
Statistics Made Easy

Decision Rule Calculator
One-tailed or two-tailed hypothesis?
Significance level
Z-statistic or t-statistic?
Decision Rule: fail to reject the null hypothesis
Explanation:
The p-value for a Z-statistic of 1.34 for a two-tailed test is 0.18025 . Since this p-value is greater than 0.05 , we fail to reject the null hypothesis .
Featured Posts

Hey there. My name is Zach Bobbitt. I have a Masters of Science degree in Applied Statistics and I’ve worked on machine learning algorithms for professional businesses in both healthcare and retail. I’m passionate about statistics, machine learning, and data visualization and I created Statology to be a resource for both students and teachers alike. My goal with this site is to help you learn statistics through using simple terms, plenty of real-world examples, and helpful illustrations.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Hypothesis Testing Calculator
Related: confidence interval calculator, type ii error.
The first step in hypothesis testing is to calculate the test statistic. The formula for the test statistic depends on whether the population standard deviation (σ) is known or unknown. If σ is known, our hypothesis test is known as a z test and we use the z distribution. If σ is unknown, our hypothesis test is known as a t test and we use the t distribution. Use of the t distribution relies on the degrees of freedom, which is equal to the sample size minus one. Furthermore, if the population standard deviation σ is unknown, the sample standard deviation s is used instead. To switch from σ known to σ unknown, click on $\boxed{\sigma}$ and select $\boxed{s}$ in the Hypothesis Testing Calculator.
Next, the test statistic is used to conduct the test using either the p-value approach or critical value approach. The particular steps taken in each approach largely depend on the form of the hypothesis test: lower tail, upper tail or two-tailed. The form can easily be identified by looking at the alternative hypothesis (H a ). If there is a less than sign in the alternative hypothesis then it is a lower tail test, greater than sign is an upper tail test and inequality is a two-tailed test. To switch from a lower tail test to an upper tail or two-tailed test, click on $\boxed{\geq}$ and select $\boxed{\leq}$ or $\boxed{=}$, respectively.
In the p-value approach, the test statistic is used to calculate a p-value. If the test is a lower tail test, the p-value is the probability of getting a value for the test statistic at least as small as the value from the sample. If the test is an upper tail test, the p-value is the probability of getting a value for the test statistic at least as large as the value from the sample. In a two-tailed test, the p-value is the probability of getting a value for the test statistic at least as unlikely as the value from the sample.
To test the hypothesis in the p-value approach, compare the p-value to the level of significance. If the p-value is less than or equal to the level of signifance, reject the null hypothesis. If the p-value is greater than the level of significance, do not reject the null hypothesis. This method remains unchanged regardless of whether it's a lower tail, upper tail or two-tailed test. To change the level of significance, click on $\boxed{.05}$. Note that if the test statistic is given, you can calculate the p-value from the test statistic by clicking on the switch symbol twice.
In the critical value approach, the level of significance ($\alpha$) is used to calculate the critical value. In a lower tail test, the critical value is the value of the test statistic providing an area of $\alpha$ in the lower tail of the sampling distribution of the test statistic. In an upper tail test, the critical value is the value of the test statistic providing an area of $\alpha$ in the upper tail of the sampling distribution of the test statistic. In a two-tailed test, the critical values are the values of the test statistic providing areas of $\alpha / 2$ in the lower and upper tail of the sampling distribution of the test statistic.
To test the hypothesis in the critical value approach, compare the critical value to the test statistic. Unlike the p-value approach, the method we use to decide whether to reject the null hypothesis depends on the form of the hypothesis test. In a lower tail test, if the test statistic is less than or equal to the critical value, reject the null hypothesis. In an upper tail test, if the test statistic is greater than or equal to the critical value, reject the null hypothesis. In a two-tailed test, if the test statistic is less than or equal the lower critical value or greater than or equal to the upper critical value, reject the null hypothesis.
When conducting a hypothesis test, there is always a chance that you come to the wrong conclusion. There are two types of errors you can make: Type I Error and Type II Error. A Type I Error is committed if you reject the null hypothesis when the null hypothesis is true. Ideally, we'd like to accept the null hypothesis when the null hypothesis is true. A Type II Error is committed if you accept the null hypothesis when the alternative hypothesis is true. Ideally, we'd like to reject the null hypothesis when the alternative hypothesis is true.
Hypothesis testing is closely related to the statistical area of confidence intervals. If the hypothesized value of the population mean is outside of the confidence interval, we can reject the null hypothesis. Confidence intervals can be found using the Confidence Interval Calculator . The calculator on this page does hypothesis tests for one population mean. Sometimes we're interest in hypothesis tests about two population means. These can be solved using the Two Population Calculator . The probability of a Type II Error can be calculated by clicking on the link at the bottom of the page.
Decision Rule Calculator
One-tailed or two-tailed hypothesis?
Significance level
Z-statistic or t-statistic?
Decision Rule: fail to reject the null hypothesis
Explanation:
The p-value for a Z-statistic of 1.34 for a two-tailed test is 0.18025 . Since this p-value is greater than 0.05 , we fail to reject the null hypothesis .
A Guide to Bartlett’s Test of Sphericity
The four assumptions of linear regression, related posts, sxy calculator for linear regression, sxx calculator for linear regression, two sample z-test calculator, one sample z-test calculator, f-test for equal variances calculator, tolerance interval calculator, area to the right of z-score calculator, area to the left of z-score calculator, x-bar (sample mean) calculator, trimmed mean calculator.
t-test Calculator
Table of contents
Welcome to our t-test calculator! Here you can not only easily perform one-sample t-tests , but also two-sample t-tests , as well as paired t-tests .
Do you prefer to find the p-value from t-test, or would you rather find the t-test critical values? Well, this t-test calculator can do both! 😊
What does a t-test tell you? Take a look at the text below, where we explain what actually gets tested when various types of t-tests are performed. Also, we explain when to use t-tests (in particular, whether to use the z-test vs. t-test) and what assumptions your data should satisfy for the results of a t-test to be valid. If you've ever wanted to know how to do a t-test by hand, we provide the necessary t-test formula, as well as tell you how to determine the number of degrees of freedom in a t-test.
When to use a t-test?
A t-test is one of the most popular statistical tests for location , i.e., it deals with the population(s) mean value(s).
There are different types of t-tests that you can perform:
- A one-sample t-test;
- A two-sample t-test; and
- A paired t-test.
In the next section , we explain when to use which. Remember that a t-test can only be used for one or two groups . If you need to compare three (or more) means, use the analysis of variance ( ANOVA ) method.
The t-test is a parametric test, meaning that your data has to fulfill some assumptions :
- The data points are independent; AND
- The data, at least approximately, follow a normal distribution .
If your sample doesn't fit these assumptions, you can resort to nonparametric alternatives. Visit our Mann–Whitney U test calculator or the Wilcoxon rank-sum test calculator to learn more. Other possibilities include the Wilcoxon signed-rank test or the sign test.
Which t-test?
Your choice of t-test depends on whether you are studying one group or two groups:
One sample t-test
Choose the one-sample t-test to check if the mean of a population is equal to some pre-set hypothesized value .
The average volume of a drink sold in 0.33 l cans — is it really equal to 330 ml?
The average weight of people from a specific city — is it different from the national average?
Two-sample t-test
Choose the two-sample t-test to check if the difference between the means of two populations is equal to some pre-determined value when the two samples have been chosen independently of each other.
In particular, you can use this test to check whether the two groups are different from one another .
The average difference in weight gain in two groups of people: one group was on a high-carb diet and the other on a high-fat diet.
The average difference in the results of a math test from students at two different universities.
This test is sometimes referred to as an independent samples t-test , or an unpaired samples t-test .
Paired t-test
A paired t-test is used to investigate the change in the mean of a population before and after some experimental intervention , based on a paired sample, i.e., when each subject has been measured twice: before and after treatment.
In particular, you can use this test to check whether, on average, the treatment has had any effect on the population .
The change in student test performance before and after taking a course.
The change in blood pressure in patients before and after administering some drug.
How to do a t-test?
So, you've decided which t-test to perform. These next steps will tell you how to calculate the p-value from t-test or its critical values, and then which decision to make about the null hypothesis.
Decide on the alternative hypothesis :
Use a two-tailed t-test if you only care whether the population's mean (or, in the case of two populations, the difference between the populations' means) agrees or disagrees with the pre-set value.
Use a one-tailed t-test if you want to test whether this mean (or difference in means) is greater/less than the pre-set value.
Compute your T-score value :
Formulas for the test statistic in t-tests include the sample size , as well as its mean and standard deviation . The exact formula depends on the t-test type — check the sections dedicated to each particular test for more details.
Determine the degrees of freedom for the t-test:
The degrees of freedom are the number of observations in a sample that are free to vary as we estimate statistical parameters. In the simplest case, the number of degrees of freedom equals your sample size minus the number of parameters you need to estimate . Again, the exact formula depends on the t-test you want to perform — check the sections below for details.
The degrees of freedom are essential, as they determine the distribution followed by your T-score (under the null hypothesis). If there are d degrees of freedom, then the distribution of the test statistics is the t-Student distribution with d degrees of freedom . This distribution has a shape similar to N(0,1) (bell-shaped and symmetric) but has heavier tails . If the number of degrees of freedom is large (>30), which generically happens for large samples, the t-Student distribution is practically indistinguishable from N(0,1).
💡 The t-Student distribution owes its name to William Sealy Gosset, who, in 1908, published his paper on the t-test under the pseudonym "Student". Gosset worked at the famous Guinness Brewery in Dublin, Ireland, and devised the t-test as an economical way to monitor the quality of beer. Cheers! 🍺🍺🍺
p-value from t-test
Recall that the p-value is the probability (calculated under the assumption that the null hypothesis is true) that the test statistic will produce values at least as extreme as the T-score produced for your sample . As probabilities correspond to areas under the density function, p-value from t-test can be nicely illustrated with the help of the following pictures:

The following formulae say how to calculate p-value from t-test. By cdf t,d we denote the cumulative distribution function of the t-Student distribution with d degrees of freedom:
p-value from left-tailed t-test:
p-value = cdf t,d (t score )
p-value from right-tailed t-test:
p-value = 1 − cdf t,d (t score )
p-value from two-tailed t-test:
p-value = 2 × cdf t,d (−|t score |)
or, equivalently: p-value = 2 − 2 × cdf t,d (|t score |)
However, the cdf of the t-distribution is given by a somewhat complicated formula. To find the p-value by hand, you would need to resort to statistical tables, where approximate cdf values are collected, or to specialized statistical software. Fortunately, our t-test calculator determines the p-value from t-test for you in the blink of an eye!
t-test critical values
Recall, that in the critical values approach to hypothesis testing, you need to set a significance level, α, before computing the critical values , which in turn give rise to critical regions (a.k.a. rejection regions).
Formulas for critical values employ the quantile function of t-distribution, i.e., the inverse of the cdf :
Critical value for left-tailed t-test: cdf t,d -1 (α)
critical region:
(-∞, cdf t,d -1 (α)]
Critical value for right-tailed t-test: cdf t,d -1 (1-α)
[cdf t,d -1 (1-α), ∞)
Critical values for two-tailed t-test: ±cdf t,d -1 (1-α/2)
(-∞, -cdf t,d -1 (1-α/2)] ∪ [cdf t,d -1 (1-α/2), ∞)
To decide the fate of the null hypothesis, just check if your T-score lies within the critical region:
If your T-score belongs to the critical region , reject the null hypothesis and accept the alternative hypothesis.
If your T-score is outside the critical region , then you don't have enough evidence to reject the null hypothesis.
How to use our t-test calculator
Choose the type of t-test you wish to perform:
A one-sample t-test (to test the mean of a single group against a hypothesized mean);
A two-sample t-test (to compare the means for two groups); or
A paired t-test (to check how the mean from the same group changes after some intervention).
Two-tailed;
Left-tailed; or
Right-tailed.
This t-test calculator allows you to use either the p-value approach or the critical regions approach to hypothesis testing!
Enter your T-score and the number of degrees of freedom . If you don't know them, provide some data about your sample(s): sample size, mean, and standard deviation, and our t-test calculator will compute the T-score and degrees of freedom for you .
Once all the parameters are present, the p-value, or critical region, will immediately appear underneath the t-test calculator, along with an interpretation!
One-sample t-test
The null hypothesis is that the population mean is equal to some value μ 0 \mu_0 μ 0 .
The alternative hypothesis is that the population mean is:
- different from μ 0 \mu_0 μ 0 ;
- smaller than μ 0 \mu_0 μ 0 ; or
- greater than μ 0 \mu_0 μ 0 .
One-sample t-test formula :
- μ 0 \mu_0 μ 0 — Mean postulated in the null hypothesis;
- n n n — Sample size;
- x ˉ \bar{x} x ˉ — Sample mean; and
- s s s — Sample standard deviation.
Number of degrees of freedom in t-test (one-sample) = n − 1 n-1 n − 1 .
The null hypothesis is that the actual difference between these groups' means, μ 1 \mu_1 μ 1 , and μ 2 \mu_2 μ 2 , is equal to some pre-set value, Δ \Delta Δ .
The alternative hypothesis is that the difference μ 1 − μ 2 \mu_1 - \mu_2 μ 1 − μ 2 is:
- Different from Δ \Delta Δ ;
- Smaller than Δ \Delta Δ ; or
- Greater than Δ \Delta Δ .
In particular, if this pre-determined difference is zero ( Δ = 0 \Delta = 0 Δ = 0 ):
The null hypothesis is that the population means are equal.
The alternate hypothesis is that the population means are:
- μ 1 \mu_1 μ 1 and μ 2 \mu_2 μ 2 are different from one another;
- μ 1 \mu_1 μ 1 is smaller than μ 2 \mu_2 μ 2 ; and
- μ 1 \mu_1 μ 1 is greater than μ 2 \mu_2 μ 2 .
Formally, to perform a t-test, we should additionally assume that the variances of the two populations are equal (this assumption is called the homogeneity of variance ).
There is a version of a t-test that can be applied without the assumption of homogeneity of variance: it is called a Welch's t-test . For your convenience, we describe both versions.
Two-sample t-test if variances are equal
Use this test if you know that the two populations' variances are the same (or very similar).
Two-sample t-test formula (with equal variances) :
where s p s_p s p is the so-called pooled standard deviation , which we compute as:
- Δ \Delta Δ — Mean difference postulated in the null hypothesis;
- n 1 n_1 n 1 — First sample size;
- x ˉ 1 \bar{x}_1 x ˉ 1 — Mean for the first sample;
- s 1 s_1 s 1 — Standard deviation in the first sample;
- n 2 n_2 n 2 — Second sample size;
- x ˉ 2 \bar{x}_2 x ˉ 2 — Mean for the second sample; and
- s 2 s_2 s 2 — Standard deviation in the second sample.
Number of degrees of freedom in t-test (two samples, equal variances) = n 1 + n 2 − 2 n_1 + n_2 - 2 n 1 + n 2 − 2 .
Two-sample t-test if variances are unequal (Welch's t-test)
Use this test if the variances of your populations are different.
Two-sample Welch's t-test formula if variances are unequal:
- s 1 s_1 s 1 — Standard deviation in the first sample;
- s 2 s_2 s 2 — Standard deviation in the second sample.
The number of degrees of freedom in a Welch's t-test (two-sample t-test with unequal variances) is very difficult to count. We can approximate it with the help of the following Satterthwaite formula :
Alternatively, you can take the smaller of n 1 − 1 n_1 - 1 n 1 − 1 and n 2 − 1 n_2 - 1 n 2 − 1 as a conservative estimate for the number of degrees of freedom.
🔎 The Satterthwaite formula for the degrees of freedom can be rewritten as a scaled weighted harmonic mean of the degrees of freedom of the respective samples: n 1 − 1 n_1 - 1 n 1 − 1 and n 2 − 1 n_2 - 1 n 2 − 1 , and the weights are proportional to the standard deviations of the corresponding samples.
As we commonly perform a paired t-test when we have data about the same subjects measured twice (before and after some treatment), let us adopt the convention of referring to the samples as the pre-group and post-group.
The null hypothesis is that the true difference between the means of pre- and post-populations is equal to some pre-set value, Δ \Delta Δ .
The alternative hypothesis is that the actual difference between these means is:
Typically, this pre-determined difference is zero. We can then reformulate the hypotheses as follows:
The null hypothesis is that the pre- and post-means are the same, i.e., the treatment has no impact on the population .
The alternative hypothesis:
- The pre- and post-means are different from one another (treatment has some effect);
- The pre-mean is smaller than the post-mean (treatment increases the result); or
- The pre-mean is greater than the post-mean (treatment decreases the result).
Paired t-test formula
In fact, a paired t-test is technically the same as a one-sample t-test! Let us see why it is so. Let x 1 , . . . , x n x_1, ... , x_n x 1 , ... , x n be the pre observations and y 1 , . . . , y n y_1, ... , y_n y 1 , ... , y n the respective post observations. That is, x i , y i x_i, y_i x i , y i are the before and after measurements of the i -th subject.
For each subject, compute the difference, d i : = x i − y i d_i := x_i - y_i d i := x i − y i . All that happens next is just a one-sample t-test performed on the sample of differences d 1 , . . . , d n d_1, ... , d_n d 1 , ... , d n . Take a look at the formula for the T-score :
Δ \Delta Δ — Mean difference postulated in the null hypothesis;
n n n — Size of the sample of differences, i.e., the number of pairs;
x ˉ \bar{x} x ˉ — Mean of the sample of differences; and
s s s — Standard deviation of the sample of differences.
Number of degrees of freedom in t-test (paired): n − 1 n - 1 n − 1
t-test vs Z-test
We use a Z-test when we want to test the population mean of a normally distributed dataset, which has a known population variance . If the number of degrees of freedom is large, then the t-Student distribution is very close to N(0,1).
Hence, if there are many data points (at least 30), you may swap a t-test for a Z-test, and the results will be almost identical. However, for small samples with unknown variance, remember to use the t-test because, in such cases, the t-Student distribution differs significantly from the N(0,1)!
🙋 Have you concluded you need to perform the z-test? Head straight to our z-test calculator !
What is a t-test?
A t-test is a widely used statistical test that analyzes the means of one or two groups of data. For instance, a t-test is performed on medical data to determine whether a new drug really helps.
What are different types of t-tests?
Different types of t-tests are:
- One-sample t-test;
- Two-sample t-test; and
- Paired t-test.
How to find the t value in a one sample t-test?
To find the t-value:
- Subtract the null hypothesis mean from the sample mean value.
- Divide the difference by the standard deviation of the sample.
- Multiply the resultant with the square root of the sample size.
.css-slt4t3.css-slt4t3{color:#2B3148;background-color:transparent;font-family:"Roboto","Helvetica","Arial",sans-serif;font-size:20px;line-height:24px;overflow:visible;padding-top:0px;position:relative;}.css-slt4t3.css-slt4t3:after{content:'';-webkit-transform:scale(0);-moz-transform:scale(0);-ms-transform:scale(0);transform:scale(0);position:absolute;border:2px solid #EA9430;border-radius:2px;inset:-8px;z-index:1;}.css-slt4t3 .js-external-link-button.link-like,.css-slt4t3 .js-external-link-anchor{color:inherit;border-radius:1px;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;}.css-slt4t3 .js-external-link-button.link-like:hover,.css-slt4t3 .js-external-link-anchor:hover,.css-slt4t3 .js-external-link-button.link-like:active,.css-slt4t3 .js-external-link-anchor:active{text-decoration-thickness:2px;text-shadow:1px 0 0;}.css-slt4t3 .js-external-link-button.link-like:focus-visible,.css-slt4t3 .js-external-link-anchor:focus-visible{outline:transparent 2px dotted;box-shadow:0 0 0 2px #6314E6;}.css-slt4t3 p,.css-slt4t3 div{margin:0px;display:block;}.css-slt4t3 pre{margin:0px;display:block;}.css-slt4t3 pre code{display:block;width:-webkit-fit-content;width:-moz-fit-content;width:fit-content;}.css-slt4t3 pre:not(:first-child){padding-top:8px;}.css-slt4t3 ul,.css-slt4t3 ol{display:block margin:0px;padding-left:20px;}.css-slt4t3 ul li,.css-slt4t3 ol li{padding-top:8px;}.css-slt4t3 ul ul,.css-slt4t3 ol ul,.css-slt4t3 ul ol,.css-slt4t3 ol ol{padding-top:0px;}.css-slt4t3 ul:not(:first-child),.css-slt4t3 ol:not(:first-child){padding-top:4px;} .css-4okk7a{margin:auto;background-color:white;overflow:auto;overflow-wrap:break-word;word-break:break-word;}.css-4okk7a code,.css-4okk7a kbd,.css-4okk7a pre,.css-4okk7a samp{font-family:monospace;}.css-4okk7a code{padding:2px 4px;color:#444;background:#ddd;border-radius:4px;}.css-4okk7a figcaption,.css-4okk7a caption{text-align:center;}.css-4okk7a figcaption{font-size:12px;font-style:italic;overflow:hidden;}.css-4okk7a h3{font-size:1.75rem;}.css-4okk7a h4{font-size:1.5rem;}.css-4okk7a .mathBlock{font-size:24px;-webkit-padding-start:4px;padding-inline-start:4px;}.css-4okk7a .mathBlock .katex{font-size:24px;text-align:left;}.css-4okk7a .math-inline{background-color:#f0f0f0;display:inline-block;font-size:inherit;padding:0 3px;}.css-4okk7a .videoBlock,.css-4okk7a .imageBlock{margin-bottom:16px;}.css-4okk7a .imageBlock__image-align--left,.css-4okk7a .videoBlock__video-align--left{float:left;}.css-4okk7a .imageBlock__image-align--right,.css-4okk7a .videoBlock__video-align--right{float:right;}.css-4okk7a .imageBlock__image-align--center,.css-4okk7a .videoBlock__video-align--center{display:block;margin-left:auto;margin-right:auto;clear:both;}.css-4okk7a .imageBlock__image-align--none,.css-4okk7a .videoBlock__video-align--none{clear:both;margin-left:0;margin-right:0;}.css-4okk7a .videoBlock__video--wrapper{position:relative;padding-bottom:56.25%;height:0;}.css-4okk7a .videoBlock__video--wrapper iframe{position:absolute;top:0;left:0;width:100%;height:100%;}.css-4okk7a .videoBlock__caption{text-align:left;}@font-face{font-family:'KaTeX_AMS';src:url(/katex-fonts/KaTeX_AMS-Regular.woff2) format('woff2'),url(/katex-fonts/KaTeX_AMS-Regular.woff) format('woff'),url(/katex-fonts/KaTeX_AMS-Regular.ttf) format('truetype');font-weight:normal;font-style:normal;}@font-face{font-family:'KaTeX_Caligraphic';src:url(/katex-fonts/KaTeX_Caligraphic-Bold.woff2) format('woff2'),url(/katex-fonts/KaTeX_Caligraphic-Bold.woff) format('woff'),url(/katex-fonts/KaTeX_Caligraphic-Bold.ttf) format('truetype');font-weight:bold;font-style:normal;}@font-face{font-family:'KaTeX_Caligraphic';src:url(/katex-fonts/KaTeX_Caligraphic-Regular.woff2) format('woff2'),url(/katex-fonts/KaTeX_Caligraphic-Regular.woff) format('woff'),url(/katex-fonts/KaTeX_Caligraphic-Regular.ttf) format('truetype');font-weight:normal;font-style:normal;}@font-face{font-family:'KaTeX_Fraktur';src:url(/katex-fonts/KaTeX_Fraktur-Bold.woff2) format('woff2'),url(/katex-fonts/KaTeX_Fraktur-Bold.woff) format('woff'),url(/katex-fonts/KaTeX_Fraktur-Bold.ttf) format('truetype');font-weight:bold;font-style:normal;}@font-face{font-family:'KaTeX_Fraktur';src:url(/katex-fonts/KaTeX_Fraktur-Regular.woff2) format('woff2'),url(/katex-fonts/KaTeX_Fraktur-Regular.woff) format('woff'),url(/katex-fonts/KaTeX_Fraktur-Regular.ttf) format('truetype');font-weight:normal;font-style:normal;}@font-face{font-family:'KaTeX_Main';src:url(/katex-fonts/KaTeX_Main-Bold.woff2) format('woff2'),url(/katex-fonts/KaTeX_Main-Bold.woff) format('woff'),url(/katex-fonts/KaTeX_Main-Bold.ttf) format('truetype');font-weight:bold;font-style:normal;}@font-face{font-family:'KaTeX_Main';src:url(/katex-fonts/KaTeX_Main-BoldItalic.woff2) format('woff2'),url(/katex-fonts/KaTeX_Main-BoldItalic.woff) format('woff'),url(/katex-fonts/KaTeX_Main-BoldItalic.ttf) format('truetype');font-weight:bold;font-style:italic;}@font-face{font-family:'KaTeX_Main';src:url(/katex-fonts/KaTeX_Main-Italic.woff2) format('woff2'),url(/katex-fonts/KaTeX_Main-Italic.woff) format('woff'),url(/katex-fonts/KaTeX_Main-Italic.ttf) format('truetype');font-weight:normal;font-style:italic;}@font-face{font-family:'KaTeX_Main';src:url(/katex-fonts/KaTeX_Main-Regular.woff2) format('woff2'),url(/katex-fonts/KaTeX_Main-Regular.woff) format('woff'),url(/katex-fonts/KaTeX_Main-Regular.ttf) format('truetype');font-weight:normal;font-style:normal;}@font-face{font-family:'KaTeX_Math';src:url(/katex-fonts/KaTeX_Math-BoldItalic.woff2) format('woff2'),url(/katex-fonts/KaTeX_Math-BoldItalic.woff) format('woff'),url(/katex-fonts/KaTeX_Math-BoldItalic.ttf) format('truetype');font-weight:bold;font-style:italic;}@font-face{font-family:'KaTeX_Math';src:url(/katex-fonts/KaTeX_Math-Italic.woff2) format('woff2'),url(/katex-fonts/KaTeX_Math-Italic.woff) format('woff'),url(/katex-fonts/KaTeX_Math-Italic.ttf) format('truetype');font-weight:normal;font-style:italic;}@font-face{font-family:'KaTeX_SansSerif';src:url(/katex-fonts/KaTeX_SansSerif-Bold.woff2) format('woff2'),url(/katex-fonts/KaTeX_SansSerif-Bold.woff) format('woff'),url(/katex-fonts/KaTeX_SansSerif-Bold.ttf) format('truetype');font-weight:bold;font-style:normal;}@font-face{font-family:'KaTeX_SansSerif';src:url(/katex-fonts/KaTeX_SansSerif-Italic.woff2) format('woff2'),url(/katex-fonts/KaTeX_SansSerif-Italic.woff) format('woff'),url(/katex-fonts/KaTeX_SansSerif-Italic.ttf) format('truetype');font-weight:normal;font-style:italic;}@font-face{font-family:'KaTeX_SansSerif';src:url(/katex-fonts/KaTeX_SansSerif-Regular.woff2) format('woff2'),url(/katex-fonts/KaTeX_SansSerif-Regular.woff) format('woff'),url(/katex-fonts/KaTeX_SansSerif-Regular.ttf) format('truetype');font-weight:normal;font-style:normal;}@font-face{font-family:'KaTeX_Script';src:url(/katex-fonts/KaTeX_Script-Regular.woff2) format('woff2'),url(/katex-fonts/KaTeX_Script-Regular.woff) format('woff'),url(/katex-fonts/KaTeX_Script-Regular.ttf) format('truetype');font-weight:normal;font-style:normal;}@font-face{font-family:'KaTeX_Size1';src:url(/katex-fonts/KaTeX_Size1-Regular.woff2) format('woff2'),url(/katex-fonts/KaTeX_Size1-Regular.woff) format('woff'),url(/katex-fonts/KaTeX_Size1-Regular.ttf) format('truetype');font-weight:normal;font-style:normal;}@font-face{font-family:'KaTeX_Size2';src:url(/katex-fonts/KaTeX_Size2-Regular.woff2) format('woff2'),url(/katex-fonts/KaTeX_Size2-Regular.woff) format('woff'),url(/katex-fonts/KaTeX_Size2-Regular.ttf) format('truetype');font-weight:normal;font-style:normal;}@font-face{font-family:'KaTeX_Size3';src:url(/katex-fonts/KaTeX_Size3-Regular.woff2) format('woff2'),url(/katex-fonts/KaTeX_Size3-Regular.woff) format('woff'),url(/katex-fonts/KaTeX_Size3-Regular.ttf) format('truetype');font-weight:normal;font-style:normal;}@font-face{font-family:'KaTeX_Size4';src:url(/katex-fonts/KaTeX_Size4-Regular.woff2) format('woff2'),url(/katex-fonts/KaTeX_Size4-Regular.woff) format('woff'),url(/katex-fonts/KaTeX_Size4-Regular.ttf) format('truetype');font-weight:normal;font-style:normal;}@font-face{font-family:'KaTeX_Typewriter';src:url(/katex-fonts/KaTeX_Typewriter-Regular.woff2) format('woff2'),url(/katex-fonts/KaTeX_Typewriter-Regular.woff) format('woff'),url(/katex-fonts/KaTeX_Typewriter-Regular.ttf) format('truetype');font-weight:normal;font-style:normal;}.css-4okk7a .katex{font:normal 1.21em KaTeX_Main,Times New Roman,serif;line-height:1.2;text-indent:0;text-rendering:auto;}.css-4okk7a .katex *{-ms-high-contrast-adjust:none!important;border-color:currentColor;}.css-4okk7a .katex .katex-version::after{content:'0.13.13';}.css-4okk7a .katex .katex-mathml{position:absolute;clip:rect(1px, 1px, 1px, 1px);padding:0;border:0;height:1px;width:1px;overflow:hidden;}.css-4okk7a .katex .katex-html>.newline{display:block;}.css-4okk7a .katex .base{position:relative;display:inline-block;white-space:nowrap;width:-webkit-min-content;width:-moz-min-content;width:-webkit-min-content;width:-moz-min-content;width:min-content;}.css-4okk7a .katex .strut{display:inline-block;}.css-4okk7a .katex .textbf{font-weight:bold;}.css-4okk7a .katex .textit{font-style:italic;}.css-4okk7a .katex .textrm{font-family:KaTeX_Main;}.css-4okk7a .katex .textsf{font-family:KaTeX_SansSerif;}.css-4okk7a .katex .texttt{font-family:KaTeX_Typewriter;}.css-4okk7a .katex .mathnormal{font-family:KaTeX_Math;font-style:italic;}.css-4okk7a .katex .mathit{font-family:KaTeX_Main;font-style:italic;}.css-4okk7a .katex .mathrm{font-style:normal;}.css-4okk7a .katex .mathbf{font-family:KaTeX_Main;font-weight:bold;}.css-4okk7a .katex .boldsymbol{font-family:KaTeX_Math;font-weight:bold;font-style:italic;}.css-4okk7a .katex .amsrm{font-family:KaTeX_AMS;}.css-4okk7a .katex .mathbb,.css-4okk7a .katex .textbb{font-family:KaTeX_AMS;}.css-4okk7a .katex .mathcal{font-family:KaTeX_Caligraphic;}.css-4okk7a .katex .mathfrak,.css-4okk7a .katex .textfrak{font-family:KaTeX_Fraktur;}.css-4okk7a .katex .mathtt{font-family:KaTeX_Typewriter;}.css-4okk7a .katex .mathscr,.css-4okk7a .katex .textscr{font-family:KaTeX_Script;}.css-4okk7a .katex .mathsf,.css-4okk7a .katex .textsf{font-family:KaTeX_SansSerif;}.css-4okk7a .katex .mathboldsf,.css-4okk7a .katex .textboldsf{font-family:KaTeX_SansSerif;font-weight:bold;}.css-4okk7a .katex .mathitsf,.css-4okk7a .katex .textitsf{font-family:KaTeX_SansSerif;font-style:italic;}.css-4okk7a .katex .mainrm{font-family:KaTeX_Main;font-style:normal;}.css-4okk7a .katex .vlist-t{display:inline-table;table-layout:fixed;border-collapse:collapse;}.css-4okk7a .katex .vlist-r{display:table-row;}.css-4okk7a .katex .vlist{display:table-cell;vertical-align:bottom;position:relative;}.css-4okk7a .katex .vlist>span{display:block;height:0;position:relative;}.css-4okk7a .katex .vlist>span>span{display:inline-block;}.css-4okk7a .katex .vlist>span>.pstrut{overflow:hidden;width:0;}.css-4okk7a .katex .vlist-t2{margin-right:-2px;}.css-4okk7a .katex .vlist-s{display:table-cell;vertical-align:bottom;font-size:1px;width:2px;min-width:2px;}.css-4okk7a .katex .vbox{display:-webkit-inline-box;display:-webkit-inline-flex;display:-ms-inline-flexbox;display:inline-flex;-webkit-flex-direction:column;-ms-flex-direction:column;flex-direction:column;-webkit-align-items:baseline;-webkit-box-align:baseline;-ms-flex-align:baseline;align-items:baseline;}.css-4okk7a .katex .hbox{display:-webkit-inline-box;display:-webkit-inline-flex;display:-ms-inline-flexbox;display:inline-flex;-webkit-flex-direction:row;-ms-flex-direction:row;flex-direction:row;width:100%;}.css-4okk7a .katex .thinbox{display:-webkit-inline-box;display:-webkit-inline-flex;display:-ms-inline-flexbox;display:inline-flex;-webkit-flex-direction:row;-ms-flex-direction:row;flex-direction:row;width:0;max-width:0;}.css-4okk7a .katex .msupsub{text-align:left;}.css-4okk7a .katex .mfrac>span>span{text-align:center;}.css-4okk7a .katex .mfrac .frac-line{display:inline-block;width:100%;border-bottom-style:solid;}.css-4okk7a .katex .mfrac .frac-line,.css-4okk7a .katex .overline .overline-line,.css-4okk7a .katex .underline .underline-line,.css-4okk7a .katex .hline,.css-4okk7a .katex .hdashline,.css-4okk7a .katex .rule{min-height:1px;}.css-4okk7a .katex .mspace{display:inline-block;}.css-4okk7a .katex .llap,.css-4okk7a .katex .rlap,.css-4okk7a .katex .clap{width:0;position:relative;}.css-4okk7a .katex .llap>.inner,.css-4okk7a .katex .rlap>.inner,.css-4okk7a .katex .clap>.inner{position:absolute;}.css-4okk7a .katex .llap>.fix,.css-4okk7a .katex .rlap>.fix,.css-4okk7a .katex .clap>.fix{display:inline-block;}.css-4okk7a .katex .llap>.inner{right:0;}.css-4okk7a .katex .rlap>.inner,.css-4okk7a .katex .clap>.inner{left:0;}.css-4okk7a .katex .clap>.inner>span{margin-left:-50%;margin-right:50%;}.css-4okk7a .katex .rule{display:inline-block;border:solid 0;position:relative;}.css-4okk7a .katex .overline .overline-line,.css-4okk7a .katex .underline .underline-line,.css-4okk7a .katex .hline{display:inline-block;width:100%;border-bottom-style:solid;}.css-4okk7a .katex .hdashline{display:inline-block;width:100%;border-bottom-style:dashed;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sqrt>.root{margin-left:0.27777778em;margin-right:-0.55555556em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size1.size1,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size1.size1{font-size:1em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size1.size2,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size1.size2{font-size:1.2em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size1.size3,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size1.size3{font-size:1.4em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size1.size4,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size1.size4{font-size:1.6em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size1.size5,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size1.size5{font-size:1.8em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size1.size6,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size1.size6{font-size:2em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size1.size7,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size1.size7{font-size:2.4em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size1.size8,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size1.size8{font-size:2.88em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size1.size9,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size1.size9{font-size:3.456em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size1.size10,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size1.size10{font-size:4.148em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size1.size11,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size1.size11{font-size:4.976em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size2.size1,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size2.size1{font-size:0.83333333em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size2.size2,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size2.size2{font-size:1em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size2.size3,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size2.size3{font-size:1.16666667em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size2.size4,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size2.size4{font-size:1.33333333em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size2.size5,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size2.size5{font-size:1.5em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size2.size6,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size2.size6{font-size:1.66666667em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size2.size7,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size2.size7{font-size:2em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size2.size8,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size2.size8{font-size:2.4em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size2.size9,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size2.size9{font-size:2.88em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size2.size10,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size2.size10{font-size:3.45666667em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size2.size11,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size2.size11{font-size:4.14666667em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size3.size1,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size3.size1{font-size:0.71428571em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size3.size2,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size3.size2{font-size:0.85714286em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size3.size3,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size3.size3{font-size:1em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size3.size4,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size3.size4{font-size:1.14285714em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size3.size5,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size3.size5{font-size:1.28571429em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size3.size6,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size3.size6{font-size:1.42857143em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size3.size7,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size3.size7{font-size:1.71428571em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size3.size8,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size3.size8{font-size:2.05714286em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size3.size9,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size3.size9{font-size:2.46857143em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size3.size10,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size3.size10{font-size:2.96285714em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size3.size11,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size3.size11{font-size:3.55428571em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size4.size1,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size4.size1{font-size:0.625em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size4.size2,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size4.size2{font-size:0.75em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size4.size3,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size4.size3{font-size:0.875em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size4.size4,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size4.size4{font-size:1em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size4.size5,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size4.size5{font-size:1.125em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size4.size6,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size4.size6{font-size:1.25em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size4.size7,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size4.size7{font-size:1.5em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size4.size8,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size4.size8{font-size:1.8em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size4.size9,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size4.size9{font-size:2.16em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size4.size10,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size4.size10{font-size:2.5925em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size4.size11,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size4.size11{font-size:3.11em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size5.size1,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size5.size1{font-size:0.55555556em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size5.size2,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size5.size2{font-size:0.66666667em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size5.size3,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size5.size3{font-size:0.77777778em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size5.size4,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size5.size4{font-size:0.88888889em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size5.size5,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size5.size5{font-size:1em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size5.size6,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size5.size6{font-size:1.11111111em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size5.size7,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size5.size7{font-size:1.33333333em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size5.size8,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size5.size8{font-size:1.6em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size5.size9,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size5.size9{font-size:1.92em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size5.size10,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size5.size10{font-size:2.30444444em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size5.size11,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size5.size11{font-size:2.76444444em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size6.size1,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size6.size1{font-size:0.5em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size6.size2,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size6.size2{font-size:0.6em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size6.size3,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size6.size3{font-size:0.7em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size6.size4,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size6.size4{font-size:0.8em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size6.size5,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size6.size5{font-size:0.9em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size6.size6,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size6.size6{font-size:1em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size6.size7,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size6.size7{font-size:1.2em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size6.size8,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size6.size8{font-size:1.44em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size6.size9,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size6.size9{font-size:1.728em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size6.size10,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size6.size10{font-size:2.074em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size6.size11,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size6.size11{font-size:2.488em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size7.size1,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size7.size1{font-size:0.41666667em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size7.size2,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size7.size2{font-size:0.5em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size7.size3,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size7.size3{font-size:0.58333333em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size7.size4,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size7.size4{font-size:0.66666667em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size7.size5,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size7.size5{font-size:0.75em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size7.size6,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size7.size6{font-size:0.83333333em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size7.size7,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size7.size7{font-size:1em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size7.size8,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size7.size8{font-size:1.2em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size7.size9,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size7.size9{font-size:1.44em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size7.size10,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size7.size10{font-size:1.72833333em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size7.size11,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size7.size11{font-size:2.07333333em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size8.size1,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size8.size1{font-size:0.34722222em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size8.size2,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size8.size2{font-size:0.41666667em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size8.size3,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size8.size3{font-size:0.48611111em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size8.size4,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size8.size4{font-size:0.55555556em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size8.size5,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size8.size5{font-size:0.625em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size8.size6,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size8.size6{font-size:0.69444444em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size8.size7,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size8.size7{font-size:0.83333333em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size8.size8,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size8.size8{font-size:1em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size8.size9,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size8.size9{font-size:1.2em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size8.size10,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size8.size10{font-size:1.44027778em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size8.size11,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size8.size11{font-size:1.72777778em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size9.size1,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size9.size1{font-size:0.28935185em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size9.size2,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size9.size2{font-size:0.34722222em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size9.size3,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size9.size3{font-size:0.40509259em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size9.size4,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size9.size4{font-size:0.46296296em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size9.size5,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size9.size5{font-size:0.52083333em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size9.size6,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size9.size6{font-size:0.5787037em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size9.size7,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size9.size7{font-size:0.69444444em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size9.size8,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size9.size8{font-size:0.83333333em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size9.size9,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size9.size9{font-size:1em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size9.size10,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size9.size10{font-size:1.20023148em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size9.size11,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size9.size11{font-size:1.43981481em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size10.size1,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size10.size1{font-size:0.24108004em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size10.size2,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size10.size2{font-size:0.28929605em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size10.size3,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size10.size3{font-size:0.33751205em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size10.size4,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size10.size4{font-size:0.38572806em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size10.size5,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size10.size5{font-size:0.43394407em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size10.size6,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size10.size6{font-size:0.48216008em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size10.size7,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size10.size7{font-size:0.57859209em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size10.size8,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size10.size8{font-size:0.69431051em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size10.size9,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size10.size9{font-size:0.83317261em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size10.size10,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size10.size10{font-size:1em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size10.size11,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size10.size11{font-size:1.19961427em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size11.size1,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size11.size1{font-size:0.20096463em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size11.size2,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size11.size2{font-size:0.24115756em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size11.size3,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size11.size3{font-size:0.28135048em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size11.size4,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size11.size4{font-size:0.32154341em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size11.size5,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size11.size5{font-size:0.36173633em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size11.size6,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size11.size6{font-size:0.40192926em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size11.size7,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size11.size7{font-size:0.48231511em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size11.size8,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size11.size8{font-size:0.57877814em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size11.size9,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size11.size9{font-size:0.69453376em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size11.size10,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size11.size10{font-size:0.83360129em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sizing.reset-size11.size11,.css-4okk7a .katex .fontsize-ensurer.reset-size11.size11{font-size:1em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .delimsizing.size1{font-family:KaTeX_Size1;}.css-4okk7a .katex .delimsizing.size2{font-family:KaTeX_Size2;}.css-4okk7a .katex .delimsizing.size3{font-family:KaTeX_Size3;}.css-4okk7a .katex .delimsizing.size4{font-family:KaTeX_Size4;}.css-4okk7a .katex .delimsizing.mult .delim-size1>span{font-family:KaTeX_Size1;}.css-4okk7a .katex .delimsizing.mult .delim-size4>span{font-family:KaTeX_Size4;}.css-4okk7a .katex .nulldelimiter{display:inline-block;width:0.12em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .delimcenter{position:relative;}.css-4okk7a .katex .op-symbol{position:relative;}.css-4okk7a .katex .op-symbol.small-op{font-family:KaTeX_Size1;}.css-4okk7a .katex .op-symbol.large-op{font-family:KaTeX_Size2;}.css-4okk7a .katex .op-limits>.vlist-t{text-align:center;}.css-4okk7a .katex .accent>.vlist-t{text-align:center;}.css-4okk7a .katex .accent .accent-body{position:relative;}.css-4okk7a .katex .accent .accent-body:not(.accent-full){width:0;}.css-4okk7a .katex .overlay{display:block;}.css-4okk7a .katex .mtable .vertical-separator{display:inline-block;min-width:1px;}.css-4okk7a .katex .mtable .arraycolsep{display:inline-block;}.css-4okk7a .katex .mtable .col-align-c>.vlist-t{text-align:center;}.css-4okk7a .katex .mtable .col-align-l>.vlist-t{text-align:left;}.css-4okk7a .katex .mtable .col-align-r>.vlist-t{text-align:right;}.css-4okk7a .katex .svg-align{text-align:left;}.css-4okk7a .katex svg{display:block;position:absolute;width:100%;height:inherit;fill:currentColor;stroke:currentColor;fill-rule:nonzero;fill-opacity:1;stroke-width:1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke-miterlimit:4;stroke-dasharray:none;stroke-dashoffset:0;stroke-opacity:1;}.css-4okk7a .katex svg path{stroke:none;}.css-4okk7a .katex img{border-style:none;min-width:0;min-height:0;max-width:none;max-height:none;}.css-4okk7a .katex .stretchy{width:100%;display:block;position:relative;overflow:hidden;}.css-4okk7a .katex .stretchy::before,.css-4okk7a .katex .stretchy::after{content:'';}.css-4okk7a .katex .hide-tail{width:100%;position:relative;overflow:hidden;}.css-4okk7a .katex .halfarrow-left{position:absolute;left:0;width:50.2%;overflow:hidden;}.css-4okk7a .katex .halfarrow-right{position:absolute;right:0;width:50.2%;overflow:hidden;}.css-4okk7a .katex .brace-left{position:absolute;left:0;width:25.1%;overflow:hidden;}.css-4okk7a .katex .brace-center{position:absolute;left:25%;width:50%;overflow:hidden;}.css-4okk7a .katex .brace-right{position:absolute;right:0;width:25.1%;overflow:hidden;}.css-4okk7a .katex .x-arrow-pad{padding:0 0.5em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .cd-arrow-pad{padding:0 0.55556em 0 0.27778em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .x-arrow,.css-4okk7a .katex .mover,.css-4okk7a .katex .munder{text-align:center;}.css-4okk7a .katex .boxpad{padding:0 0.3em 0 0.3em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .fbox,.css-4okk7a .katex .fcolorbox{box-sizing:border-box;border:0.04em solid;}.css-4okk7a .katex .cancel-pad{padding:0 0.2em 0 0.2em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .cancel-lap{margin-left:-0.2em;margin-right:-0.2em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .sout{border-bottom-style:solid;border-bottom-width:0.08em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .angl{box-sizing:border-box;border-top:0.049em solid;border-right:0.049em solid;margin-right:0.03889em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .anglpad{padding:0 0.03889em 0 0.03889em;}.css-4okk7a .katex .eqn-num::before{counter-increment:katexEqnNo;content:'(' counter(katexEqnNo) ')';}.css-4okk7a .katex .mml-eqn-num::before{counter-increment:mmlEqnNo;content:'(' counter(mmlEqnNo) ')';}.css-4okk7a .katex .mtr-glue{width:50%;}.css-4okk7a .katex .cd-vert-arrow{display:inline-block;position:relative;}.css-4okk7a .katex .cd-label-left{display:inline-block;position:absolute;right:calc(50% + 0.3em);text-align:left;}.css-4okk7a .katex .cd-label-right{display:inline-block;position:absolute;left:calc(50% + 0.3em);text-align:right;}.css-4okk7a .katex-display{display:block;margin:1em 0;text-align:center;}.css-4okk7a .katex-display>.katex{display:block;white-space:nowrap;}.css-4okk7a .katex-display>.katex>.katex-html{display:block;position:relative;}.css-4okk7a .katex-display>.katex>.katex-html>.tag{position:absolute;right:0;}.css-4okk7a .katex-display.leqno>.katex>.katex-html>.tag{left:0;right:auto;}.css-4okk7a .katex-display.fleqn>.katex{text-align:left;padding-left:2em;}.css-4okk7a body{counter-reset:katexEqnNo mmlEqnNo;}.css-4okk7a table{width:-webkit-max-content;width:-moz-max-content;width:max-content;}.css-4okk7a .tableBlock{max-width:100%;margin-bottom:1rem;overflow-y:scroll;}.css-4okk7a .tableBlock thead,.css-4okk7a .tableBlock thead th{border-bottom:1px solid #333!important;}.css-4okk7a .tableBlock th,.css-4okk7a .tableBlock td{padding:10px;text-align:left;}.css-4okk7a .tableBlock th{font-weight:bold!important;}.css-4okk7a .tableBlock caption{caption-side:bottom;color:#555;font-size:12px;font-style:italic;text-align:center;}.css-4okk7a .tableBlock caption>p{margin:0;}.css-4okk7a .tableBlock th>p,.css-4okk7a .tableBlock td>p{margin:0;}.css-4okk7a .tableBlock [data-background-color='aliceblue']{background-color:#f0f8ff;color:#000;}.css-4okk7a .tableBlock [data-background-color='black']{background-color:#000;color:#fff;}.css-4okk7a .tableBlock [data-background-color='chocolate']{background-color:#d2691e;color:#fff;}.css-4okk7a .tableBlock [data-background-color='cornflowerblue']{background-color:#6495ed;color:#fff;}.css-4okk7a .tableBlock [data-background-color='crimson']{background-color:#dc143c;color:#fff;}.css-4okk7a .tableBlock [data-background-color='darkblue']{background-color:#00008b;color:#fff;}.css-4okk7a .tableBlock [data-background-color='darkseagreen']{background-color:#8fbc8f;color:#000;}.css-4okk7a .tableBlock [data-background-color='deepskyblue']{background-color:#00bfff;color:#000;}.css-4okk7a .tableBlock [data-background-color='gainsboro']{background-color:#dcdcdc;color:#000;}.css-4okk7a .tableBlock [data-background-color='grey']{background-color:#808080;color:#fff;}.css-4okk7a .tableBlock [data-background-color='lemonchiffon']{background-color:#fffacd;color:#000;}.css-4okk7a .tableBlock [data-background-color='lightpink']{background-color:#ffb6c1;color:#000;}.css-4okk7a .tableBlock [data-background-color='lightsalmon']{background-color:#ffa07a;color:#000;}.css-4okk7a .tableBlock [data-background-color='lightskyblue']{background-color:#87cefa;color:#000;}.css-4okk7a .tableBlock [data-background-color='mediumblue']{background-color:#0000cd;color:#fff;}.css-4okk7a .tableBlock [data-background-color='omnigrey']{background-color:#f0f0f0;color:#000;}.css-4okk7a .tableBlock [data-background-color='white']{background-color:#fff;color:#000;}.css-4okk7a .tableBlock [data-text-align='center']{text-align:center;}.css-4okk7a .tableBlock [data-text-align='left']{text-align:left;}.css-4okk7a .tableBlock [data-text-align='right']{text-align:right;}.css-4okk7a .tableBlock [data-vertical-align='bottom']{vertical-align:bottom;}.css-4okk7a .tableBlock [data-vertical-align='middle']{vertical-align:middle;}.css-4okk7a .tableBlock [data-vertical-align='top']{vertical-align:top;}.css-4okk7a .tableBlock__font-size--xxsmall{font-size:10px;}.css-4okk7a .tableBlock__font-size--xsmall{font-size:12px;}.css-4okk7a .tableBlock__font-size--small{font-size:14px;}.css-4okk7a .tableBlock__font-size--large{font-size:18px;}.css-4okk7a .tableBlock__border--some tbody tr:not(:last-child){border-bottom:1px solid #e2e5e7;}.css-4okk7a .tableBlock__border--bordered td,.css-4okk7a .tableBlock__border--bordered th{border:1px solid #e2e5e7;}.css-4okk7a .tableBlock__border--borderless tbody+tbody,.css-4okk7a .tableBlock__border--borderless td,.css-4okk7a .tableBlock__border--borderless th,.css-4okk7a .tableBlock__border--borderless tr,.css-4okk7a .tableBlock__border--borderless thead,.css-4okk7a .tableBlock__border--borderless thead th{border:0!important;}.css-4okk7a .tableBlock:not(.tableBlock__table-striped) tbody tr{background-color:unset!important;}.css-4okk7a .tableBlock__table-striped tbody tr:nth-of-type(odd){background-color:#f9fafc!important;}.css-4okk7a .tableBlock__table-compactl th,.css-4okk7a .tableBlock__table-compact td{padding:3px!important;}.css-4okk7a .tableBlock__full-size{width:100%;}.css-4okk7a .textBlock{margin-bottom:16px;}.css-4okk7a .textBlock__text-formatting--finePrint{font-size:12px;}.css-4okk7a .textBlock__text-infoBox{padding:0.75rem 1.25rem;margin-bottom:1rem;border:1px solid transparent;border-radius:0.25rem;}.css-4okk7a .textBlock__text-infoBox p{margin:0;}.css-4okk7a .textBlock__text-infoBox--primary{background-color:#cce5ff;border-color:#b8daff;color:#004085;}.css-4okk7a .textBlock__text-infoBox--secondary{background-color:#e2e3e5;border-color:#d6d8db;color:#383d41;}.css-4okk7a .textBlock__text-infoBox--success{background-color:#d4edda;border-color:#c3e6cb;color:#155724;}.css-4okk7a .textBlock__text-infoBox--danger{background-color:#f8d7da;border-color:#f5c6cb;color:#721c24;}.css-4okk7a .textBlock__text-infoBox--warning{background-color:#fff3cd;border-color:#ffeeba;color:#856404;}.css-4okk7a .textBlock__text-infoBox--info{background-color:#d1ecf1;border-color:#bee5eb;color:#0c5460;}.css-4okk7a .textBlock__text-infoBox--dark{background-color:#d6d8d9;border-color:#c6c8ca;color:#1b1e21;}.css-4okk7a .text-overline{-webkit-text-decoration:overline;text-decoration:overline;}.css-4okk7a.css-4okk7a{color:#2B3148;background-color:transparent;font-family:"Roboto","Helvetica","Arial",sans-serif;font-size:20px;line-height:24px;overflow:visible;padding-top:0px;position:relative;}.css-4okk7a.css-4okk7a:after{content:'';-webkit-transform:scale(0);-moz-transform:scale(0);-ms-transform:scale(0);transform:scale(0);position:absolute;border:2px solid #EA9430;border-radius:2px;inset:-8px;z-index:1;}.css-4okk7a .js-external-link-button.link-like,.css-4okk7a .js-external-link-anchor{color:inherit;border-radius:1px;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;}.css-4okk7a .js-external-link-button.link-like:hover,.css-4okk7a .js-external-link-anchor:hover,.css-4okk7a .js-external-link-button.link-like:active,.css-4okk7a .js-external-link-anchor:active{text-decoration-thickness:2px;text-shadow:1px 0 0;}.css-4okk7a .js-external-link-button.link-like:focus-visible,.css-4okk7a .js-external-link-anchor:focus-visible{outline:transparent 2px dotted;box-shadow:0 0 0 2px #6314E6;}.css-4okk7a p,.css-4okk7a div{margin:0px;display:block;}.css-4okk7a pre{margin:0px;display:block;}.css-4okk7a pre code{display:block;width:-webkit-fit-content;width:-moz-fit-content;width:fit-content;}.css-4okk7a pre:not(:first-child){padding-top:8px;}.css-4okk7a ul,.css-4okk7a ol{display:block margin:0px;padding-left:20px;}.css-4okk7a ul li,.css-4okk7a ol li{padding-top:8px;}.css-4okk7a ul ul,.css-4okk7a ol ul,.css-4okk7a ul ol,.css-4okk7a ol ol{padding-top:0px;}.css-4okk7a ul:not(:first-child),.css-4okk7a ol:not(:first-child){padding-top:4px;} Test setup
Choose test type
t-test for the population mean, μ, based on one independent sample . Null hypothesis H 0 : μ = μ 0
Alternative hypothesis H 1
Test details
Significance level α
The probability that we reject a true H 0 (type I error).
Degrees of freedom
Calculated as sample size minus one.
Test results

- Calculators
- Member Login
Copyright © 2024 All Rights Reserved. Made by 🐒cibey with ❤️
Hypothesis Testing Calculator
Understanding Hypothesis Testing: A Guide to the Hypothesis Testing Calculator
Hypothesis testing is a crucial statistical method used to make informed decisions about data and draw conclusions. Whether you’re a student, researcher, or professional, a Hypothesis Testing Calculator can be an invaluable tool in your statistical toolkit. Let’s explore what hypothesis testing is and how this calculator can assist you:
Hypothesis Testing Basics:
- Null Hypothesis (H0): This is the default assumption or claim that there is no significant difference or effect. It’s often denoted as H0.
- Alternative Hypothesis (Ha): This is the statement that contradicts the null hypothesis. It suggests that there is a significant difference or effect. It’s denoted as Ha.
- Significance Level (α): This is the predetermined threshold (e.g., 0.05 or 5%) used to determine statistical significance. If the calculated p-value is less than α, you reject the null hypothesis.
- p-value: This is the probability of observing the results (or more extreme results) if the null hypothesis is true. A small p-value suggests that the results are unlikely under the null hypothesis.
Key Features of the Hypothesis Testing Calculator:
- Input Parameters: The calculator typically requires you to input sample data, choose the type of test (e.g., t-test, chi-square test), specify the null and alternative hypotheses, and set the significance level.
- Calculations: Once you input the data and parameters, the calculator performs the necessary statistical tests and calculations. It generates results such as the test statistic, degrees of freedom, and the p-value.
- Interpretation: Based on the results, the calculator helps you determine whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis. It provides an interpretation of the findings, which is crucial for drawing conclusions.
- Visual Representation: Some calculators may offer visual aids like graphs or charts to help you better understand the data distribution and test results.
Significance of the Hypothesis Testing Calculator:
- Scientific Research: Researchers across various fields use hypothesis testing to validate their hypotheses and draw meaningful conclusions from data.
- Quality Control: Industries use hypothesis testing to ensure the quality and consistency of products and processes.
- Medical Studies: In medical research, hypothesis testing helps assess the effectiveness of treatments or interventions.
- Academics: Students and educators use hypothesis testing to teach and learn statistical concepts and conduct experiments.
- Data-Driven Decisions: Businesses use hypothesis testing to make data-driven decisions, such as whether to launch a new product based on market research.
Conclusion:
The Hypothesis Testing Calculator is a powerful tool that simplifies complex statistical analysis and enables data-driven decision-making. Whether you’re conducting experiments, analyzing survey data, or performing quality control, understanding hypothesis testing and using this calculator can help you make informed choices and contribute to evidence-based research and decision-making.
More Tools:
- RGB to RGBA Color Converter
- Mean, Median, Mode Calculator
- T-Test Calculator
- Sampling Calculator
- Hex to HSLA Color Converter
- RGB to HSLA Color Converter
- Body Fat Percentage Calculator (Navy Method)
Sign in to your account
Username or Email Address
Remember Me
mounthnails.com
Calculating the Null Hypothesis in Statistical Analysis
In the realm of statistical analysis, the null hypothesis plays a pivotal role in testing the validity of a research claim. It serves as a foundation for drawing meaningful conclusions from experimental data. This article aims to provide a friendly and comprehensive guide to understanding the concept of the null hypothesis and its calculation.
The null hypothesis, often denoted as H0, represents the default assumption in a statistical test. It posits that there is no significant difference between the observed data and the expected outcome under the assumption that the research claim is false.
With this conceptual understanding in place, let’s delve into the steps involved in calculating the null hypothesis:
Null Hypothesis Calculation
To calculate the null hypothesis, follow these steps:
Define the research question.
State the null hypothesis., select a significance level., calculate the test statistic..
- Determine the critical value.
Make a decision.
Interpret the results., draw conclusions..
Remember, the null hypothesis is a starting point for statistical analysis. Its rejection or acceptance helps researchers make informed decisions about the validity of their claims.
The research question is the foundation of any statistical analysis. It is a clear and concise statement of the problem or issue you are investigating. A well-defined research question will help you to:
- Focus your research.
- Identify the relevant data.
- Choose the appropriate statistical tests.
- Interpret your results.
When defining your research question, keep the following in mind:
- Make it specific. Avoid broad or general questions that cannot be easily tested.
- Make it measurable. Your research question should be able to be answered with data.
- Make it relevant. Your research question should be of interest to your audience and have real-world implications.
Once you have defined your research question, you can begin to develop your null hypothesis.
The null hypothesis is a statement that there is no significant difference between the observed data and the expected outcome under the assumption that the research claim is false. In other words, the null hypothesis is the default position that you are trying to disprove.
- Use precise language. The null hypothesis should be stated clearly and concisely, using precise and unambiguous language.
- Make it testable. The null hypothesis should be able to be tested with the data that you have collected.
- Make it falsifiable. The null hypothesis should be capable of being proven false. If the null hypothesis cannot be falsified, then it is not a useful hypothesis.
- Use the appropriate statistical notation. The null hypothesis is typically denoted by the symbol H0.
Once you have stated your null hypothesis, you can begin to select a significance level.
The significance level is the probability of rejecting the null hypothesis when it is actually true. In other words, it is the risk of making a Type I error.
- Choose a small significance level. A smaller significance level means that you are less likely to reject the null hypothesis when it is actually true. However, a smaller significance level also means that you are more likely to fail to reject the null hypothesis when it is actually false (Type II error).
- Consider the consequences of making a Type I or Type II error. The consequences of making a Type I error (rejecting the null hypothesis when it is actually true) and a Type II error (failing to reject the null hypothesis when it is actually false) should be considered when selecting a significance level.
- Use a standard significance level. In many cases, a significance level of 0.05 is used. This means that there is a 5% chance of rejecting the null hypothesis when it is actually true.
- Be consistent with your significance level. Once you have selected a significance level, use it consistently throughout your analysis.
After you have selected a significance level, you can begin to calculate the test statistic.
The test statistic is a measure of how far the observed data is from what would be expected under the null hypothesis. The test statistic is used to determine whether the null hypothesis should be rejected.
- Choose the appropriate test statistic. The appropriate test statistic depends on the type of data you have and the research question you are investigating.
- Calculate the test statistic. The formula for calculating the test statistic will vary depending on the test statistic you have chosen.
- Interpret the test statistic. The test statistic will tell you how far the observed data is from what would be expected under the null hypothesis. A large test statistic means that the observed data is very different from what would be expected under the null hypothesis.
- Compare the test statistic to the critical value. The critical value is the value of the test statistic that corresponds to the significance level you have chosen. If the test statistic is greater than the critical value, then the null hypothesis is rejected.
After you have calculated the test statistic, you can make a decision about whether to reject the null hypothesis.
� the critical value.
The critical value is the value of the test statistic that corresponds to the significance level you have chosen. If the test statistic is greater than the critical value, then the null hypothesis is rejected.
The critical value is determined by the distribution of the test statistic under the assumption that the null hypothesis is true. The distribution of the test statistic depends on the type of test statistic you have chosen.
For example, if you are using a z-test, the critical value is ±1.96 for a significance level of 0.05. This means that if the absolute value of the test statistic is greater than 1.96, then the null hypothesis is rejected.
You can find the critical value for a given test statistic and significance level in a table of critical values. These tables are available in most statistics textbooks and online.
Once you have found the critical value, you can compare it to the test statistic to make a decision about whether to reject the null hypothesis.
After you have compared the test statistic to the critical value, you can make a decision about whether to reject the null hypothesis.
If the test statistic is greater than the critical value, then the null hypothesis is rejected. This means that there is sufficient evidence to conclude that the research claim is true.
If the test statistic is less than or equal to the critical value, then the null hypothesis is not rejected. This means that there is not sufficient evidence to conclude that the research claim is true. However, it is important to note that this does not mean that the research claim is false. It simply means that there is not enough evidence to support it.
When making a decision about whether to reject the null hypothesis, it is important to consider the consequences of making a Type I or Type II error.
A Type I error is rejecting the null hypothesis when it is actually true. A Type II error is failing to reject the null hypothesis when it is actually false.
After you have made a decision about whether to reject the null hypothesis, you need to interpret the results of your analysis.
- Consider the practical significance of the results. Even if the results are statistically significant, they may not be practically significant. In other words, the effect size may be too small to be of any real-world importance.
- Replicate the study. If possible, replicate the study with a different sample. This will help to ensure that the results are reliable.
- Consider alternative explanations for the results. Are there any other factors that could explain the results? For example, if you are studying the effect of a new drug, could the results be due to the placebo effect?
- Be cautious about generalizing the results. The results of your study may not be generalizable to other populations or settings.
Interpreting the results of a statistical analysis can be complex. It is important to consult with a statistician or other expert if you are unsure about how to interpret the results.
The final step in the process of calculating the null hypothesis is to draw conclusions based on the results of your analysis.
- Summarize the results of your analysis. Briefly summarize the key findings of your study.
- State your conclusions. Based on the results of your analysis, state your conclusions about the research question.
- Discuss the implications of your conclusions. What are the implications of your conclusions for theory and practice?
- Make recommendations for future research. Based on the results of your study, what are the next steps for research in this area?
Drawing conclusions from a statistical analysis can be challenging. It is important to be careful not to overinterpret the results or to make claims that are not supported by the data.
Here are some frequently asked questions about calculators:
Question 1: What is a calculator?
Answer 1: A calculator is an electronic device that performs arithmetic operations. Calculators can be used to perform basic operations such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division, as well as more complex operations such as percentages, exponents, and trigonometry.
Question 2: What are the different types of calculators?
Answer 2: There are many different types of calculators available, including:
- Basic calculators: These calculators can perform basic arithmetic operations.
- Scientific calculators: These calculators can perform more complex operations, such as percentages, exponents, and trigonometry.
- Graphing calculators: These calculators can graph functions and equations.
- Financial calculators: These calculators are designed to perform financial calculations, such as loan payments and compound interest.
Question 3: How do I use a calculator?
Answer 3: The instructions for using a calculator will vary depending on the type of calculator you have. However, most calculators have a similar layout. The keys are typically arranged in a grid, with the numbers 0-9 along the bottom row. The arithmetic operators (+, -, x, and ÷) are typically located in the middle of the keyboard.
(continue with three more questions and answers)
Closing Paragraph for FAQ
Calculators can be a valuable tool for students, professionals, and anyone who needs to perform mathematical calculations. By understanding the different types of calculators available and how to use them, you can make the most of this powerful tool.
Here are some additional tips for using a calculator:
Here are a few tips for using a calculator effectively:
Tip 1: Use the right calculator for the job.
There are many different types of calculators available, so it is important to choose the one that is right for your needs. If you only need to perform basic arithmetic operations, then a basic calculator will suffice. However, if you need to perform more complex calculations, such as percentages, exponents, or trigonometry, then you will need a scientific calculator.
Tip 2: Learn the basics of calculator operation.
Most calculators have a similar layout, with the numbers 0-9 along the bottom row and the arithmetic operators (+, -, x, and ÷) in the middle of the keyboard. However, some calculators may have additional features, such as a memory function or a graphing function. It is important to learn the basics of calculator operation before you start using it.
Tip 3: Use parentheses to group operations.
Parentheses can be used to group operations together and to specify the order in which they should be performed. This is especially important when you are performing complex calculations. For example, if you want to calculate the expression (2 + 3) x 4, you would enter the following into your calculator: (2 + 3) x 4. This will ensure that the addition operation is performed before the multiplication operation.
(continue with two more tips)
Closing Paragraph for Tips
By following these tips, you can use your calculator effectively and efficiently. Calculators can be a valuable tool for students, professionals, and anyone who needs to perform mathematical calculations.
With a little practice, you can become a proficient calculator user.
Summary of Main Points
Calculators are electronic devices that perform arithmetic operations. They can be used to perform basic operations such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division, as well as more complex operations such as percentages, exponents, and trigonometry.
There are many different types of calculators available, including basic calculators, scientific calculators, graphing calculators, and financial calculators. It is important to choose the right calculator for the job.
To use a calculator effectively, it is important to learn the basics of calculator operation. This includes understanding the layout of the calculator and how to use the different functions.
Closing Message
Images References :

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

9.1: Null and Alternative Hypotheses
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 23459

The actual test begins by considering two hypotheses . They are called the null hypothesis and the alternative hypothesis . These hypotheses contain opposing viewpoints.
\(H_0\): The null hypothesis: It is a statement of no difference between the variables—they are not related. This can often be considered the status quo and as a result if you cannot accept the null it requires some action.
\(H_a\): The alternative hypothesis: It is a claim about the population that is contradictory to \(H_0\) and what we conclude when we reject \(H_0\). This is usually what the researcher is trying to prove.
Since the null and alternative hypotheses are contradictory, you must examine evidence to decide if you have enough evidence to reject the null hypothesis or not. The evidence is in the form of sample data.
After you have determined which hypothesis the sample supports, you make a decision. There are two options for a decision. They are "reject \(H_0\)" if the sample information favors the alternative hypothesis or "do not reject \(H_0\)" or "decline to reject \(H_0\)" if the sample information is insufficient to reject the null hypothesis.
\(H_{0}\) always has a symbol with an equal in it. \(H_{a}\) never has a symbol with an equal in it. The choice of symbol depends on the wording of the hypothesis test. However, be aware that many researchers (including one of the co-authors in research work) use = in the null hypothesis, even with > or < as the symbol in the alternative hypothesis. This practice is acceptable because we only make the decision to reject or not reject the null hypothesis.
Example \(\PageIndex{1}\)
- \(H_{0}\): No more than 30% of the registered voters in Santa Clara County voted in the primary election. \(p \leq 30\)
- \(H_{a}\): More than 30% of the registered voters in Santa Clara County voted in the primary election. \(p > 30\)
Exercise \(\PageIndex{1}\)
A medical trial is conducted to test whether or not a new medicine reduces cholesterol by 25%. State the null and alternative hypotheses.
- \(H_{0}\): The drug reduces cholesterol by 25%. \(p = 0.25\)
- \(H_{a}\): The drug does not reduce cholesterol by 25%. \(p \neq 0.25\)
Example \(\PageIndex{2}\)
We want to test whether the mean GPA of students in American colleges is different from 2.0 (out of 4.0). The null and alternative hypotheses are:
- \(H_{0}: \mu = 2.0\)
- \(H_{a}: \mu \neq 2.0\)
Exercise \(\PageIndex{2}\)
We want to test whether the mean height of eighth graders is 66 inches. State the null and alternative hypotheses. Fill in the correct symbol \((=, \neq, \geq, <, \leq, >)\) for the null and alternative hypotheses.
- \(H_{0}: \mu \_ 66\)
- \(H_{a}: \mu \_ 66\)
- \(H_{0}: \mu = 66\)
- \(H_{a}: \mu \neq 66\)
Example \(\PageIndex{3}\)
We want to test if college students take less than five years to graduate from college, on the average. The null and alternative hypotheses are:
- \(H_{0}: \mu \geq 5\)
- \(H_{a}: \mu < 5\)
Exercise \(\PageIndex{3}\)
We want to test if it takes fewer than 45 minutes to teach a lesson plan. State the null and alternative hypotheses. Fill in the correct symbol ( =, ≠, ≥, <, ≤, >) for the null and alternative hypotheses.
- \(H_{0}: \mu \_ 45\)
- \(H_{a}: \mu \_ 45\)
- \(H_{0}: \mu \geq 45\)
- \(H_{a}: \mu < 45\)
Example \(\PageIndex{4}\)
In an issue of U. S. News and World Report , an article on school standards stated that about half of all students in France, Germany, and Israel take advanced placement exams and a third pass. The same article stated that 6.6% of U.S. students take advanced placement exams and 4.4% pass. Test if the percentage of U.S. students who take advanced placement exams is more than 6.6%. State the null and alternative hypotheses.
- \(H_{0}: p \leq 0.066\)
- \(H_{a}: p > 0.066\)
Exercise \(\PageIndex{4}\)
On a state driver’s test, about 40% pass the test on the first try. We want to test if more than 40% pass on the first try. Fill in the correct symbol (\(=, \neq, \geq, <, \leq, >\)) for the null and alternative hypotheses.
- \(H_{0}: p \_ 0.40\)
- \(H_{a}: p \_ 0.40\)
- \(H_{0}: p = 0.40\)
- \(H_{a}: p > 0.40\)
COLLABORATIVE EXERCISE
Bring to class a newspaper, some news magazines, and some Internet articles . In groups, find articles from which your group can write null and alternative hypotheses. Discuss your hypotheses with the rest of the class.
In a hypothesis test , sample data is evaluated in order to arrive at a decision about some type of claim. If certain conditions about the sample are satisfied, then the claim can be evaluated for a population. In a hypothesis test, we:
- Evaluate the null hypothesis , typically denoted with \(H_{0}\). The null is not rejected unless the hypothesis test shows otherwise. The null statement must always contain some form of equality \((=, \leq \text{or} \geq)\)
- Always write the alternative hypothesis , typically denoted with \(H_{a}\) or \(H_{1}\), using less than, greater than, or not equals symbols, i.e., \((\neq, >, \text{or} <)\).
- If we reject the null hypothesis, then we can assume there is enough evidence to support the alternative hypothesis.
- Never state that a claim is proven true or false. Keep in mind the underlying fact that hypothesis testing is based on probability laws; therefore, we can talk only in terms of non-absolute certainties.
9.1 Null and Alternative Hypotheses
The actual test begins by considering two hypotheses . They are called the null hypothesis and the alternative hypothesis . These hypotheses contain opposing viewpoints.
H 0 , the — null hypothesis: a statement of no difference between sample means or proportions or no difference between a sample mean or proportion and a population mean or proportion. In other words, the difference equals 0.
H a —, the alternative hypothesis: a claim about the population that is contradictory to H 0 and what we conclude when we reject H 0 .
Since the null and alternative hypotheses are contradictory, you must examine evidence to decide if you have enough evidence to reject the null hypothesis or not. The evidence is in the form of sample data.
After you have determined which hypothesis the sample supports, you make a decision. There are two options for a decision. They are reject H 0 if the sample information favors the alternative hypothesis or do not reject H 0 or decline to reject H 0 if the sample information is insufficient to reject the null hypothesis.
Mathematical Symbols Used in H 0 and H a :
H 0 always has a symbol with an equal in it. H a never has a symbol with an equal in it. The choice of symbol depends on the wording of the hypothesis test. However, be aware that many researchers use = in the null hypothesis, even with > or < as the symbol in the alternative hypothesis. This practice is acceptable because we only make the decision to reject or not reject the null hypothesis.
Example 9.1
H 0 : No more than 30 percent of the registered voters in Santa Clara County voted in the primary election. p ≤ 30 H a : More than 30 percent of the registered voters in Santa Clara County voted in the primary election. p > 30
A medical trial is conducted to test whether or not a new medicine reduces cholesterol by 25 percent. State the null and alternative hypotheses.
Example 9.2
We want to test whether the mean GPA of students in American colleges is different from 2.0 (out of 4.0). The null and alternative hypotheses are the following: H 0 : μ = 2.0 H a : μ ≠ 2.0
We want to test whether the mean height of eighth graders is 66 inches. State the null and alternative hypotheses. Fill in the correct symbol (=, ≠, ≥, <, ≤, >) for the null and alternative hypotheses.
- H 0 : μ __ 66
- H a : μ __ 66
Example 9.3
We want to test if college students take fewer than five years to graduate from college, on the average. The null and alternative hypotheses are the following: H 0 : μ ≥ 5 H a : μ < 5
We want to test if it takes fewer than 45 minutes to teach a lesson plan. State the null and alternative hypotheses. Fill in the correct symbol ( =, ≠, ≥, <, ≤, >) for the null and alternative hypotheses.
- H 0 : μ __ 45
- H a : μ __ 45
Example 9.4
An article on school standards stated that about half of all students in France, Germany, and Israel take advanced placement exams and a third of the students pass. The same article stated that 6.6 percent of U.S. students take advanced placement exams and 4.4 percent pass. Test if the percentage of U.S. students who take advanced placement exams is more than 6.6 percent. State the null and alternative hypotheses. H 0 : p ≤ 0.066 H a : p > 0.066
On a state driver’s test, about 40 percent pass the test on the first try. We want to test if more than 40 percent pass on the first try. Fill in the correct symbol (=, ≠, ≥, <, ≤, >) for the null and alternative hypotheses.
- H 0 : p __ 0.40
- H a : p __ 0.40
Collaborative Exercise
Bring to class a newspaper, some news magazines, and some internet articles. In groups, find articles from which your group can write null and alternative hypotheses. Discuss your hypotheses with the rest of the class.
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute Texas Education Agency (TEA). The original material is available at: https://www.texasgateway.org/book/tea-statistics . Changes were made to the original material, including updates to art, structure, and other content updates.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/statistics/pages/1-introduction
- Authors: Barbara Illowsky, Susan Dean
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Statistics
- Publication date: Mar 27, 2020
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/statistics/pages/1-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/statistics/pages/9-1-null-and-alternative-hypotheses
© Jan 23, 2024 Texas Education Agency (TEA). The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.

Hypothesis Testing Calculator
Understanding Hypothesis Testing: A Guide to the Hypothesis Testing Calculator
Hypothesis testing is a crucial statistical method used to make informed decisions about data and draw conclusions. Whether you’re a student, researcher, or professional, a Hypothesis Testing Calculator can be an invaluable tool in your statistical toolkit. Let’s explore what hypothesis testing is and how this calculator can assist you:
Hypothesis Testing Basics:
- Null Hypothesis (H0): This is the default assumption or claim that there is no significant difference or effect. It’s often denoted as H0.
- Alternative Hypothesis (Ha): This is the statement that contradicts the null hypothesis. It suggests that there is a significant difference or effect. It’s denoted as Ha.
- Significance Level (α): This is the predetermined threshold (e.g., 0.05 or 5%) used to determine statistical significance. If the calculated p-value is less than α, you reject the null hypothesis.
- p-value: This is the probability of observing the results (or more extreme results) if the null hypothesis is true. A small p-value suggests that the results are unlikely under the null hypothesis.
Key Features of the Hypothesis Testing Calculator:
- Input Parameters: The calculator typically requires you to input sample data, choose the type of test (e.g., t-test, chi-square test), specify the null and alternative hypotheses, and set the significance level.
- Calculations: Once you input the data and parameters, the calculator performs the necessary statistical tests and calculations. It generates results such as the test statistic, degrees of freedom, and the p-value.
- Interpretation: Based on the results, the calculator helps you determine whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis. It provides an interpretation of the findings, which is crucial for drawing conclusions.
- Visual Representation: Some calculators may offer visual aids like graphs or charts to help you better understand the data distribution and test results.
Significance of the Hypothesis Testing Calculator:
- Scientific Research: Researchers across various fields use hypothesis testing to validate their hypotheses and draw meaningful conclusions from data.
- Quality Control: Industries use hypothesis testing to ensure the quality and consistency of products and processes.
- Medical Studies: In medical research, hypothesis testing helps assess the effectiveness of treatments or interventions.
- Academics: Students and educators use hypothesis testing to teach and learn statistical concepts and conduct experiments.
- Data-Driven Decisions: Businesses use hypothesis testing to make data-driven decisions, such as whether to launch a new product based on market research.
Conclusion:
The Hypothesis Testing Calculator is a powerful tool that simplifies complex statistical analysis and enables data-driven decision-making. Whether you’re conducting experiments, analyzing survey data, or performing quality control, understanding hypothesis testing and using this calculator can help you make informed choices and contribute to evidence-based research and decision-making.

User Preferences
Content preview.
Arcu felis bibendum ut tristique et egestas quis:
- Ut enim ad minim veniam, quis nostrud exercitation ullamco laboris
- Duis aute irure dolor in reprehenderit in voluptate
- Excepteur sint occaecat cupidatat non proident
Keyboard Shortcuts
S.3.1 hypothesis testing (critical value approach).
The critical value approach involves determining "likely" or "unlikely" by determining whether or not the observed test statistic is more extreme than would be expected if the null hypothesis were true. That is, it entails comparing the observed test statistic to some cutoff value, called the " critical value ." If the test statistic is more extreme than the critical value, then the null hypothesis is rejected in favor of the alternative hypothesis. If the test statistic is not as extreme as the critical value, then the null hypothesis is not rejected.
Specifically, the four steps involved in using the critical value approach to conducting any hypothesis test are:
- Specify the null and alternative hypotheses.
- Using the sample data and assuming the null hypothesis is true, calculate the value of the test statistic. To conduct the hypothesis test for the population mean μ , we use the t -statistic \(t^*=\frac{\bar{x}-\mu}{s/\sqrt{n}}\) which follows a t -distribution with n - 1 degrees of freedom.
- Determine the critical value by finding the value of the known distribution of the test statistic such that the probability of making a Type I error — which is denoted \(\alpha\) (greek letter "alpha") and is called the " significance level of the test " — is small (typically 0.01, 0.05, or 0.10).
- Compare the test statistic to the critical value. If the test statistic is more extreme in the direction of the alternative than the critical value, reject the null hypothesis in favor of the alternative hypothesis. If the test statistic is less extreme than the critical value, do not reject the null hypothesis.

Example S.3.1.1
Mean gpa section .
In our example concerning the mean grade point average, suppose we take a random sample of n = 15 students majoring in mathematics. Since n = 15, our test statistic t * has n - 1 = 14 degrees of freedom. Also, suppose we set our significance level α at 0.05 so that we have only a 5% chance of making a Type I error.
Right-Tailed
The critical value for conducting the right-tailed test H 0 : μ = 3 versus H A : μ > 3 is the t -value, denoted t \(\alpha\) , n - 1 , such that the probability to the right of it is \(\alpha\). It can be shown using either statistical software or a t -table that the critical value t 0.05,14 is 1.7613. That is, we would reject the null hypothesis H 0 : μ = 3 in favor of the alternative hypothesis H A : μ > 3 if the test statistic t * is greater than 1.7613. Visually, the rejection region is shaded red in the graph.
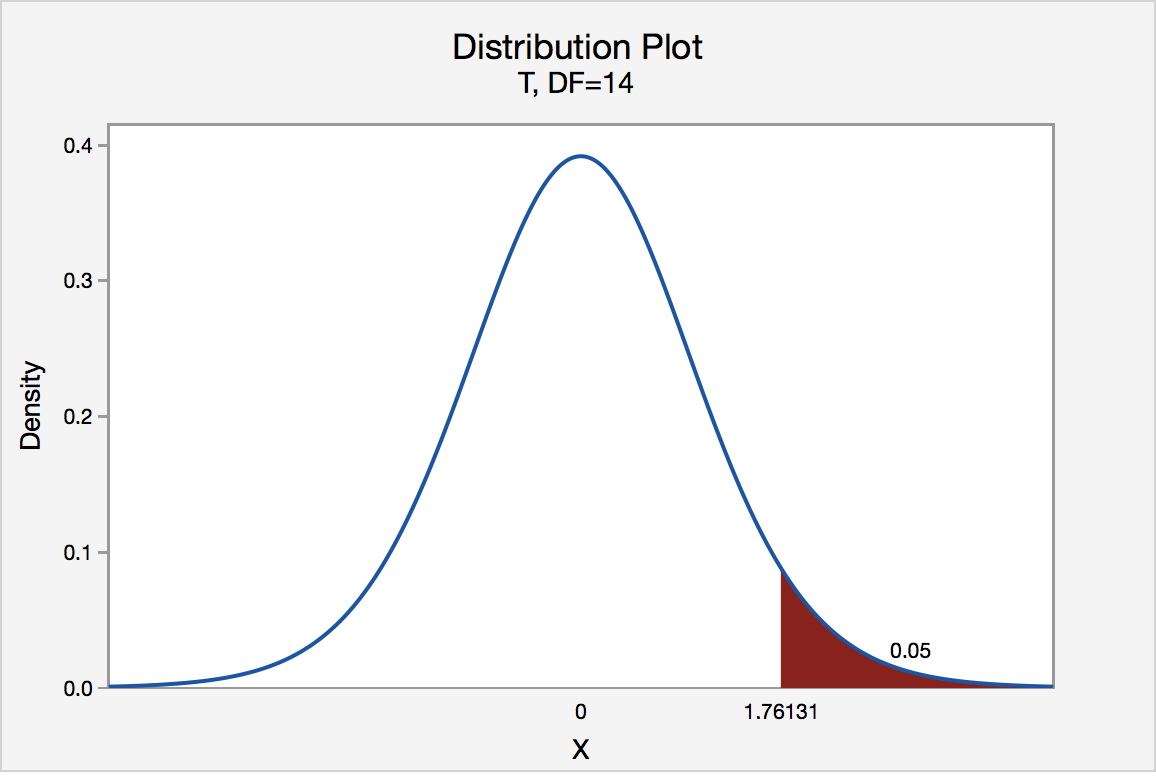
Left-Tailed
The critical value for conducting the left-tailed test H 0 : μ = 3 versus H A : μ < 3 is the t -value, denoted -t ( \(\alpha\) , n - 1) , such that the probability to the left of it is \(\alpha\). It can be shown using either statistical software or a t -table that the critical value -t 0.05,14 is -1.7613. That is, we would reject the null hypothesis H 0 : μ = 3 in favor of the alternative hypothesis H A : μ < 3 if the test statistic t * is less than -1.7613. Visually, the rejection region is shaded red in the graph.
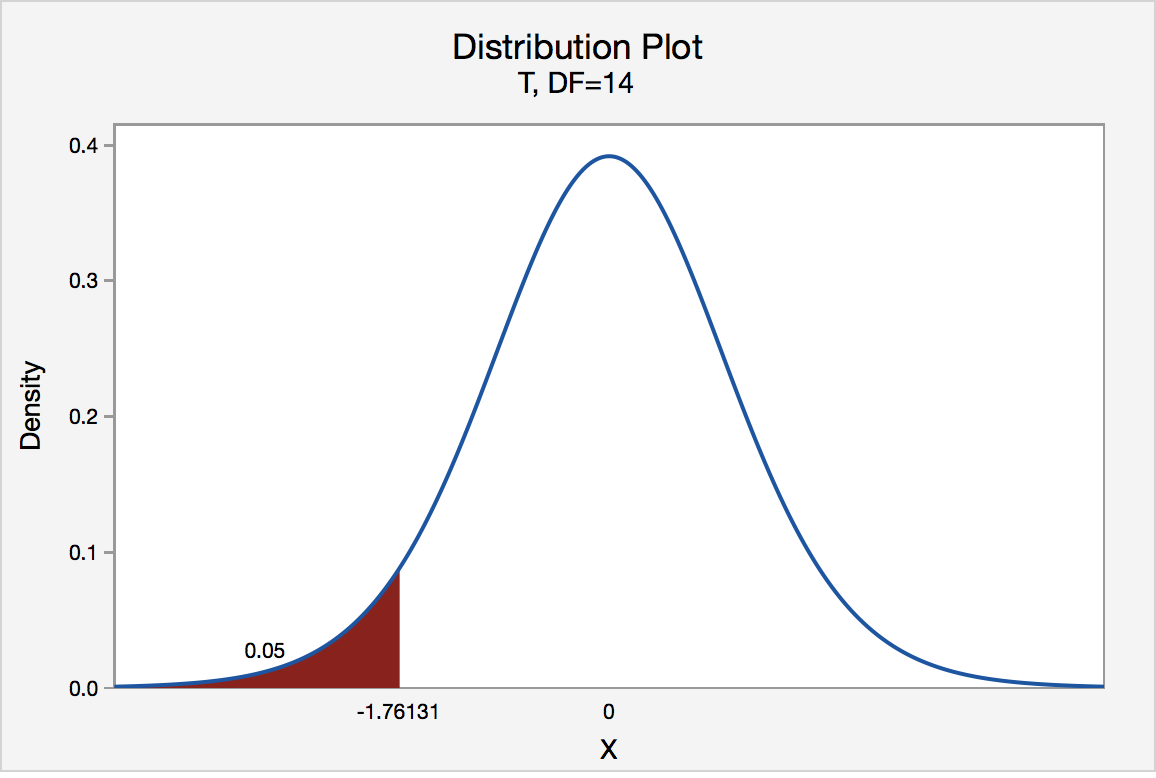
There are two critical values for the two-tailed test H 0 : μ = 3 versus H A : μ ≠ 3 — one for the left-tail denoted -t ( \(\alpha\) / 2, n - 1) and one for the right-tail denoted t ( \(\alpha\) / 2, n - 1) . The value - t ( \(\alpha\) /2, n - 1) is the t -value such that the probability to the left of it is \(\alpha\)/2, and the value t ( \(\alpha\) /2, n - 1) is the t -value such that the probability to the right of it is \(\alpha\)/2. It can be shown using either statistical software or a t -table that the critical value -t 0.025,14 is -2.1448 and the critical value t 0.025,14 is 2.1448. That is, we would reject the null hypothesis H 0 : μ = 3 in favor of the alternative hypothesis H A : μ ≠ 3 if the test statistic t * is less than -2.1448 or greater than 2.1448. Visually, the rejection region is shaded red in the graph.
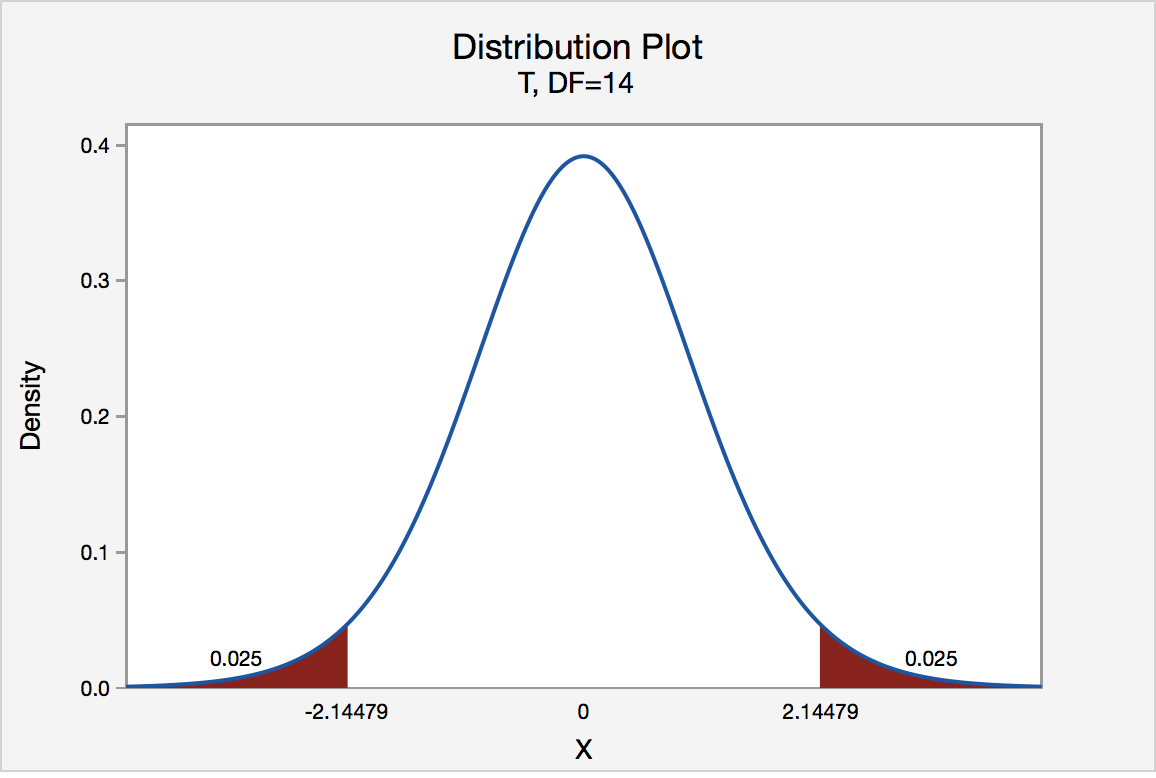

Hypothesis Testing Calculator
Navigating hypothesis testing: unveiling the potential of the hypothesis testing calculator.
Embarking on the journey of statistical exploration, hypothesis testing stands out as an indispensable method for informed decision-making and drawing meaningful conclusions from data. Whether you find yourself in the academic realm, engaged in research endeavors, or navigating the professional landscape, having a trustworthy Hypothesis Testing Calculator in your statistical toolkit can prove to be a game-changer. Let’s delve into the intricacies of hypothesis testing and uncover how this calculator can be your ally in statistical analyses.
Demystifying Hypothesis Testing:
Null Hypothesis (H0): Positioned as the default assumption, the null hypothesis asserts the absence of any significant difference or effect and is commonly represented as H0.
Alternative Hypothesis (Ha): In direct contradiction to the null hypothesis, the alternative hypothesis posits the existence of a noteworthy difference or effect, denoted as Ha.
Significance Level (α): Acting as the predetermined threshold, typically set at 0.05 or 5%, the significance level plays a pivotal role in determining statistical significance. Should the calculated p-value fall below α, the null hypothesis is rejected.
p-value: Representing the likelihood of observing the results, or more extreme outcomes, under the assumption of the null hypothesis being true, a smaller p-value suggests the unlikelihood of the results occurring by chance.
Features that Define the Hypothesis Testing Calculator:
Input Parameters: The calculator demands input of sample data, selection of the test type (e.g., t-test, chi-square test), specification of null and alternative hypotheses, and determination of the significance level.
Calculations: Once armed with the requisite data and parameters, the calculator diligently executes statistical tests and computations. The output encompasses crucial details like the test statistic, degrees of freedom, and the all-important p-value.
Interpretation: Armed with the results, the calculator aids in the decision-making process, guiding whether to reject or accept the null hypothesis. An interpretation of the findings is provided, playing a pivotal role in drawing insightful conclusions.
Visual Representation: Some calculators go the extra mile by offering visual aids such as graphs or charts, facilitating a deeper understanding of data distribution and test outcomes.
Unveiling the Significance of the Hypothesis Testing Calculator:
In Scientific Research: Researchers spanning diverse fields leverage hypothesis testing to validate their hypotheses, thereby extracting meaningful insights from data.
In Quality Control: Industries rely on hypothesis testing as a quality assurance mechanism, ensuring the consistency and excellence of products and processes.
In Medical Studies: Within the realm of medical research, hypothesis testing serves as a critical tool for evaluating the effectiveness of treatments or interventions.
In Academics: Both students and educators find value in hypothesis testing as an educational tool, enabling the comprehension of statistical concepts and the conduct of experiments.
In Data-Driven Decision-Making: Businesses, keen on making decisions grounded in data, turn to hypothesis testing to navigate choices such as launching a new product based on comprehensive market research.
Concluding Insights:
The Hypothesis Testing Calculator emerges as a formidable ally, simplifying intricate statistical analyses and fostering data-driven decision-making. Whether you are in the midst of experimental undertakings, scrutinizing survey data, or overseeing quality control protocols, a solid understanding of hypothesis testing coupled with the use of this calculator empowers you to make well-informed choices. In doing so, you not only contribute to evidence-based research but also play a pivotal role in shaping decision-making processes across various domains.

Statistics Resources
- Excel - Tutorials
- Basic Probability Rules
- Single Event Probability
- Complement Rule
- Intersections & Unions
- Compound Events
- Levels of Measurement
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Entering Data
- Central Tendency
- Data and Tests
- Displaying Data
- Discussing Statistics In-text
- SEM and Confidence Intervals
- Two-Way Frequency Tables
- Empirical Rule
- Finding Probability
- Accessing SPSS
- Chart and Graphs
- Frequency Table and Distribution
- Descriptive Statistics
- Converting Raw Scores to Z-Scores
- Converting Z-scores to t-scores
- Split File/Split Output
- Partial Eta Squared
- Downloading and Installing G*Power: Windows/PC
- Correlation
- Testing Parametric Assumptions
- One-Way ANOVA
- Two-Way ANOVA
- Repeated Measures ANOVA
- Goodness-of-Fit
- Test of Association
- Pearson's r
- Point Biserial
- Mediation and Moderation
- Simple Linear Regression
- Multiple Linear Regression
- Binomial Logistic Regression
- Multinomial Logistic Regression
- Independent Samples T-test
- Dependent Samples T-test
- Testing Assumptions
- T-tests using SPSS
- T-Test Practice
- Predictive Analytics This link opens in a new window
- Quantitative Research Questions
- Null & Alternative Hypotheses
- One-Tail vs. Two-Tail
- Alpha & Beta
- Associated Probability
- Decision Rule
- Statement of Conclusion
- Statistics Group Sessions
ASC Chat Hours
ASC Chat is usually available at the following times ( Pacific Time):
If there is not a coach on duty, submit your question via one of the below methods:
928-440-1325
Ask a Coach
Search our FAQs on the Academic Success Center's Ask a Coach page.
Reading List

In quantitative research, we can’t make claims without having some statistics to support it. In other words, it can’t be determined if the null or the alternative hypothesis is supported until the hypothesis has been explored, using the data that was collected.
There are numerous tests that can be used to test a hypothesis. Which test you use will depend on a number of factors. The purpose of this section is to discuss the basics of hypothesis testing.
Steps of Hypothesis Testing:
- State the Null & Alternative Hypotheses. These should reflect the hypothesis test that you anticipate conducting. For example, an alternative hypothesis for an ANOVA will state that there are significant differences between one or more means.
- Determine α. This refers to the amount of Type I error you are willing to make or the chance of determining that the null hypothesis is false when it is in fact true.
- State the decision rule. The decision rule states the circumstances under which the null hypothesis will be rejected. For a research paper, this will be comparing the obtained p-value (level of significance) of the test statistic to the alpha set for the hypothesis. For example, “If p < .05, the null hypothesis will be rejected.”
- Calculate the test statistic. In other words, conduct your hypothesis test with the appropriate statistical analysis. In most cases, this will be done using a statistical analysis tool, like SPSS.
- Reject the null hypothesis – In this case, the p-value for the test statistic is less than alpha. There is evidence to suggest the alternative is true.
- Fail to reject the null hypothesis – The p-value from the hypothesis test was greater than alpha. There is not sufficient evidence to suggest the null is not true.
- State the conclusion of the test in layman’s terms. This is where you connect the statistics back to the specific hypothesis being tested. For example, “The results of the hypothesis test indicate that the salary of factory workers varies based on gender.”
Was this resource helpful?
- << Previous: Quantitative Research Questions
- Next: Null & Alternative Hypotheses >>
- Last Updated: Apr 19, 2024 3:09 PM
- URL: https://resources.nu.edu/statsresources

“extremely user friendly”
“truly amazing!”
“so easy to use!”
Statistics Calculator
You want to analyze your data effortlessly? DATAtab makes it easy and online.
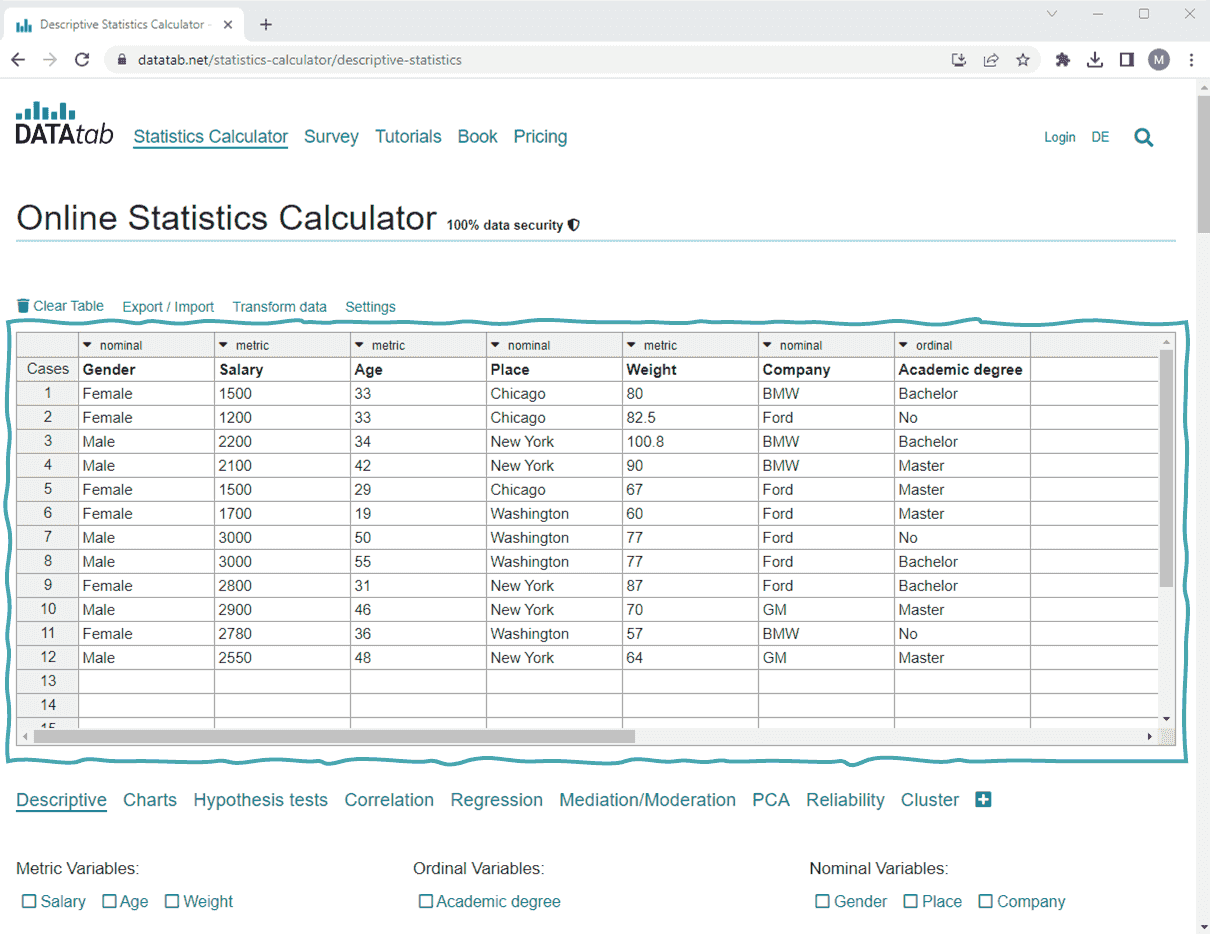
Online Statistics Calculator
What do you want to calculate online? The online statistics calculator is simple and uncomplicated! Here you can find a list of all implemented methods!
Create charts online with DATAtab
Create your charts for your data directly online and uncomplicated. To do this, insert your data into the table under Charts and select which chart you want.
The advantages of DATAtab
Statistics, as simple as never before..
DATAtab is a modern statistics software, with unique user-friendliness. Statistical analyses are done with just a few clicks, so DATAtab is perfect for statistics beginners and for professionals who want more flow in the user experience.
Directly in the browser, fully flexible.
Directly in the browser, fully flexible. DATAtab works directly in your web browser. You have no installation and maintenance effort whatsoever. Wherever and whenever you want to use DATAtab, just go to the website and get started.
All the statistical methods you need.
DATAtab offers you a wide range of statistical methods. We have selected the most central and best known statistical methods for you and do not overwhelm you with special cases.
Data security is a top priority.
All data that you insert and evaluate on DATAtab always remain on your end device. The data is not sent to any server or stored by us (not even temporarily). Furthermore, we do not pass on your data to third parties in order to analyze your user behavior.
Many tutorials with simple examples.
In order to facilitate the introduction, DATAtab offers a large number of free tutorials with focused explanations in simple language. We explain the statistical background of the methods and give step-by-step explanations for performing the analyses in the statistics calculator.
Practical Auto-Assistant.
DATAtab takes you by the hand in the world of statistics. When making statistical decisions, such as the choice of scale or measurement level or the selection of suitable methods, Auto-Assistants ensure that you get correct results quickly.
Charts, simple and clear.
With DATAtab data visualization is fun! Here you can easily create meaningful charts that optimally illustrate your results.
New in the world of statistics?
DATAtab was primarily designed for people for whom statistics is new territory. Beginners are not overwhelmed with a lot of complicated options and checkboxes, but are encouraged to perform their analyses step by step.
Online survey very simple.
DATAtab offers you the possibility to easily create an online survey, which you can then evaluate immediately with DATAtab.
Our references

Alternative to statistical software like SPSS and STATA
DATAtab was designed for ease of use and is a compelling alternative to statistical programs such as SPSS and STATA. On datatab.net, data can be statistically evaluated directly online and very easily (e.g. t-test, regression, correlation etc.). DATAtab's goal is to make the world of statistical data analysis as simple as possible, no installation and easy to use. Of course, we would also be pleased if you take a look at our second project Statisty .
Extensive tutorials
Descriptive statistics.
Here you can find out everything about location parameters and dispersion parameters and how you can describe and clearly present your data using characteristic values.
Hypothesis Test
Here you will find everything about hypothesis testing: One sample t-test , Unpaired t-test , Paired t-test and Chi-square test . You will also find tutorials for non-parametric statistical procedures such as the Mann-Whitney u-Test and Wilcoxon-Test . mann-whitney-u-test and the Wilcoxon test
The regression provides information about the influence of one or more independent variables on the dependent variable. Here are simple explanations of linear regression and logistic regression .
Correlation
Correlation analyses allow you to analyze the linear association between variables. Learn when to use Pearson correlation or Spearman rank correlation . With partial correlation , you can calculate the correlation between two variables to the exclusion of a third variable.
Partial Correlation
The partial correlation shows you the correlation between two variables to the exclusion of a third variable.
Levene Test
The Levene Test checks your data for variance equality. Thus, the levene test is used as a prerequisite test for many hypothesis tests .
The p-value is needed for every hypothesis test to be able to make a statement whether the null hypothesis is accepted or rejected.
Distributions
DATAtab provides you with tables with distributions and helpful explanations of the distribution functions. These include the Table of t-distribution and the Table of chi-squared distribution
Contingency table
With a contingency table you can get an overview of two categorical variables in the statistics.
Equivalence and non-inferiority
In an equivalence trial, the statistical test aims at showing that two treatments are not too different in characteristics and a non-inferiority trial wants to show that an experimental treatment is not worse than an established treatment.
If there is a clear cause-effect relationship between two variables, then we can speak of causality. Learn more about causality in our tutorial.
Multicollinearity
Multicollinearity is when two or more independent variables have a high correlation.
Effect size for independent t-test
Learn how to calculate the effect size for the t-test for independent samples.
Reliability analysis calculator
On DATAtab, Cohen's Kappa can be easily calculated online in the Cohen’s Kappa Calculator . there is also the Fleiss Kappa Calculator . Of course, the Cronbach's alpha can also be calculated in the Cronbach's Alpha Calculator .
Analysis of variance with repeated measurement
Repeated measures ANOVA tests whether there are statistically significant differences in three or more dependent samples.
Cite DATAtab: DATAtab Team (2024). DATAtab: Online Statistics Calculator. DATAtab e.U. Graz, Austria. URL https://datatab.net
Teach yourself statistics
Bartlett's Test Calculator
Bartlett's test is used to test the assumption that variances are equal (homogeneous) across groups. For help in using this calculator, read the Frequently-Asked Questions or review the Sample Problem .
To learn more about Bartlett's test, read Stat Trek's tutorial on Bartlett's test .
- In the dropdown box, specify the number of groups.
- Enter a value in each of the unshaded textboxes.
- Click Calculate to compute outputs.
Frequently-Asked Questions
Instructions: To find the answer to a frequently-asked question, simply click on the question.
What is Bartlett's test?
Bartlett's test is used to test the assumption that variances are equal (i.e., homogeneous) across groups. The test is easy to implement and produces valid results, assuming data points within groups are randomly sampled from a normal distribution.
Because Bartlett's test is sensitive to departures from normality, a normality test is prudent. Several ways to check for departures from normality are described at: How to Test for Normality: Three Simple Tests .
Note: Unlike Hartley's Fmax test , which also tests for homogeneity, Bartlett's test does not assume equal sample sizes across groups.
How does Bartlett's test work?
Bartlett's test is an actual hypothesis test , where we examine observed data to choose between two statistical hypotheses:
H 0 : σ 2 i = σ 2 j for all groups
H 0 : σ 2 i ≠ σ 2 j for at least one pair of groups
Like many other techniques for testing hypotheses, Bartlett's test for homogeneity involves computing a test-statistic and finding the P-value for the test statistic, given degrees of freedom and significance level . If the P-value is bigger than the significance level, we accept the null hypothesis; if it is smaller, we reject the null hypothesis.
What steps (computations) are required to execute Bartlett's test?
The steps required to conduct Bartlett's test for homogeneity are detailed below:
- Step 1. Specify the significance level ( α ).
s 2 j = [ Σ ( X i, j - X j ) 2 ] / ( n j - 1 )
where X i, j is the score for observation i in Group j , X j is the mean of Group j , n j is the number of observations in Group j , and k is the number of groups.
N = Σ n i
s 2 p = [ Σ ( n j -1 ) s 2 j ] / ( N - K )
where n j is the sample size in Group j , k is the number of groups, N is the total sample size, and s 2 j is the sample variance in Group j .
A = ( N - k ) * ln( s 2 p )
B = Σ [ ( n j - 1 ) * ln( s 2 j ) ]
C = 1 / [ 3 * ( k - 1 ) ]
D = Σ [ 1 / ( n j - 1 ) - 1 / ( N - k ) ]
T = ( A - B ) / [ 1 + ( C * D ) ]
where A is the first term in the numerator of the test statistic, B is the second term in the numerator, C is the first term in the denominator , D is the second term in the denominator, and ln is the natural logarithm.
It turns out that the test statistic (T) is distributed much like a chi-square statistic with ( k-1 ) degrees of freedom. Knowing the value of T and the degrees of freedom associated with T, we can use Stat Trek's Chi-Square Calculator to find the P-value - the probability of seeing a test statistic more extreme than T.
- Step 7. Accept or reject the null hypothesis, based on P-value and significance level. If the P-value is bigger than the significance level, we accept the null hypothesis that variances are equal across groups. Otherwise, we reject the null hypothesis.
What should I enter in the field for number of groups?
Bartlett's is designed to test the hypothesis of homogeneity among nonoverlapping sets of data. The number of groups is the number of data sets under consideration.
What should I enter for significance level?
The significance level is the probability of rejecting the null hypothesis when it is true. Researchers often choose 0.05 or 0.01 for a significance level.
What should I enter for sample size?
Sample size refers to the number of observations in a group. For each group, enter the number of observations in the space provided.
Note: Unlike some other tests for homogeneity (e.g., Hartley's Fmax test ), Bartlett's test does not require equal sample sizes across groups.
What should I enter for variance?
In the fields provided, enter an estimate of sample variance for each group. To compute sample variance ( s 2 j ) for each group, use the following formula:
where X i, j is the score for observation i in Group j , X j is the mean of Group j , and n j is the number of observations in Group j .
What is degrees of freedom?
Bartlett's test computes a test statistic (T) to test for normality. The degrees of freedom ( df ) for a chi-square test of that statistic is:
where N is the total sample size across all groups, and k is the number of groups in the sample.
What is the test statistic (T)?
The test statistic (T) is the statistic used by Bartlett's test to make a decision about whether to accept or reject the null hypothesis of equal variances between groups. When T is very big, we reject the null hypothesis; when T is small, we accept the null hypothesis.
The calculator computes a T statistic, based on user inputs. The formulas that the calculator uses to compute a T statistic are given at Bartlett's Test for Homogeneity of Variance .
What is the P-value?
If you assume that the null hypothesis of equal variance is true, the P-value is the probability of seeing a test statistic (T) that is more extreme (bigger) than the actual test statistic computed from sample data.
How does the calculator test hypotheses?
Like many other techniques for testing hypotheses, Bartlett's test for homogeneity of variance involves computing a test-statistic and finding the P-value for the test statistic, given degrees of freedom and significance level .
If the P-value is bigger than the significance level, the calculator accepts the null hypothesis. Otherwise, it rejects the null hypothesis.
Sample Problems
The table below shows sample data and variance for five groups. How would you test the assumption that variances are equal across groups?
One option would be to use Stat Trek's Bartlett's Test Calculator . Simply, take the following steps:
- Enter the number of groups (5).
- Enter the significance level. For this problem, we'll use 0.05.
- For each group, enter sample size. In this example, the sample size is 5 for each group.
- For each group, enter a sample estimate of group variance.
Then, click the Calculate button to produce the output shown below:
From the calculator, we see that the test statistic (T) is 8.91505. Assuming equal variances in groups and given a significance level of 0.05, the probability of observing a test statistic (T) bigger than 8.91505 is given by the P-value. Since the P-value (0.06326) is bigger than the significance level (0.05), we cannot reject the null hypothesis of equal variances across groups.
Note: To see the hand calculations required to solve this problem, go to Bartlett's Test for Homogeneity of Variance: Example 1 .
Oops! Something went wrong.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Decision Rule Calculator. In hypothesis testing, we want to know whether we should reject or fail to reject some statistical hypothesis. To make this decision, we compare the p-value of the test statistic to a significance level we have chosen to use for the test. If the p-value is less than the significance level, we reject the null hypothesis.
Hypothesis Testing Calculator. The first step in hypothesis testing is to calculate the test statistic. The formula for the test statistic depends on whether the population standard deviation (σ) is known or unknown. If σ is known, our hypothesis test is known as a z test and we use the z distribution. If σ is unknown, our hypothesis test is ...
Calculation Example: There are six steps you would follow in hypothesis testing: Formulate the null and alternative hypotheses in three different ways: H 0: θ = θ 0 v e r s u s H 1: θ ≠ θ 0. H 0: θ ≤ θ 0 v e r s u s H 1: θ > θ 0. H 0: θ ≥ θ 0 v e r s u s H 1: θ < θ 0.
Decision Rule Calculator. In hypothesis testing, we want to know whether we should reject or fail to reject some statistical hypothesis. To make this decision, we compare the p-value of the test statistic to a significance level we have chosen to use for the test. If the p-value is less than the significance level, we reject the null hypothesis.
The p-value calculator can help you find the p-value and evaluate how compatible your data is with the null hypothesis. We're hiring! Embed. Share via. ... Our calculator determines the p-value from the test statistic and provides the decision to be made about the null hypothesis. The standard significance level is 0.05 by default.
These next steps will tell you how to calculate the p-value from t-test or its critical values, and then which decision to make about the null hypothesis. Decide on the alternative hypothesis : Use a two-tailed t-test if you only care whether the population's mean (or, in the case of two populations, the difference between the populations ...
Sample Mean: Sample Size: Population Mean (Null Hypothesis): Population Standard Deviation: Significance Level (Alpha): Perform Test Understanding Hypothesis Testing: A Guide to the Hypothesis Testing Calculator Hypothesis testing is a crucial statistical method used to make informed decisions about data and draw conclusions. Whether you're a student, researcher, or professional, a ...
When your sample contains sufficient evidence, you can reject the null and conclude that the effect is statistically significant. Statisticians often denote the null hypothesis as H 0 or H A.. Null Hypothesis H 0: No effect exists in the population.; Alternative Hypothesis H A: The effect exists in the population.; In every study or experiment, researchers assess an effect or relationship.
There are 5 main steps in hypothesis testing: State your research hypothesis as a null hypothesis and alternate hypothesis (H o) and (H a or H 1 ). Collect data in a way designed to test the hypothesis. Perform an appropriate statistical test. Decide whether to reject or fail to reject your null hypothesis. Present the findings in your results ...
The null hypothesis should be able to be tested with the data that you have collected. Make it falsifiable. The null hypothesis should be capable of being proven false. If the null hypothesis cannot be falsified, then it is not a useful hypothesis. Use the appropriate statistical notation. The null hypothesis is typically denoted by the symbol H0.
The null and alternative hypotheses offer competing answers to your research question. When the research question asks "Does the independent variable affect the dependent variable?": The null hypothesis ( H0) answers "No, there's no effect in the population.". The alternative hypothesis ( Ha) answers "Yes, there is an effect in the ...
Review. In a hypothesis test, sample data is evaluated in order to arrive at a decision about some type of claim.If certain conditions about the sample are satisfied, then the claim can be evaluated for a population. In a hypothesis test, we: Evaluate the null hypothesis, typically denoted with \(H_{0}\).The null is not rejected unless the hypothesis test shows otherwise.
The calculated p-value is used in comparison with a predefined significance level (alpha) to make decisions about the null hypothesis. If the p-value is less than or equal to alpha, typically 0.05, the results are considered statistically significant, leading to the rejection of the null hypothesis in favor of the alternative hypothesis.
The actual test begins by considering two hypotheses.They are called the null hypothesis and the alternative hypothesis.These hypotheses contain opposing viewpoints. H 0, the —null hypothesis: a statement of no difference between sample means or proportions or no difference between a sample mean or proportion and a population mean or proportion. In other words, the difference equals 0.
For a lower-tailed test, the rule would state that the hypothesis should be rejected if the test statistic is smaller than a given critical value. In the case of a two-tailed test, the decision rule would specify rejection of the null hypothesis in the case of any extreme values of the test statistic: either values higher than an upper critical ...
The Hypothesis Testing Calculator is a powerful tool that simplifies complex statistical analysis and enables data-driven decision-making. Whether you're conducting experiments, analyzing survey data, or performing quality control, understanding hypothesis testing and using this calculator can help you make informed choices and contribute to ...
The critical value for conducting the left-tailed test H0 : μ = 3 versus HA : μ < 3 is the t -value, denoted -t( α, n - 1), such that the probability to the left of it is α. It can be shown using either statistical software or a t -table that the critical value -t0.05,14 is -1.7613. That is, we would reject the null hypothesis H0 : μ = 3 ...
Alternative Hypothesis (Ha): In direct contradiction to the null hypothesis, the alternative hypothesis posits the existence of a noteworthy difference or effect, denoted as Ha. ... Interpretation: Armed with the results, the calculator aids in the decision-making process, guiding whether to reject or accept the null hypothesis. An ...
The decision rule states the circumstances under which the null hypothesis will be rejected. For a research paper, this will be comparing the obtained p-value (level of significance) of the test statistic to the alpha set for the hypothesis. For example, "If p < .05, the null hypothesis will be rejected." Calculate the test statistic.
Online Statistics Calculator: Hypothesis testing, t-test, chi-square, regression, correlation, analysis of variance, cluster analysis ... When making statistical decisions, such as the choice of scale or measurement level or the selection of suitable methods, Auto-Assistants ensure that you get correct results quickly. ... The p-value is needed ...
The steps required to conduct Bartlett's test for homogeneity are detailed below: Step 1. Specify the significance level ( α ). Step 2. Compute the sample variance ( s 2 j ) for each group.. s 2 j = [ Σ ( X i, j - X j) 2] / ( n j - 1 ) . where X i, j is the score for observation i in Group j, X j is the mean of Group j, n j is the number of observations in Group j, and k is the number of groups.