- Features for Creative Writers
- Features for Work
- Features for Higher Education
- Features for Teachers
- Features for Non-Native Speakers
- Learn Blog Grammar Guide Community Events FAQ
- Grammar Guide

How to Write a Summary (Examples Included)

Ashley Shaw

Have you ever recommended a book to someone and given them a quick overview? Then you’ve created a summary before!
Summarizing is a common part of everyday communication. It feels easy when you’re recounting what happened on your favorite show, but what do you do when the information gets a little more complex?
Written summaries come with their own set of challenges. You might ask yourself:
- What details are unnecessary?
- How do you put this in your own words without changing the meaning?
- How close can you get to the original without plagiarizing it?
- How long should it be?
The answers to these questions depend on the type of summary you are doing and why you are doing it.
A summary in an academic setting is different to a professional summary—and both of those are very different to summarizing a funny story you want to tell your friends.
One thing they all have in common is that you need to relay information in the clearest way possible to help your reader understand. We’ll look at some different forms of summary, and give you some tips on each.
Let’s get started!
What Is a Summary?
How do you write a summary, how do you write an academic summary, what are the four types of academic summaries, how do i write a professional summary, writing or telling a summary in personal situations, summarizing summaries.
A summary is a shorter version of a larger work. Summaries are used at some level in almost every writing task, from formal documents to personal messages.
When you write a summary, you have an audience that doesn’t know every single thing you know.
When you want them to understand your argument, topic, or stance, you may need to explain some things to catch them up.
Instead of having them read the article or hear every single detail of the story or event, you instead give them a brief overview of what they need to know.
Academic, professional, and personal summaries each require you to consider different things, but there are some key rules they all have in common.
Let’s go over a few general guides to writing a summary first.

1. A summary should always be shorter than the original work, usually considerably.
Even if your summary is the length of a full paper, you are likely summarizing a book or other significantly longer work.
2. A summary should tell the reader the highlights of what they need to know without giving them unnecessary details.
3. It should also include enough details to give a clear and honest picture.
For example, if you summarize an article that says “ The Office is the greatest television show of all time,” but don’t mention that they are specifically referring to sitcoms, then you changed the meaning of the article. That’s a problem! Similarly, if you write a summary of your job history and say you volunteered at a hospital for the last three years, but you don’t add that you only went twice in that time, it becomes a little dishonest.
4. Summaries shouldn’t contain personal opinion.
While in the longer work you are creating you might use opinion, within the summary itself, you should avoid all personal opinion. A summary is different than a review. In this moment, you aren’t saying what you think of the work you are summarizing, you are just giving your audience enough information to know what the work says or did.

Now that we have a good idea of what summaries are in general, let’s talk about some specific types of summary you will likely have to do at some point in your writing life.
An academic summary is one you will create for a class or in other academic writing. The exact elements you will need to include depend on the assignment itself.
However, when you’re asked for an academic summary, this usually this means one of five things, all of which are pretty similar:
- You need to do a presentation in which you talk about an article, book, or report.
- You write a summary paper in which the entire paper is a summary of a specific work.
- You summarize a class discussion, lesson, or reading in the form of personal notes or a discussion board post.
- You do something like an annotated bibliography where you write short summaries of multiple works in preparation of a longer assignment.
- You write quick summaries within the body of another assignment . For example, in an argumentative essay, you will likely need to have short summaries of the sources you use to explain their argument before getting into how the source helps you prove your point.

Regardless of what type of summary you are doing, though, there are a few steps you should always follow:
- Skim the work you are summarizing before you read it. Notice what stands out to you.
- Next, read it in depth . Do the same things stand out?
- Put the full text away and write in a few sentences what the main idea or point was.
- Go back and compare to make sure you didn’t forget anything.
- Expand on this to write and then edit your summary.
Each type of academic summary requires slightly different things. Let’s get down to details.
How Do I Write a Summary Paper?
Sometimes teachers assign something called a summary paper . In this, the entire thing is a summary of one article, book, story, or report.
To understand how to write this paper, let’s talk a little bit about the purpose of such an assignment.
A summary paper is usually given to help a teacher see how well a student understands a reading assignment, but also to help the student digest the reading. Sometimes, it can be difficult to understand things we read right away.
However, a good way to process the information is to put it in our own words. That is the point of a summary paper.

A summary paper is:
- A way to explain in our own words what happened in a paper, book, etc.
- A time to think about what was important in the paper, etc.
- A time to think about the meaning and purpose behind the paper, etc.
Here are some things that a summary paper is not:
- A review. Your thoughts and opinions on the thing you are summarizing don’t need to be here unless otherwise specified.
- A comparison. A comparison paper has a lot of summary in it, but it is different than a summary paper. In this, you are just saying what happened, but you aren’t saying places it could have been done differently.
- A paraphrase (though you might have a little paraphrasing in there). In the section on using summary in longer papers, I talk more about the difference between summaries, paraphrases, and quotes.

Because a summary paper is usually longer than other forms of summary, you will be able to chose more detail. However, it still needs to focus on the important events. Summary papers are usually shorter papers.
Let’s say you are writing a 3–4 page summary. You are likely summarizing a full book or an article or short story, which will be much longer than 3–4 pages.
Imagine that you are the author of the work, and your editor comes to you and says they love what you wrote, but they need it to be 3–4 pages instead.
How would you tell that story (argument, idea, etc.) in that length without losing the heart or intent behind it? That is what belongs in a summary paper.
How Do I Write Useful Academic Notes?
Sometimes, you need to write a summary for yourself in the form of notes or for your classmates in the form of a discussion post.
You might not think you need a specific approach for this. After all, only you are going to see it.
However, summarizing for yourself can sometimes be the most difficult type of summary. If you try to write down everything your teacher says, your hand will cramp and you’ll likely miss a lot.
Yet, transcribing doesn’t work because studies show that writing things down (not typing them) actually helps you remember them better.
So how do you find the balance between summarizing the lessons without leaving out important points?
There are some tips for this:
- If your professor writes it on the board, it is probably important.
- What points do your textbooks include when summarizing information? Use these as a guide.
- Write the highlight of every X amount of time, with X being the time you can go without missing anything or getting tired. This could be one point per minute, or three per five minutes, etc.
How Do I Create an Annotated Biography?
An annotated bibliography requires a very specific style of writing. Often, you will write these before a longer research paper . They will ask you to find a certain amount of articles and write a short annotation for each of them.
While an annotation is more than just a summary, it usually starts with a summary of the work. This will be about 2–3 sentences long. Because you don’t have a lot of room, you really have to think about what the most important thing the work says is.
This will basically ask you to explain the point of the article in these couple of sentences, so you should focus on the main point when expressing it.
Here is an example of a summary section within an annotation about this post:
“In this post, the author explains how to write a summary in different types of settings. She walks through academic, professional, and personal summaries. Ultimately, she claims that summaries should be short explanations that get the audience caught up on the topic without leaving out details that would change the meaning.”

Can I Write a Summary Within an Essay?
Perhaps the most common type of summary you will ever do is a short summary within a longer paper.
For example, if you have to write an argumentative essay, you will likely need to use sources to help support your argument.
However, there is a good chance that your readers won’t have read those same sources.
So, you need to give them enough detail to understand your topic without spending too much time explaining and not enough making your argument.
While this depends on exactly how you are using summary in your paper, often, a good amount of summary is the same amount you would put in an annotation.
Just a few sentences will allow the reader to get an idea of the work before moving on to specific parts of it that might help your argument.
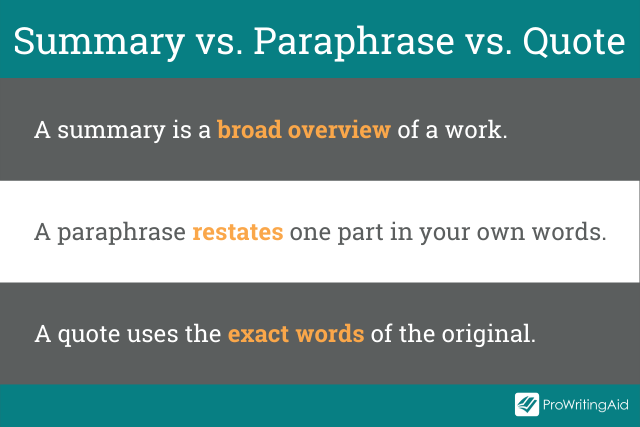
What’s the Difference Between Summarizing, Paraphrasing, and Using Quotes?
One important thing to recognize when using summaries in academic settings is that summaries are different than paraphrases or quotes.
A summary is broader and more general. A paraphrase, on the other hand, puts specific parts into your own words. A quote uses the exact words of the original. All of them, however, need to be cited.
Let’s look at an example:
Take these words by Thomas J. Watson:
”Would you like me to give you a formula for success? It’s quite simple, really. Double your rate of failure. You are thinking of failure as the enemy of success. But it isn’t as all. You can be discouraged by failure—or you can learn from it. So go ahead and make mistakes. Make all you can. Because, remember, that’s where you will find success.”
Let’s say I was told to write a summary, a paraphrase, and a quote about this statement. This is what it might look like:
Summary: Thomas J. Watson said that the key to success is actually to fail more often. (This is broad and doesn’t go into details about what he says, but it still gives him credit.)
Paraphrase: Thomas J. Watson, on asking if people would like his formula for success, said that the secret was to fail twice as much. He claimed that when you decide to learn from your mistakes instead of being disappointed by them, and when you start making a lot of them, you will actually find more success. (This includes most of the details, but it is in my own words, while still crediting the source.)
Quote: Thomas J. Watson said, ”Would you like me to give you a formula for success? It’s quite simple, really. Double your rate of failure. You are thinking of failure as the enemy of success. But it isn’t at all. You can be discouraged by failure—or you can learn from it. So go ahead and make mistakes. Make all you can. Because, remember, that’s where you will find success.” (This is the exact words of the original with quotation marks and credit given.)
Avoiding Plagiarism
One of the hardest parts about summarizing someone else’s writing is avoiding plagiarism .

That’s why I have a few rules/tips for you when summarizing anything:
1. Always cite.
If you are talking about someone else’s work in any means, cite your source. If you are summarizing the entire work, all you probably need to do (depending on style guidelines) is say the author’s name. However, if you are summarizing a specific chapter or section, you should state that specifically. Finally, you should make sure to include it in your Work Cited or Reference page.
2. Change the wording.
Sometimes when people are summarizing or paraphrasing a work, they get too close to the original, and actually use the exact words. Unless you use quotation marks, this is plagiarism. However, a good way to avoid this is to hide the article while you are summarizing it. If you don’t have it in front of you, you are less likely to accidentally use the exact words. (However, after you are done, double check that you didn’t miss anything important or give wrong details.)
3. Use a plagiarism checker.
Of course, when you are writing any summary, especially academic summaries, it can be easy to cross the line into plagiarism. If this is a place where you struggle, then ProWritingAid can help.
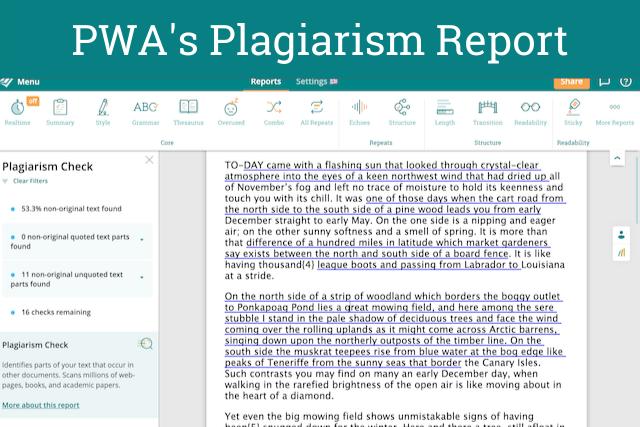
Just use our Plagiarism Report . It’ll highlight any unoriginal text in your document so you can make sure you are citing everything correctly and summarizing in your own words.
Find out more about ProWritingAid plagiarism bundles.
Along with academic summaries, you might sometimes need to write professional summaries. Often, this means writing a summary about yourself that shows why you are qualified for a position or organization.
In this section, let’s talk about two types of professional summaries: a LinkedIn summary and a summary section within a resume.
How Do I Write My LinkedIn Bio?
LinkedIn is all about professional networking. It offers you a chance to share a brief glimpse of your professional qualifications in a paragraph or two.
This can then be sent to professional connections, or even found by them without you having to reach out. This can help you get a job or build your network.
Your summary is one of the first things a future employer might see about you, and how you write yours can make you stand out from the competition.

Here are some tips on writing a LinkedIn summary :
- Before you write it, think about what you want it to do . If you are looking for a job, what kind of job? What have you done in your past that would stand out to someone hiring for that position? That is what you will want to focus on in your summary.
- Be professional . Unlike many social media platforms, LinkedIn has a reputation for being more formal. Your summary should reflect that to some extent.
- Use keywords . Your summary is searchable, so using keywords that a recruiter might be searching for can help them find you.
- Focus on the start . LinkedIn shows the first 300 characters automatically, and then offers the viewer a chance to read more. Make that start so good that everyone wants to keep reading.
- Focus on accomplishments . Think of your life like a series of albums, and this is your speciality “Greatest Hits” album. What “songs” are you putting on it?

How Do I Summarize My Experience on a Resume?
Writing a professional summary for a resume is different than any other type of summary that you may have to do.
Recruiters go through a lot of resumes every day. They don’t have time to spend ages reading yours, which means you have to wow them quickly.
To do that, you might include a section at the top of your resume that acts almost as an elevator pitch: That one thing you might say to a recruiter to get them to want to talk to you if you only had a 30-second elevator ride.

If you don’t have a lot of experience, though, you might want to skip this section entirely and focus on playing up the experience you do have.
Outside of academic and personal summaries, you use summary a lot in your day-to-day life.
Whether it is telling a good piece of trivia you just learned or a funny story that happened to you, or even setting the stage in creative writing, you summarize all the time.
How you use summary can be an important consideration in whether people want to read your work (or listen to you talk).
Here are some things to think about when telling a story:
- Pick interesting details . Too many and your point will be lost. Not enough, and you didn’t paint the scene or give them a complete idea about what happened.
- Play into the emotions . When telling a story, you want more information than the bare minimum. You want your reader to get the emotion of the story. That requires a little bit more work to accomplish.
- Focus. A summary of one story can lead to another can lead to another. Think about storytellers that you know that go off on a tangent. They never seem to finish one story without telling 100 others!

To wrap up (and to demonstrate everything I just talked about), let’s summarize this post into its most essential parts:
A summary is a great way to quickly give your audience the information they need to understand the topic you are discussing without having to know every detail.
How you write a summary is different depending on what type of summary you are doing:
- An academic summary usually gets to the heart of an article, book, or journal, and it should highlight the main points in your own words. How long it should be depends on the type of assignment it is.
- A professional summary highlights you and your professional, academic, and volunteer history. It shows people in your professional network who you are and why they should hire you, work with you, use your talents, etc.
Being able to tell a good story is another form of summary. You want to tell engaging anecdotes and facts without boring your listeners. This is a skill that is developed over time.
Take your writing to the next level:

20 Editing Tips from Professional Writers
Whether you are writing a novel, essay, article, or email, good writing is an essential part of communicating your ideas., this guide contains the 20 most important writing tips and techniques from a wide range of professional writers..
Be confident about grammar
Check every email, essay, or story for grammar mistakes. Fix them before you press send.
Ashley Shaw is a former editor and marketer/current PhD student and teacher. When she isn't studying con artists for her dissertation, she's thinking of new ways to help college students better understand and love the writing process. You can follow her on Twitter, or, if you prefer animal accounts, follow her rabbits, Audrey Hopbun and Fredra StaHare, on Instagram.
Get started with ProWritingAid
Drop us a line or let's stay in touch via :
Skip to content. | Skip to navigation
Masterlinks
- About Hunter
- One Stop for Students
- Make a Gift
- Access the Student Guide
- Apply to Become a Peer Tutor
- Access the Faculty Guide
- Request a Classroom Visit
- Refer a Student to the Center
- Request a Classroom Workshop
- The Writing Process
- The Documented Essay/Research Paper
- Writing for English Courses
- Writing Across the Curriculum
- Grammar and Mechanics
- Business and Professional Writing
- CUNY TESTING
- | Workshops
- Research Information and Resources
- Evaluating Information Sources
- Writing Tools and References
- Reading Room
- Literary Resources
- ESL Resources for Students
- ESL Resources for Faculty
- Teaching and Learning
- | Contact Us
When you underline and annotate a text, when you ask yourself questions about its contents, when you work out an outline of its structure, you are establishing your understanding of what you are reading. When you write a summary, you are demonstrating your understanding of the text and communicating it to your reader.
To summarize is to condense a text to its main points and to do so in your own words. To include every detail is neither necessary nor desirable. Instead, you should extract only those elements that you think are most important—the main idea (or thesis) and its essential supporting points, which in the original passage may have been interwoven with less important material.
Many students make the mistake of confusing summary with analysis. They are not the same thing. An analysis is a discussion of ideas, techniques, and/or meaning in a text. A summary, on the other hand, does not require you to critique or respond to the ideas in a text. When you analyze a piece of writing, you generally summarize the contents briefly in order to establish for the reader the ideas that your essay will then go on to analyze, but a summary is not a substitute for the analysis itself.
If you are writing a literature paper, for example, your teacher probably does not want you to simply write a plot summary. You may include some very brief summary within a literature paper, but only as much as necessary to make your own interpretation, your thesis, clear.
It is important to remember that a summary is not an outline or synopsis of the points that the author makes in the order that the author gives them. Instead, a summary is a distillation of the ideas or argument of the text. It is a reconstruction of the major point or points of development of a text, beginning with the thesis or main idea, followed by the points or details that support or elaborate on that idea.
If a text is organized in a linear fashion, you may be able to write a summary simply by paraphrasing the major points from the beginning of the text to the end. However, you should not assume that this will always be the case. Not all writers use such a straightforward structure. They may not state the thesis or main idea immediately at the beginning, but rather build up to it slowly, and they may introduce a point of development in one place and then return to it later in the text.
However, for the sake of clarity, a summary should present the author’s points in a straightforward structure. In order to write a good summary, you may have to gather minor points or components of an argument from different places in the text in order to summarize the text in an organized way. A point made in the beginning of an essay and then one made toward the end may need to be grouped together in your summary to concisely convey the argument that the author is making. In the end, you will have read, digested, and reconstructed the text in a shorter, more concise form.
WHEN AND HOW TO SUMMARIZE
There are many instances in which you will have to write a summary. You may be assigned to write a one or two page summary of an article or reading, or you may be asked to include a brief summary of a text as part of a response paper or critique. Also, you may write summaries of articles as part of the note-taking and planning process for a research paper, and you may want to include these summaries, or at least parts of them, in your paper. The writer of a research paper is especially dependent upon summary as a means of referring to source materials. Through the use of summary in a research paper, you can condense a broad range of information, and you can present and explain the relevance of a number of sources all dealing with the same subject.
You may also summarize your own paper in an introduction in order to present a brief overview of the ideas you will discuss throughout the rest of the paper.
Depending on the length and complexity of the original text as well as your purpose in using summary, a summary can be relatively brief—a short paragraph or even a single sentence—or quite lengthy—several paragraphs or even an entire paper.
QUALITIES OF A SUMMARY
A good summary should be comprehensive, concise, coherent, and independent . These qualities are explained below:
- A summary must be comprehensive: You should isolate all the important points in the original passage and note them down in a list. Review all the ideas on your list, and include in your summary all the ones that are indispensable to the author's development of her/his thesis or main idea.
- A summary must be concise: Eliminate repetitions in your list, even if the author restates the same points. Your summary should be considerably shorter than the source. You are hoping to create an overview; therefore, you need not include every repetition of a point or every supporting detail.
- A summary must be coherent: It should make sense as a piece of writing in its own right; it should not merely be taken directly from your list of notes or sound like a disjointed collection of points.
- A summary must be independent: You are not being asked to imitate the author of the text you are writing about. On the contrary, you are expected to maintain your own voice throughout the summary. Don't simply quote the author; instead use your own words to express your understanding of what you have read. After all, your summary is based on your interpretation of the writer's points or ideas. However, you should be careful not to create any misrepresentation or distortion by introducing comments or criticisms of your own.
TWO TECHNIQUES FOR WRITING SUMMARIES
Summarizing shorter texts (ten pages or fewer).
- Write a one-sentence summary of each paragraph.
- Formulate a single sentence that summarizes the whole text.
- Write a paragraph (or more): begin with the overall summary sentence and follow it with the paragraph summary sentences.
- Rearrange and rewrite the paragraph to make it clear and concise, to eliminate repetition and relatively minor points, and to provide transitions. The final version should be a complete, unified, and coherent.
Summarizing Longer Texts (more than ten pages)
- Outline the text. Break it down into its major sections—groups of paragraphs focused on a common topic—and list the main supporting points for each section.
- Write a one or two sentence summary of each section.
- Formulate a single sentence to summarize the whole text, looking at the author's thesis or topic sentences as a guide.
- Write a paragraph (or more): begin with the overall summary sentence and follow it with the section summary sentences.
- Rewrite and rearrange your paragraph(s) as needed to make your writing clear and concise, to eliminate relatively minor or repetitious points, and to provide transitions. Make sure your summary includes all the major supporting points of each idea. The final version should be a complete, unified, and coherent.
Document Actions
- Public Safety
- Website Feedback
- Privacy Policy
- CUNY Tobacco Policy
- Utility Menu
GA4 Tracking Code
Gen ed writes, writing across the disciplines at harvard college, what it is and why it's useful.
Summary asks writers to identify and restate in their own words the most important elements of another writer's text and, in doing do, capture the relative importance of different moments in that text as well as their logical relationship to one another. In many contexts summary is a formative assignment that's a step in a larger essay or project; in other contexts, though, it might be its own standalone assignment.
For a scholarly article, summary might mean stating the source's central claim and reconstructing the general features of its argument, using key terms and concepts. For a novel or film, it might mean unpacking plot into the linear sequence of events in a "story" and introducing the most important figures, turning points, or literary-critical concepts. The specific approach any summary exercise takes will differ based on what you're trying to do with it in your class, but it can be a really useful point of departure (or reset) at almost any point in a writing assignment. Summary is really useful for a few reasons:
It helps students test—and often improve—their understanding of a text
Being able to clearly and accurately capture a writer’s argument in your own words is always a good, if not necessary, step before engaging in analysis of it
In classes with a research essay component, summary offers good practice for generating annotated bibliographies.
Typical learning objectives for summary: identify central claims and key terms, demonstrate understanding of argument, demonstrate understanding of narrative sequences, identifying roles of evidence, paraphrase, concision, use of strong verbs
Common types of summary and related types: synopsis, argument reconstruction, abstracts, annotated bibliography
How to Teach It: Framing + Practice
While it's often a point of departure for other kinds of writing, summary itself needs framing and practice in order to make it the reliable foundation those other kinds of writing are going to build off of.
When asking students to summarize a text they've read, make it clear what the goals of the exercise will be. Is the goal to make sure everyone is on the same page about the basic outlines of a reading before discussing it in class? Is the goal to highlight the complexities of a seemingly straightforward argument? Will students be using elements of the summary in an upcoming essay or project? (See "Why It's Useful" above for ideas on framing the possible roles of summary as an exercise).
Summary can be something writers practice with or without a lot of "teaching" on the front end. Allowing students to try their hand at a summary before introducing principles can be a low-stakes way to find out where their intuitions are at with the skill. Or you can introduce the principles at the start—it's productive in both directions. Once students have drafted summaries, it can be a simple in-class exercise to have them compare their drafts with one another in groups: What were elements everyone included, or only one person, etc.? What are probably the elements any summary would include, versus the elements certain kinds of summary might focus more on? Does everyone agree on what the central claim or most important examples/evidence are? Or the order of logical development or events? Or maybe substantive differences will emerge about the nature of the source's main ideas. Getting all of these questions (and where reasonable areas of convergence and divergence lie) sorted out early in the process can bake in a lot of success to any subsequent steps of a writing assignment.
Sample Exercises and Links to Other Resources
- The in-class workshop on summary that's also posted under "Formative Writing Assignments"
- A summary and paraphrase exercise with sample text (aimed more at Humanities audiences)
- A summary prompt (that's also pointing beyond summary to the beginning of more analytical kinds of writing)
- Common Pitfalls
- Advice on Timing
- In addition to giving students the chance to work through complex sources, summary exercises can also be a great, low-stakes way to practice citation norms and styles.
- Summaries tend not to include much direct quote, but they do offer a place to practice using quick moments of quotation, e.g., with key terms, where it's important to make it clear what terms or ideas are being drawn from the source (and perhaps, in an analytical paper, directly analyzed).
- Having students summarize a source at different scales (150 words, then 50, then 1 or 2 sentences) is a great way to get them thinking about what the central ideas and most important elements of a source actually are.
- When summary is "the assignment" (and not just a step in a larger process), it's important to make that sure students know they're NOT supposed to be making an argument. Otherwise, many students might reasonably think that adding some argument is either a) fine or b) implicitly what the "best" student would move ahead with.
- Summary in general lends itself to shorter timeframes, ranging from "read source x and try summarizing it for next class" to "after we talk about source x in class you'll work on summarizing it for next week" to "now that we've talked about source x, let's take 20 minutes in small groups to sketch out what would be in a summary of it."
- These approaches can work separately or together, so timing things can work with different timelines and be adapted based on what students need.
What It Can Build Up To
- DIY Guides for Analytical Writing Assignments

- Types of Assignments
- Unpacking the Elements of Writing Prompts
- Formative Writing Assignments
- Single-Source Analysis
- Comparative Analysis
- Research Essays
- Multi-Modal or Creative Projects
- Giving Feedback to Students
Assignment Decoder
how to write a summary
A step-by-step guide to writing a great summary.
A summary of a literary work isn't just a plain-old synopsis. It's a valuable study tool, a foundational element of all kinds of essays, a common testing mechanism, and one of the basics of literary analysis.
Whether you're in high school or college, developing a deep understanding of how and when to summarize a book or text is a valuable skill. Doing so might require a little more knowledge and effort than you'd think.
That's why we're covering all aspects of summaries, from study tools to plot summaries, below.
What Is a Summary?
A summary is a brief overview of a text (or movie, speech, podcast, etcetera) that succinctly and comprehensively covers the main ideas or plot points.
Sounds simple, right? Well, there are a lot of unique characteristics that differentiate summaries from other commentary, such as analyses, book reviews, or outlines.
Summaries are:
- In your own words. It's important that you don't just copy and paste the writer's words (in fact, that's plagiarizing). Writing the key points of a work in your own words indicates your comprehension and absorption of the material.
- Objective. While a summary should be in your own words, it shouldn't contain your opinions. Instead, you should gather the main points and intentions of the writer and present them impartially. (If you include your opinions, it instead becomes an analysis or review.)
- More than paraphrasing. Many students fall into the trap of simply paraphrasing—plainly restating the ideas or events of the work. (Is our definition starting to sound contradictory? We told you it wasn't straightforward!) Rather than recounting the events or ideas in a work chronologically or in the order they're presented, instead consider the broad scope of how they all contribute to the narrative or argument.
- Short. There are no strict rules regarding length, only that it is concise. It's largely dependent on the length of the text it summarizes: longer texts, longer summaries. It also depends on the assignment or objective. However, most are about one to two paragraphs in length.
- Comprehensive. Yes, it's another seemingly contradictory descriptor, but an important one. Summaries are comprehensive, meaning they cover all of the main plot points or ideas in a work (so they inherently contain "spoilers"). You should present those ideas in a way that condenses them into an inclusive, but not exhaustive, recounting in order to keep it short.
- Straightforward (even if the text isn't). A good summary should be easy to comprehend, presenting the reader with a simple but all-encompassing understanding of the work at hand. With complex texts, summaries can be particularly useful because they distill big, complicated ideas into a bite-sized package.
When to Write a Summary
Like so many elements of literary analysis, summaries are misunderstood. We've already explained why they aren't as simple as most people think, but neither are their uses.
Summary writing is a useful skill in a variety of circumstances, both in and outside the English and Language Arts classrooms.
Readers, writers, teachers, and students can use summaries:
- As a study tactic. The ability to summarize a book or text indicates that you've absorbed and understand the material. Plus, writing down notes (as in a summary) is a great way to retain material. Try summarizing at the end of a book chapter, after each section of an article, or periodically in textbooks. Doing so will help you digest the material you've just read, confirming you understood and retained the information therein. Stopping frequently to summarize is most effective because you're less likely to forget important plot points or ideas.
- As an assignment. Teachers and professors often ask students to summarize a text as a test to confirm they read and understood the material. Before heading into class—especially if you have a test or quiz scheduled—try practicing summarizing the text. Write it down (rather than practicing it out loud or in your head) so that you can review your ideas and ensure you're presenting them succinctly and sensibly.
- As part of an essay. If you're referencing a book or article in your own paper, you might need to summarize the source as the foundation for your argument. In this case, your summary should be particularly short so the reader doesn't lose sight of your own argument and intention. Introduce the name of the work and its author, then use one sentence (two at most) to describe their objective and how it relates to your own.
- As part of a review. Summaries are very useful in an academic setting, but they have their place outside of it too. Whether you're on a book review site or just sharing a recommendation with a friend, being able to succinctly write a book summary (with or without spoilers) will help others to make their own judgements of a book.
Your Step-by-Step Guide for How to Write a Summary
Step 1: read the work .
Summaries are often perceived as a workaround for reading the work itself. That's not a great strategy under most circumstances because you tend to lose a lot of the details and nuance of a work, but it's particularly impractical to do so when writing about the work.
Remember, a summary is supposed to present your perception of the work as a whole. So in order to develop that perception, you have to first read the original text.
Step 2: Take Notes
As you read the work, simultaneously take notes. If you own the book, it might be helpful to add your notes to the margins or highlight passages that are particularly relevant or capture a key idea. If you don't own the book, try taking notes on your computer or in a notebook. You can still notate important passages by writing down the page and paragraph number or writing an abbreviated version of the quotation. Alternatively, try marking key passages with sticky notes or tabs.
It might also be helpful to write out a short outline of the work as you go. While you won't want to use this verbatim (remember, you shouldn't just paraphrase the work), it can help you establish and remember the text's framework.
Step 3: Identify the Author's Thesis Statement, Objective, or Main Point
In some works, such as a journal article, a writer will provide a thesis statement. A thesis statement is a one-sentence synopsis of the author's argument and intention. A thesis statement can be really helpful in forming the backbone of your own summary, just as it forms the backbone of the essay.
However, even when a thesis statement isn't present—like in a novel—the writer always has an objective or main idea. You should always identify this idea and use it to form the foundation of your summary.
The main point might be apparent at the outset of the work. Other times, the author won't present it until the conclusion. Sometimes you might identify multiple objectives throughout the work. That's why it's important, as you read, to note any ideas that might be the main idea. Even those that aren't the most important will likely remain relevant.
Step 4: Note Other Important Elements
If something stands out to you about the work and seems to play an important role in the text's overall narrative or structure, make a note about it. This could be a recurring theme, an incident in the storyline, or a deviation from the overall argument.
As you identify and note important elements and moments in the work, the structure of your summary should begin to fall into place.
Step 5: Prepare to Write Your Summary
Once you've finished reading the work, review your notes and highlight the key points that came to light. Remember, your summary should be objective, so disregard any opinions you might have noted about the work. You should introduce the thesis or objective, briefly encapsulate the important ideas and moments from the work, and end with a conclusion that ties those ideas to the objective. Keep this structure in mind as you begin.
Step 6: Begin by Introducing the Work
As you begin, introduce the work, its author, and, if relevant, the context.
Depending on your situation—for example, if your teacher or professor has asked you to summarize a work as part of an assignment or quiz—this might seem redundant. However, it is standard practice to begin by introducing the work, even if the reader already knows what you're writing about.
Example: In The Great Gatsby , F. Scott Fitzgerald...
Step 7: Present the Thesis, Main Idea, or Central Argument
Once you've introduced the work, your priority is to clearly define the author's thesis, important point, or central argument. As mentioned above, sometimes the author presents this idea clearly and succinctly at the outset of their work; at other times, it's buried deep in the text.
Regardless of how the main idea is presented in the work, it should be front and center in your summary. Some teachers might refer to this as a "topic sentence" or "introductory sentence." This is the central point around which you will construct the rest of your writing. As you progress, you'll highlight other ideas or occurrences that relate or contribute to this main idea, so it's important that your representation of it is easily understood.
Example: In The Great Gatsby , F. Scott Fitzgerald uses the story of Jay Gatsby as a symbol of the social stratification, greed, and indulgence of 1920s America.
Step 8: Briefly Discuss the Important Elements of the Work
After identifying the thesis or central argument, you should provide a brief overview of the work's other elements, ideas, and plot points. For the most part, the information you present throughout this section should bolster the thesis presented previously. Each sentence should serve as a supporting point for the topic sentence. Don't simply list ideas or plot points, but show how they're connected and inform the work as a whole. Of course, there may also be important elements of the work that are not directly tied to the main idea; it's ok to include these if you feel they are vital to understanding the work.
When writing the body, you should consciously and intentionally leave out unnecessary details. They tend to bog down your writing and lose the reader.
Example: The narrator, Nick Carraway, moves to New York's "West Egg," where he reunites with his cousin, Daisy, and her husband, Tom Buchanan. Fitzgerald clearly delineates social lines between West Egg (new money) and East Egg (old money), where Tom and Daisy reside.
Nick attends a lavish party thrown by his neighbor, Jay Gatsby, and learns Jay formerly had a relationship with Daisy. The two reignite their forbidden affair. Tom reveals to Daisy that Gatsby earned his money illegally, through smuggling alcohol, and is actually a man of humble Midwestern origins. Daisy and Gatsby try to run away together, but Daisy accidentally runs over Tom's mistress. Tom, eager to exact revenge, convinces his mistress' husband that Gatsby was to blame in her death, and he murders Gatsby before committing suicide. Few of Gatsby's many friends attend his funeral.
Step 9: Write a Conclusion that Ties It All Together
Much like you introduce the author's major point at the outset of your summary, you should revisit it as you close out your writing. If you presented the author's main idea in the introduction, and then bolstered that main idea by recollecting plot points or important elements from the work, your conclusion should then reiterate how those elements relate to the main idea.
Example: Though Gatsby subscribed to the extravagance of his peers, his efforts to fit into the upper echelon of West and East Egg were negated by his humble origins; always out of place, he was rejected for his social class as much as his perceived crimes.
Step 10: Edit
Before submitting your work, read it in full, and edit out any superfluous and redundant information. It's likely that unnecessary details snuck in as you were writing, and you might find that certain plot points just feel unnecessary within the scope of your finished product.
In addition to editing for content, be sure to edit it closely for grammatical or spelling errors. Even if your summary is well thought out, its expertise is compromised if it's full of errors!
How to Write a Plot Summary
The step-by-step guide to writing an effective summary, outlined above, applies to most summaries. However, each type has its own unique elements outside of those standard requirements.
A plot or book summary, for example, should encapsulate the plot of a short story or novel. When writing one, there are unique strategies to follow.
Dos of Writing a Plot Summary
- Note plot points as the book or story unfolds. Especially in longer novels, it can be difficult to keep track of the twists and turns in the storyline. That's why we recommend taking notes as you read.
- Use online study guides for inspiration. Websites like SuperSummary provide in-depth summaries free of charge. While this is a good starting point when writing your own, it should only be for inspiration. Don't copy examples online (that's plagiarism!).
- Be sure to cover the three main arcs of every story: the exposition, climax, and conclusion. The exposition is the moment when the conflict or driving narrative is introduced. The climax is when that conflict comes to a head, and the narrative reaches its most dramatic moments. The conclusion is when the conflict is resolved or the story comes to an end. You should also include any inciting incidents (the first domino in a plot point).
- Connect the dots. Throughout, you should demonstrate an understanding of how events and characters are related, rather than introducing each element as an independent variable. Remember, you should tie each plot point back to the main idea.
Don'ts of Writing a Plot Summary
- Don't just regurgitate the storyline. Rather than drone through the story plot point by plot point, you should highlight key moments in the narrative and direct them back to the author's objective.
- Avoid repetitive phrases like "then" or "next." A key indication you're just repeating the storyline point by point is utilizing a phrase like "then" or "next." While you should recount the major incidents of the narrative, it shouldn't feel so formulaic.
- Don't let it drag on. Books are long, but summarizing a book should still be short. While it depends on the assignment and the work in question, your summary should be 200 to 600 words, max.
Example : In The Great Gatsby , F. Scott Fitzgerald uses the story of Jay Gatsby as a symbol of the social stratification, greed, and indulgence of 1920s America. The narrator, Nick Carraway, moves to New York's "West Egg," where he reunites with his cousin, Daisy, and her husband, Tom Buchanan. Fitzgerald clearly delineates social lines between West Egg (new money) and East Egg (old money), where Tom and Daisy reside.
Nick attends a lavish party thrown by his neighbor, Jay Gatsby, and learns he formerly had a relationship with Daisy. When the two reignite their forbidden affair, disaster ensues. Tom reveals to Daisy that Gatsby earned his money illegally, through smuggling alcohol, and is actually a man of humble Midwestern origins. Daisy and Gatsby try to run away together, but Daisy accidentally runs over Tom's mistress. Tom, eager to exact revenge, convinces his mistress' husband that Gatsby was to blame in her death, and he murders Gatsby before committing suicide. Few of Gatsby's many friends attend his funeral.
Though Gatsby subscribed to the extravagance of his peers, his efforts to fit into the upper echelon of West and East Egg were negated by his humble origins; always out of place, he was rejected for his social class as much as his perceived crimes.
For an in-depth analysis of The Great Gatsby , check out the our study guide (we have an audio guide, too!).
How to Summarize an Article or Essay
The nature of an article or essay is quite different from a novel or short story, and in many ways, your summary should be too. The outline above remains the same, but the details are different.
Here's what you should and shouldn't do when writing your article summary.
Dos of Writing an Article Summary
- Skim the original article first. To develop a basic understanding of the article and the writer's objectives, skim the content before reading it closely. Doing so will help you to identify some of the key points and then pay attention to the arguments around them when you read the article in full.
- Then read the article closely, marking key passages and ideas. Noting important ideas as you read will help you develop a deeper understanding of the writer's intentions.
- Note headings and subheadings, which likely identify important points. In articles and essays, the author often utilizes subheadings to introduce their most important ideas. These subheadings can help guide your own writing.
- Keep it short. The rule of brevity applies to article summaries too. In fact, because articles are usually short compared to novels or books, your text should be correlatively brief. And if you're utilizing the work as part of your own essay or argument, just a couple sentences will do.
Don'ts of Writing an Article Summary
- Don't ignore the conclusion. When reading a long article or essay, it can be tempting to overlook the conclusion and focus on the body paragraphs of the article. However, the conclusion is often where the author most clearly outlines their findings and why they matter. It can serve as a great foundation for your own writing.
- Don't copy anything from the article directly—always paraphrase. If you copy any passages word-for-word from the article, be sure to identify them as quotations and attribute them to the author. Even this should be done sparingly. Instead, you should encapsulate their ideas within your own, abbreviated words.
- Don't forget to include proper citations. If you do include a direct quotation from the article, be sure to properly cite them. You can learn how to properly cite quotations in our Academic Citation Resource Guide .
Example Summary of "Gatsby as a Drowned Sailor" : In her essay, "Gatsby as a Drowned Sailor," Margaret Lukens posits that a major, and often overlooked, motif in The Great Gatsby is that of the "drowned sailor." The novel, she points out, is immersed in nautical symbols and themes, particularly in the scenes surrounding Jay Gatsby. For example, Gatsby grew up on the shores of Lake Superior, now owns a house on the Long Island Sound, and supposedly spends much of his time on his boat.
Lukens nods to the nautical imagery throughout Gatsby's lavish party, as well as Nick's interactions with Gatsby. Many of these, she argues, foreshadow Gatsby's death in his pool. Even his funeral is a testament to the motif, with the few attendees soaked to the skin with rain. Lukens presents a thorough case for the overarching nautical motif in The Great Gatsby and her argument that though Gatsby hooked a big one, ultimately it was "the one that got away."
FAQs: How to Write a Book Summary
How do you summarize without plagiarizing .
By its very nature, a summary isn't plagiarizing because it should be written in your own words. However, there are cases where it might be difficult to identify an appropriate synonym, and the phrase remains somewhat close to the original. In this scenario, just be sure to differentiate the rest of the phrase as much as possible. And if you need to include a direct quote from the work, be sure to appropriately cite it.
How to write a summary and a reaction?
In some cases, your teacher may ask you to write a summary and a reaction. Whereas a summary is objective, a reaction is a matter of opinion. So in this case, you should present the actions or ideas of the work, then respond to those actions and ideas with your personal thoughts.
Why write a summary?
A summary is a helpful tool many educators use to test their students' comprehension of a text. However, it is also a useful study tactic because recounting what you read can help you organize and retain information.

- Walden University
- Faculty Portal
Common Assignments: Summary
For each source listed, you will begin with a summary of the information you found in that specific source. The summary section gives your reader an overview of the important information from that source. Remember that you are focusing on a source's method and results, not paraphrasing the article's argument or evidence.
The questions below can help you produce an appropriate, scholarly summary:
- What is the topic of the source?
- What actions did the author perform within the study and why?
- What were the methods of the author?
- What was the theoretical basis for the study?
- What were the conclusions of the study?
Remember, a summary should be similar to an abstract of a source and written in past tense (e.g. "The authors found that…" or "The studies showed…"), but it should not be the source's abstract. Each summary should be written in your own words.
Summarizing Video Playlist
Note that these videos were created while APA 6 was the style guide edition in use. There may be some examples of writing that have not been updated to APA 7 guidelines.

Related Resources
Didn't find what you need? Email us at [email protected] .
- Previous Page: Formatting
- Next Page: Critique/Analysis
- Office of Student Disability Services
Walden Resources
Departments.
- Academic Residencies
- Academic Skills
- Career Planning and Development
- Customer Care Team
- Field Experience
- Military Services
- Student Success Advising
- Writing Skills
Centers and Offices
- Center for Social Change
- Office of Academic Support and Instructional Services
- Office of Degree Acceleration
- Office of Research and Doctoral Services
- Office of Student Affairs
Student Resources
- Doctoral Writing Assessment
- Form & Style Review
- Quick Answers
- ScholarWorks
- SKIL Courses and Workshops
- Walden Bookstore
- Walden Catalog & Student Handbook
- Student Safety/Title IX
- Legal & Consumer Information
- Website Terms and Conditions
- Cookie Policy
- Accessibility
- Accreditation
- State Authorization
- Net Price Calculator
- Contact Walden
Walden University is a member of Adtalem Global Education, Inc. www.adtalem.com Walden University is certified to operate by SCHEV © 2024 Walden University LLC. All rights reserved.
How To Write A High-Impact Executive Summary
By Derek Jansen | January 2018

In this post, I’ll deconstruct the often-misunderstood executive summary and show you how to develop a high-impact executive summary for your assignment, research report or even your dissertation or thesis.
So, what is an executive summary?
An executive summary (sometimes called an abstract ) is quite simply a summary of summaries. In other words, an executive summary provides a concise summary of each of your assignment or report chapters/sections . More specifically, it should communicate the key points/insights/findings/suggestions from the following chapters:
- Introduction
- Recommendations
- Implementation (if applicable)
- Reflection (if applicable)
I’ll discuss which key points from each section need to be addressed a bit later. On a separate note – if you’re writing an executive summary for a dissertation or thesis, all of the concepts described in this post will still apply to you, however, you’ll include an additional paragraph about your methodology, and you’ll likely spend more word count discussing your analysis findings.
The 4 Important Attributes Of An Exec Summary
Before I discuss what goes into the executive summary, let’s quickly look at 4 attributes that make for a strong executive summary:
#1 – It should be able to stand alone.
The executive summary should be able to stand independently as an informative document . In other words, the reader should be able to grasp your broad argument without having to read the full document. Further reading should be purely for attaining more detail. Simply put, the executive summary should be a “Mini-Me” of the assignment.
This independence means that anything you write in the executive summary will need to be re-stated in the body of your assignment. A common mistake that students make is to introduce key points in the executive summary and then not discuss them again in the document – accordingly, the marker must view the main document as missing these key points. Simply put – make sure you discuss key points in both the executive summary and the main body . It will feel repetitive at times – this is normal.

#2 – It should be written for the intelligent layman.
When crafting your executive summary, its useful to keep the intelligent layman front of mind. What I mean by this is that you should write your summary assuming that your reader (i.e. the marker) will be intelligent but won’t be familiar with your topic and/or industry. This means that you should explain any technical concepts, avoid jargon and explain acronyms before using them.
#3 – It should be concise.
Typically, your executive summary should be a one-pager (one and a half pages at worst). To summarise a 3000 – 5000-word document into one page is no easy task, so you’ll need to:
- Present only the most important information (key insights, recommendations, etc).
- Write concisely – i.e. with brevity and completeness.
To the first point, I’ll explain what the “most important” information is for each chapter shortly. To the second point (writing concisely), there are various ways to do this, including:
- Using simple, straightforward language.
- Using the active voice.
- Removing bloaty adverbs and adjectives.
- Reducing prepositional phrases.
- Avoiding noun strings.
Does this sound like gibberish to you? Don’t worry! The Writing Center at the University of Wisconson-Madison provides a practical guide to writing more concisely, which you can download here.
On a related note, you typically would not include headings, citations or bulleted/numbered lists in your executive summary. These visual components tend to use a lot of space, which comes at a premium, as you know.
#4 – It should be written last.
Given that your executive summary is a summary of summaries, it needs to be written last , only once you’ve identified all your key insights, recommendations and so on. This probably sounds obvious, but many students start writing the summary first (potentially because of its position in the document) and then end up re-writing it multiple times, or they don’t rewrite it and consequently end up with an executive summary which is misaligned with the main document.
Simply put, you should leave this section until everything else is completed. Once your core body content is completed, you should read through the entire document again and create a bullet-point list of all the key points . From this list, you should then craft your executive summary . The approach will also help you identify gaps, contradictions and misalignments in your main document.

So, what goes into an executive summary?
Right, let’s get into the meat of it and consider what exactly should go into your executive summary. As I’ve mentioned, you need to present only the absolutely key point points from each of your chapters, but what does this mean exactly?
Each chapter will typically take the form of 1 paragraph (with no headings) in your executive summary. So, 5 chapters means 5 paragraphs. Naturally, some will be longer than others (let this be informed by the mark allocation), but assuming one page contains 500 words, you’re aiming for roughly 100 words per paragraph (assuming a 5-paragraph structure). See why conciseness is key!
Now, let’s look at what the key points are for each chapter in the case of a typical MBA assignment or report. In the case of a dissertation or thesis, the paragraph structure would still mimic the chapter structure – you’d just have more chapters, and therefore, more paragraphs.
Paragraph 1: Introduction
This paragraph should cover the following points:
- A very brief explanation of the business (what does it do, for whom and where?).
- Clear identification and explanation of the problem or opportunity that will be the focus of the assignment/report.
- A clear statement of the purpose of the assignment (i.e. what research questions will you seek to answer?).
- Brief mention of what data sources were utilised (i.e. secondary research) and any fieldwork undertaken (i.e. primary research ).
In other words, your first paragraph should introduce the business, the problem/opportunity to be addressed, why it’s important, and how you approached your analysis. This paragraph should make it clear to the reader what the assignment is all about at a broad level. Here’s a practical example:
This assignment focuses on ABC Ltd, a XXX business based in XXX, which provides XXX to XXX customers. To date, the firm has relied almost exclusively on XXX marketing channel. Consequently, ABC Ltd has little understanding of consumer segments, wants, and needs. This marketing channel is now under regulatory threat due to XXX. The core challenge, therefore, is that whilst ABC Ltd seeks to grow its market share, it has little understanding of its market characteristics or competitive set, and its sole marketing channel under regulatory threat. Accordingly, the objective of this assignment is XXX. The assignment draws on survey, interview, and industry data.
Paragraph 2: Analysis and findings
In this paragraph, you should discuss the following:
- What exactly did you analyse? For example, you might have analysed the macro context (i.e. PESTLE analysis), followed by the meso (i.e. competitor or industry analysis) and then the micro (i.e. internal organisational analysis).
- What were your key findings in relation to the purpose of the assignment? For example, you may have identified 4 potential causes of a problem and would then state them.
In other words, your second paragraph should concisely explain what you analysed and what your main findings were . An example of this:
Segmentation analysis, consisting of macro, industry and firm-level analyses, revealed a strong segmentation variable in the form of XXX, with distinct needs in each segment. Macro analysis revealed XXX, while industry and firm-level analyses suggested XXX. Subsequently, three potential target segments were established, namely XXX, XXX and XXX. These were then evaluated using the Directional Policy Matrix, and the results indicated XXX.
From a presentation perspective, you might structure this section as:
- Analysis 1, findings from analysis 1.
- Analysis 2, findings from analysis 2.
- Analysis 3, findings from analysis 3.
Importantly, you should only discuss the findings that are directly linked to the research questions (i.e. the purpose of the assignment) – don’t digress into interesting but less relevant findings. Given that the analysis chapter typically counts for a large proportion of marks, you could viably write 2-3 paragraphs for this. Be guided by the mark allocation.
Lastly, you should ensure that the findings you present here align well with the recommendations you’ll make in the next paragraph. Think about what your recommendations are, and, if necessary, reverse engineer this paragraph to create a strong link and logical flow from analysis to recommendations.

Paragraph 3: Recommendations
With the key findings from your analysis presented in the preceding paragraph, you should now discuss the following:
- What are your key recommendations?
- How do these solve the problems you found in your analysis?
- Were there any further conclusions?
Simply put, this paragraph (or two) should present the main recommendations and justify their use (i.e. explain how they resolve the key issue). As mentioned before, it’s critically important that your recommendations tightly align with (and resolve) the key issues that you identified in the analysis. An example:
Based on the Directional Policy Matrix analysis, it is recommended that the firm target XXX segment, because of XXX. On this basis, a positioning of XXX is proposed, as this aligns with the segment’s key needs. Furthermore, a provisional high-level marketing mix is proposed. The key aspects of the marketing mix include XXX, XXX and XXX, as these align with the firm’s positioning of XXX. By adopting these recommendations, the key issue of XXX will be resolved.
Also, note that (typically) the tone changes from past to present tense when you get to the recommendations section.
Paragraph 4: Implementation
If your assignment brief requires an implementation/project plan-type section, this paragraph will typically include the following points:
- Time requirements (how long will it take?)
- People requirements (what skills are needed and where do you find them?)
- Money requirements (what budget is required?)
- How will the project or change be managed? (i.e. project management plan)
- What risks exist and how will these be managed?
Depending on what level of detail is required by your assignment brief, you may need to present more, less or other details in this section. As always, be guided by the assignment brief.
A practical example:
A high-level implementation plan is proposed, including a stakeholder analysis, project plan and business case. Resource requirements are presented, detailing XXX, XXX and XXX requirements. A risk analysis is presented, revealing key risks including XXX, XXX and XXX. Risk management solutions are proposed, including XXX and XXX.

Paragraph 5: Reflection
As with the implementation chapter, the need for a reflection chapter/section will vary between assignments and universities. If your assignment has this requirement, it’s typically good to cover the following points:
- What were your key learnings? What were your ah-ha moments?
- What has changed in the real world as a consequence of these learnings? I.e. how has your actual behaviour and approach to “X” changed, if any?
- What are the benefits and/or disadvantages of this change, if any?
This section is very personal, and so each person’s reflections will be different. Don’t take the above points as gospel.
Time to test it out.
Once you’ve written up your executive summary and feel confident that it’s in good shape, it’s time to test it out on an unsuspecting intelligent layman. This is a critically important step, since you, as the writer, are simply too close to the work to judge whether it all makes sense to a first-time reader. In fact, you are the least suitable person on the planet!
So, find someone who is not familiar with your assignment topic (and ideally, not familiar with your industry), and ask them to have a read through your executive summary. Friends and family will usually tell you its great, regardless of the quality, so you need to test them on their understanding. Do this by asking them to give the details back to you in their own words. Poke and prod – can they tell you what the key issues and recommendations were (in their own words!). You’ll quickly spot the gaps this way, and be able to flesh out any weak areas.
Wrapping up.
In this post, I’ve discussed how to write the all too often undercooked executive summary. I’ve discussed some important attributes of a strong executive summary, as well as the contents that typically go into it. To recap on the key points:
The key attributes of a high-impact executive summary:
- It should be able to stand alone.
- It should be written for the intelligent layman.
- It should be concise.
- It should be written last.
The key contents of a high-impact executive summary:
Each paragraph should cover a chapter from the document. For example, In the case of a typical assignment, it would be something like:
- Summary of the introduction chapter.
- Summary of the analysis chapter.
- Summary of the recommendations and/or conclusions chapter.
- Depending – summary of the implementation and reflection.
Lastly, don’t forget to test out your executive summary on an unsuspecting layman or two. This is probably the most important step of them all!
If you have any questions or suggestions, we’d love to hear from you. Please get in touch here or leave a comment below.
You Might Also Like:

Thanks so much for your methodical process and explanation of Executive Summary. It is exactly what I was researching for.
Regards Saane
It’s a pleasure!
This was really helpful with how to structure my assignment.
Thank you so much for the step by step process. It’s so helpful for beginners like me.
Great! This post is very informative and gives clear guidance on to write an executive summary. Thanks very much for sharing this information, it’s very helpful.
Thanks for the feedback, Anna. Best of luck with your writing 🙂
Thank you for the great article, really helped explain what was needed.
Great insight and tips . Thanks
Thank you so much for sharing this. It was exactly what I was looking for.
Thank you for your help
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
44 Summary Writing
What is a summary.
A summary is a comprehensive and objective restatement of the main ideas of a text (an article, book, movie, event, etc.) Stephen Wilhoit, in his textbook A Brief Guide to Writing from Readings , suggests that keeping the qualities of a good summary in mind helps students avoid the pitfalls of unclear or disjointed summaries. These qualities include:
Neutrality – The writer avoids inserting his or her opinion into the summary, or interpreting the original text’s content in any way. This requires that the writer avoids language that is evaluative, such as: good, bad, effective, ineffective, interesting, boring, etc. Also, keep “I” out of the summary; instead, summary should be written in grammatical 3rd person (For example: “he”, “she”, “the author”, “they”, etc).
Brevity – The summary should not be longer than the original text, but rather highlight the most important information from that text while leaving out unnecessary details while still maintaining accuracy.
Independence – The summary should make sense to someone who has not read the original source. There should be no confusion about the main content and organization of the original source. This also requires that the summary be accurate.
By mastering the craft of summarizing, students put themselves in the position to do well on many assignments in college, not just English essays. In most fields (from the humanities to the soft and hard sciences) summary is a required task. Being able to summarize lab results accurately and briefly, for example, is critical in a chemistry or engineering class. Summarizing the various theories of sociology or education helps a person apply them to his or her fieldwork. In college, it’s imperative we learn how to summarize well because we are asked to do it so often.
College students are asked to summarize material for many different types of assignments. In some instances, summarizing one source is often the sole purpose of the entire assignment. Students might also be asked to summarize as just one aspect of a larger project, such as a literature review, an abstract in a research paper, or a works consulted entry in an annotated bibliography.
Some summary assignments will expect students to condense material more than others. For example, when summary is the sole purpose of the assignment, the student might be asked to include key supporting evidence, where as an abstract might require students to boil down the source text to its bare-bones essentials.
What Makes Something a Summary?
When you ask yourself, after reading an article (and maybe even reading it two or three times), “What was that article about?” and you end up jotting down–from memory, without returning to the original article to use its language or phrases–three things that stood out as the author’s main points, you are summarizing. Summaries have several key characteristics.
You’re summarizing well when you
- use your own words
- significantly condense the original text
- provide accurate representations of the main points of the text they summarize
- avoid personal opinion.
Summaries are much shorter than the original material—a general rule is that they should be no more than 10% to 15% the length of the original, and they are often even shorter than this.
It can be easy and feel natural, when summarizing an article, to include our own opinions. We may agree or disagree strongly with what this author is saying, or we may want to compare their information with the information presented in another source, or we may want to share our own opinion on the topic. Often, our opinions slip into summaries even when we work diligently to keep them separate. These opinions are not the job of a summary, though. A summary should only highlight the main points of the article.
First , it no longer correctly represents the original text, so it misleads your reader about the ideas presented in that text. A summary should give your reader an accurate idea of what they can expect if we pick up the original article to read.
Second , it undermines your own credibility as an author to not represent this information accurately. If readers cannot trust an author to accurately represent source information, they may not be as likely to trust that author to thoroughly and accurately present a reasonable point.
How Should I Organize a Summary?
Like traditional essays, summaries have an introduction, a body, and a conclusion. What these components look like will vary some based on the purpose of the summary you’re writing. The introduction, body, and conclusion of work focused specifically around summarizing something is going to be a little different than in work where summary is not the primary goal.
Introducing a Summary
One of the trickier parts of creating a summary is making it clear that this is a summary of someone else’s work; these ideas are not your original ideas. You will almost always begin a summary with an introduction to the author, article, and publication so the reader knows what we are about to read. This information will appear again in your bibliography, but is also useful here so the reader can follow the conversation happening in your paper. You will want to provide it in both places.
In summary-focused work, this introduction should accomplish a few things:
- Introduce the name of the author whose work you are summarizing.
- Introduce the title of the text being summarized.
- Introduce where this text was presented (if it’s an art installation, where is it being shown? If it’s an article, where was that article published? Not all texts will have this component–for example, when summarizing a book written by one author, the title of the book and name of that author are sufficient information for your readers to easily locate the work you are summarizing).
- State the main ideas of the text you are summarizing—just the big-picture components.
- Give context when necessary. Is this text responding to a current event? That might be important to know. Does this author have specific qualifications that make them an expert on this topic? This might also be relevant information.
So, for example, if you were to get an assignment asking you to summarize Matthew Hutson’s Atlantic article, “ Beyond the Five Senses ,” an introduction for that summary might look something like this:
In his July 2017 article in The Atlantic , “Beyond the Five Senses,” Matthew Hutson explores ways in which potential technologies might expand our sensory perception of the world. He notes that some technologies, such as cochlear implants, are already accomplishing a version of this for people who do not have full access to one of the five senses. In much of the article, though, he seems more interested in how technology might expand the ways in which we sense things. Some of these technologies are based in senses that can be seen in nature, such as echolocation, and others seem more deeply rooted in science fiction. However, all of the examples he gives consider how adding new senses to the ones we already experience might change how we perceive the world around us.
However, you will probably find yourself more frequently using summary as just one component of work with a wide range of goals (not just a goal to “summarize X”).
Summary introductions in these situations still generally need to
- name the author
- name the text being summarized
- state just the relevant context, if there is any (maybe the author has a specific credential that makes their work on this topic carry more weight than it would otherwise, or maybe the study they generated is now being used as a benchmark for additional research)
- introduce the author’s full name (first and last names) the first time you summarize part of their text. If you summarize pieces of the same text more than once in a work you are writing, each time you use their text after that initial introduction of the source, you will only use the author’s last name as you introduce that next summary component.
Presenting the “Meat” (or Body) of a Summary
Again, this will look a little different depending on the purpose of the summary work you are doing. Regardless of how you are using summary, you will introduce the main ideas throughout your text with transitional phrasing, such as “One of [Author’s] biggest points is…,” or “[Author’s] primary concern about this solution is….”
If you are responding to a “write a summary of X” assignment, the body of that summary will expand on the main ideas you stated in the introduction of the summary, although this will all still be very condensed compared to the original. What are the key points the author makes about each of those big-picture main ideas? Depending on the kind of text you are summarizing, you may want to note how the main ideas are supported (although, again, be careful to avoid making your own opinion about those supporting sources known).
When you are summarizing with an end goal that is broader than just summary, the body of your summary will still present the idea from the original text that is relevant to the point you are making (condensed and in your own words).
Since it is much more common to summarize just a single idea or point from a text in this type of summarizing (rather than all of its main points), it is important to make sure you understand the larger points of the original text. For example, you might find that an article provides an example that opposes its main point in order to demonstrate the range of conversations happening on the topic it covers. This opposing point, though, isn’t the main point of the article, so just summarizing this one opposing example would not be an accurate representation of the ideas and points in that text.
Concluding a Summary
For writing in which summary is the sole purpose, here are some ideas for your conclusion.
- Now that we’ve gotten a little more information about the main ideas of this piece, are there any connections or loose ends to tie up that will help your reader fully understand the points being made in this text? This is the place to put those.
- This is also a good place to state (or restate) the things that are most important for your readers to remember after reading your summary.
- Depending on your assignment, rather than providing a formal concluding paragraph where you restate the main points and make connections between them, you may want to simply paraphrase the author’s concluding section or final main idea. Check your assignment sheet to see what kind of conclusion your instructor is asking for.
When your writing has a primary goal other than summary, your conclusion should
- discuss the summary you’ve just presented. How does it support, illustrate, or give new information about the point you are making in your writing? Connect it to your own main point for that paragraph so readers understand clearly why it deserves the space it takes up in your work. (Note that this is still not giving your opinion on the material you’ve summarized, just making connections between it and your own main points.)
Summary Template
Here is a basic summary template for use with any text (article, video, chapter, textbook, etc.) that you are reading and need to briefly summarize in your own words for yourself or for your readers. Use the tips when inserting information from the article that you have read into the template to make filling in the blanks much easier. Feel free to change any wording that you think needs modifying or that sounds ineffective in your final version. The summary essay rubric that follows is correlated to this template so that you can use it as a checklist.
In “Title of Article,” a (state year) adaptation/excerpt/chapter/article from Publication where it appeared , Author (first and last name) argues/explains/describes/ outlines/highlights that Thesis (main point of article) in your own words. First, he/she/ they claim(s) first supporting point. For instance, specific example from the text to illustrate this point (can be paraphrase or quote). Next, he/she/they examine(s) second supporting point. For example, specific example from the text to illustrate this point (can be paraphrase or quote). Third, he/she/they suggest(s) third supporting point. For instance, specific example from the text to illustrate this point (can be paraphrase or quote). To conclude he/she/they state(s) sum up the conclusion (may be a solution, a forecast for the future, etc.)
Sample Summary Essay Rubric
This chapter is adapted from A Guide to Rhetoric , Chapter 5.1, “ Writing Summaries, ” by Melanie Gagich, CC-BY-NC-SA 4.0.
Write What Matters Copyright © 2020 by Liza Long; Amy Minervini; and Joel Gladd is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Have a thesis expert improve your writing
Check your thesis for plagiarism in 10 minutes, generate your apa citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Working with sources
- How to Write a Summary | Guide & Examples
How to Write a Summary | Guide & Examples
Published on 25 September 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on 12 May 2023.
Summarising , or writing a summary, means giving a concise overview of a text’s main points in your own words. A summary is always much shorter than the original text.
There are five key steps that can help you to write a summary:
- Read the text
- Break it down into sections
- Identify the key points in each section
- Write the summary
- Check the summary against the article
Writing a summary does not involve critiquing or analysing the source. You should simply provide an accurate account of the most important information and ideas (without copying any text from the original).

Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
When to write a summary, step 1: read the text, step 2: break the text down into sections, step 3: identify the key points in each section, step 4: write the summary, step 5: check the summary against the article, frequently asked questions.
There are many situations in which you might have to summarise an article or other source:
- As a stand-alone assignment to show you’ve understood the material
- To keep notes that will help you remember what you’ve read
- To give an overview of other researchers’ work in a literature review
When you’re writing an academic text like an essay , research paper , or dissertation , you’ll integrate sources in a variety of ways. You might use a brief quote to support your point, or paraphrase a few sentences or paragraphs.
But it’s often appropriate to summarize a whole article or chapter if it is especially relevant to your own research, or to provide an overview of a source before you analyse or critique it.
In any case, the goal of summarising is to give your reader a clear understanding of the original source. Follow the five steps outlined below to write a good summary.
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
You should read the article more than once to make sure you’ve thoroughly understood it. It’s often effective to read in three stages:
- Scan the article quickly to get a sense of its topic and overall shape.
- Read the article carefully, highlighting important points and taking notes as you read.
- Skim the article again to confirm you’ve understood the key points, and reread any particularly important or difficult passages.
There are some tricks you can use to identify the key points as you read:
- Start by reading the abstract . This already contains the author’s own summary of their work, and it tells you what to expect from the article.
- Pay attention to headings and subheadings . These should give you a good sense of what each part is about.
- Read the introduction and the conclusion together and compare them: What did the author set out to do, and what was the outcome?
To make the text more manageable and understand its sub-points, break it down into smaller sections.
If the text is a scientific paper that follows a standard empirical structure, it is probably already organised into clearly marked sections, usually including an introduction, methods, results, and discussion.
Other types of articles may not be explicitly divided into sections. But most articles and essays will be structured around a series of sub-points or themes.
Now it’s time go through each section and pick out its most important points. What does your reader need to know to understand the overall argument or conclusion of the article?
Keep in mind that a summary does not involve paraphrasing every single paragraph of the article. Your goal is to extract the essential points, leaving out anything that can be considered background information or supplementary detail.
In a scientific article, there are some easy questions you can ask to identify the key points in each part.
If the article takes a different form, you might have to think more carefully about what points are most important for the reader to understand its argument.
In that case, pay particular attention to the thesis statement —the central claim that the author wants us to accept, which usually appears in the introduction—and the topic sentences that signal the main idea of each paragraph.
Now that you know the key points that the article aims to communicate, you need to put them in your own words.
To avoid plagiarism and show you’ve understood the article, it’s essential to properly paraphrase the author’s ideas. Do not copy and paste parts of the article, not even just a sentence or two.
The best way to do this is to put the article aside and write out your own understanding of the author’s key points.
Examples of article summaries
Let’s take a look at an example. Below, we summarise this article , which scientifically investigates the old saying ‘an apple a day keeps the doctor away’.
An article summary like the above would be appropriate for a stand-alone summary assignment. However, you’ll often want to give an even more concise summary of an article.
For example, in a literature review or research paper, you may want to briefly summarize this study as part of a wider discussion of various sources. In this case, we can boil our summary down even further to include only the most relevant information.
Citing the source you’re summarizing
When including a summary as part of a larger text, it’s essential to properly cite the source you’re summarizing. The exact format depends on your citation style , but it usually includes an in-text citation and a full reference at the end of your paper.
You can easily create your citations and references in APA or MLA using our free citation generators.
APA Citation Generator MLA Citation Generator
Finally, read through the article once more to ensure that:
- You’ve accurately represented the author’s work
- You haven’t missed any essential information
- The phrasing is not too similar to any sentences in the original.
If you’re summarising many articles as part of your own work, it may be a good idea to use a plagiarism checker to double-check that your text is completely original and properly cited. Just be sure to use one that’s safe and reliable.
A summary is a short overview of the main points of an article or other source, written entirely in your own words.
Save yourself some time with the free summariser.
A summary is always much shorter than the original text. The length of a summary can range from just a few sentences to several paragraphs; it depends on the length of the article you’re summarising, and on the purpose of the summary.
With the summariser tool you can easily adjust the length of your summary.
You might have to write a summary of a source:
- As a stand-alone assignment to prove you understand the material
- For your own use, to keep notes on your reading
- To provide an overview of other researchers’ work in a literature review
- In a paper , to summarise or introduce a relevant study
To avoid plagiarism when summarising an article or other source, follow these two rules:
- Write the summary entirely in your own words by paraphrasing the author’s ideas.
- Reference the source with an in-text citation and a full reference so your reader can easily find the original text.
An abstract concisely explains all the key points of an academic text such as a thesis , dissertation or journal article. It should summarise the whole text, not just introduce it.
An abstract is a type of summary , but summaries are also written elsewhere in academic writing . For example, you might summarise a source in a paper , in a literature review , or as a standalone assignment.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, May 12). How to Write a Summary | Guide & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 29 April 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/working-sources/how-to-write-a-summary/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to paraphrase | step-by-step guide & examples, how to quote | citing quotes in harvard & apa, apa referencing (7th ed.) quick guide | in-text citations & references.

Understanding Assignments
What this handout is about.
The first step in any successful college writing venture is reading the assignment. While this sounds like a simple task, it can be a tough one. This handout will help you unravel your assignment and begin to craft an effective response. Much of the following advice will involve translating typical assignment terms and practices into meaningful clues to the type of writing your instructor expects. See our short video for more tips.
Basic beginnings
Regardless of the assignment, department, or instructor, adopting these two habits will serve you well :
- Read the assignment carefully as soon as you receive it. Do not put this task off—reading the assignment at the beginning will save you time, stress, and problems later. An assignment can look pretty straightforward at first, particularly if the instructor has provided lots of information. That does not mean it will not take time and effort to complete; you may even have to learn a new skill to complete the assignment.
- Ask the instructor about anything you do not understand. Do not hesitate to approach your instructor. Instructors would prefer to set you straight before you hand the paper in. That’s also when you will find their feedback most useful.
Assignment formats
Many assignments follow a basic format. Assignments often begin with an overview of the topic, include a central verb or verbs that describe the task, and offer some additional suggestions, questions, or prompts to get you started.
An Overview of Some Kind
The instructor might set the stage with some general discussion of the subject of the assignment, introduce the topic, or remind you of something pertinent that you have discussed in class. For example:
“Throughout history, gerbils have played a key role in politics,” or “In the last few weeks of class, we have focused on the evening wear of the housefly …”
The Task of the Assignment
Pay attention; this part tells you what to do when you write the paper. Look for the key verb or verbs in the sentence. Words like analyze, summarize, or compare direct you to think about your topic in a certain way. Also pay attention to words such as how, what, when, where, and why; these words guide your attention toward specific information. (See the section in this handout titled “Key Terms” for more information.)
“Analyze the effect that gerbils had on the Russian Revolution”, or “Suggest an interpretation of housefly undergarments that differs from Darwin’s.”
Additional Material to Think about
Here you will find some questions to use as springboards as you begin to think about the topic. Instructors usually include these questions as suggestions rather than requirements. Do not feel compelled to answer every question unless the instructor asks you to do so. Pay attention to the order of the questions. Sometimes they suggest the thinking process your instructor imagines you will need to follow to begin thinking about the topic.
“You may wish to consider the differing views held by Communist gerbils vs. Monarchist gerbils, or Can there be such a thing as ‘the housefly garment industry’ or is it just a home-based craft?”
These are the instructor’s comments about writing expectations:
“Be concise”, “Write effectively”, or “Argue furiously.”
Technical Details
These instructions usually indicate format rules or guidelines.
“Your paper must be typed in Palatino font on gray paper and must not exceed 600 pages. It is due on the anniversary of Mao Tse-tung’s death.”
The assignment’s parts may not appear in exactly this order, and each part may be very long or really short. Nonetheless, being aware of this standard pattern can help you understand what your instructor wants you to do.
Interpreting the assignment
Ask yourself a few basic questions as you read and jot down the answers on the assignment sheet:
Why did your instructor ask you to do this particular task?
Who is your audience.
- What kind of evidence do you need to support your ideas?
What kind of writing style is acceptable?
- What are the absolute rules of the paper?
Try to look at the question from the point of view of the instructor. Recognize that your instructor has a reason for giving you this assignment and for giving it to you at a particular point in the semester. In every assignment, the instructor has a challenge for you. This challenge could be anything from demonstrating an ability to think clearly to demonstrating an ability to use the library. See the assignment not as a vague suggestion of what to do but as an opportunity to show that you can handle the course material as directed. Paper assignments give you more than a topic to discuss—they ask you to do something with the topic. Keep reminding yourself of that. Be careful to avoid the other extreme as well: do not read more into the assignment than what is there.
Of course, your instructor has given you an assignment so that they will be able to assess your understanding of the course material and give you an appropriate grade. But there is more to it than that. Your instructor has tried to design a learning experience of some kind. Your instructor wants you to think about something in a particular way for a particular reason. If you read the course description at the beginning of your syllabus, review the assigned readings, and consider the assignment itself, you may begin to see the plan, purpose, or approach to the subject matter that your instructor has created for you. If you still aren’t sure of the assignment’s goals, try asking the instructor. For help with this, see our handout on getting feedback .
Given your instructor’s efforts, it helps to answer the question: What is my purpose in completing this assignment? Is it to gather research from a variety of outside sources and present a coherent picture? Is it to take material I have been learning in class and apply it to a new situation? Is it to prove a point one way or another? Key words from the assignment can help you figure this out. Look for key terms in the form of active verbs that tell you what to do.
Key Terms: Finding Those Active Verbs
Here are some common key words and definitions to help you think about assignment terms:
Information words Ask you to demonstrate what you know about the subject, such as who, what, when, where, how, and why.
- define —give the subject’s meaning (according to someone or something). Sometimes you have to give more than one view on the subject’s meaning
- describe —provide details about the subject by answering question words (such as who, what, when, where, how, and why); you might also give details related to the five senses (what you see, hear, feel, taste, and smell)
- explain —give reasons why or examples of how something happened
- illustrate —give descriptive examples of the subject and show how each is connected with the subject
- summarize —briefly list the important ideas you learned about the subject
- trace —outline how something has changed or developed from an earlier time to its current form
- research —gather material from outside sources about the subject, often with the implication or requirement that you will analyze what you have found
Relation words Ask you to demonstrate how things are connected.
- compare —show how two or more things are similar (and, sometimes, different)
- contrast —show how two or more things are dissimilar
- apply—use details that you’ve been given to demonstrate how an idea, theory, or concept works in a particular situation
- cause —show how one event or series of events made something else happen
- relate —show or describe the connections between things
Interpretation words Ask you to defend ideas of your own about the subject. Do not see these words as requesting opinion alone (unless the assignment specifically says so), but as requiring opinion that is supported by concrete evidence. Remember examples, principles, definitions, or concepts from class or research and use them in your interpretation.
- assess —summarize your opinion of the subject and measure it against something
- prove, justify —give reasons or examples to demonstrate how or why something is the truth
- evaluate, respond —state your opinion of the subject as good, bad, or some combination of the two, with examples and reasons
- support —give reasons or evidence for something you believe (be sure to state clearly what it is that you believe)
- synthesize —put two or more things together that have not been put together in class or in your readings before; do not just summarize one and then the other and say that they are similar or different—you must provide a reason for putting them together that runs all the way through the paper
- analyze —determine how individual parts create or relate to the whole, figure out how something works, what it might mean, or why it is important
- argue —take a side and defend it with evidence against the other side
More Clues to Your Purpose As you read the assignment, think about what the teacher does in class:
- What kinds of textbooks or coursepack did your instructor choose for the course—ones that provide background information, explain theories or perspectives, or argue a point of view?
- In lecture, does your instructor ask your opinion, try to prove their point of view, or use keywords that show up again in the assignment?
- What kinds of assignments are typical in this discipline? Social science classes often expect more research. Humanities classes thrive on interpretation and analysis.
- How do the assignments, readings, and lectures work together in the course? Instructors spend time designing courses, sometimes even arguing with their peers about the most effective course materials. Figuring out the overall design to the course will help you understand what each assignment is meant to achieve.
Now, what about your reader? Most undergraduates think of their audience as the instructor. True, your instructor is a good person to keep in mind as you write. But for the purposes of a good paper, think of your audience as someone like your roommate: smart enough to understand a clear, logical argument, but not someone who already knows exactly what is going on in your particular paper. Remember, even if the instructor knows everything there is to know about your paper topic, they still have to read your paper and assess your understanding. In other words, teach the material to your reader.
Aiming a paper at your audience happens in two ways: you make decisions about the tone and the level of information you want to convey.
- Tone means the “voice” of your paper. Should you be chatty, formal, or objective? Usually you will find some happy medium—you do not want to alienate your reader by sounding condescending or superior, but you do not want to, um, like, totally wig on the man, you know? Eschew ostentatious erudition: some students think the way to sound academic is to use big words. Be careful—you can sound ridiculous, especially if you use the wrong big words.
- The level of information you use depends on who you think your audience is. If you imagine your audience as your instructor and they already know everything you have to say, you may find yourself leaving out key information that can cause your argument to be unconvincing and illogical. But you do not have to explain every single word or issue. If you are telling your roommate what happened on your favorite science fiction TV show last night, you do not say, “First a dark-haired white man of average height, wearing a suit and carrying a flashlight, walked into the room. Then a purple alien with fifteen arms and at least three eyes turned around. Then the man smiled slightly. In the background, you could hear a clock ticking. The room was fairly dark and had at least two windows that I saw.” You also do not say, “This guy found some aliens. The end.” Find some balance of useful details that support your main point.
You’ll find a much more detailed discussion of these concepts in our handout on audience .
The Grim Truth
With a few exceptions (including some lab and ethnography reports), you are probably being asked to make an argument. You must convince your audience. It is easy to forget this aim when you are researching and writing; as you become involved in your subject matter, you may become enmeshed in the details and focus on learning or simply telling the information you have found. You need to do more than just repeat what you have read. Your writing should have a point, and you should be able to say it in a sentence. Sometimes instructors call this sentence a “thesis” or a “claim.”
So, if your instructor tells you to write about some aspect of oral hygiene, you do not want to just list: “First, you brush your teeth with a soft brush and some peanut butter. Then, you floss with unwaxed, bologna-flavored string. Finally, gargle with bourbon.” Instead, you could say, “Of all the oral cleaning methods, sandblasting removes the most plaque. Therefore it should be recommended by the American Dental Association.” Or, “From an aesthetic perspective, moldy teeth can be quite charming. However, their joys are short-lived.”
Convincing the reader of your argument is the goal of academic writing. It doesn’t have to say “argument” anywhere in the assignment for you to need one. Look at the assignment and think about what kind of argument you could make about it instead of just seeing it as a checklist of information you have to present. For help with understanding the role of argument in academic writing, see our handout on argument .
What kind of evidence do you need?
There are many kinds of evidence, and what type of evidence will work for your assignment can depend on several factors–the discipline, the parameters of the assignment, and your instructor’s preference. Should you use statistics? Historical examples? Do you need to conduct your own experiment? Can you rely on personal experience? See our handout on evidence for suggestions on how to use evidence appropriately.
Make sure you are clear about this part of the assignment, because your use of evidence will be crucial in writing a successful paper. You are not just learning how to argue; you are learning how to argue with specific types of materials and ideas. Ask your instructor what counts as acceptable evidence. You can also ask a librarian for help. No matter what kind of evidence you use, be sure to cite it correctly—see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial .
You cannot always tell from the assignment just what sort of writing style your instructor expects. The instructor may be really laid back in class but still expect you to sound formal in writing. Or the instructor may be fairly formal in class and ask you to write a reflection paper where you need to use “I” and speak from your own experience.
Try to avoid false associations of a particular field with a style (“art historians like wacky creativity,” or “political scientists are boring and just give facts”) and look instead to the types of readings you have been given in class. No one expects you to write like Plato—just use the readings as a guide for what is standard or preferable to your instructor. When in doubt, ask your instructor about the level of formality they expect.
No matter what field you are writing for or what facts you are including, if you do not write so that your reader can understand your main idea, you have wasted your time. So make clarity your main goal. For specific help with style, see our handout on style .
Technical details about the assignment
The technical information you are given in an assignment always seems like the easy part. This section can actually give you lots of little hints about approaching the task. Find out if elements such as page length and citation format (see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial ) are negotiable. Some professors do not have strong preferences as long as you are consistent and fully answer the assignment. Some professors are very specific and will deduct big points for deviations.
Usually, the page length tells you something important: The instructor thinks the size of the paper is appropriate to the assignment’s parameters. In plain English, your instructor is telling you how many pages it should take for you to answer the question as fully as you are expected to. So if an assignment is two pages long, you cannot pad your paper with examples or reword your main idea several times. Hit your one point early, defend it with the clearest example, and finish quickly. If an assignment is ten pages long, you can be more complex in your main points and examples—and if you can only produce five pages for that assignment, you need to see someone for help—as soon as possible.
Tricks that don’t work
Your instructors are not fooled when you:
- spend more time on the cover page than the essay —graphics, cool binders, and cute titles are no replacement for a well-written paper.
- use huge fonts, wide margins, or extra spacing to pad the page length —these tricks are immediately obvious to the eye. Most instructors use the same word processor you do. They know what’s possible. Such tactics are especially damning when the instructor has a stack of 60 papers to grade and yours is the only one that low-flying airplane pilots could read.
- use a paper from another class that covered “sort of similar” material . Again, the instructor has a particular task for you to fulfill in the assignment that usually relates to course material and lectures. Your other paper may not cover this material, and turning in the same paper for more than one course may constitute an Honor Code violation . Ask the instructor—it can’t hurt.
- get all wacky and “creative” before you answer the question . Showing that you are able to think beyond the boundaries of a simple assignment can be good, but you must do what the assignment calls for first. Again, check with your instructor. A humorous tone can be refreshing for someone grading a stack of papers, but it will not get you a good grade if you have not fulfilled the task.
Critical reading of assignments leads to skills in other types of reading and writing. If you get good at figuring out what the real goals of assignments are, you are going to be better at understanding the goals of all of your classes and fields of study.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Common Writing Assignments

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
These OWL resources will help you understand and complete specific types of writing assignments, such as annotated bibliographies, book reports, and research papers. This section also includes resources on writing academic proposals for conference presentations, journal articles, and books.
Understanding Writing Assignments
This resource describes some steps you can take to better understand the requirements of your writing assignments. This resource works for either in-class, teacher-led discussion or for personal use.
Argument Papers
This resource outlines the generally accepted structure for introductions, body paragraphs, and conclusions in an academic argument paper. Keep in mind that this resource contains guidelines and not strict rules about organization. Your structure needs to be flexible enough to meet the requirements of your purpose and audience.
Research Papers
This handout provides detailed information about how to write research papers including discussing research papers as a genre, choosing topics, and finding sources.
Exploratory Papers
This resource will help you with exploratory/inquiry essay assignments.
Annotated Bibliographies
This handout provides information about annotated bibliographies in MLA, APA, and CMS.
Book Report
This resource discusses book reports and how to write them.
Definitions
This handout provides suggestions and examples for writing definitions.
Essays for Exams
While most OWL resources recommend a longer writing process (start early, revise often, conduct thorough research, etc.), sometimes you just have to write quickly in test situations. However, these exam essays can be no less important pieces of writing than research papers because they can influence final grades for courses, and/or they can mean the difference between getting into an academic program (GED, SAT, GRE). To that end, this resource will help you prepare and write essays for exams.
Book Review
This resource discusses book reviews and how to write them.
Academic Proposals
This resource will help undergraduate, graduate, and professional scholars write proposals for academic conferences, articles, and books.
In this section
Subsections.
Module 4: Writing in College
Writing assignments, learning objectives.
- Describe common types and expectations of writing tasks given in a college class

Figure 1 . All college classes require some form of writing. Investing some time in refining your writing skills so that you are a more confident, skilled, and efficient writer will pay dividends in the long run.
What to Do With Writing Assignments
Writing assignments can be as varied as the instructors who assign them. Some assignments are explicit about what exactly you’ll need to do, in what order, and how it will be graded. Others are more open-ended, leaving you to determine the best path toward completing the project. Most fall somewhere in the middle, containing details about some aspects but leaving other assumptions unstated. It’s important to remember that your first resource for getting clarification about an assignment is your instructor—they will be very willing to talk out ideas with you, to be sure you’re prepared at each step to do well with the writing.
Writing in college is usually a response to class materials—an assigned reading, a discussion in class, an experiment in a lab. Generally speaking, these writing tasks can be divided into three broad categories: summary assignments, defined-topic assignments, and undefined-topic assignments.
Link to Learning
Empire State College offers an Assignment Calculator to help you plan ahead for your writing assignment. Just plug in the date you plan to get started and the date it is due, and the calculator will help break it down into manageable chunks.
Summary Assignments
Being asked to summarize a source is a common task in many types of writing. It can also seem like a straightforward task: simply restate, in shorter form, what the source says. A lot of advanced skills are hidden in this seemingly simple assignment, however.
An effective summary does the following:
- reflects your accurate understanding of a source’s thesis or purpose
- differentiates between major and minor ideas in a source
- demonstrates your ability to identify key phrases to quote
- shows your ability to effectively paraphrase most of the source’s ideas
- captures the tone, style, and distinguishing features of a source
- does not reflect your personal opinion about the source
That last point is often the most challenging: we are opinionated creatures, by nature, and it can be very difficult to keep our opinions from creeping into a summary. A summary is meant to be completely neutral.
In college-level writing, assignments that are only summary are rare. That said, many types of writing tasks contain at least some element of summary, from a biology report that explains what happened during a chemical process, to an analysis essay that requires you to explain what several prominent positions about gun control are, as a component of comparing them against one another.
Writing Effective Summaries
Start with a clear identification of the work.
This automatically lets your readers know your intentions and that you’re covering the work of another author.
- In the featured article “Five Kinds of Learning,” the author, Holland Oates, justifies his opinion on the hot topic of learning styles — and adds a few himself.
Summarize the Piece as a Whole
Omit nothing important and strive for overall coherence through appropriate transitions. Write using “summarizing language.” Your reader needs to be reminded that this is not your own work. Use phrases like the article claims, the author suggests, etc.
- Present the material in a neutral fashion. Your opinions, ideas, and interpretations should be left in your brain — don’t put them into your summary. Be conscious of choosing your words. Only include what was in the original work.
- Be concise. This is a summary — it should be much shorter than the original piece. If you’re working on an article, give yourself a target length of 1/4 the original article.
Conclude with a Final Statement
This is not a statement of your own point of view, however; it should reflect the significance of the book or article from the author’s standpoint.
- Without rewriting the article, summarize what the author wanted to get across. Be careful not to evaluate in the conclusion or insert any of your own assumptions or opinions.
Understanding the Assignment and Getting Started

Figure 2 . Many writing assignments will have a specific prompt that sends you first to your textbook, and then to outside resources to gather information.
Often, the handout or other written text explaining the assignment—what professors call the assignment prompt —will explain the purpose of the assignment and the required parameters (length, number and type of sources, referencing style, etc.).
Also, don’t forget to check the rubric, if there is one, to understand how your writing will be assessed. After analyzing the prompt and the rubric, you should have a better sense of what kind of writing you are expected to produce.
Sometimes, though—especially when you are new to a field—you will encounter the baffling situation in which you comprehend every single sentence in the prompt but still have absolutely no idea how to approach the assignment! In a situation like that, consider the following tips:
- Focus on the verbs . Look for verbs like compare, explain, justify, reflect , or the all-purpose analyze . You’re not just producing a paper as an artifact; you’re conveying, in written communication, some intellectual work you have done. So the question is, what kind of thinking are you supposed to do to deepen your learning?
- Put the assignment in context . Many professors think in terms of assignment sequences. For example, a social science professor may ask you to write about a controversial issue three times: first, arguing for one side of the debate; second, arguing for another; and finally, from a more comprehensive and nuanced perspective, incorporating text produced in the first two assignments. A sequence like that is designed to help you think through a complex issue. If the assignment isn’t part of a sequence, think about where it falls in the span of the course (early, midterm, or toward the end), and how it relates to readings and other assignments. For example, if you see that a paper comes at the end of a three-week unit on the role of the Internet in organizational behavior, then your professor likely wants you to synthesize that material.
- Try a free-write . A free-write is when you just write, without stopping, for a set period of time. That doesn’t sound very “free”; it actually sounds kind of coerced, right? The “free” part is what you write—it can be whatever comes to mind. Professional writers use free-writing to get started on a challenging (or distasteful) writing task or to overcome writer’s block or a powerful urge to procrastinate. The idea is that if you just make yourself write, you can’t help but produce some kind of useful nugget. Thus, even if the first eight sentences of your free write are all variations on “I don’t understand this” or “I’d really rather be doing something else,” eventually you’ll write something like “I guess the main point of this is…,” and—booyah!—you’re off and running.
- Ask for clarification . Even the most carefully crafted assignments may need some verbal clarification, especially if you’re new to a course or field. Professors generally love questions, so don’t be afraid to ask. Try to convey to your instructor that you want to learn and you’re ready to work, and not just looking for advice on how to get an A.
Defined-Topic Assignments
Many writing tasks will ask you to address a particular topic or a narrow set of topic options. Defined-topic writing assignments are used primarily to identify your familiarity with the subject matter. (Discuss the use of dialect in Their Eyes Were Watching God , for example.)
Remember, even when you’re asked to “show how” or “illustrate,” you’re still being asked to make an argument. You must shape and focus your discussion or analysis so that it supports a claim that you discovered and formulated and that all of your discussion and explanation develops and supports.
Undefined-Topic Assignments
Another writing assignment you’ll potentially encounter is one in which the topic may be only broadly identified (“water conservation” in an ecology course, for instance, or “the Dust Bowl” in a U.S. History course), or even completely open (“compose an argumentative research essay on a subject of your choice”).

Figure 3 . For open-ended assignments, it’s best to pick something that interests you personally.
Where defined-topic essays demonstrate your knowledge of the content , undefined-topic assignments are used to demonstrate your skills— your ability to perform academic research, to synthesize ideas, and to apply the various stages of the writing process.
The first hurdle with this type of task is to find a focus that interests you. Don’t just pick something you feel will be “easy to write about” or that you think you already know a lot about —those almost always turn out to be false assumptions. Instead, you’ll get the most value out of, and find it easier to work on, a topic that intrigues you personally or a topic about which you have a genuine curiosity.
The same getting-started ideas described for defined-topic assignments will help with these kinds of projects, too. You can also try talking with your instructor or a writing tutor (at your college’s writing center) to help brainstorm ideas and make sure you’re on track.
Getting Started in the Writing Process
Writing is not a linear process, so writing your essay, researching, rewriting, and adjusting are all part of the process. Below are some tips to keep in mind as you approach and manage your assignment.
Figure 4 . Writing is a recursive process that begins with examining the topic and prewriting.
Write down topic ideas. If you have been assigned a particular topic or focus, it still might be possible to narrow it down or personalize it to your own interests.
If you have been given an open-ended essay assignment, the topic should be something that allows you to enjoy working with the writing process. Select a topic that you’ll want to think about, read about, and write about for several weeks, without getting bored.

Figure 5 . Just getting started is sometimes the most difficult part of writing. Freewriting and planning to write multiple drafts can help you dive in.
If you’re writing about a subject you’re not an expert on and want to make sure you are presenting the topic or information realistically, look up the information or seek out an expert to ask questions.
- Note: Be cautious about information you retrieve online, especially if you are writing a research paper or an article that relies on factual information. A quick Google search may turn up unreliable, misleading sources. Be sure you consider the credibility of the sources you consult (we’ll talk more about that later in the course). And keep in mind that published books and works found in scholarly journals have to undergo a thorough vetting process before they reach publication and are therefore safer to use as sources.
- Check out a library. Yes, believe it or not, there is still information to be found in a library that hasn’t made its way to the Web. For an even greater breadth of resources, try a college or university library. Even better, research librarians can often be consulted in person, by phone, or even by email. And they love helping students. Don’t be afraid to reach out with questions!
Write a Rough Draft
It doesn’t matter how many spelling errors or weak adjectives you have in it. Your draft can be very rough! Jot down those random uncategorized thoughts. Write down anything you think of that you want included in your writing and worry about organizing and polishing everything later.
If You’re Having Trouble, Try F reewriting
Set a timer and write continuously until that time is up. Don’t worry about what you write, just keeping moving your pencil on the page or typing something (anything!) into the computer.
- Outcome: Writing in College. Provided by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY-NC-SA: Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike
- Writing in College: From Competence to Excellence. Authored by : Amy Guptill. Provided by : SUNY Open Textbooks. Located at : http://textbooks.opensuny.org/writing-in-college-from-competence-to-excellence/ . License : CC BY-NC-SA: Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike
- Image of man writing. Authored by : Matt Zhang. Located at : https://flic.kr/p/pAg6t9 . License : CC BY-NC-ND: Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives
- Writing Strategies. Provided by : Lumen Learning. Located at : https://courses.lumenlearning.com/lumencollegesuccess/chapter/writing-strategies/ . License : CC BY-NC-SA: Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike
- Image of woman reading. Authored by : Aaron Osborne. Located at : https://flic.kr/p/dPLmVV . License : CC BY: Attribution
- Image of sketches of magnifying glass. Authored by : Matt Cornock. Located at : https://flic.kr/p/eBSLmg . License : CC BY-NC: Attribution-NonCommercial
- How to Write a Summary. Authored by : WikiHow. Located at : http://www.wikihow.com/Write-a-Summary . License : CC BY-NC-SA: Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike
- How to Write. Provided by : WikiHow. License : CC BY-NC-SA: Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike
- Image of typing. Authored by : Kiran Foster. Located at : https://flic.kr/p/9M2WW4 . License : CC BY: Attribution


- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

4.3: Writing Assignments
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 58278
- Lumen Learning
Learning Objectives
- Describe common types and expectations of writing tasks given in a college class

What to Do With Writing Assignments
Writing assignments can be as varied as the instructors who assign them. Some assignments are explicit about what exactly you’ll need to do, in what order, and how it will be graded. Others are more open-ended, leaving you to determine the best path toward completing the project. Most fall somewhere in the middle, containing details about some aspects but leaving other assumptions unstated. It’s important to remember that your first resource for getting clarification about an assignment is your instructor—she or he will be very willing to talk out ideas with you, to be sure you’re prepared at each step to do well with the writing.
Writing in college is usually a response to class materials—an assigned reading, a discussion in class, an experiment in a lab. Generally speaking, these writing tasks can be divided into three broad categories: summary assignments, defined-topic assignments, and undefined-topic assignments.
Link to Learning
This Assignment Calculator can help you plan ahead for your writing assignment. Just plug in the date you plan to get started and the date it is due, and it will help break it down into manageable chunks.
Summary Assignments
Being asked to summarize a source is a common task in many types of writing. It can also seem like a straightforward task: simply restate, in shorter form, what the source says. A lot of advanced skills are hidden in this seemingly simple assignment, however.
An effective summary does the following:
- reflects your accurate understanding of a source’s thesis or purpose
- differentiates between major and minor ideas in a source
- demonstrates your ability to identify key phrases to quote
- demonstrates your ability to effectively paraphrase most of the source’s ideas
- captures the tone, style, and distinguishing features of a source
- does not reflect your personal opinion about the source
That last point is often the most challenging: we are opinionated creatures, by nature, and it can be very difficult to keep our opinions from creeping into a summary, which is meant to be completely neutral.
In college-level writing, assignments that are only summary are rare. That said, many types of writing tasks contain at least some element of summary, from a biology report that explains what happened during a chemical process, to an analysis essay that requires you to explain what several prominent positions about gun control are, as a component of comparing them against one another.
Writing Effective Summaries
Start with a clear identification of the work.
This automatically lets your readers know your intentions and that you’re covering the work of another author.
- In the featured article “Five Kinds of Learning,” the author, Holland Oates, justifies his opinion on the hot topic of learning styles — and adds a few himself.
Summarize the Piece as a Whole
Omit nothing important and strive for overall coherence through appropriate transitions. Write using “summarizing language.” Your reader needs to be reminded that this is not your own work. Use phrases like the article claims, the author suggests, etc.
- Present the material in a neutral fashion. Your opinions, ideas, and interpretations should be left in your brain — don’t put them into your summary. Be conscious of choosing your words. Only include what was in the original work.
- Be concise. This is a summary — it should be much shorter than the original piece. If you’re working on an article, give yourself a target length of 1/4 the original article.
Conclude with a Final Statement
This is not a statement of your own point of view, however; it should reflect the significance of the book or article from the author’s standpoint.
- Without rewriting the article, summarize what the author wanted to get across. Be careful not to evaluate in the conclusion or insert any of your own assumptions or opinions.
Understanding the Assignment and Getting Started

Often, the handout or other written text explaining the assignment—what professors call the assignment prompt —will explain the purpose of the assignment and the required parameters (length, number and type of sources, referencing style, etc.).
Also, don’t forget to check the rubric, if there is one, to understand how your writing will be assessed. After analyzing the prompt and the rubric, you should have a better sense of what kind of writing you are expected to produce.
Sometimes, though—especially when you are new to a field—you will encounter the baffling situation in which you comprehend every single sentence in the prompt but still have absolutely no idea how to approach the assignment! In a situation like that, consider the following tips:
- Focus on the verbs . Look for verbs like compare, explain, justify, reflect , or the all-purpose analyze . You’re not just producing a paper as an artifact; you’re conveying, in written communication, some intellectual work you have done. So the question is, what kind of thinking are you supposed to do to deepen your learning?
- Put the assignment in context . Many professors think in terms of assignment sequences. For example, a social science professor may ask you to write about a controversial issue three times: first, arguing for one side of the debate; second, arguing for another; and finally, from a more comprehensive and nuanced perspective, incorporating text produced in the first two assignments. A sequence like that is designed to help you think through a complex issue. If the assignment isn’t part of a sequence, think about where it falls in the span of the course (early, midterm, or toward the end), and how it relates to readings and other assignments. For example, if you see that a paper comes at the end of a three-week unit on the role of the Internet in organizational behavior, then your professor likely wants you to synthesize that material.
- Try a free-write . A free-write is when you just write, without stopping, for a set period of time. That doesn’t sound very “free”; it actually sounds kind of coerced, right? The “free” part is what you write—it can be whatever comes to mind. Professional writers use free-writing to get started on a challenging (or distasteful) writing task or to overcome writer’s block or a powerful urge to procrastinate. The idea is that if you just make yourself write, you can’t help but produce some kind of useful nugget. Thus, even if the first eight sentences of your free write are all variations on “I don’t understand this” or “I’d really rather be doing something else,” eventually you’ll write something like “I guess the main point of this is…,” and—booyah!—you’re off and running.
- Ask for clarification . Even the most carefully crafted assignments may need some verbal clarification, especially if you’re new to a course or field. Professors generally love questions, so don’t be afraid to ask. Try to convey to your instructor that you want to learn and you’re ready to work, and not just looking for advice on how to get an A.
Defined-Topic Assignments
Many writing tasks will ask you to address a particular topic or a narrow set of topic options. Defined-topic writing assignments are used primarily to identify your familiarity with the subject matter. (Discuss the use of dialect in Their Eyes Were Watching God , for example.)
Remember, even when you’re asked to “show how” or “illustrate,” you’re still being asked to make an argument. You must shape and focus your discussion or analysis so that it supports a claim that you discovered and formulated and that all of your discussion and explanation develops and supports.
Undefined-Topic Assignments
Another writing assignment you’ll potentially encounter is one in which the topic may be only broadly identified (“water conservation” in an ecology course, for instance, or “the Dust Bowl” in a U.S. History course), or even completely open (“compose an argumentative research essay on a subject of your choice”).

Where defined-topic essays demonstrate your knowledge of the content , undefined-topic assignments are used to demonstrate your skills— your ability to perform academic research, to synthesize ideas, and to apply the various stages of the writing process.
The first hurdle with this type of task is to find a focus that interests you. Don’t just pick something you feel will be “easy to write about” or that you think you already know a lot about —those almost always turn out to be false assumptions. Instead, you’ll get the most value out of, and find it easier to work on, a topic that intrigues you personally or a topic about which you have a genuine curiosity.
The same getting-started ideas described for defined-topic assignments will help with these kinds of projects, too. You can also try talking with your instructor or a writing tutor (at your college’s writing center) to help brainstorm ideas and make sure you’re on track.
Getting Started in the Writing Process
Writing is not a linear process, so writing your essay, researching, rewriting, and adjusting are all part of the process. Below are some tips to keep in mind as you approach and manage your assignment.

Write down topic ideas. If you have been assigned a particular topic or focus, it still might be possible to narrow it down or personalize it to your own interests.
If you have been given an open-ended essay assignment, the topic should be something that allows you to enjoy working with the writing process. Select a topic that you’ll want to think about, read about, and write about for several weeks, without getting bored.

If you’re writing about a subject you’re not an expert on and want to make sure you are presenting the topic or information realistically, look up the information or seek out an expert to ask questions.
- Note: Be cautious about information you retrieve online, especially if you are writing a research paper or an article that relies on factual information. A quick Google search may turn up unreliable, misleading sources. Be sure you consider the credibility of the sources you consult (we’ll talk more about that later in the course). And keep in mind that published books and works found in scholarly journals have to undergo a thorough vetting process before they reach publication and are therefore safer to use as sources.
- Check out a library. Yes, believe it or not, there is still information to be found in a library that hasn’t made its way to the Web. For an even greater breadth of resources, try a college or university library. Even better, research librarians can often be consulted in person, by phone, or even by email. And they love helping students. Don’t be afraid to reach out with questions!
Write a Rough Draft
It doesn’t matter how many spelling errors or weak adjectives you have in it. Your draft can be very rough! Jot down those random uncategorized thoughts. Write down anything you think of that you want included in your writing and worry about organizing and polishing everything later.
If You’re Having Trouble, Try F reewriting
Set a timer and write continuously until that time is up. Don’t worry about what you write, just keeping moving your pencil on the page or typing something (anything!) into the computer.
Contributors and Attributions
- Outcome: Writing in College. Provided by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY-NC-SA: Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike
- Writing in College: From Competence to Excellence. Authored by : Amy Guptill. Provided by : SUNY Open Textbooks. Located at : textbooks.opensuny.org/writing-in-college-from-competence-to-excellence/. License : CC BY-NC-SA: Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike
- Image of man writing. Authored by : Matt Zhang. Located at : https://flic.kr/p/pAg6t9 . License : CC BY-NC-ND: Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives
- Writing Strategies. Provided by : Lumen Learning. Located at : courses.lumenlearning.com/lumencollegesuccess/chapter/writing-strategies/. License : CC BY-NC-SA: Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike
- Image of woman reading. Authored by : Aaron Osborne. Located at : https://flic.kr/p/dPLmVV . License : CC BY: Attribution
- Image of sketches of magnifying glass. Authored by : Matt Cornock. Located at : https://flic.kr/p/eBSLmg . License : CC BY-NC: Attribution-NonCommercial
- How to Write a Summary. Authored by : WikiHow. Located at : http://www.wikihow.com/Write-a-Summary . License : CC BY-NC-SA: Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike
- How to Write. Provided by : WikiHow. License : CC BY-NC-SA: Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike
- Image of typing. Authored by : Kiran Foster. Located at : https://flic.kr/p/9M2WW4 . License : CC BY: Attribution
Writing a Summary or Rhetorical Précis to Analyze Nonfiction Texts
Download this Handout PDF
Academic writers across all disciplines analyze texts. They summarize and critique published articles, evaluate papers’ arguments, and reflect on essays. In order to do these things, they have to read complex texts carefully and understand them clearly.
This page is about how you can read and analyze nonfiction texts. When you’ve read a text well, you can then discuss it in class, think critically about it, incorporate it into your writing, consider it in light of other texts, and advance or push against its ideas. We believe two productive strategies for approaching this kind of reading and analysis are active reading and rhetorical précis writing. This page provides a guide to these strategies and practical ways to help you evaluate, compare, and reflect upon nonfiction texts.
Active Reading
Introduction to the rhetorical précis, parts of a rhetorical précis, using a rhetorical précis to guide analysis.
Active reading requires you to slow your reading down, engage more intentionally with the text, think about it, and focus your attention on its ideas. When you read actively, you can’t just flip pages and daydream about tomorrow’s plans. Much has been written about active reading, but generally we recommend that when you read you:
- Skim over the text before reading it. Look to see how long it is, where it’s published, how it may be divided into sections, what kind of works cited list it has, whether there are appendices, etc. Use the title to help you predict what the text is about and what it argues. This overview will help you to understand the context, genre, and purpose of this piece as well as help you gauge how long it will take you to read it and how it might be relevant to your class, paper, or project.
- Take notes about the text’s key ideas and your responses to those ideas. Depending on the text and your preferences, these notes could be made on your copy of the text or article or in a separate place. Notes will help you remember and process what the text is about and what you think about it.
In addition to these strategies, we firmly believe that one of the best ways to understand a book, article, essay, blog post, etc. is to write a summary of it. Specifically, we recommend that you use your reading to generate a rhetorical précis.
“Précis” is French for “specific” or “precise.” It’s also a particular kind of writing. When you write a précis you have to exactly and succinctly account for the most important parts of a text. If you write a successful précis, it is a good indication that you’ve read that text closely and that you understand its major moves and arguments. Writing a précis is an excellent way to show that you’ve closely read a text.
Disclaimer: There are different kinds of précis for different contexts. A legal précis is different from what we’re talking about here. Some précis are longer or shorter than others. If you are writing a précis as a course assignment, be sure to follow your instructor’s guidance on what this should consist of and how it should be formatted.
Sometimes rhetorical précis writing is a course requirement. However, even if you aren’t required to write a précis for a class, writing one can help you in a number of ways. Writing a précis guides your reading and directs your attention to the key aspects of a text. Précis writing prepares you to discuss a text and sets you up for that important next step: analysis. A rhetorical précis can even help you structure your annotated bibliography annotations or provide you with summary sentences to include in a paper as you account for your sources.
A rhetorical précis, as developed by Margaret K. Woodworth and described in her 1988 article “The Rhetorical Précis” (published by Rhetoric Review), consists of four dense but direct sentences.
- The first sentence identifies who wrote the text, where and when it was published, and what its topic and claim are.
- The second sentence explores how the text is developed and organized.
- The third sentence explains why the author wrote this, her purpose or intended effect.
- The fourth and final sentence describes the “for whom” of the text by clarifying who the intended or assumed audience of this text is.
Let’s look more closely at those four parts.
First Sentence: Who, Where, When, and What?
Start by identifying the author and offering any information that might help clarify who this person is in relation to this text. Is this a scholar? If so, what is her field? Is she a public official or a prominent blogger? Is he a public intellectual? A reporter? A spokesperson? Has he written other stuff? Locate a bio in the journal or the book cover. Do a quick internet search. Figuring out who the writer is will help you understand some of the texts’ context.
Next up, the publication. What is its title? Is it a book in a series or an article in a special collection? Does it appear in the leisure section of a local newspaper? Sometimes the title of the journal is self-explanatory, but at other times it’s unfamiliar or not clearly connected to a specific discipline. Explain it as necessary. Add the date in parentheses after the title of the text. Unless it’s a newspaper, magazine, or time-sensitive online article, usually just the year will suffice.
The rest of the sentence should be about the article’s topic—what it is about. In order to make this part particularly precise, use a rhetorically strong verb to describe the author’s claim. For example, the author may suggest, argue, analyze, imply, urge, contrast, or claim something.
Second Sentence: How?
In this sentence, provide a very condensed outline of how the author develops, structures, and supports the argument. What kind of evidence does the article draw upon? How is the case built? Perhaps by comparing and contrasting, illustrating, defining, or providing context? Perhaps the text starts out with a narrative and then moves into a description of several research studies? This sentence should account for all the most important moves made across this piece.
Third Sentence: Why?
What does the writer want the reader to do, believe, feel, or think about all this? What was the purpose of this text? In the first sentence, you told us what that author is arguing; now it is time to consider why the author has done all of this. Use an “in order to” phrase in this sentence to very clearly indicate the purpose.
Fourth Sentence: For Whom?
In the final sentence, identify the author’s intended audience and offer some rationale for how you know that to be the audience. Look back at the publication and think about who is likely to read this kind of magazine, journal, or book. Pay attention to the language used in this piece and how much background the writer provides. What does the writer assume readers believe, know, or value? Identifying the audience helps you consider how rhetorically effective this text is.
An Annotated Sample of a Rhetorical Précis
Take a look at this annotated précis of William Cronon’s 1995 article “The Trouble with Wilderness: Or, Getting Back to the Wrong Nature.” It closely follows the précis structure outlined above.
In “The Trouble With Wilderness: Or, Getting Back to the Wrong Nature” (1995), the opening essay of the edited collection Uncommon Ground: Rethinking the Human Place in Nature, renowned environmental historian William Cronon [Comment: The information about who Cronon is was very easily located at the end of the article and through a quick internet search.] critiques the romantic idolization of supposedly untouched, vast wilderness and argues that such a perspective of wilderness negatively affects humankind’s relationship with nature. Cronon builds a historical case for wilderness as a human construct, explores the cultural and literary foundations for the belief that wilderness is a sublime frontier, identifies the problematic paradoxes inherent in this belief, and outlines the detriments of and possible paradigm–shifting solutions to this environmental problem. [Comment: One of the challenges of the second sentence is to decide what not to include. In this case, more could be said about what those paradoxes and detriments are, but since the focus here is on the “how” instead of the “what,” they have been left out. If those kinds of unidentified details are important enough, there is room to mention them more thoroughly in the third sentence.] Cronon opposes the perspective of wilderness as an idealized, non–human space in order to persuade his readers to live rightly in relationship to nature and embrace the reality that “home” as a welcoming, responsibility–requiring place encompasses both “wilderness” and “civilization.” [Comment: Often there is more than one “why,” so be on the look out for this as you actively read.] According to his specific identification, scholarly presentation, and publication venue, Cronon’s primary audience includes American environmentalist academics. [Comment: In the later third of this essay, Cronon uses the pronoun “we” to identify himself and his assumed readership. Often authors aren’t this useful in helping to identify an audience.]
Writing a good précis is a lot of work. It takes dedicated time and consideration. But, it can be useful in and of itself and productive in the development of additional academic writing. Of course, the most obvious application of a précis is connected to its function as a summary. In academic writing, we summarize sources all the time. Once you have written a précis, you can incorporate some of its sentences or ideas into your writing when you need to quickly account for a text’s argument, content, or purpose.
But a rhetorical précis is even more powerfully useful for writing analysis.
Etymologically, “analysis” comes from the Ancient Greek terms for “throughout” and “loosening.” When you analyze something, you deconstruct it, extract its parts, peer inside to see how everything fits together. You thoroughly loosen it in order to understand it better. When you’ve used a précis to lay out the primary elements of this text (the author; the argument’s what, how, and why; and the audience) in front of you, you’re ready to move on with your analysis. Analysis of nonfiction texts can take several forms, but three common ones are: evaluation and critique, comparison, and reflection.
Evaluation and Critique
Evaluating a text requires you to use your analysis to consider and critique the strengths and weaknesses of that piece of writing. Look back at the argument and audience and ask yourself some of these questions:
- Is this a persuasive argument for this group of readers?
- How well is the author’s argument developed and clarified through the structure of the text?
- Where does the logic of the argument and its supporting evidence cohere or fall apart?
- Do the author’s background, tone, evidence, and assumptions foster credibility?
- Does the piece achieve what the author intended?
Detailed answers—with examples—to any of these or similar questions could generate enough material for a close, analytical evaluation. Make sure that you are connecting your assertions about what works and doesn’t work in this text to the author, the argument’s development and purpose, and the audience. Make sure that you are looking deeply at how and why various elements of the text and its argument succeed or falter.
Through comparison, you bring together an analysis of more than one text. Start by writing a précis for each piece you have to compare. Then look at each précis side–by–side and ask yourself about how a sentence in one précis relates to the corresponding sentence in the other précis. Here are some questions to guide your thinking:
- Are all texts addressing a parallel idea?
- Are they making similar or different arguments?
- Have they employed similar methods to arrive at their arguments?
- Are they using the same kind of structure to develop those arguments?
- What is different about their intended audiences?
- Is one more or less successful or persuasive than the other?
Let what you identify as being similar and different about these texts guide your comparative analysis.
Reflection provides you with space to analyze a text in light of your experiences, perspectives, and ideas. In this kind of writing, you get to talk about yourself. In a way, a reflective analysis is kind of like a comparative analysis where the second text is you. Look back at that rhetorical précis and ask yourself questions like these, or other questions that connect what you know and have experienced with the text you have read:
- What else have you read or experienced that furthers or complicates the argument made by this text?
- How do you see that these ideas fit into the larger context of what you’ve been studying in this course?
- Why do you have a particular opinion or response towards this piece of writing?
- Moving forward, how can this text, its argument, or its presentation be influential in shaping your thinking or research?
In order to analyze a text, you need to understand key elements of it. Closely reading that text and summarizing it through a rhetorical précis can help you understand it better. In large part, the quality of your analysis will be dependent on the quality of your comprehension. So, give yourself the time you need to read carefully, think deeply, and analyze effectively.
Works Cited
Cronon, William. “The Trouble with Wilderness: Or, Getting Back to the Wrong Nature.” Environmental History , vol. 1, no. 1, pp. 7–28.
Woodworth, Margaret K. “The Rhetorical Précis.” Rhetoric Review , vol. 7, no. 1, pp. 156–64.

Academic and Professional Writing
This is an accordion element with a series of buttons that open and close related content panels.
Analysis Papers
Reading Poetry
A Short Guide to Close Reading for Literary Analysis
Using Literary Quotations
Play Reviews
Writing a Rhetorical Précis to Analyze Nonfiction Texts
Incorporating Interview Data
Grant Proposals
Planning and Writing a Grant Proposal: The Basics
Additional Resources for Grants and Proposal Writing
Job Materials and Application Essays
Writing Personal Statements for Ph.D. Programs
- Before you begin: useful tips for writing your essay
- Guided brainstorming exercises
- Get more help with your essay
- Frequently Asked Questions
Resume Writing Tips
CV Writing Tips
Cover Letters
Business Letters
Proposals and Dissertations
Resources for Proposal Writers
Resources for Dissertators
Research Papers
Planning and Writing Research Papers
Quoting and Paraphrasing
Writing Annotated Bibliographies
Creating Poster Presentations
Writing an Abstract for Your Research Paper
Thank-You Notes
Advice for Students Writing Thank-You Notes to Donors
Reading for a Review
Critical Reviews
Writing a Review of Literature
Scientific Reports
Scientific Report Format
Sample Lab Assignment
Writing for the Web
Writing an Effective Blog Post
Writing for Social Media: A Guide for Academics

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Table of contents. When to write a summary. Step 1: Read the text. Step 2: Break the text down into sections. Step 3: Identify the key points in each section. Step 4: Write the summary. Step 5: Check the summary against the article. Other interesting articles. Frequently asked questions about summarizing.
A summary should include all of the main points or ideas in the work but avoid smaller details or ideas. You don't want to provide every aspect of the plot or smaller points in your summary. Your summary should be written using your own words. Present the main ideas objectively, avoiding your own opinion and thoughts about the work.
If your assignment requires an argument with a thesis statement and supporting evidence—as many academic writing assignments do—then you should limit the amount of summary in your paper. You might use summary to provide background, set the stage, or illustrate supporting evidence, but keep it very brief: a few sentences should do the trick.
1. Read and take notes. First things first: Read or watch the original work you'll be summarizing. While you do, take brief pauses and explain to yourself what you just read or watched. As the main ideas start becoming clear to you, take notes. This will make the writing process easier. 2.
Even if your summary is the length of a full paper, you are likely summarizing a book or other significantly longer work. 2. A summary should tell the reader the highlights of what they need to know without giving them unnecessary details. 3. It should also include enough details to give a clear and honest picture.
The Writing Center Summary: Using it Wisely What this handout is about Knowing how to summarize something you have read, seen, or heard is a valuable skill, one you have probably used in many writing assignments. It is important, though, to recognize when you must go beyond describing, explaining, and restating texts and offer a more complex
A summary must be independent: You are not being asked to imitate the author of the text you are writing about. On the contrary, you are expected to maintain your own voice throughout the summary. Don't simply quote the author; instead use your own words to express your understanding of what you have read. After all, your summary is based on ...
Summary asks writers to identify and restate in their own words the most important elements of another writer's text and, in doing do, capture the relative importance of different moments in that text as well as their logical relationship to one another. In many contexts summary is a formative assignment that's a step in a larger essay or ...
A final once-over in which you reverse outline the piece, writing the main point or function of each section in the margins. * See terms and conditions. When you fully understand both the argument and its construction, you're ready to write the summary. Start with the main idea or argument. Follow it with the major points that you've ...
Using a summary in an assignment is a way to convey the main ideas or relevant themes of another piece of research. If you want to analyse ideas, research, data, and information created by researchers and draw conclusions from across the published research you may use a summary in your writing to do this. Summarising is a critical thinking tool ...
A summary is written in your own words . It contains few or no quotes. A summary is always shorter than the original text, often about 1/3 as long as the original. It is the ultimate "fat-free" writing. An article or paper may be summarized in a few sentences or a couple of paragraphs. A book may be summarized in an article or a short paper.
Step 2: Take Notes. As you read the work, simultaneously take notes. If you own the book, it might be helpful to add your notes to the margins or highlight passages that are particularly relevant or capture a key idea. If you don't own the book, try taking notes on your computer or in a notebook.
The Process of Summarizing. Note that these videos were created while APA 6 was the style guide edition in use. There may be some examples of writing that have not been updated to APA 7 guidelines. The Process of Summarizing (video, 5:06) Transcript. Definition and Examples of Summary (video, 4:35) Transcript.
Typically, your executive summary should be a one-pager (one and a half pages at worst). To summarise a 3000 - 5000-word document into one page is no easy task, so you'll need to: Present only the most important information (key insights, recommendations, etc). Write concisely - i.e. with brevity and completeness.
44 Summary Writing What is a Summary? A summary is a comprehensive and objective restatement of the main ideas of a text (an article, book, movie, event, etc.) ... Some summary assignments will expect students to condense material more than others. For example, when summary is the sole purpose of the assignment, the student might be asked to ...
Table of contents. When to write a summary. Step 1: Read the text. Step 2: Break the text down into sections. Step 3: Identify the key points in each section. Step 4: Write the summary. Step 5: Check the summary against the article. Frequently asked questions.
1. Find the main idea. A useful summary distills the source material down to its most important point to inform the reader. Pick the major point you want to communicate to the reader, and use your limited sentences wisely to convey it. Take down a few notes to help outline your thoughts in an organized manner. 2.
What this handout is about. The first step in any successful college writing venture is reading the assignment. While this sounds like a simple task, it can be a tough one. This handout will help you unravel your assignment and begin to craft an effective response. Much of the following advice will involve translating typical assignment terms ...
A summary is written in your own words . It contains few or no quotes. A summary is always shorter than the original text, often about 1/3 as long as the original. It is the ultimate "fat-free" writing. An article or paper may be summarized in a few sentences or a couple of paragraphs. A book may be summarized in an article or a short paper.
Common Writing Assignments. These OWL resources will help you understand and complete specific types of writing assignments, such as annotated bibliographies, book reports, and research papers. This section also includes resources on writing academic proposals for conference presentations, journal articles, and books.
Writing in college is usually a response to class materials—an assigned reading, a discussion in class, an experiment in a lab. Generally speaking, these writing tasks can be divided into three broad categories: summary assignments, defined-topic assignments, and undefined-topic assignments.
In college-level writing, assignments that are only summary are rare. That said, many types of writing tasks contain at least some element of summary, from a biology report that explains what happened during a chemical process, to an analysis essay that requires you to explain what several prominent positions about gun control are, as a ...
ASSIGNMENT 1. DUE DATE: 30/04/2024NB: WRITE NEATLY AND UNDERLINE ALL YOUR ANSWERS.1. A steel beam of an unequal flanges cross section is resting on an elasticfoundation whose modulus of foundation (KS) is 6.5 N/mm2. The beam is 12 mlong, and it is subjected to a concentrated load of 300 kN and anti-clockwisemoment of 0.5 ...
Writing a good précis is a lot of work. It takes dedicated time and consideration. But, it can be useful in and of itself and productive in the development of additional academic writing. Of course, the most obvious application of a précis is connected to its function as a summary. In academic writing, we summarize sources all the time.
Read the six steps on how to write a summary. Read the sample summary. Complete the "Practice Writing a Summary" worksheet and submit it to the English Learning Center for a signature. Complete a summary for "Spanglish Spoken Here.". Follow the instructions under the Final Summary Requirements. This summary will be graded by a lab ...