- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support

What Is a Case Study?
Weighing the pros and cons of this method of research
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Cara Lustik is a fact-checker and copywriter.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Cara-Lustik-1000-77abe13cf6c14a34a58c2a0ffb7297da.jpg)
Verywell / Colleen Tighe
- Pros and Cons
What Types of Case Studies Are Out There?
Where do you find data for a case study, how do i write a psychology case study.
A case study is an in-depth study of one person, group, or event. In a case study, nearly every aspect of the subject's life and history is analyzed to seek patterns and causes of behavior. Case studies can be used in many different fields, including psychology, medicine, education, anthropology, political science, and social work.
The point of a case study is to learn as much as possible about an individual or group so that the information can be generalized to many others. Unfortunately, case studies tend to be highly subjective, and it is sometimes difficult to generalize results to a larger population.
While case studies focus on a single individual or group, they follow a format similar to other types of psychology writing. If you are writing a case study, we got you—here are some rules of APA format to reference.
At a Glance
A case study, or an in-depth study of a person, group, or event, can be a useful research tool when used wisely. In many cases, case studies are best used in situations where it would be difficult or impossible for you to conduct an experiment. They are helpful for looking at unique situations and allow researchers to gather a lot of˜ information about a specific individual or group of people. However, it's important to be cautious of any bias we draw from them as they are highly subjective.
What Are the Benefits and Limitations of Case Studies?
A case study can have its strengths and weaknesses. Researchers must consider these pros and cons before deciding if this type of study is appropriate for their needs.
One of the greatest advantages of a case study is that it allows researchers to investigate things that are often difficult or impossible to replicate in a lab. Some other benefits of a case study:
- Allows researchers to capture information on the 'how,' 'what,' and 'why,' of something that's implemented
- Gives researchers the chance to collect information on why one strategy might be chosen over another
- Permits researchers to develop hypotheses that can be explored in experimental research
On the other hand, a case study can have some drawbacks:
- It cannot necessarily be generalized to the larger population
- Cannot demonstrate cause and effect
- It may not be scientifically rigorous
- It can lead to bias
Researchers may choose to perform a case study if they want to explore a unique or recently discovered phenomenon. Through their insights, researchers develop additional ideas and study questions that might be explored in future studies.
It's important to remember that the insights from case studies cannot be used to determine cause-and-effect relationships between variables. However, case studies may be used to develop hypotheses that can then be addressed in experimental research.
Case Study Examples
There have been a number of notable case studies in the history of psychology. Much of Freud's work and theories were developed through individual case studies. Some great examples of case studies in psychology include:
- Anna O : Anna O. was a pseudonym of a woman named Bertha Pappenheim, a patient of a physician named Josef Breuer. While she was never a patient of Freud's, Freud and Breuer discussed her case extensively. The woman was experiencing symptoms of a condition that was then known as hysteria and found that talking about her problems helped relieve her symptoms. Her case played an important part in the development of talk therapy as an approach to mental health treatment.
- Phineas Gage : Phineas Gage was a railroad employee who experienced a terrible accident in which an explosion sent a metal rod through his skull, damaging important portions of his brain. Gage recovered from his accident but was left with serious changes in both personality and behavior.
- Genie : Genie was a young girl subjected to horrific abuse and isolation. The case study of Genie allowed researchers to study whether language learning was possible, even after missing critical periods for language development. Her case also served as an example of how scientific research may interfere with treatment and lead to further abuse of vulnerable individuals.
Such cases demonstrate how case research can be used to study things that researchers could not replicate in experimental settings. In Genie's case, her horrific abuse denied her the opportunity to learn a language at critical points in her development.
This is clearly not something researchers could ethically replicate, but conducting a case study on Genie allowed researchers to study phenomena that are otherwise impossible to reproduce.
There are a few different types of case studies that psychologists and other researchers might use:
- Collective case studies : These involve studying a group of individuals. Researchers might study a group of people in a certain setting or look at an entire community. For example, psychologists might explore how access to resources in a community has affected the collective mental well-being of those who live there.
- Descriptive case studies : These involve starting with a descriptive theory. The subjects are then observed, and the information gathered is compared to the pre-existing theory.
- Explanatory case studies : These are often used to do causal investigations. In other words, researchers are interested in looking at factors that may have caused certain things to occur.
- Exploratory case studies : These are sometimes used as a prelude to further, more in-depth research. This allows researchers to gather more information before developing their research questions and hypotheses .
- Instrumental case studies : These occur when the individual or group allows researchers to understand more than what is initially obvious to observers.
- Intrinsic case studies : This type of case study is when the researcher has a personal interest in the case. Jean Piaget's observations of his own children are good examples of how an intrinsic case study can contribute to the development of a psychological theory.
The three main case study types often used are intrinsic, instrumental, and collective. Intrinsic case studies are useful for learning about unique cases. Instrumental case studies help look at an individual to learn more about a broader issue. A collective case study can be useful for looking at several cases simultaneously.
The type of case study that psychology researchers use depends on the unique characteristics of the situation and the case itself.
There are a number of different sources and methods that researchers can use to gather information about an individual or group. Six major sources that have been identified by researchers are:
- Archival records : Census records, survey records, and name lists are examples of archival records.
- Direct observation : This strategy involves observing the subject, often in a natural setting . While an individual observer is sometimes used, it is more common to utilize a group of observers.
- Documents : Letters, newspaper articles, administrative records, etc., are the types of documents often used as sources.
- Interviews : Interviews are one of the most important methods for gathering information in case studies. An interview can involve structured survey questions or more open-ended questions.
- Participant observation : When the researcher serves as a participant in events and observes the actions and outcomes, it is called participant observation.
- Physical artifacts : Tools, objects, instruments, and other artifacts are often observed during a direct observation of the subject.
If you have been directed to write a case study for a psychology course, be sure to check with your instructor for any specific guidelines you need to follow. If you are writing your case study for a professional publication, check with the publisher for their specific guidelines for submitting a case study.
Here is a general outline of what should be included in a case study.
Section 1: A Case History
This section will have the following structure and content:
Background information : The first section of your paper will present your client's background. Include factors such as age, gender, work, health status, family mental health history, family and social relationships, drug and alcohol history, life difficulties, goals, and coping skills and weaknesses.
Description of the presenting problem : In the next section of your case study, you will describe the problem or symptoms that the client presented with.
Describe any physical, emotional, or sensory symptoms reported by the client. Thoughts, feelings, and perceptions related to the symptoms should also be noted. Any screening or diagnostic assessments that are used should also be described in detail and all scores reported.
Your diagnosis : Provide your diagnosis and give the appropriate Diagnostic and Statistical Manual code. Explain how you reached your diagnosis, how the client's symptoms fit the diagnostic criteria for the disorder(s), or any possible difficulties in reaching a diagnosis.
Section 2: Treatment Plan
This portion of the paper will address the chosen treatment for the condition. This might also include the theoretical basis for the chosen treatment or any other evidence that might exist to support why this approach was chosen.
- Cognitive behavioral approach : Explain how a cognitive behavioral therapist would approach treatment. Offer background information on cognitive behavioral therapy and describe the treatment sessions, client response, and outcome of this type of treatment. Make note of any difficulties or successes encountered by your client during treatment.
- Humanistic approach : Describe a humanistic approach that could be used to treat your client, such as client-centered therapy . Provide information on the type of treatment you chose, the client's reaction to the treatment, and the end result of this approach. Explain why the treatment was successful or unsuccessful.
- Psychoanalytic approach : Describe how a psychoanalytic therapist would view the client's problem. Provide some background on the psychoanalytic approach and cite relevant references. Explain how psychoanalytic therapy would be used to treat the client, how the client would respond to therapy, and the effectiveness of this treatment approach.
- Pharmacological approach : If treatment primarily involves the use of medications, explain which medications were used and why. Provide background on the effectiveness of these medications and how monotherapy may compare with an approach that combines medications with therapy or other treatments.
This section of a case study should also include information about the treatment goals, process, and outcomes.
When you are writing a case study, you should also include a section where you discuss the case study itself, including the strengths and limitiations of the study. You should note how the findings of your case study might support previous research.
In your discussion section, you should also describe some of the implications of your case study. What ideas or findings might require further exploration? How might researchers go about exploring some of these questions in additional studies?
Need More Tips?
Here are a few additional pointers to keep in mind when formatting your case study:
- Never refer to the subject of your case study as "the client." Instead, use their name or a pseudonym.
- Read examples of case studies to gain an idea about the style and format.
- Remember to use APA format when citing references .
Crowe S, Cresswell K, Robertson A, Huby G, Avery A, Sheikh A. The case study approach . BMC Med Res Methodol . 2011;11:100.
Crowe S, Cresswell K, Robertson A, Huby G, Avery A, Sheikh A. The case study approach . BMC Med Res Methodol . 2011 Jun 27;11:100. doi:10.1186/1471-2288-11-100
Gagnon, Yves-Chantal. The Case Study as Research Method: A Practical Handbook . Canada, Chicago Review Press Incorporated DBA Independent Pub Group, 2010.
Yin, Robert K. Case Study Research and Applications: Design and Methods . United States, SAGE Publications, 2017.
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."

Understanding Case Study Method in Research: A Comprehensive Guide

Table of Contents
Have you ever wondered how researchers uncover the nuanced layers of individual experiences or the intricate workings of a particular event? One of the keys to unlocking these mysteries lies in the qualitative research focusing on a single subject in its real-life context.">case study method , a research strategy that might seem straightforward at first glance but is rich with complexity and insightful potential. Let’s dive into the world of case studies and discover why they are such a valuable tool in the arsenal of research methods.
What is a Case Study Method?
At its core, the case study method is a form of qualitative research that involves an in-depth, detailed examination of a single subject, such as an individual, group, organization, event, or phenomenon. It’s a method favored when the boundaries between phenomenon and context are not clearly evident, and where multiple sources of data are used to illuminate the case from various perspectives. This method’s strength lies in its ability to provide a comprehensive understanding of the case in its real-life context.
Historical Context and Evolution of Case Studies
Case studies have been around for centuries, with their roots in medical and psychological research. Over time, their application has spread to disciplines like sociology, anthropology, business, and education. The evolution of this method has been marked by a growing appreciation for qualitative data and the rich, contextual insights it can provide, which quantitative methods may overlook.
Characteristics of Case Study Research
What sets the case study method apart are its distinct characteristics:
- Intensive Examination: It provides a deep understanding of the case in question, considering the complexity and uniqueness of each case.
- Contextual Analysis: The researcher studies the case within its real-life context, recognizing that the context can significantly influence the phenomenon.
- Multiple Data Sources: Case studies often utilize various data sources like interviews, observations, documents, and reports, which provide multiple perspectives on the subject.
- Participant’s Perspective: This method often focuses on the perspectives of the participants within the case, giving voice to those directly involved.
Types of Case Studies
There are different types of case studies, each suited for specific research objectives:
- Exploratory: These are conducted before large-scale research projects to help identify questions, select measurement constructs, and develop hypotheses.
- Descriptive: These involve a detailed, in-depth description of the case, without attempting to determine cause and effect.
- Explanatory: These are used to investigate cause-and-effect relationships and understand underlying principles of certain phenomena.
- Intrinsic: This type is focused on the case itself because the case presents an unusual or unique issue.
- Instrumental: Here, the case is secondary to understanding a broader issue or phenomenon.
- Collective: These involve studying a group of cases collectively or comparably to understand a phenomenon, population, or general condition.
The Process of Conducting a Case Study
Conducting a case study involves several well-defined steps:
- Defining Your Case: What or who will you study? Define the case and ensure it aligns with your research objectives.
- Selecting Participants: If studying people, careful selection is crucial to ensure they fit the case criteria and can provide the necessary insights.
- Data Collection: Gather information through various methods like interviews, observations, and reviewing documents.
- Data Analysis: Analyze the collected data to identify patterns, themes, and insights related to your research question.
- Reporting Findings: Present your findings in a way that communicates the complexity and richness of the case study, often through narrative.
Case Studies in Practice: Real-world Examples
Case studies are not just academic exercises; they have practical applications in every field. For instance, in business, they can explore consumer behavior or organizational strategies. In psychology, they can provide detailed insight into individual behaviors or conditions. Education often uses case studies to explore teaching methods or learning difficulties.
Advantages of Case Study Research
While the case study method has its critics, it offers several undeniable advantages:
- Rich, Detailed Data: It captures data too complex for quantitative methods.
- Contextual Insights: It provides a better understanding of the phenomena in its natural setting.
- Contribution to Theory: It can generate and refine theory, offering a foundation for further research.
Limitations and Criticism
However, it’s important to acknowledge the limitations and criticisms:
- Generalizability : Findings from case studies may not be widely generalizable due to the focus on a single case.
- Subjectivity: The researcher’s perspective may influence the study, which requires careful reflection and transparency.
- Time-Consuming: They require a significant amount of time to conduct and analyze properly.
Concluding Thoughts on the Case Study Method
The case study method is a powerful tool that allows researchers to delve into the intricacies of a subject in its real-world environment. While not without its challenges, when executed correctly, the insights garnered can be incredibly valuable, offering depth and context that other methods may miss. Robert K\. Yin ’s advocacy for this method underscores its potential to illuminate and explain contemporary phenomena, making it an indispensable part of the researcher’s toolkit.
Reflecting on the case study method, how do you think its application could change with the advancements in technology and data analytics? Could such a traditional method be enhanced or even replaced in the future?
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
Average rating 0 / 5. Vote count: 0
No votes so far! Be the first to rate this post.
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Submit Comment
Research Methods in Psychology
1 Introduction to Psychological Research – Objectives and Goals, Problems, Hypothesis and Variables
- Nature of Psychological Research
- The Context of Discovery
- Context of Justification
- Characteristics of Psychological Research
- Goals and Objectives of Psychological Research
2 Introduction to Psychological Experiments and Tests
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Extraneous Variables
- Experimental and Control Groups
- Introduction of Test
- Types of Psychological Test
- Uses of Psychological Tests
3 Steps in Research
- Research Process
- Identification of the Problem
- Review of Literature
- Formulating a Hypothesis
- Identifying Manipulating and Controlling Variables
- Formulating a Research Design
- Constructing Devices for Observation and Measurement
- Sample Selection and Data Collection
- Data Analysis and Interpretation
- Hypothesis Testing
- Drawing Conclusion
4 Types of Research and Methods of Research
- Historical Research
- Descriptive Research
- Correlational Research
- Qualitative Research
- Ex-Post Facto Research
- True Experimental Research
- Quasi-Experimental Research
5 Definition and Description Research Design, Quality of Research Design
- Research Design
- Purpose of Research Design
- Design Selection
- Criteria of Research Design
- Qualities of Research Design
6 Experimental Design (Control Group Design and Two Factor Design)
- Experimental Design
- Control Group Design
- Two Factor Design
7 Survey Design
- Survey Research Designs
- Steps in Survey Design
- Structuring and Designing the Questionnaire
- Interviewing Methodology
- Data Analysis
- Final Report
8 Single Subject Design
- Single Subject Design: Definition and Meaning
- Phases Within Single Subject Design
- Requirements of Single Subject Design
- Characteristics of Single Subject Design
- Types of Single Subject Design
- Advantages of Single Subject Design
- Disadvantages of Single Subject Design
9 Observation Method
- Definition and Meaning of Observation
- Characteristics of Observation
- Types of Observation
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Observation
- Guides for Observation Method
10 Interview and Interviewing
- Definition of Interview
- Types of Interview
- Aspects of Qualitative Research Interviews
- Interview Questions
- Convergent Interviewing as Action Research
- Research Team
11 Questionnaire Method
- Definition and Description of Questionnaires
- Types of Questionnaires
- Purpose of Questionnaire Studies
- Designing Research Questionnaires
- The Methods to Make a Questionnaire Efficient
- The Types of Questionnaire to be Included in the Questionnaire
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Questionnaire
- When to Use a Questionnaire?
12 Case Study
- Definition and Description of Case Study Method
- Historical Account of Case Study Method
- Designing Case Study
- Requirements for Case Studies
- Guideline to Follow in Case Study Method
- Other Important Measures in Case Study Method
- Case Reports
13 Report Writing
- Purpose of a Report
- Writing Style of the Report
- Report Writing – the Do’s and the Don’ts
- Format for Report in Psychology Area
- Major Sections in a Report
14 Review of Literature
- Purposes of Review of Literature
- Sources of Review of Literature
- Types of Literature
- Writing Process of the Review of Literature
- Preparation of Index Card for Reviewing and Abstracting
15 Methodology
- Definition and Purpose of Methodology
- Participants (Sample)
- Apparatus and Materials
16 Result, Analysis and Discussion of the Data
- Definition and Description of Results
- Statistical Presentation
- Tables and Figures
17 Summary and Conclusion
- Summary Definition and Description
- Guidelines for Writing a Summary
- Writing the Summary and Choosing Words
- A Process for Paraphrasing and Summarising
- Summary of a Report
- Writing Conclusions
18 References in Research Report
- Reference List (the Format)
- References (Process of Writing)
- Reference List and Print Sources
- Electronic Sources
- Book on CD Tape and Movie
- Reference Specifications
- General Guidelines to Write References
Share on Mastodon
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Perspective
- Published: 22 November 2022
Single case studies are a powerful tool for developing, testing and extending theories
- Lyndsey Nickels ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-0311-3524 1 , 2 ,
- Simon Fischer-Baum ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-6067-0538 3 &
- Wendy Best ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-8375-5916 4
Nature Reviews Psychology volume 1 , pages 733–747 ( 2022 ) Cite this article
672 Accesses
5 Citations
26 Altmetric
Metrics details
- Neurological disorders
Psychology embraces a diverse range of methodologies. However, most rely on averaging group data to draw conclusions. In this Perspective, we argue that single case methodology is a valuable tool for developing and extending psychological theories. We stress the importance of single case and case series research, drawing on classic and contemporary cases in which cognitive and perceptual deficits provide insights into typical cognitive processes in domains such as memory, delusions, reading and face perception. We unpack the key features of single case methodology, describe its strengths, its value in adjudicating between theories, and outline its benefits for a better understanding of deficits and hence more appropriate interventions. The unique insights that single case studies have provided illustrate the value of in-depth investigation within an individual. Single case methodology has an important place in the psychologist’s toolkit and it should be valued as a primary research tool.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
55,14 € per year
only 4,60 € per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
Comparing meta-analyses and preregistered multiple-laboratory replication projects
The fundamental importance of method to theory
A critical evaluation of the p-factor literature
Corkin, S. Permanent Present Tense: The Unforgettable Life Of The Amnesic Patient, H. M . Vol. XIX, 364 (Basic Books, 2013).
Lilienfeld, S. O. Psychology: From Inquiry To Understanding (Pearson, 2019).
Schacter, D. L., Gilbert, D. T., Nock, M. K. & Wegner, D. M. Psychology (Worth Publishers, 2019).
Eysenck, M. W. & Brysbaert, M. Fundamentals Of Cognition (Routledge, 2018).
Squire, L. R. Memory and brain systems: 1969–2009. J. Neurosci. 29 , 12711–12716 (2009).
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Corkin, S. What’s new with the amnesic patient H.M.? Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 3 , 153–160 (2002).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Schubert, T. M. et al. Lack of awareness despite complex visual processing: evidence from event-related potentials in a case of selective metamorphopsia. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 117 , 16055–16064 (2020).
Behrmann, M. & Plaut, D. C. Bilateral hemispheric processing of words and faces: evidence from word impairments in prosopagnosia and face impairments in pure alexia. Cereb. Cortex 24 , 1102–1118 (2014).
Plaut, D. C. & Behrmann, M. Complementary neural representations for faces and words: a computational exploration. Cogn. Neuropsychol. 28 , 251–275 (2011).
Haxby, J. V. et al. Distributed and overlapping representations of faces and objects in ventral temporal cortex. Science 293 , 2425–2430 (2001).
Hirshorn, E. A. et al. Decoding and disrupting left midfusiform gyrus activity during word reading. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 113 , 8162–8167 (2016).
Kosakowski, H. L. et al. Selective responses to faces, scenes, and bodies in the ventral visual pathway of infants. Curr. Biol. 32 , 265–274.e5 (2022).
Harlow, J. Passage of an iron rod through the head. Boston Med. Surgical J . https://doi.org/10.1176/jnp.11.2.281 (1848).
Broca, P. Remarks on the seat of the faculty of articulated language, following an observation of aphemia (loss of speech). Bull. Soc. Anat. 6 , 330–357 (1861).
Google Scholar
Dejerine, J. Contribution A L’étude Anatomo-pathologique Et Clinique Des Différentes Variétés De Cécité Verbale: I. Cécité Verbale Avec Agraphie Ou Troubles Très Marqués De L’écriture; II. Cécité Verbale Pure Avec Intégrité De L’écriture Spontanée Et Sous Dictée (Société de Biologie, 1892).
Liepmann, H. Das Krankheitsbild der Apraxie (“motorischen Asymbolie”) auf Grund eines Falles von einseitiger Apraxie (Fortsetzung). Eur. Neurol. 8 , 102–116 (1900).
Article Google Scholar
Basso, A., Spinnler, H., Vallar, G. & Zanobio, M. E. Left hemisphere damage and selective impairment of auditory verbal short-term memory. A case study. Neuropsychologia 20 , 263–274 (1982).
Humphreys, G. W. & Riddoch, M. J. The fractionation of visual agnosia. In Visual Object Processing: A Cognitive Neuropsychological Approach 281–306 (Lawrence Erlbaum, 1987).
Whitworth, A., Webster, J. & Howard, D. A Cognitive Neuropsychological Approach To Assessment And Intervention In Aphasia (Psychology Press, 2014).
Caramazza, A. On drawing inferences about the structure of normal cognitive systems from the analysis of patterns of impaired performance: the case for single-patient studies. Brain Cogn. 5 , 41–66 (1986).
Caramazza, A. & McCloskey, M. The case for single-patient studies. Cogn. Neuropsychol. 5 , 517–527 (1988).
Shallice, T. Cognitive neuropsychology and its vicissitudes: the fate of Caramazza’s axioms. Cogn. Neuropsychol. 32 , 385–411 (2015).
Shallice, T. From Neuropsychology To Mental Structure (Cambridge Univ. Press, 1988).
Coltheart, M. Assumptions and methods in cognitive neuropscyhology. In The Handbook Of Cognitive Neuropsychology: What Deficits Reveal About The Human Mind (ed. Rapp, B.) 3–22 (Psychology Press, 2001).
McCloskey, M. & Chaisilprungraung, T. The value of cognitive neuropsychology: the case of vision research. Cogn. Neuropsychol. 34 , 412–419 (2017).
McCloskey, M. The future of cognitive neuropsychology. In The Handbook Of Cognitive Neuropsychology: What Deficits Reveal About The Human Mind (ed. Rapp, B.) 593–610 (Psychology Press, 2001).
Lashley, K. S. In search of the engram. In Physiological Mechanisms in Animal Behavior 454–482 (Academic Press, 1950).
Squire, L. R. & Wixted, J. T. The cognitive neuroscience of human memory since H.M. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 34 , 259–288 (2011).
Stone, G. O., Vanhoy, M. & Orden, G. C. V. Perception is a two-way street: feedforward and feedback phonology in visual word recognition. J. Mem. Lang. 36 , 337–359 (1997).
Perfetti, C. A. The psycholinguistics of spelling and reading. In Learning To Spell: Research, Theory, And Practice Across Languages 21–38 (Lawrence Erlbaum, 1997).
Nickels, L. The autocue? self-generated phonemic cues in the treatment of a disorder of reading and naming. Cogn. Neuropsychol. 9 , 155–182 (1992).
Rapp, B., Benzing, L. & Caramazza, A. The autonomy of lexical orthography. Cogn. Neuropsychol. 14 , 71–104 (1997).
Bonin, P., Roux, S. & Barry, C. Translating nonverbal pictures into verbal word names. Understanding lexical access and retrieval. In Past, Present, And Future Contributions Of Cognitive Writing Research To Cognitive Psychology 315–522 (Psychology Press, 2011).
Bonin, P., Fayol, M. & Gombert, J.-E. Role of phonological and orthographic codes in picture naming and writing: an interference paradigm study. Cah. Psychol. Cogn./Current Psychol. Cogn. 16 , 299–324 (1997).
Bonin, P., Fayol, M. & Peereman, R. Masked form priming in writing words from pictures: evidence for direct retrieval of orthographic codes. Acta Psychol. 99 , 311–328 (1998).
Bentin, S., Allison, T., Puce, A., Perez, E. & McCarthy, G. Electrophysiological studies of face perception in humans. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 8 , 551–565 (1996).
Jeffreys, D. A. Evoked potential studies of face and object processing. Vis. Cogn. 3 , 1–38 (1996).
Laganaro, M., Morand, S., Michel, C. M., Spinelli, L. & Schnider, A. ERP correlates of word production before and after stroke in an aphasic patient. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 23 , 374–381 (2011).
Indefrey, P. & Levelt, W. J. M. The spatial and temporal signatures of word production components. Cognition 92 , 101–144 (2004).
Valente, A., Burki, A. & Laganaro, M. ERP correlates of word production predictors in picture naming: a trial by trial multiple regression analysis from stimulus onset to response. Front. Neurosci. 8 , 390 (2014).
Kittredge, A. K., Dell, G. S., Verkuilen, J. & Schwartz, M. F. Where is the effect of frequency in word production? Insights from aphasic picture-naming errors. Cogn. Neuropsychol. 25 , 463–492 (2008).
Domdei, N. et al. Ultra-high contrast retinal display system for single photoreceptor psychophysics. Biomed. Opt. Express 9 , 157 (2018).
Poldrack, R. A. et al. Long-term neural and physiological phenotyping of a single human. Nat. Commun. 6 , 8885 (2015).
Coltheart, M. The assumptions of cognitive neuropsychology: reflections on Caramazza (1984, 1986). Cogn. Neuropsychol. 34 , 397–402 (2017).
Badecker, W. & Caramazza, A. A final brief in the case against agrammatism: the role of theory in the selection of data. Cognition 24 , 277–282 (1986).
Fischer-Baum, S. Making sense of deviance: Identifying dissociating cases within the case series approach. Cogn. Neuropsychol. 30 , 597–617 (2013).
Nickels, L., Howard, D. & Best, W. On the use of different methodologies in cognitive neuropsychology: drink deep and from several sources. Cogn. Neuropsychol. 28 , 475–485 (2011).
Dell, G. S. & Schwartz, M. F. Who’s in and who’s out? Inclusion criteria, model evaluation, and the treatment of exceptions in case series. Cogn. Neuropsychol. 28 , 515–520 (2011).
Schwartz, M. F. & Dell, G. S. Case series investigations in cognitive neuropsychology. Cogn. Neuropsychol. 27 , 477–494 (2010).
Cohen, J. A power primer. Psychol. Bull. 112 , 155–159 (1992).
Martin, R. C. & Allen, C. Case studies in neuropsychology. In APA Handbook Of Research Methods In Psychology Vol. 2 Research Designs: Quantitative, Qualitative, Neuropsychological, And Biological (eds Cooper, H. et al.) 633–646 (American Psychological Association, 2012).
Leivada, E., Westergaard, M., Duñabeitia, J. A. & Rothman, J. On the phantom-like appearance of bilingualism effects on neurocognition: (how) should we proceed? Bilingualism 24 , 197–210 (2021).
Arnett, J. J. The neglected 95%: why American psychology needs to become less American. Am. Psychol. 63 , 602–614 (2008).
Stolz, J. A., Besner, D. & Carr, T. H. Implications of measures of reliability for theories of priming: activity in semantic memory is inherently noisy and uncoordinated. Vis. Cogn. 12 , 284–336 (2005).
Cipora, K. et al. A minority pulls the sample mean: on the individual prevalence of robust group-level cognitive phenomena — the instance of the SNARC effect. Preprint at psyArXiv https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/bwyr3 (2019).
Andrews, S., Lo, S. & Xia, V. Individual differences in automatic semantic priming. J. Exp. Psychol. Hum. Percept. Perform. 43 , 1025–1039 (2017).
Tan, L. C. & Yap, M. J. Are individual differences in masked repetition and semantic priming reliable? Vis. Cogn. 24 , 182–200 (2016).
Olsson-Collentine, A., Wicherts, J. M. & van Assen, M. A. L. M. Heterogeneity in direct replications in psychology and its association with effect size. Psychol. Bull. 146 , 922–940 (2020).
Gratton, C. & Braga, R. M. Editorial overview: deep imaging of the individual brain: past, practice, and promise. Curr. Opin. Behav. Sci. 40 , iii–vi (2021).
Fedorenko, E. The early origins and the growing popularity of the individual-subject analytic approach in human neuroscience. Curr. Opin. Behav. Sci. 40 , 105–112 (2021).
Xue, A. et al. The detailed organization of the human cerebellum estimated by intrinsic functional connectivity within the individual. J. Neurophysiol. 125 , 358–384 (2021).
Petit, S. et al. Toward an individualized neural assessment of receptive language in children. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 63 , 2361–2385 (2020).
Jung, K.-H. et al. Heterogeneity of cerebral white matter lesions and clinical correlates in older adults. Stroke 52 , 620–630 (2021).
Falcon, M. I., Jirsa, V. & Solodkin, A. A new neuroinformatics approach to personalized medicine in neurology: the virtual brain. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 29 , 429–436 (2016).
Duncan, G. J., Engel, M., Claessens, A. & Dowsett, C. J. Replication and robustness in developmental research. Dev. Psychol. 50 , 2417–2425 (2014).
Open Science Collaboration. Estimating the reproducibility of psychological science. Science 349 , aac4716 (2015).
Tackett, J. L., Brandes, C. M., King, K. M. & Markon, K. E. Psychology’s replication crisis and clinical psychological science. Annu. Rev. Clin. Psychol. 15 , 579–604 (2019).
Munafò, M. R. et al. A manifesto for reproducible science. Nat. Hum. Behav. 1 , 0021 (2017).
Oldfield, R. C. & Wingfield, A. The time it takes to name an object. Nature 202 , 1031–1032 (1964).
Oldfield, R. C. & Wingfield, A. Response latencies in naming objects. Q. J. Exp. Psychol. 17 , 273–281 (1965).
Brysbaert, M. How many participants do we have to include in properly powered experiments? A tutorial of power analysis with reference tables. J. Cogn. 2 , 16 (2019).
Brysbaert, M. Power considerations in bilingualism research: time to step up our game. Bilingualism https://doi.org/10.1017/S1366728920000437 (2020).
Machery, E. What is a replication? Phil. Sci. 87 , 545–567 (2020).
Nosek, B. A. & Errington, T. M. What is replication? PLoS Biol. 18 , e3000691 (2020).
Li, X., Huang, L., Yao, P. & Hyönä, J. Universal and specific reading mechanisms across different writing systems. Nat. Rev. Psychol. 1 , 133–144 (2022).
Rapp, B. (Ed.) The Handbook Of Cognitive Neuropsychology: What Deficits Reveal About The Human Mind (Psychology Press, 2001).
Code, C. et al. Classic Cases In Neuropsychology (Psychology Press, 1996).
Patterson, K., Marshall, J. C. & Coltheart, M. Surface Dyslexia: Neuropsychological And Cognitive Studies Of Phonological Reading (Routledge, 2017).
Marshall, J. C. & Newcombe, F. Patterns of paralexia: a psycholinguistic approach. J. Psycholinguist. Res. 2 , 175–199 (1973).
Castles, A. & Coltheart, M. Varieties of developmental dyslexia. Cognition 47 , 149–180 (1993).
Khentov-Kraus, L. & Friedmann, N. Vowel letter dyslexia. Cogn. Neuropsychol. 35 , 223–270 (2018).
Winskel, H. Orthographic and phonological parafoveal processing of consonants, vowels, and tones when reading Thai. Appl. Psycholinguist. 32 , 739–759 (2011).
Hepner, C., McCloskey, M. & Rapp, B. Do reading and spelling share orthographic representations? Evidence from developmental dysgraphia. Cogn. Neuropsychol. 34 , 119–143 (2017).
Hanley, J. R. & Sotiropoulos, A. Developmental surface dysgraphia without surface dyslexia. Cogn. Neuropsychol. 35 , 333–341 (2018).
Zihl, J. & Heywood, C. A. The contribution of single case studies to the neuroscience of vision: single case studies in vision neuroscience. Psych. J. 5 , 5–17 (2016).
Bouvier, S. E. & Engel, S. A. Behavioral deficits and cortical damage loci in cerebral achromatopsia. Cereb. Cortex 16 , 183–191 (2006).
Zihl, J. & Heywood, C. A. The contribution of LM to the neuroscience of movement vision. Front. Integr. Neurosci. 9 , 6 (2015).
Dotan, D. & Friedmann, N. Separate mechanisms for number reading and word reading: evidence from selective impairments. Cortex 114 , 176–192 (2019).
McCloskey, M. & Schubert, T. Shared versus separate processes for letter and digit identification. Cogn. Neuropsychol. 31 , 437–460 (2014).
Fayol, M. & Seron, X. On numerical representations. Insights from experimental, neuropsychological, and developmental research. In Handbook of Mathematical Cognition (ed. Campbell, J.) 3–23 (Psychological Press, 2005).
Bornstein, B. & Kidron, D. P. Prosopagnosia. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat. 22 , 124–131 (1959).
Kühn, C. D., Gerlach, C., Andersen, K. B., Poulsen, M. & Starrfelt, R. Face recognition in developmental dyslexia: evidence for dissociation between faces and words. Cogn. Neuropsychol. 38 , 107–115 (2021).
Barton, J. J. S., Albonico, A., Susilo, T., Duchaine, B. & Corrow, S. L. Object recognition in acquired and developmental prosopagnosia. Cogn. Neuropsychol. 36 , 54–84 (2019).
Renault, B., Signoret, J.-L., Debruille, B., Breton, F. & Bolgert, F. Brain potentials reveal covert facial recognition in prosopagnosia. Neuropsychologia 27 , 905–912 (1989).
Bauer, R. M. Autonomic recognition of names and faces in prosopagnosia: a neuropsychological application of the guilty knowledge test. Neuropsychologia 22 , 457–469 (1984).
Haan, E. H. F., de, Young, A. & Newcombe, F. Face recognition without awareness. Cogn. Neuropsychol. 4 , 385–415 (1987).
Ellis, H. D. & Lewis, M. B. Capgras delusion: a window on face recognition. Trends Cogn. Sci. 5 , 149–156 (2001).
Ellis, H. D., Young, A. W., Quayle, A. H. & De Pauw, K. W. Reduced autonomic responses to faces in Capgras delusion. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B 264 , 1085–1092 (1997).
Collins, M. N., Hawthorne, M. E., Gribbin, N. & Jacobson, R. Capgras’ syndrome with organic disorders. Postgrad. Med. J. 66 , 1064–1067 (1990).
Enoch, D., Puri, B. K. & Ball, H. Uncommon Psychiatric Syndromes 5th edn (Routledge, 2020).
Tranel, D., Damasio, H. & Damasio, A. R. Double dissociation between overt and covert face recognition. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 7 , 425–432 (1995).
Brighetti, G., Bonifacci, P., Borlimi, R. & Ottaviani, C. “Far from the heart far from the eye”: evidence from the Capgras delusion. Cogn. Neuropsychiat. 12 , 189–197 (2007).
Coltheart, M., Langdon, R. & McKay, R. Delusional belief. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 62 , 271–298 (2011).
Coltheart, M. Cognitive neuropsychiatry and delusional belief. Q. J. Exp. Psychol. 60 , 1041–1062 (2007).
Coltheart, M. & Davies, M. How unexpected observations lead to new beliefs: a Peircean pathway. Conscious. Cogn. 87 , 103037 (2021).
Coltheart, M. & Davies, M. Failure of hypothesis evaluation as a factor in delusional belief. Cogn. Neuropsychiat. 26 , 213–230 (2021).
McCloskey, M. et al. A developmental deficit in localizing objects from vision. Psychol. Sci. 6 , 112–117 (1995).
McCloskey, M., Valtonen, J. & Cohen Sherman, J. Representing orientation: a coordinate-system hypothesis and evidence from developmental deficits. Cogn. Neuropsychol. 23 , 680–713 (2006).
McCloskey, M. Spatial representations and multiple-visual-systems hypotheses: evidence from a developmental deficit in visual location and orientation processing. Cortex 40 , 677–694 (2004).
Gregory, E. & McCloskey, M. Mirror-image confusions: implications for representation and processing of object orientation. Cognition 116 , 110–129 (2010).
Gregory, E., Landau, B. & McCloskey, M. Representation of object orientation in children: evidence from mirror-image confusions. Vis. Cogn. 19 , 1035–1062 (2011).
Laine, M. & Martin, N. Cognitive neuropsychology has been, is, and will be significant to aphasiology. Aphasiology 26 , 1362–1376 (2012).
Howard, D. & Patterson, K. The Pyramids And Palm Trees Test: A Test Of Semantic Access From Words And Pictures (Thames Valley Test Co., 1992).
Kay, J., Lesser, R. & Coltheart, M. PALPA: Psycholinguistic Assessments Of Language Processing In Aphasia. 2: Picture & Word Semantics, Sentence Comprehension (Erlbaum, 2001).
Franklin, S. Dissociations in auditory word comprehension; evidence from nine fluent aphasic patients. Aphasiology 3 , 189–207 (1989).
Howard, D., Swinburn, K. & Porter, G. Putting the CAT out: what the comprehensive aphasia test has to offer. Aphasiology 24 , 56–74 (2010).
Conti-Ramsden, G., Crutchley, A. & Botting, N. The extent to which psychometric tests differentiate subgroups of children with SLI. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 40 , 765–777 (1997).
Bishop, D. V. M. & McArthur, G. M. Individual differences in auditory processing in specific language impairment: a follow-up study using event-related potentials and behavioural thresholds. Cortex 41 , 327–341 (2005).
Bishop, D. V. M., Snowling, M. J., Thompson, P. A. & Greenhalgh, T., and the CATALISE-2 consortium. Phase 2 of CATALISE: a multinational and multidisciplinary Delphi consensus study of problems with language development: terminology. J. Child. Psychol. Psychiat. 58 , 1068–1080 (2017).
Wilson, A. J. et al. Principles underlying the design of ‘the number race’, an adaptive computer game for remediation of dyscalculia. Behav. Brain Funct. 2 , 19 (2006).
Basso, A. & Marangolo, P. Cognitive neuropsychological rehabilitation: the emperor’s new clothes? Neuropsychol. Rehabil. 10 , 219–229 (2000).
Murad, M. H., Asi, N., Alsawas, M. & Alahdab, F. New evidence pyramid. Evidence-based Med. 21 , 125–127 (2016).
Greenhalgh, T., Howick, J. & Maskrey, N., for the Evidence Based Medicine Renaissance Group. Evidence based medicine: a movement in crisis? Br. Med. J. 348 , g3725–g3725 (2014).
Best, W., Ping Sze, W., Edmundson, A. & Nickels, L. What counts as evidence? Swimming against the tide: valuing both clinically informed experimentally controlled case series and randomized controlled trials in intervention research. Evidence-based Commun. Assess. Interv. 13 , 107–135 (2019).
Best, W. et al. Understanding differing outcomes from semantic and phonological interventions with children with word-finding difficulties: a group and case series study. Cortex 134 , 145–161 (2021).
OCEBM Levels of Evidence Working Group. The Oxford Levels of Evidence 2. CEBM https://www.cebm.ox.ac.uk/resources/levels-of-evidence/ocebm-levels-of-evidence (2011).
Holler, D. E., Behrmann, M. & Snow, J. C. Real-world size coding of solid objects, but not 2-D or 3-D images, in visual agnosia patients with bilateral ventral lesions. Cortex 119 , 555–568 (2019).
Duchaine, B. C., Yovel, G., Butterworth, E. J. & Nakayama, K. Prosopagnosia as an impairment to face-specific mechanisms: elimination of the alternative hypotheses in a developmental case. Cogn. Neuropsychol. 23 , 714–747 (2006).
Hartley, T. et al. The hippocampus is required for short-term topographical memory in humans. Hippocampus 17 , 34–48 (2007).
Pishnamazi, M. et al. Attentional bias towards and away from fearful faces is modulated by developmental amygdala damage. Cortex 81 , 24–34 (2016).
Rapp, B., Fischer-Baum, S. & Miozzo, M. Modality and morphology: what we write may not be what we say. Psychol. Sci. 26 , 892–902 (2015).
Yong, K. X. X., Warren, J. D., Warrington, E. K. & Crutch, S. J. Intact reading in patients with profound early visual dysfunction. Cortex 49 , 2294–2306 (2013).
Rockland, K. S. & Van Hoesen, G. W. Direct temporal–occipital feedback connections to striate cortex (V1) in the macaque monkey. Cereb. Cortex 4 , 300–313 (1994).
Haynes, J.-D., Driver, J. & Rees, G. Visibility reflects dynamic changes of effective connectivity between V1 and fusiform cortex. Neuron 46 , 811–821 (2005).
Tanaka, K. Mechanisms of visual object recognition: monkey and human studies. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 7 , 523–529 (1997).
Fischer-Baum, S., McCloskey, M. & Rapp, B. Representation of letter position in spelling: evidence from acquired dysgraphia. Cognition 115 , 466–490 (2010).
Houghton, G. The problem of serial order: a neural network model of sequence learning and recall. In Current Research In Natural Language Generation (eds Dale, R., Mellish, C. & Zock, M.) 287–319 (Academic Press, 1990).
Fieder, N., Nickels, L., Biedermann, B. & Best, W. From “some butter” to “a butter”: an investigation of mass and count representation and processing. Cogn. Neuropsychol. 31 , 313–349 (2014).
Fieder, N., Nickels, L., Biedermann, B. & Best, W. How ‘some garlic’ becomes ‘a garlic’ or ‘some onion’: mass and count processing in aphasia. Neuropsychologia 75 , 626–645 (2015).
Schröder, A., Burchert, F. & Stadie, N. Training-induced improvement of noncanonical sentence production does not generalize to comprehension: evidence for modality-specific processes. Cogn. Neuropsychol. 32 , 195–220 (2015).
Stadie, N. et al. Unambiguous generalization effects after treatment of non-canonical sentence production in German agrammatism. Brain Lang. 104 , 211–229 (2008).
Schapiro, A. C., Gregory, E., Landau, B., McCloskey, M. & Turk-Browne, N. B. The necessity of the medial temporal lobe for statistical learning. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 26 , 1736–1747 (2014).
Schapiro, A. C., Kustner, L. V. & Turk-Browne, N. B. Shaping of object representations in the human medial temporal lobe based on temporal regularities. Curr. Biol. 22 , 1622–1627 (2012).
Baddeley, A., Vargha-Khadem, F. & Mishkin, M. Preserved recognition in a case of developmental amnesia: implications for the acaquisition of semantic memory? J. Cogn. Neurosci. 13 , 357–369 (2001).
Snyder, J. J. & Chatterjee, A. Spatial-temporal anisometries following right parietal damage. Neuropsychologia 42 , 1703–1708 (2004).
Ashkenazi, S., Henik, A., Ifergane, G. & Shelef, I. Basic numerical processing in left intraparietal sulcus (IPS) acalculia. Cortex 44 , 439–448 (2008).
Lebrun, M.-A., Moreau, P., McNally-Gagnon, A., Mignault Goulet, G. & Peretz, I. Congenital amusia in childhood: a case study. Cortex 48 , 683–688 (2012).
Vannuscorps, G., Andres, M. & Pillon, A. When does action comprehension need motor involvement? Evidence from upper limb aplasia. Cogn. Neuropsychol. 30 , 253–283 (2013).
Jeannerod, M. Neural simulation of action: a unifying mechanism for motor cognition. NeuroImage 14 , S103–S109 (2001).
Blakemore, S.-J. & Decety, J. From the perception of action to the understanding of intention. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2 , 561–567 (2001).
Rizzolatti, G. & Craighero, L. The mirror-neuron system. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 27 , 169–192 (2004).
Forde, E. M. E., Humphreys, G. W. & Remoundou, M. Disordered knowledge of action order in action disorganisation syndrome. Neurocase 10 , 19–28 (2004).
Mazzi, C. & Savazzi, S. The glamor of old-style single-case studies in the neuroimaging era: insights from a patient with hemianopia. Front. Psychol. 10 , 965 (2019).
Coltheart, M. What has functional neuroimaging told us about the mind (so far)? (Position Paper Presented to the European Cognitive Neuropsychology Workshop, Bressanone, 2005). Cortex 42 , 323–331 (2006).
Page, M. P. A. What can’t functional neuroimaging tell the cognitive psychologist? Cortex 42 , 428–443 (2006).
Blank, I. A., Kiran, S. & Fedorenko, E. Can neuroimaging help aphasia researchers? Addressing generalizability, variability, and interpretability. Cogn. Neuropsychol. 34 , 377–393 (2017).
Niv, Y. The primacy of behavioral research for understanding the brain. Behav. Neurosci. 135 , 601–609 (2021).
Crawford, J. R. & Howell, D. C. Comparing an individual’s test score against norms derived from small samples. Clin. Neuropsychol. 12 , 482–486 (1998).
Crawford, J. R., Garthwaite, P. H. & Ryan, K. Comparing a single case to a control sample: testing for neuropsychological deficits and dissociations in the presence of covariates. Cortex 47 , 1166–1178 (2011).
McIntosh, R. D. & Rittmo, J. Ö. Power calculations in single-case neuropsychology: a practical primer. Cortex 135 , 146–158 (2021).
Patterson, K. & Plaut, D. C. “Shallow draughts intoxicate the brain”: lessons from cognitive science for cognitive neuropsychology. Top. Cogn. Sci. 1 , 39–58 (2009).
Lambon Ralph, M. A., Patterson, K. & Plaut, D. C. Finite case series or infinite single-case studies? Comments on “Case series investigations in cognitive neuropsychology” by Schwartz and Dell (2010). Cogn. Neuropsychol. 28 , 466–474 (2011).
Horien, C., Shen, X., Scheinost, D. & Constable, R. T. The individual functional connectome is unique and stable over months to years. NeuroImage 189 , 676–687 (2019).
Epelbaum, S. et al. Pure alexia as a disconnection syndrome: new diffusion imaging evidence for an old concept. Cortex 44 , 962–974 (2008).
Fischer-Baum, S. & Campana, G. Neuroplasticity and the logic of cognitive neuropsychology. Cogn. Neuropsychol. 34 , 403–411 (2017).
Paul, S., Baca, E. & Fischer-Baum, S. Cerebellar contributions to orthographic working memory: a single case cognitive neuropsychological investigation. Neuropsychologia 171 , 108242 (2022).
Feinstein, J. S., Adolphs, R., Damasio, A. & Tranel, D. The human amygdala and the induction and experience of fear. Curr. Biol. 21 , 34–38 (2011).
Crawford, J., Garthwaite, P. & Gray, C. Wanted: fully operational definitions of dissociations in single-case studies. Cortex 39 , 357–370 (2003).
McIntosh, R. D. Simple dissociations for a higher-powered neuropsychology. Cortex 103 , 256–265 (2018).
McIntosh, R. D. & Brooks, J. L. Current tests and trends in single-case neuropsychology. Cortex 47 , 1151–1159 (2011).
Best, W., Schröder, A. & Herbert, R. An investigation of a relative impairment in naming non-living items: theoretical and methodological implications. J. Neurolinguistics 19 , 96–123 (2006).
Franklin, S., Howard, D. & Patterson, K. Abstract word anomia. Cogn. Neuropsychol. 12 , 549–566 (1995).
Coltheart, M., Patterson, K. E. & Marshall, J. C. Deep Dyslexia (Routledge, 1980).
Nickels, L., Kohnen, S. & Biedermann, B. An untapped resource: treatment as a tool for revealing the nature of cognitive processes. Cogn. Neuropsychol. 27 , 539–562 (2010).
Download references
Acknowledgements
The authors thank all of those pioneers of and advocates for single case study research who have mentored, inspired and encouraged us over the years, and the many other colleagues with whom we have discussed these issues.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Psychological Sciences & Macquarie University Centre for Reading, Macquarie University, Sydney, New South Wales, Australia
Lyndsey Nickels
NHMRC Centre of Research Excellence in Aphasia Recovery and Rehabilitation, Australia
Psychological Sciences, Rice University, Houston, TX, USA
Simon Fischer-Baum
Psychology and Language Sciences, University College London, London, UK
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
L.N. led and was primarily responsible for the structuring and writing of the manuscript. All authors contributed to all aspects of the article.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Lyndsey Nickels .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information.
Nature Reviews Psychology thanks Yanchao Bi, Rob McIntosh, and the other, anonymous, reviewer for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Nickels, L., Fischer-Baum, S. & Best, W. Single case studies are a powerful tool for developing, testing and extending theories. Nat Rev Psychol 1 , 733–747 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s44159-022-00127-y
Download citation
Accepted : 13 October 2022
Published : 22 November 2022
Issue Date : December 2022
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1038/s44159-022-00127-y
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.

A case study is a research method that extensively explores a particular subject, situation, or individual through in-depth analysis, often to gain insights into real-world phenomena or complex issues. It involves the comprehensive examination of multiple data sources, such as interviews, observations, documents, and artifacts, to provide a rich and holistic understanding of the subject under investigation.
Case studies are conducted to:
- Investigate a specific problem, event, or phenomenon
- Explore unique or atypical situations
- Examine the complexities and intricacies of a subject in its natural context
- Develop theories, propositions, or hypotheses for further research
- Gain practical insights for decision-making or problem-solving
A typical case study consists of the following components:
- Introduction: Provides a brief background and context for the study, including the purpose and research questions.
- Case Description: Describes the subject of the case study, including its relevant characteristics, settings, and participants.
- Data Collection: Details the methods used to gather data, such as interviews, observations, surveys, or document analysis.
- Data Analysis: Explains the techniques employed to analyze the collected data and derive meaningful insights.
- Findings: Presents the key discoveries and outcomes of the case study in a logical and organized manner.
- Discussion: Interprets the findings, relates them to existing theories or frameworks, discusses their implications, and addresses any limitations.
- Conclusion: Summarizes the main findings, highlights the significance of the research, and suggests potential avenues for future investigations.
Case studies offer several benefits, including:
- Providing a deep understanding of complex and context-dependent phenomena
- Generating detailed and rich qualitative data
- Allowing researchers to explore multiple perspectives and factors influencing the subject
- Offering practical insights for professionals and practitioners
- Allowing for the examination of rare or unique occurrences that cannot be replicated in experimental settings

What Is a Case Study in Psychology?
Categories Research Methods
A case study is a research method used in psychology to investigate a particular individual, group, or situation in depth . It involves a detailed analysis of the subject, gathering information from various sources such as interviews, observations, and documents.
In a case study, researchers aim to understand the complexities and nuances of the subject under investigation. They explore the individual’s thoughts, feelings, behaviors, and experiences to gain insights into specific psychological phenomena.
This type of research can provide great detail regarding a particular case, allowing researchers to examine rare or unique situations that may not be easily replicated in a laboratory setting. They offer a holistic view of the subject, considering various factors influencing their behavior or mental processes.
By examining individual cases, researchers can generate hypotheses, develop theories, and contribute to the existing body of knowledge in psychology. Case studies are often utilized in clinical psychology, where they can provide valuable insights into the diagnosis, treatment, and outcomes of specific psychological disorders.
Case studies offer a comprehensive and in-depth understanding of complex psychological phenomena, providing researchers with valuable information to inform theory, practice, and future research.
Table of Contents
Examples of Case Studies in Psychology
Case studies in psychology provide real-life examples that illustrate psychological concepts and theories. They offer a detailed analysis of specific individuals, groups, or situations, allowing researchers to understand psychological phenomena better. Here are a few examples of case studies in psychology:
Phineas Gage
This famous case study explores the effects of a traumatic brain injury on personality and behavior. A railroad construction worker, Phineas Gage survived a severe brain injury that dramatically changed his personality.
This case study helped researchers understand the role of the frontal lobe in personality and social behavior.
Little Albert
Conducted by behaviorist John B. Watson, the Little Albert case study aimed to demonstrate classical conditioning. In this study, a young boy named Albert was conditioned to fear a white rat by pairing it with a loud noise.
This case study provided insights into the process of fear conditioning and the impact of early experiences on behavior.
Genie’s case study focused on a girl who experienced extreme social isolation and deprivation during her childhood. This study shed light on the critical period for language development and the effects of severe neglect on cognitive and social functioning.
These case studies highlight the value of in-depth analysis and provide researchers with valuable insights into various psychological phenomena. By examining specific cases, psychologists can uncover unique aspects of human behavior and contribute to the field’s knowledge and understanding.
Types of Case Studies in Psychology
Psychology case studies come in various forms, each serving a specific purpose in research and analysis. Understanding the different types of case studies can help researchers choose the most appropriate approach.
Descriptive Case Studies
These studies aim to describe a particular individual, group, or situation. Researchers use descriptive case studies to explore and document specific characteristics, behaviors, or experiences.
For example, a descriptive case study may examine the life and experiences of a person with a rare psychological disorder.
Exploratory Case Studies
Exploratory case studies are conducted when there is limited existing knowledge or understanding of a particular phenomenon. Researchers use these studies to gather preliminary information and generate hypotheses for further investigation.
Exploratory case studies often involve in-depth interviews, observations, and analysis of existing data.
Explanatory Case Studies
These studies aim to explain the causal relationship between variables or events. Researchers use these studies to understand why certain outcomes occur and to identify the underlying mechanisms or processes.
Explanatory case studies often involve comparing multiple cases to identify common patterns or factors.
Instrumental Case Studies
Instrumental case studies focus on using a particular case to gain insights into a broader issue or theory. Researchers select cases that are representative or critical in understanding the phenomenon of interest.
Instrumental case studies help researchers develop or refine theories and contribute to the general knowledge in the field.
By utilizing different types of case studies, psychologists can explore various aspects of human behavior and gain a deeper understanding of psychological phenomena. Each type of case study offers unique advantages and contributes to the overall body of knowledge in psychology.
How to Collect Data for a Case Study
There are a variety of ways that researchers gather the data they need for a case study. Some sources include:
- Directly observing the subject
- Collecting information from archival records
- Conducting interviews
- Examining artifacts related to the subject
- Examining documents that provide information about the subject
The way that this information is collected depends on the nature of the study itself
Prospective Research
In a prospective study, researchers observe the individual or group in question. These observations typically occur over a period of time and may be used to track the progress or progression of a phenomenon or treatment.
Retrospective Research
A retrospective case study involves looking back on a phenomenon. Researchers typically look at the outcome and then gather data to help them understand how the individual or group reached that point.
Benefits of a Case Study
Case studies offer several benefits in the field of psychology. They provide researchers with a unique opportunity to delve deep into specific individuals, groups, or situations, allowing for a comprehensive understanding of complex phenomena.
Case studies offer valuable insights that can inform theory development and practical applications by examining real-life examples.
Complex Data
One of the key benefits of case studies is their ability to provide complex and detailed data. Researchers can gather in-depth information through various methods such as interviews, observations, and analysis of existing records.
This depth of data allows for a thorough exploration of the factors influencing behavior and the underlying mechanisms at play.
Unique Data
Additionally, case studies allow researchers to study rare or unique cases that may not be easily replicated in experimental settings. This enables the examination of phenomena that are difficult to study through other psychology research methods .
By focusing on specific cases, researchers can uncover patterns, identify causal relationships, and generate hypotheses for further investigation.
General Knowledge
Case studies can also contribute to the general knowledge of psychology by providing real-world examples that can be used to support or challenge existing theories. They offer a bridge between theory and practice, allowing researchers to apply theoretical concepts to real-life situations and vice versa.
Case studies offer a range of benefits in psychology, including providing rich and detailed data, studying unique cases, and contributing to theory development. These benefits make case studies valuable in understanding human behavior and psychological phenomena.
Limitations of a Case Study
While case studies offer numerous benefits in the field of psychology, they also have certain limitations that researchers need to consider. Understanding these limitations is crucial for interpreting the findings and generalizing the results.
Lack of Generalizability
One limitation of case studies is the issue of generalizability. Since case studies focus on specific individuals, groups, and situations, applying the findings to a larger population can be challenging. The unique characteristics and circumstances of the case may not be representative of the broader population, making it difficult to draw universal conclusions.
Researcher bias is another possible limitation. The researcher’s subjective interpretation and personal beliefs can influence the data collection, analysis, and interpretation process. This bias can affect the objectivity and reliability of the findings, raising questions about the study’s validity.
Case studies are often time-consuming and resource-intensive. They require extensive data collection, analysis, and interpretation, which can be lengthy. This can limit the number of cases that can be studied and may result in a smaller sample size, reducing the study’s statistical power.
Case studies are retrospective in nature, relying on past events and experiences. This reliance on memory and self-reporting can introduce recall bias and inaccuracies in the data. Participants may forget or misinterpret certain details, leading to incomplete or unreliable information.
Despite these limitations, case studies remain a valuable research tool in psychology. By acknowledging and addressing these limitations, researchers can enhance the validity and reliability of their findings, contributing to a more comprehensive understanding of human behavior and psychological phenomena.
While case studies have limitations, they remain valuable when researchers acknowledge and address these concerns, leading to more reliable and valid findings in psychology.
Alpi, K. M., & Evans, J. J. (2019). Distinguishing case study as a research method from case reports as a publication type. Journal of the Medical Library Association , 107(1). https://doi.org/10.5195/jmla.2019.615
Crowe, S., Cresswell, K., Robertson, A., Huby, G., Avery, A., & Sheikh, A. (2011). The case study approach. BMC Medical Research Methodology , 11(1), 100. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2288-11-100
Paparini, S., Green, J., Papoutsi, C., Murdoch, J., Petticrew, M., Greenhalgh, T., Hanckel, B., & Shaw, S. (2020). Case study research for better evaluations of complex interventions: Rationale and challenges. BMC Medicine , 18(1), 301. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12916-020-01777-6
Willemsen, J. (2023). What is preventing psychotherapy case studies from having a greater impact on evidence-based practice, and how to address the challenges? Frontiers in Psychiatry , 13, 1101090. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2022.1101090
Yin, Robert K. Case Study Research and Applications: Design and Methods . United States, SAGE Publications, 2017.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Psicol Reflex Crit
- v.34; 2021 Dec
Appraising psychotherapy case studies in practice-based evidence: introducing Case Study Evaluation-tool (CaSE)
Greta kaluzeviciute.
Department of Psychosocial and Psychoanalytic Studies, University of Essex, Wivenhoe Park, Colchester, CO4 3SQ UK
Associated Data
Not applicable.
Systematic case studies are often placed at the low end of evidence-based practice (EBP) due to lack of critical appraisal. This paper seeks to attend to this research gap by introducing a novel Case Study Evaluation-tool (CaSE). First, issues around knowledge generation and validity are assessed in both EBP and practice-based evidence (PBE) paradigms. Although systematic case studies are more aligned with PBE paradigm, the paper argues for a complimentary, third way approach between the two paradigms and their ‘exemplary’ methodologies: case studies and randomised controlled trials (RCTs). Second, the paper argues that all forms of research can produce ‘valid evidence’ but the validity itself needs to be assessed against each specific research method and purpose. Existing appraisal tools for qualitative research (JBI, CASP, ETQS) are shown to have limited relevance for the appraisal of systematic case studies through a comparative tool assessment. Third, the paper develops purpose-oriented evaluation criteria for systematic case studies through CaSE Checklist for Essential Components in Systematic Case Studies and CaSE Purpose-based Evaluative Framework for Systematic Case Studies. The checklist approach aids reviewers in assessing the presence or absence of essential case study components (internal validity). The framework approach aims to assess the effectiveness of each case against its set out research objectives and aims (external validity), based on different systematic case study purposes in psychotherapy. Finally, the paper demonstrates the application of the tool with a case example and notes further research trajectories for the development of CaSE tool.
Introduction
Due to growing demands of evidence-based practice, standardised research assessment and appraisal tools have become common in healthcare and clinical treatment (Hannes, Lockwood, & Pearson, 2010 ; Hartling, Chisholm, Thomson, & Dryden, 2012 ; Katrak, Bialocerkowski, Massy-Westropp, Kumar, & Grimmer, 2004 ). This allows researchers to critically appraise research findings on the basis of their validity, results, and usefulness (Hill & Spittlehouse, 2003 ). Despite the upsurge of critical appraisal in qualitative research (Williams, Boylan, & Nunan, 2019 ), there are no assessment or appraisal tools designed for psychotherapy case studies.
Although not without controversies (Michels, 2000 ), case studies remain central to the investigation of psychotherapy processes (Midgley, 2006 ; Willemsen, Della Rosa, & Kegerreis, 2017 ). This is particularly true of systematic case studies, the most common form of case study in contemporary psychotherapy research (Davison & Lazarus, 2007 ; McLeod & Elliott, 2011 ).
Unlike the classic clinical case study, systematic cases usually involve a team of researchers, who gather data from multiple different sources (e.g., questionnaires, observations by the therapist, interviews, statistical findings, clinical assessment, etc.), and involve a rigorous data triangulation process to assess whether the data from different sources converge (McLeod, 2010 ). Since systematic case studies are methodologically pluralistic, they have a greater interest in situating patients within the study of a broader population than clinical case studies (Iwakabe & Gazzola, 2009 ). Systematic case studies are considered to be an accessible method for developing research evidence-base in psychotherapy (Widdowson, 2011 ), especially since they correct some of the methodological limitations (e.g. lack of ‘third party’ perspectives and bias in data analysis) inherent to classic clinical case studies (Iwakabe & Gazzola, 2009 ). They have been used for the purposes of clinical training (Tuckett, 2008 ), outcome assessment (Hilliard, 1993 ), development of clinical techniques (Almond, 2004 ) and meta-analysis of qualitative findings (Timulak, 2009 ). All these developments signal a revived interest in the case study method, but also point to the obvious lack of a research assessment tool suitable for case studies in psychotherapy (Table (Table1 1 ).
Key concept: systematic case study
To attend to this research gap, this paper first reviews issues around the conceptualisation of validity within the paradigms of evidence-based practice (EBP) and practice-based evidence (PBE). Although case studies are often positioned at the low end of EBP (Aveline, 2005 ), the paper suggests that systematic cases are a valuable form of evidence, capable of complimenting large-scale studies such as randomised controlled trials (RCTs). However, there remains a difficulty in assessing the quality and relevance of case study findings to broader psychotherapy research.
As a way forward, the paper introduces a novel Case Study Evaluation-tool (CaSE) in the form of CaSE Purpose - based Evaluative Framework for Systematic Case Studies and CaSE Checklist for Essential Components in Systematic Case Studies . The long-term development of CaSE would contribute to psychotherapy research and practice in three ways.
Given the significance of methodological pluralism and diverse research aims in systematic case studies, CaSE will not seek to prescribe explicit case study writing guidelines, which has already been done by numerous authors (McLeod, 2010 ; Meganck, Inslegers, Krivzov, & Notaerts, 2017 ; Willemsen et al., 2017 ). Instead, CaSE will enable the retrospective assessment of systematic case study findings and their relevance (or lack thereof) to broader psychotherapy research and practice. However, there is no reason to assume that CaSE cannot be used prospectively (i.e. producing systematic case studies in accordance to CaSE evaluative framework, as per point 3 in Table Table2 2 ).
How can Case Study Evaluation-tool (CaSE) be used in psychotherapy research and practice?
The development of a research assessment or appraisal tool is a lengthy, ongoing process (Long & Godfrey, 2004 ). It is particularly challenging to develop a comprehensive purpose - oriented evaluative framework, suitable for the assessment of diverse methodologies, aims and outcomes. As such, this paper should be treated as an introduction to the broader development of CaSE tool. It will introduce the rationale behind CaSE and lay out its main approach to evidence and evaluation, with further development in mind. A case example from the Single Case Archive (SCA) ( https://singlecasearchive.com ) will be used to demonstrate the application of the tool ‘in action’. The paper notes further research trajectories and discusses some of the limitations around the use of the tool.
Separating the wheat from the chaff: what is and is not evidence in psychotherapy (and who gets to decide?)
The common approach: evidence-based practice.
In the last two decades, psychotherapy has become increasingly centred around the idea of an evidence-based practice (EBP). Initially introduced in medicine, EBP has been defined as ‘conscientious, explicit and judicious use of current best evidence in making decisions about the care of individual patients’ (Sackett, Rosenberg, Gray, Haynes, & Richardson, 1996 ). EBP revolves around efficacy research: it seeks to examine whether a specific intervention has a causal (in this case, measurable) effect on clinical populations (Barkham & Mellor-Clark, 2003 ). From a conceptual standpoint, Sackett and colleagues defined EBP as a paradigm that is inclusive of many methodologies, so long as they contribute towards clinical decision-making process and accumulation of best currently available evidence in any given set of circumstances (Gabbay & le May, 2011 ). Similarly, the American Psychological Association (APA, 2010 ) has recently issued calls for evidence-based systematic case studies in order to produce standardised measures for evaluating process and outcome data across different therapeutic modalities.
However, given EBP’s focus on establishing cause-and-effect relationships (Rosqvist, Thomas, & Truax, 2011 ), it is unsurprising that qualitative research is generally not considered to be ‘gold standard’ or ‘efficacious’ within this paradigm (Aveline, 2005 ; Cartwright & Hardie, 2012 ; Edwards, 2013 ; Edwards, Dattilio, & Bromley, 2004 ; Longhofer, Floersch, & Hartmann, 2017 ). Qualitative methods like systematic case studies maintain an appreciation for context, complexity and meaning making. Therefore, instead of measuring regularly occurring causal relations (as in quantitative studies), the focus is on studying complex social phenomena (e.g. relationships, events, experiences, feelings, etc.) (Erickson, 2012 ; Maxwell, 2004 ). Edwards ( 2013 ) points out that, although context-based research in systematic case studies is the bedrock of psychotherapy theory and practice, it has also become shrouded by an unfortunate ideological description: ‘anecdotal’ case studies (i.e. unscientific narratives lacking evidence, as opposed to ‘gold standard’ evidence, a term often used to describe the RCT method and the therapeutic modalities supported by it), leading to a further need for advocacy in and defence of the unique epistemic process involved in case study research (Fishman, Messer, Edwards, & Dattilio, 2017 ).
The EBP paradigm prioritises the quantitative approach to causality, most notably through its focus on high generalisability and the ability to deal with bias through randomisation process. These conditions are associated with randomised controlled trials (RCTs) but are limited (or, as some argue, impossible) in qualitative research methods such as the case study (Margison et al., 2000 ) (Table (Table3 3 ).
Key concept: evidence-based practice (EBP)
‘Evidence’ from an EBP standpoint hovers over the epistemological assumption of procedural objectivity : knowledge can be generated in a standardised, non-erroneous way, thus producing objective (i.e. with minimised bias) data. This can be achieved by anyone, as long as they are able to perform the methodological procedure (e.g. RCT) appropriately, in a ‘clearly defined and accepted process that assists with knowledge production’ (Douglas, 2004 , p. 131). If there is a well-outlined quantitative form for knowledge production, the same outcome should be achieved regardless of who processes or interprets the information. For example, researchers using Cochrane Review assess the strength of evidence using meticulously controlled and scrupulous techniques; in turn, this minimises individual judgment and creates unanimity of outcomes across different groups of people (Gabbay & le May, 2011 ). The typical process of knowledge generation (through employing RCTs and procedural objectivity) in EBP is demonstrated in Fig. Fig.1 1 .

Typical knowledge generation process in evidence–based practice (EBP)
In EBP, the concept of validity remains somewhat controversial, with many critics stating that it limits rather than strengthens knowledge generation (Berg, 2019 ; Berg & Slaattelid, 2017 ; Lilienfeld, Ritschel, Lynn, Cautin, & Latzman, 2013 ). This is because efficacy research relies on internal validity . At a general level, this concept refers to the congruence between the research study and the research findings (i.e. the research findings were not influenced by anything external to the study, such as confounding variables, methodological errors and bias); at a more specific level, internal validity determines the extent to which a study establishes a reliable causal relationship between an independent variable (e.g. treatment) and independent variable (outcome or effect) (Margison et al., 2000 ). This approach to validity is demonstrated in Fig. Fig.2 2 .

Internal validity
Social scientists have argued that there is a trade-off between research rigour and generalisability: the more specific the sample and the more rigorously defined the intervention, the outcome is likely to be less applicable to everyday, routine practice. As such, there remains a tension between employing procedural objectivity which increases the rigour of research outcomes and applying such outcomes to routine psychotherapy practice where scientific standards of evidence are not uniform.
According to McLeod ( 2002 ), inability to address questions that are most relevant for practitioners contributed to a deepening research–practice divide in psychotherapy. Studies investigating how practitioners make clinical decisions and the kinds of evidence they refer to show that there is a strong preference for knowledge that is not generated procedurally, i.e. knowledge that encompasses concrete clinical situations, experiences and techniques. A study by Stewart and Chambless ( 2007 ) sought to assess how a larger population of clinicians (under APA, from varying clinical schools of thought and independent practices, sample size 591) make treatment decisions in private practice. The study found that large-scale statistical data was not the primary source of information sought by clinicians. The most important influences were identified as past clinical experiences and clinical expertise ( M = 5.62). Treatment materials based on clinical case observations and theory ( M = 4.72) were used almost as frequently as psychotherapy outcome research findings ( M = 4.80) (i.e. evidence-based research). These numbers are likely to fluctuate across different forms of psychotherapy; however, they are indicative of the need for research about routine clinical settings that does not isolate or generalise the effect of an intervention but examines the variations in psychotherapy processes.
The alternative approach: practice-based evidence
In an attempt to dissolve or lessen the research–practice divide, an alternative paradigm of practice-based evidence (PBE) has been suggested (Barkham & Mellor-Clark, 2003 ; Fox, 2003 ; Green & Latchford, 2012 ; Iwakabe & Gazzola, 2009 ; Laska, Motulsky, Wertz, Morrow, & Ponterotto, 2014 ; Margison et al., 2000 ). PBE represents a shift in how we think about evidence and knowledge generation in psychotherapy. PBE treats research as a local and contingent process (at least initially), which means it focuses on variations (e.g. in patient symptoms) and complexities (e.g. of clinical setting) in the studied phenomena (Fox, 2003 ). Moreover, research and theory-building are seen as complementary rather than detached activities from clinical practice. That is to say, PBE seeks to examine how and which treatments can be improved in everyday clinical practice by flagging up clinically salient issues and developing clinical techniques (Barkham & Mellor-Clark, 2003 ). For this reason, PBE is concerned with the effectiveness of research findings: it evaluates how well interventions work in real-world settings (Rosqvist et al., 2011 ). Therefore, although it is not unlikely for RCTs to be used in order to generate practice-informed evidence (Horn & Gassaway, 2007 ), qualitative methods like the systematic case study are seen as ideal for demonstrating the effectiveness of therapeutic interventions with individual patients (van Hennik, 2020 ) (Table (Table4 4 ).
Key concept: practice-based evidence (PBE)
PBE’s epistemological approach to ‘evidence’ may be understood through the process of concordant objectivity (Douglas, 2004 ): ‘Instead of seeking to eliminate individual judgment, … [concordant objectivity] checks to see whether the individual judgments of people in fact do agree’ (p. 462). This does not mean that anyone can contribute to the evaluation process like in procedural objectivity, where the main criterion is following a set quantitative protocol or knowing how to operate a specific research design. Concordant objectivity requires that there is a set of competent observers who are closely familiar with the studied phenomenon (e.g. researchers and practitioners who are familiar with depression from a variety of therapeutic approaches).
Systematic case studies are a good example of PBE ‘in action’: they allow for the examination of detailed unfolding of events in psychotherapy practice, making it the most pragmatic and practice-oriented form of psychotherapy research (Fishman, 1999 , 2005 ). Furthermore, systematic case studies approach evidence and results through concordant objectivity (Douglas, 2004 ) by involving a team of researchers and rigorous data triangulation processes (McLeod, 2010 ). This means that, although systematic case studies remain focused on particular clinical situations and detailed subjective experiences (similar to classic clinical case studies; see Iwakabe & Gazzola, 2009 ), they still involve a series of validity checks and considerations on how findings from a single systematic case pertain to broader psychotherapy research (Fishman, 2005 ). The typical process of knowledge generation (through employing systematic case studies and concordant objectivity) in PBE is demonstrated in Fig. Fig.3. 3 . The figure exemplifies a bidirectional approach to research and practice, which includes the development of research-supported psychological treatments (through systematic reviews of existing evidence) as well as the perspectives of clinical practitioners in the research process (through the study of local and contingent patient and/or treatment processes) (Teachman et al., 2012 ; Westen, Novotny, & Thompson-Brenner, 2004 ).

Typical knowledge generation process in practice-based evidence (PBE)
From a PBE standpoint, external validity is a desirable research condition: it measures extent to which the impact of interventions apply to real patients and therapists in everyday clinical settings. As such, external validity is not based on the strength of causal relationships between treatment interventions and outcomes (as in internal validity); instead, the use of specific therapeutic techniques and problem-solving decisions are considered to be important for generalising findings onto routine clinical practice (even if the findings are explicated from a single case study; see Aveline, 2005 ). This approach to validity is demonstrated in Fig. Fig.4 4 .

External validity
Since effectiveness research is less focused on limiting the context of the studied phenomenon (indeed, explicating the context is often one of the research aims), there is more potential for confounding factors (e.g. bias and uncontrolled variables) which in turn can reduce the study’s internal validity (Barkham & Mellor-Clark, 2003 ). This is also an important challenge for research appraisal. Douglas ( 2004 ) argues that appraising research in terms of its effectiveness may produce significant disagreements or group illusions, since what might work for some practitioners may not work for others: ‘It cannot guarantee that values are not influencing or supplanting reasoning; the observers may have shared values that cause them to all disregard important aspects of an event’ (Douglas, 2004 , p. 462). Douglas further proposes that an interactive approach to objectivity may be employed as a more complex process in debating the evidential quality of a research study: it requires a discussion among observers and evaluators in the form of peer-review, scientific discourse, as well as research appraisal tools and instruments. While these processes of rigour are also applied in EBP, there appears to be much more space for debate, disagreement and interpretation in PBE’s approach to research evaluation, partly because the evaluation criteria themselves are subject of methodological debate and are often employed in different ways by researchers (Williams et al., 2019 ). This issue will be addressed more explicitly again in relation to CaSE development (‘Developing purpose-oriented evaluation criteria for systematic case studies’ section).
A third way approach to validity and evidence
The research–practice divide shows us that there may be something significant in establishing complementarity between EBP and PBE rather than treating them as mutually exclusive forms of research (Fishman et al., 2017 ). For one, EBP is not a sufficient condition for delivering research relevant to practice settings (Bower, 2003 ). While RCTs can demonstrate that an intervention works on average in a group, clinicians who are facing individual patients need to answer a different question: how can I make therapy work with this particular case ? (Cartwright & Hardie, 2012 ). Systematic case studies are ideal for filling this gap: they contain descriptions of microprocesses (e.g. patient symptoms, therapeutic relationships, therapist attitudes) in psychotherapy practice that are often overlooked in large-scale RCTs (Iwakabe & Gazzola, 2009 ). In particular, systematic case studies describing the use of specific interventions with less researched psychological conditions (e.g. childhood depression or complex post-traumatic stress disorder) can deepen practitioners’ understanding of effective clinical techniques before the results of large-scale outcome studies are disseminated.
Secondly, establishing a working relationship between systematic case studies and RCTs will contribute towards a more pragmatic understanding of validity in psychotherapy research. Indeed, the very tension and so-called trade-off between internal and external validity is based on the assumption that research methods are designed on an either/or basis; either they provide a sufficiently rigorous study design or they produce findings that can be applied to real-life practice. Jimenez-Buedo and Miller ( 2010 ) call this assumption into question: in their view, if a study is not internally valid, then ‘little, or rather nothing, can be said of the outside world’ (p. 302). In this sense, internal validity may be seen as a pre-requisite for any form of applied research and its external validity, but it need not be constrained to the quantitative approach of causality. For example, Levitt, Motulsky, Wertz, Morrow, and Ponterotto ( 2017 ) argue that, what is typically conceptualised as internal validity, is, in fact, a much broader construct, involving the assessment of how the research method (whether qualitative or quantitative) is best suited for the research goal, and whether it obtains the relevant conclusions. Similarly, Truijens, Cornelis, Desmet, and De Smet ( 2019 ) suggest that we should think about validity in a broader epistemic sense—not just in terms of psychometric measures, but also in terms of the research design, procedure, goals (research questions), approaches to inquiry (paradigms, epistemological assumptions), etc.
The overarching argument from research cited above is that all forms of research—qualitative and quantitative—can produce ‘valid evidence’ but the validity itself needs to be assessed against each specific research method and purpose. For example, RCTs are accompanied with a variety of clearly outlined appraisal tools and instruments such as CASP (Critical Appraisal Skills Programme) that are well suited for the assessment of RCT validity and their implications for EBP. Systematic case studies (or case studies more generally) currently have no appraisal tools in any discipline. The next section evaluates whether existing qualitative research appraisal tools are relevant for systematic case studies in psychotherapy and specifies the missing evaluative criteria.
The relevance of existing appraisal tools for qualitative research to systematic case studies in psychotherapy
What is a research tool.
Currently, there are several research appraisal tools, checklists and frameworks for qualitative studies. It is important to note that tools, checklists and frameworks are not equivalent to one another but actually refer to different approaches to appraising the validity of a research study. As such, it is erroneous to assume that all forms of qualitative appraisal feature the same aims and methods (Hannes et al., 2010 ; Williams et al., 2019 ).
Generally, research assessment falls into two categories: checklists and frameworks . Checklist approaches are often contrasted with quantitative research, since the focus is on assessing the internal validity of research (i.e. researcher’s independence from the study). This involves the assessment of bias in sampling, participant recruitment, data collection and analysis. Framework approaches to research appraisal, on the other hand, revolve around traditional qualitative concepts such as transparency, reflexivity, dependability and transferability (Williams et al., 2019 ). Framework approaches to appraisal are often challenging to use because they depend on the reviewer’s familiarisation and interpretation of the qualitative concepts.
Because of these different approaches, there is some ambiguity in terminology, particularly between research appraisal instruments and research appraisal tools . These terms are often used interchangeably in appraisal literature (Williams et al., 2019 ). In this paper, research appraisal tool is defined as a method-specific (i.e. it identifies a specific research method or component) form of appraisal that draws from both checklist and framework approaches. Furthermore, a research appraisal tool seeks to inform decision making in EBP or PBE paradigms and provides explicit definitions of the tool’s evaluative framework (thus minimising—but by no means eliminating—the reviewers’ interpretation of the tool). This definition will be applied to CaSE (Table (Table5 5 ).
Key concept: research appraisal tool
In contrast, research appraisal instruments are generally seen as a broader form of appraisal in the sense that they may evaluate a variety of methods (i.e. they are non-method specific or they do not target a particular research component), and are aimed at checking whether the research findings and/or the study design contain specific elements (e.g. the aims of research, the rationale behind design methodology, participant recruitment strategies, etc.).
There is often an implicit difference in audience between appraisal tools and instruments. Research appraisal instruments are often aimed at researchers who want to assess the strength of their study; however, the process of appraisal may not be made explicit in the study itself (besides mentioning that the tool was used to appraise the study). Research appraisal tools are aimed at researchers who wish to explicitly demonstrate the evidential quality of the study to the readers (which is particularly common in RCTs). All forms of appraisal used in the comparative exercise below are defined as ‘tools’, even though they have different appraisal approaches and aims.
Comparing different qualitative tools
Hannes et al. ( 2010 ) identified CASP (Critical Appraisal Skills Programme-tool), JBI (Joanna Briggs Institute-tool) and ETQS (Evaluation Tool for Qualitative Studies) as the most frequently used critical appraisal tools by qualitative researchers. All three instruments are available online and are free of charge, which means that any researcher or reviewer can readily utilise CASP, JBI or ETQS evaluative frameworks to their research. Furthermore, all three instruments were developed within the context of organisational, institutional or consortium support (Tables (Tables6, 6 , ,7 7 and and8 8 ).
CASP (Critical Appraisal Skills Programme-tool)
JBI (Joanna Briggs Institute-tool)
ETQS (Evaluation Tool for Qualitative Studies)
It is important to note that neither of the three tools is specific to systematic case studies or psychotherapy case studies (which would include not only systematic but also experimental and clinical cases). This means that using CASP, JBI or ETQS for case study appraisal may come at a cost of overlooking elements and components specific to the systematic case study method.
Based on Hannes et al. ( 2010 ) comparative study of qualitative appraisal tools as well as the different evaluation criteria explicated in CASP, JBI and ETQS evaluative frameworks, I assessed how well each of the three tools is attuned to the methodological , clinical and theoretical aspects of systematic case studies in psychotherapy. The latter components were based on case study guidelines featured in the journal of Pragmatic Case Studies in Psychotherapy as well as components commonly used by published systematic case studies across a variety of other psychotherapy journals (e.g. Psychotherapy Research , Research In Psychotherapy : Psychopathology Process And Outcome , etc.) (see Table Table9 9 for detailed descriptions of each component).
Comparing the relevance of JBI (Joanna Briggs Institute), CASP (Critical Appraisal Skills Program) and ETQS (Evaluation Tool for Qualitative Studies) for appraising components specific to systematic case studies
The evaluation criteria for each tool in Table Table9 9 follows Joanna Briggs Institute (JBI) ( 2017a , 2017b ); Critical Appraisal Skills Programme (CASP) ( 2018 ); and ETQS Questionnaire (first published in 2004 but revised continuously since). Table Table10 10 demonstrates how each tool should be used (i.e. recommended reviewer responses to checklists and questionnaires).
Recommended reviewer responses to JBI (Joanna Briggs Institute), CASP (Critical Appraisal Skills Program) and ETQS (Evaluation Tool for Qualitative Studies)
Using CASP, JBI and ETQS for systematic case study appraisal
Although JBI, CASP and ETQS were all developed to appraise qualitative research, it is evident from the above comparison that there are significant differences between the three tools. For example, JBI and ETQS are well suited to assess researcher’s interpretations (Hannes et al. ( 2010 ) defined this as interpretive validity , a subcategory of internal validity ): the researcher’s ability to portray, understand and reflect on the research participants’ experiences, thoughts, viewpoints and intentions. JBI has an explicit requirement for participant voices to be clearly represented, whereas ETQS involves a set of questions about key characteristics of events, persons, times and settings that are relevant to the study. Furthermore, both JBI and ETQS seek to assess the researcher’s influence on the research, with ETQS particularly focusing on the evaluation of reflexivity (the researcher’s personal influence on the interpretation and collection of data). These elements are absent or addressed to a lesser extent in the CASP tool.
The appraisal of transferability of findings (what this paper previously referred to as external validity ) is addressed only by ETQS and CASP. Both tools have detailed questions about the value of research to practice and policy as well as its transferability to other populations and settings. Methodological research aspects are also extensively addressed by CASP and ETQS, but less so by JBI (which relies predominantly on congruity between research methodology and objectives without any particular assessment criteria for other data sources and/or data collection methods). Finally, the evaluation of theoretical aspects (referred to by Hannes et al. ( 2010 ) as theoretical validity ) is addressed only by JBI and ETQS; there are no assessment criteria for theoretical framework in CASP.
Given these differences, it is unsurprising that CASP, JBI and ETQS have limited relevance for systematic case studies in psychotherapy. First, it is evident that neither of the three tools has specific evaluative criteria for the clinical component of systematic case studies. Although JBI and ETQS feature some relevant questions about participants and their context, the conceptualisation of patients (and/or clients) in psychotherapy involves other kinds of data elements (e.g. diagnostic tools and questionnaires as well as therapist observations) that go beyond the usual participant data. Furthermore, much of the clinical data is intertwined with the therapist’s clinical decision-making and thinking style (Kaluzeviciute & Willemsen, 2020 ). As such, there is a need to appraise patient data and therapist interpretations not only on a separate basis, but also as two forms of knowledge that are deeply intertwined in the case narrative.
Secondly, since systematic case studies involve various forms of data, there is a need to appraise how these data converge (or how different methods complement one another in the case context) and how they can be transferred or applied in broader psychotherapy research and practice. These systematic case study components are attended to a degree by CASP (which is particularly attentive of methodological components) and ETQS (particularly specific criteria for research transferability onto policy and practice). These components are not addressed or less explicitly addressed by JBI. Overall, neither of the tools is attuned to all methodological, theoretical and clinical components of the systematic case study. Specifically, there are no clear evaluation criteria for the description of research teams (i.e. different data analysts and/or clinicians); the suitability of the systematic case study method; the description of patient’s clinical assessment; the use of other methods or data sources; the general data about therapeutic progress.
Finally, there is something to be said about the recommended reviewer responses (Table (Table10). 10 ). Systematic case studies can vary significantly in their formulation and purpose. The methodological, theoretical and clinical components outlined in Table Table9 9 follow guidelines made by case study journals; however, these are recommendations, not ‘set in stone’ case templates. For this reason, the straightforward checklist approaches adopted by JBI and CASP may be difficult to use for case study researchers and those reviewing case study research. The ETQS open-ended questionnaire approach suggested by Long and Godfrey ( 2004 ) enables a comprehensive, detailed and purpose-oriented assessment, suitable for the evaluation of systematic case studies. That said, there remains a challenge of ensuring that there is less space for the interpretation of evaluative criteria (Williams et al., 2019 ). The combination of checklist and framework approaches would, therefore, provide a more stable appraisal process across different reviewers.
Developing purpose-oriented evaluation criteria for systematic case studies
The starting point in developing evaluation criteria for Case Study Evaluation-tool (CaSE) is addressing the significance of pluralism in systematic case studies. Unlike RCTs, systematic case studies are pluralistic in the sense that they employ divergent practices in methodological procedures ( research process ), and they may include significantly different research aims and purpose ( the end - goal ) (Kaluzeviciute & Willemsen, 2020 ). While some systematic case studies will have an explicit intention to conceptualise and situate a single patient’s experiences and symptoms within a broader clinical population, others will focus on the exploration of phenomena as they emerge from the data. It is therefore important that CaSE is positioned within a purpose - oriented evaluative framework , suitable for the assessment of what each systematic case is good for (rather than determining an absolute measure of ‘good’ and ‘bad’ systematic case studies). This approach to evidence and appraisal is in line with the PBE paradigm. PBE emphasises the study of clinical complexities and variations through local and contingent settings (e.g. single case studies) and promotes methodological pluralism (Barkham & Mellor-Clark, 2003 ).
CaSE checklist for essential components in systematic case studies
In order to conceptualise purpose-oriented appraisal questions, we must first look at what unites and differentiates systematic case studies in psychotherapy. The commonly used theoretical, clinical and methodological systematic case study components were identified earlier in Table Table9. 9 . These components will be seen as essential and common to most systematic case studies in CaSE evaluative criteria. If these essential components are missing in a systematic case study, then it may be implied there is a lack of information, which in turn diminishes the evidential quality of the case. As such, the checklist serves as a tool for checking whether a case study is, indeed, systematic (as opposed to experimental or clinical; see Iwakabe & Gazzola, 2009 for further differentiation between methodologically distinct case study types) and should be used before CaSE Purpose - based Evaluative Framework for Systematic Case Studie s (which is designed for the appraisal of different purposes common to systematic case studies).
As noted earlier in the paper, checklist approaches to appraisal are useful when evaluating the presence or absence of specific information in a research study. This approach can be used to appraise essential components in systematic case studies, as shown below. From a pragmatic point view (Levitt et al., 2017 ; Truijens et al., 2019 ), CaSE Checklist for Essential Components in Systematic Case Studies can be seen as a way to ensure the internal validity of systematic case study: the reviewer is assessing whether sufficient information is provided about the case design, procedure, approaches to inquiry, etc., and whether they are relevant to the researcher’s objectives and conclusions (Table (Table11 11 ).
Case Study Evaluation-tool (CaSE) checklist for essential components in systematic case studies. Recommended responses: Yes, No, unclear or not applicable
CaSE purpose-based evaluative framework for systematic case studies
Identifying differences between systematic case studies means identifying the different purposes systematic case studies have in psychotherapy. Based on the earlier work by social scientist Yin ( 1984 , 1993 ), we can differentiate between exploratory (hypothesis generating, indicating a beginning phase of research), descriptive (particularising case data as it emerges) and representative (a case that is typical of a broader clinical population, referred to as the ‘explanatory case’ by Yin) cases.
Another increasingly significant strand of systematic case studies is transferable (aggregating and transferring case study findings) cases. These cases are based on the process of meta-synthesis (Iwakabe & Gazzola, 2009 ): by examining processes and outcomes in many different case studies dealing with similar clinical issues, researchers can identify common themes and inferences. In this way, single case studies that have relatively little impact on clinical practice, research or health care policy (in the sense that they capture psychotherapy processes rather than produce generalisable claims as in Yin’s representative case studies) can contribute to the generation of a wider knowledge base in psychotherapy (Iwakabe, 2003 , 2005 ). However, there is an ongoing issue of assessing the evidential quality of such transferable cases. According to Duncan and Sparks ( 2020 ), although meta-synthesis and meta-analysis are considered to be ‘gold standard’ for assessing interventions across disparate studies in psychotherapy, they often contain case studies with significant research limitations, inappropriate interpretations and insufficient information. It is therefore important to have a research appraisal process in place for selecting transferable case studies.
Two other types of systematic case study research include: critical (testing and/or confirming existing theories) cases, which are described as an excellent method for falsifying existing theoretical concepts and testing whether therapeutic interventions work in practice with concrete patients (Kaluzeviciute, 2021 ), and unique (going beyond the ‘typical’ cases and demonstrating deviations) cases (Merriam, 1998 ). These two systematic case study types are often seen as less valuable for psychotherapy research given that unique/falsificatory findings are difficult to generalise. But it is clear that practitioners and researchers in our field seek out context-specific data, as well as detailed information on the effectiveness of therapeutic techniques in single cases (Stiles, 2007 ) (Table (Table12 12 ).
Key concept: purpose–based systematic case studies
Each purpose-based case study contributes to PBE in different ways. Representative cases provide qualitatively rich, in-depth data about a clinical phenomenon within its particular context. This offers other clinicians and researchers access to a ‘closed world’ (Mackrill & Iwakabe, 2013 ) containing a wide range of attributes about a conceptual type (e.g. clinical condition or therapeutic technique). Descriptive cases generally seek to demonstrate a realistic snapshot of therapeutic processes, including complex dynamics in therapeutic relationships, and instances of therapeutic failure (Maggio, Molgora, & Oasi, 2019 ). Data in descriptive cases should be presented in a transparent manner (e.g. if there are issues in standardising patient responses to a self-report questionnaire, this should be made explicit). Descriptive cases are commonly used in psychotherapy training and supervision. Unique cases are relevant for both clinicians and researchers: they often contain novel treatment approaches and/or introduce new diagnostic considerations about patients who deviate from the clinical population. Critical cases demonstrate the application of psychological theories ‘in action’ with particular patients; as such, they are relevant to clinicians, researchers and policymakers (Mackrill & Iwakabe, 2013 ). Exploratory cases bring new insight and observations into clinical practice and research. This is particularly useful when comparing (or introducing) different clinical approaches and techniques (Trad & Raine, 1994 ). Findings from exploratory cases often include future research suggestions. Finally, transferable cases provide one solution to the generalisation issue in psychotherapy research through the previously mentioned process of meta-synthesis. Grouped together, transferable cases can contribute to theory building and development, as well as higher levels of abstraction about a chosen area of psychotherapy research (Iwakabe & Gazzola, 2009 ).
With this plurality in mind, it is evident that CaSE has a challenging task of appraising research components that are distinct across six different types of purpose-based systematic case studies. The purpose-specific evaluative criteria in Table Table13 13 was developed in close consultation with epistemological literature associated with each type of case study, including: Yin’s ( 1984 , 1993 ) work on establishing the typicality of representative cases; Duncan and Sparks’ ( 2020 ) and Iwakabe and Gazzola’s ( 2009 ) case selection criteria for meta-synthesis and meta-analysis; Stake’s ( 1995 , 2010 ) research on particularising case narratives; Merriam’s ( 1998 ) guidelines on distinctive attributes of unique case studies; Kennedy’s ( 1979 ) epistemological rules for generalising from case studies; Mahrer’s ( 1988 ) discovery oriented case study approach; and Edelson’s ( 1986 ) guidelines for rigorous hypothesis generation in case studies.
Case Study Evaluation-tool (CaSE) purpose-based evaluative framework for systematic case studies. Recommended responses: open-ended questionnaire
Research on epistemic issues in case writing (Kaluzeviciute, 2021 ) and different forms of scientific thinking in psychoanalytic case studies (Kaluzeviciute & Willemsen, 2020 ) was also utilised to identify case study components that would help improve therapist clinical decision-making and reflexivity.
For the analysis of more complex research components (e.g. the degree of therapist reflexivity), the purpose-based evaluation will utilise a framework approach, in line with comprehensive and open-ended reviewer responses in ETQS (Evaluation Tool for Qualitative Studies) (Long & Godfrey, 2004 ) (Table (Table13). 13 ). That is to say, the evaluation here is not so much about the presence or absence of information (as in the checklist approach) but the degree to which the information helps the case with its unique purpose, whether it is generalisability or typicality. Therefore, although the purpose-oriented evaluation criteria below encompasses comprehensive questions at a considerable level of generality (in the sense that not all components may be required or relevant for each case study), it nevertheless seeks to engage with each type of purpose-based systematic case study on an individual basis (attending to research or clinical components that are unique to each of type of case study).
It is important to note that, as this is an introductory paper to CaSE, the evaluative framework is still preliminary: it involves some of the core questions that pertain to the nature of all six purpose-based systematic case studies. However, there is a need to develop a more comprehensive and detailed CaSE appraisal framework for each purpose-based systematic case study in the future.
Using CaSE on published systematic case studies in psychotherapy: an example
To illustrate the use of CaSE Purpose - based Evaluative Framework for Systematic Case Studies , a case study by Lunn, Daniel, and Poulsen ( 2016 ) titled ‘ Psychoanalytic Psychotherapy With a Client With Bulimia Nervosa ’ was selected from the Single Case Archive (SCA) and analysed in Table Table14. 14 . Based on the core questions associated with the six purpose-based systematic case study types in Table Table13(1 13 (1 to 6), the purpose of Lunn et al.’s ( 2016 ) case was identified as critical (testing an existing theoretical suggestion).
Using Case Study Evaluation-tool (CaSE): Lunn et al. ( 2016 )’s case ‘ Psychoanalytic psychotherapy with a client with bulimia nervosa ’
Sometimes, case study authors will explicitly define the purpose of their case in the form of research objectives (as was the case in Lunn et al.’s study); this helps identifying which purpose-based questions are most relevant for the evaluation of the case. However, some case studies will require comprehensive analysis in order to identify their purpose (or multiple purposes). As such, it is recommended that CaSE reviewers first assess the degree and manner in which information about the studied phenomenon, patient data, clinical discourse and research are presented before deciding on the case purpose.
Although each purpose-based systematic case study will contribute to different strands of psychotherapy (theory, practice, training, etc.) and focus on different forms of data (e.g. theory testing vs extensive clinical descriptions), the overarching aim across all systematic case studies in psychotherapy is to study local and contingent processes, such as variations in patient symptoms and complexities of the clinical setting. The comprehensive framework approach will therefore allow reviewers to assess the degree of external validity in systematic case studies (Barkham & Mellor-Clark, 2003 ). Furthermore, assessing the case against its purpose will let reviewers determine whether the case achieves its set goals (research objectives and aims). The example below shows that Lunn et al.’s ( 2016 ) case is successful in functioning as a critical case as the authors provide relevant, high-quality information about their tested therapeutic conditions.
Finally, it is also possible to use CaSE to gather specific type of systematic case studies for one’s research, practice, training, etc. For example, a CaSE reviewer might want to identify as many descriptive case studies focusing on negative therapeutic relationships as possible for their clinical supervision. The reviewer will therefore only need to refer to CaSE questions in Table Table13(2) 13 (2) on descriptive cases. If the reviewed cases do not align with the questions in Table Table13(2), 13 (2), then they are not suitable for the CaSE reviewer who is looking for “know-how” knowledge and detailed clinical narratives.
Concluding comments
This paper introduces a novel Case Study Evaluation-tool (CaSE) for systematic case studies in psychotherapy. Unlike most appraisal tools in EBP, CaSE is positioned within purpose-oriented evaluation criteria, in line with the PBE paradigm. CaSE enables reviewers to assess what each systematic case is good for (rather than determining an absolute measure of ‘good’ and ‘bad’ systematic case studies). In order to explicate a purpose-based evaluative framework, six different systematic case study purposes in psychotherapy have been identified: representative cases (purpose: typicality), descriptive cases (purpose: particularity), unique cases (purpose: deviation), critical cases (purpose: falsification/confirmation), exploratory cases (purpose: hypothesis generation) and transferable cases (purpose: generalisability). Each case was linked with an existing epistemological network, such as Iwakabe and Gazzola’s ( 2009 ) work on case selection criteria for meta-synthesis. The framework approach includes core questions specific to each purpose-based case study (Table 13 (1–6)). The aim is to assess the external validity and effectiveness of each case study against its set out research objectives and aims. Reviewers are required to perform a comprehensive and open-ended data analysis, as shown in the example in Table Table14 14 .
Along with CaSE Purpose - based Evaluative Framework (Table (Table13), 13 ), the paper also developed CaSE Checklist for Essential Components in Systematic Case Studies (Table (Table12). 12 ). The checklist approach is meant to aid reviewers in assessing the presence or absence of essential case study components, such as the rationale behind choosing the case study method and description of patient’s history. If essential components are missing in a systematic case study, then it may be implied that there is a lack of information, which in turn diminishes the evidential quality of the case. Following broader definitions of validity set out by Levitt et al. ( 2017 ) and Truijens et al. ( 2019 ), it could be argued that the checklist approach allows for the assessment of (non-quantitative) internal validity in systematic case studies: does the researcher provide sufficient information about the case study design, rationale, research objectives, epistemological/philosophical paradigms, assessment procedures, data analysis, etc., to account for their research conclusions?
It is important to note that this paper is set as an introduction to CaSE; by extension, it is also set as an introduction to research evaluation and appraisal processes for case study researchers in psychotherapy. As such, it was important to provide a step-by-step epistemological rationale and process behind the development of CaSE evaluative framework and checklist. However, this also means that further research needs to be conducted in order to develop the tool. While CaSE Purpose - based Evaluative Framework involves some of the core questions that pertain to the nature of all six purpose-based systematic case studies, there is a need to develop individual and comprehensive CaSE evaluative frameworks for each of the purpose-based systematic case studies in the future. This line of research is likely to enhance CaSE target audience: clinicians interested in reviewing highly particular clinical narratives will attend to descriptive case study appraisal frameworks; researchers working with qualitative meta-synthesis will find transferable case study appraisal frameworks most relevant to their work; while teachers on psychotherapy and counselling modules may seek out unique case study appraisal frameworks.
Furthermore, although CaSE Checklist for Essential Components in Systematic Case Studies and CaSE Purpose - based Evaluative Framework for Systematic Case Studies are presented in a comprehensive, detailed manner, with definitions and examples that would enable reviewers to have a good grasp of the appraisal process, it is likely that different reviewers may have different interpretations or ideas of what might be ‘substantial’ case study data. This, in part, is due to the methodologically pluralistic nature of the case study genre itself; what is relevant for one case study may not be relevant for another, and vice-versa. To aid with the review process, future research on CaSE should include a comprehensive paper on using the tool. This paper should involve evaluation examples with all six purpose-based systematic case studies, as well as a ‘search’ exercise (using CaSE to assess the relevance of case studies for one’s research, practice, training, etc.).
Finally, further research needs to be developed on how (and, indeed, whether) systematic case studies should be reviewed with specific ‘grades’ or ‘assessments’ that go beyond the qualitative examination in Table Table14. 14 . This would be particularly significant for the processes of qualitative meta-synthesis and meta-analysis. These research developments will further enhance CaSE tool, and, in turn, enable psychotherapy researchers to appraise their findings within clear, purpose-based evaluative criteria appropriate for systematic case studies.
Acknowledgments
I would like to thank Prof Jochem Willemsen (Faculty of Psychology and Educational Sciences, Université catholique de Louvain-la-Neuve), Prof Wayne Martin (School of Philosophy and Art History, University of Essex), Dr Femke Truijens (Institute of Psychology, Erasmus University Rotterdam) and the reviewers of Psicologia: Reflexão e Crítica / Psychology : Research and Review for their feedback, insight and contributions to the manuscript.
Author’s contributions
GK is the sole author of the manuscript. The author(s) read and approved the final manuscript.
Arts and Humanities Research Council (AHRC) and Consortium for Humanities and the Arts South-East England (CHASE) Doctoral Training Partnership, Award Number [AH/L50 3861/1].
Availability of data and materials
Declarations.
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
- Almond R. “I Can Do It (All) Myself”: Clinical technique with defensive narcissistic self–sufficiency. Psychoanalytic Psychology. 2004; 21 (3):371–384. doi: 10.1037/0736-9735.21.3.371. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- American Psychological Association . Evidence–based case study. 2010. [ Google Scholar ]
- Aveline M. Clinical case studies: Their place in evidence–based practice. Psychodynamic Practice: Individuals, Groups and Organisations. 2005; 11 (2):133–152. doi: 10.1080/14753630500108174. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Barkham M, Mellor-Clark J. Bridging evidence-based practice and practice-based evidence: Developing a rigorous and relevant knowledge for the psychological therapies. Clinical Psychology & Psychotherapy. 2003; 10 (6):319–327. doi: 10.1002/cpp.379. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Berg H. How does evidence–based practice in psychology work? – As an ethical demarcation. Philosophical Psychology. 2019; 32 (6):853–873. doi: 10.1080/09515089.2019.1632424. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Berg H, Slaattelid R. Facts and values in psychotherapy—A critique of the empirical reduction of psychotherapy within evidence-based practice. Journal of Evaluation in Clinical Practice. 2017; 23 (5):1075–1080. doi: 10.1111/jep.12739. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bower P. Efficacy in evidence-based practice. Clinical Psychology and Psychotherapy. 2003; 10 (6):328–336. doi: 10.1002/cpp.380. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cartwright, N., & Hardie, J. (2012). What are RCTs good for? In N. Cartwright, & J. Hardie (Eds.), Evidence–based policy: A practical guide to doing it better . Oxford University Press. 10.1093/acprof:osobl/9780199841608.003.0008.
- Critical Appraisal Skills Programme (CASP) Qualitative checklist. 2018. [ Google Scholar ]
- Davison, G. C., & Lazarus, A. A. (2007). Clinical case studies are important in the science and practice of psychotherapy. In S. O. Lilienfeld, & W. T. O’Donohue (Eds.), The great ideas of clinical science: 17 principles that every mental health professional should understand , (pp. 149–162). Routledge/Taylor & Francis Group.
- Douglas H. The irreducible complexity of objectivity. Synthese. 2004; 138 (3):453–473. doi: 10.1023/B:SYNT.0000016451.18182.91. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Duncan BL, Sparks JA. When meta–analysis misleads: A critical case study of a meta–analysis of client feedback. Psychological Services. 2020; 17 (4):487–496. doi: 10.1037/ser0000398. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Edelson, M. (1986). Causal explanation in science and in psychoanalysis—Implications for writing a case study. Psychoanalytic Study of Child , 41 (1), 89–127. 10.1080/00797308.1986.11823452. [ PubMed ]
- Edwards DJA. Collaborative versus adversarial stances in scientific discourse: Implications for the role of systematic case studies in the development of evidence–based practice in psychotherapy. Pragmatic Case Studies in Psychotherapy. 2013; 3 (1):6–34. [ Google Scholar ]
- Edwards DJA, Dattilio FM, Bromley DB. Developing evidence–based practice: The role of case–based research. Professional Psychology: Research and Practice. 2004; 35 (6):589–597. doi: 10.1037/0735-7028.35.6.589. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Erickson F. Comments on causality in qualitative inquiry. Qualitative Inquiry. 2012; 18 (8):686–688. doi: 10.1177/1077800412454834. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Fishman, D. B. (1999). The case for pragmatic psychology . New York University Press.
- Fishman DB. Editor’s introduction to PCSP––From single case to database: A new method for enhancing psychotherapy practice. Pragmatic Case Studies in Psychotherapy. 2005; 1 (1):1–50. [ Google Scholar ]
- Fishman, D. B., Messer, S. B., Edwards, D. J. A., & Dattilio, F. M. (Eds.) (2017). Case studies within psychotherapy trials: Integrating qualitative and quantitative methods . Oxford University Press.
- Fox, N. J. (2003). Practice–based evidence: Towards collaborative and transgressive research. Sociology , 37 (1), 81–102. 10.1177/0038038503037001388.
- Gabbay, J., & le May, A. (2011). Practice–based evidence for healthcare: Clinical mindlines . Routledge.
- Green, L. W., & Latchford, G. (2012). Maximising the benefits of psychotherapy: A practice–based evidence approach . Wiley–Blackwell. 10.1002/9781119967590.
- Hannes K, Lockwood C, Pearson A. A comparative analysis of three online appraisal instruments’ ability to assess validity in qualitative research. Qualitative Health Research. 2010; 20 (12):1736–1743. doi: 10.1177/1049732310378656. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hartling L, Chisholm A, Thomson D, Dryden DM. A descriptive analysis of overviews of reviews published between 2000 and 2011. PLoS One. 2012; 7 (11):e49667. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0049667. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hill A, Spittlehouse C. What is critical appraisal? Evidence–Based Medicine. 2003; 3 (2):1–8. [ Google Scholar ]
- Hilliard RB. Single–case methodology in psychotherapy process and outcome research. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology. 1993; 61 (3):373–380. doi: 10.1037/0022-006X.61.3.373. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Horn SD, Gassaway J. Practice–based evidence study design for comparative effectiveness research. Medical Care. 2007; 45 (10):S50–S57. doi: 10.1097/MLR.0b013e318070c07b. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Iwakabe S. Paper presented at the 19th Annual Conference of the Society for Exploration of Psychotherapy Integration, New York. 2003. Common change events in stages of psychotherapy: A qualitative analysis of case reports. [ Google Scholar ]
- Iwakabe S. Pragmatic meta–analysis of case studies. Annual Progress of Family Psychology. 2005; 23 :154–169. [ Google Scholar ]
- Iwakabe S, Gazzola N. From single–case studies to practice–based knowledge: Aggregating and synthesizing case studies. Psychotherapy Research. 2009; 19 (4-5):601–611. doi: 10.1080/10503300802688494. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Jimenez-Buedo M, Miller L. Why a Trade–Off? The relationship between the external and internal validity of experiments. THEORIA: An International Journal for Theory History and Foundations of Science. 2010; 25 (3):301–321. [ Google Scholar ]
- Joanna Briggs Institute (JBI) Critical appraisal checklist for qualitative research. 2017. [ Google Scholar ]
- Joanna Briggs Institute (JBI) Checklist for case reports. 2017. [ Google Scholar ]
- Kaluzeviciute, G. (2021). Validity, Evidence and Appraisal in Systematic Psychotherapy Case Studies . Paper presented at the Research Forum of Department of Psychosocial and Psychoanalytic Studies, University of Essex, Colchester, UK. 10.13140/RG.2.2.33502.15683
- Kaluzeviciute G, Willemsen J. Scientific thinking styles: The different ways of thinking in psychoanalytic case studies. The International Journal of Psychoanalysis. 2020; 101 (5):900–922. doi: 10.1080/00207578.2020.1796491. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Katrak P, Bialocerkowski AE, Massy-Westropp N, Kumar SVS, Grimmer K. A systematic review of the content of critical appraisal tools. BMC Medical Research Methodology. 2004; 4 (1):22. doi: 10.1186/1471-2288-4-22. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kennedy MM. Generalising from single case studies. Evaluation Quarterly. 1979; 3 (4):661–678. doi: 10.1177/0193841X7900300409. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Laska KM, Gurman AS, Wampold BE. Expanding the lens of evidence–based practice in psychotherapy: A common factors perspective. Psychotherapy. 2014; 51 (4):467–481. doi: 10.1037/a0034332. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Levitt HM, Motulsky SL, Wertz FJ, Morrow SL, Ponterotto JG. Recommendations for designing and reviewing qualitative research in psychology: Promoting methodological integrity. Qualitative Psychology. 2017; 4 (1):2–22. doi: 10.1037/qup0000082. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lilienfeld SO, Ritschel LA, Lynn SJ, Cautin RL, Latzman RD. Why many clinical psychologists are resistant to evidence–based practice: root causes and constructive remedies. Clinical Psychology Review. 2013; 33 (7):883–900. doi: 10.1016/j.cpr.2012.09.008. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Long AF, Godfrey M. An evaluation tool to assess the quality of qualitative research studies. International Journal of Social Research Methodology. 2004; 7 (2):181–196. doi: 10.1080/1364557032000045302. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Longhofer J, Floersch J, Hartmann EA. Case for the case study: How and why they matter. Clinical Social Work Journal. 2017; 45 (3):189–200. doi: 10.1007/s10615-017-0631-8. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lunn S, Daniel SIF, Poulsen S. Psychoanalytic psychotherapy with a client with bulimia nervosa. Psychotherapy. 2016; 53 (2):206–215. doi: 10.1037/pst0000052. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Mackrill T, Iwakabe S. Making a case for case studies in psychotherapy training: A small step towards establishing an empirical basis for psychotherapy training. Counselling Psychotherapy Quarterly. 2013; 26 (3–4):250–266. doi: 10.1080/09515070.2013.832148. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Maggio S, Molgora S, Oasi O. Analyzing psychotherapeutic failures: A research on the variables involved in the treatment with an individual setting of 29 cases. Frontiers in Psychology. 2019; 10 :1250. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2019.01250. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Mahrer AR. Discovery–oriented psychotherapy research: Rationale, aims, and methods. American Psychologist. 1988; 43 (9):694–702. doi: 10.1037/0003-066X.43.9.694. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Margison FB, et al. Measurement and psychotherapy: Evidence–based practice and practice–based evidence. British Journal of Psychiatry. 2000; 177 (2):123–130. doi: 10.1192/bjp.177.2.123. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Maxwell JA. Causal explanation, qualitative research, and scientific inquiry in education. Educational Researcher. 2004; 33 (2):3–11. doi: 10.3102/0013189X033002003. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- McLeod J. Case studies and practitioner research: Building knowledge through systematic inquiry into individual cases. Counselling and Psychotherapy Research: Linking research with practice. 2002; 2 (4):264–268. doi: 10.1080/14733140212331384755. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- McLeod, J. (2010). Case study research in counselling and psychotherapy . SAGE Publications. 10.4135/9781446287897.
- McLeod J, Elliott R. Systematic case study research: A practice–oriented introduction to building an evidence base for counselling and psychotherapy. Counselling and Psychotherapy Research. 2011; 11 (1):1–10. doi: 10.1080/14733145.2011.548954. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Meganck R, Inslegers R, Krivzov J, Notaerts L. Beyond clinical case studies in psychoanalysis: A review of psychoanalytic empirical single case studies published in ISI–ranked journals. Frontiers in Psychology. 2017; 8 :1749. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2017.01749. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Merriam, S. B. (1998). Qualitative research and case study applications in education . Jossey–Bass Publishers.
- Michels R. The case history. Journal of the American Psychoanalytic Association. 2000; 48 (2):355–375. doi: 10.1177/00030651000480021201. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Midgley N. Re–reading “Little Hans”: Freud’s case study and the question of competing paradigms in psychoanalysis. Journal of the American Psychoanalytic Association. 2006; 54 (2):537–559. doi: 10.1177/00030651060540021601. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rosqvist, J., Thomas, J. C., & Truax, P. (2011). Effectiveness versus efficacy studies. In J. C. Thomas, & M. Hersen (Eds.), Understanding research in clinical and counseling psychology , (pp. 319–354). Routledge/Taylor & Francis Group.
- Sackett DL, Rosenberg WM, Gray JAM, Haynes RB, Richardson WS. Evidence based medicine: what it is and what it isn’t. BMJ. 1996; 312 (7023):71–72. doi: 10.1136/bmj.312.7023.71. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Stake, R. E. (1995). The art of case study research . SAGE Publications.
- Stake, R. E. (2010). Qualitative research: Studying how things work . The Guilford Press.
- Stewart RE, Chambless DL. Does psychotherapy research inform treatment decisions in private practice? Journal of Clinical Psychology. 2007; 63 (3):267–281. doi: 10.1002/jclp.20347. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Stiles WB. Theory–building case studies of counselling and psychotherapy. Counselling and Psychotherapy Research. 2007; 7 (2):122–127. doi: 10.1080/14733140701356742. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Teachman BA, Drabick DA, Hershenberg R, Vivian D, Wolfe BE, Goldfried MR. Bridging the gap between clinical research and clinical practice: introduction to the special section. Psychotherapy. 2012; 49 (2):97–100. doi: 10.1037/a0027346. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Thorne S, Jensen L, Kearney MH, Noblit G, Sandelowski M. Qualitative metasynthesis: Reflections on methodological orientation and ideological agenda. Qualitative Health Research. 2004; 14 (10):1342–1365. doi: 10.1177/1049732304269888. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Timulak L. Meta–analysis of qualitative studies: A tool for reviewing qualitative research findings in psychotherapy. Psychotherapy Research. 2009; 19 (4–5):591–600. doi: 10.1080/10503300802477989. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Trad PV, Raine MJ. A prospective interpretation of unconscious processes during psychoanalytic psychotherapy. Psychoanalytic Psychology. 1994; 11 (1):77–100. doi: 10.1037/h0079522. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Truijens, F., Cornelis, S., Desmet, M., & De Smet, M. (2019). Validity beyond measurement: Why psychometric validity is insufficient for valid psychotherapy research. Frontiers in Psychology , 10 . 10.3389/fpsyg.2019.00532. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ]
- Tuckett, D. (Ed.) (2008). The new library of psychoanalysis. Psychoanalysis comparable and incomparable: The evolution of a method to describe and compare psychoanalytic approaches . Routledge/Taylor & Francis Group. 10.4324/9780203932551.
- van Hennik R. Practice based evidence based practice, part II: Navigating complexity and validity from within. Journal of Family Therapy. 2020; 43 (1):27–45. doi: 10.1111/1467-6427.12291. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Westen D, Novotny CM, Thompson-Brenner H. The empirical status of empirically supported psychotherapies: Assumptions, findings, and reporting in controlled clinical trials. Psychological Bulletin. 2004; 130 (4):631–663. doi: 10.1037/0033-2909.130.4.631. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Widdowson, M. (2011). Case study research methodology. International Journal of Transactional Analysis Research & Practice , 2 (1). 10.29044/v2i1p25.
- Willemsen, J., Della Rosa, E., & Kegerreis, S. (2017). Clinical case studies in psychoanalytic and psychodynamic treatment. Frontiers in Psychology , 8 (108). 10.3389/fpsyg.2017.00108. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ]
- Williams, V., Boylan, A., & Nunan, D. (2019). Critical appraisal of qualitative research: Necessity, partialities and the issue of bias. BMJ Evidence–Based Medicine . 10.1136/bmjebm-2018-111132. [ PubMed ]
- Yin, R. K. (1984). Case study research: Design and methods . SAGE Publications.
- Yin, R. K. (1993). Applications of case study research . SAGE Publications.
- Living reference work entry
- First Online: 02 February 2024
- Cite this living reference work entry

- Li Shouxin 2
It is a method of psychological study that involves the observation and investigation of specific individuals or organizations. It is a type of qualitative research method. A case can be a typical individual, a prominent event, or a representative group (Fig. 1 ). Founder of the School of Psychoanalysis, Sigmund Freud, applied this method to conduct in-depth studies of the creative process and personality characteristics of many famous people in history. There are two types of case study: (1) Follow-up study: It uses follow-up approach, such as keeping systematic biographies from the birth of a child, through a relatively long period of observation, helps to summarize the characteristics of the child’s psychological and behavioral development and the influencing factors. (2) Retrospective study: It uses a retrospective approach; for example, when studying a juvenile delinquent, by visiting and surveying the juvenile delinquent’s teachers, classmates, parents, and correctional staff, so...
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
Institutional subscriptions
Further Reading
Kantowitz BH, Roediger HL, Elmes DG (2015) Experimental psychology, 10th edn. Cengage Learning, Boston
Google Scholar
Zhang X-M, Shu H (2014) Experimental psychology. Beijing Normal University Publishing Group, Beijing
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Psychology, Shandong Normal University, Jinan, China
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Li Shouxin .
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 Encyclopedia of China Publishing House
About this entry
Cite this entry.
Shouxin, L. (2024). Case Study. In: The ECPH Encyclopedia of Psychology. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-6000-2_409-1
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-6000-2_409-1
Received : 04 January 2024
Accepted : 05 January 2024
Published : 02 February 2024
Publisher Name : Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN : 978-981-99-6000-2
Online ISBN : 978-981-99-6000-2
eBook Packages : Springer Reference Behavioral Science and Psychology Reference Module Humanities and Social Sciences Reference Module Business, Economics and Social Sciences
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
15 Famous Experiments and Case Studies in Psychology

Psychology has seen thousands upon thousands of research studies over the years. Most of these studies have helped shape our current understanding of human thoughts, behavior, and feelings.
The psychology case studies in this list are considered classic examples of psychological case studies and experiments, which are still being taught in introductory psychology courses up to this day.
Some studies, however, were downright shocking and controversial that you’d probably wonder why such studies were conducted back in the day. Imagine participating in an experiment for a small reward or extra class credit, only to be left scarred for life. These kinds of studies, however, paved the way for a more ethical approach to studying psychology and implementation of research standards such as the use of debriefing in psychology research .
Case Study vs. Experiment
Before we dive into the list of the most famous studies in psychology, let us first review the difference between case studies and experiments.
- It is an in-depth study and analysis of an individual, group, community, or phenomenon. The results of a case study cannot be applied to the whole population, but they can provide insights for further studies.
- It often uses qualitative research methods such as observations, surveys, and interviews.
- It is often conducted in real-life settings rather than in controlled environments.
- An experiment is a type of study done on a sample or group of random participants, the results of which can be generalized to the whole population.
- It often uses quantitative research methods that rely on numbers and statistics.
- It is conducted in controlled environments, wherein some things or situations are manipulated.
See Also: Experimental vs Observational Studies
Famous Experiments in Psychology
1. the marshmallow experiment.
Psychologist Walter Mischel conducted the marshmallow experiment at Stanford University in the 1960s to early 1970s. It was a simple test that aimed to define the connection between delayed gratification and success in life.
The instructions were fairly straightforward: children ages 4-6 were presented a piece of marshmallow on a table and they were told that they would receive a second piece if they could wait for 15 minutes without eating the first marshmallow.
About one-third of the 600 participants succeeded in delaying gratification to receive the second marshmallow. Mischel and his team followed up on these participants in the 1990s, learning that those who had the willpower to wait for a larger reward experienced more success in life in terms of SAT scores and other metrics.
This case study also supported self-control theory , a theory in criminology that holds that people with greater self-control are less likely to end up in trouble with the law!
The classic marshmallow experiment, however, was debunked in a 2018 replication study done by Tyler Watts and colleagues.
This more recent experiment had a larger group of participants (900) and a better representation of the general population when it comes to race and ethnicity. In this study, the researchers found out that the ability to wait for a second marshmallow does not depend on willpower alone but more so on the economic background and social status of the participants.
2. The Bystander Effect
In 1694, Kitty Genovese was murdered in the neighborhood of Kew Gardens, New York. It was told that there were up to 38 witnesses and onlookers in the vicinity of the crime scene, but nobody did anything to stop the murder or call for help.
Such tragedy was the catalyst that inspired social psychologists Bibb Latane and John Darley to formulate the phenomenon called bystander effect or bystander apathy .
Subsequent investigations showed that this story was exaggerated and inaccurate, as there were actually only about a dozen witnesses, at least two of whom called the police. But the case of Kitty Genovese led to various studies that aim to shed light on the bystander phenomenon.
Latane and Darley tested bystander intervention in an experimental study . Participants were asked to answer a questionnaire inside a room, and they would either be alone or with two other participants (who were actually actors or confederates in the study). Smoke would then come out from under the door. The reaction time of participants was tested — how long would it take them to report the smoke to the authorities or the experimenters?
The results showed that participants who were alone in the room reported the smoke faster than participants who were with two passive others. The study suggests that the more onlookers are present in an emergency situation, the less likely someone would step up to help, a social phenomenon now popularly called the bystander effect.
3. Asch Conformity Study
Have you ever made a decision against your better judgment just to fit in with your friends or family? The Asch Conformity Studies will help you understand this kind of situation better.
In this experiment, a group of participants were shown three numbered lines of different lengths and asked to identify the longest of them all. However, only one true participant was present in every group and the rest were actors, most of whom told the wrong answer.
Results showed that the participants went for the wrong answer, even though they knew which line was the longest one in the first place. When the participants were asked why they identified the wrong one, they said that they didn’t want to be branded as strange or peculiar.
This study goes to show that there are situations in life when people prefer fitting in than being right. It also tells that there is power in numbers — a group’s decision can overwhelm a person and make them doubt their judgment.
4. The Bobo Doll Experiment
The Bobo Doll Experiment was conducted by Dr. Albert Bandura, the proponent of social learning theory .
Back in the 1960s, the Nature vs. Nurture debate was a popular topic among psychologists. Bandura contributed to this discussion by proposing that human behavior is mostly influenced by environmental rather than genetic factors.
In the Bobo Doll Experiment, children were divided into three groups: one group was shown a video in which an adult acted aggressively toward the Bobo Doll, the second group was shown a video in which an adult play with the Bobo Doll, and the third group served as the control group where no video was shown.
The children were then led to a room with different kinds of toys, including the Bobo Doll they’ve seen in the video. Results showed that children tend to imitate the adults in the video. Those who were presented the aggressive model acted aggressively toward the Bobo Doll while those who were presented the passive model showed less aggression.
While the Bobo Doll Experiment can no longer be replicated because of ethical concerns, it has laid out the foundations of social learning theory and helped us understand the degree of influence adult behavior has on children.
5. Blue Eye / Brown Eye Experiment
Following the assassination of Martin Luther King Jr. in 1968, third-grade teacher Jane Elliott conducted an experiment in her class. Although not a formal experiment in controlled settings, A Class Divided is a good example of a social experiment to help children understand the concept of racism and discrimination.
The class was divided into two groups: blue-eyed children and brown-eyed children. For one day, Elliott gave preferential treatment to her blue-eyed students, giving them more attention and pampering them with rewards. The next day, it was the brown-eyed students’ turn to receive extra favors and privileges.
As a result, whichever group of students was given preferential treatment performed exceptionally well in class, had higher quiz scores, and recited more frequently; students who were discriminated against felt humiliated, answered poorly in tests, and became uncertain with their answers in class.
This study is now widely taught in sociocultural psychology classes.
6. Stanford Prison Experiment
One of the most controversial and widely-cited studies in psychology is the Stanford Prison Experiment , conducted by Philip Zimbardo at the basement of the Stanford psychology building in 1971. The hypothesis was that abusive behavior in prisons is influenced by the personality traits of the prisoners and prison guards.
The participants in the experiment were college students who were randomly assigned as either a prisoner or a prison guard. The prison guards were then told to run the simulated prison for two weeks. However, the experiment had to be stopped in just 6 days.
The prison guards abused their authority and harassed the prisoners through verbal and physical means. The prisoners, on the other hand, showed submissive behavior. Zimbardo decided to stop the experiment because the prisoners were showing signs of emotional and physical breakdown.
Although the experiment wasn’t completed, the results strongly showed that people can easily get into a social role when others expect them to, especially when it’s highly stereotyped .
7. The Halo Effect
Have you ever wondered why toothpastes and other dental products are endorsed in advertisements by celebrities more often than dentists? The Halo Effect is one of the reasons!
The Halo Effect shows how one favorable attribute of a person can gain them positive perceptions in other attributes. In the case of product advertisements, attractive celebrities are also perceived as intelligent and knowledgeable of a certain subject matter even though they’re not technically experts.
The Halo Effect originated in a classic study done by Edward Thorndike in the early 1900s. He asked military commanding officers to rate their subordinates based on different qualities, such as physical appearance, leadership, dependability, and intelligence.
The results showed that high ratings of a particular quality influences the ratings of other qualities, producing a halo effect of overall high ratings. The opposite also applied, which means that a negative rating in one quality also correlated to negative ratings in other qualities.
Experiments on the Halo Effect came in various formats as well, supporting Thorndike’s original theory. This phenomenon suggests that our perception of other people’s overall personality is hugely influenced by a quality that we focus on.
8. Cognitive Dissonance
There are experiences in our lives when our beliefs and behaviors do not align with each other and we try to justify them in our minds. This is cognitive dissonance , which was studied in an experiment by Leon Festinger and James Carlsmith back in 1959.
In this experiment, participants had to go through a series of boring and repetitive tasks, such as spending an hour turning pegs in a wooden knob. After completing the tasks, they were then paid either $1 or $20 to tell the next participants that the tasks were extremely fun and enjoyable. Afterwards, participants were asked to rate the experiment. Those who were given $1 rated the experiment as more interesting and fun than those who received $20.
The results showed that those who received a smaller incentive to lie experienced cognitive dissonance — $1 wasn’t enough incentive for that one hour of painstakingly boring activity, so the participants had to justify that they had fun anyway.
Famous Case Studies in Psychology
9. little albert.
In 1920, behaviourist theorists John Watson and Rosalie Rayner experimented on a 9-month-old baby to test the effects of classical conditioning in instilling fear in humans.
This was such a controversial study that it gained popularity in psychology textbooks and syllabi because it is a classic example of unethical research studies done in the name of science.
In one of the experiments, Little Albert was presented with a harmless stimulus or object, a white rat, which he wasn’t scared of at first. But every time Little Albert would see the white rat, the researchers would play a scary sound of hammer and steel. After about 6 pairings, Little Albert learned to fear the rat even without the scary sound.
Little Albert developed signs of fear to different objects presented to him through classical conditioning . He even generalized his fear to other stimuli not present in the course of the experiment.
10. Phineas Gage
Phineas Gage is such a celebrity in Psych 101 classes, even though the way he rose to popularity began with a tragic accident. He was a resident of Central Vermont and worked in the construction of a new railway line in the mid-1800s. One day, an explosive went off prematurely, sending a tamping iron straight into his face and through his brain.
Gage survived the accident, fortunately, something that is considered a feat even up to this day. He managed to find a job as a stagecoach after the accident. However, his family and friends reported that his personality changed so much that “he was no longer Gage” (Harlow, 1868).
New evidence on the case of Phineas Gage has since come to light, thanks to modern scientific studies and medical tests. However, there are still plenty of mysteries revolving around his brain damage and subsequent recovery.
11. Anna O.
Anna O., a social worker and feminist of German Jewish descent, was one of the first patients to receive psychoanalytic treatment.
Her real name was Bertha Pappenheim and she inspired much of Sigmund Freud’s works and books on psychoanalytic theory, although they hadn’t met in person. Their connection was through Joseph Breuer, Freud’s mentor when he was still starting his clinical practice.
Anna O. suffered from paralysis, personality changes, hallucinations, and rambling speech, but her doctors could not find the cause. Joseph Breuer was then called to her house for intervention and he performed psychoanalysis, also called the “talking cure”, on her.
Breuer would tell Anna O. to say anything that came to her mind, such as her thoughts, feelings, and childhood experiences. It was noted that her symptoms subsided by talking things out.
However, Breuer later referred Anna O. to the Bellevue Sanatorium, where she recovered and set out to be a renowned writer and advocate of women and children.
12. Patient HM
H.M., or Henry Gustav Molaison, was a severe amnesiac who had been the subject of countless psychological and neurological studies.
Henry was 27 when he underwent brain surgery to cure the epilepsy that he had been experiencing since childhood. In an unfortunate turn of events, he lost his memory because of the surgery and his brain also became unable to store long-term memories.
He was then regarded as someone living solely in the present, forgetting an experience as soon as it happened and only remembering bits and pieces of his past. Over the years, his amnesia and the structure of his brain had helped neuropsychologists learn more about cognitive functions .
Suzanne Corkin, a researcher, writer, and good friend of H.M., recently published a book about his life. Entitled Permanent Present Tense , this book is both a memoir and a case study following the struggles and joys of Henry Gustav Molaison.
13. Chris Sizemore
Chris Sizemore gained celebrity status in the psychology community when she was diagnosed with multiple personality disorder, now known as dissociative identity disorder.
Sizemore has several alter egos, which included Eve Black, Eve White, and Jane. Various papers about her stated that these alter egos were formed as a coping mechanism against the traumatic experiences she underwent in her childhood.
Sizemore said that although she has succeeded in unifying her alter egos into one dominant personality, there were periods in the past experienced by only one of her alter egos. For example, her husband married her Eve White alter ego and not her.
Her story inspired her psychiatrists to write a book about her, entitled The Three Faces of Eve , which was then turned into a 1957 movie of the same title.
14. David Reimer
When David was just 8 months old, he lost his penis because of a botched circumcision operation.
Psychologist John Money then advised Reimer’s parents to raise him as a girl instead, naming him Brenda. His gender reassignment was supported by subsequent surgery and hormonal therapy.
Money described Reimer’s gender reassignment as a success, but problems started to arise as Reimer was growing up. His boyishness was not completely subdued by the hormonal therapy. When he was 14 years old, he learned about the secrets of his past and he underwent gender reassignment to become male again.
Reimer became an advocate for children undergoing the same difficult situation he had been. His life story ended when he was 38 as he took his own life.
15. Kim Peek
Kim Peek was the inspiration behind Rain Man , an Oscar-winning movie about an autistic savant character played by Dustin Hoffman.
The movie was released in 1988, a time when autism wasn’t widely known and acknowledged yet. So it was an eye-opener for many people who watched the film.
In reality, Kim Peek was a non-autistic savant. He was exceptionally intelligent despite the brain abnormalities he was born with. He was like a walking encyclopedia, knowledgeable about travel routes, US zip codes, historical facts, and classical music. He also read and memorized approximately 12,000 books in his lifetime.
This list of experiments and case studies in psychology is just the tip of the iceberg! There are still countless interesting psychology studies that you can explore if you want to learn more about human behavior and dynamics.
You can also conduct your own mini-experiment or participate in a study conducted in your school or neighborhood. Just remember that there are ethical standards to follow so as not to repeat the lasting physical and emotional harm done to Little Albert or the Stanford Prison Experiment participants.
Asch, S. E. (1956). Studies of independence and conformity: I. A minority of one against a unanimous majority. Psychological Monographs: General and Applied, 70 (9), 1–70. https://doi.org/10.1037/h0093718
Bandura, A., Ross, D., & Ross, S. A. (1961). Transmission of aggression through imitation of aggressive models. The Journal of Abnormal and Social Psychology, 63 (3), 575–582. https://doi.org/10.1037/h0045925
Elliott, J., Yale University., WGBH (Television station : Boston, Mass.), & PBS DVD (Firm). (2003). A class divided. New Haven, Conn.: Yale University Films.
Festinger, L., & Carlsmith, J. M. (1959). Cognitive consequences of forced compliance. The Journal of Abnormal and Social Psychology, 58 (2), 203–210. https://doi.org/10.1037/h0041593
Haney, C., Banks, W. C., & Zimbardo, P. G. (1973). A study of prisoners and guards in a simulated prison. Naval Research Review , 30 , 4-17.
Latane, B., & Darley, J. M. (1968). Group inhibition of bystander intervention in emergencies. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 10 (3), 215–221. https://doi.org/10.1037/h0026570
Mischel, W. (2014). The Marshmallow Test: Mastering self-control. Little, Brown and Co.
Thorndike, E. (1920) A Constant Error in Psychological Ratings. Journal of Applied Psychology , 4 , 25-29. http://dx.doi.org/10.1037/h0071663
Watson, J. B., & Rayner, R. (1920). Conditioned emotional reactions. Journal of experimental psychology , 3 (1), 1.

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 15 Animism Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 10 Magical Thinking Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ Social-Emotional Learning (Definition, Examples, Pros & Cons)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ What is Educational Psychology?
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Research Methods In Psychology
Saul Mcleod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul Mcleod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
Research methods in psychology are systematic procedures used to observe, describe, predict, and explain behavior and mental processes. They include experiments, surveys, case studies, and naturalistic observations, ensuring data collection is objective and reliable to understand and explain psychological phenomena.

Hypotheses are statements about the prediction of the results, that can be verified or disproved by some investigation.
There are four types of hypotheses :
- Null Hypotheses (H0 ) – these predict that no difference will be found in the results between the conditions. Typically these are written ‘There will be no difference…’
- Alternative Hypotheses (Ha or H1) – these predict that there will be a significant difference in the results between the two conditions. This is also known as the experimental hypothesis.
- One-tailed (directional) hypotheses – these state the specific direction the researcher expects the results to move in, e.g. higher, lower, more, less. In a correlation study, the predicted direction of the correlation can be either positive or negative.
- Two-tailed (non-directional) hypotheses – these state that a difference will be found between the conditions of the independent variable but does not state the direction of a difference or relationship. Typically these are always written ‘There will be a difference ….’
All research has an alternative hypothesis (either a one-tailed or two-tailed) and a corresponding null hypothesis.
Once the research is conducted and results are found, psychologists must accept one hypothesis and reject the other.
So, if a difference is found, the Psychologist would accept the alternative hypothesis and reject the null. The opposite applies if no difference is found.
Sampling techniques
Sampling is the process of selecting a representative group from the population under study.
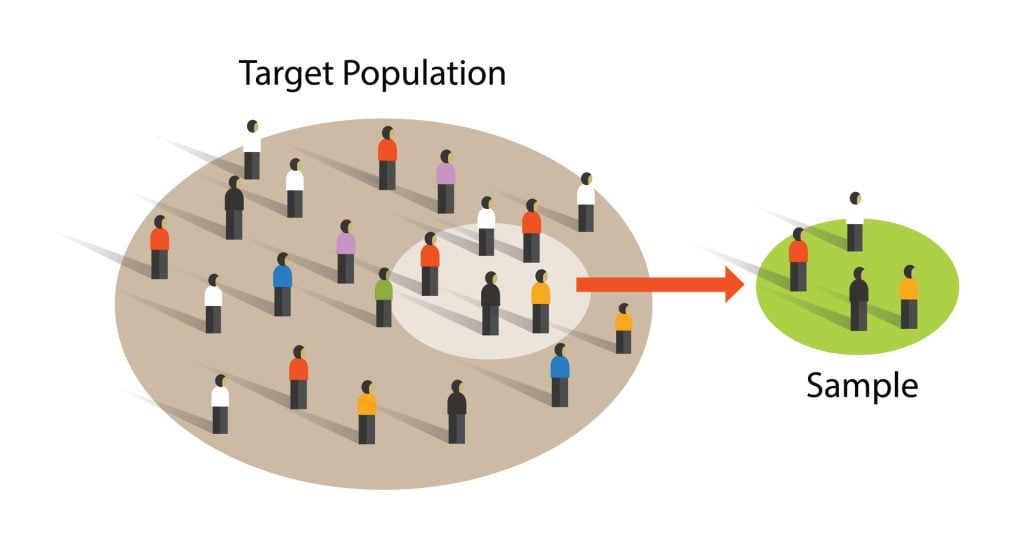
A sample is the participants you select from a target population (the group you are interested in) to make generalizations about.
Representative means the extent to which a sample mirrors a researcher’s target population and reflects its characteristics.
Generalisability means the extent to which their findings can be applied to the larger population of which their sample was a part.
- Volunteer sample : where participants pick themselves through newspaper adverts, noticeboards or online.
- Opportunity sampling : also known as convenience sampling , uses people who are available at the time the study is carried out and willing to take part. It is based on convenience.
- Random sampling : when every person in the target population has an equal chance of being selected. An example of random sampling would be picking names out of a hat.
- Systematic sampling : when a system is used to select participants. Picking every Nth person from all possible participants. N = the number of people in the research population / the number of people needed for the sample.
- Stratified sampling : when you identify the subgroups and select participants in proportion to their occurrences.
- Snowball sampling : when researchers find a few participants, and then ask them to find participants themselves and so on.
- Quota sampling : when researchers will be told to ensure the sample fits certain quotas, for example they might be told to find 90 participants, with 30 of them being unemployed.
Experiments always have an independent and dependent variable .
- The independent variable is the one the experimenter manipulates (the thing that changes between the conditions the participants are placed into). It is assumed to have a direct effect on the dependent variable.
- The dependent variable is the thing being measured, or the results of the experiment.
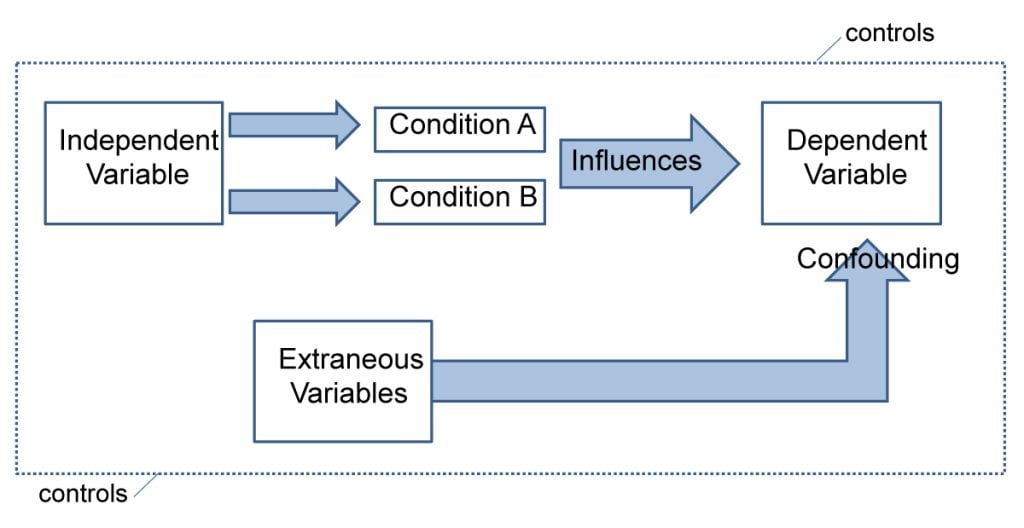
Operationalization of variables means making them measurable/quantifiable. We must use operationalization to ensure that variables are in a form that can be easily tested.
For instance, we can’t really measure ‘happiness’, but we can measure how many times a person smiles within a two-hour period.
By operationalizing variables, we make it easy for someone else to replicate our research. Remember, this is important because we can check if our findings are reliable.
Extraneous variables are all variables which are not independent variable but could affect the results of the experiment.
It can be a natural characteristic of the participant, such as intelligence levels, gender, or age for example, or it could be a situational feature of the environment such as lighting or noise.
Demand characteristics are a type of extraneous variable that occurs if the participants work out the aims of the research study, they may begin to behave in a certain way.
For example, in Milgram’s research , critics argued that participants worked out that the shocks were not real and they administered them as they thought this was what was required of them.
Extraneous variables must be controlled so that they do not affect (confound) the results.
Randomly allocating participants to their conditions or using a matched pairs experimental design can help to reduce participant variables.
Situational variables are controlled by using standardized procedures, ensuring every participant in a given condition is treated in the same way
Experimental Design
Experimental design refers to how participants are allocated to each condition of the independent variable, such as a control or experimental group.
- Independent design ( between-groups design ): each participant is selected for only one group. With the independent design, the most common way of deciding which participants go into which group is by means of randomization.
- Matched participants design : each participant is selected for only one group, but the participants in the two groups are matched for some relevant factor or factors (e.g. ability; sex; age).
- Repeated measures design ( within groups) : each participant appears in both groups, so that there are exactly the same participants in each group.
- The main problem with the repeated measures design is that there may well be order effects. Their experiences during the experiment may change the participants in various ways.
- They may perform better when they appear in the second group because they have gained useful information about the experiment or about the task. On the other hand, they may perform less well on the second occasion because of tiredness or boredom.
- Counterbalancing is the best way of preventing order effects from disrupting the findings of an experiment, and involves ensuring that each condition is equally likely to be used first and second by the participants.
If we wish to compare two groups with respect to a given independent variable, it is essential to make sure that the two groups do not differ in any other important way.

Experimental Methods
All experimental methods involve an iv (independent variable) and dv (dependent variable)..
- Field experiments are conducted in the everyday (natural) environment of the participants. The experimenter still manipulates the IV, but in a real-life setting. It may be possible to control extraneous variables, though such control is more difficult than in a lab experiment.
- Natural experiments are when a naturally occurring IV is investigated that isn’t deliberately manipulated, it exists anyway. Participants are not randomly allocated, and the natural event may only occur rarely.
Case studies are in-depth investigations of a person, group, event, or community. It uses information from a range of sources, such as from the person concerned and also from their family and friends.
Many techniques may be used such as interviews, psychological tests, observations and experiments. Case studies are generally longitudinal: in other words, they follow the individual or group over an extended period of time.
Case studies are widely used in psychology and among the best-known ones carried out were by Sigmund Freud . He conducted very detailed investigations into the private lives of his patients in an attempt to both understand and help them overcome their illnesses.
Case studies provide rich qualitative data and have high levels of ecological validity. However, it is difficult to generalize from individual cases as each one has unique characteristics.
Correlational Studies
Correlation means association; it is a measure of the extent to which two variables are related. One of the variables can be regarded as the predictor variable with the other one as the outcome variable.
Correlational studies typically involve obtaining two different measures from a group of participants, and then assessing the degree of association between the measures.
The predictor variable can be seen as occurring before the outcome variable in some sense. It is called the predictor variable, because it forms the basis for predicting the value of the outcome variable.
Relationships between variables can be displayed on a graph or as a numerical score called a correlation coefficient.
- If an increase in one variable tends to be associated with an increase in the other, then this is known as a positive correlation .
- If an increase in one variable tends to be associated with a decrease in the other, then this is known as a negative correlation .
- A zero correlation occurs when there is no relationship between variables.
After looking at the scattergraph, if we want to be sure that a significant relationship does exist between the two variables, a statistical test of correlation can be conducted, such as Spearman’s rho.
The test will give us a score, called a correlation coefficient . This is a value between 0 and 1, and the closer to 1 the score is, the stronger the relationship between the variables. This value can be both positive e.g. 0.63, or negative -0.63.
A correlation between variables, however, does not automatically mean that the change in one variable is the cause of the change in the values of the other variable. A correlation only shows if there is a relationship between variables.
Correlation does not always prove causation, as a third variable may be involved.
Interview Methods
Interviews are commonly divided into two types: structured and unstructured.
A fixed, predetermined set of questions is put to every participant in the same order and in the same way.
Responses are recorded on a questionnaire, and the researcher presets the order and wording of questions, and sometimes the range of alternative answers.
The interviewer stays within their role and maintains social distance from the interviewee.
There are no set questions, and the participant can raise whatever topics he/she feels are relevant and ask them in their own way. Questions are posed about participants’ answers to the subject
Unstructured interviews are most useful in qualitative research to analyze attitudes and values.
Though they rarely provide a valid basis for generalization, their main advantage is that they enable the researcher to probe social actors’ subjective point of view.
Questionnaire Method
Questionnaires can be thought of as a kind of written interview. They can be carried out face to face, by telephone, or post.
The choice of questions is important because of the need to avoid bias or ambiguity in the questions, ‘leading’ the respondent or causing offense.
- Open questions are designed to encourage a full, meaningful answer using the subject’s own knowledge and feelings. They provide insights into feelings, opinions, and understanding. Example: “How do you feel about that situation?”
- Closed questions can be answered with a simple “yes” or “no” or specific information, limiting the depth of response. They are useful for gathering specific facts or confirming details. Example: “Do you feel anxious in crowds?”
Its other practical advantages are that it is cheaper than face-to-face interviews and can be used to contact many respondents scattered over a wide area relatively quickly.
Observations
There are different types of observation methods :
- Covert observation is where the researcher doesn’t tell the participants they are being observed until after the study is complete. There could be ethical problems or deception and consent with this particular observation method.
- Overt observation is where a researcher tells the participants they are being observed and what they are being observed for.
- Controlled : behavior is observed under controlled laboratory conditions (e.g., Bandura’s Bobo doll study).
- Natural : Here, spontaneous behavior is recorded in a natural setting.
- Participant : Here, the observer has direct contact with the group of people they are observing. The researcher becomes a member of the group they are researching.
- Non-participant (aka “fly on the wall): The researcher does not have direct contact with the people being observed. The observation of participants’ behavior is from a distance
Pilot Study
A pilot study is a small scale preliminary study conducted in order to evaluate the feasibility of the key s teps in a future, full-scale project.
A pilot study is an initial run-through of the procedures to be used in an investigation; it involves selecting a few people and trying out the study on them. It is possible to save time, and in some cases, money, by identifying any flaws in the procedures designed by the researcher.
A pilot study can help the researcher spot any ambiguities (i.e. unusual things) or confusion in the information given to participants or problems with the task devised.
Sometimes the task is too hard, and the researcher may get a floor effect, because none of the participants can score at all or can complete the task – all performances are low.
The opposite effect is a ceiling effect, when the task is so easy that all achieve virtually full marks or top performances and are “hitting the ceiling”.
Research Design
In cross-sectional research , a researcher compares multiple segments of the population at the same time
Sometimes, we want to see how people change over time, as in studies of human development and lifespan. Longitudinal research is a research design in which data-gathering is administered repeatedly over an extended period of time.
In cohort studies , the participants must share a common factor or characteristic such as age, demographic, or occupation. A cohort study is a type of longitudinal study in which researchers monitor and observe a chosen population over an extended period.
Triangulation means using more than one research method to improve the study’s validity.
Reliability
Reliability is a measure of consistency, if a particular measurement is repeated and the same result is obtained then it is described as being reliable.
- Test-retest reliability : assessing the same person on two different occasions which shows the extent to which the test produces the same answers.
- Inter-observer reliability : the extent to which there is an agreement between two or more observers.
Meta-Analysis
A meta-analysis is a systematic review that involves identifying an aim and then searching for research studies that have addressed similar aims/hypotheses.
This is done by looking through various databases, and then decisions are made about what studies are to be included/excluded.
Strengths: Increases the conclusions’ validity as they’re based on a wider range.
Weaknesses: Research designs in studies can vary, so they are not truly comparable.
Peer Review
A researcher submits an article to a journal. The choice of the journal may be determined by the journal’s audience or prestige.
The journal selects two or more appropriate experts (psychologists working in a similar field) to peer review the article without payment. The peer reviewers assess: the methods and designs used, originality of the findings, the validity of the original research findings and its content, structure and language.
Feedback from the reviewer determines whether the article is accepted. The article may be: Accepted as it is, accepted with revisions, sent back to the author to revise and re-submit or rejected without the possibility of submission.
The editor makes the final decision whether to accept or reject the research report based on the reviewers comments/ recommendations.
Peer review is important because it prevent faulty data from entering the public domain, it provides a way of checking the validity of findings and the quality of the methodology and is used to assess the research rating of university departments.
Peer reviews may be an ideal, whereas in practice there are lots of problems. For example, it slows publication down and may prevent unusual, new work being published. Some reviewers might use it as an opportunity to prevent competing researchers from publishing work.
Some people doubt whether peer review can really prevent the publication of fraudulent research.
The advent of the internet means that a lot of research and academic comment is being published without official peer reviews than before, though systems are evolving on the internet where everyone really has a chance to offer their opinions and police the quality of research.
Types of Data
- Quantitative data is numerical data e.g. reaction time or number of mistakes. It represents how much or how long, how many there are of something. A tally of behavioral categories and closed questions in a questionnaire collect quantitative data.
- Qualitative data is virtually any type of information that can be observed and recorded that is not numerical in nature and can be in the form of written or verbal communication. Open questions in questionnaires and accounts from observational studies collect qualitative data.
- Primary data is first-hand data collected for the purpose of the investigation.
- Secondary data is information that has been collected by someone other than the person who is conducting the research e.g. taken from journals, books or articles.
Validity means how well a piece of research actually measures what it sets out to, or how well it reflects the reality it claims to represent.
Validity is whether the observed effect is genuine and represents what is actually out there in the world.
- Concurrent validity is the extent to which a psychological measure relates to an existing similar measure and obtains close results. For example, a new intelligence test compared to an established test.
- Face validity : does the test measure what it’s supposed to measure ‘on the face of it’. This is done by ‘eyeballing’ the measuring or by passing it to an expert to check.
- Ecological validit y is the extent to which findings from a research study can be generalized to other settings / real life.
- Temporal validity is the extent to which findings from a research study can be generalized to other historical times.
Features of Science
- Paradigm – A set of shared assumptions and agreed methods within a scientific discipline.
- Paradigm shift – The result of the scientific revolution: a significant change in the dominant unifying theory within a scientific discipline.
- Objectivity – When all sources of personal bias are minimised so not to distort or influence the research process.
- Empirical method – Scientific approaches that are based on the gathering of evidence through direct observation and experience.
- Replicability – The extent to which scientific procedures and findings can be repeated by other researchers.
- Falsifiability – The principle that a theory cannot be considered scientific unless it admits the possibility of being proved untrue.
Statistical Testing
A significant result is one where there is a low probability that chance factors were responsible for any observed difference, correlation, or association in the variables tested.
If our test is significant, we can reject our null hypothesis and accept our alternative hypothesis.
If our test is not significant, we can accept our null hypothesis and reject our alternative hypothesis. A null hypothesis is a statement of no effect.
In Psychology, we use p < 0.05 (as it strikes a balance between making a type I and II error) but p < 0.01 is used in tests that could cause harm like introducing a new drug.
A type I error is when the null hypothesis is rejected when it should have been accepted (happens when a lenient significance level is used, an error of optimism).
A type II error is when the null hypothesis is accepted when it should have been rejected (happens when a stringent significance level is used, an error of pessimism).
Ethical Issues
- Informed consent is when participants are able to make an informed judgment about whether to take part. It causes them to guess the aims of the study and change their behavior.
- To deal with it, we can gain presumptive consent or ask them to formally indicate their agreement to participate but it may invalidate the purpose of the study and it is not guaranteed that the participants would understand.
- Deception should only be used when it is approved by an ethics committee, as it involves deliberately misleading or withholding information. Participants should be fully debriefed after the study but debriefing can’t turn the clock back.
- All participants should be informed at the beginning that they have the right to withdraw if they ever feel distressed or uncomfortable.
- It causes bias as the ones that stayed are obedient and some may not withdraw as they may have been given incentives or feel like they’re spoiling the study. Researchers can offer the right to withdraw data after participation.
- Participants should all have protection from harm . The researcher should avoid risks greater than those experienced in everyday life and they should stop the study if any harm is suspected. However, the harm may not be apparent at the time of the study.
- Confidentiality concerns the communication of personal information. The researchers should not record any names but use numbers or false names though it may not be possible as it is sometimes possible to work out who the researchers were.
Related Articles

Research Methodology
Qualitative Data Coding

What Is a Focus Group?

Cross-Cultural Research Methodology In Psychology

A-Level Psychology
A-level Psychology AQA Revision Notes

What Is Internal Validity In Research?

Research Methodology , Statistics
What Is Face Validity In Research? Importance & How To Measure
- Privacy Policy

Home » Case Study – Methods, Examples and Guide
Case Study – Methods, Examples and Guide
Table of Contents

A case study is a research method that involves an in-depth examination and analysis of a particular phenomenon or case, such as an individual, organization, community, event, or situation.
It is a qualitative research approach that aims to provide a detailed and comprehensive understanding of the case being studied. Case studies typically involve multiple sources of data, including interviews, observations, documents, and artifacts, which are analyzed using various techniques, such as content analysis, thematic analysis, and grounded theory. The findings of a case study are often used to develop theories, inform policy or practice, or generate new research questions.
Types of Case Study
Types and Methods of Case Study are as follows:
Single-Case Study
A single-case study is an in-depth analysis of a single case. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to understand a specific phenomenon in detail.
For Example , A researcher might conduct a single-case study on a particular individual to understand their experiences with a particular health condition or a specific organization to explore their management practices. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as content analysis or thematic analysis. The findings of a single-case study are often used to generate new research questions, develop theories, or inform policy or practice.
Multiple-Case Study
A multiple-case study involves the analysis of several cases that are similar in nature. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to identify similarities and differences between the cases.
For Example, a researcher might conduct a multiple-case study on several companies to explore the factors that contribute to their success or failure. The researcher collects data from each case, compares and contrasts the findings, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as comparative analysis or pattern-matching. The findings of a multiple-case study can be used to develop theories, inform policy or practice, or generate new research questions.
Exploratory Case Study
An exploratory case study is used to explore a new or understudied phenomenon. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to generate hypotheses or theories about the phenomenon.
For Example, a researcher might conduct an exploratory case study on a new technology to understand its potential impact on society. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as grounded theory or content analysis. The findings of an exploratory case study can be used to generate new research questions, develop theories, or inform policy or practice.
Descriptive Case Study
A descriptive case study is used to describe a particular phenomenon in detail. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to provide a comprehensive account of the phenomenon.
For Example, a researcher might conduct a descriptive case study on a particular community to understand its social and economic characteristics. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as content analysis or thematic analysis. The findings of a descriptive case study can be used to inform policy or practice or generate new research questions.
Instrumental Case Study
An instrumental case study is used to understand a particular phenomenon that is instrumental in achieving a particular goal. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to understand the role of the phenomenon in achieving the goal.
For Example, a researcher might conduct an instrumental case study on a particular policy to understand its impact on achieving a particular goal, such as reducing poverty. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as content analysis or thematic analysis. The findings of an instrumental case study can be used to inform policy or practice or generate new research questions.
Case Study Data Collection Methods
Here are some common data collection methods for case studies:
Interviews involve asking questions to individuals who have knowledge or experience relevant to the case study. Interviews can be structured (where the same questions are asked to all participants) or unstructured (where the interviewer follows up on the responses with further questions). Interviews can be conducted in person, over the phone, or through video conferencing.
Observations
Observations involve watching and recording the behavior and activities of individuals or groups relevant to the case study. Observations can be participant (where the researcher actively participates in the activities) or non-participant (where the researcher observes from a distance). Observations can be recorded using notes, audio or video recordings, or photographs.
Documents can be used as a source of information for case studies. Documents can include reports, memos, emails, letters, and other written materials related to the case study. Documents can be collected from the case study participants or from public sources.
Surveys involve asking a set of questions to a sample of individuals relevant to the case study. Surveys can be administered in person, over the phone, through mail or email, or online. Surveys can be used to gather information on attitudes, opinions, or behaviors related to the case study.
Artifacts are physical objects relevant to the case study. Artifacts can include tools, equipment, products, or other objects that provide insights into the case study phenomenon.
How to conduct Case Study Research
Conducting a case study research involves several steps that need to be followed to ensure the quality and rigor of the study. Here are the steps to conduct case study research:
- Define the research questions: The first step in conducting a case study research is to define the research questions. The research questions should be specific, measurable, and relevant to the case study phenomenon under investigation.
- Select the case: The next step is to select the case or cases to be studied. The case should be relevant to the research questions and should provide rich and diverse data that can be used to answer the research questions.
- Collect data: Data can be collected using various methods, such as interviews, observations, documents, surveys, and artifacts. The data collection method should be selected based on the research questions and the nature of the case study phenomenon.
- Analyze the data: The data collected from the case study should be analyzed using various techniques, such as content analysis, thematic analysis, or grounded theory. The analysis should be guided by the research questions and should aim to provide insights and conclusions relevant to the research questions.
- Draw conclusions: The conclusions drawn from the case study should be based on the data analysis and should be relevant to the research questions. The conclusions should be supported by evidence and should be clearly stated.
- Validate the findings: The findings of the case study should be validated by reviewing the data and the analysis with participants or other experts in the field. This helps to ensure the validity and reliability of the findings.
- Write the report: The final step is to write the report of the case study research. The report should provide a clear description of the case study phenomenon, the research questions, the data collection methods, the data analysis, the findings, and the conclusions. The report should be written in a clear and concise manner and should follow the guidelines for academic writing.
Examples of Case Study
Here are some examples of case study research:
- The Hawthorne Studies : Conducted between 1924 and 1932, the Hawthorne Studies were a series of case studies conducted by Elton Mayo and his colleagues to examine the impact of work environment on employee productivity. The studies were conducted at the Hawthorne Works plant of the Western Electric Company in Chicago and included interviews, observations, and experiments.
- The Stanford Prison Experiment: Conducted in 1971, the Stanford Prison Experiment was a case study conducted by Philip Zimbardo to examine the psychological effects of power and authority. The study involved simulating a prison environment and assigning participants to the role of guards or prisoners. The study was controversial due to the ethical issues it raised.
- The Challenger Disaster: The Challenger Disaster was a case study conducted to examine the causes of the Space Shuttle Challenger explosion in 1986. The study included interviews, observations, and analysis of data to identify the technical, organizational, and cultural factors that contributed to the disaster.
- The Enron Scandal: The Enron Scandal was a case study conducted to examine the causes of the Enron Corporation’s bankruptcy in 2001. The study included interviews, analysis of financial data, and review of documents to identify the accounting practices, corporate culture, and ethical issues that led to the company’s downfall.
- The Fukushima Nuclear Disaster : The Fukushima Nuclear Disaster was a case study conducted to examine the causes of the nuclear accident that occurred at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant in Japan in 2011. The study included interviews, analysis of data, and review of documents to identify the technical, organizational, and cultural factors that contributed to the disaster.
Application of Case Study
Case studies have a wide range of applications across various fields and industries. Here are some examples:
Business and Management
Case studies are widely used in business and management to examine real-life situations and develop problem-solving skills. Case studies can help students and professionals to develop a deep understanding of business concepts, theories, and best practices.
Case studies are used in healthcare to examine patient care, treatment options, and outcomes. Case studies can help healthcare professionals to develop critical thinking skills, diagnose complex medical conditions, and develop effective treatment plans.
Case studies are used in education to examine teaching and learning practices. Case studies can help educators to develop effective teaching strategies, evaluate student progress, and identify areas for improvement.
Social Sciences
Case studies are widely used in social sciences to examine human behavior, social phenomena, and cultural practices. Case studies can help researchers to develop theories, test hypotheses, and gain insights into complex social issues.
Law and Ethics
Case studies are used in law and ethics to examine legal and ethical dilemmas. Case studies can help lawyers, policymakers, and ethical professionals to develop critical thinking skills, analyze complex cases, and make informed decisions.
Purpose of Case Study
The purpose of a case study is to provide a detailed analysis of a specific phenomenon, issue, or problem in its real-life context. A case study is a qualitative research method that involves the in-depth exploration and analysis of a particular case, which can be an individual, group, organization, event, or community.
The primary purpose of a case study is to generate a comprehensive and nuanced understanding of the case, including its history, context, and dynamics. Case studies can help researchers to identify and examine the underlying factors, processes, and mechanisms that contribute to the case and its outcomes. This can help to develop a more accurate and detailed understanding of the case, which can inform future research, practice, or policy.
Case studies can also serve other purposes, including:
- Illustrating a theory or concept: Case studies can be used to illustrate and explain theoretical concepts and frameworks, providing concrete examples of how they can be applied in real-life situations.
- Developing hypotheses: Case studies can help to generate hypotheses about the causal relationships between different factors and outcomes, which can be tested through further research.
- Providing insight into complex issues: Case studies can provide insights into complex and multifaceted issues, which may be difficult to understand through other research methods.
- Informing practice or policy: Case studies can be used to inform practice or policy by identifying best practices, lessons learned, or areas for improvement.
Advantages of Case Study Research
There are several advantages of case study research, including:
- In-depth exploration: Case study research allows for a detailed exploration and analysis of a specific phenomenon, issue, or problem in its real-life context. This can provide a comprehensive understanding of the case and its dynamics, which may not be possible through other research methods.
- Rich data: Case study research can generate rich and detailed data, including qualitative data such as interviews, observations, and documents. This can provide a nuanced understanding of the case and its complexity.
- Holistic perspective: Case study research allows for a holistic perspective of the case, taking into account the various factors, processes, and mechanisms that contribute to the case and its outcomes. This can help to develop a more accurate and comprehensive understanding of the case.
- Theory development: Case study research can help to develop and refine theories and concepts by providing empirical evidence and concrete examples of how they can be applied in real-life situations.
- Practical application: Case study research can inform practice or policy by identifying best practices, lessons learned, or areas for improvement.
- Contextualization: Case study research takes into account the specific context in which the case is situated, which can help to understand how the case is influenced by the social, cultural, and historical factors of its environment.
Limitations of Case Study Research
There are several limitations of case study research, including:
- Limited generalizability : Case studies are typically focused on a single case or a small number of cases, which limits the generalizability of the findings. The unique characteristics of the case may not be applicable to other contexts or populations, which may limit the external validity of the research.
- Biased sampling: Case studies may rely on purposive or convenience sampling, which can introduce bias into the sample selection process. This may limit the representativeness of the sample and the generalizability of the findings.
- Subjectivity: Case studies rely on the interpretation of the researcher, which can introduce subjectivity into the analysis. The researcher’s own biases, assumptions, and perspectives may influence the findings, which may limit the objectivity of the research.
- Limited control: Case studies are typically conducted in naturalistic settings, which limits the control that the researcher has over the environment and the variables being studied. This may limit the ability to establish causal relationships between variables.
- Time-consuming: Case studies can be time-consuming to conduct, as they typically involve a detailed exploration and analysis of a specific case. This may limit the feasibility of conducting multiple case studies or conducting case studies in a timely manner.
- Resource-intensive: Case studies may require significant resources, including time, funding, and expertise. This may limit the ability of researchers to conduct case studies in resource-constrained settings.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Questionnaire – Definition, Types, and Examples

Observational Research – Methods and Guide

Quantitative Research – Methods, Types and...

Qualitative Research Methods

Explanatory Research – Types, Methods, Guide

Survey Research – Types, Methods, Examples
2.2 Approaches to Research
Learning objectives.
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Describe the different research methods used by psychologists
- Discuss the strengths and weaknesses of case studies, naturalistic observation, surveys, and archival research
- Compare longitudinal and cross-sectional approaches to research
- Compare and contrast correlation and causation
There are many research methods available to psychologists in their efforts to understand, describe, and explain behavior and the cognitive and biological processes that underlie it. Some methods rely on observational techniques. Other approaches involve interactions between the researcher and the individuals who are being studied—ranging from a series of simple questions to extensive, in-depth interviews—to well-controlled experiments.
Each of these research methods has unique strengths and weaknesses, and each method may only be appropriate for certain types of research questions. For example, studies that rely primarily on observation produce incredible amounts of information, but the ability to apply this information to the larger population is somewhat limited because of small sample sizes. Survey research, on the other hand, allows researchers to easily collect data from relatively large samples. While this allows for results to be generalized to the larger population more easily, the information that can be collected on any given survey is somewhat limited and subject to problems associated with any type of self-reported data. Some researchers conduct archival research by using existing records. While this can be a fairly inexpensive way to collect data that can provide insight into a number of research questions, researchers using this approach have no control on how or what kind of data was collected. All of the methods described thus far are correlational in nature. This means that researchers can speak to important relationships that might exist between two or more variables of interest. However, correlational data cannot be used to make claims about cause-and-effect relationships.
Correlational research can find a relationship between two variables, but the only way a researcher can claim that the relationship between the variables is cause and effect is to perform an experiment. In experimental research, which will be discussed later in this chapter, there is a tremendous amount of control over variables of interest. While this is a powerful approach, experiments are often conducted in artificial settings. This calls into question the validity of experimental findings with regard to how they would apply in real-world settings. In addition, many of the questions that psychologists would like to answer cannot be pursued through experimental research because of ethical concerns.
Clinical or Case Studies
In 2011, the New York Times published a feature story on Krista and Tatiana Hogan, Canadian twin girls. These particular twins are unique because Krista and Tatiana are conjoined twins, connected at the head. There is evidence that the two girls are connected in a part of the brain called the thalamus, which is a major sensory relay center. Most incoming sensory information is sent through the thalamus before reaching higher regions of the cerebral cortex for processing.
Link to Learning
Watch this CBC video about Krista's and Tatiana's lives to learn more.
The implications of this potential connection mean that it might be possible for one twin to experience the sensations of the other twin. For instance, if Krista is watching a particularly funny television program, Tatiana might smile or laugh even if she is not watching the program. This particular possibility has piqued the interest of many neuroscientists who seek to understand how the brain uses sensory information.
These twins represent an enormous resource in the study of the brain, and since their condition is very rare, it is likely that as long as their family agrees, scientists will follow these girls very closely throughout their lives to gain as much information as possible (Dominus, 2011).
Over time, it has become clear that while Krista and Tatiana share some sensory experiences and motor control, they remain two distinct individuals, which provides invaluable insight for researchers interested in the mind and the brain (Egnor, 2017).
In observational research, scientists are conducting a clinical or case study when they focus on one person or just a few individuals. Indeed, some scientists spend their entire careers studying just 10–20 individuals. Why would they do this? Obviously, when they focus their attention on a very small number of people, they can gain a precious amount of insight into those cases. The richness of information that is collected in clinical or case studies is unmatched by any other single research method. This allows the researcher to have a very deep understanding of the individuals and the particular phenomenon being studied.
If clinical or case studies provide so much information, why are they not more frequent among researchers? As it turns out, the major benefit of this particular approach is also a weakness. As mentioned earlier, this approach is often used when studying individuals who are interesting to researchers because they have a rare characteristic. Therefore, the individuals who serve as the focus of case studies are not like most other people. If scientists ultimately want to explain all behavior, focusing attention on such a special group of people can make it difficult to generalize any observations to the larger population as a whole. Generalizing refers to the ability to apply the findings of a particular research project to larger segments of society. Again, case studies provide enormous amounts of information, but since the cases are so specific, the potential to apply what’s learned to the average person may be very limited.
Naturalistic Observation
If you want to understand how behavior occurs, one of the best ways to gain information is to simply observe the behavior in its natural context. However, people might change their behavior in unexpected ways if they know they are being observed. How do researchers obtain accurate information when people tend to hide their natural behavior? As an example, imagine that your professor asks everyone in your class to raise their hand if they always wash their hands after using the restroom. Chances are that almost everyone in the classroom will raise their hand, but do you think hand washing after every trip to the restroom is really that universal?
This is very similar to the phenomenon mentioned earlier in this chapter: many individuals do not feel comfortable answering a question honestly. But if we are committed to finding out the facts about hand washing, we have other options available to us.
Suppose we send a classmate into the restroom to actually watch whether everyone washes their hands after using the restroom. Will our observer blend into the restroom environment by wearing a white lab coat, sitting with a clipboard, and staring at the sinks? We want our researcher to be inconspicuous—perhaps standing at one of the sinks pretending to put in contact lenses while secretly recording the relevant information. This type of observational study is called naturalistic observation : observing behavior in its natural setting. To better understand peer exclusion, Suzanne Fanger collaborated with colleagues at the University of Texas to observe the behavior of preschool children on a playground. How did the observers remain inconspicuous over the duration of the study? They equipped a few of the children with wireless microphones (which the children quickly forgot about) and observed while taking notes from a distance. Also, the children in that particular preschool (a “laboratory preschool”) were accustomed to having observers on the playground (Fanger, Frankel, & Hazen, 2012).
It is critical that the observer be as unobtrusive and as inconspicuous as possible: when people know they are being watched, they are less likely to behave naturally. If you have any doubt about this, ask yourself how your driving behavior might differ in two situations: In the first situation, you are driving down a deserted highway during the middle of the day; in the second situation, you are being followed by a police car down the same deserted highway ( Figure 2.7 ).
It should be pointed out that naturalistic observation is not limited to research involving humans. Indeed, some of the best-known examples of naturalistic observation involve researchers going into the field to observe various kinds of animals in their own environments. As with human studies, the researchers maintain their distance and avoid interfering with the animal subjects so as not to influence their natural behaviors. Scientists have used this technique to study social hierarchies and interactions among animals ranging from ground squirrels to gorillas. The information provided by these studies is invaluable in understanding how those animals organize socially and communicate with one another. The anthropologist Jane Goodall , for example, spent nearly five decades observing the behavior of chimpanzees in Africa ( Figure 2.8 ). As an illustration of the types of concerns that a researcher might encounter in naturalistic observation, some scientists criticized Goodall for giving the chimps names instead of referring to them by numbers—using names was thought to undermine the emotional detachment required for the objectivity of the study (McKie, 2010).
The greatest benefit of naturalistic observation is the validity , or accuracy, of information collected unobtrusively in a natural setting. Having individuals behave as they normally would in a given situation means that we have a higher degree of ecological validity, or realism, than we might achieve with other research approaches. Therefore, our ability to generalize the findings of the research to real-world situations is enhanced. If done correctly, we need not worry about people or animals modifying their behavior simply because they are being observed. Sometimes, people may assume that reality programs give us a glimpse into authentic human behavior. However, the principle of inconspicuous observation is violated as reality stars are followed by camera crews and are interviewed on camera for personal confessionals. Given that environment, we must doubt how natural and realistic their behaviors are.
The major downside of naturalistic observation is that they are often difficult to set up and control. In our restroom study, what if you stood in the restroom all day prepared to record people’s hand washing behavior and no one came in? Or, what if you have been closely observing a troop of gorillas for weeks only to find that they migrated to a new place while you were sleeping in your tent? The benefit of realistic data comes at a cost. As a researcher you have no control of when (or if) you have behavior to observe. In addition, this type of observational research often requires significant investments of time, money, and a good dose of luck.
Sometimes studies involve structured observation. In these cases, people are observed while engaging in set, specific tasks. An excellent example of structured observation comes from Strange Situation by Mary Ainsworth (you will read more about this in the chapter on lifespan development). The Strange Situation is a procedure used to evaluate attachment styles that exist between an infant and caregiver. In this scenario, caregivers bring their infants into a room filled with toys. The Strange Situation involves a number of phases, including a stranger coming into the room, the caregiver leaving the room, and the caregiver’s return to the room. The infant’s behavior is closely monitored at each phase, but it is the behavior of the infant upon being reunited with the caregiver that is most telling in terms of characterizing the infant’s attachment style with the caregiver.
Another potential problem in observational research is observer bias . Generally, people who act as observers are closely involved in the research project and may unconsciously skew their observations to fit their research goals or expectations. To protect against this type of bias, researchers should have clear criteria established for the types of behaviors recorded and how those behaviors should be classified. In addition, researchers often compare observations of the same event by multiple observers, in order to test inter-rater reliability : a measure of reliability that assesses the consistency of observations by different observers.
Often, psychologists develop surveys as a means of gathering data. Surveys are lists of questions to be answered by research participants, and can be delivered as paper-and-pencil questionnaires, administered electronically, or conducted verbally ( Figure 2.9 ). Generally, the survey itself can be completed in a short time, and the ease of administering a survey makes it easy to collect data from a large number of people.
Surveys allow researchers to gather data from larger samples than may be afforded by other research methods . A sample is a subset of individuals selected from a population , which is the overall group of individuals that the researchers are interested in. Researchers study the sample and seek to generalize their findings to the population. Generally, researchers will begin this process by calculating various measures of central tendency from the data they have collected. These measures provide an overall summary of what a typical response looks like. There are three measures of central tendency: mode, median, and mean. The mode is the most frequently occurring response, the median lies at the middle of a given data set, and the mean is the arithmetic average of all data points. Means tend to be most useful in conducting additional analyses like those described below; however, means are very sensitive to the effects of outliers, and so one must be aware of those effects when making assessments of what measures of central tendency tell us about a data set in question.
There is both strength and weakness of the survey in comparison to case studies. By using surveys, we can collect information from a larger sample of people. A larger sample is better able to reflect the actual diversity of the population, thus allowing better generalizability. Therefore, if our sample is sufficiently large and diverse, we can assume that the data we collect from the survey can be generalized to the larger population with more certainty than the information collected through a case study. However, given the greater number of people involved, we are not able to collect the same depth of information on each person that would be collected in a case study.
Another potential weakness of surveys is something we touched on earlier in this chapter: People don't always give accurate responses. They may lie, misremember, or answer questions in a way that they think makes them look good. For example, people may report drinking less alcohol than is actually the case.
Any number of research questions can be answered through the use of surveys. One real-world example is the research conducted by Jenkins, Ruppel, Kizer, Yehl, and Griffin (2012) about the backlash against the US Arab-American community following the terrorist attacks of September 11, 2001. Jenkins and colleagues wanted to determine to what extent these negative attitudes toward Arab-Americans still existed nearly a decade after the attacks occurred. In one study, 140 research participants filled out a survey with 10 questions, including questions asking directly about the participant’s overt prejudicial attitudes toward people of various ethnicities. The survey also asked indirect questions about how likely the participant would be to interact with a person of a given ethnicity in a variety of settings (such as, “How likely do you think it is that you would introduce yourself to a person of Arab-American descent?”). The results of the research suggested that participants were unwilling to report prejudicial attitudes toward any ethnic group. However, there were significant differences between their pattern of responses to questions about social interaction with Arab-Americans compared to other ethnic groups: they indicated less willingness for social interaction with Arab-Americans compared to the other ethnic groups. This suggested that the participants harbored subtle forms of prejudice against Arab-Americans, despite their assertions that this was not the case (Jenkins et al., 2012).
Archival Research
Some researchers gain access to large amounts of data without interacting with a single research participant. Instead, they use existing records to answer various research questions. This type of research approach is known as archival research . Archival research relies on looking at past records or data sets to look for interesting patterns or relationships.
For example, a researcher might access the academic records of all individuals who enrolled in college within the past ten years and calculate how long it took them to complete their degrees, as well as course loads, grades, and extracurricular involvement. Archival research could provide important information about who is most likely to complete their education, and it could help identify important risk factors for struggling students ( Figure 2.10 ).
In comparing archival research to other research methods, there are several important distinctions. For one, the researcher employing archival research never directly interacts with research participants. Therefore, the investment of time and money to collect data is considerably less with archival research. Additionally, researchers have no control over what information was originally collected. Therefore, research questions have to be tailored so they can be answered within the structure of the existing data sets. There is also no guarantee of consistency between the records from one source to another, which might make comparing and contrasting different data sets problematic.
Longitudinal and Cross-Sectional Research
Sometimes we want to see how people change over time, as in studies of human development and lifespan. When we test the same group of individuals repeatedly over an extended period of time, we are conducting longitudinal research. Longitudinal research is a research design in which data-gathering is administered repeatedly over an extended period of time. For example, we may survey a group of individuals about their dietary habits at age 20, retest them a decade later at age 30, and then again at age 40.
Another approach is cross-sectional research. In cross-sectional research , a researcher compares multiple segments of the population at the same time. Using the dietary habits example above, the researcher might directly compare different groups of people by age. Instead of studying a group of people for 20 years to see how their dietary habits changed from decade to decade, the researcher would study a group of 20-year-old individuals and compare them to a group of 30-year-old individuals and a group of 40-year-old individuals. While cross-sectional research requires a shorter-term investment, it is also limited by differences that exist between the different generations (or cohorts) that have nothing to do with age per se, but rather reflect the social and cultural experiences of different generations of individuals that make them different from one another.
To illustrate this concept, consider the following survey findings. In recent years there has been significant growth in the popular support of same-sex marriage. Many studies on this topic break down survey participants into different age groups. In general, younger people are more supportive of same-sex marriage than are those who are older (Jones, 2013). Does this mean that as we age we become less open to the idea of same-sex marriage, or does this mean that older individuals have different perspectives because of the social climates in which they grew up? Longitudinal research is a powerful approach because the same individuals are involved in the research project over time, which means that the researchers need to be less concerned with differences among cohorts affecting the results of their study.
Often longitudinal studies are employed when researching various diseases in an effort to understand particular risk factors. Such studies often involve tens of thousands of individuals who are followed for several decades. Given the enormous number of people involved in these studies, researchers can feel confident that their findings can be generalized to the larger population. The Cancer Prevention Study-3 (CPS-3) is one of a series of longitudinal studies sponsored by the American Cancer Society aimed at determining predictive risk factors associated with cancer. When participants enter the study, they complete a survey about their lives and family histories, providing information on factors that might cause or prevent the development of cancer. Then every few years the participants receive additional surveys to complete. In the end, hundreds of thousands of participants will be tracked over 20 years to determine which of them develop cancer and which do not.
Clearly, this type of research is important and potentially very informative. For instance, earlier longitudinal studies sponsored by the American Cancer Society provided some of the first scientific demonstrations of the now well-established links between increased rates of cancer and smoking (American Cancer Society, n.d.) ( Figure 2.11 ).
As with any research strategy, longitudinal research is not without limitations. For one, these studies require an incredible time investment by the researcher and research participants. Given that some longitudinal studies take years, if not decades, to complete, the results will not be known for a considerable period of time. In addition to the time demands, these studies also require a substantial financial investment. Many researchers are unable to commit the resources necessary to see a longitudinal project through to the end.
Research participants must also be willing to continue their participation for an extended period of time, and this can be problematic. People move, get married and take new names, get ill, and eventually die. Even without significant life changes, some people may simply choose to discontinue their participation in the project. As a result, the attrition rates, or reduction in the number of research participants due to dropouts, in longitudinal studies are quite high and increase over the course of a project. For this reason, researchers using this approach typically recruit many participants fully expecting that a substantial number will drop out before the end. As the study progresses, they continually check whether the sample still represents the larger population, and make adjustments as necessary.
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/psychology-2e/pages/1-introduction
- Authors: Rose M. Spielman, William J. Jenkins, Marilyn D. Lovett
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Psychology 2e
- Publication date: Apr 22, 2020
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/psychology-2e/pages/1-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/psychology-2e/pages/2-2-approaches-to-research
© Jan 6, 2024 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.

How to Get Started on Your First Psychology Experiment
Acquiring even a little expertise in advance makes science research easier..
Updated May 16, 2024 | Reviewed by Ray Parker
- Why Education Is Important
- Find a Child Therapist
- Students often struggle at the beginning of research projects—knowing how to begin.
- Research projects can sometimes be inspired by everyday life or personal concerns.
- Becoming something of an "expert" on a topic in advance makes designing a study go more smoothly.

One of the most rewarding and frustrating parts of my long career as a psychology professor at a small liberal arts college has been guiding students through the senior capstone research experience required near the end of their college years. Each psychology major must conduct an independent experiment in which they collect data to test a hypothesis, analyze the data, write a research paper, and present their results at a college poster session or at a professional conference.
The rewarding part of the process is clear: The students' pride at seeing their poster on display and maybe even getting their name on an article in a professional journal allows us professors to get a glimpse of students being happy and excited—for a change. I also derive great satisfaction from watching a student discover that he or she has an aptitude for research and perhaps start shifting their career plans accordingly.
The frustrating part comes at the beginning of the research process when students are attempting to find a topic to work on. There is a lot of floundering around as students get stuck by doing something that seems to make sense: They begin by trying to “think up a study.”
The problem is that even if the student's research interest is driven by some very personal topic that is deeply relevant to their own life, they simply do not yet know enough to know where to begin. They do not know what has already been done by others, nor do they know how researchers typically attack that topic.
Students also tend to think in terms of mission statements (I want to cure eating disorders) rather than in terms of research questions (Why are people of some ages or genders more susceptible to eating disorders than others?).
Needless to say, attempting to solve a serious, long-standing societal problem in a few weeks while conducting one’s first psychology experiment can be a showstopper.
Even a Little Bit of Expertise Can Go a Long Way
My usual approach to helping students get past this floundering stage is to tell them to try to avoid thinking up a study altogether. Instead, I tell them to conceive of their mission as becoming an “expert” on some topic that they find interesting. They begin by reading journal articles, writing summaries of these articles, and talking to me about them. As the student learns more about the topic, our conversations become more sophisticated and interesting. Researchable questions begin to emerge, and soon, the student is ready to start writing a literature review that will sharpen the focus of their research question.
In short, even a little bit of expertise on a subject makes it infinitely easier to craft an experiment on that topic because the research done by others provides a framework into which the student can fit his or her own work.
This was a lesson I learned early in my career when I was working on my own undergraduate capstone experience. Faced with the necessity of coming up with a research topic and lacking any urgent personal issues that I was trying to resolve, I fell back on what little psychological expertise I had already accumulated.
In a previous psychology course, I had written a literature review on why some information fails to move from short-term memory into long-term memory. The journal articles that I had read for this paper relied primarily on laboratory studies with mice, and the debate that was going on between researchers who had produced different results in their labs revolved around subtle differences in the way that mice were released into the experimental apparatus in the studies.
Because I already had done some homework on this, I had a ready-made research question available: What if the experimental task was set up so that the researcher had no influence on how the mouse entered the apparatus at all? I was able to design a simple animal memory experiment that fit very nicely into the psychological literature that was already out there, and this prevented a lot of angst.
Please note that my undergraduate research project was guided by the “expertise” that I had already acquired rather than by a burning desire to solve some sort of personal or social problem. I guarantee that I had not been walking around as an undergraduate student worrying about why mice forget things, but I was nonetheless able to complete a fun and interesting study.

My first experiment may not have changed the world, but it successfully launched my research career, and I fondly remember it as I work with my students 50 years later.

Frank McAndrew, Ph.D., is the Cornelia H. Dudley Professor of Psychology at Knox College.
- Find a Therapist
- Find a Treatment Center
- Find a Psychiatrist
- Find a Support Group
- Find Online Therapy
- International
- New Zealand
- South Africa
- Switzerland
- Asperger's
- Bipolar Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Eating Disorders
- Passive Aggression
- Personality
- Goal Setting
- Positive Psychology
- Stopping Smoking
- Low Sexual Desire
- Relationships
- Child Development
- Self Tests NEW
- Therapy Center
- Diagnosis Dictionary
- Types of Therapy

At any moment, someone’s aggravating behavior or our own bad luck can set us off on an emotional spiral that threatens to derail our entire day. Here’s how we can face our triggers with less reactivity so that we can get on with our lives.
- Emotional Intelligence
- Gaslighting
- Affective Forecasting
- Neuroscience

- Liberty University
- Jerry Falwell Library
- Special Collections
- < Previous
Home > ETD > Doctoral > 5638
Doctoral Dissertations and Projects
A case study of early childhood educators' self-determination in implementing social emotional learning pedagogy.
Ingrid Brouwer , Liberty University Follow
School of Education
Doctor of Philosophy in Education (PhD)
Denise Nixon
early childhood teachers, intrinsic motivation, social-emotional learning, self-determination theory, autonomy, relatedness, competence
Disciplines
Education | Educational Assessment, Evaluation, and Research
Recommended Citation
Brouwer, Ingrid, "A Case Study of Early Childhood Educators' Self-Determination in Implementing Social Emotional Learning Pedagogy" (2024). Doctoral Dissertations and Projects . 5638. https://digitalcommons.liberty.edu/doctoral/5638
The purpose of this single common case study will be to answer the question, “How does intrinsic motivation and self-determination in the ability to make choices and manage one’s behavior guide the implementation of social-emotional teaching practices into the early childhood classroom?” for the participants at Mount Uinta (pseudonym). The theory guiding this study will be Deci and Ryan’s Self-determination Theory (SDT), as it will validate the three basic psychological needs to strengthen learners’ autonomy, competence, and a sense of positive relatedness in social-emotional learning and teaching. Reaching the goal of implementing intrinsic motivation and professional development (PD) for early childhood teachers can complement the teaching of SEL skills. The method for the selected research will be qualitative, using exploration and understanding of a group of teachers and the social problem of teacher intrinsic motivation and self-determination. Detailed information will be collected using a variety of data collection methods for this single common case study, by conducting interviews with the staff, holding focus groups, and collecting teacher reflection surveys on their level of preparedness to incorporate SEL into early childhood classrooms. The analysis will be conducted via two-cycle coding methods, including emotion coding and pattern matching to form an understanding of teacher self-determination.
Since May 22, 2024
Included in
Educational Assessment, Evaluation, and Research Commons
- Collections
- Faculty Expert Gallery
- Theses and Dissertations
- Conferences and Events
- Open Educational Resources (OER)
- Explore Disciplines
Advanced Search
- Notify me via email or RSS .
Faculty Authors
- Submit Research
- Expert Gallery Login
Student Authors
- Undergraduate Submissions
- Graduate Submissions
- Honors Submissions
Home | About | FAQ | My Account | Accessibility Statement
Privacy Copyright
- Open access
- Published: 24 February 2024
Physical activity improves stress load, recovery, and academic performance-related parameters among university students: a longitudinal study on daily level
- Monika Teuber 1 ,
- Daniel Leyhr 1 , 2 &
- Gorden Sudeck 1 , 3
BMC Public Health volume 24 , Article number: 598 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
4323 Accesses
30 Altmetric
Metrics details
Physical activity has been proven to be beneficial for physical and psychological health as well as for academic achievement. However, especially university students are insufficiently physically active because of difficulties in time management regarding study, work, and social demands. As they are at a crucial life stage, it is of interest how physical activity affects university students' stress load and recovery as well as their academic performance.
Student´s behavior during home studying in times of COVID-19 was examined longitudinally on a daily basis during a ten-day study period ( N = 57, aged M = 23.5 years, SD = 2.8, studying between the 1st to 13th semester ( M = 5.8, SD = 4.1)). Two-level regression models were conducted to predict daily variations in stress load, recovery and perceived academic performance depending on leisure-time physical activity and short physical activity breaks during studying periods. Parameters of the individual home studying behavior were also taken into account as covariates.
While physical activity breaks only positively affect stress load (functional stress b = 0.032, p < 0.01) and perceived academic performance (b = 0.121, p < 0.001), leisure-time physical activity affects parameters of stress load (functional stress: b = 0.003, p < 0.001, dysfunctional stress: b = -0.002, p < 0.01), recovery experience (b = -0.003, p < 0.001) and perceived academic performance (b = 0.012, p < 0.001). Home study behavior regarding the number of breaks and longest stretch of time also shows associations with recovery experience and perceived academic performance.
Conclusions
Study results confirm the importance of different physical activities for university students` stress load, recovery experience and perceived academic performance in home studying periods. Universities should promote physical activity to keep their students healthy and capable of performing well in academic study: On the one hand, they can offer opportunities to be physically active in leisure time. On the other hand, they can support physical activity breaks during the learning process and in the immediate location of study.
Peer Review reports
Introduction
Physical activity (PA) takes a particularly key position in health promotion and prevention. It reduces risks for several diseases, overweight, and all-cause mortality [ 1 ] and is beneficial for physical, psychological and social health [ 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 ] as well as for academic achievement [ 6 , 7 ]. However, PA levels decrease from childhood through adolescence and into adulthood [ 8 , 9 , 10 ]. Especially university students are insufficiently physically active according to health-oriented PA guidelines [ 11 ] because of academic workloads as well as difficulties in time management regarding study, work, and social demands [ 12 ]. Due to their independence and increasing self-responsibility, university students are at a crucial life stage. In this essential and still educational stage of the students´ development, it is important to study their PA behavior. Furthermore, PA as health behavior represents one influencing factor which is considered in the analytical framework of the impact of health and health behaviors on educational outcomes which was developed by the authors Suhrcke and de Paz Nieves [ 13 , 14 ]. In light of this, the present study examines how PA affects university students' academic situations.
Along with the promotion of PA, the reduction of sedentary behavior has also become a crucial part of modern health promotion and prevention strategies. Spending too much time sitting increases many health risks, including the risk of obesity [ 15 ], diabetes [ 16 ] and other chronic diseases [ 15 ], damage to muscular balances, bone metabolism and musculoskeletal system [ 17 ] and even early death [ 15 ]. University students are a population that has shown the greatest increase in sedentary behavior over the last two decades [ 18 ]. In Germany, they show the highest percentage of sitting time among all working professional groups [ 19 ]. Long times sitting in classes, self-study learning, and through smartphone use, all of which are connected to the university setting and its associated behaviors, might be the cause of this [ 20 , 21 ]. This goes along with technological advances which allow students to study in the comfort of their own homes without changing locations [ 22 ].
To counter a sedentary lifestyle, PA is crucial. In addition to its physical health advantages, PA is essential for coping with the intellectual and stress-related demands of academic life. PA shows positive associations with stress load and academic performance. It is positively associated with learning and educational success [ 6 ] and even shows stress-regulatory potential [ 23 ]. In contrast, sedentary behavior is associated with lower cognitive performance [ 24 ]. Moreover, theoretical derivations show that too much sitting could have a negative impact on brain health and diminish the positive effects of PA [ 16 ]. Given the theoretical background of the stressor detachment model [ 25 ] and the cybernetic approach to stress management in the workplace [ 26 ], PA can promote recovery experience, it can enhance academic performance, and it is a way to reduce the impact of study-related stressors on strain. Load-related stress response can be bilateral: On the one hand, it can be functional if it is beneficial to help cope with the study demands. On the other hand, it can be dysfunctional if it puts a strain on personal resources and can lead to load-related states of strain [ 27 ]. Thus, both, the promotion of PA and reduction of sedentary behavior are important for stress load, recovery, and performance in student life, which can be of particular importance for students in an academic context.
A simple but (presumably) effective way to integrate PA and reduce sedentary behavior in student life are short PA breaks. Due to the exercises' simplicity and short duration, students can perform them wherever they are — together in a lecture or alone at home. Short PA breaks could prevent an accumulation of negative stressors during the day and can help with prolonged sitting as well as inactivity. Especially in the university setting, evidence of the positive effects of PA breaks exists for self-perceived physical and psychological well-being of the university students [ 28 ]. PA breaks buffer university students’ perceived stress [ 29 ] and show positive impacts on recovery need [ 30 ] and better mood ratings [ 31 , 32 ]. In addition, there is evidence for reduction in tension [ 30 ], overall muscular discomfort [ 33 ], daytime sleepiness or fatigue [ 33 , 34 ] and increase in vigor [ 34 ] and experienced energy [ 30 ]. This is in line with cognitive, affective, behavioral, and biological effects of PA, all categorized as palliative-regenerative coping strategies, which addresses the consequences of stress-generating appraisal processes aiming to alleviate these consequences (palliative) or restore the baseline of the relevant reaction parameter (regenerative) [ 35 , 36 ]. This is achieved by, for example, reducing stress-induced cortisol release or tension through physical activity (reaction reduction) [ 35 ]. Such mechanisms are also in accordance with the previously mentioned stressor detachment model [ 25 ]. Lastly, there is a health-strengthening effect that impacts the entire stress-coping-health process, relying on the compensatory effects of PA which is in accordance to the stress-buffering effect of exercise [ 37 ]. Health, in turn, effects educational outcomes [ 13 , 14 ]. Therefore, stress regulating effects are also accompanied with the before mentioned analytical framework of the impact of health and health behaviors on educational outcomes [ 13 , 14 ].
Focusing on the effects of PA, this study is guided by an inquiry into how PA affects university students' stress load and recovery as well as their perceived academic performance. For that reason, the student´s behavior during home studying in times of COVID-19 is examined, a time in which reinforced prolonged sitting, inactivity, and a negative stress load response was at a high [ 38 , 39 , 40 , 41 , 42 ]. Looking separately on the relation of PA with different parameters based on the mentioned evidence, we assume that PA has a positive impact on stress load, recovery, and perceived academic performance-related parameters. Furthermore, a side effect of the home study behavior on the mentioned parameters is assumed regarding the accumulation of negative stressors during home studying. These associations are presented in Fig. 1 and summarized in the following hypotheses:
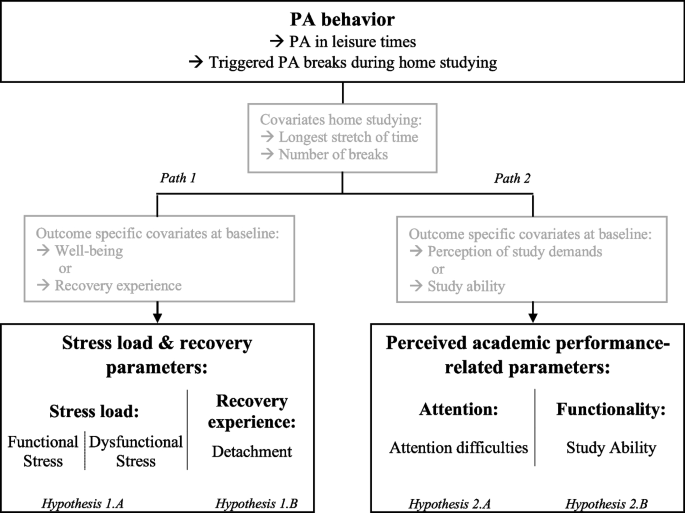
Overview of the assumed effects and investigated hypotheses of physical activity (PA) behavior on variables of stress load and recovery and perceived academic performance-related parameters
Hypothesis 1 (path 1): Given that stress load always occurs as a duality—beneficial if it is functional for coping, or exhausting if it puts a strain on personal resources [ 27 ] – we consider two variables for stress load: functional stress and dysfunctional stress. In order to reduce the length of the daily surveys, we focused the measure of recovery only on the most obvious and accessible component of recovery experience, namely psychological detachment. PA (whether performed in leisure-time or during PA breaks) encourages functional stress and reduce dysfunctional stress (1.A) and has a positive effect on recovery experience through psychological detachment (1.B).
Hypothesis 2 (path 2): The academic performance-related parameters attention difficulties and study ability are positively influenced by PA (whether done in leisure-time or during PA breaks). We have chosen to assess attention difficulties for a cognitive parameter because poor control over the stream of occurring stimuli have been associated with impairment in executive functions or academic failure [ 43 , 44 , 45 , 46 ]. Furthermore, we have assessed the study ability to refer to the self-perceived feeling of functionality regarding the demands of students. PA reduces self-reported attention difficulties (2.A) and improves perceived study ability, indicating that a student feels capable of performing well in academic study (2.B).
Hypothesis 3: We assume that a longer time spent on studying at home (so called home studying) could result in higher accumulation of stressors throughout the day which could elicit immediate stress responses, while breaks in general could reduce the influence of work-related stressors on strain and well-being [ 47 , 48 ]. Therefore, the following covariates are considered for secondary effects:
the daily longest stretch of time without a break spent on home studying
the daily number of breaks during home studying
Study setting
The study was carried out during the COVID-19 pandemic containment phase. It took place in the middle of the lecture period between 25th of November and 4th of December 2020. Student life was characterized by home studying and digital learning. A so called “digital semester” was in effect at the University of Tübingen when the study took place. Hence, courses were mainly taught online (e.g., live or via a recorded lecture). Other events and actions at the university were not permitted. As such, the university sports department closed in-person sports activities. For leisure time in general, there were contact restrictions (social distancing), the performance of sports activities in groups was not permitted, and sports facilities were closed.
Thus, the university sports department of the University of Tübingen launched various online sports courses and the student health management introduced an opportunity for a new digital form of PA breaks. This opportunity provided PA breaks via videos with guided physical exercises and health-promoting explanations for a PA break for everyday home studying: the so called “Bewegungssnack digital” [in English “exercise snack digital” (ESD)] [ 49 ]. The ESD videos took 5–7 min and were categorized into three thematic foci: activation, relaxation, and coordination. Exercises were demonstrated by one or two student exercise leaders, accompanied by textual descriptions of the relevant execution features of each exercise.
Participants
Participants were recruited within the framework of an intervention study, which was conducted to investigate whether a digital nudging intervention has a beneficial effect on taking PA breaks during home study periods [ 49 ]. Students at the University of Tübingen which counts 27,532 enrolled students were approached for participation through a variety of digital means: via an email sent to those who registered for ESD course on the homepage of the university sports department and to all students via the university email distribution list; via advertisement on social media of the university sports department (Facebook, Instagram, YouTube, homepage). Five tablets, two smart watches, and one iPad were raffled off to participants who engaged actively during the full study period in an effort to motivate them to stick with it to the end. In any case, participants knew that the study was voluntary and that they would not suffer any personal disadvantages should they opt out. There was a written informed consent prompt together with a prompt for the approval of the data protection regulations immediately within the first questionnaire (T0) presented in a mandatory selection field. Positive ethical approval for the study was given by the first author´s institution´s ethics committee of the faculty of the University of Tübingen.
Participants ( N = 57) who completed the daily surveys on at least half of the days of the study period, were included in the sample (male = 6, female = 47, diverse = 1, not stated = 3). As not all subjects provided data on all ten study days, the total number of observations was between 468 and 540, depending on the variable under study (see Table 1 ). The average number of observations per subject was around eight. Their age was between 18 and 32 years ( M = 23.52, SD = 2.81) and they were studying between the 1st to 13th semester ( M = 5.76, SD = 4.11) within the following major courses of study: mathematical-scientific majors (34.0%), social science majors (22.6%), philosophical majors (18.9%), medicine (13.2%), theology (5.7%), economics (3.8%), or law (1.9%). 20.4% of the students had on-site classroom teaching on university campus for at least one day a week despite the mandated digital semester, as there were exceptions for special forms of teaching.
Design and procedures
To examine these hypothesized associations, a longitudinal study design with daily surveys was chosen following the suggestion of the day-level study of Feuerhahn et al. (2014) and also of Sonnentag (2001) measuring recovery potential of (exercise) activities during leisure time [ 50 , 51 ]. Considering that there are also differences between people at the beginning of the study period, initial base-line value variables respective to the outcomes measured before the study period were considered as independent covariates. Therefore, the well-being at baseline serves as a control for stress load (2.A), the psychological detachment at baseline serves as a control for daily psychological detachment (2.B), the perception of study demands serves as a control for self-reported attention difficulties (1.A), and the perceived study ability at baseline serves as a control for daily study ability (2.B).
Subjects were asked to continue with their normal home study routine and additionally perform ESD at any time in their daily routine. Data were collected one to two days before (T0) as well as daily during the ten-day study period (Wednesday to Friday). The daily surveys (t 1 -t 10 ) were sent by email at 7 p.m. every evening. Each day, subjects were asked to answer questions about their home studying behavior, study related requirements, recovery experience from study tasks, attention, and PA, including ESD participation. The surveys were conducted online using the UNIPARK software and were recorded and analyzed anonymously.
Measures and covariates
In total, five outcome variables, two independent variables, and seven covariates were included in different analyses: three variables were used for stress load and recovery parameters, two variables for academic performance-related parameters, two variables for PA behavior, two variables for study behavior, four variables for outcome specific baseline values and one variable for age.
Outcome variables
Stress load & recovery parameters (hypothesis 1).
Stress load was included in the analysis with two variables: functional stress and dysfunctional stress. Followingly, a questionnaire containing a word list of adjectives for the recording of emotions and stress during work (called “Erfassung von Emotionen und Beanspruchung “ in German, also known as EEB [ 52 ]) was used. It is an instrument which were developed and validated in the context of occupational health promotion. The items are based on mental-workload research and the assessment of the stress potential of work organization [ 52 ]. Within the questionnaire, four mental and motivational stress items were combined to form a functional stress scale (energetic, willing to perform, attentive, focused) (α = 0.89) and four negative emotional and physical stress items were combined to form dysfunctional stress scale (nervous, physically tensioned, excited, physically unwell) (α = 0.71). Participants rated the items according to how they felt about home studying in general on the following scale (adjustment from “work” to “home studying”): hardly, somewhat, to some extent, fairly, strongly, very strongly, exceptionally.
Recovery experience was measured via psychological detachment. Therefore, the dimension “detachment” of the Recovery Experience Questionnaire (RECQ [ 53 ]) was adjusted to home studying. The introductory question was "How did you experience your free time (including short breaks between learning) during home studying today?". Students responded to four statements based on the extent to which they agreed or disagreed (not at all true, somewhat true, moderately true, mostly true, completely true). The statements covered subjects such as forgetting about studying, not thinking about studying, detachment from studying, and keeping a distance from student tasks. The four items were combined into a score for psychological detachment (α = 0.94).
Academic performance-related parameters (hypothesis 2)
Attention was assessed via the subscale “difficulty maintaining focused attention performance” of the “Attention and Performance Self-Assessment” (ASPA, AP-F2 [ 54 ]). It contains nine items with statements about disturbing situations regarding concentration (e.g. “Even a small noise from the environment could disturb me while reading.”). Participants had to answer how often such situations happened to them on a given day on the following scale: never, rarely, sometimes, often, always. The nine items were combined into the AP-F2 score (α = 0.87).
The perceived study ability was assessed using the study ability index (SAI [ 55 ]). The study ability index captures the current state of perceived functioning in studying. It is based on the Work Ability Index by Hasselhorn and Freude ([ 56 ]) and consists of an adjusted short scale of three adapted items in the context of studying. Firstly, (a) the perceived academic performance was asked after in comparison to the best study-related academic performance ever achieved (from 0 = completely unable to function to 10 = currently best functioning). Secondly, the other two items were aimed at assessing current study-related performance in relation to (b) study tasks that have to be mastered cognitively and (c) the psychological demands of studying. Both items were answered on a five-point Likert scale (1 = very poor, 2 = rather poor, 3 = moderate, 4 = rather good, 5 = very good). A sum index, the SAI, was formed which can indicate values between 2 and 20, with higher values corresponding to higher assessed functioning in studies (α = 0.86). In a previous study it already showed satisfying reliability (α = 0.72) [ 55 ].
Independent variables
Pa behavior.
Two indicators for PA behavior were included via self-reports: the time spent on ESD and the time spent on leisure-time PA (LTPA). Participants were asked the following overarching question daily: “How much time did you spend on physical activity today and in what context”. For the independent variable time spent on PA breaks, participants could answer the option “I participated in the Bewegungssnack digital” with the amount of time they spent on it (in minutes). To assess the time spent on LTPA besides PA breaks, participants could report their time for four different contexts of PA which comprised two forms: Firstly, structured supervised exercise was reported via time spent on (a) university sports courses and (b) other organized sports activities. Secondly, self-organized PA was indicated via (c) independent PA at home, such as a workout or other physically demanding activity such as cleaning or tidying up, as well as via (d) independent PA outside, like walking, cycling, jogging, a workout or something similar. Referring to the different domains of health enhancing PA [ 57 ], the reported minutes of these four types of PA were summed up to a total LTPA value. The total LTPA value was included in the analysis as a metric variable in minutes.
Covariates (hypothesis 3)
Regarding hypothesis 3 and home study behavior, the longest daily stretch of time without a break spent on home studying (in hours) and the daily number of breaks during home studying was assessed. Therein, participants had to answer the overarching question “How much time did you spend on your home studying today?” and give responses to the items: (1) longest stretch of time for home studying (without a break), and (2) number of short and long breaks you took during home studying.
In principle, efforts were made to control for potential confounders at the individual level (level 2) either by including the baseline measure (T0) of the respective variable or by including variables assessing related trait-like characteristics for respective outcomes. The reason why related trait-like characteristics were used for the outcomes was because brief assessments were used for daily surveys that were not concurrently employed in the baseline assessment. To enable the continued use of controlling for person-specific baseline characteristics in the analysis of daily associations, trait-like characteristics available from the baseline assessment were utilized as the best possible approximation.To sum up, four outcome specific baseline value variables were measured before the study period (at T0). The psychological detachment with the RECQ (α = 0.87) [ 53 ] was assessed at the beginning to monitor daily psychological detachment. Further, the SAI [ 55 ] was assessed at the beginning of the study period to monitor daily study ability. To monitor daily stress load, which in part measures mental stress aspects and negative emotional stress aspects, the well-being was assessed at the beginning using the WHO-Five Well-being Index (WHO-5 [ 58 ]). It is a one-dimensional self-report measure with five items. The index value is the sum of all items, with higher values indicating better well-being. As the well-being and stress load tolerance may linked with each other, this variable was assumed to be a good fit with the daily stress load indicating mental and emotional stress aspects. With respect to student life, daily academic performance-related attention was monitored with an instrument for the perception of study demands and resources (termed “Berliner Anforderungen Ressourcen-Inventar – Studierende” in German, the so-called BARI-S [ 59 ]). It contains eight items which capture overwork in studies, time pressure during studies, and the incompatibility of studies and private life. All together they form the BARI-S demand scale (α = 0.85) which was included in the analysis. As overwork and time pressure may result in attention difficulties (e.g. Elfering et al., 2013), this variable was assumed to have a good fit with academic performance-related attention [ 60 ]. Additionally, age in years at T0 was considered as a sociodemographic factor.
Statistical analysis
Since the study design provided ten measurement points for various people, the hierarchical structure of the nested data called for two-level analyses. Pre-analyses of Random-Intercept-Only models for each of the outcome variables (hypothesis 1 to 3) revealed an Intra-Class-Correlation ( ICC ) of at least 0.10 (range 0.26 – 0.64) and confirmed the necessity to perform multilevel analyses [ 61 ]. Specifically, the day-level variables belong to Level 1 (ESD time, LTPA time, longest stretch of time without a break spent on home studying, daily number of breaks during home studying). To analyze day-specific effects within the person, these variables were centered on the person mean (cw = centered within) [ 50 , 62 , 63 , 64 ]. This means that the analyses’ findings are based on a person’s deviations from their average values. The variables assessed at T0 belong to Level 2, which describe the person level (psychological detachment baseline, SAI baseline, well-being, study demands scale, age). These covariates on person level were centered around the grand mean [ 50 ] indicating that the analyses’ findings are based how far an individual deviates from the sample's mean values. As a result, the models’ intercept reflects the outcome value of an average student in the sample at his/her daily average behavior in PA and home study when all parameters are zero. For descriptive statistics SPSS 28.0.1.1 (IBM) and for inferential statistics R (version 4.1.2) were used. The hierarchical models were calculated using the package lme4 with the lmer-function in R in the following steps [ 65 ]. The Null Model was analyzed for all models first, with the corresponding intercept as the only predictor. Afterwards, all variables were entered. The regression coefficient estimates (”b”) were considered for statistical significance for the models and the respective BIC was provided.
In total, five regression models with ‘PA break time’ and ‘LTPA time’ as independent variables were computed due to the five measured outcomes of the present study. Three models belonged to hypothesis 1 and two models to hypothesis 2.
Hypothesis 1: To test hypothesis 1.A two outcome variables were chosen for two separate models: ‘functional stress’ and ‘dysfunctional stress’. Besides the PA behavior variables, the ‘number of breaks’, the ‘longest stretch of time without a break spent on home studying’, ‘age’, and the ‘well-being’ at the beginning of the study as corresponding baseline variable to the output variable were also included as independent variables in both models. The outcome variable ‘psychological detachment’ was utilized in conjunction with the aforementioned independent variables to test hypotheses 1.B, with one exception: psychological detachment at the start of the study was chosen as the corresponding baseline variable.
Hypothesis 2: To investigate hypothesis 2.A the outcome variable ‘attention difficulties’ was selected. Hypothesis 2.B was tested with the outcome variables ‘study ability’. Both models included both PA behavior variables as well as the ‘number of breaks’, the ‘longest stretch of time without a break spent on home studying’, ‘age’ and one corresponding baseline variable each: the ‘study demand scale’ at the start of the study for ‘attention difficulties’ and the ‘SAI’ at the beginning of the study for the daily ‘study ability’.
Hypothesis 3: In addition to both PA behavior variables, age and one baseline variable that matched the outcome variable, the covariates ‘daily longest stretch of time spent on home studying’ and ‘daily number of breaks during home studying’ were included in the models for all five outcome variables.
Handling missing data
The dataset had up to 18% missing values (most exhibit the variables ‘daily longest stretch of time without a break spent on home studying’ with 17.89% followed by ‘daily number of breaks during homes studying’ with 16.67%, and ‘functional / dysfunctional stress’ with 12.45%). Therefore, a sensitivity analysis was performed using the multiple imputation mice-package in the statistical program R [ 66 ], the package howManyImputation based on Von Hippel (2020, [ 67 ]), and the additional broom package [ 68 ]. The results of the models remained the same, with one exception for the Attention Difficulties Model: The daily longest stretch of time without a break spent on home studying showed a significant association (Table 1 in supplement). Due to this almost perfect consistency of results between analyses based on the dataset with missing data and those with imputed data alongside the lack of information provided by the packages for imputed datasets, we decided to stick with the main analysis including the missing data. Thus, in the following the results of the main analysis without imputations are presented.
Table 1 shows the descriptive statistics of the variables used in the analysis. An overview of the analysed models is presented in Table 2 .
Effects on stress load and recovery (hypothesis 1)
Hypothesis 1.A: The Model Functional Stress explained 13% of the variance by fixed factors (marginal R 2 = 0.13), and 52% by both fixed and random factors (conditional R 2 = 0.52). The time spent on ESD as well as the time spent on PA in leisure showed a positive significant influence on functional stress (b = 0.032, p < 0.01). The same applied to LTPA (b = 0.003, p < 0.001). The Model Dysfunctional Stress (marginal R 2 = 0.027, conditional R 2 = 0.647) showed only one significant result. The dysfunctional stress was only significantly negatively influenced by the time spent on LTPA (b = 0.002, p < 0.01).
Hypothesis 1.B: With the Model Detachment, fixed factors contributed 18% of the explained variance and fixed and random factors 46% of the explained variance for psychological detachment. Only the amount of time spent on LTPA revealed a positive impact on psychological detachment (b = 0.003, p < 0.001).
Effects on academic performance-related parameters (hypothesis 2)
Hypothesis 2.A: The Model Attention Difficulties showed 13% of the variance explained by fixed factors, and 51% explained by both fixed and random factors. It showed a significant negative association only for the time spent on LTPA (b = 0.003, p < 0.001).
Hypothesis 2.B: The Model SAI showed 18% of the variance explained by fixed factors, and 39% explained by both fixed and random factors. There were significant positive associations for time spent on ESD (b = 0.121, p < 0.001) and time spent on LTPA (b = 0.012, p < 0.001). The same applied to LTPA (b = 0.012, p < 0.001).
Effects of home study behavior (hypothesis 3)
Regarding the independent covariates for the outcome variables functional and dysfunctional stress, there were no significant results for the number of breaks during homes studying or the longest stretch of time without a break spent on home studying. Considering the outcome variable ‘psychological detachment’, there were significant results with negative impact for both study behavior variables: breaks during home studying (b = 0.058, p < 0.01) and daily longest stretch of time without a break (b = 0.120, p < 0.01). Evaluating the outcome variables ‘attention difficulties’, there were no significant results for the number of breaks during home studying or the longest stretch of time without a break spent on home studying. Testing the independent study behavior variables for the SAI, it increased with increasing number in daily breaks during homes studying relative to the person´s mean (b = 0.183, p < 0.05). No significant effect was found for the longest stretch of time without a break spent on home studying ( p = 0.07).
The baseline covariates of the models showed expected associations and thus confirmed their inclusion. The baseline variables well-being showed a significant impact on functional stress (b = 0.089, p < 0.001), psychological detachment showed a positive effect on the daily output variables psychological detachment (b = 0.471, p < 0.001), study demand scale showed a positive association on difficulties in attention (b = 0.240, p < 0.01), and baseline SAI had a positive effect on the daily SAI (b = 0.335, p < 0.001).
The present study theorized that PA breaks and LTPA positively influence the academic situation of university students. Therefore, impact on stress load (‘functional stress’ and ‘dysfunctional stress’) and ‘psychological detachment’ as well as academic performance-related parameters ‘self-reported attention difficulties’ and ‘perceived study ability’ was taken into account. The first and second hypotheses assumed that both PA breaks and LTPA are positively associated with the aforementioned parameters and were confirmed for LTPA for all parameters and for PA breaks for functional stress and perceived study ability. The third hypothesis assumed that home study behavior regarding the daily number of breaks during home studying and longest stretch of time without a break spent on home studying has side effects. Detected negative effects for both covariates on psychological detachment and positive effects for the daily number of breaks on perceived study ability were partly unexpected in their direction. These results emphasize the key position of PA in the context of modern health promotion especially for students in an academic context.
Regarding hypothesis 1 and the detected positive associations for stress load and recovery parameters with PA, the results are in accordance with the stress-regulatory potential of PA from the state of research [ 23 ]. For hypothesis 1.A, there is a positive influence of PA breaks and LTPA on functional stress and a negative influence of LTPA on dysfunctional stress. Given the bilateral role of stress load, the results indicate that PA breaks and LTPA are beneficial for coping with study demands, and may help to promote feelings of joy, pride, and learning progress [ 27 ]. This is in line with previous evidence that PA breaks in lectures can buffer university students’ perceived stress [ 29 ], lead to better mood ratings [ 29 , 31 ], and increase in motivation [ 28 , 69 ], vigor [ 34 ], energy [ 30 ], and self-perceived physical and psychological well-being [ 28 ]. Looking at dysfunctional stress, the result point that LTPA counteract load-related states of strain such as inner tension, irritability and nervous restlessness or feelings of boredom [ 27 ]. In contrast, short PA breaks during the day could not have enough impact in countering dysfunctional stress at the end of the day regarding the accumulation of negative stressors during home studying which might have occurred after the participant took PA breaks. Other studies have been able to show a reduction in tension [ 30 ] and general muscular discomfort [ 33 ] after PA breaks. However, this was measured as an immediate effect of PA breaks and not with general evening surveys. Blasche and colleagues [ 34 ] measured effects immediately and 20 min after different kind of breaks and found that PA breaks led to an additional short‐ and medium‐term increase in vigor while the relaxation break lead to an additional medium‐term decrease in fatigue compared to an unstructured open break. This is consistent with the results of the present study that an effect of PA breaks is only observed for functional stress and not for dysfunctional stress. Furthermore, there is evidence that long sitting during lectures leads to increased fatigue and lower concentration [ 31 , 70 ], which could be counteracted by PA breaks. For both types of stress loads, functional and dysfunctional stress, there is an influence of students´ well-being in this study. This shows that the stress load is affected by the way students have mentally felt over the last two weeks. The relevance of monitoring this seems important especially in the time of COVID-19 as, for example, 65.3% of the students of a cross-sectional online survey at an Australian university reported low to very low well-being during that time [ 71 ]. However, since PA and well-being can support functional stress load, they should be of the highest priority—not only as regards the pandemic, but also in general.
Looking at hypothesis 1.B; while there is a positive influence of LTPA on experienced psychological detachment, no significant influence for PA breaks was detected. The fact that only LTPA has a positive effect can be explained by the voluntary character of the activity [ 50 ]. The voluntary character ensures that stressors no longer affect the student and, thus, recovery as detachment can take place. Home studying is not present in leisure times, and thus detachment from study is easier. The PA break videos, on the other hand, were shot in a university setting, which would have made it more difficult to detach from study. In order to further understand how PA breaks affect recovery and whether there is a distinction between PA breaks and LTPA, future research should also consider other types of recovery (e.g. relaxation, mastery, and control). Additionally, different types of PA breaks, such as group PA breaks taken on-site versus video-based PA breaks, should be taken into account.
Considering the confirmed positive associations for academic performance-related parameters of hypothesis 2, the results are in accordance with the evidence of positive associations between PA and learning and educational success [ 6 ], as well as between PA breaks and better cognitive functioning [ 28 ]. Looking at the self-reported attention difficulties of hypothesis 2.A, only LTPA can counteract it. PA breaks showed no effects, contrary to the results of a study of Löffler and collegues (2011, [ 31 ]), in which acute effects of PA breaks could be found for higher attention and cognitive performance. Furthermore, the perception of study demands before the study periods has a positive impact on difficulties in attention. That means that overload in studies, time pressure during studies, and incompatibility of studies and private life leads to higher difficulties with attention in home studying. In these conditions, PA breaks might have been seen as interfering, resulting in the expected beneficial effects of exercise on attention and task-related participation behavior [ 72 , 73 ] therefore remaining undetected. With respect to the COVID-19 pandemic, accompanying education changes, and an increase in student´s worries [ 74 , 75 ], the perception of study demands could be affected. This suggests that especially in times of constraint and changes, it is important to promote PA in order to counteract attention difficulties. This also applies to post-pandemic phase.
Regarding the perceived academic performance of hypothesis 2.B, both PA breaks and LTPA have a positive effect on perceived study ability. This result confirms the positive short-term effects on cognition tasks [ 76 ]. It is also in line with the positive function of PA breaks in interrupting sedentary behavior and therefore counteracting the negative association between sitting behavior and lower cognitive performance [ 24 ]. Additionally, this result also fits with the previously mentioned positive relationship between LTPA and functional stress and between PA breaks and functional stress.
According to hypothesis 3, in relation to the mentioned stress load and recovery parameters, there are negative effects of the daily number of breaks during home studying and the longest stretch of time without a break spent on home studying on psychological detachment. As stressors result in negative activation, which impede psychological detachment from study during non-studying time [ 25 ], it was expected and confirmed that the longest stretch of time without a break spent on home studying has a negative effect on detachment. Initially unexpected, the number of breaks has a negative influence on psychological detachment, as breaks could prevent the accumulation of strain reactions. However, if the breaks had no recovery effect through successful detachment, the number might not have any influence on recovery via detachment. This is indicated by the PA breaks, which had no impact on psychological detachment. Since there are other ways to recover from stress besides psychological detachment, such as relaxation, mastery, and control [ 53 ], PA breaks must have had an additional impact in relation to the positive results for functional stress.
In relation to the mentioned academic performance-related parameters, only the number of breaks has a positive influence on the perceived study ability. This indicates that not only PA breaks but also breaks in general lead to better perceived functionality in studying. Paulus and colleagues (2021) found out that an increase in cognitive skills is not only attributed to PA breaks and standing breaks, but also to open breaks with no special instructions [ 28 ]. Either way, they found better improvement in self-perceived physical and psychological well-being of the university students with PA breaks than with open breaks. This is also reflected in the present study with the aforementioned positive effects of PA breaks on functional stress, which does not apply to the number of breaks.
Overall, it must be considered that the there is a more complex network of associations between the examined parameters. The hypothesized separate relation of PA with different parameters do not consider associations between parameters of stress load / recovery and academic performance although there might be a interdependency. Furthermore, moderation aspects were not examined. For example, PA could be a moderator which buffer negative effects of stress on the study ability [ 55 ]. Moreover, perceived study ability might moderate stress levels and academic performance. Further studies should try to approach and understand the different relationships between the parameters in its complexity.
Limitations
Certain limitations must be taken into account. Regarding the imbalanced design toward more female students in the sample (47 female versus 6 male), possible sampling bias cannot be excluded. Gender research on students' emotional states during COVID-19, when this study took place, or students´ acceptance of PA breaks is diverse and only partially supplied with inconsistent findings. For example, during the COVID-19 pandemic, some studies reported that female students were associated with lower well-being [ 71 ] or worse mental health trajectories [ 75 , 77 ]. Another study with a large sample of students from 62 countries reported that male students were more strongly affected by the pandemic because they were significantly less satisfied with their academic life [ 74 ]. However, Keating and colleges (2020) discovered that, despite the COVID-19 pandemic, females rated some aspects of PA breaks during lectures more positively than male students did. However, this was also based on a female slanted sample [ 78 ]. Further studies are needed to get more insights into gender bias.
Furthermore, the small sample size combined with up to 16% missing values comprises a significant short-coming. There were a lot of possibilities which could cause such missing data, like refused, forgotten or missed participation, technical problems, or deviation of the personal code for the questionnaire between survey times. Although the effects could be excluded by sensitive analysis due to missing data, the sample is still small. To generalize the findings, future replication studies are needed.
Additionally, PA breaks were only captured through participation in the ESD, the specially instructed PA break via video. Effects of other short PA breaks were not include in the study. However, participants were called to participate in ESD whenever possible, so the likelihood that they did take part in PA breaks in addition to the ESD could be ignored.
With respect to the baseline variables, it must be considered that two variables (stress load, attention difficulties) were adjusted not with their identical variable in T0, but with other conceptually associated variables (well-being index, BARI-S). Indeed, contrary to the assumption the well-being index does only show an association with functional stress, indicating that it does not control dysfunctional stress. Although the other three assumed associations were confirmed there might be a discrepancy between the daily measured variables and the variables measured in T0. Further studies should either proof the association between these used variables or measure the same variables in T0 for control the daily value of these variables.
Moreover, the measuring instruments comprised the self-assessed perception of the students and thus do not provide an objective information. This must be considered, especially for measuring cognitive and academic-performance-related measures. Here, existing objective tests, such as multiple choice exams after a video-taped lecture [ 72 ] might have also been used. Nevertheless, such methods were mostly used in a lab setting and do not reflect reality. Due to economic reasons and the natural learning environment, such procedures were not applied in this study. However, the circumstances of COVID-19 pandemic allowed a kind of lab setting in real life, as there were a lot of restrictions in daily life which limited the influence of other covariates. The study design provides a real natural home studying environment, producing results that are applicable to the healthy way that students learn in the real world. As this study took place under the conditions of COVID-19, new transformations in studying were also taken into account, as home studying and digital learning are increasingly part of everyday study.
However, the restrictions during the COVID-19 pandemic could result in a greater extent of leisure time per se. As the available leisure time in general was not measured on daily level, it is not possible to distinguish if the examined effects on the outcomes are purely attributable to PA. It is possible that being more physical active is the result of having a greater extent of leisure time and not that PA but the leisure time itself effected the examined outcomes. To address this issue in future studies, it is necessary to measure the proportion of PA in relation to the leisure time available.
Furthermore, due to the retrospective nature of the daily assessments of the variables, there may be overstated associations which must be taken into account. Anyway, the daily level of the study design provides advantages regarding the ability to observe changes in an individual's characteristics over the period of the study. This design made it possible to find out the necessity to analyze the hierarchical structure of the intraindividual data nested within the interindividual data. The performed multilevel analyses made it possible to reflect the outcome of an average student in the sample at his/her daily average behavior in PA and home study.
Conclusion and practical implications
The current findings confirm the importance of PA for university students` stress load, recovery experience, and academic performance-related parameters in home studying. Briefly summarized, it can be concluded that PA breaks positively affect stress load and perceived study ability. LTPA has a positive impact on stress load, recovery experience, and academic performance-related parameters regarding attention difficulties and perceived study ability. Following these results, universities should promote PA in both fashions in order to keep their students healthy and functioning: On the one hand, they should offer opportunities to be physically active in leisure time. This includes time, environment, and structural aspects. The university sport department, which offers sport courses and provides sport facilities on university campuses for students´ leisure time, is one good example. On the other hand, they should support PA breaks during the learning process and in the immediate location of study. This includes, for example, providing instructor videos for PA breaks to use while home studying, and furthermore having instructors to lead in-person PA breaks in on-site learning settings like universities´ libraries or even lectures and seminars. This not only promotes PA, but also reduces sedentary behavior and thereby reduces many other health risks. Further research should focus not only on the effect of PA behavior but also of sedentary behavior as well as the amount of leisure time per se. They should also try to implement objective measures for example on academic performance parameters and investigate different effect directions and possible moderation effects to get a deeper understanding of the complex network of associations in which PA plays a crucial role.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
Attention and Performance Self-Assessment
"Berliner Anforderungen Ressourcen-Inventar – Studierende" (instrument for the perception of study demands and resources)
Centered within
Grand centered
“Erfassung von Emotionen und Beanspruchung “ (questionnaire containing a word list of adjectives for the recording of emotions and stress during work)
Exercise snack digital (special physical activity break offer)
Intra-Class-Correlation
Leisure time physical activity
- Physical activity
Recovery Experience Questionnaire
Study ability index
World Health Organization-Five Well-being index
Knight JA. Physical inactivity: associated diseases and disorders. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 2012;42(3):320–37.
PubMed Google Scholar
Kemel PN, Porter JE, Coombs N. Improving youth physical, mental and social health through physical activity: a systematic literature review. Health Promot J Austr. 2002;33(3):590–601.
Article Google Scholar
Gothe NP, Ehlers DK, Salerno EA, Fanning J, Kramer AF, McAuley E. Physical activity, sleep and quality of life in older adults: influence of physical, mental and social well-being. Behav Sleep Med. 2020;18(6):797–808.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Eime RM, Young JA, Harvey JT, Charity MJ, Payne WR. A systematic review of the psychological and social benefits of participation in sport for children and adolescents: informing development of a conceptual model of health through sport. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act. 2013;10(1):1–21.
Google Scholar
Iannotti RJ, Janssen I, Haug E, Kololo H, Annaheim B, Borraccino A. Interrelationships of adolescent physical activity, screen-based sedentary behaviour, and social and psychological health. Int J Public Health. 2009;54:191–8.
Dadaczynski K, Schiemann S. Welchen Einfluss haben körperliche Aktivität und Fitness im Kindes-und Jugendalter auf Bildungsoutcomes? German J Exerc Sport Res. 2015;4(45):190–9.
Kari JT, Pehkonen J, Hutri-Kähönen N, Raitakari OT, Tammelin TH. Longitudinal associations between physical activity and educational outcomes. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2017;49(11).
Grim M, Hortz B, Petosa R. Impact evaluation of a pilot web-based intervention to increase physical activity. Am J Health Promot. 2011;25(4):227–30.
Irwin JD. Prevalence of university students’ sufficient physical activity: A systematic review. Percept Mot Skills. 2004;98:927–43.
Kwan MY, Cairney J, Faulkner GE, Pullenayegum EE. Physical activity and other health-risk behaviors during the transition into early adulthood: a longitudinal cohort study. Am J Prev Med. 2012;42(1):14–20.
John JM, Gropper H, Thiel A. The role of critical life events in the talent development pathways of athletes and musicians: A systematic review. Psychol Sport Exerc. 2019;45.
Bopp M, Bopp C, Schuchert M. Active transportation to and on campus is associated with objectively measured fitness outcomes among college students. J Phys Act Health. 2015;12(3):418–23.
Dadaczynski K. Stand der Forschung zum Zusammenhang von Gesundheit und Bildung. Überblick und Implikationen für die schulische Gesundheitsförderung. Zeitschrift für Gesundheitspsychologie. 2012;20(3):141–53
Suhrcke M, de Paz NC. The impact of health and health behaviours on educational outcomes in high-income countries: a review of the evidence. Copenhagen: WHO Regional Offi ce for Europe; 2011.
Lynch BM, Owen N. Too much sitting and chronic disease risk: steps to move the science forward. Ann Intern Med. 2015;16(2):146–7.
Voss MW, Carr LJ, Clark R, Weng T. Revenge of the “sit” II: Does lifestyle impact neuronal and cognitive health through distinct mechanisms associated with sedentary behavior and physical activity? Ment Health Phys Act. 2014;7(1):9–24.
Huber G. Ist Sitzen eine tödliche Aktivität? B&G Bewegungstherapie und Gesundheitssport. 2014;30(01):13–6.
Peterson NE, Sirard JR, Kulbok PA, DeBoer MD, Erickson JM. Sedentary behavior and physical activity of young adult university students. Res Nurs Health. 2018;4(1):30–8.
Rupp R, Dold C, Bucksch J. Sitzzeitreduktion und Bewegungsaktivierung in der Hochschullehre – Entwicklung und Implementierung der Mehrebenen-Intervention Kopf-Stehen. Die Hochschullehre. 2019;5:525–42.
Ickes MJ, McMullen J, Pflug C, Westgate PM. Impact of a University-based Program on Obese College Students’ Physical Activity Behaviors, Attitudes, and Self-efficacy. Am J Health Educ. 2016;47(1):47–55.
Lepp A, Barkley JE, Karpinski AC. The relationship between cell phone use and academic performance in a sample of US college students. Sage Open. 2015;5(1).
Stapp AC, Prior LF. The Impact of Physically Active Brain Breaks on College Students’ Activity Levels and Perceptions. J Physic Activ Res. 2018;3(1):60–7.
Fuchs R, Klaperski S. Sportliche Aktivität und Stressregulation. In: Fuchs R, Schlicht W, editors. Sportaktivität und seelische Gesundheit Göttingen: Hogrefe; 2012. p. 100–21.
Falck RS, Davis JC, Liu-Ambrose T. What is the association between sedentary behaviour and cognitive function? A systematic review. Br J Sports Med. 2017;51(10):800–11.
Sonnentag S, Fritz C. Recovery from job stress: The stressor-detachment model as an integrative framework. J Organ Behav. 2015;36:72–103.
Edwards JR. A cybernetic theory of stress, coping, and well-being in organizations. Acad Manag Rev. 1992;17(2):238–74.
Wieland R. Status-Bericht: Psychische Gesundheit in der betrieblichen Gesundheitsförderung – eine arbeitspsychologische Perspektive. In: Nold H, Wenninger G, editors. Rückengesundheit und psychische Gesundheit. Rückengesundheit und psychische Gesundheit.: Asanger Verlag; 2013.
Paulus M, Kunkel J, Schmidt SCE, Bachert P, Wäsche H, Neumann R, et al. Standing breaks in lectures improve university students’ self-perceived physical, mental, and cognitive condition. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18.
Marschin V, Herbert C. A Short, Multimodal Activity Break Incorporated Into the Learning Context During the Covid-19 Pandemic: Effects of Physical Activity and Positive Expressive Writing on University Students’ Mental Health — Results and Recommendations From a Pilot Study. Front Psychol. 2021;12.
Gollner E, Savil M, Schnabel F, Braun C, Blasche G. Unterschiede in der Wirksamkeit von Kurzpausenaktivitäten im Vergleich von Bewegungspausen zu psychoregulativen Pausen bei kognitiver Belastung. Bewegungstherapie Gesundheitssport. 2019;35:134–43.
Löffler SN, Dominok E, von Haaren B, Schellhorn R, Gidion G. Aktivierung, Konzentration, Entspannung: Interventionsmöglichkeiten zur Förderung fitnessrelevanter Kompetenzen im Studium: KIT Scientific Publishing; 2011.
Marschin V, Herbert C. A short, multimodal activity break incorporated into the learning context during the Covid-19 pandemic: effects of physical activity and positive expressive writing on university students' mental health—results and recommendations from a pilot study. Front Psychol. 2021.
Kowalsky RJ, Farney TM, Hearon CM. Resistance Exercise Breaks Improve Ratings of Discomfort and Sleepiness in College Students. Res Q Exerc Sport. 2022;94(1):210–5.
Blasche G, Szabo B, Wagner-Menghin M, Ekmekcioglu C, Gollner E. Comparison of rest-break interventions during a mentally demanding task. Stress Health. 2018;34(5):629–38.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Fuchs R, Klaperski S. Stressregulation durch Sport und Bewegung. In: Fuchs R, Gerber M, editors. Handbuch Stressregulation und Sport. Berlin: Springer; 2018. p. 205–26.
Chapter Google Scholar
Kaluza G, Renneberg B. Stressbewältigung. In: Bengel J, Jerusalem M, editors. HandbuchGesundheitspsychologie und medizinische Psychologie. Göttingen: Hogrefe; 2009. p. 265–72.
Klaperski S. Exercise, Stress and Health: The Stress-Buffering Effect of Exercise. In: Fuchs R, Gerber M, editors. Handbuch Stressregulation und Sport. Berlin: Springer; 2018. p. 227–50.
Lesser IA, Nienhuis CP. The impact of COVID-19 on physical activity behavior and well-being of Canadians. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020;17(11):3899.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Moore SA, Faulkner G, Rhodes RE, Brussoni M, Chulak-Bozzer T, Ferguson LJ, et al. Impact of the COVID-19 virus outbreak on movement and play behaviours of Canadian children and youth: a national survey. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act. 2020;17(1):1–11.
Rodríguez-Larrad A, Mañas A, Labayen I, González-Gross M, Espin A, Aznar S, et al. Impact of COVID-19 confinement on physical activity and sedentary behaviour in Spanish university students: Role of gender. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18(2):369.
Stanton R, To QG, Khalesi S, Williams SL, Alley SJ, Thwaite TL, et al. Depression, anxiety and stress during COVID-19: associations with changes in physical activity, sleep, tobacco and alcohol use in Australian adults. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020;17(11):4065.
Zheng C, Huang WY, Sheridan S, Sit CHP, Chen XK, Wong SHS. COVID-19 pandemic brings a sedentary lifestyle in young adults: a cross-sectional and longitudinal study. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020;17(17):6035.
Commodari E. Attention Skills and Risk of Developing Learning Difficulties. Curr Psychol. 2012;31:17–34.
Commodari E, Guarnera M. Attention and reading skills. Percept Mot Skills. 2005;100:3753–86.
Raaijmakers MAJ, Smidts DP, Sergeant JA, Maassen GH, Posthumus JA, van Engeland H, et al. Executive functions in preschool children with aggressive behavior: impairments in inhibitory control. J Abnorm Child Psychol. 2008;36:1097–107.
Vellutino FR, Scanlon DM, Sipay ER, Small SG, Pratt A, Chen RS, et al. Cognitive profiles of difficulty to remediate and readily remediate poor readers: early intervention as a vehicle for distinguishing between cognitive and experiential deficits as basic of specific reading disability. J Educ Psychol. 1996;88:601–38.
Ilies R, Dimotakis N, De Pater IE. Psychological and physiological reactions to high workloads: Implications for well-being. Pers Psychol. 2010;63(2):407–36.
Rodell JB, Judge TA. Can “good” stressors spark “bad” behaviors? The mediating role of emotions in links of challenge and hindrance stressors with citizenship and counterproductive behaviors. J Appl Psychol. 2009;94(6).
Teuber M, Leyhr D, Moll J, Sudeck G. Nudging digital physical activity breaks for home studying of university students—A randomized controlled trial during the COVID-19 pandemic with daily activity measures. Front Sports Active Living. 2022;4.
Feuerhahn N, Sonnentag S, Woll A. Exercise after work, psychological mediators, and affect: A day-level study. Eur J Work Organ Psy. 2014;23(1):62–79.
Sonnentag S. Work, Recovery Activities, ans Individual Well-Being: A Diary Study. J Occup Health Psychol. 2001;6(3):196–210.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Wieland R. Gestaltung gesundheitsförderlicher Arbeitsbedingungen. In: Kleinbeck U, Schmidt K-H, editors. Arbeitspsychologie (Enzyklopädie der Psychologie, Serie Wirtschafts-, Organisations- und Arbeitspsychologie). 1. Göttingen: Hogrefe; 2010. p. 869–919.
Sonnentag S, Fritz C. The Recovery Experience Questionnaire: development and validation of a measure for assessing recuperation and unwinding from work. J Occup Health Psychol. 2007;12(3):204–21.
Bankstahl US, Görtelmeyer R. Measuring subjective complaints of attention and performance failures development and psychometric validation in tinnitus of the self-assessment scale APSA. Health and Quality of Life Outcomes. 2013;11(86).
Teuber M, Arzberger I, Sudeck G. Körperliche Aktivität, Gesundheit und Funktionsfähigkeit im Studium: Sportliche Freizeitaktivitäten und aktive Fortbewegung als Ressource im Studium? In: Göring A, Mayer J, Jetzke M, editors. Sport und Studienerfolg - Analysen zur Bedeutung sportlicher Aktivität im Setting Hochschule. Hochschulsport: Bildung und Wissenschaft, 4. Göttingen: Universitätsverlag Göttingen; 2020. p. 27–49.
Hasselhorn H-M, Freude G. Der Work-Ability-Index: ein Leitfaden In: Arbeitsmedizin BfAu, editor. Dortmund/Berlin/Dresden: Wirtschaftsverl. NW, Verlag für Neue Wissenschaft GmbH; 2007.
Rütten A, Pfeifer K. Nationale Empfehlungen für Bewegung und Bewegungsförderung. Köln: Bundeszentrale für Gesundheitliche Aufklärung (BZgA); 2017.
Brähler E, Mühlan H, Albani C, Schmidt S. Teststatistische Prüfung und Normierung der deutschen Versionen des EUROHIS-QOL Lebensqualität-Index und des WHO-5 Wohlbefindens-Index. Diagnostica. 2007;53(2):83–96.
Gusy B, Wörfel F, Lohmann K. Erschöpfung und Engagement im Studium. Zeitschrift für Gesundheitspsychologie. 2016;24(1):41–53.
Elfering A, Grebner S, de Tribolet-Hardy F. The long arm of time pressure at work: Cognitive failure and commuting near-accidents. Eur J Work Organ Psy. 2013;22(6):737–49.
Kreft IG, de Leeuw J. Introducing multilevel modeling. London: Sage; 1998.
Book Google Scholar
Bates D, Mächler M, Bolker BM, Walker SC. Fitting Linear Mixed-Effects Models Using lme4. J Stat Softw. 2015;67(1):1–48.
Hofmann DA, Gavin MB. Centering decisions in hierarchical linear models: Implications for research in organizations. J Manag. 1998;24(5):623–41.
Nezlek J. Diary Studies in Social and Personality Psychology: An Introduction With Some Recommendations and Suggestions. Social Psychological Bulletin. 2020;15(2).
Knapp G. Gemischte Modelle in R. Begleitskriptum zur Weiterbildung. In: Dortmund TU, editor. Braunschweig2019.
Van Buuren S, Groothuis-Oudshoorn K. mice: Multivariate imputation by chained equations in R. J Stat Softw. 2011;45:1–67.
von Hippel PT. How Many Imputations Do You Need? A Twostage Calculation Using a Quadratic Rule. Sociological Methods & Research. 2020;49(3):699–718.
Article MathSciNet Google Scholar
Robinson D. broom: An R package for converting statistical analysis objects into tidy data frames. arXiv preprint arXiv:14123565. 2014.
Young-Jones A, McCain J, Hart B. Let’s Take a Break: The Impact of Physical Activity on Academic Motivation. Int J Teach Learn High Educ. 2022;33(3):110–8.
Barr-Anderson DJ, AuYoung M, Whitt-Glover MC, Glenn BA, Yancey AK. Integration of short bouts of physical activity into organizational routine: A systematic review of the literature. Am J Prev Med. 2011;40(1):76–93.
Dodd RH, Dadaczynski K, Okan O, McCaffery KJ, Pickles K. Psychological Wellbeing and Academic Experience of University Students in Australia during COVID-19. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2021;18.
Fenesi B, Lucibello K, Kim JA, Heisz JJ. Sweat so you don’t forget: exercise breaks during a university lecture increase on-task attention and learning. J Appl Res Mem Cogn. 2018;7(2):261–9.
Ruhland S, Lange KW. Effect of classroom-based physical activity interventions on attention and on-task behavior in schoolchildren: A systematic review. Sports Med Health Sci. 2021;3:125–33.
Aristovnik A, Keržič D, Ravšelj D, Tomaževič N, Umek L. Impacts of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Life of Higher Education Students: A Global Perspective. Sustainability. 2020;12(20).
Browning MHEM, Larson LR, Sharaievska I, Rigolon A, McAnirlin O, Mullenbach L, et al. Psychological impacts from COVID-19 among university students: Risk factors across seven states in the United States. PLoS ONE 2021;16(1).
Chang Y-K, Labban JD, Gapin JI, Etnier JL. The effects of acute exercise on cognitive performance: a meta-analysis. Brain Res. 2012;1453:87–101.
Elmer T, Mepham K, Stadtfeld C. Students under lockdown: Comparisons of students’ social networks and mental health before and during the COVID-19 crisis in Switzerland. PLoS ONE. 2020;15(7):e0236337.
Keating R, Ahern S, Bisgood L, Mernagh K, Nicolson GH, Barrett EM. Stand up, stand out. Feasibility of an active break targeting prolonged sitting in university students. J Am Coll Health. 2020;70(7).
Download references
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Juliane Moll, research associate of the Student Health Management of University of Tübingen, for the support in the coordination and realization study. We would like to express our thanks also to Ingrid Arzberger, Head of University Sports at the University of Tübingen, for providing the resources and co-applying for the funding. We acknowledge support by Open Access Publishing Fund of University of Tübingen.
Open Access funding enabled and organized by Projekt DEAL. This research regarding the conduction of the study was funded by the Techniker Krankenkasse, health insurance fund.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Institute of Sports Science, Faculty of Economics and Social Sciences, University of Tübingen, Tübingen, Germany
Monika Teuber, Daniel Leyhr & Gorden Sudeck
Methods Center, Faculty of Economics and Social Sciences, University of Tübingen, Tübingen, Germany
Daniel Leyhr
Interfaculty Research Institute for Sports and Physical Activity, University of Tübingen, Tübingen, Germany
Gorden Sudeck
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
M.T. and G.S. designed the study. M.T. coordinated and carried out participant recruitment and data collection. M.T. analyzed the data and M.T. and D.L. interpreted the data. M.T. drafted the initial version of the manuscript and prepared the figure and all tables. All authors contributed to reviewing and editing the manuscript and have read and agreed to the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Monika Teuber .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
The study involves human participants and was reviewed and approved by the Ethics Committee of the Faculty of Social Sciences and Economics, University of Tübingen (ref. A2.54-127_kr). The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study. All methods were carried out in accordance with relevant guidelines and regulations.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Supplementary file 1., supplementary file 2., rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Teuber, M., Leyhr, D. & Sudeck, G. Physical activity improves stress load, recovery, and academic performance-related parameters among university students: a longitudinal study on daily level. BMC Public Health 24 , 598 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-024-18082-z
Download citation
Received : 30 June 2023
Accepted : 12 February 2024
Published : 24 February 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-024-18082-z
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Physical activity breaks
- Stress load
- Psychological detachment
- Academic performance
- Study ability
- University students
BMC Public Health
ISSN: 1471-2458
- General enquiries: [email protected]
Root out friction in every digital experience, super-charge conversion rates, and optimize digital self-service
Uncover insights from any interaction, deliver AI-powered agent coaching, and reduce cost to serve
Increase revenue and loyalty with real-time insights and recommendations delivered to teams on the ground
Know how your people feel and empower managers to improve employee engagement, productivity, and retention
Take action in the moments that matter most along the employee journey and drive bottom line growth
Whatever they’re are saying, wherever they’re saying it, know exactly what’s going on with your people
Get faster, richer insights with qual and quant tools that make powerful market research available to everyone
Run concept tests, pricing studies, prototyping + more with fast, powerful studies designed by UX research experts
Track your brand performance 24/7 and act quickly to respond to opportunities and challenges in your market
Explore the platform powering Experience Management
- Free Account
- For Digital
- For Customer Care
- For Human Resources
- For Researchers
- Financial Services
- All Industries
Popular Use Cases
Customer Experience
Employee Experience
- Net Promoter Score
- Voice of Customer
- Customer Success Hub
- Product Documentation
- Training & Certification
- XM Institute
- Popular Resources
- Customer Stories
- Artificial Intelligence
- Market Research
- Partnerships
- Marketplace
The annual gathering of the experience leaders at the world’s iconic brands building breakthrough business results, live in Salt Lake City.
- English/AU & NZ
- Español/Europa
- Español/América Latina
- Português Brasileiro
- REQUEST DEMO
Best strategy & research books to read in 2024
In a world where staying ahead of the curve is crucial, diving into the right resources can make all the difference. But the big question is of course ‘where do I start?’
Our ebook, 24 Essential Books for Researchers in 2024 , is your go-to list.
24 research books that will help you understand the hallmarks of effective strategy, uncover hidden truths of human behavior through big data, and delve into the creative magic behind branding in everyday life. You will be able to recognize the subtle forces influencing our decisions and unlock the psychology of consumer behavior.
As a sneak peek, here’s everything you need to know about five standout strategy books from our list that will each sharpen your strategic thinking and inspire you to create your own competitive advantage.
Free eBook: 24 Essential Books for Researchers in 2024
1. Good Strategy Bad Strategy: The Difference and Why It Matters

By Richard Rumelt
What better place to start than the fundamental differences between winning and losing strategies?
UCLA professor and revered strategy legend, Richard Rumelt, breaks down the bad strategy elements to avoid, like vague objectives and empty slogans, and the good strategy components to never miss. From a solid diagnosis of the challenge to a guiding policy to tackle it and coherent actions to carry it out – complemented by frameworks from leading minds like Michael Porter – Rumelt wants his reader to understand the core principles of strategic thinking.
Brilliantly complementing these principles – which can, in many ways, be seen as modern extensions of the strategic principles found in "The Art of War" by Sun Tzu, one of the best strategy books in history – Rumelt’s real-life case studies make his approach incredibly easy to grasp.
For market researchers, Rumelt’s framework – focusing on clear, actionable strategies over generic goals – will sharpen your strategic planning and refine your analytical approach. Read it and gain a true understanding of what simply makes a good strategy good and how you can streamline your efforts to achieve tangible, measurable results.
Find it on Amazon
2. Everybody Lies: Big Data, New Data, and What the Internet Can Tell Us About Who We Really Are

By Seth Stephens-Davidowitz
Popularly known as “Everybody Lies”, this New York Times bestseller and the Economist book of the year delves into how big data unveils hidden truths about our behavior and desires.
With his background as a Google data scientist, Stephens-Davidowitz leverages online data from search engines and social media to reveal the often surprising – and sometimes uncomfortable – realities that traditional surveys often miss. It’s a fascinating demonstration of big data’s power to uncover genuine insights about everyday life, from economics to ethics, sports to race, and sex to gender.
Highlighting the potential of non-traditional data sources – specifically, online behavior – to reveal deeper consumer insights, market researchers will find this book to be a true eye-opener. Stephens-Davidowitz details techniques researchers can use to develop more precise and effective marketing strategies that truly resonate with an audience.
3. Alchemy: The Dark Art and Curious Science of Creating Magic in Brands, Business, and Life

By Rory Sutherland
A renowned adman and behavioral science pioneer, Rory Sutherland puts his brilliant mind to print to explore how embracing the irrational and creative aspects of marketing can lead to extraordinary success.
At its core, “Alchemy” argues against businesses and organizations taking a purely logical approach – after all, magic and logic aren’t the greatest match. Instead, Sutherland campaigns for the transformative power of unconventional thinking, using leading-edge scientific research, absurdly entertaining storytelling and practical case studies to bring this approach to life.
With a strong emphasis on creativity and intuition, “Alchemy” should give any market researcher reason to break away from data-driven norms and experiment with bold, unconventional ideas.
4. The Illusion of Choice: 16 ½ Psychological Biases That Influence What We Buy

By Richard Shotton
Another proponent for the importance of psychology and behavioral science in marketing, Richard Shotton’s "The Illusion of Choice" reveals how tiny, unnoticed factors shape our day-to-day decisions.
Shotton identifies the 16½ most important psychological biases that everyone in business needs to be aware of today – and how any business can use them to find a competitive advantage. The book brilliantly blends theory and practical insights, demonstrating to readers how minor tweaks in presentation and context can have a huge bearing on the choices we make.
"The Illusion of Choice" is a goldmine for market researchers. Revealing the psychological tricks behind decision-making, this book will undoubtedly empower you to design better surveys and marketing strategies to ultimately build a more successful company. Shotton's insights will help you predict consumer responses more accurately and craft more persuasive messages; you’ll understand data on a deeper level and learn how to ethically influence consumer behavior.
5. Decoded: The Science Behind Why We Buy

By Phil Barden
Leveraging an over 25-year career in marketing, and working with some of the world’s most successful companies and business leaders, Phil Barden’s groundbreaking book uncovers the psychological mechanisms that drive our purchasing decisions.
Barden draws on neuroscience and behavioral economics to explore why we choose certain products over others, breaking down complex scientific concepts into easy-to-understand insights. With the help of real-world examples, Barden shows how these principles play out in everyday buying behavior with brands that you will no doubt know very well.
Barden’s exploration of the subconscious factors influencing consumer choices provides valuable tools for any market researcher wanting to deliver more effective work. His book’s popularity stems from its practicality: by understanding the science behind why people buy, you can better predict consumer behavior and tailor your approaches to resonate more deeply with your target audience.
If you're a fan of "Blue Ocean Strategy: How to Create Uncontested Market Space and Make the Competition Irrelevant" by W. Chan Kim and Renée Mauborgne, you will get a lot out of this book.
Download your gateway to smarter, more impactful research
Whether you’re enhancing your professional toolkit or seeking fresh perspectives, these strategy books are your gateway to smarter, more impactful research in 2024.
Free eBook: 24 essential books for researchers in 2024
Qualtrics // Experience Management
Qualtrics, the leader and creator of the experience management category, is a cloud-native software platform that empowers organizations to deliver exceptional experiences and build deep relationships with their customers and employees.
With insights from Qualtrics, organizations can identify and resolve the greatest friction points in their business, retain and engage top talent, and bring the right products and services to market. Nearly 20,000 organizations around the world use Qualtrics’ advanced AI to listen, understand, and take action. Qualtrics uses its vast universe of experience data to form the largest database of human sentiment in the world. Qualtrics is co-headquartered in Provo, Utah and Seattle.
Related Articles
May 20, 2024
Improving state government customer experience: Insights from rankings and research analysis
May 13, 2024
X4 2024 Customer Experience Showcase: Strengthening the power of human connection
X4 2024 employee experience showcase: powering the future of work with ai.
Experience Management
X4 2024 Strategy & Research Showcase: Introducing the future of insights generation
May 6, 2024
New innovations for the XM Platform showcased at X4 2024
May 3, 2024
X4 2024: Reimagining human experiences with AI
May 2, 2024
X4 2024: Humanized Intelligence
April 16, 2024
A better way to measure and improve patient access
Stay up to date with the latest xm thought leadership, tips and news., request demo.
Ready to learn more about Qualtrics?

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A case study is an in-depth study of one person, group, or event. In a case study, nearly every aspect of the subject's life and history is analyzed to seek patterns and causes of behavior. Case studies can be used in many different fields, including psychology, medicine, education, anthropology, political science, and social work.
Case studies are in-depth investigations of a person, group, event, or community. Typically, data is gathered from various sources using several methods (e.g., observations & interviews). The case study research method originated in clinical medicine (the case history, i.e., the patient's personal history). In psychology, case studies are ...
One notable example is Freud's study on Little Hans. This case study explored a 5-year-old boy's fear of horses and related it back to Freud's theories about psychosexual stages. Another classic example is Genie Wiley (a pseudonym), a feral child who was subjected to severe social isolation during her early years.
The case study method is an in-depth research strategy focusing on the detailed examination of a specific subject, situation, or group over time. It's employed across various disciplines to narrow broad research fields into manageable topics, enabling researchers to conduct detailed investigations in real-world contexts. This method is characterized by its intensive examination of individual ...
In APA Handbook Of Research Methods In Psychology Vol. 2 Research Designs: Quantitative, Qualitative, Neuropsychological, And Biological (eds Cooper, H. et al.) 633-646 (American Psychological ...
Summary. The case study approach has a rich history in psychology as a method for observing the ways in which individuals may demonstrate abnormal thinking and behavior, for collecting evidence concerning the circumstances and consequences surrounding such disorders, and for providing data to generate and test models of human behavior (see Yin ...
Clinical Case Studies (CCS), peer-reviewed & published bi-monthly electronic only, is the only journal devoted entirely to innovative psychotherapy case studies & presents cases involving individual, couples, & family therapy.The easy-to-follow case presentation format allows you to learn how interesting & challenging cases were assessed & conceptualized, & how treatment followed such ...
Purpose. Case studies are conducted to: Investigate a specific problem, event, or phenomenon. Explore unique or atypical situations. Examine the complexities and intricacies of a subject in its natural context. Develop theories, propositions, or hypotheses for further research. Gain practical insights for decision-making or problem-solving.
A case study is a research method used in psychology to investigate a particular individual, group, or situation in depth. It involves a detailed analysis of the subject, gathering information from various sources such as interviews, observations, and documents. In a case study, researchers aim to understand the complexities and nuances of the ...
The latter components were based on case study guidelines featured in the journal of Pragmatic Case Studies in Psychotherapy as well as components commonly used by published systematic case studies across a variety of other psychotherapy journals (e.g. Psychotherapy Research, Research In Psychotherapy: Psychopathology Process And Outcome, etc ...
It is a method of psychological study that involves the observation and investigation of specific individuals or organizations. It is a type of qualitative research method. A case can be a typical individual, a prominent event, or a representative group (Fig. 1). Founder of the School of Psychoanalysis, Sigmund Freud, applied this method to ...
A case study is one of the most commonly used methodologies of social research. This article attempts to look into the various dimensions of a case study research strategy, the different epistemological strands which determine the particular case study type and approach adopted in the field, discusses the factors which can enhance the effectiveness of a case study research, and the debate ...
Psychology case studies are important because they can help support psychological theories and assist with developing treatments or confirming diagnoses. They can also allow future psychologists to have additional in-depth empirical research to review in order to expand their own case study research.
Kitty Genovese. Sadly, it is not really Kitty Genovese the person who has become one of psychology's classic case studies, but rather the terrible fate that befell her. In 1964 in New York, Genovese was returning home from her job as a bar maid when she was attacked and eventually murdered by Winston Mosely.
Revised on November 20, 2023. A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject, such as a person, group, place, event, organization, or phenomenon. Case studies are commonly used in social, educational, clinical, and business research. A case study research design usually involves qualitative methods, but quantitative methods are ...
Professional Psychology: Research and Practice December 2015 by Jenna T. LeJeune and Jason B. Luoma; Psychotherapists as Gatekeepers: An Evidence-Based Case Study Highlighting the Role and Process of Letter Writing for Transgender Clients (PDF, 76KB) Psychotherapy September 2015 by Stephanie L. Budge
6. Stanford Prison Experiment. One of the most controversial and widely-cited studies in psychology is the Stanford Prison Experiment, conducted by Philip Zimbardo at the basement of the Stanford psychology building in 1971. The hypothesis was that abusive behavior in prisons is influenced by the personality traits of the prisoners and prison ...
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc. Research methods in psychology are systematic procedures used to observe, describe, predict, and explain behavior and mental processes. They include experiments, surveys, case studies, and naturalistic observations, ensuring data collection is objective and reliable to understand and explain psychological phenomena.
Parallel in purpose to the Practice Review articles, I would like to issue an open invitation for authors to submit an Evidence-Based Case Study for possible publication in Psychotherapy.I believe developing such a series of Evidence-Based Case Studies will be extremely useful in several ways.. First, such investigation will provide much needed information to bridge the gap between research ...
Defnition: A case study is a research method that involves an in-depth examination and analysis of a particular phenomenon or case, such as an individual, organization, community, event, or situation. It is a qualitative research approach that aims to provide a detailed and comprehensive understanding of the case being studied.
2 Psychological Research. Introduction; 2.1 Why Is Research Important? 2.2 Approaches to Research; 2.3 Analyzing Findings; ... Discuss the strengths and weaknesses of case studies, naturalistic observation, surveys, and archival research ... In one study, 140 research participants filled out a survey with 10 questions, including questions ...
Sara, a 35-year-old married female. Sara was referred to treatment after having a stillbirth. Sara showed symptoms of grief, or complicated bereavement, and was diagnosed with major depression, recurrent. The clinician recommended interpersonal psychotherapy (IPT) for a duration of 12 weeks. Bleiberg, K.L., & Markowitz, J.C. (2008).
The frustrating part comes at the beginning of the research process when students are attempting to find a topic to work on. There is a lot of floundering around as students get stuck by doing ...
The purpose of this single common case study will be to answer the question, "How does intrinsic motivation and self-determination in the ability to make choices and manage one's behavior guide the implementation of social-emotional teaching practices into the early childhood classroom?" for the participants at Mount Uinta (pseudonym). The theory guiding this study will be Deci and Ryan ...
Physical activity has been proven to be beneficial for physical and psychological health as well as for academic achievement. However, especially university students are insufficiently physically active because of difficulties in time management regarding study, work, and social demands. As they are at a crucial life stage, it is of interest how physical activity affects university students ...
24 research books that will help you understand the hallmarks of effective strategy, uncover hidden truths of human behavior through big data, and delve into the creative magic behind branding in everyday life. You will be able to recognize the subtle forces influencing our decisions and unlock the psychology of consumer behavior.
Kent, S. (1993). Domestic Architecture and the Use of Space: An Interdisciplinary Cross-Cultural Study. Cambridge University Press. Kumar, A. (2005). Vaastu: The Art And Science Of Living: The Art and Sciene of Living. Sterling Publishers Pvt. Ltd. Marc, O. (1975). Psychology of the House. Thames & Hudson. Master Choa Kok Sui. (2006).