- Assignment Clause
Get free proposals from vetted lawyers in our marketplace.


Contract Clauses
- Acceleration Clause
- Arbitration Clause
- Cancellation Clause
- Choice of Law Clause
- Confidentiality Clause
- Consideration Clause
- Definitions Clause
- Dispute Resolution Clause
- Entire Agreement Clause
- Escalation Clause
- Exclusivity Clause
- Exculpatory Clause
- Force Majeure Clause
- Governing Law Clause
- Indemnification Clause
- Indemnity Clause
- Insurance Clause
- Integration Clause
- Merger Clause
- Non-Competition Clause
- Non-Disparagement Clause
- Non-Exclusivity Clause
- Non-Solicitation Clause
- Privacy Clause
- Release Clause
- Severability Clause
- Subordination Clause
- Subrogation Clause
- Survival Clause
- Termination Clause
- Time of Essence Clause
Jump to Section
Assignment clause defined.
Assignment clauses are legally binding provisions in contracts that give a party the chance to engage in a transfer of ownership or assign their contractual obligations and rights to a different contracting party.
In other words, an assignment clause can reassign contracts to another party. They can commonly be seen in contracts related to business purchases.
Here’s an article about assignment clauses.
Assignment Clause Explained
Assignment contracts are helpful when you need to maintain an ongoing obligation regardless of ownership. Some agreements have limitations or prohibitions on assignments, while other parties can freely enter into them.
Here’s another article about assignment clauses.
Purpose of Assignment Clause
The purpose of assignment clauses is to establish the terms around transferring contractual obligations. The Uniform Commercial Code (UCC) permits the enforceability of assignment clauses.
Assignment Clause Examples
Examples of assignment clauses include:
- Example 1 . A business closing or a change of control occurs
- Example 2 . New services providers taking over existing customer contracts
- Example 3 . Unique real estate obligations transferring to a new property owner as a condition of sale
- Example 4 . Many mergers and acquisitions transactions, such as insurance companies taking over customer policies during a merger
Here’s an article about the different types of assignment clauses.
Assignment Clause Samples
Sample 1 – sales contract.
Assignment; Survival . Neither party shall assign all or any portion of the Contract without the other party’s prior written consent, which consent shall not be unreasonably withheld; provided, however, that either party may, without such consent, assign this Agreement, in whole or in part, in connection with the transfer or sale of all or substantially all of the assets or business of such Party relating to the product(s) to which this Agreement relates. The Contract shall bind and inure to the benefit of the successors and permitted assigns of the respective parties. Any assignment or transfer not in accordance with this Contract shall be void. In order that the parties may fully exercise their rights and perform their obligations arising under the Contract, any provisions of the Contract that are required to ensure such exercise or performance (including any obligation accrued as of the termination date) shall survive the termination of the Contract.
Reference :
Security Exchange Commission - Edgar Database, EX-10.29 3 dex1029.htm SALES CONTRACT , Viewed May 10, 2021, < https://www.sec.gov/Archives/edgar/data/1492426/000119312510226984/dex1029.htm >.
Sample 2 – Purchase and Sale Agreement
Assignment . Purchaser shall not assign this Agreement or any interest therein to any Person, without the prior written consent of Seller, which consent may be withheld in Seller’s sole discretion. Notwithstanding the foregoing, upon prior written notice to Seller, Purchaser may designate any Affiliate as its nominee to receive title to the Property, or assign all of its right, title and interest in this Agreement to any Affiliate of Purchaser by providing written notice to Seller no later than five (5) Business Days prior to the Closing; provided, however, that (a) such Affiliate remains an Affiliate of Purchaser, (b) Purchaser shall not be released from any of its liabilities and obligations under this Agreement by reason of such designation or assignment, (c) such designation or assignment shall not be effective until Purchaser has provided Seller with a fully executed copy of such designation or assignment and assumption instrument, which shall (i) provide that Purchaser and such designee or assignee shall be jointly and severally liable for all liabilities and obligations of Purchaser under this Agreement, (ii) provide that Purchaser and its designee or assignee agree to pay any additional transfer tax as a result of such designation or assignment, (iii) include a representation and warranty in favor of Seller that all representations and warranties made by Purchaser in this Agreement are true and correct with respect to such designee or assignee as of the date of such designation or assignment, and will be true and correct as of the Closing, and (iv) otherwise be in form and substance satisfactory to Seller and (d) such Assignee is approved by Manager as an assignee of the Management Agreement under Article X of the Management Agreement. For purposes of this Section 16.4, “Affiliate” shall include any direct or indirect member or shareholder of the Person in question, in addition to any Person that would be deemed an Affiliate pursuant to the definition of “Affiliate” under Section 1.1 hereof and not by way of limitation of such definition.
Security Exchange Commission - Edgar Database, EX-10.8 3 dex108.htm PURCHASE AND SALE AGREEMENT , Viewed May 10, 2021, < https://www.sec.gov/Archives/edgar/data/1490985/000119312510160407/dex108.htm >.
Sample 3 – Share Purchase Agreement
Assignment . Neither this Agreement nor any right or obligation hereunder may be assigned by any Party without the prior written consent of the other Parties, and any attempted assignment without the required consents shall be void.
Security Exchange Commission - Edgar Database, EX-4.12 3 dex412.htm SHARE PURCHASE AGREEMENT , Viewed May 10, 2021, < https://www.sec.gov/Archives/edgar/data/1329394/000119312507148404/dex412.htm >.
Sample 4 – Asset Purchase Agreement
Assignment . This Agreement and any of the rights, interests, or obligations incurred hereunder, in part or as a whole, at any time after the Closing, are freely assignable by Buyer. This Agreement and any of the rights, interests, or obligations incurred hereunder, in part or as a whole, are assignable by Seller only upon the prior written consent of Buyer, which consent shall not be unreasonably withheld. This Agreement will be binding upon, inure to the benefit of and be enforceable by the parties and their respective successors and permitted assigns.
Security Exchange Commission - Edgar Database, EX-2.1 2 dex21.htm ASSET PURCHASE AGREEMENT , Viewed May 10, 2021, < https://www.sec.gov/Archives/edgar/data/1428669/000119312510013625/dex21.htm >.
Sample 5 – Asset Purchase Agreement
Assignment; Binding Effect; Severability
This Agreement may not be assigned by any party hereto without the other party’s written consent; provided, that Buyer may transfer or assign in whole or in part to one or more Buyer Designee its right to purchase all or a portion of the Purchased Assets, but no such transfer or assignment will relieve Buyer of its obligations hereunder. This Agreement shall be binding upon and inure to the benefit of and be enforceable by the successors, legal representatives and permitted assigns of each party hereto. The provisions of this Agreement are severable, and in the event that any one or more provisions are deemed illegal or unenforceable the remaining provisions shall remain in full force and effect unless the deletion of such provision shall cause this Agreement to become materially adverse to either party, in which event the parties shall use reasonable commercial efforts to arrive at an accommodation that best preserves for the parties the benefits and obligations of the offending provision.
Security Exchange Commission - Edgar Database, EX-2.4 2 dex24.htm ASSET PURCHASE AGREEMENT , Viewed May 10, 2021, < https://www.sec.gov/Archives/edgar/data/1002047/000119312511171858/dex24.htm >.
Common Contracts with Assignment Clauses
Common contracts with assignment clauses include:
- Real estate contracts
- Sales contract
- Asset purchase agreement
- Purchase and sale agreement
- Bill of sale
- Assignment and transaction financing agreement
Assignment Clause FAQs
Assignment clauses are powerful when used correctly. Check out the assignment clause FAQs below to learn more:
What is an assignment clause in real estate?
Assignment clauses in real estate transfer legal obligations from one owner to another party. They also allow house flippers to engage in a contract negotiation with a seller and then assign the real estate to the buyer while collecting a fee for their services. Real estate lawyers assist in the drafting of assignment clauses in real estate transactions.
What does no assignment clause mean?
No assignment clauses prohibit the transfer or assignment of contract obligations from one part to another.
What’s the purpose of the transfer and assignment clause in the purchase agreement?
The purpose of the transfer and assignment clause in the purchase agreement is to protect all involved parties’ rights and ensure that assignments are not to be unreasonably withheld. Contract lawyers can help you avoid legal mistakes when drafting your business contracts’ transfer and assignment clauses.
ContractsCounsel is not a law firm, and this post should not be considered and does not contain legal advice. To ensure the information and advice in this post are correct, sufficient, and appropriate for your situation, please consult a licensed attorney. Also, using or accessing ContractsCounsel's site does not create an attorney-client relationship between you and ContractsCounsel.
Nicholas M.
Meet some of our Lawyers
Alen Aydinian is a seasoned real estate attorney with a wealth of experience in handling transactional matters, real estate transactions, and lease agreements. As a licensed real estate broker, Alen Aydinian brings a unique perspective to the table, allowing clients to benefit from both legal expertise and practical industry knowledge. He is a trusted advisor in the realm of real estate transactions and lease agreements. Whether representing buyers, sellers, landlords, or tenants, Alen Aydinian is committed to providing strategic counsel and dedicated advocacy every step of the way. Clients rely on him for sound legal guidance, proactive problem-solving, and unwavering support throughout the transaction process.
I am a solo-practitioner with a practice mostly consisting of serving as a fractional general counsel to start ups and growth stage companies. With a practical business background, I aim to bring real-world, economically driven solutions to my client's legal problems and pride myself on efficient yet effective work.
Billy Joe M.
I graduated from the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign in 2006 with a degree in Political Science, Finance, and Economics. I stayed around Champaign for law school and graduated in 2009. I then worked at a big law firm in downtown Chicago. It was boring, so I quit in early 2011. I thought that I could not be happy practicing law - I was wrong. After I quit the traditional law firm life, I began representing my own clients. I realize now that I love helping normal people, small business owners, and non-profits address a variety of legal issues. I hope to hear from you.
Mr. Mehdipour attended the University of California San Diego where he received his degree in political science. After graduating from UCSD, Mr. Mehdipour attended Southwestern University School of Law where he received his JD. Upon passing the bar, Mr. Mehdipour gained invaluable experience both in a law firm and business setting. Mr. Mehdipour uses his prior business and legal experiences to negotiate the most advantageous results for his clients.
Nicholas A.
I help small business owners build and protect their dreams. I always thought that I would just be a litigator. Then I joined an intellectual property clinic in law school. We were helping nonprofits and small businesses reach their goals. I fell in love with the work and decided to open my own firm so I could keep helping them. When I decided to start Victrix Legal, I decided that it would be a modern law firm designed to serve professionals. It would be different from every other law firm. In my experience, my law firms are designed to promote inefficiency and reactionary lawyering. Because in most firms, you make more money when you spend more time on a project. And you lose money if your client doesn't get sued. In my opinion, that's a built-in conflict of interest. My firm is different. I use flat fees for most basic projects to keep costs predictable for you and incentivize efficiency. I offer long-term advisory plans and legal audits to prevent issues from happening. I want my clients to see me as their business partner, not just the guy they call when they are in trouble. If any of that interests you, please reach out to me. I offer free consultations. Let's set aside some time and talk about what your legal needs are.
My clients know me as more than just an attorney. First and foremost, my background is much broader than that. Prior to attending the Valparaiso University School of Law, I earned a Master of Business Administration and ran a small business as a certified public accountant. Thanks to this experience, I possess unique insight which in turn allows me to better assist my clients with a wide range of business and tax matters today. In total, I have over 20 years of experience in financial management, tax law, and business consulting, and I’m proud to say that I’m utilizing the knowledge I’ve gained to assist the community of Round Rock in a variety of ways. In my current practice, I provide counsel to small to medium-sized businesses, nonprofit organizations, and everyday individuals. Though my primary areas of practice are estate planning, elder law, business consulting, and tax planning, I pride myself on assisting my clients in a comprehensive manner. Whenever I take on a new client, I make an effort to get to know them on a personal level. This, of course, begins with listening. It is important that I fully understand their vision so I can help them successfully translate it into a concrete plan of action that meets their goals and expectations. I appreciate the individual attributes of each client and know firsthand that thoughtful, creative, and customized planning can maximize both financial security and personal happiness. During my time as a certified public accountant, I cultivated an invaluable skill set. After all, while my legal education has given me a deep understanding of tax law, I would not be the tax attorney I am today without my background in accounting. Due to my far-reaching experience, I am competent in unraveling even the most complex tax mysteries and disputes. My CPA training benefits my estate planning practice, too. In the process of drafting comprehensive wills and trusts, I carefully account for every asset and plan for any tax burdens that may arise, often facilitating a much smoother inheritance for the heirs of my clients. Prior to becoming certified as a CPA, I made sure to establish a solid foundation in business both in and out of the classroom, and the acumen I’ve attained has served me well. Not only am I better able to run my own practice than I otherwise would be; I am able to help other small business owners fulfill their dreams, as well.
Find the best lawyer for your project

Quick, user friendly and one of the better ways I've come across to get ahold of lawyers willing to take new clients.
CONTRACT lawyers by city
- Atlanta Contract Lawyers
- Austin Contract Lawyers
- Boston Contract Lawyers
- Chicago Contract Lawyers
- Dallas Contract Lawyers
- Denver Contract Lawyers
- Fort Lauderdale Contract Lawyers
- Houston Contract Lawyers
- Las Vegas Contract Lawyers
- Los Angeles Contract Lawyers
- Memphis Contract Lawyers
- Miami Contract Lawyers
- New York Contract Lawyers
- Oklahoma City Contract Lawyers
- Orlando Contract Lawyers
- Philadelphia Contract Lawyers
- Phoenix Contract Lawyers
- Richmond Contract Lawyers
- Salt Lake City Contract Lawyers
- San Antonio Contract Lawyers
- San Diego Contract Lawyers
- San Francisco Contract Lawyers
- Seattle Contract Lawyers
- Tampa Contract Lawyers
Contracts Counsel was incredibly helpful and easy to use. I submitted a project for a lawyer's help within a day I had received over 6 proposals from qualified lawyers. I submitted a bid that works best for my business and we went forward with the project.
I never knew how difficult it was to obtain representation or a lawyer, and ContractsCounsel was EXACTLY the type of service I was hoping for when I was in a pinch. Working with their service was efficient, effective and made me feel in control. Thank you so much and should I ever need attorney services down the road, I'll certainly be a repeat customer.
I got 5 bids within 24h of posting my project. I choose the person who provided the most detailed and relevant intro letter, highlighting their experience relevant to my project. I am very satisfied with the outcome and quality of the two agreements that were produced, they actually far exceed my expectations.
How It Works
Post Your Project
Get Free Bids to Compare
Hire Your Lawyer
Find lawyers and attorneys by city
(404) 738-5471

Ultimate Checklist for Understanding Contract Assignment Rules
- February 28, 2024
- Moton Legal Group

In contracts, understanding assignment is key. Simply put, an assignment in contract law is when one party (the assignor) transfers their rights and responsibilities under a contract to another party (the assignee). This can include anything from leasing agreements to business operations. But why is this important? It’s because it allows for flexibility in business and personal dealings, a critical component in our world.
Here’s a quick rundown: – Contract Basics: The foundational agreements between parties. – Assignment Importance: Allowing the transfer of obligations and benefits to keep up with life’s changes.
Contracts are a staple in both personal and business worlds, acting as the backbone to many transactions and agreements encountered daily. Understanding the nuances, like assignments, can empower you to navigate these waters with confidence and ease. Whether you’re a business owner in the Southeast looking to expand or an individual managing personal agreements, grasp these basics, and you’re on the right path.
Understanding Contract Assignment
Contract Assignment sounds complicated, right? But, let’s break it down into simple terms. In contracts and legal agreements, knowing about assignment can save you a lot of headaches down the road. Whether you’re a business owner, a landlord, or just someone who deals with contracts, this is for you.
Legal Definition
At its core, contract assignment is about transferring rights or obligations under a contract from one party to another. Think of it as passing a baton in a relay race. The original party (the assignor) hands off their responsibilities or benefits to someone else (the assignee). But, there’s a twist – the race keeps going with the new runner without starting over.
Contract Law
In contract law, assignment comes into play in various ways. For example, if you’re a freelancer and you’ve agreed to complete a project but suddenly find yourself overbooked, you might assign that contract to another freelancer. This way, the job gets done, and your client is happy. However, not all contracts can be freely assigned. Some require the other party’s consent, and others can’t be assigned at all, especially if they involve personal skills or confidential trust.
Property Law
When it comes to property law, assignment often surfaces in landlord-tenant relationships. Say you’re renting a shop for your business, but you decide to move. If your lease allows it, you might assign your lease to another business. This means they take over your lease, stepping into your shoes, with all the rights and obligations that come with it.
The concept might seem straightforward, but there are important legal requirements and potential pitfalls to be aware of. For instance, an assignment could be prohibited by the contract itself, or it may significantly change the original deal’s terms in a way that’s not allowed. Plus, when you’re dealing with something that requires a unique skill set, like an artist or a consultant, those services typically can’t be passed on to someone else without agreement from all parties involved.
To navigate these complexities, understanding the fundamentals of assignment in contract law and property law is crucial. It ensures that when you’re ready to pass that baton, you’re doing it in a way that’s legal, effective, and doesn’t leave you tripping up before you reach the finish line.
The goal here is to make sure everyone involved understands what’s happening and agrees to it. That way, assignments can be a useful tool to manage your contracts and property agreements, keeping things moving smoothly even when changes come up.
For more detailed exploration on this topic, consider checking the comprehensive guide on Assignment (law)). This resource dives deeper into the nuances of contract assignment, offering insights and examples that can help clarify this complex area of law.
By grasping these basics, you’re well on your way to mastering the art of contract assignment. Whether you’re dealing with leases, business deals, or any agreement in between, knowing how to effectively assign a contract can be a game-changer.
Key Differences Between Assignment and Novation
When diving into contracts, two terms that often cause confusion are assignment and novation . While both deal with transferring obligations and rights under a contract, they are fundamentally different in several key aspects. Understanding these differences is crucial for anyone involved in contract management or negotiation.
Rights Transfer
Assignment involves the transfer of benefits or rights from one party (the assignor) to another (the assignee). However, it’s important to note that only the benefits of the contract can be assigned, not the burdens. For instance, if someone has the right to receive payments under a contract, they can assign this right to someone else.
Novation , on the other hand, is more comprehensive. It involves transferring both the rights and obligations under a contract from one party to a new party. With novation, the original party is completely released from the contract, and a new contractual relationship is formed between the remaining and the new party. This is a key distinction because, in novation, all parties must agree to this new arrangement.
Obligations Transfer
Assignment doesn’t transfer the original party’s obligations under the contract. The assignor (the original party who had the rights under the contract) might still be liable if the assignee fails to fulfill the contract terms.
In contrast, novation transfers all obligations to the new party. Once a novation is complete, the new party takes over all rights and obligations, leaving the original party with no further legal liabilities or rights under the contract.
Written Agreement
While assignments can sometimes be informal or even verbal, novation almost always requires a written agreement. This is because novation affects more parties’ rights and obligations and has a more significant impact on the contractual relationship. A written agreement ensures that all parties are clear about the terms of the novation and their respective responsibilities.
In practice, the need for a written agreement in novation serves as a protection for all parties involved. It ensures that the transfer of obligations is clearly documented and legally enforceable.
For example, let’s say Alex agrees to paint Bailey’s house for $1,000. Later, Alex decides they can’t complete the job and wants Chris to take over. If Bailey agrees, they can sign a novation agreement where Chris agrees to paint the house under the same conditions. Alex is then relieved from the original contract, and Chris becomes responsible for completing the painting job.
Understanding the difference between assignment and novation is critical for anyone dealing with contracts. While both processes allow for the transfer of rights or obligations, they do so in different ways and with varying implications for all parties involved. Knowing when and how to use each can help ensure that your contractual relationships are managed effectively and legally sound.
For further in-depth information and real-life case examples on assignment in contract law, you can explore detailed resources such as Assignment (law) on Wikipedia).
Next, we’ll delve into the legal requirements for a valid assignment, touching on express prohibition, material change, future rights, and the rare skill requirement. Understanding these will further equip you to navigate the complexities of contract assignments successfully.
Legal Requirements for a Valid Assignment
When dealing with assignment in contract law , it’s crucial to understand the legal backbone that supports a valid assignment. This ensures that the assignment stands up in a court of law if disputes arise. Let’s break down the must-know legal requirements: express prohibition, material change, future rights, and rare skill requirement.
Express Prohibition
The first stop on our checklist is to look for an express prohibition against assignment in the contract. This is a clause that outright states assignments are not allowed without the other party’s consent. If such language exists and you proceed with an assignment, you could be breaching the contract. Always read the fine print or have a legal expert review the contract for you.
Material Change
Next up is the material change requirement. The law states that an assignment cannot significantly alter the duties, increase the burdens, or impair the chances of the other party receiving due performance under the contract. For instance, if the contract involves personal services tailored to the specific party, assigning it to someone else might change the expected outcome, making such an assignment invalid.
Future Rights
Another important aspect is future rights . The rule here is straightforward: you can’t assign what you don’t have. This means that a promise to assign rights you may acquire in the future is generally not enforceable at present. An effective assignment requires that the rights exist at the time of the assignment.
Rare Skill Requirement
Lastly, let’s talk about the rare skill requirement . Some contracts are so specialized that they cannot be assigned to another party without compromising the contract’s integrity. This is often the case with contracts that rely on an individual’s unique skills or trust. Think of an artist commissioned for a portrait or a lawyer hired for their specialized legal expertise. In these scenarios, assignments are not feasible as they could severely impact the contract’s intended outcome.
Understanding these legal requirements is pivotal for navigating the complexities of assignment in contract law. By ensuring compliance with these principles, you can effectively manage contract assignments, safeguarding your interests and those of the other contracting party.
For anyone looking to delve deeper into the intricacies of contract law, you can explore detailed resources such as Assignment (law) on Wikipedia).
Moving forward, we’ll explore the common types of contract assignments, from landlord-tenant agreements to business contracts and intellectual property transfers. This will give you a clearer picture of how assignments work across different legal landscapes.
Common Types of Contract Assignments
When we dive into assignment in contract law , we find it touches nearly every aspect of our business and personal lives. Let’s simplify this complex topic by looking at some of the most common types of contract assignments you might encounter.
Landlord-Tenant Agreements
Imagine you’re renting a fantastic apartment but have to move because of a new job. Instead of breaking your lease, you can assign your lease to someone else. This means the new tenant takes over your lease, including rent payments and maintenance responsibilities. However, it’s crucial that the landlord agrees to this switch. If done right, it’s a win-win for everyone involved.

Business Contracts
In the business world, contract assignments are a daily occurrence. For example, if a company agrees to provide services but then realizes it’s overbooked, it can assign the contract to another company that can fulfill the obligations. This way, the project is completed on time, and the client remains happy. It’s a common practice that ensures flexibility and efficiency in business operations.

Intellectual Property
Intellectual property (IP) assignments are fascinating and complex. If an inventor creates a new product, they can assign their patent rights to a company in exchange for a lump sum or royalties. This transfer allows the company to produce and sell the invention, while the inventor benefits financially. However, it’s critical to note that with trademarks, the goodwill associated with the mark must also be transferred to maintain its value.
Understanding these types of assignments helps clarify the vast landscape of contract law. Whether it’s a cozy apartment, a crucial business deal, or a groundbreaking invention, assignments play a pivotal role in ensuring these transitions happen smoothly.
As we navigate through the realm of contract assignments, each type has its own set of rules and best practices. The key is to ensure all parties are on the same page and that the assignment is executed properly to avoid any legal pitfalls.
Diving deeper into the subject, next, we will explore how to execute a contract assignment effectively, ensuring all legal requirements are met and the process runs as smoothly as possible.
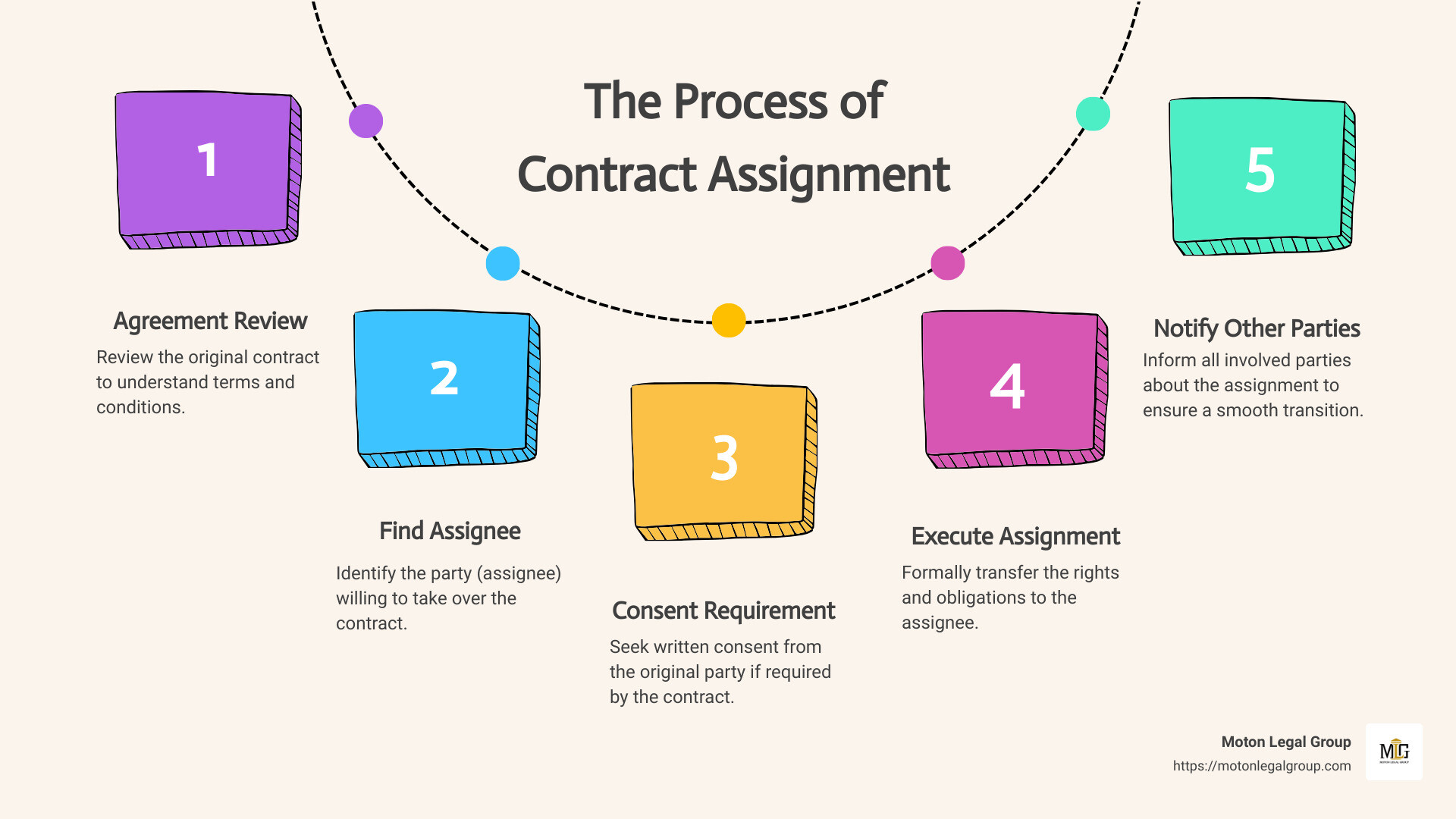
How to Execute a Contract Assignment Effectively
Executing a contract assignment effectively is crucial to ensure that all legal requirements are met and the process runs smoothly. Here’s a straightforward guide to help you navigate this process without any hiccups.
Written Consent
First and foremost, get written consent . This might seem like a no-brainer, but it’s surprising how often this step is overlooked. If the original contract requires the consent of the other party for an assignment to be valid, make sure you have this in black and white. Not just a handshake or a verbal agreement. This ensures clarity and avoids any ambiguity or disputes down the line.
Notice of Assignment
Next up, provide a notice of assignment to all relevant parties. This is not just common courtesy; it’s often a legal requirement. It informs all parties involved about the change in the assignment of rights or obligations under the contract. Think of it as updating your address with the post office; everyone needs to know where to send the mail now.
Privity of Estate
Understanding privity of estate is key in real estate transactions and leases. It refers to the legal relationship that exists between parties under a contract. When you assign a contract, the assignee steps into your shoes, but the original terms of the contract still apply. This means the assignee needs to be aware of and comply with the original agreement’s requirements.
Secondary Liability
Lastly, let’s talk about secondary liability . Just because you’ve assigned a contract doesn’t always mean you’re off the hook. In some cases, the original party (the assignor) may still hold some liability if the assignee fails to perform under the contract. It’s essential to understand the terms of your assignment agreement and whether it includes a release from liability for the assignor.
Executing a contract assignment effectively is all about dotting the I’s and crossing the T’s . By following these steps—securing written consent, issuing a notice of assignment, understanding privity of estate, and clarifying secondary liability—you’re setting yourself up for a seamless transition.
The goal is to ensure all parties are fully informed and agreeable to the changes being made. This not only helps in maintaining good relationships but also in avoiding potential legal issues down the line.
We’ll dive into some of the frequently asked questions about contract assignment to clear any lingering doubts.
Frequently Asked Questions about Contract Assignment
When navigating contracts, questions often arise, particularly about the concepts of assignment and novation. Let’s break these down into simpler terms.
What does assignment of a contract mean?
In the realm of assignment in contract law , think of assignment as passing the baton in a relay race. It’s where one party (the assignor) transfers their rights and benefits under a contract to another party (the assignee). However, unlike a relay race, the original party might still be on the hook for obligations unless the contract says otherwise. It’s like handing off the baton but still running alongside the new runner just in case.
Is an assignment legally binding?
Absolutely, an assignment is as binding as a pinky promise in the playground – but with legal muscle behind it. Once an assignment meets the necessary legal criteria (like not significantly changing the obligor’s duties or having express consent if required), it’s set in stone. This means both the assignee and the assignor must honor this transfer of rights or face potential legal actions. It’s a serious commitment, not just a casual exchange.
What is the difference between assignment and novation?
Now, this is where it gets a bit more intricate. If assignment is passing the baton, novation is forming a new team mid-race. It involves replacing an old obligation with a new one or adding a new party to take over an old one’s duties. Crucially, novation extinguishes the old contract and requires all original and new parties to agree. It’s a clean slate – the original party walks away, and the new party steps in, no strings attached.
While both assignment and novation change the playing field of a contract, novation requires a unanimous thumbs up from everyone involved, completely freeing the original party from their obligations. On the other hand, an assignment might leave the original party watching from the sidelines, ready to jump back in if needed.
Understanding these facets of assignment in contract law is crucial, whether you’re diving into a new agreement or navigating an existing one. Knowledge is power – especially when it comes to contracts.
As we wrap up these FAQs, the legal world of contracts is vast and sometimes complex, but breaking it down into bite-sized pieces can help demystify the process and empower you in your legal undertakings.
Here’s a helpful resource for further reading on the difference between assignment and cession.
Now, let’s continue on to the conclusion to tie all these insights together.
Navigating assignment in contract law can seem like a daunting task at first glance. However, with the right information and guidance, it becomes an invaluable tool in ensuring that your rights and obligations are protected and effectively managed in any contractual relationship.
At Moton Legal Group, we understand the intricacies of contract law and are dedicated to providing you with the expertise and support you need to navigate these waters. Whether you’re dealing with a straightforward contract assignment or facing more complex legal challenges, our team is here to help. We pride ourselves on our ability to demystify legal processes and make them accessible to everyone.
The key to successfully managing any contract assignment lies in understanding your rights, the obligations involved, and the potential impacts on all parties. It’s about ensuring that the assignment is executed in a way that is legally sound and aligns with your interests.
If you’re in need of assistance with a contract review, looking to understand more about how contract assignments work, or simply seeking legal advice on your contractual rights and responsibilities, Moton Legal Group is here for you. Our team of experienced attorneys is committed to providing the clarity, insight, and support you need to navigate the complexities of contract law with confidence.
For more information on how we can assist you with your contract review and other legal needs, visit our contract review service page .
In the constantly evolving landscape of contract law, having a trusted legal partner can make all the difference. Let Moton Legal Group be your guide, ensuring that your contractual dealings are handled with the utmost care, professionalism, and expertise. Together, we can navigate the complexities of contract law and secure the best possible outcomes for your legal matters.
Thank you for joining us on this journey through the fundamentals of assignment in contract law. We hope you found this information helpful and feel more empowered to handle your contractual affairs with confidence.
For more information Call :
Reach out now.
" * " indicates required fields
Recent Blog Posts:

Understanding Rescission in Contract Law: A Detailed Guide

Understanding Privity in Contract Law: A Beginner’s Guide

Beginner’s Guide to Offer and Acceptance in Contract Law

Understanding Mutual Assent in Contract Law: A Comprehensive Guide

Understanding Capacity in Contract Law: A Comprehensive Guide

Understanding Verbal Contract Law: A Step-by-Step Guide

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
Margin Size
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

14.2: Assignment of Contract Rights
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 21985

\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
Learning Objectives
- Understand what an assignment is and how it is made.
- Recognize the effect of the assignment.
- Know when assignments are not allowed.
- Understand the concept of assignor’s warranties
The Concept of a Contract Assignment
Contracts create rights and duties. By an assignment , an obligee (one who has the right to receive a contract benefit) transfers a right to receive a contract benefit owed by the obligor (the one who has a duty to perform) to a third person ( assignee ); the obligee then becomes an assignor (one who makes an assignment).
The Restatement (Second) of Contracts defines an assignment of a right as “a manifestation of the assignor’s intention to transfer it by virtue of which the assignor’s right to performance by the obligor is extinguished in whole or in part and the assignee acquires the right to such performance.”Restatement (Second) of Contracts, Section 317(1). The one who makes the assignment is both an obligee and a transferor. The assignee acquires the right to receive the contractual obligations of the promisor, who is referred to as the obligor (see Figure 14.1 "Assignment of Rights" ). The assignor may assign any right unless (1) doing so would materially change the obligation of the obligor, materially burden him, increase his risk, or otherwise diminish the value to him of the original contract; (2) statute or public policy forbids the assignment; or (3) the contract itself precludes assignment. The common law of contracts and Articles 2 and 9 of the Uniform Commercial Code (UCC) govern assignments. Assignments are an important part of business financing, such as factoring. A factor is one who purchases the right to receive income from another.
Figure 14.1 Assignment of Rights

Method of Assignment
Manifesting assent.
To effect an assignment, the assignor must make known his intention to transfer the rights to the third person. The assignor’s intention must be that the assignment is effective without need of any further action or any further manifestation of intention to make the assignment. In other words, the assignor must intend and understand himself to be making the assignment then and there; he is not promising to make the assignment sometime in the future.
Under the UCC, any assignments of rights in excess of $5,000 must be in writing, but otherwise, assignments can be oral and consideration is not required: the assignor could assign the right to the assignee for nothing (not likely in commercial transactions, of course). Mrs. Franklin has the right to receive $750 a month from the sale of a house she formerly owned; she assigns the right to receive the money to her son Jason, as a gift. The assignment is good, though such a gratuitous assignment is usually revocable, which is not the case where consideration has been paid for an assignment.
Acceptance and Revocation
For the assignment to become effective, the assignee must manifest his acceptance under most circumstances. This is done automatically when, as is usually the case, the assignee has given consideration for the assignment (i.e., there is a contract between the assignor and the assignee in which the assignment is the assignor’s consideration), and then the assignment is not revocable without the assignee’s consent. Problems of acceptance normally arise only when the assignor intends the assignment as a gift. Then, for the assignment to be irrevocable, either the assignee must manifest his acceptance or the assignor must notify the assignee in writing of the assignment.
Notice to the obligor is not required, but an obligor who renders performance to the assignor without notice of the assignment (that performance of the contract is to be rendered now to the assignee) is discharged. Obviously, the assignor cannot then keep the consideration he has received; he owes it to the assignee. But if notice is given to the obligor and she performs to the assignor anyway, the assignee can recover from either the obligor or the assignee, so the obligor could have to perform twice, as in Exercise 2 at the chapter’s end, Aldana v. Colonial Palms Plaza . Of course, an obligor who receives notice of the assignment from the assignee will want to be sure the assignment has really occurred. After all, anybody could waltz up to the obligor and say, “I’m the assignee of your contract with the bank. From now on, pay me the $500 a month, not the bank.” The obligor is entitled to verification of the assignment.
Effect of Assignment
General rule.
An assignment of rights effectively makes the assignee stand in the shoes of the assignor. He gains all the rights against the obligor that the assignor had, but no more. An obligor who could avoid the assignor’s attempt to enforce the rights could avoid a similar attempt by the assignee. Likewise, under UCC Section 9-318(1), the assignee of an account is subject to all terms of the contract between the debtor and the creditor-assignor. Suppose Dealer sells a car to Buyer on a contract where Buyer is to pay $300 per month and the car is warranted for 50,000 miles. If the car goes on the fritz before then and Dealer won’t fix it, Buyer could fix it for, say, $250 and deduct that $250 from the amount owed Dealer on the next installment (called a setoff). Now, if Dealer assigns the contract to Assignee, Assignee stands in Dealer’s shoes, and Buyer could likewise deduct the $250 from payment to Assignee.
The “shoe rule” does not apply to two types of assignments. First, it is inapplicable to the sale of a negotiable instrument to a holder in due course. Second, the rule may be waived: under the UCC and at common law, the obligor may agree in the original contract not to raise defenses against the assignee that could have been raised against the assignor.Uniform Commercial Code, Section 9-206. While a waiver of defenses makes the assignment more marketable from the assignee’s point of view, it is a situation fraught with peril to an obligor, who may sign a contract without understanding the full import of the waiver. Under the waiver rule, for example, a farmer who buys a tractor on credit and discovers later that it does not work would still be required to pay a credit company that purchased the contract; his defense that the merchandise was shoddy would be unavailing (he would, as used to be said, be “having to pay on a dead horse”).
For that reason, there are various rules that limit both the holder in due course and the waiver rule. Certain defenses, the so-called real defenses (infancy, duress, and fraud in the execution, among others), may always be asserted. Also, the waiver clause in the contract must have been presented in good faith, and if the assignee has actual notice of a defense that the buyer or lessee could raise, then the waiver is ineffective. Moreover, in consumer transactions, the UCC’s rule is subject to state laws that protect consumers (people buying things used primarily for personal, family, or household purposes), and many states, by statute or court decision, have made waivers of defenses ineffective in such consumer transactions . Federal Trade Commission regulations also affect the ability of many sellers to pass on rights to assignees free of defenses that buyers could raise against them. Because of these various limitations on the holder in due course and on waivers, the “shoe rule” will not govern in consumer transactions and, if there are real defenses or the assignee does not act in good faith, in business transactions as well.
When Assignments Are Not Allowed
The general rule—as previously noted—is that most contract rights are assignable. But there are exceptions. Five of them are noted here.
Material Change in Duties of the Obligor
When an assignment has the effect of materially changing the duties that the obligor must perform, it is ineffective. Changing the party to whom the obligor must make a payment is not a material change of duty that will defeat an assignment, since that, of course, is the purpose behind most assignments. Nor will a minor change in the duties the obligor must perform defeat the assignment.
Several residents in the town of Centerville sign up on an annual basis with the Centerville Times to receive their morning paper. A customer who is moving out of town may assign his right to receive the paper to someone else within the delivery route. As long as the assignee pays for the paper, the assignment is effective; the only relationship the obligor has to the assignee is a routine delivery in exchange for payment. Obligors can consent in the original contract, however, to a subsequent assignment of duties. Here is a clause from the World Team Tennis League contract: “It is mutually agreed that the Club shall have the right to sell, assign, trade and transfer this contract to another Club in the League, and the Player agrees to accept and be bound by such sale, exchange, assignment or transfer and to faithfully perform and carry out his or her obligations under this contract as if it had been entered into by the Player and such other Club.” Consent is not necessary when the contract does not involve a personal relationship.
Assignment of Personal Rights
When it matters to the obligor who receives the benefit of his duty to perform under the contract, then the receipt of the benefit is a personal right that cannot be assigned. For example, a student seeking to earn pocket money during the school year signs up to do research work for a professor she admires and with whom she is friendly. The professor assigns the contract to one of his colleagues with whom the student does not get along. The assignment is ineffective because it matters to the student (the obligor) who the person of the assignee is. An insurance company provides auto insurance covering Mohammed Kareem, a sixty-five-year-old man who drives very carefully. Kareem cannot assign the contract to his seventeen-year-old grandson because it matters to the insurance company who the person of its insured is. Tenants usually cannot assign (sublet) their tenancies without the landlord’s permission because it matters to the landlord who the person of their tenant is. Section 14.4.1 "Nonassignable Rights" , Nassau Hotel Co. v. Barnett & Barse Corp. , is an example of the nonassignability of a personal right.
Assignment Forbidden by Statute or Public Policy
Various federal and state laws prohibit or regulate some contract assignment. The assignment of future wages is regulated by state and federal law to protect people from improvidently denying themselves future income because of immediate present financial difficulties. And even in the absence of statute, public policy might prohibit some assignments.
Contracts That Prohibit Assignment
Assignability of contract rights is useful, and prohibitions against it are not generally favored. Many contracts contain general language that prohibits assignment of rights or of “the contract.” Both the Restatement and UCC Section 2-210(3) declare that in the absence of any contrary circumstances, a provision in the agreement that prohibits assigning “the contract” bars “only the delegation to the assignee of the assignor’s performance.”Restatement (Second) of Contracts, Section 322. In other words, unless the contract specifically prohibits assignment of any of its terms, a party is free to assign anything except his or her own duties.
Even if a contractual provision explicitly prohibits it, a right to damages for breach of the whole contract is assignable under UCC Section 2-210(2) in contracts for goods. Likewise, UCC Section 9-318(4) invalidates any contract provision that prohibits assigning sums already due or to become due. Indeed, in some states, at common law, a clause specifically prohibiting assignment will fail. For example, the buyer and the seller agree to the sale of land and to a provision barring assignment of the rights under the contract. The buyer pays the full price, but the seller refuses to convey. The buyer then assigns to her friend the right to obtain title to the land from the seller. The latter’s objection that the contract precludes such an assignment will fall on deaf ears in some states; the assignment is effective, and the friend may sue for the title.
Future Contracts
The law distinguishes between assigning future rights under an existing contract and assigning rights that will arise from a future contract. Rights contingent on a future event can be assigned in exactly the same manner as existing rights, as long as the contingent rights are already incorporated in a contract. Ben has a long-standing deal with his neighbor, Mrs. Robinson, to keep the latter’s walk clear of snow at twenty dollars a snowfall. Ben is saving his money for a new printer, but when he is eighty dollars shy of the purchase price, he becomes impatient and cajoles a friend into loaning him the balance. In return, Ben assigns his friend the earnings from the next four snowfalls. The assignment is effective. However, a right that will arise from a future contract cannot be the subject of a present assignment.
Partial Assignments
An assignor may assign part of a contractual right, but only if the obligor can perform that part of his contractual obligation separately from the remainder of his obligation. Assignment of part of a payment due is always enforceable. However, if the obligor objects, neither the assignor nor the assignee may sue him unless both are party to the suit. Mrs. Robinson owes Ben one hundred dollars. Ben assigns fifty dollars of that sum to his friend. Mrs. Robinson is perplexed by this assignment and refuses to pay until the situation is explained to her satisfaction. The friend brings suit against Mrs. Robinson. The court cannot hear the case unless Ben is also a party to the suit. This ensures all parties to the dispute are present at once and avoids multiple lawsuits.
Successive Assignments
It may happen that an assignor assigns the same interest twice (see Figure 14.2 "Successive Assignments" ). With certain exceptions, the first assignee takes precedence over any subsequent assignee. One obvious exception is when the first assignment is ineffective or revocable. A subsequent assignment has the effect of revoking a prior assignment that is ineffective or revocable. Another exception: if in good faith the subsequent assignee gives consideration for the assignment and has no knowledge of the prior assignment, he takes precedence whenever he obtains payment from, performance from, or a judgment against the obligor, or whenever he receives some tangible evidence from the assignor that the right has been assigned (e.g., a bank deposit book or an insurance policy).
Some states follow the different English rule: the first assignee to give notice to the obligor has priority, regardless of the order in which the assignments were made. Furthermore, if the assignment falls within the filing requirements of UCC Article 9 (see Chapter 33 "Secured Transactions and Suretyship" ), the first assignee to file will prevail.
Figure 14.2 Successive Assignments

Assignor’s Warranties
An assignor has legal responsibilities in making assignments. He cannot blithely assign the same interests pell-mell and escape liability. Unless the contract explicitly states to the contrary, a person who assigns a right for value makes certain assignor’s warranties to the assignee: that he will not upset the assignment, that he has the right to make it, and that there are no defenses that will defeat it. However, the assignor does not guarantee payment; assignment does not by itself amount to a warranty that the obligor is solvent or will perform as agreed in the original contract. Mrs. Robinson owes Ben fifty dollars. Ben assigns this sum to his friend. Before the friend collects, Ben releases Mrs. Robinson from her obligation. The friend may sue Ben for the fifty dollars. Or again, if Ben represents to his friend that Mrs. Robinson owes him (Ben) fifty dollars and assigns his friend that amount, but in fact Mrs. Robinson does not owe Ben that much, then Ben has breached his assignor’s warranty. The assignor’s warranties may be express or implied.
Key Takeaway
Generally, it is OK for an obligee to assign the right to receive contractual performance from the obligor to a third party. The effect of the assignment is to make the assignee stand in the shoes of the assignor, taking all the latter’s rights and all the defenses against nonperformance that the obligor might raise against the assignor. But the obligor may agree in advance to waive defenses against the assignee, unless such waiver is prohibited by law.
There are some exceptions to the rule that contract rights are assignable. Some, such as personal rights, are not circumstances where the obligor’s duties would materially change, cases where assignability is forbidden by statute or public policy, or, with some limits, cases where the contract itself prohibits assignment. Partial assignments and successive assignments can happen, and rules govern the resolution of problems arising from them.
When the assignor makes the assignment, that person makes certain warranties, express or implied, to the assignee, basically to the effect that the assignment is good and the assignor knows of no reason why the assignee will not get performance from the obligor.
- If Able makes a valid assignment to Baker of his contract to receive monthly rental payments from Tenant, how is Baker’s right different from what Able’s was?
- Able made a valid assignment to Baker of his contract to receive monthly purchase payments from Carr, who bought an automobile from Able. The car had a 180-day warranty, but the car malfunctioned within that time. Able had quit the auto business entirely. May Carr withhold payments from Baker to offset the cost of needed repairs?
- Assume in the case in Exercise 2 that Baker knew Able was selling defective cars just before his (Able’s) withdrawal from the auto business. How, if at all, does that change Baker’s rights?
- Why are leases generally not assignable? Why are insurance contracts not assignable?
- Find a Lawyer
- Legal Topics
- Contract Law
Contract Assignment Agreement
(This may not be the same place you live)
What Is a Contract Assignment?
In a contract assignment, one of the two parties may transfer their right to the other’s performance to a third party. This is known as “contract assignment.” Typically, all rights under a contract may be assigned. A provision in the agreement that states the contract may not be assigned usually refers to the delegation of the assignor’s (individual who assigns) obligations under that agreement, not their rights.
In modern law, the term “assignment of contract” usually means assigning both rights and duties under a contract.
What Is a Contract Assignment Agreement?
Who are the various parties involved in a contract assignment, how is a contract assignment created, when is a contract assignment prohibited, what should a contract assignment agreement contain, what are some common disputes related to assignment agreements, what is a breach of contract, what are the ways you can breach a contract, do i need a lawyer for help with a contract assignment agreement.
A contract assignment agreement may be created in cases involving a contract assignment. An assignment is where the recipient of products, services, or other rights transfers (assigns) their rights to another party. The party transferring their rights is the assignor, while the party performing the services is dubbed the obligor. The party obtaining the transferred rights is called the assignee.
Contract assignments are often utilized in cases similar to beneficiary and gift-giving situations. Yet, there is frequently a substantial business or commercial component to contract assignments (such as those projects involving commercial building and contracting).
There are two parties to the agreement in a contract, X and Y. The parties may agree to let X assign X’s rights to a third party . Once the third party enters the picture, each party has a particular name. For example, suppose X, a seller of bookmarks, contracts with Y, a purchaser of bookmarks. Y wants to have Y’s right to X’s performance (selling bookmarks every month) to another individual.
This third individual, Z, is dubbed the assignee. X is named the obligor , and Y is named the assignor since Y has assigned its right to X’s performance . X, the obligor, is bound to continue to perform its duties under the contract.
There are no “magical words” required to make an assignment. The law demands that the would-be assignor intend to wholly and immediately transfer their rights in the agreement. In addition, writing is generally not needed to make an assignment. As long as X and Y adequately comprehend what right is being assigned, an assignment is formed.
Comments that demonstrate a transfer is to take place suffice, such as “I plan to transfer my rights under this agreement,” “I plan to give my rights to Z,” or “I plan to confer an assignment on Z.” In addition, consideration, which is a bargained-for exchange needed for a contract to be proper, is not needed for the assignment.
In specific examples, an assignment of contract rights can be restricted. If the agreement includes a clause forbidding assignment of “the contract” without establishing more, the law construes this language as banning only delegation of the assignor’s duties, not their rights.
If the assignment language states “assignment of contractual rights is forbidden,” the obligor may sue for damages if the assignor tries to assign the agreement. If the contract language says that attempts to assign “will be null,” the parties can ban the assignment of rights.
Under current contract law, the expression “I assign the contract” is usually interpreted to mean that one is assigning rights and duties. What is an assignment of duties? An assignment of duties emerges where Y, dubbed the obligor or delegator, promises to perform for X, the obligee. Y then entrusts their duty to perform to Z, the delegate. Under the law, most duties can be delegated.
A contract assignment should include:
- Names of the parties involved
- Depictions of the rights or contract benefits being assigned
- When the assignment takes effect, and whether or not it lapses
- Conditions regarding legal action if a breach or violation of contract should ensue
Most jurisdictions don’t demand a contract assignment to be in writing. Of course, it’s always best to put the agreement in writing to create a record of the transaction if there are any future problems.
Some typical legal problems involving contract assignments include:
- Failure to transfer the rights to the assignee
- Refusal to cooperate with the contract assignment terms
- Use of deception, misrepresentation, or force when dealing with assignment agreement documents
- Blunders or mistakes concerning definitions of the assignment subject
Conflicts oftentimes require legal action in a court of law to settle the legal problems. This can result in a monetary damages award to cover losses caused by a breach of contract. Alternatively, some courts may enforce other remedies such as cancellation or rewriting of the agreement.
A breach of contract may arise when a party to a good agreement has failed to fulfill their side of the deal.
For example, the terms of a contract guide the parties in what they must do and how they should do it to maintain their promise. If a party does not do what the agreement instructs them to do, then the non-breaching party will be entitled to take legal action and file a lawsuit against them in court.
A breach of contract can arise as either a partial or a complete breach. A court will also consider whether the breach was substantial or only a minor one. This will allow the court to decide what type of damages the breaching party should have to expend.
There are three major ways for which a party can be held liable for breach of contract. This includes when:
- There is an anticipatory breach: Often referred to as anticipatory repudiation, this kind of breach happens when the breaching party tells the non-breaching party that they will not be fulfilling the terms of their contract. Once the other party is informed, they can sue for breach of contract.
- A party has committed a minor breach: A minor breach of contract happens when a party fails to perform a small contract detail. The total contract has not been violated and can still be substantially performed in this circumstance. This also comes up when there is a technical mistake with the agreement (e.g., a false date, price, or typo within the terms of the agreement).
- If there is a material or fundamental breach: These are the most standard sorts of breaches cited as the basis of a breach of contract action. When the breach is so substantial, it essentially cancels the contract because it renders performance by either party impossible.
Some other ways that a contract can be breached include when the contract is dishonest, if the contract was formed illegally or is unconscionable, and when there is a mistake of fact present in the agreement terms. The parties may also include conditions unique to their respective agreement, which specify when a party’s actions can be deemed a breach.
Further, state regulations and the type of contract (e.g., lease agreement, sales contract, government contract, etc.) may indicate other ways a contract can be breached.
Contract agreements often require much attention to detail and foresight for anticipating future events. It’s in your best interests to hire a contract lawyer if you need help with any contract matters. Your lawyer can help you with your records and represent you if you ever need to file a claim in court for damages.

Save Time and Money - Speak With a Lawyer Right Away
- Buy one 30-minute consultation call or subscribe for unlimited calls
- Subscription includes access to unlimited consultation calls at a reduced price
- Receive quick expert feedback or review your DIY legal documents
- Have peace of mind without a long wait or industry standard retainer
- Get the right guidance - Schedule a call with a lawyer today!
Need a Contract Lawyer in your Area?
- Connecticut
- Massachusetts
- Mississippi
- New Hampshire
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- West Virginia

Ty McDuffey
LegalMatch Legal Writer
Updating Author
Ty began working at LegalMatch in November 2021. Ty holds a Professional Writing Degree from Missouri State University with a minor in Economics. Ty received his Juris Doctorate from the University of Missouri-Kansas City School of Law in May of 2021. Before joining LegalMatch, Ty worked as a law clerk and freelance writer. Ty is a native of Lake of the Ozarks, Missouri, and currently resides in Kansas City. Read More

Jose Rivera
Managing Editor
Original Author
Related Articles
- When Can a Party Assign Contractual Rights to Another Party?
- What Are Contractual Rights?
- When a Party to a Contract Makes a Unilateral Mistake
- Unilateral Mistake Examples
- Retainer Fee Contracts
- What is a Non-disclosure Agreement
- Breach of a Confidentiality Agreement
- Non-Disclosure Agreement Violation
- Lawyers for Contracts: Contract Dispute Attorney Near Me
- Contract Mistake Lawyers
- Contract Error Lawsuits
- Breach of Real Estate Contract
- Fraud in Contract Law
- Contract Coercion
- Legally Binding Contracts
- Contract Violation Lawyers
- Binding Agreement
- Duty to Read a Contract
- What are Employment Contracts?
- Resolving Contract Conflicts
- State Employment Contracts
- Land Contract Agreements
- Installment Contract
- What is a Land Contract?
- What is a Service Contract?
- Service-Level Agreement Disputes
- Contract Obligations
- Legal Contracts
- Indemnity Clause Law
- Indemnification
Discover the Trustworthy LegalMatch Advantage
- No fee to present your case
- Choose from lawyers in your area
- A 100% confidential service
How does LegalMatch work?
Law Library Disclaimer

16 people have successfully posted their cases
Understanding an assignment and assumption agreement
Need to assign your rights and duties under a contract? Learn more about the basics of an assignment and assumption agreement.
Get your assignment of agreement

by Belle Wong, J.D.
Belle Wong, is a freelance writer specializing in small business, personal finance, banking, and tech/SAAS. She ...
Read more...
Updated on: November 24, 2023 · 3 min read
The assignment and assumption agreement
The basics of assignment and assumption, filling in the assignment and assumption agreement.
While every business should try its best to meet its contractual obligations, changes in circumstance can happen that could necessitate transferring your rights and duties under a contract to another party who would be better able to meet those obligations.

If you find yourself in such a situation, and your contract provides for the possibility of assignment, an assignment and assumption agreement can be a good option for preserving your relationship with the party you initially contracted with, while at the same time enabling you to pass on your contractual rights and duties to a third party.
An assignment and assumption agreement is used after a contract is signed, in order to transfer one of the contracting party's rights and obligations to a third party who was not originally a party to the contract. The party making the assignment is called the assignor, while the third party accepting the assignment is known as the assignee.
In order for an assignment and assumption agreement to be valid, the following criteria need to be met:
- The initial contract must provide for the possibility of assignment by one of the initial contracting parties.
- The assignor must agree to assign their rights and duties under the contract to the assignee.
- The assignee must agree to accept, or "assume," those contractual rights and duties.
- The other party to the initial contract must consent to the transfer of rights and obligations to the assignee.
A standard assignment and assumption contract is often a good starting point if you need to enter into an assignment and assumption agreement. However, for more complex situations, such as an assignment and amendment agreement in which several of the initial contract terms will be modified, or where only some, but not all, rights and duties will be assigned, it's a good idea to retain the services of an attorney who can help you draft an agreement that will meet all your needs.
When you're ready to enter into an assignment and assumption agreement, it's a good idea to have a firm grasp of the basics of assignment:
- First, carefully read and understand the assignment and assumption provision in the initial contract. Contracts vary widely in their language on this topic, and each contract will have specific criteria that must be met in order for a valid assignment of rights to take place.
- All parties to the agreement should carefully review the document to make sure they each know what they're agreeing to, and to help ensure that all important terms and conditions have been addressed in the agreement.
- Until the agreement is signed by all the parties involved, the assignor will still be obligated for all responsibilities stated in the initial contract. If you are the assignor, you need to ensure that you continue with business as usual until the assignment and assumption agreement has been properly executed.
Unless you're dealing with a complex assignment situation, working with a template often is a good way to begin drafting an assignment and assumption agreement that will meet your needs. Generally speaking, your agreement should include the following information:
- Identification of the existing agreement, including details such as the date it was signed and the parties involved, and the parties' rights to assign under this initial agreement
- The effective date of the assignment and assumption agreement
- Identification of the party making the assignment (the assignor), and a statement of their desire to assign their rights under the initial contract
- Identification of the third party accepting the assignment (the assignee), and a statement of their acceptance of the assignment
- Identification of the other initial party to the contract, and a statement of their consent to the assignment and assumption agreement
- A section stating that the initial contract is continued; meaning, that, other than the change to the parties involved, all terms and conditions in the original contract stay the same
In addition to these sections that are specific to an assignment and assumption agreement, your contract should also include standard contract language, such as clauses about indemnification, future amendments, and governing law.
Sometimes circumstances change, and as a business owner you may find yourself needing to assign your rights and duties under a contract to another party. A properly drafted assignment and assumption agreement can help you make the transfer smoothly while, at the same time, preserving the cordiality of your initial business relationship under the original contract.
You may also like

What does 'inc.' mean in a company name?
'Inc.' in a company name means the business is incorporated, but what does that entail, exactly? Here's everything you need to know about incorporating your business.
October 9, 2023 · 10min read

How to write a will: A comprehensive guide to will writing
Writing a will is one of the most important things you can do for yourself and for your loved ones, and it can be done in just minutes. Are you ready to get started?
May 17, 2024 · 11min read

How to Start an LLC in 7 Easy Steps (2024 Guide)
2024 is one of the best years ever to start an LLC, and you can create yours in only a few steps.
May 16, 2024 · 22min read
Assignability Of Contracts: Everything You Need to Know
The assignability of contracts is when one side of a contract agreement transfers the contract to another entity, so that the new entity fulfills the terms of the contract. 3 min read updated on February 01, 2023
The assignability of contracts is when one side of a contract agreement transfers the contract to another entity, so that the new entity fulfills the terms of the contract. Being able to assign contracts depends on a variety of factors, mainly the language contained in the contract.
How Contract Assignments Work
Some contracts prohibit assignment altogether, while others may allow it with the other party's consent. An example of a basic contract assignment may look like this:
- Bob contracts with a dairy to deliver a gallon of cream to his house every day.
- The dairy assigns Bob's contract to another dairy.
- As long as Bob is notified of the change in provider and gets his gallon of cream every day, his contract is with the new dairy.
Because the law has a preference for the free alienation of property, parties are free to assign contract rights and delegate contractual obligations.
Assigning a contract to another doesn't always take away the assigning party's liability. Some contracts include a clause that at least one of the original parties guarantees performance — or fulfills the contract terms — no matter what the assignment.
The performance, however, can't be changed in contract assignment. There's a limit to substitution, so the new party has no power to change the performance per the rights stated in the contract. For example, if the obliging party has pledged to perform only if some event happens (with no certainty that it will happen), no assignment should increase the risk to the obliging party if the event doesn't happen through no fault of the obligor.
The nature of a contract's obligations determines its assignability.
When Assignments Won't Be Enforced
In certain cases, contracts can't be assigned.
- A clause in the contract prohibits assignment. This is usually called an anti-assignment clause.
- Assignments can't take place if they materially alter what's expected under the contract. If the assignment affects the expected performance as outlined in the contract, lowers the value of returns (including anticipated returns), or increases risks for the other contract party (the one who's not assigning contractual rights), it's unlikely that any court will enforce the arrangement.
- If an assignment violates public policy or the law, it won't be enforced. For instance, the federal government prohibits certain claim assignments against the government, and many states prohibit an employee from assigning future wages.
Other assignments may not be illegal, but they could still violate public policy. As an example, personal injury claims can't be assigned because doing so might encourage litigation.
When looking into whether one party can transfer a contract or some rights and obligations in the contract, the transferring party has to check into applicable laws and statutes. That party must also check the contract's express language to determine whether or not it can transfer the assignment without obtaining consent from the non-transferring party.
If the contract requires that consent is given and the transferring party doesn't get that consent, it risks a contract breach as well as an invalid, ineffective transfer.
How to Assign a Contract
Follow these steps to assign contracts, when it's allowed for you to do so.
- Carefully study the contract for prohibitions or limitations, such as anti-assignment clauses. In some cases, there isn't a separate anti-assignment clause, but it may be stated in another way, such as language that says, "This contract may not be assigned."
- Execute the assignment. As long as you're free to assign the contract, prepare and enter into the assignment, which is basically an agreement transferring your rights and obligations.
- Notify the obligor, or the non-transferring party. After you assign contract rights to the assignee, notify the other party that was the original contractor, also known as the obligor. This notice relieves you of any liability as stated in the contract, as long as the contract doesn't say differently — for instance, the contract states that you, as the assignor, guarantee performance under the contract.
Before trying to assign a contract to a third party, it's very important to understand if you're allowed to do so. You'll have to research legal statutes as well as the language in the contract to ensure you follow rules and regulations. Otherwise, you risk a breach of contract .
If you need help with contract assignments, you can post your legal need on UpCounsel's marketplace. UpCounsel accepts only the top 5 percent of lawyers to its site. Lawyers on UpCounsel come from law schools such as Harvard Law and Yale Law and average 14 years of legal experience, including work with or on behalf of companies like Google, Menlo Ventures, and Airbnb.
Hire the top business lawyers and save up to 60% on legal fees
Content Approved by UpCounsel
- Consent to Assignment
- Assignment Contract Law
- Assignment of Contract Rights
- Assignment of Rights and Obligations Under a Contract
- Assignment Of Contracts
- Legal Assignment
- Assignment Law
- Assignment of Rights Example
- Third Party Contracts
- What Is the Definition of Assigns
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- Building Your Business
- Operations & Success
What Is an Assignment of Contract?
Assignment of Contract Explained
Hero Images / Getty Images
Assignment of contract allows one person to assign, or transfer, their rights, obligations, or property to another. An assignment of contract clause is often included in contracts to give either party the opportunity to transfer their part of the contract to someone else in the future. Many assignment clauses require that both parties agree to the assignment.
Learn more about assignment of contract and how it works.
What Is Assignment of Contract?
Assignment of contract means the contract and the property, rights, or obligations within it can be assigned to another party. An assignment of contract clause can typically be found in a business contract. This type of clause is common in contracts with suppliers or vendors and in intellectual property (patent, trademark , and copyright) agreements.
How Does Assignment of Contract Work?
An assignment may be made to anyone, but it is typically made to a subsidiary or a successor. A subsidiary is a business owned by another business, while a successor is the business that follows a sale, acquisition, or merger.
Let’s suppose Ken owns a lawn mowing service and he has a contract with a real estate firm to mow at each of their offices every week in the summer. The contract includes an assignment clause, so when Ken goes out of business, he assigns the contract to his sister-in-law Karrie, who also owns a lawn mowing service.
Before you try to assign something in a contract, check the contract to make sure it's allowed, and notify the other party in the contract.
Assignment usually is included in a specific clause in a contract. It typically includes transfer of both accountability and responsibility to another party, but liability usually remains with the assignor (the person doing the assigning) unless there is language to the contrary.
What Does Assignment of Contract Cover?
Generally, just about anything of value in a contract can be assigned, unless there is a specific law or public policy disallowing the assignment.
Rights and obligations of specific people can’t be assigned because special skills and abilities can’t be transferred. This is called specific performance. For example, Billy Joel wouldn't be able to transfer or assign a contract to perform at Madison Square Garden to someone else—they wouldn't have his special abilities.
Assignments won’t stand up in court if the assignment significantly changes the terms of the contract. For example, if Karrie’s business is tree trimming, not lawn mowing, the contract can’t be assigned to her.
Assigning Intellectual Property
Intellectual property (such as copyrights, patents, and trademarks) has value, and these assets are often assigned. The U.S. Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) says patents are personal property and that patent rights can be assigned. Trademarks, too, can be assigned. The assignment must be registered with the USPTO's Electronic Trademark Assignment System (ETAS) .
The U.S. Copyright Office doesn't keep a database of copyright assignments, but they will record the document if you follow their procedure.
Alternatives to Assignment of Contract
There are other types of transfers that may be functional alternatives to assignment.
Licensing is an agreement whereby one party leases the rights to use a piece of property (for example, intellectual property) from another. For instance, a business that owns a patent may license another company to make products using that patent.
Delegation permits someone else to act on your behalf. For example, Ken’s lawn service might delegate Karrie to do mowing for him without assigning the entire contract to her. Ken would still receive the payment and control the work.
Do I Need an Assignment of Contract?
Assignment of contract can be a useful clause to include in a business agreement. The most common cases of assignment of contract in a business situation are:
- Assignment of a trademark, copyright, or patent
- Assignments to a successor company in the case of the sale of the business
- Assignment in a contract with a supplier or customer
- Assignment in an employment contract or work for hire agreement
Before you sign a contract, look to see if there is an assignment clause, and get the advice of an attorney if you want to assign something in a contract.
Key Takeaways
- Assignment of contract is the ability to transfer rights, property, or obligations to another.
- Assignment of contract is a clause often found in business contracts.
- A party may assign a contract to another party if the contract permits it and no law forbids it.
Legal Information Institute. " Assignment ." Accessed Jan. 2, 2021.
Legal Information Institute. " Specific Performance ." Accessed Jan. 2, 2021.
U.S. Patent and Trademark Office. " 301 Ownership/Assignability of Patents and Applications [R-10.2019] ." Accessed Jan. 2, 2021.
Licensing International. " What is Licensing ." Accessed Jan. 2, 2021.
What are Contract Terms & Legal Jargon? Master the Basics

- April 9, 2024
Check out Volody's Free CLM Software
Understanding contract terms is essential in navigating the complex world of legal agreements. These terms form the basis of any contract, outlining the parties’ rights, responsibilities, and obligations.
Deciding how long a contract will last, what it’s about, and making sure it’s enforceable crucial for legal binding. To better understand this topic, let’s take a closer look at what contract terms are and why they matter.
Understanding the basics of contract terms and legal language helps businesses ensure all their business and commercial contracts are clear and safe.
What are Contract Terms?

Contract terms are the building blocks of any agreement. They establish the rights and obligations of each party involved and define the scope and limitations of the contract. Whether you are drafting, negotiating, or reviewing a contract, a clear understanding of contract terms is essential.
Definition of contractual terms
In a legal agreement, a contract term is a part of the agreement that lays out what each party involved has agreed to do. It includes things like rights, duties, and conditions.
Contract terms can either be written out in the contract (referred to as “ express terms “) or understood based on common laws (referred to as “ implied terms “).
Contract terms are binding and enforceable, and failure to comply with these terms can result in a breach of contract. Before agreeing to any contract, it’s essential to thoroughly read and comprehend the terms. This ensures that both parties understand their duties and rights.
Importance of Contract Terms
Contract terms are essential for establishing clear expectations and obligations between parties. They provide a framework for the relationship and help prevent misunderstandings and disputes. Breach of contract can have serious consequences, including financial penalties , damaged business relationships, and potential legal action.
When people agree to the terms of a contract, they promise to be honest and fair in fulfilling their duties. This honesty and fairness, known as “good faith,” is really important in contract law. It means everyone involved should behave in a trustworthy and fair way when dealing with each other.
Knowing what’s in the contract helps everyone understand their responsibilities and what they can expect from each other. This keeps things smooth and makes sure nobody drops the ball.
Related Article: Contract Law: Understanding Legal Agreements
Different Types of Contract Terminology

Contract terms can take various forms and serve different purposes. Understanding the different types of terms of the contract is crucial for accurately interpreting and applying them. Let’s explore the three main types of contract terms: condition, warranty, and innominate term.
- Condition: A condition is a fundamental term of a contract that goes to the root of the agreement. Breaching a condition allows the innocent party to terminate the contract and seek damages. For example, in a sale of goods contract, the condition may be the delivery in a satisfactory condition. If the goods are delivered in a damaged state, it would be a breach of condition.
- Warranty: A warranty in a contract is a secondary term that isn’t crucial to the main purpose of the agreement. If someone breaches a warranty , the other party can ask for compensation, but they can’t cancel the contract. For instance, in a car sale contract, there might be a warranty for the car’s paint job. If there’s a small problem with the paint, it counts as a breach of warranty.
- Innominate term: An innominate term is a term that can’t be labeled as either a condition or a warranty. If the breach is really bad and affects the core of the agreement, it might be seen as a condition. But if it’s not that serious, it might be seen as a warranty. The court will look at how much the breach affects things to decide how to classify it.
Knowing the various kinds of contract terms helps parties understand how important each term is and how it can affect the entire contract. By understanding contract terms correctly, parties can better protect their rights and navigate potential contract breaches or disputes.
Related Article: What Is A Contract? Definition, Importance And Key Terms
Common Legal Terms Used in Contracts
Legal contracts often contain complex legal terminology that can be challenging to understand for those without a legal background. Getting to know typical legal jargon can help you understand contracts better so you can work with them effectively. Here are some common contract terms you should be aware of, including the concept of a legally binding contract:
- Intellectual property (IP): Intellectual property refers to intangible creations of the human intellect, such as inventions, literary and artistic works, trademarks , and trade secrets. Contracts often contain provisions related to the protection and use of intellectual property rights.
- Sale of goods: It involves one party transferring ownership of tangible items to another through agreements. These contracts usually state the price, quantity, quality, and delivery terms of the goods being sold.
- Force majeure: Force majeure refers to unforeseeable circumstances that prevent a party from fulfilling its contractual obligations . These circumstances may include natural disasters, strikes, or government actions. Force majeure clauses in contracts outline the rights and responsibilities of the parties in such situations.
- Confidentiality: Confidentiality clauses keep private information safe making sure details aren’t shared without permission. These provisions are particularly important in agreements involving trade secrets, proprietary information, or personal data.
- Jurisdiction: Jurisdiction refers to the legal authority of a court to hear and decide a particular case. Contracts often specify the jurisdiction that will govern any contractual disputes arising from the contract. This choice of jurisdiction determines which laws will apply and where legal proceedings will take place.
- Assignment: Assignment refers to the transfer of rights or obligations under a contract from one party to another. Contracts may include provisions that allow or restrict the assignment of rights or obligations.
Learning these usual legal words will help you feel sure about reading and understanding contract agreements. This way, you’ll understand precisely the rights and duties stated in the contract.
Related Article: How To Enforce Contract Legally? Expert Tips
The Difference Between Contract Terms and Contract Clauses

Contract terms and contract clauses are both important components of a contract, but they serve different purposes. Understanding the distinction between the two is crucial for effectively interpreting and applying contract language.
How Terms and Clauses Interact Within a Contract
The terms and clauses within a contract work together to establish the rights, obligations, and conditions of the agreement. Terms give the big picture and lay down the basic rules, while clauses get into the nitty-gritty details and cover specific topics.
The interaction between terms and clauses ensures comprehensive, clear, and enforceable contracts. Clauses may refer to specific terms within the contract, providing further clarification or exceptions to the general terms.
By understanding how terms and clauses interact, parties can effectively navigate the contract and ensure that the agreement accurately reflects their intentions and protects their interests.
Related Article: 7 Key Contract Clauses Found In Business Contracts
Contract Negotiation Strategies

Contract negotiation is a critical process that allows parties to reach mutually agreeable terms and conditions. Effective negotiation strategies can help parties achieve favorable outcomes and avoid potential disputes. Here are some key strategies to consider when engaging in contract negotiations:
- Preparation: Thoroughly research and understand the subject matter, market conditions, and industry standards related to the contract. This preparation will give you a solid foundation for negotiation and allow you to advocate for your interests effectively.
- Identify priorities: Determine your key objectives and priorities for the negotiation. Identify the terms that are most important to you and be prepared to make concessions on less critical issues.
- Flexibility and compromise: Negotiation requires a willingness to compromise and find mutually beneficial solutions . Be open to alternative proposals and creative solutions that can address the interests of both parties.
- Active listening and effective communication: Actively listen to the third party’s concerns and perspectives. Clearly articulate your interests and communicate your positions respectfully and constructively.
- Seek win-win outcomes: Focus on reaching outcomes that are beneficial for both parties. Look for opportunities to create value and build long-term relationships.
- Understand alternatives: Consider your alternatives if the negotiation doesn’t result in a satisfactory agreement. Understanding your alternatives strengthens your position and provides leverage during the negotiation process.
- Review and seek professional advice: Carefully review the proposed terms and seek legal advice if necessary. Legal professionals can guide on the legal implications of the terms and help identify potential risks or pitfalls.
By employing these negotiation strategies, parties can increase the chances of reaching favorable terms and building collaborative relationships.
Related Article: Contract Negotiation: Proven Strategies For Collaboration
Best Practices in Contract Management

Implementing best practices in contract management can help legal teams and law firms maximize the benefits of their contract management processes and systems. Here are some best practices to consider:
1. Ensuring Compliance and Mitigating Risks
Ensuring compliance with contractual obligations and mitigating risks are critical aspects of contract management for businesses. Here are some strategies to consider:
- Stay updated on legal and regulatory requirements: Regularly review and stay informed about relevant laws, regulations, and industry standards that may impact your contractual obligations. This includes understanding the legal implications of contract standard terms and ensuring compliance with data privacy and security regulations.
- Implement audit trails: Utilize contract management software or systems that maintain comprehensive audit trails of all contract-related activities. This ensures transparency and provides a record of all changes, approvals, and communication related to contracts.
- Conduct regular contract reviews: Periodically review your contracts to ensure compliance with contractual obligations and identify any potential risks, discrepancies, or areas for improvement. This includes reviewing contract terms, performance metrics, and key dates.
- Establish risk mitigation strategies: Develop strategies to proactively address potential risks or disputes . This may involve including appropriate termination clauses in contracts, maintaining backup copies of contracts, or implementing contingency plans for potential contract breaches.
By ensuring compliance with contractual obligations and proactively mitigating risks, small businesses can reduce the likelihood of disputes, penalties, or financial losses. This helps maintain business relationships, protect legal rights, and ensure the successful execution of contractual commitments.
2. Leveraging Automation for Efficiency
Leveraging automation tools and technologies can significantly improve the efficiency of your contracting processes. Here are some ways to leverage automation for greater operational efficiency:
- Use contract management software: Businesses can use contract lifecycle management (CLM) software . A CLM software automates tasks like creating contracts, getting approvals, and remembering important dates. This means they don’t have to do as much manual work for everyday contract management jobs.
- Integrate systems: Connect your CLM software with other business systems like CRM or ERP platforms. This way, data can move automatically between them, making workflows smoother. You won’t have to type in data manually, which cuts down on mistakes and speeds up how long it takes to handle each contract.
- Automate approval workflows: Set up automated approval workflows that route contracts to the appropriate stakeholders for review and approval. This ensures that contracts move through the approval process efficiently and reduces delays.
- Use electronic signatures: Utilize electronic signature technology to automate the signing process, eliminating the need for paper-based signatures and manual document routing.
By leveraging automation tools and technologies, small businesses can streamline their contract management processes, reduce administrative tasks, and improve overall operational efficiency. This allows businesses to allocate more time and resources to core business activities and strategic initiatives.
3. Continual Improvement and Adaptation Strategies
Continuously improving and adapting strategies are crucial to ensure that the contracting processes stay in line with business needs. Here are some strategies to consider:
- Regularly review and assess processes: Continually review your contract management processes to identify areas for improvement or potential bottlenecks. This can include soliciting feedback from stakeholders, conducting performance audits, and analyzing key metrics.
- Stay updated on industry trends: Make sure you know about new trends, the best ways of doing things, and any new technology that comes out. This helps you change your contract management processes to match the industry trends and use new features.
- Embrace CLM solution: Continually evaluate new contract management features or functionalities offered by contract management software providers. Adopting new features can enhance your contract management processes and provide additional value to your business.
- Foster a culture of continuous improvement: Promote a culture where everyone is always looking for ways to make things better. Encourage everyone to share new ideas, find ways to make processes work better, and put those improvements into action.
By implementing continual improvement and adaptation strategies, small businesses can ensure that their contract management processes remain effective, efficient, and aligned with business goals. This allows businesses to adapt to changing market conditions, technology advancements, and industry trends.
Related Article: Best Contract Management Software: Top 10 CLM In 2024
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the most important contract terms to be aware of.
The most important contract terms to be aware of include breach of the contract, indemnity, confidentiality, jurisdiction, and assignment. These terms define the rights, obligations, and potential consequences in a contractual agreement.
What are some common mistakes made in contract drafting?
Common mistakes in contract drafting include drafting errors, oversight of important terms, unclear language, and failure to specify key details. These mistakes can lead to misunderstandings, disputes, and potential legal issues.
Can contract terms be negotiated after signing?
Yes, contract terms can be renegotiated after signing. This can be done through an amendment process or by negotiating changes after the contract is signed. Both contracting parties need to agree to the modifications, and it’s important to document and execute any changes properly.
What role do contract clauses play in dispute resolution?
Contract clauses play a significant role in dispute resolution by outlining the procedures and mechanisms for resolving conflicts. Clauses such as arbitration clauses, mediation, and dispute resolution procedures help parties navigate potential disputes and avoid costly court proceedings.
How often should contracts be reviewed or updated?
Contracts should be reviewed and updated regularly to make sure they stay useful and work well. How often this happens can change based on the contract itself and what’s going on, like if laws or business stuff changes.
Understanding contract terms and legal jargon is crucial for navigating agreements effectively. By mastering the basics, you establish a solid foundation for drafting, negotiating, and managing contracts.
Clarity, precision, and attention to detail are key in ensuring smooth contract execution. Remember, contract terms and clauses have distinct roles and interactions within an agreement. With a firm grasp of contract essentials, you can confidently engage in negotiations and protect your interests with confidence.
Volody Products

Volody is a legal tech company specializing in providing software to help businesses digitize and automate their legal processes. Built by professionals with decades of experience, our products, such as Contract Lifecycle Management Software, Document Management Software, and Litigation Management Software, aim to reduce legal workload and eliminate low-value manual processes. With AI & ML at their core, Volody products are engineered to provide astute and agile solutions that adeptly meet the evolving requirements of the corporate world. That’s why global giants like Vodafone Idea, HDFC, Honda Cars, Linde Group, Oberoi Realty, etc., have chosen Volody as their legal tech provider.
Want more content like this? Sign up for our monthly newsletter.
You might also like:

Contractual Liability: A Comprehensive Guide

Can AI Replace Lawyers? Exploring the Future of Legal AI

How to Manage Legal Teams? 8 Strategies for Effective Management
Smart Contract Management Software
- Choose right CLM
- Contract management
- Explainer videos
- All CLM Software
- Litigation Management Software
- SDD Software
- Workflow approval
- Stronger contracts
- Contract analysis
- Automate drafting
- Dashboard & reporting
- Obligation management
- Contract repository
- Transportation
- Pharmaceutical
- Manufacturing
- Procurement
Other Pages

Eco House 604, Vishveshwar Nagar Rd, Churi Wadi, Goregaon, Mumbai 400063
+91 8080-809-301
INC Business Lawyers 1103 – 11871 Horseshoe Way, 2nd Floor, Richmond BC V7A 5H5 CANADA
+1 917-724-2760
Volody Products Inc 2578 Broadway #534 New York, NY 10025-8844 United States
- Cookie & Policy
- 2024 VOLODY
Volody's Free Trial of CLM Software
Experience the transformative power of Volody’s CLM platform for free!
- Customizable Templates
- Approval Workflows
- Obligation Management
- Central Repository
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
Legal Templates
Home Business Assignment Agreement
Assignment Agreement Template
Use our assignment agreement to transfer contractual obligations.

Updated February 1, 2024 Reviewed by Brooke Davis
An assignment agreement is a legal document that transfers rights, responsibilities, and benefits from one party (the “assignor”) to another (the “assignee”). You can use it to reassign debt, real estate, intellectual property, leases, insurance policies, and government contracts.
What Is an Assignment Agreement?
What to include in an assignment agreement, how to assign a contract, how to write an assignment agreement, assignment agreement sample.

Partnership Interest
An assignment agreement effectively transfers the rights and obligations of a person or entity under an initial contract to another. The original party is the assignor, and the assignee takes on the contract’s duties and benefits.
It’s often a requirement to let the other party in the original deal know the contract is being transferred. It’s essential to create this form thoughtfully, as a poorly written assignment agreement may leave the assignor obligated to certain aspects of the deal.
The most common use of an assignment agreement occurs when the assignor no longer can or wants to continue with a contract. Instead of leaving the initial party or breaking the agreement, the assignor can transfer the contract to another individual or entity.
For example, imagine a small residential trash collection service plans to close its operations. Before it closes, the business brokers a deal to send its accounts to a curbside pickup company providing similar services. After notifying account holders, the latter company continues the service while receiving payment.
Create a thorough assignment agreement by including the following information:
- Effective Date: The document must indicate when the transfer of rights and obligations occurs.
- Parties: Include the full name and address of the assignor, assignee, and obligor (if required).
- Assignment: Provide details that identify the original contract being assigned.
- Third-Party Approval: If the initial contract requires the approval of the obligor, note the date the approval was received.
- Signatures: Both parties must sign and date the printed assignment contract template once completed. If a notary is required, wait until you are in the presence of the official and present identification before signing. Failure to do so may result in having to redo the assignment contract.
Review the Contract Terms
Carefully review the terms of the existing contract. Some contracts may have specific provisions regarding assignment. Check for any restrictions or requirements related to assigning the contract.
Check for Anti-Assignment Clauses
Some contracts include anti-assignment clauses that prohibit or restrict the ability to assign the contract without the consent of the other party. If there’s such a clause, you may need the consent of the original parties to proceed.
Determine Assignability
Ensure that the contract is assignable. Some contracts, especially those involving personal services or unique skills, may not be assignable without the other party’s agreement.
Get Consent from the Other Party (if Required)
If the contract includes an anti-assignment clause or requires consent for assignment, seek written consent from the other party. This can often be done through a formal amendment to the contract.
Prepare an Assignment Agreement
Draft an assignment agreement that clearly outlines the transfer of rights and obligations from the assignor (the party assigning the contract) to the assignee (the party receiving the assignment). Include details such as the names of the parties, the effective date of the assignment, and the specific rights and obligations being transferred.
Include Original Contract Information
Attach a copy of the original contract or reference its key terms in the assignment agreement. This helps in clearly identifying the contract being assigned.
Execution of the Assignment Agreement
Both the assignor and assignee should sign the assignment agreement. Signatures should be notarized if required by the contract or local laws.
Notice to the Other Party
Provide notice of the assignment to the non-assigning party. This can be done formally through a letter or as specified in the contract.
File the Assignment
File the assignment agreement with the appropriate parties or entities as required. This may include filing with the original contracting party or relevant government authorities.
Communicate with Third Parties
Inform any relevant third parties, such as suppliers, customers, or service providers, about the assignment to ensure a smooth transition.
Keep Copies for Records
Keep copies of the assignment agreement, original contract, and any related communications for your records.
Here’s a list of steps on how to write an assignment agreement:
Step 1 – List the Assignor’s and Assignee’s Details
List all of the pertinent information regarding the parties involved in the transfer. This information includes their full names, addresses, phone numbers, and other relevant contact information.
This step clarifies who’s transferring the initial contract and who will take on its responsibilities.
Step 2 – Provide Original Contract Information
Describing and identifying the contract that is effectively being reassigned is essential. This step avoids any confusion after the transfer has been completed.
Step 3 – State the Consideration
Provide accurate information regarding the amount the assignee pays to assume the contract. This figure should include taxes and any relevant peripheral expenses. If the assignee will pay the consideration over a period, indicate the method and installments.
Step 4 – Provide Any Terms and Conditions
The terms and conditions of any agreement are crucial to a smooth transaction. You must cover issues such as dispute resolution, governing law, obligor approval, and any relevant clauses.
Step 5 – Obtain Signatures
Both parties must sign the agreement to ensure it is legally binding and that they have read and understood the contract. If a notary is required, wait to sign off in their presence.

Related Documents
- Purchase Agreement : Outlines the terms and conditions of an item sale.
- Business Contract : An agreement in which each party agrees to an exchange, typically involving money, goods, or services.
- Lease/Rental Agreement : A lease agreement is a written document that officially recognizes a legally binding relationship between two parties -- a landlord and a tenant.
- Legal Resources
- Partner With Us
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell My Personal Information

The document above is a sample. Please note that the language you see here may change depending on your answers to the document questionnaire.
Thank you for downloading!
How would you rate your free template?
Click on a star to rate
Gatekeeper's COVID-19 Resource Centre
This website stores cookies on your computer. These cookies are used to improve your website and to provide more personlised services to you, both on this website and through other media.
To find out more about the cookies we use see our Privacy Policy .

- Book a Demo
- Gatekeeper for Legal Teams
- Gatekeeper for Procurement Teams
- Gatekeeper for Finance Teams
- Gatekeeper for Vendor Management Teams
- Gatekeeper for Operations Teams
- Gatekeeper for IT Teams
- Gatekeeper for Sales Teams
- Complete Guide to Contract Management (ebook)
- Contract Management Template Bundle (Excel)
- Contract Management RFP Templates (Excel)
- 2023 Gartner® Magic Quadrant™ Report
- An Introduction to Vendor Management (ebook)
- VCLM: A holistic approach to managing agreements
- Customer Knowledge Base How-to Guides for Using Gatekeeper
- Request my demo
Contract Management , Contracts , Compliance , Visibility
Contract Terminology: Contract terms you need to know
Rod Linsley Jun 11, 2018 4:52:15 PM
Assuming you’re not a legal professional, if you’ve ever read through a contract in detail, you’ll likely have come across a number of unfamiliar contract terminology that you’ve probably not seen in any other circumstances.
There’s a broad range of contractual terms, including various latin phrases, which are used in legal documents and will be understood by those drafting them on behalf of businesses.
This legalese can be a impenetrable to the layman and can create an unnecessary barrier to all parties being able to fully understand the content of a contract.
To help you overcome any unfamiliarity with clauses in a contract, we’ve created this handy jargon-buster, which outlines the commonly understood meanings of contract terminology.
It’s worth pointing out that it’s not exhaustive and you should still consult with a legal professional if you’re looking to create or amend an official document, even if it's edits to common contract terms.

Contract terminology Glossary
You can visit our contract terminology glossary for a comprehensive list of legalese. Below are some of the most important phrases you need to know.
Ab Initio (Ab Init ): Latin, meaning from the beginning.
Alternative Dispute Resolution (ADR) : methods of attempting to resolve a dispute without going to court. Arbitration, Mediation and negotiation are types of ADR. Contracts may contain a clause requiring the Parties to that contract to follow specific processes if a contract-related disagreement occurs. Such a clause may prevent a Party from starting court proceedings at all or without first following the prescribed process.
Arbitration : a method of dispute resolution where a private tribunal determines the resolution of a dispute between the Parties to a contract.
Assignment / Novation : the Parties to a contract may, under agreed conditions, transfer or assign (novate) any of their liabilities, rights or obligations under the contract to a third party.
Bankruptcy : the official legal status of a person or organisation that cannot repay the debts owed to creditors.
Bona Fide : Latin, meaning in good faith. Usually implies a level of trust that the Parties to a contract are acting honestly without any hidden motives.
Breach of Contract : failure by a Party to a contract to comply with one or more Conditions of the contract. A breach of contract will make the whole thing Void and can lead to Damages being awarded against the breaching Party.
Capitalised Terms : A word or a group of words can be defined to have specific meaning in a contract, to prevent misinterpretation of that word or group of words. By convention, such definitions are indicated by capitalising the first letter of each word in the term, such as 'Building' or 'High Value Property'. The definitions may be pre-defined, appearing in a specific definitions clause, where each defined term is followed by the desired meaning of that term. Definitions may also or instead be post-defined, appearing in the body of any particular clause after a group of words, such as 'Duties are to commence between 6am and 8am ('Start Time')'.
Caveat Emptor : Latin, meaning let the buyer beware. The buyer is responsible for ensuring that what they are acquiring under a contract is really what they want. An error of judgement by the buyer in this regard is not grounds for making the contract.
Condition : an essential or fundamental term in a contract. Failure of a condition results in Breach of Contract.
Confidential : a secret or something that should not be disclosed except under specified circumstances.
Consideration : the benefit given by each Party to a contract to the other Party in exchange for the contractual promise of another Party to the contract. The benefit exchanged can be something physical like equipment, monetary, behavioural like an action or inaction, anything that has some value to the provider of the benefit.
Counterpart : a copy of a contract, often created so that each Party to the contract may have its own copy. A contract may contain a Counterparts clause allowing the Parties to each sign their own copy of the contract rather than require all Parties to sign the one copy.
Cure Period : when a Default occurs, the breaching Party may have a certain period of time to cure the Default before the non-breaching Party is allowed to exercise Remedies. The non-breaching Party may need to give notice to the breaching Party before the time period.
Damages : an amount of money sought or awarded to a Party to a contract to compensate for the loss that Party has suffered due to a Breach of Contract.
Deed : a special type of legally binding and enforceable contract that does not require Consideration to pass from one Party to another.
Default : the circumstances where a Party to a contract is considered to be in Breach of Contract.
Deliverables : a collective name for all those tangible things that a Party to a contract is required to supply, often by an agreed date.
Entire Agreement : a clause in a contract stating that the written document is the complete understanding between the Parties. Any statement or promise made by a Party to the contract that is not in that written document will not be considered part of the legally binding contract, and cannot be relied upon in relation to the contract.
Excuse : something that forgives performance and bars enforcement of a contract. If performance of a contractual obligation of a Party to the contract is excused, this relieves the non-performing Party of liability with respect to that obligation.
Express Terms : the terms actually written in a contract or verbally agreed before or at the time the contract is made. See Implied Terms.
Force Majeure : the circumstances or situations described in a contract that may prevent one or more of the Parties to the contract from performing their contractual obligations. The occurrence of such circumstances or situations may excuse the affected Party.
Governing Law : the union, country or state / provincial laws applicable to a contract. The Governing Law will be used by the courts to interpret and make decisions about the contract in the event of a contractual dispute where the Parties are not based in the same union, country or state / province. This clause is normally coupled with a Jurisdiction clause.
Implied Terms : the terms that are implied in a contract by law, custom and practice without actually being mentioned in writing or verbally by any Party to the contract. Terms implied by custom and practice can always be overridden by Express Terms, but some terms implied by law cannot be overridden at all.
Indemnity : a contractual obligation on a Party to a contract to compensate for any loss another Party to the contract may suffer in the circumstances that are the subject of the Indemnity, such as payment of reasonable court costs in the settlement of a contractual dispute.
Injunction : a court order sought by a Party to a contract to make another Party to the contract do or stop doing something. It is sought urgently where the whole purpose of the contract would be defeated and Damages would not adequately compensate the Party seeking the Injunction for the loss it is likely to suffer from the other Party’s actions or omissions.
Insolvency : the situation where a person or business is unable to meet their financial obligations. See Bankruptcy, Liquidation and Receivership.
Intellectual Property Rights (IPR) : legal rights relating to the ownership of intellectual, industrial or artistic work, including, Inter Alia, patents (inventions), designs (graphics), trademarks (names or marks used to identify goods) and copyrights (rights of authorship).
Inter Alia : Latin, meaning among other things. This is often used in contracts to indicate that what is being specifically referred to is part of a larger group without having to name all the elements of the group.
Joint and Several Liability : in a contract where the Parties act together as partners, as well as being responsible together, each Party is also individually liable for the entire contract.
Jurisdiction : the place where a Party to a contract without any Alternative Dispute Resolution clause must bring court proceedings if there is a dispute about the contract.
Key Performance Indicator (KPI) : a qualitative or quantitative factor that can be measured to assist in determining whether or not a contract is, or is on track for, meeting its objectives. KPIs should be regularly and systematically reviewed in order to identify any issues or concerns as early as possible.
Liability : a Party to a contract's legal obligation, on its Breach of Contract, to compensate another Party to the contract for any harm so caused.
License : a method by which the owner of physical or Intellectual Property (the licensor) allows someone else (the licensee) to use it in some prescribed manner, typically but not always for a royalty or a fee.
Limited liability : a Party to a contract's financial liability may be limited to a fixed sum, commonly some fraction or multiple of the value of the fees paid by another Party to the contract over the preceding 12 months.
Liquidated Damages : a contract provision that estimates and fixes in advance the sum payable as Damages for a Party to the contract's Breach of Contract.
Liquidation : the formal dissolution of a business by the sale or transfer of its assets to pay a debt. This often occurs as a result of Insolvency, but a solvent business can be liquidated if it no longer wishes to continue trading.
Litigation : the conduct of court proceedings to resolve a dispute.
Mala Fide : Latin, meaning in bad faith, opposite of Bona Fide.
Material Breach : a Breach of Contract which has a serious, not merely trivial or inconsequential, effect on the benefit which the non-breaching Party to the contract would otherwise have gained from the contract.
Mediation : a form of Alternative Dispute Resolution where an independent person meets with the Parties to a contract to help them formulate their own resolution to a conflict.
Mutatis Mutandis : Latin, meaning changing whatever ought to be changed.
Obligation : something which must or must not be done by one or more Parties to a contract.
Party : Any individual, group or organisation participating in a contract. 'Parties' has a corresponding meaning.
Period : The length of time a contract is expected to be in force (see also 'Term').
Pro Rata : Latin, meaning for the rate, or assigning an amount to a fraction according to its share of the whole.
Pro Tempore (Pro Tem) : Latin, meaning for the time being.
Quid pro quo : Latin, meaning something for something. The basis for definition of Consideration in a contract, where each Party to the contract should offer something to the other.
Receivership : the appointment of a licensed insolvency practitioner to take over the running of a business that cannot meet its financial commitments.
Recitals : A section in a contract that states who the Parties are and their reasons for entering into the contract. Sometimes called 'Background' or 'Preamble'.
Remedies : the measures, including Damages and Injunctions, that can be taken by a court to help a Party to a contract in the event of Breach of Contract by another Party to the contract.
Representations : statements or promises made as a fact by one Party to a contract to another Party to the contract.
Rights : the things a Party to a contract is entitled to do or not do as the case may be.
Risk of Loss : allocation of responsibility for covering the risk of damage to or loss of goods being transported long distances after a sale has been completed, but before delivery has occurred. If the seller bears risk of loss during transport, the seller has a responsibility to provide substitute goods should the goods get lost or destroyed in transit. If the buyer bears risk of loss, the buyer generally must pay for the goods, even though they never arrive. Often parties cover the risk of loss with insurance.
Severability : the allowance a contract for removal or correction of portions of the contract that are incorrectly or illegally drawn up, allowing the remainder of the contract to be valid and enforceable.
Term : either (a) the length of time for which a contract operates (see Period) or (b) any contract clause (see Condition).
Termination for cause : a contract may identify the conditions under which a Party to the contract could terminate a contract due to another Party's material breach of the contract, such as becoming bankrupt or insolvent, failing to comply with confidentiality provisions, or failing to perform obligations due to a force majeure event. Depending on the nature of the breach, the non-breaching Party may terminate the contract immediately with or without notice, or provide the breaching Party with prior notice and an opportunity to cure the breach within a certain time frame, after which the contract may be terminated if the breach remains uncured.
Termination for convenience : a contract may allow one or more Parties to the contract to unilaterally terminate the contract without providing the other Parties to the contract with any reason. Such termination may only be allowed at certain times such as on the contract anniversary or following the end of any initial term, may require some minimum notice period, and could require payment of an early termination fee by the 'buying' Party or the refund by the 'selling' Party of the unused portion of any prepaid fees.
Territory : any geographical area where a contract has force.
Third Party : an individual, group, organisation or other legal entity (eg. a company) that is not a Party.
Time is of the Essence : a statement indicating that the times specified in a contract are so critical that if one Party to the contract does not comply with the timing requirements, another Party to the contract can immediately Terminate for Cause.
Variation : the method agreed by the Parties to a contract for making changes to the contract after it has been signed. It usually requires that any change to the contract be in writing signed by all Parties.
Void : making a contract unenforceable in law.
Waiver : an intentional surrendering of rights by a Party to a contract. A 'no waiver' clause can be agreed stating that no provision in the contract may be waived, except by means of a writing signed by the Party to the contract against whom a waiver is sought.
Warranties : promises made in a contract. Failure of a warranty results in liability to pay Damages.

Rod is a seasoned Contracts Management and Procurement professional with a senior IT Management background, specialising in ICT contracts
Enjoyed this post? Don't forget to share.
Ready to improve your contract & vendor management .

Supplier Management
Contract management, vendor management, contract lifecycle, popular posts, what is contract management - everything you need to know, managing contracts using excel: free templates for 2024, contract management kpis - contract performance metrics that matter, recent posts, the benefits of contract lifecycle management, what is enterprise contract management, how to track contract performance, what is vendor management, related content, contract renewals best practices for 2024, contract management and the cloud, subscribe to our newsletter.
Sign up today to receive the latest GateKeeper content in your inbox.
Subscribe to Email Updates
- REQUEST MY DEMO

- SPECIALISMS
- Contract Lifecycle Management
- Vendor Lifecycle Management
- Contract Management Software
- Vendor Management Software
- Artificial Intelligence
- OCR Search & Analysis
- Enterprise Contract Management
- USEFUL LINKS
- What is VCLM?
- How to manage vendors
- How to review a contract
- Complete Guide to CLM
- How to build a Business Case
- How to run an RFP
- Vision & Values
- Partner Program
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Service
- Legality of E-Signatures
- Data Processing Agreement
- Data Feed Terms
Copyright © 2015 - 2024. Gatekeeper™ is a registered trademark.
Request your free demo of Gatekeeper
Top rated clm software.

Before Gatekeeper, our contracts were everywhere and nowhere. Anastasiia Sergeeva, Legal Operations Manager, BlaBlaCar
Gatekeeper is that friendly tap on the shoulder, to remind me what needs our attention. Donna Roccoforte, Paralegal, Hakkasan Group
Great System. Vetted over 25 other systems and Gatekeeper rose to the top. Randall S. Wood, Associate Corporate Counsel, Cricut
Book your Free Demo of Gatekeeper
Thank you for requesting your demo.
Next Step - Book a Call
Please book a convenient time for a quick call to discuss your requirements.
- France (FR)
- Germany (DE)
- Netherlands
United Kingdom
- United States
The Business Contract Terms (Assignment of Receivables) Regulations 2018: still more to do?

The Business Contract Terms (Assignment of Receivables) Regulations 2018 (the " Regulations ") are now in force. The Regulations are intended to make it easier for small businesses to access receivables-based finance by making ineffective any prohibitions, conditions and restrictions on the assignment of receivables [1] arising under contracts for the supply of goods, services or intangible assets.
The Regulations have a somewhat chequered history. The Law Commission advocated legislation to limit the effectiveness of anti-assignment clauses in 2005, however, the proposal failed to gain momentum and lay dormant for more than a decade. Draft legislation finally appeared in 2017, but was withdrawn following criticism by the Loan Market Association and others. The final form of the Regulations addresses some of the criticisms, but adds complexity in what is already a complex area of the law.
The Effect of the Regulations
A term in a contract to which the Regulations apply is ineffective to the extent that it prohibits or imposes a condition or other restriction on the assignment of a receivable arising under that contract or another contract between the same parties. That does not necessarily mean that the term will be entirely void as a result: contractual prohibitions on assignment often do not distinguish between the right to performance of the contract and the right to be paid amounts arising under it. Prohibitions of this type will remain effective to prevent an assignment of the right to performance, even if they are ineffective to prevent the assignment of receivables arising under the contract.
The Regulations provide that a term which prevents an assignee from determining the validity or the value of the receivable or restricts its ability to enforce the receivable will be deemed to be a condition or other restriction on assignment. This, for example, includes provisions which prevent an assignee from obtaining particulars and evidence of any potential defence or set-off by a party to the contract. Therefore, the Regulations permit disclosure of matters which might otherwise be caught by confidentiality provisions in the underlying contract.
When do the Regulations apply?
Subject to specified exceptions, the Regulations apply to any contract entered into on or after 31 December 2018.
Certain types of contract are excluded from the Regulations. For example, the Regulations do not apply :
- to contracts for certain prescribed financial services or to other specific types of contract, including those in relation to real estate, certain derivatives, certain project finance and energy agreements and operating leases.
- to contracts entered into in connection with the acquisition, disposal or transfer of an ownership interest in all or part of a business, firm or undertaking, provided the relevant contract includes a statement to that effect. The need for such a statement applies even where the purpose of the contract is obvious on its face.
- where one or more of the parties is a consumer, or where none of the parties has entered into the contract in the course of carrying on a business in the UK.
The Regulations do not apply if the supplier is a "large enterprise" or a "special purpose vehicle" (the " SME Test ") at the time of the assignment. For this purpose, a special purpose vehicle is a firm that carries out a primary purpose in relation to the holding of assets (except trading stock) or financing commercial transactions, which in either case involves it incurring a liability of £10m or more.
The question of whether a limited company is a "large enterprise" depends in part on turnover, balance sheet total and number of employees assessed by reference the most recent annual accounts filed by the company or its parent prior to the assignment. Therefore, at the time the supplier and the debtor enter into a contract, they will not necessarily know whether a contractual prohibition on the assignment of receivables will be effective.
The definition of a "large enterprise" may be difficult to apply in some circumstances and to some entities. For example, the Regulations imply that limited partnerships are included in scope and some commentators argue that in this situation it would be the general partner entity which would be assessed under the SME Test, however, this is not expressly provided for by the Regulations.
If another governing law is imposed by a party wholly or mainly for the purpose of enabling it to evade the operation of the Regulations, the Regulations state that they will nevertheless have effect. Aside from the practical difficulty in determining whether the choice of law was imposed for this purpose, the effect of this provision is not entirely clear. Under Rome I, the law governing an assigned claim determines its assignability and the relationship between the assignee and the debtor [2] . Therefore, the fundamental question of whether the debtor should pay the supplier or the assignee remains determined by the governing law of the contract, but subject it seems (at least as far as the English courts are concerned) to the mandatory provisions of the Regulations.
The Regulations only affect prohibitions, restrictions and conditions on assignment contained in the contract under which the receivable arises or another contract between the same parties. For example, they would not restrict the effectiveness of a negative pledge or a restriction on the disposal of receivables contained in a financing document with a third party lender.
The term "assignment" is not defined in the Regulations and, assuming it has its normal legal meaning, does not include the creation of a charge or trust. Therefore, it appears that the Regulations do not apply to the creation of a charge or a trust.
What if the Regulations do not apply?
As a result of the SME Test and the exclusion of certain types of contracts, there will be many situations in which the Regulations are not relevant to the assignment of a receivable. Where the Regulations do not apply, the current law recognises the effectiveness of contractual prohibitions on the assignment of receivables [3] . However, case law suggests that a prohibition on assignment will not normally be construed as preventing the creation of a trust. Receivables purchase agreements will therefore often provide for the supplier to hold the receivable and/or its proceeds on trust for the assignee to the extent that the assignment is ineffective. In response, some debtors include specific prohibitions on the creation of trusts over receivables in their contracts. However, assignees will try to circumvent the practical effect of even the most widely drafted prohibition by taking a power of attorney enabling them to bring an action against the debtor in the name of the supplier.
The law is still developing in response to this escalating arms race between assignees and debtors. In part this is due to an inevitable tension between the interest of the assignee in having its proprietary interest in the receivable recognised and the interest of the debtor in choosing whether it deals with anyone other than its original contractual counterparty.
This has led some to argue that the common law should recognise all assignments of receivables notwithstanding prohibitions on assignment, at least as between the assignor and the assignee. [4] Arguably, this approach would balance the legitimate interests of all parties.
Still more to do?
Where they apply, the Regulations will make it easier for SMEs to assign their receivables and to raise finance. However, the Regulations do not mean that assignees can ignore the terms of the underlying contractual arrangements between suppliers and debtors; for one thing any existing rights of set-off will continue to bind the assignee [5] . Also, because the Regulations do not apply to contracts entered into before 31 December 2018, prohibitions on assignment will continue to apply to many receivables owed to SME suppliers for a while yet.
Assessing whether a supplier is an SME involves reviewing the most recent relevant annual accounts and the status of the supplier in this respect may change throughout the term of a contract. There are also various types of contract to which the Regulations do not apply and, in some cases, applying those exceptions is not straightforward. The Regulations add an additional layer of complexity to the law.
In practice, the question that assignees ask their lawyers is very simple: what action can they take to recover? The Regulations may enable the answer to be more positive, but they also make it more nuanced. There is more work for legislation or precedent to do to simplify the law in this area.
[1] "Receivable" is defined in broad terms as a right (whether or not earned by performance) to be paid any amount under a contract for the supply of goods, services or intangible assets.
[2] Regulation (EC) No 593/2008: Article 14(2), Rome I
[3] Linden Gardens Trust Ltd v Lenesta Sludge Disposals Ltd [1994] 1 AC 85
[4] See in particular Professor Roy Goode's article " Contractual Prohibitions Against Assignment " [2009] LMCLQ 300 cited by approval by Lady Justice Gloster in First Abu Dhabi Bank PJSC and BP Oil International Limited [2018] EWCA Civ 14
[5] In recovery situations, set-off and disputes in relation to liability are often more significant issues for the debtor from a commercial perspective than the question of whether a prohibition on assignment is legally effective.

COMMENTS
Assignment Clause Examples. Examples of assignment clauses include: Example 1. A business closing or a change of control occurs. Example 2. New services providers taking over existing customer contracts. Example 3. Unique real estate obligations transferring to a new property owner as a condition of sale. Example 4.
An assignment of contract occurs when one party to an existing contract (the "assignor") hands off the contract's obligations and benefits to another party (the "assignee"). Ideally, the assignor wants the assignee to step into his shoes and assume all of his contractual obligations and rights. In order to do that, the other party to the ...
It's essential to understand the terms of your assignment agreement and whether it includes a release from liability for the assignor. Executing a contract assignment effectively is all about dotting the I's and crossing the T's. By following these steps—securing written consent, issuing a notice of assignment, understanding privity of ...
The best approach when you're assigning a contract is to make a written assignment agreement with the assignee. A lawyer can help you draft an agreement tailored to your circumstances, with language that clearly spells out your rights and obligations and the rights and obligations of the assignee. That way, you are less likely to be left ...
As a preliminary matter, it is important to realize that contracts are, by law, assignable and delegable. This means that the rights conveyed by the contract may be transferred to another party by assignment, unless an express restriction on assignment exists within the contract, or unless an assignment would violate public policy. Likewise ...
Assignment of rights changes the foundational terms of the agreement. The assignment is illegal in some way. If assignment of contract takes place, but the contract actually prohibits it, the assignment will automatically be voided. When a transfer of contract rights will somehow change the basics of the contract, assignment cannot happen.
The Concept of a Contract Assignment. Contracts create rights and duties. By an assignment, an obligee ... Likewise, under UCC Section 9-318(1), the assignee of an account is subject to all terms of the contract between the debtor and the creditor-assignor. Suppose Dealer sells a car to Buyer on a contract where Buyer is to pay $300 per month ...
A contract assignment agreement may be created in cases involving a contract assignment. An assignment is where the recipient of products, services, or other rights transfers (assigns) their rights to another party. The party transferring their rights is the assignor, while the party performing the services is dubbed the obligor.
The assignment and assumption agreement. An assignment and assumption agreement is used after a contract is signed, in order to transfer one of the contracting party's rights and obligations to a third party who was not originally a party to the contract. The party making the assignment is called the assignor, while the third party accepting ...
As long as you're free to assign the contract, prepare and enter into the assignment, which is basically an agreement transferring your rights and obligations. Notify the obligor, or the non-transferring party. After you assign contract rights to the assignee, notify the other party that was the original contractor, also known as the obligor.
A contract assignment agreement is a binding document between two parties that sets out the terms of the assignment of a contract. It is typically used when one party wishes to assign their rights, responsibilities, obligations, and benefits under a contract to another party. Use this contract assignment agreement template to create a binding ...
An assignment of contract is a legal term in which someone transfers, or assigns, property or rights to another. ... Assignments won't stand up in court if the assignment significantly changes the terms of the contract. For example, if Karrie's business is tree trimming, not lawn mowing, the contract can't be assigned to her. ...
Contract terms are the building blocks of any agreement. They establish the rights and obligations of each party involved and define the scope and limitations of the contract. Whether you are drafting, negotiating, or reviewing a contract, a clear understanding of contract terms is essential.
What to Include in an Assignment Agreement. Create a thorough assignment agreement by including the following information: Effective Date: The document must indicate when the transfer of rights and obligations occurs. Parties: Include the full name and address of the assignor, assignee, and obligor (if required). Assignment: Provide details that identify the original contract being assigned.
A Letter of assignment can be used to affect the assignment and is signed by the outgoing party and the incoming party. It contains special provisions to transfer all of the rights and benefits under the contract to the incoming party. However, in practice, the assignor will usually subcontract, or delegate, their obligations under the contract ...
THE BUSINESS CONTRACT TERMS (ASSIGNMENT OF RECEIVABLES) REGULATIONS 2018 (THE REGULATIONS) The Regulations, which came into force on 24 November 2018, are intended to ... If the Contract is silent on assignment, or the grant of security then, other than for personal contracts (contracts where the rights are so personal to the parties ...
Contract terminology Glossary. You can visit our contract terminology glossary for a comprehensive list of legalese. Below are some of the most important phrases you need to know. Ab Initio (Ab Init ): Latin, meaning from the beginning. Alternative Dispute Resolution (ADR): methods of attempting to resolve a dispute without going to court.
The Business Contract Terms (Assignment of Receivables) Regulations 2018 (the "Regulations") are now in force. The Regulations are intended to make it easier for small businesses to access receivables-based finance by making ineffective any prohibitions, conditions and restrictions on the assignment of receivables [1] arising under contracts ...
Since 1 January 2019, the Business Contract Terms (Assignment of Receivables) Regulations 2018 (the "Regulations") have prevented parties from…
The Business Contract Terms (Assignment of Receivables) Regulations 2018 (the "Regulations") came into force on 24 November 2018. The aim of the Regulations is to make it easier for small and medium-sized enterprises to access invoice financing. To that effect, the Regulations provide that, under certain contracts, clauses purporting to ...