
English Current

ESL Lesson Plans, Tests, & Ideas
- North American Idioms
- Business Idioms
- Idioms Quiz
- Idiom Requests
- Proverbs Quiz & List
- Phrasal Verbs Quiz
- Basic Phrasal Verbs
- North American Idioms App
- A(n)/The: Help Understanding Articles
- The First & Second Conditional
- The Difference between 'So' & 'Too'
- The Difference between 'a few/few/a little/little'
- The Difference between "Other" & "Another"
- Check Your Level
- English Vocabulary
- Verb Tenses (Intermediate)
- Articles (A, An, The) Exercises
- Prepositions Exercises
- Irregular Verb Exercises
- Gerunds & Infinitives Exercises
- Discussion Questions
- Speech Topics
- Argumentative Essay Topics
- Top-rated Lessons
- Intermediate
- Upper-Intermediate
- Reading Lessons
- View Topic List
- Expressions for Everyday Situations
- Travel Agency Activity
- Present Progressive with Mr. Bean
- Work-related Idioms
- Adjectives to Describe Employees
- Writing for Tone, Tact, and Diplomacy
- Speaking Tactfully
- Advice on Monetizing an ESL Website
- Teaching your First Conversation Class
- How to Teach English Conversation
- Teaching Different Levels
- Teaching Grammar in Conversation Class
- Members' Home
- Update Billing Info.
- Cancel Subscription
- North American Proverbs Quiz & List
- North American Idioms Quiz
- Idioms App (Android)
- 'Be used to'" / 'Use to' / 'Get used to'
- Ergative Verbs and the Passive Voice
- Keywords & Verb Tense Exercises
- Irregular Verb List & Exercises
- Non-Progressive (State) Verbs
- Present Perfect vs. Past Simple
- Present Simple vs. Present Progressive
- Past Perfect vs. Past Simple
- Subject Verb Agreement
- The Passive Voice
- Subject & Object Relative Pronouns
- Relative Pronouns Where/When/Whose
- Commas in Adjective Clauses
- A/An and Word Sounds
- 'The' with Names of Places
- Understanding English Articles
- Article Exercises (All Levels)
- Yes/No Questions
- Wh-Questions
- How far vs. How long
- Affect vs. Effect
- A few vs. few / a little vs. little
- Boring vs. Bored
- Compliment vs. Complement
- Die vs. Dead vs. Death
- Expect vs. Suspect
- Experiences vs. Experience
- Go home vs. Go to home
- Had better vs. have to/must
- Have to vs. Have got to
- I.e. vs. E.g.
- In accordance with vs. According to
- Lay vs. Lie
- Make vs. Do
- In the meantime vs. Meanwhile
- Need vs. Require
- Notice vs. Note
- 'Other' vs 'Another'
- Pain vs. Painful vs. In Pain
- Raise vs. Rise
- So vs. Such
- So vs. So that
- Some vs. Some of / Most vs. Most of
- Sometimes vs. Sometime
- Too vs. Either vs. Neither
- Weary vs. Wary
- Who vs. Whom
- While vs. During
- While vs. When
- Wish vs. Hope
- 10 Common Writing Mistakes
- 34 Common English Mistakes
- First & Second Conditionals
- Comparative & Superlative Adjectives
- Determiners: This/That/These/Those
- Check Your English Level
- Grammar Quiz (Advanced)
- Vocabulary Test - Multiple Questions
- Vocabulary Quiz - Choose the Word
- Verb Tense Review (Intermediate)
- Verb Tense Exercises (All Levels)
- Conjunction Exercises
- List of Topics
- Business English
- Games for the ESL Classroom
- Pronunciation
- Teaching Your First Conversation Class
- How to Teach English Conversation Class
Argumentative Essays: The Counter-Argument & Refutation
An argumentative essay presents an argument for or against a topic. For example, if your topic is working from home , then your essay would either argue in favor of working from home (this is the for side) or against working from home.
Like most essays, an argumentative essay begins with an introduction that ends with the writer's position (or stance) in the thesis statement .
Introduction Paragraph
(Background information....)
- Thesis statement : Employers should give their workers the option to work from home in order to improve employee well-being and reduce office costs.
This thesis statement shows that the two points I plan to explain in my body paragraphs are 1) working from home improves well-being, and 2) it allows companies to reduce costs. Each topic will have its own paragraph. Here's an example of a very basic essay outline with these ideas:
- Background information
Body Paragraph 1
- Topic Sentence : Workers who work from home have improved well-being .
- Evidence from academic sources
Body Paragraph 2
- Topic Sentence : Furthermore, companies can reduce their expenses by allowing employees to work at home .
- Summary of key points
- Restatement of thesis statement
Does this look like a strong essay? Not really . There are no academic sources (research) used, and also...
You Need to Also Respond to the Counter-Arguments!
The above essay outline is very basic. The argument it presents can be made much stronger if you consider the counter-argument , and then try to respond (refute) its points.
The counter-argument presents the main points on the other side of the debate. Because we are arguing FOR working from home, this means the counter-argument is AGAINST working from home. The best way to find the counter-argument is by reading research on the topic to learn about the other side of the debate. The counter-argument for this topic might include these points:
- Distractions at home > could make it hard to concentrate
- Dishonest/lazy people > might work less because no one is watching
Next, we have to try to respond to the counter-argument in the refutation (or rebuttal/response) paragraph .
The Refutation/Response Paragraph
The purpose of this paragraph is to address the points of the counter-argument and to explain why they are false, somewhat false, or unimportant. So how can we respond to the above counter-argument? With research !
A study by Bloom (2013) followed workers at a call center in China who tried working from home for nine months. Its key results were as follows:
- The performance of people who worked from home increased by 13%
- These workers took fewer breaks and sick-days
- They also worked more minutes per shift
In other words, this study shows that the counter-argument might be false. (Note: To have an even stronger essay, present data from more than one study.) Now we have a refutation.
Where Do We Put the Counter-Argument and Refutation?
Commonly, these sections can go at the beginning of the essay (after the introduction), or at the end of the essay (before the conclusion). Let's put it at the beginning. Now our essay looks like this:
Counter-argument Paragraph
- Dishonest/lazy people might work less because no one is watching
Refutation/Response Paragraph
- Study: Productivity increased by 14%
- (+ other details)
Body Paragraph 3
- Topic Sentence : In addition, people who work from home have improved well-being .
Body Paragraph 4
The outline is stronger now because it includes the counter-argument and refutation. Note that the essay still needs more details and research to become more convincing.

Working from home may increase productivity.
Extra Advice on Argumentative Essays
It's not a compare and contrast essay.
An argumentative essay focuses on one topic (e.g. cats) and argues for or against it. An argumentative essay should not have two topics (e.g. cats vs dogs). When you compare two ideas, you are writing a compare and contrast essay. An argumentative essay has one topic (cats). If you are FOR cats as pets, a simplistic outline for an argumentative essay could look something like this:
- Thesis: Cats are the best pet.
- are unloving
- cause allergy issues
- This is a benefit > Many working people do not have time for a needy pet
- If you have an allergy, do not buy a cat.
- But for most people (without allergies), cats are great
- Supporting Details
Use Language in Counter-Argument That Shows Its Not Your Position
The counter-argument is not your position. To make this clear, use language such as this in your counter-argument:
- Opponents might argue that cats are unloving.
- People who dislike cats would argue that cats are unloving.
- Critics of cats could argue that cats are unloving.
- It could be argued that cats are unloving.
These underlined phrases make it clear that you are presenting someone else's argument , not your own.
Choose the Side with the Strongest Support
Do not choose your side based on your own personal opinion. Instead, do some research and learn the truth about the topic. After you have read the arguments for and against, choose the side with the strongest support as your position.
Do Not Include Too Many Counter-arguments
Include the main (two or three) points in the counter-argument. If you include too many points, refuting these points becomes quite difficult.
If you have any questions, leave a comment below.
- Matthew Barton / Creator of Englishcurrent.com
Additional Resources :
- Writing a Counter-Argument & Refutation (Richland College)
- Language for Counter-Argument and Refutation Paragraphs (Brown's Student Learning Tools)
EnglishCurrent is happily hosted on Dreamhost . If you found this page helpful, consider a donation to our hosting bill to show your support!
23 comments on “ Argumentative Essays: The Counter-Argument & Refutation ”
Thank you professor. It is really helpful.
Can you also put the counter argument in the third paragraph
It depends on what your instructor wants. Generally, a good argumentative essay needs to have a counter-argument and refutation somewhere. Most teachers will probably let you put them anywhere (e.g. in the start, middle, or end) and be happy as long as they are present. But ask your teacher to be sure.
Thank you for the information Professor
how could I address a counter argument for “plastic bags and its consumption should be banned”?
For what reasons do they say they should be banned? You need to address the reasons themselves and show that these reasons are invalid/weak.
Thank you for this useful article. I understand very well.
Thank you for the useful article, this helps me a lot!
Thank you for this useful article which helps me in my study.
Thank you, professor Mylene 102-04
it was very useful for writing essay
Very useful reference body support to began writing a good essay. Thank you!
Really very helpful. Thanks Regards Mayank
Thank you, professor, it is very helpful to write an essay.
It is really helpful thank you
It was a very helpful set of learning materials. I will follow it and use it in my essay writing. Thank you, professor. Regards Isha
Thanks Professor
This was really helpful as it lays the difference between argumentative essay and compare and contrast essay.. Thanks for the clarification.
This is such a helpful guide in composing an argumentative essay. Thank you, professor.
This was really helpful proof, thankyou!
Thanks this was really helpful to me
This was very helpful for us to generate a good form of essay
thank you so much for this useful information.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

8 Effective Strategies to Write Argumentative Essays
In a bustling university town, there lived a student named Alex. Popular for creativity and wit, one challenge seemed insurmountable for Alex– the dreaded argumentative essay!
One gloomy afternoon, as the rain tapped against the window pane, Alex sat at his cluttered desk, staring at a blank document on the computer screen. The assignment loomed large: a 350-600-word argumentative essay on a topic of their choice . With a sigh, he decided to seek help of mentor, Professor Mitchell, who was known for his passion for writing.
Entering Professor Mitchell’s office was like stepping into a treasure of knowledge. Bookshelves lined every wall, faint aroma of old manuscripts in the air and sticky notes over the wall. Alex took a deep breath and knocked on his door.
“Ah, Alex,” Professor Mitchell greeted with a warm smile. “What brings you here today?”
Alex confessed his struggles with the argumentative essay. After hearing his concerns, Professor Mitchell said, “Ah, the argumentative essay! Don’t worry, Let’s take a look at it together.” As he guided Alex to the corner shelf, Alex asked,
Table of Contents
“What is an Argumentative Essay?”
The professor replied, “An argumentative essay is a type of academic writing that presents a clear argument or a firm position on a contentious issue. Unlike other forms of essays, such as descriptive or narrative essays, these essays require you to take a stance, present evidence, and convince your audience of the validity of your viewpoint with supporting evidence. A well-crafted argumentative essay relies on concrete facts and supporting evidence rather than merely expressing the author’s personal opinions . Furthermore, these essays demand comprehensive research on the chosen topic and typically follows a structured format consisting of three primary sections: an introductory paragraph, three body paragraphs, and a concluding paragraph.”
He continued, “Argumentative essays are written in a wide range of subject areas, reflecting their applicability across disciplines. They are written in different subject areas like literature and philosophy, history, science and technology, political science, psychology, economics and so on.
Alex asked,
“When is an Argumentative Essay Written?”
The professor answered, “Argumentative essays are often assigned in academic settings, but they can also be written for various other purposes, such as editorials, opinion pieces, or blog posts. Some situations to write argumentative essays include:
1. Academic assignments
In school or college, teachers may assign argumentative essays as part of coursework. It help students to develop critical thinking and persuasive writing skills .
2. Debates and discussions
Argumentative essays can serve as the basis for debates or discussions in academic or competitive settings. Moreover, they provide a structured way to present and defend your viewpoint.
3. Opinion pieces
Newspapers, magazines, and online publications often feature opinion pieces that present an argument on a current issue or topic to influence public opinion.
4. Policy proposals
In government and policy-related fields, argumentative essays are used to propose and defend specific policy changes or solutions to societal problems.
5. Persuasive speeches
Before delivering a persuasive speech, it’s common to prepare an argumentative essay as a foundation for your presentation.
Regardless of the context, an argumentative essay should present a clear thesis statement , provide evidence and reasoning to support your position, address counterarguments, and conclude with a compelling summary of your main points. The goal is to persuade readers or listeners to accept your viewpoint or at least consider it seriously.”
Handing over a book, the professor continued, “Take a look on the elements or structure of an argumentative essay.”
Elements of an Argumentative Essay
An argumentative essay comprises five essential components:
Claim in argumentative writing is the central argument or viewpoint that the writer aims to establish and defend throughout the essay. A claim must assert your position on an issue and must be arguable. It can guide the entire argument.
2. Evidence
Evidence must consist of factual information, data, examples, or expert opinions that support the claim. Also, it lends credibility by strengthening the writer’s position.
3. Counterarguments
Presenting a counterclaim demonstrates fairness and awareness of alternative perspectives.
4. Rebuttal
After presenting the counterclaim, the writer refutes it by offering counterarguments or providing evidence that weakens the opposing viewpoint. It shows that the writer has considered multiple perspectives and is prepared to defend their position.
The format of an argumentative essay typically follows the structure to ensure clarity and effectiveness in presenting an argument.
How to Write An Argumentative Essay
Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to write an argumentative essay:
1. Introduction
- Begin with a compelling sentence or question to grab the reader’s attention.
- Provide context for the issue, including relevant facts, statistics, or historical background.
- Provide a concise thesis statement to present your position on the topic.
2. Body Paragraphs (usually three or more)
- Start each paragraph with a clear and focused topic sentence that relates to your thesis statement.
- Furthermore, provide evidence and explain the facts, statistics, examples, expert opinions, and quotations from credible sources that supports your thesis.
- Use transition sentences to smoothly move from one point to the next.
3. Counterargument and Rebuttal
- Acknowledge opposing viewpoints or potential objections to your argument.
- Also, address these counterarguments with evidence and explain why they do not weaken your position.
4. Conclusion
- Restate your thesis statement and summarize the key points you’ve made in the body of the essay.
- Leave the reader with a final thought, call to action, or broader implication related to the topic.
5. Citations and References
- Properly cite all the sources you use in your essay using a consistent citation style.
- Also, include a bibliography or works cited at the end of your essay.
6. Formatting and Style
- Follow any specific formatting guidelines provided by your instructor or institution.
- Use a professional and academic tone in your writing and edit your essay to avoid content, spelling and grammar mistakes .
Remember that the specific requirements for formatting an argumentative essay may vary depending on your instructor’s guidelines or the citation style you’re using (e.g., APA, MLA, Chicago). Always check the assignment instructions or style guide for any additional requirements or variations in formatting.
Did you understand what Prof. Mitchell explained Alex? Check it now!
Fill the Details to Check Your Score

Prof. Mitchell continued, “An argumentative essay can adopt various approaches when dealing with opposing perspectives. It may offer a balanced presentation of both sides, providing equal weight to each, or it may advocate more strongly for one side while still acknowledging the existence of opposing views.” As Alex listened carefully to the Professor’s thoughts, his eyes fell on a page with examples of argumentative essay.
Example of an Argumentative Essay
Alex picked the book and read the example. It helped him to understand the concept. Furthermore, he could now connect better to the elements and steps of the essay which Prof. Mitchell had mentioned earlier. Aren’t you keen to know how an argumentative essay should be like? Here is an example of a well-crafted argumentative essay , which was read by Alex. After Alex finished reading the example, the professor turned the page and continued, “Check this page to know the importance of writing an argumentative essay in developing skills of an individual.”
Importance of an Argumentative Essay
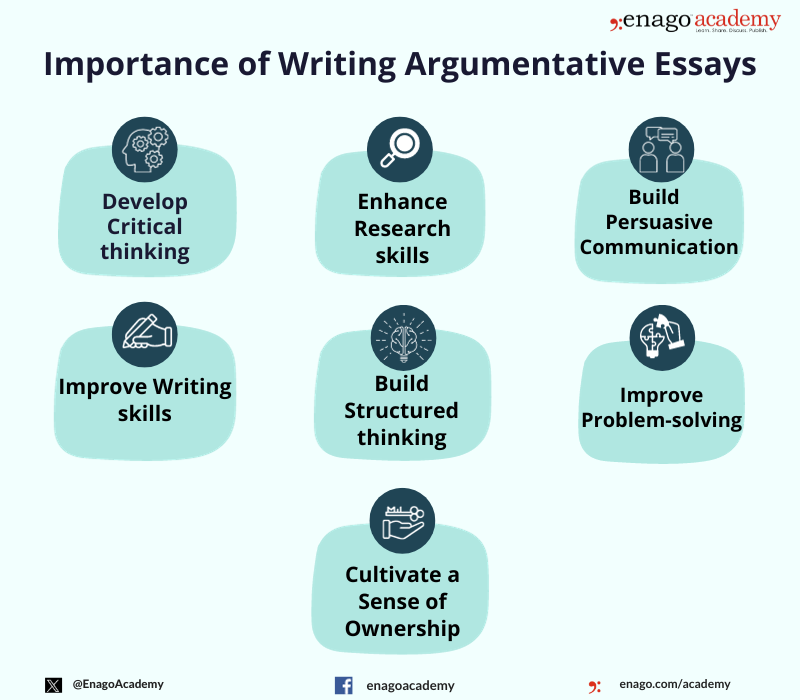
After understanding the benefits, Alex was convinced by the ability of the argumentative essays in advocating one’s beliefs and favor the author’s position. Alex asked,
“How are argumentative essays different from the other types?”
Prof. Mitchell answered, “Argumentative essays differ from other types of essays primarily in their purpose, structure, and approach in presenting information. Unlike expository essays, argumentative essays persuade the reader to adopt a particular point of view or take a specific action on a controversial issue. Furthermore, they differ from descriptive essays by not focusing vividly on describing a topic. Also, they are less engaging through storytelling as compared to the narrative essays.
Alex said, “Given the direct and persuasive nature of argumentative essays, can you suggest some strategies to write an effective argumentative essay?
Turning the pages of the book, Prof. Mitchell replied, “Sure! You can check this infographic to get some tips for writing an argumentative essay.”
Effective Strategies to Write an Argumentative Essay

As days turned into weeks, Alex diligently worked on his essay. He researched, gathered evidence, and refined his thesis. It was a long and challenging journey, filled with countless drafts and revisions.
Finally, the day arrived when Alex submitted their essay. As he clicked the “Submit” button, a sense of accomplishment washed over him. He realized that the argumentative essay, while challenging, had improved his critical thinking and transformed him into a more confident writer. Furthermore, Alex received feedback from his professor, a mix of praise and constructive criticism. It was a humbling experience, a reminder that every journey has its obstacles and opportunities for growth.
Frequently Asked Questions
An argumentative essay can be written as follows- 1. Choose a Topic 2. Research and Collect Evidences 3. Develop a Clear Thesis Statement 4. Outline Your Essay- Introduction, Body Paragraphs and Conclusion 5. Revise and Edit 6. Format and Cite Sources 7. Final Review
One must choose a clear, concise and specific statement as a claim. It must be debatable and establish your position. Avoid using ambiguous or unclear while making a claim. To strengthen your claim, address potential counterarguments or opposing viewpoints. Additionally, use persuasive language and rhetoric to make your claim more compelling
Starting an argument essay effectively is crucial to engage your readers and establish the context for your argument. Here’s how you can start an argument essay are: 1. Begin With an Engaging Hook 2. Provide Background Information 3. Present Your Thesis Statement 4. Briefly Outline Your Main 5. Establish Your Credibility
The key features of an argumentative essay are: 1. Clear and Specific Thesis Statement 2. Credible Evidence 3. Counterarguments 4. Structured Body Paragraph 5. Logical Flow 6. Use of Persuasive Techniques 7. Formal Language
An argumentative essay typically consists of the following main parts or sections: 1. Introduction 2. Body Paragraphs 3. Counterargument and Rebuttal 4. Conclusion 5. References (if applicable)
The main purpose of an argumentative essay is to persuade the reader to accept or agree with a particular viewpoint or position on a controversial or debatable topic. In other words, the primary goal of an argumentative essay is to convince the audience that the author's argument or thesis statement is valid, logical, and well-supported by evidence and reasoning.
Great article! The topic is simplified well! Keep up the good work
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles
![argumentative essay for and against What is Academic Integrity and How to Uphold it [FREE CHECKLIST]](https://www.enago.com/academy/wp-content/uploads/2024/05/FeatureImages-59-210x136.png)
Ensuring Academic Integrity and Transparency in Academic Research: A comprehensive checklist for researchers
Academic integrity is the foundation upon which the credibility and value of scientific findings are…

- AI in Academia
AI vs. AI: How to detect image manipulation and avoid academic misconduct
The scientific community is facing a new frontier of controversy as artificial intelligence (AI) is…

- Industry News
- Publishing News
Unified AI Guidelines Crucial as Academic Writing Embraces Generative Tools
As generative artificial intelligence (AI) tools like ChatGPT are advancing at an accelerating pace, their…

- Diversity and Inclusion
Need for Diversifying Academic Curricula: Embracing missing voices and marginalized perspectives
In classrooms worldwide, a single narrative often dominates, leaving many students feeling lost. These stories,…

- Reporting Research
How to Effectively Cite a PDF (APA, MLA, AMA, and Chicago Style)
The pressure to “publish or perish” is a well-known reality for academics, striking fear into…
How to Optimize Your Research Process: A step-by-step guide
How to Improve Lab Report Writing: Best practices to follow with and without…
Digital Citations: A comprehensive guide to citing of websites in APA, MLA, and CMOS…

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

As a researcher, what do you consider most when choosing an image manipulation detector?
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
How to Write an Argumentative Essay

4-minute read
- 30th April 2022
An argumentative essay is a structured, compelling piece of writing where an author clearly defines their stance on a specific topic. This is a very popular style of writing assigned to students at schools, colleges, and universities. Learn the steps to researching, structuring, and writing an effective argumentative essay below.
Requirements of an Argumentative Essay
To effectively achieve its purpose, an argumentative essay must contain:
● A concise thesis statement that introduces readers to the central argument of the essay
● A clear, logical, argument that engages readers
● Ample research and evidence that supports your argument
Approaches to Use in Your Argumentative Essay
1. classical.
● Clearly present the central argument.
● Outline your opinion.
● Provide enough evidence to support your theory.
2. Toulmin
● State your claim.
● Supply the evidence for your stance.
● Explain how these findings support the argument.
● Include and discuss any limitations of your belief.
3. Rogerian
● Explain the opposing stance of your argument.
● Discuss the problems with adopting this viewpoint.
● Offer your position on the matter.
● Provide reasons for why yours is the more beneficial stance.
● Include a potential compromise for the topic at hand.
Tips for Writing a Well-Written Argumentative Essay
● Introduce your topic in a bold, direct, and engaging manner to captivate your readers and encourage them to keep reading.
● Provide sufficient evidence to justify your argument and convince readers to adopt this point of view.
● Consider, include, and fairly present all sides of the topic.
● Structure your argument in a clear, logical manner that helps your readers to understand your thought process.
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
● Discuss any counterarguments that might be posed.
● Use persuasive writing that’s appropriate for your target audience and motivates them to agree with you.
Steps to Write an Argumentative Essay
Follow these basic steps to write a powerful and meaningful argumentative essay :
Step 1: Choose a topic that you’re passionate about
If you’ve already been given a topic to write about, pick a stance that resonates deeply with you. This will shine through in your writing, make the research process easier, and positively influence the outcome of your argument.
Step 2: Conduct ample research to prove the validity of your argument
To write an emotive argumentative essay , finding enough research to support your theory is a must. You’ll need solid evidence to convince readers to agree with your take on the matter. You’ll also need to logically organize the research so that it naturally convinces readers of your viewpoint and leaves no room for questioning.
Step 3: Follow a simple, easy-to-follow structure and compile your essay
A good structure to ensure a well-written and effective argumentative essay includes:
Introduction
● Introduce your topic.
● Offer background information on the claim.
● Discuss the evidence you’ll present to support your argument.
● State your thesis statement, a one-to-two sentence summary of your claim.
● This is the section where you’ll develop and expand on your argument.
● It should be split into three or four coherent paragraphs, with each one presenting its own idea.
● Start each paragraph with a topic sentence that indicates why readers should adopt your belief or stance.
● Include your research, statistics, citations, and other supporting evidence.
● Discuss opposing viewpoints and why they’re invalid.
● This part typically consists of one paragraph.
● Summarize your research and the findings that were presented.
● Emphasize your initial thesis statement.
● Persuade readers to agree with your stance.
We certainly hope that you feel inspired to use these tips when writing your next argumentative essay . And, if you’re currently elbow-deep in writing one, consider submitting a free sample to us once it’s completed. Our expert team of editors can help ensure that it’s concise, error-free, and effective!
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
9-minute read
How to Use Infographics to Boost Your Presentation
Is your content getting noticed? Capturing and maintaining an audience’s attention is a challenge when...
8-minute read
Why Interactive PDFs Are Better for Engagement
Are you looking to enhance engagement and captivate your audience through your professional documents? Interactive...
7-minute read
Seven Key Strategies for Voice Search Optimization
Voice search optimization is rapidly shaping the digital landscape, requiring content professionals to adapt their...
Five Creative Ways to Showcase Your Digital Portfolio
Are you a creative freelancer looking to make a lasting impression on potential clients or...
How to Ace Slack Messaging for Contractors and Freelancers
Effective professional communication is an important skill for contractors and freelancers navigating remote work environments....
3-minute read
How to Insert a Text Box in a Google Doc
Google Docs is a powerful collaborative tool, and mastering its features can significantly enhance your...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.
Argumentative Essay Examples to Inspire You (+ Free Formula)
.webp)
Table of contents

Meredith Sell
Have you ever been asked to explain your opinion on a controversial issue?
- Maybe your family got into a discussion about chemical pesticides
- Someone at work argues against investing resources into your project
- Your partner thinks intermittent fasting is the best way to lose weight and you disagree
Proving your point in an argumentative essay can be challenging, unless you are using a proven formula.
Argumentative essay formula & example
In the image below, you can see a recommended structure for argumentative essays. It starts with the topic sentence, which establishes the main idea of the essay. Next, this hypothesis is developed in the development stage. Then, the rebuttal, or the refutal of the main counter argument or arguments. Then, again, development of the rebuttal. This is followed by an example, and ends with a summary. This is a very basic structure, but it gives you a bird-eye-view of how a proper argumentative essay can be built.

Writing an argumentative essay (for a class, a news outlet, or just for fun) can help you improve your understanding of an issue and sharpen your thinking on the matter. Using researched facts and data, you can explain why you or others think the way you do, even while other reasonable people disagree.
Free AI argumentative essay generator > Free AI argumentative essay generator >
What Is an Argumentative Essay?
An argumentative essay is an explanatory essay that takes a side.
Instead of appealing to emotion and personal experience to change the reader’s mind, an argumentative essay uses logic and well-researched factual information to explain why the thesis in question is the most reasonable opinion on the matter.
Over several paragraphs or pages, the author systematically walks through:
- The opposition (and supporting evidence)
- The chosen thesis (and its supporting evidence)
At the end, the author leaves the decision up to the reader, trusting that the case they’ve made will do the work of changing the reader’s mind. Even if the reader’s opinion doesn’t change, they come away from the essay with a greater understanding of the perspective presented — and perhaps a better understanding of their original opinion.
All of that might make it seem like writing an argumentative essay is way harder than an emotionally-driven persuasive essay — but if you’re like me and much more comfortable spouting facts and figures than making impassioned pleas, you may find that an argumentative essay is easier to write.
Plus, the process of researching an argumentative essay means you can check your assumptions and develop an opinion that’s more based in reality than what you originally thought. I know for sure that my opinions need to be fact checked — don’t yours?
So how exactly do we write the argumentative essay?
How do you start an argumentative essay
First, gain a clear understanding of what exactly an argumentative essay is. To formulate a proper topic sentence, you have to be clear on your topic, and to explore it through research.
Students have difficulty starting an essay because the whole task seems intimidating, and they are afraid of spending too much time on the topic sentence. Experienced writers, however, know that there is no set time to spend on figuring out your topic. It's a real exploration that is based to a large extent on intuition.
6 Steps to Write an Argumentative Essay (Persuasion Formula)
Use this checklist to tackle your essay one step at a time:

1. Research an issue with an arguable question
To start, you need to identify an issue that well-informed people have varying opinions on. Here, it’s helpful to think of one core topic and how it intersects with another (or several other) issues. That intersection is where hot takes and reasonable (or unreasonable) opinions abound.
I find it helpful to stage the issue as a question.
For example:
Is it better to legislate the minimum size of chicken enclosures or to outlaw the sale of eggs from chickens who don’t have enough space?
Should snow removal policies focus more on effectively keeping roads clear for traffic or the environmental impacts of snow removal methods?
Once you have your arguable question ready, start researching the basic facts and specific opinions and arguments on the issue. Do your best to stay focused on gathering information that is directly relevant to your topic. Depending on what your essay is for, you may reference academic studies, government reports, or newspaper articles.
Research your opposition and the facts that support their viewpoint as much as you research your own position . You’ll need to address your opposition in your essay, so you’ll want to know their argument from the inside out.
2. Choose a side based on your research
You likely started with an inclination toward one side or the other, but your research should ultimately shape your perspective. So once you’ve completed the research, nail down your opinion and start articulating the what and why of your take.
What: I think it’s better to outlaw selling eggs from chickens whose enclosures are too small.
Why: Because if you regulate the enclosure size directly, egg producers outside of the government’s jurisdiction could ship eggs into your territory and put nearby egg producers out of business by offering better prices because they don’t have the added cost of larger enclosures.
This is an early form of your thesis and the basic logic of your argument. You’ll want to iterate on this a few times and develop a one-sentence statement that sums up the thesis of your essay.
Thesis: Outlawing the sale of eggs from chickens with cramped living spaces is better for business than regulating the size of chicken enclosures.
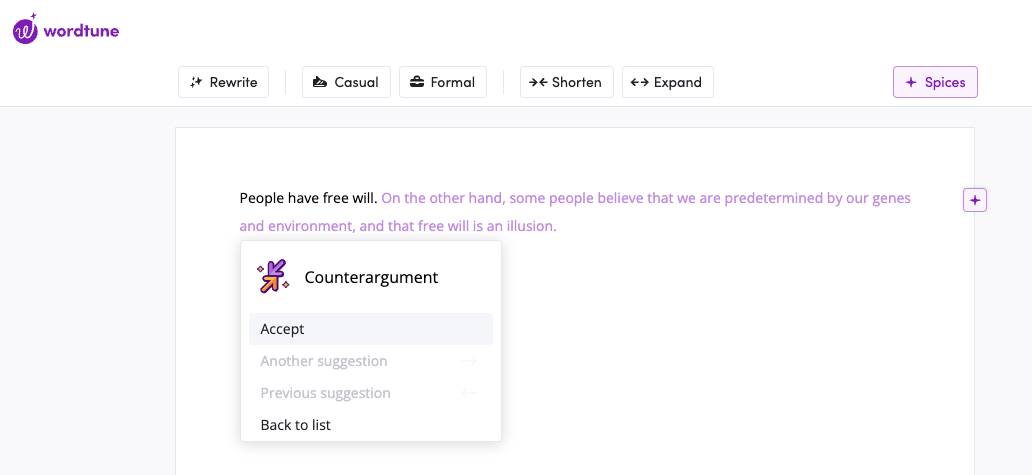
Now that you’ve articulated your thesis , spell out the counterargument(s) as well. Putting your opposition’s take into words will help you throughout the rest of the essay-writing process. (You can start by choosing the counter argument option with Wordtune Spices .)

Counterargument: Outlawing the sale of eggs from chickens with too small enclosures will immediately drive up egg prices for consumers, making the low-cost protein source harder to afford — especially for low-income consumers.
There may be one main counterargument to articulate, or several. Write them all out and start thinking about how you’ll use evidence to address each of them or show why your argument is still the best option.
3. Organize the evidence — for your side and the opposition
You did all of that research for a reason. Now’s the time to use it.
Hopefully, you kept detailed notes in a document, complete with links and titles of all your source material. Go through your research document and copy the evidence for your argument and your opposition’s into another document.
List the main points of your argument. Then, below each point, paste the evidence that backs them up.
If you’re writing about chicken enclosures, maybe you found evidence that shows the spread of disease among birds kept in close quarters is worse than among birds who have more space. Or maybe you found information that says eggs from free-range chickens are more flavorful or nutritious. Put that information next to the appropriate part of your argument.
Repeat the process with your opposition’s argument: What information did you find that supports your opposition? Paste it beside your opposition’s argument.
You could also put information here that refutes your opposition, but organize it in a way that clearly tells you — at a glance — that the information disproves their point.
Counterargument: Outlawing the sale of eggs from chickens with too small enclosures will immediately drive up egg prices for consumers.
BUT: Sicknesses like avian flu spread more easily through small enclosures and could cause a shortage that would drive up egg prices naturally, so ensuring larger enclosures is still a better policy for consumers over the long term.
As you organize your research and see the evidence all together, start thinking through the best way to order your points.
Will it be better to present your argument all at once or to break it up with opposition claims you can quickly refute? Would some points set up other points well? Does a more complicated point require that the reader understands a simpler point first?
Play around and rearrange your notes to see how your essay might flow one way or another.
4. Freewrite or outline to think through your argument
Is your brain buzzing yet? At this point in the process, it can be helpful to take out a notebook or open a fresh document and dump whatever you’re thinking on the page.
Where should your essay start? What ground-level information do you need to provide your readers before you can dive into the issue?
Use your organized evidence document from step 3 to think through your argument from beginning to end, and determine the structure of your essay.
There are three typical structures for argumentative essays:
- Make your argument and tackle opposition claims one by one, as they come up in relation to the points of your argument - In this approach, the whole essay — from beginning to end — focuses on your argument, but as you make each point, you address the relevant opposition claims individually. This approach works well if your opposition’s views can be quickly explained and refuted and if they directly relate to specific points in your argument.
- Make the bulk of your argument, and then address the opposition all at once in a paragraph (or a few) - This approach puts the opposition in its own section, separate from your main argument. After you’ve made your case, with ample evidence to convince your readers, you write about the opposition, explaining their viewpoint and supporting evidence — and showing readers why the opposition’s argument is unconvincing. Once you’ve addressed the opposition, you write a conclusion that sums up why your argument is the better one.
- Open your essay by talking about the opposition and where it falls short. Build your entire argument to show how it is superior to that opposition - With this structure, you’re showing your readers “a better way” to address the issue. After opening your piece by showing how your opposition’s approaches fail, you launch into your argument, providing readers with ample evidence that backs you up.
As you think through your argument and examine your evidence document, consider which structure will serve your argument best. Sketch out an outline to give yourself a map to follow in the writing process. You could also rearrange your evidence document again to match your outline, so it will be easy to find what you need when you start writing.
5. Write your first draft
You have an outline and an organized document with all your points and evidence lined up and ready. Now you just have to write your essay.
In your first draft, focus on getting your ideas on the page. Your wording may not be perfect (whose is?), but you know what you’re trying to say — so even if you’re overly wordy and taking too much space to say what you need to say, put those words on the page.
Follow your outline, and draw from that evidence document to flesh out each point of your argument. Explain what the evidence means for your argument and your opposition. Connect the dots for your readers so they can follow you, point by point, and understand what you’re trying to say.
As you write, be sure to include:
1. Any background information your reader needs in order to understand the issue in question.
2. Evidence for both your argument and the counterargument(s). This shows that you’ve done your homework and builds trust with your reader, while also setting you up to make a more convincing argument. (If you find gaps in your research while you’re writing, Wordtune Spices can source statistics or historical facts on the fly!)

Get Wordtune for free > Get Wordtune for free >
3. A conclusion that sums up your overall argument and evidence — and leaves the reader with an understanding of the issue and its significance. This sort of conclusion brings your essay to a strong ending that doesn’t waste readers’ time, but actually adds value to your case.
6. Revise (with Wordtune)
The hard work is done: you have a first draft. Now, let’s fine tune your writing.
I like to step away from what I’ve written for a day (or at least a night of sleep) before attempting to revise. It helps me approach clunky phrases and rough transitions with fresh eyes. If you don’t have that luxury, just get away from your computer for a few minutes — use the bathroom, do some jumping jacks, eat an apple — and then come back and read through your piece.
As you revise, make sure you …
- Get the facts right. An argument with false evidence falls apart pretty quickly, so check your facts to make yours rock solid.
- Don’t misrepresent the opposition or their evidence. If someone who holds the opposing view reads your essay, they should affirm how you explain their side — even if they disagree with your rebuttal.
- Present a case that builds over the course of your essay, makes sense, and ends on a strong note. One point should naturally lead to the next. Your readers shouldn’t feel like you’re constantly changing subjects. You’re making a variety of points, but your argument should feel like a cohesive whole.
- Paraphrase sources and cite them appropriately. Did you skip citations when writing your first draft? No worries — you can add them now. And check that you don’t overly rely on quotations. (Need help paraphrasing? Wordtune can help. Simply highlight the sentence or phrase you want to adjust and sort through Wordtune’s suggestions.)
- Tighten up overly wordy explanations and sharpen any convoluted ideas. Wordtune makes a great sidekick for this too 😉

Words to start an argumentative essay
The best way to introduce a convincing argument is to provide a strong thesis statement . These are the words I usually use to start an argumentative essay:
- It is indisputable that the world today is facing a multitude of issues
- With the rise of ____, the potential to make a positive difference has never been more accessible
- It is essential that we take action now and tackle these issues head-on
- it is critical to understand the underlying causes of the problems standing before us
- Opponents of this idea claim
- Those who are against these ideas may say
- Some people may disagree with this idea
- Some people may say that ____, however
When refuting an opposing concept, use:
- These researchers have a point in thinking
- To a certain extent they are right
- After seeing this evidence, there is no way one can agree with this idea
- This argument is irrelevant to the topic
Are you convinced by your own argument yet? Ready to brave the next get-together where everyone’s talking like they know something about intermittent fasting , chicken enclosures , or snow removal policies?
Now if someone asks you to explain your evidence-based but controversial opinion, you can hand them your essay and ask them to report back after they’ve read it.
Share This Article:
.webp)
Eight Steps to Craft an Irresistible LinkedIn Profile
.webp)
7 Common Errors in Writing + How to Fix Them (With Examples)

How To Prepare For Studying Abroad (From Someone Who’s Done It)
Looking for fresh content, thank you your submission has been received.

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
Margin Size
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

9.3: The Argumentative Essay
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 58378
- Lumen Learning
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
Learning Objectives
- Examine types of argumentative essays
Argumentative Essays
You may have heard it said that all writing is an argument of some kind. Even if you’re writing an informative essay, you still have the job of trying to convince your audience that the information is important. However, there are times you’ll be asked to write an essay that is specifically an argumentative piece.
An argumentative essay is one that makes a clear assertion or argument about some topic or issue. When you’re writing an argumentative essay, it’s important to remember that an academic argument is quite different from a regular, emotional argument. Note that sometimes students forget the academic aspect of an argumentative essay and write essays that are much too emotional for an academic audience. It’s important for you to choose a topic you feel passionately about (if you’re allowed to pick your topic), but you have to be sure you aren’t too emotionally attached to a topic. In an academic argument, you’ll have a lot more constraints you have to consider, and you’ll focus much more on logic and reasoning than emotions.

Argumentative essays are quite common in academic writing and are often an important part of writing in all disciplines. You may be asked to take a stand on a social issue in your introduction to writing course, but you could also be asked to take a stand on an issue related to health care in your nursing courses or make a case for solving a local environmental problem in your biology class. And, since argument is such a common essay assignment, it’s important to be aware of some basic elements of a good argumentative essay.
When your professor asks you to write an argumentative essay, you’ll often be given something specific to write about. For example, you may be asked to take a stand on an issue you have been discussing in class. Perhaps, in your education class, you would be asked to write about standardized testing in public schools. Or, in your literature class, you might be asked to argue the effects of protest literature on public policy in the United States.
However, there are times when you’ll be given a choice of topics. You might even be asked to write an argumentative essay on any topic related to your field of study or a topic you feel that is important personally.
Whatever the case, having some knowledge of some basic argumentative techniques or strategies will be helpful as you write. Below are some common types of arguments.
Causal Arguments
- In this type of argument, you argue that something has caused something else. For example, you might explore the causes of the decline of large mammals in the world’s ocean and make a case for your cause.
Evaluation Arguments
- In this type of argument, you make an argumentative evaluation of something as “good” or “bad,” but you need to establish the criteria for “good” or “bad.” For example, you might evaluate a children’s book for your education class, but you would need to establish clear criteria for your evaluation for your audience.
Proposal Arguments
- In this type of argument, you must propose a solution to a problem. First, you must establish a clear problem and then propose a specific solution to that problem. For example, you might argue for a proposal that would increase retention rates at your college.
Narrative Arguments
- In this type of argument, you make your case by telling a story with a clear point related to your argument. For example, you might write a narrative about your experiences with standardized testing in order to make a case for reform.
Rebuttal Arguments
- In a rebuttal argument, you build your case around refuting an idea or ideas that have come before. In other words, your starting point is to challenge the ideas of the past.

Definition Arguments
- In this type of argument, you use a definition as the starting point for making your case. For example, in a definition argument, you might argue that NCAA basketball players should be defined as professional players and, therefore, should be paid.
https://assessments.lumenlearning.co...essments/20277
Essay Examples
- Click here to read an argumentative essay on the consequences of fast fashion . Read it and look at the comments to recognize strategies and techniques the author uses to convey her ideas.
- In this example, you’ll see a sample argumentative paper from a psychology class submitted in APA format. Key parts of the argumentative structure have been noted for you in the sample.
Link to Learning
For more examples of types of argumentative essays, visit the Argumentative Purposes section of the Excelsior OWL .
Contributors and Attributions
- Argumentative Essay. Provided by : Excelsior OWL. Located at : https://owl.excelsior.edu/rhetorical-styles/argumentative-essay/ . License : CC BY: Attribution
- Image of a man with a heart and a brain. Authored by : Mohamed Hassan. Provided by : Pixabay. Located at : pixabay.com/illustrations/decision-brain-heart-mind-4083469/. License : Other . License Terms : pixabay.com/service/terms/#license
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Argumentative Essays

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
What is an argumentative essay?
The argumentative essay is a genre of writing that requires the student to investigate a topic; collect, generate, and evaluate evidence; and establish a position on the topic in a concise manner.
Please note : Some confusion may occur between the argumentative essay and the expository essay. These two genres are similar, but the argumentative essay differs from the expository essay in the amount of pre-writing (invention) and research involved. The argumentative essay is commonly assigned as a capstone or final project in first year writing or advanced composition courses and involves lengthy, detailed research. Expository essays involve less research and are shorter in length. Expository essays are often used for in-class writing exercises or tests, such as the GED or GRE.
Argumentative essay assignments generally call for extensive research of literature or previously published material. Argumentative assignments may also require empirical research where the student collects data through interviews, surveys, observations, or experiments. Detailed research allows the student to learn about the topic and to understand different points of view regarding the topic so that she/he may choose a position and support it with the evidence collected during research. Regardless of the amount or type of research involved, argumentative essays must establish a clear thesis and follow sound reasoning.
The structure of the argumentative essay is held together by the following.
- A clear, concise, and defined thesis statement that occurs in the first paragraph of the essay.
In the first paragraph of an argument essay, students should set the context by reviewing the topic in a general way. Next the author should explain why the topic is important ( exigence ) or why readers should care about the issue. Lastly, students should present the thesis statement. It is essential that this thesis statement be appropriately narrowed to follow the guidelines set forth in the assignment. If the student does not master this portion of the essay, it will be quite difficult to compose an effective or persuasive essay.
- Clear and logical transitions between the introduction, body, and conclusion.
Transitions are the mortar that holds the foundation of the essay together. Without logical progression of thought, the reader is unable to follow the essay’s argument, and the structure will collapse. Transitions should wrap up the idea from the previous section and introduce the idea that is to follow in the next section.
- Body paragraphs that include evidential support.
Each paragraph should be limited to the discussion of one general idea. This will allow for clarity and direction throughout the essay. In addition, such conciseness creates an ease of readability for one’s audience. It is important to note that each paragraph in the body of the essay must have some logical connection to the thesis statement in the opening paragraph. Some paragraphs will directly support the thesis statement with evidence collected during research. It is also important to explain how and why the evidence supports the thesis ( warrant ).
However, argumentative essays should also consider and explain differing points of view regarding the topic. Depending on the length of the assignment, students should dedicate one or two paragraphs of an argumentative essay to discussing conflicting opinions on the topic. Rather than explaining how these differing opinions are wrong outright, students should note how opinions that do not align with their thesis might not be well informed or how they might be out of date.
- Evidential support (whether factual, logical, statistical, or anecdotal).
The argumentative essay requires well-researched, accurate, detailed, and current information to support the thesis statement and consider other points of view. Some factual, logical, statistical, or anecdotal evidence should support the thesis. However, students must consider multiple points of view when collecting evidence. As noted in the paragraph above, a successful and well-rounded argumentative essay will also discuss opinions not aligning with the thesis. It is unethical to exclude evidence that may not support the thesis. It is not the student’s job to point out how other positions are wrong outright, but rather to explain how other positions may not be well informed or up to date on the topic.
- A conclusion that does not simply restate the thesis, but readdresses it in light of the evidence provided.
It is at this point of the essay that students may begin to struggle. This is the portion of the essay that will leave the most immediate impression on the mind of the reader. Therefore, it must be effective and logical. Do not introduce any new information into the conclusion; rather, synthesize the information presented in the body of the essay. Restate why the topic is important, review the main points, and review your thesis. You may also want to include a short discussion of more research that should be completed in light of your work.
A complete argument
Perhaps it is helpful to think of an essay in terms of a conversation or debate with a classmate. If I were to discuss the cause of World War II and its current effect on those who lived through the tumultuous time, there would be a beginning, middle, and end to the conversation. In fact, if I were to end the argument in the middle of my second point, questions would arise concerning the current effects on those who lived through the conflict. Therefore, the argumentative essay must be complete, and logically so, leaving no doubt as to its intent or argument.
The five-paragraph essay
A common method for writing an argumentative essay is the five-paragraph approach. This is, however, by no means the only formula for writing such essays. If it sounds straightforward, that is because it is; in fact, the method consists of (a) an introductory paragraph (b) three evidentiary body paragraphs that may include discussion of opposing views and (c) a conclusion.
Longer argumentative essays
Complex issues and detailed research call for complex and detailed essays. Argumentative essays discussing a number of research sources or empirical research will most certainly be longer than five paragraphs. Authors may have to discuss the context surrounding the topic, sources of information and their credibility, as well as a number of different opinions on the issue before concluding the essay. Many of these factors will be determined by the assignment.
Search form
A for and against essay.
Look at the essay and do the exercises to improve your writing skills.
Instructions
Do the preparation exercise first. Then do the other exercises.
Preparation

Check your understanding: multiple selection
Check your writing: reordering - essay structure, check your writing: typing - linking words, worksheets and downloads.
What are your views on reality TV? Are these types of shows popular in your country?

Sign up to our newsletter for LearnEnglish Teens
We will process your data to send you our newsletter and updates based on your consent. You can unsubscribe at any time by clicking the "unsubscribe" link at the bottom of every email. Read our privacy policy for more information.
Get science-backed answers as you write with Paperpal's Research feature
What is an Argumentative Essay? How to Write It (With Examples)

We define an argumentative essay as a type of essay that presents arguments about both sides of an issue. The purpose is to convince the reader to accept a particular viewpoint or action. In an argumentative essay, the writer takes a stance on a controversial or debatable topic and supports their position with evidence, reasoning, and examples. The essay should also address counterarguments, demonstrating a thorough understanding of the topic.
Table of Contents
- What is an argumentative essay?
- Argumentative essay structure
- Argumentative essay outline
- Types of argument claims
How to write an argumentative essay?
- Argumentative essay writing tips
- Good argumentative essay example
How to write a good thesis
- How to Write an Argumentative Essay with Paperpal?
Frequently Asked Questions
What is an argumentative essay.
An argumentative essay is a type of writing that presents a coherent and logical analysis of a specific topic. 1 The goal is to convince the reader to accept the writer’s point of view or opinion on a particular issue. Here are the key elements of an argumentative essay:
- Thesis Statement : The central claim or argument that the essay aims to prove.
- Introduction : Provides background information and introduces the thesis statement.
- Body Paragraphs : Each paragraph addresses a specific aspect of the argument, presents evidence, and may include counter arguments.
Articulate your thesis statement better with Paperpal. Start writing now!
- Evidence : Supports the main argument with relevant facts, examples, statistics, or expert opinions.
- Counterarguments : Anticipates and addresses opposing viewpoints to strengthen the overall argument.
- Conclusion : Summarizes the main points, reinforces the thesis, and may suggest implications or actions.

Argumentative essay structure
Aristotelian, Rogerian, and Toulmin are three distinct approaches to argumentative essay structures, each with its principles and methods. 2 The choice depends on the purpose and nature of the topic. Here’s an overview of each type of argumentative essay format.
Have a looming deadline for your argumentative essay? Write 2x faster with Paperpal – Start now!
Argumentative essay outline
An argumentative essay presents a specific claim or argument and supports it with evidence and reasoning. Here’s an outline for an argumentative essay, along with examples for each section: 3
1. Introduction :
- Hook : Start with a compelling statement, question, or anecdote to grab the reader’s attention.
Example: “Did you know that plastic pollution is threatening marine life at an alarming rate?”
- Background information : Provide brief context about the issue.
Example: “Plastic pollution has become a global environmental concern, with millions of tons of plastic waste entering our oceans yearly.”
- Thesis statement : Clearly state your main argument or position.
Example: “We must take immediate action to reduce plastic usage and implement more sustainable alternatives to protect our marine ecosystem.”
2. Body Paragraphs :
- Topic sentence : Introduce the main idea of each paragraph.
Example: “The first step towards addressing the plastic pollution crisis is reducing single-use plastic consumption.”
- Evidence/Support : Provide evidence, facts, statistics, or examples that support your argument.
Example: “Research shows that plastic straws alone contribute to millions of tons of plastic waste annually, and many marine animals suffer from ingestion or entanglement.”
- Counterargument/Refutation : Acknowledge and refute opposing viewpoints.
Example: “Some argue that banning plastic straws is inconvenient for consumers, but the long-term environmental benefits far outweigh the temporary inconvenience.”
- Transition : Connect each paragraph to the next.
Example: “Having addressed the issue of single-use plastics, the focus must now shift to promoting sustainable alternatives.”
3. Counterargument Paragraph :
- Acknowledgement of opposing views : Recognize alternative perspectives on the issue.
Example: “While some may argue that individual actions cannot significantly impact global plastic pollution, the cumulative effect of collective efforts must be considered.”
- Counterargument and rebuttal : Present and refute the main counterargument.
Example: “However, individual actions, when multiplied across millions of people, can substantially reduce plastic waste. Small changes in behavior, such as using reusable bags and containers, can have a significant positive impact.”
4. Conclusion :
- Restatement of thesis : Summarize your main argument.
Example: “In conclusion, adopting sustainable practices and reducing single-use plastic is crucial for preserving our oceans and marine life.”
- Call to action : Encourage the reader to take specific steps or consider the argument’s implications.
Example: “It is our responsibility to make environmentally conscious choices and advocate for policies that prioritize the health of our planet. By collectively embracing sustainable alternatives, we can contribute to a cleaner and healthier future.”

Types of argument claims
A claim is a statement or proposition a writer puts forward with evidence to persuade the reader. 4 Here are some common types of argument claims, along with examples:
- Fact Claims : These claims assert that something is true or false and can often be verified through evidence. Example: “Water boils at 100°C at sea level.”
- Value Claims : Value claims express judgments about the worth or morality of something, often based on personal beliefs or societal values. Example: “Organic farming is more ethical than conventional farming.”
- Policy Claims : Policy claims propose a course of action or argue for a specific policy, law, or regulation change. Example: “Schools should adopt a year-round education system to improve student learning outcomes.”
- Cause and Effect Claims : These claims argue that one event or condition leads to another, establishing a cause-and-effect relationship. Example: “Excessive use of social media is a leading cause of increased feelings of loneliness among young adults.”
- Definition Claims : Definition claims assert the meaning or classification of a concept or term. Example: “Artificial intelligence can be defined as machines exhibiting human-like cognitive functions.”
- Comparative Claims : Comparative claims assert that one thing is better or worse than another in certain respects. Example: “Online education is more cost-effective than traditional classroom learning.”
- Evaluation Claims : Evaluation claims assess the quality, significance, or effectiveness of something based on specific criteria. Example: “The new healthcare policy is more effective in providing affordable healthcare to all citizens.”
Understanding these argument claims can help writers construct more persuasive and well-supported arguments tailored to the specific nature of the claim.
If you’re wondering how to start an argumentative essay, here’s a step-by-step guide to help you with the argumentative essay format and writing process.
- Choose a Topic: Select a topic that you are passionate about or interested in. Ensure that the topic is debatable and has two or more sides.
- Define Your Position: Clearly state your stance on the issue. Consider opposing viewpoints and be ready to counter them.
- Conduct Research: Gather relevant information from credible sources, such as books, articles, and academic journals. Take notes on key points and supporting evidence.
- Create a Thesis Statement: Develop a concise and clear thesis statement that outlines your main argument. Convey your position on the issue and provide a roadmap for the essay.
- Outline Your Argumentative Essay: Organize your ideas logically by creating an outline. Include an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion. Each body paragraph should focus on a single point that supports your thesis.
- Write the Introduction: Start with a hook to grab the reader’s attention (a quote, a question, a surprising fact). Provide background information on the topic. Present your thesis statement at the end of the introduction.
- Develop Body Paragraphs: Begin each paragraph with a clear topic sentence that relates to the thesis. Support your points with evidence and examples. Address counterarguments and refute them to strengthen your position. Ensure smooth transitions between paragraphs.
- Address Counterarguments: Acknowledge and respond to opposing viewpoints. Anticipate objections and provide evidence to counter them.
- Write the Conclusion: Summarize the main points of your argumentative essay. Reinforce the significance of your argument. End with a call to action, a prediction, or a thought-provoking statement.
- Revise, Edit, and Share: Review your essay for clarity, coherence, and consistency. Check for grammatical and spelling errors. Share your essay with peers, friends, or instructors for constructive feedback.
- Finalize Your Argumentative Essay: Make final edits based on feedback received. Ensure that your essay follows the required formatting and citation style.
Struggling to start your argumentative essay? Paperpal can help – try now!
Argumentative essay writing tips
Here are eight strategies to craft a compelling argumentative essay:
- Choose a Clear and Controversial Topic : Select a topic that sparks debate and has opposing viewpoints. A clear and controversial issue provides a solid foundation for a strong argument.
- Conduct Thorough Research : Gather relevant information from reputable sources to support your argument. Use a variety of sources, such as academic journals, books, reputable websites, and expert opinions, to strengthen your position.
- Create a Strong Thesis Statement : Clearly articulate your main argument in a concise thesis statement. Your thesis should convey your stance on the issue and provide a roadmap for the reader to follow your argument.
- Develop a Logical Structure : Organize your essay with a clear introduction, body paragraphs, and conclusion. Each paragraph should focus on a specific point of evidence that contributes to your overall argument. Ensure a logical flow from one point to the next.
- Provide Strong Evidence : Support your claims with solid evidence. Use facts, statistics, examples, and expert opinions to support your arguments. Be sure to cite your sources appropriately to maintain credibility.
- Address Counterarguments : Acknowledge opposing viewpoints and counterarguments. Addressing and refuting alternative perspectives strengthens your essay and demonstrates a thorough understanding of the issue. Be mindful of maintaining a respectful tone even when discussing opposing views.
- Use Persuasive Language : Employ persuasive language to make your points effectively. Avoid emotional appeals without supporting evidence and strive for a respectful and professional tone.
- Craft a Compelling Conclusion : Summarize your main points, restate your thesis, and leave a lasting impression in your conclusion. Encourage readers to consider the implications of your argument and potentially take action.

Good argumentative essay example
Let’s consider a sample of argumentative essay on how social media enhances connectivity:
In the digital age, social media has emerged as a powerful tool that transcends geographical boundaries, connecting individuals from diverse backgrounds and providing a platform for an array of voices to be heard. While critics argue that social media fosters division and amplifies negativity, it is essential to recognize the positive aspects of this digital revolution and how it enhances connectivity by providing a platform for diverse voices to flourish. One of the primary benefits of social media is its ability to facilitate instant communication and connection across the globe. Platforms such as Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram break down geographical barriers, enabling people to establish and maintain relationships regardless of physical location and fostering a sense of global community. Furthermore, social media has transformed how people stay connected with friends and family. Whether separated by miles or time zones, social media ensures that relationships remain dynamic and relevant, contributing to a more interconnected world. Moreover, social media has played a pivotal role in giving voice to social justice movements and marginalized communities. Movements such as #BlackLivesMatter, #MeToo, and #ClimateStrike have gained momentum through social media, allowing individuals to share their stories and advocate for change on a global scale. This digital activism can shape public opinion and hold institutions accountable. Social media platforms provide a dynamic space for open dialogue and discourse. Users can engage in discussions, share information, and challenge each other’s perspectives, fostering a culture of critical thinking. This open exchange of ideas contributes to a more informed and enlightened society where individuals can broaden their horizons and develop a nuanced understanding of complex issues. While criticisms of social media abound, it is crucial to recognize its positive impact on connectivity and the amplification of diverse voices. Social media transcends physical and cultural barriers, connecting people across the globe and providing a platform for marginalized voices to be heard. By fostering open dialogue and facilitating the exchange of ideas, social media contributes to a more interconnected and empowered society. Embracing the positive aspects of social media allows us to harness its potential for positive change and collective growth.
- Clearly Define Your Thesis Statement: Your thesis statement is the core of your argumentative essay. Clearly articulate your main argument or position on the issue. Avoid vague or general statements.
- Provide Strong Supporting Evidence: Back up your thesis with solid evidence from reliable sources and examples. This can include facts, statistics, expert opinions, anecdotes, or real-life examples. Make sure your evidence is relevant to your argument, as it impacts the overall persuasiveness of your thesis.
- Anticipate Counterarguments and Address Them: Acknowledge and address opposing viewpoints to strengthen credibility. This also shows that you engage critically with the topic rather than presenting a one-sided argument.
How to Write an Argumentative Essay with Paperpal?
Writing a winning argumentative essay not only showcases your ability to critically analyze a topic but also demonstrates your skill in persuasively presenting your stance backed by evidence. Achieving this level of writing excellence can be time-consuming. This is where Paperpal, your AI academic writing assistant, steps in to revolutionize the way you approach argumentative essays. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to use Paperpal to write your essay:
- Sign Up or Log In: Begin by creating an account or logging into paperpal.com .
- Navigate to Paperpal Copilot: Once logged in, proceed to the Templates section from the side navigation bar.
- Generate an essay outline: Under Templates, click on the ‘Outline’ tab and choose ‘Essay’ from the options and provide your topic to generate an outline.
- Develop your essay: Use this structured outline as a guide to flesh out your essay. If you encounter any roadblocks, click on Brainstorm and get subject-specific assistance, ensuring you stay on track.
- Refine your writing: To elevate the academic tone of your essay, select a paragraph and use the ‘Make Academic’ feature under the ‘Rewrite’ tab, ensuring your argumentative essay resonates with an academic audience.
- Final Touches: Make your argumentative essay submission ready with Paperpal’s language, grammar, consistency and plagiarism checks, and improve your chances of acceptance.
Paperpal not only simplifies the essay writing process but also ensures your argumentative essay is persuasive, well-structured, and academically rigorous. Sign up today and transform how you write argumentative essays.
The length of an argumentative essay can vary, but it typically falls within the range of 1,000 to 2,500 words. However, the specific requirements may depend on the guidelines provided.
You might write an argumentative essay when: 1. You want to convince others of the validity of your position. 2. There is a controversial or debatable issue that requires discussion. 3. You need to present evidence and logical reasoning to support your claims. 4. You want to explore and critically analyze different perspectives on a topic.
Argumentative Essay: Purpose : An argumentative essay aims to persuade the reader to accept or agree with a specific point of view or argument. Structure : It follows a clear structure with an introduction, thesis statement, body paragraphs presenting arguments and evidence, counterarguments and refutations, and a conclusion. Tone : The tone is formal and relies on logical reasoning, evidence, and critical analysis. Narrative/Descriptive Essay: Purpose : These aim to tell a story or describe an experience, while a descriptive essay focuses on creating a vivid picture of a person, place, or thing. Structure : They may have a more flexible structure. They often include an engaging introduction, a well-developed body that builds the story or description, and a conclusion. Tone : The tone is more personal and expressive to evoke emotions or provide sensory details.
- Gladd, J. (2020). Tips for Writing Academic Persuasive Essays. Write What Matters .
- Nimehchisalem, V. (2018). Pyramid of argumentation: Towards an integrated model for teaching and assessing ESL writing. Language & Communication , 5 (2), 185-200.
- Press, B. (2022). Argumentative Essays: A Step-by-Step Guide . Broadview Press.
- Rieke, R. D., Sillars, M. O., & Peterson, T. R. (2005). Argumentation and critical decision making . Pearson/Allyn & Bacon.
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
- Empirical Research: A Comprehensive Guide for Academics
- How to Write a Scientific Paper in 10 Steps
- What is a Literature Review? How to Write It (with Examples)
- Life Sciences Papers: 9 Tips for Authors Writing in Biological Sciences
Make Your Research Paper Error-Free with Paperpal’s Online Spell Checker
The do’s & don’ts of using generative ai tools ethically in academia, you may also like, how to write a high-quality conference paper, how paperpal is enhancing academic productivity and accelerating..., academic editing: how to self-edit academic text with..., 4 ways paperpal encourages responsible writing with ai, what are scholarly sources and where can you..., how to write a hypothesis types and examples , what is academic writing: tips for students, what is hedging in academic writing , how to use ai to enhance your college..., how to use paperpal to generate emails &....

Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, 3 strong argumentative essay examples, analyzed.
General Education

Need to defend your opinion on an issue? Argumentative essays are one of the most popular types of essays you’ll write in school. They combine persuasive arguments with fact-based research, and, when done well, can be powerful tools for making someone agree with your point of view. If you’re struggling to write an argumentative essay or just want to learn more about them, seeing examples can be a big help.
After giving an overview of this type of essay, we provide three argumentative essay examples. After each essay, we explain in-depth how the essay was structured, what worked, and where the essay could be improved. We end with tips for making your own argumentative essay as strong as possible.
What Is an Argumentative Essay?
An argumentative essay is an essay that uses evidence and facts to support the claim it’s making. Its purpose is to persuade the reader to agree with the argument being made.
A good argumentative essay will use facts and evidence to support the argument, rather than just the author’s thoughts and opinions. For example, say you wanted to write an argumentative essay stating that Charleston, SC is a great destination for families. You couldn’t just say that it’s a great place because you took your family there and enjoyed it. For it to be an argumentative essay, you need to have facts and data to support your argument, such as the number of child-friendly attractions in Charleston, special deals you can get with kids, and surveys of people who visited Charleston as a family and enjoyed it. The first argument is based entirely on feelings, whereas the second is based on evidence that can be proven.
The standard five paragraph format is common, but not required, for argumentative essays. These essays typically follow one of two formats: the Toulmin model or the Rogerian model.
- The Toulmin model is the most common. It begins with an introduction, follows with a thesis/claim, and gives data and evidence to support that claim. This style of essay also includes rebuttals of counterarguments.
- The Rogerian model analyzes two sides of an argument and reaches a conclusion after weighing the strengths and weaknesses of each.
3 Good Argumentative Essay Examples + Analysis
Below are three examples of argumentative essays, written by yours truly in my school days, as well as analysis of what each did well and where it could be improved.
Argumentative Essay Example 1
Proponents of this idea state that it will save local cities and towns money because libraries are expensive to maintain. They also believe it will encourage more people to read because they won’t have to travel to a library to get a book; they can simply click on what they want to read and read it from wherever they are. They could also access more materials because libraries won’t have to buy physical copies of books; they can simply rent out as many digital copies as they need.
However, it would be a serious mistake to replace libraries with tablets. First, digital books and resources are associated with less learning and more problems than print resources. A study done on tablet vs book reading found that people read 20-30% slower on tablets, retain 20% less information, and understand 10% less of what they read compared to people who read the same information in print. Additionally, staring too long at a screen has been shown to cause numerous health problems, including blurred vision, dizziness, dry eyes, headaches, and eye strain, at much higher instances than reading print does. People who use tablets and mobile devices excessively also have a higher incidence of more serious health issues such as fibromyalgia, shoulder and back pain, carpal tunnel syndrome, and muscle strain. I know that whenever I read from my e-reader for too long, my eyes begin to feel tired and my neck hurts. We should not add to these problems by giving people, especially young people, more reasons to look at screens.
Second, it is incredibly narrow-minded to assume that the only service libraries offer is book lending. Libraries have a multitude of benefits, and many are only available if the library has a physical location. Some of these benefits include acting as a quiet study space, giving people a way to converse with their neighbors, holding classes on a variety of topics, providing jobs, answering patron questions, and keeping the community connected. One neighborhood found that, after a local library instituted community events such as play times for toddlers and parents, job fairs for teenagers, and meeting spaces for senior citizens, over a third of residents reported feeling more connected to their community. Similarly, a Pew survey conducted in 2015 found that nearly two-thirds of American adults feel that closing their local library would have a major impact on their community. People see libraries as a way to connect with others and get their questions answered, benefits tablets can’t offer nearly as well or as easily.
While replacing libraries with tablets may seem like a simple solution, it would encourage people to spend even more time looking at digital screens, despite the myriad issues surrounding them. It would also end access to many of the benefits of libraries that people have come to rely on. In many areas, libraries are such an important part of the community network that they could never be replaced by a simple object.
The author begins by giving an overview of the counter-argument, then the thesis appears as the first sentence in the third paragraph. The essay then spends the rest of the paper dismantling the counter argument and showing why readers should believe the other side.
What this essay does well:
- Although it’s a bit unusual to have the thesis appear fairly far into the essay, it works because, once the thesis is stated, the rest of the essay focuses on supporting it since the counter-argument has already been discussed earlier in the paper.
- This essay includes numerous facts and cites studies to support its case. By having specific data to rely on, the author’s argument is stronger and readers will be more inclined to agree with it.
- For every argument the other side makes, the author makes sure to refute it and follow up with why her opinion is the stronger one. In order to make a strong argument, it’s important to dismantle the other side, which this essay does this by making the author's view appear stronger.
- This is a shorter paper, and if it needed to be expanded to meet length requirements, it could include more examples and go more into depth with them, such as by explaining specific cases where people benefited from local libraries.
- Additionally, while the paper uses lots of data, the author also mentions their own experience with using tablets. This should be removed since argumentative essays focus on facts and data to support an argument, not the author’s own opinion or experiences. Replacing that with more data on health issues associated with screen time would strengthen the essay.
- Some of the points made aren't completely accurate , particularly the one about digital books being cheaper. It actually often costs a library more money to rent out numerous digital copies of a book compared to buying a single physical copy. Make sure in your own essay you thoroughly research each of the points and rebuttals you make, otherwise you'll look like you don't know the issue that well.

Argumentative Essay Example 2
There are multiple drugs available to treat malaria, and many of them work well and save lives, but malaria eradication programs that focus too much on them and not enough on prevention haven’t seen long-term success in Sub-Saharan Africa. A major program to combat malaria was WHO’s Global Malaria Eradication Programme. Started in 1955, it had a goal of eliminating malaria in Africa within the next ten years. Based upon previously successful programs in Brazil and the United States, the program focused mainly on vector control. This included widely distributing chloroquine and spraying large amounts of DDT. More than one billion dollars was spent trying to abolish malaria. However, the program suffered from many problems and in 1969, WHO was forced to admit that the program had not succeeded in eradicating malaria. The number of people in Sub-Saharan Africa who contracted malaria as well as the number of malaria deaths had actually increased over 10% during the time the program was active.
One of the major reasons for the failure of the project was that it set uniform strategies and policies. By failing to consider variations between governments, geography, and infrastructure, the program was not nearly as successful as it could have been. Sub-Saharan Africa has neither the money nor the infrastructure to support such an elaborate program, and it couldn’t be run the way it was meant to. Most African countries don't have the resources to send all their people to doctors and get shots, nor can they afford to clear wetlands or other malaria prone areas. The continent’s spending per person for eradicating malaria was just a quarter of what Brazil spent. Sub-Saharan Africa simply can’t rely on a plan that requires more money, infrastructure, and expertise than they have to spare.
Additionally, the widespread use of chloroquine has created drug resistant parasites which are now plaguing Sub-Saharan Africa. Because chloroquine was used widely but inconsistently, mosquitoes developed resistance, and chloroquine is now nearly completely ineffective in Sub-Saharan Africa, with over 95% of mosquitoes resistant to it. As a result, newer, more expensive drugs need to be used to prevent and treat malaria, which further drives up the cost of malaria treatment for a region that can ill afford it.
Instead of developing plans to treat malaria after the infection has incurred, programs should focus on preventing infection from occurring in the first place. Not only is this plan cheaper and more effective, reducing the number of people who contract malaria also reduces loss of work/school days which can further bring down the productivity of the region.
One of the cheapest and most effective ways of preventing malaria is to implement insecticide-treated bed nets (ITNs). These nets provide a protective barrier around the person or people using them. While untreated bed nets are still helpful, those treated with insecticides are much more useful because they stop mosquitoes from biting people through the nets, and they help reduce mosquito populations in a community, thus helping people who don’t even own bed nets. Bed nets are also very effective because most mosquito bites occur while the person is sleeping, so bed nets would be able to drastically reduce the number of transmissions during the night. In fact, transmission of malaria can be reduced by as much as 90% in areas where the use of ITNs is widespread. Because money is so scarce in Sub-Saharan Africa, the low cost is a great benefit and a major reason why the program is so successful. Bed nets cost roughly 2 USD to make, last several years, and can protect two adults. Studies have shown that, for every 100-1000 more nets are being used, one less child dies of malaria. With an estimated 300 million people in Africa not being protected by mosquito nets, there’s the potential to save three million lives by spending just a few dollars per person.
Reducing the number of people who contract malaria would also reduce poverty levels in Africa significantly, thus improving other aspects of society like education levels and the economy. Vector control is more effective than treatment strategies because it means fewer people are getting sick. When fewer people get sick, the working population is stronger as a whole because people are not put out of work from malaria, nor are they caring for sick relatives. Malaria-afflicted families can typically only harvest 40% of the crops that healthy families can harvest. Additionally, a family with members who have malaria spends roughly a quarter of its income treatment, not including the loss of work they also must deal with due to the illness. It’s estimated that malaria costs Africa 12 billion USD in lost income every year. A strong working population creates a stronger economy, which Sub-Saharan Africa is in desperate need of.
This essay begins with an introduction, which ends with the thesis (that malaria eradication plans in Sub-Saharan Africa should focus on prevention rather than treatment). The first part of the essay lays out why the counter argument (treatment rather than prevention) is not as effective, and the second part of the essay focuses on why prevention of malaria is the better path to take.
- The thesis appears early, is stated clearly, and is supported throughout the rest of the essay. This makes the argument clear for readers to understand and follow throughout the essay.
- There’s lots of solid research in this essay, including specific programs that were conducted and how successful they were, as well as specific data mentioned throughout. This evidence helps strengthen the author’s argument.
- The author makes a case for using expanding bed net use over waiting until malaria occurs and beginning treatment, but not much of a plan is given for how the bed nets would be distributed or how to ensure they’re being used properly. By going more into detail of what she believes should be done, the author would be making a stronger argument.
- The introduction of the essay does a good job of laying out the seriousness of the problem, but the conclusion is short and abrupt. Expanding it into its own paragraph would give the author a final way to convince readers of her side of the argument.

Argumentative Essay Example 3
There are many ways payments could work. They could be in the form of a free-market approach, where athletes are able to earn whatever the market is willing to pay them, it could be a set amount of money per athlete, or student athletes could earn income from endorsements, autographs, and control of their likeness, similar to the way top Olympians earn money.
Proponents of the idea believe that, because college athletes are the ones who are training, participating in games, and bringing in audiences, they should receive some sort of compensation for their work. If there were no college athletes, the NCAA wouldn’t exist, college coaches wouldn’t receive there (sometimes very high) salaries, and brands like Nike couldn’t profit from college sports. In fact, the NCAA brings in roughly $1 billion in revenue a year, but college athletes don’t receive any of that money in the form of a paycheck. Additionally, people who believe college athletes should be paid state that paying college athletes will actually encourage them to remain in college longer and not turn pro as quickly, either by giving them a way to begin earning money in college or requiring them to sign a contract stating they’ll stay at the university for a certain number of years while making an agreed-upon salary.
Supporters of this idea point to Zion Williamson, the Duke basketball superstar, who, during his freshman year, sustained a serious knee injury. Many argued that, even if he enjoyed playing for Duke, it wasn’t worth risking another injury and ending his professional career before it even began for a program that wasn’t paying him. Williamson seems to have agreed with them and declared his eligibility for the NCAA draft later that year. If he was being paid, he may have stayed at Duke longer. In fact, roughly a third of student athletes surveyed stated that receiving a salary while in college would make them “strongly consider” remaining collegiate athletes longer before turning pro.
Paying athletes could also stop the recruitment scandals that have plagued the NCAA. In 2018, the NCAA stripped the University of Louisville's men's basketball team of its 2013 national championship title because it was discovered coaches were using sex workers to entice recruits to join the team. There have been dozens of other recruitment scandals where college athletes and recruits have been bribed with anything from having their grades changed, to getting free cars, to being straight out bribed. By paying college athletes and putting their salaries out in the open, the NCAA could end the illegal and underhanded ways some schools and coaches try to entice athletes to join.
People who argue against the idea of paying college athletes believe the practice could be disastrous for college sports. By paying athletes, they argue, they’d turn college sports into a bidding war, where only the richest schools could afford top athletes, and the majority of schools would be shut out from developing a talented team (though some argue this already happens because the best players often go to the most established college sports programs, who typically pay their coaches millions of dollars per year). It could also ruin the tight camaraderie of many college teams if players become jealous that certain teammates are making more money than they are.
They also argue that paying college athletes actually means only a small fraction would make significant money. Out of the 350 Division I athletic departments, fewer than a dozen earn any money. Nearly all the money the NCAA makes comes from men’s football and basketball, so paying college athletes would make a small group of men--who likely will be signed to pro teams and begin making millions immediately out of college--rich at the expense of other players.
Those against paying college athletes also believe that the athletes are receiving enough benefits already. The top athletes already receive scholarships that are worth tens of thousands per year, they receive free food/housing/textbooks, have access to top medical care if they are injured, receive top coaching, get travel perks and free gear, and can use their time in college as a way to capture the attention of professional recruiters. No other college students receive anywhere near as much from their schools.
People on this side also point out that, while the NCAA brings in a massive amount of money each year, it is still a non-profit organization. How? Because over 95% of those profits are redistributed to its members’ institutions in the form of scholarships, grants, conferences, support for Division II and Division III teams, and educational programs. Taking away a significant part of that revenue would hurt smaller programs that rely on that money to keep running.
While both sides have good points, it’s clear that the negatives of paying college athletes far outweigh the positives. College athletes spend a significant amount of time and energy playing for their school, but they are compensated for it by the scholarships and perks they receive. Adding a salary to that would result in a college athletic system where only a small handful of athletes (those likely to become millionaires in the professional leagues) are paid by a handful of schools who enter bidding wars to recruit them, while the majority of student athletics and college athletic programs suffer or even shut down for lack of money. Continuing to offer the current level of benefits to student athletes makes it possible for as many people to benefit from and enjoy college sports as possible.
This argumentative essay follows the Rogerian model. It discusses each side, first laying out multiple reasons people believe student athletes should be paid, then discussing reasons why the athletes shouldn’t be paid. It ends by stating that college athletes shouldn’t be paid by arguing that paying them would destroy college athletics programs and cause them to have many of the issues professional sports leagues have.
- Both sides of the argument are well developed, with multiple reasons why people agree with each side. It allows readers to get a full view of the argument and its nuances.
- Certain statements on both sides are directly rebuffed in order to show where the strengths and weaknesses of each side lie and give a more complete and sophisticated look at the argument.
- Using the Rogerian model can be tricky because oftentimes you don’t explicitly state your argument until the end of the paper. Here, the thesis doesn’t appear until the first sentence of the final paragraph. That doesn’t give readers a lot of time to be convinced that your argument is the right one, compared to a paper where the thesis is stated in the beginning and then supported throughout the paper. This paper could be strengthened if the final paragraph was expanded to more fully explain why the author supports the view, or if the paper had made it clearer that paying athletes was the weaker argument throughout.

3 Tips for Writing a Good Argumentative Essay
Now that you’ve seen examples of what good argumentative essay samples look like, follow these three tips when crafting your own essay.
#1: Make Your Thesis Crystal Clear
The thesis is the key to your argumentative essay; if it isn’t clear or readers can’t find it easily, your entire essay will be weak as a result. Always make sure that your thesis statement is easy to find. The typical spot for it is the final sentence of the introduction paragraph, but if it doesn’t fit in that spot for your essay, try to at least put it as the first or last sentence of a different paragraph so it stands out more.
Also make sure that your thesis makes clear what side of the argument you’re on. After you’ve written it, it’s a great idea to show your thesis to a couple different people--classmates are great for this. Just by reading your thesis they should be able to understand what point you’ll be trying to make with the rest of your essay.
#2: Show Why the Other Side Is Weak
When writing your essay, you may be tempted to ignore the other side of the argument and just focus on your side, but don’t do this. The best argumentative essays really tear apart the other side to show why readers shouldn’t believe it. Before you begin writing your essay, research what the other side believes, and what their strongest points are. Then, in your essay, be sure to mention each of these and use evidence to explain why they’re incorrect/weak arguments. That’ll make your essay much more effective than if you only focused on your side of the argument.
#3: Use Evidence to Support Your Side
Remember, an essay can’t be an argumentative essay if it doesn’t support its argument with evidence. For every point you make, make sure you have facts to back it up. Some examples are previous studies done on the topic, surveys of large groups of people, data points, etc. There should be lots of numbers in your argumentative essay that support your side of the argument. This will make your essay much stronger compared to only relying on your own opinions to support your argument.
Summary: Argumentative Essay Sample
Argumentative essays are persuasive essays that use facts and evidence to support their side of the argument. Most argumentative essays follow either the Toulmin model or the Rogerian model. By reading good argumentative essay examples, you can learn how to develop your essay and provide enough support to make readers agree with your opinion. When writing your essay, remember to always make your thesis clear, show where the other side is weak, and back up your opinion with data and evidence.
What's Next?
Do you need to write an argumentative essay as well? Check out our guide on the best argumentative essay topics for ideas!
You'll probably also need to write research papers for school. We've got you covered with 113 potential topics for research papers.
Your college admissions essay may end up being one of the most important essays you write. Follow our step-by-step guide on writing a personal statement to have an essay that'll impress colleges.

Christine graduated from Michigan State University with degrees in Environmental Biology and Geography and received her Master's from Duke University. In high school she scored in the 99th percentile on the SAT and was named a National Merit Finalist. She has taught English and biology in several countries.
Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”
Are you seeking one-on-one college counseling and/or essay support? Limited spots are now available. Click here to learn more.
160 Good Argumentative Essay Topics for Students in 2024
April 3, 2024
The skill of writing an excellent argumentative essay is a crucial one for every high school or college student to master. In sum, argumentative essays teach students how to organize their thoughts logically and present them in a convincing way. This skill is helpful not only for those pursuing degrees in law , international relations , or public policy , but for any student who wishes to develop their critical thinking faculties. In this article, we’ll cover what makes a good argument essay and offer several argumentative essay topics for high school and college students. Let’s begin!
What is an Argumentative Essay?
An argumentative essay is an essay that uses research to present a reasoned argument on a particular subject . As with the persuasive essay , the purpose of an argumentative essay is to sway the reader to the writer’s position. However, a strong persuasive essay makes its point through diligent research and emotion while a strong argumentative essay should be based solely on facts, not feelings.
Moreover, each fact should be supported by clear evidence from credible sources . Furthermore, a good argumentative essay will have an easy-to-follow structure. When organizing your argumentative essay, use this format as a guide:
- Introduction
- Supporting body paragraphs
- Paragraph(s) addressing common counterarguments
Argumentative Essay Format
In the introduction , the writer presents their position and thesis statement —a sentence that summarizes the paper’s main points. The body paragraphs then draw upon supporting evidence to back up this initial statement, with each paragraph focusing on its own point. The length of your paper will determine the amount of examples you need. In general, you’ll likely need at least two to three. Additionally, your examples should be as detailed as possible, citing specific research, case studies, statistics, or anecdotes.
In the counterargument paragraph , the writer acknowledges and refutes opposing viewpoints. Finally, in the conclusion , the writer restates the main argument made in the thesis statement and summarizes the points of the essay. Additionally, the conclusion may offer a final proposal to persuade the reader of the essay’s position.
How to Write an Effective Argumentative Essay, Step by Step
- Choose your topic. Use the list below to help you pick a topic. Ideally, a good argumentative essay topic will be meaningful to you—writing is always stronger when you are interested in the subject matter. In addition, the topic should be complex with plenty of “pro” and “con” arguments. Avoid choosing a topic that is either widely accepted as fact or too narrow. For example, “Is the earth round?” would not be a solid choice.
- Research. Use the library, the web, and any other resources to gather information about your argumentative essay topic. Research widely but smartly. As you go, take organized notes, marking the source of every quote and where it may fit in the scheme of your larger essay. Moreover, remember to look for (and research) possible counterarguments.
- Outline . Using the argument essay format above, create an outline for your essay. Then, brainstorm a thesis statement covering your argument’s main points, and begin to put your examples in order, focusing on logical flow. It’s often best to place your strongest example last.
- Write . Draw on your research and outline to create a first draft. Remember, your first draft doesn’t need to be perfect. (As Voltaire says, “Perfect is the enemy of good.”) Accordingly, just focus on getting the words down on paper.
- Does my thesis statement need to be adjusted?
- Which examples feel strongest? Weakest?
- Do the transitions flow smoothly?
- Do I have a strong opening paragraph?
- Does the conclusion reinforce my argument?
Tips for Revising an Argument Essay
Evaluating your own work can be difficult, so you might consider the following strategies:
- Read your work aloud to yourself.
- Record yourself reading your paper, and listen to the recording.
- Reverse outline your paper. Firstly, next to each paragraph, write a short summary of that paragraph’s main points/idea. Then, read through your reverse outline. Does it have a logical flow? If not, where should you adjust?
- Print out your paper and cut it into paragraphs. What happens when you rearrange the paragraphs?
Good Argumentative Essay Topics for Middle School, High School, and College Students
Family argumentative essay topics.
- Should the government provide financial incentives for families to have children to address the declining birth rate?
- Should we require parents to provide their children with a certain level of nutrition and physical activity to prevent childhood obesity?
- Should parents implement limits on how much time their children spend playing video games?
- Should cell phones be banned from family/holiday gatherings?
- Should we hold parents legally responsible for their children’s actions?
- Should children have the right to sue their parents for neglect?
- Should parents have the right to choose their child’s religion?
- Are spanking and other forms of physical punishment an effective method of discipline?
- Should courts allow children to choose where they live in cases of divorce?
- Should parents have the right to monitor teens’ activity on social media?
- Should parents control their child’s medical treatment, even if it goes against the child’s wishes?
- Should parents be allowed to post pictures of their children on social media without their consent?
- Should fathers have a legal say in whether their partners do or do not receive an abortion?
- Can television have positive developmental benefits on children?
- Should the driving age be raised to prevent teen car accidents?
- Should adult children be legally required to care for their aging parents?
Education Argument Essay Topics
- Should schools ban the use of technology like ChatGPT?
- Are zoos unethical, or necessary for conservation and education?
- To what degree should we hold parents responsible in the event of a school shooting?
- Should schools offer students a set number of mental health days?
- Should school science curriculums offer a course on combating climate change?
- Should public libraries be allowed to ban certain books? If so, what types?
- What role, if any, should prayer play in public schools?
- Should schools push to abolish homework?
- Are gifted and talented programs in schools more harmful than beneficial due to their exclusionary nature?
- Should universities do away with Greek life?
- Should schools remove artwork, such as murals, that some perceive as offensive?
- Should the government grant parents the right to choose alternative education options for their children and use taxpayer funds to support these options?
- Is homeschooling better than traditional schooling for children’s academic and social development?
- Should we require schools to teach sex education to reduce teen pregnancy rates?
- Should we require schools to provide sex education that includes information about both homosexual and heterosexual relationships?
- Should colleges use affirmative action and other race-conscious policies to address diversity on campus?
- Should public schools remove the line “under God” from the Pledge of Allegiance?
- Should college admissions officers be allowed to look at students’ social media accounts?
- Should schools abolish their dress codes, many of which unfairly target girls, LGBTQ students, and students of color?
- Should schools be required to stock free period products in bathrooms?
- Should legacy students receive preferential treatment during the college admissions process?
- Are school “voluntourism” trips ethical?
Government Argumentative Essay Topics
- Should the U.S. decriminalize prostitution?
- Should the U.S. issue migration visas to all eligible applicants?
- Should the federal government cancel all student loan debt?
- Should we lower the minimum voting age? If so, to what?
- Should the federal government abolish all laws penalizing drug production and use?
- Should the U.S. use its military power to deter a Chinese invasion of Taiwan?
- Should the U.S. supply Ukraine with further military intelligence and supplies?
- Should the North and South of the U.S. split up into two regions?
- Should Americans hold up nationalism as a critical value?
- Should we permit Supreme Court justices to hold their positions indefinitely?
- Should Supreme Court justices be democratically elected?
- Is the Electoral College still a productive approach to electing the U.S. president?
- Should the U.S. implement a national firearm registry?
- Is it ethical for countries like China and Israel to mandate compulsory military service for all citizens?
- Should the U.S. government implement a ranked-choice voting system?
- Should institutions that benefited from slavery be required to provide reparations?
- Based on the 1619 project, should history classes change how they teach about the founding of the U.S.?
- Should term limits be imposed on Senators and Representatives? If so, how long?
- Should women be allowed into special forces units?
- Should the federal government implement stronger, universal firearm licensing laws?
- Do public sex offender registries help prevent future sex crimes?
- Should the government be allowed to regulate family size?
- Should all adults legally be considered mandated reporters?
- Should the government fund public universities to make higher education more accessible to low-income students?
- Should the government fund universal preschool to improve children’s readiness for kindergarten?
Health/Bioethics Argumentative Essay Topics
- Should the U.S. government offer its own healthcare plan?
- In the case of highly infectious pandemics, should we focus on individual freedoms or public safety when implementing policies to control the spread?
- Should we legally require parents to vaccinate their children to protect public health?
- Is it ethical for parents to use genetic engineering to create “designer babies” with specific physical and intellectual traits?
- Should the government fund research on embryonic stem cells for medical treatments?
- Should the government legalize assisted suicide for terminally ill patients?
- Should organ donation be mandatory?
- Is cloning animals ethical?
- Should cancer screenings start earlier? If so, what age?
- Is surrogacy ethical?
- Should birth control require a prescription?
- Should minors have access to emergency contraception?
- Should hospitals be for-profit or nonprofit institutions?
Good Argumentative Essay Topics — Continued
Social media argumentative essay topics.
- Should the federal government increase its efforts to minimize the negative impact of social media?
- Do social media and smartphones strengthen one’s relationships?
- Should antitrust regulators take action to limit the size of big tech companies?
- Should social media platforms ban political advertisements?
- Should the federal government hold social media companies accountable for instances of hate speech discovered on their platforms?
- Do apps such as TikTok and Instagram ultimately worsen the mental well-being of teenagers?
- Should governments oversee how social media platforms manage their users’ data?
- Should social media platforms like Facebook enforce a minimum age requirement for users?
- Should social media companies be held responsible for cases of cyberbullying?
- Should the United States ban TikTok?
- Is social media harmful to children?
- Should employers screen applicants’ social media accounts during the hiring process?
Religion Argument Essay Topics
- Should religious institutions be tax-exempt?
- Should religious symbols such as the hijab or crucifix be allowed in public spaces?
- Should religious freedoms be protected, even when they conflict with secular laws?
- Should the government regulate religious practices?
- Should we allow churches to engage in political activities?
- Religion: a force for good or evil in the world?
- Should the government provide funding for religious schools?
- Is it ethical for healthcare providers to deny abortions based on religious beliefs?
- Should religious organizations be allowed to discriminate in their hiring practices?
- Should we allow people to opt out of medical treatments based on their religious beliefs?
- Should the U.S. government hold religious organizations accountable for cases of sexual abuse within their community?
- Should religious beliefs be exempt from anti-discrimination laws?
- Should religious individuals be allowed to refuse services to others based on their beliefs or lifestyles? (As in this famous case .)
- Should the US ban religion-based federal holidays?
- Should public schools be allowed to teach children about religious holidays?
Science Argument Essay Topics
- Would the world be safer if we eliminated nuclear weapons?
- Should scientists bring back extinct animals? If so, which ones?
- Should we hold companies fiscally responsible for their carbon footprint?
- Should we ban pesticides in favor of organic farming methods?
- Should the federal government ban all fossil fuels, despite the potential economic impact on specific industries and communities?
- What renewable energy source should the U.S. invest more money in?
- Should the FDA outlaw GMOs?
- Should we worry about artificial intelligence surpassing human intelligence?
- Should the alternative medicine industry be more stringently regulated?
- Is colonizing Mars a viable option?
- Is the animal testing worth the potential to save human lives?
Sports Argument Essay Topics
- Should colleges compensate student-athletes?
- How should sports teams and leagues address the gender pay gap?
- Should youth sports teams do away with scorekeeping?
- Should we ban aggressive contact sports like boxing and MMA?
- Should professional sports associations mandate that athletes stand during the national anthem?
- Should high schools require their student-athletes to maintain a certain GPA?
- Should transgender athletes compete in sports according to their gender identity?
- Should schools ban football due to the inherent danger it poses to players?
- Should performance-enhancing drugs be allowed in sports?
- Do participation trophies foster entitlement and unrealistic expectations?
- Should sports teams be divided by gender?
- Should professional athletes be allowed to compete in the Olympics?
- Should women be allowed on NFL teams?
Technology Argumentative Essay Topics
- Should sites like DALL-E compensate the artists whose work it was trained on?
- Should the federal government make human exploration of space a more significant priority?
- Is it ethical for the government to use surveillance technology to monitor citizens?
- Should websites require proof of age from their users? If so, what age?
- Should we consider A.I.-generated images and text pieces of art?
- Does the use of facial recognition technology violate individuals’ privacy?
- Is online learning as effective as in-person learning?
- Does computing harm the environment?
- Should buying, sharing, and selling collected personal data be illegal?
- Are electric cars really better for the environment?
- Should car companies be held responsible for self-driving car accidents?
- Should private jets be banned?
- Do violent video games contribute to real-life violence?
Business Argument Essay Topics
- Should the U.S. government phase out the use of paper money in favor of a fully digital currency system?
- Should the federal government abolish its patent and copyright laws?
- Should we replace the Federal Reserve with free-market institutions?
- Is free-market ideology responsible for the U.S. economy’s poor performance over the past decade?
- Will cryptocurrencies overtake natural resources like gold and silver?
- Is capitalism the best economic system? What system would be better?
- Should the U.S. government enact a universal basic income?
- Should we require companies to provide paid parental leave to their employees?
- Should the government raise the minimum wage? If so, to what?
- Should antitrust regulators break up large companies to promote competition?
- Is it ethical for companies to prioritize profits over social responsibility?
- Should gig-economy workers like Uber and Lyft drivers be considered employees or independent contractors?
- Should the federal government regulate the gig economy to ensure fair treatment of workers?
- Should the government require companies to disclose the environmental impact of their products?
- Should companies be allowed to fire employees based on political views or activities?
- Should tipping practices be phased out?
- Should employees who choose not to have children be given the same amount of paid leave as parents?
- Should MLMs (multi-level marketing companies) be illegal?
- Should employers be allowed to factor tattoos and personal appearance into hiring decisions?
In Conclusion – Argument Essay Topics
Using the tips above, you can effectively structure and pen a compelling argumentative essay that will wow your instructor and classmates. Remember to craft a thesis statement that offers readers a roadmap through your essay, draw on your sources wisely to back up any claims, and read through your paper several times before it’s due to catch any last-minute proofreading errors. With time, diligence, and patience, your essay will be the most outstanding assignment you’ve ever turned in…until the next one rolls around.
Looking for more fresh and engaging topics for use in the classroom? You might consider checking out the following:
- 125 Good Debate Topics for High School Students
- 150 Good Persuasive Speech Topics
- 7 Best Places to Study
- Guide to the IB Extended Essay
- How to Write the AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay
- AP Lit Reading List
- How to Write the AP Lang Synthesis Essay
- 49 Most Interesting Biology Research Topics
- High School Success
Lauren Green
With a Bachelor of Arts in Creative Writing from Columbia University and an MFA in Fiction from the Michener Center for Writers at the University of Texas at Austin, Lauren has been a professional writer for over a decade. She is the author of the chapbook A Great Dark House (Poetry Society of America, 2023) and a forthcoming novel (Viking/Penguin).
- 2-Year Colleges
- Application Strategies
- Best Colleges by Major
- Best Colleges by State
- Big Picture
- Career & Personality Assessment
- College Essay
- College Search/Knowledge
- College Success
- Costs & Financial Aid
- Data Visualizations
- Dental School Admissions
- Extracurricular Activities
- Graduate School Admissions
- High Schools
- Law School Admissions
- Medical School Admissions
- Navigating the Admissions Process
- Online Learning
- Private High School Spotlight
- Summer Program Spotlight
- Summer Programs
- Teacher Tools
- Test Prep Provider Spotlight
“Innovative and invaluable…use this book as your college lifeline.”
— Lynn O'Shaughnessy
Nationally Recognized College Expert
College Planning in Your Inbox
Join our information-packed monthly newsletter.
A for and against essay – a balanced essay
List three advantages and three disadvantages.

Write the composition using linking expressions
Discuss the pros and cons of streaming video platforms like netflix or hbo.
Everyone knows about streaming platforms. Netflix, Amazon Prime, Hulu, HBO, and the list goes on. It’s true that they offer their audiences numerous advantages, but maybe they are not for everyone, and before you sign up for one of them, you should also consider their disadvantages.
The main advantage of streaming video services is that you can take your favourite shows and movies anywhere, you just need a phone or tablet and an internet connection, and you are good to go. Another advantage is the great availability; you can access almost any show or film you can think of, and you don’t have to wait a week to see another episode of your favourite series. Furthermore , if you are learning a language, you can easily find movies in the original version and decide whether you want to add subtitles.
However , not everything is positive about these platforms; there are also some disadvantages that we should consider. An important disadvantage is that if you go somewhere with a poor internet connection or with no internet connection, then you’d better go straight to bed or read a book because you’re not going to watch your series. In addition , although you can watch almost anything, there are significant limitations. Not everything you want to watch is there; for instance , if you love old movies, you will probably not find what you are looking for, and if you have Netflix, forget about watching Game of Thrones. Another negative point is that since so many films and series episodes are available, you may end up sleeping less than you need.
In conclusion , streaming video platforms are great, and they are the present and future of TV entertainment, but people who want to use one of these platforms should know that not everything is positive about these services.
Use linking expressions…
to list advantages and disadvantages:
- The main advantage of … is that …
- An important advantage of … is that …
- Another advantage is that …
- Another point in favour of … is that …
- Another negative point is that …
to add more points:
- In addition,
- Furthermore,
to introduce examples:
- For example,
- For instance,
to introduce contrasting points:
- On the other hand,
to introduce the conclusion:
- In conclusion,
Don’t give your opinion unless you are asked to do it
This is a ‘for and against’ essay where you will discuss two contrasting views about a topic. You should only give your opinion if you are explicitly instructed to do so.
Related tests:
50 Argumentative Essay Topics
Illustration by Catherine Song. ThoughtCo.
- M.Ed., Education Administration, University of Georgia
- B.A., History, Armstrong State University
An argumentative essay requires you to decide on a topic and argue for or against it. You'll need to back up your viewpoint with well-researched facts and information as well. One of the hardest parts is deciding which topic to write about, but there are plenty of ideas available to get you started. Then you need to take a position, do some research, and present your viewpoint convincingly.
Choosing a Great Argumentative Essay Topic
Students often find that most of their work on these essays is done before they even start writing. This means that it's best if you have a general interest in your subject. Otherwise, you might get bored or frustrated while trying to gather information. You don't need to know everything, though; part of what makes this experience rewarding is learning something new.
It's best if you have a general interest in your subject, but the argument you choose doesn't have to be one that you agree with.
The subject you choose may not necessarily be one you are in full agreement with, either. You may even be asked to write a paper from the opposing point of view. Researching a different viewpoint helps students broaden their perspectives.
Ideas for Argument Essays
Sometimes, the best ideas are sparked by looking at many different options. Explore this list of possible topics and see if a few pique your interest. Write those down as you come across them, then think about each for a few minutes.
Which would you enjoy researching? Do you have a firm position on a particular subject? Is there a point you would like to make sure you get across? Did the topic give you something new to think about? Can you see why someone else may feel differently?
List of 50 Possible Argumentative Essay Topics
A number of these topics are rather controversial—that's the point. In an argumentative essay , opinions matter, and controversy is based on opinions. Just make sure your opinions are backed up by facts in the essay. If these topics are a little too controversial or you don't find the right one for you, try browsing through persuasive essay and speech topics as well.
- Is global climate change caused by humans?
- Is the death penalty effective?
- Is the U.S. election process fair?
- Is torture ever acceptable?
- Should men get paternity leave from work?
- Are school uniforms beneficial?
- Does the U.S. have a fair tax system?
- Do curfews keep teens out of trouble?
- Is cheating out of control?
- Are we too dependent on computers?
- Should animals be used for research?
- Should cigarette smoking be banned?
- Are cell phones dangerous?
- Are law enforcement cameras an invasion of privacy?
- Do we have a throwaway society ?
- Is child behavior better or worse than it was years ago?
- Should companies market to children?
- Should the government have a say in our diets?
- Does access to condoms prevent teen pregnancy?
- Should members of Congress have term limits?
- Are actors and professional athletes paid too much?
- Are CEOs paid too much?
- Should athletes be held to high moral standards?
- Do violent video games cause behavior problems?
- Should creationism be taught in public schools?
- Are beauty pageants exploitative ?
- Should English be the official language of the United States?
- Should the racing industry be forced to use biofuels?
- Should the alcohol-drinking age be increased or decreased?
- Should everyone be required to recycle?
- Is it okay for prisoners to vote (as they are in some states)?
- Should same-sex marriage be legalized in more countries?
- Are there benefits to attending a single-sex school ?
- Does boredom lead to trouble?
- Should schools be in session year-round ?
- Does religion cause war?
- Should the government provide health care?
- Should abortion be illegal?
- Should more companies expand their reproductive health benefits for employees?
- Is homework harmful or helpful?
- Is the cost of college too high?
- Is college admission too competitive?
- Should euthanasia be illegal?
- Should the federal government legalize marijuana use nationally ?
- Should rich people be required to pay more taxes?
- Should schools require foreign language or physical education?
- Is affirmative action fair?
- Is public prayer okay in schools?
- Are schools and teachers responsible for low test scores?
- Is greater gun control a good idea?
How to Craft a Persuasive Argument
After you've decided on your essay topic, gather evidence to make your argument as strong as possible. Your research could even help shape the position your essay ultimately takes. As you craft your essay, remember to utilize persuasive writing techniques , such as invoking emotional language or citing facts from authoritative figures.
- 100 Persuasive Essay Topics
- 100 Persuasive Speech Topics for Students
- Tips on How to Write an Argumentative Essay
- Preparing an Argument Essay: Exploring Both Sides of an Issue
- Bad Essay Topics for College Admissions
- How to Write a Narrative Essay or Speech
- Controversial Speech Topics
- How to Write a Solid Thesis Statement
- MBA Essay Tips
- High School Debate Topics
- How to Write a Persuasive Essay
- How to Ace Your University of Wisconsin Personal Statements
- 25 Essay Topics for American Government Classes
- A Sample Essay for Common Application Option #7: Topic of Your Choice
- Common Application Essay Option 6: Losing Track of Time
- Topic In Composition and Speech

Writing an Argumentative Research Paper
- Library Resources
- Books & EBooks
- What is an Argumentative Research Essay?
- Choosing a Topic
- How to Write a Thesis Statement Libguide
- Structure & Outline
- Types of Sources
- OER Resources
- Copyright, Plagiarism, and Fair Use
Examples of argumentative essays
Skyline College libguides: MLA Sample Argumentative Papers
Ebooks in Galileo
Video Tutorial
Structure & Outline
Usually written in the five-paragraph structure, the argumentative essay format consists of an introduction, 2-3 body paragraphs, and a conclusion.
A works cited page or reference page (depending on format) will be included at the end of the essay along with in-text citations within the essay.
When writing an argumentative research essay, create an outline to structure the research you find as well as help with the writing process. The outline of an argumentative essay should include an introduction with thesis statement, 3 main body paragraphs with supporting evidence and opposing viewpoints with evidence to disprove, along with an conclusion.
The example below is just a basic outline and structure
I. Introduction: tells what you are going to write about. Basic information about the issue along with your thesis statement.
A. Basic information
B. Thesis Statement
II. Body 1 : Reason 1 write about the first reason that proves your claim on the issue and give supporting evidence
A. supporting evidence
B. Supporting evidence
II. Body 2 .: Reason 2 write about the third reason that proves your claim on the issue and give supporting evidence
A. supporting evidence
III. Body 3 : Reason 3 write about the fourth reason that proves your claim on the issue and give supporting evidence
IV. Counter arguments and responses. Write about opposing viewpoints and use evidence to refute their argument and persuade audience in your direction or viewpoint
A. Arguments from other side of the issue
B. Refute the arguments
V. Conclusion
- << Previous: How to Write a Thesis Statement Libguide
- Next: Conducting Research >>
- Last Updated: Jan 24, 2024 1:23 PM
- URL: https://wiregrass.libguides.com/c.php?g=1188383
When you write an academic essay, you make an argument: you propose a thesis and offer some reasoning, using evidence, that suggests why the thesis is true. When you counter-argue, you consider a possible argument against your thesis or some aspect of your reasoning. This is a good way to test your ideas when drafting, while you still have time to revise them. And in the finished essay, it can be a persuasive and (in both senses of the word) disarming tactic. It allows you to anticipate doubts and pre-empt objections that a skeptical reader might have; it presents you as the kind of person who weighs alternatives before arguing for one, who confronts difficulties instead of sweeping them under the rug, who is more interested in discovering the truth than winning a point.
Not every objection is worth entertaining, of course, and you shouldn't include one just to include one. But some imagining of other views, or of resistance to one's own, occurs in most good essays. And instructors are glad to encounter counterargument in student papers, even if they haven't specifically asked for it.
The Turn Against
Counterargument in an essay has two stages: you turn against your argument to challenge it and then you turn back to re-affirm it. You first imagine a skeptical reader, or cite an actual source, who might resist your argument by pointing out
- a problem with your demonstration, e.g., that a different conclusion could be drawn from the same facts, a key assumption is unwarranted, a key term is used unfairly, certain evidence is ignored or played down;
- one or more disadvantages or practical drawbacks to what you propose;
- an alternative explanation or proposal that makes more sense.
You introduce this turn against with a phrase like One might object here that... or It might seem that... or It's true that... or Admittedly,... or Of course,... or with an anticipated challenging question: But how...? or But why...? or But isn't this just...? or But if this is so, what about...? Then you state the case against yourself as briefly but as clearly and forcefully as you can, pointing to evidence where possible. (An obviously feeble or perfunctory counterargument does more harm than good.)
The Turn Back
Your return to your own argument—which you announce with a but, yet, however, nevertheless or still —must likewise involve careful reasoning, not a flippant (or nervous) dismissal. In reasoning about the proposed counterargument, you may
- refute it, showing why it is mistaken—an apparent but not real problem;
- acknowledge its validity or plausibility, but suggest why on balance it's relatively less important or less likely than what you propose, and thus doesn't overturn it;
- concede its force and complicate your idea accordingly—restate your thesis in a more exact, qualified, or nuanced way that takes account of the objection, or start a new section in which you consider your topic in light of it. This will work if the counterargument concerns only an aspect of your argument; if it undermines your whole case, you need a new thesis.
Where to Put a Counterargument
Counterargument can appear anywhere in the essay, but it most commonly appears
- as part of your introduction—before you propose your thesis—where the existence of a different view is the motive for your essay, the reason it needs writing;
- as a section or paragraph just after your introduction, in which you lay out the expected reaction or standard position before turning away to develop your own;
- as a quick move within a paragraph, where you imagine a counterargument not to your main idea but to the sub-idea that the paragraph is arguing or is about to argue;
- as a section or paragraph just before the conclusion of your essay, in which you imagine what someone might object to what you have argued.
But watch that you don't overdo it. A turn into counterargument here and there will sharpen and energize your essay, but too many such turns will have the reverse effect by obscuring your main idea or suggesting that you're ambivalent.
Counterargument in Pre-Writing and Revising
Good thinking constantly questions itself, as Socrates observed long ago. But at some point in the process of composing an essay, you need to switch off the questioning in your head and make a case. Having such an inner conversation during the drafting stage, however, can help you settle on a case worth making. As you consider possible theses and begin to work on your draft, ask yourself how an intelligent person might plausibly disagree with you or see matters differently. When you can imagine an intelligent disagreement, you have an arguable idea.
And, of course, the disagreeing reader doesn't need to be in your head: if, as you're starting work on an essay, you ask a few people around you what they think of topic X (or of your idea about X) and keep alert for uncongenial remarks in class discussion and in assigned readings, you'll encounter a useful disagreement somewhere. Awareness of this disagreement, however you use it in your essay, will force you to sharpen your own thinking as you compose. If you come to find the counterargument truer than your thesis, consider making it your thesis and turning your original thesis into a counterargument. If you manage to draft an essay without imagining a counterargument, make yourself imagine one before you revise and see if you can integrate it.
Gordon Harvey (adapted from The Academic Essay: A Brief Anatomy), for the Writing Center at Harvard University

Friday essay: ‘me against you’ – Jon Ronson investigates the perpetual outrage of the culture wars
Senior Lecturer, Discipline of English and Writing, University of Sydney
Disclosure statement
Alexander Howard does not work for, consult, own shares in or receive funding from any company or organization that would benefit from this article, and has disclosed no relevant affiliations beyond their academic appointment.
University of Sydney provides funding as a member of The Conversation AU.
View all partners
The culture wars are perpetually waged in response to new and imagined threats, but they’ve been around forever. They just keep taking on new forms. In Australia, we’re seeing heated zero-sum disputes about everything from gender and sexuality, and race and religious freedom in schools , to climate change and the right to protest.
Just last week, western Sydney’s Cumberland Council voted to ban same-sex parenting books in eight Australian libraries – a ban that was overturned at a late-night council meeting two nights ago, as police watched over competing protests (for and against), outside the council building.
During COVID, conspiracy theories and related ways of thinking accelerated – helped by social media. But neither COVID nor social media caused this shift. Things were already falling apart, and that event and those platforms accelerated processes already underway. We are reaping the rewards of something toxic that has been brewing for a while, which is perhaps borne out by our tendencies to cast everything in binary terms: me against you, us and them.

Maybe we are whipping ourselves up into a state of perpetual outrage and distraction because, in the end, we desperately don’t want to acknowledge the complexities of how bad things are getting – in a world beset by accelerating climate disasters, humanitarian catastrophes, widening wealth gaps and cost-of-living and housing crises.
In 2024, populist and authoritarian leaders around the world have succeeded by leaning into conspiracy theories, misinformation and disinformation. And the recent introduction of artificial intelligence only makes it easier for these things to spread. How did we get here?
Inflamed passions
Forks, Washington, is famous for being the home of Bella and Edward, the fictitious vampire couple in Stephenie Myer’s popular Twilight franchise.
In real life, it is a place where “nothing much happens”, as investigative journalist Jon Ronson says in the second series of his award-winning podcast, Things Fell Apart , about the origins and accelerants of the culture wars.
This changed on June 3 2020, when an innocent family on a Twilight-themed holiday found themselves trapped in the woods, surrounded by a bevy of heavily armed townspeople with short fuses and itchy trigger fingers.
The word on the social media grapevine was that Forks was about to be swamped by violent leftists hellbent on nothing less than the total annihilation of America. Mistakenly identified as members of the decentralised leftist collective Antifa, the family narrowly avoided a violent confrontation. Passions were inflamed, the situation on a knife edge.
The unwitting, traumatised family had, Ronson reveals, “become collateral damage in a culture war inflamed by a national media that had become too polarised and ideological”.
“It feels to me that for great numbers of people […] ideology and activism have started to matter more than evidence,” he told the Guardian in recent days, emphasising the importance of the “nuanced truth” in his work. He says he’s not against activist journalism, which has done “a lot of good”. But he says “the old rules of journalism – evidence, fairness – still need to apply”.

The stories in Ronson’s podcast – focusing on Qanon, COVID deniers and conspiracy theorists – depict the faultlines of America. We’re not as far down the road, but the culture wars continue to spill into Australia.
The Albanese government has attempted to defuse them. In his response to last year’s Australian Law Reform Commission report on religious educational institutions and anti-discrimination laws, the prime minister was categorical : “Australians do not want to see the culture wars and the division out there.”
However, as the ferocious and damaging culture war over the Voice to Parliament referendum shows, the country has a long way to go.
And in recent days, responding to the Cumberland Council book ban spearheaded by councillor Steve Christou, New South Wales arts minister John Graham condemned “this councillor importing this US culture war into our country and playing it out on the shelves of the local library”.

Culture wars are not new
Ronson offers two provisional definitions of culture wars. In the first series of Things Fell Apart, he described them as issues “people yell at each other about on social media”. In the second series, which focuses on a series of seemingly random events that accelerated the culture wars over 30 days during COVID, Ronson refines his definition: they are struggles “for dominance between conflicting values”.
The historical origins of the term can be traced back to Europe in the 19th century.
On June 29 1868, Pope Pius IX issued invitations for the creation of a Vatican Council. The founding of the First Vatican Council led, in turn, to the Declaration of Papal Infallibility . This edict, which threatened the separation of church and state, went down badly with Europe’s ruling classes.
Prussia’s Otto von Bismarck was one of those who took umbrage. As an empire-builder, Bismarck was perturbed by what he perceived as an attack on his authority and a threat to national sovereignty. A seven-year political standoff between Chancellor Bismark and the Pius IX subsequently ensued.
The German word for this confrontation – which impinged on virtually every sphere of public and social life – is Kulturkampf , which translates as “struggles of cultures”. It has since been taken up by many critics and cultural commentators.
One was sociologist James Davison Hunter, who introduced the term into American public discourse with his 1991 book Culture Wars: The Struggle to Define America . Hunter defines cultural warfare
very simply as political and social hostility rooted in different systems of moral understanding. The end to which these hostilities tend is the domination of one cultural and moral ethos over all others.
Abortion, education, affirmative action. Religion and the ongoing fight for gay rights. These are some of the polarising social and political issues Hunter discusses in his account of the American culture wars of the late 20th century.
Meanwhile, here in Australia at the time, John Howard and the Liberal Party were embarking on a decades-long campaign against the purported perils of political correctness and multiculturalism – while attacking anyone who had the temerity to criticise Australia’s colonial history . Years later, in 2006, after ten years as prime minister, Howard would literally claim victory in Australia’s culture wars – but of course they’re still raging today.
Within a year of Hunter’s book, “culture wars” were headline news. On August 17 1992, the right-wing politician Pat Buchanan delivered a fiery and divisive primetime address on the opening night of the Republican National Convention in Houston, Texas. He painted a picture of a nation under siege and described “a cultural war, as critical to the kind of nation we shall be as was the Cold War itself, for this war is for the soul of America”.
Environmental extremists. Purveyors of pornographic filth. Radical feminists. Bill and Hilary Clinton. The list of those deemed to be attacking and undermining America is seemingly endless and strangely familiar. “My friends,” he implored, “we must take back our cities, and take back our culture, and take back our country”.
Howard framed Australia’s culture war in similar terms 14 years later, in 2006, claiming his government had seen the end of a “divisive, phoney debate about national identity”. He continued: “We’ve drawn back from being too obsessed with diversity to a point where Australians are now better able to appreciate the enduring values of the national character that we proudly celebrate and preserve.”
Ronson mulls over Buchanan’s proto-Trumpian speech and its mixed reception in contemporary conservative circles in series one of Things Fell Apart.
Journalist Irving Kristol dismissed Buchanan as out of touch, noting: “I regret to inform him that those wars are over, and the Left has won.” During the 70s and 80s in America, Ronson clarifies, the Left had taken control of education, entertainment and the media.
Abortion was legal, school textbooks were becoming more diverse, gay activism was beginning a path to victory, and Hollywood was celebrating those values. “In the early 80s, as conservatives were feeling aggrieved that the culture was running away from them, a strange kind of storytelling began to blossom.”
Did the Satanic Panic birth QAnon?
Ronson illustrates this with a story from the 1980s – the so-called Satanic Panic – that may explain the roots of QAnon , the 21st-century conspiracy theory that essentially revolves around the idea “Democrats and Hollywood elites derive their power from secretly drinking the blood of kidnapped children”.
He traces it back to Bob Larson, a Christian conservative broadcaster in Phoenix, Arizona who was concerned about death metal music, and started to see Satanic patterns everywhere. He encouraged his listeners to reach out if they had ever had firsthand contact with Satanism – and they had.
In regular streets all over America, secret cabals were ritually abusing children in the name of Satan. They told stories of cannibalism and dead cats nailed to pulpits.

A credulous Larson incorporated what he heard into a novel, Dead Air , about a heroic radio host who spends his spare time rescuing vulnerable children from the clutches of devil-worshipping cults. Published in 1991, it was advertised as being based on true events.
Roughly 90% of Americans believed in a higher power in the 1980s. Ronson recounts how “mainstream broadcasters saw huge ratings potential, not by debunking the satanic claims, but by entertaining the idea that they might be true”.
Over 12,000 cases of ritualistic abuse were reported. People were falsely accused of bizarre and far-fetched acts of child abuse, and lives were ruined.
Keep this in mind as we move into the 21st century. On October 30 2016, a white supremacist Twitter user, posing as a Jewish lawyer from New York, falsely claimed local police were investigating evidence from disgraced politician Anthony Weiner ’s laptop implicating Hilary Clinton in an international child enslavement ring.
The allegation quickly gained traction across various social media platforms, giving rise to a modern spin on an old antisemitic conspiracy theory about blood libels: the infamous Pizzagate . Online speculation intensified, and the situation eventually spilled over into the real world.
At this point, things turned violent. In a scene that could almost have been lifted verbatim from the pages of Dead Air, a self-styled investigator armed with a high-power assault rifle shot up a pizzeria in Washington, D.C. The assailant, who worked as a jobbing screenwriter and actor, had come to believe children were being held hostage in the restaurant’s basement. The only problem: the restaurant didn’t even have a basement.

Despite having been thoroughly debunked, this particular conspiracy theory persists today. Indeed, as researcher Mike Rothschild outlines, “the sordid aspects of Pizzagate, like the abuse of children and the centrality of the Clintons and their inner circle” constitute an important part of the mythology associated with QAnon.
Rothschild argues “no conspiracy theory more encapsulates the full-throated madness of the Donald Trump era than QAnon.” At the same time, QAnon, which has been referred to as “Pizzagate on bathsalts” , also heralded the arrival of what journalist Anna Merlan has identified as the “conspiracy singularity”.
This was the moment, a few months into the coronavirus pandemic, when a multitude of different conspiracy theories, some of which had been lurking in the darker recesses of the internet for decades, began to bleed into each other in strange and surprising ways. Malevolent reptilians masquerading as humans, chemtrails in the sky, the sinking of the Titanic . Everything suddenly seemed to come together. This convergence, Merlan writes, gave rise to “a grand unified theory of suspicion”.
‘Excited delirium’ and George Floyd
The 2024 season of Things Fell Apart is interested in this strange moment of conspiratorial convergence, and strives to understand, to borrow a term from American historian Richard Hofstader , “movements of suspicious discontent”.
It centres on a number of seemingly unrelated events that occurred in May and June 2020, and accelerated the culture wars. Taken together, these events refute Irving Kristol’s assertion about culture wars being a thing of the past. If anything, we are, as Ronson demonstrates, more culturally divided than ever before, living as we do in an age of violent dispute and rampant untruth.
So, for instance, we see the link between a strange, since-discredited diagnosis given to African American sex workers found dead in Miami in the 1980s (“excited delirium”), the killing of George Floyd by a white police officer on May 25 2020, and the Black Lives Matter movement.
In 1980, Miami’s coroner explained the deaths, later attributed to a serial killer (which the evidence pointed to), by “discovering” a condition that rendered men impervious to pain and caused instant death in women. Excited delirium, the discredited term, continues to be used in some police training programs – and was voiced by a police officer on the scene while Derek Chauvin choked the life out of George Floyd.
Of course, the protests by Black Lives Matter and Antifa that followed his murder “gave rise to a whole new wave of culture wars”.

Cultural critic and activist Naomi Klein describes how, during this incredibly volatile period, it felt like everything started to bifurcate. Society seemed to split into two camps, with “each side defining itself against the other – whatever one says and believes, the other seems obliged to say and believe the opposite”.
The Great Reset
The sixth episode of Ronson’s podcast focuses on the culture war that exploded over the Great Reset , a hastily cobbled together economic recovery plan drawn up by the World Economic Forum in response to the pandemic. “It is our defining moment – we will be dealing with its fallout for years, and many things will change forever,” it read in part.
Launched in June 2020 by Prince Charles and the head of the Davos summit (the World Economic Forum’s annual meeting), the plan took the pandemic as an opportunity to promote several long-favoured ideas that will supposedly save us. For example, artificial intelligence, bio-tech, autonomous vehicles, green capitalism and energy capture.
Conspiratorial placards and chants decrying the Great Reset soon began to appear at anti-lockdown rallies across the globe. If these protesters were to be believed, World Economic Forum CEO Klaus Schwab and his band of unscrupulous Davos cronies were about to strip us of our belongings, make us live in tiny boxes, and force us to subside on a diet consisting entirely of edible insects. (As with almost all conspiracy theories, as Ronson readily admits, there were elements of truth to some of these claims.)
“When they started showing up at the early anti-lockdown protests,” Naomi Klein recalls in her 2023 book Doppelganger, they spoke “as if a great secret was being revealed”. Klein thinks this rather odd, given the Great Reset came with a slick, high-profile marketing campaign. Nonetheless, as Klein writes,
journalists and politicians on the right, and “independent researchers” on the left, acted as it they had uncovered a conspiracy that wily elites were trying to hide from them. If so, it was the first conspiracy with its own marketing agency and explainer videos.
The question Ronson poses in this episode speaks directly to Klein’s droll observations: “why was this happening?” Part of the answer lies in the way people on both sides of the political spectrum were accessing and processing information.

‘Something in us … is waiting to be addicted’
Twitter only exploits and magnifies social problems that are already there, wrote commentator Richard Seymour in 2019. “If we’ve found ourselves addicted to social media, in spite or because of its frequent nastiness, as I have, then there is something in us that is waiting to be addicted.”
It was social media that exposed millions of people to the work of conspiracy theorist Mikki Willis, the former actor and model behind the ongoing Plandemic series, which intimates COVID-19 was deliberately engineered as part of a concerted attempt to murder millions and curtail civil liberties.

Released May 4 2020, the first of these slickly produced films – which was independently released on YouTube, at just 26 minutes long – includes an extensive interview with discredited virologist Judy Mikovits. In little over a week, Plandemic accrued more than 8 million views on Twitter, Facebook, Instagram and YouTube. On May 5, a day after its release, a QAnon Facebook group dedicated to the conspiracy movement posted the film to its 25,000 members, imploring them to watch it as quickly as possible.
Four years later, Mikki Willis, who has extensive links to the anti-vax movement, is an established presence on the conspiracy theory circuit, and was recently a guest on culture warrior Alex Jones’s InfoWars. He was also present at the January 6 2021 insurrection in Washington DC. He denies knowing anything about QAnon, but in the same breath thanks the movement’s followers for promoting his work.
Ronson sees Willis’ influence reflected across his series, in culture battles as disparate as the Great Reset and trans rights. “When I watched all his documentaries I noticed he had turned everything we covered through the series into one uber-conspiracy,” Ronson told the Guardian .
But what especially interests him is Willis’ devotion to literary scholar Joseph Campbell and his “hero’s journey”, intended as a way of explaining how narratives work – but taken on by Willis as an inspirational self-help book. It’s the sort of thing we might associate with an alt-right guru like Jordan Peterson: a guide to how life should work.
Willis tells Ronson how he stumbled across Campbell’s work in a secondhand bookstore in Los Angeles. He was particularly taken with the thesis Campbell advances in his most famous work, The Hero with a Thousand Faces . Published in 1949, this book has inspired countless critics and writers, including George Lucas, who liberally cribbed from it when developing Star Wars.
A work of comparative mythology, Campbell’s book divides the world up into a series of recognisable archetypes. In the end, at least from Campbell’s perspective, it all comes down to an old-fashioned struggle between heroes and villains, between the forces of good and evil:
A hero ventures forth from the world of common day into a region of supernatural wonder: fabulous forces are there encountered and a decisive victory is won: the hero comes back from this mysterious adventure with the power to bestow boons on his fellow man.
Conspiracy theorists tend to see patterns everywhere, so it’s easy to see the appeal. Campbell provides a readily discernible framework for approaching and comprehending often bewilderingly complex – and occasionally entirely random – events.
Offering adventure and excitement, Campbell’s schema also comes tantalisingly preloaded with the promise of recognition and eventual adulation. But it also tends towards reduction and oversimplification, and encourages us to understand the world around us in terms of binary opposition. This, I think, should give us pause for thought.
Heroes, villains and the truth
At a glance, Plandemic’s millions and millions of views in a matter of days in 2020 can be explained by clickbait tactics and algorithmical orchestrations. But the more time I spend thinking about it, the more I wonder if we all, to some degree or other, want to believe in binaries, and to understand everything in terms of a clash between heroes and villains.
We do it because it’s easy and, in a way, comforting. Like a balm, this manner of thinking affords us temporary solace and the illusion of respite – at a frightening time, when everything is going from bad to worse. This strikes me as deeply troubling.
The constrictive, ultimately destructive binary thinking that structures much of everyday existence, online or otherwise, only intensifies with the ever-changing and overwhelming media landscape, which continually bombards us with piecemeal fragments of a selectively curated approximation of something that, to the naked eye, passes for reality.
And perhaps, stuck as we seem to be in our silos and personalised echo chambers, we are less likely to try to negotiate an agreed understanding somewhere in the murky middle. I’m not sure how we fix this, or if it can be fixed.
As Things Fell Apart ends, Ronson muses:
When untruths spread, the ripples can be devastating. So it feels more important than ever to hold onto the truth, like driftwood in the ocean, because if not, we might drown.
I agree. But I can’t shake the nagging suspicion that the 20th-century philosopher Theodor Adorno , who is himself the subject of a long-running conspiracy theory with a decidedly antisemitic slant, might have been right all along when he suggested “we live in a world in which we can no longer imagine a better one”.
Read more: Is America enduring a 'slow civil war'? Jeff Sharlet visits Trump rallies, a celebrity megachurch and the manosphere to find out
- Climate change
- Culture wars
- Hero's journey
- Joseph Campbell
- Naomi Klein
- Friday essay
- George Floyd
- Pat Buchanan
- Satanic panic
- Cumberland City Council
Want to write?
Write an article and join a growing community of more than 183,700 academics and researchers from 4,959 institutions.
Register now
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Guest Essay
Elite Colleges Walked Into the Israel Divestment Trap

By Gary Sernovitz
Mr. Sernovitz is a managing director of Lime Rock Management, a private equity firm that invests in oil and gas and clean energy companies and whose investors include colleges and universities.
“ Disclose, divest, we will not stop, we will not rest ” is a frequent chant ringing through pro-Palestinian college protests. Of all the actions one could advocate in the war between Israel and Hamas, protesters at Columbia listed, as their first demand, that it divest from companies and institutions that, in their view, “profit from Israeli apartheid.”
Israeli companies aren’t the only target. A proposal Columbia students put forward in December calls for divestment from Microsoft, Airbnb, Amazon and Alphabet, among others. Microsoft is tagged for supplying cloud software services to Israel; Airbnb is targeted for posting rentals in Israeli settlements in the West Bank, listings the platform said it would remove in 2018 . The company reversed this policy months later to settle lawsuits.
Administrators at some universities, including Brown and Northwestern , have agreed to talks with students about divestment as part of agreements to end campus encampments. Other schools have said point blank that they will not accede. The University of Michigan Regents, for one, in March reaffirmed “its longstanding policy to shield the endowment from political pressures and base investment decisions on financial factors such as risk and return.”
“Longstanding” is a debatable term, as it was only three years ago that the regents decided the endowment should stop investing in funds focused on certain fossil fuels (which affected the firm I work at). Before the war in Gaza, it had been pretty easy for universities to make compromises around divestment demands, but those expedient choices are haunting them now. Every investment in elite schools’ endowments is up for debate.
College endowment managers no doubt feel beleaguered that pressing moral questions regularly end up on their desks. For that desk is already covered with spreadsheets on another question: how to generate returns for universities that are nonprofits, unfathomably expensive, and desperate to not be just finishing schools for the rich. Last fiscal year, endowments over $5 billion provided 17.7 percent of their university’s budgets . This school year, Williams College charged $81,200 in tuition and fees . But spending per student was $135,600. The endowment helps make up the difference.
Yet activists view endowments with a sense of ownership. They are part of a community that owns this money. They also go after endowments because they lack better targets. It says something about the authority of ideas in our age that students lobby institutions dedicated to the advancement and propagation of knowledge mainly over what they do with their excess cash.
The mother to all divestment movements was the one that aimed at apartheid in South Africa in the 1970s and ’80s. (In 1981, Barack Obama g ave his first public speech at a divestment rally at Occidental College.) It largely worked: Over 100 colleges in the U.S. eventually agreed to at least partly divest from companies that did business in the country. Years later, many believe divestment played some role in ending apartheid in South Africa.
From 2020 to 2022, as evidence of climate change grew increasingly unavoidable, student demands for divestment from fossil fuels claimed more victories, especially at the Ivy League and other colleges with large endowments — and not coincidentally large groups of activist students telling them what to do with them. Schools’ exposure to oil and gas investments was often less than 5 percent of their endowment, so finding a way to wind down investing, in some form, in the sector was easy to do.
Every divesting institution found its own path, some more logically consistent and sincere than others. I watched some of this unfold firsthand as some schools stopped investing in our oil and gas funds while others invested in our clean energy funds. But almost all the schools succeeded in minimizing real disruption to the endowment and inducing student activists to move on.
Unlike the effects of the South Africa movement, the early impact of oil and gas divestment by colleges and others has been negligible, or even counterproductive: Oil and gas companies have needed little external financial capital , and hostility to the divestment movement has led Republican-led states such as Florida to restrict E.S.G. investing , which focuses on environmental, social and governance factors. (Note that Florida’s State Board of Administration manages almost exactly the same amount of money as the 10 largest private college endowments combined.)
What the fossil fuel divestiture did establish, however, was that university leaders can be made to concede that their endowments will, in certain circumstances, be guided by the school’s collective values, and that current students can shape those values. And by getting endowments to not invest in the sector in some way , the protesters hardened an abstract moral judgment: that the oil and gas business, and the faceless bureaucrats who work for it, are wrong . Divestment champions hope the symbolic removal of an industry’s “social license” can take on its own power, emboldening government policymakers to regulate that industry or dissuading students from seeking jobs in it.
Now the reason for divestment is Israel rather than oil. For many students it’s part of the same conversation , as I saw in a scrawled word salad sign on display at Tulane’s pro-Palestinian encampment: “From the Gulf to the sea, no genocide for oil greed.”
University leaders could follow the same playbook as they did on fossil fuels and find ways to symbolically divest without disrupting their endowments in any notable way. Based on the size of G.D.P., not investing is Israel directly would be like not investing in Colorado. And despite the chants that charge otherwise, many endowments appear to have little to no direct exposure to Israel or to many of the American companies protesters want to blacklist.
But there’s a key difference between avoiding fossil fuels and shunning Israel. The institutions that divested from oil and gas made sure to describe it as financially prudent, albeit sometimes with shallow investment logic. This time, Israel’s social license is the only thing that is on the table. And if Israel is on the table, what other countries should lose their social license? How many years must pass since what some believe to be a country’s settler colonialist period or messy wars that kill innocent civilians to make it investable?
And if divestment against Israel is carried out, when should it end? Oil and gas divesting is meant never to end; oil and gas consumption is meant to end. Divestment from South Africa ended with apartheid. So university leaders will be forced to ask an often heterogeneous group of students what would earn Israel its social license back. A cease-fire? A new Israeli government? A two-state solution? The end of Israel as a Jewish state?
The effort to identify every investment with ties to Israel is also fraught. Columbia activists could find information only on pocket-change-size ownership of certain companies, such as $69,000 of Microsoft stock. So protesters are also demanding that colleges disclose all their investments, presumably so students can research the morality of each one. However, some firms that manage parts of an endowment’s money, particularly hedge funds, don’t report individual holdings to investors: asking them for it is like asking for the secret recipe for Coke.
But even if an endowment could provide a list of every underlying investment, it would likely then be inundated for more calls to divest, for more discovered connections — however small — to Israel, and for reasons related to other offenses discoverable with an online search. Why would there not be a Taiwanese student group demanding divestment from China, to dissuade an invasion? Other students demanding divestment from Big Tech, citing students’ mental health? Others demanding divestment from all of it, the hedge funds and private equity funds whose asset managers are not exactly healing American income inequality?
The answer, of course, is that endowments can’t be in the moral adjudication business — and they should never have headed this way. This does not mean that investing should be a returns-at-any-cost exercise. But it does mean that the real world does not always provide objective answers to how to balance benefits and consequences of companies providing products and services: Carbon emissions are bad, but energy consumption is necessary. Microsoft software for the Israeli government may displease you, but Microsoft saying it won’t sell software to Israel would displease others — and probably get itself banned from working with New York State agencies .
Listen to the protesters on divestment. They will not stop. They will not rest.
But neither will the markets. They open every morning, Monday through Friday, and university budgets’ demands on endowments never go away. Tuitions are rising . Costs always go up . Colleges should debate deep moral issues and discuss the hard compromises to solve the world’s ills. But we should move those efforts to the lecture halls, away from the investment offices. Divesting is an easy chant. Investing is hard enough as it is.
Gary Sernovitz is a managing director of Lime Rock Management, a private equity firm that invests in oil and gas and clean energy companies and whose investors include colleges and universities. He is also the author of “The Counting House,” a novel about the travails of a university chief investment officer.
The Times is committed to publishing a diversity of letters to the editor. We’d like to hear what you think about this or any of our articles. Here are some tips . And here’s our email: [email protected] .
Follow the New York Times Opinion section on Facebook , Instagram , TikTok , WhatsApp , X and Threads .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Make a claim. Provide the grounds (evidence) for the claim. Explain the warrant (how the grounds support the claim) Discuss possible rebuttals to the claim, identifying the limits of the argument and showing that you have considered alternative perspectives. The Toulmin model is a common approach in academic essays.
An argumentative essay presents an argument for or against a topic. For example, if your topic is working from home, then your essay would either argue in favor of working from home (this is the for side) or against working from home.. Like most essays, an argumentative essay begins with an introduction that ends with the writer's position (or stance) in the thesis statement.
An argumentative essay attempts to convince a reader to agree with a particular argument (the writer's thesis statement). The writer takes a firm stand one way or another on a topic and then uses hard evidence to support that stance. An argumentative essay seeks to prove to the reader that one argument —the writer's argument— is the ...
An argumentative essay comprises five essential components: 1. Claim. Claim in argumentative writing is the central argument or viewpoint that the writer aims to establish and defend throughout the essay. A claim must assert your position on an issue and must be arguable. It can guide the entire argument.
Tips for Writing a Well-Written Argumentative Essay. Introduce your topic in a bold, direct, and engaging manner to captivate your readers and encourage them to keep reading. Provide sufficient evidence to justify your argument and convince readers to adopt this point of view. Consider, include, and fairly present all sides of the topic.
Argumentative essay formula & example. In the image below, you can see a recommended structure for argumentative essays. It starts with the topic sentence, which establishes the main idea of the essay. Next, this hypothesis is developed in the development stage. Then, the rebuttal, or the refutal of the main counter argument or arguments.
When you're writing a persuasive essay, you need more than just an opinion to make your voice heard. Even the strongest stance won't be compelling if it's not structured properly and reinforced with solid reasoning and evidence. Learn what elements every argumentative essay should include and how to structure it depending on your audience in this easy step-by-step guide.
In an academic argument, you'll have a lot more constraints you have to consider, and you'll focus much more on logic and reasoning than emotions. Figure 1. When writing an argumentative essay, students must be able to separate emotion based arguments from logic based arguments in order to appeal to an academic audience.
Focus Area #3: Writing the Conclusion. It's common to conclude an argumentative essay by reiterating the thesis statement in some way, either by reminding the reader what the overarching argument was in the first place or by reviewing the main points and evidence that you covered.
The argumentative essay is commonly assigned as a capstone or final project in first year writing or advanced composition courses and involves lengthy, detailed research. Expository essays involve less research and are shorter in length. Expository essays are often used for in-class writing exercises or tests, such as the GED or GRE.
Worksheets and downloads. A for and against essay - exercises 945.25 KB. A for and against essay - answers 293.66 KB. A for and against essay - essay 786.07 KB. A for and against essay - writing practice 497.45 KB.
An argumentative essay presents a specific claim or argument and supports it with evidence and reasoning. Here's an outline for an argumentative essay, along with examples for each section: 3. 1. Introduction: Hook: Start with a compelling statement, question, or anecdote to grab the reader's attention.
Argumentative Essay Example 2. Malaria is an infectious disease caused by parasites that are transmitted to people through female Anopheles mosquitoes. Each year, over half a billion people will become infected with malaria, with roughly 80% of them living in Sub-Saharan Africa.
Try our student writing prompts. In 2017, we compiled a list of 401 argumentative writing prompts, all drawn from our daily Student Opinion column. Now, we're rounding up 130 more we've ...
Lauren Green. With a Bachelor of Arts in Creative Writing from Columbia University and an MFA in Fiction from the Michener Center for Writers at the University of Texas at Austin, Lauren has been a professional writer for over a decade. She is the author of the chapbook A Great Dark House (Poetry Society of America, 2023) and a forthcoming ...
This is a 'for and against' essay where you will discuss two contrasting views about a topic. You should only give your opinion if you are explicitly instructed to do so. Learn how to write a good for and against essay. With step by step instructions, two sample argumentative compositions and a few exercises to work on expressions and ...
Developing an argument requires a significant understanding of the subject matter from all angles. Let's take a look at the steps to writing an argumentative essay: 1. Choose appropriate argumentative essay topics. Although topics for an argumentative essay are highly diverse, they are based on a controversial stance.
19. Snail Mail: Do you think handwritten cards and letters still have value in the digital age? 20. Cyberbullying: Should social media companies do more to prevent online harassment? 21. Phone ...
An argumentative essay requires you to decide on a topic and argue for or against it. You'll need to back up your viewpoint with well-researched facts and information as well. One of the hardest parts is deciding which topic to write about, but there are plenty of ideas available to get you started.
When writing an argumentative research essay, create an outline to structure the research you find as well as help with the writing process. The outline of an argumentative essay should include an introduction with thesis statement, 3 main body paragraphs with supporting evidence and opposing viewpoints with evidence to disprove, along with an ...
Counterargument. When you write an academic essay, you make an argument: you propose a thesis and offer some reasoning, using evidence, that suggests why the thesis is true. When you counter-argue, you consider a possible argument against your thesis or some aspect of your reasoning. This is a good way to test your ideas when drafting, while ...
Jon Ronson says he's 'not against' activist journalism, but evidence and fairness still need to apply. The stories in Ronson's podcast - focusing on Qanon, COVID deniers and conspiracy ...
Mr. Sernovitz is a managing director of Lime Rock Management, a private equity firm that invests in oil and gas and clean energy companies and whose investors include colleges and universities ...