What is the difference between assignment and homework ?
Quick word challenge
Quiz Review
Score: 0 / 5

What's the difference between assignment and job ?
Definition:
- (n.) An allotting or an appointment to a particular person or use; or for a particular time, as of a cause or causes in court.
- (n.) A transfer of title or interest by writing, as of lease, bond, note, or bill of exchange; a transfer of the whole of some particular estate or interest in lands.
- (n.) The writing by which an interest is transferred.
- (n.) The transfer of the property of a bankrupt to certain persons called assignees, in whom it is vested for the benefit of creditors.
Example Sentences:
- (1) Structure assignment of the isomeric immonium ions 5 and 6, generated via FAB from N-isobutyl glycine and N-methyl valine, can be achieved by their collision induced dissociation characteristics.
- (2) A statement from the company said it had assigned all its assets for the benefit of creditors, in accordance with Massachusetts' law.
- (3) Five days later, the animals were randomly assigned to one of four treatment groups: Group 1 received intracranial implantation of controlled-release polymers containing dexamethasone; Group 2 received intraperitoneal implantation of controlled-release polymers containing dexamethasone; Group 3 received serial intraperitoneal injections of dexamethasone; and Group 4 received sham treatment.
- (4) Students are assigned to tutorial groups, and much of the educational thrust of the program is built upon interactions within these groups.
- (5) The second triplet, which was stable in the dark at 4.2 K following illumination, was assigned to the radical pair Donor+I-.
- (6) After the first stage of analysis the spin systems of 60 of the 77 residues were assigned to the appropriate residue type, providing an ample basis for subsequent sequence-specific assignments.
- (7) In an effort to identify the optimal dose and strain of measles vaccination for early immunization, Peruvian infants were randomly assigned to receive one of three measles vaccines in varying doses at 5 to 6 or 8 to 9 months of age.
- (8) Independent t test results indicated nurses assigned more importance to psychosocial support and skills training than did patients; patients assigned more importance to sensation--discomfort than did nurses.
- (9) Families were randomly assigned to one of two forms of conjoint therapy: an Insight-oriented treatment (N = 10) or a Problem-Solving intervention (N = 10).
- (10) Patients were randomly assigned to receive 10 minutes before surgery either I.V.
- (11) Some additional amino proton resonances have also been assigned.
- (12) These chemical shift assignments have been achieved using 1H-detected two-dimensional heteronuclear 1H-13C correlation techniques.
- (13) 7 male and 39 female undergraduates were alternately assigned to rooms painted red or Baker-Miller Pink.
- (14) These data agree with the recent assignment of DIA1 to chromosome G22 by Fisher et al.
- (15) The sequential resonance assignment of the 1H NMR spectrum of the antihypertensive and antiviral protein BDS-I from the sea anemone Anemonia sulcata is presented.
- (16) Following a baseline examination, the furcation-involved molars were randomly assigned in each patient to either a test or a control treatment procedure.
- (17) The letter to Florence Nightingale was written by Bernita Decker as part of a nursing course assignment for our Nurse Educator advisor, Betty Pugh.
- (18) This initial observation of release of eosinophil chemotactic factor of anaphylaxis in vivo along with histamine assigns the mast cell a central role in cold urticaria.
- (19) This assignment was supported by peptide mapping with a tryptophan-specific reagent.
- (20) Both amino acids were found to have the L-configuration by GC analysis on a chiral column and alanine was assigned to be the N-terminal amino acid by Edman degradation.
- (n.) A sudden thrust or stab; a jab.
- (n.) A piece of chance or occasional work; any definite work undertaken in gross for a fixed price; as, he did the job for a thousand dollars.
- (n.) A public transaction done for private profit; something performed ostensibly as a part of official duty, but really for private gain; a corrupt official business.
- (n.) Any affair or event which affects one, whether fortunately or unfortunately.
- (n.) A situation or opportunity of work; as, he lost his job.
- (v. t.) To strike or stab with a pointed instrument.
- (v. t.) To thrust in, as a pointed instrument.
- (v. t.) To do or cause to be done by separate portions or lots; to sublet (work); as, to job a contract.
- (v. t.) To buy and sell, as a broker; to purchase of importers or manufacturers for the purpose of selling to retailers; as, to job goods.
- (v. t.) To hire or let by the job or for a period of service; as, to job a carriage.
- (v. i.) To do chance work for hire; to work by the piece; to do petty work.
- (v. i.) To seek private gain under pretense of public service; to turn public matters to private advantage.
- (v. i.) To carry on the business of a jobber in merchandise or stocks.
- (n.) The hero of the book of that name in the Old Testament; the typical patient man.
- (1) Not only do they give employers no reason to turn them into proper jobs, but mini-jobs offer workers little incentive to work more because then they would have to pay tax.
- (2) That means deciding what job they’d like to have and outlining the steps they’ll need to take to achieve it.
- (3) The idea that 80% of an engineer's time is spent on the day job and 20% pursuing a personal project is a mathematician's solution to innovation, Brin says.
- (4) Of course the job is not done and we will continue to remain vigilant to all risks, particularly when the global economic situation is so uncertain,” the chancellor said in a statement.
- (5) To this figure an additional 250,000 older workers must be added, who are no longer registered as unemployed but nevertheless would be interested in finding another job.
- (6) When compared with self-reported exposures, the sensitivity of both job-exposure matrices was low (on average, below 0.51), while the specificity was generally high (on average, above 0.90).
- (7) David Cameron has insisted that membership of the European Union is in Britain's national interest and vital for "millions of jobs and millions of families", as he urged his own backbenchers not to back calls for a referendum on the UK's relationship with Brussels.
- (8) "We do not think the Astra management have done a good job on behalf of shareholders.
- (9) No one has jobs,” said Annie, 45, who runs a street stall selling fried chicken and rice in the Matongi neighbourhood.
- (10) For enrolled nurses an increase in "Intrinsic Job Satisfaction" was less well maintained and no differences were found over time on "Patient Focus".
- (11) If black people could only sort out these self-inflicted problems themselves, everything would be OK. After all, doesn't every business say it welcomes job applicants from all backgrounds?
- (12) It did the job of triggering growth, but it also fueled real-estate speculation, similar to what was going on in the mid-2000s here.” Slowing economic growth may be another concern.
- (13) I hope they fight for the money to make their jobs worth doing, because it's only with the money (a drop in the ocean though it may be) that they'll be able to do anything.
- (14) Guardian Australia reported last week that morale at the national laboratory had fallen dramatically, with one in three staff “seriously considering” leaving their jobs in the wake of the cuts.
- (15) Which must make yesterday's jobs figures doubly alarming for the coalition.
- (16) Such a decision put hundreds of British jobs at risk and would once again deprive Londoners of the much-loved hop-on, hop-off service.
- (17) This defeat, though, is hardly a good calling card for the main job.
- (18) Here's Dominic's full story: US unemployment rate drops to lowest level in six years as 288,000 jobs added Michael McKee (@mckonomy) BNP economists say jobless rate would have been 6.8% if not for drop in participation rate May 2, 2014 2.20pm BST ING's Rob Carnell is also struck by the "extraordinary weakness" of US wage growth .
- (19) He's called out for his lack of imagination in a stinging review by a leading food critic (Oliver Platt) and - after being introduced to Twitter by his tech-savvy son (Emjay Anthony) - accidentally starts a flame war that will lead to him losing his job.
- (20) Pearson had been informed after that bizarre incident that he was out of a job only to be told that he was back in work a few hours later .
Words possibly related to " assignment "
dispatching
consignment
appointment
reassignment
subrogation
Words possibly related to " job "
CompareWords

Understanding Assignments
What this handout is about.
The first step in any successful college writing venture is reading the assignment. While this sounds like a simple task, it can be a tough one. This handout will help you unravel your assignment and begin to craft an effective response. Much of the following advice will involve translating typical assignment terms and practices into meaningful clues to the type of writing your instructor expects. See our short video for more tips.
Basic beginnings
Regardless of the assignment, department, or instructor, adopting these two habits will serve you well :
- Read the assignment carefully as soon as you receive it. Do not put this task off—reading the assignment at the beginning will save you time, stress, and problems later. An assignment can look pretty straightforward at first, particularly if the instructor has provided lots of information. That does not mean it will not take time and effort to complete; you may even have to learn a new skill to complete the assignment.
- Ask the instructor about anything you do not understand. Do not hesitate to approach your instructor. Instructors would prefer to set you straight before you hand the paper in. That’s also when you will find their feedback most useful.
Assignment formats
Many assignments follow a basic format. Assignments often begin with an overview of the topic, include a central verb or verbs that describe the task, and offer some additional suggestions, questions, or prompts to get you started.
An Overview of Some Kind
The instructor might set the stage with some general discussion of the subject of the assignment, introduce the topic, or remind you of something pertinent that you have discussed in class. For example:
“Throughout history, gerbils have played a key role in politics,” or “In the last few weeks of class, we have focused on the evening wear of the housefly …”
The Task of the Assignment
Pay attention; this part tells you what to do when you write the paper. Look for the key verb or verbs in the sentence. Words like analyze, summarize, or compare direct you to think about your topic in a certain way. Also pay attention to words such as how, what, when, where, and why; these words guide your attention toward specific information. (See the section in this handout titled “Key Terms” for more information.)
“Analyze the effect that gerbils had on the Russian Revolution”, or “Suggest an interpretation of housefly undergarments that differs from Darwin’s.”
Additional Material to Think about
Here you will find some questions to use as springboards as you begin to think about the topic. Instructors usually include these questions as suggestions rather than requirements. Do not feel compelled to answer every question unless the instructor asks you to do so. Pay attention to the order of the questions. Sometimes they suggest the thinking process your instructor imagines you will need to follow to begin thinking about the topic.
“You may wish to consider the differing views held by Communist gerbils vs. Monarchist gerbils, or Can there be such a thing as ‘the housefly garment industry’ or is it just a home-based craft?”
These are the instructor’s comments about writing expectations:
“Be concise”, “Write effectively”, or “Argue furiously.”
Technical Details
These instructions usually indicate format rules or guidelines.
“Your paper must be typed in Palatino font on gray paper and must not exceed 600 pages. It is due on the anniversary of Mao Tse-tung’s death.”
The assignment’s parts may not appear in exactly this order, and each part may be very long or really short. Nonetheless, being aware of this standard pattern can help you understand what your instructor wants you to do.
Interpreting the assignment
Ask yourself a few basic questions as you read and jot down the answers on the assignment sheet:
Why did your instructor ask you to do this particular task?
Who is your audience.
- What kind of evidence do you need to support your ideas?
What kind of writing style is acceptable?
- What are the absolute rules of the paper?
Try to look at the question from the point of view of the instructor. Recognize that your instructor has a reason for giving you this assignment and for giving it to you at a particular point in the semester. In every assignment, the instructor has a challenge for you. This challenge could be anything from demonstrating an ability to think clearly to demonstrating an ability to use the library. See the assignment not as a vague suggestion of what to do but as an opportunity to show that you can handle the course material as directed. Paper assignments give you more than a topic to discuss—they ask you to do something with the topic. Keep reminding yourself of that. Be careful to avoid the other extreme as well: do not read more into the assignment than what is there.
Of course, your instructor has given you an assignment so that they will be able to assess your understanding of the course material and give you an appropriate grade. But there is more to it than that. Your instructor has tried to design a learning experience of some kind. Your instructor wants you to think about something in a particular way for a particular reason. If you read the course description at the beginning of your syllabus, review the assigned readings, and consider the assignment itself, you may begin to see the plan, purpose, or approach to the subject matter that your instructor has created for you. If you still aren’t sure of the assignment’s goals, try asking the instructor. For help with this, see our handout on getting feedback .
Given your instructor’s efforts, it helps to answer the question: What is my purpose in completing this assignment? Is it to gather research from a variety of outside sources and present a coherent picture? Is it to take material I have been learning in class and apply it to a new situation? Is it to prove a point one way or another? Key words from the assignment can help you figure this out. Look for key terms in the form of active verbs that tell you what to do.
Key Terms: Finding Those Active Verbs
Here are some common key words and definitions to help you think about assignment terms:
Information words Ask you to demonstrate what you know about the subject, such as who, what, when, where, how, and why.
- define —give the subject’s meaning (according to someone or something). Sometimes you have to give more than one view on the subject’s meaning
- describe —provide details about the subject by answering question words (such as who, what, when, where, how, and why); you might also give details related to the five senses (what you see, hear, feel, taste, and smell)
- explain —give reasons why or examples of how something happened
- illustrate —give descriptive examples of the subject and show how each is connected with the subject
- summarize —briefly list the important ideas you learned about the subject
- trace —outline how something has changed or developed from an earlier time to its current form
- research —gather material from outside sources about the subject, often with the implication or requirement that you will analyze what you have found
Relation words Ask you to demonstrate how things are connected.
- compare —show how two or more things are similar (and, sometimes, different)
- contrast —show how two or more things are dissimilar
- apply—use details that you’ve been given to demonstrate how an idea, theory, or concept works in a particular situation
- cause —show how one event or series of events made something else happen
- relate —show or describe the connections between things
Interpretation words Ask you to defend ideas of your own about the subject. Do not see these words as requesting opinion alone (unless the assignment specifically says so), but as requiring opinion that is supported by concrete evidence. Remember examples, principles, definitions, or concepts from class or research and use them in your interpretation.
- assess —summarize your opinion of the subject and measure it against something
- prove, justify —give reasons or examples to demonstrate how or why something is the truth
- evaluate, respond —state your opinion of the subject as good, bad, or some combination of the two, with examples and reasons
- support —give reasons or evidence for something you believe (be sure to state clearly what it is that you believe)
- synthesize —put two or more things together that have not been put together in class or in your readings before; do not just summarize one and then the other and say that they are similar or different—you must provide a reason for putting them together that runs all the way through the paper
- analyze —determine how individual parts create or relate to the whole, figure out how something works, what it might mean, or why it is important
- argue —take a side and defend it with evidence against the other side
More Clues to Your Purpose As you read the assignment, think about what the teacher does in class:
- What kinds of textbooks or coursepack did your instructor choose for the course—ones that provide background information, explain theories or perspectives, or argue a point of view?
- In lecture, does your instructor ask your opinion, try to prove their point of view, or use keywords that show up again in the assignment?
- What kinds of assignments are typical in this discipline? Social science classes often expect more research. Humanities classes thrive on interpretation and analysis.
- How do the assignments, readings, and lectures work together in the course? Instructors spend time designing courses, sometimes even arguing with their peers about the most effective course materials. Figuring out the overall design to the course will help you understand what each assignment is meant to achieve.
Now, what about your reader? Most undergraduates think of their audience as the instructor. True, your instructor is a good person to keep in mind as you write. But for the purposes of a good paper, think of your audience as someone like your roommate: smart enough to understand a clear, logical argument, but not someone who already knows exactly what is going on in your particular paper. Remember, even if the instructor knows everything there is to know about your paper topic, they still have to read your paper and assess your understanding. In other words, teach the material to your reader.
Aiming a paper at your audience happens in two ways: you make decisions about the tone and the level of information you want to convey.
- Tone means the “voice” of your paper. Should you be chatty, formal, or objective? Usually you will find some happy medium—you do not want to alienate your reader by sounding condescending or superior, but you do not want to, um, like, totally wig on the man, you know? Eschew ostentatious erudition: some students think the way to sound academic is to use big words. Be careful—you can sound ridiculous, especially if you use the wrong big words.
- The level of information you use depends on who you think your audience is. If you imagine your audience as your instructor and they already know everything you have to say, you may find yourself leaving out key information that can cause your argument to be unconvincing and illogical. But you do not have to explain every single word or issue. If you are telling your roommate what happened on your favorite science fiction TV show last night, you do not say, “First a dark-haired white man of average height, wearing a suit and carrying a flashlight, walked into the room. Then a purple alien with fifteen arms and at least three eyes turned around. Then the man smiled slightly. In the background, you could hear a clock ticking. The room was fairly dark and had at least two windows that I saw.” You also do not say, “This guy found some aliens. The end.” Find some balance of useful details that support your main point.
You’ll find a much more detailed discussion of these concepts in our handout on audience .
The Grim Truth
With a few exceptions (including some lab and ethnography reports), you are probably being asked to make an argument. You must convince your audience. It is easy to forget this aim when you are researching and writing; as you become involved in your subject matter, you may become enmeshed in the details and focus on learning or simply telling the information you have found. You need to do more than just repeat what you have read. Your writing should have a point, and you should be able to say it in a sentence. Sometimes instructors call this sentence a “thesis” or a “claim.”
So, if your instructor tells you to write about some aspect of oral hygiene, you do not want to just list: “First, you brush your teeth with a soft brush and some peanut butter. Then, you floss with unwaxed, bologna-flavored string. Finally, gargle with bourbon.” Instead, you could say, “Of all the oral cleaning methods, sandblasting removes the most plaque. Therefore it should be recommended by the American Dental Association.” Or, “From an aesthetic perspective, moldy teeth can be quite charming. However, their joys are short-lived.”
Convincing the reader of your argument is the goal of academic writing. It doesn’t have to say “argument” anywhere in the assignment for you to need one. Look at the assignment and think about what kind of argument you could make about it instead of just seeing it as a checklist of information you have to present. For help with understanding the role of argument in academic writing, see our handout on argument .
What kind of evidence do you need?
There are many kinds of evidence, and what type of evidence will work for your assignment can depend on several factors–the discipline, the parameters of the assignment, and your instructor’s preference. Should you use statistics? Historical examples? Do you need to conduct your own experiment? Can you rely on personal experience? See our handout on evidence for suggestions on how to use evidence appropriately.
Make sure you are clear about this part of the assignment, because your use of evidence will be crucial in writing a successful paper. You are not just learning how to argue; you are learning how to argue with specific types of materials and ideas. Ask your instructor what counts as acceptable evidence. You can also ask a librarian for help. No matter what kind of evidence you use, be sure to cite it correctly—see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial .
You cannot always tell from the assignment just what sort of writing style your instructor expects. The instructor may be really laid back in class but still expect you to sound formal in writing. Or the instructor may be fairly formal in class and ask you to write a reflection paper where you need to use “I” and speak from your own experience.
Try to avoid false associations of a particular field with a style (“art historians like wacky creativity,” or “political scientists are boring and just give facts”) and look instead to the types of readings you have been given in class. No one expects you to write like Plato—just use the readings as a guide for what is standard or preferable to your instructor. When in doubt, ask your instructor about the level of formality they expect.
No matter what field you are writing for or what facts you are including, if you do not write so that your reader can understand your main idea, you have wasted your time. So make clarity your main goal. For specific help with style, see our handout on style .
Technical details about the assignment
The technical information you are given in an assignment always seems like the easy part. This section can actually give you lots of little hints about approaching the task. Find out if elements such as page length and citation format (see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial ) are negotiable. Some professors do not have strong preferences as long as you are consistent and fully answer the assignment. Some professors are very specific and will deduct big points for deviations.
Usually, the page length tells you something important: The instructor thinks the size of the paper is appropriate to the assignment’s parameters. In plain English, your instructor is telling you how many pages it should take for you to answer the question as fully as you are expected to. So if an assignment is two pages long, you cannot pad your paper with examples or reword your main idea several times. Hit your one point early, defend it with the clearest example, and finish quickly. If an assignment is ten pages long, you can be more complex in your main points and examples—and if you can only produce five pages for that assignment, you need to see someone for help—as soon as possible.
Tricks that don’t work
Your instructors are not fooled when you:
- spend more time on the cover page than the essay —graphics, cool binders, and cute titles are no replacement for a well-written paper.
- use huge fonts, wide margins, or extra spacing to pad the page length —these tricks are immediately obvious to the eye. Most instructors use the same word processor you do. They know what’s possible. Such tactics are especially damning when the instructor has a stack of 60 papers to grade and yours is the only one that low-flying airplane pilots could read.
- use a paper from another class that covered “sort of similar” material . Again, the instructor has a particular task for you to fulfill in the assignment that usually relates to course material and lectures. Your other paper may not cover this material, and turning in the same paper for more than one course may constitute an Honor Code violation . Ask the instructor—it can’t hurt.
- get all wacky and “creative” before you answer the question . Showing that you are able to think beyond the boundaries of a simple assignment can be good, but you must do what the assignment calls for first. Again, check with your instructor. A humorous tone can be refreshing for someone grading a stack of papers, but it will not get you a good grade if you have not fulfilled the task.
Critical reading of assignments leads to skills in other types of reading and writing. If you get good at figuring out what the real goals of assignments are, you are going to be better at understanding the goals of all of your classes and fields of study.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift

Assignment vs. Project — What's the Difference?
Difference Between Assignment and Project
Table of contents, key differences, comparison chart, compare with definitions, common curiosities, can assignments be used to assess understanding or proficiency in a subject, do projects typically involve extensive research, planning, and execution, is an assignment a specific task or piece of work allocated to someone, is the scope of an assignment typically more focused and specific than that of a project, is a project a larger and more complex undertaking than an assignment, do projects often encourage collaborative efforts and integration of various skills, can a project require more time, resources, and effort compared to an assignment, is an assignment usually of shorter duration compared to a project, can projects involve multiple stages and components, can an assignment have clear and defined objectives, share your discovery.

Author Spotlight
Popular Comparisons

Trending Comparisons

New Comparisons

Trending Terms

- Organizations
- Planning & Activities
- Product & Services
- Structure & Systems
- Career & Education
- Entertainment
- Fashion & Beauty
- Political Institutions
- SmartPhones
- Protocols & Formats
- Communication
- Web Applications
- Household Equipments
- Career and Certifications
- Diet & Fitness
- Mathematics & Statistics
- Processed Foods
- Vegetables & Fruits
Difference Between Job and Work
• Categorized under Words | Difference Between Job and Work
Job vs Work
“Work” and “job” are two words that have similar yet different meanings. Although they are used interchangeably, their meanings may differ according to how they are used.
The use of the word “job” to describe a piece of work was first recorded in the 1550s. It comes from the Middle English word “gobben” which means “lump or mass.” It is a noun that is used to refer to work that an individual does for a living.
“Job” is defined as “an activity that an individual performs in exchange for a specific fee or payment.” It is also referred to as an occupation, profession, career, or trade. It is a responsibility of an individual towards his employer that he must perform well because he is paid for it. A job is a formal kind of work. When one is hired for a job, he has to get into a contract with his employer, and he has to abide by the regulations of the company. In a job, the goals and targets are more specific and well laid out for the employees to follow and achieve.
It refers to a specific type of employment wherein the individual’s role or position is clearly defined. It involves working on a specific task with the expectation of being compensated for the job done. The term “job” is also used in lieu of the word “work,” but work has separate connotations.
The word “work” is used as a noun as well as a verb. The noun work first appeared in the 1650s to refer to an industrial place. It comes from the Old English word “worc” or “weorc” which means “something done, action, or business.” “Work” is defined as “a physical or mental activity that is performed in order to accomplish or produce something.” It is something that an individual does in the performance of his job or of his responsibilities towards his employers or other people.
It has a broader meaning and can refer to all kinds of activities that an individual does. It can be something that one does in the performance of his responsibilities to his family such as cooking their food and cleaning the house. It can also be something that one does because he loves doing it like gardening or helping out in church. An individual does not always have to be paid for his work unlike a job in which he is paid for accomplishing.
1.A job is an activity that an individual performs in exchange for payment while work is an activity that an individual performs in order to produce or accomplish something. 2.Individuals perform their jobs in order to get monetary compensation while people work on something not only to earn but also as part of their responsibility towards others which does not involve any compensation. 3.“Work” is a general term that refers to all activities that one does while “job” is more specific. 4.The word “work” comes from the Old English word “weorc” or “worc” while the word “job” comes from the Middle English word “gobben.”
- Recent Posts
- Difference Between Mocha and Coffee - January 11, 2012
- Difference Between Verb and Predicate - January 2, 2012
- Difference Between Tropical Meteorology and Monsoon Meteorology - January 2, 2012
Sharing is caring!
- Pinterest 1

Read More ESL Articles
Search differencebetween.net :.
- Difference Between Your and You’re
- Difference Between Sleep and Asleep
- Difference Between Licence and License
- Difference Between Payed and Paid
- Difference Between Guaranty and Guarantee
Cite APA 7 M, E. (2018, April 24). Difference Between Job and Work. Difference Between Similar Terms and Objects. http://www.differencebetween.net/language/words-language/difference-between-job-and-work/. MLA 8 M, Emelda. "Difference Between Job and Work." Difference Between Similar Terms and Objects, 24 April, 2018, http://www.differencebetween.net/language/words-language/difference-between-job-and-work/.
10 Comments
that was a gud differences but were can i find more
Good explanation. Thank you.
Job : means work in the sense of job or employment, for example, David finally got a new job . job is an accounting term , which means you can say (a job , one job , two jobs ) .
Work : Work means when it refers to tasks that involves work or where you work , for example : I have a lot of work at this time. Countless work is a word , so you can not say ( to work , one work , two works ) .
Explaining a term by the term itself “erreur de débutant”
suppose someone is working in an organisation with no contract but is paid,is that a job or work?
Your job is what you were trained to do. Your work is what you were born to do. You can be fire from your job but never from your work. Your job is your career, your work is your life assignment. In other words, your job/skills prepares you for your work /gifts. Your work is more related to your purpose in life.
- Ade July 2, 2020 • 2:36 am Reply
OK, please ZB saying “work” is our purpose in life…does it mean same thing as our call or ministry?
So, can I then say that having the urge of helping small ministries, or granting financial help or showing empathy to people… Is my purpose in life? Kindly reply.
Exactly meaning of the world is being used for complete details of the trade.
Leave a Response
Name ( required )
Email ( required )
Please note: comment moderation is enabled and may delay your comment. There is no need to resubmit your comment.
Notify me of followup comments via e-mail
Written by : Emelda M. and updated on 2018, April 24 Articles on DifferenceBetween.net are general information, and are not intended to substitute for professional advice. The information is "AS IS", "WITH ALL FAULTS". User assumes all risk of use, damage, or injury. You agree that we have no liability for any damages.
Advertisments
More in 'words'.
- Difference Between Center and Centre
- Difference Between Lodge and Resort
- Difference Between Authoritarian and Fascism
- Difference Between Advocate and Barrister
- Difference Between Advocacy and Lobbying
Top Difference Betweens
Get new comparisons in your inbox:, most emailed comparisons, editor's picks.
- Difference Between MAC and IP Address
- Difference Between Platinum and White Gold
- Difference Between Civil and Criminal Law
- Difference Between GRE and GMAT
- Difference Between Immigrants and Refugees
- Difference Between DNS and DHCP
- Difference Between Computer Engineering and Computer Science
- Difference Between Men and Women
- Difference Between Book value and Market value
- Difference Between Red and White wine
- Difference Between Depreciation and Amortization
- Difference Between Bank and Credit Union
- Difference Between White Eggs and Brown Eggs
Job Description vs Job Posting: 3 Key Differences
Job description vs job posting — what’s the difference? Many people use these terms interchangeably. They’re similar, but not the same. Here’s why.
The Definition of a Job Description
A job description is a framework for a job post. It represents all of the responsibilities for a role. When an employee signs a “job description”, it’s a legal document that helps you measure productivity and performance.
The process of writing a JD is usually a collaboration between the hiring manager, recruiter, and compensation team.
Job Posting Definition
A job posting is what you find on job boards or company career sites. It’s a recruiting tool to attract potential candidates. A job post helps candidates answer the question, “Do I want to apply for this job?”.
A recruiter or someone from the Talent Acquisition team usually writes job postings.
The Difference Between “Job Description” and “Job Posting”
Now that we’ve defined both, let’s look at 3 key differences between a job posting vs job description.
1. Explaining Roles vs. Attracting Candidates
A Job description is usually an internal doc. It explains the tasks, duties, salary, and functions of a position. You can think of it as a job manual for you and your new employee. It tells your new hires what you expect of them and how the company will measure their job performance.
The primary purpose of job postings is to attract potential applicants. A job posting is usually found outside the company (unless it’s an internal job posting ). They’re an external recruiting tool. You’ll generally post them on job boards and career sites.
2. Creating a Legal Document vs. a Marketing Piece
A job description is a legal document filed away by HR once it’s signed by a hiring manager and an employee. It’s usually in the form of a Word doc or an Excel spreadsheet. It’s organized and focused more on outlining facts, roles, responsibilities, and expectations than anything else.
A job posting is more dynamic. Job postings have images, videos, employee testimonials, and more. Job postings are marketing pieces.
Here’s a side-by-side comparison of a job description vs job posting:
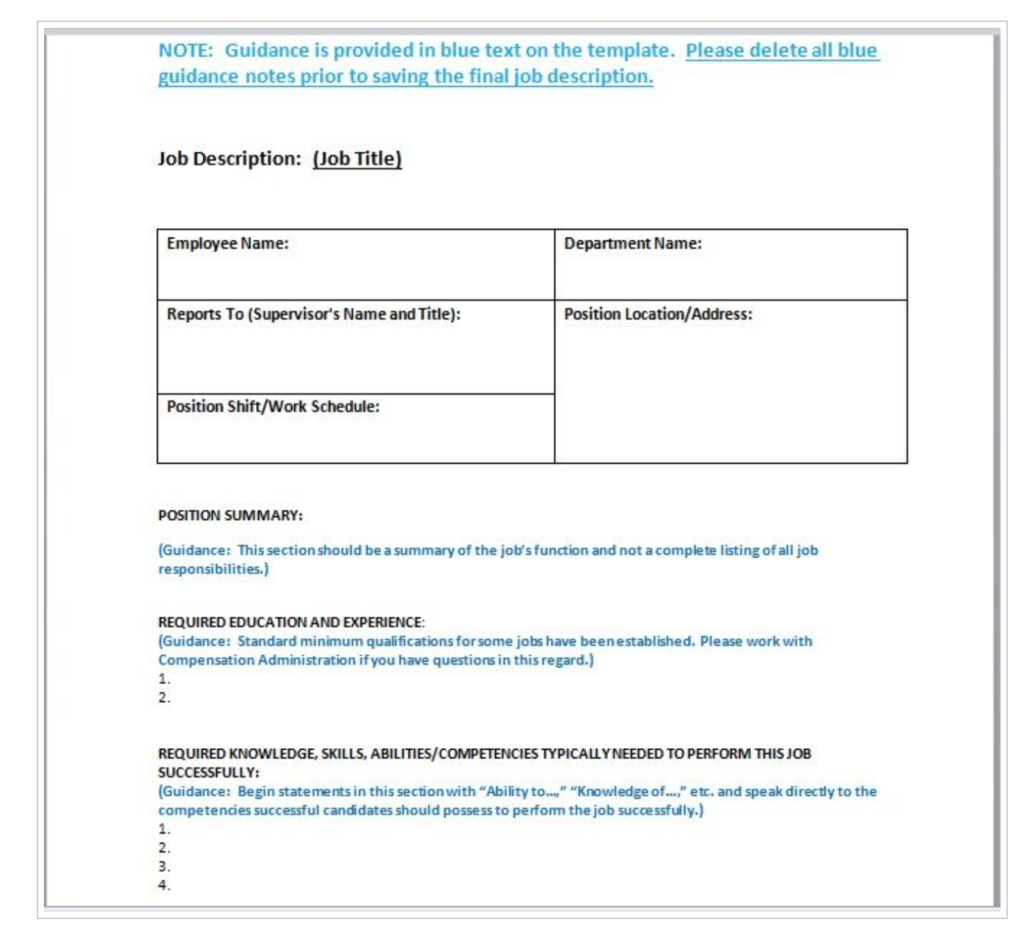
3. Using Company Jargon vs. Engaging Content
A job description is usually a long list of job requirements employees sign. They’re often hard to read. You typically use a formal tone and an academic (or legal) writing style for job descriptions. Sometimes JDs have company jargon or acronyms that might confuse candidates. So, to keep the playing field level, you want to avoid jargon and use engaging language to attract the right candidate.
One example is “KSAs” ( knowledge, skills, and abilities) :
Required KSAs:
- Three years of people and/or project management experience
- Prior people/project management experience
- Excellent written and verbal communication skills
- Ability to accomplish many complex tasks simultaneously
- Success implementing continuous improvement initiatives
KSAs are a common (and key) piece of job descriptions because this is how employee performance is measured. But, in a job posting, you might switch out “Required KSAs” with “Your Requirements”…to make it sound less like a legal document.
A job posting is engaging because it piques the attention of your target recruits (and sells your job opportunity). So, use words that get applicants excited to apply. Will they get to work with exciting people? What kind of fantastic benefits will they get? What salary will they make? Writing it in second person (“you”) helps too, because you speak directly to the candidate.
Job descriptions and job postings are very similar. But they are not the same. It’s ok to use the terms interchangeably, but make sure not to confuse the documents you’ll use in your hiring process.
Note: Here’s a blog by Ongig’s CEO, Rob Kelly, with even more info on job descriptions vs job posting s — What’s The Difference Between a Job Description, Job Posting and Job Ad?
Why I wrote this?
Ongig is on a mission to create effective and inclusive job descriptions (and job postings) so you can attract top talent. Please request a demo for a free JD analysis.
Shout-outs:
- Eight key Differences Between a Job Description and a Job Advert at Webrecruit (by Holly Watson )
- Job descriptions vs. job postings: What’s the difference? (by The Procom Staff )
- The Ideal Work Environment for Millennials (by Alba Garcia Garcia )
- What’s the Difference Between a Job Description, Posting, and Ad (by Katrina Kibben )
- What’s the Difference Between a Job Description and a Job Posting (by the University of Arkansas )
March 28, 2022 by Joanne Derecho in Job Descriptions
- AI Recruitment (1)
- Applicant Tracking System (16)
- Candidate Engagement (10)
- Candidate Experience (5)
- Company Career Site (42)
- Conferences (18)
- Diversity and Inclusion (246)
- Employee Branding (3)
- Employer Branding (42)
- Employer of Choice (4)
- Entrepreneurship (4)
- Hiring (27)
- HR Content (72)
- Job Boards (2)
- Job Description Management (7)
- Job Descriptions (162)
- Job Pages (3)
- Job Postings (9)
- Job Titles (44)
- Leadership (4)
- Microsites (6)
- Networking (5)
- Recruit Veterans (1)
- Recruiters (18)
- Recruiting Metrics (2)
- Recruiting Process (7)
- Recruiting Software (13)
- Recruiting Strategies (32)
- Recruiting Videos (12)
- Recruitment Marketing (10)
- Recruitment SEO (9)
- Social Recruiting (21)
- Talent Acquisition (9)
- Talent Airport (2)
- Technology (8)
- Trends (11)
- University Recruiting (3)
- Video Job Descriptions (9)
- Writing Job Descriptions (40)
template: single.php

What is the difference between Jobs and Assignments | WeNaturalists

Home » Education » What is the Difference Between Homework and Assignment
What is the Difference Between Homework and Assignment
The main difference between homework and assignment is that homework is a task or a work assigned to a student generally by a teacher to be completed outside the classroom setting, most probably at home, while an assignment is a task assigned to a student to be completed within the course of a particular study.
Assignments and homework vary from one another due to a wide range of distinctive elements such as the objective or the purpose of the task, main functions, and the benefits received.
Key Areas Covered
1. What is Homework – Definition, Features 2. What is Assignment – Definition, Features 3. Similarities Between Homework and Assignment – Outline of Common Characteristics 4. Difference Between Homework and Assignment – Comparison of Key Differences

What is Homework
Homework refers to the tasks assigned to the students by the schoolteachers. They expect students to carry out the task during non-school hours. Teachers often give homework to complete at home in order to make their students practice the learning material already taught. Their aim is to reinforce learning and facilitate the mastery of specific competencies and skills .
Sometimes, a student might get preparation assignments as homework. The purpose of such homework is to introduce the student to the study material that the teacher will present in future lessons. Furthermore, it would help students to obtain the maximum benefit once the new material is being taught in class.

On the other hand, homework sometimes facilitates the transfer of previously acquired skills to new situations. For example, the students might learn in class about factors that led to World war I. Then, as homework, the teacher would ask the students to find out the factors that led to World war II. Here, the teacher gives an integration homework, which requires the student to apply separately learned skills to create a single product, such as science projects, newspaper reports, or creative writing.
In addition, homework can be used to build up proper communication between parents and children, as a constructive method of punishment and also to make the parents aware of what is happening in school.
What is Assignment
If you are a student, you might think that it is not your responsibility to learn by yourself; rather, it is the job of the teacher to teach you. But, a teacher cannot teach every little thing in a particular unit or subject to the students.
Such a spoon-feeding method of imparting knowledge can negatively influence the learning capabilities and the academic career of a student. Especially in academic establishments such as colleges or universities, teachers expect the students do some research to grasp the untaught concepts and to explore the subject on their own instead of teaching everything to the students using a lecture method.

The actual purpose of giving assignments is to enhance the learning skills of the students. This enables the students to occupy their brains more and more. Academic assignments improve the creativity of the students as they naturally acquire and learn a lot when they read or practice a subject or art on their own. Therefore, the main reason for giving assignments is to provide the student with a platform to practice and explore knowledge about a subject on their own.
Similarities Between Homework and Assignment
- Both aim at enhancing the learning skills of the students.
- Teachers or professors assign them to the students.
- It is possible to grade both homework and assignments.
Difference Between Homework and Assignment
Homework is a work or a task assigned to a student by a teacher to be completed during a non-school hour, whereas an assignment is a task assigned to a student in the course of study. In contrast to homework, an assignment usually provides the student with a clue about the objectives of the assigned task.
The main purpose of an assignment is to help a student understand the studying process well. In contrast, homework basically helps the student to improve his/her skills.
Main Function
An assignment can be used to figure out what should be taught, while homework is basically used to identify the challenges encountered by students on a particular topic.
Some advantages of assignments include supporting students to revise a particular topic and boosting the students’ confidence, whereas homework becomes helpful in understanding a specific topic and when preparing for an exam.
In brief, the main difference between homework and assignment is that homework is assigned to be completed outside the classroom while assignments are assigned to be completed within the course of a particular study. Nonetheless, no matter how beneficial they can be, for most students, homework and assignments are a massive source of unhappiness and irritation.
1. Levy, Sandra. “ Why Homework Is Bad: Stress and Consequences .” Healthline , Healthline Media.
Image Courtesy:
About the Author: Anuradha
Anuradha has a BA degree in English, French, and Translation studies. She is currently reading for a Master's degree in Teaching English Literature in a Second Language Context. Her areas of interests include Arts and Literature, Language and Education, Nature and Animals, Cultures and Civilizations, Food, and Fashion.
You May Also Like These
Leave a reply cancel reply.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Jobs can be full-time or part-time and are often linked to a career or profession. Whereas an assignment generally refers to a specific task or project assigned to someone, often as part of their educational or professional responsibilities. Assignments are usually finite and have a clear end point. 12. In terms of duration and scope, a job is ...
1. Additionally, at school an assignment is a specific task for a student to do in class time or as homework, and the word also refers to the document which is produced during the assignment and handed in for correction. On the other hand a job is a task unrelated to the students studies, for example rubbish bin duty. - Peter.
The act of assigning; the allocation of a job or a set of tasks. This flow chart represents the assignment of tasks in our committee. The categorization of something as belonging to a specific category. We should not condone the assignment of asylum seekers to that of people smugglers. An assigned task.
Assignments are commonly used in the context of intellectual property, where authors or inventors assign their rights to a publisher or company. Unlike assignation, assignment does not necessarily imply a formal agreement or a legally binding transfer. Instead, it focuses on the act of transferring ownership or responsibility. 2. Academic Context:
Noun. ( en noun ) The act of assigning; the allocation of a job or a set of tasks. This flow chart represents the assignment of tasks in our committee. The categorization of something as belonging to a specific category. We should not condone the assignment of asylum seekers to that of people smugglers. An assigned task.
Avoid using "assignment" as a synonym for "task" or "job," as it can make the sentence unclear and confusing. More Examples Of Task & Assignment Used In Sentences. In order to better understand the differences between tasks and assignments, it can be helpful to see them used in various contexts.
A task is something you have to do. An assignment is usually a task that someone gives you to do. Ways to use 'task'. A task describes an activity that can be done in your daily life. But you ...
Now that we've established the difference between assignment and placement, let's dive deeper into the nuances of each concept. Define Assignment. An assignment refers to a temporary job or task given to an individual by an employer or a company. It is a specific project or duty that an employee is assigned to work on for a predetermined ...
Task, project, assignment, job. Which one is correct in my case? These words don't have exact matches in Portuguese, so sometimes I get confused about their usage. When is it more suitable to use task rather than assigment and vice versa?
We use the word assignment when talking about individual jobs in a specific place. The two words can overlap when a person's assignment (individual job) is helping carry out the mission or ...
homework. ? 1 `assignment'. An assignment is a task that someone is given to do, usually as part of their job. My first major assignment as a reporter was to cover a large-scale riot. An assignment is also a piece of academic work given to students. The course has some heavy reading assignments.
As nouns the difference between assignment and assignation. is that assignment is the act of assigning; the allocation of a job or a set of tasks while assignation is an appointment for a meeting, generally of a romantic or sexual nature.
3. Outline Main Points, Only Tease the Details. More often than not, the primary reason companies dole out homework is to get a better sense of your thought process, as well as how you structure and convey your thoughts and ideas. There's not necessarily a "right" answer, nor is there a need to get way down in the weeds.
What's the difference between assignment and job? Assignment. Definition: (n.) An allotting or an appointment to a particular person or use; or for a particular time, as of a cause or causes in court. (n.) A transfer of title or interest by writing, as of lease, bond, note, or bill of exchange; a transfer of the whole of some particular estate ...
The assignment's parts may not appear in exactly this order, and each part may be very long or really short. Nonetheless, being aware of this standard pattern can help you understand what your instructor wants you to do. Interpreting the assignment. Ask yourself a few basic questions as you read and jot down the answers on the assignment sheet:
An assignment is a task or piece of work allocated to someone as part of a job or course of study, whereas a project is a planned undertaking, typically involving research or design, that is carefully planned to achieve a particular aim. ... Key Differences. Assignment and project, while semantically related, delineate different scopes and ...
An assignment is a specific task given to a student to complete, usually with a specific deadline. It is often graded and contributes to the student's overall grade in the course. On the other hand, an activity is a more general term that refers to any task or exercise given to students, whether it is graded or not.
3."Work" is a general term that refers to all activities that one does while "job" is more specific. 4.The word "work" comes from the Old English word "weorc" or "worc" while the word "job" comes from the Middle English word "gobben.". Author. Recent Posts.
Assign is a derived term of assignment. As nouns the difference between assignment and assign is that assignment is the act of assigning; the allocation of a job or a set of tasks while assign is an assignee. As a verb assign is to designate or set apart something for some purpose.
The Difference Between "Job Description" and "Job Posting". Now that we've defined both, let's look at 3 key differences between a job posting vs job description. 1. Explaining Roles vs. Attracting Candidates. A Job description is usually an internal doc. It explains the tasks, duties, salary, and functions of a position.
A Job is a full-time or a part-time employment position offered by a WeNaturalists member, whereas an 'Assignment' is usually an opportunity that contractually ...
An assignment is a task or piece of work that is assigned to someone, typically by a teacher or supervisor. It is usually a smaller task, and often has a specific deadline. A project, on the other hand, is a larger task that involves multiple steps and often requires collaboration with others.
The main difference between homework and assignment is that homework is a task or a work assigned to a student generally by a teacher to be completed outside the classroom setting, most probably at home, while an assignment is a task assigned to a student to be completed within the course of a particular study.. Assignments and homework vary from one another due to a wide range of distinctive ...