

The Ultimate Guide to Qualitative Research - Part 1: The Basics

- Introduction and overview
- What is qualitative research?
- What is qualitative data?
- Examples of qualitative data
- Qualitative vs. quantitative research
- Mixed methods
- Qualitative research preparation
- Theoretical perspective
- Theoretical framework
- Literature reviews
Research question
- Conceptual framework
- Conceptual vs. theoretical framework
Data collection
- Qualitative research methods
- Focus groups
- Observational research
What is a case study?
Applications for case study research, what is a good case study, process of case study design, benefits and limitations of case studies.
- Ethnographical research
- Ethical considerations
- Confidentiality and privacy
- Power dynamics
- Reflexivity
Case studies
Case studies are essential to qualitative research , offering a lens through which researchers can investigate complex phenomena within their real-life contexts. This chapter explores the concept, purpose, applications, examples, and types of case studies and provides guidance on how to conduct case study research effectively.

Whereas quantitative methods look at phenomena at scale, case study research looks at a concept or phenomenon in considerable detail. While analyzing a single case can help understand one perspective regarding the object of research inquiry, analyzing multiple cases can help obtain a more holistic sense of the topic or issue. Let's provide a basic definition of a case study, then explore its characteristics and role in the qualitative research process.
Definition of a case study
A case study in qualitative research is a strategy of inquiry that involves an in-depth investigation of a phenomenon within its real-world context. It provides researchers with the opportunity to acquire an in-depth understanding of intricate details that might not be as apparent or accessible through other methods of research. The specific case or cases being studied can be a single person, group, or organization – demarcating what constitutes a relevant case worth studying depends on the researcher and their research question .
Among qualitative research methods , a case study relies on multiple sources of evidence, such as documents, artifacts, interviews , or observations , to present a complete and nuanced understanding of the phenomenon under investigation. The objective is to illuminate the readers' understanding of the phenomenon beyond its abstract statistical or theoretical explanations.
Characteristics of case studies
Case studies typically possess a number of distinct characteristics that set them apart from other research methods. These characteristics include a focus on holistic description and explanation, flexibility in the design and data collection methods, reliance on multiple sources of evidence, and emphasis on the context in which the phenomenon occurs.
Furthermore, case studies can often involve a longitudinal examination of the case, meaning they study the case over a period of time. These characteristics allow case studies to yield comprehensive, in-depth, and richly contextualized insights about the phenomenon of interest.
The role of case studies in research
Case studies hold a unique position in the broader landscape of research methods aimed at theory development. They are instrumental when the primary research interest is to gain an intensive, detailed understanding of a phenomenon in its real-life context.
In addition, case studies can serve different purposes within research - they can be used for exploratory, descriptive, or explanatory purposes, depending on the research question and objectives. This flexibility and depth make case studies a valuable tool in the toolkit of qualitative researchers.
Remember, a well-conducted case study can offer a rich, insightful contribution to both academic and practical knowledge through theory development or theory verification, thus enhancing our understanding of complex phenomena in their real-world contexts.
What is the purpose of a case study?
Case study research aims for a more comprehensive understanding of phenomena, requiring various research methods to gather information for qualitative analysis . Ultimately, a case study can allow the researcher to gain insight into a particular object of inquiry and develop a theoretical framework relevant to the research inquiry.
Why use case studies in qualitative research?
Using case studies as a research strategy depends mainly on the nature of the research question and the researcher's access to the data.
Conducting case study research provides a level of detail and contextual richness that other research methods might not offer. They are beneficial when there's a need to understand complex social phenomena within their natural contexts.
The explanatory, exploratory, and descriptive roles of case studies
Case studies can take on various roles depending on the research objectives. They can be exploratory when the research aims to discover new phenomena or define new research questions; they are descriptive when the objective is to depict a phenomenon within its context in a detailed manner; and they can be explanatory if the goal is to understand specific relationships within the studied context. Thus, the versatility of case studies allows researchers to approach their topic from different angles, offering multiple ways to uncover and interpret the data .
The impact of case studies on knowledge development
Case studies play a significant role in knowledge development across various disciplines. Analysis of cases provides an avenue for researchers to explore phenomena within their context based on the collected data.

This can result in the production of rich, practical insights that can be instrumental in both theory-building and practice. Case studies allow researchers to delve into the intricacies and complexities of real-life situations, uncovering insights that might otherwise remain hidden.
Types of case studies
In qualitative research , a case study is not a one-size-fits-all approach. Depending on the nature of the research question and the specific objectives of the study, researchers might choose to use different types of case studies. These types differ in their focus, methodology, and the level of detail they provide about the phenomenon under investigation.
Understanding these types is crucial for selecting the most appropriate approach for your research project and effectively achieving your research goals. Let's briefly look at the main types of case studies.
Exploratory case studies
Exploratory case studies are typically conducted to develop a theory or framework around an understudied phenomenon. They can also serve as a precursor to a larger-scale research project. Exploratory case studies are useful when a researcher wants to identify the key issues or questions which can spur more extensive study or be used to develop propositions for further research. These case studies are characterized by flexibility, allowing researchers to explore various aspects of a phenomenon as they emerge, which can also form the foundation for subsequent studies.
Descriptive case studies
Descriptive case studies aim to provide a complete and accurate representation of a phenomenon or event within its context. These case studies are often based on an established theoretical framework, which guides how data is collected and analyzed. The researcher is concerned with describing the phenomenon in detail, as it occurs naturally, without trying to influence or manipulate it.
Explanatory case studies
Explanatory case studies are focused on explanation - they seek to clarify how or why certain phenomena occur. Often used in complex, real-life situations, they can be particularly valuable in clarifying causal relationships among concepts and understanding the interplay between different factors within a specific context.

Intrinsic, instrumental, and collective case studies
These three categories of case studies focus on the nature and purpose of the study. An intrinsic case study is conducted when a researcher has an inherent interest in the case itself. Instrumental case studies are employed when the case is used to provide insight into a particular issue or phenomenon. A collective case study, on the other hand, involves studying multiple cases simultaneously to investigate some general phenomena.
Each type of case study serves a different purpose and has its own strengths and challenges. The selection of the type should be guided by the research question and objectives, as well as the context and constraints of the research.
The flexibility, depth, and contextual richness offered by case studies make this approach an excellent research method for various fields of study. They enable researchers to investigate real-world phenomena within their specific contexts, capturing nuances that other research methods might miss. Across numerous fields, case studies provide valuable insights into complex issues.
Critical information systems research
Case studies provide a detailed understanding of the role and impact of information systems in different contexts. They offer a platform to explore how information systems are designed, implemented, and used and how they interact with various social, economic, and political factors. Case studies in this field often focus on examining the intricate relationship between technology, organizational processes, and user behavior, helping to uncover insights that can inform better system design and implementation.
Health research
Health research is another field where case studies are highly valuable. They offer a way to explore patient experiences, healthcare delivery processes, and the impact of various interventions in a real-world context.

Case studies can provide a deep understanding of a patient's journey, giving insights into the intricacies of disease progression, treatment effects, and the psychosocial aspects of health and illness.
Asthma research studies
Specifically within medical research, studies on asthma often employ case studies to explore the individual and environmental factors that influence asthma development, management, and outcomes. A case study can provide rich, detailed data about individual patients' experiences, from the triggers and symptoms they experience to the effectiveness of various management strategies. This can be crucial for developing patient-centered asthma care approaches.
Other fields
Apart from the fields mentioned, case studies are also extensively used in business and management research, education research, and political sciences, among many others. They provide an opportunity to delve into the intricacies of real-world situations, allowing for a comprehensive understanding of various phenomena.
Case studies, with their depth and contextual focus, offer unique insights across these varied fields. They allow researchers to illuminate the complexities of real-life situations, contributing to both theory and practice.
Whatever field you're in, ATLAS.ti puts your data to work for you
Download a free trial of ATLAS.ti to turn your data into insights.
Understanding the key elements of case study design is crucial for conducting rigorous and impactful case study research. A well-structured design guides the researcher through the process, ensuring that the study is methodologically sound and its findings are reliable and valid. The main elements of case study design include the research question , propositions, units of analysis, and the logic linking the data to the propositions.
The research question is the foundation of any research study. A good research question guides the direction of the study and informs the selection of the case, the methods of collecting data, and the analysis techniques. A well-formulated research question in case study research is typically clear, focused, and complex enough to merit further detailed examination of the relevant case(s).
Propositions
Propositions, though not necessary in every case study, provide a direction by stating what we might expect to find in the data collected. They guide how data is collected and analyzed by helping researchers focus on specific aspects of the case. They are particularly important in explanatory case studies, which seek to understand the relationships among concepts within the studied phenomenon.
Units of analysis
The unit of analysis refers to the case, or the main entity or entities that are being analyzed in the study. In case study research, the unit of analysis can be an individual, a group, an organization, a decision, an event, or even a time period. It's crucial to clearly define the unit of analysis, as it shapes the qualitative data analysis process by allowing the researcher to analyze a particular case and synthesize analysis across multiple case studies to draw conclusions.
Argumentation
This refers to the inferential model that allows researchers to draw conclusions from the data. The researcher needs to ensure that there is a clear link between the data, the propositions (if any), and the conclusions drawn. This argumentation is what enables the researcher to make valid and credible inferences about the phenomenon under study.
Understanding and carefully considering these elements in the design phase of a case study can significantly enhance the quality of the research. It can help ensure that the study is methodologically sound and its findings contribute meaningful insights about the case.
Ready to jumpstart your research with ATLAS.ti?
Conceptualize your research project with our intuitive data analysis interface. Download a free trial today.
Conducting a case study involves several steps, from defining the research question and selecting the case to collecting and analyzing data . This section outlines these key stages, providing a practical guide on how to conduct case study research.
Defining the research question
The first step in case study research is defining a clear, focused research question. This question should guide the entire research process, from case selection to analysis. It's crucial to ensure that the research question is suitable for a case study approach. Typically, such questions are exploratory or descriptive in nature and focus on understanding a phenomenon within its real-life context.
Selecting and defining the case
The selection of the case should be based on the research question and the objectives of the study. It involves choosing a unique example or a set of examples that provide rich, in-depth data about the phenomenon under investigation. After selecting the case, it's crucial to define it clearly, setting the boundaries of the case, including the time period and the specific context.
Previous research can help guide the case study design. When considering a case study, an example of a case could be taken from previous case study research and used to define cases in a new research inquiry. Considering recently published examples can help understand how to select and define cases effectively.
Developing a detailed case study protocol
A case study protocol outlines the procedures and general rules to be followed during the case study. This includes the data collection methods to be used, the sources of data, and the procedures for analysis. Having a detailed case study protocol ensures consistency and reliability in the study.
The protocol should also consider how to work with the people involved in the research context to grant the research team access to collecting data. As mentioned in previous sections of this guide, establishing rapport is an essential component of qualitative research as it shapes the overall potential for collecting and analyzing data.
Collecting data
Gathering data in case study research often involves multiple sources of evidence, including documents, archival records, interviews, observations, and physical artifacts. This allows for a comprehensive understanding of the case. The process for gathering data should be systematic and carefully documented to ensure the reliability and validity of the study.
Analyzing and interpreting data
The next step is analyzing the data. This involves organizing the data , categorizing it into themes or patterns , and interpreting these patterns to answer the research question. The analysis might also involve comparing the findings with prior research or theoretical propositions.
Writing the case study report
The final step is writing the case study report . This should provide a detailed description of the case, the data, the analysis process, and the findings. The report should be clear, organized, and carefully written to ensure that the reader can understand the case and the conclusions drawn from it.
Each of these steps is crucial in ensuring that the case study research is rigorous, reliable, and provides valuable insights about the case.
The type, depth, and quality of data in your study can significantly influence the validity and utility of the study. In case study research, data is usually collected from multiple sources to provide a comprehensive and nuanced understanding of the case. This section will outline the various methods of collecting data used in case study research and discuss considerations for ensuring the quality of the data.
Interviews are a common method of gathering data in case study research. They can provide rich, in-depth data about the perspectives, experiences, and interpretations of the individuals involved in the case. Interviews can be structured , semi-structured , or unstructured , depending on the research question and the degree of flexibility needed.
Observations
Observations involve the researcher observing the case in its natural setting, providing first-hand information about the case and its context. Observations can provide data that might not be revealed in interviews or documents, such as non-verbal cues or contextual information.
Documents and artifacts
Documents and archival records provide a valuable source of data in case study research. They can include reports, letters, memos, meeting minutes, email correspondence, and various public and private documents related to the case.

These records can provide historical context, corroborate evidence from other sources, and offer insights into the case that might not be apparent from interviews or observations.
Physical artifacts refer to any physical evidence related to the case, such as tools, products, or physical environments. These artifacts can provide tangible insights into the case, complementing the data gathered from other sources.
Ensuring the quality of data collection
Determining the quality of data in case study research requires careful planning and execution. It's crucial to ensure that the data is reliable, accurate, and relevant to the research question. This involves selecting appropriate methods of collecting data, properly training interviewers or observers, and systematically recording and storing the data. It also includes considering ethical issues related to collecting and handling data, such as obtaining informed consent and ensuring the privacy and confidentiality of the participants.
Data analysis
Analyzing case study research involves making sense of the rich, detailed data to answer the research question. This process can be challenging due to the volume and complexity of case study data. However, a systematic and rigorous approach to analysis can ensure that the findings are credible and meaningful. This section outlines the main steps and considerations in analyzing data in case study research.
Organizing the data
The first step in the analysis is organizing the data. This involves sorting the data into manageable sections, often according to the data source or the theme. This step can also involve transcribing interviews, digitizing physical artifacts, or organizing observational data.
Categorizing and coding the data
Once the data is organized, the next step is to categorize or code the data. This involves identifying common themes, patterns, or concepts in the data and assigning codes to relevant data segments. Coding can be done manually or with the help of software tools, and in either case, qualitative analysis software can greatly facilitate the entire coding process. Coding helps to reduce the data to a set of themes or categories that can be more easily analyzed.
Identifying patterns and themes
After coding the data, the researcher looks for patterns or themes in the coded data. This involves comparing and contrasting the codes and looking for relationships or patterns among them. The identified patterns and themes should help answer the research question.
Interpreting the data
Once patterns and themes have been identified, the next step is to interpret these findings. This involves explaining what the patterns or themes mean in the context of the research question and the case. This interpretation should be grounded in the data, but it can also involve drawing on theoretical concepts or prior research.
Verification of the data
The last step in the analysis is verification. This involves checking the accuracy and consistency of the analysis process and confirming that the findings are supported by the data. This can involve re-checking the original data, checking the consistency of codes, or seeking feedback from research participants or peers.
Like any research method , case study research has its strengths and limitations. Researchers must be aware of these, as they can influence the design, conduct, and interpretation of the study.
Understanding the strengths and limitations of case study research can also guide researchers in deciding whether this approach is suitable for their research question . This section outlines some of the key strengths and limitations of case study research.
Benefits include the following:
- Rich, detailed data: One of the main strengths of case study research is that it can generate rich, detailed data about the case. This can provide a deep understanding of the case and its context, which can be valuable in exploring complex phenomena.
- Flexibility: Case study research is flexible in terms of design , data collection , and analysis . A sufficient degree of flexibility allows the researcher to adapt the study according to the case and the emerging findings.
- Real-world context: Case study research involves studying the case in its real-world context, which can provide valuable insights into the interplay between the case and its context.
- Multiple sources of evidence: Case study research often involves collecting data from multiple sources , which can enhance the robustness and validity of the findings.
On the other hand, researchers should consider the following limitations:
- Generalizability: A common criticism of case study research is that its findings might not be generalizable to other cases due to the specificity and uniqueness of each case.
- Time and resource intensive: Case study research can be time and resource intensive due to the depth of the investigation and the amount of collected data.
- Complexity of analysis: The rich, detailed data generated in case study research can make analyzing the data challenging.
- Subjectivity: Given the nature of case study research, there may be a higher degree of subjectivity in interpreting the data , so researchers need to reflect on this and transparently convey to audiences how the research was conducted.
Being aware of these strengths and limitations can help researchers design and conduct case study research effectively and interpret and report the findings appropriately.

Ready to analyze your data with ATLAS.ti?
See how our intuitive software can draw key insights from your data with a free trial today.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Methodology
- Case Study | Definition, Examples & Methods
Case Study | Definition, Examples & Methods
Published on 5 May 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on 30 January 2023.
A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject, such as a person, group, place, event, organisation, or phenomenon. Case studies are commonly used in social, educational, clinical, and business research.
A case study research design usually involves qualitative methods , but quantitative methods are sometimes also used. Case studies are good for describing , comparing, evaluating, and understanding different aspects of a research problem .
Table of contents
When to do a case study, step 1: select a case, step 2: build a theoretical framework, step 3: collect your data, step 4: describe and analyse the case.
A case study is an appropriate research design when you want to gain concrete, contextual, in-depth knowledge about a specific real-world subject. It allows you to explore the key characteristics, meanings, and implications of the case.
Case studies are often a good choice in a thesis or dissertation . They keep your project focused and manageable when you don’t have the time or resources to do large-scale research.
You might use just one complex case study where you explore a single subject in depth, or conduct multiple case studies to compare and illuminate different aspects of your research problem.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Once you have developed your problem statement and research questions , you should be ready to choose the specific case that you want to focus on. A good case study should have the potential to:
- Provide new or unexpected insights into the subject
- Challenge or complicate existing assumptions and theories
- Propose practical courses of action to resolve a problem
- Open up new directions for future research
Unlike quantitative or experimental research, a strong case study does not require a random or representative sample. In fact, case studies often deliberately focus on unusual, neglected, or outlying cases which may shed new light on the research problem.
If you find yourself aiming to simultaneously investigate and solve an issue, consider conducting action research . As its name suggests, action research conducts research and takes action at the same time, and is highly iterative and flexible.
However, you can also choose a more common or representative case to exemplify a particular category, experience, or phenomenon.
While case studies focus more on concrete details than general theories, they should usually have some connection with theory in the field. This way the case study is not just an isolated description, but is integrated into existing knowledge about the topic. It might aim to:
- Exemplify a theory by showing how it explains the case under investigation
- Expand on a theory by uncovering new concepts and ideas that need to be incorporated
- Challenge a theory by exploring an outlier case that doesn’t fit with established assumptions
To ensure that your analysis of the case has a solid academic grounding, you should conduct a literature review of sources related to the topic and develop a theoretical framework . This means identifying key concepts and theories to guide your analysis and interpretation.
There are many different research methods you can use to collect data on your subject. Case studies tend to focus on qualitative data using methods such as interviews, observations, and analysis of primary and secondary sources (e.g., newspaper articles, photographs, official records). Sometimes a case study will also collect quantitative data .
The aim is to gain as thorough an understanding as possible of the case and its context.
In writing up the case study, you need to bring together all the relevant aspects to give as complete a picture as possible of the subject.
How you report your findings depends on the type of research you are doing. Some case studies are structured like a standard scientific paper or thesis, with separate sections or chapters for the methods , results , and discussion .
Others are written in a more narrative style, aiming to explore the case from various angles and analyse its meanings and implications (for example, by using textual analysis or discourse analysis ).
In all cases, though, make sure to give contextual details about the case, connect it back to the literature and theory, and discuss how it fits into wider patterns or debates.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, January 30). Case Study | Definition, Examples & Methods. Scribbr. Retrieved 14 May 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/research-methods/case-studies/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, correlational research | guide, design & examples, a quick guide to experimental design | 5 steps & examples, descriptive research design | definition, methods & examples.
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Assignments
- Annotated Bibliography
- Analyzing a Scholarly Journal Article
- Group Presentations
- Dealing with Nervousness
- Using Visual Aids
- Grading Someone Else's Paper
- Types of Structured Group Activities
- Group Project Survival Skills
- Leading a Class Discussion
- Multiple Book Review Essay
- Reviewing Collected Works
- Writing a Case Analysis Paper
- Writing a Case Study
- About Informed Consent
- Writing Field Notes
- Writing a Policy Memo
- Writing a Reflective Paper
- Writing a Research Proposal
- Generative AI and Writing
- Acknowledgments
A case study research paper examines a person, place, event, condition, phenomenon, or other type of subject of analysis in order to extrapolate key themes and results that help predict future trends, illuminate previously hidden issues that can be applied to practice, and/or provide a means for understanding an important research problem with greater clarity. A case study research paper usually examines a single subject of analysis, but case study papers can also be designed as a comparative investigation that shows relationships between two or more subjects. The methods used to study a case can rest within a quantitative, qualitative, or mixed-method investigative paradigm.
Case Studies. Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Mills, Albert J. , Gabrielle Durepos, and Eiden Wiebe, editors. Encyclopedia of Case Study Research . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2010 ; “What is a Case Study?” In Swanborn, Peter G. Case Study Research: What, Why and How? London: SAGE, 2010.
How to Approach Writing a Case Study Research Paper
General information about how to choose a topic to investigate can be found under the " Choosing a Research Problem " tab in the Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper writing guide. Review this page because it may help you identify a subject of analysis that can be investigated using a case study design.
However, identifying a case to investigate involves more than choosing the research problem . A case study encompasses a problem contextualized around the application of in-depth analysis, interpretation, and discussion, often resulting in specific recommendations for action or for improving existing conditions. As Seawright and Gerring note, practical considerations such as time and access to information can influence case selection, but these issues should not be the sole factors used in describing the methodological justification for identifying a particular case to study. Given this, selecting a case includes considering the following:
- The case represents an unusual or atypical example of a research problem that requires more in-depth analysis? Cases often represent a topic that rests on the fringes of prior investigations because the case may provide new ways of understanding the research problem. For example, if the research problem is to identify strategies to improve policies that support girl's access to secondary education in predominantly Muslim nations, you could consider using Azerbaijan as a case study rather than selecting a more obvious nation in the Middle East. Doing so may reveal important new insights into recommending how governments in other predominantly Muslim nations can formulate policies that support improved access to education for girls.
- The case provides important insight or illuminate a previously hidden problem? In-depth analysis of a case can be based on the hypothesis that the case study will reveal trends or issues that have not been exposed in prior research or will reveal new and important implications for practice. For example, anecdotal evidence may suggest drug use among homeless veterans is related to their patterns of travel throughout the day. Assuming prior studies have not looked at individual travel choices as a way to study access to illicit drug use, a case study that observes a homeless veteran could reveal how issues of personal mobility choices facilitate regular access to illicit drugs. Note that it is important to conduct a thorough literature review to ensure that your assumption about the need to reveal new insights or previously hidden problems is valid and evidence-based.
- The case challenges and offers a counter-point to prevailing assumptions? Over time, research on any given topic can fall into a trap of developing assumptions based on outdated studies that are still applied to new or changing conditions or the idea that something should simply be accepted as "common sense," even though the issue has not been thoroughly tested in current practice. A case study analysis may offer an opportunity to gather evidence that challenges prevailing assumptions about a research problem and provide a new set of recommendations applied to practice that have not been tested previously. For example, perhaps there has been a long practice among scholars to apply a particular theory in explaining the relationship between two subjects of analysis. Your case could challenge this assumption by applying an innovative theoretical framework [perhaps borrowed from another discipline] to explore whether this approach offers new ways of understanding the research problem. Taking a contrarian stance is one of the most important ways that new knowledge and understanding develops from existing literature.
- The case provides an opportunity to pursue action leading to the resolution of a problem? Another way to think about choosing a case to study is to consider how the results from investigating a particular case may result in findings that reveal ways in which to resolve an existing or emerging problem. For example, studying the case of an unforeseen incident, such as a fatal accident at a railroad crossing, can reveal hidden issues that could be applied to preventative measures that contribute to reducing the chance of accidents in the future. In this example, a case study investigating the accident could lead to a better understanding of where to strategically locate additional signals at other railroad crossings so as to better warn drivers of an approaching train, particularly when visibility is hindered by heavy rain, fog, or at night.
- The case offers a new direction in future research? A case study can be used as a tool for an exploratory investigation that highlights the need for further research about the problem. A case can be used when there are few studies that help predict an outcome or that establish a clear understanding about how best to proceed in addressing a problem. For example, after conducting a thorough literature review [very important!], you discover that little research exists showing the ways in which women contribute to promoting water conservation in rural communities of east central Africa. A case study of how women contribute to saving water in a rural village of Uganda can lay the foundation for understanding the need for more thorough research that documents how women in their roles as cooks and family caregivers think about water as a valuable resource within their community. This example of a case study could also point to the need for scholars to build new theoretical frameworks around the topic [e.g., applying feminist theories of work and family to the issue of water conservation].
Eisenhardt, Kathleen M. “Building Theories from Case Study Research.” Academy of Management Review 14 (October 1989): 532-550; Emmel, Nick. Sampling and Choosing Cases in Qualitative Research: A Realist Approach . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2013; Gerring, John. “What Is a Case Study and What Is It Good for?” American Political Science Review 98 (May 2004): 341-354; Mills, Albert J. , Gabrielle Durepos, and Eiden Wiebe, editors. Encyclopedia of Case Study Research . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2010; Seawright, Jason and John Gerring. "Case Selection Techniques in Case Study Research." Political Research Quarterly 61 (June 2008): 294-308.
Structure and Writing Style
The purpose of a paper in the social sciences designed around a case study is to thoroughly investigate a subject of analysis in order to reveal a new understanding about the research problem and, in so doing, contributing new knowledge to what is already known from previous studies. In applied social sciences disciplines [e.g., education, social work, public administration, etc.], case studies may also be used to reveal best practices, highlight key programs, or investigate interesting aspects of professional work.
In general, the structure of a case study research paper is not all that different from a standard college-level research paper. However, there are subtle differences you should be aware of. Here are the key elements to organizing and writing a case study research paper.
I. Introduction
As with any research paper, your introduction should serve as a roadmap for your readers to ascertain the scope and purpose of your study . The introduction to a case study research paper, however, should not only describe the research problem and its significance, but you should also succinctly describe why the case is being used and how it relates to addressing the problem. The two elements should be linked. With this in mind, a good introduction answers these four questions:
- What is being studied? Describe the research problem and describe the subject of analysis [the case] you have chosen to address the problem. Explain how they are linked and what elements of the case will help to expand knowledge and understanding about the problem.
- Why is this topic important to investigate? Describe the significance of the research problem and state why a case study design and the subject of analysis that the paper is designed around is appropriate in addressing the problem.
- What did we know about this topic before I did this study? Provide background that helps lead the reader into the more in-depth literature review to follow. If applicable, summarize prior case study research applied to the research problem and why it fails to adequately address the problem. Describe why your case will be useful. If no prior case studies have been used to address the research problem, explain why you have selected this subject of analysis.
- How will this study advance new knowledge or new ways of understanding? Explain why your case study will be suitable in helping to expand knowledge and understanding about the research problem.
Each of these questions should be addressed in no more than a few paragraphs. Exceptions to this can be when you are addressing a complex research problem or subject of analysis that requires more in-depth background information.
II. Literature Review
The literature review for a case study research paper is generally structured the same as it is for any college-level research paper. The difference, however, is that the literature review is focused on providing background information and enabling historical interpretation of the subject of analysis in relation to the research problem the case is intended to address . This includes synthesizing studies that help to:
- Place relevant works in the context of their contribution to understanding the case study being investigated . This would involve summarizing studies that have used a similar subject of analysis to investigate the research problem. If there is literature using the same or a very similar case to study, you need to explain why duplicating past research is important [e.g., conditions have changed; prior studies were conducted long ago, etc.].
- Describe the relationship each work has to the others under consideration that informs the reader why this case is applicable . Your literature review should include a description of any works that support using the case to investigate the research problem and the underlying research questions.
- Identify new ways to interpret prior research using the case study . If applicable, review any research that has examined the research problem using a different research design. Explain how your use of a case study design may reveal new knowledge or a new perspective or that can redirect research in an important new direction.
- Resolve conflicts amongst seemingly contradictory previous studies . This refers to synthesizing any literature that points to unresolved issues of concern about the research problem and describing how the subject of analysis that forms the case study can help resolve these existing contradictions.
- Point the way in fulfilling a need for additional research . Your review should examine any literature that lays a foundation for understanding why your case study design and the subject of analysis around which you have designed your study may reveal a new way of approaching the research problem or offer a perspective that points to the need for additional research.
- Expose any gaps that exist in the literature that the case study could help to fill . Summarize any literature that not only shows how your subject of analysis contributes to understanding the research problem, but how your case contributes to a new way of understanding the problem that prior research has failed to do.
- Locate your own research within the context of existing literature [very important!] . Collectively, your literature review should always place your case study within the larger domain of prior research about the problem. The overarching purpose of reviewing pertinent literature in a case study paper is to demonstrate that you have thoroughly identified and synthesized prior studies in relation to explaining the relevance of the case in addressing the research problem.
III. Method
In this section, you explain why you selected a particular case [i.e., subject of analysis] and the strategy you used to identify and ultimately decide that your case was appropriate in addressing the research problem. The way you describe the methods used varies depending on the type of subject of analysis that constitutes your case study.
If your subject of analysis is an incident or event . In the social and behavioral sciences, the event or incident that represents the case to be studied is usually bounded by time and place, with a clear beginning and end and with an identifiable location or position relative to its surroundings. The subject of analysis can be a rare or critical event or it can focus on a typical or regular event. The purpose of studying a rare event is to illuminate new ways of thinking about the broader research problem or to test a hypothesis. Critical incident case studies must describe the method by which you identified the event and explain the process by which you determined the validity of this case to inform broader perspectives about the research problem or to reveal new findings. However, the event does not have to be a rare or uniquely significant to support new thinking about the research problem or to challenge an existing hypothesis. For example, Walo, Bull, and Breen conducted a case study to identify and evaluate the direct and indirect economic benefits and costs of a local sports event in the City of Lismore, New South Wales, Australia. The purpose of their study was to provide new insights from measuring the impact of a typical local sports event that prior studies could not measure well because they focused on large "mega-events." Whether the event is rare or not, the methods section should include an explanation of the following characteristics of the event: a) when did it take place; b) what were the underlying circumstances leading to the event; and, c) what were the consequences of the event in relation to the research problem.
If your subject of analysis is a person. Explain why you selected this particular individual to be studied and describe what experiences they have had that provide an opportunity to advance new understandings about the research problem. Mention any background about this person which might help the reader understand the significance of their experiences that make them worthy of study. This includes describing the relationships this person has had with other people, institutions, and/or events that support using them as the subject for a case study research paper. It is particularly important to differentiate the person as the subject of analysis from others and to succinctly explain how the person relates to examining the research problem [e.g., why is one politician in a particular local election used to show an increase in voter turnout from any other candidate running in the election]. Note that these issues apply to a specific group of people used as a case study unit of analysis [e.g., a classroom of students].
If your subject of analysis is a place. In general, a case study that investigates a place suggests a subject of analysis that is unique or special in some way and that this uniqueness can be used to build new understanding or knowledge about the research problem. A case study of a place must not only describe its various attributes relevant to the research problem [e.g., physical, social, historical, cultural, economic, political], but you must state the method by which you determined that this place will illuminate new understandings about the research problem. It is also important to articulate why a particular place as the case for study is being used if similar places also exist [i.e., if you are studying patterns of homeless encampments of veterans in open spaces, explain why you are studying Echo Park in Los Angeles rather than Griffith Park?]. If applicable, describe what type of human activity involving this place makes it a good choice to study [e.g., prior research suggests Echo Park has more homeless veterans].
If your subject of analysis is a phenomenon. A phenomenon refers to a fact, occurrence, or circumstance that can be studied or observed but with the cause or explanation to be in question. In this sense, a phenomenon that forms your subject of analysis can encompass anything that can be observed or presumed to exist but is not fully understood. In the social and behavioral sciences, the case usually focuses on human interaction within a complex physical, social, economic, cultural, or political system. For example, the phenomenon could be the observation that many vehicles used by ISIS fighters are small trucks with English language advertisements on them. The research problem could be that ISIS fighters are difficult to combat because they are highly mobile. The research questions could be how and by what means are these vehicles used by ISIS being supplied to the militants and how might supply lines to these vehicles be cut off? How might knowing the suppliers of these trucks reveal larger networks of collaborators and financial support? A case study of a phenomenon most often encompasses an in-depth analysis of a cause and effect that is grounded in an interactive relationship between people and their environment in some way.
NOTE: The choice of the case or set of cases to study cannot appear random. Evidence that supports the method by which you identified and chose your subject of analysis should clearly support investigation of the research problem and linked to key findings from your literature review. Be sure to cite any studies that helped you determine that the case you chose was appropriate for examining the problem.
IV. Discussion
The main elements of your discussion section are generally the same as any research paper, but centered around interpreting and drawing conclusions about the key findings from your analysis of the case study. Note that a general social sciences research paper may contain a separate section to report findings. However, in a paper designed around a case study, it is common to combine a description of the results with the discussion about their implications. The objectives of your discussion section should include the following:
Reiterate the Research Problem/State the Major Findings Briefly reiterate the research problem you are investigating and explain why the subject of analysis around which you designed the case study were used. You should then describe the findings revealed from your study of the case using direct, declarative, and succinct proclamation of the study results. Highlight any findings that were unexpected or especially profound.
Explain the Meaning of the Findings and Why They are Important Systematically explain the meaning of your case study findings and why you believe they are important. Begin this part of the section by repeating what you consider to be your most important or surprising finding first, then systematically review each finding. Be sure to thoroughly extrapolate what your analysis of the case can tell the reader about situations or conditions beyond the actual case that was studied while, at the same time, being careful not to misconstrue or conflate a finding that undermines the external validity of your conclusions.
Relate the Findings to Similar Studies No study in the social sciences is so novel or possesses such a restricted focus that it has absolutely no relation to previously published research. The discussion section should relate your case study results to those found in other studies, particularly if questions raised from prior studies served as the motivation for choosing your subject of analysis. This is important because comparing and contrasting the findings of other studies helps support the overall importance of your results and it highlights how and in what ways your case study design and the subject of analysis differs from prior research about the topic.
Consider Alternative Explanations of the Findings Remember that the purpose of social science research is to discover and not to prove. When writing the discussion section, you should carefully consider all possible explanations revealed by the case study results, rather than just those that fit your hypothesis or prior assumptions and biases. Be alert to what the in-depth analysis of the case may reveal about the research problem, including offering a contrarian perspective to what scholars have stated in prior research if that is how the findings can be interpreted from your case.
Acknowledge the Study's Limitations You can state the study's limitations in the conclusion section of your paper but describing the limitations of your subject of analysis in the discussion section provides an opportunity to identify the limitations and explain why they are not significant. This part of the discussion section should also note any unanswered questions or issues your case study could not address. More detailed information about how to document any limitations to your research can be found here .
Suggest Areas for Further Research Although your case study may offer important insights about the research problem, there are likely additional questions related to the problem that remain unanswered or findings that unexpectedly revealed themselves as a result of your in-depth analysis of the case. Be sure that the recommendations for further research are linked to the research problem and that you explain why your recommendations are valid in other contexts and based on the original assumptions of your study.
V. Conclusion
As with any research paper, you should summarize your conclusion in clear, simple language; emphasize how the findings from your case study differs from or supports prior research and why. Do not simply reiterate the discussion section. Provide a synthesis of key findings presented in the paper to show how these converge to address the research problem. If you haven't already done so in the discussion section, be sure to document the limitations of your case study and any need for further research.
The function of your paper's conclusion is to: 1) reiterate the main argument supported by the findings from your case study; 2) state clearly the context, background, and necessity of pursuing the research problem using a case study design in relation to an issue, controversy, or a gap found from reviewing the literature; and, 3) provide a place to persuasively and succinctly restate the significance of your research problem, given that the reader has now been presented with in-depth information about the topic.
Consider the following points to help ensure your conclusion is appropriate:
- If the argument or purpose of your paper is complex, you may need to summarize these points for your reader.
- If prior to your conclusion, you have not yet explained the significance of your findings or if you are proceeding inductively, use the conclusion of your paper to describe your main points and explain their significance.
- Move from a detailed to a general level of consideration of the case study's findings that returns the topic to the context provided by the introduction or within a new context that emerges from your case study findings.
Note that, depending on the discipline you are writing in or the preferences of your professor, the concluding paragraph may contain your final reflections on the evidence presented as it applies to practice or on the essay's central research problem. However, the nature of being introspective about the subject of analysis you have investigated will depend on whether you are explicitly asked to express your observations in this way.
Problems to Avoid
Overgeneralization One of the goals of a case study is to lay a foundation for understanding broader trends and issues applied to similar circumstances. However, be careful when drawing conclusions from your case study. They must be evidence-based and grounded in the results of the study; otherwise, it is merely speculation. Looking at a prior example, it would be incorrect to state that a factor in improving girls access to education in Azerbaijan and the policy implications this may have for improving access in other Muslim nations is due to girls access to social media if there is no documentary evidence from your case study to indicate this. There may be anecdotal evidence that retention rates were better for girls who were engaged with social media, but this observation would only point to the need for further research and would not be a definitive finding if this was not a part of your original research agenda.
Failure to Document Limitations No case is going to reveal all that needs to be understood about a research problem. Therefore, just as you have to clearly state the limitations of a general research study , you must describe the specific limitations inherent in the subject of analysis. For example, the case of studying how women conceptualize the need for water conservation in a village in Uganda could have limited application in other cultural contexts or in areas where fresh water from rivers or lakes is plentiful and, therefore, conservation is understood more in terms of managing access rather than preserving access to a scarce resource.
Failure to Extrapolate All Possible Implications Just as you don't want to over-generalize from your case study findings, you also have to be thorough in the consideration of all possible outcomes or recommendations derived from your findings. If you do not, your reader may question the validity of your analysis, particularly if you failed to document an obvious outcome from your case study research. For example, in the case of studying the accident at the railroad crossing to evaluate where and what types of warning signals should be located, you failed to take into consideration speed limit signage as well as warning signals. When designing your case study, be sure you have thoroughly addressed all aspects of the problem and do not leave gaps in your analysis that leave the reader questioning the results.
Case Studies. Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Gerring, John. Case Study Research: Principles and Practices . New York: Cambridge University Press, 2007; Merriam, Sharan B. Qualitative Research and Case Study Applications in Education . Rev. ed. San Francisco, CA: Jossey-Bass, 1998; Miller, Lisa L. “The Use of Case Studies in Law and Social Science Research.” Annual Review of Law and Social Science 14 (2018): TBD; Mills, Albert J., Gabrielle Durepos, and Eiden Wiebe, editors. Encyclopedia of Case Study Research . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2010; Putney, LeAnn Grogan. "Case Study." In Encyclopedia of Research Design , Neil J. Salkind, editor. (Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2010), pp. 116-120; Simons, Helen. Case Study Research in Practice . London: SAGE Publications, 2009; Kratochwill, Thomas R. and Joel R. Levin, editors. Single-Case Research Design and Analysis: New Development for Psychology and Education . Hilldsale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, 1992; Swanborn, Peter G. Case Study Research: What, Why and How? London : SAGE, 2010; Yin, Robert K. Case Study Research: Design and Methods . 6th edition. Los Angeles, CA, SAGE Publications, 2014; Walo, Maree, Adrian Bull, and Helen Breen. “Achieving Economic Benefits at Local Events: A Case Study of a Local Sports Event.” Festival Management and Event Tourism 4 (1996): 95-106.
Writing Tip
At Least Five Misconceptions about Case Study Research
Social science case studies are often perceived as limited in their ability to create new knowledge because they are not randomly selected and findings cannot be generalized to larger populations. Flyvbjerg examines five misunderstandings about case study research and systematically "corrects" each one. To quote, these are:
Misunderstanding 1 : General, theoretical [context-independent] knowledge is more valuable than concrete, practical [context-dependent] knowledge. Misunderstanding 2 : One cannot generalize on the basis of an individual case; therefore, the case study cannot contribute to scientific development. Misunderstanding 3 : The case study is most useful for generating hypotheses; that is, in the first stage of a total research process, whereas other methods are more suitable for hypotheses testing and theory building. Misunderstanding 4 : The case study contains a bias toward verification, that is, a tendency to confirm the researcher’s preconceived notions. Misunderstanding 5 : It is often difficult to summarize and develop general propositions and theories on the basis of specific case studies [p. 221].
While writing your paper, think introspectively about how you addressed these misconceptions because to do so can help you strengthen the validity and reliability of your research by clarifying issues of case selection, the testing and challenging of existing assumptions, the interpretation of key findings, and the summation of case outcomes. Think of a case study research paper as a complete, in-depth narrative about the specific properties and key characteristics of your subject of analysis applied to the research problem.
Flyvbjerg, Bent. “Five Misunderstandings About Case-Study Research.” Qualitative Inquiry 12 (April 2006): 219-245.
- << Previous: Writing a Case Analysis Paper
- Next: Writing a Field Report >>
- Last Updated: May 7, 2024 9:45 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide/assignments

Research Writing and Analysis
- NVivo Group and Study Sessions
- SPSS This link opens in a new window
- Statistical Analysis Group sessions
- Using Qualtrics
- Dissertation and Data Analysis Group Sessions
- Defense Schedule - Commons Calendar This link opens in a new window
- Research Process Flow Chart
- Research Alignment Chapter 1 This link opens in a new window
- Step 1: Seek Out Evidence
- Step 2: Explain
- Step 3: The Big Picture
- Step 4: Own It
- Step 5: Illustrate
- Annotated Bibliography
- Literature Review This link opens in a new window
- Systematic Reviews & Meta-Analyses
- How to Synthesize and Analyze
- Synthesis and Analysis Practice
- Synthesis and Analysis Group Sessions
- Problem Statement
- Purpose Statement
- Conceptual Framework
- Theoretical Framework
- Quantitative Research Questions
- Qualitative Research Questions
- Trustworthiness of Qualitative Data
- Analysis and Coding Example- Qualitative Data
- Thematic Data Analysis in Qualitative Design
- Dissertation to Journal Article This link opens in a new window
- International Journal of Online Graduate Education (IJOGE) This link opens in a new window
- Journal of Research in Innovative Teaching & Learning (JRIT&L) This link opens in a new window
Writing a Case Study

What is a case study?

A Case study is:
- An in-depth research design that primarily uses a qualitative methodology but sometimes includes quantitative methodology.
- Used to examine an identifiable problem confirmed through research.
- Used to investigate an individual, group of people, organization, or event.
- Used to mostly answer "how" and "why" questions.
What are the different types of case studies?

Note: These are the primary case studies. As you continue to research and learn
about case studies you will begin to find a robust list of different types.
Who are your case study participants?

What is triangulation ?
Validity and credibility are an essential part of the case study. Therefore, the researcher should include triangulation to ensure trustworthiness while accurately reflecting what the researcher seeks to investigate.

How to write a Case Study?
When developing a case study, there are different ways you could present the information, but remember to include the five parts for your case study.

Was this resource helpful?
- << Previous: Thematic Data Analysis in Qualitative Design
- Next: Journal Article Reporting Standards (JARS) >>
- Last Updated: May 16, 2024 8:25 AM
- URL: https://resources.nu.edu/researchtools

How to write a case study — examples, templates, and tools

It’s a marketer’s job to communicate the effectiveness of a product or service to potential and current customers to convince them to buy and keep business moving. One of the best methods for doing this is to share success stories that are relatable to prospects and customers based on their pain points, experiences, and overall needs.
That’s where case studies come in. Case studies are an essential part of a content marketing plan. These in-depth stories of customer experiences are some of the most effective at demonstrating the value of a product or service. Yet many marketers don’t use them, whether because of their regimented formats or the process of customer involvement and approval.
A case study is a powerful tool for showcasing your hard work and the success your customer achieved. But writing a great case study can be difficult if you’ve never done it before or if it’s been a while. This guide will show you how to write an effective case study and provide real-world examples and templates that will keep readers engaged and support your business.
In this article, you’ll learn:
What is a case study?
How to write a case study, case study templates, case study examples, case study tools.
A case study is the detailed story of a customer’s experience with a product or service that demonstrates their success and often includes measurable outcomes. Case studies are used in a range of fields and for various reasons, from business to academic research. They’re especially impactful in marketing as brands work to convince and convert consumers with relatable, real-world stories of actual customer experiences.
The best case studies tell the story of a customer’s success, including the steps they took, the results they achieved, and the support they received from a brand along the way. To write a great case study, you need to:
- Celebrate the customer and make them — not a product or service — the star of the story.
- Craft the story with specific audiences or target segments in mind so that the story of one customer will be viewed as relatable and actionable for another customer.
- Write copy that is easy to read and engaging so that readers will gain the insights and messages intended.
- Follow a standardized format that includes all of the essentials a potential customer would find interesting and useful.
- Support all of the claims for success made in the story with data in the forms of hard numbers and customer statements.
Case studies are a type of review but more in depth, aiming to show — rather than just tell — the positive experiences that customers have with a brand. Notably, 89% of consumers read reviews before deciding to buy, and 79% view case study content as part of their purchasing process. When it comes to B2B sales, 52% of buyers rank case studies as an important part of their evaluation process.
Telling a brand story through the experience of a tried-and-true customer matters. The story is relatable to potential new customers as they imagine themselves in the shoes of the company or individual featured in the case study. Showcasing previous customers can help new ones see themselves engaging with your brand in the ways that are most meaningful to them.
Besides sharing the perspective of another customer, case studies stand out from other content marketing forms because they are based on evidence. Whether pulling from client testimonials or data-driven results, case studies tend to have more impact on new business because the story contains information that is both objective (data) and subjective (customer experience) — and the brand doesn’t sound too self-promotional.

Case studies are unique in that there’s a fairly standardized format for telling a customer’s story. But that doesn’t mean there isn’t room for creativity. It’s all about making sure that teams are clear on the goals for the case study — along with strategies for supporting content and channels — and understanding how the story fits within the framework of the company’s overall marketing goals.
Here are the basic steps to writing a good case study.
1. Identify your goal
Start by defining exactly who your case study will be designed to help. Case studies are about specific instances where a company works with a customer to achieve a goal. Identify which customers are likely to have these goals, as well as other needs the story should cover to appeal to them.
The answer is often found in one of the buyer personas that have been constructed as part of your larger marketing strategy. This can include anything from new leads generated by the marketing team to long-term customers that are being pressed for cross-sell opportunities. In all of these cases, demonstrating value through a relatable customer success story can be part of the solution to conversion.
2. Choose your client or subject
Who you highlight matters. Case studies tie brands together that might otherwise not cross paths. A writer will want to ensure that the highlighted customer aligns with their own company’s brand identity and offerings. Look for a customer with positive name recognition who has had great success with a product or service and is willing to be an advocate.
The client should also match up with the identified target audience. Whichever company or individual is selected should be a reflection of other potential customers who can see themselves in similar circumstances, having the same problems and possible solutions.
Some of the most compelling case studies feature customers who:
- Switch from one product or service to another while naming competitors that missed the mark.
- Experience measurable results that are relatable to others in a specific industry.
- Represent well-known brands and recognizable names that are likely to compel action.
- Advocate for a product or service as a champion and are well-versed in its advantages.
Whoever or whatever customer is selected, marketers must ensure they have the permission of the company involved before getting started. Some brands have strict review and approval procedures for any official marketing or promotional materials that include their name. Acquiring those approvals in advance will prevent any miscommunication or wasted effort if there is an issue with their legal or compliance teams.
3. Conduct research and compile data
Substantiating the claims made in a case study — either by the marketing team or customers themselves — adds validity to the story. To do this, include data and feedback from the client that defines what success looks like. This can be anything from demonstrating return on investment (ROI) to a specific metric the customer was striving to improve. Case studies should prove how an outcome was achieved and show tangible results that indicate to the customer that your solution is the right one.
This step could also include customer interviews. Make sure that the people being interviewed are key stakeholders in the purchase decision or deployment and use of the product or service that is being highlighted. Content writers should work off a set list of questions prepared in advance. It can be helpful to share these with the interviewees beforehand so they have time to consider and craft their responses. One of the best interview tactics to keep in mind is to ask questions where yes and no are not natural answers. This way, your subject will provide more open-ended responses that produce more meaningful content.
4. Choose the right format
There are a number of different ways to format a case study. Depending on what you hope to achieve, one style will be better than another. However, there are some common elements to include, such as:
- An engaging headline
- A subject and customer introduction
- The unique challenge or challenges the customer faced
- The solution the customer used to solve the problem
- The results achieved
- Data and statistics to back up claims of success
- A strong call to action (CTA) to engage with the vendor
It’s also important to note that while case studies are traditionally written as stories, they don’t have to be in a written format. Some companies choose to get more creative with their case studies and produce multimedia content, depending on their audience and objectives. Case study formats can include traditional print stories, interactive web or social content, data-heavy infographics, professionally shot videos, podcasts, and more.
5. Write your case study
We’ll go into more detail later about how exactly to write a case study, including templates and examples. Generally speaking, though, there are a few things to keep in mind when writing your case study.
- Be clear and concise. Readers want to get to the point of the story quickly and easily, and they’ll be looking to see themselves reflected in the story right from the start.
- Provide a big picture. Always make sure to explain who the client is, their goals, and how they achieved success in a short introduction to engage the reader.
- Construct a clear narrative. Stick to the story from the perspective of the customer and what they needed to solve instead of just listing product features or benefits.
- Leverage graphics. Incorporating infographics, charts, and sidebars can be a more engaging and eye-catching way to share key statistics and data in readable ways.
- Offer the right amount of detail. Most case studies are one or two pages with clear sections that a reader can skim to find the information most important to them.
- Include data to support claims. Show real results — both facts and figures and customer quotes — to demonstrate credibility and prove the solution works.
6. Promote your story
Marketers have a number of options for distribution of a freshly minted case study. Many brands choose to publish case studies on their website and post them on social media. This can help support SEO and organic content strategies while also boosting company credibility and trust as visitors see that other businesses have used the product or service.
Marketers are always looking for quality content they can use for lead generation. Consider offering a case study as gated content behind a form on a landing page or as an offer in an email message. One great way to do this is to summarize the content and tease the full story available for download after the user takes an action.
Sales teams can also leverage case studies, so be sure they are aware that the assets exist once they’re published. Especially when it comes to larger B2B sales, companies often ask for examples of similar customer challenges that have been solved.
Now that you’ve learned a bit about case studies and what they should include, you may be wondering how to start creating great customer story content. Here are a couple of templates you can use to structure your case study.
Template 1 — Challenge-solution-result format
- Start with an engaging title. This should be fewer than 70 characters long for SEO best practices. One of the best ways to approach the title is to include the customer’s name and a hint at the challenge they overcame in the end.
- Create an introduction. Lead with an explanation as to who the customer is, the need they had, and the opportunity they found with a specific product or solution. Writers can also suggest the success the customer experienced with the solution they chose.
- Present the challenge. This should be several paragraphs long and explain the problem the customer faced and the issues they were trying to solve. Details should tie into the company’s products and services naturally. This section needs to be the most relatable to the reader so they can picture themselves in a similar situation.
- Share the solution. Explain which product or service offered was the ideal fit for the customer and why. Feel free to delve into their experience setting up, purchasing, and onboarding the solution.
- Explain the results. Demonstrate the impact of the solution they chose by backing up their positive experience with data. Fill in with customer quotes and tangible, measurable results that show the effect of their choice.
- Ask for action. Include a CTA at the end of the case study that invites readers to reach out for more information, try a demo, or learn more — to nurture them further in the marketing pipeline. What you ask of the reader should tie directly into the goals that were established for the case study in the first place.
Template 2 — Data-driven format
- Start with an engaging title. Be sure to include a statistic or data point in the first 70 characters. Again, it’s best to include the customer’s name as part of the title.
- Create an overview. Share the customer’s background and a short version of the challenge they faced. Present the reason a particular product or service was chosen, and feel free to include quotes from the customer about their selection process.
- Present data point 1. Isolate the first metric that the customer used to define success and explain how the product or solution helped to achieve this goal. Provide data points and quotes to substantiate the claim that success was achieved.
- Present data point 2. Isolate the second metric that the customer used to define success and explain what the product or solution did to achieve this goal. Provide data points and quotes to substantiate the claim that success was achieved.
- Present data point 3. Isolate the final metric that the customer used to define success and explain what the product or solution did to achieve this goal. Provide data points and quotes to substantiate the claim that success was achieved.
- Summarize the results. Reiterate the fact that the customer was able to achieve success thanks to a specific product or service. Include quotes and statements that reflect customer satisfaction and suggest they plan to continue using the solution.
- Ask for action. Include a CTA at the end of the case study that asks readers to reach out for more information, try a demo, or learn more — to further nurture them in the marketing pipeline. Again, remember that this is where marketers can look to convert their content into action with the customer.
While templates are helpful, seeing a case study in action can also be a great way to learn. Here are some examples of how Adobe customers have experienced success.
Juniper Networks
One example is the Adobe and Juniper Networks case study , which puts the reader in the customer’s shoes. The beginning of the story quickly orients the reader so that they know exactly who the article is about and what they were trying to achieve. Solutions are outlined in a way that shows Adobe Experience Manager is the best choice and a natural fit for the customer. Along the way, quotes from the client are incorporated to help add validity to the statements. The results in the case study are conveyed with clear evidence of scale and volume using tangible data.

The story of Lenovo’s journey with Adobe is one that spans years of planning, implementation, and rollout. The Lenovo case study does a great job of consolidating all of this into a relatable journey that other enterprise organizations can see themselves taking, despite the project size. This case study also features descriptive headers and compelling visual elements that engage the reader and strengthen the content.
Tata Consulting
When it comes to using data to show customer results, this case study does an excellent job of conveying details and numbers in an easy-to-digest manner. Bullet points at the start break up the content while also helping the reader understand exactly what the case study will be about. Tata Consulting used Adobe to deliver elevated, engaging content experiences for a large telecommunications client of its own — an objective that’s relatable for a lot of companies.
Case studies are a vital tool for any marketing team as they enable you to demonstrate the value of your company’s products and services to others. They help marketers do their job and add credibility to a brand trying to promote its solutions by using the experiences and stories of real customers.
When you’re ready to get started with a case study:
- Think about a few goals you’d like to accomplish with your content.
- Make a list of successful clients that would be strong candidates for a case study.
- Reach out to the client to get their approval and conduct an interview.
- Gather the data to present an engaging and effective customer story.
Adobe can help
There are several Adobe products that can help you craft compelling case studies. Adobe Experience Platform helps you collect data and deliver great customer experiences across every channel. Once you’ve created your case studies, Experience Platform will help you deliver the right information to the right customer at the right time for maximum impact.
To learn more, watch the Adobe Experience Platform story .
Keep in mind that the best case studies are backed by data. That’s where Adobe Real-Time Customer Data Platform and Adobe Analytics come into play. With Real-Time CDP, you can gather the data you need to build a great case study and target specific customers to deliver the content to the right audience at the perfect moment.
Watch the Real-Time CDP overview video to learn more.
Finally, Adobe Analytics turns real-time data into real-time insights. It helps your business collect and synthesize data from multiple platforms to make more informed decisions and create the best case study possible.
Request a demo to learn more about Adobe Analytics.
https://business.adobe.com/blog/perspectives/b2b-ecommerce-10-case-studies-inspire-you
https://business.adobe.com/blog/basics/business-case
https://business.adobe.com/blog/basics/what-is-real-time-analytics

Sales CRM Terms
What is Case Study Analysis? (Explained With Examples)
Oct 11, 2023

Case Study Analysis is a widely used research method that examines in-depth information about a particular individual, group, organization, or event. It is a comprehensive investigative approach that aims to understand the intricacies and complexities of the subject under study. Through the analysis of real-life scenarios and inquiry into various data sources, Case Study Analysis provides valuable insights and knowledge that can be used to inform decision-making and problem-solving strategies.
1°) What is Case Study Analysis?
Case Study Analysis is a research methodology that involves the systematic investigation of a specific case or cases to gain a deep understanding of the subject matter. This analysis encompasses collecting and analyzing various types of data, including qualitative and quantitative information. By examining multiple aspects of the case, such as its context, background, influences, and outcomes, researchers can draw meaningful conclusions and provide valuable insights for various fields of study.
When conducting a Case Study Analysis, researchers typically begin by selecting a case or multiple cases that are relevant to their research question or area of interest. This can involve choosing a specific organization, individual, event, or phenomenon to study. Once the case is selected, researchers gather relevant data through various methods, such as interviews, observations, document analysis, and artifact examination.
The data collected during a Case Study Analysis is then carefully analyzed and interpreted. Researchers use different analytical frameworks and techniques to make sense of the information and identify patterns, themes, and relationships within the data. This process involves coding and categorizing the data, conducting comparative analysis, and drawing conclusions based on the findings.
One of the key strengths of Case Study Analysis is its ability to provide a rich and detailed understanding of a specific case. This method allows researchers to delve deep into the complexities and nuances of the subject matter, uncovering insights that may not be captured through other research methods. By examining the case in its natural context, researchers can gain a holistic perspective and explore the various factors and variables that contribute to the case.
1.1 - Definition of Case Study Analysis
Case Study Analysis can be defined as an in-depth examination and exploration of a particular case or cases to unravel relevant details and complexities associated with the subject being studied. It involves a comprehensive and detailed analysis of various factors and variables that contribute to the case, aiming to answer research questions and uncover insights that can be applied in real-world scenarios.
When conducting a Case Study Analysis, researchers employ a range of research methods and techniques to collect and analyze data. These methods can include interviews, surveys, observations, document analysis, and experiments, among others. By using multiple sources of data, researchers can triangulate their findings and ensure the validity and reliability of their analysis.
Furthermore, Case Study Analysis often involves the use of theoretical frameworks and models to guide the research process. These frameworks provide a structured approach to analyzing the case and help researchers make sense of the data collected. By applying relevant theories and concepts, researchers can gain a deeper understanding of the underlying factors and dynamics at play in the case.
1.2 - Advantages of Case Study Analysis
Case Study Analysis offers numerous advantages that make it a popular research method across different disciplines. One significant advantage is its ability to provide rich and detailed information about a specific case, allowing researchers to gain a holistic understanding of the subject matter. Additionally, Case Study Analysis enables researchers to explore complex issues and phenomena in their natural context, capturing the intricacies and nuances that may not be captured through other research methods.
Moreover, Case Study Analysis allows researchers to investigate rare or unique cases that may not be easily replicated or studied through experimental methods. This method is particularly useful when studying phenomena that are complex, multifaceted, or involve multiple variables. By examining real-world cases, researchers can gain insights that can be applied to similar situations or inform future research and practice.
Furthermore, this research method allows for the analysis of multiple sources of data, such as interviews, observations, documents, and artifacts, which can contribute to a comprehensive and well-rounded examination of the case. Case Study Analysis also facilitates the exploration and identification of patterns, trends, and relationships within the data, generating valuable insights and knowledge for future reference and application.
1.3 - Disadvantages of Case Study Analysis
While Case Study Analysis offers various advantages, it also comes with certain limitations and challenges. One major limitation is the potential for researcher bias, as the interpretation of data and findings can be influenced by preconceived notions and personal perspectives. Researchers must be aware of their own biases and take steps to minimize their impact on the analysis.
Additionally, Case Study Analysis may suffer from limited generalizability, as it focuses on specific cases and contexts, which might not be applicable or representative of broader populations or situations. The findings of a case study may not be easily generalized to other settings or individuals, and caution should be exercised when applying the results to different contexts.
Moreover, Case Study Analysis can require significant time and resources due to its in-depth nature and the need for meticulous data collection and analysis. This can pose challenges for researchers working with limited budgets or tight deadlines. However, the thoroughness and depth of the analysis often outweigh the resource constraints, as the insights gained from a well-conducted case study can be highly valuable.
Finally, ethical considerations also play a crucial role in Case Study Analysis, as researchers must ensure the protection of participant confidentiality and privacy. Researchers must obtain informed consent from participants and take measures to safeguard their identities and personal information. Ethical guidelines and protocols should be followed to ensure the rights and well-being of the individuals involved in the case study.
2°) Examples of Case Study Analysis
Real-world examples of Case Study Analysis demonstrate the method's practical application and showcase its usefulness across various fields. The following examples provide insights into different scenarios where Case Study Analysis has been employed successfully.
2.1 - Example in a Startup Context
In a startup context, a Case Study Analysis might explore the factors that contributed to the success of a particular startup company. It would involve examining the organization's background, strategies, market conditions, and key decision-making processes. This analysis could reveal valuable lessons and insights for aspiring entrepreneurs and those interested in understanding the intricacies of startup success.
2.2 - Example in a Consulting Context
In the consulting industry, Case Study Analysis is often utilized to understand and develop solutions for complex business problems. For instance, a consulting firm might conduct a Case Study Analysis on a company facing challenges in its supply chain management. This analysis would involve identifying the underlying issues, evaluating different options, and proposing recommendations based on the findings. This approach enables consultants to apply their expertise and provide practical solutions to their clients.
2.3 - Example in a Digital Marketing Agency Context
Within a digital marketing agency, Case Study Analysis can be used to examine successful marketing campaigns. By analyzing various factors such as target audience, message effectiveness, channel selection, and campaign metrics, this analysis can provide valuable insights into the strategies and tactics that contribute to successful marketing initiatives. Digital marketers can then apply these insights to optimize future campaigns and drive better results for their clients.
2.4 - Example with Analogies
Case Study Analysis can also be utilized with analogies to investigate specific scenarios and draw parallels to similar situations. For instance, a Case Study Analysis could explore the response of different countries to natural disasters and draw analogies to inform disaster management strategies in other regions. These analogies can help policymakers and researchers develop more effective approaches to mitigate the impact of disasters and protect vulnerable populations.
In conclusion, Case Study Analysis is a powerful research method that provides a comprehensive understanding of a particular individual, group, organization, or event. By analyzing real-life cases and exploring various data sources, researchers can unravel complexities, generate valuable insights, and inform decision-making processes. With its advantages and limitations, Case Study Analysis offers a unique approach to gaining in-depth knowledge and practical application across numerous fields.
About the author

Arnaud Belinga

Close deals x2 faster with
Breakcold sales crm.
SEE PRICING
*No credit card required
Related Articles

What is the 80-20 rule? (Explained With Examples)

What is the ABCD Sales Method? (Explained With Examples)

What is an Accelerated Sales Cycle? (Explained With Examples)

What is Account-Based Marketing (ABM)? (Explained With Examples)

What is an Account Manager? (Explained With Examples)

What is Account Mapping? (Explained With Examples)

What is Account-Based Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is Ad Targeting? (Explained With Examples)

What is the Addressable Market? (Explained With Examples)

What is the Adoption Curve? (Explained With Examples)

What is an AE (Account Executive)? (Explained With Examples)

What is Affiliate Marketing? (Explained With Examples)

What is AI in Sales? (Explained With Examples)

What is an AI-Powered CRM? (Explained With Examples)

What is an Alternative Close? (Explained With Examples)

What is the Annual Contract Value? (ACV - Explained With Examples)

What are Appointments Set? (Explained With Examples)

What is an Assumptive Close? (Explained With Examples)

What is Automated Outreach? (Explained With Examples)

What is Average Revenue Per Account (ARPA)? (Explained With Examples)

What is B2B (Business-to-Business)? (Explained With Examples)

What is B2G (Business-to-Government)? (Explained With Examples)

What is B2P (Business-to-Partner)? (Explained With Examples)

What is BANT (Budget, Authority, Need, Timing)? (Explained With Examples)

What is Behavioral Economics in Sales? (Explained With Examples)

What is Benchmark Data? (Explained With Examples)

What is Benefit Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What are Benefit Statements? (Explained With Examples)

What is Beyond the Obvious? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Bootstrapped Startup? (Explained With Examples)

What is the Bottom of the Funnel (BOFU)? (Explained With Examples)

What is Bounce Rate? (Explained With Examples)

What is Brand Awareness? (Explained With Examples)

What is the Break-Even Point? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Breakup Email? (Explained With Examples)

What is Business Development? (Explained With Examples)

What are Business Insights? (Explained With Examples)

What is Business Process Automation? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Buyer Persona? (Explained With Examples)

What is the Buyer's Journey? (Explained With Examples)

What is the Buying Cycle? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Buying Signal? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Buying Team? (Explained With Examples)

What is a C-Level Executive? (Explained With Examples)

What is Call Logging? (Explained With Examples)

What is Call Recording? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Call-to-Action (CTA)? (Explained With Examples)

What is Challenger Sales? (Explained With Examples)

What is Chasing Lost Deals? (Explained With Examples)

What is Churn Prevention? (Explained With Examples)

What is Churn Rate? (Explained With Examples)

What is Click-Through Rate (CTR)? (Explained With Examples)

What is Client Acquisition? (Explained With Examples)

What is the Closing Ratio? (Explained With Examples)

What is the Ben Franklin Close? (Explained With Examples)

What is Cognitive Bias in Sales? (Explained With Examples)

What is Cognitive Dissonance in Sales? (Explained With Examples)

What is Cold Calling? (Explained With Examples)

What is Cold Outreach? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Competitive Advantage? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Competitive Analysis? (Explained With Examples)

What is Competitive Positioning? (Explained With Examples)

What is Conceptual Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is Consultative Closing? (Explained With Examples)

What is Consultative Negotiation? (Explained With Examples)

What is Consultative Prospecting? (Explained With Examples)

What is Consultative Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is Content Marketing? (Explained With Examples)

What is Content Syndication? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Conversion Funnel? (Explained With Examples)

What is Conversion Optimization? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Conversion Path? (Explained With Examples)

What is Conversion Rate? (Explained With Examples)

What is Cost-Per-Click (CPC)? (Explained With Examples)

What is a CRM (Customer Relationship Management)? (Explained With Examples)

What is Cross-Cultural Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Cross-Sell Ratio? (Explained With Examples)

What is Cross-Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC)? (Explained With Examples)

What is Customer-Centric Marketing? (Explained With Examples)

What is Customer-Centric Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is Customer Journey Mapping? (Explained With Examples)

What is the Customer Journey? (Explained With Examples)

What is the Customer Lifetime Value (CLV)? (Explained With Examples)

What is Customer Profiling? (Explained With Examples)

What is Customer Retention? (Explained With Examples)

What is Dark Social? (Explained With Examples)

What is Data Enrichment? (Explained With Examples)

What is Data Segmentation? (Explained With Examples)

What is Database Marketing? (Explained With Examples)

What are Decision Criteria? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Decision Maker? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Decision-Making Unit (DMU)? (Explained With Examples)

What is Demand Generation? (Explained With Examples)

What is Digital Marketing? (Explained With Examples)

What is Direct Marketing? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Discovery Call? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Discovery Meeting? (Explained With Examples)

What are Discovery Questions? (Explained With Examples)

What is Door-to-Door Sales? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Drip Campaign? (Explained With Examples)

What is Dunning? (Explained With Examples)

What is an Early Adopter? (Explained With Examples)

What is Elevator Pitch? (Explained With Examples)

What is Email Hygiene? (Explained With Examples)

What is Email Marketing? (Explained With Examples)

What is Emotional Intelligence Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is Engagement Marketing? (Explained With Examples)

What is Engagement Rate? (Explained With Examples)

What is Engagement Strategy? (Explained With Examples)

What is Feature-Benefit Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is Field Sales? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Follow-Up? (Explained With Examples)

What is Forecast Accuracy? (Explained With Examples)


What is a Funnel? (Explained With Examples)

What is Gamification in Sales? (Explained With Examples)

What is Gatekeeper Strategy? (Explained With Examples)

What is Gatekeeper? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Go-to Market Strategy? (Explained With Examples)

What is Growth Hacking? (Explained With Examples)

What is Growth Marketing? (Explained With Examples)

What is Guerrilla Marketing? (Explained With Examples)

What is High-Ticket Sales? (Explained With Examples)

What is Holistic Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is Ideal Customer Profile (ICP)? (Explained With Examples)

What is Inbound Lead Generation? (Explained With Examples)

What is an Inbound Lead? (Explained With Examples)

What is Inbound Marketing? (Explained With Examples)

What is Inbound Sales? (Explained With Examples)

What is Influencer Marketing? (Explained With Examples)

What is Inside Sales Representative? (Explained With Examples)

What is Inside Sales? (Explained With Examples)

What is Insight Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Key Account? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Key Performance Indicator (KPI)? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Landing Page? (Explained With Examples)

What is Lead Database? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Lead Enrichment? (Explained With Examples)

What is Lead Generation? (Explained With Examples)

What is Lead Nurturing? (Explained With Examples)

What is Lead Qualification? (Explained With Examples)

What is Lead Scoring? (Explained With Examples)

What are LinkedIn InMails? (Explained With Examples)

What is LinkedIn Sales Navigator? (Explained With Examples)

What is Lost Opportunity? (Explained With Examples)

What is Market Positioning? (Explained With Examples)

What is Market Research? (Explained With Examples)

What is Market Segmentation? (Explained With Examples)

What is MEDDIC? (Explained With Examples)

What is Middle Of The Funnel (MOFU)? (Explained With Examples)

What is Motivational Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is a MQL (Marketing Qualified Lead)? (Explained With Examples)

What is MRR Growth? (Explained With Examples)

What is MRR (Monthly Recurring Revenue)? (Explained With Examples)

What is N.E.A.T. Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is Neil Rackham's Sales Tactics? (Explained With Examples)

What is Networking? (Explained With Examples)

What is NLP Sales Techniques? (Explained With Examples)

What is the Net Promotion Score? (NPS - Explained With Examples)

What is Objection Handling Framework? (Explained With Examples)

What is On-Hold Messaging? (Explained With Examples)

What is Onboarding in Sales? (Explained With Examples)

What is Online Advertising? (Explained With Examples)

What is Outbound Sales? (Explained With Examples)

What is Pain Points Analysis? (Explained With Examples)

What is Permission Marketing? (Explained With Examples)

What is Personality-Based Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is Persuasion Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is Pipeline Management? (Explained With Examples)

What is Pipeline Velocity? (Explained With Examples)

What is Predictive Lead Scoring? (Explained With Examples)

What is Price Negotiation? (Explained With Examples)

What is Price Objection? (Explained With Examples)

What is Price Sensitivity? (Explained With Examples)

What is Problem-Solution Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is Product Knowledge? (Explained With Examples)

What is Product-Led-Growth? (Explained With Examples)

What is Prospecting? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Qualified Lead? (Explained With Examples)

What is Question-Based Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is Referral Marketing? (Explained With Examples)

What is Relationship Building? (Explained With Examples)

What is Revenue Forecast? (Explained With Examples)

What is a ROI? (Explained With Examples)

What is Sales Automation? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Sales Bonus Plan? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Sales Champion? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Sales Collateral? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Sales Commission Structure Plan? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Sales CRM? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Sales Cycle? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Sales Demo? (Explained With Examples)

What is Sales Enablement? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Sales Flywheel? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Sales Funnel? (Explained With Examples)

What are Sales KPIs? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Sales Meetup? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Sales Pipeline? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Sales Pitch? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Sales Playbook? (Explained With Examples)
Try breakcold now, are you ready to accelerate your sales pipeline.
Join over +1000 agencies, startups & consultants closing deals with Breakcold Sales CRM
Get Started for free
Sales CRM Features
Sales CRM Software
Sales Pipeline
Sales Lead Tracking
CRM with social media integrations
Social Selling Software
Contact Management
CRM Unified Email LinkedIn Inbox
Breakcold works for many industries
CRM for Agencies
CRM for Startups
CRM for Consultants
CRM for Small Business
CRM for LinkedIn
CRM for Coaches
Sales CRM & Sales Pipeline Tutorials
The 8 Sales Pipeline Stages
The Best CRMs for Agencies
The Best CRMs for Consultants
The Best LinkedIn CRMs
How to close deals in 2024, not in 2010
CRM automation: from 0 to PRO in 5 minutes
LinkedIn Inbox Management
LinkedIn Account-Based Marketing (2024 Tutorial with video)
Tools & more
Sales Pipeline Templates
Alternatives
Integrations
CRM integration with LinkedIn
© 2024 Breakcold
Privacy Policy
Terms of Service
How to Write a Case Study Analysis
Step-By-Step Instructions
Lucy Lambriex/Getty Images
- Student Resources
- Business Degree Options
- Choosing A Business School
- Business School Admissions
- MBA Programs & Rankings
- Business Careers and Internships
- Homework Help
- Private School
- College Admissions
- College Life
- Graduate School
- Distance Learning
When writing a business case study analysis , you must first have a good understanding of the case study . Before you begin the steps below, read the business case carefully, taking notes all the while. It may be necessary to read the case several times to get all of the details and fully grasp the issues facing the group, company, or industry.
As you are reading, do your best to identify key issues, key players, and the most pertinent facts. After you are comfortable with the information, use the following step-by-step instructions (geared toward a single-company analysis) to write your report. To write about an industry, just adapt the steps listed here to discuss the segment as a whole.
Step 1: Investigate the Company’s History and Growth
A company’s past can greatly affect the present and future state of the organization. To begin, investigate the company’s founding, critical incidents, structure, and growth. Create a timeline of events, issues, and achievements. This timeline will come in handy for the next step.
Step 2: Identify Strengths and Weaknesses
Using the information you gathered in step one, continue by examining and making a list of the value creation functions of the company. For example, the company may be weak in product development but strong in marketing. Make a list of problems that have occurred and note the effects they have had on the company. You should also list areas where the company has excelled. Note the effects of these incidents as well.
You're essentially conducting a partial SWOT analysis to get a better understanding of the company's strengths and weaknesses. A SWOT analysis involves documenting things like internal strengths (S) and weaknesses (W) and external opportunities (O) and threats (T).
Step 3: Examine the External Environment
The third step involves identifying opportunities and threats within the company’s external environment. This is where the second part of the SWOT analysis (the O and the T) comes into play. Special items to note include competition within the industry, bargaining powers, and the threat of substitute products. Some examples of opportunities include expansion into new markets or new technology. Some examples of threats include increasing competition and higher interest rates.
Step 4: Analyze Your Findings
Using the information in steps 2 and 3, create an evaluation for this portion of your case study analysis. Compare the strengths and weaknesses within the company to the external threats and opportunities. Determine if the company is in a strong competitive position, and decide if it can continue at its current pace successfully.
Step 5: Identify Corporate-Level Strategy
To identify a company’s corporate-level strategy, identify and evaluate the company’s mission , goals, and actions toward those goals. Analyze the company’s line of business and its subsidiaries and acquisitions. You also want to debate the pros and cons of the company strategy to determine whether or not a change might benefit the company in the short or long term.
Step 6: Identify Business-Level Strategy
Thus far, your case study analysis has identified the company’s corporate-level strategy. To perform a complete analysis, you will need to identify the company’s business-level strategy. (Note: If it is a single business, without multiple companies under one umbrella, and not an industry-wide review, the corporate strategy and the business-level strategy are the same.) For this part, you should identify and analyze each company’s competitive strategy, marketing strategy, costs, and general focus.
Step 7: Analyze Implementations
This portion requires that you identify and analyze the structure and control systems that the company is using to implement its business strategies. Evaluate organizational change, levels of hierarchy, employee rewards, conflicts, and other issues that are important to the company you are analyzing.
Step 8: Make Recommendations
The final part of your case study analysis should include your recommendations for the company. Every recommendation you make should be based on and supported by the context of your analysis. Never share hunches or make a baseless recommendation.
You also want to make sure that your suggested solutions are actually realistic. If the solutions cannot be implemented due to some sort of restraint, they are not realistic enough to make the final cut.
Finally, consider some of the alternative solutions that you considered and rejected. Write down the reasons why these solutions were rejected.
Step 9: Review
Look over your analysis when you have finished writing. Critique your work to make sure every step has been covered. Look for grammatical errors , poor sentence structure, or other things that can be improved. It should be clear, accurate, and professional.
Business Case Study Analysis Tips
Keep these strategic tips in mind:
- Know the case study backward and forward before you begin your case study analysis.
- Give yourself enough time to write the case study analysis. You don't want to rush through it.
- Be honest in your evaluations. Don't let personal issues and opinions cloud your judgment.
- Be analytical, not descriptive.
- Proofread your work, and even let a test reader give it a once-over for dropped words or typos that you no longer can see.
- How to Write and Format a Business Case Study
- MBA Case Studies From Top Business Schools
- Business Case Competitions: Purpose, Types and Rules
- Components of a Business Plan
- How to Write a Case Brief
- How to Get Good Grades in Business School
- What Is Proposal Writing?
- What to Expect From MBA Classes
- How to Write a 10-Page Research Paper
- How To Write a Top-Scoring ACT Essay for the Enhanced Writing Test
- How to Write a Letter of Recommendation
- How to Write a Descriptive Paragraph
- How to Write a Functional Behavior Analysis
- What You Can Do With an MBA
- How to Write a Business Report for English Learners
- Critical Thinking Definition, Skills, and Examples
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
What Is a Case Study?
Weighing the pros and cons of this method of research
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Cara Lustik is a fact-checker and copywriter.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Cara-Lustik-1000-77abe13cf6c14a34a58c2a0ffb7297da.jpg)
Verywell / Colleen Tighe
- Pros and Cons
What Types of Case Studies Are Out There?
Where do you find data for a case study, how do i write a psychology case study.
A case study is an in-depth study of one person, group, or event. In a case study, nearly every aspect of the subject's life and history is analyzed to seek patterns and causes of behavior. Case studies can be used in many different fields, including psychology, medicine, education, anthropology, political science, and social work.
The point of a case study is to learn as much as possible about an individual or group so that the information can be generalized to many others. Unfortunately, case studies tend to be highly subjective, and it is sometimes difficult to generalize results to a larger population.
While case studies focus on a single individual or group, they follow a format similar to other types of psychology writing. If you are writing a case study, we got you—here are some rules of APA format to reference.
At a Glance
A case study, or an in-depth study of a person, group, or event, can be a useful research tool when used wisely. In many cases, case studies are best used in situations where it would be difficult or impossible for you to conduct an experiment. They are helpful for looking at unique situations and allow researchers to gather a lot of˜ information about a specific individual or group of people. However, it's important to be cautious of any bias we draw from them as they are highly subjective.
What Are the Benefits and Limitations of Case Studies?
A case study can have its strengths and weaknesses. Researchers must consider these pros and cons before deciding if this type of study is appropriate for their needs.
One of the greatest advantages of a case study is that it allows researchers to investigate things that are often difficult or impossible to replicate in a lab. Some other benefits of a case study:
- Allows researchers to capture information on the 'how,' 'what,' and 'why,' of something that's implemented
- Gives researchers the chance to collect information on why one strategy might be chosen over another
- Permits researchers to develop hypotheses that can be explored in experimental research
On the other hand, a case study can have some drawbacks:
- It cannot necessarily be generalized to the larger population
- Cannot demonstrate cause and effect
- It may not be scientifically rigorous
- It can lead to bias
Researchers may choose to perform a case study if they want to explore a unique or recently discovered phenomenon. Through their insights, researchers develop additional ideas and study questions that might be explored in future studies.
It's important to remember that the insights from case studies cannot be used to determine cause-and-effect relationships between variables. However, case studies may be used to develop hypotheses that can then be addressed in experimental research.
Case Study Examples
There have been a number of notable case studies in the history of psychology. Much of Freud's work and theories were developed through individual case studies. Some great examples of case studies in psychology include:
- Anna O : Anna O. was a pseudonym of a woman named Bertha Pappenheim, a patient of a physician named Josef Breuer. While she was never a patient of Freud's, Freud and Breuer discussed her case extensively. The woman was experiencing symptoms of a condition that was then known as hysteria and found that talking about her problems helped relieve her symptoms. Her case played an important part in the development of talk therapy as an approach to mental health treatment.
- Phineas Gage : Phineas Gage was a railroad employee who experienced a terrible accident in which an explosion sent a metal rod through his skull, damaging important portions of his brain. Gage recovered from his accident but was left with serious changes in both personality and behavior.
- Genie : Genie was a young girl subjected to horrific abuse and isolation. The case study of Genie allowed researchers to study whether language learning was possible, even after missing critical periods for language development. Her case also served as an example of how scientific research may interfere with treatment and lead to further abuse of vulnerable individuals.
Such cases demonstrate how case research can be used to study things that researchers could not replicate in experimental settings. In Genie's case, her horrific abuse denied her the opportunity to learn a language at critical points in her development.
This is clearly not something researchers could ethically replicate, but conducting a case study on Genie allowed researchers to study phenomena that are otherwise impossible to reproduce.
There are a few different types of case studies that psychologists and other researchers might use:
- Collective case studies : These involve studying a group of individuals. Researchers might study a group of people in a certain setting or look at an entire community. For example, psychologists might explore how access to resources in a community has affected the collective mental well-being of those who live there.
- Descriptive case studies : These involve starting with a descriptive theory. The subjects are then observed, and the information gathered is compared to the pre-existing theory.
- Explanatory case studies : These are often used to do causal investigations. In other words, researchers are interested in looking at factors that may have caused certain things to occur.
- Exploratory case studies : These are sometimes used as a prelude to further, more in-depth research. This allows researchers to gather more information before developing their research questions and hypotheses .
- Instrumental case studies : These occur when the individual or group allows researchers to understand more than what is initially obvious to observers.
- Intrinsic case studies : This type of case study is when the researcher has a personal interest in the case. Jean Piaget's observations of his own children are good examples of how an intrinsic case study can contribute to the development of a psychological theory.
The three main case study types often used are intrinsic, instrumental, and collective. Intrinsic case studies are useful for learning about unique cases. Instrumental case studies help look at an individual to learn more about a broader issue. A collective case study can be useful for looking at several cases simultaneously.
The type of case study that psychology researchers use depends on the unique characteristics of the situation and the case itself.
There are a number of different sources and methods that researchers can use to gather information about an individual or group. Six major sources that have been identified by researchers are:
- Archival records : Census records, survey records, and name lists are examples of archival records.
- Direct observation : This strategy involves observing the subject, often in a natural setting . While an individual observer is sometimes used, it is more common to utilize a group of observers.
- Documents : Letters, newspaper articles, administrative records, etc., are the types of documents often used as sources.
- Interviews : Interviews are one of the most important methods for gathering information in case studies. An interview can involve structured survey questions or more open-ended questions.
- Participant observation : When the researcher serves as a participant in events and observes the actions and outcomes, it is called participant observation.
- Physical artifacts : Tools, objects, instruments, and other artifacts are often observed during a direct observation of the subject.
If you have been directed to write a case study for a psychology course, be sure to check with your instructor for any specific guidelines you need to follow. If you are writing your case study for a professional publication, check with the publisher for their specific guidelines for submitting a case study.
Here is a general outline of what should be included in a case study.
Section 1: A Case History
This section will have the following structure and content:
Background information : The first section of your paper will present your client's background. Include factors such as age, gender, work, health status, family mental health history, family and social relationships, drug and alcohol history, life difficulties, goals, and coping skills and weaknesses.
Description of the presenting problem : In the next section of your case study, you will describe the problem or symptoms that the client presented with.
Describe any physical, emotional, or sensory symptoms reported by the client. Thoughts, feelings, and perceptions related to the symptoms should also be noted. Any screening or diagnostic assessments that are used should also be described in detail and all scores reported.
Your diagnosis : Provide your diagnosis and give the appropriate Diagnostic and Statistical Manual code. Explain how you reached your diagnosis, how the client's symptoms fit the diagnostic criteria for the disorder(s), or any possible difficulties in reaching a diagnosis.
Section 2: Treatment Plan
This portion of the paper will address the chosen treatment for the condition. This might also include the theoretical basis for the chosen treatment or any other evidence that might exist to support why this approach was chosen.
- Cognitive behavioral approach : Explain how a cognitive behavioral therapist would approach treatment. Offer background information on cognitive behavioral therapy and describe the treatment sessions, client response, and outcome of this type of treatment. Make note of any difficulties or successes encountered by your client during treatment.
- Humanistic approach : Describe a humanistic approach that could be used to treat your client, such as client-centered therapy . Provide information on the type of treatment you chose, the client's reaction to the treatment, and the end result of this approach. Explain why the treatment was successful or unsuccessful.
- Psychoanalytic approach : Describe how a psychoanalytic therapist would view the client's problem. Provide some background on the psychoanalytic approach and cite relevant references. Explain how psychoanalytic therapy would be used to treat the client, how the client would respond to therapy, and the effectiveness of this treatment approach.
- Pharmacological approach : If treatment primarily involves the use of medications, explain which medications were used and why. Provide background on the effectiveness of these medications and how monotherapy may compare with an approach that combines medications with therapy or other treatments.
This section of a case study should also include information about the treatment goals, process, and outcomes.
When you are writing a case study, you should also include a section where you discuss the case study itself, including the strengths and limitiations of the study. You should note how the findings of your case study might support previous research.
In your discussion section, you should also describe some of the implications of your case study. What ideas or findings might require further exploration? How might researchers go about exploring some of these questions in additional studies?
Need More Tips?
Here are a few additional pointers to keep in mind when formatting your case study:
- Never refer to the subject of your case study as "the client." Instead, use their name or a pseudonym.
- Read examples of case studies to gain an idea about the style and format.
- Remember to use APA format when citing references .
Crowe S, Cresswell K, Robertson A, Huby G, Avery A, Sheikh A. The case study approach . BMC Med Res Methodol . 2011;11:100.
Crowe S, Cresswell K, Robertson A, Huby G, Avery A, Sheikh A. The case study approach . BMC Med Res Methodol . 2011 Jun 27;11:100. doi:10.1186/1471-2288-11-100
Gagnon, Yves-Chantal. The Case Study as Research Method: A Practical Handbook . Canada, Chicago Review Press Incorporated DBA Independent Pub Group, 2010.
Yin, Robert K. Case Study Research and Applications: Design and Methods . United States, SAGE Publications, 2017.
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
Business growth
Marketing tips
16 case study examples (+ 3 templates to make your own)
I like to think of case studies as a business's version of a resume. It highlights what the business can do, lends credibility to its offer, and contains only the positive bullet points that paint it in the best light possible.
Imagine if the guy running your favorite taco truck followed you home so that he could "really dig into how that burrito changed your life." I see the value in the practice. People naturally prefer a tried-and-true burrito just as they prefer tried-and-true products or services.
To help you showcase your success and flesh out your burrito questionnaire, I've put together some case study examples and key takeaways.
What is a case study?
A case study is an in-depth analysis of how your business, product, or service has helped past clients. It can be a document, a webpage, or a slide deck that showcases measurable, real-life results.
For example, if you're a SaaS company, you can analyze your customers' results after a few months of using your product to measure its effectiveness. You can then turn this analysis into a case study that further proves to potential customers what your product can do and how it can help them overcome their challenges.
It changes the narrative from "I promise that we can do X and Y for you" to "Here's what we've done for businesses like yours, and we can do it for you, too."
16 case study examples
While most case studies follow the same structure, quite a few try to break the mold and create something unique. Some businesses lean heavily on design and presentation, while others pursue a detailed, stat-oriented approach. Some businesses try to mix both.
There's no set formula to follow, but I've found that the best case studies utilize impactful design to engage readers and leverage statistics and case details to drive the point home. A case study typically highlights the companies, the challenges, the solution, and the results. The examples below will help inspire you to do it, too.
1. .css-yjptlz-Link{all:unset;box-sizing:border-box;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;cursor:pointer;-webkit-transition:all 300ms ease-in-out;transition:all 300ms ease-in-out;outline-offset:1px;-webkit-text-fill-color:currentColor;outline:1px solid transparent;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']{color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']:hover{color:#2b2358;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']:focus{color:#3d4592;outline-color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']{color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']:hover{color:#a8a5a0;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']:focus{color:#fffdf9;outline-color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']{color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']:hover{color:#2b2358;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']:focus{color:#3d4592;outline-color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']{color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']:hover{color:#a8a5a0;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']:focus{color:#fffdf9;outline-color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='inherit']{font-weight:inherit;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='normal']{font-weight:400;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='bold']{font-weight:700;} Volcanica Coffee and AdRoll

People love a good farm-to-table coffee story, and boy am I one of them. But I've shared this case study with you for more reasons than my love of coffee. I enjoyed this study because it was written as though it was a letter.
In this case study, the founder of Volcanica Coffee talks about the journey from founding the company to personally struggling with learning and applying digital marketing to finding and enlisting AdRoll's services.
It felt more authentic, less about AdRoll showcasing their worth and more like a testimonial from a grateful and appreciative client. After the story, the case study wraps up with successes, milestones, and achievements. Note that quite a few percentages are prominently displayed at the top, providing supporting evidence that backs up an inspiring story.
Takeaway: Highlight your goals and measurable results to draw the reader in and provide concise, easily digestible information.
2. .css-yjptlz-Link{all:unset;box-sizing:border-box;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;cursor:pointer;-webkit-transition:all 300ms ease-in-out;transition:all 300ms ease-in-out;outline-offset:1px;-webkit-text-fill-color:currentColor;outline:1px solid transparent;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']{color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']:hover{color:#2b2358;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']:focus{color:#3d4592;outline-color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']{color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']:hover{color:#a8a5a0;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']:focus{color:#fffdf9;outline-color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']{color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']:hover{color:#2b2358;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']:focus{color:#3d4592;outline-color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']{color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']:hover{color:#a8a5a0;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']:focus{color:#fffdf9;outline-color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='inherit']{font-weight:inherit;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='normal']{font-weight:400;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='bold']{font-weight:700;} Taylor Guitars and Airtable

This Airtable case study on Taylor Guitars comes as close as one can to an optimal structure. It features a video that represents the artistic nature of the client, highlighting key achievements and dissecting each element of Airtable's influence.
It also supplements each section with a testimonial or quote from the client, using their insights as a catalyst for the case study's narrative. For example, the case study quotes the social media manager and project manager's insights regarding team-wide communication and access before explaining in greater detail.
Takeaway: Highlight pain points your business solves for its client, and explore that influence in greater detail.
3. .css-yjptlz-Link{all:unset;box-sizing:border-box;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;cursor:pointer;-webkit-transition:all 300ms ease-in-out;transition:all 300ms ease-in-out;outline-offset:1px;-webkit-text-fill-color:currentColor;outline:1px solid transparent;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']{color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']:hover{color:#2b2358;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']:focus{color:#3d4592;outline-color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']{color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']:hover{color:#a8a5a0;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']:focus{color:#fffdf9;outline-color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']{color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']:hover{color:#2b2358;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']:focus{color:#3d4592;outline-color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']{color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']:hover{color:#a8a5a0;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']:focus{color:#fffdf9;outline-color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='inherit']{font-weight:inherit;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='normal']{font-weight:400;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='bold']{font-weight:700;} EndeavourX and Figma

My favorite part of Figma's case study is highlighting why EndeavourX chose its solution. You'll notice an entire section on what Figma does for teams and then specifically for EndeavourX.
It also places a heavy emphasis on numbers and stats. The study, as brief as it is, still manages to pack in a lot of compelling statistics about what's possible with Figma.
Takeaway: Showcase the "how" and "why" of your product's differentiators and how they benefit your customers.
4. .css-yjptlz-Link{all:unset;box-sizing:border-box;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;cursor:pointer;-webkit-transition:all 300ms ease-in-out;transition:all 300ms ease-in-out;outline-offset:1px;-webkit-text-fill-color:currentColor;outline:1px solid transparent;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']{color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']:hover{color:#2b2358;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']:focus{color:#3d4592;outline-color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']{color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']:hover{color:#a8a5a0;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']:focus{color:#fffdf9;outline-color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']{color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']:hover{color:#2b2358;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']:focus{color:#3d4592;outline-color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']{color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']:hover{color:#a8a5a0;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']:focus{color:#fffdf9;outline-color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='inherit']{font-weight:inherit;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='normal']{font-weight:400;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='bold']{font-weight:700;} ActiveCampaign and Zapier

Zapier's case study leans heavily on design, using graphics to present statistics and goals in a manner that not only remains consistent with the branding but also actively pushes it forward, drawing users' eyes to the information most important to them.
The graphics, emphasis on branding elements, and cause/effect style tell the story without requiring long, drawn-out copy that risks boring readers. Instead, the cause and effect are concisely portrayed alongside the client company's information for a brief and easily scannable case study.
Takeaway: Lean on design to call attention to the most important elements of your case study, and make sure it stays consistent with your branding.
5. .css-yjptlz-Link{all:unset;box-sizing:border-box;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;cursor:pointer;-webkit-transition:all 300ms ease-in-out;transition:all 300ms ease-in-out;outline-offset:1px;-webkit-text-fill-color:currentColor;outline:1px solid transparent;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']{color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']:hover{color:#2b2358;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']:focus{color:#3d4592;outline-color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']{color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']:hover{color:#a8a5a0;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']:focus{color:#fffdf9;outline-color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']{color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']:hover{color:#2b2358;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']:focus{color:#3d4592;outline-color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']{color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']:hover{color:#a8a5a0;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']:focus{color:#fffdf9;outline-color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='inherit']{font-weight:inherit;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='normal']{font-weight:400;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='bold']{font-weight:700;} Ironclad and OpenAI
In true OpenAI fashion, this case study is a block of text. There's a distinct lack of imagery, but the study features a narrated video walking readers through the product.
The lack of imagery and color may not be the most inviting, but utilizing video format is commendable. It helps thoroughly communicate how OpenAI supported Ironclad in a way that allows the user to sit back, relax, listen, and be impressed.
Takeaway: Get creative with the media you implement in your case study. Videos can be a very powerful addition when a case study requires more detailed storytelling.
6. .css-yjptlz-Link{all:unset;box-sizing:border-box;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;cursor:pointer;-webkit-transition:all 300ms ease-in-out;transition:all 300ms ease-in-out;outline-offset:1px;-webkit-text-fill-color:currentColor;outline:1px solid transparent;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']{color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']:hover{color:#2b2358;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']:focus{color:#3d4592;outline-color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']{color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']:hover{color:#a8a5a0;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']:focus{color:#fffdf9;outline-color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']{color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']:hover{color:#2b2358;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']:focus{color:#3d4592;outline-color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']{color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']:hover{color:#a8a5a0;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']:focus{color:#fffdf9;outline-color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='inherit']{font-weight:inherit;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='normal']{font-weight:400;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='bold']{font-weight:700;} Shopify and GitHub

GitHub's case study on Shopify is a light read. It addresses client pain points and discusses the different aspects its product considers and improves for clients. It touches on workflow issues, internal systems, automation, and security. It does a great job of representing what one company can do with GitHub.
To drive the point home, the case study features colorful quote callouts from the Shopify team, sharing their insights and perspectives on the partnership, the key issues, and how they were addressed.
Takeaway: Leverage quotes to boost the authoritativeness and trustworthiness of your case study.
7 . .css-yjptlz-Link{all:unset;box-sizing:border-box;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;cursor:pointer;-webkit-transition:all 300ms ease-in-out;transition:all 300ms ease-in-out;outline-offset:1px;-webkit-text-fill-color:currentColor;outline:1px solid transparent;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']{color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']:hover{color:#2b2358;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']:focus{color:#3d4592;outline-color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']{color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']:hover{color:#a8a5a0;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']:focus{color:#fffdf9;outline-color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']{color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']:hover{color:#2b2358;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']:focus{color:#3d4592;outline-color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']{color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']:hover{color:#a8a5a0;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']:focus{color:#fffdf9;outline-color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='inherit']{font-weight:inherit;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='normal']{font-weight:400;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='bold']{font-weight:700;} Audible and Contentful

Contentful's case study on Audible features almost every element a case study should. It includes not one but two videos and clearly outlines the challenge, solution, and outcome before diving deeper into what Contentful did for Audible. The language is simple, and the writing is heavy with quotes and personal insights.
This case study is a uniquely original experience. The fact that the companies in question are perhaps two of the most creative brands out there may be the reason. I expected nothing short of a detailed analysis, a compelling story, and video content.
Takeaway: Inject some brand voice into the case study, and create assets that tell the story for you.
8 . .css-yjptlz-Link{all:unset;box-sizing:border-box;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;cursor:pointer;-webkit-transition:all 300ms ease-in-out;transition:all 300ms ease-in-out;outline-offset:1px;-webkit-text-fill-color:currentColor;outline:1px solid transparent;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']{color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']:hover{color:#2b2358;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']:focus{color:#3d4592;outline-color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']{color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']:hover{color:#a8a5a0;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']:focus{color:#fffdf9;outline-color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']{color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']:hover{color:#2b2358;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']:focus{color:#3d4592;outline-color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']{color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']:hover{color:#a8a5a0;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']:focus{color:#fffdf9;outline-color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='inherit']{font-weight:inherit;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='normal']{font-weight:400;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='bold']{font-weight:700;} Zoom and Asana
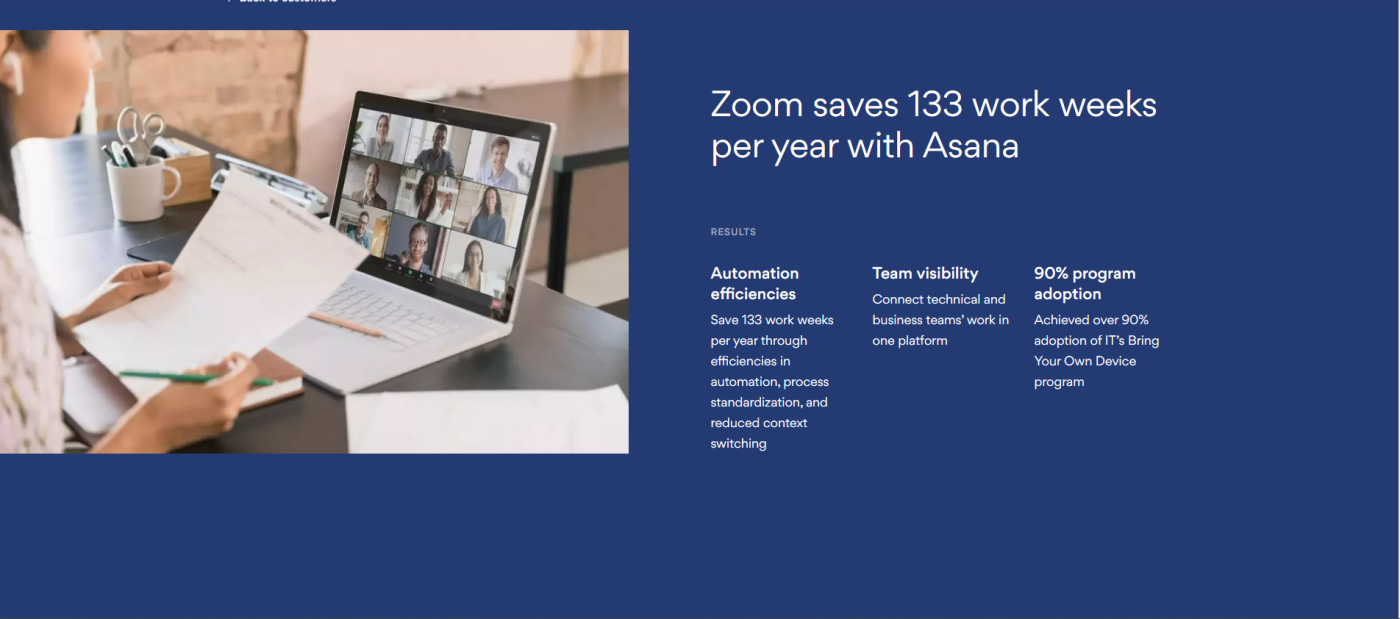
Asana's case study on Zoom is longer than the average piece and features detailed data on Zoom's growth since 2020. Instead of relying on imagery and graphics, it features several quotes and testimonials.
It's designed to be direct, informative, and promotional. At some point, the case study reads more like a feature list. There were a few sections that felt a tad too promotional for my liking, but to each their own burrito.
Takeaway: Maintain a balance between promotional and informative. You want to showcase the high-level goals your product helped achieve without losing the reader.
9 . .css-yjptlz-Link{all:unset;box-sizing:border-box;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;cursor:pointer;-webkit-transition:all 300ms ease-in-out;transition:all 300ms ease-in-out;outline-offset:1px;-webkit-text-fill-color:currentColor;outline:1px solid transparent;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']{color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']:hover{color:#2b2358;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']:focus{color:#3d4592;outline-color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']{color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']:hover{color:#a8a5a0;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']:focus{color:#fffdf9;outline-color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']{color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']:hover{color:#2b2358;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']:focus{color:#3d4592;outline-color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']{color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']:hover{color:#a8a5a0;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']:focus{color:#fffdf9;outline-color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='inherit']{font-weight:inherit;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='normal']{font-weight:400;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='bold']{font-weight:700;} Hickies and Mailchimp

I've always been a fan of Mailchimp's comic-like branding, and this case study does an excellent job of sticking to their tradition of making information easy to understand, casual, and inviting.
It features a short video that briefly covers Hickies as a company and Mailchimp's efforts to serve its needs for customer relationships and education processes. Overall, this case study is a concise overview of the partnership that manages to convey success data and tell a story at the same time. What sets it apart is that it does so in a uniquely colorful and brand-consistent manner.
Takeaway: Be concise to provide as much value in as little text as possible.
10. .css-yjptlz-Link{all:unset;box-sizing:border-box;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;cursor:pointer;-webkit-transition:all 300ms ease-in-out;transition:all 300ms ease-in-out;outline-offset:1px;-webkit-text-fill-color:currentColor;outline:1px solid transparent;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']{color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']:hover{color:#2b2358;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']:focus{color:#3d4592;outline-color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']{color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']:hover{color:#a8a5a0;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']:focus{color:#fffdf9;outline-color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']{color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']:hover{color:#2b2358;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']:focus{color:#3d4592;outline-color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']{color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']:hover{color:#a8a5a0;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']:focus{color:#fffdf9;outline-color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='inherit']{font-weight:inherit;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='normal']{font-weight:400;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='bold']{font-weight:700;} NVIDIA and Workday
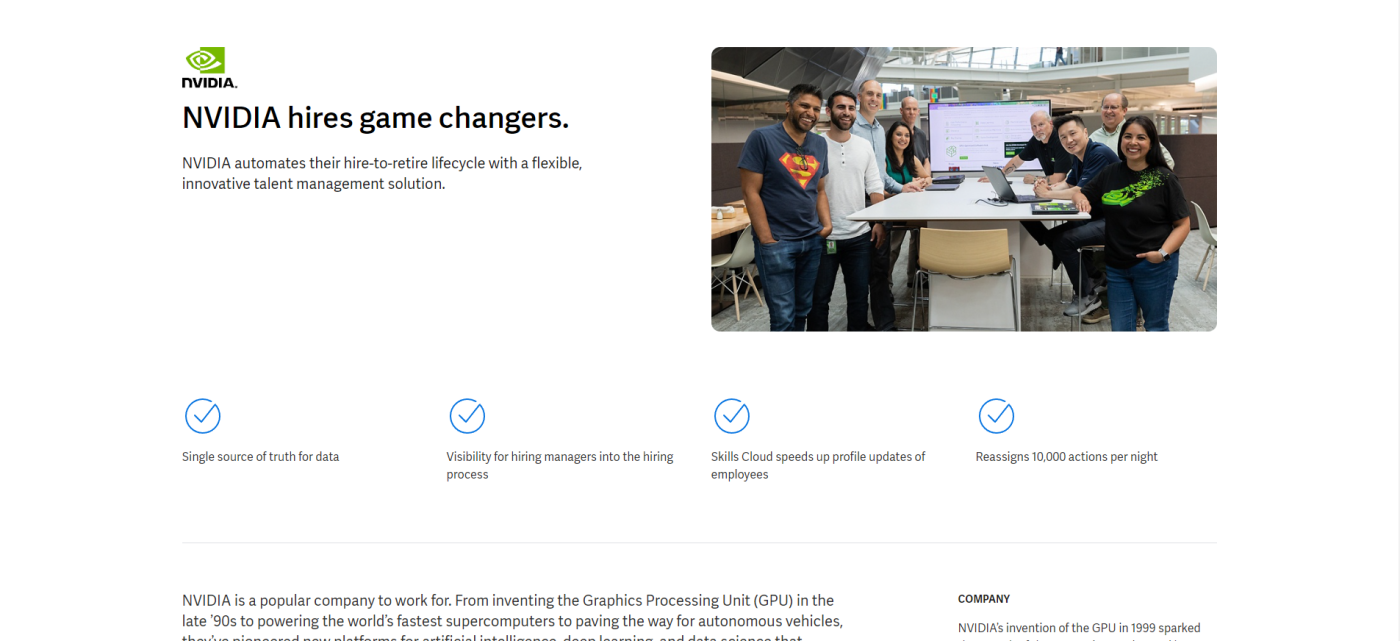
The gaming industry is notoriously difficult to recruit for, as it requires a very specific set of skills and experience. This case study focuses on how Workday was able to help fill that recruitment gap for NVIDIA, one of the biggest names in the gaming world.
Though it doesn't feature videos or graphics, this case study stood out to me in how it structures information like "key products used" to give readers insight into which tools helped achieve these results.
Takeaway: If your company offers multiple products or services, outline exactly which ones were involved in your case study, so readers can assess each tool.
11. .css-yjptlz-Link{all:unset;box-sizing:border-box;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;cursor:pointer;-webkit-transition:all 300ms ease-in-out;transition:all 300ms ease-in-out;outline-offset:1px;-webkit-text-fill-color:currentColor;outline:1px solid transparent;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']{color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']:hover{color:#2b2358;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']:focus{color:#3d4592;outline-color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']{color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']:hover{color:#a8a5a0;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']:focus{color:#fffdf9;outline-color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']{color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']:hover{color:#2b2358;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']:focus{color:#3d4592;outline-color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']{color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']:hover{color:#a8a5a0;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']:focus{color:#fffdf9;outline-color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='inherit']{font-weight:inherit;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='normal']{font-weight:400;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='bold']{font-weight:700;} KFC and Contentful
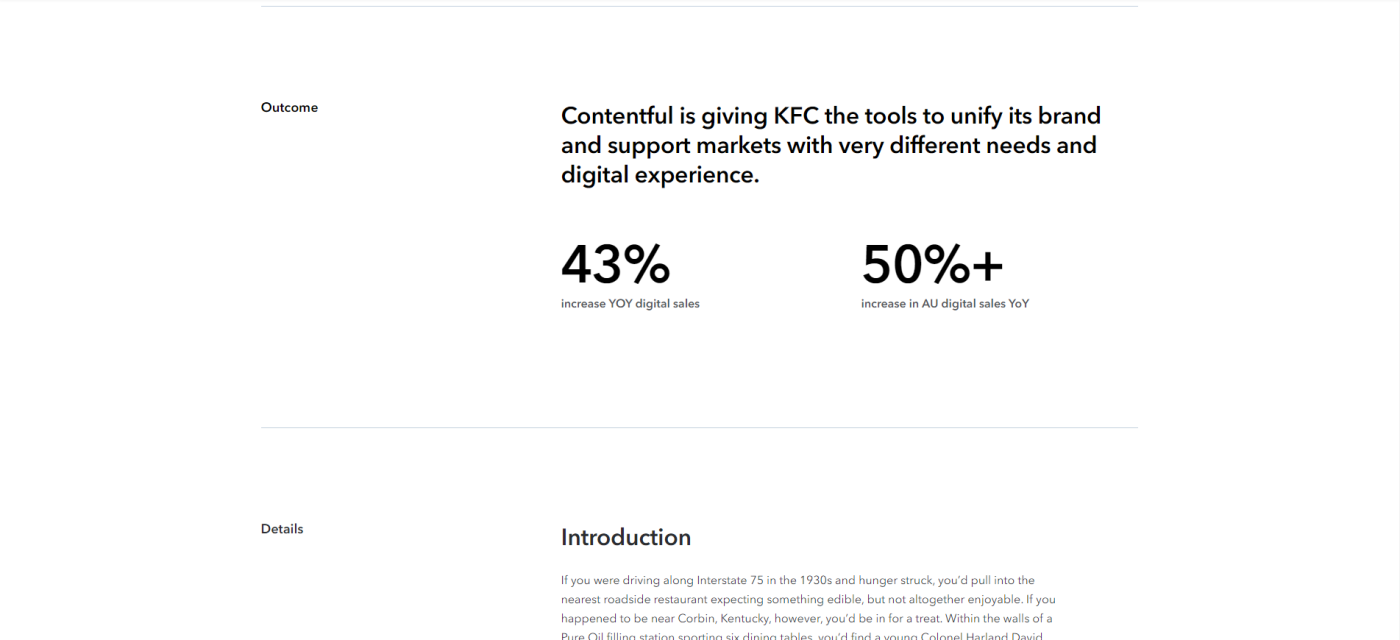
I'm personally not a big KFC fan, but that's only because I refuse to eat out of a bucket. My aversion to the bucket format aside, Contentful follows its consistent case study format in this one, outlining challenges, solutions, and outcomes before diving into the nitty-gritty details of the project.
Say what you will about KFC, but their primary product (chicken) does present a unique opportunity for wordplay like "Continuing to march to the beat of a digital-first drum(stick)" or "Delivering deep-fried goodness to every channel."
Takeaway: Inject humor into your case study if there's room for it and if it fits your brand.
12. .css-yjptlz-Link{all:unset;box-sizing:border-box;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;cursor:pointer;-webkit-transition:all 300ms ease-in-out;transition:all 300ms ease-in-out;outline-offset:1px;-webkit-text-fill-color:currentColor;outline:1px solid transparent;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']{color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']:hover{color:#2b2358;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']:focus{color:#3d4592;outline-color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']{color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']:hover{color:#a8a5a0;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']:focus{color:#fffdf9;outline-color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']{color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']:hover{color:#2b2358;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']:focus{color:#3d4592;outline-color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']{color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']:hover{color:#a8a5a0;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']:focus{color:#fffdf9;outline-color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='inherit']{font-weight:inherit;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='normal']{font-weight:400;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='bold']{font-weight:700;} Intuit and Twilio

Twilio does an excellent job of delivering achievements at the very beginning of the case study and going into detail in this two-minute read. While there aren't many graphics, the way quotes from the Intuit team are implemented adds a certain flair to the study and breaks up the sections nicely.
It's simple, concise, and manages to fit a lot of information in easily digestible sections.
Takeaway: Make sure each section is long enough to inform but brief enough to avoid boring readers. Break down information for each section, and don't go into so much detail that you lose the reader halfway through.
13. .css-yjptlz-Link{all:unset;box-sizing:border-box;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;cursor:pointer;-webkit-transition:all 300ms ease-in-out;transition:all 300ms ease-in-out;outline-offset:1px;-webkit-text-fill-color:currentColor;outline:1px solid transparent;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']{color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']:hover{color:#2b2358;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']:focus{color:#3d4592;outline-color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']{color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']:hover{color:#a8a5a0;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']:focus{color:#fffdf9;outline-color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']{color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']:hover{color:#2b2358;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']:focus{color:#3d4592;outline-color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']{color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']:hover{color:#a8a5a0;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']:focus{color:#fffdf9;outline-color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='inherit']{font-weight:inherit;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='normal']{font-weight:400;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='bold']{font-weight:700;} Spotify and Salesforce

Salesforce created a video that accurately summarizes the key points of the case study. Beyond that, the page itself is very light on content, and sections are as short as one paragraph.
I especially like how information is broken down into "What you need to know," "Why it matters," and "What the difference looks like." I'm not ashamed of being spoon-fed information. When it's structured so well and so simply, it makes for an entertaining read.
14. .css-yjptlz-Link{all:unset;box-sizing:border-box;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;cursor:pointer;-webkit-transition:all 300ms ease-in-out;transition:all 300ms ease-in-out;outline-offset:1px;-webkit-text-fill-color:currentColor;outline:1px solid transparent;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']{color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']:hover{color:#2b2358;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']:focus{color:#3d4592;outline-color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']{color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']:hover{color:#a8a5a0;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']:focus{color:#fffdf9;outline-color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']{color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']:hover{color:#2b2358;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']:focus{color:#3d4592;outline-color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']{color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']:hover{color:#a8a5a0;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']:focus{color:#fffdf9;outline-color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='inherit']{font-weight:inherit;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='normal']{font-weight:400;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='bold']{font-weight:700;} Benchling and Airtable

Benchling is an impressive entity in its own right. Biotech R&D and health care nuances go right over my head. But the research and digging I've been doing in the name of these burritos (case studies) revealed that these products are immensely complex.
And that's precisely why this case study deserves a read—it succeeds at explaining a complex project that readers outside the industry wouldn't know much about.
Takeaway: Simplify complex information, and walk readers through the company's operations and how your business helped streamline them.
15. .css-yjptlz-Link{all:unset;box-sizing:border-box;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;cursor:pointer;-webkit-transition:all 300ms ease-in-out;transition:all 300ms ease-in-out;outline-offset:1px;-webkit-text-fill-color:currentColor;outline:1px solid transparent;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']{color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']:hover{color:#2b2358;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']:focus{color:#3d4592;outline-color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']{color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']:hover{color:#a8a5a0;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']:focus{color:#fffdf9;outline-color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']{color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']:hover{color:#2b2358;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']:focus{color:#3d4592;outline-color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']{color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']:hover{color:#a8a5a0;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']:focus{color:#fffdf9;outline-color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='inherit']{font-weight:inherit;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='normal']{font-weight:400;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='bold']{font-weight:700;} Chipotle and Hubble

The concision of this case study is refreshing. It features two sections—the challenge and the solution—all in 316 words. This goes to show that your case study doesn't necessarily need to be a four-figure investment with video shoots and studio time.
Sometimes, the message is simple and short enough to convey in a handful of paragraphs.
Takeaway: Consider what you should include instead of what you can include. Assess the time, resources, and effort you're able and willing to invest in a case study, and choose which elements you want to include from there.
16. .css-yjptlz-Link{all:unset;box-sizing:border-box;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;cursor:pointer;-webkit-transition:all 300ms ease-in-out;transition:all 300ms ease-in-out;outline-offset:1px;-webkit-text-fill-color:currentColor;outline:1px solid transparent;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']{color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']:hover{color:#2b2358;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='ocean']:focus{color:#3d4592;outline-color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']{color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']:hover{color:#a8a5a0;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='white']:focus{color:#fffdf9;outline-color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']{color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']:hover{color:#2b2358;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='primary']:focus{color:#3d4592;outline-color:#3d4592;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']{color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']:hover{color:#a8a5a0;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-color='secondary']:focus{color:#fffdf9;outline-color:#fffdf9;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='inherit']{font-weight:inherit;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='normal']{font-weight:400;}.css-yjptlz-Link[data-weight='bold']{font-weight:700;} Hudl and Zapier
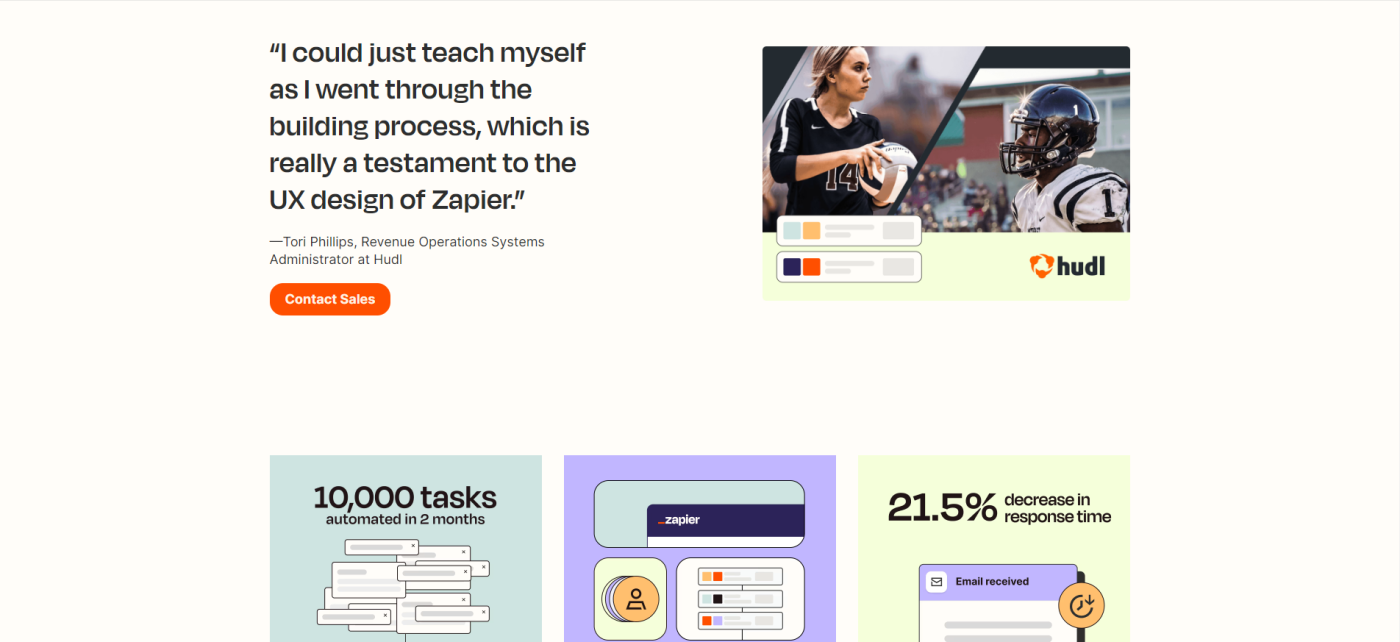
I may be biased, but I'm a big fan of seeing metrics and achievements represented in branded graphics. It can be a jarring experience to navigate a website, then visit a case study page and feel as though you've gone to a completely different website.
The case study is essentially the summary, and the blog article is the detailed analysis that provides context beyond X achievement or Y goal.
Takeaway: Keep your case study concise and informative. Create other resources to provide context under your blog, media or press, and product pages.
3 case study templates
Now that you've had your fill of case studies (if that's possible), I've got just what you need: an infinite number of case studies, which you can create yourself with these case study templates.
Case study template 1

If you've got a quick hit of stats you want to show off, try this template. The opening section gives space for a short summary and three visually appealing stats you can highlight, followed by a headline and body where you can break the case study down more thoroughly. This one's pretty simple, with only sections for solutions and results, but you can easily continue the formatting to add more sections as needed.
Case study template 2

For a case study template with a little more detail, use this one. Opening with a striking cover page for a quick overview, this one goes on to include context, stakeholders, challenges, multiple quote callouts, and quick-hit stats.
Case study template 3

Whether you want a little structural variation or just like a nice dark green, this template has similar components to the last template but is designed to help tell a story. Move from the client overview through a description of your company before getting to the details of how you fixed said company's problems.
Tips for writing a case study
Examples are all well and good, but you don't learn how to make a burrito just by watching tutorials on YouTube without knowing what any of the ingredients are. You could , but it probably wouldn't be all that good.
Have an objective: Define your objective by identifying the challenge, solution, and results. Assess your work with the client and focus on the most prominent wins. You're speaking to multiple businesses and industries through the case study, so make sure you know what you want to say to them.
Focus on persuasive data: Growth percentages and measurable results are your best friends. Extract your most compelling data and highlight it in your case study.
Use eye-grabbing graphics: Branded design goes a long way in accurately representing your brand and retaining readers as they review the study. Leverage unique and eye-catching graphics to keep readers engaged.
Simplify data presentation: Some industries are more complex than others, and sometimes, data can be difficult to understand at a glance. Make sure you present your data in the simplest way possible. Make it concise, informative, and easy to understand.
Use automation to drive results for your case study
A case study example is a source of inspiration you can leverage to determine how to best position your brand's work. Find your unique angle, and refine it over time to help your business stand out. Ask anyone: the best burrito in town doesn't just appear at the number one spot. They find their angle (usually the house sauce) and leverage it to stand out.
Case study FAQ
Got your case study template? Great—it's time to gather the team for an awkward semi-vague data collection task. While you do that, here are some case study quick answers for you to skim through while you contemplate what to call your team meeting.
What is an example of a case study?
An example of a case study is when a software company analyzes its results from a client project and creates a webpage, presentation, or document that focuses on high-level results, challenges, and solutions in an attempt to showcase effectiveness and promote the software.
How do you write a case study?
To write a good case study, you should have an objective, identify persuasive and compelling data, leverage graphics, and simplify data. Case studies typically include an analysis of the challenge, solution, and results of the partnership.
What is the format of a case study?
While case studies don't have a set format, they're often portrayed as reports or essays that inform readers about the partnership and its results.
Related reading:
Get productivity tips delivered straight to your inbox
We’ll email you 1-3 times per week—and never share your information.

Hachem Ramki
Hachem is a writer and digital marketer from Montreal. After graduating with a degree in English, Hachem spent seven years traveling around the world before moving to Canada. When he's not writing, he enjoys Basketball, Dungeons and Dragons, and playing music for friends and family.
- Content marketing
Related articles

12 Linkedin Lead Gen Form examples to inspire your next campaign
12 Linkedin Lead Gen Form examples to...

14 types of email marketing to experiment with
14 types of email marketing to experiment...
8 business anniversary marketing ideas and examples worth celebrating
8 business anniversary marketing ideas and...
A guide to verticalization: What it is, when to try it, and how to get started
A guide to verticalization: What it is, when...
Improve your productivity automatically. Use Zapier to get your apps working together.

Case Study Analysis: Examples + How-to Guide & Writing Tips
A case study analysis is a typical assignment in business management courses. The task aims to show high school and college students how to analyze a current situation, determine what problems exist, and develop the best possible strategy to achieve the desired outcome.
Many students feel anxious about writing case analyses because being told to analyze a case study and provide a solution can seem like a big task. That is especially so when working with real-life scenarios. However, you can rest assured writing a case analysis paper is easier than you think. Just keep reading this article and you will find case study examples for students and the advice provided by Custom-writing experts!
- 👣 Main Steps
- 🕵 Preparing the Case
🔬 Analyzing the Case
- 📑 Format & Structure
- 🙅 Things to Avoid
- 🏁 Conclusion
🔗 References
👣 writing a case study analysis: main steps.
Business management is built on case analysis. Every single economic result shows that the methods and instruments employed were either well-timed and expedient, in the event of success, or not, in case of failure. These two options indicate whether the strategy is efficient (and should be followed) or requires corrections (or complete change). Such an approach to the case study will make your writing piece more proficient and valuable for the reader. The following steps will direct your plan for writing a case study analysis.
Step 1: Preliminary work
- Make notes and highlight the numbers and ideas that could be quoted.
- Single out as many problems as you can, and briefly mark their underlying issues. Then make a note of those responsible. In the report, you will use two to five of the problems, so you will have a selection to choose from.
- Outline a possible solution to each of the problems you found. Course readings and outside research shall be used here. Highlight your best and worst solution for further reference.
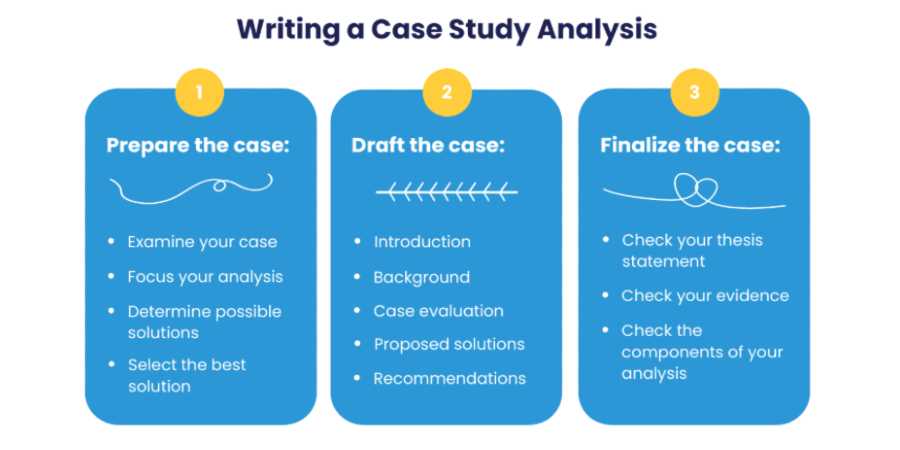
Step 2: Drafting the Case
- Provide a general description of the situation and its history.
- Name all the problems you are going to discuss.
- Specify the theory used for the analysis.
- Present the assumptions that emerged during the analysis, if any.
- Describe the detected problems in more detail.
- Indicate their link to, and effect on, the general situation.
- Explain why the problems emerged and persist.
- List realistic and feasible solutions to the problems you outlined, in the order of importance.
- Specify your predicted results of such changes.
- Support your choice with reliable evidence (i.e., textbook readings, the experience of famous companies, and other external research).
- Define the strategies required to fulfill your proposed solution.
- Indicate the responsible people and the realistic terms for its implementation.
- Recommend the issues for further analysis and supervision.
Step 3: Finalizing the Case
Like any other piece of writing, a case analysis requires post-editing. Carefully read it through, looking for inconsistencies and gaps in meaning. Your purpose is to make it look complete, precise, and convincing.
🕵 Preparing a Case for Analysis
Your professor might give you various case study examples from which to choose, or they may just assign you a particular case study. To conduct a thorough data analysis, you must first read the case study. This might appear to be obvious. However, you’d be surprised at how many students don’t take adequate time to complete this part.
Read the case study very thoroughly, preferably several times. Highlight, underline, flag key information, and make notes to refer to later when you are writing your analysis report.
If you don’t have a complete knowledge of the case study your professor has assigned, you won’t conduct a proper analysis of it. Even if you make use of a business case study template or refer to a sample analysis, it won’t help if you aren’t intimately familiar with your case study.
You will also have to conduct research. When it comes to research, you will need to do the following:
- Gather hard, quantitative data (e.g. 67% of the staff participated in the meeting).
- Design research tools , such as questionnaires and surveys (this will aid in gathering data).
- Determine and suggest the best specific, workable solutions.
It would be best if you also learned how to analyze a case study. Once you have read through the case study, you need to determine the focus of your analysis. You can do this by doing the following:
Compare your chosen solutions to the solutions offered by the experts who analyzed the case study you were given or to online assignments for students who were dealing with a similar task. The experts’ solutions will probably be more advanced than yours simply because these people are more experienced. However, don’t let this discourage you; the whole point of doing this analysis is to learn. Use the opportunity to learn from others’ valuable experience, and your results will be better next time.
If you are still in doubt, the University of South Carolina offers a great guide on forming a case study analysis.
📑 Case Analysis Format & Structure
When you are learning how to write a case study analysis, it is important to get the format of your analysis right. Understanding the case study format is vital for both the professor and the student. The person planning and handing out such an assignment should ensure that the student doesn’t have to use any external sources .
In turn, students have to remember that a well-written case analysis provides all the data, making it unnecessary for the reader to go elsewhere for information.
Regardless of whether you use a case study template, you will need to follow a clear and concise format when writing your analysis report. There are some possible case study frameworks available. Still, a case study should contain eight sections laid out in the following format:
- Describe the purpose of the current case study;
- Provide a summary of the company;
- Briefly introduce the problems and issues found in the case study
- Discuss the theory you will be using in the analysis;
- Present the key points of the study and present any assumptions made during the analysis.
- Present each problem you have singled out;
- Justify your inclusion of each problem by providing supporting evidence from the case study and by discussing relevant theory and what you have learned from your course content;
- Divide the section (and following sections) into subsections, one for each of your selected problems.
- Present a summary of each problem you have identified;
- Present plausible solutions for each of the problems, keeping in mind that each problem will likely have more than one possible solution;
- Provide the pros and cons of each solution in a way that is practical.
- Conclusion . This is a summary of your findings and discussion.
- Decide which solution best fits each of the issues you identified;
- Explain why you chose this solution and how it will effectively solve the problem;
- Be persuasive when you write this section so that you can drive your point home;
- Be sure to bring together theory and what you have learned throughout your course to support your recommendations.
- Provide an explanation of what must be done, who should take action, and when the solution should be carried out;
- Where relevant, you should provide an estimate of the cost in implementing the solution, including both the financial investment and the cost in terms of time.
- References. While you generally do not need to refer to many external sources when writing a case study analysis, you might use a few. When you do, you will need to properly reference these sources, which is most often done in one of the main citation styles, including APA, MLA, or Harvard. There is plenty of help when citing references, and you can follow these APA guidelines , these MLA guidelines , or these Harvard guidelines .
- Appendices. This is the section you include after your case study analysis if you used any original data in the report. These data, presented as charts, graphs, and tables, are included here because to present them in the main body of the analysis would be disruptive to the reader. The University of Southern California provides a great description of appendices and when to make use of them.
When you’ve finished your first draft, be sure to proofread it. Look not only for potential grammar and spelling errors but also for discrepancies or holes in your argument.
You should also know what you need to avoid when writing your analysis.
🙅 Things to Avoid in Case Analysis
Whenever you deal with a case study, remember that there are some pitfalls to avoid! Beware of the following mistakes:
- Excessive use of colloquial language . Even though it is a study of an actual case, it should sound formal.
- Lack of statistical data . Give all the important data, both in percentages and in numbers.
- Excessive details. State only the most significant facts, rather than drowning the reader in every fact you find.
- Inconsistency in the methods you have used . In a case study, theory plays a relatively small part, so you must develop a specific case study research methodology.
- Trivial means of research . It is critical that you design your own case study research method in whatever form best suits your analysis, such as questionnaires and surveys.
It is useful to see a few examples of case analysis papers. After all, a sample case study report can provide you with some context so you can see how to approach each aspect of your paper.
👀 Case Study Examples for Students
It might be easier to understand how a case study analysis works if you have an example to look at. Fortunately, examples of case studies are easy to come by. Take a look at this video for a sample case study analysis for the Coca-Cola Company.
If you want another example, then take a look at the one below!
Business Case Analysis: Example
CRM’s primary focus is customers and customer perception of the brand or the company. The focus may shift depending on customers’ needs. The main points that Center Parcs should consider are an increase in customer satisfaction and its market share. Both of these points will enhance customer perception of the product as a product of value. Increased customer satisfaction will indicate that the company provides quality services, and increased market share can reduce the number of switching (or leaving) customers, thus fostering customer loyalty.
Case Study Topics
- Equifax case study: the importance of cybersecurity measures .
- Study a case illustrating ethical issues of medical research.
- Examine the case describing the complications connected with nursing and residential care.
- Analyze the competitive strategy of Delta Airlines .
- Present a case study of an ethical dilemma showing the conflict between the spirit and the letter of the law.
- Explore the aspects of Starbucks’ marketing strategyin a case study.
- Research a case of community-based clinic organization and development.
- Customer service of United Airlines: a case study .
- Analyze a specific schizophrenia case and provide your recommendations.
- Provide a case study of a patient with hyperglycemia.
- Examine the growth strategy of United Healthcare.
- Present a case study demonstrating ethical issues in business.
- Study a case of the 5% shareholding rule application and its impact on the company.
- Case study of post-traumatic stress disorder .
- Analyze a case examining the issues of cross-cultural management .
- Write a case study exploring the ethical issues the finance manager of a long-term care facility can face and the possible reaction to them.
- Write a case study analyzing the aspects of a new president of a firm election.
- Discuss the specifics of supply chain management in the case of Tehindo company.
- Study a case of a life crisis in a family and the ways to cope with it.
- Case study of Tea Leaves and More: supply chain issues .
- Explore the case of ketogenic diet implementation among sportspeople.
- Analyze the case of Webster Jewelry shop and suggest some changes.
- Examine the unique aspects of Tea and More brand management .
- Adidas case study: an ethical dilemma .
- Research the challenges of Brazos Valley Food Bank and suggest possible solutions.
- Describe the case of dark web monitoring for business.
- Study a case of permissive parenting style .
- Case study of Starbucks employees.
- Analyze a case of workplace discrimination and suggest a strategy to avoid it.
- Examine a case of the consumer decision-making process and define the factors that influence it.
- Present a case study of Netflix illustrating the crucial role of management innovation for company development.
- Discuss a case describing a workplace ethical issue and propose ways to resolve it.
- Case study of the 2008 financial crisis: Graham’s value investing principles in the modern economic climate.
- Write a case study analyzing the harmful consequences of communication issues in a virtual team.
- Analyze a case that highlights the importance of a proper functional currency choice.
- Examine the case of Hitachi Power Systems management.
- Present a case study of medication research in a healthcare facility.
- Study the case of Fiji Water and the challenges the brand faces.
- Research a social problem case and suggest a solution.
- Analyze a case that reveals the connection between alcohol use and borderline personality disorder.
- Transglobal Airline case study: break-even analysis.
- Examine the case of Chiquita Brands International from the moral and business ethics points of view.
- Present a case study of applying for Social Security benefits.
- Study the case of a mass hacker attack on Microsoft clients and suggest possible ways to prevent future attacks.
- Case study of leadership effectiveness .
- Analyze a case presenting a clinical moral dilemma and propose ways to resolve it.
- Describe the case of Cowbell Brewing Company and discuss the strategy that made them successful.
- Write a case study of WeWork company and analyze the strengths and weaknesses of its strategy.
- Case study of medical ethical decision-making.
- Study the case of The Georges hotel and suggest ways to overcome its managerial issues.
🏁 Concluding Remarks
Writing a case study analysis can seem incredibly overwhelming, especially if you have never done it before. Just remember, you can do it provided you follow a plan, keep to the format described here, and study at least one case analysis example.
If you still need help analyzing a case study, your professor is always available to answer your questions and point you in the right direction. You can also get help with any aspect of the project from a custom writing company. Just tackle the research and hand over the writing, write a rough draft and have it checked by a professional, or completely hand the project off to an expert writer.
Regardless of the path you choose, you will turn in something of which you can be proud!
✏️ Case Study Analysis FAQ
Students (especially those who study business) often need to write a case study analysis. It is a kind of report that describes a business case. It includes multiple aspects, for example, the problems that exist, possible solutions, forecasts, etc.
There should be 3 main points covered in a case study analysis:
- The challenge(s) description,
- Possible solutions,
- Outcomes (real and/or foreseen).
Firstly, study some examples available online and in the library. Case study analysis should be a well-structured paper with all the integral components in place. Thus, you might want to use a template and/or an outline to start correctly.
A case study analysis is a popular task for business students. They typically hand it in the format of a paper with several integral components:
- Description of the problem
- Possible ways out
- Results and/or forecasts
Students sometimes tell about the outcome of their research within an oral presentation.
- Case Study: Academia
- Windows of vulnerability: a case study analysis (IEEE)
- A (Very) Brief Refresher on the Case Study Method: SAGE
- The case study approach: Medical Research Methodology
- Strengths and Limitations of Case Studies: Stanford University
- A Sample APA Paper: Radford University
- How to Write a Case Study APA Style: Seattle PI
- The Case Analysis: GVSU
- How to Outline: Purdue OWL
- Incorporating Interview Data: UW-Madison Writing Center
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to LinkedIn
- Share to email

If you are a student, you might need to learn how to write a literature review at some point. But don’t think it’s the same as the book review or other types of academic writing you had to do in high school! A literature review is a close examination of...

So, have you been recently assigned a research project? Or, even worse, is it already due soon? The following research paper hacks will help you do it in record time. In the article, you’ll see ten things you can do to conduct a study and compose a piece like a...

Eating a delicacy, watching a good movie, and proving a point to an audience are the three things that make life seem better. Today, you’ll deal with the last one. You’re about to become a professional at public speaking and attention grabbing. Here, you can learn how to write a...
![analysis of case study Library Research Paper: Example & Writing Guide [2024]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/library-with-books-284x122.jpeg)
What is a library research paper? It’s nothing more than an academic writing project that summarizes the information on a specific topic taken from primary and secondary sources. There are numerous library research examples you can find online. But to complete this assignment, you should simply follow these essential steps:...
![analysis of case study Research Analysis Paper: How to Analyze a Research Article [2024]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/opened-book-library-table-284x153.jpg)
Do you need to write a research analysis paper but have no idea how to do that? Then you’re in the right place. While completing this type of assignment, your key aim is to critically analyze a research article. An article from a serious scientific journal would be a good...
![analysis of case study American Antiquity Style Guide: Citation Rules & Examples [2024]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/education-concept-books-laptop-library-284x153.jpg)
American Antiquity is a professional quarterly journal, which contains various papers on the American archeology. It is incredibly popular among archeologists and the students majoring in history. The organization adopted the rules of The Society for American Archaeology (SAA) citation style. As a result: The journal includes numerous references that...

The most tedious and time-consuming part of any school or college written assignment is the bibliography. Sometimes, it can even be challenging! For example, if you’re confused by the variety of citation styles. This is probably when the most students wonder “Is there someone who could complete my assignment?” That...

An appendix is the part of the paper that contains supplementary material. The information from an appendix in paper writing is not essential. If the readers ignore this part, they still have to get the paper’s idea. Appendices help the readers to understand the research better. They might be useful...

Writing an abstract is one of the skills you need to master to succeed in your studies. An abstract is a summary of an academic text. It contains information about the aims and the outcomes of the research. The primary purpose of an abstract is to help readers understand what...

So you have to write a literature review. You find your favorite novel and then start analyzing it. This is how it’s usually done, right? It’s not. You have to learn the elements of literature review and how to deal with them.
![analysis of case study How to Write a Research Paper Step by Step [2024 Upd.]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/research-charts-284x153.jpg)
Only two words, but you already feel a chill down your spine. A research paper is no joke. It’s a super detailed piece of academic writing where you analyze a chosen issue in-depth. The main aim of such torture is to show how knowledgeable you are and that your opinion...

A research proposal is a text that suggests a topic or research problem, justifies the need to study it, and describes the ways and methods of conducting the study. Scholars usually write proposals to get funding for their research. In their turn, students might have to do that to get...
Quite an impressive piece The steps and procedures outlined here are well detailed and the examples facilitates understanding.
it was very helpful. I have an assessment to write where in I need to mention different effective components that are needed to compile a high quality case study assessment.
It is very important and helpful.
Thanks a lot. A knowledge shared with a structured template. Stay the course
Thanks for this valuable knowledge.I loved this. keep sharing. to know more about click Air India Case Study – Why Air India failed ?
This is going to be a great help in my monthly analysis requirements for my subject. Thank you so much.
Thank you very much for this insightful guidelines… It has really been a great tool for writing my project. Thanks once again.
This article was very helpful, even though I’ll have a clearer mind only after I do the case study myself but I felt very much motivated after reading this, as now I can at least have a plan of what to do compared to the clueless me I was before I read it. I hope if I have any questions or doubts about doing a case study I can clear it out here.
- Discounts and promotions
- Delivery and payment
Cart is empty!
Case study definition

Case study, a term which some of you may know from the "Case Study of Vanitas" anime and manga, is a thorough examination of a particular subject, such as a person, group, location, occasion, establishment, phenomena, etc. They are most frequently utilized in research of business, medicine, education and social behaviour. There are a different types of case studies that researchers might use:
• Collective case studies
• Descriptive case studies
• Explanatory case studies
• Exploratory case studies
• Instrumental case studies
• Intrinsic case studies
Case studies are usually much more sophisticated and professional than regular essays and courseworks, as they require a lot of verified data, are research-oriented and not necessarily designed to be read by the general public.
How to write a case study?
It very much depends on the topic of your case study, as a medical case study and a coffee business case study have completely different sources, outlines, target demographics, etc. But just for this example, let's outline a coffee roaster case study. Firstly, it's likely going to be a problem-solving case study, like most in the business and economics field are. Here are some tips for these types of case studies:
• Your case scenario should be precisely defined in terms of your unique assessment criteria.
• Determine the primary issues by analyzing the scenario. Think about how they connect to the main ideas and theories in your piece.
• Find and investigate any theories or methods that might be relevant to your case.
• Keep your audience in mind. Exactly who are your stakeholder(s)? If writing a case study on coffee roasters, it's probably gonna be suppliers, landlords, investors, customers, etc.
• Indicate the best solution(s) and how they should be implemented. Make sure your suggestions are grounded in pertinent theories and useful resources, as well as being realistic, practical, and attainable.
• Carefully proofread your case study. Keep in mind these four principles when editing: clarity, honesty, reality and relevance.
Are there any online services that could write a case study for me?
Luckily, there are!
We completely understand and have been ourselves in a position, where we couldn't wrap our head around how to write an effective and useful case study, but don't fear - our service is here.
We are a group that specializes in writing all kinds of case studies and other projects for academic customers and business clients who require assistance with its creation. We require our writers to have a degree in your topic and carefully interview them before they can join our team, as we try to ensure quality above all. We cover a great range of topics, offer perfect quality work, always deliver on time and aim to leave our customers completely satisfied with what they ordered.
The ordering process is fully online, and it goes as follows:
• Select the topic and the deadline of your case study.
• Provide us with any details, requirements, statements that should be emphasized or particular parts of the writing process you struggle with.
• Leave the email address, where your completed order will be sent to.
• Select your payment type, sit back and relax!
With lots of experience on the market, professionally degreed writers, online 24/7 customer support and incredibly low prices, you won't find a service offering a better deal than ours.
Artificial intelligence in strategy
Can machines automate strategy development? The short answer is no. However, there are numerous aspects of strategists’ work where AI and advanced analytics tools can already bring enormous value. Yuval Atsmon is a senior partner who leads the new McKinsey Center for Strategy Innovation, which studies ways new technologies can augment the timeless principles of strategy. In this episode of the Inside the Strategy Room podcast, he explains how artificial intelligence is already transforming strategy and what’s on the horizon. This is an edited transcript of the discussion. For more conversations on the strategy issues that matter, follow the series on your preferred podcast platform .
Joanna Pachner: What does artificial intelligence mean in the context of strategy?
Yuval Atsmon: When people talk about artificial intelligence, they include everything to do with analytics, automation, and data analysis. Marvin Minsky, the pioneer of artificial intelligence research in the 1960s, talked about AI as a “suitcase word”—a term into which you can stuff whatever you want—and that still seems to be the case. We are comfortable with that because we think companies should use all the capabilities of more traditional analysis while increasing automation in strategy that can free up management or analyst time and, gradually, introducing tools that can augment human thinking.
Joanna Pachner: AI has been embraced by many business functions, but strategy seems to be largely immune to its charms. Why do you think that is?
Subscribe to the Inside the Strategy Room podcast
Yuval Atsmon: You’re right about the limited adoption. Only 7 percent of respondents to our survey about the use of AI say they use it in strategy or even financial planning, whereas in areas like marketing, supply chain, and service operations, it’s 25 or 30 percent. One reason adoption is lagging is that strategy is one of the most integrative conceptual practices. When executives think about strategy automation, many are looking too far ahead—at AI capabilities that would decide, in place of the business leader, what the right strategy is. They are missing opportunities to use AI in the building blocks of strategy that could significantly improve outcomes.
I like to use the analogy to virtual assistants. Many of us use Alexa or Siri but very few people use these tools to do more than dictate a text message or shut off the lights. We don’t feel comfortable with the technology’s ability to understand the context in more sophisticated applications. AI in strategy is similar: it’s hard for AI to know everything an executive knows, but it can help executives with certain tasks.
When executives think about strategy automation, many are looking too far ahead—at AI deciding the right strategy. They are missing opportunities to use AI in the building blocks of strategy.
Joanna Pachner: What kind of tasks can AI help strategists execute today?
Yuval Atsmon: We talk about six stages of AI development. The earliest is simple analytics, which we refer to as descriptive intelligence. Companies use dashboards for competitive analysis or to study performance in different parts of the business that are automatically updated. Some have interactive capabilities for refinement and testing.
The second level is diagnostic intelligence, which is the ability to look backward at the business and understand root causes and drivers of performance. The level after that is predictive intelligence: being able to anticipate certain scenarios or options and the value of things in the future based on momentum from the past as well as signals picked in the market. Both diagnostics and prediction are areas that AI can greatly improve today. The tools can augment executives’ analysis and become areas where you develop capabilities. For example, on diagnostic intelligence, you can organize your portfolio into segments to understand granularly where performance is coming from and do it in a much more continuous way than analysts could. You can try 20 different ways in an hour versus deploying one hundred analysts to tackle the problem.
Predictive AI is both more difficult and more risky. Executives shouldn’t fully rely on predictive AI, but it provides another systematic viewpoint in the room. Because strategic decisions have significant consequences, a key consideration is to use AI transparently in the sense of understanding why it is making a certain prediction and what extrapolations it is making from which information. You can then assess if you trust the prediction or not. You can even use AI to track the evolution of the assumptions for that prediction.
Those are the levels available today. The next three levels will take time to develop. There are some early examples of AI advising actions for executives’ consideration that would be value-creating based on the analysis. From there, you go to delegating certain decision authority to AI, with constraints and supervision. Eventually, there is the point where fully autonomous AI analyzes and decides with no human interaction.
Because strategic decisions have significant consequences, you need to understand why AI is making a certain prediction and what extrapolations it’s making from which information.
Joanna Pachner: What kind of businesses or industries could gain the greatest benefits from embracing AI at its current level of sophistication?
Yuval Atsmon: Every business probably has some opportunity to use AI more than it does today. The first thing to look at is the availability of data. Do you have performance data that can be organized in a systematic way? Companies that have deep data on their portfolios down to business line, SKU, inventory, and raw ingredients have the biggest opportunities to use machines to gain granular insights that humans could not.
Companies whose strategies rely on a few big decisions with limited data would get less from AI. Likewise, those facing a lot of volatility and vulnerability to external events would benefit less than companies with controlled and systematic portfolios, although they could deploy AI to better predict those external events and identify what they can and cannot control.
Third, the velocity of decisions matters. Most companies develop strategies every three to five years, which then become annual budgets. If you think about strategy in that way, the role of AI is relatively limited other than potentially accelerating analyses that are inputs into the strategy. However, some companies regularly revisit big decisions they made based on assumptions about the world that may have since changed, affecting the projected ROI of initiatives. Such shifts would affect how you deploy talent and executive time, how you spend money and focus sales efforts, and AI can be valuable in guiding that. The value of AI is even bigger when you can make decisions close to the time of deploying resources, because AI can signal that your previous assumptions have changed from when you made your plan.
Joanna Pachner: Can you provide any examples of companies employing AI to address specific strategic challenges?
Yuval Atsmon: Some of the most innovative users of AI, not coincidentally, are AI- and digital-native companies. Some of these companies have seen massive benefits from AI and have increased its usage in other areas of the business. One mobility player adjusts its financial planning based on pricing patterns it observes in the market. Its business has relatively high flexibility to demand but less so to supply, so the company uses AI to continuously signal back when pricing dynamics are trending in a way that would affect profitability or where demand is rising. This allows the company to quickly react to create more capacity because its profitability is highly sensitive to keeping demand and supply in equilibrium.
Joanna Pachner: Given how quickly things change today, doesn’t AI seem to be more a tactical than a strategic tool, providing time-sensitive input on isolated elements of strategy?
Yuval Atsmon: It’s interesting that you make the distinction between strategic and tactical. Of course, every decision can be broken down into smaller ones, and where AI can be affordably used in strategy today is for building blocks of the strategy. It might feel tactical, but it can make a massive difference. One of the world’s leading investment firms, for example, has started to use AI to scan for certain patterns rather than scanning individual companies directly. AI looks for consumer mobile usage that suggests a company’s technology is catching on quickly, giving the firm an opportunity to invest in that company before others do. That created a significant strategic edge for them, even though the tool itself may be relatively tactical.
Joanna Pachner: McKinsey has written a lot about cognitive biases and social dynamics that can skew decision making. Can AI help with these challenges?
Yuval Atsmon: When we talk to executives about using AI in strategy development, the first reaction we get is, “Those are really big decisions; what if AI gets them wrong?” The first answer is that humans also get them wrong—a lot. [Amos] Tversky, [Daniel] Kahneman, and others have proven that some of those errors are systemic, observable, and predictable. The first thing AI can do is spot situations likely to give rise to biases. For example, imagine that AI is listening in on a strategy session where the CEO proposes something and everyone says “Aye” without debate and discussion. AI could inform the room, “We might have a sunflower bias here,” which could trigger more conversation and remind the CEO that it’s in their own interest to encourage some devil’s advocacy.
We also often see confirmation bias, where people focus their analysis on proving the wisdom of what they already want to do, as opposed to looking for a fact-based reality. Just having AI perform a default analysis that doesn’t aim to satisfy the boss is useful, and the team can then try to understand why that is different than the management hypothesis, triggering a much richer debate.
In terms of social dynamics, agency problems can create conflicts of interest. Every business unit [BU] leader thinks that their BU should get the most resources and will deliver the most value, or at least they feel they should advocate for their business. AI provides a neutral way based on systematic data to manage those debates. It’s also useful for executives with decision authority, since we all know that short-term pressures and the need to make the quarterly and annual numbers lead people to make different decisions on the 31st of December than they do on January 1st or October 1st. Like the story of Ulysses and the sirens, you can use AI to remind you that you wanted something different three months earlier. The CEO still decides; AI can just provide that extra nudge.
Joanna Pachner: It’s like you have Spock next to you, who is dispassionate and purely analytical.
Yuval Atsmon: That is not a bad analogy—for Star Trek fans anyway.
Joanna Pachner: Do you have a favorite application of AI in strategy?
Yuval Atsmon: I have worked a lot on resource allocation, and one of the challenges, which we call the hockey stick phenomenon, is that executives are always overly optimistic about what will happen. They know that resource allocation will inevitably be defined by what you believe about the future, not necessarily by past performance. AI can provide an objective prediction of performance starting from a default momentum case: based on everything that happened in the past and some indicators about the future, what is the forecast of performance if we do nothing? This is before we say, “But I will hire these people and develop this new product and improve my marketing”— things that every executive thinks will help them overdeliver relative to the past. The neutral momentum case, which AI can calculate in a cold, Spock-like manner, can change the dynamics of the resource allocation discussion. It’s a form of predictive intelligence accessible today and while it’s not meant to be definitive, it provides a basis for better decisions.
Joanna Pachner: Do you see access to technology talent as one of the obstacles to the adoption of AI in strategy, especially at large companies?
Yuval Atsmon: I would make a distinction. If you mean machine-learning and data science talent or software engineers who build the digital tools, they are definitely not easy to get. However, companies can increasingly use platforms that provide access to AI tools and require less from individual companies. Also, this domain of strategy is exciting—it’s cutting-edge, so it’s probably easier to get technology talent for that than it might be for manufacturing work.
The bigger challenge, ironically, is finding strategists or people with business expertise to contribute to the effort. You will not solve strategy problems with AI without the involvement of people who understand the customer experience and what you are trying to achieve. Those who know best, like senior executives, don’t have time to be product managers for the AI team. An even bigger constraint is that, in some cases, you are asking people to get involved in an initiative that may make their jobs less important. There could be plenty of opportunities for incorporating AI into existing jobs, but it’s something companies need to reflect on. The best approach may be to create a digital factory where a different team tests and builds AI applications, with oversight from senior stakeholders.
The big challenge is finding strategists to contribute to the AI effort. You are asking people to get involved in an initiative that may make their jobs less important.
Joanna Pachner: Do you think this worry about job security and the potential that AI will automate strategy is realistic?
Yuval Atsmon: The question of whether AI will replace human judgment and put humanity out of its job is a big one that I would leave for other experts.
The pertinent question is shorter-term automation. Because of its complexity, strategy would be one of the later domains to be affected by automation, but we are seeing it in many other domains. However, the trend for more than two hundred years has been that automation creates new jobs, although ones requiring different skills. That doesn’t take away the fear some people have of a machine exposing their mistakes or doing their job better than they do it.
Joanna Pachner: We recently published an article about strategic courage in an age of volatility that talked about three types of edge business leaders need to develop. One of them is an edge in insights. Do you think AI has a role to play in furnishing a proprietary insight edge?
Yuval Atsmon: One of the challenges most strategists face is the overwhelming complexity of the world we operate in—the number of unknowns, the information overload. At one level, it may seem that AI will provide another layer of complexity. In reality, it can be a sharp knife that cuts through some of the clutter. The question to ask is, Can AI simplify my life by giving me sharper, more timely insights more easily?
Joanna Pachner: You have been working in strategy for a long time. What sparked your interest in exploring this intersection of strategy and new technology?
Yuval Atsmon: I have always been intrigued by things at the boundaries of what seems possible. Science fiction writer Arthur C. Clarke’s second law is that to discover the limits of the possible, you have to venture a little past them into the impossible, and I find that particularly alluring in this arena.
AI in strategy is in very nascent stages but could be very consequential for companies and for the profession. For a top executive, strategic decisions are the biggest way to influence the business, other than maybe building the top team, and it is amazing how little technology is leveraged in that process today. It’s conceivable that competitive advantage will increasingly rest in having executives who know how to apply AI well. In some domains, like investment, that is already happening, and the difference in returns can be staggering. I find helping companies be part of that evolution very exciting.
Explore a career with us
Related articles.

Strategic courage in an age of volatility

Bias Busters Collection

Published: 5 April 2024 Contributors: Tim Mucci, Cole Stryker
Big data analytics refers to the systematic processing and analysis of large amounts of data and complex data sets, known as big data, to extract valuable insights. Big data analytics allows for the uncovering of trends, patterns and correlations in large amounts of raw data to help analysts make data-informed decisions. This process allows organizations to leverage the exponentially growing data generated from diverse sources, including internet-of-things (IoT) sensors, social media, financial transactions and smart devices to derive actionable intelligence through advanced analytic techniques.
In the early 2000s, advances in software and hardware capabilities made it possible for organizations to collect and handle large amounts of unstructured data. With this explosion of useful data, open-source communities developed big data frameworks to store and process this data. These frameworks are used for distributed storage and processing of large data sets across a network of computers. Along with additional tools and libraries, big data frameworks can be used for:
- Predictive modeling by incorporating artificial intelligence (AI) and statistical algorithms
- Statistical analysis for in-depth data exploration and to uncover hidden patterns
- What-if analysis to simulate different scenarios and explore potential outcomes
- Processing diverse data sets, including structured, semi-structured and unstructured data from various sources.
Four main data analysis methods – descriptive, diagnostic, predictive and prescriptive – are used to uncover insights and patterns within an organization's data. These methods facilitate a deeper understanding of market trends, customer preferences and other important business metrics.
IBM named a Leader in the 2024 Gartner® Magic Quadrant™ for Augmented Data Quality Solutions.
Structured vs unstructured data
What is data management?
The main difference between big data analytics and traditional data analytics is the type of data handled and the tools used to analyze it. Traditional analytics deals with structured data, typically stored in relational databases . This type of database helps ensure that data is well-organized and easy for a computer to understand. Traditional data analytics relies on statistical methods and tools like structured query language (SQL) for querying databases.
Big data analytics involves massive amounts of data in various formats, including structured, semi-structured and unstructured data. The complexity of this data requires more sophisticated analysis techniques. Big data analytics employs advanced techniques like machine learning and data mining to extract information from complex data sets. It often requires distributed processing systems like Hadoop to manage the sheer volume of data.
These are the four methods of data analysis at work within big data:
The "what happened" stage of data analysis. Here, the focus is on summarizing and describing past data to understand its basic characteristics.
The “why it happened” stage. By delving deep into the data, diagnostic analysis identifies the root patterns and trends observed in descriptive analytics.
The “what will happen” stage. It uses historical data, statistical modeling and machine learning to forecast trends.
Describes the “what to do” stage, which goes beyond prediction to provide recommendations for optimizing future actions based on insights derived from all previous.
The following dimensions highlight the core challenges and opportunities inherent in big data analytics.
The sheer volume of data generated today, from social media feeds, IoT devices, transaction records and more, presents a significant challenge. Traditional data storage and processing solutions are often inadequate to handle this scale efficiently. Big data technologies and cloud-based storage solutions enable organizations to store and manage these vast data sets cost-effectively, protecting valuable data from being discarded due to storage limitations.
Data is being produced at unprecedented speeds, from real-time social media updates to high-frequency stock trading records. The velocity at which data flows into organizations requires robust processing capabilities to capture, process and deliver accurate analysis in near real-time. Stream processing frameworks and in-memory data processing are designed to handle these rapid data streams and balance supply with demand.
Today's data comes in many formats, from structured to numeric data in traditional databases to unstructured text, video and images from diverse sources like social media and video surveillance. This variety demans flexible data management systems to handle and integrate disparate data types for comprehensive analysis. NoSQL databases , data lakes and schema -on-read technologies provide the necessary flexibility to accommodate the diverse nature of big data.
Data reliability and accuracy are critical, as decisions based on inaccurate or incomplete data can lead to negative outcomes. Veracity refers to the data's trustworthiness, encompassing data quality, noise and anomaly detection issues. Techniques and tools for data cleaning, validation and verification are integral to ensuring the integrity of big data, enabling organizations to make better decisions based on reliable information.
Big data analytics aims to extract actionable insights that offer tangible value. This involves turning vast data sets into meaningful information that can inform strategic decisions, uncover new opportunities and drive innovation. Advanced analytics, machine learning and AI are key to unlocking the value contained within big data, transforming raw data into strategic assets.
Data professionals, analysts, scientists and statisticians prepare and process data in a data lakehouse, which combines the performance of a data lakehouse with the flexibility of a data lake to clean data and ensure its quality. The process of turning raw data into valuable insights encompasses several key stages:
- Collect data: The first step involves gathering data, which can be a mix of structured and unstructured forms from myriad sources like cloud, mobile applications and IoT sensors. This step is where organizations adapt their data collection strategies and integrate data from varied sources into central repositories like a data lake, which can automatically assign metadata for better manageability and accessibility.
- Process data: After being collected, data must be systematically organized, extracted, transformed and then loaded into a storage system to ensure accurate analytical outcomes. Processing involves converting raw data into a format that is usable for analysis, which might involve aggregating data from different sources, converting data types or organizing data into structure formats. Given the exponential growth of available data, this stage can be challenging. Processing strategies may vary between batch processing, which handles large data volumes over extended periods and stream processing, which deals with smaller real-time data batches.
- Clean data: Regardless of size, data must be cleaned to ensure quality and relevance. Cleaning data involves formatting it correctly, removing duplicates and eliminating irrelevant entries. Clean data prevents the corruption of output and safeguard’s reliability and accuracy.
- Analyze data: Advanced analytics, such as data mining, predictive analytics, machine learning and deep learning, are employed to sift through the processed and cleaned data. These methods allow users to discover patterns, relationships and trends within the data, providing a solid foundation for informed decision-making.
Under the Analyze umbrella, there are potentially many technologies at work, including data mining, which is used to identify patterns and relationships within large data sets; predictive analytics, which forecasts future trends and opportunities; and deep learning , which mimics human learning patterns to uncover more abstract ideas.
Deep learning uses an artificial neural network with multiple layers to model complex patterns in data. Unlike traditional machine learning algorithms, deep learning learns from images, sound and text without manual help. For big data analytics, this powerful capability means the volume and complexity of data is not an issue.
Natural language processing (NLP) models allow machines to understand, interpret and generate human language. Within big data analytics, NLP extracts insights from massive unstructured text data generated across an organization and beyond.
Structured Data
Structured data refers to highly organized information that is easily searchable and typically stored in relational databases or spreadsheets. It adheres to a rigid schema, meaning each data element is clearly defined and accessible in a fixed field within a record or file. Examples of structured data include:
- Customer names and addresses in a customer relationship management (CRM) system
- Transactional data in financial records, such as sales figures and account balances
- Employee data in human resources databases, including job titles and salaries
Structured data's main advantage is its simplicity for entry, search and analysis, often using straightforward database queries like SQL. However, the rapidly expanding universe of big data means that structured data represents a relatively small portion of the total data available to organizations.
Unstructured Data
Unstructured data lacks a pre-defined data model, making it more difficult to collect, process and analyze. It comprises the majority of data generated today, and includes formats such as:
- Textual content from documents, emails and social media posts
- Multimedia content, including images, audio files and videos
- Data from IoT devices, which can include a mix of sensor data, log files and time-series data
The primary challenge with unstructured data is its complexity and lack of uniformity, requiring more sophisticated methods for indexing, searching and analyzing. NLP, machine learning and advanced analytics platforms are often employed to extract meaningful insights from unstructured data.
Semi-structured data
Semi-structured data occupies the middle ground between structured and unstructured data. While it does not reside in a relational database, it contains tags or other markers to separate semantic elements and enforce hierarchies of records and fields within the data. Examples include:
- JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) and XML (eXtensible Markup Language) files, which are commonly used for web data interchange
- Email, where the data has a standardized format (e.g., headers, subject, body) but the content within each section is unstructured
- NoSQL databases, can store and manage semi-structured data more efficiently than traditional relational databases
Semi-structured data is more flexible than structured data but easier to analyze than unstructured data, providing a balance that is particularly useful in web applications and data integration tasks.
Ensuring data quality and integrity, integrating disparate data sources, protecting data privacy and security and finding the right talent to analyze and interpret data can present challenges to organizations looking to leverage their extensive data volumes. What follows are the benefits organizations can realize once they see success with big data analytics:
Real-time intelligence
One of the standout advantages of big data analytics is the capacity to provide real-time intelligence. Organizations can analyze vast amounts of data as it is generated from myriad sources and in various formats. Real-time insight allows businesses to make quick decisions, respond to market changes instantaneously and identify and act on opportunities as they arise.
Better-informed decisions
With big data analytics, organizations can uncover previously hidden trends, patterns and correlations. A deeper understanding equips leaders and decision-makers with the information needed to strategize effectively, enhancing business decision-making in supply chain management, e-commerce, operations and overall strategic direction.
Cost savings
Big data analytics drives cost savings by identifying business process efficiencies and optimizations. Organizations can pinpoint wasteful expenditures by analyzing large datasets, streamlining operations and enhancing productivity. Moreover, predictive analytics can forecast future trends, allowing companies to allocate resources more efficiently and avoid costly missteps.
Better customer engagement
Understanding customer needs, behaviors and sentiments is crucial for successful engagement and big data analytics provides the tools to achieve this understanding. Companies gain insights into consumer preferences and tailor their marketing strategies by analyzing customer data.
Optimized risk management strategies
Big data analytics enhances an organization's ability to manage risk by providing the tools to identify, assess and address threats in real time. Predictive analytics can foresee potential dangers before they materialize, allowing companies to devise preemptive strategies.
As organizations across industries seek to leverage data to drive decision-making, improve operational efficiencies and enhance customer experiences, the demand for skilled professionals in big data analytics has surged. Here are some prominent career paths that utilize big data analytics:
Data scientist
Data scientists analyze complex digital data to assist businesses in making decisions. Using their data science training and advanced analytics technologies, including machine learning and predictive modeling, they uncover hidden insights in data.
Data analyst
Data analysts turn data into information and information into insights. They use statistical techniques to analyze and extract meaningful trends from data sets, often to inform business strategy and decisions.
Data engineer
Data engineers prepare, process and manage big data infrastructure and tools. They also develop, maintain, test and evaluate data solutions within organizations, often working with massive datasets to assist in analytics projects.
Machine learning engineer
Machine learning engineers focus on designing and implementing machine learning applications. They develop sophisticated algorithms that learn from and make predictions on data.
Business intelligence analyst
Business intelligence (BI) analysts help businesses make data-driven decisions by analyzing data to produce actionable insights. They often use BI tools to convert data into easy-to-understand reports and visualizations for business stakeholders.
Data visualization specialist
These specialists focus on the visual representation of data. They create data visualizations that help end users understand the significance of data by placing it in a visual context.
Data architect
Data architects design, create, deploy and manage an organization's data architecture. They define how data is stored, consumed, integrated and managed by different data entities and IT systems.
IBM and Cloudera have partnered to create an industry-leading, enterprise-grade big data framework distribution plus a variety of cloud services and products — all designed to achieve faster analytics at scale.
IBM Db2 Database on IBM Cloud Pak for Data combines a proven, AI-infused, enterprise-ready data management system with an integrated data and AI platform built on the security-rich, scalable Red Hat OpenShift foundation.
IBM Big Replicate is an enterprise-class data replication software platform that keeps data consistent in a distributed environment, on-premises and in the hybrid cloud, including SQL and NoSQL databases.
A data warehouse is a system that aggregates data from different sources into a single, central, consistent data store to support data analysis, data mining, artificial intelligence and machine learning.
Business intelligence gives organizations the ability to get answers they can understand. Instead of using best guesses, they can base decisions on what their business data is telling them — whether it relates to production, supply chain, customers or market trends.
Cloud computing is the on-demand access of physical or virtual servers, data storage, networking capabilities, application development tools, software, AI analytic tools and more—over the internet with pay-per-use pricing. The cloud computing model offers customers flexibility and scalability compared to traditional infrastructure.
Purpose-built data-driven architecture helps support business intelligence across the organization. IBM analytics solutions allow organizations to simplify raw data access, provide end-to-end data management and empower business users with AI-driven self-service analytics to predict outcomes.
- Open supplemental data
- Reference Manager
- Simple TEXT file
People also looked at
Original research article, local perspectives on marine ecotourism development in a water-insecure island region: the case of bocas del toro, panama.

- 1 Ocean Nexus, Dalhousie University, Marine Affairs Program, Halifax, NS, Canada
- 2 Center for Tropical Island Biodiversity Studies, The School for Field Studies, Bocas del Toro, Panama
As a dimension of a blue economy, marine ecotourism should, in theory, not only increase economic viability and environmental sustainability but, most importantly, pursue socially equitable outcomes. In tropical and sub-tropical island regions, where substantial tourism development is often coupled with widespread strains on public infrastructure and services, including water access, there exists a need to better understand the expansion of this industry is felt at the community level; more importantly by individuals who are reliant on these infrastructures and services. Through a case study of the Bocas del Toro Archipelago, where water insecurity is becoming acute, we draw on and mobilize stories from local community members, alongside non-participant observations and document collection, to 1) document the experience of some community members with water insecurity and shortages, including how they perceive the roles played by the central government and marine ecotourism sector, and 2) examine how community members feel about how communities feel about policies and investment priorities of the central government regarding water insecurity, including the extent to which they view marine ecotourism development as undermining or promoting local needs. Our results underline the complex nature of marine ecotourism governance and infrastructure development outcomes in a resource-insecure island region, demonstrating that current issues are greatly impacted by historical and social underpinnings of neo-colonialism and systemic racism, misalignments of community vs. government development priorities, and eroded political trust, that shape local experiences with sustainable development and local residents’ perceptions of the ability of marine ecotourism to address issues of water insecurity. Moreover, while our focus is on the marine ecotourism industry, the significance of these findings contributes to a growing body of literature that places local experiences at the forefront of research into the implications of sustainable development in island regions.
Introduction
The marine ecotourism industry is considered to be a dimension of a ‘blue economy’; an ocean-wide sustainable development strategy proposed by Small Island Developing States (SIDS) in 2012 to “promote economic growth, social inclusion, and preservation or improvement of livelihoods, while at the same time ensuring environmental sustainability” ( World Bank and UN DESA, 2017 , p.1). In theory, marine ecotourism should not only increase economic viability and environmental sustainability but, most importantly, pursue social equity—a “distinctive system of individualized justice” ( Minow, 2021 , p.173). In island regions, where substantial tourism appeal is often coupled with widespread issues of water insecurity ( Cole, 2012 ; Gössling et al., 2012 ; Gossling, 2015 ), this study explores questions regarding the ability of a blue economy strategy, rooted in marine ecotourism, to equitably address both development and well-being in the eyes of those local to island regions. In this paper, we refer exclusively to tropical and sub-tropical islands when discussing ‘islands’ or ‘island regions.’
In island regions, local blue economies are often heavily reliant on the marine tourism industry ( UNWTO, 2023 ). However, as per Leposa (2020) , large volumes of tourists, and the services required to support them (e.g., transportation, accommodation, food and beverage, recreation, etc.), can exacerbate existing issues of local public utility access, often due to infrastructural deficiencies or inherent vulnerabilities to climate change. Important to this study, in particular, is the relationship between the marine ecotourism industry and the availability and management of water resources.
To our knowledge there exist few studies that sit at the intersection of marine ecotourism and water insecurity in island regions specifically; less so those that are guided by, and draw conclusions from, the experiences of those individuals that most closely feel their impacts. As the push for blue economic development continues to grow ( Cisneros-Montemayor et al., 2021 ; Pace et al., 2023 ), and water insecurity becomes increasingly prevalent in climate-vulnerable regions ( Winters et al., 2022 ; Crisman and Winters, 2023 ), failing to capture how the two intersect and are felt at the community level could pose risks of conducting research with communities as the ‘subject’ rather than active participants and beneficiaries of the research process ( Israel et al., 2019 ), and/or informing policies that do not capture the nuances of community interests and needs ( Freudenberg and Tsui, 2014 ; Cisneros-Montemayor et al., 2019 ).
Marine ecotourism can be described as a “nature-based; environmentally educated; and sustainably managed” ocean tourism industry involving activities such as recreational fishing, snorkelling, whale watching, and SCUBA diving, for example ( Blamey, 2001 , p.6). Modern definitions also include dimensions of local benefits ( Sakellariadou, 2014 ; Das and Chatterjee, 2015 ; Ramos-García et al., 2017 ; Tuwo et al., 2021 ). This can entail increasing market demand for locally produced goods, the use of, and investment in, local facilities and infrastructure, opportunities for local entrepreneurship, and the generation of new revenue streams that remain within a community, for example ( Sakellariadou, 2014 ).
Unlike traditional mass tourism models, marine ecotourism adopts aspects of environmental conservation and promotes community involvement. However, when these tenets are not upheld, due to a variety of reasons (e.g., poor management, lack of community involvement, limited enforcement regimes, etc.), the industry can promote unsustainable practices on all fronts—economic, social, and environmental ( Hoyman and McCall, 2013 ; Rahman et al., 2022 ; Zeng et al., 2022 ). As such, recent scholarship has called for a re-prioritization of social sustainability within blue economic development ( Pascual et al., 2014 ; Bennett et al., 2019 ; Leposa, 2020 ; Nugraheni et al., 2020 ; Osterblum et al., 2020 ; Campbell et al., 2021 ; Cisneros-Montemayor et al., 2021 ), with concerns raised regarding the implication of developing marine industries in areas where there is significant need to consume and manage resources sustainably.
The United Nations (UN) refers to water security as the ability of a population to safeguard sustainable access to adequate quantities and quality of water for the support of livelihoods, human well-being and socio-economic development ( UN Water, 2013 ). In this sense, water in security is the condition in which at least one of the above variables (i.e., quantity, quality, or accessibility) is not met, threatening human well-being. While many island regions have some degree of established water infrastructure, the coincidence of ‘dry season’ and peak tourist landings can perpetuate regional instabilities in water security, where local residents compete for this essential yet scarce resource; both with tourists and between communities ( Gheuens et al., 2019 ).
In this study, we draw on and mobilize stories of local residents in a heavily touristed island to better understand how the relationship between marine ecotourism and water insecurity manifests at the community level. We explore the case of Panama’s Bocas del Toro Archipelago (henceforth referred to as ‘Bocas del Toro’ or ‘the archipelago’), where substantial tourism appeal and infrastructural issues coexist, as a microcosm of the paradox of pursuing a marine ecotourism-based blue economy in a water insecure island region. Through integrating non-participant observations and collected documents with a series of semi-structured interview responses we aim to 1) document the experience of some community members with water insecurity and shortages, including how they perceive the roles played by the central government and marine ecotourism sector, and 2) examine whether community members feel as though water insecurity and shortages have influenced policies and economic investment and the extent to which marine ecotourism development may undermine or promote changes.
Our results underline the dynamic and complex nature of marine ecotourism governance and infrastructure development outcomes in a resource-insecure island region, highlighting the historical, political, and social underpinnings that shape perceptions of, and poor experiences with, blue economic. While our focus is on the marine ecotourism industry, the significance of these findings contributes to a growing body of literature that places local experiences at the forefront of research into the implications of sustainable development in island regions.
Island development and marine ecotourism
Although often associated with ‘paradise’ ( Baldacchino, 2012 ), island nations are considered, by the UN, to be some of the world’s ‘least developed’ nations (UN, n.d.), with island regions often referred to as ‘vulnerable,’ given their narrow resource bases, remoteness, and susceptibility to natural hazards and external economic shocks ( Baldacchino, 2012 ; Belmar et al., 2016 ; Lucas et al., 2017 ; Nunn and Kumar, 2017 ). That said, it is important to note that this explicitly reflects the barriers that may limit attempts to garner increased economic prosperity and/or development capacity rather than island societies as a whole.
As described by ( Grydehøj et al., 2021 , p.4), in reflecting upon Hau’ofa (1994) , the modern development and governance of island resources is also often heavily steeped in colonialism, where Western standards for ‘successful’ development are far too narrow in their economic, geographic, and cultural views. Dating back to the 15th century, island states have faced oppression from the United States, France, Spain, England, and the Netherlands ( Keegan and Diamond, 1987 ; Leposa, 2020 ). While there remain proponents of some aspects of the colonial legacy ( Feyrer and Sacerdote, 2009 ), Kay (2010) maintains that colonialism, in Latin America specifically, has led to harmful endo -colonial relations that sit at the root of present-day developmental inequities. In the Caribbean, Sealy (2018) notes that colonization has not only impacted the regional ethnic makeup, but that the perpetuation of globalization as a neo-colonial structure has created a larger dependence on investments from the Global North. Overall, there exists a small body of literature that discusses the role of the blue economy in perpetuating or combating neo-colonialism. However, scholarship surrounding the colonization of islands maintains that neo-colonialism can propagate harmful outcomes of sustainable development projects such as marine ecotourism ( Heim, 2017 ; Durokifa and Ijeoma, 2018 ; Grydehøj et al., 2021 ).
Typically, ‘tourism intensive’ island regions derive a substantial proportion of their economic development from the marine ecotourism industry ( Adamiak and Szyda, 2022 ). McElroy (2006) refers to tourist-driven island economies as SITES (‘Small Island Tourist Economies’), describing the expansion of tourism as a prominent development strategy for small economies, where there exist large dependencies on the industry. While, marine ecotourism can lead to a host of benefits, research in the island context specifically, more often notes the potential consequences of such development in destinations considered to be on the ‘global periphery’ ( Dodds and Graci, 2012 ). For example, while ecotourism may produce local job opportunities, Das and Chatterjee (2015) posit that community members are more often placed in low-skill and/or low-pay roles. Moreover, Harrison and Prasad (2011) found that in Fiji, for example, there exist high levels of benefit leakages to foreign investors. In Bocas del Toro, specifically ( Scott et al., 2024 , p.2), explain that tourism-related development can lead to inequitable impacts through the promotion of real estate ventures in culturally significant areas, like mangroves, where investors may view the local environment as “obstacles to achieving ‘paradise.’”
Bocas del Toro, Panama
Located off the Caribbean coast of Panama, Bocas del Toro is one of the country’s top ecotourism destinations. It consists of approximately nine islands and 200 islets and is home to a population of approximately 22,500 across the larger Bocas del Toro district ( INEC, 2021 ). Attributable to a history of colonialism, the construction of the Panama Canal, and the cultivation of a plantation economy, among other reasons, the region is also home to a variety of distinct racial and cultural groups including Ngäbe peoples (those indigenous to present-day Panama and Costa Rica), Panamanians, Afro-Antilleans, and Chinese individuals, for example ( Guerrón-Montero, 2006 ; Carse, 2014 ; Suman and Spalding, 2018 ). Moreover, Bocas del Toro’s most developed islands have become increasingly inhabited by lifestyle migrants—relatively affluent individuals with the capacity to move to destinations, typically in the Global South, with warmer climates, a lower cost of living, and a seemingly higher quality of life—from the United States ( Benson, 2013 ; Spalding, 2013 ).
Although not formally considered an autonomous state, Bocas del Toro displays many of the hallmark characteristics of a SIDS as per the UN Office of the High Representative for the Least Developed Countries, Landlocked Developing Countries and Small Island Developing States ( UN-OHRLLS, 2022 ). It is home to both a distinct societal makeup and unique marine ecosystems ( Seemann et al., 2014 ; Pleasant and Spalding, 2021 ), and faces documented issues of infrastructural development and geographic isolation from larger global markets ( Tilmans et al., 2014 ; Pleasant and Spalding, 2021 ).
Bocas del Toro’s economy is predominantly supported by the tourism industry; across the larger Bocas del Toro province, tourism makes up 95% of all economic activity, greatly exceeding the national average ( Klytchnikova and Dorosh, 2013 ). The most lucrative form of tourism is referred to by the Autoridad de Turismo de Panama (Tourism Authority of Panama; ATP) as ‘island ecotourism’ ( ATP, 2020 ), with the most popular destinations being Starfish Beach, Red Frog Beach, and Isla Bastimentos National Marine Park ( Camarca de Turismo de Bocas del Toro, 2022 ). While the ATP does not explicitly refer to ‘marine ecotourism’ in their reporting, for the purposes of this study, ‘island ecotourism’ and ‘marine ecotourism’ will be considered synonymous, as their accepted definitions align greatly.
Common marine ecotourism-based businesses in the region include boat tours and taxis, restaurants, hostels, and gift shops, with much of the region’s tourism development concentrated in Bocas Town, Isla Colón, where an average of 150,000 tourists visited annually pre-COVID-19 pandemic ( Gray et al., 2015 ). Strikingly, although Bocas del Toro now sees approximately 225,000 tourists per year, the Bocas del Toro province remains one of the poorest in the nation ( CECOMRO, 2018 ; ATP, 2020 ).
Moreover, to appreciate the nuances of Bocas del Toro’s current socioeconomic landscape, one must also understand its economic history, which is closely tied to colonial resource extraction. In the early 20 th century, the construction of the Panama Canal and the establishment of the U.S. Canal Zone cemented the United States as a major player in the Panamanian economy. In Bocas del Toro, specifically, this presence was predominantly felt through the establishment of the United Fruit Company (UFC), an American-owned corporation trading in Latin American-grown fruit, namely bananas ( Pleasant and Spalding, 2021 ). Typically supporting the UFC’s operations were Afro-Caribbean and Ngäbe workers, as well as labour migrants from China and Italy ( Spalding, 2011 ). This created harmful shifts in power, as Black and Indigenous individuals were often exploited and marginalized through the imposition of a globally capitalistic system ( Amin, 1978 ). While small-scale operations remain (now Chiquita Brands International), the UFC’s presence in the archipelago declined greatly by 1990 due to war, crop diseases, and labour losses (as a result of poor pay and working conditions) ( Guerrón-Montero, 2006 ), making way for a burgeoning tourism industry by the 2000s, as many large-scale housing developments were left vacant and global interest in the region increased following the 1991 earthquake.
Today, the archipelago’s socioeconomic and environmental systems are inextricably linked to the marine ecotourism industry, attracting individuals looking to experience its vibrant culture, beautiful beaches, and ocean life ( Klytchnikova and Dorosh, 2013 ; Spalding et al., 2015 ; Lucas, 2019 ; ATP, 2020 ; Mach and Vahradian, 2021 ; Pleasant and Spalding, 2021 ; Bocas del Toro Tourism, 2023 ). That said, tourism infrastructure across Bocas del Toro has been deemed ‘suboptimal’ by the ATP, specifically as it pertains to the limitation of physical space and the overload of basic services, such as water provisioning ( ATP, 2020 ). Critical to this study, Bocas del Toro is also home to widespread issues of water insecurity; the majority of households across archipelago do not have access to running water supplied by the Instituto de Acueductos y Alcantarillados Nacionales (Institute of Aquaducts and Sewers; IDAAN), with 23% of the population instead turning to bottled water or drinking unfiltered rainwater respectively ( CNA, 2016 ) ( Figure 1 ). In fact, just 1.9% of the total residences connected to IDAAN’s services reside in the Bocas del Toro province ( IDAAN, 2022 ). As such, water insecurity is among the region’s most precarious issues.
Figure 1 Regional water insecurity across the Bocas del Toro Archipelago represented by the percentage of households in each census region without access to running water. The population density of each region in relation to the archipelago’s total population is also represented. Uncoloured areas represent regions outside of the archipelago or those not captured by the Panamanian Census. Created using the 2010 Panamanian Census Data, accessed from the STRI GIS Data Portal (2019) .
In this study we employ a multi-method approach—the combining of two or more methods to expand one’s research base when investigating a research question or phenomenon ( Roller and Lavrakas, 2015 )—that is firmly rooted in local experiences and perceptions. This includes the use of semi-structured interviews, non-participant observation, and document collection. While our approach pulls from that of political ecology, we do not attempt to formally mobilize methods typically used in such studies (e.g., Cole, 2012 ), but rather utilize participant responses to deduce the governance processes, historical events, etc., that frame their experiences with marine ecotourism and water insecurity. It should be noted that the data collection period in Bocas del Toro (May 25 th , 2023 to June 27 th , 2023) also coincided with a water shortage; declared an environmental emergency on June 9 th , 2023.
Semi-structured interviews
A member of our research team travelled to Bocas del Toro from May 25 th , 2023 to June 9 th , 2023 to conduct semi-structured interviews; asking participants open-ended questions to elicit information regarding one’s research topic ( Adeoye-Olatunde and Olenik, 2021 ). During this time, a total of 16 individuals, including members of the Bocas del Toro Chamber of Tourism, property owners, business owners, tour guides, labourers, and concerned citizens, were interviewed. Participants in this process—those older than 18 years of age and who have lived in the region for over 5 years—were identified through a purposive snowball method ( Weiss, 1994 ), beginning with contacts provided by a local informant.
Topics discussed (i.e., water shortages, infrastructure, economic and tourism development, and overall welfare) were drawn from a pre-determined interview guide developed through preliminary document collection and with guidance from researchers in the region (see Supplementary Table 3 ). While the guide was used to facilitate conversation, it adapted as more information was provided and new events occurred (i.e., the onset of an environmental emergency during the interview period). Interviews lasted an average of one hour and, depending on the participant’s level of comfort, were conducted in both English and Spanish (with an interpreter translating responses). Due to participant location and the accessibility of each island, interviews took place across three of Bocas del Toro’s nine main islands—Isla Colón, Isla Carenero, and Isla San Cristóbal ( Table 1 ).
Table 1 Socioeconomic and geographic description of interview locations/study sites.
Non-participant observation
To support responses collected during interviews, non-participant observation—observing and documenting an event without actively participating in activities ( Becker and Geer, 1957 )—was used to explore how ecotourist attractions function across the archipelago and further understand how communities respond to, and navigate, water shortages. Observed events were identified through community contacts established during the interview period as well as local WhatsApp groups; typically used to share important information across the region. They included waiting in line at public wells, visiting an ecotourist attraction, observing protests regarding water access, and attending a public meeting with IDAAN (further event details available in Supplementary Table 4 ). The average observation process lasted approximately one hour and involved taking notes regarding what did and did not occur, what demographic of individuals were present, and the overall tone of those present.
Document collection
Given that this is the first study to investigate topics of marine ecotourism and water insecurity in Bocas del Toro, supplementary grey literature was sought out to provide wider context and breadth to the study. Documents were found by searching for qualitative phrases related to drought, water, and tourism in Bocas del Toro in Google and the Bocas Breeze Newspaper database. Documents collected include government policies, local news articles, and regional reports.
The analysis of the data was guided by an inductive, constant comparative approach, as per Hodkinson (2008) and Glaser (1965) , whereby we sought to increase our understanding of potential underlying theories and identify emergent themes through a constant back-and-forth engagement with the data. In practice, this first involved transcribing and digitizing interview responses and observation notes. The data was then coded categorically (e.g., the codes ‘GOV-TOURISM’ and ‘GOV-WATER’ were utilized whenever a participant described how they felt about and experienced tourism and water governance respectively), and supplemental documents were reviewed to compare and contrast with interview and observational data.
In an effort to mirror the anecdotal nature of the data collected, here we weave together interview responses, observational notes, and document insights to describe how the economic development of Bocas del Toro, governance processes, experiences with water shortages, and future development in the region, shape local experiences with, and perceptions of, marine ecotourism and water insecurity. Figure 2 demonstrates a timeline of events and governance developments described by participants, as well as relevant events to contextualize the case.
Figure 2 Timeline of events and developments regarding ecotourism and water security in Bocas del Toro, Panama. The timeline presented is not exhaustive of all related moments in history, but rather those relevant to this particular study. Entries on the left of the timeline represent historical events, while those on the left represent policies and plans. ATP refers to the Tourism Authority of Panama; IDAAN refers to the Institute of Aquaducts and Sewers.
Beaches as the new bananas–shifting to a tourism-based economy
With increased neoliberal capital interest, government incentives to purchase land for tourism, and an abundance of global interest, tourism in Bocas del Toro effectively ‘exploded’ by the year 2000, signifying, as put by Pleasant and Spalding (2021) , a shift from a banana-based export economy created by the UFC to a tourism-centric economy based on the region’s beaches and biodiversity. Despite this shift, the UFC’s presence in Bocas del Toro remains prominent, as it had become integrated into the region’s social and infrastructural fabric (e.g., the creation of communication networks, railway systems, power plants, medical facilities, and housing developments) (United Fruit Historical Society, n.d.). Furthermore, when asked about the UFC in Bocas del Toro, participants described how a dependency on a singular industry and foreign entity resulted in harmful losses of traditional livelihoods, such as fishing and agriculture—”we used to be farmers who could feed ourselves, now we’ve lost this completely,” said one property owner.
Among those participants directly employed by the tourism industry, all spoke positively about the renewed economic benefit it brings. As one tour operator put it, “the money is in tourism, the experiences.” Of those participants situated outside of the industry, a majority also acknowledged that marine ecotourism does play a major role in supporting the local economy— “tourism is good,” noted a construction worker we spoke with, “yeah it’s good because it makes work and brings in money to us when it’s done right.”
That said, there remains great skepticism across all participants surrounding the industry’s future in Bocas del Toro:
“I used to fully believe that tourism was the key to successful cities with no opportunities.
But then we have fragile societies like we have in Latin America, and there’s not a strong
government that actually tries to implement human development. It is not taking us to the
right place,” said a member of the Bocas del Toro Chamber of Tourism.
When asked what she believes to be the largest development project in the community, one business owner responded:
“Tourists. But it grew alone. It grows alone … It’s incredible. Bocas [del Toro] has been developed in many ways, but not in basic things. It keeps growing, growing, growing, and I don’t see [public utilities] growing with it.”
Navigating an era of sustainable development – tourism and water governance
In contextualizing participant responses, we offer a brief exploration of relevant actors, plans, and policies as they pertain to marine ecotourism and water governance in Bocas del Toro. The overarching development of Panama’s marine sector is directed by the Ministerio de Relaciones Exteriores (Ministry of Foreign Affairs), Ministerio de Ambiente (Ministry of the Environment; MiAMBIENTE), and the UN Development Programme via the Política Nacional de Océanos de Panamá ( National Ocean Policy of Panama; NOP). Ratified in 2022, the goal of the NOP is to pursue a ‘Blue Panama,’ where “marine and coastal resources are protected, conserved, valued, and used sustainably, positively impacting the quality of life of citizens in an inclusive and participatory manner” ( MiAMBIENTE, 2022 , p.13). To do so, blue economic development, internally defined as the “sustainable use of marine and coastal resources…, approaching marine-coastal activities under the prism of balance between the three social, economic and environmental dimensions,” is prioritized as one of 4 strategic axes ( MiAMBIENTE, 2022 , p.21). Central to this, under Goal M. 27, is the “promotion of sustainable tourism development linked to the oceans” ( MiAMBIENTE, 2022 , p.21), where the NOP yields much of the responsibility around this directive to the ATP.
Since 2008, the ATP has been responsible for “the development, promotion, and regulation of tourism as an activity”; maintaining tourist resources, protecting the ecological balance of the land, and respecting the customs of its inhabitants ( Decreto Ley No.4, 2008 , p.1). When asked about their feelings towards the ATP, virtually all participants expressed concern regarding tourism governance in Bocas del Toro, and its ability to “make things happen.” According to one individual, tourism in Bocas del Toro is “governed by people who don’t have morals, they are just selfish. If it doesn’t make them money, they don’t do it.” At the community level, tourism in Bocas del Toro is monitored by the Cámara Turismo Bocas del Toro (Bocas del Toro Chamber of Tourism), a non-profit community organization that works to organize the local tourism sector and protect its longevity ( CTB, 2023 ). Nonetheless, the Chamber of Tourism is not afforded government funds or jurisdiction to carry out and/or enforce such endeavours and does not play a large role in high-level decision-making regarding tourism in the archipelago ( ATP, 2020 ). According to a member of the Chamber of Tourism, this creates issues surrounding community input, whereby the community is neither adequately consulted nor are their ideas accurately integrated into development plans:
“We are a private sector, but we have no say or worth in the final decision. [The ATP] says: ‘We met with the Chamber of Tourism and the chamber is approving [the development]’. But later, when we come and tell you all the things wrong with the plan, they say ‘Oh no, you came up with this idea, the Chamber approved it’…We don’t want that; we don’t need that. We need real things.”
At large, plans for tourism development in Bocas del Toro are organized under the Plan Maestro de Desarrollo Turístico Sostenible 2020-2050 (Master Plan for Sustainable Tourism Development 2020-2050; MPSTD), with goals to promote Panamanian tourism, improve global competitiveness, decentralize tourism operations, and develop state tourism policies ( ATP, 2020 ). In Bocas del Toro, the MPSTD’s Action Plan includes a total of 19 actions and 75 projects. Of this, 6 projects fall under Action 2.4.4. Improvement of Basic Infrastructures, including a project to, in tandem with IDAAN, “improve the drinking water supply system on Isla Colón” by 2022 ( ATP, 2020 , p.316). Despite this, participants were wary as to whether these plans would ever “hit the ground,” as put by one individual. “The [MPSTD] is a plan,” said a member of the Chamber of Tourism, “but if you do nothing to implement it, it’s not going to change. I haven’t seen any real action.” “You don’t need the government. The government is not going to do it. Because the government has no brain to think,” expressed another member of the community.
The implementation of these projects is largely overseen by IDAAN, with more specific water infrastructure improvement plans for Bocas del Toro listed in Panama’s Plan Nacional de Seguridad Hídrica 2015-2050 (National Plan for Water Security 2015-2050; NPWS). The NPWS serves as a roadmap for ensuring that “every person in [Panama] has sustained access to quality water and basic sanitation,” with a focus on “eliminating inequalities of access in an inclusive and equitable manner” ( CNA, 2016 , p.65). In pursuit of this, the NPSW budgets 3.3 billion USD to address issues of drinking water in Isla Colón exclusively, including improvements to catchments and sewage systems ( CNA, 2016 ). However, while the NPSW projects that all individuals in the Bocas del Toro province will have access to drinking water by 2025, as will be described in subsequent sections, participants note that, as of 2023, they are skeptical as to whether this goal will ever be reached. As one business owner put it, “it’s only plans plans. But when you go to practice? No, nothing happens.”
Accessing water in Bocas del Toro – a myriad of methods
Very limited formal documentation on water infrastructure and distribution processes in Bocas del Toro is publicly available; as put by one participant, “nobody really knows exactly how the water works [in Bocas del Toro].” Despite this, with insights from community members, we attempt here to establish a clearer picture of water distribution across the study sites ( Figure 3 ), highlighting the intensity of water insecurity in Bocas del Toro and inform how marine ecotourism might impact water access.
Figure 3 Maps of approximate locations of examples of water infrastructure across Isla Colón/Isla Carenero (A) , and Isla San Cristóbal (B) as described by participants. Image 1—a newly constructed water reserve tank. Image 2—a typical public well in Isla Colón. Image 3—Big Creek Reservoir. Image 4—IDAAN water processing station. Image 5—a typical rain catchment system in Isla Colón. Image 6—a water tanker deployed during water shortages. Image 7—water line that connects Isla Colón and Isla Carenero. Image 8—a typical rain catchment system in Isla Carenero. Image 9—water catchment station in Isla San Cristóbal. Image 10—underground pipe system in Isla San Cristóbal. Images 1-3 and 5-10 were taken by Abigael Kim. Image 4 is reprinted from the IDAAN Water Treatment Plant Database ( https://sig-idaan.hub.arcgis.com/apps/0a722564d72f421798b33b902ebef781/explore ).
Residents of Isla Colón typically access water through IDAAN’s public distribution system, and/or via public or private wells. IDAAN services over 9,000 individuals across the southern region of Isla Colón through an underground pipe system powered by gravity and a select number of pumps. While it is widely understood this water, supplied by a local reservoir (‘Big Creek’) ( Figure 3 , Point 3), is filtered at a nearby plant ( Figure 3 , Point 4), the efficacy of this process remains highly debated ( Corea, 2016 ; Telemetro, 2022 ; Albaez, 2023 ; Godoy, 2023 ; Ortiz, 2023 ). When asked whether she would drink water from her tap, one shop owner responded, “I’m not gonna do that,” while her partner added that the water is often “yellow or brown” in colour. This system is also subject to the impacts of ‘dry season’ in the Caribbean (October to April), when services are often limited by IDAAN to two hours in the morning and evening. Regions of the island not serviced by IDAAN rely on rainwater collection ( Figure 3 , Point 5) or the use of public or private wells ( Figure 3 , Point 2). As of today, there exist eight IDAAN wells in Isla Colón, with only four in constant operation, while private wells on the island are typically located in regions populated by lifestyle migrants and affluent families. That said, virtually all wells across the archipelago require electricity, of which the local supply is highly unpredictable.
In Isla Carenero, those residing along the island’s perimeter typically rely on underwater pipes that distribute water sourced from IDAAN’s system in Isla Colón ( Figure 3 , Point 7). That said, participants noted that this process is unreliable, as there is often not enough water pressure from Big Creek to reach the shores of Isla Carenero. According to a local restaurant owner, “[Isla] Carenero has huge water problems. When there is no water there, [they] struggle the most.” Participants from Isla Carenero also noted that it is common to utilize rain collection systems ( Figure 3 , Point 8) or to travel to Isla Colón to purchase jugs of water. Furthermore, many restaurants and tourist operations on the island utilize private wells to service their patrons, while lifestyle migrants are also known to have access to private wells.
Isla Colón and Isla Carenero are the only islands (out of nine that are inhabited) to have direct access to IDAAN’s services. Other islands, like Isla San Cristóbal, rely on community-led initiatives or the purchasing of water jugs from Isla Colón. As described by a local tour guide, approximately 600 individuals on Isla San Cristóbal access water via a natural catchment system and man-made storage and distribution point developed through a fundraising project by local and international organizations ( Figure 3 , Point 9). The storage point collects water from the island’s northern mountain region, filters it for solids, and distributes it to the community via gravity and underground pipes ( Figure 3 , Point 10). According to a local tour guide, this process is quite reliable; during times of drought, residents of other islands have looked to him for water.
Frustrations run high – a history of water shortages
Bocas del Toro has faced (documented) water shortages in 2016, 2017, 2019, 2022, and 2023. One restaurant owner noted that, while “water has always been an issue in [Bocas del Toro],” the problem “has never been this bad.” Following a prolonged period of drought and water restrictions, as well as pressure from MiAMBIENTE, a State of Environmental Emergency was declared by the Cabinet of Panama in both 2022 (November 8 th ) and 2023 (May 30 th ) ( Resolución de Gabinete No. 127, 2022 ; Resolución de Gabinete No. 48, 2023 ). Doing so authorizes IDAAN to enact the region’s ‘Contingency Plan’, involving the assignment of water trucks to distribute potable water to affected businesses and residences on Isla Colón and Isla Carenero, the increase of water conduction line diameters, the activation of additional wells, and the increase of regional technical support ( IDAAN, n.d. ).
During this type of Environmental Emergency, those without private well access typically purchase water jugs from local shops, fill their household tanks at public wells, or fill up smaller jugs from IDAAN trucks ( Figure 3 , Point 6). However, participants mentioned that such alternative methods are not sufficient, leaving many without water for days on end. One souvenir vendor, for example, mentioned that she had not been able to shower in “over 8 days.” Moreover, as lines for local wells grow, business owners mentioned that these trucks are extremely challenging to access, having to “choose between running [their] shops and getting water.”
Overall, aside from climate change as a catalyst, there is no largely agreed-upon answer or government consensus as to why water management and infrastructure are so precarious or why Bocas del Toro feels droughts so intensely. However, participants speculated that they have something to do with the coinciding of ‘dry season’ and tourist season in the fall. As mentioned in the Bocas Breeze Newspaper in response to the 2016 shortage:
“In recent years, sometimes it doesn’t rain for a while or excited tourists flood the island in
record numbers and when you turn the faucet, you are met with the depressing sound of a
‘drip, drip, (silence)…’ Maybe you left your toilet running and your tank has gone empty, or
perhaps the town reservoir has gone dry” (2016).
Undoubtedly at the center of these frustrations is IDAAN, more specifically as it pertains to the uneven distribution of water and lack of government accountability. According to IDAAN, water trucks are to deliver water to both city centres and residential areas. However, almost all participants mentioned that this system is not well executed, citing disparities in where water was being delivered during the 2023 shortage. “Unfortunately, there is a bad distribution of the water and trucks,” one tour operator said, “they don’t have a good plan for giving out the water, so they pass me by.” More specifically, many participants mentioned that hotels are often prioritized, and speculated that truck drivers were being paid a premium by these establishments to visit them first. “A government truck should be for the community,” said one community member, “but it doesn’t happen in Panama.”
Participants also expressed frustration with IDAAN’s accountability during these shortages. “I don’t look to the government for water,” said one individual, “I pray to God.” During the 2023 shortage, in particular, many community members were left with unanswered questions, as the regional IDAAN phone line for Bocas del Toro was disconnected, and public meetings with IDAAN were continuously cancelled. As was seen on multiple occasions during the 2023 shortage, such feelings often led to public displays of frustration, in the form of road blockades and protests; “we don’t just wait for water, we have to block the streets for water,” said one shop owner.
In June 2023, after over a month without reliable access to running water, IDAAN announced the connection of two additional wells to supplement Big Creek while precipitation levels remained low ( Ortiz, 2023 ). Despite these developments, residents of both Isla Colón and Isla Carenero still face water insecurity at large, with water remaining a contentious issue across the archipelago.
A potential paradox? – Future plans for water infrastructure and marine ecotourism
Looking towards 2050, Bocas del Toro is the topic of numerous development projects in both marine ecotourism and water infrastructure. However, participants expressed disappointment about the priorities of the central government’s plans and were skeptical of their potential outcomes.
In 2022, under the NPSW, IDAAN announced a 10 million USD investment in the “study, design, construction, operation, and maintenance of improvements to the components of the aqueduct in Isla Colón” ( Ortiz, 2023 , p.1). According to Albaez (2023) , this includes a 3-Phase Plan to develop a more reliable 24-hour public, potable water supply system:
● Phase 1—Well drilling/maintenance and construction of a water storage tank with a 700,000-gallon capacity.
● Phase 2—Construction of well-housing units and pumping equipment.
● Phase 3—Construction of supplementary desalinization plant and improvements to water treatment plant and dispensers.
Despite reports that 60% of the project has been completed as of May 2023 ( Ortiz, 2023 ), including the totality of Phase 1 and the maintenance of public well systems from Phase 2, none of the participants indicated that they had seen improvements in their water supply, but instead questioned the efficacy of IDAAN’s projects. For example, one participant referred to the early release of 5 million USD of the 3-Phase Plan investment during the 2022 shortage to rapidly increase water infrastructure quality and capacity ( Resolución de Gabinete No. 127, 2022 ), of which they had yet to see the effects of:
“They would come around and promise us that they would solve the problem, and it never
happened … They released 5 million dollars. Where does it go? It’s like ice in the sun, nobody knows where it goes … A week after they got the money the water came like lemonade, and we got it once a day”.
All participants were critical of where the Government of Panama’s plans for the development of water infrastructure sit on the list of priorities, as compared to tourism. Those directly employed by the tourism industry made note of the Urban Development of Cities with a Tourist Vocation Plan; a 6-year 100 million USD loan (2019-2023) for the development of tourism infrastructure, management, and governance, including that of public utilities in Isla Colón ( Inter-American Development Bank , n.d.). However, when asked whether they had seen any benefits from this investment, all pointed to the development of more hotels, attractions, and restaurants rather than improvements to existing infrastructure. “When I see that [investment] here, it’s in building hotels,” mentioned one property owner, “but they’re not building up the community with it, you know? ‘Why is that?’ I ask all the time”. Another participant mentioned that “[Bocas del Toro] is so marketed as a tourism place that there is nothing else [the government] does. We have culture and needs but they don’t see.”
While not explicitly discussed with participants, an important development in this case came in July of 2023, when Panama signed on to the UN’s Water Capacity Development Initiative (CDI) for SDG 6; the first country in the world to do so. The CDI serves as a vehicle for inter-agency cooperation on capacity development related to freshwater, sanitation, and hygiene ( UN Water, 2021 , p.1). Its goal is to enable the UN system, and its partners, to coordinate support for participating countries based on their unique needs. While it is too early to predict the efficacy of this initiative, it does indeed promote “national-level ownership” and capacity building, rather than a “simple transfer of mechanisms” ( UN Water, 2021 , p.1). As Panama continues to pursue a blue economy rooted in marine ecotourism as well as improved water security, questions remain as to whether there is indeed a balance to be struck between the two; one that aligns government aspirations for development with the realities and needs of those living in Bocas del Toro.
Contextualized around the potential paradox of developing a blue economy in a resource-insecure island region, this study examines how the relationship between marine ecotourism and water insecurity, in particular, manifests at the community level through a case study of Bocas del Toro, Panama. Guided by local experiences and perceptions, our findings highlight the role that socio-historical shifts, central plans and policies, and ongoing crises play in shaping the realities of local residents and their attitudes toward sustainable development and the government as a whole. In this section, we situate key findings within the literature, teasing out applicable lessons learned, making inquiries into the reasoning behind our results, and contemplating areas for future research.
The role of colonialism and race in marine ecotourism and water governance
Our results further perpetuate the widely accepted notion that issues of island development and resource governance must be considered within the context of colonization and systemic racism. In particular, studies in the ‘island tourism’ field (e.g., Cywiński (2015) ; Guerrón-Montero (2006) ; Grydehøj et al. (2021) ) would describe the lasting impacts of losses in traditional livelihoods at the hands of the UFC, and its role in directing Bocas del Toro’s economic development, as a function of neo -colonialism. Along this vein, Grimwood et al ( Grimwood et al., 2019 , p.1) posit that the production and consumption of tourism have the propensity to “(re)inscribe colonizing structures, systems, and narratives across time and space,” while ( Eyisi et al., 2024 , p.154) note that the pace and manner of tourism development is often an artifact of “tourists from colonizers becoming the source market for the colonized”. For example, a study of wildlife tourism by ( Mach et al., 2023 , p.1474) found that wildlife tourism boat guides learned what tourists (many being from Europe and North America) “wanted to see and seemed to enjoy most (e.g. pretty beaches and charismatic wildlife) and itineraries evolved accordingly,” often changing the actual names of destination, commonly used between locals to simple English, in order attract more tourists (e.g., ‘Sloth Island’).
A discussion of colonialism in this context, that being inherently racially formed, also brings us to the role of systemic racism. While the Panamanian government has enacted laws surrounding racial discrimination, in an effort to reconcile past and present harms [e.g., the dispossession of Afro-Caribbean farming communities ( Chapman, 2014 ), infringements upon Ngäbe land rights ( Finley-Brook and Thomas, 2010 ), and the attempted assimilation of Afro-Caribbean identity into mestizo society ( Corinealdi, 2022 )], Afro-Panamanians and Ngäbe individuals still make up some of the poorest groups in the nation, often residing in some of the least invested-in regions, with limited access to social services, water included ( INEC, 2021 ). While drawing a causal relationship between race and water insecurity is not within the scope of this research, the 2020 UN World Water Report does explicitly relate water insecurity and intersectionality, especially regarding race and class ( UN Water, 2020 ). Peer-reviewed studies on this issue, however, overwhelmingly exist in the North American context (e.g., Deitz and Meehan, 2019 ; Dickin and Gabrielsson, 2023 ; Harrington et al., 2023 ; Méndez-Barrientos et al., 2023 ; Workman and Shah, 2023 ). For example, a spatial analysis of water insecurity across the United States by Deitz and Meehan (2019) found that deficiencies in household water infrastructure are concentrated in regions typically inhabited by racialized groups. Specific to Bocas del Toro, our research highlights disparities in access to water between social and racial groups, as determined by foreign and ethno-racial status. For example, participants note that, during water shortages, wealthier lifestyle migrants and hotel operators have the financial capital to purchase water and/or pay truck drivers to deliver it.
The government-community disconnect
Central to this case is an evident disconnect between the Government of Panama’s aspirations for marine ecotourism development in Bocas del Toro and the needs of those living in the region, with many participants believing the government to be prioritizing marine ecotourism development over plans to improve water infrastructure. While a more intensive study, one which highlights the interconnectedness of climate change impacts and water management within larger government policies, is required to support this notion, our findings suggest that local realities may perpetuate the narrative that the government is ‘leaving behind’ social sustainability in pursuit of a viable marine ecotourism industry. In the Caribbean context, Peterson ( Peterson, 2020 , p.20) argues that “growth, rather than development, remains the overriding focus,” whereby “the quality of life for residents and, in turn, the quality of experience for visitors have not always met the various principles of sustainable tourism.” Furthermore, Srivastava and Mehta (2023) and Scott et al. (2024) propose that this outcome can indeed be “further exacerbated by neoliberal development policies and the notion of [Bocas del Toro] as a ‘resource frontier.’
As found by Wortman et al. (2016) ’s examination of local opinions on foreign tourism investment in Mauritius, our results suggest that the sheer profitability of the marine ecotourism sector may incentivize governments to continue to pursue its growth in terms of investment and future planning. They describe the tourism industry as “a variant of outward-oriented development strategies,” where the services required to host a successful industry may eclipse the services required by the local population. This is of extreme relevance in island regions, where tourism is a major contributor to national economies, motivating governments to continue to pursue ‘tourism-led growth,’ as put by Lee and Chien (2008) , and attracting increasing amounts of foreign direct investment ( Tecel et al., 2020 ; Broner et al., 2023 ).
If Bocas del Toro’s marine ecotourism sector continues to grow without the development of essential infrastructure alongside it, the region may indeed hit the point of ‘over-tourism’, where the arrival of excessive numbers of tourists at a destination imposes negative impacts on local communities ( Dioko, 2017 ). Peterson (2023) notes that over-tourism, in the Caribbean specifically, is often an artifact of “neo-liberal outward-oriented tourism policy., largely based on private and political interests to the exclusion of societal values and community interests.” Notably, reaching this point may, in fact, incentivize governing bodies to prioritize the development of public utility infrastructure to ensure that marine ecotourism remains an economically viable industry.
The importance of trust
The prevalence of mistrust in the Government of Panama expressed by participants can be described as a lack of ‘political trust’; trust in institutions and governance actors stemming from group membership, government policies, and/or general political support or satisfaction ( Bauer and Freitag, 2016 ). Our results demonstrate that local perceptions of corruption can mold residents’ opinions of marine ecotourism development, and its ability to act on issues of water insecurity. While we are not aware of any studies that explore the role of government corruption in affecting local perceptions of sustainable development, more broadly, Karst and Nepal (2022) note that a lack of established trust between communities and actors that oversee ecotourism development can lead to an array of management challenges and stakeholder conflicts.
Political trust is also often tied to the ability of actors to deliver quality public services and respond to citizen demands ( Murtin et al., 2018 ). In this study, participant responses indicate skepticism regarding the effectiveness and accountability of government actors and policies. As described by Fragkou and McEvoy (2016) , in an investigation of community attitudes surrounding water scarcity in Latin America, traumatic and frequent experiences with water scarcity can foster concerns regarding political accountability, further erode trust in utility providers, and perpetuate poor opinions of future developments that could potentially improve water access, like desalinization plants. Enqvist and Ziervogel (2019) also found that when compounded with historically tense relationships between communities and policymakers, the mishandling of water shortages can signal to local residents that government action is ineffective and subsequently untrustworthy. Eyisi et al. (2024) review of tourism in Nigeria also found that negative opinions of tourism development can be tied to a history of unfulfilled government promises. In the case of Bocas del Toro, participants often pointed out a lack of follow-through on the MPSTD. Nilsen et al. (2023) describe what it means to be a ‘periphery’ region on an intra -national scale, where the development of rural or isolated regions may fall victim to an ‘urban bias’ ( Lipton, 1977 ). We witness this in Bocas del Toro as participants note that management schemes from the national level often overlook their interests as compared to more urbanized provinces closer to the core of Panama City.
Study limitations and future research avenues
While we believe the stories and perceptions shared with us to be of the utmost value to understanding our research questions, we acknowledge that our results represent the experiences of 16 individuals across the archipelago. Although a smaller sample size can enhance the validity of an in-depth inquiry ( Crouch and McKenzie, 2006 ), a larger sample size can better account for diversity within and between stakeholder groups ( Boddy, 2016 ). As the pool of research in this field begins to expand, we recommend that not only do future studies adequately account for community experiences and perceptions, but that they aim to include a variety of stake- and rights-holders, determining sample size as a “matter of judgment and experience … evaluating the quality of the information collected against the uses to which it will be put,” as per Sandelowski ( Sandelowski, 1995 , p.179).
This research begins to fill knowledge gaps in the literature surrounding marine ecotourism development and access to water in island regions. To ensure that community realities and interests do not effectively ‘fall through the cracks,’ there exists a need to pursue community-centric research on the impact of a blue economic agenda on a variety of essential public utilities and human needs (e.g., electricity, food, housing). Furthermore, valuable insights can be drawn from studies that compare and contrast, in-depth, cases across island regions to better understand the norms of the community impacts of blue economic development in resource-scarce societies. Concerning Bocas del Toro specifically, there is a great need for continued research into all areas of marine ecotourism development and the equitable distribution of resources (both in relation to one another and independently), as ours is one of a handful of studies within the region (e.g., Spalding, 2013 ; Spalding et al., 2015 ; Spalding, 2017 ; Mach and Vahradian, 2021 ; Pleasant and Spalding, 2021 ; Mach et al., 2023 ; Sandelowski, 1995 ; Pigram, 2000 ; McElroy, 2006 ; Pascual et al., 2014 ; Sakellariadou, 2014 ; Roller and Lavrakas, 2015 ; Pierskalla, 2016 ; Nunn and Kumar, 2017 ; Ramos-García et al., 2017 ; Murtin et al., 2018 ; Nugraheni et al., 2020 ; Osterblum et al., 2020 ; Peterson, 2020 ; Phelan et al., 2020 ; Mach and Vahradian, 2021 ; Minow, 2021 ; Pleasant and Spalding, 2021 ; Ministerio de Ambiente de Panamá, 2022 ; Rahman et al., 2022 ; Resolución de Gabinete No. 127, 2022 ; Méndez-Barrientos et al., 2023 ; Nilsen et al., 2023 ; Ortiz, 2023 ; Pace et al., 2023 ; Resolución de Gabinete No. 48, 2023 ; Scott et al., 2024 ).
In this study, we mobilize local experiences with marine ecotourism and water insecurity to better understand how the relationship between the two manifests at the community level. Our results highlight issues, of colonialism and systemic racism, misalignments of development priorities, and eroded trust, that shape local experiences with sustainable development, and residents’ perceptions of the ability of marine ecotourism to address issues of water insecurity.
Moving forward, as the Government of Panama pursues a ‘Blue Panama,’ and the global community continues to adopt the blue economy as a framework for sustainable ocean development, there exists a need to re-center and internalize social sustainability, primarily issues of equity, as the leading goal of blue economic development. More specifically, in order to adhere to the original intent of a blue economy, this must not only include the prioritization of social equity throughout marine ecotourism and water governance, but also address the issues that underpin such misalignments, as found in this study. This can include an approach that focuses on the power disparities between groups through a socio-historical lens. Singh et al. (2023) refer to this as an ‘anti-inequity’ approach, whereby it is critical to investigate and understand the processes that perpetuate inequities in, in this case, water security.
Overall, this research has demonstrated that the ‘balance’ between community well-being and development in the pursuit of a blue economy in island regions is a matter far greater than ‘growth,’ ‘infrastructure,’ or ‘development’. There exist important historical and social underpinnings that define the relationship between decision-makers and the communities in which they make decisions for, who proves to benefit from a blue economy, and perceptions of sustainable development as a whole. Ultimately, marine ecotourism cannot be considered part of a blue economy strategy if it does not prioritize social equity. As such it is pivotal that future research within this field understand how relevant plans and policies may manifest at the community level, directly from those communities that may face existing barriers to social well-being and sustainability.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/ Supplementary Material . Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Marine Affairs Program Ethics Review Standing Committee, Dalhousie University. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
AK: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. CS: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. WS: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This study was funded by the Nippon Foundation, Ocean Nexus.
Acknowledgments
We sincerely thank the communities and participants of Bocas del Toro for allowing, actively participating in, and supporting the data collection for this study. We also thank the staff of The School for Field Studies, Panama, for hosting us during our time in the field, as well as Laura Bruce and Sydney Rubinstein for their support as interpreters. Commentary and edits on the original manuscript were also provided by Ricardo de Ycaza (Oregon State University). We are grateful for the time and input from the reviewers of this paper, which have greatly improved the manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmars.2024.1377053/full#supplementary-material
Adamiak C., Szyda B. (2022). Combining conventional statistics and big data to map global tourism destinations before COVID-19. J. Travel Res. 6, 1848–1871. doi: 10.1177/00472875211051418
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Adeoye-Olatunde O. A., Olenik N. L. (2021). Research and scholarly methods: Semi- structured interviews. J. Am. Coll. Clin. Pharm. 4, 1358–1367. doi: 10.1002/jac5.1441
Albaez A. (2023) IDAAN advances in the contingency plan for water supply in Isla Colón (province of Bocas del Toro: Radio Panama). Available online at: https://radioPanama.com.pa/idaan-avanza-en-plan-de-contingencia-de-abastecimiento-de-agua-en-isla-colon-provincia-de-bocas-del-toro/ (Accessed July 22, 2023).
Google Scholar
Amin S. (1978). Unequal development: An essay on the social formations of peripheral capitalism. Sci. Soc. 42, 219–222.
ATP (2020) Plan Maestro de Turismo Sostenible (Panama City: Autoridad de Tourismo de Panama). Available online at: https://www.atp.gob.pa/Plan_Maestro_de_Turismo_Sostenible_2020-2025.pdf (Accessed May 8, 2023).
Baldacchino G. (2012). The Lure of the island: A spatial analysis of power relations. J. Mar. Island Cultures 1, 55–62. doi: 10.1016/j.imic.2012.11.003
Bauer P. C., Freitag M. (2016). ““Measuring trust,”,” in The Oxford Handbook of Social and Political Trust . Ed. Uslaner E. (Oxford University Press, New York).
Becker H. S., Geer B. (1957). Participant observation and interviewing: A comparison. Hum. Organ. 16, 28–32. doi: 10.17730/humo.16.3.k687822132323013
Belmar Y. N., McNamara K. E., Morrison T. H. (2016). Water security in small island developing states: The limited utility of evolving governance paradigms. WIREs Water 3, 181–193. doi: 10.1002/wat2.1129
Bennett N. J., Cisneros-Montemayor A. M., Blythe J., Silver J. J., Singh G., Andrews N., et al. (2019). Towards a sustainable and equitable blue economy. Nat. Sustainability. 2, 1665–1685. doi: 10.1038/s41893-019-0404-1
Benson M. C. (2013). Postcoloniality and privilege in new lifestyle flows: The case of north Americans in Panama. Mobilities 8, 313–330. doi: 10.1080/17450101.2013.810403
Blamey R. K. (2001). ““Principles of ecotourism,“,” in The Encyclopedia of Ecotourism . Ed. Weaver D. B. (New York: CABI Publishing), 5–22.
Bocas del Toro Tourism (2023) Isla Colón . Available online at: https://go.bocasdeltoro.travel/es/destinos/isla-colon/ (Accessed May 3, 2023).
Boddy C. R. (2016). Sample size for qualitative research. Qual. Market Res. 19, 426–432. doi: 10.1108/QMR-06-2016-0053
Broner F., Didier T., Schmukler S. L., von Peter G. (2023). Bilateral international investments: The big sur? J. Int. Economics 145, 103795. doi: 10.1016/j.jinteco.2023.103795
Camarca de Turismo de Bocas del Toro (2022). Estudio del Destino 2020 Bocas del Toro, Panama. Available at: https://camaraturismobocas.org/estudio-del-destino-2020/ .
Campbell L. M., Fairbanks L., Murray G., Stoll J. S., D’Anna L., Bingham J. (2021). From Blue Economy to Blue Communities: Reorienting aquaculture expansion for community wellbeing. Mar. Policy 124, 104361. doi: 10.1016/j.marpol.2020.104361
Carse A. (2014). Beyond the big ditch : politics, ecology, and infrastructure at the Panama Canal. (Massachusetts: The MIT Press). doi: 10.7551/mitpress/9780262028110.001.0001
CECOMRO (2018) Visiones Regionales al 2050 de Bocas del Toro (Centro de Competitividad de la Región Occidental: David). Available online at: https://www.cecomro.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/03/VISION-2050-REGION-OCCIDENTAL.pdf (Accessed May 3, 202).
Chapman P. (2014). Bananas: How the United Fruit Company Shaped the World (Scotland: Open Road + Grove/Atlantic).
Cisneros-Montemayor A. M., Moreno-Báez M., Reygondeau G., Cheung W. W. L., Crosman K. M., González-Espinosa P. C., et al. (2021). Enabling conditions for an equitable and sustainable blue economy. Nature. 591, 396–401. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-03327-3
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Cisneros-Montemayor A. M., Moreno-Báez M., Voyer M., Allison E. H., Cheung W. W. L., Hessing-Lewis M., et al. (2019). Social equity and benefits as the nexus of a transformative Blue Economy: A sectoral review of implications. Mar. Policy. 109, 103702. doi: 10.1016/j.marpol.2019.103702
Cole S. (2012). A political ecology of water equity and tourism. Ann. Tourism Res. 39, 1221–1241. doi: 10.1016/j.annals.2012.01.003
CNA. (2016). Plan Nacional de Seguridad Hídrica 2015-2050 (Panama City: Republic of Panama). Available online at: https://www.undp.org/es/Panama/publications/plan-nacional-de-seguridad-h%C3%ADdrica-2015-2050-agua-para-todos (Accessed August 9, 2023).
Corea N. (2016). Moving 55,000 Cubic Meters of Sediment Means More Water for Bocas Town (The Bocas Breeze Newspaper). Available online at: https://thebocasbreeze.com/community/moving-55000-cubic-meters-sediment-means-water-bocas-town/ (Accessed July 30, 2023).
Corinealdi K. (2022). Panama in Black: Afro-Caribbean World Making in the Twentieth Century (North Carolina: Duke University Press). doi: 10.1215/9781478023128
Crisman T. L., Winters Z. S. (2023). Caribbean small island developing states must incorporate water quality and quantity in adaptive management of the water-energy-food nexus. Front. Environ. Sci. 11. doi: 10.3389/fenvs.2023.1212552
Crouch M., McKenzie H. (2006). The logic of small samples in interview-based qualitative research. Soc. Sci. Inf. 45, 483–499. doi: 10.1177/0539018406069584
CTB (2023) Sobre Nosotros . Available online at: https://camaraturismobocas.org/sobre-nosotros/ (Accessed May 3, 2023).
Cywiński P. (2015). Tourist neo-colonialism as an indication of the future of islands. The example of borobodur (Central Java). Miscellanea Geographica 19, 21–24. doi: 10.1515/mgrsd-2015-0011
Das M., Chatterjee B. (2015). Ecotourism: A panacea or a predicament? Tourism Manage. Perspect. 14, 3–16. doi: 10.1016/j.tmp.2015.01.002
Decreto Ley No.4 (2008). Available online at: https://www.atp.gob.pa/wp-content/uploads/2020/11/decretoley_atp2008.pdf (Accessed March 25, 2023).
Deitz S., Meehan K. (2019). Plumbing poverty: Mapping hot spots of racial and geographic inequality in U.S. Household water insecurity. Ann. Am. Assoc. Geographers 109, 1092–1109. doi: 10.1080/24694452.2018.1530587
Dickin S., Gabrielsson S. (2023). Inequalities in water, sanitation and hygiene: Challenges and opportunities for measurement and monitoring. Water Secur. 20, 100143. doi: 10.1016/j.wasec.2023.100143
Dioko L. A. (2017). The problem of rapid tourism growth—An overview of the strategic question. Worldwide Hospitality Tourism Themes 9, 252–259. doi: 10.1108/WHATT-02-2017-0005
Dodds R., Graci S. (2012). Sustainable Tourism in Island Destinations (New York: Routledge). doi: 10.4324/9781849776660
Durokifa A. A., Ijeoma E. C. (2018). Neo-colonialism and Millennium Development Goals (MDGs) in Africa: A blend of an old wine in a new bottle. Afr. J. Science Technology Innovation Dev. 10, 355–366. doi: 10.1080/20421338.2018.1463654
Enqvist J. P., Ziervogel G. (2019). Water governance and justice in Cape Town: An overview. WIREs Water 6, 1354. doi: 10.1002/wat2.1354
Eyisi A. P., Ololo N. G., Aruomah M. O. (2024). The impacts of colonialism on residents’ perceptions of tourism in Southeastern Nigeria. Tourism Hospitality Res. 24, 152–165. doi: 10.1177/14673584221128139
Feyrer J., Sacerdote B. (2009). Colonialism and modern income: Islands as natural experiments. Rev. Economics Stat 91, 245–262. doi: 10.1162/rest.91.2.245
Finley-Brook M., Thomas C. (2010). Treatment of displaced indigenous populations in two large hydro projects in Panama. Water Alternatives 3, 269–290.
Fragkou M. C., McEvoy J. (2016). Trust matters: Why augmenting water supplies via desalination may not overcome perceptual water scarcity. Desalination 397, 1–8. doi: 10.1016/j.desal.2016.06.007
Freudenberg N., Tsui E. (2014). Evidence, power, and policy change in community-based participatory research. Am. J. Public Health (1971) 104, 11–14. doi: 10.2105/AJPH.2013.301471
Gheuens J., Nagabhatla N., Perera E. D. P. (2019). Disaster-risk, water security challenges and strategies in small island developing states (SIDS). Water 11, 637. doi: 10.3390/w11040637
Glaser B. G. (1965). The constant comparative method of qualitative analysis. Soc. Problems 12, 436–445. doi: 10.2307/798843
Godoy Y. (2023) Panama will develop water and sanitation project (Telemetro). Available online at: https://www.telemetro.com/nacionales/Panama-desarrollara-proyecto-agua-y-saneamiento-n5902526 (Accessed July 22, 2023).
Gossling S. (2015). New performance indicators for water management in tourism. Tourism Manage. (1982) 46, 233–244. doi: 10.1016/j.tourman.2014.06.018
Gössling S., Peeters P., Hall C. M., Ceron J.-P., Dubois G., Lehmann L. V., et al. (2012). Tourism and water use: Supply, demand, and security. An international review. Tourism Manage. (1982) 33, 1–15. doi: 10.1016/j.tourman.2011.03.015
Gray E., Burke L., Lambert J. (2015). Valuing the costs and benefits of improved wastewater management: An economic valuation resource guide for the wider caribbean region (World Resource Institute). Available at: https://clmeplus.org/app/uploads/2020/04/CReW_C2_WRI_Valuing_Wastewater_PART_I_-Summary_Revised_April16.pdf .
Grimwood B. S. R., Stinson M. J., King L. J. (2019). A decolonizing settler story. Ann. Tourism Res. 79, 102763. doi: 10.1016/j.annals.2019.102763
Grydehøj A., Bevacqua M. L., Chibana M., Nadarajah Y., Simonsen A., Su P., et al. (2021). Practicing decolonial political geography: Island perspectives on neocolonialism and the China threat discourse. Political Geogr. 85, 102330. doi: 10.1016/j.polgeo.2020.102330
Guerrón-Montero C. (2006). Racial democracy and nationalism in Panama. Ethnology 45, 209–228. doi: 10.2307/20456595
Harrington C., Montana P., Schmidt J. J., Swain A. (2023). Race, ethnicity, and the case for intersectional water security. Global Environ. Politics 23, 1–10. doi: 10.1162/glep_a_00702
Harrison D., Prasad B. (2011). “The contribution of tourism to the development of Fiji and other pacific island countries,” in Handbook of Tourism Economics (Queensland: WORLD SCIENTIFIC), 741–761. doi: 10.1142/9789814327084_0032
Hau’ofa E. (1994). Our sea of islands. Contemp. Pacific 6, 148–161.
Heim O. (2017). Island logic and the decolonization of the pacific. Interventions 19, 914–929. doi: 10.1080/1369801X.2017.1401945
Hodkinson P. (2008). “Grounded Theory and inductive research,” in Researching Social Life , vol. 5. (London: SAGE Publications Ltd), 80–100.
Hoyman M. M., McCall J. R. (2013). Is there trouble in paradise? The perspectives of Galapagos community leaders on managing economic development and environmental conservation through ecotourism policies and the Special Law of 1998. J. Ecotourism 12, 33–48. doi: 10.1080/14724049.2012.749882
IDAAN IDAAN maintains a contingency plan for water supply on Isla Colón (IDAAN). Available online at: https://www.idaan.gob.pa/idaan-mantiene-plan-de-contingencia-de-abastecimiento-de-agua-en-isla-colon/ (Accessed July 22, 2023).
IDAAN (2022) Facturcion Total Clientes Medidos, Medidor Promediado y no Medidos en Balboas y Volumen en Galones (No. 2) . Available online at: https://www.idaan.gob.pa/wp-content/uploads/2022/04/FACTURACION-TOTAL-CLIENTES-MEDIDOS-MEDIDOR-PROMEDIADO-Y-NO-MEDIDOS-EN-BALBOAS-Y-VOLUMEN-EN-GALONES.pdf .
INEC. (2021). Population . Available online at: https://www.inec.gob.pa/publicaciones/Default3.aspx?ID_PUBLICACION=1196andID_CATEGORIA=17andID_SUBCATEGORIA=45 (Accessed October 11, 2023).
Inter-American Development Bank Comprehensive urban development program with tourist vocations . Available online at: https://www.iadb.org/en/whats-our-impact/PN-L1154 (Accessed October 15, 2023).
Israel B. A., Schulz A. J., Coombe C. M., Parker E. A., Reyes A. G., Rowe Z., et al. (2019). Community-based participatory research. Urban Health 272, 272–282. doi: 10.1093/oso/9780190915858.003.0029
Karst H. E., Nepal S. K. (2022). Social-ecological wellbeing of communities engaged in ecotourism: Perspectives from Sakteng Wildlife Sanctuary, Bhutan. J. Sustain. Tourism 30, 1177–1199. doi: 10.1080/09669582.2021.1913500
Kay C. (2010). Latin American Theories of Development and Underdevelopment (New York: Routledge). doi: 10.4324/9780203835418
Keegan W. F., Diamond J. M. (1987). Colonization of islands by humans: A biogeographical perspective. Adv. Archaeological Method Theory 10, 49–92. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-003110-8.50005-0
Klytchnikova I., Dorosh P. (2013). Tourism sector in Panama: Regional economic impacts and the potential to benefit the poor. Natural Resour. Forum 37, 70–79. doi: 10.1111/1477-8947.12019
Lee C.-C., Chien M.-S. (2008). Structural breaks, tourism development, and economic growth: Evidence from Taiwan. Mathematics Comput. Simulation 77, 358–368. doi: 10.1016/j.matcom.2007.03.004
Leposa N. (2020). Problematic blue growth: A thematic synthesis of social sustainability problems related to growth in the marine and coastal tourism. Sustainability Sci. 15, 1233–1244. doi: 10.1007/s11625-020-00796-9
Lipton M. (1977). ““Why poor people stay poor: A study of urban bias in world development,”,” in Milestones and Turning Points in Development Thinking . Ed. Jolly R. (Palgrave Macmillan, London), 148.
Lucas A. (2019) Tourism in Bocas del Toro, contradictory paths (Alba Sud). Available online at: https://www.albasud.org/noticia/es/1111/turismo-en-bocas-del-toro-caminos-contradictorios (Accessed May 3, 2023).
Lucas H., Fifita S., Talab I., Marschel C., Cabeza L. F. (2017). Critical challenges and capacity building needs for renewable energy deployment in Pacific Small Island Developing States (Pacific SIDS). Renewable Energy 107, 42–52. doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2017.01.029
Mach L., McPherson B., Hayes R. (2023). Wildlife tourism maps and the governance of environmental collapse. Tourism Geographies 25, 1465–1482. doi: 10.1080/14616688.2023.2231423
Mach L., Vahradian D. (2021). Tourists want to be spooked, not schooled: Sustaining indigenous tourism in the Bastimentos Island National Marine Park, Bocas del Toro, Panama. J. Ecotourism 20, 130–144. doi: 10.1080/14724049.2019.1585439
McElroy J. L. (2006). Small island tourist economies across the life cycle. Asia Pacific Viewpoint 47, 61–77. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-8373.2006.00303.x
Méndez-Barrientos L. E., Fencl A. L., Workman C. L., Shah S. H. (2023). Race, citizenship, and belonging in the pursuit of water and climate justice in California. Environ. Plann. E: Nat. Space 6, 1614–1635. doi: 10.1177/25148486221133282
MiAMBIENTE. (2022). Política Nacional de Océanos de Panamá (Panama City: MiAmbiente). Available online at: https://www.undp.org/sites/g/files/zskgke326/files/2023-03/UNDP-PA-Politica-Oceanos-Documento.pdf (Accessed October 15, 2023).
Minow M. (2021). Equality vs. equity. Am. J. Law Equality 1, 167–193. doi: 10.1162/ajle_a_00019
Murtin F., Fleischer L., Siegerink V., Aassve A., Algan Y., Boarini R., et al. (2018) Trust and its determinants: Evidence from the Trustlab experiment (OECD Working Paper). Available online at: https://www.oecd-ilibrary.org/economics/trust-and-its-determinants_869ef2ec-en (Accessed October 10, 2023).
Nilsen T., Grillitsch M., Hauge A. (2023). Varieties of periphery and local agency in regional development. Regional Stud. 57, 749–762. doi: 10.1080/00343404.2022.2106364
Nugraheni A. I. P., Priyambodo T. K., Sutikno B., Kusworo H. A. (2020). The social dimensions’ Aspects of sustainable tourism development analysis: A systematic literature review. Digital Press Soc. Sci. Humanities 4, 1. doi: 10.29037/digitalpress.44348
Nunn P., Kumar R. (2017). Understanding climate-human interactions in Small Island Developing States (SIDS): Implications for future livelihood sustainability. Int. J. Climate Change Strategies Manage. 10, 245–271. doi: 10.1108/IJCCSM-01-2017-0012
Ortiz N. (2023) From Crises To Solutions: Tackling The Water Challenges Of An Island Paradise (The Bocas Breeze Newspaper). Available online at: https://thebocasbreeze.com/community/water-solutions/ (Accessed August 30, 2023).
Osterblum H., Wabnitz C. C., Tladi D., Allison E., Arnaud-Haond S., Bebbington J., et al. (2020) Towards Ocean Equity. High Level Panel for a Sustainable Ocean Economy Working Paper . Available online at: https://digitalarchive.worldfishcenter.org/handle/20.500.12348/4486 (Accessed January 1, 2023).
Pace L. A., Saritas O., Deidun A. (2023). Exploring future research and innovation directions for a sustainable blue economy. Mar. Policy 148, 105433. doi: 10.1016/j.marpol.2022.105433\
Pascual U., Phelps J., Garmendia E., Brown K., Corbera E., Martin A., et al. (2014). Social equity matters in payments for ecosystem services. BioScience. 64, 1027–1036. doi: 10.1093/biosci/biu146
Peterson R. R. (2020). Over the caribbean top: Community well-being and over-tourism in small island tourism economies. Int. J. Community Well-Being 6, 89–126. doi: 10.1007/s42413-020-00094-3
Peterson R. R. (2023). Over the caribbean top: Community well-being and over-tourism in small island tourism economies. Int. J. Community Well-Being 6, 89–126. doi: 10.1007/s42413-020-00094-3
Phelan A., Ruhanen L., Mair J. (2020). Ecosystem services approach for community-based ecotourism: towards an equitable and sustainable blue economy. J. Sustain. Tourism 28, 1665–1685. doi: 10.1080/09669582.2020.1747475
Pierskalla J. H. (2016). The politics of urban bias: Rural threats and the dual dilemma of political survival. Stud. Comp. Int. Dev. 51, 286–307. doi: 10.1007/s12116-015-9194-2
Pigram J. (2000) Water Resources Management: In Island Environments: The Challenge of Tourism Development (Wisconsin: Centre for Water Policy Research). Available online at: https://mail.perfectbg.com/TouristDocuments.nsf/0/9a3404dbc7a13563c2257061003bc83f/$FILE/waterresourse.pdf (Accessed October 7, 2023).
Pleasant T., Spalding A. (2021). Development and dependency in the periphery: From bananas to tourism in Bocas del Toro, Panama. World Dev. Perspect. 24, 100363. doi: 10.1016/j.wdp.2021.100363
Rahman M. K., Masud M. M., Akhtar R., Hossain M. M. (2022). Impact of community participation on sustainable development of marine protected areas: Assessment of ecotourism development. Int. J. Tourism Res. 24, 33–43. doi: 10.1002/jtr.2480
Ramos-García J., Ibarra-Michel J. P., Velarde-Valdez M. (2017). Community-based ecotourism management: the case of a cooperative in Mazatlán, Sinaloa, Mexico. Czech J. Tourism 6, 155–170. doi: 10.1515/cjot-2017–0008
Resolución de Gabinete No. 127 (2022). Available online at: https://www.gacetaoficial.gob.pa/pdfTemp/29660_A/GacetaNo_29660a_20221109.pdf .
Resolución de Gabinete No. 48 (2023). Available online at: https://www.gacetaoficial.gob.pa/pdfTemp/29793/GacetaNo_29793_20230531.pdf .
Roller M. R., Lavrakas P. H. (2015). “A multi-method approach in qualitative research,” in Applied Qualitative Research Design: A Total Quality Framework Approach (New York: Guilford Publications), 288–289.
Sakellariadou F. (2014). The concept of marine ecotourism: A case study in a mediterranean island. Int. J. Climate Change: Impacts Responses 6, 33–39. doi: 10.18848/1835-7156/CGP/v06i01/37218
Sandelowski M. (1995). Sample size in qualitative research. Res. Nurs. Health 18, 179–183. doi: 10.1002/nur.4770180211
Scott C. P., Mach L., Lucas K. M., Myers A. E. (2024). Whose cultural ecosystem service values matter? Exploring power inequities in diverse mangrove communities. Hum. Ecology : Interdiscip. J . 52, 81–97. doi: 10.1007/s10745-023-00462-5
Sealy W. (2018). From colonialism to transnationalism: The neo-colonial structure of caribbean tourism. J. On Tourism Sustainability 1, 81–92.
Seemann J., González C. T., Carballo-Bolaños R., Berry K., Heiss G. A., Struck U., et al. (2014). Assessing the ecological effects of human impacts on coral reefs in Bocas del Toro, Panama. Environ. Monit. Assessment. 186, 1747–1763. doi: 10.1007/s10661-013-3490-y
Singh G. G., Keefer J., Ota Y. (2023). An inequity assessment framework for planning coastal and marine conservation and development interventions. Front. Mar. Sci. 10. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2023.1256500
Spalding A. K. (2017). Exploring the evolution of land tenure and land use change in panama: Linking land policy with development outcomes. Land Use Policy 61, 543–552. doi: 10.1016/j.landusepol.2016.11.023
Spalding A. K. (2011). Re-Making Lives Abroad: Lifestyle Migration and Socio-Environmental Change in Bocas del Toro (Panama: [Alberta]: University of Lethbridge).
Spalding A. K. (2013). Lifestyle Migration to Bocas del Toro, Panama: Exploring migration strategies and introducing local implications of the search for paradise. Int. Rev. Soc. Res. 3, 67–86. doi: 10.1515/irsr-2013-0005
Spalding A. K., Suman D. O., Mellado M. E. (2015). Navigating the evolution of marine policy in Panama: Current policies and community responses in the Pearl Islands and Bocas del Toro Archipelagos of Panama. Mar. Policy 62, 161–168. doi: 10.1016/j.marpol.2015.09.020
Srivastava S., Mehta L. (2023). The social life of mangroves: Neoliberal development and mangrove conservation in the changing landscape of Kutch. Environ. Planning. E Nat. Space (Print) 6, 2229–2248. doi: 10.1177/25148486211045360
STRI GIS Data Portal (2019). Available online at: https://stridata-si.opendata.arcgis.com/datasets/e9b8ba21a21d4ac7be98bbff2c67d3f2_0/explore .
Suman D. O., Spalding A. K. (2018). Coastal Resources of Bocas del Toro, PANAMA: Tourism and Development Pressures and the Quest for Sustainability (Miami: University of Miami).
Tecel A., Katircioğlu S., Taheri E., Victor Bekun F. (2020). Causal interactions among tourism, foreign direct investment, domestic credits, and economic growth: Evidence from selected Mediterranean countries. Portuguese Economic J. 19, 195–212. doi: 10.1007/s10258-020-00181-5
Telemetro (2022) State of Environmental Emergency declared on Colón and Carenero islands due to lack of water (Telemetro). Available online at: https://www.telemetro.com/nacionales/declaran-estado-emergencia-ambiental-islas-colon-y-carenero-falta-agua-n5799895 (Accessed July 22, 2023).
Tilmans S., Diaz-Hernandez A., Nyman E., Davis J. (2014). The potential for financing small-scale wastewater treatment through resource recovery: Experience from Bocas del Toro, Panama. J. Water Sanitation Hygiene Dev. 4, 449–459. doi: 10.2166/washdev.2014.138
Tuwo A., Yunus M., Aprianto R., Tresnati J. (2021). Marine ecotourism development in South Sulawesi, Indonesia. IOP Conf. Series. Earth Environ. Sci. 763, 12068. doi: 10.1088/1755-1315/763/1/012068
UN Water (2013) What is Water Security (Geneva: UN Water). Available online at: https://www.unwater.org/sites/default/files/app/uploads/2017/05/unwater_poster_Oct2013.pdf (Accessed October 16, 2023).
UN Water (2020) Water and Climate Change: United Nations World Water Development Report 2020 (UNESCO). Available online at: https://unesdoc.unesco.org/ark:/48223/pf0000372985.locale=en (Accessed October 16, 2023).
UN Water (2021) SDG 6 Capacity Development Initiative: Concept Note (Geneva: UN Water). Available online at: https://sdgs.un.org/partnerships/un-water-sdg-6-capacity-development-initiative#:~:text=The%20SDG%206%20Capacity%20Development%20Initiative%20supports%20coordination%20on%20SDG,the%20SDG%206%20Global%20Acceleration (Accessed July 23, 2023).
UNWTO. (2023). Inbound tourism expenditure over exports of goods and services. Available online at https://www.unwto.org/news/international-tourism-to-reach-pre-pandemic-levels-in-2024 .
UN-OHRLLS. (2022). List of LDCs. In: Office of the high representative for the least developed countries, landlocked developing countries and small island developing states . Available at: https://www.un.org/ohrlls/content/list-ldcs (Accessed November 8, 2023).
Weiss R. S. (1994). Learning from strangers : The art and method of qualitative interview studies (New York: Free Press).
Winters Z. S., Crisman T. L., Dumke D. T. (2022). Sustainability of the Water-energy-food nexus in caribbean small island developing states. Water (Basel) 14, 322. doi: 10.3390/w14030322
Workman C. L., Shah S. H. (2023). Water infrastructure as intrusion: race, exclusion, and nostalgic futures in North Carolina. Ann. Am. Assoc. Geographers 113, 1639–1651. doi: 10.1080/24694452.2022.2149461
World Bank and UN DESA (2017) The Potential of the Blue Economy—Increasing Long- term Benefits of the Sustainable Use of Marine Resources for SIDS and Coastal Least Developed Countries (Washington: World Bank). Available online at: https://openknowledge.worldbank.org/server/api/core/bitstreams/cee24b6c-2e2f-5579-b1a4-457011419425/content (Accessed November 9, 2023).
Wortman T., Donaldson R., van Westen G. (2016). “They are stealing my island”: Residents’ opinions on foreign investment in the residential tourism industry in Tamarin, Mauritius. Singapore J. Trop. Geogr. 37, 139–157. doi: 10.1111/sjtg.12151
Zeng X., Chen M., Zeng C., Cheng S., Wang Z., Liu S., et al. (2022). Assessing the management effectiveness of China’s marine protected areas: Challenges and recommendations. Ocean Coast. Management. 224, 106172. doi: 10.1016/j.ocecoaman.2022.106172
Keywords: marine ecotourism, water security, blue economy, island systems, Bocas del Toro, sustainable development
Citation: Kim A, Scott CP and Swartz W (2024) Local perspectives on marine ecotourism development in a water-insecure island region: the case of Bocas del Toro, Panama. Front. Mar. Sci. 11:1377053. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2024.1377053
Received: 26 January 2024; Accepted: 02 May 2024; Published: 17 May 2024.
Reviewed by:
Copyright © 2024 Kim, Scott and Swartz. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY) . The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Abigael Kim, [email protected]
† These authors have contributed equally to this work
This article is part of the Research Topic
The Potentials and Pitfalls from National Blue Economy Plans Towards Sustainable Development
Wegovy users keep weight off for 4 years, new analysis finds
Patients taking Novo Nordisk’s Wegovy obesity treatment maintained an average of 10% weight loss after four years, potentially boosting the drugmaker’s case to insurers and governments to cover the cost of the effective but expensive drug.
The Danish drugmaker presented the new long-term data on Tuesday at the European Congress on Obesity in Venice, Italy, in a new analysis from a large study for which substantial results had been published last year.
“This is the longest study we’ve conducted so far of semaglutide for weight loss,” Martin Holst Lange, Novo’s head of development, said in an interview, referring to the active ingredient in Wegovy and the company’s diabetes drug Ozempic.
“We see that once the majority of the weight loss is accrued, you don’t go back and start to increase in weight if you stay on the drug,” he added.
The data could go some way to convince insurers and governments to reimburse Wegovy, which ranges from $200 to almost $2,000 a month in the 10 countries it has been launched in so far.
Wegovy was the first to market from a newer generation of medicines known as GLP-1 agonists, originally developed for diabetes, that provide a new way to address record obesity rates. Eli Lilly launched its rival drug Zepbound in the United States in December. Neither company has been able to produce enough to meet unprecedented demand .
Dr. Simon Cork, Senior Lecturer in Physiology from Anglia Ruskin University, said Britain’s public health service’s decision to limit coverage of the medicine to two years was “because of questionable long-term effectiveness”.
The new data showing benefits continuing to four years may go some way to negating that argument, he said.
How Wegovy benefits the heart
The 17,604-patient trial tested Wegovy not for weight loss but for its heart protective benefits for overweight and obese patients who had pre-existing heart disease but not diabetes. Participants were not required to track diet and exercise because it was not an obesity study.
Around 17% of trial participants stopped using Wegovy due to side effects, the most common of which was nausea, Novo said in another analysis in the trial published by the drugmaker on Tuesday.
Patients in the trial, called Select, lost an average of nearly 10% of their total body weight after 65 weeks on Wegovy. That percentage weight-loss was roughly sustained year-on-year until the end of about four years, where weight loss stood at 10.2%, the company said.
A third new analysis on Select published by Novo on Tuesday showed that the heart protective benefits of Wegovy to patients in the trial occurred regardless of their weight before starting on the drug and regardless of how much weight they lose on it.
“We now also understand that while we know that body weight loss is important, it’s not the only thing driving the cardiovascular benefit of semaglutide treatment”, Lange told Reuters in the interview.
The Select study, released in August, showed that Wegovy reduced the risk of a major cardiovascular event such as a stroke by 20% in overweight or obese people with a history of heart disease.
Novo says researchers are still working to understand the mechanisms of the cardiovascular protection that semaglutide provides.
Wegovy and Zepbound are being tested to assess their benefits in a variety of other medical uses such as lowering heart attack risk and for sleep apnea and kidney disease.
The weight loss in the heart trial was less than the average of 15% weight loss in earlier Wegovy obesity studies before the drug was launched in the United States in June 2021.
Wegovy users keep weight off for four years, Novo Nordisk study says
- Medium Text
- Company Novo Nordisk A/S Follow
- Company Eli Lilly and Co Follow
- Company Roche Holding AG Follow
HEART BENEFITS
Sign up here.
Reporting by Maggie Fick Editing by Bill Berkrot and Louise Heavens
Our Standards: The Thomson Reuters Trust Principles. New Tab , opens new tab

Thomson Reuters
Maggie is a Britain-based reporter covering the European pharmaceuticals industry with a global perspective. In 2023, Maggie's coverage of Danish drugmaker Novo Nordisk and its race to increase production of its new weight-loss drug helped the Health & Pharma team win a Reuters Journalists of the Year award in the Beat Coverage of the Year category. Since November 2023, she has also been participating in Reuters coverage related to the Israel-Hamas war. Previously based in Nairobi and Cairo for Reuters and in Lagos for the Financial Times, Maggie got her start in journalism in 2010 as a freelancer for The Associated Press in South Sudan.

Business Chevron

Nestle India shareholders vote against increase in royalty to Swiss parent
Shareholders in Nestle India have rejected a company proposal to increase royalty payments to its Swiss parent Nestle , the company said late on Friday.


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
In case study research, the unit of analysis can be an individual, a group, an organization, a decision, an event, or even a time period. It's crucial to clearly define the unit of analysis, as it shapes the qualitative data analysis process by allowing the researcher to analyze a particular case and synthesize analysis across multiple case ...
A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject, such as a person, group, place, event, organization, or phenomenon. Learn how to choose, collect, and analyze data for a case study, and see examples of different types of case studies.
Case study is unbounded and relies on gathering external information; case analysis is a self-contained subject of analysis. The scope of a case study chosen as a method of research is bounded. However, the researcher is free to gather whatever information and data is necessary to investigate its relevance to understanding the research problem.
Learn how to conduct a case study research, a qualitative method that involves an in-depth examination and analysis of a particular phenomenon or case. Find out the types, methods, data collection, analysis, and reporting of case study research.
Case study protocol is a formal document capturing the entire set of procedures involved in the collection of empirical material . It extends direction to researchers for gathering evidences, empirical material analysis, and case study reporting . This section includes a step-by-step guide that is used for the execution of the actual study.
Case study examples. Case studies are proven marketing strategies in a wide variety of B2B industries. Here are just a few examples of a case study: Amazon Web Services, Inc. provides companies with cloud computing platforms and APIs on a metered, pay-as-you-go basis. This case study example illustrates the benefits Thomson Reuters experienced ...
The purpose of case study research is twofold: (1) to provide descriptive information and (2) to suggest theoretical relevance. Rich description enables an in-depth or sharpened understanding of the case. It is unique given one characteristic: case studies draw from more than one data source. Case studies are inherently multimodal or mixed ...
Learn how to investigate, examine, and propose solutions for a business problem using a case study. Follow the guidelines to prepare, draft, and finalize your analysis with supporting evidence.
Learn how to conduct a case study, a detailed study of a specific subject in its real-world context. Find out when to use a case study, how to select a case, build a theoretical framework, collect and analyse data, and write up the case study.
A case study research paper examines a person, place, event, condition, phenomenon, or other type of subject of analysis in order to extrapolate key themes and results that help predict future trends, illuminate previously hidden issues that can be applied to practice, and/or provide a means for understanding an important research problem with greater clarity.
A case study is one of the most commonly used methodologies of social research. This article attempts to look into the various dimensions of a case study research strategy, the different epistemological strands which determine the particular case study type and approach adopted in the field, discusses the factors which can enhance the effectiveness of a case study research, and the debate ...
A Case study is: An in-depth research design that primarily uses a qualitative methodology but sometimes includes quantitative methodology. Used to examine an identifiable problem confirmed through research. Used to investigate an individual, group of people, organization, or event. Used to mostly answer "how" and "why" questions.
The case study is a detailed analysis of a given phenomenon. On the other hand, a research study is a broader exploration of a topic. Case studies typically use qualitative research methods like documents, observations, and interviews. A research study follows a more standardized structure, and uses more rigorous and systematic research ...
How to Analyze a Case Study Adapted from Ellet, W. (2007). The case study handbook. Boston, MA: Harvard Business School. A business case simulates a real situation and has three characteristics: 1. a significant issue, 2. enough information to reach a reasonable conclusion, 3. no stated conclusion. A case may include 1. irrelevant information 2.
Case study examples. While templates are helpful, seeing a case study in action can also be a great way to learn. Here are some examples of how Adobe customers have experienced success. Juniper Networks. One example is the Adobe and Juniper Networks case study, which puts the reader in the customer's shoes.
Case Study Analysis is a widely used research method that examines in-depth information about a particular individual, group, organization, or event. It is a comprehensive investigative approach that aims to understand the intricacies and complexities of the subject under study. Through the analysis of real-life scenarios and inquiry into ...
Step 4: Analyze Your Findings. Using the information in steps 2 and 3, create an evaluation for this portion of your case study analysis. Compare the strengths and weaknesses within the company to the external threats and opportunities. Determine if the company is in a strong competitive position, and decide if it can continue at its current ...
A case study is an in-depth study of one person, group, or event. In a case study, nearly every aspect of the subject's life and history is analyzed to seek patterns and causes of behavior. Case studies can be used in many different fields, including psychology, medicine, education, anthropology, political science, and social work.
For example, the case study quotes the social media manager and project manager's insights regarding team-wide communication and access before explaining in greater detail. Takeaway: Highlight pain points your business solves for its client, and explore that influence in greater detail. 3. EndeavourX and Figma.
Résumé. Case study is a common methodology in the social sciences (management, psychology, science of education, political science, sociology). A lot of methodological papers have been dedicated to case study but, paradoxically, the question "what is a case?" has been less studied.
Case studies help attract attention to your products, b. We've put together 15 real-life case study examples to inspire you. These examples cover a variety of industries and formats, plus templates to inspire you. ... It provides an in-depth analysis of your company's problem-solving process. Disadvantages of a case study:
A case study analysis is a typical assignment in business management courses. The task aims to show high school and college students how to analyze a current situation, determine what problems exist, and develop the best possible strategy to achieve the desired outcome.
The ordering process is fully online, and it goes as follows: • Select the topic and the deadline of your case study. • Provide us with any details, requirements, statements that should be emphasized or particular parts of the writing process you struggle with. • Leave the email address, where your completed order will be sent to.
Companies use dashboards for competitive analysis or to study performance in different parts of the business that are automatically updated. Some have interactive capabilities for refinement and testing. ... The neutral momentum case, which AI can calculate in a cold, Spock-like manner, can change the dynamics of the resource allocation ...
What is big data analytics? Big data analytics refers to the systematic processing and analysis of large amounts of data and complex data sets, known as big data, to extract valuable insights. Big data analytics allows for the uncovering of trends, patterns and correlations in large amounts of raw data to help analysts make data-informed decisions.
The Role of Traditional Knowledge Due to Climate Change Adaptation and Economic Wellbeing in Island Communities: A Case Study of Terengganu, Malaysia Previous Article in Journal Predictive Modeling and Validation of Carbon Emissions from China's Coastal Construction Industry: A BO-XGBoost Ensemble Approach
Through a case study of the Bocas del Toro Archipelago, where water insecurity is becoming acute, we draw on and mobilize stories from local community members, alongside non-participant observations and document collection, to 1) document the experience of some community members with water insecurity and shortages, including how they perceive ...
Case Study Analysis 3.4. Business Environment Analysis Chapter 4. mHealth Apps Market Segment Analysis, By Type, 2018 - 2030 (USD Million) 4.1. Definitions and Scope 4.2. Type Segment Dashboard
The weight loss in the heart trial was less than the average of 15% weight loss in earlier Wegovy obesity studies before the drug was launched in the United States in June 2021. Patients taking ...
Patients taking Novo Nordisk's Wegovy obesity treatment maintained an average of 10% weight loss after four years, potentially boosting the drugmaker's case to insurers and governments to cover ...