scale of things back on earth, that is an incomprehensibly large number. Furthermore, scientists have stated that these gargantuan water-clouds are ancient, dating back to 12 billion years. For reference, the current consensus on the age of the universe is 13.7 billion years. This means water was formed just 1.6 billion years after the start of the universe.
Further Reading:
- Water – An Overview of Water, its Sources, and the Importance of Water
- Water Pollution & its Control – Causes, Effects & Control Measures
Frequently Asked Questions on Facts About Water
What is an interesting fact about water.
12 billion light-years away lies a blackhole with a gargantuan cloud of water vapour – and the amount of water present in that cloud is 140 trillion times all the water in the world’s ocean.
List some facts about water.
Less than 0.5% of the Earth’s water is readily available freshwater.
Explore more intriguing facts about water by registering at BYJU’S Biology .
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser or activate Google Chrome Frame to improve your experience.

Thanks for signing up as a global citizen. In order to create your account we need you to provide your email address. You can check out our Privacy Policy to see how we safeguard and use the information you provide us with. If your Facebook account does not have an attached e-mail address, you'll need to add that before you can sign up.
This account has been deactivated.
Please contact us at [email protected] if you would like to re-activate your account.
Maybe you’ve heard that a human can survive without water for only three days or that nearly 1 in 5 people don’t wash their hands after using a toilet.
But how much do you really know about water and sanitation?
Ensuring access to clean water and proper sanitation was among the UN Millennium Development Goals (MDG) that are furthest from being accomplished, with billions of people still lacking access to basic human needs like clean water and a safe place to poo.
Unlike many of the other global goals that saw improvements toward ending extreme poverty, the number of people facing water scarcity is actually projected to rise .
Yet, other millennium development goals — like education, food, and environment — continue to receive more attention and money.
To increase awareness and knowledge about these issues, Global Citizen has put together a list of important stats everyone should know about water and sanitation:
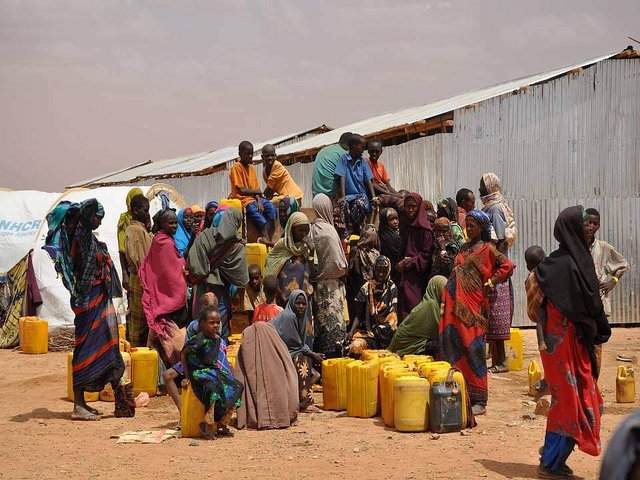

1/ 4.5 billion people around the world lack access to hygienic sanitation
Only 2 out of every 5 people used safely managed sanitation services in 2015, according to a 2017 report from the World Health Organization (WHO) and the United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF). For a toilet to be considered a “safely managed sanitation service,” it must provide a safe place for someone to defecate, be separate from another household, and the feces must be treated either on or off site.
Still, 2.3 billion people lack even basic sanitation services. Basic sanitation refers to the use of improve facilities that are not shared with other households. This does not include hanging latrines, bucket latrines, or pit latrines without a slab or platform.
2/ 844 million people lack access to clean drinking water
According to a 2017 report by UNICEF and the WHO, 884 million people still lack basic access to clean water. Basic access to safely managed drinking water means that there is at least one source of drinking water located on the premises, available when a person needs it and free from contamination. As of 2015, 71% (or 5.2 billion) of the world’s population had access to clean water it, meaning the rest either has to travel over 30 minutes to find drinking water or uses untreated water sources.
Of the millions who lack a source of drinking water, 159 million people still collect their drinking water directly from surface water sources , such as ponds, lakes or rivers. Fifty-eight percent of those people live in sub-Saharan Africa. Drinking this untreated water can increase one’s risk of ingesting bacteria, viruses and other contaminants, which can cause cramps, nausea, diarrhea and more serious and fatal illnesses .
Read More: This Cheap Plastic Uses Sunlight to Turn Sewage Into Drinkable Water
3/ Diarrheal disease is the second leading cause of death for children under the age of 5
Diarrhea is deadly for young children and elderly people whose bodies are weaker at fighting off infections and coping with dehydration. Around the world, diarrhea kills more children than AIDS, malaria, and measles combined, according to the Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) . Children with HIV are 11 times more likely to die from diarrhea than a child without HIV.
Contaminated water sources from animals or sick people and food prepared by contaminated hands are major pathways for diarrhea. The causes of diarrhea shares some similarities with pneumonia , the leading cause of death among post-neonatal children, according to the WHO.
However, the link to unsafe sanitation and water sources is unique to diarrhea.
4/ 1 child under age five dies from a diarrheal disease every 1.5 minutes.
Diarrhea kills around 2,195 children each day , according to the CDC. That’s about 91 children every hour, equating to one child every minute and a half.
Of those deaths, 88% can be attributed to unsafe water, inadequate sanitation, and insufficient hygiene, according to UNICEF .
Deaths due to diarrhea are preventable. According to a study from 2014, the number of diarrheal deaths would fall by 34% if everyone everywhere had access to clean water, by 28% if there was universal access to adequate toilets, and by 23% if good hygiene practices were universally practiced.
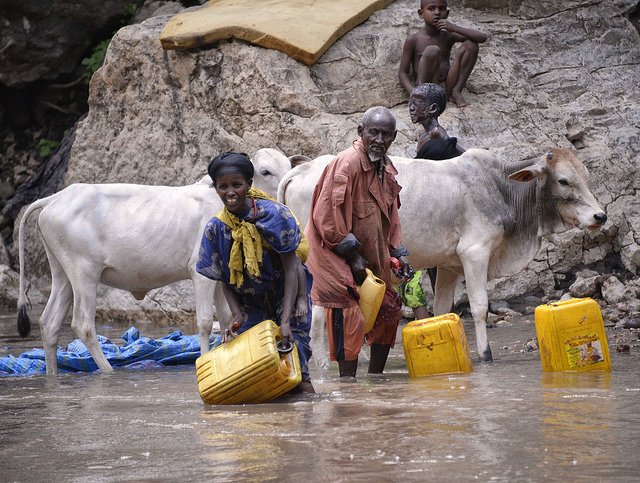

5/ Almost half of people living in rural areas around the world do not have improved sanitation facilities
Although 2.1 billion people have gained access to improved sanitation since 1990, the world fell short of the MDGs for both developed and developing regions. People living in rural areas are particularly in need of improved sanitation facilities: almost 50% do not have improved sanitation facilities, a stark difference from the 18% of people in urban areas who lack improved sanitation access.
Take Action: Tell World Leaders: Provide Access to Sanitation for all
6/ 892 million still practice open defecation
The UNICEF and WHO report defines open defecation as the disposal of human feces in open spaces — forests, bushes, bodies of water, fields, etc — or with garbage.
This practice puts women, children, and their communities at risk. Open defecation is an easy pathway toward diarrhea and related infections and is linked to stunting in children . Women and girls are particularly vulnerable to sexual assault when they go to the bathroom in an unprotected place, and many can injure themselves by waiting until dark to defecate.
To reach the Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) of ending open defecation by 2030 , countries and organizations must focus on behavioral and cultural changes around open defecation.
In India, where nearly half the population still doesn’t use a toilet, UNICEF has implemented programs like ‘ Stop Stunting ’ and ‘ Take Poo to the Loo ' to raise awareness of the risks of open defecation.
Read More: Bollywood's Latest Hit Deals With Love, Romance, and Toilets
7/ Funding for WASH must triple to meet SDG target goals
Without more funding, the world will not reach its SDG for water and sanitation by 2030 .
The WHO and UNICEF estimate that 9 out of 10 countries where more than 5% of people lack basic sanitation are progressing too slowly and won’t achieve universal basic sanitation by 2030 .
In worse news: in one out of every seven of these countries the use of basic sanitation is actually decreasing.
The World Band estimates that total global investments must triple to the target goal of $114 billion USD each year in order to meet the SDG requirements for water, sanitation and hygiene (WASH).

Take Action: Call on businesses and world leaders to fill the funding gap for water and sanitation
Without this additional funding, these statistics listed above are unlikely to improve. Many more children will continue to needlessly die due to poor-quality water, bathroom facilities and hygiene practices. With more people living in cities than ever before, improved sanitation and waste management systems have never been more important.
Aid toward water and sanitation is vital, but it is also tricky. Change depends not only on increase aid funding but also on addressing unhealthy social norms and behaviors practiced around the world.
With more money and more support, we could see a world in 2030 where everyone has access to clean drinking water and everyone washes their hands.
Defeat Poverty
7 Important Facts You Should Know About Water and Sanitation
Aug. 24, 2017
469 Water Essay Topic Ideas & Examples
Looking for interesting topics related to water? This study field is broad, exciting, and definitely worth exploring!

🏆 Best Water Topic Ideas & Essay Examples
👍 top water essay examples, 📌 easy topics related to water, 💡 water essay topics, ✍ water topics for research papers, 🥇 interesting water topics to write about, ❓ essay questions about water.
In your essay about water, you might want to focus on water as one of the most valuable natural resources. Consider exploring the issues of water pollution, purification, conservation, or management. Whether you need to prepare an essay, a research paper, or a presentation, our article will be helpful. Here we’ve collected water essay topics and titles. Water essay examples are added to inspire you even more!
- Should Bottled Water Be Banned? Plastics is one of the products that are leading in polluting the environment. Plastics are detrimental to the environment; they affect the soil, water, air and eventually lead to climate change and global warming.
- Water Pollution: Causes, Effects and Possible Solutions This is why clean water is required in all the places to make sure the people and all the living creatures in the planet live a good and healthy life.
- Air and Water Pollution in the Modern World The high number of vehicles in the city has greatly promoted air pollution in the area. Poor sewerage system, high pollution from industries and automobiles are among the major causes of air and water pollutions […]
- Water Scarcity as a Global Issue: Causes and Solutions Common causes of water scarcity include overpopulation e in regions that have limited water resources, global warming, destruction of water catchment areas by human activities, and pollution of water sources.
- Water Pollution: Causes, Effects, and Prevention Farmers should be encouraged to embrace this kind of farming which ensures that the manure used is biodegradable and do not end up accumulating in the water bodies once they are washed off by floods.
- Accessibility to Safe Drinking Water The first is to dig wells in the rural and arid areas to aid the people to have access to water. The other alternative is to treat water and use it in the home.
- The Process of the Water Cycle It is the primary process that drives the movement of water from water bodies into the atmosphere in form of water vapor.
- Evian Water Company’s Analysis Due to the popularity of its water, the company managed to expand, and in 1978, it made its way to the market of the United States of America.
- Fire and Water Symbols in “Sula” by Toni Morrison Water and fire are used by the author as symbols of destruction and purification respectively, which allows the readers to better understand the main characters in the context of the communist oppression.
- Water Shortage’ Major Causes and Implication Summary of the article This article is a discussion regarding one major problem that is an issue of concern in the 21st century which according to the author, the world is currently facing a major […]
- Water Recycling Recycled water is obtained from waste water and contaminated water that has been subjected to thorough treatment to ensure that it is proper for use for different purposes.
- Water Advertisement The waterfall in the background reinforces the psychological need for water and adds to the freshness of the advertisement and water itself.
- Water Cycle: Lesson Plan for 5th Graders The purpose of the program is to introduce students to the water cycle systems, stages, and importance. The student should be able to define and explain the water cycle stages.
- The Effect of Plastic Water Bottles on the Environment In addition, the proponents of plastic use have argued that recycling is an effective method of mitigating the effects of plastic to the environment.
- Water Purification Process Since the process is aimed at eliminating all the impurities present in the water, it is necessary to apply chemical and physical methods of separation in an orderly manner.
- The Thematic Concept in Water Names Like the narrator, a reader may think that the story presents a happy ending, as the young woman “went to join the kingdom of her beloved”. The woman wants the girls to find the answer […]
- Masafi Water Company and Al Ain Water Company Manufacturing of Masafi and Al Ain Water: The resource of Masafi water is the mountain and this is why the water is rich in minerals.
- Environmental Impact of Bottled Water The process of manufacturing the water bottles, such as the dependence on fossil fuels, is causing a lot of direct as well indirect destructing to the environment.
- Water Transport Systems in the World The development of the three and four Masted ships in the 16th century was a major event in the history of the water transportation system.
- How Does Water Hyacinth Harm the Local Ecosystem? Water hyacinth Flowers Water hyacinth has great harm on the local ecosystem and affects aquatic life and water quality. The life of other plants and animals is jeopardized by the rapid growth of water hyacinth.
- Saving Water and Methods of Its Protection That is, the plan will effectively manage the water usage at the current state of the company as well as in the future. If protection and conservation of water is not done, there will be […]
- Determination of Quinine in Tonic Water with Fluorescence Spectroscopy In general, luminescence is understood as the glow of substances not accompanied by heat production but initiated by the absorption of photons.
- Water Cycle Process On the reaching the atmosphere water molecules bond together again and come back to the earth surface through the process of precipitation.
- Water Pollution in the Philippines: Metropolitan Manila Area In this brief economic analysis of water pollution in Metro Manila, it is proposed to look at the industrial use of waters and the household use to understand the impact that the population growth and […]
- Sustainable Strategies in Water Quality Control With regards to the first strategy, it is important to touch the hearts and minds of the next generation’s leaders and policy makers. They have to see and experience the benefits of their actions.
- Water Resource Management: How to Save Water Resources We need to address the difficult problems of evaluating and protecting the global commons, which are complicated and interrelated while maintaining the free trade systems of the world.
- Fiji Water: A Comprehensive Analysis The paper is analytical in nature and it displays some of the aspects that make the product unique and relevant in the market, some of the challenges that the product’s company encounters, how the company […]
- Coca-Cola India and Water Pollution Issues The first difficulty that the representatives of the Coca-Cola Company happened to face due to their campaign in the territory of India was caused by the concerns of the local government.
- Fiji Water Strategic Analysis The second alternative could involve the idea of putting underground and sea bed pipes to facilitate the transportation of the water commodity from Fiji to the lucrative international markets, such as the US.
- Dehydration and Importance of Water There are plenty of fluids in the body that mainly consist of water; one of these is saliva. Water also transports oxygen from the lungs to other parts of the body that are in need […]
- Fiji Water Report The aim of this report is to analyze the future options of Fiji waters company growing up as a company that will be conscious to the environment and ensure its’ sustainability.
- Water Shortages in the World Management of water supply in developing countries is poor as compared to that of developed world. In addition, pollution of water in developing countries is quite prevalent as compared to that of developed world.
- Best Water Management Practices The use of spray irrigations to water gardens contributes to the loss of water. The government has invested in the creation of public awareness of the various water conservation strategies.
- Water Conservation and Drought Issues in Resorts The idea of the conservation of natural resources and water, in particular, became popular in the previous century. The understanding of the need for nature protection commenced in the 1960s.
- Roman Aqueducts “The Relevance of Water to the Social Political Climate of the Roman” The main question in this paper is: what were the names and functions of the aqueducts in ancient Rome? The need to build aqueducts in Rome was prompted by the need for mass supply of […]
- Ethics of Bottled Water The manufacture of bottled water began in Europe in the 1970s. The availability of bottled water allows consumers to buy water when they need it.
- Analysis of Lab: Heat of Fusion of Water In this experiment, information was collected regarding the mass of the calorimeter and bowl, the mass of the empty calorimeter, the water, and the contents: all raw data are shown in Table 1.
- The Water System: Rivers, Streams and Lakes The techniques used to compare rivers in the world involve an analysis of the size of the drainage area, the length of the main stem and the mean discharge.
- The Effect of pH on Water Holding Capacity of Chicken In the present laboratory work, the main issue is to investigate the potential relationship between WHC as a measure of moisture content and chicken pH; specifically, the question is to identify the effect of meat […]
- Water Purification in Saudi Arabia The scope of this report is to bring out all sorts of features used for water purification in Saudi Arabia and their effectiveness in providing pure water in all regions of Saudi Arabia. Desalination is […]
- Sustainability: Domestic Water Usage Much of the hot water is used when cleaning and washing, with the shower making up to 43% of the 41 gallons and washing clothes making up to 29%.
- Tipperary Mineral Water Company In addition, consumers’ desire to lead a healthy lifestyle has greatly increased the market growth and demand for mineral water by a rate of 8. The main consumers of mineral water in this market are […]
- Anomalous Expansion of Water: A Home Experiment This investigation proves the hypothesis that water expands anomalously when cooled and increases in volume as it nears its freezing point of zero degree Celsius.
- Las Vegas Water Shortage The lake happens to be the primary source of water for Las Vegas and this is an alarming development for the urban area which has a rapid population growth and is projected to be about […]
- Muslim Civilisation: The Mechanical Water Clock of Ibn Al-Haytham This forth stage is the one that determines the survival of the state, as the society is already discontented with the rule, hence disintegration of the state.
- The Issue of Bottled Water Consumption The steady rise in the demand for bottled water is causing hips of unnecessary garbage and resulting in the consumption of vast quantities of energy according to the report by Earth Policy Institute.
- Water’s Role in Society and Its Applications The water table is forced higher by a dam to intensify the force of the water’s descent. In the future, water should be modified to act as a source of fuel for different machinery to […]
- The Physical and Chemical Properties of Water Considering the structure in the figure above, it is evident that a molecule of water has a line of symmetry that can be traced through the water molecule, acting as a bisector of the angle […]
- Parent Purchase Bottled Water With all the sweat and tears, I can feel that you must be really tired with all the work that you do. This total number of bottled water consumed excludes the water that you take […]
- Virtual Water and Water-Energy-Food Nexus The content of the “real” water in the product is usually insignificant in comparison to the amount of used virtual water.
- Synopsis of “Water” Short Story by Lee Hoffman From the story it is clearly indicated that, Evan was very disappointed with what Redmor treated the people of this area; and decided to take a ravage especially because his friend Hank was shot.
- Demo Park Water Administration Project Management In this assignment, the main areas for group work were the creation of a project plan and the identification, as well as the demonstration of its importance.
- Marketing Plan for Water Sensitive Nail Polish This part presents the information collected in 2014 as the company focuses on the demand behavior of the new nail polish.
- Bottled Water Industry and Aquafina Another reason of the boom in the consumption of bottled water is its taste because a large number of people prefer its taste to that of tap water.
- Key Factors of Competitive Success in the Water Bottling Industry The introduction of enhanced or functional water products, by a number of major bottling firms such as Coca-Cola and PepsiCo, has provided further competition, threatening to squeeze profitability for them.
- Water Properties as a Solvent: An Experiment Lab In the second part of the work, a mixture of 10 g of solid calcium hydroxide and 50 mL of drinking water in a beaker was initially created.
- The Water Cube Project and Design-Build Approaches Despite the variety of designs that the engineers could use in the construction, the choice of a Water Cube helped to embolden the Chinese culture in the building.
- Third World War Will Be Over Water The severity of the case of water scarcity can be best explained by the inclusion of the problem of water as one of the main goals of one of the greatest development frameworks in the […]
- Motivations to Choose Bottled Water The growth of the bottled water industry is attracting a lot of global attention because more companies are jostling to have a significant share of the market.
- Water and Environment Engineering The village is situated in the Northwestern part of the state, near the seacoast. However, one of the village residents made an offer to the turtle and the latter allowed humans to use water from […]
- Cashion Water Quality: Spatial Distribution of Water Pollution Incidents This essay discusses the quality of water as per the report of 2021 obtained from the municipality, the quality issue and the source of pollution, and how the pollution impacts human health and the environment […]
- Case Study: Human Body Water Balance Sodium is reabsorbed in the thick climbing appendage of the loop of Henle. The rest of the Na+ retention happens in the distal nephron.
- Seawater vs. Brackish Water Reverse Osmosis The concentrations of seawater and brackish water differ considerably; hence, there is a distinction involving the concentrate acquired from seawater desalination plants and brackish water desalination plants.
- Water Consumption by Individuals and Households Water demand rate for a household differs from that by industry within the same day and as well differs from the entire per-capital demand of a community.
- Bling H2O: Brand of Mineral Water Besides, it has a median age of 35 and is the economic hub of Australia, for example, out of the 54 banks operating in the continent, 44 have their headquarters in Sydney.
- Water-Saving Technologies in the Middle East Our planet is made of 70% water and yet most areas of the world are without water. However, to conserve the cost of this important resource, certain steps are being taken by the respective governments […]
- Water Pollution: OIL Spills Aspects The effects of the oil spill on a species of ducks called the Harlequin ducks were formulated and the author attempted to trace out the immediate and residual effects of the oil on the birds.
- Integrated Sustainable Water Management in the UAE The UAE Water Security Strategy 2036 was unveiled by the Ministry of Energy in 2017 to ensure that access to water during an emergency and normal conditions are sustainable within the internal standards, local regulations, […]
- Fiji Water Company Analysis The differences in the kind of approach a company adopts in the handling of its CSR communication is due to an apparent sensitivity of the CSR topic, as well as company ambiguity and inadequate knowledge […]
- Water: Nature’s Gift to Humanity However, the role of this element is not only in the formation of life but also its maintenance since this seemingly ordinary liquid plays an enormously essential role in the existence of the human and […]
- Water Management: Best Practices Australia is one of the developed countries that are faced with the problem of dwindling supplies of clean water as some of the reliable rivers become smaller in size than they were in the past.
- Environmental Science: Smart Water Management Among the essential elements in human life is water, which is required for maintaining the water balance in the body and for cleanliness, as well as for many economic sectors, from agriculture to metallurgy.
- Systemic Effects (Risks) of Water Fluoridation: Fluoridation Assignment Fluoride contributes to teeth development depending on the site where it is applied and the mode of entry into the system. Thus, proponents argue it is one of the safest and most effective solutions to […]
- Ineffective Water Resource Management in the Hotel Industry In the context of the problem of water overuse for service production and revenue generation, the most appropriate type of assessment is a water audit.
- Innovations on Energy and Water Co-Benefits In addition, the number of harmful emissions that are harmful to both people and the planet will be significantly reduced. The introduction of social innovations is to develop strategies that will solve social problems.
- The Himalayan Melting Glacier Contribution to Water Scarcity in Mount Everest Planetary phenomena such as the tilt of the Earth, its distance from the Sun, temperature, and atmospheric cycles belong to the first category.
- Food and Water Shortage: The Negative Effects As a result, one of the biggest challenges in the 21st century is the food and water shortage, which might lead to violence and the death of many people.
- Sustaining Our Water Resources: Pharmaceuticals in Water Supply The presence of pharmaceuticals in the water supply is primarily harmful to fish and aquatic wildlife as they may impact the hormone system of living creatures, causing reproductive failure.
- The Article “Where the Water Goes” by David Owen This paper highlights misconceptions about the drying of lake Mead, the importance of the Colorado River, and the causes of its scarcity in Las Vegas.
- Plan Elements for Sustainable Management of Water Resources It was taken into account because it provides greater imperiousness, where the rising development of Arzaville community structures and roadways disrupts the local water cycle and floods bays and guts with significant amounts of stormwater […]
- Clouds: The Water Cycle and Social Sciences As a result, when the weight increases and the droplets grow, they are released in the form of precipitations. Moreover, the movement of the water can be applied to a sociological element.
- Water Pollution as a Crime Against the Environment In particular, water pollution is a widespread crime against the environment, even though it is a severe felony that can result in harm to many people and vast territories.
- Water Contamination Issue in Medical Anthropology The role of water is so important that any economic or political disturbance can result in the worsening health problems of the population. The most recent and evident example of the failure in disease management […]
- Water Consumption and Sleep Hygiene Practices First, I will discuss that safe and sufficient water facilitates the practice of hygiene and well-being and is a critical determining factor for health.
- Understanding the Water Regulations in Kenya The Constitution, therefore, mandates the national government the role of ensuring that all the water resources, including the international waters, are well managed and utilized to better the lives of the citizens in the nation.
- India’s Water Supply Improvement Plan In India, the concept of a “water crisis” is firmly established, and the future of the country largely depends on how it will be possible to dispose of the available sources of fresh water.
- Water and Energy Problems in Mining Industry The goal is to find and recommend solutions for mining companies to easily access quality ore deposits in inaccessible areas. According to the second interviewee, accessibility to water and electricity are among the major challenges […]
- The Water Treatment System Project The purpose of this project was to create a water treatment system that will allow for establishing and maintaining the provision of high-quality drinking water. In turn, the second part of the project includes information […]
- Sustainable Development and Water-Food-Energy Nexus in Sweden The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations states that the securities of food, energy, and water are interconnected and depend on each other.
- Water Quality Issues: Case Study Analysis The quality of water is an essential part of the infrastructure of a city or state, which affects the health of the population and the level of well-being.
- America’s Growing Clean Water Crisis and the Resulting Diseases The current water crisis in Flint, Michigan, has focused a lot of attention on the state of water infrastructure. Lastly, there will be a not adequate amount of water to help in dissolving the nutrients […]
- The Sea Water Impact on the Human Cell Hence, consuming it causes a high amount of salt without the human cell, which leads to a steep concentration gradient within the cell, thereby causing water to be drawn out, which is detrimental to the […]
- Factors of the Water Crisis in Flint, Michigan The factors that caused the water crisis in this city can be considered negligence of the authorities, ambiguous and contradictory instructions of environmental protection agencies, and corruption.
- Increasing Global Access to Clean Water and Sanitation As noticed by researchers, innovative solutions to achieve global clean water and sanitation are needed, and the positive partnership of various organizations and groups from different spheres and levels may help with this task.
- Environmental Racism: The Water Crisis in Flint, Michigan The situation is a manifestation of environmental racism and classism since most of the city’s population is people of color and poor. Thus, the water crisis in Flint, Michigan, is a manifestation of environmental racism […]
- Flint Water Crisis: Municipal Water Supply System The city of Flint was a thriving industrial center in the third quarter of the last century; however, it had economic difficulties due to the closure of several General Motors factories in the 1980s and […]
- Water Quality Report: Overview Water quality reports provide information in regards to the quality of the drinking water, possible contaminants, and ways to reduce risks.
- The Flint Water Crisis and Its Impact The contaminated water has lead to a number of diseases and disabilities, which, in turn, has left the city’s population with a large number of healthcare bills. In conclusion, the Flint Water Crisis is an […]
- Overcoming Shortage of Drinking Water It is also possible to process saltwater into freshwater, which is the most promising way to solve the problem of water scarcity.
- Financial Attractiveness of Domestic Solar Hot Water Systems: Article Review The peculiarity of the article is that the study of the authors aims to resolve urgent needs by increasing the demand for goods.
- Singapore International Water Week A good example of these conferences is the Singapore International Water Week and it forms the basis for this detailed report The SIWW 2022 brings together professionals, technocrats, and government leaders to share their experiences […]
- The Safe Drinking Water Act 1974: The Main Concept The act also directs EPA to report on the eminence of drinking water in the U. The SDWA calls for the EPA to publish an annual report on the drinking water in the US.
- The Safe Drinking Water Act 1974: Overview The main provisions in this law were to ensure that water supplied from the source to the faucets was free from natural and artificial contaminants through water treatment and consistent supply to the public.
- The Flint Water Crisis From Marxist Perspective To understand the causes of the crisis and ways to prevent such problems in the future, it is possible to employ the Marxist approach.
- Is Tap Water Better and Safer for People and the Environment Than Bottled Water? In this study, I have decided to explore if tap water is better and safer for people and the environment than bottled one. Further, I will look at the impact of bottled water on people […]
- Importance of Mercury Water Pollution Problem Solutions The severity of the mercury contamination consequences depends on the age of the person exposed to the contamination, the way of contamination, the health condition, and many other factors.
- The Influence of Water Quality on the Population of Salmonid Fish It is expected that populations of wild salmonid fish may decline rapidly due to water pollution instead of farmed species because the effects of water pollution are deleterious.
- Rainwater Harvesting to Replenish Underground Water in India Due to the increased rates of deforestation in Rajasthan monsoon, rains started to wash down the surface levels of the soil, making the ground less fertile and eroded.
- Typical Reasonably Homogeneous Equilibrium in Water It is important that the diffusion coefficient used to link the iodine concentrations in one phase to that in another account for the existence of iodide and polyiodide salts.
- Creative and Critical Thinking in Case of Lack of Water In order to identify the significance of creative and critical thinking in the situation presented, it is necessary to dwell on the definition of the process of creative thinking.
- Water Scarcity in Africa and Mental Disorders Partially, the reason for the lack of meaningful changes in the policies preventing the causes lies in the social stigma towards patients with mental problems.
- Concept of Water Companies Furthermore, in this market formation, it is assumed that the prices do not control the market, which is contrary to the search for a life partner.
- The Safe Drinking Water Act: The Discussion Post The discussion post acknowledges that the Safe Drinking Water Act has remained a powerful guideline that must be followed by different stakeholders to ensure quality and clean drinking water is available to the greatest number […]
- Dehydration and Water in People’s Life It is of utmost importance since it cannot be stored in the body and replenishing of the water must occur constantly.
- Energy and Air Emission Effects of Water Supply Contemporary systems meant to heat water/air explore both the heat pumps and the solar plates that are combined to form a unit with the aim of optimizing on the energy efficiency as well as solar […]
- Adjustable Speed Drives Improving Circulating Water System This was concluded to be because of the many vortices that were generated as a result of the hindrance in the flow of water due to the shape defect.
- Effect of Sea Water and Corrosion on Concrete On the other hand, substantial tautness, for instance due to meandering will shatter the tiny firm pattern, ending up in fracturing and disjointing of the concrete.
- Oil and Water Flow in a Petroleum Reservoir While the physical model is to the scale of the original reservoir’s dimensions, a mathematical model is different. The mathematical model allows one to learn the fluid flow equation without having to develop a laboratory […]
- Behavior Change: More Water, No Coffee By the way, this was the first day when I did not feel any lack of energy due to the lack of coffee.
- Efficient Solar Refrigeration: A Technology Platform for Clean Energy and Water Refrigeration cycle capable to be driven by low grade energy, substituting gas-phase ejector used in conventional mechanical compressor.
- Salt and Drinking Water Shortage Therefore, humanity could reveal that given that the salt would not be willing to negotiate, it is possible to extort the water from the Martians as the resources of Earth are not as essential.
- Flint Water Crisis: Environmental Racism and Racial Capitalism The Flint crisis is a result of the neoliberal approach of the local state as opposed to the typical factors of environmental injustice; a polluter or a reckless emitter cutting costs. The two main factors […]
- Oil-Water Separation Techniques in Qatar’s Desalination Plants In many areas of the Middle East, the proper functioning of the vital social mechanism depends on the stable supply of fresh water.
- Annotated Bibliography on Water Management The importance of water management and its application in the oil industry is the primary focus of Adham et al.in this article.
- Recycled Water – Is It Safe for Drinking? There are a number of barriers that always work against the desire to obtain safe drinking water from recycling plants.
- Remote Sensing Monitoring the Ground Water Quality The overall view of the water quality index of the present study area revealed that most of the study area with > 50 standard rating of water quality index exhibited poor, very poor and unfit […]
- A Means of Water Conservation: Irrigation System Strategy An irrigation system strategy is a cost effective strategy that achieves water efficiency that crops get sufficient water whilst minimizing negative effects of irrigation.
- The Consequences of Using Tap and Bottled Water Using the word ‘walking’, the professor means searching for the required information, while ‘talking’ is a dialogue with the authors of the sources.’Cooking’ is implementing the information in the paper to achieve new conclusions, and […]
- Thirstier Mineral Water: Australian Market Analysis Due to the demand of the pure water, a group of students carried out research to come up with a natural drinking mineral water to meet Australian population demands.
- The Health Condition of Water Filtration for the Prevention of Gastroenteritis The medical care authorities prescribe that to lessen the danger of burning-through dirtied or defiled water is satisfactorily sifting water prior to drinking. The properties of the water channel should be checked to ensure that […]
- Marketing of the Bottled Water Industry in the US The growth of the industry can then be attributed to the level of comfort that people have become accustomed to. The bottled water industry is a feasible option for investors who would like to concentrate […]
- Abu Dhabi Water and Electricity Authority The subject of the contract is the performance of construction works by Contractor for ADWEA. The term of the contract includes the time needed to execute and complete all works.
- Proper Water Flow Requirements In order to ascertain the proper flow of water, standard typical sprinkler testing should be carried out on all the established water systems.
- Water Scarcity Problem in Sub-Saharan Africa Since the world has water in abundance, it is necessary that more be done to address the shortage of clean water.
- Water Quality Importance In a lot of areas, the water available to the public is contaminated; that is it has substances that can be of great harm to public health.
- Anglo American PLC: Water Usage Sustainability Anglo American PLC, which is a well-known mining company operating as the second-largest mining company in the industry, intends to embellish the rate of sustainability to retain its global position in the critical competitive mining […]
- Newark Water Crisis: Water Pollution Problem The main problem was rooted in the fact that lead levels in the drinking water were highly elevated, which is dangerous and detrimental to the population’s health.
- Water Quality and the Water Board Scenario As a member of this water board one first needs to find out the level of quality of water and its source before the eruption of the drought, the clear cause of water shortage, impacts […]
- Water Fluoridation Plant Analysis On the other hand, the flow meter provides the rates of water flow to the dosing facility, which interprets the amount of fluoride needed in the water.
- Determination of M2+ Ions in Mineral Water Titrometry is one of the techniques that chemical analysts use to determine the concentration of metal ions in mineral water. A buffer is necessary to provide suitable pH for the complexing of EDTA with metal.
- House Energy Audit: Water and Energy Consumption Review for the House 265 kWh/kL water supply The actual daily consumption in a period of 8 days of the above-mentioned utilities are calculated and recorded in the following table 2.
- Pre-Construction Design Specifications: Water Piping Sub-System The criteria of complexity and implementation are related to the flexible PDS criteria of the system being powering set-up, repeatability of measurement, reduced temperature setup time, and progressive heating/cooling supply temperature.
- Woburn’s Municipal Water Supply System During the subsequent 20years, “problems with the taste, odor, and supply of water from the city wells continued to arise”. To remove the fine particles, chemicals such as polymers, salts and aluminum are included in […]
- Toxicology: Is Water a Toxic Substance? It is well known that the solubility of ethanol in water is unlimited. Toxicity could be a characteristic of the formation of the reactive oxygen species which can also be present in water.
- The Effects of a High Consumption of Water The null hypothesis would be that increasing the daily intake of water to eight glasses a day has a positive effect on the body, especially on the skin.
- FIJI Water: The Leading Producer of Bottled Water At the same time, the overall corporate culture and the company’s contribution to the development of the community are rather effective.
- Biorefinery Processes and Products (Microalgae and Water Hyacinth) The biomass pulp is directed to the second biorefinery process where grains and enzymes are fed into the tank. The fermentation and bio-reactions lead to the formation of bio-products which are fed into the fourth […]
- Water-Absorbing Polymers: Review Thus, to improve wetting properties of the sandy soils, prevent leaching of nutrients, and improve the yields of onions, the use of water-absorbing polymers is essential.
- How a Desalination Plant Removes Salts, Minerals From Water The main objective of such processes is to convert salty water into one that is suitable for human use or in some cases for irrigation purposes.
- Water for Environmental Health and Promotion The recognition of the effect of the epidemiological triangle is quite crucial, as people ought to realize the interrelationship of the host, environment and agent in the process of spreading diseases and the effect that […]
- Conventional Water Treatment It is essential to note the contrast between the quality of source water and the quality of the desired treated water for better selection of the treatment process.
- Water Supply and Sanitation Systems Devikilum Village The rate of pumping will depend on the rate of water recovery from the sources, and hence prior arrangement of pumping rate must be considered when installing the pump. Due to its availability and low […]
- Reduced Flow of Stream Water The algae will flourish almost to the surface of the stream and this may appear like scum that is easy to notice.
- “Nutrient Water” Type Drinks and Whole Milk: Evidence-Based Claims The report then goes on to conclude as to the findings of the various journals on which of the two is the better option and finally a recommendation as to the circumstances when their use […]
- Women Groups in Ikombe County: Water Tanks Delivery Funding Phase one which will be implemented in the first year will target to provide four women groups with water tanks. The last phase will be accomplished in the fifth year and will provide tanks to […]
- Diet and Water as an Overlooked Essential Nutrient Water is a very important nutrient in the body because it maintains homeostasis, and enhances the transport of other nutrients and minerals from their point of absorption to other parts of the body.
- Designing a Controlled Water Cooling System The scope of the project is to design and build a system for cooling and heating water in tanks/reservoirs for domestic customers.
- Warm Water and the Characteristics of Plaster The sample which implied using chilled water has shown the latest initial, and effect of retardation) and final set ). 015 for the warm water sample, and 0.
- Aquadaf Technology – High Rate Water Clarification In this study we will focus on Aquadaf technology to explain how the high rate water clarification process works, the efficiency of the process and the economical aspect of it.
- Fluoride in Drinking Water, Its Costs and Benefits to Oral Health The studies shown below were meant to determine the effects of fluoride in drinking water There was a case study conducted by Milciuvinene and her colleagues in Lithuania that showed there was a positive effect […]
- Water Desalination in Saudi Arabia
- Irrigation Water and Carbon Footprint
- Domestic Water Usage Monitoring System
- Nutrition: The Importance of Water for Daily Life
- Water Policy Design in Toronto
- People Affected by Fires and Natural Disasters Need Help With Food, Water, Shelter
- Landscaping Membranes for Oil-Water Separation
- Water Treatment System for Saline Bores in Cape York
- Testing the Safety of Water in Canada
- The Mega Corporation: Clean Water
- Clean Water Change the Lives of People in Developing Countries
- Privatization of Water in St. Louis
- Finance for Drinking Water Infrastructure
- BP: Water Use in Oil and Gas Industry
- Visiting Black Rock Water Reclamation Plan
- Water Scarcity: Industrial Projects of Countries That Affect the External Environment
- Mapping Environmental Justice: Water and Waste Management
- California and Water Shortage
- Water Policy: The Impacts of Water Trading
- Water Services and Fire Fighting in Maryland
- Water Service in the UK: History and Sources
- Water Distribution in California
- Monet’s Water Lilies: What Would Clive Bell Say?
- Western Region Water Corporation’s Analysis
- Water: The Element of Life
- Evaluation of the Popularity of Bottled Water Over the Tap Water
- Water and Energy Requirements of Curcubita Maxima
- Modern Water Purification Methods for the Middle East
- 321 Water as a Bottle With a Built-in Filter
- Energy, Water and Capital as Factors Influencing Business
- Water Purification: Process and Other Nuances
- Thomas Cole’s Revelations Through Landscape and Water
- Thames Water Company’s Pollution Issue and Ecocentrism
- Restoration of the Natural Water Flow in the Everglades
- Fresh Water System for El Salvador
- Las Vegas Water Policy
- Water Pollution in a Community: Mitigation Plan
- Mediterranean Deep Water & Levantine Intermediate Water
- North California Water Problem and Solution to It
- Modern Global Issues: Drinking Water Shortage
- Sharjah Electricity & Water Authority’s Creative Improvement Strategies
- Domestic Water Consumption : Effect, Outcome, Feedback
- Liquid Waste Disposal and Ground Water Contamination
- Polluted Water and Human Diseases
- Water Resource Exploitation in the Arid Lands as an Global Political Problem
- Water-Based Recreational Opportunities
- Market Analysis of Bottled Water
- Water Efficiency in Food Production: Food Security, and Quality of Life
- Food Distribution and Water Pollution
- Water, Energy and Food Sustainability in Middle East
- Domestication of Water: History of Swimming Pools
- Analysis of Water in Wetlands for Phosphate, Nitrite, and Bacteria
- Food and Water Access. Human Security Perspective
- Flow: For Love of Water
- Environmental Policy: Water Sanitation
- Masafi Alkalife pH9 Water Advertisement
- The Ongoing Problem of Lead in Drinking Water in Newark, New Jersey
- Jordan’s Water Crisis and Response
- Water and Its Role in Biochemical Processes
- Baja California Water Crisis and Its Impact
- Columbia Roxx Water Company: Operations and Management Plan
- The Documentary Film “Flow: For Love of Water”
- Natural Sciences: Water Expansion During Freezing
- Water Treatment Impact on Wheat Plant Growth
- Insects and Walking on Water
- Water Shortage in Somalia: Reasons and Solutions
- Dubai Electricity and Water Authority’s Internship
- Fiji Water’ Environmental Effects
- Bolivian Water Price Determination
- Energy and Water Projects in the Middle East and North Africa
- Irrigation Water Reduction Using Water-Absorbing Polymers
- Public Water Supply System in New York
- The Paths of Water: Hydrological Cycle
- Website Usage: Bottled Water Company in Nigeria Case
- All the Water on Europa: Astronomy Picture of the Day
- Battled Water and Jewelry: Product Analysis
- Water Management: Soft-Path Approach in Abu Dhabi
- Integrated Sustainable Water Resource Management
- Heavy Crude Oil Emulsification in Water
- Year-Round Water Access in South Asian Countries
- Dubai Electricity and Water Authority: Sustainable Management
- Dubai Electricity and Water Authority’s Strategic Options
- Trends in Water Supply and Sustainable Consumption
- Water Maze Experiment for Hydergine Drugs Testing
- Ablution Water Recycling in Mosques
- Privatized Kuwaiti Ministry of Electricity and Water
- Abu Dhabi Climate, Water Usage and Food Production
- Chemical Contamination of Ground or Surface Water
- Water Billing IT Solutions Company Business Plan
- Nuclear Magnetic Resonance and Water Quality
- Turbidity and Total Suspended Solids of Water: Lentic and Lotic Sites
- Dubai Electricity and Water Authority’s Tech Innovations
- Dubai Electricity & Water Authority’s Asset Lifecycle
- Dubai Electricity & Water Authority’s Cost Management
- Drinking Water Distribution System
- The Chippewa Cree Tribe’s Water Rights
- Tribal Water Rights and Influence on the State Future
- Water Quality as a Concern for Urban Areas
- Solar-Powered Water Cooler System
- How Saudi Arabia Can Overcome Economic Water Crisis?
- Water Pollution and Associated Health Risks
- California Water Shortages and Long-Term Solutions
- Lake Erie Water Pollution
- Dubai Electricity and Water Authority: Consultation
- Preserving of the Drinkable Water Worldwide
- Dubai Electricity and Water Authority’s Employees
- Drinking Water Availability and Quality in the USA
- Dubai Electricity and Water Authority’s Empowerment
- American Water Company: Users and Systems Specialists Role
- Water Price Hike and Its Effects on the UK Economy
- Water Drinking Increasing Skin Moisture Balance
- Water Crisis Resolution and Investments
- Food and Water Quality Testing Device
- UAE Federal Electricity and Water Authority’s Policies
- Water and Soil Resources Issues in the Middle East
- Mountain Valley Spring Water Advertising
- Sunflower Plant Growth With Minimal Water Requirements
- Water & Air Pollution and Health Issues in Brazil
- Pure Home Water Company: Business Model
- Pure Home Water Company’s Environment
- Disposable Water Bottle Usage by Youth Population
- The Gardens of Islam: Water and Shade
- Water Cycle and Environmental Factors
- Potable Water Supply in the Gulf Region
- Water Resources: History and Potential Impacts
- Storm Water Pollution Prevention Plan
- The Jordan River Water Issues and Hydropolitics
- Water-Energy Nexus Explained
- Water Pollution in the US: Causes and Control
- Smart Water Grids and Water Sustainability
- Water Control Issue in the United Arab Emirates
- Food and Water Waste Disposal in NYC
- Dubai Electricity and Water Authority: Employee Performance
- Economic View on Water and Pollution
- Barwon Water Company’s Management and Service Analysis
- Water Transportation Industry’s Impact on Wildlife
- The Nile River: Water Issues and Hydropolitics
- Water Crisis, Oceans and Sea Turtles Issues
- Water Tailing Technologies Issues
- Sharjah Electricity & Water Authority’s Customer Satisfaction
- Water Pollution and Management in the UAE
- Abu Dhabi Water & Electricity Authority’s Pre-Assessment Audit
- EPA Rules Effect on Perchlorate in Drinking Water
- Quality Management of the Dubai Electricity and Water Authority
- Abu Dhabi Water and Electricity Company’ Demand Forecasting
- Environmental Health: Lead Exposure in Water
- Water Yield Re-Estimation From the Catchment Due to Bushfire
- The Human Right to Water: History, Meaning and Controversy
- “Vitamin-Enriched” Bottled Water: PEST Analysis
- World Water Needs: Water Scarcity Problem in Australia
- The Water Nexus Model in the UAE
- Water Related Conflicts in Africa
- Clean Water Problem in Singapore
- Water Consumption on the Household Level
- Water Paradox: “The Wealth of Nations” by Adam Smith
- Water Scarcity, Marketing, and Privatisation
- Reduce Chemical Spills by Using Green Water Purification
- Reducing Chemical Contamination on Water
- Effective Methods to Increase Water Quality
- Sanitation of Reserve Resources: Unsafe Drinking Water
- Abu Dhabi Water & Electricity Authority’ Quality Planning
- Water Resources Ecology: Current Issues and Strategies
- Blue Gold: World Water War Documentary
- Thirstier Mineral Water – Marketing
- Safe Drinking Water Importance
- Water Crisis in the Documentary “Chinatown”
- Mars: Water and the Martian Landscape
- Saving Energy Systems: Water Heater Technology
- Jordan River’ Water Issues and Hydropolitics
- Water Symbolism in Christianity and Islam
- Banning Hosepipe Use as a Poor Solution to a Water Shortage
- Criminology: Water Boarding Torture
- Blue Gold: Global Water Crisis
- City of Newark Public Water Supply System
- Irrigation and Sustainable Water Use for Improved Crop Yield
- Water Distribution in Boston
- Environmental Studies: Water Contamination in China
- Is Bottled Water Ethical?
- Kantian Perspective on Water Privatisation
- Water Purification Process
- Water Quality & Drinking Water Treatment
- Dialysis Water Treatment System
- Kant’s Philosophy: Water and Ethics
- Water Pollution and Its Challenges
- The Three Methods of Water Supply
- Management of Water Supply Projects in Malaysia
- Drinking and Bathing Water in Sabah
- Project Management: Sydney Water Company
- Perchlorate in Drinking Water
- Impact of PPP Projects in Energy and Water Sectors in the MENA Region
- Potential Reduction in Irrigation Water Through the Use of Water-Absorbent Polymers in Agriculture in UAE
- Water Pollution Sources, Effects and Control
- Water Resources Deterioration Consequences in the GCC Countries
- Society’s Impact on Water Recourses
- Effects of Lead and Lead Compounds on Soil, Water, and Air
- Knowledge Management: Maroochy Water Services
- Promotional Strategy for the New Water Based Theme Park in Darling Harbor
- Marketing Strategy for Bottled Water in Hong Kong
- Water Boarding as a Form of Criminal Interrogation in the US
- Scarcity of Water in Saudi Arabia, Africa and Australia
- The Ancient and the Medieval Worlds: The Use of Water Power
- Power Water Corporation (PWC): Compiling a Business Strategy
- Availability of Water Resources in United Arab Emirates
- Chloramine in Drinking Water: When the Threat of Pollution Emerges
- The Hydrologic Cycle and Water on Earth
- British Petroleum Company: Deepwater Horizon Oil Spill
- Chloramine Breakdown in Drinking Water and Possible Consequences
- Water Management in Houston
- Cold Water Creek Comprehensive Case
- “Water and Pollution” Class Game
- Global Water Scarcity Causes and Solutions
- Technologies in Improving Air Quality Management Due to Waste Water
- Environmental Justice and Water: Quality, Affordability and Sustainable Use. Facing the Dilemmas of the XXI Century
- Water Quality and Treatment
- Water in Crisis: Public Health Concerns in Africa
- Water War in the Middle East
- Reclamation of Grey Water & Refinery Oily Wastewater Using Bioprocesses Treatment
- Factors Affecting Access to Water Resources in South Asia, the Middle East and the Nile River Basin
- Water War in Bolivia
- Bottled Water: Tropical Spring Water Company
- Protecting Water Resources in South Asia
- Can Hot Water Freeze Faster Than Cold Water?
- Water Wars in Bolivia
- Water Consumption in the World
- Political Ecology and Water Resources
- Design Systems. Water Supply & Sanitation
- Drinking Water and Culture in the Valley of Mexico
- Water Usage in University of Ottawa
- Air and Water Pollution
- Critical Book Analysis – Blue Gold: The Battle Against Corporate Theft of the World’s Water by Maude Barlow and Tony Clarke
- Green Buildings and Their Efficiency Water Consumption
- Water Resources and Usage
- The Planning Action to Bring Water to the Town Population
- The “Bling H2O” as the Luxury Bottled Water
- Privatization of the World’s Water and Wars of Water
- The Effect of Animal Reburial on the Soil Structure and Water
- Analysis of High Recovery Brackish Water Desalination Processes using Fuel Cells by Rajindar Singh
- The Entrance of Bling H2O Into the Bottled Water Market
- Australian, Perth Water Supply Crisis
- Bottled Water Effect on Environment and Culture
- Environmental and Cultural Impact of Bottled Water
- The Privatization or Commodification of Water
- Western Water Company Overview
- Water Resources in Economic
- Water Regional Police Services Project Implementation
- Biblical Living Water Explained
- Providing Access to Clean Water
- The Global Water Shortage
- Water Consumption in the UAE: Analyzing the Past Mistakes, Designing the Future Strategy
- Fat- and Water-Soluble Vitamins
- Mineral and Water Function
- Causes of Water Pollution and the Present Environmental Solution
- Water Balance in Berkeley and Terre Haute
- Water Pollution & Diseases (Undeveloped Nations)
- Trend Analysis: Water Scarcity Issue
- Water and Water Pollution in Point of Economics’ View
- Water Scarcity and Its Effects on the Environment
- The Water Distribution System of Springfield City
- Safety of Recycled Water for Drinking
- Diffusion of Water as the Important Factor in the Development Egypt and in United States
- Environmental Justice Issues Affecting African Americans: Water Pollution
- Threats to Water Availability in Canada
- Economics of Water Bottling
- Dubai Water & Electricity Company
- Pesticide Usage and Water Scarcity
- Why the Water Bears are the Most Appropriate Animals to Send to Mars for Human Research
- Water Pollution and Wind Energy
- Description of the Water Resource Problem (Origins)
- Air and Water Pollution in Los Angeles
- Classification of Water-Related Diseases
- Water Pollution Causes and Climate Impacts
- Como Agua Para Chocolate: Like Water for Chocolate
- Water Distribution System in Spain
- Water Distribution System Used by the State of Texas
- Company Profile: Western Water
- Water Crisis in UAE
- Water Pollution Origins and Ways of Resolving
- Mud Lick Creek Project – Fresh Water Pollution
- Water Quality Issues in Developing Countries
- Comparison of Secondary and Tertiary Waste Water Management
- Housing; Safety of Beach Water Users
- Water Distribution System in Boston
- Water Resources Management
- Does Salt Affect the Freezing Point of Water?
- What Is the Biggest Problem Concerning Water Today?
- Does Too Much Water Help Plants Grow More Rapidly?
- How Can Leaders Tackle With Water Pollution in China?
- How Are Farmers Growing More Crops With Less Water Than Before?
- What Is the Healthiest Type of Water to Drink?
- How Does Human Activity in Watersheds Affect the Water Quality of Lakes?
- Will We Ever Run Out of Water?
- How Does the Temperature of Water Affect How Fast Sugar Can Dissolve?
- How Harmful Can Bottled Water Be?
- What Factors Affect the Cooling of Hot Water in a Container?
- What Are the Two Main Problems With Water?
- Why Diverting Water From the Great Lakes Region Is a Bad Idea?
- What Are the Benefits of Drinking Water?
- How Much Water Should People Drink?
- Why Bottled Water Should Be Free?
- What Is the Proper Way to Drink Water?
- What Is the Best Time to Drink Water?
- Who Is the Biggest Water Company?
- What Are the Challenges for Water Industry?
- What Is the Value of the Water Industry?
- Why Do 785 Million People Lack Access To Clean Water?
- What Is the Best Selling Water?
- Which Type of Water Is the Purest and Safest To Drink?
- How Are Water Companies Funded?
- How Does Drinking Water Pollution Impact the World?
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, March 4). 469 Water Essay Topic Ideas & Examples. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/water-essay-topics/
"469 Water Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." IvyPanda , 4 Mar. 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/topic/water-essay-topics/.
IvyPanda . (2024) '469 Water Essay Topic Ideas & Examples'. 4 March.
IvyPanda . 2024. "469 Water Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." March 4, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/water-essay-topics/.
1. IvyPanda . "469 Water Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." March 4, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/water-essay-topics/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "469 Water Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." March 4, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/water-essay-topics/.
- Air Pollution Research Ideas
- Environment Research Topics
- Agriculture Essay Ideas
- Environmental Protection Titles
- Climate Change Titles
- Hazardous Waste Essay Topics
- Hygiene Essay Topics
- Oceanography Research Ideas
- Play & Activities
- Life Skills
- Learning & Education
- Play & Learning

- Growth & Development
- Rhymes & Songs
- Preschool Locator
Importance Of Water – 10 Lines, Short And Long Essay For Children
Key Points To Note: Essay On Importance Of Water For Lower Primary Classes
10 lines on the importance of water for kids, a paragraph on the importance of water, short essay on the importance of water for kids, long essay on the importance of water for children, interesting facts about water for children, what will your child learn from this essay.
There will be no living beings on this planet without water. Since each living organism requires water to survive, we should always take care to make sure that this resource is available. This is why children are made to write an essay in English about the importance of water in classes 1, 2 and 3.
Essay writing is a crucial skill. It helps improve children’s vocabulary and writing skills. This article can assist children who’ve been searching for details on water in English. Crafting an essay on such a topic allows kids to be open to the importance of water in their minds, and it will make them respect the key resource on our planet.
Writing an essay on the significance of water is not a very tough task. Make sure you remember the below-mentioned points while writing an essay:
- Start by explaining why water is vital to everyone.
- Discuss some fascinating water facts.
- Explain why it is important to preserve water.
- Talk about ways you can preserve water. Mention the easy tips and ideas that people can follow.
- Also, don’t forget to end on a positive note.
We must learn the true value of water while writing an essay on water in English. Below are 10 points on the importance of water:
- Water is essential for all flora and fauna on this planet.
- If there’s no water, life on this planet would be impossible.
- Water accounts for about 60% of a human’s weight.
- Water is used for showering, cleaning, cooking, etc.
- The two categories of water on our planet are salty and fresh water.
- Water covers about 71% of the Earth’s surface.
- For consumption, we solely utilise fresh water.
- We should not misuse water because the scarcity of drinking water is a major issue worldwide.
- We must save water by preserving and utilising rainwater, among other things.
- We must prevent water pollution by participating in a water management initiative.
When kids write about the importance of water, it generates a flood of fantastic ideas in their heads, and they learn a lot from it. Usually, this is a common essay for classes 1 & 2.
Water is an extremely important element for the survival of all living organisms on our planet. The significance of water is crucial in more than one way. Furthermore, there’s no substitute for water. Regardless of the huge amount of water on the planet, usable and drinking water is very limited. Even though water covers 71% of the earth’s crust, just around 3% of it is suitable for human use. However, we waste water and pollute it, which has created issues like water scarcity for all. There is a continuous depletion of groundwater as well.
A hungry person can stay without eating food, but a thirsty one cannot go on without water since living without fluids is impossible. This essay on water for class 3 will help kids learn about the importance of water.
Everyone, including humans and plants, requires water. People, creatures, and flora all need water. Life cannot exist without water; everyone and everything will perish if no water is available. Water helps in maintaining our body temperature and aids in digestion too. Aquatic animals use oxygen and nutrients present in water for their survival.
There are two kinds of water available on our planet – fresh water and salt water, and the ocean is all salt water. Humankind uses most water for irrigation, home, and business purposes. The quantity of drinkable or fresh water on earth is diminishing daily; therefore, we must save it. We should store water and then use it wisely. We must not leave the tap running or wash our automobiles with water pipes for long hours.
FEATURE IMAGE SSID: (1931142059) (ALT<(Essay On Importance of Water – 10 Lines, Short and Long Essay for Children>)
Water represents life. Water is a precious resource, a fundamental human requirement, and a valuable asset that all living things possess. Every child should understand the importance of water in daily life.
There are many reasons why water is considered one of the most important and valuable resources on our planet. Let us look at this in a more detailed manner.
Significance Of Water
Water is the cornerstone of human survival when it comes to life. A human body requires water every single day. We might be capable of not eating for seven days; however, we won’t last even three days without drinking water. Furthermore, approximately 60% of human bodies are made up of water which aids our body’s normal functioning. As a result, ingesting impure water will cause major health issues in humans. Therefore, the amount and quality of water we drink are critical to everyone’s physical health and wellness.
Furthermore, our everyday activities would be incomplete without water, like brushing our teeth or preparing meals. Also, many companies use water on a massive scale as almost every single activity of their procedure requires water.
Water has an important function in the lives of all living organisms. From the tiniest insect to the largest whale, each life requires water to stay alive. Water is not just a human need but also flora and fauna. Water is necessary for the planet’s life to function. We should not be self-centred and utilise it for our purposes without caring for the consequences.
Water For Life Processes
- Water plays a crucial part in most biological functions as a solvent. Several waste materials are also eliminated as a solution via urination and sweat.
- Water aids in maintaining body temperature. We take plenty of fluids when it’s hot outside, which keeps the body temperature stable. Water also escapes from the body’s surface as sweat, which removes heat from the body and gets to normal temperature.
- Water is required for plants to make food.
Uses Of Water
- In our daily lives, water is utilised for drinking, dishwashing, baking, showering, and wiping.
- We need water daily for our home gardens too.
- A hydroelectric power plant uses water to create energy.
- Water is being used to irrigate crops and create a variety of items.
- Many water sports include swimming, sailing, kayaking, etc.
- Water can also be used to put out fires.
- Water is necessary for the correct operation of farmed fish, dairies, and many other non-farm operations.
- The majority of fresh water is frozen.
- The oceans contain just about all the water on the planet.
- The salt content of salty water fluctuates.
- One single drop could hold a great deal of life.
- Comets might have also provided some water in the earth’s history.
Your child will learn how to improve their writing and creative abilities. They will also discover how important water is for their bodies and the ecosystem and the various ways they might use it. They will learn about the importance of water on this planet, not just for humans but for all living things. Last but not least, students will learn about several water-related facts.
1. What Will Happen If Water Vanishes?
Complete vegetation would die rapidly without water, making the earth brown instead of greenish-blue. As clouds will fail to develop and there will be no rainfall, the climate will be dominated entirely by atmospheric circulation. Life as we know it would cease to exist.
2. Why Should We Not Waste Water?
Water is scarce, despite its abundance, and cannot be regenerated. We must utilise it with caution.
To summarise, water is indeed the foundation of all living things on the planet. Recognising fresh water’s importance and educating people about it is necessary.
Importance of Education for Classes 1, 2 & 3 Kids Essay On Healthy Food Essay for Lower Primary Children Essay On Cleanliness is Next To Godliness for Class 1,2 and 3 Kids
- Essays for Class 1
- Essays for Class 2
- Essays for Class 3
5 Recommended Books To Add To Your Child’s Reading List and Why
5 absolute must-watch movies and shows for kids, 15 indoor toys that have multiple uses and benefits, leave a reply cancel reply.
Log in to leave a comment

Most Popular
The best toys for newborns according to developmental paediatricians, the best toys for three-month-old baby brain development, recent comments.

FirstCry Intelli Education is an Early Learning brand, with products and services designed by educators with decades of experience, to equip children with skills that will help them succeed in the world of tomorrow.

Story Related Activities Designed to Bring the Story to Life and Create Fun Memories.

Online Preschool is the Only Way Your Child's Learning Can Continue This Year, Don't Wait Any Longer - Get Started!
©2021 All rights reserved
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Use

Welcome to the world of Intelli!
We have some FREE Activity E-books waiting for you. Fill in your details below so we can send you tailor- made activities for you and your little one.

Welcome to the world of intelli!
FREE guides and worksheets coming your way on whatsapp. Subscribe Below !!
THANK YOU!!!
Here are your free guides and worksheets.
- 50 US States

42 Interesting Facts About Paper
Last updated on June 29th, 2021
Paper is a thin sheet material. Nowadays, it is usually produced by machines however initially it was hand manufactured. It is usually made of cellulose fibres formed on a wire screen from water suspension. We use paper daily, whether at home for jotting down the shopping list, at school, or work for filing reports. The form surrounds us literally, but how much do you know about it? Here is a collection of 25 facts about paper.
1. Paper was invented from hemp by the Chinese, around 100 B.C. Later, they started creating paper using other forms of plant fibers such as bamboo and tree bark. Prior to the invention of paper, papyrus served as a writing surface.
2. The Chinese also are credited with being the first people to use paper currency and toilet paper.
3. The production of the paper focuses on softwood trees that account for approximately eighty-five percent of the form. The wood pulp in softwood trees contains cellulose fibers and is most preferred since they can produce adequate strength for paper.
4. The favorable softwood trees for papermaking include pine, fir, and spruce. Trees come in varied sizes, making it difficult to establish how a single tree can produce many sheets of paper. However, on average, one pine tree can make around 80,000 sheets of paper.
5. It can take five liters of water to make one sheet of paper. Although water and writing may sound like a bizarre combination, ninety-nine percent removal of water will make the remaining one percent paper the way we see it.
6. You can put paper into seven different categories. These are printing paper, writing paper, drawing paper, wrapping paper, handmade paper, blotting paper, and specialty paper.
7. Paper-making was a huge secret the Chinese kept to themselves until the sixth century when the idea was brought to Japan by a Buddhist monk called Dam Jing. The Japanese quickly learned this tactic and began making the valuable item using pulp obtained from mulberry bark.

8. It is believed that the knowledge of paper-making was later passed to the Arab world in 751 CE after the famous Battle of Talas. During this time, two Chinese who were paper-makers were captured as prisoners.
9. The paper-making technique employed by people of the Middle East tangled macerating and garnering rags in water to create homogeneous pulp, which would be sifted to obtain macerated fiber sheets. The sheets were then pressed, dried, and covered with a film of rice starch.

10. The idea of paper production and usage spread from the Middle East to Europe in the 13th Century. It was then that Europe established the first water-powered paper mills.
11. Much growth in paper industry took place in New York and New England during the late nineteenth century. For this reason, Holyoke and Massachusetts came to be known as ‘The Paper City.’
12. Philadelphia was an important center for paper-making in the nineteenth century as it had lots of specialty paper-makers such as manufacturers of roofing paper and wallpapers.
13. Mass communication began with the industrial manufacture of paper in the 19th Century. This was a result of the mass-circulation of newspapers and novels. During the same period, there was an explosion of literacy among the middle class.

14. The first monthly newspaper “Notizie Scritte,” was printed in Venice in the year 1556. The monthly publication would go for one Vatican coin known as Gazzetta thus the name ‘gazette’ can be used when referring to a newspaper.
15. Paper is widely recommended for packaging by manufacturers as it is appealing and easy to carry. For two-thirds of consumers, cardboard and paper-based packaging make items more alluring than other packaging materials.
16. Paper containers are bio-degradable and can be reused in many other forms such as fiber-boards. Therefore, people are encouraged to embrace them as compared to plastic containers.

17. Paper is one of the few truly renewable resources. Paper fibers can be recycled up to twelve times before they get too short for paper-making. Recycling paper makes it possible to save up to 0.4 hectares of forest. Furthermore, paper is made from trees, a renewable source.
18. Producing paper from waste paper is economical. 85% of the water used in normal paper production is saved when the paper is recycled as well as a significant reduction in water pollution. Recycling paper also means you saving trees. Statistics show that approximately 0.4 hectares of forest can be saved when a ton of paper is recycled.
19. The production of recycled paper contributes to cleaner air. Compared to the production of standard paper, recycled paper production reduces air pollution to up to 73%.
20. About two-thirds of the paper we use gets to be recycled.
21. Similar to the initial production of paper, the recycling process involves extraction. First, the recyclable paper is separated from the non-recyclable one; then, the recyclable paper is washed in soapy water. The soapy water cleans away the ink, glue, staples, and plastic films.
22. Paper production is energy-intensive. According to statistics, paper production is ranked top three of all manufacturing industries as the most energy-intensive. This however can be significantly reduced when paper is recycled.
23. During decomposition, paper releases methane, a gas more potent strong than carbon dioxide. Methane gas has a heat-trapping power 21 times more than carbon dioxide. Decomposing paper is therefore amongst the largest source of methane emission across the globe. In the event of recycling, such an issue is reduced.

24. Most solid wastes in landfills consist of paper. Paper represents up to 16% of solid wastes in landfills. The fact is, there is lots of paper being thrown away as waste instead of recycling. The end result is too much waste polluting the environment.
25. When paper decomposes in a landfill, it emits methane, a greenhouse gas that is more hazardous than carbon dioxide. Paper littering is more harmful to the environment.
26. Interestingly, the global paper consumption statistics reveal that printing is not the leading paper consumer. Packing and wrapping are significant consumers taking up to fifty-five percent of the total paper production.
27. Not all paper is made from wood. This might sound confusing right? But well, the first Chinese paper was made from cloth scraps and pieces of hemp material. Today, currency notes we use are made from cotton fiber, that’s why it is strong and more durable than normal paper.
. . . continue reading on the next page
- Privacy Policy
- Legal Disclaimer
- Report Error

19 Intriguing Facts About Watersheds
Written by Brigid Gideon
Modified & Updated: 10 May 2024
Reviewed by Jessica Corbett
- Earth Sciences
- Biodiversity Facts
- Ecological Balance Facts
- Ecosystem Facts
- Environmental Impact Facts
- Intriguing Facts
- Sustainability Facts
- Water Conservation Facts
- Water Cycle Facts
- Water Pollution Facts

Watersheds are fascinating natural phenomena that play a vital role in our everyday lives, yet many people are unaware of the intricacies and importance of these systems. In simple terms, a watershed is an area of land where all the water, such as rainfall and snowmelt, drains into a single location like a lake, river, or ocean. This network of streams and rivers acts as a natural drainage system, shaping the landscape and influencing the distribution of water resources.
In this article, we’ll delve into 19 intriguing facts about watersheds that will not only broaden your geographical knowledge but also deepen your appreciation for the interconnectedness of ecosystems and the significance of water conservation. From the world’s largest watersheds to the role of watersheds in mitigating floods and providing habitats for diverse wildlife, get ready to discover the wonders of these dynamic and vital natural systems.
Key Takeaways:
- Watersheds are like Earth’s natural plumbing system, collecting and channeling water to rivers, lakes, and oceans. They’re crucial for clean drinking water and supporting diverse habitats for plants and animals.
- Protecting watersheds is essential for preventing floods, preserving water quality, and sustaining agricultural productivity. Collaboration and proper land management are key to ensuring the long-term sustainability of these vital resources.
Watersheds are vital components of Earth’s hydrological cycle.
A watershed, also known as a drainage basin or catchment area, is an area of land that collects and channels water into a common outlet, such as a river, lake, or ocean.
There are millions of watersheds around the world.
From small, local watersheds that encompass only a few square miles to massive ones that cover thousands of square miles, watersheds are found on every continent and in every corner of the globe.
Watersheds provide important ecological functions.
They play a crucial role in maintaining water quality, regulating water flow, replenishing groundwater, and supporting diverse habitats for various plant and animal species.
The size of a watershed determines its water flow and drainage characteristics.
A smaller watershed can respond more quickly to rainfall events, while larger watersheds have a greater water-holding capacity and can sustain flow during dry periods.
Watersheds are influenced by both natural and human factors.
Natural factors include climate, topography, and vegetation, while human factors include land use, urban development, and pollution.
Watersheds can be classified into different types.
Common classifications include oceanic watersheds, river watersheds, lake watersheds, and even underground watersheds where water is stored in aquifers.
The health of a watershed is crucial for supplying clean drinking water.
Water from rivers and lakes within a watershed is often the source of drinking water for nearby communities, highlighting the importance of watershed conservation and protection.
Healthy watersheds can help mitigate the impacts of flooding.
By acting as natural reservoirs and absorbing excess water, well-managed watersheds can reduce the risk of floods and their destructive consequences.
Watersheds are interconnected.
Water that flows through one watershed has the potential to impact downstream watersheds, emphasizing the need for integrated and collaborative watershed management .
Watersheds support a variety of recreational activities.
From boating and fishing to hiking and wildlife viewing, well-preserved watersheds offer numerous opportunities for outdoor enthusiasts to explore and enjoy nature.
Watersheds are susceptible to pollution.
Human activities such as agriculture, industrial processes, and improper waste disposal can introduce pollutants into watersheds, affecting water quality and harming ecosystems.
Proper land management practices are essential for watershed conservation.
Implementing measures like sustainable agriculture, reforestation, and erosion control helps protect watersheds from degradation and ensures a sustainable water supply.
Watersheds support diverse aquatic ecosystems.
From tiny microorganisms to large fish species, watersheds provide habitat for a wide range of marine and freshwater life.
Some watersheds are designated as protected areas.
National parks, wildlife refuges, and other conservation areas are often established to safeguard important watersheds and their associated ecosystems.
Climate change can have a significant impact on watersheds.
Shifts in precipitation patterns, increased frequency of extreme weather events, and rising temperatures can alter the flow and availability of water in watersheds, posing challenges for water management.
Watersheds support agricultural productivity.
Irrigation systems that rely on water obtained from rivers within watersheds play a critical role in providing water for crop production and sustaining agricultural communities .
Watersheds contribute to the economy.
Industries such as fishing, tourism, and hydroelectric power generation rely on the resources provided by healthy and well-managed watersheds.
Urbanization can have adverse effects on watersheds.
Increased impervious surfaces, such as roads and buildings, can lead to rapid runoff and reduced infiltration, disrupting the natural water balance in a watershed.
Collaboration is key for effective watershed management.
Successful watershed management requires the cooperation and coordination of various stakeholders, including government agencies, local communities, and environmental organizations, to ensure the long-term sustainability of these essential resources.
Throughout the world, watersheds play a critical role in sustaining life and supporting ecosystems. Understanding their importance and taking steps to protect and manage them is crucial for ensuring a sustainable future for our planet.
So, next time you gaze upon a river or lake, remember that it is just a small part of the intricate web of life within a watershed.
Watersheds are a fascinating natural phenomenon that play a vital role in shaping our planet’s landscapes and ecosystems. From the largest river basins to the smallest streams, these interconnected networks of waterways have a significant impact on our daily lives. Whether it’s providing us with clean drinking water, supporting diverse plant and animal species, or influencing weather patterns, watersheds are essential for the sustainability of our planet.
By understanding and appreciating the intricacies of watersheds, we can take steps to protect and conserve these valuable resources. Through responsible land use, water management practices, and increased awareness, we can ensure the long-term health and vitality of our watersheds for future generations.
1. What is a watershed?
A watershed, also known as a drainage basin or catchment area, refers to an area of land where all the rainfall and snowmelt flows into a common river or lake. It is the starting point for all the water flowing through a river system.
2. How do watersheds affect water quality?
Watersheds have a direct impact on water quality. The land within a watershed acts as a filter, removing pollutants and impurities from the water as it travels to rivers, lakes, and groundwater sources. Healthy watersheds help maintain clean and safe water supplies for both human consumption and ecosystem health.
3. Are watersheds only found near large bodies of water?
No, watersheds can be found in any region where there is precipitation. They exist everywhere, from the coastlines to inland areas. Even small streams and creeks have their own localized watersheds.
4. Can human activities impact watersheds?
Absolutely. Human activities such as deforestation, urbanization, pollution, and improper land use can have a detrimental impact on watersheds. These activities can disrupt the natural flow of water, degrade water quality, and harm ecosystem health.
5. How can we protect and conserve watersheds?
We can protect and conserve watersheds by implementing sustainable land use practices, reducing pollution and runoff, restoring and conserving wetlands, and promoting water conservation . It also involves raising awareness and educating communities about the importance of watersheds and the actions they can take to preserve them.
Watersheds play a crucial role in our environment, and understanding their intricacies can help us better appreciate their significance. If you found these facts about watersheds intriguing, you might also be interested in exploring the astonishing world of watershed divides , delving deeper into the complexities of watersheds , and learning about the extraordinary aspects of watershed management . Each of these topics offers unique insights into the interconnected nature of our water resources and the importance of their conservation.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
Share this Fact:

UnifyCosmos
20 Interesting Facts About the Human Brain That Will Amaze You
Posted: May 12, 2024 | Last updated: May 12, 2024

Prepare to be amazed as we delve into the extraordinary world of the human brain! This incredible organ not only orchestrates our thoughts, emotions, and behaviors but also holds secrets that are as fascinating as they are vital to understanding ourselves. From its astonishing capacity to generate electricity to its ability to adapt and heal, join us as we explore some of the most interesting and surprising facts about the human brain that will surely captivate your curiosity.
The Brain’s Water Content
The human brain is approximately 75% water. This high water content is crucial as it helps maintain chemical processes, delivers nutrients to brain cells, and removes waste. Dehydration, even in small amounts, can affect cognitive function and the ability to think clearly.

Neuron Count
There are roughly 86 billion neurons in the human brain. Each neuron is capable of forming thousands of connections with other neurons, leading to an almost infinite number of potential neural pathways. This vast network is what allows for the complexity of human thought, memory, and emotion.
Electrical Power
The brain operates on the same amount of power as a 10-watt light bulb, even when you’re sleeping. The electrical activity generated by the brain is enough to power a small light bulb, highlighting the organâs efficiency and energy management.

Blood Vessels Length
If stretched out, the blood vessels in the brain would be about 100,000 miles long. This extensive network ensures that brain cells receive a constant supply of oxygen and nutrients essential for optimal function.

New Neurons
The adult human brain can grow new neurons, a process known as neurogenesis. Primarily occurring in the hippocampus, this phenomenon is vital for learning and memory. It challenges the old belief that adults cannot grow new brain cells.

Brain Weight
The average adult human brain weighs about 3 pounds, which is about 2% of total body weight. Despite its weight, it uses about 20% of the body’s energy and oxygen intake, emphasizing its importance and metabolic demand.

For each neuron, there can be between 1,000 to 10,000 synapses, amounting to over 100 trillion in total. This immense network of connections is what allows for complex thought, learning, and the formation of memories.

Speed of Information
Information in the brain travels at different speeds but can be as fast as 270 miles per hour. This fast processing speed enables quick reflex responses and seamless coordination of physical actions.

Fat Content
Oxygen Usage
The brain consumes about 20% of the oxygen we breathe in. Its high oxygen use reflects its intense metabolic activity, required for maintaining normal cognitive and neurological functions.

The Visual Brain
Around 30% of the brainâs cortex is devoted to visual processing, more than any other sense. This extensive area highlights the importance of vision in human evolution and function.

Memory Capacity
The storage capacity of the human brain is considered to rival about 2.5 petabytes of binary data, which is equivalent to about three million hours of TV shows. This vast capacity allows humans to store a tremendous amount of information over a lifetime.

Protective Blood-Brain Barrier
The brain is protected by a selective barrier called the blood-brain barrier, which prevents most substances in the blood from entering the brain. This feature is essential for protecting the brain from pathogens and toxins.

The Brain’s Clock
The suprachiasmatic nucleus in the brain acts as the master clock, coordinating all the biological clocks in a human body, regulating circadian rhythms, and ensuring timely hormone release for sleep and other body functions.
Processing Power
The human brain can process images the eye sees for as little as 13 milliseconds â much faster than a blink, which takes about 100 to 400 milliseconds. This rapid processing ability is critical for quick reactions and seamless visual understanding.

Language and the Brain
The brain’s left hemisphere is predominantly responsible for language abilities in right-handed individuals. This lateralization shows how certain high-level functions are compartmentalized within the brain.

Brain Growth
The human brain continues to grow until about the age of 25. This extended period of development is crucial for the maturation of advanced cognitive functions and emotional regulation.

Temperature Regulation

Neural Plasticity
The brain has the remarkable ability to reorganize itself by forming new neural connections throughout life. This plasticity allows for learning new skills, adapting to new environments, and recovering from injuries.
Gamma Waves
The brain can produce gamma waves, which have a frequency of about 25 to 100 Hz and are associated with higher mental activity, including perception, problem-solving, and consciousness.
This article originally appeared on UnifyCosmos .

More from UnifyCosmos
Explore 21 iconic desserts from around the world, each representing a unique culinary tradition. Read more!

14 Cheese Varieties From Around the World and How to Savor Them
Embark on a flavorful journey as we explore 14 distinct cheese varieties from around the globe. Read more .

20 Basic Etiquette Rules That Make Life Better for Everyone
Basic etiquette rules are essential for creating harmonious interactions in a diverse society. Read more!
More for You
Donald Trump Prosecutors 'Know They've Got a Problem'—Legal Analyst
A Photo of Pedro Pascal and Dakota Johnson Kissing Passionately on the Street Has Gone Viral
Doctor shares what happens to our bodies moments before we die
Controversy follows Gov. Kristi Noem as she is banned by two more South Dakota tribes
I Asked 5 Chefs to Name Their Favorite Mayo, and They All Chose the Same Brand
‘American Idol’ reveals its top 3. Here’s how to vote for your favorite singer
Bad luck, rather than the Chiefs, defeated the 49ers at the Super Bowl, according to former QB Alex Smith
Trump dismisses former presidential rival Nikki Haley as a potential running mate: 'Not under consideration'
How Many Fighter Jets Does The United States Have?
The dog breed that has attacked the most people, based on data. Plus, see the rest of the top 20.
Charlie Munger lived in the same home for 70 years: Rich people who build 'really fancy houses' become 'less happy'
Common over-the-counter medicine linked to increased dementia risk
These Crispy Onion Rings Are Almost Too Good to Share
10 PC hardware misconceptions you still believe in
Explosion Rips Through 10-Story Russian Apartment Building
Caitlin Clark, much like Larry Bird, the focus of talks about race and double standards in sports
Broncos release former Super Bowl champion WR
Top 20 Best Kelly Clarkson Show Moments
25 Most Expensive Horse Breeds (Think in the Millions)
These 'Essential 8' habits slowed biological aging significantly, study shows

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Over 90% of the world's supply of fresh water is located in Antarctica. 23. Water regulates the Earth's temperature. 23. On average, 10 gallons per day of your water footprint (or 14% of your indoor use) is lost to leaks. 24. The average pool takes 22,000 gallons of water to fill. 24.
Almost all Earth's water is in the oceans. A whopping 96.5 percent of water on Earth is in our oceans, covering 71 percent of the surface of our planet. And at any given time, about 0.001 percent is floating above us in the atmosphere. If all of that water fell as rain at once, the whole planet would get about 1 inch of rain.
Water numbers. Some of water's physical properties: Weight: 62.416 pounds/cubic foot at 32°F; 1,000 kilograms/cubic meter. Weight: 61.998 pounds/cubic foot at 100°F; 993 kilograms/cubic meter. Weight: 8.33 pounds/gallon; 1 kilogram/liter. Density: 1 gram/cubic centimeter (cc) at 39.2°F, 0.95865 gram/cc at 212°F. Some water volume comparisons:
Facts About Water. 1. The average human body is made of 55 to 65 percent water. 2. Newborn babies have even more, ringing in at 78 percent water. 3. A gallon of water weighs 8.34 pounds; a cubic ...
Most people know that you can't survive without water. But the truth is slightly more nuanced. You need more than just water - you need SAFE water. You also need safe toilets to keep the environment clean, and as well as soap and water to stop the spread of disease. Find out more about why safe water, sanitation and hygiene are so important: 1.
Conservation Facts. Drought Facts. 5+. Water is life. All known lifeforms are dependent on it. According to studies, if we continue our current lifestyle, worsening water pollution and severe water shortage will affect the entire planet by 2040. Theoretically speaking, the world won't run out of water.
A.1 Water is of the utmost importance for human and animal life. It gives us water to drink. It also comes in great use for farmers and industries. Even common man requires water for various purposes like drinking, cleaning, bathing and more. Q.2 List the ways to avoid wastage of water.
Adults are 55-60 percent water. Water is involved in just about everything our body does. It's a big part of the blood that brings nutrients to all our cells. We use it to get rid of wastes. It helps us regulate our body temperature. It acts as a shock absorber for our brain and spinal cord.
The ocean covers 70 percent of Earth 's surface. It contains about 1.35 billion cubic kilometers (324 million cubic miles) of water, which is about 97 percent of all the water on Earth. The ocean makes all life on Earth possible, and makes the planet appear blue when viewed from space. Earth is the only planet in our solar system that is ...
0.5% of the Earth's Water is Freshwater. Technically, 3% of the total water on earth is freshwater. However, more than 2.5% of the same is locked up glaciers, soil, atmosphere and the polar ice caps. That leaves just 0.5% as easily accessible freshwater. A significant amount of freshwater is also found deep underground, but it may not be ...
Here's a look at 35+ surprising facts about water conversation you should know: Fact 1. The agricultural sector worldwide takes about 70% of the water from the planet's freshwater reserves. This is more than double what the industrial sector consumers, which is 23%. Fact 2.
Key Takeaways: Water covers 71% of the Earth's surface, playing a vital role in supporting life and ecosystems. It exists in three states and is essential for regulating body temperature and sustaining our bodies. Water scarcity affects over 40% of people worldwide, highlighting the importance of conserving and protecting this precious ...
7/ Funding for WASH must triple to meet SDG target goals. Without more funding, the world will not reach its SDG for water and sanitation by 2030. The WHO and UNICEF estimate that 9 out of 10 countries where more than 5% of people lack basic sanitation are progressing too slowly and won't achieve universal basic sanitation by 2030.
The first is to dig wells in the rural and arid areas to aid the people to have access to water. The other alternative is to treat water and use it in the home. The Process of the Water Cycle. It is the primary process that drives the movement of water from water bodies into the atmosphere in form of water vapor.
Fact 9. Water cycle was first mentioned about 2000 years ago - According to Chandogya Upanishad, one of Hindu's most ancient scriptures, "rivers… lead from sea to sea.". Fact 10. Water moves slowly in the cycle - Water can stay for at least 10,000 years locked up in the polar ices sheets or in underground reservoirs.
Discuss some fascinating water facts. Explain why it is important to preserve water. Talk about ways you can preserve water. Mention the easy tips and ideas that people can follow. Also, don't forget to end on a positive note. 10 Lines On The Importance Of Water For Kids. We must learn the true value of water while writing an essay on water ...
10 Facts On Freshwater. Freshwater is a precious resource that sustains life on our planet. It encompasses rivers, lakes, streams, and underground aquifers, playing a vital role in supporting diverse ecosystems and human activities. Understanding the significance of freshwater is crucial for appreciating its value and implementing sustainable ...
2. It forms saliva and mucus. Saliva helps us digest our food and keeps the mouth, nose, and eyes moist. This prevents friction and damage. Drinking water also keeps the mouth clean. Consumed ...
Giant Squid. Giant Squid: Deep-Sea Enigma: Giant squids are elusive creatures that inhabit the darkest depths of the ocean. With eyes the size of basketballs and tentacles that can reach lengths ...
Undoubtedly, it is the availability of water, due to which existence of life is possible on earth. Biologists opine that life on Earth originated in water. In fact, water has been the subject of study for a number of disciplines. All these studies have generated many fascinating facts about water. The scientific study of water is called Hydrology.
5. It can take five liters of water to make one sheet of paper. Although water and writing may sound like a bizarre combination, ninety-nine percent removal of water will make the remaining one percent paper the way we see it. 6. You can put paper into seven different categories.
Interesting and Useful Water Facts | | 1. Roughly 70 percent of an adult's body is made up of water . 2. At birth‚ water accounts for approximately 80 percent of an infant's body weight. 3. A healthy person can drink about three gallons (48 cups) of water per day. 4.
Watersheds have a direct impact on water quality. The land within a watershed acts as a filter, removing pollutants and impurities from the water as it travels to rivers, lakes, and groundwater sources. Healthy watersheds help maintain clean and safe water supplies for both human consumption and ecosystem health. 3.
1. Singapore is 1 of 3 city-states in the world. A city-state is a sovereign state centered around one city. There are only 3 modern, independent city-states in the world. The other 2 are Monaco ...
The Brain's Water Content. The human brain is approximately 75% water. This high water content is crucial as it helps maintain chemical processes, delivers nutrients to brain cells, and removes ...