

14 Crafting a Thesis Statement
Learning Objectives
- Craft a thesis statement that is clear, concise, and declarative.
- Narrow your topic based on your thesis statement and consider the ways that your main points will support the thesis.
Crafting a Thesis Statement
A thesis statement is a short, declarative sentence that states the purpose, intent, or main idea of a speech. A strong, clear thesis statement is very valuable within an introduction because it lays out the basic goal of the entire speech. We strongly believe that it is worthwhile to invest some time in framing and writing a good thesis statement. You may even want to write your thesis statement before you even begin conducting research for your speech. While you may end up rewriting your thesis statement later, having a clear idea of your purpose, intent, or main idea before you start searching for research will help you focus on the most appropriate material. To help us understand thesis statements, we will first explore their basic functions and then discuss how to write a thesis statement.
Basic Functions of a Thesis Statement
A thesis statement helps your audience by letting them know, clearly and concisely, what you are going to talk about. A strong thesis statement will allow your reader to understand the central message of your speech. You will want to be as specific as possible. A thesis statement for informative speaking should be a declarative statement that is clear and concise; it will tell the audience what to expect in your speech. For persuasive speaking, a thesis statement should have a narrow focus and should be arguable, there must be an argument to explore within the speech. The exploration piece will come with research, but we will discuss that in the main points. For now, you will need to consider your specific purpose and how this relates directly to what you want to tell this audience. Remember, no matter if your general purpose is to inform or persuade, your thesis will be a declarative statement that reflects your purpose.
How to Write a Thesis Statement
Now that we’ve looked at why a thesis statement is crucial in a speech, let’s switch gears and talk about how we go about writing a solid thesis statement. A thesis statement is related to the general and specific purposes of a speech.
Once you have chosen your topic and determined your purpose, you will need to make sure your topic is narrow. One of the hardest parts of writing a thesis statement is narrowing a speech from a broad topic to one that can be easily covered during a five- to seven-minute speech. While five to seven minutes may sound like a long time for new public speakers, the time flies by very quickly when you are speaking. You can easily run out of time if your topic is too broad. To ascertain if your topic is narrow enough for a specific time frame, ask yourself three questions.
Is your speech topic a broad overgeneralization of a topic?
Overgeneralization occurs when we classify everyone in a specific group as having a specific characteristic. For example, a speaker’s thesis statement that “all members of the National Council of La Raza are militant” is an overgeneralization of all members of the organization. Furthermore, a speaker would have to correctly demonstrate that all members of the organization are militant for the thesis statement to be proven, which is a very difficult task since the National Council of La Raza consists of millions of Hispanic Americans. A more appropriate thesis related to this topic could be, “Since the creation of the National Council of La Raza [NCLR] in 1968, the NCLR has become increasingly militant in addressing the causes of Hispanics in the United States.”
Is your speech’s topic one clear topic or multiple topics?
A strong thesis statement consists of only a single topic. The following is an example of a thesis statement that contains too many topics: “Medical marijuana, prostitution, and Women’s Equal Rights Amendment should all be legalized in the United States.” Not only are all three fairly broad, but you also have three completely unrelated topics thrown into a single thesis statement. Instead of a thesis statement that has multiple topics, limit yourself to only one topic. Here’s an example of a thesis statement examining only one topic: Ratifying the Women’s Equal Rights Amendment as equal citizens under the United States law would protect women by requiring state and federal law to engage in equitable freedoms among the sexes.
Does the topic have direction?
If your basic topic is too broad, you will never have a solid thesis statement or a coherent speech. For example, if you start off with the topic “Barack Obama is a role model for everyone,” what do you mean by this statement? Do you think President Obama is a role model because of his dedication to civic service? Do you think he’s a role model because he’s a good basketball player? Do you think he’s a good role model because he’s an excellent public speaker? When your topic is too broad, almost anything can become part of the topic. This ultimately leads to a lack of direction and coherence within the speech itself. To make a cleaner topic, a speaker needs to narrow her or his topic to one specific area. For example, you may want to examine why President Obama is a good public speaker.
Put Your Topic into a Declarative Sentence
You wrote your general and specific purpose. Use this information to guide your thesis statement. If you wrote a clear purpose, it will be easy to turn this into a declarative statement.
General purpose: To inform
Specific purpose: To inform my audience about the lyricism of former President Barack Obama’s presentation skills.
Your thesis statement needs to be a declarative statement. This means it needs to actually state something. If a speaker says, “I am going to talk to you about the effects of social media,” this tells you nothing about the speech content. Are the effects positive? Are they negative? Are they both? We don’t know. This sentence is an announcement, not a thesis statement. A declarative statement clearly states the message of your speech.
For example, you could turn the topic of President Obama’s public speaking skills into the following sentence: “Because of his unique sense of lyricism and his well-developed presentational skills, President Barack Obama is a modern symbol of the power of public speaking.” Or you could state, “Socal media has both positive and negative effects on users.”
Adding your Argument, Viewpoint, or Opinion
If your topic is informative, your job is to make sure that the thesis statement is nonargumentative and focuses on facts. For example, in the preceding thesis statement, we have a couple of opinion-oriented terms that should be avoided for informative speeches: “unique sense,” “well-developed,” and “power.” All three of these terms are laced with an individual’s opinion, which is fine for a persuasive speech but not for an informative speech. For informative speeches, the goal of a thesis statement is to explain what the speech will be informing the audience about, not attempting to add the speaker’s opinion about the speech’s topic. For an informative speech, you could rewrite the thesis statement to read, “Barack Obama’s use of lyricism in his speech, ‘A World That Stands as One,’ delivered July 2008 in Berlin demonstrates exceptional use of rhetorical strategies.
On the other hand, if your topic is persuasive, you want to make sure that your argument, viewpoint, or opinion is clearly indicated within the thesis statement. If you are going to argue that Barack Obama is a great speaker, then you should set up this argument within your thesis statement.
For example, you could turn the topic of President Obama’s public speaking skills into the following sentence: “Because of his unique sense of lyricism and his well-developed presentational skills, President Barack Obama is a modern symbol of the power of public speaking.” Once you have a clear topic sentence, you can start tweaking the thesis statement to help set up the purpose of your speech.
Thesis Checklist
Once you have written a first draft of your thesis statement, you’re probably going to end up revising your thesis statement a number of times prior to delivering your actual speech. A thesis statement is something that is constantly tweaked until the speech is given. As your speech develops, often your thesis will need to be rewritten to whatever direction the speech itself has taken. We often start with a speech going in one direction, and find out through our research that we should have gone in a different direction. When you think you finally have a thesis statement that is good to go for your speech, take a second and make sure it adheres to the criteria shown below.

Preview of Speech
The preview, as stated in the introduction portion of our readings, reminds us that we will need to let the audience know what the main points in our speech will be. You will want to follow the thesis with the preview of your speech. Your preview will allow the audience to follow your main points in a sequential manner. Spoiler alert: The preview when stated out loud will remind you of main point 1, main point 2, and main point 3 (etc. if you have more or less main points). It is a built in memory card!
For Future Reference | How to organize this in an outline |
Introduction
Attention Getter: Background information: Credibility: Thesis: Preview:
Key Takeaways
Introductions are foundational to an effective public speech.
- A thesis statement is instrumental to a speech that is well-developed and supported.
- Be sure that you are spending enough time brainstorming strong attention getters and considering your audience’s goal(s) for the introduction.
- A strong thesis will allow you to follow a roadmap throughout the rest of your speech: it is worth spending the extra time to ensure you have a strong thesis statement.
Stand up, Speak out by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Public Speaking Copyright © by Dr. Layne Goodman; Amber Green, M.A.; and Various is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
- Speech Crafting →
Public Speaking: Developing a Thesis Statement In a Speech

Understanding the purpose of a thesis statement in a speech
Diving headfirst into the world of public speaking, it’s essential to grasp the role of a thesis statement in your speech. Think of it as encapsulating the soul of your speech within one or two sentences.
It’s the declarative sentence that broadcasts your intent and main idea to captivate audiences from start to finish. More than just a preview, an effective thesis statement acts as a roadmap guiding listeners through your thought process.
Giving them that quick glimpse into what they can anticipate helps keep their attention locked in.
As you craft this central hub of information, understand that its purpose is not limited to informing alone—it could be meant also to persuade or entertain based on what you aim for with your general purpose statement.
This clear focus is pivotal—it shapes each aspect of your talk, easing understanding for the audience while setting basic goals for yourself throughout the speech-making journey. So whether you are rallying rapturous applause or instigating intellectual insight, remember—your thesis statement holds power like none other! Its clarity and strength can transition between being valuable sidekicks in introductions towards becoming triumphant heroes by concluding lines.
Identifying the main idea to develop a thesis statement
In crafting a compelling speech, identifying the main idea to develop a thesis statement acts as your compass. This process is a crucial step in speech preparation that steers you towards specific purpose.
Think of your central idea as the seed from which all other elements in your speech will grow.
To pinpoint it, start by brainstorming broad topics that interest or inspire you. From this list, choose one concept that stands out and begin to narrow it down into more specific points. It’s these refined ideas that form the heart of your thesis statement — essentially acting as signposts leading the audience through your narrative journey.
Crafting an effective thesis statement requires clarity and precision. This means keeping it concise without sacrificing substance—a tricky balancing act even for public speaking veterans! The payoff though? A well-developed thesis statement provides structure to amplifying your central idea and guiding listeners smoothly from point A to B.
It’s worth noting here: just like every speaker has their own unique style, there are multiple ways of structuring a thesis statement too. But no matter how you shape yours, ensuring it resonates with both your overarching message and audience tastes will help cement its effectiveness within your broader presentation context.
Analyzing the audience to tailor the thesis statement
Audience analysis is a crucial first step for every public speaker. This process involves adapting the message to meet the audience’s needs, a thoughtful approach that considers cultural diversity and ensures clear communication.
Adapting your speech to resonate with your target audience’s interests, level of understanding, attitudes and beliefs can significantly affect its impact.
Crafting an appealing thesis statement hinges on this initial stage of audience analysis. As you analyze your crowd, focus on shaping a specific purpose statement that reflects their preferences yet stays true to the objective of your speech—capturing your main idea in one or two impactful sentences.
This balancing act demands strategy; however, it isn’t impossible. Taking into account varying aspects such as culture and perceptions can help you tailor a well-received thesis statement. A strong handle on these elements allows you to select language and tones best suited for them while also reflecting the subject at hand.
Ultimately, putting yourself in their shoes helps increase message clarity which crucially leads to acceptance of both you as the speaker and your key points – all embodied within the concise presentation of your tailor-made thesis statement.
Brainstorming techniques to generate thesis statement ideas
Leveraging brainstorming techniques to generate robust thesis statement ideas is a power move in public speaking. This process taps into the GAP model, focusing on your speech’s Goals, Audience, and Parameters for seamless target alignment.
Dive into fertile fields of thought and let your creativity flow unhindered like expert David Zarefsky proposes.
Start by zeroing in on potential speech topics then nurture them with details till they blossom into fully-fledged arguments. It’s akin to turning stones into gems for the eye of your specific purpose statement.
Don’t shy away from pushing the envelope – sometimes out-of-the-box suggestions give birth to riveting speeches! Broaden your options if parameters are flexible but remember focus is key when aiming at narrow targets.
The beauty lies not just within topic generation but also formulation of captivating informative or persuasive speech thesis statements; both fruits harvested from a successful brainstorming session.
So flex those idea muscles, encourage intellectual growth and watch as vibrant themes spring forth; you’re one step closer to commanding attention!
Remember: Your thesis statement is the heartbeat of your speech – make it strong using brainstorming techniques and fuel its pulse with evidence-backed substance throughout your presentation.
Narrowing down the thesis statement to a specific topic
Crafting a compelling thesis statement for your speech requires narrowing down a broad topic to a specific focus that can be effectively covered within the given time frame. This step is crucial as it helps you maintain clarity and coherence throughout your presentation.
Start by brainstorming various ideas related to your speech topic and then analyze them critically to identify the most relevant and interesting points to discuss. Consider the specific purpose of your speech and ask yourself what key message you want to convey to your audience.
By narrowing down your thesis statement, you can ensure that you address the most important aspects of your chosen topic, while keeping it manageable and engaging for both you as the speaker and your audience.
Choosing the appropriate language and tone for the thesis statement
Crafting the appropriate language and tone for your thesis statement is a crucial step in developing a compelling speech. Your choice of language and tone can greatly impact how your audience perceives your message and whether they are engaged or not.
When choosing the language for your thesis statement, it’s important to consider the level of formality required for your speech. Are you speaking in a professional setting or a casual gathering? Adjusting your language accordingly will help you connect with your audience on their level and make them feel comfortable.
Additionally, selecting the right tone is essential to convey the purpose of your speech effectively. Are you aiming to inform, persuade, or entertain? Each objective requires a different tone: informative speeches may call for an objective and neutral tone, persuasive speeches might benefit from more assertive language, while entertaining speeches can be lighthearted and humorous.
Remember that clarity is key when crafting your thesis statement’s language. Using concise and straightforward wording will ensure that your main idea is easily understood by everyone in the audience.
By taking these factors into account – considering formality, adapting to objectives, maintaining clarity – you can create a compelling thesis statement that grabs attention from the start and sets the stage for an impactful speech.
Incorporating evidence to support the thesis statement
Incorporating evidence to support the thesis statement is a critical aspect of delivering an effective speech. As public speakers, we understand the importance of backing up our claims with relevant and credible information.
When it comes to incorporating evidence, it’s essential to select facts, examples, and opinions that directly support your thesis statement.
To ensure your evidence is relevant and reliable, consider conducting thorough research on the topic at hand. Look for trustworthy sources such as academic journals, respected publications, or experts in the field.
By choosing solid evidence that aligns with your message, you can enhance your credibility as a speaker.
When presenting your evidence in the speech itself, be sure to keep it concise and clear. Avoid overwhelming your audience with excessive details or data. Instead, focus on selecting key points that strengthen your argument while keeping their attention engaged.
Remember that different types of evidence can be utilized depending on the nature of your speech. You may include statistical data for a persuasive presentation or personal anecdotes for an informative talk.
The choice should reflect what will resonate best with your audience and effectively support your thesis statement.
By incorporating strong evidence into our speeches, we not only bolster our arguments but also build trust with our listeners who recognize us as reliable sources of information. So remember to choose wisely when including supporting material – credibility always matters when making an impact through public speaking.
Avoiding common mistakes when developing a thesis statement
Crafting an effective thesis statement is vital for public speakers to deliver a compelling and focused speech. To avoid common mistakes when developing a thesis statement , it is essential to be aware of some pitfalls that can hinder the impact of your message.
One mistake to steer clear of is having an incomplete thesis statement. Ensure that your thesis statement includes all the necessary information without leaving any key elements out. Additionally, avoid wording your thesis statement as a question as this can dilute its potency.
Another mistake to watch out for is making statements of fact without providing evidence or support. While it may seem easy to write about factual information, it’s important to remember that statements need to be proven and backed up with credible sources or examples.
To create a more persuasive argument, avoid using phrases like “I believe” or “I feel.” Instead, take a strong stance in your thesis statement that encourages support from the audience. This will enhance your credibility and make your message more impactful.
By avoiding these common mistakes when crafting your thesis statement, you can develop a clear, engaging, and purposeful one that captivates your audience’s attention and guides the direction of your speech effectively.
Key words: Avoiding common mistakes when developing a thesis statement – Crafting a thesis statement – Effective thesis statements – Public speaking skills – Errors in the thesis statement – Enhancing credibility
Revising the thesis statement to enhance clarity and coherence
Revising the thesis statement is a crucial step in developing a clear and coherent speech. The thesis statement serves as the main idea or argument that guides your entire speech, so it’s important to make sure it effectively communicates your message to the audience.
To enhance clarity and coherence in your thesis statement, start by refining and strengthening it through revision . Take into account any feedback you may have received from others or any new information you’ve gathered since initially developing the statement.
Consider if there are any additional points or evidence that could further support your main idea.
As you revise, focus on clarifying the language and tone of your thesis statement. Choose words that resonate with your audience and clearly convey your point of view. Avoid using technical jargon or overly complicated language that might confuse or alienate listeners.
Another important aspect of revising is ensuring that your thesis statement remains focused on a specific topic. Narrow down broad ideas into more manageable topics that can be explored thoroughly within the scope of your speech.
Lastly, consider incorporating evidence to support your thesis statement. This could include statistics, examples, expert opinions, or personal anecdotes – whatever helps strengthen and validate your main argument.
By carefully revising your thesis statement for clarity and coherence, you’ll ensure that it effectively conveys your message while capturing the attention and understanding of your audience at large.
Testing the thesis statement to ensure it meets the speech’s objectives.
Testing the thesis statement is a crucial step to ensure that it effectively meets the objectives of your speech. By testing the thesis statement , you can assess its clarity, relevance, and impact on your audience.
One way to test your thesis statement is to consider its purpose and intent. Does it clearly communicate what you want to achieve with your speech? Is it concise and specific enough to guide your content?.
Another important aspect of testing the thesis statement is analyzing whether it aligns with the needs and interests of your audience. Consider their background knowledge, values, and expectations.
Will they find the topic engaging? Does the thesis statement address their concerns or provide valuable insights?.
In addition to considering purpose and audience fit, incorporating supporting evidence into your speech is vital for testing the effectiveness of your thesis statement. Ensure that there is relevant material available that supports your claim.
To further enhance clarity and coherence in a tested thesis statement, revise it if necessary based on feedback from others or through self-reflection. This will help refine both language choices and overall effectiveness.
By thoroughly testing your thesis statement throughout these steps, you can confidently develop a clear message for an impactful speech that resonates with your audience’s needs while meeting all stated objectives.
1. What is a thesis statement in public speaking?
A thesis statement in public speaking is a concise and clear sentence that summarizes the main point or argument of a speech. It serves as a roadmap for the audience, guiding them through the speech and helping them understand its purpose.
2. How do I develop an effective thesis statement for a speech?
To develop an effective thesis statement for a speech, start by identifying your topic and determining what specific message you want to convey to your audience. Then, clearly state this message in one or two sentences that capture the main idea of your speech.
3. Why is it important to have a strong thesis statement in public speaking?
Having a strong thesis statement in public speaking helps you stay focused on your main argument throughout the speech and ensures that your audience understands what you are trying to communicate. It also helps establish credibility and authority as you present well-supported points related to your thesis.
4. Can my thesis statement change during my speech preparation?
Yes, it is possible for your thesis statement to evolve or change during the preparation process as you gather more information or refine your ideas. However, it’s important to ensure that any changes align with the overall purpose of your speech and still effectively guide the content and structure of your presentation.

Speechwriting
8 Purpose and Thesis
Speechwriting Essentials
In this chapter . . .
As discussed in the chapter on Speaking Occasion , speechwriting begins with careful analysis of the speech occasion and its given circumstances, leading to the choice of an appropriate topic. As with essay writing, the early work of speechwriting follows familiar steps: brainstorming, research, pre-writing, thesis, and so on.
This chapter focuses on techniques that are unique to speechwriting. As a spoken form, speeches must be clear about the purpose and main idea or “takeaway.” Planned redundancy means that you will be repeating these elements several times over during the speech.
Furthermore, finding purpose and thesis are essential whether you’re preparing an outline for extemporaneous delivery or a completely written manuscript for presentation. When you know your topic, your general and specific purpose, and your thesis or central idea, you have all the elements you need to write a speech that is focused, clear, and audience friendly.
Recognizing the General Purpose
Speeches have traditionally been grouped into one of three categories according to their primary purpose: 1) to inform, 2) to persuade, or 3) to inspire, honor, or entertain. These broad goals are commonly known as the general purpose of a speech . Earlier, you learned about the actor’s tool of intention or objectives. The general purpose is like a super-objective; it defines the broadest goal of a speech. These three purposes are not necessarily exclusive to the others. A speech designed to be persuasive can also be informative and entertaining. However, a speech should have one primary goal. That is its general purpose.
Why is it helpful to talk about speeches in such broad terms? Being perfectly clear about what you want your speech to do or make happen for your audience will keep you focused. You can make a clearer distinction between whether you want your audience to leave your speech knowing more (to inform), or ready to take action (to persuade), or feeling something (to inspire)
It’s okay to use synonyms for these broad categories. Here are some of them:
- To inform could be to explain, to demonstrate, to describe, to teach.
- To persuade could be to convince, to argue, to motivate, to prove.
- To inspire might be to honor, or entertain, to celebrate, to mourn.
In summary, the first question you must ask yourself when starting to prepare a speech is, “Is the primary purpose of my speech to inform, to persuade, or to inspire?”
Articulating Specific Purpose
A specific purpose statement builds upon your general purpose and makes it specific (as the name suggests). For example, if you have been invited to give a speech about how to do something, your general purpose is “to inform.” Choosing a topic appropriate to that general purpose, you decide to speak about how to protect a personal from cyberattacks. Now you are on your way to identifying a specific purpose.
A good specific purpose statement has three elements: goal, target audience, and content.
If you think about the above as a kind of recipe, then the first two “ingredients” — your goal and your audience — should be simple. Words describing the target audience should be as specific as possible. Instead of “my peers,” you could say, for example, “students in their senior year at my university.”
The third ingredient in this recipe is content, or what we call the topic of your speech. This is where things get a bit difficult. You want your content to be specific and something that you can express succinctly in a sentence. Here are some common problems that speakers make in defining the content, and the fix:
Now you know the “recipe” for a specific purpose statement. It’s made up of T o, plus an active W ord, a specific A udience, and clearly stated C ontent. Remember this formula: T + W + A + C.
A: for a group of new students
C: the term “plagiarism”
Here are some further examples a good specific purpose statement:
- To explain to a group of first-year students how to join a school organization.
- To persuade the members of the Greek society to take a spring break trip in Daytona Beach.
- To motivate my classmates in English 101 to participate in a study abroad program.
- To convince first-year students that they need at least seven hours of sleep per night to do well in their studies.
- To inspire my Church community about the accomplishments of our pastor.
The General and Specific Purpose Statements are writing tools in the sense that they help you, as a speechwriter, clarify your ideas.
Creating a Thesis Statement
Once you are clear about your general purpose and specific purpose, you can turn your attention to crafting a thesis statement. A thesis is the central idea in an essay or a speech. In speechwriting, the thesis or central idea explains the message of the content. It’s the speech’s “takeaway.” A good thesis statement will also reveal and clarify the ideas or assertions you’ll be addressing in your speech (your main points). Consider this example:
General Purpose: To persuade. Specific Purpose: To motivate my classmates in English 101 to participate in a study abroad program. Thesis: A semester-long study abroad experience produces lifelong benefits by teaching you about another culture, developing your language skills, and enhancing your future career prospects.
The difference between a specific purpose statement and a thesis statement is clear in this example. The thesis provides the takeaway (the lifelong benefits of study abroad). It also points to the assertions that will be addressed in the speech. Like the specific purpose statement, the thesis statement is a writing tool. You’ll incorporate it into your speech, usually as part of the introduction and conclusion.
All good expository, rhetorical, and even narrative writing contains a thesis. Many students and even experienced writers struggle with formulating a thesis. We struggle when we attempt to “come up with something” before doing the necessary research and reflection. A thesis only becomes clear through the thinking and writing process. As you develop your speech content, keep asking yourself: What is important here? If the audience can remember only one thing about this topic, what do I want them to remember?
Example #2: General Purpose: To inform Specific Purpose: To demonstrate to my audience the correct method for cleaning a computer keyboard. Central Idea: Your computer keyboard needs regular cleaning to function well, and you can achieve that in four easy steps.
Example # 3 General Purpose: To Inform Specific Purpose: To describe how makeup is done for the TV show The Walking Dead . Central Idea: The wildly popular zombie show The Walking Dead achieves incredibly scary and believable makeup effects, and in the next few minutes I will tell you who does it, what they use, and how they do it.
Notice in the examples above that neither the specific purpose nor the central idea ever exceeds one sentence. If your central idea consists of more than one sentence, then you are probably including too much information.
Problems to Avoid
The first problem many students have in writing their specific purpose statement has already been mentioned: specific purpose statements sometimes try to cover far too much and are too broad. For example:
“To explain to my classmates the history of ballet.”
Aside from the fact that this subject may be difficult for everyone in your audience to relate to, it’s enough for a three-hour lecture, maybe even a whole course. You’ll probably find that your first attempt at a specific purpose statement will need refining. These examples are much more specific and much more manageable given the limited amount of time you’ll have.
- To explain to my classmates how ballet came to be performed and studied in the U.S.
- To explain to my classmates the difference between Russian and French ballet.
- To explain to my classmates how ballet originated as an art form in the Renaissance.
- To explain to my classmates the origin of the ballet dancers’ clothing.
The second problem happens when the “communication verb” in the specific purpose does not match the content; for example, persuasive content is paired with “to inform” or “to explain.” Can you find the errors in the following purpose statements?
- To inform my audience why capital punishment is unconstitutional. (This is persuasive. It can’t be informative since it’s taking a side)
- To persuade my audience about the three types of individual retirement accounts. (Even though the purpose statement says “persuade,” it isn’t persuading the audience of anything. It is informative.)
- To inform my classmates that Universal Studios is a better theme park than Six Flags over Georgia. (This is clearly an opinion; hence it is a persuasive speech and not merely informative)
The third problem exists when the content part of the specific purpose statement has two parts. One specific purpose is enough. These examples cover two different topics.
- To explain to my audience how to swing a golf club and choose the best golf shoes.
- To persuade my classmates to be involved in the Special Olympics and vote to fund better classes for the intellectually disabled.
To fix this problem of combined or hybrid purposes, you’ll need to select one of the topics in these examples and speak on that one alone.
The fourth problem with both specific purpose and central idea statements is related to formatting. There are some general guidelines that need to be followed in terms of how you write out these elements of your speech:
- Don’t write either statement as a question.
- Always use complete sentences for central idea statements and infinitive phrases (beginning with “to”) for the specific purpose statement.
- Use concrete language (“I admire Beyoncé for being a talented performer and businesswoman”) and avoid subjective or slang terms (“My speech is about why I think Beyoncé is the bomb”) or jargon and acronyms (“PLA is better than CBE for adult learners.”)
There are also problems to avoid in writing the central idea statement. As mentioned above, remember that:
- The specific purpose and central idea statements are not the same thing, although they are related.
- The central idea statement should be clear and not complicated or wordy; it should “stand out” to the audience. As you practice delivery, you should emphasize it with your voice.
- The central idea statement should not be the first thing you say but should follow the steps of a good introduction as outlined in the next chapters.
You should be aware that all aspects of your speech are constantly going to change as you move toward the moment of giving your speech. The exact wording of your central idea may change, and you can experiment with different versions for effectiveness. However, your specific purpose statement should not change unless there is a good reason to do so. There are many aspects to consider in the seemingly simple task of writing a specific purpose statement and its companion, the central idea statement. Writing good ones at the beginning will save you some trouble later in the speech preparation process.
Public Speaking as Performance Copyright © 2023 by Mechele Leon is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
9.3 Putting It Together: Steps to Complete Your Introduction
Learning objectives.
- Clearly identify why an audience should listen to a speaker.
- Discuss how you can build your credibility during a speech.
- Understand how to write a clear thesis statement.
- Design an effective preview of your speech’s content for your audience.
Erin Brown-John – puzzle – CC BY-NC 2.0.
Once you have captured your audience’s attention, it’s important to make the rest of your introduction interesting, and use it to lay out the rest of the speech. In this section, we are going to explore the five remaining parts of an effective introduction: linking to your topic, reasons to listen, stating credibility, thesis statement, and preview.
Link to Topic
After the attention-getter, the second major part of an introduction is called the link to topic. The link to topic is the shortest part of an introduction and occurs when a speaker demonstrates how an attention-getting device relates to the topic of a speech. Often the attention-getter and the link to topic are very clear. For example, if you look at the attention-getting device example under historical reference above, you’ll see that the first sentence brings up the history of the Vietnam War and then shows us how that war can help us understand the Iraq War. In this case, the attention-getter clearly flows directly to the topic. However, some attention-getters need further explanation to get to the topic of the speech. For example, both of the anecdote examples (the girl falling into the manhole while texting and the boy and the filberts) need further explanation to connect clearly to the speech topic (i.e., problems of multitasking in today’s society).
Let’s look at the first anecdote example to demonstrate how we could go from the attention-getter to the topic.
In July 2009, a high school girl named Alexa Longueira was walking along a main boulevard near her home on Staten Island, New York, typing in a message on her cell phone. Not paying attention to the world around her, she took a step and fell right into an open manhole. This anecdote illustrates the problem that many people are facing in today’s world. We are so wired into our technology that we forget to see what’s going on around us—like a big hole in front of us.
In this example, the third sentence here explains that the attention-getter was an anecdote that illustrates a real issue. The fourth sentence then introduces the actual topic of the speech.
Let’s now examine how we can make the transition from the parable or fable attention-getter to the topic:
The ancient Greek writer Aesop told a fable about a boy who put his hand into a pitcher of filberts. The boy grabbed as many of the delicious nuts as he possibly could. But when he tried to pull them out, his hand wouldn’t fit through the neck of the pitcher because he was grasping so many filberts. Instead of dropping some of them so that his hand would fit, he burst into tears and cried about his predicament. The moral of the story? “Don’t try to do too much at once.” In today’s world, many of us are us are just like the boy putting his hand into the pitcher. We are constantly trying to grab so much or do so much that it prevents us from accomplishing our goals. I would like to show you three simple techniques to manage your time so that you don’t try to pull too many filberts from your pitcher.
In this example, we added three new sentences to the attention-getter to connect it to the speech topic.
Reasons to Listen
Once you have linked an attention-getter to the topic of your speech, you need to explain to your audience why your topic is important. We call this the “why should I care?” part of your speech because it tells your audience why the topic is directly important to them. Sometimes you can include the significance of your topic in the same sentence as your link to the topic, but other times you may need to spell out in one or two sentences why your specific topic is important.
People in today’s world are very busy, and they do not like their time wasted. Nothing is worse than having to sit through a speech that has nothing to do with you. Imagine sitting through a speech about a new software package you don’t own and you will never hear of again. How would you react to the speaker? Most of us would be pretty annoyed at having had our time wasted in this way. Obviously, this particular speaker didn’t do a great job of analyzing her or his audience if the audience isn’t going to use the software package—but even when speaking on a topic that is highly relevant to the audience, speakers often totally forget to explain how and why it is important.
Appearing Credible
The next part of a speech is not so much a specific “part” as an important characteristic that needs to be pervasive throughout your introduction and your entire speech. As a speaker, you want to be seen as credible (competent, trustworthy, and caring/having goodwill). As mentioned earlier in this chapter, credibility is ultimately a perception that is made by your audience. While your audience determines whether they perceive you as competent, trustworthy, and caring/having goodwill, there are some strategies you can employ to make yourself appear more credible.
First, to make yourself appear competent, you can either clearly explain to your audience why you are competent about a given subject or demonstrate your competence by showing that you have thoroughly researched a topic by including relevant references within your introduction. The first method of demonstrating competence—saying it directly—is only effective if you are actually a competent person on a given subject. If you are an undergraduate student and you are delivering a speech about the importance of string theory in physics, unless you are a prodigy of some kind, you are probably not a recognized expert on the subject. Conversely, if your number one hobby in life is collecting memorabilia about the Three Stooges, then you may be an expert about the Three Stooges. However, you would need to explain to your audience your passion for collecting Three Stooges memorabilia and how this has made you an expert on the topic.
If, on the other hand, you are not actually a recognized expert on a topic, you need to demonstrate that you have done your homework to become more knowledgeable than your audience about your topic. The easiest way to demonstrate your competence is through the use of appropriate references from leading thinkers and researchers on your topic. When you demonstrate to your audience that you have done your homework, they are more likely to view you as competent.
The second characteristic of credibility, trustworthiness, is a little more complicated than competence, for it ultimately relies on audience perceptions. One way to increase the likelihood that a speaker will be perceived as trustworthy is to use reputable sources. If you’re quoting Dr. John Smith, you need to explain who Dr. John Smith is so your audience will see the quotation as being more trustworthy. As speakers we can easily manipulate our sources into appearing more credible than they actually are, which would be unethical. When you are honest about your sources with your audience, they will trust you and your information more so than when you are ambiguous. The worst thing you can do is to out-and-out lie about information during your speech. Not only is lying highly unethical, but if you are caught lying, your audience will deem you untrustworthy and perceive everything you are saying as untrustworthy. Many speakers have attempted to lie to an audience because it will serve their own purposes or even because they believe their message is in their audience’s best interest, but lying is one of the fastest ways to turn off an audience and get them to distrust both the speaker and the message.
The third characteristic of credibility to establish during the introduction is the sense of caring/goodwill. While some unethical speakers can attempt to manipulate an audience’s perception that the speaker cares, ethical speakers truly do care about their audiences and have their audience’s best interests in mind while speaking. Often speakers must speak in front of audiences that may be hostile toward the speaker’s message. In these cases, it is very important for the speaker to explain that he or she really does believe her or his message is in the audience’s best interest. One way to show that you have your audience’s best interests in mind is to acknowledge disagreement from the start:
Today I’m going to talk about why I believe we should enforce stricter immigration laws in the United States. I realize that many of you will disagree with me on this topic. I used to believe that open immigration was a necessity for the United States to survive and thrive, but after researching this topic, I’ve changed my mind. While I may not change all of your minds today, I do ask that you listen with an open mind, set your personal feelings on this topic aside, and judge my arguments on their merits.
While clearly not all audience members will be open or receptive to opening their minds and listening to your arguments, by establishing that there is known disagreement, you are telling the audience that you understand their possible views and are not trying to attack their intellect or their opinions.
Thesis Statement
A thesis statement is a short, declarative sentence that states the purpose, intent, or main idea of a speech. A strong, clear thesis statement is very valuable within an introduction because it lays out the basic goal of the entire speech. We strongly believe that it is worthwhile to invest some time in framing and writing a good thesis statement. You may even want to write your thesis statement before you even begin conducting research for your speech. While you may end up rewriting your thesis statement later, having a clear idea of your purpose, intent, or main idea before you start searching for research will help you focus on the most appropriate material. To help us understand thesis statements, we will first explore their basic functions and then discuss how to write a thesis statement.
Basic Functions of a Thesis Statement
A thesis statement helps your audience by letting them know “in a nutshell” what you are going to talk about. With a good thesis statement you will fulfill four basic functions: you express your specific purpose, provide a way to organize your main points, make your research more effective, and enhance your delivery.
Express Your Specific Purpose
To orient your audience, you need to be as clear as possible about your meaning. A strong thesis will prepare your audience effectively for the points that will follow. Here are two examples:
- “Today, I want to discuss academic cheating.” (weak example)
- “Today, I will clarify exactly what plagiarism is and give examples of its different types so that you can see how it leads to a loss of creative learning interaction.” (strong example)
The weak statement will probably give the impression that you have no clear position about your topic because you haven’t said what that position is. Additionally, the term “academic cheating” can refer to many behaviors—acquiring test questions ahead of time, copying answers, changing grades, or allowing others to do your coursework—so the specific topic of the speech is still not clear to the audience.
The strong statement not only specifies plagiarism but also states your specific concern (loss of creative learning interaction).
Provide a Way to Organize Your Main Points
A thesis statement should appear, almost verbatim, toward the end of the introduction to a speech. A thesis statement helps the audience get ready to listen to the arrangement of points that follow. Many speakers say that if they can create a strong thesis sentence, the rest of the speech tends to develop with relative ease. On the other hand, when the thesis statement is not very clear, creating a speech is an uphill battle.
When your thesis statement is sufficiently clear and decisive, you will know where you stand about your topic and where you intend to go with your speech. Having a clear thesis statement is especially important if you know a great deal about your topic or you have strong feelings about it. If this is the case for you, you need to know exactly what you are planning on talking about in order to fit within specified time limitations. Knowing where you are and where you are going is the entire point in establishing a thesis statement; it makes your speech much easier to prepare and to present.
Let’s say you have a fairly strong thesis statement, and that you’ve already brainstormed a list of information that you know about the topic. Chances are your list is too long and has no focus. Using your thesis statement, you can select only the information that (1) is directly related to the thesis and (2) can be arranged in a sequence that will make sense to the audience and will support the thesis. In essence, a strong thesis statement helps you keep useful information and weed out less useful information.
Make Your Research More Effective
If you begin your research with only a general topic in mind, you run the risk of spending hours reading mountains of excellent literature about your topic. However, mountains of literature do not always make coherent speeches. You may have little or no idea of how to tie your research all together, or even whether you should tie it together. If, on the other hand, you conduct your research with a clear thesis statement in mind, you will be better able to zero in only on material that directly relates to your chosen thesis statement. Let’s look at an example that illustrates this point:
Many traffic accidents involve drivers older than fifty-five.
While this statement may be true, you could find industrial, medical, insurance literature that can drone on ad infinitum about the details of all such accidents in just one year. Instead, focusing your thesis statement will help you narrow the scope of information you will be searching for while gathering information. Here’s an example of a more focused thesis statement:
Three factors contribute to most accidents involving drivers over fifty-five years of age: failing eyesight, slower reflexes, and rapidly changing traffic conditions.
This framing is somewhat better. This thesis statement at least provides three possible main points and some keywords for your electronic catalog search. However, if you want your audience to understand the context of older people at the wheel, consider something like:
Mature drivers over fifty-five years of age must cope with more challenging driving conditions than existed only one generation ago: more traffic moving at higher speeds, the increased imperative for quick driving decisions, and rapidly changing ramp and cloverleaf systems. Because of these challenges, I want my audience to believe that drivers over the age of sixty-five should be required to pass a driving test every five years.
This framing of the thesis provides some interesting choices. First, several terms need to be defined, and these definitions might function surprisingly well in setting the tone of the speech. Your definitions of words like “generation,” “quick driving decisions,” and “cloverleaf systems” could jolt your audience out of assumptions they have taken for granted as truth.
Second, the framing of the thesis provides you with a way to describe the specific changes as they have occurred between, say, 1970 and 2010. How much, and in what ways, have the volume and speed of traffic changed? Why are quick decisions more critical now? What is a “cloverleaf,” and how does any driver deal cognitively with exiting in the direction seemingly opposite to the desired one? Questions like this, suggested by your own thesis statement, can lead to a strong, memorable speech.
Enhance Your Delivery
When your thesis is not clear to you, your listeners will be even more clueless than you are—but if you have a good clear thesis statement, your speech becomes clear to your listeners. When you stand in front of your audience presenting your introduction, you can vocally emphasize the essence of your speech, expressed as your thesis statement. Many speakers pause for a half second, lower their vocal pitch slightly, slow down a little, and deliberately present the thesis statement, the one sentence that encapsulates its purpose. When this is done effectively, the purpose, intent, or main idea of a speech is driven home for an audience.
How to Write a Thesis Statement
Now that we’ve looked at why a thesis statement is crucial in a speech, let’s switch gears and talk about how we go about writing a solid thesis statement. A thesis statement is related to the general and specific purposes of a speech as we discussed them in Chapter 6 “Finding a Purpose and Selecting a Topic” .
Choose Your Topic
The first step in writing a good thesis statement was originally discussed in Chapter 6 “Finding a Purpose and Selecting a Topic” when we discussed how to find topics. Once you have a general topic, you are ready to go to the second step of creating a thesis statement.
Narrow Your Topic
One of the hardest parts of writing a thesis statement is narrowing a speech from a broad topic to one that can be easily covered during a five- to ten-minute speech. While five to ten minutes may sound like a long time to new public speakers, the time flies by very quickly when you are speaking. You can easily run out of time if your topic is too broad. To ascertain if your topic is narrow enough for a specific time frame, ask yourself three questions.
First, is your thesis statement narrow or is it a broad overgeneralization of a topic? An overgeneralization occurs when we classify everyone in a specific group as having a specific characteristic. For example, a speaker’s thesis statement that “all members of the National Council of La Raza are militant” is an overgeneralization of all members of the organization. Furthermore, a speaker would have to correctly demonstrate that all members of the organization are militant for the thesis statement to be proven, which is a very difficult task since the National Council of La Raza consists of millions of Hispanic Americans. A more appropriate thesis related to this topic could be, “Since the creation of the National Council of La Raza [NCLR] in 1968, the NCLR has become increasingly militant in addressing the causes of Hispanics in the United States.”
The second question to ask yourself when narrowing a topic is whether your speech’s topic is one clear topic or multiple topics. A strong thesis statement consists of only a single topic. The following is an example of a thesis statement that contains too many topics: “Medical marijuana, prostitution, and gay marriage should all be legalized in the United States.” Not only are all three fairly broad, but you also have three completely unrelated topics thrown into a single thesis statement. Instead of a thesis statement that has multiple topics, limit yourself to only one topic. Here’s an example of a thesis statement examining only one topic: “Today we’re going to examine the legalization and regulation of the oldest profession in the state of Nevada.” In this case, we’re focusing our topic to how one state has handled the legalization and regulation of prostitution.
The last question a speaker should ask when making sure a topic is sufficiently narrow is whether the topic has direction. If your basic topic is too broad, you will never have a solid thesis statement or a coherent speech. For example, if you start off with the topic “Barack Obama is a role model for everyone,” what do you mean by this statement? Do you think President Obama is a role model because of his dedication to civic service? Do you think he’s a role model because he’s a good basketball player? Do you think he’s a good role model because he’s an excellent public speaker? When your topic is too broad, almost anything can become part of the topic. This ultimately leads to a lack of direction and coherence within the speech itself. To make a cleaner topic, a speaker needs to narrow her or his topic to one specific area. For example, you may want to examine why President Obama is a good speaker.
Put Your Topic into a Sentence
Once you’ve narrowed your topic to something that is reasonably manageable given the constraints placed on your speech, you can then formalize that topic as a complete sentence. For example, you could turn the topic of President Obama’s public speaking skills into the following sentence: “Because of his unique sense of lyricism and his well-developed presentational skills, President Barack Obama is a modern symbol of the power of public speaking.” Once you have a clear topic sentence, you can start tweaking the thesis statement to help set up the purpose of your speech.
Add Your Argument, Viewpoint, or Opinion
This function only applies if you are giving a speech to persuade. If your topic is informative, your job is to make sure that the thesis statement is nonargumentative and focuses on facts. For example, in the preceding thesis statement we have a couple of opinion-oriented terms that should be avoided for informative speeches: “unique sense,” “well-developed,” and “power.” All three of these terms are laced with an individual’s opinion, which is fine for a persuasive speech but not for an informative speech. For informative speeches, the goal of a thesis statement is to explain what the speech will be informing the audience about, not attempting to add the speaker’s opinion about the speech’s topic. For an informative speech, you could rewrite the thesis statement to read, “This speech is going to analyze Barack Obama’s use of lyricism in his speech, ‘A World That Stands as One,’ delivered July 2008 in Berlin.”
On the other hand, if your topic is persuasive, you want to make sure that your argument, viewpoint, or opinion is clearly indicated within the thesis statement. If you are going to argue that Barack Obama is a great speaker, then you should set up this argument within your thesis statement.
Use the Thesis Checklist
Once you have written a first draft of your thesis statement, you’re probably going to end up revising your thesis statement a number of times prior to delivering your actual speech. A thesis statement is something that is constantly tweaked until the speech is given. As your speech develops, often your thesis will need to be rewritten to whatever direction the speech itself has taken. We often start with a speech going in one direction, and find out through our research that we should have gone in a different direction. When you think you finally have a thesis statement that is good to go for your speech, take a second and make sure it adheres to the criteria shown in Table 9.1 “Thesis Checklist”
Table 9.1 Thesis Checklist
Preview of Speech
The final part of an introduction contains a preview of the major points to be covered within your speech. I’m sure we’ve all seen signs that have three cities listed on them with the mileage to reach each city. This mileage sign is an indication of what is to come. A preview works the same way. A preview foreshadows what the main body points will be in the speech. For example, to preview a speech on bullying in the workplace, one could say, “To understand the nature of bullying in the modern workplace, I will first define what workplace bullying is and the types of bullying, I will then discuss the common characteristics of both workplace bullies and their targets, and lastly, I will explore some possible solutions to workplace bullying.” In this case, each of the phrases mentioned in the preview would be a single distinct point made in the speech itself. In other words, the first major body point in this speech would examine what workplace bullying is and the types of bullying; the second major body point in this speech would discuss the common characteristics of both workplace bullies and their targets; and lastly, the third body point in this speech would explore some possible solutions to workplace bullying.
Key Takeaways
- Linking the attention-getter to the speech topic is essential so that you maintain audience attention and so that the relevance of the attention-getter is clear to your audience.
- Establishing how your speech topic is relevant and important shows the audience why they should listen to your speech.
- To be an effective speaker, you should convey all three components of credibility, competence, trustworthiness, and caring/goodwill, by the content and delivery of your introduction.
- A clear thesis statement is essential to provide structure for a speaker and clarity for an audience.
- An effective preview identifies the specific main points that will be present in the speech body.
- Make a list of the attention-getting devices you might use to give a speech on the importance of recycling. Which do you think would be most effective? Why?
- Create a thesis statement for a speech related to the topic of collegiate athletics. Make sure that your thesis statement is narrow enough to be adequately covered in a five- to six-minute speech.
- Discuss with a partner three possible body points you could utilize for the speech on the topic of volunteerism.
- Fill out the introduction worksheet to help work through your introduction for your next speech. Please make sure that you answer all the questions clearly and concisely.
Stand up, Speak out Copyright © 2016 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

7.2 The Topic, General Purpose, Specific Purpose, and Thesis
Before any work can be done on crafting the body of your speech or presentation, you must first do some prep work—selecting a topic, formulating a general purpose, a specific purpose statement, and crafting a central idea, or thesis statement. In doing so, you lay the foundation for your speech by making important decisions about what you will speak about and for what purpose you will speak. These decisions will influence and guide the entire speechwriting process, so it is wise to think carefully and critically during these beginning stages.
Selecting a Topic
Generally, speakers focus on one or more interrelated topics—relatively broad concepts, ideas, or problems that are relevant for particular audiences. The most common way that speakers discover topics is by simply observing what is happening around them—at their school, in their local government, or around the world. Student government leaders, for example, speak or write to other students when their campus is facing tuition or fee increases, or when students have achieved something spectacular, like lobbying campus administrators for lower student fees and succeeding. In either case, it is the situation that makes their speeches appropriate and useful for their audience of students and university employees. More importantly, they speak when there is an opportunity to change a university policy or to alter the way students think or behave in relation to a particular event on campus.
But you need not run for president or student government in order to give a meaningful speech. On the contrary, opportunities abound for those interested in engaging speech as a tool for change. Perhaps the simplest way to find a topic is to ask yourself a few questions, including:
• What important events are occurring locally, nationally and internationally? • What do I care about most? • Is there someone or something I can advocate for? • What makes me angry/happy? • What beliefs/attitudes do I want to share? • Is there some information the audience needs to know?
Students speak about what is interesting to them and their audiences. What topics do you think are relevant today? There are other questions you might ask yourself, too, but these should lead you to at least a few topical choices. The most important work that these questions do is to locate topics within your pre-existing sphere of knowledge and interest. David Zarefsky (2010) also identifies brainstorming as a way to develop speech topics, a strategy that can be helpful if the questions listed above did not yield an appropriate or interesting topic. Starting with a topic you are already interested in will likely make writing and presenting your speech a more enjoyable and meaningful experience. It means that your entire speechwriting process will focus on something you find important and that you can present this information to people who stand to benefit from your speech.
Once you have answered these questions and narrowed your responses, you are still not done selecting your topic. For instance, you might have decided that you really care about breeds of dogs. This is a very broad topic and could easily lead to a dozen different speeches. To resolve this problem, speakers must also consider the audience to whom they will speak, the scope of their presentation, and the outcome they wish to achieve.
Formulating the Purpose Statements
By honing in on a very specific topic, you begin the work of formulating your purpose statement . In short, a purpose statement clearly states what it is you would like to achieve. Purpose statements are especially helpful for guiding you as you prepare your speech. When deciding which main points, facts, and examples to include, you should simply ask yourself whether they are relevant not only to the topic you have selected, but also whether they support the goal you outlined in your purpose statement. The general purpose statement of a speech may be to inform, to persuade, to celebrate, or to entertain. Thus, it is common to frame a specific purpose statement around one of these goals. According to O’Hair, Stewart, and Rubenstein, a specific purpose statement “expresses both the topic and the general speech purpose in action form and in terms of the specific objectives you hope to achieve” (2004). For instance, the home design enthusiast might write the following specific purpose statement: At the end of my speech, the audience will learn the pro’s and con’s of flipping houses. In short, the general purpose statement lays out the broader goal of the speech while the specific purpose statement describes precisely what the speech is intended to do. Some of your professors may ask that you include the general purpose and add the specific purpose.
Writing the Thesis Statement
The specific purpose statement is a tool that you will use as you write your talk, but it is unlikely that it will appear verbatim in your speech. Instead, you will want to convert the specific purpose statement into a central idea, or thesis statement that you will share with your audience.
Depending on your instructor’s approach, a thesis statement may be written two different ways. A thesis statement may encapsulate the main points of a speech in just a sentence or two, and be designed to give audiences a quick preview of what the entire speech will be about. The thesis statement for a speech, like the thesis of a research-based essay, should be easily identifiable and ought to very succinctly sum up the main points you will present. Some instructors prefer that your thesis, or central idea, be a single, declarative statement providing the audience with an overall statement that provides the essence of the speech, followed by a separate preview statement.
If you are a Harry Potter enthusiast, you may write a thesis statement (central idea) the following way using the above approach: J.K. Rowling is a renowned author of the Harry Potter series with a Cinderella like story having gone from relatively humble beginnings, through personal struggles, and finally success and fame.
Writing the Preview Statement
However, some instructors prefer that you separate your thesis from your preview statement . A preview statement (or series of statements) is a guide to your speech. This is the part of the speech that literally tells the audience exactly what main points you will cover. If you were to open your Waze app, it would tell you exactly how to get there. Best of all, you would know what to look for! So, if we take our J.K Rowling example, let’s rewrite that using this approach separating out the thesis and preview:
J.K. Rowling is a renowned author of the Harry Potter series with a Cinderella like rags to riches story. First, I will tell you about J.K. Rowling’s humble beginnings. Then, I will describe her personal struggles as a single mom. Finally, I will explain how she overcame adversity and became one of the richest women in the United Kingdom.
There is no best way to approach this. This is up to your instructor.
Writing the Body of Your Speech
Once you have finished the important work of deciding what your speech will be about, as well as formulating the purpose statement and crafting the thesis, you should turn your attention to writing the body of your speech. All of your main points are contained in the body, and normally this section is prepared well before you ever write the introduction or conclusion. The body of your speech will consume the largest amount of time to present; and it is the opportunity for you to elaborate on facts, evidence, examples, and opinions that support your thesis statement and do the work you have outlined in the specific purpose statement. Combining these various elements into a cohesive and compelling speech, however, is not without its difficulties, the first of which is deciding which elements to include and how they ought to be organized to best suit your purpose.
clearly states what it is you would like to achieve
“expresses both the topic and the general speech purpose in action form and in terms of the specific objectives you hope to achieve" (O'Hair, Stewart, & Rubenstein, 2004)
single, declarative sentence that captures the essence or main point of your entire presentation
the part of the speech that literally tells the audience exactly what main points you will cover
Introduction to Speech Communication Copyright © 2021 by Individual authors retain copyright of their work. is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

Thesis Statements
What this handout is about.
This handout describes what a thesis statement is, how thesis statements work in your writing, and how you can craft or refine one for your draft.
Introduction
Writing in college often takes the form of persuasion—convincing others that you have an interesting, logical point of view on the subject you are studying. Persuasion is a skill you practice regularly in your daily life. You persuade your roommate to clean up, your parents to let you borrow the car, your friend to vote for your favorite candidate or policy. In college, course assignments often ask you to make a persuasive case in writing. You are asked to convince your reader of your point of view. This form of persuasion, often called academic argument, follows a predictable pattern in writing. After a brief introduction of your topic, you state your point of view on the topic directly and often in one sentence. This sentence is the thesis statement, and it serves as a summary of the argument you’ll make in the rest of your paper.
What is a thesis statement?
A thesis statement:
- tells the reader how you will interpret the significance of the subject matter under discussion.
- is a road map for the paper; in other words, it tells the reader what to expect from the rest of the paper.
- directly answers the question asked of you. A thesis is an interpretation of a question or subject, not the subject itself. The subject, or topic, of an essay might be World War II or Moby Dick; a thesis must then offer a way to understand the war or the novel.
- makes a claim that others might dispute.
- is usually a single sentence near the beginning of your paper (most often, at the end of the first paragraph) that presents your argument to the reader. The rest of the paper, the body of the essay, gathers and organizes evidence that will persuade the reader of the logic of your interpretation.
If your assignment asks you to take a position or develop a claim about a subject, you may need to convey that position or claim in a thesis statement near the beginning of your draft. The assignment may not explicitly state that you need a thesis statement because your instructor may assume you will include one. When in doubt, ask your instructor if the assignment requires a thesis statement. When an assignment asks you to analyze, to interpret, to compare and contrast, to demonstrate cause and effect, or to take a stand on an issue, it is likely that you are being asked to develop a thesis and to support it persuasively. (Check out our handout on understanding assignments for more information.)
How do I create a thesis?
A thesis is the result of a lengthy thinking process. Formulating a thesis is not the first thing you do after reading an essay assignment. Before you develop an argument on any topic, you have to collect and organize evidence, look for possible relationships between known facts (such as surprising contrasts or similarities), and think about the significance of these relationships. Once you do this thinking, you will probably have a “working thesis” that presents a basic or main idea and an argument that you think you can support with evidence. Both the argument and your thesis are likely to need adjustment along the way.
Writers use all kinds of techniques to stimulate their thinking and to help them clarify relationships or comprehend the broader significance of a topic and arrive at a thesis statement. For more ideas on how to get started, see our handout on brainstorming .
How do I know if my thesis is strong?
If there’s time, run it by your instructor or make an appointment at the Writing Center to get some feedback. Even if you do not have time to get advice elsewhere, you can do some thesis evaluation of your own. When reviewing your first draft and its working thesis, ask yourself the following :
- Do I answer the question? Re-reading the question prompt after constructing a working thesis can help you fix an argument that misses the focus of the question. If the prompt isn’t phrased as a question, try to rephrase it. For example, “Discuss the effect of X on Y” can be rephrased as “What is the effect of X on Y?”
- Have I taken a position that others might challenge or oppose? If your thesis simply states facts that no one would, or even could, disagree with, it’s possible that you are simply providing a summary, rather than making an argument.
- Is my thesis statement specific enough? Thesis statements that are too vague often do not have a strong argument. If your thesis contains words like “good” or “successful,” see if you could be more specific: why is something “good”; what specifically makes something “successful”?
- Does my thesis pass the “So what?” test? If a reader’s first response is likely to be “So what?” then you need to clarify, to forge a relationship, or to connect to a larger issue.
- Does my essay support my thesis specifically and without wandering? If your thesis and the body of your essay do not seem to go together, one of them has to change. It’s okay to change your working thesis to reflect things you have figured out in the course of writing your paper. Remember, always reassess and revise your writing as necessary.
- Does my thesis pass the “how and why?” test? If a reader’s first response is “how?” or “why?” your thesis may be too open-ended and lack guidance for the reader. See what you can add to give the reader a better take on your position right from the beginning.
Suppose you are taking a course on contemporary communication, and the instructor hands out the following essay assignment: “Discuss the impact of social media on public awareness.” Looking back at your notes, you might start with this working thesis:
Social media impacts public awareness in both positive and negative ways.
You can use the questions above to help you revise this general statement into a stronger thesis.
- Do I answer the question? You can analyze this if you rephrase “discuss the impact” as “what is the impact?” This way, you can see that you’ve answered the question only very generally with the vague “positive and negative ways.”
- Have I taken a position that others might challenge or oppose? Not likely. Only people who maintain that social media has a solely positive or solely negative impact could disagree.
- Is my thesis statement specific enough? No. What are the positive effects? What are the negative effects?
- Does my thesis pass the “how and why?” test? No. Why are they positive? How are they positive? What are their causes? Why are they negative? How are they negative? What are their causes?
- Does my thesis pass the “So what?” test? No. Why should anyone care about the positive and/or negative impact of social media?
After thinking about your answers to these questions, you decide to focus on the one impact you feel strongly about and have strong evidence for:
Because not every voice on social media is reliable, people have become much more critical consumers of information, and thus, more informed voters.
This version is a much stronger thesis! It answers the question, takes a specific position that others can challenge, and it gives a sense of why it matters.
Let’s try another. Suppose your literature professor hands out the following assignment in a class on the American novel: Write an analysis of some aspect of Mark Twain’s novel Huckleberry Finn. “This will be easy,” you think. “I loved Huckleberry Finn!” You grab a pad of paper and write:
Mark Twain’s Huckleberry Finn is a great American novel.
You begin to analyze your thesis:
- Do I answer the question? No. The prompt asks you to analyze some aspect of the novel. Your working thesis is a statement of general appreciation for the entire novel.
Think about aspects of the novel that are important to its structure or meaning—for example, the role of storytelling, the contrasting scenes between the shore and the river, or the relationships between adults and children. Now you write:
In Huckleberry Finn, Mark Twain develops a contrast between life on the river and life on the shore.
- Do I answer the question? Yes!
- Have I taken a position that others might challenge or oppose? Not really. This contrast is well-known and accepted.
- Is my thesis statement specific enough? It’s getting there–you have highlighted an important aspect of the novel for investigation. However, it’s still not clear what your analysis will reveal.
- Does my thesis pass the “how and why?” test? Not yet. Compare scenes from the book and see what you discover. Free write, make lists, jot down Huck’s actions and reactions and anything else that seems interesting.
- Does my thesis pass the “So what?” test? What’s the point of this contrast? What does it signify?”
After examining the evidence and considering your own insights, you write:
Through its contrasting river and shore scenes, Twain’s Huckleberry Finn suggests that to find the true expression of American democratic ideals, one must leave “civilized” society and go back to nature.
This final thesis statement presents an interpretation of a literary work based on an analysis of its content. Of course, for the essay itself to be successful, you must now present evidence from the novel that will convince the reader of your interpretation.
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
Anson, Chris M., and Robert A. Schwegler. 2010. The Longman Handbook for Writers and Readers , 6th ed. New York: Longman.
Lunsford, Andrea A. 2015. The St. Martin’s Handbook , 8th ed. Boston: Bedford/St Martin’s.
Ramage, John D., John C. Bean, and June Johnson. 2018. The Allyn & Bacon Guide to Writing , 8th ed. New York: Pearson.
Ruszkiewicz, John J., Christy Friend, Daniel Seward, and Maxine Hairston. 2010. The Scott, Foresman Handbook for Writers , 9th ed. Boston: Pearson Education.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift

8.2 The Topic, General Purpose, Specific Purpose, and Thesis
Before any work can be done on crafting the body of your speech or presentation, you must first do some prep work—selecting a topic, formulating a general purpose, a specific purpose statement, and crafting a central idea, or thesis statement. In doing so, you lay the foundation for your speech by making important decisions about what you will speak about and for what purpose you will speak. These decisions will influence and guide the entire speechwriting process, so it is wise to think carefully and critically during these beginning stages.
Understanding the General Purpose
Before any work on a speech can be done, the speaker needs to understand the general purpose of the speech. The general purpose is what the speaker hopes to accomplish and will help guide in the selection of a topic. The instructor generally provides the general purpose for a speech, which falls into one of three categories. A general purpose to inform would mean that the speaker is teaching the audience about a topic, increasing their understanding and awareness, or providing new information about a topic the audience might already know. Informative speeches are designed to present the facts, but not give the speaker’s opinion or any call to action. A general purpose to persuade would mean that the speaker is choosing the side of a topic and advocating for their side or belief. The speaker is asking the audience to believe in their stance, or to take an action in support of their topic. A general purpose to entertain often entails short speeches of ceremony, where the speaker is connecting the audience to the celebration. You can see how these general purposes are very different. An informative speech is just facts, the speaker would not be able to provide an opinion or direction on what to do with the information, whereas a persuasive speech includes the speaker’s opinions and direction on what to do with the information. Before a speaker chooses a topic, they must first understand the general purpose.
Selecting a Topic
Generally, speakers focus on one or more interrelated topics—relatively broad concepts, ideas, or problems that are relevant for particular audiences. The most common way that speakers discover topics is by simply observing what is happening around them—at their school, in their local government, or around the world. Opportunities abound for those interested in engaging speech as a tool for change. Perhaps the simplest way to find a topic is to ask yourself a few questions, including:
- What important events are occurring locally, nationally, and internationally?
- What do I care about most?
- Is there someone or something I can advocate for?
- What makes me angry/happy?
- What beliefs/attitudes do I want to share?
- Is there some information the audience needs to know?
Students speak about what is interesting to them and their audiences. What topics do you think are relevant today? There are other questions you might ask yourself, too, but these should lead you to at least a few topical choices. The most important work that these questions do is to locate topics within your pre-existing sphere of knowledge and interest. Topics should be ideas that interest the speaker or are part of their daily lives. In order for a topic to be effective, the speaker needs to have some credibility or connection to the topic; it would be unfair to ask the audience to donate to a cause that the speaker has never donated to. There must be a connection to the topic for the speaker to be seen as credible. David Zarefsky (2010) also identifies brainstorming as a way to develop speech topics, a strategy that can be helpful if the questions listed above did not yield an appropriate or interesting topic. Brainstorming involves looking at your daily activities to determine what you could share with an audience. Perhaps if you work out regularly or eat healthy, you could explain that to an audience, or demonstrate how to dribble a basketball. If you regularly play video games, you may advocate for us to take up video games or explain the history of video games. Anything that you find interesting or important might turn into a topic. Starting with a topic you are already interested in will make writing and presenting your speech a more enjoyable and meaningful experience. It means that your entire speechwriting process will focus on something you find important and that you can present this information to people who stand to benefit from your speech. At this point, it is also important to consider the audience before choosing a topic. While we might really enjoy a lot of different things that could be topics, if the audience has no connection to that topic, then it wouldn’t be meaningful for the speaker or audience. Since we always have a diverse audience, we want to make sure that everyone in the audience can gain some new information from the speech. Sometimes, a topic might be too complicated to cover in the amount of time we have to present, or involve too much information then that topic might not work for the assignment, and finally if the audience can not gain anything from a topic then it won’t work. Ultimately, when we choose a topic we want to pick something that we are familiar with and enjoy, we have credibility and that the audience could gain something from. Once you have answered these questions and narrowed your responses, you are still not done selecting your topic. For instance, you might have decided that you really care about breeds of dogs. This is a very broad topic and could easily lead to a dozen different speeches. To resolve this problem, speakers must also consider the audience to whom they will speak, the scope of their presentation, and the outcome they wish to achieve.
Formulating the Purpose Statements
By honing in on a very specific topic, you begin the work of formulating your purpose statement. In short, a purpose statement clearly states what it is you would like to achieve. Purpose statements are especially helpful for guiding you as you prepare your speech. When deciding which main points, facts, and examples to include, you should simply ask yourself whether they are relevant not only to the topic you have selected, but also whether they support the goal you outlined in your purpose statement. The general purpose statement of a speech may be to inform, to persuade, to celebrate, or to entertain. Thus, it is common to frame a specific purpose statement around one of these goals. According to O’Hair, Stewart, and Rubenstein, a specific purpose statement “expresses both the topic and the general speech purpose in action form and in terms of the specific objectives you hope to achieve” (2004). The specific purpose is a single sentence that states what the audience will gain from this speech, or what will happen at the end of the speech. The specific purpose is a combination of the general purpose and the topic and helps the speaker to focus in on what can be achieved in a short speech.
To go back to the topic of a dog breed, the general purpose might be to inform, a specific purpose might be: To inform the audience about how corgis became household pets. If the general purpose is to persuade the specific purpose might be: to persuade the audience that dog breeds deemed “dangerous” should not be excluded from living in the cities. In short, the general purpose statement lays out the broader goal of the speech while the specific purpose statement describes precisely what the speech is intended to do. The specific purpose should focus on the audience and be measurable, if I were to ask the audience before I began the speech how many people know how corgis became household pets, they could raise their hand, and if I ask at the end of my speech how many people know how corgis became household pets, I should see a lot more hands. The specific purpose is the “so what” of the speech, it helps the speaker focus on the audience and take a bigger idea of a topic and narrow it down to what can be accomplished in a short amount of time.
Writing the Thesis Statement
The specific purpose statement is a tool that you will use as you write your speech, but it is unlikely that it will appear verbatim in your speech. Instead, you will want to convert the specific purpose statement into a central idea, or thesis statement that you will share with your audience. Just like in a written paper, where the thesis comes in the first part of the paper, in a speech, the thesis comes within the first few sentences of the speech. The thesis must be stated and tells the audience what to expect in this speech. A thesis statement may encapsulate the main idea of a speech in just a sentence or two and be designed to give audiences a quick preview of what the entire speech will be about. The thesis statement should be a single, declarative statement followed by a separate preview statement. If you are a Harry Potter enthusiast, you may write a thesis statement (central idea) the following way using the above approach: J.K. Rowling is a renowned author of the Harry Potter series with a Cinderella-like story of a rise to fame.
Writing the Preview Statement
A preview statement (or series of statements) is a guide to your speech. This is the part of the speech that literally tells the audience exactly what main points you will cover. If you were to get on any freeway, there would be a green sign on the side of the road that tells you what cities are coming up—this is what your preview statement does; it tells the audience what points will be covered in the speech. Best of all, you would know what to look for! So, if we take our J.K Rowling example, the thesis and preview would look like this: J.K. Rowling is a renowned author of the Harry Potter series with a Cinderella-like rags-to-riches story. First, I will tell you about J.K. Rowling’s humble beginnings. Then, I will describe her personal struggles as a single mom. Finally, I will explain how she overcame adversity and became one of the richest women in the United Kingdom.
Writing the Body of Your Speech
Once you have finished the important work of deciding what your speech will be about, as well as formulating the purpose statement and crafting the thesis, you should turn your attention to writing the body of your speech. The body of your speech consists of 3–4 main points that support your thesis and help the audience to achieve the specific purpose. Creating main points helps to chunk the information you are sharing with your audience into an easy-to-understand organization. Choosing your main points will help you focus in on what information you want to share with the audience in order to prove your thesis. Since we can’t tell the audience everything about our topic, we need to choose our main points to make sure we can share the most important information with our audience. All of your main points are contained in the body, and normally this section is prepared well before you ever write the introduction or conclusion. The body of your speech will consume the largest amount of time to present, and it is the opportunity for you to elaborate on your supporting evidence, such as facts, statistics, examples, and opinions that support your thesis statement and do the work you have outlined in the specific purpose statement. Combining these various elements into a cohesive and compelling speech, however, is not without its difficulties, the first of which is deciding which elements to include and how they ought to be organized to best suit your purpose.
clearly states what it is you would like to achieve
“expresses both the topic and the general speech purpose in action form and in terms of the specific objectives you hope to achieve” (O'Hair, Stewart, & Rubenstein, 2004)
single, declarative sentence that captures the essence or main point of your entire presentation
It’s About Them: Public Speaking in the 21st Century Copyright © 2022 by LOUIS: The Louisiana Library Network is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Informative Speaking
The topic, purpose, and thesis.
Before any work can be done on crafting the body of your speech or presentation, you must first do some prep work—selecting a topic, formulating a purpose statement, and crafting a thesis statement. In doing so, you lay the foundation for your speech by making important decisions about what you will speak about and for what purpose you will speak. These decisions will influence and guide the entire speechwriting process, so it is wise to think carefully and critically during these beginning stages.
I think reading is important in any form. I think a person who’s trying to learn to like reading should start off reading about a topic they are interested in, or a person they are interested in. – Ice Cube
Questions for Selecting a Topic
- What important events are occurring locally, nationally and internationally?
- What do I care about most?
- Is there someone or something I can advocate for?
- What makes me angry/happy?
- What beliefs/attitudes do I want to share?
- Is there some information the audience needs to know?
Selecting a Topic

“The Reader” by Shakespearesmonkey. CC-BY-NC .
Generally, speakers focus on one or more interrelated topics—relatively broad concepts, ideas, or problems that are relevant for particular audiences. The most common way that speakers discover topics is by simply observing what is happening around them—at their school, in their local government, or around the world. This is because all speeches are brought into existence as a result of circumstances, the multiplicity of activities going on at any one given moment in a particular place. For instance, presidential candidates craft short policy speeches that can be employed during debates, interviews, or town hall meetings during campaign seasons. When one of the candidates realizes he or she will not be successful, the particular circumstances change and the person must craft different kinds of speeches—a concession speech, for example. In other words, their campaign for presidency, and its many related events, necessitates the creation of various speeches. Rhetorical theorist Lloyd Bitzer [1] describes this as the rhetorical situation. Put simply, the rhetorical situation is the combination of factors that make speeches and other discourse meaningful and a useful way to change the way something is. Student government leaders, for example, speak or write to other students when their campus is facing tuition or fee increases, or when students have achieved something spectacular, like lobbying campus administrators for lower student fees and succeeding. In either case, it is the situation that makes their speeches appropriate and useful for their audience of students and university employees. More importantly, they speak when there is an opportunity to change a university policy or to alter the way students think or behave in relation to a particular event on campus.
But you need not run for president or student government in order to give a meaningful speech. On the contrary, opportunities abound for those interested in engaging speech as a tool for change. Perhaps the simplest way to find a topic is to ask yourself a few questions. See the textbox entitled “Questions for Selecting a Topic” for a few questions that will help you choose a topic.
There are other questions you might ask yourself, too, but these should lead you to at least a few topical choices. The most important work that these questions do is to locate topics within your pre-existing sphere of knowledge and interest. David Zarefsky [2] also identifies brainstorming as a way to develop speech topics, a strategy that can be helpful if the questions listed in the textbox did not yield an appropriate or interesting topic.
Starting with a topic you are already interested in will likely make writing and presenting your speech a more enjoyable and meaningful experience. It means that your entire speechwriting process will focus on something you find important and that you can present this information to people who stand to benefit from your speech.
Once you have answered these questions and narrowed your responses, you are still not done selecting your topic. For instance, you might have decided that you really care about conserving habitat for bog turtles. This is a very broad topic and could easily lead to a dozen different speeches. To resolve this problem, speakers must also consider the audience to whom they will speak, the scope of their presentation, and the outcome they wish to achieve. If the bog turtle enthusiast knows that she will be talking to a local zoning board and that she hopes to stop them from allowing businesses to locate on important bog turtle habitat, her topic can easily morph into something more specific. Now, her speech topic is two-pronged: bog turtle habitat and zoning rules.

Formulating the Purpose Statements

“Bog turtle sunning” by U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service. Public domain.
By honing in on a very specific topic, you begin the work of formulating your purpose statement . In short, a purpose statement clearly states what it is you would like to achieve. Purpose statements are especially helpful for guiding you as you prepare your speech. When deciding which main points, facts, and examples to include, you should simply ask yourself whether they are relevant not only to the topic you have selected, but also whether they support the goal you outlined in your purpose statement. The general purpose statement of a speech may be to inform, to persuade, to inspire, to celebrate, to mourn, or to entertain. Thus, it is common to frame a specific purpose statement around one of these goals. According to O’Hair, Stewart, and Rubenstein, a specific purpose statement “expresses both the topic and the general speech purpose in action form and in terms of the specific objectives you hope to achieve.” [3] For instance, the bog turtle habitat activist might write the following specific purpose statement: At the end of my speech, the Clarke County Zoning Commission will understand that locating businesses in bog turtle habitat is a poor choice with a range of negative consequences. In short, the general purpose statement lays out the broader goal of the speech while the specific purpose statement describes precisely what the speech is intended to do.
Success demands singleness of purpose. – Vince Lombardi
Writing the Thesis Statement
The specific purpose statement is a tool that you will use as you write your talk, but it is unlikely that it will appear verbatim in your speech. Instead, you will want to convert the specific purpose statement into a thesis statement that you will share with your audience. A thesis statement encapsulates the main points of a speech in just a sentence or two, and it is designed to give audiences a quick preview of what the entire speech will be about. The thesis statement for a speech, like the thesis of a research- based essay, should be easily identifiable and ought to very succinctly sum up the main points you will present. Moreover, the thesis statement should reflect the general purpose of your speech; if your purpose is to persuade or educate, for instance, the thesis should alert audience members to this goal. The bog turtle enthusiast might prepare the following thesis statement based on her specific purpose statement: Bog turtle habitats are sensitive to a variety of activities, but land development is particularly harmful to unstable habitats. The Clarke County Zoning Commission should protect bog turtle habitats by choosing to prohibit business from locating in these habitats. In this example, the thesis statement outlines the main points and implies that the speaker will be arguing for certain zoning practices.
- Bitzer, L. (1968). The rhetorical situation. Philosophy & Rhetoric , 1 (1), 1 – 14. ↵
- Zarefsky, D. (2010). Public speaking: Strategies for success (6th edition). Boston: Allyn & Bacon. ↵
- O’Hair, D., Stewart, R., Rubenstein, H. (2004). A speaker’s guidebook: Text and reference (2nd edition). Boston: Bedford/St. Martin’s. ↵
- Chapter 8 The Topic, Purpose, and Thesis. Authored by : Joshua Trey Barnett. Provided by : University of Indiana, Bloomington, IN. Located at : http://publicspeakingproject.org/psvirtualtext.html . Project : The Public Speaking Project. License : CC BY-NC-ND: Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives
- The Reader. Authored by : Shakespearesmonkey. Located at : https://www.flickr.com/photos/shakespearesmonkey/4939289974/ . License : CC BY-NC: Attribution-NonCommercial
- Image of a bog turtle . Authored by : R. G. Tucker, Jr.. Provided by : United States Fish and Wildlife Service. Located at : http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Bog_turtle_sunning.jpg . License : Public Domain: No Known Copyright

Privacy Policy
My Speech Class
Public Speaking Tips & Speech Topics
Writing a Thesis Statement – Template & Examples

Amanda Green was born in a small town in the west of Scotland, where everyone knows everyone. I joined the Toastmasters 15 years ago, and I served in nearly every office in the club since then. I love helping others gain confidence and skills they can apply in every day life.
The thesis statement aims to inform your readers what your essay or speech will cover. It provides contexts and limitations on your topic.
Your thesis statement can make or break your essay. Even though it’s only one to two sentences short, it’s still the most challenging part of your paper to write. Follow these templates and examples when writing your thesis statement.
What Is a Thesis Statement?

Whether in high school or college, you’ve probably heard of the term thesis statement when writing school essays. A thesis statement is a single idea found in the introductory paragraph of every piece.
As the secret to a strong essay outline, this statement sums up the central idea of your essay. It informs the reader how you will analyze, argue, or describe a subject matter. It also directly answers the question, “What is your paper all about?”
A weak thesis statement won’t be able to tell the reader what to expect from your paper. The thesis statement is also different from the topic sentence, which is a sentence summing up every body paragraph.
Why Your Essay Needs a Thesis Statement
It would help if you spent extra time writing an effective thesis statement in your essays so that the readers will know its scope. The thesis also informs the readers of your ideas on your paper, especially if you’re writing academic papers like analytical or argumentative essays.
A clear thesis statement will make the audience understand your stance if you’re writing about a debatable topic. It will ensure that your relevant evidence is related to the paper and that your ideas can be tested.
Can We Write Your Speech?
Get your audience blown away with help from a professional speechwriter. Free proofreading and copy-editing included.
Where to Put the Thesis Statement
Thesis statements usually appear at the end of the essay introduction and before the body paragraphs.
Thesis statements are usually generated once you’ve decided on the type of essay you’re making, whether it’s an informative or argumentative essay. It would help if you also decided on the topic of your entire paper before writing the direct statement.
Tips for Writing a Thesis Statement
Consider these tips and examples when writing a thesis statement for your essay.
Determine the Type of Paper You’re Writing
Different types of papers require different methods for writing a thesis statement. Once you understand the formula, you’ll develop a strong thesis that can be supported by substantial evidence.
An argumentative thesis statement should state the position you argue for or against with all the key points. Here are some argumentative thesis statement examples.
- The war on drugs has more disadvantages than advantages because it leads to the criminalization of drug users, mandatory sentencing, and excessive imprisonment levels that directly impact the poor.
- The federal government should regulate the size of chips and sodas because of the health effects of junk food.
Meanwhile, an expository paper aims to explain. That means there should be no opinion or persuasion in this sentence. Take a look at these expository thesis statement examples.
- The government allots most of its budget to the military rather than the education system or food security.
- The rate of suicide is higher among men than women.
An analytical essay focuses on exploring a concept in-depth. That means the thesis statement may serve as a summary of your analysis. Here are some analytical thesis statement examples.
- The implications of Olivia Wilde’s movie, Don’t Worry Darling, contributes to notions of liberal feminism.
- In modern times, Korean music is heavily influencing the consumption of Filipinos.
Ask a Question
Don’t forget to ask a question whenever you write a thesis statement for your paper. If the professor assigns a topic to you, the assignment question may serve as a guide to your thesis. But if they haven’t assigned a topic, you should think about what you want to discuss and turn it into an interrogative statement.
Here are a few quick sample questions based on the types of thesis statements you will produce.
- Argumentative thesis question: Should cigarettes and other tobacco products be outlawed?
- Expository thesis question: What are the health effects of a lack of sleep?
- Analytical thesis question: How are Virginia Woolf’s works relevant to modern times?
Below is a sample thesis statement for the analytical thesis question.
- Virginia Woolf’s novels and essays have shaped women’s writing, artistic theory, and the politics of power.
As you can see, a single sentence could answer the question and produce a thesis statement. However, this answer may still be tentative. It should only guide your research process first. Along the way, your analysis and writing structure may still change.
Decide on an Answer You Can Defend or Explain
After conducting enough research on your thesis statement, it’s time to finalize your answer. Will your strong thesis statement be supported by richer ideas and evidence throughout the paper?
Importantly, your statement should definitely be something that a reader could disagree with, even if it’s an expository essay.
For example, it’s not enough to say that “Access to foreign countries has a huge effect on our culture” since the statement is too obvious. Instead, ask yourself why or how it has a huge effect. Think of a position that your readers could rationally disagree with or dispute.
Here is an example to show you what I mean.
“Access to foreign countries has enabled cultural changes by bringing people of different backgrounds and traditions together.”
Here are other examples of argumentative and analytical thesis statements.
- Argumentative: COVID-19 vaccinations should be mandatory.
- Analytical: A Little Life by Hanya Yanaghihara is an unrealistic representation of mental health struggles.
Refine Your Thesis Statement
Thesis statements are clear and concise, at most two sentences. However, they should be specific enough to summarize the key arguments of your paper and answer the essay question.
From your initial answer, you need to make some expansions that will include every point in your body paragraphs. Below is an example of an incomplete argumentative thesis statement with main points.
- COVID-19 vaccines are safe and effective.
- COVID-19 vaccines will reduce hospitalizations and deaths.
Once everything is set, it’s time to refine your thesis statement. Your goal is to write your main point and supporting details in one to two sentences. Below is an example.
- COVID-19 vaccinations should be mandatory because they are safe and effective and can help reduce hospitalizations and deaths caused by COVID-19.
Here’s another example of a complete thesis statement.
- The benefits of internet use among adolescents outweigh the downsides: It allows them to easily access information, develop their identities through self-expression, and hone critical thinking skills.
If you find this step challenging, you can hire professional essay writers to generate a thesis statement and outline for your essay needs.
Check if Your Thesis Statement Is Strong

Whether you’re writing an essay about politics or cinema, you need to maintain a solid thesis statement. Here are some questions to ask when checking your thesis.
Was I Able to Answer the Question?
As you already know, the question depends on the type of paper you’re writing. Your answer should be a clear and concise 1-2 sentence statement. Try changing the wording if the question prompt isn’t phrased as a question.
Have I Shared an Opinion That Others Might Oppose?
Your argumentative thesis statement should not merely state facts that people already know. Remember that you’re not writing a summary, so make your thesis as opinionated as possible.
Beyond being debatable, you should also have a convincing thesis statement. This is especially important if you’re writing persuasive essays.
Is It Specific Enough?
Being specific is critical to producing a solid statement. Make sure it does not contain general words like good or successful . Once your argument is strong, the process of writing essays will be much easier.
Does the Entire Essay Support the Thesis?
An ineffective thesis statement does not support the next couple of paragraphs of the entire essay. Therefore, if you say that low-income students and student-athletes should receive more assistance in terms of their crippling student debt, then your empirical evidence should support it in your argumentative paper.
The Backbone of Your Essay Is Your Thesis Statement
A thesis statement is a declarative statement that expresses your paper’s position or main topic. It fulfills the several roles of your paper, whether it’s a research paper, an essay for coursework, or a speech.
Make sure to place your thesis statement at the end of your introduction before your first body paragraph.
More Thesis Statement Examples
- Incorrect: People should eat healthily.
- Correct: Americans should start eating a balanced diet because it keeps their body healthy and prevents the risk of stroke.
- Incorrect: Everyone should stop smoking because it is bad for our health.
- Correct: Individuals must stop smoking because it causes cancer, lung disease, and diabetes.
- Incorrect: Listening to music can make people feel relaxed.
- Correct: Listening to music relieves stress as the brain synchronizes to the beat and causes alpha brainwaves.
Thesis Statement Template
Use these templates for your essays when writing a thesis statement.
Comparison/Contrast Thesis Statement Templates
- The similarities between ____________ and ____________ are [striking, pronounced], and they ____________ [deserve, merit] [thorough, rigorous, meticulous] [investigation, scrutiny, examination].
- [Despite, despite bearing, although they bear] some [superficial, minor] similarities, the differences between ____________ and ____________ are [clear, striking, remarkable, pronounced].
- While some differences between ____________ and ____________ are [evident, obvious, noticeable], the similarities are ____________.
Proposition Thesis Statement Templates
- The [belief, thought, notion, idea, proposition] that ____________ is ____________ is [an interesting, a fascinating, a thought-provoking, a provocative] one, and one that I believe in.
- ____________ is true because of ____________.
Informative Thesis Statement Template
- The ____________ is characterized by ____________, ____________, and ____________.
- An analysis of ____________ reveals that ____________.
How to Write the Best Commencement Speech – Tips & Examples
Persuasive Essay Outline – Examples, Templates & Structure
Leave a Comment
I accept the Privacy Policy
Reach out to us for sponsorship opportunities
Vivamus integer non suscipit taciti mus etiam at primis tempor sagittis euismod libero facilisi.
© 2024 My Speech Class
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
8 Chapter 8: Organizing and Outlining
Victoria Leonard, College of the Canyons
Adapted by William Kelvin, Professor of Communication Studies, Katharine O’Connor, Ph.D., and Jamie C. Votraw, Professor of Communication Studies, Florida SouthWestern State College

Figure 8.1: Outlining with Post it Notes 1
Introduction
One of your authors remembers taking an urban studies course in college. The professor was incredibly knowledgeable and passionate about the subject. Do you think that alone made her want to go to class? Unfortunately not. As great as this professor was in so many ways, the lectures were not organized. As much as she tried to take great notes and follow along, it felt like a hopeless task. Having a great topic that you are passionate about is important, but organizing your speech so that the audience can follow along is vital to the success of your speech.
When students are faced with developing a speech, they face the same challenges as a student asked to write an essay. Although the end product may be different in that you are not writing an essay or turning one in, you will go through much of the same process as you would in writing an essay.
Before you get too far into the writing process, it is important to know what steps you will have to take to write your speech. Note that the speech-writing process is formulaic: it is based on time-honored principles of rhetoric established thousands of years ago. Your initial preparation work will include the following:
- Selecting a topic
- Writing a general purpose
- Writing a specific purpose
- Writing a thesis statement
- Selecting main points
- Writing a preview statement
- Writing the body of the speech
This chapter will explain each of these steps so that you can create a thorough and well-written speech. As with anything we do that requires effort, the more you put in, the more you will get out of the writing process, in terms of both your education and your grade.
The Speech Topic, General Purpose, Specific Purpose, and Thesis
Selecting a topic.
We all want to know that our topics will be interesting to our audience. If you think back to Chapter 5, Identifying Topic, Purpose, and Audience, you will recall how important it is to be audience-centered. Does this mean that you cannot talk about a topic that your audience is unfamiliar with? No, what it does mean is that your goal as a speaker is to make that topic relevant to the audience. Whether you are writing an informative speech on earthquakes or the singer Jhené Aiko, you will need to make sure that you approach the speech in a way that helps your speech resonate with the audience. Although many of you would not have been alive when Hurricane Andrew hit Florida in 1992, this is an important topic to people who live in hurricane zones. Explaining hurricanes and hurricane preparation would be a great way to bring this topic alive for people who may not have lived through this event. Similarly, many audience members may be unfamiliar with Jhené Aiko, and that allows you to share information about her that might lead someone to want to check out her music.
If you are writing a persuasive speech, you might approach your topic selection differently. Think about what is happening in the world today. You can look at what affects you and your peers at a local, state, national, or global level. Whether you believe that gun violence is important to address because it is a problem at the national level, or you wish to address parking fees on your campus, you will have given thought to what is important to your audience. As Chapter 2 explained, your topics must fulfill the ethical goals of the speech. If you are ethical and select a topic you care about and make it relevant for the audience, you are on the right track.
Here are some questions that might help you select a topic:
- What are some current trends in music or fashion?
- What hobbies do I have that might be interesting to others?
- What objects or habits do I use every day that are beneficial to know about?
- What people are influencing the world in social media or politics?
- What authors, artists, or actors have made an impact on society?
- What events have shaped our nation or our world?
- What political debates are taking place today?
- What challenges do we face as a society or species?
- What health-related conditions should others be aware of?
- What is important for all people to be aware of in your community?
Once you have answered these questions and narrowed your responses, you are still not done selecting your topic. For instance, you might have decided that you really care about dogs. This is a very broad topic and could easily lead to a dozen different speeches. Now you must further narrow down the topic in your purpose statements.
Writing the Purpose Statements
Purpose statements allow you to do two things. First, they allow you to focus on whether you are fulfilling the assignment. Second, they allow you to narrow your topic so that you are not speaking too broadly. When creating an outline for your speech, you should include the general purpose and specific purpose statement at the beginning of your outline.
A general purpose statement is the overarching goal of a speech whether to inform, to persuade, to inspire, to celebrate, to mourn, or to entertain. It describes what your speech goal is, or what you hope to achieve. In public speaking classes, you will be asked to do any of the following: To inform, to persuade, or to entertain . Thus, your general purpose statement will be two words —the easiest points you will ever earn! But these two words are critical for you to keep in mind as you write the speech. Your authors have seen many persuasive speeches submitted inappropriately as informative speeches. Likewise, one author remembers a fascinating “persuasive speech” on the death penalty that never took a stance on the issue or asked the audience to—that would be an informative speech, right? You must always know your broad goal. Your audience should know it, too, and so should your instructor! Knowing your purpose is important because this is what you begin with to build your speech. It is also important to know your general purpose because this will determine your research approach. You might use different sources if you were writing a speech to inform versus to persuade.
A specific purpose statement is consistent with the general purpose of the speech, written according to assignment requirements, and clearly identifies desired audience outcomes. It is a declaration starting with the general purpose and then providing the topic with the precise objectives of the speech. It will be written according to your general purpose. For instance, the home design enthusiast might write the following specific purpose statement: To inform my audience about the pros and cons of flipping houses.
Specific purpose statements are integral in knowing if your speech is narrowed enough or if you need to narrow it further. Consider these examples:
- To inform my audience about musical instruments
- To inform my audience about string instruments
- To inform my audience about the violin
As you can see, the first two examples are far too broad. But is the third purpose statement sufficiently narrow? Will the speaker be covering the violin’s design, physics, history, cost, or how to play it? What do you think about these possible topics?
- To inform my audience about the life and contributions of Patricia Bath
- To inform my audience about the invention of the wheelchair
- To inform my audience about the Biloxi Wade-Ins
- To inform my audience about how Fibromyalgia affects the body

Figure 8.2: Dr. Patricia Bath 2
Hopefully, you can see that the examples above would work for an informative speech. They are specific and limited in their scope.
Your instructor will give you a time limit for your speech. Your specific purpose should help you see if you can stay within the time limit. You should put the purpose statements on your outline. Others may only ask you to put these on your topic submission. However, you do not state a general purpose or specific purpose during the delivery of your speech! These are simply guidelines for you as you write and for your instructor as they assess your writing.
Writing the Thesis Statement
A thesis statement is a single, declarative statement that encapsulates the essence of your speech. Just like in essay writing, you want your thesis statement, or central idea, to reveal what your speech is about. Thesis statements can never be written as questions, nor can they include a research citation. The thesis statement is not a list of main points, it is an over-arching idea that encapsulates them all.

Figure 8.3: Portrait of Aut h or, J.R.R. Tolkien 3
As a Lord of the Rings enthusiast, I may choose to write a speech on author J.R.R. Tolkien. Here is an example of what a thesis statement may sound like:
J.R.R. Tolkien is known as the father of modern fantasy literature and became a pop culture icon after his death.
The thesis you just read provides the audience with just enough information to help them know what they will hear ahd learn from your speech.
Selecting Main Points
The main points are the major ideas you want to cover in your speech. Since speeches have time requirements, your outline will always be limited to two to three main points. Many instructors suggest that you have no more than three main points so you can do justice to each idea and stay within the time frame. You will also lose time on each main point describing it in the preview statement, internal transitions, and review of main points in the conclusion. Plus, it can be difficult for audiences to remember many points.
Let’s determine the main points for a short speech using the J.R.R. Tolkien thesis above. Having researched his life, you might come up with an initial list like this:
- Childhood and Background
- Military service
- Literary fame and honors
As interesting as all of these topics are, there is not enough time to speak about each idea. This is where the difficult decision of narrowing a speech comes in. Brainstorming all of the points you could cover would be your first step. Then, you need to determine which of the points would be the most interesting for your audience to hear. There are also creative ways to combine ideas and touch on key points within each main point. You will see how this can be achieved in the next section as we narrow down the number of topics we will discuss about J.R.R. Tolkein.
Writing the Preview Statement
A preview statement is a guide to your speech. This is the part of the speech that literally tells the audience exactly what main points you will cover. If you were to open an app on your phone to get directions to a location, you would be told exactly how to get there. Best of all, you would know what to look for, such as landmarks. A preview statement in a speech fulfills the same goal. It is a roadmap for your speech. Let’s look at how a thesis and preview statement might look for a speech on J.R.R. Tolkien:
Thesis: J.R.R. Tolkien is known as the father of modern fantasy literature and became a pop culture icon after his death.
Preview: First, I will tell you about J.R.R. Tolkien’s humble beginnings. Then, I will describe his rise to literary fame. Finally, I will explain his lasting cultural legacy.
Notice that the thesis statement captures the essence of the speech. The preview concisely names each main point that supports the thesis. You will want to refer to these main point names, or taglines , throughout the speech. This repetition will help audience members remember each main point; use variations of these taglines in your preview statement, when introducing each point, and again in the conclusion.
Always use your words to make the audience feel that they are part of the performance. This makes them feel included and on your side. Also, occasionally audience members will have more expertise than you. Imagine how an expert would feel when you begin your speech with “Today I will teach you about…” when they already know a lot about the subject. Use inclusive language in your preview statement–“Get ready to join me on a fantastic adventure…”
Organizing the Main Points
Once you know what your speech is about, you can begin developing the body of your speech. The body of the speech is the longest and most important part of your speech because it’s where the general purpose is executed, e.g., you inform or persuade with the main points that you listed in your preview statement. In general, the body of the speech comprises about 75% to 80% of the length of your speech. This is where you will present the bulk of your research, evidence, examples, and any other supporting material you have. Chapter 7 will provide you with specifics on how to do research and support your speech.
Several patterns of organization are available to choose from when writing a speech. You should keep in mind that some patterns work only for informative speeches and others for persuasive speeches. The topical, chronological, spatial, or causal patterns discussed here are best suited to informative speeches. The patterns of organization for persuasive speeches will be discussed in Chapter 10.
Topical Pattern
The chronological pattern needed main points ordered in a specific sequence, whereas the topical pattern arranges the information of the speech into different subtopics. For example, you are currently attending college. Within your college, various student services are important for you to use while you are there. You may visit the Richard H. Rush Library and its computer lab, Academic Support Centers, Career Services and the Office of Student Financial Aid.

Figure 8.6: Valencia Campus Library Stacks 6
To organize this speech topically, it doesn’t matter which area you speak about first, but here is how you could organize it:
Topic: Student Services at Florida SouthWestern State College
Thesis Statement: Florida SouthWestern State College has five important student services, which include the library, the library computer lab, Academic Support Centers, Career Services and the Financial Aid office.
Preview : This speech will discuss each of the five important student services that Florida SouthWestern State College offers.
Main Points:
I. The Richard H. Rush Library can be accessed five days a week and online and has a multitude of books, periodicals, and other resources to use.
II.The library’s computer lab is open for students to use for several hours a day, with reliable, high-speed internet connections and webcams.
III.The Academic Support Centers have subject tutors, computers, and study rooms.
IV.CareerSource offers career services both in-person and online, with counseling and access to job listings and networking opportunities.
V. The Office of Student Financial Aid is one of the busiest offices on campus, offering students a multitude of methods by which they can supplement their personal finances by paying for both tuition and books.
Note that many novices appreciate the topical pattern because of its simplicity. However, because there is no internal logic to the ordering of points, the speech writer loses an opportunity to include a mnemonic device (phrasing that helps people remember information) in their performance. Audience members are more likely to remember information if it hangs together in an ordered, logical way, such as the following patterns employ.
Chronological (Temporal) Pattern
When organizing a speech based on time or sequence, you would use a chronological (temporal) pattern of organization. Speeches that look at the history of someone or something, or the evolution of an object or a process could be organized chronologically. For example, you could use this pattern in speaking about President Barack Obama, the Holocaust, the evolution of the cell phone, or how to carve a pumpkin. The challenge of using this pattern is to make sure your speech has distinct main points and that it does not appear to be storytelling.

Figure 8.4: Barack Obama 4
Here is an example of how your main points will help you make sure that the points are clear and distinct:
Topic: President Barack Obama
Specific Purpose: To inform my audience about the life of President Barack Obama.
Thesis: From his humble beginnings, President Barack Obama succeeded in law and politics to become the first African-American president in U.S. history.
Preview: First, let’s look at Obama’s background and career in law. Then, we will look at his rise to the presidency of the United States. Finally, we will explore his accomplishments after leaving the White House.
I. First, let’s look at the early life of Obama and his career as a lawyer and advocate.
II. Second, let’s examine how Obama transitioned from law to becoming the first African-American President of the United States.
III. Finally, let’s explore all that Obama has achieved since he left the White House.
We hope that you can see that the main points clearly define and isolate different parts of Obama’s life so that each point is distinct. Using a chronological pattern can also help you with other types of informative speech topics.

Figure 8.5: Pumpkin Carving 5
Here is an additional example to help you see different ways to use this pattern:
Topic : How to Carve a Pumpkin
Specific Purpose: To inform my audience how to carve a pumpkin.
Thesis: Carving a pumpkin with special techniques and tools can result in amazing creations.
Preview: First, I will explain the process of gutting the pumpkin in preparation for carving. Then, I will describe the way you use your special tools to carve the face you hope to create. Finally, I will show you a variety of different designs that are unique to make your pumpkin memorable.
I. First, let me explain exactly how you open up the pumpkin, remove the seeds, and clean it so it is ready to carve.
II. Second, let me describe how the tools you have on hand are used to draw and carve the face of the pumpkin.
III. Finally, let me show you several unique designs that will make your pumpkin dazzle your friends and neighbors.
Note that some instructors prefer their students not give “how-to” speeches. Always clear your topic with your instructor early on in the speech-writing process.
Spatial Pattern
A spatial pattern arranges ideas according to their physical or geographic relationships. Typically, we can begin with a starting point and look at the main points of your speech directionally from top to bottom, inside to outside, left to right, north to south, and so on. A spatial pattern allows for creativity as well as clarity. For example, a speech about an automobile could be arranged using a spatial pattern and you might describe the car from the front end to the back end or the interior to the exterior. A speech on Disneyland might begin with your starting point at the entrance on Main Street, and each subsequent main point may be organized by going through each land in the park in a directional manner. Even a speech on the horrific tsunami off the Indonesian coast of Sumatra on December 26, 2004, could be discussed spatially as you use the starting point and describe the destruction as it traveled, killing 250,000 people.
If you have never heard of the Great Pacific Garbage Patch, it is marine debris that is in the North Pacific Ocean. Just like the tsunami in the previous example, this mass could likewise be discussed using a spatial pattern.
Figure 8.7: The Great Pacific Garbage Patch 7
In an informative speech, you could arrange your points spatially like this:
Topic: Great Pacific Garbage Patch
Thesis: The Great Pacific Garbage patch is not well known to most people; it consists of marine debris that is located in the North Pacific Ocean.
Preview: First, I will describe the Eastern Garbage Patch. Finally, I will explain the Western Patch.
I. The Eastern Garbage patch is located between the states of Hawaii and California.
II. The Western Garbage Patch is located near Japan.
Causal Pattern
A causal pattern of organization can be used to describe what occurred that caused something to happen, and what the effects were. Conversely, another approach is to begin with the effects and then talk about what caused them. For example, in 1994, there was a 6.7 magnitude earthquake that occurred in the San Fernando Valley in Northridge, California.

Figure 8.8: Northridge Meadows Apartment Building Collapse 8
Let’s look at how we can arrange this speech first by using a cause-effect pattern:
Topic: Northridge Earthquake
Thesis: The Northridge, California earthquake was a devastating event that was caused by an unknown fault and resulted in the loss of life and billions of dollars of damage.
I. The Northridge earthquake was caused by a fault that was previously unknown and located nine miles beneath Northridge.
II. The Northridge earthquake resulted in the loss of 57 lives and over 40 billion dollars of damage in Northridge and surrounding communities.
Depending on your topic, you may decide it is more impactful to start with the effects and work back to the causes ( effect-cause pattern ). Let’s take the same example and flip it around:
Thesis: The Northridge, California earthquake was a devastating event that resulted in the loss of life and billions of dollars in damage and was caused by an unknown fault below Northridge.
I. The Northridge earthquake resulted in the loss of 57 lives and over 40 billion dollars of damage in Northridge and surrounding communities.
II. The Northridge earthquake was caused by a fault that was previously unknown and located nine miles beneath Northridge.
Why might you decide to use an effect-cause approach rather than a cause-effect approach? In this particular example, the effects of the earthquake were truly horrible. If you heard all of that information first, you would be much more curious to hear about what caused such devastation. Sometimes natural disasters are not that exciting, even when they are horrible. Why? Unless they affect us directly, we may not have the same attachment to the topic. This is one example where an effect-cause approach may be very impactful.
One take-home idea for you about organizing patterns is that you can usually use any pattern with any topic. Could the Great Pacific Garbage Patch be explained using the chronological or causal patterns? Could the Northridge quake be discussed using the chronological or spatial patterns? Could a pumpkin-carving speech be spatially organized? The answer to all of the above is yes. The organizational pattern you select should be one that you think will best help the audience make sense of, and remember, your ideas.
Developing the Outline
Although students are often intimidated by the process of outlining a speech, you should know that it is a formulaic process. Once you understand the formula–the same one speech instructors have long taught and used to assess throughout the nation–speech writing should be a cinch. And remember, this process is what organizes your speech. A well-organized speech leads to better delivery. Simply, outlining is a method of organizing the introduction, body with main points, and conclusion of your speech. Outlines are NOT essays; they are properly formatted outlines! They use specific symbols in a specific order to help you break down your ideas in a clear way. There are two types of outlines: the preparation outline and the speaking outline.
Outline Types
When you begin the outlining process, you will create a preparation outline. A preparation outline consists of full, complete sentences, and thus, is void of awkward sentences and sentence fragments. In a full-sentence preparation outline, only one punctuated sentence should appear beside each symbol. In many cases, this type of outline will be used in preparing your speech, but will not be allowed to be used during your speech delivery. Remember that even though this outline requires complete sentences, it is still not an essay. The examples you saw earlier in this chapter were written in complete sentences, which is exactly what a preparation outline should look like.
A speaking outline is less detailed than the preparation outline and will include brief phrases or words that help you remember your key ideas. It is also called a “key word” outline because it is not written in complete sentences–only key words are present to jog your memory as needed. It should include elements of the introduction, body, and conclusion, as well as your transitions. Speaking outlines may be written on index cards to be used when you deliver your speech.
Confirm with your professor about specific submission requirements for preparation and speaking outlines.
Outline Components
Introduction and conclusion.
In Chapter 9, we identified the components of effective introductions and conclusions. Do you remember what they were? Your preparation outline should delineate the five elements of an introduction and the four elements of a conclusion . Recall, a complete introduction includes an attention-getter, relates the topic to the audience, establishes speaker credibility, states the thesis, and previews the main points. A quality conclusion will signal the speech is ending, restate the thesis, review the main points, and finish with a memorable ending.
Main Points
Main points are the main ideas in the speech. In other words, the main points are what your audience should remember from your talk, and they are phrased as single, declarative sentences. These are never phrased as a question, nor can they be a quote or form of citation. Any supporting material you have will be put in your outline as a subpoint. Since this is a public speaking class, your instructor will decide how long your speeches will be, but in general, you can assume that no speech will be longer than 10 minutes in length. Given that alone, we can make one assumption: All speeches will fall between 2 to 3 main points based simply on length. If you are working on an outline and you have ten main points, something is wrong, and you need to revisit your ideas to see how you need to reorganize your points.
All main points are preceded by Roman numerals (I, II, III, IV, V). Subpoints are preceded by capital letters (A, B, C, etc.), sub-sub points by Arabic numerals (1, 2, 3, etc.), then sub-sub-sub points by lowercase letters (a, b, c, etc.). You may expand further than this. Here is a short template:
I. First main point
- First subpoint
- Second subpoint
- First sub-subpoint
- First sub-sub-subpoint
- Second sub-sub-subpoint
- Second main point
- Third main point
References List
A quality speech requires a speaker to cite evidence to support their claims. Your professor will likely require that you incorporate evidence from your research in both your outline and speech. In Chapter 7, we reviewed how to gather information, incorporate the research into your speech, and cite your sources, both in your written outline and during oral delivery. An ethical and credible speaker gives credit where credit is due and shares source information with the audience. Accordingly, the last piece of your preparation outline is the References List. The references list will include full written citations for all resources used in the composition and presentation of your speech. The structure of the references list follows a specific format dictated by the American Psychological Association 7th Ed. (remember, the Communication Studies discipline uses this APA formatting). Since formatting varies by source type, it is useful to refer to a reference guide to determine the exact citation formatting when writing your references list.
Written Oral Citations
There is a good chance your professor will ask you to include oral citations in your speech delivery. If so, you should include these in your preparation outline. The written oral citation is where you share your evidence and details of how you plan to cite the source during the delivery. Often, this is written in a similar format as “According to an article titled [title], written by [author] in [year], [resource content].” You should include enough source-identifying information for your audience to verify the accuracy and credibility of the content. In your outline, write out the specific source-information you will use to orally cite the source in your speech. Discuss the required number of oral citations with your professor and include all of them in your written outline. At FSW, we require three oral citations.
Outlining Principles
Next, we will cover the principles of outline which are outlining “rules” that you want to follow to be most effective. (Your English teachers will thank us, too!). First, read through this example outline for a main point about dogs. We will recall this example as we move through the principles. Don’t skip this example. Read it now!

Figure 6.9: Big and Small Dog 9
Topic: Dogs
Thesis: There are many types of dogs that individuals can select from before deciding which would make the best family pet.
Preview: First, I will describe the characteristics of large breed dogs, then I will discuss the characteristics of small breed dogs.
- Some large breed dogs need daily activity.
- Some large breed dogs are dog friendly.
- After eating is one of the times drooling is bad.
- The drooling is horrible after they drink, so beware!
- Great Pyrenees Mountain dogs drool as well.
- If you live in an apartment, these breeds could pose a problem.
Transition statement: Now that we’ve explored the characteristics of large breed dogs, let’s contrast this with small breeds.
- Some small breed dogs need daily activity.
- Some small breed dogs are dog friendly.
- They will jump on people.
- They will wag their tails and nuzzle.
- Beagles love strangers.
- Cockapoos also love strangers.
This dog example will help us showcase the following outlining principles.
Subordination and Coordination
The example above helps us to explain the concepts of subordination and coordination . Subordination is used in outline organization so the content is in a hierarchical order. This means that your outline shows subordination by indention. All of the points that are “beneath” (indented in the format) are called subordinate points. For example, if you have a job with a supervisor, you are subordinate to the supervisor. The supervisor is subordinate to the owner of the company. Your outline content works in a similar way. Using the dog example outlined in the previous section of this chapter, subpoints A, B, and C described characteristics of large breed dogs, and those points are all subordinate to main point I. Similarly, subpoints i and ii beneath subpoint C.1. both described dogs that drool, so those are subordinate to subpoint C. If we had discussed “food” under point C, you would know that something didn’t make sense! Overall, to check your outline for coherence, think of the outline as a staircase; walking down the outline one step at a time.
Tech tip: You can use the Ruler function of word processing software such as Microsoft Word or Google Docs to create tabs that align subordinated points with each other and keep the following lines of text properly aligned. If you only use the tab key, text that flows beyond the first line will usually not align with the proper tab stop for a given sub-point. Some instructors may provide you with a template, but experiment with the Ruler function on your own. It’s very useful!
You will also see that there is a coordination of points. Coordination is used in outline organization so that all of the numbers or letters represent the same idea. You know they coordinate because they align vertically and there is no diagonal relationship between the symbols. In the dog example, A, B, and C were all characteristics of large breed dogs, so those are all coordinated and represent the same “idea.” Had C been “German Shepherd,” then the outline would have been incorrect because that is a type of dog, not a characteristic, therefore, breaking the rules of subordination and coordination.
Figure 8.10 below provides you with a visual graphic of the subordination and coordination process. You will see that the topic of this very brief outline is bread. The main point tells you that there are different types of bread: sourdough, wheat, white, and egg.
To check this brief outline for subordination, you would look to see what subpoints fall beneath the main point. Do all of the sub-points represent a type of bread? You will see that they do! Next, to check for coordination, you would look at all of the subpoints that have a vertical relationship to each other. Are the subpoints these four types of bread? They are. The image also allows you to see what happens when you make a mistake. The third example shows the subpoints as sourdough, wheat, white, and jelly. Clearly, jelly is not a type of bread. Thus, there is a lack of both subordination and coordination in this short example. Make sure you spend some time checking the subordination and coordination of your own subpoints all the way throughout the outline until you have reached your last level of subordination. Now, study the image so that these principles of outlining are crystal clear; please ask your professor questions about this because it is a major part of speechmaking.
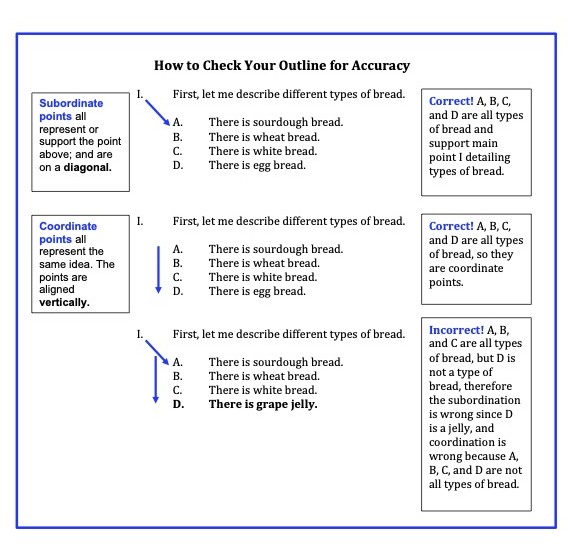
Figure 8.10: Checking Your Outline 10
You may be wondering why we bother with subordination and coordination. It actually helps both your listeners and your instructors. Listening is difficult. Any techniques that help audiences make sense of information are welcome. As soon as you begin talking, audiences listen for cues on how you are structuring information. If you organize clearly using logical relationships, your audience will be better able to follow your ideas. Further, for busy instructors examining many students’ outlines, when students’ grasp of subordination and coordination jump off the page due to their proper visual alignment, we know that students understand how to organize information for verbal delivery.
Parallelism
Another important rule in outlining is known as parallelism . This means that, when possible, you begin your sentences in a similar way, using a similar grammatical structure. For example, in the previous example on dogs, some of the sentences began with “some large breed dogs.” This type of structure adds clarity to your speech. Students often worry that parallelism will sound boring. It’s actually the opposite! It adds clarity. However, if you had ten sentences in a row, we would never recommend you begin them all the same way. That is where transitions come into the picture and break up any monotony that could occur.
The principle of division is an important part of outlining. Division is a principle of outlining that requires a balance between two subpoints in an outline. For each idea in your speech, you should have enough subordinate ideas to explain the point in detail and you must have enough meaningful information so that you can divide it into a minimum of two subpoints (A and B). If subpoint A has enough information that you can explain it, then it, too, should be able to be divided into two subpoints (1 and 2). So, in other words, division means this: If you have an A, then you need a B; if you have a 1, then you need a 2, and so on. What if you cannot divide the point? In a case like that, you would simply incorporate the information in the point above.
Connecting Your 2-3 Main Points
There are different types of transitions , which are words or phrases that help you connect all sections of your speech. To guarantee the flow of the speech, you will write transition statements to make connections between all sections of the outline. You will use these transitions throughout the outline, including between the introduction and the body, between the 2-3 main points, and between the body and the conclusion.
- Internal Reviews (Summaries) and Previews are short descriptions of what a speaker has said and will say that are delivered between main points.
Internal Reviews give your audience a cue that you have finished a main point and are moving on to the next main point. These also help remind the audience of what you have spoken about throughout your speech. For example, an internal review may sound like this, “So far, we have seen that the pencil has a long and interesting history. We also looked at the many uses the pencil has that you may not have known about previously.”
Internal Previews lay out what will occur next in your speech. They are longer than transitional words or signposts. For example, “Next, let us explore what types of pencils there are to pick from that will be best for your specific project.”
- Signposts are transitional words that are not full sentences, but connect ideas using words like “first,” “next,” “also,” “moreover,” etc. Signposts are used within the main point you are discussing, and they help the audience know when you are moving to a new idea.
- A nonverbal transition is a transition that does not use words. Rather, movement, such as pausing as you move from one point to another is one way to use a nonverbal transition. You can also use inflection by raising the pitch of your voice on a signpost to indicate that you are transitioning.
The most effective transitions typically combine many or all of the elements discussed here. Here is an example:
Now ( signpost ) that I have told you about the history of the pencil, as well as its many uses, ( internal review ) let’s look at what types of pencils you can pick from (mime picking up a pencil and moving a few steps for nonverbal transition ) that might be best for your project ( internal preview ).
Although this wasn’t the splashiest chapter in the text, it is one of the most critical chapters in speechmaking. Communicating your ideas in an organized and developed fashion means your audience will easily understand you. Each one of the principles and examples provided should be referenced as you work to develop your own speech. Remember that your speech will have a general purpose (typically to inform or persuade) and a specific purpose that details exactly what you hope to accomplish in the speech. Your speech’s thesis statement will be the central idea, what audiences most remember. The thesis is not just a list of main points, but it is a larger idea encompassing the two to three main points supporting it in the speech. Speeches should follow an organizational pattern, use standard formatting practices, and progress from full-sentence preparation outlines to key word speaking outlines before your performance. To see how all of these pieces come together, check out the sample preparation outline included at the bottom of the chapter. When writing your own preparation outline, use this sample as a guide. Consider each component a puzzle piece needed to make your outline complete.
Reflection Questions
- How has the information regarding general and specific purpose statements helped you to narrow your topic for your speech?
- Using brainstorming, can you generate a list of possible main points for your speech topic? Then, how will you decide which are the best choices to speak on?
- Which pattern(s) of organization do you think would be best for your informative speech? Why?
- Researchers say writing in small bursts is better. Do you agree that it is more effective to write your outline in small chunks of time rather than writing an entire speech in one day? Why or why not?
Body of the Speech
Coordination
General Purpose Statement
Internal Review (Summary)
Internal Preview
Nonverbal Transition
Preparation Outline
Preview Statement
Speaking Outline
Specific Purpose Statement
Subordination
Thesis Statement
Transitions
Written Oral Citation
Sample Speaking Outline
General Purpose: To inform
Specific Purpose: By the end of this speech, my audience will be able to explain bottle bricking, bottle brick benches, and their purposes.
Introduction —
I. Attention Getter: How many of you have thrown away a piece of plastic in the last 24 hours? Perhaps you pulled cellophane off a pack of gum or emptied out a produce bag. You probably don’t think about it, but those little pieces of plastic have two potential destinations – if they’re obedient, they go to a landfill. If they’re rogue, they can end up in waterways.
II. Thesis Statement: Today we will learn about a revolutionary way of dealing with plastic trash called bottle bricking.
III. Relevance Statement: As our planet’s ecological crises worsen, each of us should reflect on our impact on the environment. According to the Sea Education Society, a non-profit dedicated to reducing pollution through environmental education, there are more than one million pieces of plastic per square mile in the most polluted parts of the Atlantic Ocean, as Kirsten Silven of Earthtimes.org reported in (2011). If you want to take steps to preserve our world’s natural beauty for future generations, this speech is for you.
IV. Credibility Statement: When I first learned about bottle bricks I was incredulous. I thought “what is the point of stuffing plastic into plastic bottles?”. But soon the idea took hold of me and I was volunteering with local groups, eventually inspiring the creation of a Bottle Brick Bench at a high school I worked at.
V. Preview Main Points Statement: In this speech, we will learn how a bottle brick is made, how they are turned into benches, and the purpose behind this seemingly strange activity.
Transition: Before we go any further, let’s learn how to make a bottle brick.
Body —
- You will soon notice it everywhere.
- The trash must be clean and dry.
- Other hard-plastic bottles work, also.
- The bottles must be clean and dry.
- The stick should be long enough to reach the bottom of the bottle.
- Pick a smooth stick or give it a handle.
Transition: Now we know how to transform our trash into tools. But, what can bottle bricks be used for? One answer: a bench.
- Most creators argue you should use reclaimed stone (urbanite).
- Bricks make up the backrest.
- Cob is like mud.
- The benches make us realize how much plastic we toss, writes Brennan Blazer Bird on earthbench.org (2014) , home of the Peace on Earthbench Movement that the 25-year-old ecological educator founded.
- Later, people might think about it the plastic away they throw away
- Currently we have little use for soft plastic; most film plastics are not recyclable.
- Benches are a sign for change, and they are comfortable.
- Plastic “sequestered” in a bottle avoids landfills and the ocean.
- In landfills it gets into drinking water.
- All five subtropical ocean gyres have plastic “garbage patches,” according to 5gyres, a nonprofit dedicated to eliminating plastic pollution in the gyres (5gyres.org, 2014) .
- To have fun! The Harvest Collective called natural building such as earthbenches “incredibly fun and inspiring” on its website theharvestcollective.org (2014) .
Transition: So now that we understand why someone would make a bottle brick bench, let’s see if we’ve successfully “stuffed” this knowledge into our heads. [ I can make a bottle-stuffing motion to have fun during transition. ]
Conclusion —
- Signal end of the speech: I think it’s safe to say that every one of us throws away plastic on a regular basis has some degree of concern for the health of our planet.
- Review Main Points: Today we’ve learned how to make bottle bricks, how to put them into a bottle brick bench, and the reasons for doing so.
- Restate Thesis: Today we have seen that we can turn our seemingly useless, polluting trash into safe, useful technology. Maybe we can use such forward-thinking attitudes to promote sustainable cycles in all aspects of society.
- Specify desired audience response: I know that you aren’t all going to rush home and start bricking, but I’d like you to remember the basic premises underlying bottle bricks. But, by all means, if you’re interested in adding to the Peace on Earth Bench for Movement, visit earthbench.org or talk to me in class sometime.
- Strong closing (clincher): Who knows, maybe when you’re about to graduate you will be able to sit on a Bottle Brick Bench on campus reminding us all that we, through our individual choices, have the power to transform our species’ problems into solutions.
Introduction to Public Speaking Copyright © by Jamie C. Votraw, M.A.; Katharine O'Connor, Ph.D.; and William F. Kelvin, Ph.D.. All Rights Reserved.
Share This Book
How to Write a Solid Thesis Statement
The important sentence expresses your central assertion or argument
arabianEye / Getty Images
- Writing Research Papers
- Writing Essays
- English Grammar
- M.Ed., Education Administration, University of Georgia
- B.A., History, Armstrong State University
A thesis statement provides the foundation for your entire research paper or essay. This statement is the central assertion that you want to express in your essay. A successful thesis statement is one that is made up of one or two sentences clearly laying out your central idea and expressing an informed, reasoned answer to your research question.
Usually, the thesis statement will appear at the end of the first paragraph of your paper. There are a few different types, and the content of your thesis statement will depend upon the type of paper you’re writing.
Key Takeaways: Writing a Thesis Statement
- A thesis statement gives your reader a preview of your paper's content by laying out your central idea and expressing an informed, reasoned answer to your research question.
- Thesis statements will vary depending on the type of paper you are writing, such as an expository essay, argument paper, or analytical essay.
- Before creating a thesis statement, determine whether you are defending a stance, giving an overview of an event, object, or process, or analyzing your subject
Expository Essay Thesis Statement Examples
An expository essay "exposes" the reader to a new topic; it informs the reader with details, descriptions, or explanations of a subject. If you are writing an expository essay , your thesis statement should explain to the reader what she will learn in your essay. For example:
- The United States spends more money on its military budget than all the industrialized nations combined.
- Gun-related homicides and suicides are increasing after years of decline.
- Hate crimes have increased three years in a row, according to the FBI.
- Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) increases the risk of stroke and arterial fibrillation (irregular heartbeat).
These statements provide a statement of fact about the topic (not just opinion) but leave the door open for you to elaborate with plenty of details. In an expository essay, you don't need to develop an argument or prove anything; you only need to understand your topic and present it in a logical manner. A good thesis statement in an expository essay always leaves the reader wanting more details.
Types of Thesis Statements
Before creating a thesis statement, it's important to ask a few basic questions, which will help you determine the kind of essay or paper you plan to create:
- Are you defending a stance in a controversial essay ?
- Are you simply giving an overview or describing an event, object, or process?
- Are you conducting an analysis of an event, object, or process?
In every thesis statement , you will give the reader a preview of your paper's content, but the message will differ a little depending on the essay type .
Argument Thesis Statement Examples
If you have been instructed to take a stance on one side of a controversial issue, you will need to write an argument essay . Your thesis statement should express the stance you are taking and may give the reader a preview or a hint of your evidence. The thesis of an argument essay could look something like the following:
- Self-driving cars are too dangerous and should be banned from the roadways.
- The exploration of outer space is a waste of money; instead, funds should go toward solving issues on Earth, such as poverty, hunger, global warming, and traffic congestion.
- The U.S. must crack down on illegal immigration.
- Street cameras and street-view maps have led to a total loss of privacy in the United States and elsewhere.
These thesis statements are effective because they offer opinions that can be supported by evidence. If you are writing an argument essay, you can craft your own thesis around the structure of the statements above.
Analytical Essay Thesis Statement Examples
In an analytical essay assignment, you will be expected to break down a topic, process, or object in order to observe and analyze your subject piece by piece. Examples of a thesis statement for an analytical essay include:
- The criminal justice reform bill passed by the U.S. Senate in late 2018 (" The First Step Act ") aims to reduce prison sentences that disproportionately fall on nonwhite criminal defendants.
- The rise in populism and nationalism in the U.S. and European democracies has coincided with the decline of moderate and centrist parties that have dominated since WWII.
- Later-start school days increase student success for a variety of reasons.
Because the role of the thesis statement is to state the central message of your entire paper, it is important to revisit (and maybe rewrite) your thesis statement after the paper is written. In fact, it is quite normal for your message to change as you construct your paper.
- 4 Teaching Philosophy Statement Examples
- Examples of Great Introductory Paragraphs
- 100 Persuasive Essay Topics
- 50 Argumentative Essay Topics
- How to Write a Good Thesis Statement
- What Is Expository Writing?
- An Introduction to Academic Writing
- Definition and Examples of Analysis in Composition
- Write an Attention-Grabbing Opening Sentence for an Essay
- How To Write an Essay
- Tips on How to Write an Argumentative Essay
- How to Write a Response Paper
- The Ultimate Guide to the 5-Paragraph Essay
- Understanding What an Expository Essay Is
- The Introductory Paragraph: Start Your Paper Off Right
- Tips for Writing an Art History Paper
How to Write a Thesis Statement for a Speech

Good thesis statements define your general idea and inform your audience about your main points. Hence, writing a thesis statement is a key to getting attention of the listeners and engaging them in thinking about your topic. Knowing how to write a thesis statement for a speech is a vital skill, as far as it predetermines the outcome of your speech. Will your listeners be interested in what you are talking about? Are they going to remember it? Is it going to influence their ideas? Consider these questions when you will be writing a speech for your next occasion.
Writing a Good Thesis for a Speech: How Is It Different From Other Theses?
When writing a speech, you mostly think of argumentative thesis statement. It has a lot in common with thesis statement for a research paper or argumentative essay thesis: you need to put forward your idea and add details, which are to demonstrate where your research or analysis is going to move. However, if a thesis for research paper has to be well-grounded and profound, the goal of thesis for a speech is different: it has to grab attention of your audience and get them involved in your topic. Argumentative speech is supposed to deal with proving certain point, which you consider to be controversial. Thus, in order to get a working thesis statement, you have to demonstrate why your topic is interesting, what is the reason for you to talk about it. As opposed to thesis statement for argumentative essay, thesis for argumentative speech should not just outline ideas you are going to handle but also make listeners stop fiddling with their smart phones and pay attention to what you are talking about. Make it catchy so that the audience get engaged into your topic from the very beginning. Provoke thoughts and discussions. Give people an opportunity to relate to your topic by including issues that occur in their lives. That will insure contact between you and your audience.
As PapersMaster mentioned above, writing a thesis statement for your speech resembles creating a thesis statement for an essay. It might be a good idea to try using online essay writer in order to clarify a structure of a good thesis statement. Automatic essay writer might not provide a perfect thesis for your particular case, nevertheless you can see what are the key ingredients that should be included into it.
When you ask yourself a question: “ How do I write my thesis for a speech?”, try thinking about the greatest speeches you have ever heard. You might think of the famous “I have a dream” by Martin Luther King , or anything else you find powerful and inspiring. Try to understand what turns this words into a great force. Look into theses of these speeches and analyze why they appeal to so many hearts. All in all, use your heart and your brain, and the result will pleasantly surprise you.

We have taken appropriate security measures to protect you against loss, misuse or alteration of the information we have collected from you.
Please read our Privacy and Cookies Policy to learn more.
Our guarantees
Your academic success is our goal.
- About Company
- How it Works
- Testimonials
- Write My Essay
- Research Paper Writing Service
- Term Paper Writing Sevice
- Dissertation Writing Service
- Homework Writing Service
- Assignment Writing Service
- Report Writing Service
- Article Writing Service
- Privacy and Cookies Policy
- Terms of Use
- Revision Policy
- Money Back Guarantee
- Secure Payment System
PapersMASTER
- +1 (844) 869-8779
- [email protected]
We try to make your user experience better. By staying on our website, you agree to our use of cookies. See more .

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
Margin Size
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

6.1: The Topic, General Purpose, Specific Purpose, and Thesis
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 54935
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
Before any work can be done on crafting the body of your speech or presentation, you must first do some prep work—selecting a topic, formulating a general purpose, a specific purpose statement, and crafting a central idea, or thesis statement. In doing so, you lay the foundation for your speech by making important decisions about what you will speak about and for what purpose you will speak. These decisions will influence and guide the entire speechwriting process, so it is wise to think carefully and critically during these beginning stages.
Selecting a Topic
Generally, speakers focus on one or more interrelated topics—relatively broad concepts, ideas, or problems that are relevant for particular audiences. The most common way that speakers discover topics is by simply observing what is happening around them—at their school, in their local government, or around the world. Student government leaders, for example, speak or write to other students when their campus is facing tuition or fee increases, or when students have achieved something spectacular, like lobbying campus administrators for lower student fees and succeeding. In either case, it is the situation that makes their speeches appropriate and useful for their audience of students and university employees. More importantly, they speak when there is an opportunity to change a university policy or to alter the way students think or behave in relation to a particular event on campus.
But you need not run for president or student government in order to give a meaningful speech. On the contrary, opportunities abound for those interested in engaging speech as a tool for change. Perhaps the simplest way to find a topic is to ask yourself a few questions. See the textbox entitled “Questions for Selecting a Topic” for a few questions that will help you choose a topic.
Students speak about what is interesting to them and their audiences. What topics do you think are relevant today? There are other questions you might ask yourself, too, but these should lead you to at least a few topical choices. The most important work that these questions do is to locate topics within your pre-existing sphere of knowledge and interest. David Zarefsky (2010) also identifies brainstorming as a way to develop speech topics, a strategy that can be helpful if the questions listed in the textbox did not yield an appropriate or interesting topic. Starting with a topic you are already interested in will likely make writing and presenting your speech a more enjoyable and meaningful experience. It means that your entire speechwriting process will focus on something you find important and that you can present this information to people who stand to benefit from your speech.
Questions for Selecting a Topic
- What important events are occurring locally, nationally and internationally?
- What do I care about most?
- Is there someone or something I can advocate for?
- What makes me angry/happy?
- What beliefs/attitudes do I want to share?
- Is there some information the audience needs to know?
Once you have answered these questions and narrowed your responses, you are still not done selecting your topic. For instance, you might have decided that you really care about breeds of dogs. This is a very broad topic and could easily lead to a dozen different speeches. To resolve this problem, speakers must also consider the audience to whom they will speak, the scope of their presentation, and the outcome they wish to achieve.
Formulating the Purpose Statements
By honing in on a very specific topic, you begin the work of formulating your purpose statement. In short, a purpose statement clearly states what it is you would like to achieve. Purpose statements are especially helpful for guiding you as you prepare your speech. When deciding which main points, facts, and examples to include, you should simply ask yourself whether they are relevant not only to the topic you have selected, but also whether they support the goal you outlined in your purpose statement. The general purpose statement of a speech may be to inform, to persuade, to celebrate, or to entertain. Thus, it is common to frame a specific purpose statement around one of these goals. According to O’Hair, Stewart, and Rubenstein, a specific purpose statement “expresses both the topic and the general speech purpose in action form and in terms of the specific objectives you hope to achieve (2004). For instance, the home design enthusiast might write the following specific purpose statement: At the end of my speech, the audience will learn the pro’s and con’s of flipping houses . In short, the general purpose statement lays out the broader goal of the speech while the specific purpose statement describes precisely what the speech is intended to do. Some of your professors may ask that you include the general purpose and add the specific purpose.
Writing the Thesis Statement
The specific purpose statement is a tool that you will use as you write your talk, but it is unlikely that it will appear verbatim in your speech. Instead, you will want to convert the specific purpose statement into a central idea, or thesis statement that you will share with your audience.
Depending on your instructor’s approach, a thesis statement may be written two different ways. A thesis statement may encapsulate the main points of a speech in just a sentence or two, and be designed to give audiences a quick preview of what the entire speech will be about. The thesis statement for a speech, like the thesis of a research-based essay, should be easily identifiable and ought to very succinctly sum up the main points you will present. Some instructors prefer that your thesis, or central idea, be a single, declarative statement providing the audience with an overall statement that provides the essence of the speech, followed by a separate preview statement.
If you are a Harry Potter enthusiast, you may write a thesis statement (central idea) the following way using the above approach: J.K. Rowling is a renowned author of the Harry Potter series with a Cinderella like story having gone from relatively humble beginnings, through personal struggles, and finally success and fame .
Writing the Preview Statement
However, some instructors prefer that you separate your thesis from your preview statement. A preview statement (or series of statements) is a guide to your speech. This is the part of the speech that literally tells the audience exactly what main points you will cover. If you were to open your Waze app, it would tell you exactly how to get there. Best of all, you would know what to look for! So, if we take our J.K Rowling example, let’s rewrite that using this approach separating out the thesis and preview:
J.K. Rowling is a renowned author of the Harry Potter series with a Cinderella like rags to riches story. First, I will tell you about J.K. Rowling’s humble beginnings. Then, I will describe her personal struggles as a single mom. Finally, I will explain how she overcame adversity and became one of the richest women in the United Kingdom.
There is no best way to approach this. This is up to your instructor.
Writing the Body of Your Speech
Once you have finished the important work of deciding what your speech will be about, as well as formulating the purpose statement and crafting the thesis, you should turn your attention to writing the body of your speech. All of your main points are contained in the body, and normally this section is prepared well before you ever write the introduction or conclusion. The body of your speech will consume the largest amount of time to present; and it is the opportunity for you to elaborate on facts, evidence, examples, and opinions that support your thesis statement and do the work you have outlined in the specific purpose statement. Combining these various elements into a cohesive and compelling speech, however, is not without its difficulties, the first of which is deciding which elements to include and how they ought to be organized to best suit your purpose.
Good design is making something intelligible and memorable. Great design is making something memorable and meaningful.
~ Dieter Rams
Contributors and Attributions
- Template:ContribCCComm105

- University of Pennsylvania
- School of Arts and Sciences
- Penn Calendar
Search form

On Thesis Statements
The thesis statement.
This is not an exhaustive list of bad thesis statements, but here're five kinds of problems I've seen most often. Notice that the last two, #4 and #5, are not necessarily incorrect or illegitimate thesis statements, but, rather, inappropriate for the purposes of this course. They may be useful forms for papers on different topics in other courses.
A thesis takes a position on an issue. It is different from a topic sentence in that a thesis statement is not neutral. It announces, in addition to the topic, the argument you want to make or the point you want to prove. This is your own opinion that you intend to back up. This is your reason and motivation for writing.
Bad Thesis 1
Bad Thesis 2 : This paper will consider the advantages and disadvantages of certain restrictions on free speech.
Better Thesis 1 : Stanley Fish's argument that free speech exists more as a political prize than as a legal reality ignores the fact that even as a political prize it still serves the social end of creating a general cultural atmosphere of tolerance that may ultimately promote free speech in our nation just as effectively as any binding law.
Better Thesis 2 : Even though there may be considerable advantages to restricting hate speech, the possibility of chilling open dialogue on crucial racial issues is too great and too high a price to pay.
A thesis should be as specific as possible, and it should be tailored to reflect the scope of the paper. It is not possible, for instance, to write about the history of English literature in a 5 page paper. In addition to choosing simply a smaller topic, strategies to narrow a thesis include specifying a method or perspective or delineating certain limits.
Bad Thesis 2 : The government has the right to limit free speech.
Better Thesis 1 : There should be no restrictions on the 1st amendment if those restrictions are intended merely to protect individuals from unspecified or otherwise unquantifiable or unverifiable "emotional distress."
Better Thesis 2 : The government has the right to limit free speech in cases of overtly racist or sexist language because our failure to address such abuses would effectively suggest that our society condones such ignorant and hateful views.
A thesis must be arguable. And in order for it to be arguable, it must present a view that someone might reasonably contest. Sometimes a thesis ultimately says, "we should be good," or "bad things are bad." Such thesis statements are tautological or so universally accepted that there is no need to prove the point.
Bad Thesis 2 : There are always alternatives to using racist speech.
Better Thesis 1 : If we can accept that emotional injuries can be just as painful as physical ones we should limit speech that may hurt people's feelings in ways similar to the way we limit speech that may lead directly to bodily harm.
Better Thesis 2 : The "fighting words" exception to free speech is not legitimate because it wrongly considers speech as an action.
A good argumentative thesis provides not only a position on an issue, but also suggests the structure of the paper. The thesis should allow the reader to imagine and anticipate the flow of the paper, in which a sequence of points logically prove the essay's main assertion. A list essay provides no such structure, so that different points and paragraphs appear arbitrary with no logical connection to one another.
Bad Thesis 2 : None of the arguments in favor of regulating pornography are persuasive.
Better Thesis 1 : Among the many reasons we need to limit hate speech the most compelling ones all refer to our history of discrimination and prejudice, and it is, ultimately, for the purpose of trying to repair our troubled racial society that we need hate speech legislation.
Better Thesis 2 : None of the arguments in favor of regulating pornography are persuasive because they all base their points on the unverifiable and questionable assumption that the producers of pornography necessarily harbor ill will specifically to women.
In an other course this would not be at all unacceptable, and, in fact, possibly even desirable. But in this kind of course, a thesis statement that makes a factual claim that can be verified only with scientific, sociological, psychological or other kind of experimental evidence is not appropriate. You need to construct a thesis that you are prepared to prove using the tools you have available, without having to consult the world's leading expert on the issue to provide you with a definitive judgment.
Bad Thesis 2 : Hate speech can cause emotional pain and suffering in victims just as intense as physical battery.
Better Thesis 1 : Whether or not the cultural concept of free speech bears any relation to the reality of 1st amendment legislation and jurisprudence, its continuing social function as a promoter of tolerance and intellectual exchange trumps the call for politicization (according to Fish's agenda) of the term.
Better Thesis 2 : The various arguments against the regulation of hate speech depend on the unspoken and unexamined assumption that emotional pain is either trivial.

How to write a PhD thesis: a step-by-step guide
A draft isn’t a perfect, finished product; it is your opportunity to start getting words down on paper, writes Kelly Louise Preece
Kelly Louise Preece

Created in partnership with

You may also like

Popular resources
.css-1txxx8u{overflow:hidden;max-height:81px;text-indent:0px;} How to develop a researcher mindset as a PhD student
Formative, summative or diagnostic assessment a guide, emotions and learning: what role do emotions play in how and why students learn, how to assess and enhance students’ ai literacy, how hard can it be testing ai detection tools.
Congratulations; you’ve finished your research! Time to write your PhD thesis. This resource will take you through an eight-step plan for drafting your chapters and your thesis as a whole.

Organise your material
Before you start, it’s important to get organised. Take a step back and look at the data you have, then reorganise your research. Which parts of it are central to your thesis and which bits need putting to one side? Label and organise everything using logical folders – make it easy for yourself! Academic and blogger Pat Thomson calls this “Clean up to get clearer” . Thomson suggests these questions to ask yourself before you start writing:
- What data do you have? You might find it useful to write out a list of types of data (your supervisor will find this list useful too.) This list is also an audit document that can go in your thesis. Do you have any for the “cutting room floor”? Take a deep breath and put it in a separate non-thesis file. You can easily retrieve it if it turns out you need it.
- What do you have already written? What chunks of material have you written so far that could form the basis of pieces of the thesis text? They will most likely need to be revised but they are useful starting points. Do you have any holding text? That is material you already know has to be rewritten but contains information that will be the basis of a new piece of text.
- What have you read and what do you still need to read? Are there new texts that you need to consult now after your analysis? What readings can you now put to one side, knowing that they aren’t useful for this thesis – although they might be useful at another time?
- What goes with what? Can you create chunks or themes of materials that are going to form the basis of some chunks of your text, perhaps even chapters?
Once you have assessed and sorted what you have collected and generated you will be in much better shape to approach the big task of composing the dissertation.
Decide on a key message
A key message is a summary of new information communicated in your thesis. You should have started to map this out already in the section on argument and contribution – an overarching argument with building blocks that you will flesh out in individual chapters.
You have already mapped your argument visually, now you need to begin writing it in prose. Following another of Pat Thomson’s exercises, write a “tiny text” thesis abstract. This doesn’t have to be elegant, or indeed the finished product, but it will help you articulate the argument you want your thesis to make. You create a tiny text using a five-paragraph structure:
- The first sentence addresses the broad context. This locates the study in a policy, practice or research field.
- The second sentence establishes a problem related to the broad context you have set out. It often starts with “But”, “Yet” or “However”.
- The third sentence says what specific research has been done. This often starts with “This research” or “I report…”
- The fourth sentence reports the results. Don’t try to be too tricky here, just start with something like: “This study shows,” or “Analysis of the data suggests that…”
- The fifth and final sentence addresses the “So What?” question and makes clear the claim to contribution.
Here’s an example that Thomson provides:
Secondary school arts are in trouble, as the fall in enrolments in arts subjects dramatically attests. However, there is patchy evidence about the benefits of studying arts subjects at school and this makes it hard to argue why the drop in arts enrolments matters. This thesis reports on research which attempts to provide some answers to this problem – a longitudinal study which followed two groups of senior secondary students, one group enrolled in arts subjects and the other not, for three years. The results of the study demonstrate the benefits of young people’s engagement in arts activities, both in and out of school, as well as the connections between the two. The study not only adds to what is known about the benefits of both formal and informal arts education but also provides robust evidence for policymakers and practitioners arguing for the benefits of the arts. You can find out more about tiny texts and thesis abstracts on Thomson’s blog.
- Writing tips for higher education professionals
- Resource collection on academic writing
- What is your academic writing temperament?
Write a plan
You might not be a planner when it comes to writing. You might prefer to sit, type and think through ideas as you go. That’s OK. Everybody works differently. But one of the benefits of planning your writing is that your plan can help you when you get stuck. It can help with writer’s block (more on this shortly!) but also maintain clarity of intention and purpose in your writing.
You can do this by creating a thesis skeleton or storyboard , planning the order of your chapters, thinking of potential titles (which may change at a later stage), noting down what each chapter/section will cover and considering how many words you will dedicate to each chapter (make sure the total doesn’t exceed the maximum word limit allowed).
Use your plan to help prompt your writing when you get stuck and to develop clarity in your writing.
Some starting points include:
- This chapter will argue that…
- This section illustrates that…
- This paragraph provides evidence that…
Of course, we wish it werethat easy. But you need to approach your first draft as exactly that: a draft. It isn’t a perfect, finished product; it is your opportunity to start getting words down on paper. Start with whichever chapter you feel you want to write first; you don’t necessarily have to write the introduction first. Depending on your research, you may find it easier to begin with your empirical/data chapters.
Vitae advocates for the “three draft approach” to help with this and to stop you from focusing on finding exactly the right word or transition as part of your first draft.

This resource originally appeared on Researcher Development .
Kelly Louse Preece is head of educator development at the University of Exeter.
If you would like advice and insight from academics and university staff delivered direct to your inbox each week, sign up for the Campus newsletter .
How to develop a researcher mindset as a PhD student
A diy guide to starting your own journal, contextual learning: linking learning to the real world, what does a university faculty senate do, hybrid learning through podcasts: a practical approach, how exactly does research get funded.
Register for free
and unlock a host of features on the THE site
Things you buy through our links may earn Vox Media a commission.
Roaring Kitty’s Second Act Has Begun

Keith Gill’s second act has gone well for him. Gill, the meme-stock trader nonpareil better known as Roaring Kitty and DeepFuckingValue, made his triumphant return to shitposting last month. GameStop, his stock of choice, has skyrocketed, inflating his net worth to around $300 million . Wall Street has, predictably, found itself at a loss over how to handle all this. E*Trade , owned by a Too Big To Fail bank, is considering kicking him off their platform, and Gill is already under investigation for the high crime of posting memes . But what’s more surprising is that Gill and his horde of self-identified apes, the fanatical investors who act more like rowdy Philadelphia sports fans than buttoned-up investors, has not just divided the financial world — but there has been a split on Reddit, the online forum that birthed the meme-stock movement in the first place.
The original meme-stock rally of early 2021 was fueled, in large part, by Gill’s argument that Wall Street had gotten GameStop’s fundamental business wrong, and was too pessimistic about it going bankrupt. Over time, this would become unhinged from a stuffy thesis about valuation and turn into a rallying cry that buying shares of a middling brick-and-mortar video-game seller was somehow akin to the French Revolution . And it kind of worked, with a major hedge fund that was betting against GameStop, Melvin Capital, shutting down in the process. Ground zero for the thesis turned movement was one of Reddit’s most infamous forums, WallStreetBets, a profane and often hilarious gathering of traders who pile into a stock (or, frequently, all-or-nothing bets on options) not necessarily because it is the best investment thesis on the forum, but because it is the funniest and the most audacious. Often, as in the case of GameStop, there is also the adrenaline rush that comes with betting large sums of money on extremely risky plays.
This new phase of the meme-stock frenzy, though, has not taken place on Reddit. On June 2, Gill posted a screenshot of his position in GameStop. Gill owned 5 million shares, and had options that could grant him another 120,000 more — giving him roughly 5 percent of the company, a giant stake for an individual investor. The disclosure sent the stock up nearly 100 percent. (It also spawned theories about how he could have so much money, with short seller Andrew Left speculating that someone else was funding him). Look closely, though, and the post is on a different Reddit forum called Superstonks, rather than WallStreetBets. (“Stonk” is a joke misspelling of “stock” that revels in the dumbness of it all.)
Superstonks is one of several forums that came into being after the apes clashed with WallStreetBets moderators they deemed insufficiently pro-GME. In response, WallStreetBets subsequently throttled discussion of the video game retailer around 2021. “GME people started being jerks and getting conspiratorial and weird and accusing us of favoritism or the opposite,” one WSB moderator told me. At first, WSB tried to limit GameStop to a single thread, but, the moderator told me, that didn’t contain the apes’ accusations that WSB was biased against them. While Superstonks isn’t as widely known as WallStreetBets, it’s a subreddit that is even more dedicated to meme-stock rallies, conspiracy theories, and anything that can make GameStop’s shares go higher.
During the first meme-stock rally, the apes had arguably exposed a flaw in how Wall Street worked. These were a novel type of trader — certainly not a doom-and-gloom bear, and more out of control than a bull — that bought and held a stock for seemingly irrational reasons. But the WallStreetBets of 2021 wasn’t just pure testosterone and YOLO risk-taking. In October that year, the Securities and Exchange Commission noted in its report on GameStop that there was an actual investment idea — one that wouldn’t be so out of place at a garden variety hedge fund. “Some of this discussion argued that GME was undervalued based on fundamental analysis and therefore constituted an attractive investment, while other discussion focused on its ability to transition to an e-commerce company,” according to the report.
That’s all fine, but it was still the apes who sent GameStop up 1,000 percent , at least until it came crashing down. Whether they were daredevils or nihilists, the apes — who were certainly encouraged by Gill — made GameStop into something more personal, and they were out for blood. On WallStreetBets, hedge funds shorting GameStop became enemies. At the time, hedge funds were so convinced that GameStop was headed for bankruptcy that it was among the most bet-against stocks in the U.S. Since so many big-money investors would profit off GameStop’s failure — shorting the stock, in Wall Street parlance — that created a situation that kept the company’s price as low as it was, in the apes’ eyes. The apes then developed a plan to crush those short sellers, like Melvin Capital. The “mother of all short squeezes” — or MOASS, for the gleefully profane — was a plan to bleed money out of any trader betting that GameStop’s price would go down by forcing them into bankruptcy by making their anti-GameStop bets too expensive to hold onto. Or, as the SEC put it: “Unusually high levels of short interest in GME presented the potential for a coordinated ‘short squeeze.”
It’s not exactly clear why Gill is out to make GameStop’s share price go up this time, except for the obvious reason. Some short-sellers had returned to betting against the stock, and they’ve already lost more than $1 billion collectively . But it is far from the most hated stock out there. Since Gill is mostly communicating through memes these days (and ignoring requests for comment), his followers have taken to speaking for him, piecing together a master plan that makes good on the MOASS. (In theory, this plan would wipe out short-sellers in one final master stroke. But in the fever-pitch world of Superstonk, this has gotten a less-than-enthusiastic response .)
Over on WallStreetBets, it’s almost as if GameStop doesn’t exist. “We don’t have a problem with ballsy gambling at all. That’s kinda the WSB schtick,” one moderator told me. “I hope they sell the rip and make their money, even if they’re not allowed to post about it.” The weird and vaguely frightening thing about this meme rally is that it’s not really clear how this all ends. The apes may have one move — make a number go up as loudly as possible — but they’ve shown that they’re more than whatever platform or forum they have been posting on. “I know [Gill] has a bigger position than ever. I know most of you have bigger positions than ever,” one Superstonk ape wrote . “I know that I’ll never give up or give in and that you won’t either.”
- the money game
Most Viewed Stories
- It’s Good That Caitlin Clark Is Getting Pushed Around in the WNBA
- Trump Is Colluding With Putin in Plain Sight
- Why Has Melania Been Hiding in Trump Tower for Two Weeks?
- Who’s the Trump VP Pick? Latest Odds for Every Shortlist Candidate.
- Trump vs. Biden Polls: How the Conviction Affected the Race
- The Problem With Darling 58
Editor’s Picks

Most Popular
- It’s Good That Caitlin Clark Is Getting Pushed Around in the WNBA By Will Leitch
- Trump Is Colluding With Putin in Plain Sight By Jonathan Chait
- Why Has Melania Been Hiding in Trump Tower for Two Weeks? By Margaret Hartmann
- Who’s the Trump VP Pick? Latest Odds for Every Shortlist Candidate. By Margaret Hartmann
- Trump vs. Biden Polls: How the Conviction Affected the Race By Ed Kilgore
- The Problem With Darling 58 By Kate Morgan

What is your email?
This email will be used to sign into all New York sites. By submitting your email, you agree to our Terms and Privacy Policy and to receive email correspondence from us.
Sign In To Continue Reading
Create your free account.
Password must be at least 8 characters and contain:
- Lower case letters (a-z)
- Upper case letters (A-Z)
- Numbers (0-9)
- Special Characters (!@#$%^&*)
As part of your account, you’ll receive occasional updates and offers from New York , which you can opt out of anytime.

1 Minute Speech on Global Warming
Ai generator.
Good morning everyone,
Today, I want to talk about global warming. Global warming refers to the long-term increase in Earth’s average temperature due to human activities, particularly the burning of fossil fuels and deforestation. This rise in temperature is causing significant changes to our climate.
The impacts of global warming are widespread and alarming. We’re witnessing more frequent and severe weather events like hurricanes, droughts, and wildfires. Polar ice caps are melting, leading to rising sea levels that threaten coastal communities. These changes disrupt ecosystems, endanger wildlife, and affect agriculture, water supplies, and human health.
It’s crucial that we take action now to combat global warming. This means reducing our carbon footprint by using renewable energy, conserving energy, and supporting policies aimed at protecting the environment. Each of us can make a difference through small changes in our daily lives, like using public transport, recycling, and reducing waste.
Let’s commit to being part of the solution and work together to ensure a healthier planet for future generations.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Crafting a Thesis Statement. A thesis statement is a short, declarative sentence that states the purpose, intent, or main idea of a speech. A strong, clear thesis statement is very valuable within an introduction because it lays out the basic goal of the entire speech. We strongly believe that it is worthwhile to invest some time in framing and ...
A speech thesis statement is a succinct and focused declaration that encapsulates the central argument, purpose, or message of a speech. It outlines the primary idea the speaker intends to convey to the audience, serving as a guide for the content and structure of the speech.
What is a Thesis Statement in a Speech. A thesis statement is the speaker's whole speech condensed into one statement. It should include the overall point of the speech as well as any subpoints ...
Revising the thesis statement to enhance clarity and coherence. Revising the thesis statement is a crucial step in developing a clear and coherent speech. The thesis statement serves as the main idea or argument that guides your entire speech, so it's important to make sure it effectively communicates your message to the audience.
A thesis is the central idea in an essay or a speech. In speechwriting, the thesis or central idea explains the message of the content. It's the speech's "takeaway." A good thesis statement will also reveal and clarify the ideas or assertions you'll be addressing in your speech (your main points). Consider this example:
Step 2: Write your initial answer. After some initial research, you can formulate a tentative answer to this question. At this stage it can be simple, and it should guide the research process and writing process. The internet has had more of a positive than a negative effect on education.
A thesis statement should appear, almost verbatim, toward the end of the introduction to a speech. A thesis statement helps the audience get ready to listen to the arrangement of points that follow. Many speakers say that if they can create a strong thesis sentence, the rest of the speech tends to develop with relative ease.
A thesis statement may encapsulate the main points of a speech in just a sentence or two, and be designed to give audiences a quick preview of what the entire speech will be about. The thesis statement for a speech, like the thesis of a research-based essay, should be easily identifiable and ought to very succinctly sum up the main points you ...
A thesis statement: tells the reader how you will interpret the significance of the subject matter under discussion. is a road map for the paper; in other words, it tells the reader what to expect from the rest of the paper. directly answers the question asked of you. A thesis is an interpretation of a question or subject, not the subject itself.
Thesis Statements. A thesis is the main claim you are making in an argument, similar to the hypothesis in a scientific experiment. It is what you are trying to prove or persuade your audience to believe or do. It's helpful to develop a working thesis to guide your composition process. "Working" is the operative word here; your ideas are ...
The thesis must be stated and tells the audience what to expect in this speech. A thesis statement may encapsulate the main idea of a speech in just a sentence or two and be designed to give audiences a quick preview of what the entire speech will be about. The thesis statement should be a single, declarative statement followed by a separate ...
A thesis statement encapsulates the main points of a speech in just a sentence or two, and it is designed to give audiences a quick preview of what the entire speech will be about. The thesis statement for a speech, like the thesis of a research- based essay, should be easily identifiable and ought to very succinctly sum up the main points you ...
A thesis statement is a very common component of an essay, particularly in the humanities. It usually comprises 1 or 2 sentences in the introduction of your essay, and should clearly and concisely summarize the central points of your academic essay. A thesis is a long-form piece of academic writing, often taking more than a full semester to ...
The thesis statement aims to inform your readers what your essay or speech will cover. It provides contexts and limitations on your topic. Your thesis statement can make or break your essay. Even though it's only one to two sentences short, it's still the most challenging part of your paper to write.
Writing the Thesis Statement. A thesis statement is a single, declarative statement that encapsulates the essence of your speech. Just like in essay writing, you want your thesis statement, or central idea, to reveal what your speech is about. Thesis statements can never be written as questions, nor can they include a research citation.
A thesis statement provides the foundation for your entire research paper or essay. This statement is the central assertion that you want to express in your essay. A successful thesis statement is one that is made up of one or two sentences clearly laying out your central idea and expressing an informed, reasoned answer to your research question.
credibility statement. You will then introduce your thesis statement, and finish with a preview of what is to come next. Attention Getters An attention getter is the device a speaker uses at the beginning of a speech to draw the audience in and encourage interest in the speech topic.
A persuasive speech thesis statement is a concise declaration that clearly expresses the main argument or stance of your speech. Unlike an informative speech thesis statement which simply informs, a persuasive speech thesis aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take a certain action.
Good thesis statements define your general idea and inform your audience about your main points. Hence, writing a thesis statement is a key to getting attention of the listeners and engaging them in thinking about your topic. Knowing how to write a thesis statement for a speech is a vital skill, as far as it predetermines the outcome of your ...
A thesis statement may encapsulate the main points of a speech in just a sentence or two, and be designed to give audiences a quick preview of what the entire speech will be about. The thesis statement for a speech, like the thesis of a research-based essay, should be easily identifiable and ought to very succinctly sum up the main points you ...
An informative speech thesis statement conveys the main idea of your speech, providing an overview of what listeners should expect. It aims to educate, enlighten, and provide essential details on a specific topic without persuading or arguing a perspective. Today, we'll explore the mysterious world of the deep sea and the creatures that ...
Bad Thesis 1. : Americans today are not prepared to give up on the concept of free speech. Bad Thesis 2: Hate speech can cause emotional pain and suffering in victims just as intense as physical battery. Better Thesis 1: Whether or not the cultural concept of free speech bears any relation to the reality of 1st amendment legislation and ...
You create a tiny text using a five-paragraph structure: The first sentence addresses the broad context. This locates the study in a policy, practice or research field. The second sentence establishes a problem related to the broad context you have set out. It often starts with "But", "Yet" or "However".
Gill, the meme-stock trader nonpareil better known as Roaring Kitty and DeepFuckingValue, made his triumphant return to shitposting last month. GameStop, his stock of choice, has skyrocketed ...
1 Minute Speech on Global Warming. Good morning everyone, Today, I want to talk about global warming. Global warming refers to the long-term increase in Earth's average temperature due to human activities, particularly the burning of fossil fuels and deforestation. This rise in temperature is causing significant changes to our climate.
Each year millions of students enter the growing cohort of adults with some college but no degree. As enrollment struggles mount, institutions are starting to pay attention. About 2.3 million students stopped out of college between January 2021 and July 2022, a 2.9 percent increase from the year prior, according to a report out today from the National Student Clearinghouse (NSC) Research Center.