Get science-backed answers as you write with Paperpal's Research feature

How to Write a Research Paper Introduction (with Examples)

The research paper introduction section, along with the Title and Abstract, can be considered the face of any research paper. The following article is intended to guide you in organizing and writing the research paper introduction for a quality academic article or dissertation.
The research paper introduction aims to present the topic to the reader. A study will only be accepted for publishing if you can ascertain that the available literature cannot answer your research question. So it is important to ensure that you have read important studies on that particular topic, especially those within the last five to ten years, and that they are properly referenced in this section. 1 What should be included in the research paper introduction is decided by what you want to tell readers about the reason behind the research and how you plan to fill the knowledge gap. The best research paper introduction provides a systemic review of existing work and demonstrates additional work that needs to be done. It needs to be brief, captivating, and well-referenced; a well-drafted research paper introduction will help the researcher win half the battle.
The introduction for a research paper is where you set up your topic and approach for the reader. It has several key goals:
- Present your research topic
- Capture reader interest
- Summarize existing research
- Position your own approach
- Define your specific research problem and problem statement
- Highlight the novelty and contributions of the study
- Give an overview of the paper’s structure
The research paper introduction can vary in size and structure depending on whether your paper presents the results of original empirical research or is a review paper. Some research paper introduction examples are only half a page while others are a few pages long. In many cases, the introduction will be shorter than all of the other sections of your paper; its length depends on the size of your paper as a whole.
- Break through writer’s block. Write your research paper introduction with Paperpal Copilot
Table of Contents
What is the introduction for a research paper, why is the introduction important in a research paper, craft a compelling introduction section with paperpal. try now, 1. introduce the research topic:, 2. determine a research niche:, 3. place your research within the research niche:, craft accurate research paper introductions with paperpal. start writing now, frequently asked questions on research paper introduction, key points to remember.
The introduction in a research paper is placed at the beginning to guide the reader from a broad subject area to the specific topic that your research addresses. They present the following information to the reader
- Scope: The topic covered in the research paper
- Context: Background of your topic
- Importance: Why your research matters in that particular area of research and the industry problem that can be targeted
The research paper introduction conveys a lot of information and can be considered an essential roadmap for the rest of your paper. A good introduction for a research paper is important for the following reasons:
- It stimulates your reader’s interest: A good introduction section can make your readers want to read your paper by capturing their interest. It informs the reader what they are going to learn and helps determine if the topic is of interest to them.
- It helps the reader understand the research background: Without a clear introduction, your readers may feel confused and even struggle when reading your paper. A good research paper introduction will prepare them for the in-depth research to come. It provides you the opportunity to engage with the readers and demonstrate your knowledge and authority on the specific topic.
- It explains why your research paper is worth reading: Your introduction can convey a lot of information to your readers. It introduces the topic, why the topic is important, and how you plan to proceed with your research.
- It helps guide the reader through the rest of the paper: The research paper introduction gives the reader a sense of the nature of the information that will support your arguments and the general organization of the paragraphs that will follow. It offers an overview of what to expect when reading the main body of your paper.
What are the parts of introduction in the research?
A good research paper introduction section should comprise three main elements: 2
- What is known: This sets the stage for your research. It informs the readers of what is known on the subject.
- What is lacking: This is aimed at justifying the reason for carrying out your research. This could involve investigating a new concept or method or building upon previous research.
- What you aim to do: This part briefly states the objectives of your research and its major contributions. Your detailed hypothesis will also form a part of this section.
How to write a research paper introduction?
The first step in writing the research paper introduction is to inform the reader what your topic is and why it’s interesting or important. This is generally accomplished with a strong opening statement. The second step involves establishing the kinds of research that have been done and ending with limitations or gaps in the research that you intend to address. Finally, the research paper introduction clarifies how your own research fits in and what problem it addresses. If your research involved testing hypotheses, these should be stated along with your research question. The hypothesis should be presented in the past tense since it will have been tested by the time you are writing the research paper introduction.
The following key points, with examples, can guide you when writing the research paper introduction section:
- Highlight the importance of the research field or topic
- Describe the background of the topic
- Present an overview of current research on the topic
Example: The inclusion of experiential and competency-based learning has benefitted electronics engineering education. Industry partnerships provide an excellent alternative for students wanting to engage in solving real-world challenges. Industry-academia participation has grown in recent years due to the need for skilled engineers with practical training and specialized expertise. However, from the educational perspective, many activities are needed to incorporate sustainable development goals into the university curricula and consolidate learning innovation in universities.
- Reveal a gap in existing research or oppose an existing assumption
- Formulate the research question
Example: There have been plausible efforts to integrate educational activities in higher education electronics engineering programs. However, very few studies have considered using educational research methods for performance evaluation of competency-based higher engineering education, with a focus on technical and or transversal skills. To remedy the current need for evaluating competencies in STEM fields and providing sustainable development goals in engineering education, in this study, a comparison was drawn between study groups without and with industry partners.
- State the purpose of your study
- Highlight the key characteristics of your study
- Describe important results
- Highlight the novelty of the study.
- Offer a brief overview of the structure of the paper.
Example: The study evaluates the main competency needed in the applied electronics course, which is a fundamental core subject for many electronics engineering undergraduate programs. We compared two groups, without and with an industrial partner, that offered real-world projects to solve during the semester. This comparison can help determine significant differences in both groups in terms of developing subject competency and achieving sustainable development goals.
Write a Research Paper Introduction in Minutes with Paperpal
Paperpal Copilot is a generative AI-powered academic writing assistant. It’s trained on millions of published scholarly articles and over 20 years of STM experience. Paperpal Copilot helps authors write better and faster with:
- Real-time writing suggestions
- In-depth checks for language and grammar correction
- Paraphrasing to add variety, ensure academic tone, and trim text to meet journal limits
With Paperpal Copilot, create a research paper introduction effortlessly. In this step-by-step guide, we’ll walk you through how Paperpal transforms your initial ideas into a polished and publication-ready introduction.

How to use Paperpal to write the Introduction section
Step 1: Sign up on Paperpal and click on the Copilot feature, under this choose Outlines > Research Article > Introduction
Step 2: Add your unstructured notes or initial draft, whether in English or another language, to Paperpal, which is to be used as the base for your content.
Step 3: Fill in the specifics, such as your field of study, brief description or details you want to include, which will help the AI generate the outline for your Introduction.
Step 4: Use this outline and sentence suggestions to develop your content, adding citations where needed and modifying it to align with your specific research focus.
Step 5: Turn to Paperpal’s granular language checks to refine your content, tailor it to reflect your personal writing style, and ensure it effectively conveys your message.
You can use the same process to develop each section of your article, and finally your research paper in half the time and without any of the stress.
The purpose of the research paper introduction is to introduce the reader to the problem definition, justify the need for the study, and describe the main theme of the study. The aim is to gain the reader’s attention by providing them with necessary background information and establishing the main purpose and direction of the research.
The length of the research paper introduction can vary across journals and disciplines. While there are no strict word limits for writing the research paper introduction, an ideal length would be one page, with a maximum of 400 words over 1-4 paragraphs. Generally, it is one of the shorter sections of the paper as the reader is assumed to have at least a reasonable knowledge about the topic. 2 For example, for a study evaluating the role of building design in ensuring fire safety, there is no need to discuss definitions and nature of fire in the introduction; you could start by commenting upon the existing practices for fire safety and how your study will add to the existing knowledge and practice.
When deciding what to include in the research paper introduction, the rest of the paper should also be considered. The aim is to introduce the reader smoothly to the topic and facilitate an easy read without much dependency on external sources. 3 Below is a list of elements you can include to prepare a research paper introduction outline and follow it when you are writing the research paper introduction. Topic introduction: This can include key definitions and a brief history of the topic. Research context and background: Offer the readers some general information and then narrow it down to specific aspects. Details of the research you conducted: A brief literature review can be included to support your arguments or line of thought. Rationale for the study: This establishes the relevance of your study and establishes its importance. Importance of your research: The main contributions are highlighted to help establish the novelty of your study Research hypothesis: Introduce your research question and propose an expected outcome. Organization of the paper: Include a short paragraph of 3-4 sentences that highlights your plan for the entire paper
Cite only works that are most relevant to your topic; as a general rule, you can include one to three. Note that readers want to see evidence of original thinking. So it is better to avoid using too many references as it does not leave much room for your personal standpoint to shine through. Citations in your research paper introduction support the key points, and the number of citations depend on the subject matter and the point discussed. If the research paper introduction is too long or overflowing with citations, it is better to cite a few review articles rather than the individual articles summarized in the review. A good point to remember when citing research papers in the introduction section is to include at least one-third of the references in the introduction.
The literature review plays a significant role in the research paper introduction section. A good literature review accomplishes the following: Introduces the topic – Establishes the study’s significance – Provides an overview of the relevant literature – Provides context for the study using literature – Identifies knowledge gaps However, remember to avoid making the following mistakes when writing a research paper introduction: Do not use studies from the literature review to aggressively support your research Avoid direct quoting Do not allow literature review to be the focus of this section. Instead, the literature review should only aid in setting a foundation for the manuscript.
Remember the following key points for writing a good research paper introduction: 4
- Avoid stuffing too much general information: Avoid including what an average reader would know and include only that information related to the problem being addressed in the research paper introduction. For example, when describing a comparative study of non-traditional methods for mechanical design optimization, information related to the traditional methods and differences between traditional and non-traditional methods would not be relevant. In this case, the introduction for the research paper should begin with the state-of-the-art non-traditional methods and methods to evaluate the efficiency of newly developed algorithms.
- Avoid packing too many references: Cite only the required works in your research paper introduction. The other works can be included in the discussion section to strengthen your findings.
- Avoid extensive criticism of previous studies: Avoid being overly critical of earlier studies while setting the rationale for your study. A better place for this would be the Discussion section, where you can highlight the advantages of your method.
- Avoid describing conclusions of the study: When writing a research paper introduction remember not to include the findings of your study. The aim is to let the readers know what question is being answered. The actual answer should only be given in the Results and Discussion section.
To summarize, the research paper introduction section should be brief yet informative. It should convince the reader the need to conduct the study and motivate him to read further. If you’re feeling stuck or unsure, choose trusted AI academic writing assistants like Paperpal to effortlessly craft your research paper introduction and other sections of your research article.
1. Jawaid, S. A., & Jawaid, M. (2019). How to write introduction and discussion. Saudi Journal of Anaesthesia, 13(Suppl 1), S18.
2. Dewan, P., & Gupta, P. (2016). Writing the title, abstract and introduction: Looks matter!. Indian pediatrics, 53, 235-241.
3. Cetin, S., & Hackam, D. J. (2005). An approach to the writing of a scientific Manuscript1. Journal of Surgical Research, 128(2), 165-167.
4. Bavdekar, S. B. (2015). Writing introduction: Laying the foundations of a research paper. Journal of the Association of Physicians of India, 63(7), 44-6.
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
- Scientific Writing Style Guides Explained
- 5 Reasons for Rejection After Peer Review
- Ethical Research Practices For Research with Human Subjects
- 8 Most Effective Ways to Increase Motivation for Thesis Writing
Practice vs. Practise: Learn the Difference
Academic paraphrasing: why paperpal’s rewrite should be your first choice , you may also like, how to write a high-quality conference paper, academic editing: how to self-edit academic text with..., measuring academic success: definition & strategies for excellence, phd qualifying exam: tips for success , ai in education: it’s time to change the..., is it ethical to use ai-generated abstracts without..., what are journal guidelines on using generative ai..., quillbot review: features, pricing, and free alternatives, what is an academic paper types and elements , should you use ai tools like chatgpt for....
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- 4. The Introduction
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Applying Critical Thinking
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
The introduction leads the reader from a general subject area to a particular topic of inquiry. It establishes the scope, context, and significance of the research being conducted by summarizing current understanding and background information about the topic, stating the purpose of the work in the form of the research problem supported by a hypothesis or a set of questions, explaining briefly the methodological approach used to examine the research problem, highlighting the potential outcomes your study can reveal, and outlining the remaining structure and organization of the paper.
Key Elements of the Research Proposal. Prepared under the direction of the Superintendent and by the 2010 Curriculum Design and Writing Team. Baltimore County Public Schools.
Importance of a Good Introduction
Think of the introduction as a mental road map that must answer for the reader these four questions:
- What was I studying?
- Why was this topic important to investigate?
- What did we know about this topic before I did this study?
- How will this study advance new knowledge or new ways of understanding?
According to Reyes, there are three overarching goals of a good introduction: 1) ensure that you summarize prior studies about the topic in a manner that lays a foundation for understanding the research problem; 2) explain how your study specifically addresses gaps in the literature, insufficient consideration of the topic, or other deficiency in the literature; and, 3) note the broader theoretical, empirical, and/or policy contributions and implications of your research.
A well-written introduction is important because, quite simply, you never get a second chance to make a good first impression. The opening paragraphs of your paper will provide your readers with their initial impressions about the logic of your argument, your writing style, the overall quality of your research, and, ultimately, the validity of your findings and conclusions. A vague, disorganized, or error-filled introduction will create a negative impression, whereas, a concise, engaging, and well-written introduction will lead your readers to think highly of your analytical skills, your writing style, and your research approach. All introductions should conclude with a brief paragraph that describes the organization of the rest of the paper.
Hirano, Eliana. “Research Article Introductions in English for Specific Purposes: A Comparison between Brazilian, Portuguese, and English.” English for Specific Purposes 28 (October 2009): 240-250; Samraj, B. “Introductions in Research Articles: Variations Across Disciplines.” English for Specific Purposes 21 (2002): 1–17; Introductions. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; “Writing Introductions.” In Good Essay Writing: A Social Sciences Guide. Peter Redman. 4th edition. (London: Sage, 2011), pp. 63-70; Reyes, Victoria. Demystifying the Journal Article. Inside Higher Education.
Structure and Writing Style
I. Structure and Approach
The introduction is the broad beginning of the paper that answers three important questions for the reader:
- What is this?
- Why should I read it?
- What do you want me to think about / consider doing / react to?
Think of the structure of the introduction as an inverted triangle of information that lays a foundation for understanding the research problem. Organize the information so as to present the more general aspects of the topic early in the introduction, then narrow your analysis to more specific topical information that provides context, finally arriving at your research problem and the rationale for studying it [often written as a series of key questions to be addressed or framed as a hypothesis or set of assumptions to be tested] and, whenever possible, a description of the potential outcomes your study can reveal.
These are general phases associated with writing an introduction: 1. Establish an area to research by:
- Highlighting the importance of the topic, and/or
- Making general statements about the topic, and/or
- Presenting an overview on current research on the subject.
2. Identify a research niche by:
- Opposing an existing assumption, and/or
- Revealing a gap in existing research, and/or
- Formulating a research question or problem, and/or
- Continuing a disciplinary tradition.
3. Place your research within the research niche by:
- Stating the intent of your study,
- Outlining the key characteristics of your study,
- Describing important results, and
- Giving a brief overview of the structure of the paper.
NOTE: It is often useful to review the introduction late in the writing process. This is appropriate because outcomes are unknown until you've completed the study. After you complete writing the body of the paper, go back and review introductory descriptions of the structure of the paper, the method of data gathering, the reporting and analysis of results, and the conclusion. Reviewing and, if necessary, rewriting the introduction ensures that it correctly matches the overall structure of your final paper.
II. Delimitations of the Study
Delimitations refer to those characteristics that limit the scope and define the conceptual boundaries of your research . This is determined by the conscious exclusionary and inclusionary decisions you make about how to investigate the research problem. In other words, not only should you tell the reader what it is you are studying and why, but you must also acknowledge why you rejected alternative approaches that could have been used to examine the topic.
Obviously, the first limiting step was the choice of research problem itself. However, implicit are other, related problems that could have been chosen but were rejected. These should be noted in the conclusion of your introduction. For example, a delimitating statement could read, "Although many factors can be understood to impact the likelihood young people will vote, this study will focus on socioeconomic factors related to the need to work full-time while in school." The point is not to document every possible delimiting factor, but to highlight why previously researched issues related to the topic were not addressed.
Examples of delimitating choices would be:
- The key aims and objectives of your study,
- The research questions that you address,
- The variables of interest [i.e., the various factors and features of the phenomenon being studied],
- The method(s) of investigation,
- The time period your study covers, and
- Any relevant alternative theoretical frameworks that could have been adopted.
Review each of these decisions. Not only do you clearly establish what you intend to accomplish in your research, but you should also include a declaration of what the study does not intend to cover. In the latter case, your exclusionary decisions should be based upon criteria understood as, "not interesting"; "not directly relevant"; “too problematic because..."; "not feasible," and the like. Make this reasoning explicit!
NOTE: Delimitations refer to the initial choices made about the broader, overall design of your study and should not be confused with documenting the limitations of your study discovered after the research has been completed.
ANOTHER NOTE : Do not view delimitating statements as admitting to an inherent failing or shortcoming in your research. They are an accepted element of academic writing intended to keep the reader focused on the research problem by explicitly defining the conceptual boundaries and scope of your study. It addresses any critical questions in the reader's mind of, "Why the hell didn't the author examine this?"
III. The Narrative Flow
Issues to keep in mind that will help the narrative flow in your introduction :
- Your introduction should clearly identify the subject area of interest . A simple strategy to follow is to use key words from your title in the first few sentences of the introduction. This will help focus the introduction on the topic at the appropriate level and ensures that you get to the subject matter quickly without losing focus, or discussing information that is too general.
- Establish context by providing a brief and balanced review of the pertinent published literature that is available on the subject. The key is to summarize for the reader what is known about the specific research problem before you did your analysis. This part of your introduction should not represent a comprehensive literature review--that comes next. It consists of a general review of the important, foundational research literature [with citations] that establishes a foundation for understanding key elements of the research problem. See the drop-down menu under this tab for " Background Information " regarding types of contexts.
- Clearly state the hypothesis that you investigated . When you are first learning to write in this format it is okay, and actually preferable, to use a past statement like, "The purpose of this study was to...." or "We investigated three possible mechanisms to explain the...."
- Why did you choose this kind of research study or design? Provide a clear statement of the rationale for your approach to the problem studied. This will usually follow your statement of purpose in the last paragraph of the introduction.
IV. Engaging the Reader
A research problem in the social sciences can come across as dry and uninteresting to anyone unfamiliar with the topic . Therefore, one of the goals of your introduction is to make readers want to read your paper. Here are several strategies you can use to grab the reader's attention:
- Open with a compelling story . Almost all research problems in the social sciences, no matter how obscure or esoteric , are really about the lives of people. Telling a story that humanizes an issue can help illuminate the significance of the problem and help the reader empathize with those affected by the condition being studied.
- Include a strong quotation or a vivid, perhaps unexpected, anecdote . During your review of the literature, make note of any quotes or anecdotes that grab your attention because they can used in your introduction to highlight the research problem in a captivating way.
- Pose a provocative or thought-provoking question . Your research problem should be framed by a set of questions to be addressed or hypotheses to be tested. However, a provocative question can be presented in the beginning of your introduction that challenges an existing assumption or compels the reader to consider an alternative viewpoint that helps establish the significance of your study.
- Describe a puzzling scenario or incongruity . This involves highlighting an interesting quandary concerning the research problem or describing contradictory findings from prior studies about a topic. Posing what is essentially an unresolved intellectual riddle about the problem can engage the reader's interest in the study.
- Cite a stirring example or case study that illustrates why the research problem is important . Draw upon the findings of others to demonstrate the significance of the problem and to describe how your study builds upon or offers alternatives ways of investigating this prior research.
NOTE: It is important that you choose only one of the suggested strategies for engaging your readers. This avoids giving an impression that your paper is more flash than substance and does not distract from the substance of your study.
Freedman, Leora and Jerry Plotnick. Introductions and Conclusions. University College Writing Centre. University of Toronto; Introduction. The Structure, Format, Content, and Style of a Journal-Style Scientific Paper. Department of Biology. Bates College; Introductions. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Introductions. The Writer’s Handbook. Writing Center. University of Wisconsin, Madison; Introductions, Body Paragraphs, and Conclusions for an Argument Paper. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; “Writing Introductions.” In Good Essay Writing: A Social Sciences Guide . Peter Redman. 4th edition. (London: Sage, 2011), pp. 63-70; Resources for Writers: Introduction Strategies. Program in Writing and Humanistic Studies. Massachusetts Institute of Technology; Sharpling, Gerald. Writing an Introduction. Centre for Applied Linguistics, University of Warwick; Samraj, B. “Introductions in Research Articles: Variations Across Disciplines.” English for Specific Purposes 21 (2002): 1–17; Swales, John and Christine B. Feak. Academic Writing for Graduate Students: Essential Skills and Tasks . 2nd edition. Ann Arbor, MI: University of Michigan Press, 2004 ; Writing Your Introduction. Department of English Writing Guide. George Mason University.
Writing Tip
Avoid the "Dictionary" Introduction
Giving the dictionary definition of words related to the research problem may appear appropriate because it is important to define specific terminology that readers may be unfamiliar with. However, anyone can look a word up in the dictionary and a general dictionary is not a particularly authoritative source because it doesn't take into account the context of your topic and doesn't offer particularly detailed information. Also, placed in the context of a particular discipline, a term or concept may have a different meaning than what is found in a general dictionary. If you feel that you must seek out an authoritative definition, use a subject specific dictionary or encyclopedia [e.g., if you are a sociology student, search for dictionaries of sociology]. A good database for obtaining definitive definitions of concepts or terms is Credo Reference .
Saba, Robert. The College Research Paper. Florida International University; Introductions. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina.
Another Writing Tip
When Do I Begin?
A common question asked at the start of any paper is, "Where should I begin?" An equally important question to ask yourself is, "When do I begin?" Research problems in the social sciences rarely rest in isolation from history. Therefore, it is important to lay a foundation for understanding the historical context underpinning the research problem. However, this information should be brief and succinct and begin at a point in time that illustrates the study's overall importance. For example, a study that investigates coffee cultivation and export in West Africa as a key stimulus for local economic growth needs to describe the beginning of exporting coffee in the region and establishing why economic growth is important. You do not need to give a long historical explanation about coffee exports in Africa. If a research problem requires a substantial exploration of the historical context, do this in the literature review section. In your introduction, make note of this as part of the "roadmap" [see below] that you use to describe the organization of your paper.
Introductions. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; “Writing Introductions.” In Good Essay Writing: A Social Sciences Guide . Peter Redman. 4th edition. (London: Sage, 2011), pp. 63-70.
Yet Another Writing Tip
Always End with a Roadmap
The final paragraph or sentences of your introduction should forecast your main arguments and conclusions and provide a brief description of the rest of the paper [the "roadmap"] that let's the reader know where you are going and what to expect. A roadmap is important because it helps the reader place the research problem within the context of their own perspectives about the topic. In addition, concluding your introduction with an explicit roadmap tells the reader that you have a clear understanding of the structural purpose of your paper. In this way, the roadmap acts as a type of promise to yourself and to your readers that you will follow a consistent and coherent approach to addressing the topic of inquiry. Refer to it often to help keep your writing focused and organized.
Cassuto, Leonard. “On the Dissertation: How to Write the Introduction.” The Chronicle of Higher Education , May 28, 2018; Radich, Michael. A Student's Guide to Writing in East Asian Studies . (Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Writing n. d.), pp. 35-37.
- << Previous: Executive Summary
- Next: The C.A.R.S. Model >>
- Last Updated: May 15, 2024 9:53 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide
How to write an effective introduction for your research paper
Last updated
20 January 2024
Reviewed by
However, the introduction is a vital element of your research paper . It helps the reader decide whether your paper is worth their time. As such, it's worth taking your time to get it right.
In this article, we'll tell you everything you need to know about writing an effective introduction for your research paper.
- The importance of an introduction in research papers
The primary purpose of an introduction is to provide an overview of your paper. This lets readers gauge whether they want to continue reading or not. The introduction should provide a meaningful roadmap of your research to help them make this decision. It should let readers know whether the information they're interested in is likely to be found in the pages that follow.
Aside from providing readers with information about the content of your paper, the introduction also sets the tone. It shows readers the style of language they can expect, which can further help them to decide how far to read.
When you take into account both of these roles that an introduction plays, it becomes clear that crafting an engaging introduction is the best way to get your paper read more widely. First impressions count, and the introduction provides that impression to readers.
- The optimum length for a research paper introduction
While there's no magic formula to determine exactly how long a research paper introduction should be, there are a few guidelines. Some variables that impact the ideal introduction length include:
Field of study
Complexity of the topic
Specific requirements of the course or publication
A commonly recommended length of a research paper introduction is around 10% of the total paper’s length. So, a ten-page paper has a one-page introduction. If the topic is complex, it may require more background to craft a compelling intro. Humanities papers tend to have longer introductions than those of the hard sciences.
The best way to craft an introduction of the right length is to focus on clarity and conciseness. Tell the reader only what is necessary to set up your research. An introduction edited down with this goal in mind should end up at an acceptable length.
- Evaluating successful research paper introductions
A good way to gauge how to create a great introduction is by looking at examples from across your field. The most influential and well-regarded papers should provide some insights into what makes a good introduction.
Dissecting examples: what works and why
We can make some general assumptions by looking at common elements of a good introduction, regardless of the field of research.
A common structure is to start with a broad context, and then narrow that down to specific research questions or hypotheses. This creates a funnel that establishes the scope and relevance.
The most effective introductions are careful about the assumptions they make regarding reader knowledge. By clearly defining key terms and concepts instead of assuming the reader is familiar with them, these introductions set a more solid foundation for understanding.
To pull in the reader and make that all-important good first impression, excellent research paper introductions will often incorporate a compelling narrative or some striking fact that grabs the reader's attention.
Finally, good introductions provide clear citations from past research to back up the claims they're making. In the case of argumentative papers or essays (those that take a stance on a topic or issue), a strong thesis statement compels the reader to continue reading.
Common pitfalls to avoid in research paper introductions
You can also learn what not to do by looking at other research papers. Many authors have made mistakes you can learn from.
We've talked about the need to be clear and concise. Many introductions fail at this; they're verbose, vague, or otherwise fail to convey the research problem or hypothesis efficiently. This often comes in the form of an overemphasis on background information, which obscures the main research focus.
Ensure your introduction provides the proper emphasis and excitement around your research and its significance. Otherwise, fewer people will want to read more about it.
- Crafting a compelling introduction for a research paper
Let’s take a look at the steps required to craft an introduction that pulls readers in and compels them to learn more about your research.
Step 1: Capturing interest and setting the scene
To capture the reader's interest immediately, begin your introduction with a compelling question, a surprising fact, a provocative quote, or some other mechanism that will hook readers and pull them further into the paper.
As they continue reading, the introduction should contextualize your research within the current field, showing readers its relevance and importance. Clarify any essential terms that will help them better understand what you're saying. This keeps the fundamentals of your research accessible to all readers from all backgrounds.
Step 2: Building a solid foundation with background information
Including background information in your introduction serves two major purposes:
It helps to clarify the topic for the reader
It establishes the depth of your research
The approach you take when conveying this information depends on the type of paper.
For argumentative papers, you'll want to develop engaging background narratives. These should provide context for the argument you'll be presenting.
For empirical papers, highlighting past research is the key. Often, there will be some questions that weren't answered in those past papers. If your paper is focused on those areas, those papers make ideal candidates for you to discuss and critique in your introduction.
Step 3: Pinpointing the research challenge
To capture the attention of the reader, you need to explain what research challenges you'll be discussing.
For argumentative papers, this involves articulating why the argument you'll be making is important. What is its relevance to current discussions or problems? What is the potential impact of people accepting or rejecting your argument?
For empirical papers, explain how your research is addressing a gap in existing knowledge. What new insights or contributions will your research bring to your field?
Step 4: Clarifying your research aims and objectives
We mentioned earlier that the introduction to a research paper can serve as a roadmap for what's within. We've also frequently discussed the need for clarity. This step addresses both of these.
When writing an argumentative paper, craft a thesis statement with impact. Clearly articulate what your position is and the main points you intend to present. This will map out for the reader exactly what they'll get from reading the rest.
For empirical papers, focus on formulating precise research questions and hypotheses. Directly link them to the gaps or issues you've identified in existing research to show the reader the precise direction your research paper will take.
Step 5: Sketching the blueprint of your study
Continue building a roadmap for your readers by designing a structured outline for the paper. Guide the reader through your research journey, explaining what the different sections will contain and their relationship to one another.
This outline should flow seamlessly as you move from section to section. Creating this outline early can also help guide the creation of the paper itself, resulting in a final product that's better organized. In doing so, you'll craft a paper where each section flows intuitively from the next.
Step 6: Integrating your research question
To avoid letting your research question get lost in background information or clarifications, craft your introduction in such a way that the research question resonates throughout. The research question should clearly address a gap in existing knowledge or offer a new perspective on an existing problem.
Tell users your research question explicitly but also remember to frequently come back to it. When providing context or clarification, point out how it relates to the research question. This keeps your focus where it needs to be and prevents the topic of the paper from becoming under-emphasized.
Step 7: Establishing the scope and limitations
So far, we've talked mostly about what's in the paper and how to convey that information to readers. The opposite is also important. Information that's outside the scope of your paper should be made clear to the reader in the introduction so their expectations for what is to follow are set appropriately.
Similarly, be honest and upfront about the limitations of the study. Any constraints in methodology, data, or how far your findings can be generalized should be fully communicated in the introduction.
Step 8: Concluding the introduction with a promise
The final few lines of the introduction are your last chance to convince people to continue reading the rest of the paper. Here is where you should make it very clear what benefit they'll get from doing so. What topics will be covered? What questions will be answered? Make it clear what they will get for continuing.
By providing a quick recap of the key points contained in the introduction in its final lines and properly setting the stage for what follows in the rest of the paper, you refocus the reader's attention on the topic of your research and guide them to read more.
- Research paper introduction best practices
Following the steps above will give you a compelling introduction that hits on all the key points an introduction should have. Some more tips and tricks can make an introduction even more polished.
As you follow the steps above, keep the following tips in mind.
Set the right tone and style
Like every piece of writing, a research paper should be written for the audience. That is to say, it should match the tone and style that your academic discipline and target audience expect. This is typically a formal and academic tone, though the degree of formality varies by field.
Kno w the audience
The perfect introduction balances clarity with conciseness. The amount of clarification required for a given topic depends greatly on the target audience. Knowing who will be reading your paper will guide you in determining how much background information is required.
Adopt the CARS (create a research space) model
The CARS model is a helpful tool for structuring introductions. This structure has three parts. The beginning of the introduction establishes the general research area. Next, relevant literature is reviewed and critiqued. The final section outlines the purpose of your study as it relates to the previous parts.
Master the art of funneling
The CARS method is one example of a well-funneled introduction. These start broadly and then slowly narrow down to your specific research problem. It provides a nice narrative flow that provides the right information at the right time. If you stray from the CARS model, try to retain this same type of funneling.
Incorporate narrative element
People read research papers largely to be informed. But to inform the reader, you have to hold their attention. A narrative style, particularly in the introduction, is a great way to do that. This can be a compelling story, an intriguing question, or a description of a real-world problem.
Write the introduction last
By writing the introduction after the rest of the paper, you'll have a better idea of what your research entails and how the paper is structured. This prevents the common problem of writing something in the introduction and then forgetting to include it in the paper. It also means anything particularly exciting in the paper isn’t neglected in the intro.
Should you be using a customer insights hub?
Do you want to discover previous research faster?
Do you share your research findings with others?
Do you analyze research data?
Start for free today, add your research, and get to key insights faster
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 11 January 2024
Last updated: 15 January 2024
Last updated: 17 January 2024
Last updated: 12 May 2023
Last updated: 30 April 2024
Last updated: 18 May 2023
Last updated: 25 November 2023
Last updated: 13 May 2024
Latest articles
Related topics, .css-je19u9{-webkit-align-items:flex-end;-webkit-box-align:flex-end;-ms-flex-align:flex-end;align-items:flex-end;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-flex-direction:row;-ms-flex-direction:row;flex-direction:row;-webkit-box-flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-flex-wrap:wrap;-ms-flex-wrap:wrap;flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-box-pack:center;-ms-flex-pack:center;-webkit-justify-content:center;justify-content:center;row-gap:0;text-align:center;max-width:671px;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}}@media (max-width: 799px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}} decide what to .css-1kiodld{max-height:56px;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-1kiodld{display:none;}} build next, decide what to build next.

Users report unexpectedly high data usage, especially during streaming sessions.

Users find it hard to navigate from the home page to relevant playlists in the app.

It would be great to have a sleep timer feature, especially for bedtime listening.

I need better filters to find the songs or artists I’m looking for.
Log in or sign up
Get started for free
- If you are writing in a new discipline, you should always make sure to ask about conventions and expectations for introductions, just as you would for any other aspect of the essay. For example, while it may be acceptable to write a two-paragraph (or longer) introduction for your papers in some courses, instructors in other disciplines, such as those in some Government courses, may expect a shorter introduction that includes a preview of the argument that will follow.
- In some disciplines (Government, Economics, and others), it’s common to offer an overview in the introduction of what points you will make in your essay. In other disciplines, you will not be expected to provide this overview in your introduction.
- Avoid writing a very general opening sentence. While it may be true that “Since the dawn of time, people have been telling love stories,” it won’t help you explain what’s interesting about your topic.
- Avoid writing a “funnel” introduction in which you begin with a very broad statement about a topic and move to a narrow statement about that topic. Broad generalizations about a topic will not add to your readers’ understanding of your specific essay topic.
- Avoid beginning with a dictionary definition of a term or concept you will be writing about. If the concept is complicated or unfamiliar to your readers, you will need to define it in detail later in your essay. If it’s not complicated, you can assume your readers already know the definition.
- Avoid offering too much detail in your introduction that a reader could better understand later in the paper.
- picture_as_pdf Introductions
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
- Research Papers
How to Write a Research Introduction
Last Updated: December 6, 2023 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Megan Morgan, PhD . Megan Morgan is a Graduate Program Academic Advisor in the School of Public & International Affairs at the University of Georgia. She earned her PhD in English from the University of Georgia in 2015. There are 7 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 2,653,290 times.
The introduction to a research paper can be the most challenging part of the paper to write. The length of the introduction will vary depending on the type of research paper you are writing. An introduction should announce your topic, provide context and a rationale for your work, before stating your research questions and hypothesis. Well-written introductions set the tone for the paper, catch the reader's interest, and communicate the hypothesis or thesis statement.
Introducing the Topic of the Paper

- In scientific papers this is sometimes known as an "inverted triangle", where you start with the broadest material at the start, before zooming in on the specifics. [2] X Research source
- The sentence "Throughout the 20th century, our views of life on other planets have drastically changed" introduces a topic, but does so in broad terms.
- It provides the reader with an indication of the content of the essay and encourages them to read on.

- For example, if you were writing a paper about the behaviour of mice when exposed to a particular substance, you would include the word "mice", and the scientific name of the relevant compound in the first sentences.
- If you were writing a history paper about the impact of the First World War on gender relations in Britain, you should mention those key words in your first few lines.

- This is especially important if you are attempting to develop a new conceptualization that uses language and terminology your readers may be unfamiliar with.

- If you use an anecdote ensure that is short and highly relevant for your research. It has to function in the same way as an alternative opening, namely to announce the topic of your research paper to your reader.
- For example, if you were writing a sociology paper about re-offending rates among young offenders, you could include a brief story of one person whose story reflects and introduces your topic.
- This kind of approach is generally not appropriate for the introduction to a natural or physical sciences research paper where the writing conventions are different.
Establishing the Context for Your Paper

- It is important to be concise in the introduction, so provide an overview on recent developments in the primary research rather than a lengthy discussion.
- You can follow the "inverted triangle" principle to focus in from the broader themes to those to which you are making a direct contribution with your paper.
- A strong literature review presents important background information to your own research and indicates the importance of the field.

- By making clear reference to existing work you can demonstrate explicitly the specific contribution you are making to move the field forward.
- You can identify a gap in the existing scholarship and explain how you are addressing it and moving understanding forward.

- For example, if you are writing a scientific paper you could stress the merits of the experimental approach or models you have used.
- Stress what is novel in your research and the significance of your new approach, but don't give too much detail in the introduction.
- A stated rationale could be something like: "the study evaluates the previously unknown anti-inflammatory effects of a topical compound in order to evaluate its potential clinical uses".
Specifying Your Research Questions and Hypothesis

- The research question or questions generally come towards the end of the introduction, and should be concise and closely focused.
- The research question might recall some of the key words established in the first few sentences and the title of your paper.
- An example of a research question could be "what were the consequences of the North American Free Trade Agreement on the Mexican export economy?"
- This could be honed further to be specific by referring to a particular element of the Free Trade Agreement and the impact on a particular industry in Mexico, such as clothing manufacture.
- A good research question should shape a problem into a testable hypothesis.

- If possible try to avoid using the word "hypothesis" and rather make this implicit in your writing. This can make your writing appear less formulaic.
- In a scientific paper, giving a clear one-sentence overview of your results and their relation to your hypothesis makes the information clear and accessible. [10] X Trustworthy Source PubMed Central Journal archive from the U.S. National Institutes of Health Go to source
- An example of a hypothesis could be "mice deprived of food for the duration of the study were expected to become more lethargic than those fed normally".

- This is not always necessary and you should pay attention to the writing conventions in your discipline.
- In a natural sciences paper, for example, there is a fairly rigid structure which you will be following.
- A humanities or social science paper will most likely present more opportunities to deviate in how you structure your paper.
Research Introduction Help

Community Q&A
- Use your research papers' outline to help you decide what information to include when writing an introduction. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 1
- Consider drafting your introduction after you have already completed the rest of your research paper. Writing introductions last can help ensure that you don't leave out any major points. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0

- Avoid emotional or sensational introductions; these can create distrust in the reader. Thanks Helpful 50 Not Helpful 12
- Generally avoid using personal pronouns in your introduction, such as "I," "me," "we," "us," "my," "mine," or "our." Thanks Helpful 31 Not Helpful 7
- Don't overwhelm the reader with an over-abundance of information. Keep the introduction as concise as possible by saving specific details for the body of your paper. Thanks Helpful 24 Not Helpful 14
You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://library.sacredheart.edu/c.php?g=29803&p=185916
- ↑ https://www.aresearchguide.com/inverted-pyramid-structure-in-writing.html
- ↑ https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide/introduction
- ↑ https://writing.wisc.edu/Handbook/PlanResearchPaper.html
- ↑ https://dept.writing.wisc.edu/wac/writing-an-introduction-for-a-scientific-paper/
- ↑ https://writing.wisc.edu/handbook/assignments/planresearchpaper/
- ↑ http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3178846/
About This Article

To introduce your research paper, use the first 1-2 sentences to describe your general topic, such as “women in World War I.” Include and define keywords, such as “gender relations,” to show your reader where you’re going. Mention previous research into the topic with a phrase like, “Others have studied…”, then transition into what your contribution will be and why it’s necessary. Finally, state the questions that your paper will address and propose your “answer” to them as your thesis statement. For more information from our English Ph.D. co-author about how to craft a strong hypothesis and thesis, keep reading! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Abdulrahman Omar
Oct 5, 2018
Did this article help you?
May 9, 2021
Lavanya Gopakumar
Oct 1, 2016
Dengkai Zhang
May 14, 2018
Leslie Mae Cansana
Sep 22, 2016

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Don’t miss out! Sign up for
wikiHow’s newsletter

- Walden University
- Faculty Portal
General Research Paper Guidelines: Introduction
Introduction.
Generally, all academic introductory sections should introduce readers to your topic and scope, moving readers from a broad overview to your specific, narrow focus. In an academic introduction, you should also indicate your perspective on or argument about your given topic and explain to readers why the study of your topic is important. An introduction can range from a single paragraph to multiple paragraphs, depending on the length and scope of your draft.
For research papers, in particular, you want to make sure your introduction not only meets the general guidelines above but also does the following:
- Includes a central argument, problem statement, or thesis statement, detailing the intent, rationale, and/or purpose of your research.
- Addresses why your problem or topic is important.
- Outlines the design, method, and/or key characteristics of your research.
- Describes important results or conclusions of your research.
- Provides a brief, yet clear overview of the structure of the paper.
- Previous Page: Abstract
- Next Page: Literature Review
- Office of Student Disability Services
Walden Resources
Departments.
- Academic Residencies
- Academic Skills
- Career Planning and Development
- Customer Care Team
- Field Experience
- Military Services
- Student Success Advising
- Writing Skills
Centers and Offices
- Center for Social Change
- Office of Academic Support and Instructional Services
- Office of Degree Acceleration
- Office of Research and Doctoral Services
- Office of Student Affairs
Student Resources
- Doctoral Writing Assessment
- Form & Style Review
- Quick Answers
- ScholarWorks
- SKIL Courses and Workshops
- Walden Bookstore
- Walden Catalog & Student Handbook
- Student Safety/Title IX
- Legal & Consumer Information
- Website Terms and Conditions
- Cookie Policy
- Accessibility
- Accreditation
- State Authorization
- Net Price Calculator
- Contact Walden
Walden University is a member of Adtalem Global Education, Inc. www.adtalem.com Walden University is certified to operate by SCHEV © 2024 Walden University LLC. All rights reserved.
How to Write the Introduction to a Scientific Paper?
- Open Access
- First Online: 24 October 2021
Cite this chapter
You have full access to this open access chapter

- Samiran Nundy 4 ,
- Atul Kakar 5 &
- Zulfiqar A. Bhutta 6
65k Accesses
142 Altmetric
An Introduction to a scientific paper familiarizes the reader with the background of the issue at hand. It must reflect why the issue is topical and its current importance in the vast sea of research being done globally. It lays the foundation of biomedical writing and is the first portion of an article according to the IMRAD pattern ( I ntroduction, M ethodology, R esults, a nd D iscussion) [1].
I once had a professor tell a class that he sifted through our pile of essays, glancing at the titles and introductions, looking for something that grabbed his attention. Everything else went to the bottom of the pile to be read last, when he was tired and probably grumpy from all the marking. Don’t get put at the bottom of the pile, he said. Anonymous
You have full access to this open access chapter, Download chapter PDF
Similar content being viewed by others

The Introduction Section

Abstract and Keywords

Writing and publishing a scientific paper
1 what is the importance of an introduction.
An Introduction to a scientific paper familiarizes the reader with the background of the issue at hand. It must reflect why the issue is topical and its current importance in the vast sea of research being done globally. It lays the foundation of biomedical writing and is the first portion of an article according to the IMRAD pattern ( I ntroduction, M ethodology, R esults, a nd D iscussion) [ 1 ].
It provides the flavour of the article and many authors have used phrases to describe it for example—'like a gate of the city’ [ 2 ], ‘the beginning is half of the whole’ [ 3 ], ‘an introduction is not just wrestling with words to fit the facts, but it also strongly modulated by perception of the anticipated reactions of peer colleagues’, [ 4 ] and ‘an introduction is like the trailer to a movie’. A good introduction helps captivate the reader early.

2 What Are the Principles of Writing a Good Introduction?
A good introduction will ‘sell’ an article to a journal editor, reviewer, and finally to a reader [ 3 ]. It should contain the following information [ 5 , 6 ]:
The known—The background scientific data
The unknown—Gaps in the current knowledge
Research hypothesis or question
Methodologies used for the study
The known consist of citations from a review of the literature whereas the unknown is the new work to be undertaken. This part should address how your work is the required missing piece of the puzzle.
3 What Are the Models of Writing an Introduction?
The Problem-solving model
First described by Swales et al. in 1979, in this model the writer should identify the ‘problem’ in the research, address the ‘solution’ and also write about ‘the criteria for evaluating the problem’ [ 7 , 8 ].
The CARS model that stands for C reating A R esearch S pace [ 9 , 10 ].
The two important components of this model are:
Establishing a territory (situation)
Establishing a niche (problem)
Occupying a niche (the solution)
In this popular model, one can add a fourth point, i.e., a conclusion [ 10 ].
4 What Is Establishing a Territory?
This includes: [ 9 ]
Stating the general topic and providing some background about it.
Providing a brief and relevant review of the literature related to the topic.
Adding a paragraph on the scope of the topic including the need for your study.
5 What Is Establishing a Niche?
Establishing a niche includes:
Stating the importance of the problem.
Outlining the current situation regarding the problem citing both global and national data.
Evaluating the current situation (advantages/ disadvantages).
Identifying the gaps.
Emphasizing the importance of the proposed research and how the gaps will be addressed.
Stating the research problem/ questions.
Stating the hypotheses briefly.
Figure 17.1 depicts how the introduction needs to be written. A scientific paper should have an introduction in the form of an inverted pyramid. The writer should start with the general information about the topic and subsequently narrow it down to the specific topic-related introduction.
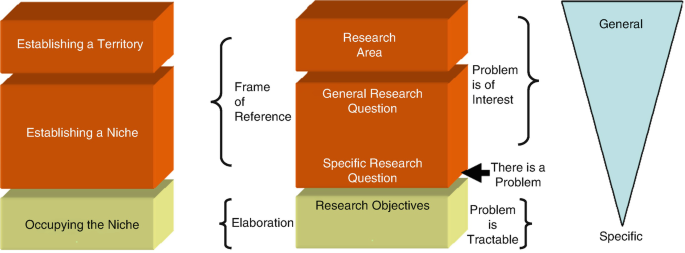
Flow of ideas from the general to the specific
6 What Does Occupying a Niche Mean?
This is the third portion of the introduction and defines the rationale of the research and states the research question. If this is missing the reviewers will not understand the logic for publication and is a common reason for rejection [ 11 , 12 ]. An example of this is given below:
Till date, no study has been done to see the effectiveness of a mesh alone or the effectiveness of double suturing along with a mesh in the closure of an umbilical hernia regarding the incidence of failure. So, the present study is aimed at comparing the effectiveness of a mesh alone versus the double suturing technique along with a mesh.
7 How Long Should the Introduction Be?
For a project protocol, the introduction should be about 1–2 pages long and for a thesis it should be 3–5 pages in a double-spaced typed setting. For a scientific paper it should be less than 10–15% of the total length of the manuscript [ 13 , 14 ].
8 How Many References Should an Introduction Have?
All sections in a scientific manuscript except the conclusion should contain references. It has been suggested that an introduction should have four or five or at the most one-third of the references in the whole paper [ 15 ].
9 What Are the Important Points Which Should be not Missed in an Introduction?
An introduction paves the way forward for the subsequent sections of the article. Frequently well-planned studies are rejected by journals during review because of the simple reason that the authors failed to clarify the data in this section to justify the study [ 16 , 17 ]. Thus, the existing gap in knowledge should be clearly brought out in this section (Fig. 17.2 ).
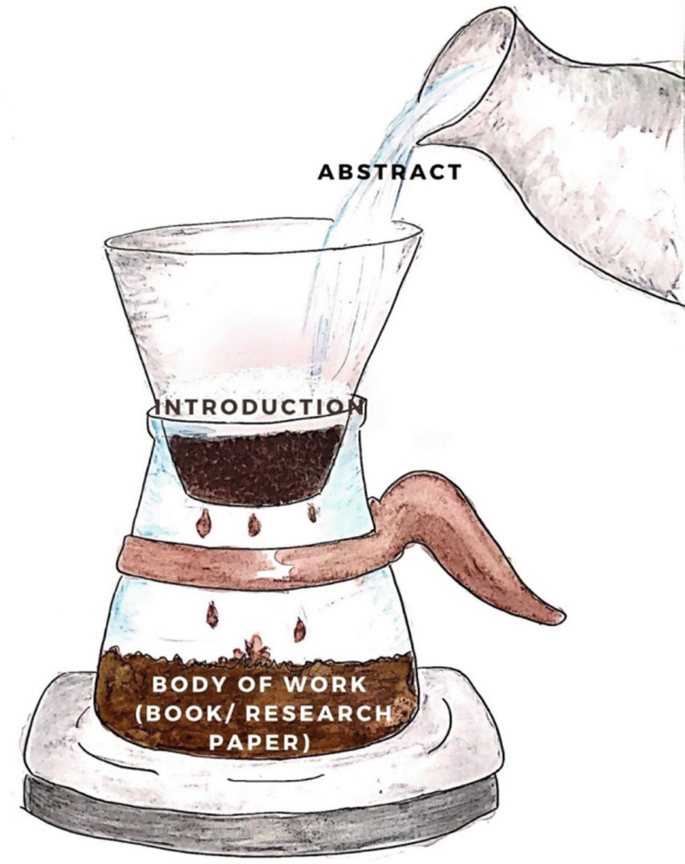
How should the abstract, introduction, and discussion look
The following points are important to consider:
The introduction should be written in simple sentences and in the present tense.
Many of the terms will be introduced in this section for the first time and these will require abbreviations to be used later.
The references in this section should be to papers published in quality journals (e.g., having a high impact factor).
The aims, problems, and hypotheses should be clearly mentioned.
Start with a generalization on the topic and go on to specific information relevant to your research.
10 Example of an Introduction

11 Conclusions
An Introduction is a brief account of what the study is about. It should be short, crisp, and complete.
It has to move from a general to a specific research topic and must include the need for the present study.
The Introduction should include data from a literature search, i.e., what is already known about this subject and progress to what we hope to add to this knowledge.
Moore A. What’s in a discussion section? Exploiting 2-dimensionality in the online world. Bioassays. 2016;38(12):1185.
Article Google Scholar
Annesley TM. The discussion section: your closing argument. Clin Chem. 2010;56(11):1671–4.
Article CAS Google Scholar
Bavdekar SB. Writing the discussion section: describing the significance of the study findings. J Assoc Physicians India. 2015;63(11):40–2.
PubMed Google Scholar
Foote M. The proof of the pudding: how to report results and write a good discussion. Chest. 2009;135(3):866–8.
Kearney MH. The discussion section tells us where we are. Res Nurs Health. 2017;40(4):289–91.
Ghasemi A, Bahadoran Z, Mirmiran P, Hosseinpanah F, Shiva N, Zadeh-Vakili A. The principles of biomedical scientific writing: discussion. Int J Endocrinol Metab. 2019;17(3):e95415.
Swales JM, Feak CB. Academic writing for graduate students: essential tasks and skills. Ann Arbor, MI: University of Michigan Press; 2004.
Google Scholar
Colombo M, Bucher L, Sprenger J. Determinants of judgments of explanatory power: credibility, generality, and statistical relevance. Front Psychol. 2017;8:1430.
Mozayan MR, Allami H, Fazilatfar AM. Metadiscourse features in medical research articles: subdisciplinary and paradigmatic influences in English and Persian. Res Appl Ling. 2018;9(1):83–104.
Hyland K. Metadiscourse: mapping interactions in academic writing. Nordic J English Stud. 2010;9(2):125.
Hill AB. The environment and disease: association or causation? Proc Royal Soc Med. 2016;58(5):295–300.
Alpert JS. Practicing medicine in Plato’s cave. Am J Med. 2006;119(6):455–6.
Walsh K. Discussing discursive discussions. Med Educ. 2016;50(12):1269–70.
Polit DF, Beck CT. Generalization in quantitative and qualitative research: myths and strategies. Int J Nurs Stud. 2010;47(11):1451–8.
Jawaid SA, Jawaid M. How to write introduction and discussion. Saudi J Anaesth. 2019;13(Suppl 1):S18–9.
Jawaid SA, Baig M. How to write an original article. In: Jawaid SA, Jawaid M, editors. Scientific writing: a guide to the art of medical writing and scientific publishing. Karachi: Published by Med-Print Services; 2018. p. 135–50.
Hall GM, editor. How to write a paper. London: BMJ Books, BMJ Publishing Group; 2003. Structure of a scientific paper. p. 1–5.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Surgical Gastroenterology and Liver Transplantation, Sir Ganga Ram Hospital, New Delhi, India
Samiran Nundy
Department of Internal Medicine, Sir Ganga Ram Hospital, New Delhi, India
Institute for Global Health and Development, The Aga Khan University, South Central Asia, East Africa and United Kingdom, Karachi, Pakistan
Zulfiqar A. Bhutta
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Rights and permissions
Open Access This chapter is licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ ), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license and indicate if changes were made.
The images or other third party material in this chapter are included in the chapter's Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the chapter's Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder.
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s)
About this chapter
Nundy, S., Kakar, A., Bhutta, Z.A. (2022). How to Write the Introduction to a Scientific Paper?. In: How to Practice Academic Medicine and Publish from Developing Countries?. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-5248-6_17
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-5248-6_17
Published : 24 October 2021
Publisher Name : Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN : 978-981-16-5247-9
Online ISBN : 978-981-16-5248-6
eBook Packages : Medicine Medicine (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
- Privacy Policy

Home » Research Paper – Structure, Examples and Writing Guide
Research Paper – Structure, Examples and Writing Guide
Table of Contents

Research Paper
Definition:
Research Paper is a written document that presents the author’s original research, analysis, and interpretation of a specific topic or issue.
It is typically based on Empirical Evidence, and may involve qualitative or quantitative research methods, or a combination of both. The purpose of a research paper is to contribute new knowledge or insights to a particular field of study, and to demonstrate the author’s understanding of the existing literature and theories related to the topic.
Structure of Research Paper
The structure of a research paper typically follows a standard format, consisting of several sections that convey specific information about the research study. The following is a detailed explanation of the structure of a research paper:
The title page contains the title of the paper, the name(s) of the author(s), and the affiliation(s) of the author(s). It also includes the date of submission and possibly, the name of the journal or conference where the paper is to be published.
The abstract is a brief summary of the research paper, typically ranging from 100 to 250 words. It should include the research question, the methods used, the key findings, and the implications of the results. The abstract should be written in a concise and clear manner to allow readers to quickly grasp the essence of the research.

Introduction
The introduction section of a research paper provides background information about the research problem, the research question, and the research objectives. It also outlines the significance of the research, the research gap that it aims to fill, and the approach taken to address the research question. Finally, the introduction section ends with a clear statement of the research hypothesis or research question.
Literature Review
The literature review section of a research paper provides an overview of the existing literature on the topic of study. It includes a critical analysis and synthesis of the literature, highlighting the key concepts, themes, and debates. The literature review should also demonstrate the research gap and how the current study seeks to address it.
The methods section of a research paper describes the research design, the sample selection, the data collection and analysis procedures, and the statistical methods used to analyze the data. This section should provide sufficient detail for other researchers to replicate the study.
The results section presents the findings of the research, using tables, graphs, and figures to illustrate the data. The findings should be presented in a clear and concise manner, with reference to the research question and hypothesis.
The discussion section of a research paper interprets the findings and discusses their implications for the research question, the literature review, and the field of study. It should also address the limitations of the study and suggest future research directions.
The conclusion section summarizes the main findings of the study, restates the research question and hypothesis, and provides a final reflection on the significance of the research.
The references section provides a list of all the sources cited in the paper, following a specific citation style such as APA, MLA or Chicago.
How to Write Research Paper
You can write Research Paper by the following guide:
- Choose a Topic: The first step is to select a topic that interests you and is relevant to your field of study. Brainstorm ideas and narrow down to a research question that is specific and researchable.
- Conduct a Literature Review: The literature review helps you identify the gap in the existing research and provides a basis for your research question. It also helps you to develop a theoretical framework and research hypothesis.
- Develop a Thesis Statement : The thesis statement is the main argument of your research paper. It should be clear, concise and specific to your research question.
- Plan your Research: Develop a research plan that outlines the methods, data sources, and data analysis procedures. This will help you to collect and analyze data effectively.
- Collect and Analyze Data: Collect data using various methods such as surveys, interviews, observations, or experiments. Analyze data using statistical tools or other qualitative methods.
- Organize your Paper : Organize your paper into sections such as Introduction, Literature Review, Methods, Results, Discussion, and Conclusion. Ensure that each section is coherent and follows a logical flow.
- Write your Paper : Start by writing the introduction, followed by the literature review, methods, results, discussion, and conclusion. Ensure that your writing is clear, concise, and follows the required formatting and citation styles.
- Edit and Proofread your Paper: Review your paper for grammar and spelling errors, and ensure that it is well-structured and easy to read. Ask someone else to review your paper to get feedback and suggestions for improvement.
- Cite your Sources: Ensure that you properly cite all sources used in your research paper. This is essential for giving credit to the original authors and avoiding plagiarism.
Research Paper Example
Note : The below example research paper is for illustrative purposes only and is not an actual research paper. Actual research papers may have different structures, contents, and formats depending on the field of study, research question, data collection and analysis methods, and other factors. Students should always consult with their professors or supervisors for specific guidelines and expectations for their research papers.
Research Paper Example sample for Students:
Title: The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health among Young Adults
Abstract: This study aims to investigate the impact of social media use on the mental health of young adults. A literature review was conducted to examine the existing research on the topic. A survey was then administered to 200 university students to collect data on their social media use, mental health status, and perceived impact of social media on their mental health. The results showed that social media use is positively associated with depression, anxiety, and stress. The study also found that social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO (Fear of Missing Out) are significant predictors of mental health problems among young adults.
Introduction: Social media has become an integral part of modern life, particularly among young adults. While social media has many benefits, including increased communication and social connectivity, it has also been associated with negative outcomes, such as addiction, cyberbullying, and mental health problems. This study aims to investigate the impact of social media use on the mental health of young adults.
Literature Review: The literature review highlights the existing research on the impact of social media use on mental health. The review shows that social media use is associated with depression, anxiety, stress, and other mental health problems. The review also identifies the factors that contribute to the negative impact of social media, including social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO.
Methods : A survey was administered to 200 university students to collect data on their social media use, mental health status, and perceived impact of social media on their mental health. The survey included questions on social media use, mental health status (measured using the DASS-21), and perceived impact of social media on their mental health. Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics and regression analysis.
Results : The results showed that social media use is positively associated with depression, anxiety, and stress. The study also found that social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO are significant predictors of mental health problems among young adults.
Discussion : The study’s findings suggest that social media use has a negative impact on the mental health of young adults. The study highlights the need for interventions that address the factors contributing to the negative impact of social media, such as social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO.
Conclusion : In conclusion, social media use has a significant impact on the mental health of young adults. The study’s findings underscore the need for interventions that promote healthy social media use and address the negative outcomes associated with social media use. Future research can explore the effectiveness of interventions aimed at reducing the negative impact of social media on mental health. Additionally, longitudinal studies can investigate the long-term effects of social media use on mental health.
Limitations : The study has some limitations, including the use of self-report measures and a cross-sectional design. The use of self-report measures may result in biased responses, and a cross-sectional design limits the ability to establish causality.
Implications: The study’s findings have implications for mental health professionals, educators, and policymakers. Mental health professionals can use the findings to develop interventions that address the negative impact of social media use on mental health. Educators can incorporate social media literacy into their curriculum to promote healthy social media use among young adults. Policymakers can use the findings to develop policies that protect young adults from the negative outcomes associated with social media use.
References :
- Twenge, J. M., & Campbell, W. K. (2019). Associations between screen time and lower psychological well-being among children and adolescents: Evidence from a population-based study. Preventive medicine reports, 15, 100918.
- Primack, B. A., Shensa, A., Escobar-Viera, C. G., Barrett, E. L., Sidani, J. E., Colditz, J. B., … & James, A. E. (2017). Use of multiple social media platforms and symptoms of depression and anxiety: A nationally-representative study among US young adults. Computers in Human Behavior, 69, 1-9.
- Van der Meer, T. G., & Verhoeven, J. W. (2017). Social media and its impact on academic performance of students. Journal of Information Technology Education: Research, 16, 383-398.
Appendix : The survey used in this study is provided below.
Social Media and Mental Health Survey
- How often do you use social media per day?
- Less than 30 minutes
- 30 minutes to 1 hour
- 1 to 2 hours
- 2 to 4 hours
- More than 4 hours
- Which social media platforms do you use?
- Others (Please specify)
- How often do you experience the following on social media?
- Social comparison (comparing yourself to others)
- Cyberbullying
- Fear of Missing Out (FOMO)
- Have you ever experienced any of the following mental health problems in the past month?
- Do you think social media use has a positive or negative impact on your mental health?
- Very positive
- Somewhat positive
- Somewhat negative
- Very negative
- In your opinion, which factors contribute to the negative impact of social media on mental health?
- Social comparison
- In your opinion, what interventions could be effective in reducing the negative impact of social media on mental health?
- Education on healthy social media use
- Counseling for mental health problems caused by social media
- Social media detox programs
- Regulation of social media use
Thank you for your participation!
Applications of Research Paper
Research papers have several applications in various fields, including:
- Advancing knowledge: Research papers contribute to the advancement of knowledge by generating new insights, theories, and findings that can inform future research and practice. They help to answer important questions, clarify existing knowledge, and identify areas that require further investigation.
- Informing policy: Research papers can inform policy decisions by providing evidence-based recommendations for policymakers. They can help to identify gaps in current policies, evaluate the effectiveness of interventions, and inform the development of new policies and regulations.
- Improving practice: Research papers can improve practice by providing evidence-based guidance for professionals in various fields, including medicine, education, business, and psychology. They can inform the development of best practices, guidelines, and standards of care that can improve outcomes for individuals and organizations.
- Educating students : Research papers are often used as teaching tools in universities and colleges to educate students about research methods, data analysis, and academic writing. They help students to develop critical thinking skills, research skills, and communication skills that are essential for success in many careers.
- Fostering collaboration: Research papers can foster collaboration among researchers, practitioners, and policymakers by providing a platform for sharing knowledge and ideas. They can facilitate interdisciplinary collaborations and partnerships that can lead to innovative solutions to complex problems.
When to Write Research Paper
Research papers are typically written when a person has completed a research project or when they have conducted a study and have obtained data or findings that they want to share with the academic or professional community. Research papers are usually written in academic settings, such as universities, but they can also be written in professional settings, such as research organizations, government agencies, or private companies.
Here are some common situations where a person might need to write a research paper:
- For academic purposes: Students in universities and colleges are often required to write research papers as part of their coursework, particularly in the social sciences, natural sciences, and humanities. Writing research papers helps students to develop research skills, critical thinking skills, and academic writing skills.
- For publication: Researchers often write research papers to publish their findings in academic journals or to present their work at academic conferences. Publishing research papers is an important way to disseminate research findings to the academic community and to establish oneself as an expert in a particular field.
- To inform policy or practice : Researchers may write research papers to inform policy decisions or to improve practice in various fields. Research findings can be used to inform the development of policies, guidelines, and best practices that can improve outcomes for individuals and organizations.
- To share new insights or ideas: Researchers may write research papers to share new insights or ideas with the academic or professional community. They may present new theories, propose new research methods, or challenge existing paradigms in their field.
Purpose of Research Paper
The purpose of a research paper is to present the results of a study or investigation in a clear, concise, and structured manner. Research papers are written to communicate new knowledge, ideas, or findings to a specific audience, such as researchers, scholars, practitioners, or policymakers. The primary purposes of a research paper are:
- To contribute to the body of knowledge : Research papers aim to add new knowledge or insights to a particular field or discipline. They do this by reporting the results of empirical studies, reviewing and synthesizing existing literature, proposing new theories, or providing new perspectives on a topic.
- To inform or persuade: Research papers are written to inform or persuade the reader about a particular issue, topic, or phenomenon. They present evidence and arguments to support their claims and seek to persuade the reader of the validity of their findings or recommendations.
- To advance the field: Research papers seek to advance the field or discipline by identifying gaps in knowledge, proposing new research questions or approaches, or challenging existing assumptions or paradigms. They aim to contribute to ongoing debates and discussions within a field and to stimulate further research and inquiry.
- To demonstrate research skills: Research papers demonstrate the author’s research skills, including their ability to design and conduct a study, collect and analyze data, and interpret and communicate findings. They also demonstrate the author’s ability to critically evaluate existing literature, synthesize information from multiple sources, and write in a clear and structured manner.
Characteristics of Research Paper
Research papers have several characteristics that distinguish them from other forms of academic or professional writing. Here are some common characteristics of research papers:
- Evidence-based: Research papers are based on empirical evidence, which is collected through rigorous research methods such as experiments, surveys, observations, or interviews. They rely on objective data and facts to support their claims and conclusions.
- Structured and organized: Research papers have a clear and logical structure, with sections such as introduction, literature review, methods, results, discussion, and conclusion. They are organized in a way that helps the reader to follow the argument and understand the findings.
- Formal and objective: Research papers are written in a formal and objective tone, with an emphasis on clarity, precision, and accuracy. They avoid subjective language or personal opinions and instead rely on objective data and analysis to support their arguments.
- Citations and references: Research papers include citations and references to acknowledge the sources of information and ideas used in the paper. They use a specific citation style, such as APA, MLA, or Chicago, to ensure consistency and accuracy.
- Peer-reviewed: Research papers are often peer-reviewed, which means they are evaluated by other experts in the field before they are published. Peer-review ensures that the research is of high quality, meets ethical standards, and contributes to the advancement of knowledge in the field.
- Objective and unbiased: Research papers strive to be objective and unbiased in their presentation of the findings. They avoid personal biases or preconceptions and instead rely on the data and analysis to draw conclusions.
Advantages of Research Paper
Research papers have many advantages, both for the individual researcher and for the broader academic and professional community. Here are some advantages of research papers:
- Contribution to knowledge: Research papers contribute to the body of knowledge in a particular field or discipline. They add new information, insights, and perspectives to existing literature and help advance the understanding of a particular phenomenon or issue.
- Opportunity for intellectual growth: Research papers provide an opportunity for intellectual growth for the researcher. They require critical thinking, problem-solving, and creativity, which can help develop the researcher’s skills and knowledge.
- Career advancement: Research papers can help advance the researcher’s career by demonstrating their expertise and contributions to the field. They can also lead to new research opportunities, collaborations, and funding.
- Academic recognition: Research papers can lead to academic recognition in the form of awards, grants, or invitations to speak at conferences or events. They can also contribute to the researcher’s reputation and standing in the field.
- Impact on policy and practice: Research papers can have a significant impact on policy and practice. They can inform policy decisions, guide practice, and lead to changes in laws, regulations, or procedures.
- Advancement of society: Research papers can contribute to the advancement of society by addressing important issues, identifying solutions to problems, and promoting social justice and equality.
Limitations of Research Paper
Research papers also have some limitations that should be considered when interpreting their findings or implications. Here are some common limitations of research papers:
- Limited generalizability: Research findings may not be generalizable to other populations, settings, or contexts. Studies often use specific samples or conditions that may not reflect the broader population or real-world situations.
- Potential for bias : Research papers may be biased due to factors such as sample selection, measurement errors, or researcher biases. It is important to evaluate the quality of the research design and methods used to ensure that the findings are valid and reliable.
- Ethical concerns: Research papers may raise ethical concerns, such as the use of vulnerable populations or invasive procedures. Researchers must adhere to ethical guidelines and obtain informed consent from participants to ensure that the research is conducted in a responsible and respectful manner.
- Limitations of methodology: Research papers may be limited by the methodology used to collect and analyze data. For example, certain research methods may not capture the complexity or nuance of a particular phenomenon, or may not be appropriate for certain research questions.
- Publication bias: Research papers may be subject to publication bias, where positive or significant findings are more likely to be published than negative or non-significant findings. This can skew the overall findings of a particular area of research.
- Time and resource constraints: Research papers may be limited by time and resource constraints, which can affect the quality and scope of the research. Researchers may not have access to certain data or resources, or may be unable to conduct long-term studies due to practical limitations.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

How to Cite Research Paper – All Formats and...

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Paper Format – Types, Examples and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples
Writing Center: Rough Drafting
- Brainstorming and Planning
- Thesis Statements
- Rough Drafting
- Editing and Revising
- Citations and Style
- Additional Resources
- ENGL 110 Resources
- Writing in the Major
The Essential Elements of a Paper
Every paper must include:.
- An Introduction: This element should grab the reader's attention, briefly introduce the topic, and state your main claim (thesis statement).
- Body: This element includes all your supporting points and evidence. This is where you build your argument to support the thesis statement.
- A Conclusion: This element should restate your main claim, summarize your main points, and provide the reader with something to take away.
Typically, you need a seperate paragraph for each of these elements . The Body will usually include multiple paragraphs, although it does not have to.
Introduction
An Introduction should grab the reader's attention, briefly introduce the topic, and state your main claim.
Your thesis statement should be the final sentence in the introductory paragraph.
- Writing an Introduction Paragraph
What is the body of a paper?
The body of the paper includes all the paragraphs between the introduction and conclusion paragraphs. This can range from one paragraph to as many as you need to make your point.
Body Paragraph Structure:
- Every body paragraph should communicate ONE main idea.
- Body paragraphs include the same elements as the paper overall (See The Essential Elements of a Paper ): a topic sentence (introduction), support (body), and a concluding sentence (conclusion)!
Topic Sentences:
Topic sentences are incredibly important because they help you keep your paper organized and your reader follow your argument. The topic sentence should include the main point of the paragraph (like a mini thesis statement).
See below for more information on Topic Sentences!
- Topic Sentence Guide
The support in your paper includes both evidence and analysis. You need to provide your readers with reasons for your topic sentence. Often, this includes information from outside sources, such as books, articles, websites, and journals. It is not enough to simply throw infromation at your reader. You must also analyze the information. Tell your reader why your evidence is significant: how it impacts the main point of that paragraph and the thesis statement for the entire paper.
See below for information on Quote Integration!
- Quote Integration Guide
Concluding Sentences:
The concluding sentence wraps up the paragraph by reminding the reader about the main claim in that paragraph. Often, this looks like a restatement of your topic sentence. Also, this sentence can work to connect the main point of that paragraph back to the thesis statement.
A Conclusion should restate your main claim, summarize your main points, and provide the reader with something to take away.
The Conclusion is the last part of the paper that your reader encounters. If they remember only one thing from your paper, what is that you would want them to remember? Include that in your conclusion. This usually includes why your reader should care about the point you have just made (your thesis statement) and if applicable, what the reader should do now that they have that information.
- Writing a Conclusion Paragraph
Essay Structure Overview

The Essay Wheel

Essay Wheel Video!
Create an Outline
Before rough drafting, consider creating an outline.
Click here for more information on creating an outline.
- << Previous: Thesis Statements
- Next: Editing and Revising >>
- Last Updated: May 13, 2024 2:54 PM
- URL: https://libguides.messiah.edu/c.php?g=1350954
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Welcome to the Purdue Online Writing Lab

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
The Online Writing Lab at Purdue University houses writing resources and instructional material, and we provide these as a free service of the Writing Lab at Purdue. Students, members of the community, and users worldwide will find information to assist with many writing projects. Teachers and trainers may use this material for in-class and out-of-class instruction.
The Purdue On-Campus Writing Lab and Purdue Online Writing Lab assist clients in their development as writers—no matter what their skill level—with on-campus consultations, online participation, and community engagement. The Purdue Writing Lab serves the Purdue, West Lafayette, campus and coordinates with local literacy initiatives. The Purdue OWL offers global support through online reference materials and services.
A Message From the Assistant Director of Content Development
The Purdue OWL® is committed to supporting students, instructors, and writers by offering a wide range of resources that are developed and revised with them in mind. To do this, the OWL team is always exploring possibilties for a better design, allowing accessibility and user experience to guide our process. As the OWL undergoes some changes, we welcome your feedback and suggestions by email at any time.
Please don't hesitate to contact us via our contact page if you have any questions or comments.
All the best,
Social Media
Facebook twitter.
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Published: 08 May 2024
Accurate structure prediction of biomolecular interactions with AlphaFold 3
- Josh Abramson ORCID: orcid.org/0009-0000-3496-6952 1 na1 ,
- Jonas Adler ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-9928-3407 1 na1 ,
- Jack Dunger 1 na1 ,
- Richard Evans ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-4675-8469 1 na1 ,
- Tim Green ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-3227-1505 1 na1 ,
- Alexander Pritzel ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-4233-9040 1 na1 ,
- Olaf Ronneberger ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-4266-1515 1 na1 ,
- Lindsay Willmore ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-4314-0778 1 na1 ,
- Andrew J. Ballard ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-4956-5304 1 ,
- Joshua Bambrick ORCID: orcid.org/0009-0003-3908-0722 2 ,
- Sebastian W. Bodenstein 1 ,
- David A. Evans 1 ,
- Chia-Chun Hung ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-5264-9165 2 ,
- Michael O’Neill 1 ,
- David Reiman ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-1605-7197 1 ,
- Kathryn Tunyasuvunakool ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-8594-1074 1 ,
- Zachary Wu ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-2429-9812 1 ,
- Akvilė Žemgulytė 1 ,
- Eirini Arvaniti 3 ,
- Charles Beattie ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-1840-054X 3 ,
- Ottavia Bertolli ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-8578-3216 3 ,
- Alex Bridgland 3 ,
- Alexey Cherepanov ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-5227-0622 4 ,
- Miles Congreve 4 ,
- Alexander I. Cowen-Rivers 3 ,
- Andrew Cowie ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-4491-1434 3 ,
- Michael Figurnov ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-1386-8741 3 ,
- Fabian B. Fuchs 3 ,
- Hannah Gladman 3 ,
- Rishub Jain 3 ,
- Yousuf A. Khan ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-0201-2796 3 ,
- Caroline M. R. Low 4 ,
- Kuba Perlin 3 ,
- Anna Potapenko 3 ,
- Pascal Savy 4 ,
- Sukhdeep Singh 3 ,
- Adrian Stecula ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-6914-6743 4 ,
- Ashok Thillaisundaram 3 ,
- Catherine Tong ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-7570-4801 4 ,
- Sergei Yakneen ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-7827-9839 4 ,
- Ellen D. Zhong ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-6345-1907 3 ,
- Michal Zielinski 3 ,
- Augustin Žídek ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-0748-9684 3 ,
- Victor Bapst 1 na2 ,
- Pushmeet Kohli ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-7466-7997 1 na2 ,
- Max Jaderberg ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-9033-2695 2 na2 ,
- Demis Hassabis ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-2812-9917 1 , 2 na2 &
- John M. Jumper ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-6169-6580 1 na2
Nature ( 2024 ) Cite this article
230k Accesses
1 Citations
1152 Altmetric
Metrics details
We are providing an unedited version of this manuscript to give early access to its findings. Before final publication, the manuscript will undergo further editing. Please note there may be errors present which affect the content, and all legal disclaimers apply.
- Drug discovery
- Machine learning
- Protein structure predictions
- Structural biology
The introduction of AlphaFold 2 1 has spurred a revolution in modelling the structure of proteins and their interactions, enabling a huge range of applications in protein modelling and design 2–6 . In this paper, we describe our AlphaFold 3 model with a substantially updated diffusion-based architecture, which is capable of joint structure prediction of complexes including proteins, nucleic acids, small molecules, ions, and modified residues. The new AlphaFold model demonstrates significantly improved accuracy over many previous specialised tools: far greater accuracy on protein-ligand interactions than state of the art docking tools, much higher accuracy on protein-nucleic acid interactions than nucleic-acid-specific predictors, and significantly higher antibody-antigen prediction accuracy than AlphaFold-Multimer v2.3 7,8 . Together these results show that high accuracy modelling across biomolecular space is possible within a single unified deep learning framework.
You have full access to this article via your institution.
Similar content being viewed by others

Highly accurate protein structure prediction with AlphaFold
De novo generation of multi-target compounds using deep generative chemistry
Augmenting large language models with chemistry tools
Author information.
These authors contributed equally: Josh Abramson, Jonas Adler, Jack Dunger, Richard Evans, Tim Green, Alexander Pritzel, Olaf Ronneberger, Lindsay Willmore
These authors jointly supervised this work: Victor Bapst, Pushmeet Kohli, Max Jaderberg, Demis Hassabis, John M. Jumper
Authors and Affiliations
Core Contributor, Google DeepMind, London, UK
Josh Abramson, Jonas Adler, Jack Dunger, Richard Evans, Tim Green, Alexander Pritzel, Olaf Ronneberger, Lindsay Willmore, Andrew J. Ballard, Sebastian W. Bodenstein, David A. Evans, Michael O’Neill, David Reiman, Kathryn Tunyasuvunakool, Zachary Wu, Akvilė Žemgulytė, Victor Bapst, Pushmeet Kohli, Demis Hassabis & John M. Jumper
Core Contributor, Isomorphic Labs, London, UK
Joshua Bambrick, Chia-Chun Hung, Max Jaderberg & Demis Hassabis
Google DeepMind, London, UK
Eirini Arvaniti, Charles Beattie, Ottavia Bertolli, Alex Bridgland, Alexander I. Cowen-Rivers, Andrew Cowie, Michael Figurnov, Fabian B. Fuchs, Hannah Gladman, Rishub Jain, Yousuf A. Khan, Kuba Perlin, Anna Potapenko, Sukhdeep Singh, Ashok Thillaisundaram, Ellen D. Zhong, Michal Zielinski & Augustin Žídek
Isomorphic Labs, London, UK
Alexey Cherepanov, Miles Congreve, Caroline M. R. Low, Pascal Savy, Adrian Stecula, Catherine Tong & Sergei Yakneen
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding authors
Correspondence to Max Jaderberg , Demis Hassabis or John M. Jumper .
Supplementary information
Supplementary information.
This Supplementary Information file contains the following 9 sections: (1) Notation; (2) Data pipeline; (3) Model architecture; (4) Auxiliary heads; (5) Training and inference; (6) Evaluation; (7) Differences to AlphaFold2 and AlphaFold-Multimer; (8) Supplemental Results; and (9) Appendix: CCD Code and PDB ID tables.
Reporting Summary
Rights and permissions.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Abramson, J., Adler, J., Dunger, J. et al. Accurate structure prediction of biomolecular interactions with AlphaFold 3. Nature (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-024-07487-w
Download citation
Received : 19 December 2023
Accepted : 29 April 2024
Published : 08 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-024-07487-w
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
This article is cited by
Major alphafold upgrade offers boost for drug discovery.
- Ewen Callaway
Nature (2024)
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines . If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Sign up for the Nature Briefing: Translational Research newsletter — top stories in biotechnology, drug discovery and pharma.
- Open access
- Published: 16 May 2024
Integrating qualitative research within a clinical trials unit: developing strategies and understanding their implementation in contexts
- Jeremy Segrott ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-6215-0870 1 ,
- Sue Channon 2 ,
- Amy Lloyd 4 ,
- Eleni Glarou 2 , 3 ,
- Josie Henley 5 ,
- Jacqueline Hughes 2 ,
- Nina Jacob 2 ,
- Sarah Milosevic 2 ,
- Yvonne Moriarty 2 ,
- Bethan Pell 6 ,
- Mike Robling 2 ,
- Heather Strange 2 ,
- Julia Townson 2 ,
- Qualitative Research Group &
- Lucy Brookes-Howell 2
Trials volume 25 , Article number: 323 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
Metrics details
Background/aims
The value of using qualitative methods within clinical trials is widely recognised. How qualitative research is integrated within trials units to achieve this is less clear. This paper describes the process through which qualitative research has been integrated within Cardiff University’s Centre for Trials Research (CTR) in Wales, UK. We highlight facilitators of, and challenges to, integration.
We held group discussions on the work of the Qualitative Research Group (QRG) within CTR. The content of these discussions, materials for a presentation in CTR, and documents relating to the development of the QRG were interpreted at a workshop attended by group members. Normalisation Process Theory (NPT) was used to structure analysis. A writing group prepared a document for input from members of CTR, forming the basis of this paper.
Actions to integrate qualitative research comprised: its inclusion in Centre strategies; formation of a QRG with dedicated funding/roles; embedding of qualitative research within operating systems; capacity building/training; monitoring opportunities to include qualitative methods in studies; maximising the quality of qualitative research and developing methodological innovation. Facilitators of these actions included: the influence of the broader methodological landscape within trial/study design and its promotion of the value of qualitative research; and close physical proximity of CTR qualitative staff/students allowing sharing of methodological approaches. Introduction of innovative qualitative methods generated interest among other staff groups. Challenges included: pressure to under-resource qualitative components of research, preference for a statistical stance historically in some research areas and funding structures, and difficulties faced by qualitative researchers carving out individual academic profiles when working across trials/studies.
Conclusions
Given that CTUs are pivotal to the design and conduct of RCTs and related study types across multiple disciplines, integrating qualitative research into trials units is crucial if its contribution is to be fully realised. We have made explicit one trials unit’s experience of embedding qualitative research and present this to open dialogue on ways to operationalise and optimise qualitative research in trials. NPT provides a valuable framework with which to theorise these processes, including the importance of sense-making and legitimisation when introducing new practices within organisations.
Peer Review reports
The value of using qualitative methods within randomised control trials (RCTs) is widely recognised [ 1 , 2 , 3 ]. Qualitative research generates important evidence on factors affecting trial recruitment/retention [ 4 ] and implementation, aiding interpretation of quantitative data [ 5 ]. Though RCTs have traditionally been viewed as sitting within a positivist paradigm, recent methodological innovations have developed new trial designs that draw explicitly on both quantitative and qualitative methods. For instance, in the field of complex public health interventions, realist RCTs seek to understand the mechanisms through which interventions generate hypothesised impacts, and how interactions across different implementation contexts form part of these mechanisms. Proponents of realist RCTs—which integrate experimental and realist paradigms—highlight the importance of using quantitative and qualitative methods to fully realise these aims and to generate an understanding of intervention mechanisms and how context shapes them [ 6 ].
A need for guidance on how to conduct good quality qualitative research is being addressed, particularly in relation to feasibility studies for RCTs [ 7 ] and process evaluations embedded within trials of complex interventions [ 5 ]. There is also guidance on the conduct of qualitative research within trials at different points in the research cycle, including development, conduct and reporting [ 8 , 9 ].
A high proportion of trials are based within or involve clinical trials units (CTUs). In the UK the UKCRC Registered CTU Network describes them as:
… specialist units which have been set up with a specific remit to design, conduct, analyse and publish clinical trials and other well-designed studies. They have the capability to provide specialist expert statistical, epidemiological, and other methodological advice and coordination to undertake successful clinical trials. In addition, most CTUs will have expertise in the coordination of trials involving investigational medicinal products which must be conducted in compliance with the UK Regulations governing the conduct of clinical trials resulting from the EU Directive for Clinical Trials.
Thus, CTUs provide the specialist methodological expertise needed for the conduct of trials, and in the case of trials of investigational medicinal products, their involvement may be mandated to ensure compliance with relevant regulations. As the definition above suggests, CTUs also conduct and support other types of study apart from RCTs, providing a range of methodological and subject-based expertise.
However, despite their central role in the conduct and design of trials, (and other evaluation designs) little has been written about how CTUs have integrated qualitative work within their organisation at a time when such methods are, as stated above, now recognised as an important aspect of RCTs and evaluation studies more generally. This is a significant gap, since integration at the organisational level arguably shapes how qualitative research is integrated within individual studies, and thus it is valuable to understand how CTUs have approached the task. There are different ways of involving qualitative work in trials units, such as partnering with other departments (e.g. social science) or employing qualitative researchers directly. Qualitative research can be imagined and configured in different ways—as a method that generates data to inform future trial and intervention design, as an embedded component within an RCT or other evaluation type, or as a parallel strand of research focusing on lived experiences of illness, for instance. Understanding how trials units have integrated qualitative research is valuable, as it can shed light on which strategies show promise, and in which contexts, and how qualitative research is positioned within the field of trials research, foregrounding the value of qualitative research. However, although much has been written about its use within trials, few accounts exist of how trials units have integrated qualitative research within their systems and structures.
This paper discusses the process of embedding qualitative research within the work of one CTU—Cardiff University’s Centre for Trials Research (CTR). It highlights facilitators of this process and identifies challenges to integration. We use the Normalisation Process Theory (NPT) as a framework to structure our experience and approach. The key gap addressed by this paper is the implementation of strategies to integrate qualitative research (a relatively newly adopted set of practices and processes) within CTU systems and structures. We acknowledge from the outset that there are multiple ways of approaching this task. What follows therefore is not a set of recommendations for a preferred or best way to integrate qualitative research, as this will comprise diverse actions according to specific contexts. Rather, we examine the processes through which integration occurred in our own setting and highlight the potential value of these insights for others engaged in the work of promoting qualitative research within trials units.
Background to the integration of qualitative research within CTR
The CTR was formed in 2015 [ 10 ]. It brought together three existing trials units at Cardiff University: the South East Wales Trials Unit, the Wales Cancer Trials Unit, and the Haematology Clinical Trials Unit. From its inception, the CTR had a stated aim of developing a programme of qualitative research and integrating it within trials and other studies. In the sections below, we map these approaches onto the framework offered by Normalisation Process Theory to understand the processes through which they helped achieve embedding and integration of qualitative research.
CTR’s aims (including those relating to the development of qualitative research) were included within its strategy documents and communicated to others through infrastructure funding applications, annual reports and its website. A Qualitative Research Group (QRG), which had previously existed within the South East Wales Trials Unit, with dedicated funding for methodological specialists and group lead academics, was a key mechanism through which the development of a qualitative portfolio was put into action. Integration of qualitative research within Centre systems and processes occurred through the inclusion of qualitative research in study adoption processes and representation on committees. The CTR’s study portfolio provided a basis to track qualitative methods in new and existing studies, identify opportunities to embed qualitative methods within recently adopted studies (at the funding application stage) and to manage staff resources. Capacity building and training were an important focus of the QRG’s work, including training courses, mentoring, creation of an academic network open to university staff and practitioners working in the field of healthcare, presentations at CTR staff meetings and securing of PhD studentships. Standard operating procedures and methodological guidance on the design and conduct of qualitative research (e.g. templates for developing analysis plans) aimed to create a shared understanding of how to undertake high-quality research, and a means to monitor the implementation of rigorous approaches. As the QRG expanded its expertise it sought to develop innovative approaches, including the use of visual [ 11 ] and ethnographic methods [ 12 ].
Understanding implementation—Normalisation Process Theory (NPT)
Normalisation Process Theory (NPT) provides a model with which to understand the implementation of new sets of practices and their normalisation within organisational settings. The term ‘normalisation’ refers to how new practices become routinised (part of the everyday work of an organisation) through embedding and integration [ 13 , 14 ]. NPT defines implementation as ‘the social organisation of work’ and is concerned with the social processes that take place as new practices are introduced. Embedding involves ‘making practices routine elements of everyday life’ within an organisation. Integration takes the form of ‘sustaining embedded practices in social contexts’, and how these processes lead to the practices becoming (or not becoming) ‘normal and routine’ [ 14 ]. NPT is concerned with the factors which promote or ‘inhibit’ attempts to embed and integrate the operationalisation of new practices [ 13 , 14 , 15 ].
Embedding new practices is therefore achieved through implementation—which takes the form of interactions in specific contexts. Implementation is operationalised through four ‘generative mechanisms’— coherence , cognitive participation , collective action and reflexive monitoring [ 14 ]. Each mechanism is characterised by components comprising immediate and organisational work, with actions of individuals and organisations (or groups of individuals) interdependent. The mechanisms operate partly through forms of investment (i.e. meaning, commitment, effort, and comprehension) [ 14 ].
Coherence refers to how individuals/groups make sense of, and give meaning to, new practices. Sense-making concerns the coherence of a practice—whether it ‘holds together’, and its differentiation from existing activities [ 15 ]. Communal and individual specification involve understanding new practices and their potential benefits for oneself or an organisation. Individuals consider what new practices mean for them in terms of tasks and responsibilities ( internalisation ) [ 14 ].
NPT frames the second mechanism, cognitive participation , as the building of a ‘community of practice’. For a new practice to be initiated, individuals and groups within an organisation must commit to it [ 14 , 15 ]. Cognitive participation occurs through enrolment —how people relate to the new practice; legitimation —the belief that it is right for them to be involved; and activation —defining which actions are necessary to sustain the practice and their involvement [ 14 ]. Making the new practices work may require changes to roles (new responsibilities, altered procedures) and reconfiguring how colleagues work together (changed relationships).
Third, Collective Action refers to ‘the operational work that people do to enact a set of practices’ [ 14 ]. Individuals engage with the new practices ( interactional workability ) reshaping how members of an organisation interact with each other, through creation of new roles and expectations ( relational interaction ) [ 15 ]. Skill set workability concerns how the work of implementing a new set of practices is distributed and the necessary roles and skillsets defined [ 14 ]. Contextual integration draws attention to the incorporation of a practice within social contexts, and the potential for aspects of these contexts, such as systems and procedures, to be modified as a result [ 15 ].
Reflexive monitoring is the final implementation mechanism. Collective and individual appraisal evaluate the value of a set of practices, which depends on the collection of information—formally and informally ( systematisation ). Appraisal may lead to reconfiguration in which procedures of the practice are redefined or reshaped [ 14 , 15 ].
We sought to map the following: (1) the strategies used to embed qualitative research within the Centre, (2) key facilitators, and (3) barriers to their implementation. Through focused group discussions during the monthly meetings of the CTR QRG and in discussion with the CTR senior management team throughout 2019–2020 we identified nine types of documents (22 individual documents in total) produced within the CTR which had relevant information about the integration of qualitative research within its work (Table 1 ). The QRG had an ‘open door’ policy to membership and welcomed all staff/students with an interest in qualitative research. It included researchers who were employed specifically to undertake qualitative research and other staff with a range of study roles, including trial managers, statisticians, and data managers. There was also diversity in terms of career stage, including PhD students, mid-career researchers and members of the Centre’s Executive team. Membership was therefore largely self-selected, and comprised of individuals with a role related to, or an interest in, embedding qualitative research within trials. However, the group brought together diverse methodological perspectives and was not solely comprised of methodological ‘champions’ whose job it was to promote the development of qualitative research within the centre. Thus whilst the group (and by extension, the authors of this paper) had a shared appreciation of the value of qualitative research within a trials centre, they also brought varied methodological perspectives and ways of engaging with it.
All members of the QRG ( n = 26) were invited to take part in a face-to-face, day-long workshop in February 2019 on ‘How to optimise and operationalise qualitative research in trials: reflections on CTR structure’. The workshop was attended by 12 members of staff and PhD students, including members of the QRG and the CTR’s senior management team. Recruitment to the workshop was therefore inclusive, and to some extent opportunistic, but all members of the QRG were able to contribute to discussions during regular monthly group meetings and the drafting of the current paper.
The aim of the workshop was to bring together information from the documents in Table 1 to generate discussion around the key strategies (and their component activities) that had been adopted to integrate qualitative research into CTR, as well as barriers to, and facilitators of, their implementation. The agenda for the workshop involved four key areas: development and history of the CTR model; mapping the current model within CTR; discussing the structure of other CTUs; and exploring the advantages and disadvantages of the CTR model.
During the workshop, we discussed the use of NPT to conceptualise how qualitative research had been embedded within CTR’s systems and practices. The group produced spider diagrams to map strategies and actions on to the four key domains (or ‘generative mechanisms’ of NPT) summarised above, to aid the understanding of how they had functioned, and the utility of NPT as a framework. This is summarised in Table 2 .
Detailed notes were made during the workshop. A core writing group then used these notes and the documents in Table 1 to develop a draft of the current paper. This was circulated to all members of the CTR QRG ( n = 26) and stored within a central repository accessible to them to allow involvement and incorporate the views of those who were not able to attend the workshop. This draft was again presented for comments in the monthly CTR QRG meeting in February 2021 attended by n = 10. The Standards for QUality Improvement Reporting Excellence 2.0 (SQUIRE) guidelines were used to inform the structure and content of the paper (see supplementary material) [ 16 ].
In the following sections, we describe the strategies CTR adopted to integrate qualitative research. These are mapped against NPT’s four generative mechanisms to explore the processes through which the strategies promoted integration, and facilitators of and barriers to their implementation. A summary of the strategies and their functioning in terms of the generative mechanisms is provided in Table 2 .
Coherence—making sense of qualitative research
In CTR, many of the actions taken to build a portfolio of qualitative research were aimed at enabling colleagues, and external actors, to make sense of this set of methodologies. Centre-level strategies and grant applications for infrastructure funding highlighted the value of qualitative research, the added benefits it would bring, and positioned it as a legitimate set of practices alongside existing methods. For example, a 2014 application for renewal of trials unit infrastructure funding stated:
We are currently in the process of undertaking […] restructuring for our qualitative research team and are planning similar for trial management next year. The aim of this restructuring is to establish greater hierarchical management and opportunities for staff development and also provide a structure that can accommodate continuing growth.
Within the CTR, various forms of communication on the development of qualitative research were designed to enable staff and students to make sense of it, and to think through its potential value for them, and ways in which they might engage with it. These included presentations at staff meetings, informal meetings between project teams and the qualitative group lead, and the visibility of qualitative research on the public-facing Centre website and Centre committees and systems. For instance, qualitative methods were included (and framed as a distinct set of practices) within study adoption forms and committee agendas. Information for colleagues described how qualitative methods could be incorporated within funding applications for RCTs and other evaluation studies to generate new insights into questions research teams were already keen to answer, such as influences on intervention implementation fidelity. Where externally based chief investigators approached the Centre to be involved in new grant applications, the existence of the qualitative team and group lead enabled the inclusion of qualitative research to be actively promoted at an early stage, and such opportunities were highlighted in the Centre’s brochure for new collaborators. Monthly qualitative research network meetings—advertised across CTR and to external research collaborators, were also designed to create a shared understanding of qualitative research methods and their utility within trials and other study types (e.g. intervention development, feasibility studies, and observational studies). Training events (discussed in more detail below) also aided sense-making.
Several factors facilitated the promotion of qualitative research as a distinctive and valuable entity. Among these was the influence of the broader methodological landscape within trial design which was promoting the value of qualitative research, such as guidance on the evaluation of complex interventions by the Medical Research Council [ 17 ], and the growing emphasis placed on process evaluations within trials (with qualitative methods important in understanding participant experience and influences on implementation) [ 5 ]. The attention given to lived experience (both through process evaluations and the move to embed public involvement in trials) helped to frame qualitative research within the Centre as something that was appropriate, legitimate, and of value. Recognition by research funders of the value of qualitative research within studies was also helpful in normalising and legitimising its adoption within grant applications.
The inclusion of qualitative methods within influential methodological guidance helped CTR researchers to develop a ‘shared language’ around these methods, and a way that a common understanding of the role of qualitative research could be generated. One barrier to such sense-making work was the varying extent to which staff and teams had existing knowledge or experience of qualitative research. This varied across methodological and subject groups within the Centre and reflected the history of the individual trials units which had merged to form the Centre.
Cognitive participation—legitimising qualitative research
Senior CTR leaders promoted the value and legitimacy of qualitative research. Its inclusion in centre strategies, infrastructure funding applications, and in public-facing materials (e.g. website, investigator brochures), signalled that it was appropriate for individuals to conduct qualitative research within their roles, or to support others in doing so. Legitimisation also took place through informal channels, such as senior leadership support for qualitative research methods in staff meetings and participation in QRG seminars. Continued development of the QRG (with dedicated infrastructure funding) provided a visible identity and equivalence with other methodological groups (e.g. trial managers, statisticians).
Staff were asked to engage with qualitative research in two main ways. First, there was an expansion in the number of staff for whom qualitative research formed part of their formal role and responsibilities. One of the three trials units that merged to form CTR brought with it a qualitative team comprising methodological specialists and a group lead. CTR continued the expansion of this group with the creation of new roles and an enlarged nucleus of researchers for whom qualitative research was the sole focus of their work. In part, this was linked to the successful award of projects that included a large qualitative component, and that were coordinated by CTR (see Table 3 which describes the PUMA study).
Members of the QRG were encouraged to develop their own research ideas and to gain experience as principal investigators, and group seminars were used to explore new ideas and provide peer support. This was communicated through line management, appraisal, and informal peer interaction. Boundaries were not strictly demarcated (i.e. staff located outside the qualitative team were already using qualitative methods), but the new team became a central focus for developing a growing programme of work.
Second, individuals and studies were called upon to engage in new ways with qualitative research, and with the qualitative team. A key goal for the Centre was that groups developing new research ideas should give more consideration in general to the potential value and inclusion of qualitative research within their funding applications. Specifically, they were asked to do this by thinking about qualitative research at an early point in their application’s development (rather than ‘bolting it on’ after other elements had been designed) and to draw upon the expertise and input of the qualitative team. An example was the inclusion of questions on qualitative methods within the Centre’s study adoption form and representation from the qualitative team at the committee which reviewed new adoption requests. Where adoption requests indicated the inclusion of qualitative methods, colleagues were encouraged to liaise with the qualitative team, facilitating the integration of its expertise from an early stage. Qualitative seminars offered an informal and supportive space in which researchers could share initial ideas and refine their methodological approach. The benefits of this included the provision of sufficient time for methodological specialists to be involved in the design of the proposed qualitative component and ensuring adequate costings had been drawn up. At study adoption group meetings, scrutiny of new proposals included consideration of whether new research proposals might be strengthened through the use of qualitative methods where these had not initially been included. Meetings of the QRG—which reviewed the Centre’s portfolio of new studies and gathered intelligence on new ideas—also helped to identify, early on, opportunities to integrate qualitative methods. Communication across teams was useful in identifying new research ideas and embedding qualitative researchers within emerging study development groups.
Actions to promote greater use of qualitative methods in funding applications fed through into a growing number of studies with a qualitative component. This helped to increase the visibility and legitimacy of qualitative methods within the Centre. For example, the PUMA study [ 12 ], which brought together a large multidisciplinary team to develop and evaluate a Paediatric early warning system, drew heavily on qualitative methods, with the qualitative research located within the QRG. The project introduced an extensive network of collaborators and clinical colleagues to qualitative methods and how they could be used during intervention development and the generation of case studies. Further information about the PUMA study is provided in Table 3 .
Increasing the legitimacy of qualitative work across an extensive network of staff, students and collaborators was a complex process. Set within the continuing dominance of quantitative methods with clinical trials, there were variations in the extent to which clinicians and other collaborators embraced the value of qualitative methods. Research funding schemes, which often continued to emphasise the quantitative element of randomised controlled trials, inevitably fed through into the focus of new research proposals. Staff and external collaborators were sometimes uncertain about the added value that qualitative methods would bring to their trials. Across the CTR there were variations in the speed at which qualitative research methods gained legitimacy, partly based on disciplinary traditions and their influences. For instance, population health trials, often located within non-health settings such as schools or community settings, frequently involved collaboration with social scientists who brought with them experience in qualitative methods. Methodological guidance in this field, such as MRC guidance on process evaluations, highlighted the value of qualitative methods and alternatives to the positivist paradigm, such as the value of realist RCTs. In other, more clinical areas, positivist paradigms had greater dominance. Established practices and methodological traditions across different funders also influenced the ease of obtaining funding to include qualitative research within studies. For drugs trials (CTIMPs), the influence of regulatory frameworks on study design, data collection and the allocation of staff resources may have played a role. Over time, teams gained repeated experience of embedding qualitative research (and researchers) within their work and took this learning with them to subsequent studies. For example, the senior clinician quoted within the PUMA case study (Table 3 below) described how they had gained an appreciation of the rigour of qualitative research and an understanding of its language. Through these repeated interactions, embedding of qualitative research within studies started to become the norm rather than the exception.
Collective action—operationalising qualitative research
Collective action concerns the operationalisation of new practices within organisations—the allocation and management of the work, how individuals interact with each other, and the work itself. In CTR the formation of a Qualitative Research Group helped to allocate and organise the work of building a portfolio of studies. Researchers across the Centre were called upon to interact with qualitative research in new ways. Presentations at staff meetings and the inclusion of qualitative research methods in portfolio study adoption forms were examples of this ( interactive workability ). It was operationalised by encouraging study teams to liaise with the qualitative research lead. Development of standard operating procedures, templates for costing qualitative research and methodological guidance (e.g. on analysis plans) also helped encourage researchers to interact with these methods in new ways. For some qualitative researchers who had been trained in the social sciences, working within a trials unit meant that they needed to interact in new and sometimes unfamiliar ways with standard operating procedures, risk assessments, and other trial-based systems. Thus, training needs and capacity-building efforts were multidirectional.
Whereas there had been a tendency for qualitative research to be ‘bolted on’ to proposals for RCTs, the systems described above were designed to embed thinking about the value and design of the qualitative component from the outset. They were also intended to integrate members of the qualitative team with trial teams from an early stage to promote effective integration of qualitative methods within larger trials and build relationships over time.
Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs), formal and informal training, and interaction between the qualitative team and other researchers increased the relational workability of qualitative methods within the Centre—the confidence individuals felt in including these methods within their studies, and their accountability for doing so. For instance, study adoption forms prompted researchers to interact routinely with the qualitative team at an early stage, whilst guidance on costing grants provided clear expectations about the resources needed to deliver a proposed set of qualitative data collection.
Formation of the Qualitative Research Group—comprised of methodological specialists, created new roles and skillsets ( skill set workability ). Research teams were encouraged to draw on these when writing funding applications for projects that included a qualitative component. Capacity-building initiatives were used to increase the number of researchers with the skills needed to undertake qualitative research, and for these individuals to develop their expertise over time. This was achieved through formal training courses, academic seminars, mentoring from experienced colleagues, and informal knowledge exchange. Links with external collaborators and centres engaged in building qualitative research supported these efforts. Within the Centre, the co-location of qualitative researchers with other methodological and trial teams facilitated knowledge exchange and building of collaborative relationships, whilst grouping of the qualitative team within a dedicated office space supported a collective identity and opportunities for informal peer support.
Some aspects of the context in which qualitative research was being developed created challenges to operationalisation. Dependence on project grants to fund qualitative methodologists meant that there was a continuing need to write further grant applications whilst limiting the amount of time available to do so. Similarly, researchers within the team whose role was funded largely by specific research projects could sometimes find it hard to create sufficient time to develop their personal methodological interests. However, the cultivation of a methodologically varied portfolio of work enabled members of the team to build significant expertise in different approaches (e.g. ethnography, discourse analysis) that connected individual studies.
Reflexive monitoring—evaluating the impact of qualitative research
Inclusion of questions/fields relating to qualitative research within the Centre’s study portfolio database was a key way in which information was collected ( systematisation ). It captured numbers of funding applications and funded studies, research design, and income generation. Alongside this database, a qualitative resource planner spreadsheet was used to link individual members of the qualitative team with projects and facilitate resource planning, further reinforcing the core responsibilities and roles of qualitative researchers within CTR. As with all staff in the Centre, members of the qualitative team were placed on ongoing rather than fixed-term contracts, reflecting their core role within CTR. Planning and strategy meetings used the database and resource planner to assess the integration of qualitative research within Centre research, identify opportunities for increasing involvement, and manage staff recruitment and sustainability of researcher posts. Academic meetings and day-to-day interaction fulfilled informal appraisal of the development of the group, and its position within the Centre. Individual appraisal was also important, with members of the qualitative team given opportunities to shape their role, reflect on progress, identify training needs, and further develop their skillset, particularly through line management systems.
These forms of systematisation and appraisal were used to reconfigure the development of qualitative research and its integration within the Centre. For example, group strategies considered how to achieve long-term integration of qualitative research from its initial embedding through further promoting the belief that it formed a core part of the Centre’s business. The visibility and legitimacy of qualitative research were promoted through initiatives such as greater prominence on the Centre’s website. Ongoing review of the qualitative portfolio and discussion at academic meetings enabled the identification of areas where increased capacity would be helpful, both for qualitative staff, and more broadly within the Centre. This prompted the qualitative group to develop an introductory course to qualitative methods open to all Centre staff and PhD students, aimed at increasing understanding and awareness. As the qualitative team built its expertise and experience it also sought to develop new and innovative approaches to conducting qualitative research. This included the use of visual and diary-based methods [ 11 ] and the adoption of ethnography to evaluate system-level clinical interventions [ 12 ]. Restrictions on conventional face-to-face qualitative data collection due to the COVID-19 pandemic prompted rapid adoption of virtual/online methods for interviews, observation, and use of new internet platforms such as Padlet—a form of digital note board.
In this paper, we have described the work undertaken by one CTU to integrate qualitative research within its studies and organisational culture. The parallel efforts of many trials units to achieve these goals arguably come at an opportune time. The traditional designs of RCTs have been challenged and re-imagined by the increasing influence of realist evaluation [ 6 , 18 ] and the widespread acceptance that trials need to understand implementation and intervention theory as well as assess outcomes [ 17 ]. Hence the widespread adoption of embedded mixed methods process evaluations within RCTs. These broad shifts in methodological orthodoxies, the production of high-profile methodological guidance, and the expectations of research funders all create fertile ground for the continued expansion of qualitative methods within trials units. However, whilst much has been written about the importance of developing qualitative research and the possible approaches to integrating qualitative and quantitative methods within studies, much less has been published on how to operationalise this within trials units. Filling this lacuna is important. Our paper highlights how the integration of a new set of practices within an organisation can become embedded as part of its ‘normal’ everyday work whilst also shaping the practices being integrated. In the case of CTR, it could be argued that the integration of qualitative research helped shape how this work was done (e.g. systems to assess progress and innovation).
In our trials unit, the presence of a dedicated research group of methodological specialists was a key action that helped realise the development of a portfolio of qualitative research and was perhaps the most visible evidence of a commitment to do so. However, our experience demonstrates that to fully realise the goal of developing qualitative research, much work focuses on the interaction between this ‘new’ set of methods and the organisation into which it is introduced. Whilst the team of methodological specialists was tasked with, and ‘able’ to do the work, the ‘work’ itself needed to be integrated and embedded within the existing system. Thus, alongside the creation of a team and methodological capacity, promoting the legitimacy of qualitative research was important to communicate to others that it was both a distinctive and different entity, yet similar and equivalent to more established groups and practices (e.g. trial management, statistics, data management). The framing of qualitative research within strategies, the messages given out by senior leaders (formally and informally) and the general visibility of qualitative research within the system all helped to achieve this.
Normalisation Process Theory draws our attention to the concepts of embedding (making a new practice routine, normal within an organisation) and integration —the long-term sustaining of these processes. An important process through which embedding took place in our centre concerned the creation of messages and systems that called upon individuals and research teams to interact with qualitative research. Research teams were encouraged to think about qualitative research and consider its potential value for their studies. Critically, they were asked to do so at specific points, and in particular ways. Early consideration of qualitative methods to maximise and optimise their inclusion within studies was emphasised, with timely input from the qualitative team. Study adoption systems, centre-level processes for managing financial and human resources, creation of a qualitative resource planner, and awareness raising among staff, helped to reinforce this. These processes of embedding and integration were complex and they varied in intensity and speed across different areas of the Centre’s work. In part this depended on existing research traditions, the extent of prior experience of working with qualitative researchers and methods, and the priorities of subject areas and funders. Centre-wide systems, sometimes linked to CTR’s operation as a CTU, also helped to legitimise and embed qualitative research, lending it equivalence with other research activity. For example, like all CTUs, CTR was required to conform with the principles of Good Clinical Practice, necessitating the creation of a quality management system, operationalised through standard operating procedures for all areas of its work. Qualitative research was included, and became embedded, within these systems, with SOPs produced to guide activities such as qualitative analysis.
NPT provides a helpful way of understanding how trials units might integrate qualitative research within their work. It highlights how new practices interact with existing organisational systems and the work needed to promote effective interaction. That is, alongside the creation of a team or programme of qualitative research, much of the work concerns how members of an organisation understand it, engage with it, and create systems to sustain it. Embedding a new set of practices may be just as important as the quality or characteristics of the practices themselves. High-quality qualitative research is of little value if it is not recognised and drawn upon within new studies for instance. NPT also offers a helpful lens with which to understand how integration and embedding occur, and the mechanisms through which they operate. For example, promoting the legitimacy of a new set of practices, or creating systems that embed it, can help sustain these practices by creating an organisational ambition and encouraging (or requiring) individuals to interact with them in certain ways, redefining their roles accordingly. NPT highlights the ways in which integration of new practices involves bi-directional exchanges with the organisation’s existing practices, with each having the potential to re-shape the other as interaction takes place. For instance, in CTR, qualitative researchers needed to integrate and apply their methods within the quality management and other systems of a CTU, such as the formalisation of key processes within standard operating procedures, something less likely to occur outside trials units. Equally, project teams (including those led by externally based chief investigators) increased the integration of qualitative methods within their overall study design, providing opportunities for new insights on intervention theory, implementation and the experiences of practitioners and participants.
We note two aspects of the normalisation processes within CTR that are slightly less well conceptualised by NPT. The first concerns the emphasis within coherence on identifying the distinctiveness of new practices, and how they differ from existing activities. Whilst differentiation was an important aspect of the integration of qualitative research in CTR, such integration could be seen as operating partly through processes of de-differentiation, or at least equivalence. That is, part of the integration of qualitative research was to see it as similar in terms of rigour, coherence, and importance to other forms of research within the Centre. To be viewed as similar, or at least comparable to existing practices, was to be legitimised.
Second, whilst NPT focuses mainly on the interaction between a new set of practices and the organisational context into which it is introduced, our own experience of introducing qualitative research into a trials unit was shaped by broader organisational and methodological contexts. For example, the increasing emphasis placed upon understanding implementation processes and the experiences of research participants in the field of clinical trials (e.g. by funders), created an environment conducive to the development of qualitative research methods within our Centre. Attempts to integrate qualitative research within studies were also cross-organisational, given that many of the studies managed within the CTR drew together multi-institutional teams. This provided important opportunities to integrate qualitative research within a portfolio of studies that extended beyond CTR and build a network of collaborators who increasingly included qualitative methods within their funding proposals. The work of growing and integrating qualitative research within a trials unit is an ongoing one in which ever-shifting macro-level influences can help or hinder, and where the organisations within which we work are never static in terms of barriers and facilitators.
The importance of utilising qualitative methods within RCTs is now widely recognised. Increased emphasis on the evaluation of complex interventions, the influence of realist methods directing greater attention to complexity and the widespread adoption of mixed methods process evaluations are key drivers of this shift. The inclusion of qualitative methods within individual trials is important and previous research has explored approaches to their incorporation and some of the challenges encountered. Our paper highlights that the integration of qualitative methods at the organisational level of the CTU can shape how they are taken up by individual trials. Within CTR, it can be argued that qualitative research achieved high levels of integration, as conceptualised by Normalisation Process Theory. Thus, qualitative research became recognised as a coherent and valuable set of practices, secured legitimisation as an appropriate focus of individual and organisational activity and benefitted from forms of collective action which operationalised these organisational processes. Crucially, the routinisation of qualitative research appeared to be sustained, something which NPT suggests helps define integration (as opposed to initial embedding). However, our analysis suggested that the degree of integration varied by trial area. This variation reflected a complex mix of factors including disciplinary traditions, methodological guidance, existing (un)familiarity with qualitative research, and the influence of regulatory frameworks for certain clinical trials.
NPT provides a valuable framework with which to understand how these processes of embedding and integration occur. Our use of NPT draws attention to the importance of sense-making and legitimisation as important steps in introducing a new set of practices within the work of an organisation. Integration also depends, across each mechanism of NPT, on the building of effective relationships, which allow individuals and teams to work together in new ways. By reflecting on our experiences and the decisions taken within CTR we have made explicit one such process for embedding qualitative research within a trials unit, whilst acknowledging that approaches may differ across trials units. Mindful of this fact, and the focus of the current paper on one trials unit’s experience, we do not propose a set of recommendations for others who are working to achieve similar goals. Rather, we offer three overarching reflections (framed by NPT) which may act as a useful starting point for trials units (and other infrastructures) seeking to promote the adoption of qualitative research.
First, whilst research organisations such as trials units are highly heterogenous, processes of embedding and integration, which we have foregrounded in this paper, are likely to be important across different contexts in sustaining the use of qualitative research. Second, developing a plan for the integration of qualitative research will benefit from mapping out the characteristics of the extant system. For example, it is valuable to know how familiar staff are with qualitative research and any variations across teams within an organisation. Thirdly, NPT frames integration as a process of implementation which operates through key generative mechanisms— coherence , cognitive participation , collective action and reflexive monitoring . These mechanisms can help guide understanding of which actions help achieve embedding and integration. Importantly, they span multiple aspects of how organisations, and the individuals within them, work. The ways in which people make sense of a new set of practices ( coherence ), their commitment towards it ( cognitive participation ), how it is operationalised ( collective action ) and the evaluation of its introduction ( reflexive monitoring ) are all important. Thus, for example, qualitative research, even when well organised and operationalised within an organisation, is unlikely to be sustained if appreciation of its value is limited, or people are not committed to it.
We present our experience of engaging with the processes described above to open dialogue with other trials units on ways to operationalise and optimise qualitative research in trials. Understanding how best to integrate qualitative research within these settings may help to fully realise the significant contribution which it makes the design and conduct of trials.
Availability of data and materials
Some documents cited in this paper are either freely available from the Centre for Trials Research website or can be requested from the author for correspondence.
O’Cathain A, Thomas KJ, Drabble SJ, Rudolph A, Hewison J. What can qualitative research do for randomised controlled trials? A systematic mapping review. BMJ Open. 2013;3(6):e002889.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
O’Cathain A, Thomas KJ, Drabble SJ, Rudolph A, Goode J, Hewison J. Maximising the value of combining qualitative research and randomised controlled trials in health research: the QUAlitative Research in Trials (QUART) study – a mixed methods study. Health Technol Assess. 2014;18(38):1–197.
Clement C, Edwards SL, Rapport F, Russell IT, Hutchings HA. Exploring qualitative methods reported in registered trials and their yields (EQUITY): systematic review. Trials. 2018;19(1):589.
Hennessy M, Hunter A, Healy P, Galvin S, Houghton C. Improving trial recruitment processes: how qualitative methodologies can be used to address the top 10 research priorities identified within the PRioRiTy study. Trials. 2018;19:584.
Moore GF, Audrey S, Barker M, Bond L, Bonell C, Hardeman W, et al. Process evaluation of complex interventions: Medical Research Council guidance. BMJ. 2015;350(mar19 6):h1258.
Bonell C, Fletcher A, Morton M, Lorenc T, Moore L. Realist randomised controlled trials: a new approach to evaluating complex public health interventions. Soc Sci Med. 2012;75(12):2299–306.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
O’Cathain A, Hoddinott P, Lewin S, Thomas KJ, Young B, Adamson J, et al. Maximising the impact of qualitative research in feasibility studies for randomised controlled trials: guidance for researchers. Pilot Feasibility Stud. 2015;1:32.
Cooper C, O’Cathain A, Hind D, Adamson J, Lawton J, Baird W. Conducting qualitative research within Clinical Trials Units: avoiding potential pitfalls. Contemp Clin Trials. 2014;38(2):338–43.
Rapport F, Storey M, Porter A, Snooks H, Jones K, Peconi J, et al. Qualitative research within trials: developing a standard operating procedure for a clinical trials unit. Trials. 2013;14:54.
Cardiff University. Centre for Trials Research. Available from: https://www.cardiff.ac.uk/centre-for-trials-research . Accessed 10 May 2024.
Pell B, Williams D, Phillips R, Sanders J, Edwards A, Choy E, et al. Using visual timelines in telephone interviews: reflections and lessons learned from the star family study. Int J Qual Methods. 2020;19:160940692091367.
Thomas-Jones E, Lloyd A, Roland D, Sefton G, Tume L, Hood K, et al. A prospective, mixed-methods, before and after study to identify the evidence base for the core components of an effective Paediatric Early Warning System and the development of an implementation package containing those core recommendations for use in th. BMC Pediatr. 2018;18:244.
May C, Finch T, Mair F, Ballini L, Dowrick C, Eccles M, et al. Understanding the implementation of complex interventions in health care: the normalization process model. BMC Health Serv Res. 2007;7:148.
May C, Finch T. Implementing, embedding, and integrating practices: an outline of normalization process theory. Sociology. 2009;43(3):535–54.
Article Google Scholar
May CR, Mair F, Finch T, Macfarlane A, Dowrick C, Treweek S, et al. Development of a theory of implementation and integration: normalization process theory. Implement Sci. 2009;4:29.
Ogrinc G, Davies L, Goodman D, Batalden PB, Davidoff F, Stevens D. SQUIRE 2.0 (Standards for QUality Improvement Reporting Excellence): Revised publication guidelines from a detailed consensus process. BMJ Quality and Safety. 2016;25:986-92.
Craig P, Dieppe P, Macintyre S, Michie S, Nazareth I, Petticrew M. Developing and evaluating complex interventions: the new Medical Research Council guidance. BMJ. 2008;337:a1655.
Jamal F, Fletcher A, Shackleton N, Elbourne D, Viner R, Bonell C. The three stages of building and testing mid-level theories in a realist RCT: a theoretical and methodological case-example. Trials. 2015;16(1):466.
Download references
Acknowledgements
Members of the Centre for Trials Research (CTR) Qualitative Research Group were collaborating authors: C Drew (Senior Research Fellow—Senior Trial Manager, Brain Health and Mental Wellbeing Division), D Gillespie (Director, Infection, Inflammation and Immunity Trials, Principal Research Fellow), R Hale (now Research Associate, School of Social Sciences, Cardiff University), J Latchem-Hastings (now Lecturer and Postdoctoral Fellow, School of Healthcare Sciences, Cardiff University), R Milton (Research Associate—Trial Manager), B Pell (now PhD student, DECIPHer Centre, Cardiff University), H Prout (Research Associate—Qualitative), V Shepherd (Senior Research Fellow), K Smallman (Research Associate), H Stanton (Research Associate—Senior Data Manager). Thanks are due to Kerry Hood and Aimee Grant for their involvement in developing processes and systems for qualitative research within CTR.
No specific grant was received to support the writing of this paper.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Centre for Trials Research, DECIPHer Centre, Cardiff University, Neuadd Meirionnydd, Heath Park, Cardiff, CF14 4YS, UK
Jeremy Segrott
Centre for Trials Research, Cardiff University, Neuadd Meirionnydd, Heath Park, Cardiff, CF14 4YS, UK
Sue Channon, Eleni Glarou, Jacqueline Hughes, Nina Jacob, Sarah Milosevic, Yvonne Moriarty, Mike Robling, Heather Strange, Julia Townson & Lucy Brookes-Howell
Division of Population Medicine, School of Medicine, Cardiff University, Neuadd Meirionnydd, Heath Park, Cardiff, CF14 4YS, UK
Eleni Glarou
Wales Centre for Public Policy, Cardiff University, Sbarc I Spark, Maindy Road, Cardiff, CF24 4HQ, UK
School of Social Sciences, Cardiff University, King Edward VII Avenue, Cardiff, CF10 3WA, UK
Josie Henley
DECIPHer Centre, School of Social Sciences, Cardiff University, Sbarc I Spark, Maindy Road, Cardiff, CF24 4HQ, UK
Bethan Pell
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Qualitative Research Group
- , D. Gillespie
- , J. Latchem-Hastings
- , R. Milton
- , V. Shepherd
- , K. Smallman
- & H. Stanton
Contributions
JS contributed to the design of the work and interpretation of data and was responsible for leading the drafting and revision of the paper. SC contributed to the design of the work, the acquisition of data and the drafting and revision of the paper. AL contributed to the design of the work, the acquisition of data and the drafting and revision of the paper. EG contributed to a critical review of the manuscript and provided additional relevant references. JH provided feedback on initial drafts of the paper and contributed to subsequent revisions. JHu provided feedback on initial drafts of the paper and contributed to subsequent revisions. NG provided feedback on initial drafts of the paper and contributed to subsequent revisions. SM was involved in the acquisition and analysis of data and provided a critical review of the manuscript. YM was involved in the acquisition and analysis of data and provided a critical review of the manuscript. MR was involved in the interpretation of data and critical review and revision of the paper. HS contributed to the conception and design of the work, the acquisition and analysis of data, and the revision of the manuscript. JT provided feedback on initial drafts of the paper and contributed to subsequent revisions. LB-H made a substantial contribution to the design and conception of the work, led the acquisition and analysis of data, and contributed to the drafting and revision of the paper.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Jeremy Segrott .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Ethical approval was not sought as no personal or identifiable data was collected.
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
All authors are or were members of staff or students in the Centre for Trials Research. JS is an associate editor of Trials .
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Supplementary material 1., rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Segrott, J., Channon, S., Lloyd, A. et al. Integrating qualitative research within a clinical trials unit: developing strategies and understanding their implementation in contexts. Trials 25 , 323 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13063-024-08124-7
Download citation
Received : 20 October 2023
Accepted : 17 April 2024
Published : 16 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s13063-024-08124-7
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Qualitative research
- Qualitative methods
- Trials units
- Normalisation Process Theory
- Randomised controlled trials
ISSN: 1745-6215
- Submission enquiries: Access here and click Contact Us
- General enquiries: [email protected]

Cultural Relativity and Acceptance of Embryonic Stem Cell Research
Article sidebar.

Main Article Content
There is a debate about the ethical implications of using human embryos in stem cell research, which can be influenced by cultural, moral, and social values. This paper argues for an adaptable framework to accommodate diverse cultural and religious perspectives. By using an adaptive ethics model, research protections can reflect various populations and foster growth in stem cell research possibilities.
INTRODUCTION
Stem cell research combines biology, medicine, and technology, promising to alter health care and the understanding of human development. Yet, ethical contention exists because of individuals’ perceptions of using human embryos based on their various cultural, moral, and social values. While these disagreements concerning policy, use, and general acceptance have prompted the development of an international ethics policy, such a uniform approach can overlook the nuanced ethical landscapes between cultures. With diverse viewpoints in public health, a single global policy, especially one reflecting Western ethics or the ethics prevalent in high-income countries, is impractical. This paper argues for a culturally sensitive, adaptable framework for the use of embryonic stem cells. Stem cell policy should accommodate varying ethical viewpoints and promote an effective global dialogue. With an extension of an ethics model that can adapt to various cultures, we recommend localized guidelines that reflect the moral views of the people those guidelines serve.
Stem cells, characterized by their unique ability to differentiate into various cell types, enable the repair or replacement of damaged tissues. Two primary types of stem cells are somatic stem cells (adult stem cells) and embryonic stem cells. Adult stem cells exist in developed tissues and maintain the body’s repair processes. [1] Embryonic stem cells (ESC) are remarkably pluripotent or versatile, making them valuable in research. [2] However, the use of ESCs has sparked ethics debates. Considering the potential of embryonic stem cells, research guidelines are essential. The International Society for Stem Cell Research (ISSCR) provides international stem cell research guidelines. They call for “public conversations touching on the scientific significance as well as the societal and ethical issues raised by ESC research.” [3] The ISSCR also publishes updates about culturing human embryos 14 days post fertilization, suggesting local policies and regulations should continue to evolve as ESC research develops. [4] Like the ISSCR, which calls for local law and policy to adapt to developing stem cell research given cultural acceptance, this paper highlights the importance of local social factors such as religion and culture.
I. Global Cultural Perspective of Embryonic Stem Cells
Views on ESCs vary throughout the world. Some countries readily embrace stem cell research and therapies, while others have stricter regulations due to ethical concerns surrounding embryonic stem cells and when an embryo becomes entitled to moral consideration. The philosophical issue of when the “someone” begins to be a human after fertilization, in the morally relevant sense, [5] impacts when an embryo becomes not just worthy of protection but morally entitled to it. The process of creating embryonic stem cell lines involves the destruction of the embryos for research. [6] Consequently, global engagement in ESC research depends on social-cultural acceptability.
a. US and Rights-Based Cultures
In the United States, attitudes toward stem cell therapies are diverse. The ethics and social approaches, which value individualism, [7] trigger debates regarding the destruction of human embryos, creating a complex regulatory environment. For example, the 1996 Dickey-Wicker Amendment prohibited federal funding for the creation of embryos for research and the destruction of embryos for “more than allowed for research on fetuses in utero.” [8] Following suit, in 2001, the Bush Administration heavily restricted stem cell lines for research. However, the Stem Cell Research Enhancement Act of 2005 was proposed to help develop ESC research but was ultimately vetoed. [9] Under the Obama administration, in 2009, an executive order lifted restrictions allowing for more development in this field. [10] The flux of research capacity and funding parallels the different cultural perceptions of human dignity of the embryo and how it is socially presented within the country’s research culture. [11]
b. Ubuntu and Collective Cultures
African bioethics differs from Western individualism because of the different traditions and values. African traditions, as described by individuals from South Africa and supported by some studies in other African countries, including Ghana and Kenya, follow the African moral philosophies of Ubuntu or Botho and Ukama , which “advocates for a form of wholeness that comes through one’s relationship and connectedness with other people in the society,” [12] making autonomy a socially collective concept. In this context, for the community to act autonomously, individuals would come together to decide what is best for the collective. Thus, stem cell research would require examining the value of the research to society as a whole and the use of the embryos as a collective societal resource. If society views the source as part of the collective whole, and opposes using stem cells, compromising the cultural values to pursue research may cause social detachment and stunt research growth. [13] Based on local culture and moral philosophy, the permissibility of stem cell research depends on how embryo, stem cell, and cell line therapies relate to the community as a whole. Ubuntu is the expression of humanness, with the person’s identity drawn from the “’I am because we are’” value. [14] The decision in a collectivistic culture becomes one born of cultural context, and individual decisions give deference to others in the society.
Consent differs in cultures where thought and moral philosophy are based on a collective paradigm. So, applying Western bioethical concepts is unrealistic. For one, Africa is a diverse continent with many countries with different belief systems, access to health care, and reliance on traditional or Western medicines. Where traditional medicine is the primary treatment, the “’restrictive focus on biomedically-related bioethics’” [is] problematic in African contexts because it neglects bioethical issues raised by traditional systems.” [15] No single approach applies in all areas or contexts. Rather than evaluating the permissibility of ESC research according to Western concepts such as the four principles approach, different ethics approaches should prevail.
Another consideration is the socio-economic standing of countries. In parts of South Africa, researchers have not focused heavily on contributing to the stem cell discourse, either because it is not considered health care or a health science priority or because resources are unavailable. [16] Each country’s priorities differ given different social, political, and economic factors. In South Africa, for instance, areas such as maternal mortality, non-communicable diseases, telemedicine, and the strength of health systems need improvement and require more focus [17] Stem cell research could benefit the population, but it also could divert resources from basic medical care. Researchers in South Africa adhere to the National Health Act and Medicines Control Act in South Africa and international guidelines; however, the Act is not strictly enforced, and there is no clear legislation for research conduct or ethical guidelines. [18]
Some parts of Africa condemn stem cell research. For example, 98.2 percent of the Tunisian population is Muslim. [19] Tunisia does not permit stem cell research because of moral conflict with a Fatwa. Religion heavily saturates the regulation and direction of research. [20] Stem cell use became permissible for reproductive purposes only recently, with tight restrictions preventing cells from being used in any research other than procedures concerning ART/IVF. Their use is conditioned on consent, and available only to married couples. [21] The community's receptiveness to stem cell research depends on including communitarian African ethics.
c. Asia
Some Asian countries also have a collective model of ethics and decision making. [22] In China, the ethics model promotes a sincere respect for life or human dignity, [23] based on protective medicine. This model, influenced by Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), [24] recognizes Qi as the vital energy delivered via the meridians of the body; it connects illness to body systems, the body’s entire constitution, and the universe for a holistic bond of nature, health, and quality of life. [25] Following a protective ethics model, and traditional customs of wholeness, investment in stem cell research is heavily desired for its applications in regenerative therapies, disease modeling, and protective medicines. In a survey of medical students and healthcare practitioners, 30.8 percent considered stem cell research morally unacceptable while 63.5 percent accepted medical research using human embryonic stem cells. Of these individuals, 89.9 percent supported increased funding for stem cell research. [26] The scientific community might not reflect the overall population. From 1997 to 2019, China spent a total of $576 million (USD) on stem cell research at 8,050 stem cell programs, increased published presence from 0.6 percent to 14.01 percent of total global stem cell publications as of 2014, and made significant strides in cell-based therapies for various medical conditions. [27] However, while China has made substantial investments in stem cell research and achieved notable progress in clinical applications, concerns linger regarding ethical oversight and transparency. [28] For example, the China Biosecurity Law, promoted by the National Health Commission and China Hospital Association, attempted to mitigate risks by introducing an institutional review board (IRB) in the regulatory bodies. 5800 IRBs registered with the Chinese Clinical Trial Registry since 2021. [29] However, issues still need to be addressed in implementing effective IRB review and approval procedures.
The substantial government funding and focus on scientific advancement have sometimes overshadowed considerations of regional cultures, ethnic minorities, and individual perspectives, particularly evident during the one-child policy era. As government policy adapts to promote public stability, such as the change from the one-child to the two-child policy, [30] research ethics should also adapt to ensure respect for the values of its represented peoples.
Japan is also relatively supportive of stem cell research and therapies. Japan has a more transparent regulatory framework, allowing for faster approval of regenerative medicine products, which has led to several advanced clinical trials and therapies. [31] South Korea is also actively engaged in stem cell research and has a history of breakthroughs in cloning and embryonic stem cells. [32] However, the field is controversial, and there are issues of scientific integrity. For example, the Korean FDA fast-tracked products for approval, [33] and in another instance, the oocyte source was unclear and possibly violated ethical standards. [34] Trust is important in research, as it builds collaborative foundations between colleagues, trial participant comfort, open-mindedness for complicated and sensitive discussions, and supports regulatory procedures for stakeholders. There is a need to respect the culture’s interest, engagement, and for research and clinical trials to be transparent and have ethical oversight to promote global research discourse and trust.
d. Middle East
Countries in the Middle East have varying degrees of acceptance of or restrictions to policies related to using embryonic stem cells due to cultural and religious influences. Saudi Arabia has made significant contributions to stem cell research, and conducts research based on international guidelines for ethical conduct and under strict adherence to guidelines in accordance with Islamic principles. Specifically, the Saudi government and people require ESC research to adhere to Sharia law. In addition to umbilical and placental stem cells, [35] Saudi Arabia permits the use of embryonic stem cells as long as they come from miscarriages, therapeutic abortions permissible by Sharia law, or are left over from in vitro fertilization and donated to research. [36] Laws and ethical guidelines for stem cell research allow the development of research institutions such as the King Abdullah International Medical Research Center, which has a cord blood bank and a stem cell registry with nearly 10,000 donors. [37] Such volume and acceptance are due to the ethical ‘permissibility’ of the donor sources, which do not conflict with religious pillars. However, some researchers err on the side of caution, choosing not to use embryos or fetal tissue as they feel it is unethical to do so. [38]
Jordan has a positive research ethics culture. [39] However, there is a significant issue of lack of trust in researchers, with 45.23 percent (38.66 percent agreeing and 6.57 percent strongly agreeing) of Jordanians holding a low level of trust in researchers, compared to 81.34 percent of Jordanians agreeing that they feel safe to participate in a research trial. [40] Safety testifies to the feeling of confidence that adequate measures are in place to protect participants from harm, whereas trust in researchers could represent the confidence in researchers to act in the participants’ best interests, adhere to ethical guidelines, provide accurate information, and respect participants’ rights and dignity. One method to improve trust would be to address communication issues relevant to ESC. Legislation surrounding stem cell research has adopted specific language, especially concerning clarification “between ‘stem cells’ and ‘embryonic stem cells’” in translation. [41] Furthermore, legislation “mandates the creation of a national committee… laying out specific regulations for stem-cell banking in accordance with international standards.” [42] This broad regulation opens the door for future global engagement and maintains transparency. However, these regulations may also constrain the influence of research direction, pace, and accessibility of research outcomes.
e. Europe
In the European Union (EU), ethics is also principle-based, but the principles of autonomy, dignity, integrity, and vulnerability are interconnected. [43] As such, the opportunity for cohesion and concessions between individuals’ thoughts and ideals allows for a more adaptable ethics model due to the flexible principles that relate to the human experience The EU has put forth a framework in its Convention for the Protection of Human Rights and Dignity of the Human Being allowing member states to take different approaches. Each European state applies these principles to its specific conventions, leading to or reflecting different acceptance levels of stem cell research. [44]
For example, in Germany, Lebenzusammenhang , or the coherence of life, references integrity in the unity of human culture. Namely, the personal sphere “should not be subject to external intervention.” [45] Stem cell interventions could affect this concept of bodily completeness, leading to heavy restrictions. Under the Grundgesetz, human dignity and the right to life with physical integrity are paramount. [46] The Embryo Protection Act of 1991 made producing cell lines illegal. Cell lines can be imported if approved by the Central Ethics Commission for Stem Cell Research only if they were derived before May 2007. [47] Stem cell research respects the integrity of life for the embryo with heavy specifications and intense oversight. This is vastly different in Finland, where the regulatory bodies find research more permissible in IVF excess, but only up to 14 days after fertilization. [48] Spain’s approach differs still, with a comprehensive regulatory framework. [49] Thus, research regulation can be culture-specific due to variations in applied principles. Diverse cultures call for various approaches to ethical permissibility. [50] Only an adaptive-deliberative model can address the cultural constructions of self and achieve positive, culturally sensitive stem cell research practices. [51]
II. Religious Perspectives on ESC
Embryonic stem cell sources are the main consideration within religious contexts. While individuals may not regard their own religious texts as authoritative or factual, religion can shape their foundations or perspectives.
The Qur'an states:
“And indeed We created man from a quintessence of clay. Then We placed within him a small quantity of nutfa (sperm to fertilize) in a safe place. Then We have fashioned the nutfa into an ‘alaqa (clinging clot or cell cluster), then We developed the ‘alaqa into mudgha (a lump of flesh), and We made mudgha into bones, and clothed the bones with flesh, then We brought it into being as a new creation. So Blessed is Allah, the Best of Creators.” [52]
Many scholars of Islam estimate the time of soul installment, marked by the angel breathing in the soul to bring the individual into creation, as 120 days from conception. [53] Personhood begins at this point, and the value of life would prohibit research or experimentation that could harm the individual. If the fetus is more than 120 days old, the time ensoulment is interpreted to occur according to Islamic law, abortion is no longer permissible. [54] There are a few opposing opinions about early embryos in Islamic traditions. According to some Islamic theologians, there is no ensoulment of the early embryo, which is the source of stem cells for ESC research. [55]
In Buddhism, the stance on stem cell research is not settled. The main tenets, the prohibition against harming or destroying others (ahimsa) and the pursuit of knowledge (prajña) and compassion (karuna), leave Buddhist scholars and communities divided. [56] Some scholars argue stem cell research is in accordance with the Buddhist tenet of seeking knowledge and ending human suffering. Others feel it violates the principle of not harming others. Finding the balance between these two points relies on the karmic burden of Buddhist morality. In trying to prevent ahimsa towards the embryo, Buddhist scholars suggest that to comply with Buddhist tenets, research cannot be done as the embryo has personhood at the moment of conception and would reincarnate immediately, harming the individual's ability to build their karmic burden. [57] On the other hand, the Bodhisattvas, those considered to be on the path to enlightenment or Nirvana, have given organs and flesh to others to help alleviate grieving and to benefit all. [58] Acceptance varies on applied beliefs and interpretations.
Catholicism does not support embryonic stem cell research, as it entails creation or destruction of human embryos. This destruction conflicts with the belief in the sanctity of life. For example, in the Old Testament, Genesis describes humanity as being created in God’s image and multiplying on the Earth, referencing the sacred rights to human conception and the purpose of development and life. In the Ten Commandments, the tenet that one should not kill has numerous interpretations where killing could mean murder or shedding of the sanctity of life, demonstrating the high value of human personhood. In other books, the theological conception of when life begins is interpreted as in utero, [59] highlighting the inviolability of life and its formation in vivo to make a religious point for accepting such research as relatively limited, if at all. [60] The Vatican has released ethical directives to help apply a theological basis to modern-day conflicts. The Magisterium of the Church states that “unless there is a moral certainty of not causing harm,” experimentation on fetuses, fertilized cells, stem cells, or embryos constitutes a crime. [61] Such procedures would not respect the human person who exists at these stages, according to Catholicism. Damages to the embryo are considered gravely immoral and illicit. [62] Although the Catholic Church officially opposes abortion, surveys demonstrate that many Catholic people hold pro-choice views, whether due to the context of conception, stage of pregnancy, threat to the mother’s life, or for other reasons, demonstrating that practicing members can also accept some but not all tenets. [63]
Some major Jewish denominations, such as the Reform, Conservative, and Reconstructionist movements, are open to supporting ESC use or research as long as it is for saving a life. [64] Within Judaism, the Talmud, or study, gives personhood to the child at birth and emphasizes that life does not begin at conception: [65]
“If she is found pregnant, until the fortieth day it is mere fluid,” [66]
Whereas most religions prioritize the status of human embryos, the Halakah (Jewish religious law) states that to save one life, most other religious laws can be ignored because it is in pursuit of preservation. [67] Stem cell research is accepted due to application of these religious laws.
We recognize that all religions contain subsets and sects. The variety of environmental and cultural differences within religious groups requires further analysis to respect the flexibility of religious thoughts and practices. We make no presumptions that all cultures require notions of autonomy or morality as under the common morality theory , which asserts a set of universal moral norms that all individuals share provides moral reasoning and guides ethical decisions. [68] We only wish to show that the interaction with morality varies between cultures and countries.
III. A Flexible Ethical Approach
The plurality of different moral approaches described above demonstrates that there can be no universally acceptable uniform law for ESC on a global scale. Instead of developing one standard, flexible ethical applications must be continued. We recommend local guidelines that incorporate important cultural and ethical priorities.
While the Declaration of Helsinki is more relevant to people in clinical trials receiving ESC products, in keeping with the tradition of protections for research subjects, consent of the donor is an ethical requirement for ESC donation in many jurisdictions including the US, Canada, and Europe. [69] The Declaration of Helsinki provides a reference point for regulatory standards and could potentially be used as a universal baseline for obtaining consent prior to gamete or embryo donation.
For instance, in Columbia University’s egg donor program for stem cell research, donors followed standard screening protocols and “underwent counseling sessions that included information as to the purpose of oocyte donation for research, what the oocytes would be used for, the risks and benefits of donation, and process of oocyte stimulation” to ensure transparency for consent. [70] The program helped advance stem cell research and provided clear and safe research methods with paid participants. Though paid participation or covering costs of incidental expenses may not be socially acceptable in every culture or context, [71] and creating embryos for ESC research is illegal in many jurisdictions, Columbia’s program was effective because of the clear and honest communications with donors, IRBs, and related stakeholders. This example demonstrates that cultural acceptance of scientific research and of the idea that an egg or embryo does not have personhood is likely behind societal acceptance of donating eggs for ESC research. As noted, many countries do not permit the creation of embryos for research.
Proper communication and education regarding the process and purpose of stem cell research may bolster comprehension and garner more acceptance. “Given the sensitive subject material, a complete consent process can support voluntary participation through trust, understanding, and ethical norms from the cultures and morals participants value. This can be hard for researchers entering countries of different socioeconomic stability, with different languages and different societal values. [72]
An adequate moral foundation in medical ethics is derived from the cultural and religious basis that informs knowledge and actions. [73] Understanding local cultural and religious values and their impact on research could help researchers develop humility and promote inclusion.
IV. Concerns
Some may argue that if researchers all adhere to one ethics standard, protection will be satisfied across all borders, and the global public will trust researchers. However, defining what needs to be protected and how to define such research standards is very specific to the people to which standards are applied. We suggest that applying one uniform guide cannot accurately protect each individual because we all possess our own perceptions and interpretations of social values. [74] Therefore, the issue of not adjusting to the moral pluralism between peoples in applying one standard of ethics can be resolved by building out ethics models that can be adapted to different cultures and religions.
Other concerns include medical tourism, which may promote health inequities. [75] Some countries may develop and approve products derived from ESC research before others, compromising research ethics or drug approval processes. There are also concerns about the sale of unauthorized stem cell treatments, for example, those without FDA approval in the United States. Countries with robust research infrastructures may be tempted to attract medical tourists, and some customers will have false hopes based on aggressive publicity of unproven treatments. [76]
For example, in China, stem cell clinics can market to foreign clients who are not protected under the regulatory regimes. Companies employ a marketing strategy of “ethically friendly” therapies. Specifically, in the case of Beike, China’s leading stem cell tourism company and sprouting network, ethical oversight of administrators or health bureaus at one site has “the unintended consequence of shifting questionable activities to another node in Beike's diffuse network.” [77] In contrast, Jordan is aware of stem cell research’s potential abuse and its own status as a “health-care hub.” Jordan’s expanded regulations include preserving the interests of individuals in clinical trials and banning private companies from ESC research to preserve transparency and the integrity of research practices. [78]
The social priorities of the community are also a concern. The ISSCR explicitly states that guidelines “should be periodically revised to accommodate scientific advances, new challenges, and evolving social priorities.” [79] The adaptable ethics model extends this consideration further by addressing whether research is warranted given the varying degrees of socioeconomic conditions, political stability, and healthcare accessibilities and limitations. An ethical approach would require discussion about resource allocation and appropriate distribution of funds. [80]
While some religions emphasize the sanctity of life from conception, which may lead to public opposition to ESC research, others encourage ESC research due to its potential for healing and alleviating human pain. Many countries have special regulations that balance local views on embryonic personhood, the benefits of research as individual or societal goods, and the protection of human research subjects. To foster understanding and constructive dialogue, global policy frameworks should prioritize the protection of universal human rights, transparency, and informed consent. In addition to these foundational global policies, we recommend tailoring local guidelines to reflect the diverse cultural and religious perspectives of the populations they govern. Ethics models should be adapted to local populations to effectively establish research protections, growth, and possibilities of stem cell research.
For example, in countries with strong beliefs in the moral sanctity of embryos or heavy religious restrictions, an adaptive model can allow for discussion instead of immediate rejection. In countries with limited individual rights and voice in science policy, an adaptive model ensures cultural, moral, and religious views are taken into consideration, thereby building social inclusion. While this ethical consideration by the government may not give a complete voice to every individual, it will help balance policies and maintain the diverse perspectives of those it affects. Embracing an adaptive ethics model of ESC research promotes open-minded dialogue and respect for the importance of human belief and tradition. By actively engaging with cultural and religious values, researchers can better handle disagreements and promote ethical research practices that benefit each society.
This brief exploration of the religious and cultural differences that impact ESC research reveals the nuances of relative ethics and highlights a need for local policymakers to apply a more intense adaptive model.
[1] Poliwoda, S., Noor, N., Downs, E., Schaaf, A., Cantwell, A., Ganti, L., Kaye, A. D., Mosel, L. I., Carroll, C. B., Viswanath, O., & Urits, I. (2022). Stem cells: a comprehensive review of origins and emerging clinical roles in medical practice. Orthopedic reviews , 14 (3), 37498. https://doi.org/10.52965/001c.37498
[2] Poliwoda, S., Noor, N., Downs, E., Schaaf, A., Cantwell, A., Ganti, L., Kaye, A. D., Mosel, L. I., Carroll, C. B., Viswanath, O., & Urits, I. (2022). Stem cells: a comprehensive review of origins and emerging clinical roles in medical practice. Orthopedic reviews , 14 (3), 37498. https://doi.org/10.52965/001c.37498
[3] International Society for Stem Cell Research. (2023). Laboratory-based human embryonic stem cell research, embryo research, and related research activities . International Society for Stem Cell Research. https://www.isscr.org/guidelines/blog-post-title-one-ed2td-6fcdk ; Kimmelman, J., Hyun, I., Benvenisty, N. et al. Policy: Global standards for stem-cell research. Nature 533 , 311–313 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/533311a
[4] International Society for Stem Cell Research. (2023). Laboratory-based human embryonic stem cell research, embryo research, and related research activities . International Society for Stem Cell Research. https://www.isscr.org/guidelines/blog-post-title-one-ed2td-6fcdk
[5] Concerning the moral philosophies of stem cell research, our paper does not posit a personal moral stance nor delve into the “when” of human life begins. To read further about the philosophical debate, consider the following sources:
Sandel M. J. (2004). Embryo ethics--the moral logic of stem-cell research. The New England journal of medicine , 351 (3), 207–209. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMp048145 ; George, R. P., & Lee, P. (2020, September 26). Acorns and Embryos . The New Atlantis. https://www.thenewatlantis.com/publications/acorns-and-embryos ; Sagan, A., & Singer, P. (2007). The moral status of stem cells. Metaphilosophy , 38 (2/3), 264–284. http://www.jstor.org/stable/24439776 ; McHugh P. R. (2004). Zygote and "clonote"--the ethical use of embryonic stem cells. The New England journal of medicine , 351 (3), 209–211. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMp048147 ; Kurjak, A., & Tripalo, A. (2004). The facts and doubts about beginning of the human life and personality. Bosnian journal of basic medical sciences , 4 (1), 5–14. https://doi.org/10.17305/bjbms.2004.3453
[6] Vazin, T., & Freed, W. J. (2010). Human embryonic stem cells: derivation, culture, and differentiation: a review. Restorative neurology and neuroscience , 28 (4), 589–603. https://doi.org/10.3233/RNN-2010-0543
[7] Socially, at its core, the Western approach to ethics is widely principle-based, autonomy being one of the key factors to ensure a fundamental respect for persons within research. For information regarding autonomy in research, see: Department of Health, Education, and Welfare, & National Commission for the Protection of Human Subjects of Biomedical and Behavioral Research (1978). The Belmont Report. Ethical principles and guidelines for the protection of human subjects of research.; For a more in-depth review of autonomy within the US, see: Beauchamp, T. L., & Childress, J. F. (1994). Principles of Biomedical Ethics . Oxford University Press.
[8] Sherley v. Sebelius , 644 F.3d 388 (D.C. Cir. 2011), citing 45 C.F.R. 46.204(b) and [42 U.S.C. § 289g(b)]. https://www.cadc.uscourts.gov/internet/opinions.nsf/6c690438a9b43dd685257a64004ebf99/$file/11-5241-1391178.pdf
[9] Stem Cell Research Enhancement Act of 2005, H. R. 810, 109 th Cong. (2001). https://www.govtrack.us/congress/bills/109/hr810/text ; Bush, G. W. (2006, July 19). Message to the House of Representatives . National Archives and Records Administration. https://georgewbush-whitehouse.archives.gov/news/releases/2006/07/20060719-5.html
[10] National Archives and Records Administration. (2009, March 9). Executive order 13505 -- removing barriers to responsible scientific research involving human stem cells . National Archives and Records Administration. https://obamawhitehouse.archives.gov/the-press-office/removing-barriers-responsible-scientific-research-involving-human-stem-cells
[11] Hurlbut, W. B. (2006). Science, Religion, and the Politics of Stem Cells. Social Research , 73 (3), 819–834. http://www.jstor.org/stable/40971854
[12] Akpa-Inyang, Francis & Chima, Sylvester. (2021). South African traditional values and beliefs regarding informed consent and limitations of the principle of respect for autonomy in African communities: a cross-cultural qualitative study. BMC Medical Ethics . 22. 10.1186/s12910-021-00678-4.
[13] Source for further reading: Tangwa G. B. (2007). Moral status of embryonic stem cells: perspective of an African villager. Bioethics , 21(8), 449–457. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-8519.2007.00582.x , see also Mnisi, F. M. (2020). An African analysis based on ethics of Ubuntu - are human embryonic stem cell patents morally justifiable? African Insight , 49 (4).
[14] Jecker, N. S., & Atuire, C. (2021). Bioethics in Africa: A contextually enlightened analysis of three cases. Developing World Bioethics , 22 (2), 112–122. https://doi.org/10.1111/dewb.12324
[15] Jecker, N. S., & Atuire, C. (2021). Bioethics in Africa: A contextually enlightened analysis of three cases. Developing World Bioethics, 22(2), 112–122. https://doi.org/10.1111/dewb.12324
[16] Jackson, C.S., Pepper, M.S. Opportunities and barriers to establishing a cell therapy programme in South Africa. Stem Cell Res Ther 4 , 54 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1186/scrt204 ; Pew Research Center. (2014, May 1). Public health a major priority in African nations . Pew Research Center’s Global Attitudes Project. https://www.pewresearch.org/global/2014/05/01/public-health-a-major-priority-in-african-nations/
[17] Department of Health Republic of South Africa. (2021). Health Research Priorities (revised) for South Africa 2021-2024 . National Health Research Strategy. https://www.health.gov.za/wp-content/uploads/2022/05/National-Health-Research-Priorities-2021-2024.pdf
[18] Oosthuizen, H. (2013). Legal and Ethical Issues in Stem Cell Research in South Africa. In: Beran, R. (eds) Legal and Forensic Medicine. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-32338-6_80 , see also: Gaobotse G (2018) Stem Cell Research in Africa: Legislation and Challenges. J Regen Med 7:1. doi: 10.4172/2325-9620.1000142
[19] United States Bureau of Citizenship and Immigration Services. (1998). Tunisia: Information on the status of Christian conversions in Tunisia . UNHCR Web Archive. https://webarchive.archive.unhcr.org/20230522142618/https://www.refworld.org/docid/3df0be9a2.html
[20] Gaobotse, G. (2018) Stem Cell Research in Africa: Legislation and Challenges. J Regen Med 7:1. doi: 10.4172/2325-9620.1000142
[21] Kooli, C. Review of assisted reproduction techniques, laws, and regulations in Muslim countries. Middle East Fertil Soc J 24 , 8 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s43043-019-0011-0 ; Gaobotse, G. (2018) Stem Cell Research in Africa: Legislation and Challenges. J Regen Med 7:1. doi: 10.4172/2325-9620.1000142
[22] Pang M. C. (1999). Protective truthfulness: the Chinese way of safeguarding patients in informed treatment decisions. Journal of medical ethics , 25(3), 247–253. https://doi.org/10.1136/jme.25.3.247
[23] Wang, L., Wang, F., & Zhang, W. (2021). Bioethics in China’s biosecurity law: Forms, effects, and unsettled issues. Journal of law and the biosciences , 8(1). https://doi.org/10.1093/jlb/lsab019 https://academic.oup.com/jlb/article/8/1/lsab019/6299199
[24] Wang, Y., Xue, Y., & Guo, H. D. (2022). Intervention effects of traditional Chinese medicine on stem cell therapy of myocardial infarction. Frontiers in pharmacology , 13 , 1013740. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2022.1013740
[25] Li, X.-T., & Zhao, J. (2012). Chapter 4: An Approach to the Nature of Qi in TCM- Qi and Bioenergy. In Recent Advances in Theories and Practice of Chinese Medicine (p. 79). InTech.
[26] Luo, D., Xu, Z., Wang, Z., & Ran, W. (2021). China's Stem Cell Research and Knowledge Levels of Medical Practitioners and Students. Stem cells international , 2021 , 6667743. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/6667743
[27] Luo, D., Xu, Z., Wang, Z., & Ran, W. (2021). China's Stem Cell Research and Knowledge Levels of Medical Practitioners and Students. Stem cells international , 2021 , 6667743. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/6667743
[28] Zhang, J. Y. (2017). Lost in translation? accountability and governance of Clinical Stem Cell Research in China. Regenerative Medicine , 12 (6), 647–656. https://doi.org/10.2217/rme-2017-0035
[29] Wang, L., Wang, F., & Zhang, W. (2021). Bioethics in China’s biosecurity law: Forms, effects, and unsettled issues. Journal of law and the biosciences , 8(1). https://doi.org/10.1093/jlb/lsab019 https://academic.oup.com/jlb/article/8/1/lsab019/6299199
[30] Chen, H., Wei, T., Wang, H. et al. Association of China’s two-child policy with changes in number of births and birth defects rate, 2008–2017. BMC Public Health 22 , 434 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-022-12839-0
[31] Azuma, K. Regulatory Landscape of Regenerative Medicine in Japan. Curr Stem Cell Rep 1 , 118–128 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40778-015-0012-6
[32] Harris, R. (2005, May 19). Researchers Report Advance in Stem Cell Production . NPR. https://www.npr.org/2005/05/19/4658967/researchers-report-advance-in-stem-cell-production
[33] Park, S. (2012). South Korea steps up stem-cell work. Nature . https://doi.org/10.1038/nature.2012.10565
[34] Resnik, D. B., Shamoo, A. E., & Krimsky, S. (2006). Fraudulent human embryonic stem cell research in South Korea: lessons learned. Accountability in research , 13 (1), 101–109. https://doi.org/10.1080/08989620600634193 .
[35] Alahmad, G., Aljohani, S., & Najjar, M. F. (2020). Ethical challenges regarding the use of stem cells: interviews with researchers from Saudi Arabia. BMC medical ethics, 21(1), 35. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12910-020-00482-6
[36] Association for the Advancement of Blood and Biotherapies. https://www.aabb.org/regulatory-and-advocacy/regulatory-affairs/regulatory-for-cellular-therapies/international-competent-authorities/saudi-arabia
[37] Alahmad, G., Aljohani, S., & Najjar, M. F. (2020). Ethical challenges regarding the use of stem cells: Interviews with researchers from Saudi Arabia. BMC medical ethics , 21 (1), 35. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12910-020-00482-6
[38] Alahmad, G., Aljohani, S., & Najjar, M. F. (2020). Ethical challenges regarding the use of stem cells: Interviews with researchers from Saudi Arabia. BMC medical ethics , 21(1), 35. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12910-020-00482-6
Culturally, autonomy practices follow a relational autonomy approach based on a paternalistic deontological health care model. The adherence to strict international research policies and religious pillars within the regulatory environment is a great foundation for research ethics. However, there is a need to develop locally targeted ethics approaches for research (as called for in Alahmad, G., Aljohani, S., & Najjar, M. F. (2020). Ethical challenges regarding the use of stem cells: interviews with researchers from Saudi Arabia. BMC medical ethics, 21(1), 35. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12910-020-00482-6), this decision-making approach may help advise a research decision model. For more on the clinical cultural autonomy approaches, see: Alabdullah, Y. Y., Alzaid, E., Alsaad, S., Alamri, T., Alolayan, S. W., Bah, S., & Aljoudi, A. S. (2022). Autonomy and paternalism in Shared decision‐making in a Saudi Arabian tertiary hospital: A cross‐sectional study. Developing World Bioethics , 23 (3), 260–268. https://doi.org/10.1111/dewb.12355 ; Bukhari, A. A. (2017). Universal Principles of Bioethics and Patient Rights in Saudi Arabia (Doctoral dissertation, Duquesne University). https://dsc.duq.edu/etd/124; Ladha, S., Nakshawani, S. A., Alzaidy, A., & Tarab, B. (2023, October 26). Islam and Bioethics: What We All Need to Know . Columbia University School of Professional Studies. https://sps.columbia.edu/events/islam-and-bioethics-what-we-all-need-know
[39] Ababneh, M. A., Al-Azzam, S. I., Alzoubi, K., Rababa’h, A., & Al Demour, S. (2021). Understanding and attitudes of the Jordanian public about clinical research ethics. Research Ethics , 17 (2), 228-241. https://doi.org/10.1177/1747016120966779
[40] Ababneh, M. A., Al-Azzam, S. I., Alzoubi, K., Rababa’h, A., & Al Demour, S. (2021). Understanding and attitudes of the Jordanian public about clinical research ethics. Research Ethics , 17 (2), 228-241. https://doi.org/10.1177/1747016120966779
[41] Dajani, R. (2014). Jordan’s stem-cell law can guide the Middle East. Nature 510, 189. https://doi.org/10.1038/510189a
[42] Dajani, R. (2014). Jordan’s stem-cell law can guide the Middle East. Nature 510, 189. https://doi.org/10.1038/510189a
[43] The EU’s definition of autonomy relates to the capacity for creating ideas, moral insight, decisions, and actions without constraint, personal responsibility, and informed consent. However, the EU views autonomy as not completely able to protect individuals and depends on other principles, such as dignity, which “expresses the intrinsic worth and fundamental equality of all human beings.” Rendtorff, J.D., Kemp, P. (2019). Four Ethical Principles in European Bioethics and Biolaw: Autonomy, Dignity, Integrity and Vulnerability. In: Valdés, E., Lecaros, J. (eds) Biolaw and Policy in the Twenty-First Century. International Library of Ethics, Law, and the New Medicine, vol 78. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-05903-3_3
[44] Council of Europe. Convention for the protection of Human Rights and Dignity of the Human Being with regard to the Application of Biology and Medicine: Convention on Human Rights and Biomedicine (ETS No. 164) https://www.coe.int/en/web/conventions/full-list?module=treaty-detail&treatynum=164 (forbidding the creation of embryos for research purposes only, and suggests embryos in vitro have protections.); Also see Drabiak-Syed B. K. (2013). New President, New Human Embryonic Stem Cell Research Policy: Comparative International Perspectives and Embryonic Stem Cell Research Laws in France. Biotechnology Law Report , 32 (6), 349–356. https://doi.org/10.1089/blr.2013.9865
[45] Rendtorff, J.D., Kemp, P. (2019). Four Ethical Principles in European Bioethics and Biolaw: Autonomy, Dignity, Integrity and Vulnerability. In: Valdés, E., Lecaros, J. (eds) Biolaw and Policy in the Twenty-First Century. International Library of Ethics, Law, and the New Medicine, vol 78. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-05903-3_3
[46] Tomuschat, C., Currie, D. P., Kommers, D. P., & Kerr, R. (Trans.). (1949, May 23). Basic law for the Federal Republic of Germany. https://www.btg-bestellservice.de/pdf/80201000.pdf
[47] Regulation of Stem Cell Research in Germany . Eurostemcell. (2017, April 26). https://www.eurostemcell.org/regulation-stem-cell-research-germany
[48] Regulation of Stem Cell Research in Finland . Eurostemcell. (2017, April 26). https://www.eurostemcell.org/regulation-stem-cell-research-finland
[49] Regulation of Stem Cell Research in Spain . Eurostemcell. (2017, April 26). https://www.eurostemcell.org/regulation-stem-cell-research-spain
[50] Some sources to consider regarding ethics models or regulatory oversights of other cultures not covered:
Kara MA. Applicability of the principle of respect for autonomy: the perspective of Turkey. J Med Ethics. 2007 Nov;33(11):627-30. doi: 10.1136/jme.2006.017400. PMID: 17971462; PMCID: PMC2598110.
Ugarte, O. N., & Acioly, M. A. (2014). The principle of autonomy in Brazil: one needs to discuss it ... Revista do Colegio Brasileiro de Cirurgioes , 41 (5), 374–377. https://doi.org/10.1590/0100-69912014005013
Bharadwaj, A., & Glasner, P. E. (2012). Local cells, global science: The rise of embryonic stem cell research in India . Routledge.
For further research on specific European countries regarding ethical and regulatory framework, we recommend this database: Regulation of Stem Cell Research in Europe . Eurostemcell. (2017, April 26). https://www.eurostemcell.org/regulation-stem-cell-research-europe
[51] Klitzman, R. (2006). Complications of culture in obtaining informed consent. The American Journal of Bioethics, 6(1), 20–21. https://doi.org/10.1080/15265160500394671 see also: Ekmekci, P. E., & Arda, B. (2017). Interculturalism and Informed Consent: Respecting Cultural Differences without Breaching Human Rights. Cultura (Iasi, Romania) , 14 (2), 159–172.; For why trust is important in research, see also: Gray, B., Hilder, J., Macdonald, L., Tester, R., Dowell, A., & Stubbe, M. (2017). Are research ethics guidelines culturally competent? Research Ethics , 13 (1), 23-41. https://doi.org/10.1177/1747016116650235
[52] The Qur'an (M. Khattab, Trans.). (1965). Al-Mu’minun, 23: 12-14. https://quran.com/23
[53] Lenfest, Y. (2017, December 8). Islam and the beginning of human life . Bill of Health. https://blog.petrieflom.law.harvard.edu/2017/12/08/islam-and-the-beginning-of-human-life/
[54] Aksoy, S. (2005). Making regulations and drawing up legislation in Islamic countries under conditions of uncertainty, with special reference to embryonic stem cell research. Journal of Medical Ethics , 31: 399-403.; see also: Mahmoud, Azza. "Islamic Bioethics: National Regulations and Guidelines of Human Stem Cell Research in the Muslim World." Master's thesis, Chapman University, 2022. https://doi.org/10.36837/ chapman.000386
[55] Rashid, R. (2022). When does Ensoulment occur in the Human Foetus. Journal of the British Islamic Medical Association , 12 (4). ISSN 2634 8071. https://www.jbima.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/01/2-Ethics-3_-Ensoulment_Rafaqat.pdf.
[56] Sivaraman, M. & Noor, S. (2017). Ethics of embryonic stem cell research according to Buddhist, Hindu, Catholic, and Islamic religions: perspective from Malaysia. Asian Biomedicine,8(1) 43-52. https://doi.org/10.5372/1905-7415.0801.260
[57] Jafari, M., Elahi, F., Ozyurt, S. & Wrigley, T. (2007). 4. Religious Perspectives on Embryonic Stem Cell Research. In K. Monroe, R. Miller & J. Tobis (Ed.), Fundamentals of the Stem Cell Debate: The Scientific, Religious, Ethical, and Political Issues (pp. 79-94). Berkeley: University of California Press. https://escholarship.org/content/qt9rj0k7s3/qt9rj0k7s3_noSplash_f9aca2e02c3777c7fb76ea768ba458f0.pdf https://doi.org/10.1525/9780520940994-005
[58] Lecso, P. A. (1991). The Bodhisattva Ideal and Organ Transplantation. Journal of Religion and Health , 30 (1), 35–41. http://www.jstor.org/stable/27510629 ; Bodhisattva, S. (n.d.). The Key of Becoming a Bodhisattva . A Guide to the Bodhisattva Way of Life. http://www.buddhism.org/Sutras/2/BodhisattvaWay.htm
[59] There is no explicit religious reference to when life begins or how to conduct research that interacts with the concept of life. However, these are relevant verses pertaining to how the fetus is viewed. (( King James Bible . (1999). Oxford University Press. (original work published 1769))
Jerimiah 1: 5 “Before I formed thee in the belly I knew thee; and before thou camest forth out of the womb I sanctified thee…”
In prophet Jerimiah’s insight, God set him apart as a person known before childbirth, a theme carried within the Psalm of David.
Psalm 139: 13-14 “…Thou hast covered me in my mother's womb. I will praise thee; for I am fearfully and wonderfully made…”
These verses demonstrate David’s respect for God as an entity that would know of all man’s thoughts and doings even before birth.
[60] It should be noted that abortion is not supported as well.
[61] The Vatican. (1987, February 22). Instruction on Respect for Human Life in Its Origin and on the Dignity of Procreation Replies to Certain Questions of the Day . Congregation For the Doctrine of the Faith. https://www.vatican.va/roman_curia/congregations/cfaith/documents/rc_con_cfaith_doc_19870222_respect-for-human-life_en.html
[62] The Vatican. (2000, August 25). Declaration On the Production and the Scientific and Therapeutic Use of Human Embryonic Stem Cells . Pontifical Academy for Life. https://www.vatican.va/roman_curia/pontifical_academies/acdlife/documents/rc_pa_acdlife_doc_20000824_cellule-staminali_en.html ; Ohara, N. (2003). Ethical Consideration of Experimentation Using Living Human Embryos: The Catholic Church’s Position on Human Embryonic Stem Cell Research and Human Cloning. Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology . Retrieved from https://article.imrpress.com/journal/CEOG/30/2-3/pii/2003018/77-81.pdf.
[63] Smith, G. A. (2022, May 23). Like Americans overall, Catholics vary in their abortion views, with regular mass attenders most opposed . Pew Research Center. https://www.pewresearch.org/short-reads/2022/05/23/like-americans-overall-catholics-vary-in-their-abortion-views-with-regular-mass-attenders-most-opposed/
[64] Rosner, F., & Reichman, E. (2002). Embryonic stem cell research in Jewish law. Journal of halacha and contemporary society , (43), 49–68.; Jafari, M., Elahi, F., Ozyurt, S. & Wrigley, T. (2007). 4. Religious Perspectives on Embryonic Stem Cell Research. In K. Monroe, R. Miller & J. Tobis (Ed.), Fundamentals of the Stem Cell Debate: The Scientific, Religious, Ethical, and Political Issues (pp. 79-94). Berkeley: University of California Press. https://escholarship.org/content/qt9rj0k7s3/qt9rj0k7s3_noSplash_f9aca2e02c3777c7fb76ea768ba458f0.pdf https://doi.org/10.1525/9780520940994-005
[65] Schenker J. G. (2008). The beginning of human life: status of embryo. Perspectives in Halakha (Jewish Religious Law). Journal of assisted reproduction and genetics , 25 (6), 271–276. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10815-008-9221-6
[66] Ruttenberg, D. (2020, May 5). The Torah of Abortion Justice (annotated source sheet) . Sefaria. https://www.sefaria.org/sheets/234926.7?lang=bi&with=all&lang2=en
[67] Jafari, M., Elahi, F., Ozyurt, S. & Wrigley, T. (2007). 4. Religious Perspectives on Embryonic Stem Cell Research. In K. Monroe, R. Miller & J. Tobis (Ed.), Fundamentals of the Stem Cell Debate: The Scientific, Religious, Ethical, and Political Issues (pp. 79-94). Berkeley: University of California Press. https://escholarship.org/content/qt9rj0k7s3/qt9rj0k7s3_noSplash_f9aca2e02c3777c7fb76ea768ba458f0.pdf https://doi.org/10.1525/9780520940994-005
[68] Gert, B. (2007). Common morality: Deciding what to do . Oxford Univ. Press.
[69] World Medical Association (2013). World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki: ethical principles for medical research involving human subjects. JAMA , 310(20), 2191–2194. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2013.281053 Declaration of Helsinki – WMA – The World Medical Association .; see also: National Commission for the Protection of Human Subjects of Biomedical and Behavioral Research. (1979). The Belmont report: Ethical principles and guidelines for the protection of human subjects of research . U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. https://www.hhs.gov/ohrp/regulations-and-policy/belmont-report/read-the-belmont-report/index.html
[70] Zakarin Safier, L., Gumer, A., Kline, M., Egli, D., & Sauer, M. V. (2018). Compensating human subjects providing oocytes for stem cell research: 9-year experience and outcomes. Journal of assisted reproduction and genetics , 35 (7), 1219–1225. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10815-018-1171-z https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6063839/ see also: Riordan, N. H., & Paz Rodríguez, J. (2021). Addressing concerns regarding associated costs, transparency, and integrity of research in recent stem cell trial. Stem Cells Translational Medicine , 10 (12), 1715–1716. https://doi.org/10.1002/sctm.21-0234
[71] Klitzman, R., & Sauer, M. V. (2009). Payment of egg donors in stem cell research in the USA. Reproductive biomedicine online , 18 (5), 603–608. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1472-6483(10)60002-8
[72] Krosin, M. T., Klitzman, R., Levin, B., Cheng, J., & Ranney, M. L. (2006). Problems in comprehension of informed consent in rural and peri-urban Mali, West Africa. Clinical trials (London, England) , 3 (3), 306–313. https://doi.org/10.1191/1740774506cn150oa
[73] Veatch, Robert M. Hippocratic, Religious, and Secular Medical Ethics: The Points of Conflict . Georgetown University Press, 2012.
[74] Msoroka, M. S., & Amundsen, D. (2018). One size fits not quite all: Universal research ethics with diversity. Research Ethics , 14 (3), 1-17. https://doi.org/10.1177/1747016117739939
[75] Pirzada, N. (2022). The Expansion of Turkey’s Medical Tourism Industry. Voices in Bioethics , 8 . https://doi.org/10.52214/vib.v8i.9894
[76] Stem Cell Tourism: False Hope for Real Money . Harvard Stem Cell Institute (HSCI). (2023). https://hsci.harvard.edu/stem-cell-tourism , See also: Bissassar, M. (2017). Transnational Stem Cell Tourism: An ethical analysis. Voices in Bioethics , 3 . https://doi.org/10.7916/vib.v3i.6027
[77] Song, P. (2011) The proliferation of stem cell therapies in post-Mao China: problematizing ethical regulation, New Genetics and Society , 30:2, 141-153, DOI: 10.1080/14636778.2011.574375
[78] Dajani, R. (2014). Jordan’s stem-cell law can guide the Middle East. Nature 510, 189. https://doi.org/10.1038/510189a
[79] International Society for Stem Cell Research. (2024). Standards in stem cell research . International Society for Stem Cell Research. https://www.isscr.org/guidelines/5-standards-in-stem-cell-research
[80] Benjamin, R. (2013). People’s science bodies and rights on the Stem Cell Frontier . Stanford University Press.
Mifrah Hayath
SM Candidate Harvard Medical School, MS Biotechnology Johns Hopkins University
Olivia Bowers
MS Bioethics Columbia University (Disclosure: affiliated with Voices in Bioethics)
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License .

Impact of the use of cannabis as a medicine in pregnancy, on the unborn child: a systematic review and meta-analysis protocol
- Find this author on Google Scholar
- Find this author on PubMed
- Search for this author on this site
- For correspondence: [email protected]
- Info/History
- Preview PDF
Introduction: The use of cannabis for medicinal purposes is on the rise. As more people place their trust in the safety of prescribed alternative plant-based medicine and find it easily accessible, there is a growing concern that pregnant women may be increasingly using cannabis for medicinal purposes to manage their pregnancy symptoms and other health conditions. The aim of this review is to investigate the use of cannabis for medicinal purposes during pregnancy, describe the characteristics of the demographic population, and to measure the impact on the unborn child and up to twelve months postpartum. Methods and analyses: Research on pregnant women who use cannabis for medicinal purposes only and infants up to one year after birth who experienced in utero exposure to cannabis for medicinal purposes will be included in this review. Reviews, randomised controlled trials, case control, cross-sectional and cohort studies, that have been peer reviewed and published between 1996 and April 2024 as a primary research paper that investigates prenatal use of cannabis for medicinal purposes on foetal, perinatal, and neonatal outcomes, will be selected for review. Excluding cover editorials, letters, commentaries, protocols, conference papers and book chapters. Effects of illicit drugs use, alcohol misuse and nicotine exposure on neonate outcome will be controlled by excluding studies reporting on the concomitant use of such substances with cannabis for medicinal purposes during pregnancy. All titles and abstracts will be reviewed independently and in duplicate by at least two researchers. Records will be excluded based on title and abstract screening as well as publication type. Where initial disagreement exists between reviewers regarding the inclusion of a study, team members will review disputed articles status until consensus is gained. Selected studies will then be assessed by at least two independent researchers for risk bias assessment using validated tools. Data will be extracted and analysed following a systematic review and meta-analysis methodology. The statistical analysis will combine three or more outcomes that are reported in a consistent manner. The systematic review and meta-analysis will follow the PRISMA guidelines to facilitate transparent reporting [1].
Competing Interest Statement
The authors have declared no competing interest.
Funding Statement
This study did not receive any funding.
Author Declarations
I confirm all relevant ethical guidelines have been followed, and any necessary IRB and/or ethics committee approvals have been obtained.
The details of the IRB/oversight body that provided approval or exemption for the research described are given below:
The study will use ONLY openly available human data from studies published in biomedical and scientific journals.
I confirm that all necessary patient/participant consent has been obtained and the appropriate institutional forms have been archived, and that any patient/participant/sample identifiers included were not known to anyone (e.g., hospital staff, patients or participants themselves) outside the research group so cannot be used to identify individuals.
I understand that all clinical trials and any other prospective interventional studies must be registered with an ICMJE-approved registry, such as ClinicalTrials.gov. I confirm that any such study reported in the manuscript has been registered and the trial registration ID is provided (note: if posting a prospective study registered retrospectively, please provide a statement in the trial ID field explaining why the study was not registered in advance).
I have followed all appropriate research reporting guidelines, such as any relevant EQUATOR Network research reporting checklist(s) and other pertinent material, if applicable.
Data Availability
All data produced in the present work are contained in the manuscript.
View the discussion thread.
Thank you for your interest in spreading the word about medRxiv.
NOTE: Your email address is requested solely to identify you as the sender of this article.

Citation Manager Formats
- EndNote (tagged)
- EndNote 8 (xml)
- RefWorks Tagged
- Ref Manager
- Tweet Widget
- Facebook Like
- Google Plus One
- Addiction Medicine (324)
- Allergy and Immunology (627)
- Anesthesia (163)
- Cardiovascular Medicine (2371)
- Dentistry and Oral Medicine (289)
- Dermatology (206)
- Emergency Medicine (379)
- Endocrinology (including Diabetes Mellitus and Metabolic Disease) (836)
- Epidemiology (11768)
- Forensic Medicine (10)
- Gastroenterology (702)
- Genetic and Genomic Medicine (3736)
- Geriatric Medicine (350)
- Health Economics (633)
- Health Informatics (2395)
- Health Policy (932)
- Health Systems and Quality Improvement (896)
- Hematology (341)
- HIV/AIDS (782)
- Infectious Diseases (except HIV/AIDS) (13308)
- Intensive Care and Critical Care Medicine (767)
- Medical Education (365)
- Medical Ethics (104)
- Nephrology (398)
- Neurology (3501)
- Nursing (198)
- Nutrition (524)
- Obstetrics and Gynecology (674)
- Occupational and Environmental Health (663)
- Oncology (1823)
- Ophthalmology (537)
- Orthopedics (218)
- Otolaryngology (287)
- Pain Medicine (232)
- Palliative Medicine (66)
- Pathology (446)
- Pediatrics (1033)
- Pharmacology and Therapeutics (426)
- Primary Care Research (420)
- Psychiatry and Clinical Psychology (3175)
- Public and Global Health (6138)
- Radiology and Imaging (1280)
- Rehabilitation Medicine and Physical Therapy (747)
- Respiratory Medicine (826)
- Rheumatology (379)
- Sexual and Reproductive Health (372)
- Sports Medicine (323)
- Surgery (402)
- Toxicology (50)
- Transplantation (172)
- Urology (145)

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Table of contents. Step 1: Introduce your topic. Step 2: Describe the background. Step 3: Establish your research problem. Step 4: Specify your objective (s) Step 5: Map out your paper. Research paper introduction examples. Frequently asked questions about the research paper introduction.
The research paper introduction section, along with the Title and Abstract, can be considered the face of any research paper. The following article is intended to guide you in organizing and writing the research paper introduction for a quality academic article or dissertation. The research paper introduction aims to present the topic to the ...
Research Paper Introduction. Research paper introduction is the first section of a research paper that provides an overview of the study, its purpose, and the research question(s) or hypothesis(es) being investigated. It typically includes background information about the topic, a review of previous research in the field, and a statement of the research objectives.
The introduction leads the reader from a general subject area to a particular topic of inquiry. It establishes the scope, context, and significance of the research being conducted by summarizing current understanding and background information about the topic, stating the purpose of the work in the form of the research problem supported by a hypothesis or a set of questions, explaining briefly ...
When writing your research paper introduction, there are several key elements you should include to ensure it is comprehensive and informative. A hook or attention-grabbing statement to capture the reader's interest. It can be a thought-provoking question, a surprising statistic, or a compelling anecdote that relates to your research topic.
Step 2: Building a solid foundation with background information. Including background information in your introduction serves two major purposes: It helps to clarify the topic for the reader. It establishes the depth of your research. The approach you take when conveying this information depends on the type of paper.
In general, your introductions should contain the following elements: When you're writing an essay, it's helpful to think about what your reader needs to know in order to follow your argument. Your introduction should include enough information so that readers can understand the context for your thesis. For example, if you are analyzing ...
A clear format will ensure that your research paper is understood by your readers. Follow: 1. Context — your introduction. 2. Content — your results. 3. Conclusion — your discussion. Plan ...
The 4-step approach to writing the Introduction section. As a rule of thumb, this section accounts for about 10% of the total word count of the body of a typical research paper, or about 400 words spread over three paragraphs in a 4000-word paper.1 With that, let us now understand how to write the Introduction section step-by-step: 1.
Table of contents. Step 1: Hook your reader. Step 2: Give background information. Step 3: Present your thesis statement. Step 4: Map your essay's structure. Step 5: Check and revise. More examples of essay introductions. Other interesting articles. Frequently asked questions about the essay introduction.
The five parts of introductions. According to John W. Creswell, the five components of a good introduction are the following: " (a) establishing the problem leading to the study, (b) reviewing the literature about the problem, (c) identifying deficiencies in the literature about the problem, (d) targeting an audience and noting the ...
Download Article. 1. Announce your research topic. You can start your introduction with a few sentences which announce the topic of your paper and give an indication of the kind of research questions you will be asking. This is a good way to introduce your readers to your topic and pique their interest.
Hannah Skaggs. Hannah, a writer and editor since 2017, specializes in clear and concise academic and business writing. She has mentored countless scholars and companies in writing authoritative and engaging content. A great research paper introduction starts with a catchy hook and ends with a road map for the research. At every step, QuillBot ...
For research papers, in particular, you want to make sure your introduction not only meets the general guidelines above but also does the following: Includes a central argument, problem statement, or thesis statement, detailing the intent, rationale, and/or purpose of your research. Addresses why your problem or topic is important.
The introduction is an important and challenging part of any research paper as it establishes your writing style, the quality of your research, and your credibility as a scholar. It is your first chance to make a good impression on your reader. The introduction gives the reader background and context to convey the importance of your research. It
A scientific paper should have an introduction in the form of an inverted pyramid. The writer should start with the general information about the topic and subsequently narrow it down to the specific topic-related introduction. Fig. 17.1. Flow of ideas from the general to the specific. Full size image.
The key thing is. to guide the reader into your topic and situate your ideas. Step 2: Describe the background. This part of the introduction differs depending on what approach your paper is ...
• Repeat the paper title at the top of the first page of text. • Begin with an introduction to provide background and context. • Use descriptive headings to identify other sections (e.g., Method, Results, Discussion for quantitative research papers). • Sections and headings vary depending on paper type and complexity.
The structure of a research paper typically follows a standard format, consisting of several sections that convey specific information about the research study. ... Write your Paper: Start by writing the introduction, followed by the literature review, methods, results, discussion, and conclusion. Ensure that your writing is clear, concise, and ...
Every paper must include: An Introduction: This element should grab the reader's attention, briefly introduce the topic, and state your main claim (thesis statement). Body: This element includes all your supporting points and evidence. This is where you build your argument to support the thesis statement. A Conclusion: This element should restate your main claim, summarize your main points ...
Mission. The Purdue On-Campus Writing Lab and Purdue Online Writing Lab assist clients in their development as writers—no matter what their skill level—with on-campus consultations, online participation, and community engagement. The Purdue Writing Lab serves the Purdue, West Lafayette, campus and coordinates with local literacy initiatives.
The introduction of AlphaFold 21 has spurred a revolution in modelling the structure of proteins and their interactions, enabling a huge range of applications in protein modelling and design2-6.
The value of using qualitative methods within clinical trials is widely recognised. How qualitative research is integrated within trials units to achieve this is less clear. This paper describes the process through which qualitative research has been integrated within Cardiff University's Centre for Trials Research (CTR) in Wales, UK. We highlight facilitators of, and challenges to, integration.
Prior to GPT-4o, you could use Voice Mode to talk to ChatGPT with latencies of 2.8 seconds (GPT-3.5) and 5.4 seconds (GPT-4) on average. To achieve this, Voice Mode is a pipeline of three separate models: one simple model transcribes audio to text, GPT-3.5 or GPT-4 takes in text and outputs text, and a third simple model converts that text back to audio.
Voices in Bioethics is currently seeking submissions on philosophical and practical topics, both current and timeless. Papers addressing access to healthcare, the bioethical implications of recent Supreme Court rulings, environmental ethics, data privacy, cybersecurity, law and bioethics, economics and bioethics, reproductive ethics, research ethics, and pediatric bioethics are sought.
Introduction: The use of cannabis for medicinal purposes is on the rise. As more people place their trust in the safety of prescribed alternative plant-based medicine and find it easily accessible, there is a growing concern that pregnant women may be increasingly using cannabis for medicinal purposes to manage their pregnancy symptoms and other health conditions. The aim of this review is to ...