ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Innovative application of new media in visual communication design and resistance to innovation.

- 1 College of Fine Arts, Shanxi University, Taiyuan, China
- 2 School of Languages, Civilization and Philosophy, Universiti Utara Malaysia, Changlun, Kedah, Malaysia
- 3 Prince Sattam Bin Abdulaziz University, Al-Kharj, Saudi Arabia
- 4 Catholic University of Cuenca, Cuenca, Ecuador
- 5 Indonesia Language Education Study Program, Universitas Sebelas Maret, Surakarta, Indonesia
It has become essential to create and apply new media in visual communication design due to social media existence. This study aims to investigate the role of innovative applications of new media in visual communication design in educational institutions. Traditional media design in visual communication lacks to disseminate information more effectively, which requires innovative change. Therefore, this study attempts to highlight the role of innovative application of new media in visual communication by considering visual expression design with information technology (IT), flexible layout, diversified modes of transmission, and interactivity of integration. For this purpose, this study adopted a quantitative research approach in which a cross-sectional research design is followed. A questionnaire survey is carried out to collect data from educational institutions in China. Partial Least Square-Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM) is used for data analysis. Results of the study indicated that innovative applications of new media have central importance in visual communication. However, resistance to innovative change has a negative role in the relationship between innovative applications of new media and visual communication design. Results of the study highlighted that visual expression design with IT, flexible layout, diversified modes of transmission, and interactivity of integration have a positive effect on visual communication design. Therefore, among the educational intuitions of China, implementing innovative applications related to the new media can lead to visual communication design. The results of this study provided several insights for the practitioners to promote communication methods among educational institutions.

Introduction
Visual communication is the conveyance of ideas and information by using a broad range of forms that can be visually observed. These include different signs, diagrams, graphic designs, illustrations, animations, colors, and electronic resources ( Kujur and Singh, 2020 ; Ji and Lin, 2022 ). Visual communication is a powerful communication tool that is central to communication ( Ji and Lin, 2022 ; Xiangwei, 2022 ). It is based on animated Graphics Interchange Formats (GIFs), screenshots, different types of videos, pie charts, and infographics, along with slide deck presentations. All these types of visual communication have a vital role in the communication process through different methods. Along with other institutions, visual communication is standard in educational institutions as it provides different ways for teachers to teach effectively and lead to effective learning. Visual communication is an effective tool in educational institutions ( Matusitz, 2005 ), but it is lacking in Chinese institutions.
Visual communication requires innovative applications ( Goransson and Fagerholm, 2018 ; Liu, 2018 ). Mainly, new media applications in visual communication design are most important to introduce in Chinese educational institutions. Traditional communication design lacks different elements, which may lead to a lack of communication. The problems in traditional communication design can be well managed with the help of innovative applications of new media. New and traditional media complement each other and develop together ( Yue, 2020 ). However, new media has the potential to create a better communication environment which can lead to the accuracy of communication. The innovative applications in new media can cover a broader range than traditional media. Advance technology in new media has several forms which can perform better than traditional media in different ways ( Yue, 2020 ).
Earlier studies investigated visual communication through different aspects ( Russmann, 2019 ; Duan, 2022 ). However, the element of innovation is rarely addressed. Different studies on visual communication design, such as Guan-Chen and Ko (2022) , discussed the wireless data transmission technology about the Blockchain big data information presentation. Wang (2021) highlights visual communication design with the help of artificial intelligence and innovation development. Arsyadi (2019) discussed visual communication design in classrooms to facilitate instructors teaching at educational institutions. Huang and Zhou (2022) conducted a research study on visual communication design by considering the training program of universities. All these studies highlighted the essential findings and provided several implications.
However, the role of innovative applications of new media is not investigated. To get maximum benefits from visual communication, the role of innovative applications is required. Previously, research has investigated the impact of narrative theory on perspective development in graphic designing courses ( Yang and Hsu, 2017 ). The study did not find the impact of the application of new media on visual communication design. Therefore, based on narrative theory, the current research examines the impact of the application of new media on visual communication design. This study attempts to highlight the role of the innovative application of new media in visual communication. Thus, to address the role of new media on visual communication, this study addressed four significant elements; visual expression design with information technology (IT), flexible layout, diversified modes of transmission, and interactivity of integration.
The innovative application of new media faces resistance to innovative ideas. The implementation of innovative ideas faces resistance to innovative change. The employees working in educational institutions resist innovative change. Previous studies also mentioned that resistance to innovation causes a decrease in the implementation of innovative ideas among institutions ( Koch, 2021 ; Friedman and Ormiston, 2022 ; Naveed, 2022 ). Similarly, in visual communication design, resistance to innovative change is one of the significant problems. Hence, this study is one of the attempts to address the effect of resistance to innovative change in visual communication design. Finally, this study aims to investigate the role of innovative applications of new media in visual communication design in educational institutions. This study has vital theoretical contributions, which further lead to several practical implications for fostering visual communication design through the innovative application of new media.
Literature review
Visual expression design with information technology.
IT (information technology) is the use of networking among storage, computers, and other physical infrastructures, devices, and processes that create, secure, store, exchange, and process all forms of electronic data. IT intended for financial gain encompasses both telecommunication and computer technology. As a past study conducted by Cebollada (2021) , the visual form of data has a significant role in all forms of electronic data. It is because visual expressions are based on values, ideas, and feelings that are visually presented. In addition, Erickson (2020) described that visual expression design is something perceptible that is perceived on a screen.
According to the present study, visual expression design with IT refers to acceptable, tolerable, standard, and decent designs in every aspect of IT, mainly to depict the actual meaning of the cause behind the creation of the design. Raposo (2018) says that visual communication is an art that combines words, thoughts, images, and ideas to express a message or to convey information aiming to produce a particular effect. Visual expression design with IT is more effective, persuasive, convincing, and result-oriented because IT adds significant meaning to the growth of the business and commerce sector by generating the maximum possible outcome.
Flexible layout
To create consistency, avoidance of unnecessary items is necessary. However, a container must be able to hold all the items that are specified and unspecified. Sumual (2021) represented that a potent layout is always invisible to users and provides more comfort to get things done more quickly. A user-friendly and flexible layout is one of the primary purposes of any developer. A study on creating a dynamic layout for a virtual environment for walking conducted by Vasylevska (2013) says that a dynamically practical layout is called a flexible layout. It provides adequate methods to distribute, align, and space among items in a container or stack even when the size of the items is dynamic or unknown. Hence, a flexible layout is an art to fit the requirements of a system. Phoon (2018) presented that a flexible layout helps expand items to cover free space or shrinks the items to avoid overflow.
Moreover, Pourvaziri et al. (2021) described that regular layouts are limited which are vertically or horizontally based. While the flexible layout is direction-agnostic, it allows the automatic position of items by wrapping. In addition, Haddou and Benyoucef (2019) described that a flexible layout is always ready to accept products of uncertain sizes. Therefore, a flexible layout is crucial for accomplishing dynamic manufacturing cells, particularly in an environment with dynamic production.
Diversified modes of transmission
In telecommunication, transmission refers to the spreading or broadcasting of information. A transmission system sends a signal from place A to place B. Figure 1 shows a telecommunication network representing the current transmission mode. Figure 2 show the complete networking of telecommunication.
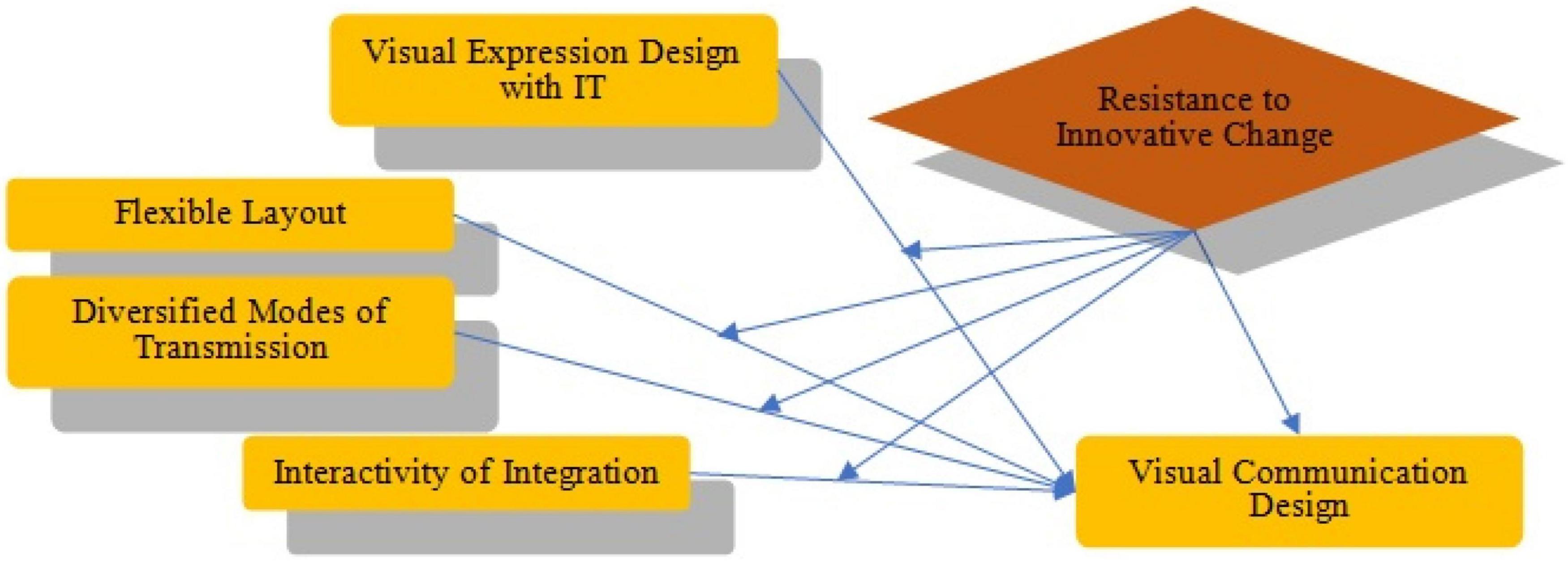
Figure 1. Research model.
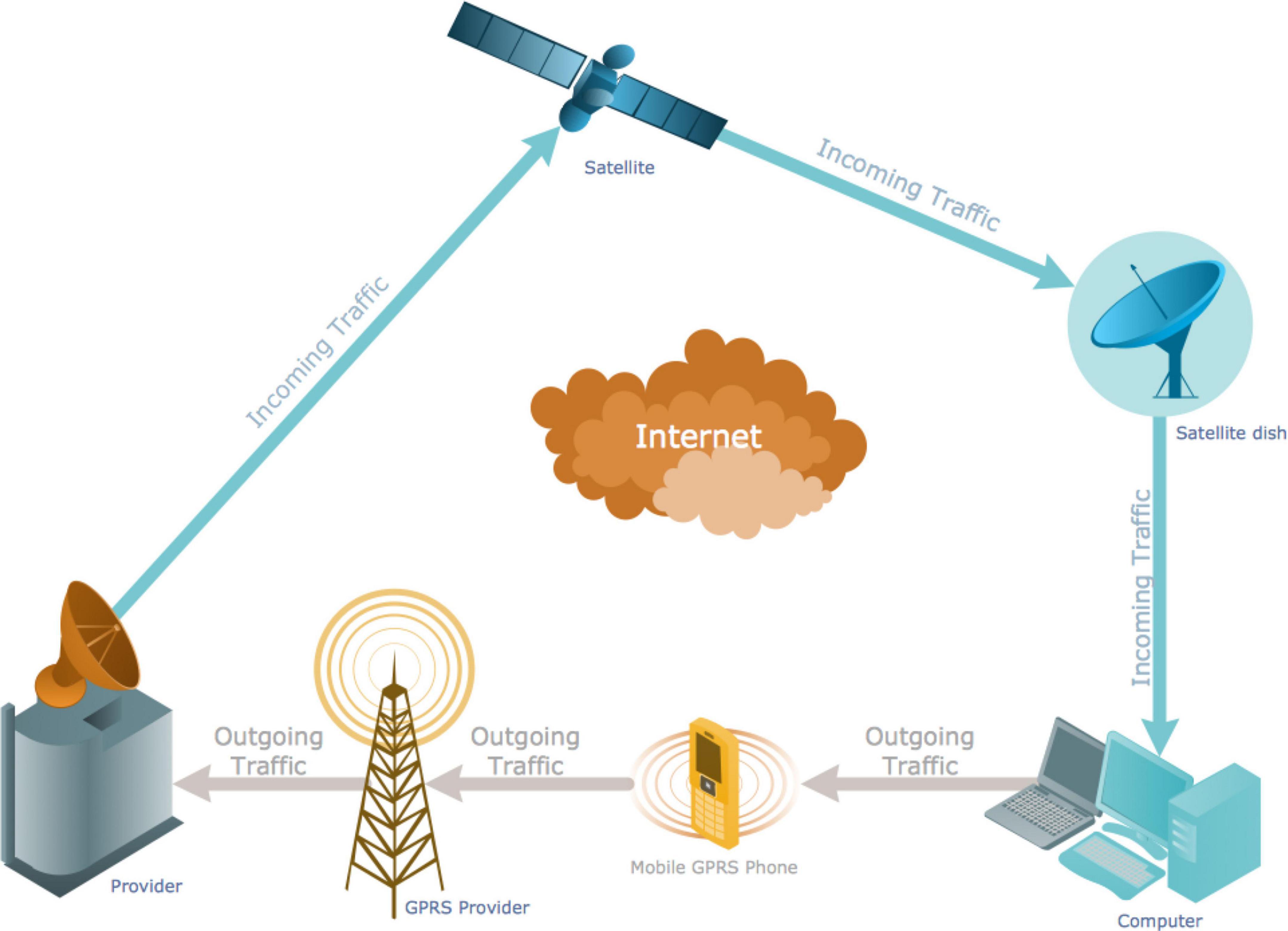
Figure 2. Telecommunication network. Source: https://www.conceptdraw.com/How-To-Guide/picture/Computer-and-Networks-Telecommunication-Network-Diagrams-GPRS-network-scheme.png . VED-IT, Visual Expression Design with IT; FL, Flexible Layout; DMT, Diversified Modes of Transmission; II, Interactivity of Integration; VCD, Visual Communication Design; RI, Resistance to Innovative Change.
The transmission system sends information consisting of video or audio or some other type of data, in digital or analog form using optical or electromagnetic signals between various sites. Bezruk et al. (2012) researched multi-criteria optimization in telecommunication network planning, designing, and controlling. They described the following four types of telecommunication networks: (a) public-switched telephone networks, (b) radio networks, (c) packet-switched networks, and (d) computer networks.
The traditional modes of transmission are relatively simple. However, in computers, transmission modes are comparatively complex and more efficient ( Cheng, 2019 ). Furthermore, according to Liu (2017) , in computers, simple mode, half-duplex mode, and full-duplex mode are the three primary modes of transmission. Gao (2015) also determined that communication in simple mode is unidirectional, which means that between two devices, one will transmit while the other will receive. Lari and Gandomani (2022) explored that in a half-duplex mode of transmission, both the devices can transmit and receive data but not simultaneously. While in full-duplex, both the devices can simultaneously transmit and receive data.
Interactivity of integration
Innovation in visual communication design is necessary to use modern technologies because the innovative designs of products have become hot items produced by professional designers. Moreover, Chen and Zheng (2021) concluded that visual communication design’s professionally designed items are integrated with modern technologies. A previous study by Yue (2020) explored that interactivity of integration in visual communication design helps bring unique information that can be linked to design requiring more innovative creations. The interactivity of integration also refers to the process of designing in which a designer can display his/her work in a customized way; hence, viewers’ attention is increased to see more exciting content generated by the designer. In addition, Kim and Lee (2019) proved that interactivity of integration attracts viewers to participate in the designing process. Sometimes using advanced technologies that help achieve a higher sense of integration and incorporation aims to achieve higher quality and ensure that more decadent designs promote audiences.
Resistance to innovative change
Like any change, innovation is also a change that requires intention, effort, and motive; it needs leadership and vision. Furthermore, it generates resistance. In several cases, an increase is the primary goal, meaning innovation is mandatory in these cases. Kostis (2018) described that innovative changes have consequences that influence the performance in either positive or negative ways. According to Zhou et al. (2019) , resistance to innovative change refers to the limitation that decreases or stops increasing the performance volume. In other words, resistance to innovation change is a factor that spectacle the progressive boundaries of an institution. King (2007) determined that resistance to innovative change decreases the demanding work contexts that ultimately result in organizational outcomes. In addition, resistance to innovation change is defined as the act toward the acceptance and usage of any modernization that results in continuing the current situation and resisting any abnormality from prevailing beliefs. However, resistance to innovative change is categorized based on various factors such as rational, logical, emotional, psychological, and sociological resistance. According to Talwar (2020) , lack of trust, poor communication, emotional response, fear of failure, surprises, constant change, and listening to employees are the common reasons for resistance to innovative change.
Visual communication design
Scholars have long been concerned about the design principles such as unity, proportion, complexity, and symmetry ( Wang and Hsu, 2020 ; Yanarates and Zhou, 2021 ; Haapala, 2022 ). According to Liang (2021) , visual communication design is a process that combines technology and visual arts to communicate thoughts and creative ideas. Typically, every visual communication design begins with a message transformed into visual communication that goes beyond complete pictures and words. Zhang and Wu (2021) presented that broadcast, film, advertising, web, publishing, television, and industry are the visual channels and formats for creative visual material. Modern means of communication such as social media platforms and websites keep bringing current visual communications design to attract their audience.
Furthermore, typography and art also significantly positively affect visual communication design. Hence the fundamental purpose of visual communication design is to convey information. However, there is a difference between graphic design and visual communication design. According to Emans and Murdoch-Kitt (2018) , every image that people see is graphic design. Only the images that convey a message are visual communication design, while the images that do not convey a message are graphic design.
Development of hypotheses
Visual expression design with information technology and visual communication design.
A study by Jia (2017) explored that visual expression design plays a significant role in educational institutions. Educational institutions, especially in China, without visual expression design, fail to meet their targets, particularly concerning learning and teaching methods. In addition, Saris (2020) determined that learning becomes more compelling and persuasive for students through clear, attractive, engaging, and appropriate visual expression design. Several previous studies are also evident that increasing the value of visual expression design, especially in educational institutions, increases the value of the institutions ( Wu, 2019 ; Huang, 2021 ). Furthermore, visual expression design with IT adds significant meaning to the visual communication design. Prior literature also revealed that visual expression design with IT adds significant meaning to educational materials such as videos, infographics, animated GIFs, and slide presentations that make the massage or information clear, concise, and succinct; hence, learners easily understand. Previous literature shows that an increase in the value of visual expression design with IT also increases the value of visual communication design. Hence, it is enclosed.
H1: Visual expression design with IT positively correlates with visual communication design.
Flexible layout and visual communication design
A flexible layout helps to design a visual communication design. According to the present study, the flexible layout has a significant favorable influence on the teaching methods, especially for teachers in China. It is observed that innovation in teaching and education increases the performance of the teachers and the educational institutions. Furthermore, Huang L. (2020) determined that during the COVID-19 outbreak, the flexible learning process was entirely ensuring for quality of education and increased the value of visual communication design by adding significant positive meaning to the online learning process. Ozkan (2021) explored that the faculty of an educational institution feel more comfortable with movement in the flexibility and engagement in technology-enhanced classrooms. In addition, Zahlbruckner (2021) determined that flexible layout significantly affects visual communication design. Results of the previous study show that increasing the value of flexible layouts also increases the value of visual communication design. Hence, it is enclosed.
H2: Flexible layout has a positive relationship with visual communication design.
Diversified modes of transmission and visual communication design
For higher education institutions, diversified modes of transmission play a crucial role ( Flückiger, 2021 ). In countries like China, educational institutions are responsible for students’ behavior, personality building, career orientation, and socio-economic values. Therefore, diversified modes of transmission in educational institutions in the country are more significant. Previous literature shows that educational institutions in China having good value for diversified modes of transmission remain successful in building visual communication designs that are advantageous both for the teaching methods and learning process ( Talidong and Toquero, 2021 ). Furthermore, Wu (2021) determined that diversified modes of transmission have positive effects on the health of teachers and students. During the COVID-19 outbreak, the value for visual communication design increased due to the variety of diversified modes of transmission. Hence, it is clear from the results of the previous study that increasing the value of diversified modes of transmission also increases the value of visual communication design. Therefore, it is enclosed that:
H3: Diversified modes of transmission have a positive relationship with visual communication design.
The interactivity of integration and visual communication design
Yadav and Prakash (2022) determined that interactivity of integration plays a significant role, especially in the sustainable development of educational institutions. Furthermore, interactivity of integration helps assess the management of educational institutions in countries like China and India. Turnbull (2021) also agreed that interactivity of integration helps to deal with the challenges such as communication gaps. The present study concluded from the previous literature that several kinds of barriers, such as physical, emotional, cultural, perceptual, language, and interpersonal barriers, are the real reasons that ultimately lead to communication gaps. However, decreased value of interactivity of integration is the real cause behind these barriers ( Vakulenko, 2021 ). Studies also determined that the value of the visual communication design increases with the increase in the interactivity of integration. Furthermore, the educational institutions in China have better versions of visual communication design that increased value for interactivity of integration. Therefore, it is enclosed that:
H4: Interactivity of integration has a positive relationship with visual communication design.
Resistance to innovative change and visual communication design
Kujur and Singh (2020) investigated that effective visual communication design, especially in an educational institution, particularly in a country like China, helps students and learners to understand their lessons and other information. Faculty often need visual communication designs that can convey their message correctly to their pupils. Moreover, the faculty also demands innovation in visual communication design. However, Frost (2019) determined that resistance to innovative change in the learning process and teaching methods eventually results in a communication gap. In addition, Demuyakor (2020) also explored that during the COVID-19 outbreak, the learning process in higher institutions of education in China was diminished. It was due to resistance to innovative change because of COVID-19. Outcomes of the previous literature result in a decrease in the value of resistance to innovative change and a decrease in the value of visual communication design. Hence, it is enclosed:
H5: Resistance to innovative change has a negative relationship with visual communication design.
Moderation relationship
Educational institutions in China having increased value of resistance to innovative change have adverse effects on the relationship between visual expression design with IT and visual communication design. Huang W. (2020) determined that resistance to innovative change results in reduced performance in educational institutions. Moreover, the moderation role of resistance to innovative change decreases the value of the visual expression design with IT and visual communication design. Xie (2022) concluded that resistance to innovative change decreases the value of talent in learners; hence, the value of intelligent computing decreases. Hence, it is enclosed:
H6: Resistance to innovative change moderates the relationship between visual expression design with IT and visual communication design
Resistance to innovative change in the educational institutions in China results in adverse effects on the relationship between flexible layout and visual communication design. Liu (2020) investigated that a flexible classroom layout pattern adds significant meaning to students’ learning process in educational institutions. Moreover, the moderating role of resistance to innovative change decreases the value of flexible layout, eventually decreasing the value of visual communication design. Prior literature on the educational system also shows that resistance to innovative change decreases the value of educational institutions ( Yan, 2012 ). Hence, it is enclosed:
H7: Resistance to innovative change moderates the relationship between flexible layout and visual communication design
Educational institutions in China having increased value of resistance to innovative change have adverse effects on the relationship between diversified modes of transmission and visual communication design. According to Kaur (2020) , resistance to innovative change always creates boundaries between the target and the current performance of an educational institution. Furthermore, the moderating role of resistance to innovative change decreases the value of diversified modes of transmission, ultimately resulting in a decrease in the value of visual communication design. Results of the previous study show that resistance to innovative change has sufficient influence on diversified modes of transmission and visual communication design ( Haotian, 2020 ). Hence, it is enclosed:
H8: Resistance to innovative change moderates the relationship between diversified modes of transmission and visual communication design
In China, educational institutions that carry resistance to innovative change show adverse effects on the relationship between interactivity of integration and visual communication design. Shahbaz (2019) determined that needless interference with selective perception, loss of freedom, security, threats to the power of influence, skill obsolescence, need fulfillment, habit, and economic implications are the reasons behind resistance to innovative change. In addition, Blin and Munro (2008) explored that the moderation role of the resistance to innovative change decreases the value of interactivity of integration, ultimately resulting in a decrease in the value of visual communication design. Hence, it is enclosed:
H9: Resistance to innovative change moderates the relationship between interactivity of integration and visual communication design
Research methodology
The current study examined the relationship among visual expression design with IT, flexible layout, diversified modes of transmission, interactivity of integration, visual communication design, and resistance to innovative change. The nature of this relationship is supported by a cross-sectional research design. Therefore, the current study followed a cross-sectional research design by following the quantitative research approach. While using a cross-sectional research design, this study carried out a questionnaire survey to collect data from respondents.
The population of the study is based on the educational institutions in China. The teachers and employees working in these institutions were considered the study’s respondents. Few previous studies investigated visual expression design with IT, flexible layout, diversified modes of transmission, interactivity of integration, visual communication design, and resistance to innovative change. However, these elements are rarely discussed among Chinese educational institutions. Therefore, this study conducted a questionnaire survey to collect data from Chinese educational institutions. The questionnaires were distributed by using simple random sampling among the educational institutions. This study distributed 500 questionnaires and 225 questionnaires were returned; 10 questionnaires were missing by a significant part, therefore, excluded from the survey; and 215 valid responses were used in the data analysis.
Visual communication design is measured by considering the effectiveness in educational institutions. Five items are used to measure visual communication design. Visual expression design with IT is measured by using the role of IT in visual expression design. Flexible layout is measured by using the different layouts and their effectiveness in visual communication among the educational institutions. Visual expression design with IT and flexible layout are measured using five items each.
Furthermore, four items are used to measure diversified modes of transmission, and these items are designed using different transmission modes. The interactivity of integration is also measured using four scale items based on the interactivity, which are regarding time and technology. Finally, four items are used to measure resistance to innovative change. These items are developed by considering the resistance to innovative change by the employees. After the development of the questionnaire, face validity and content validity are confirmed by reviewing the questionnaire from experts in a related field. After that, a pilot study is carried out by using 100 questionnaires. Additionally, exploratory factor analysis (EFA) is also employed.
Data analysis
The current study analyzed data using Partial Least Square-Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM). PLS-SEM is the most well-known data analysis technique recommended by several previous studies ( Hair, 2020 ; Hair et al., 2021 ). PLS-SEM is based on two significant steps: (1) measurement model assessment and (2) structural model assessment. However, before data analysis, the current study performed initial data screening in which missing values and outliers are examined. After data screening, the data statistics are given in Table 1 .
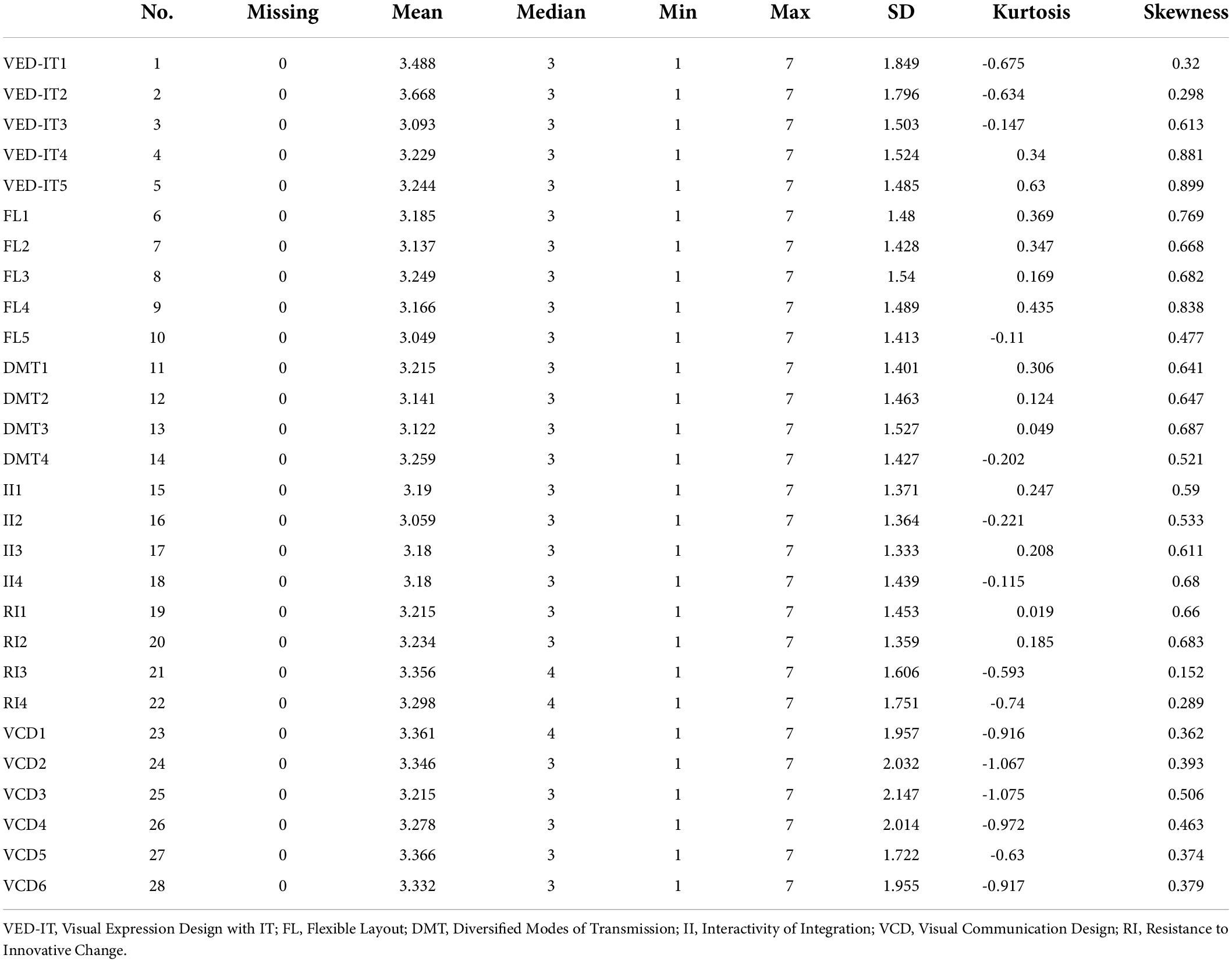
Table 1. Data statistics.
Measurement model assessment
The PLS measurement model is highlighted in Figure 3 . In this step of data analysis, reliability and validity are considered. While considering the reliability, this study preferred to examine factor loadings and composite reliability (CR). According to the literature, factor loadings must not be less than 0.7 ( Hameed, 2020 , 2021 ; Hair et al., 2021 ). Results shown in Table 2 highlighted that all the scale items have factor loading higher than 0.7.
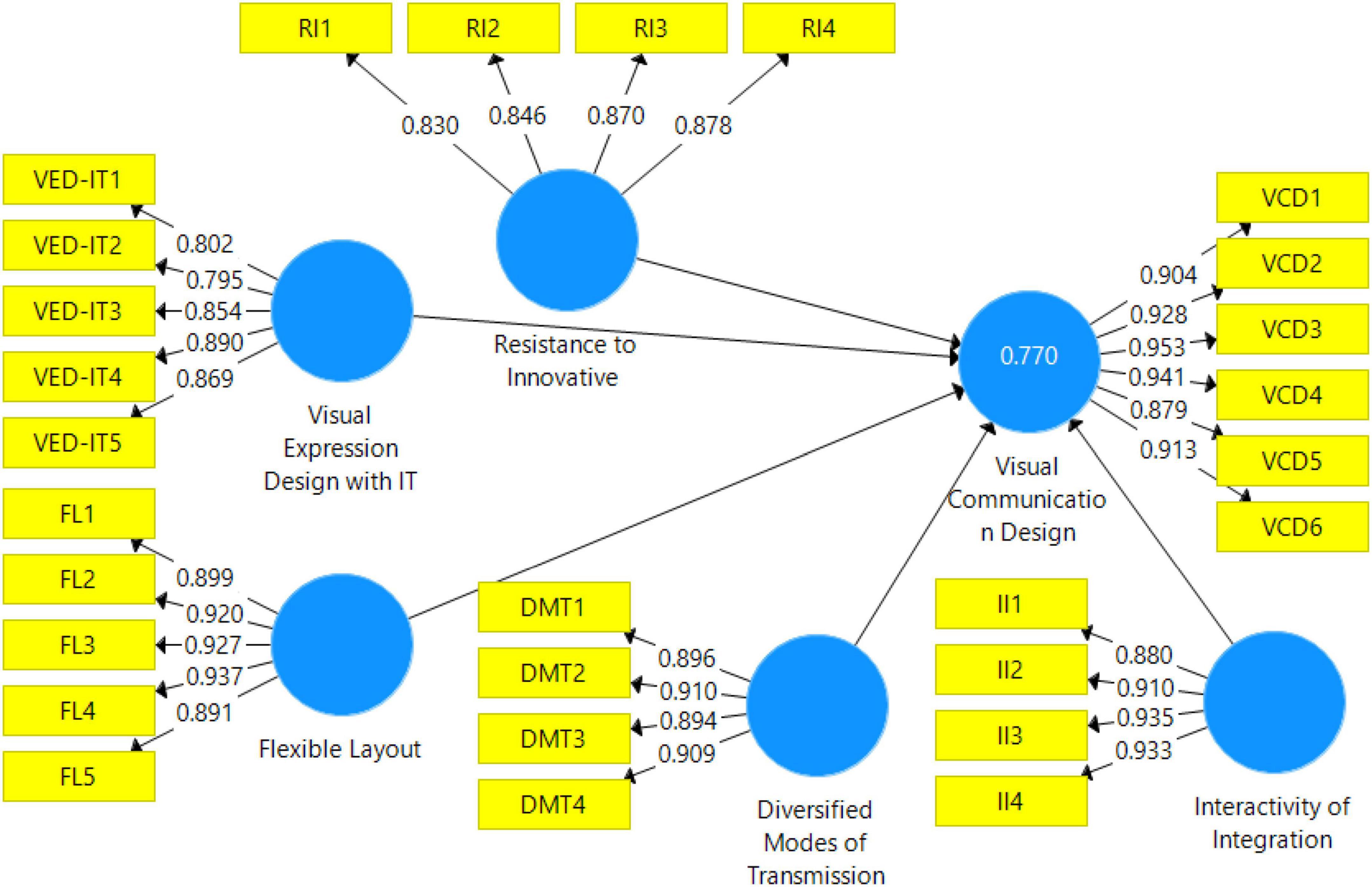
Figure 3. Measurement model. VED-IT, Visual Expression Design with IT; FL, Flexible Layout; DMT, Diversified Modes of Transmission; II, Interactivity of Integration; VCD, Visual Communication Design; RI, Resistance to Innovative Change.
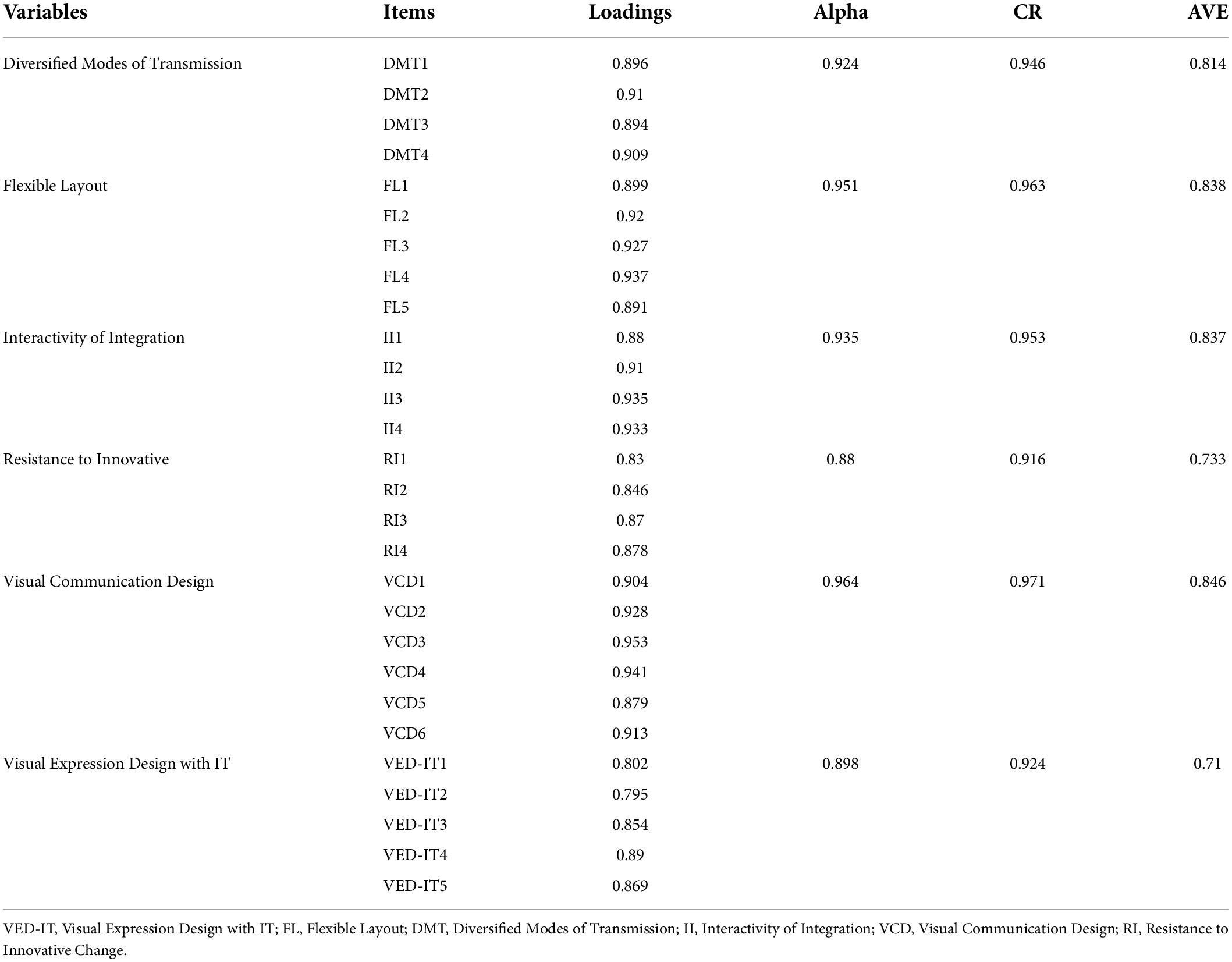
Table 2. Factor loadings, reliability, and convergent validity.
Furthermore, composite reliability (CR) is reported in Table 2 . It must be higher than 0.7 for all variables. This study achieved the minimum level of CR, as shown in Table 2 . Additionally, to check the convergent validity, this study preferred the average variance extracted (AVE), which must be higher than 0.5. AVE higher than 0.5 confirmed the convergent validity, as shown in Table 2 .
Finally, in the measurement model, this study considered discriminant validity, which is essential before examining the relationship between variables. Two methods are used to confirm the discriminant validity. First, the heterotrait-monotrait ratio of correlations (HTMT) 0.9 is considered because all the values must not be higher than 0.9. HTMT is highlighted in Table 3 . AVE square root is considered, which is highlighted in Table 4 .
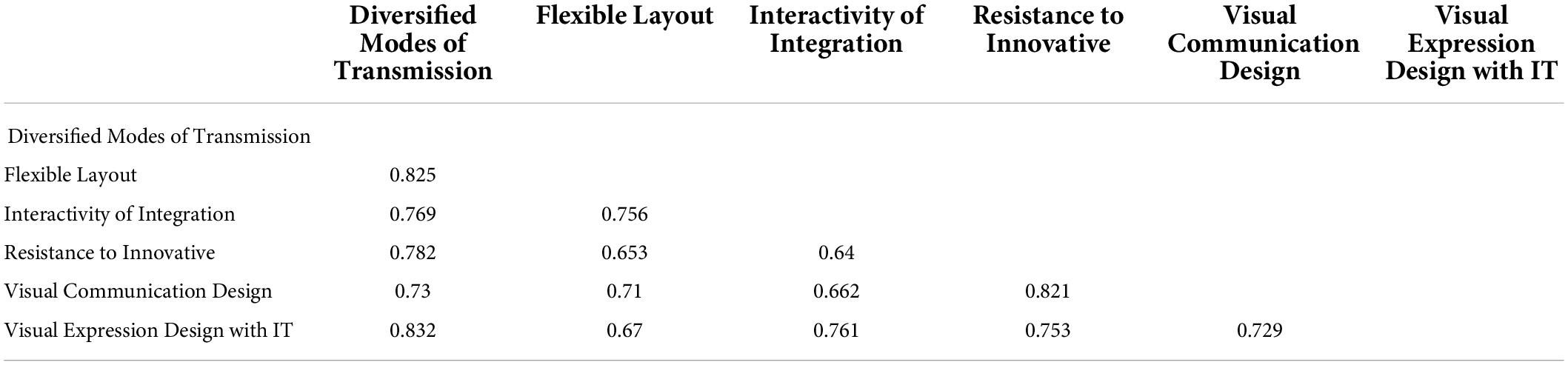
Table 3. Discriminant validity (HTMT).
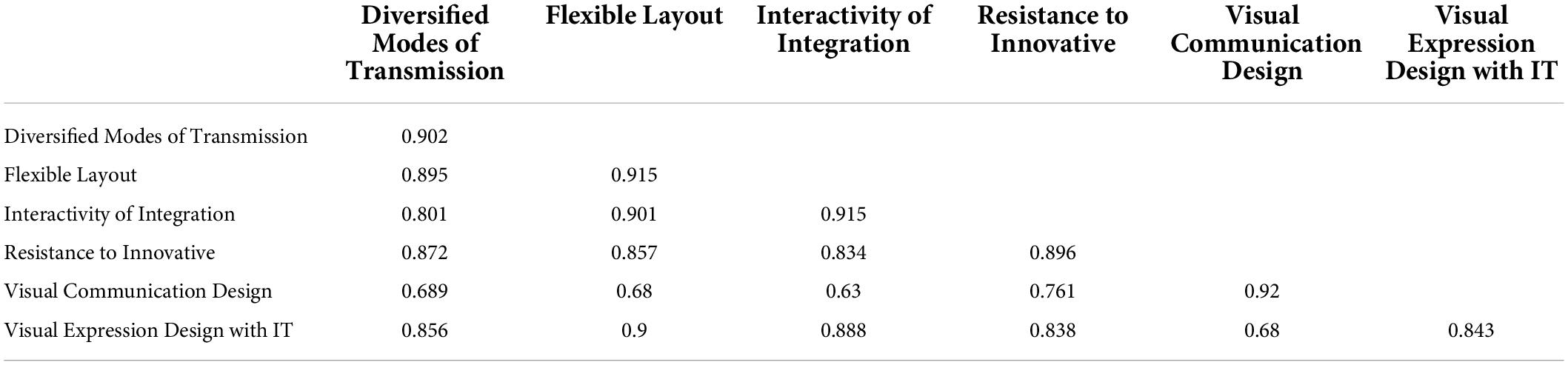
Table 4. Discriminant validity (AVE Square Root).
Structural model assessment
The structural model examines the relationship between visual expression design with IT, flexible layout, diversified modes of transmission, interactivity of integration, visual communication design, and resistance to innovative change. Figure 4 shows the structural model assessment, and the results are reported in Table 5 . This study considered a t-value of 1.96 to accept the hypotheses. Results show that visual expression design with IT positively affects visual communication design with a t-value of 9.808. A flexible layout positively affects visual communication design with a t-value of 5.445.
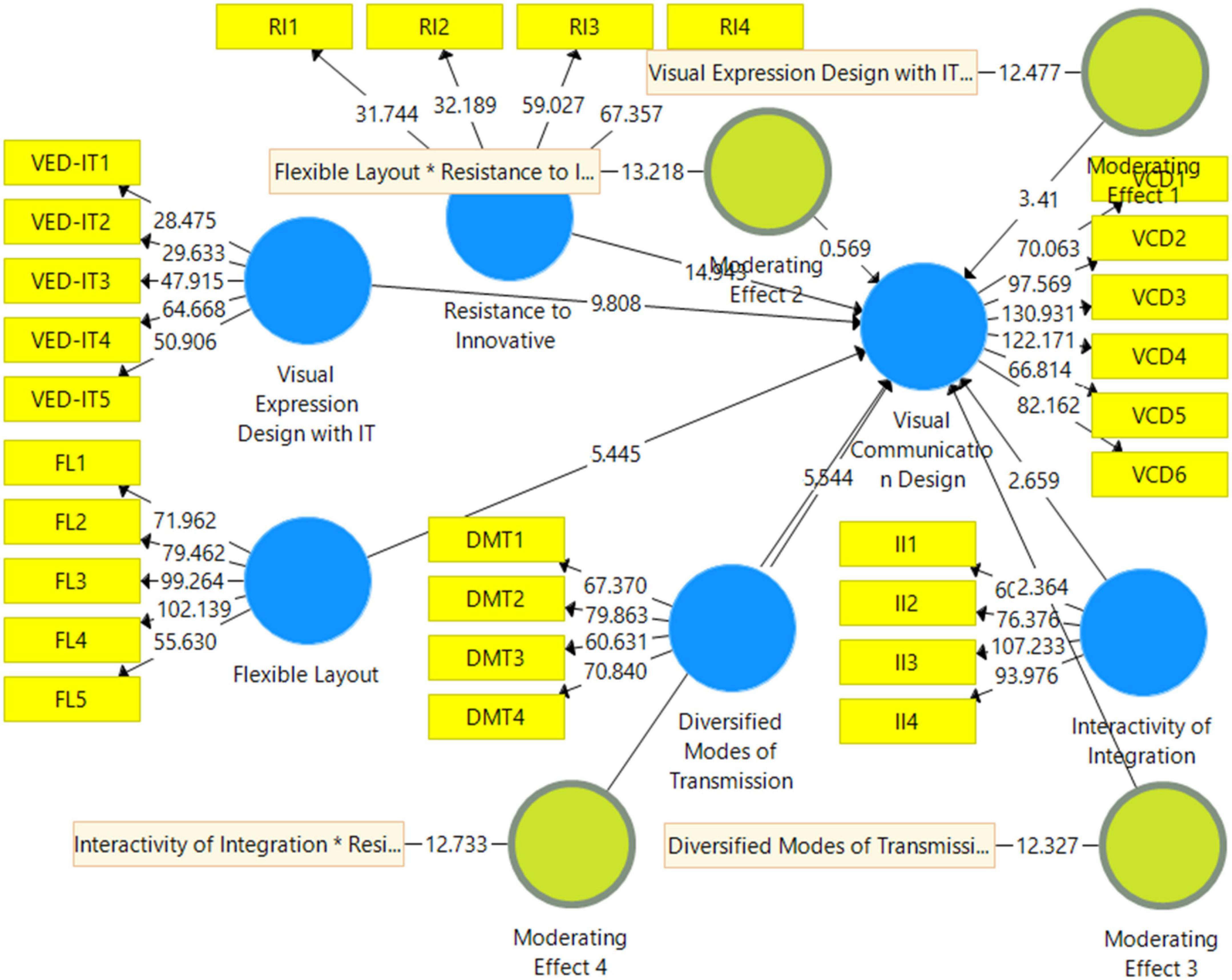
Figure 4. Structural model.
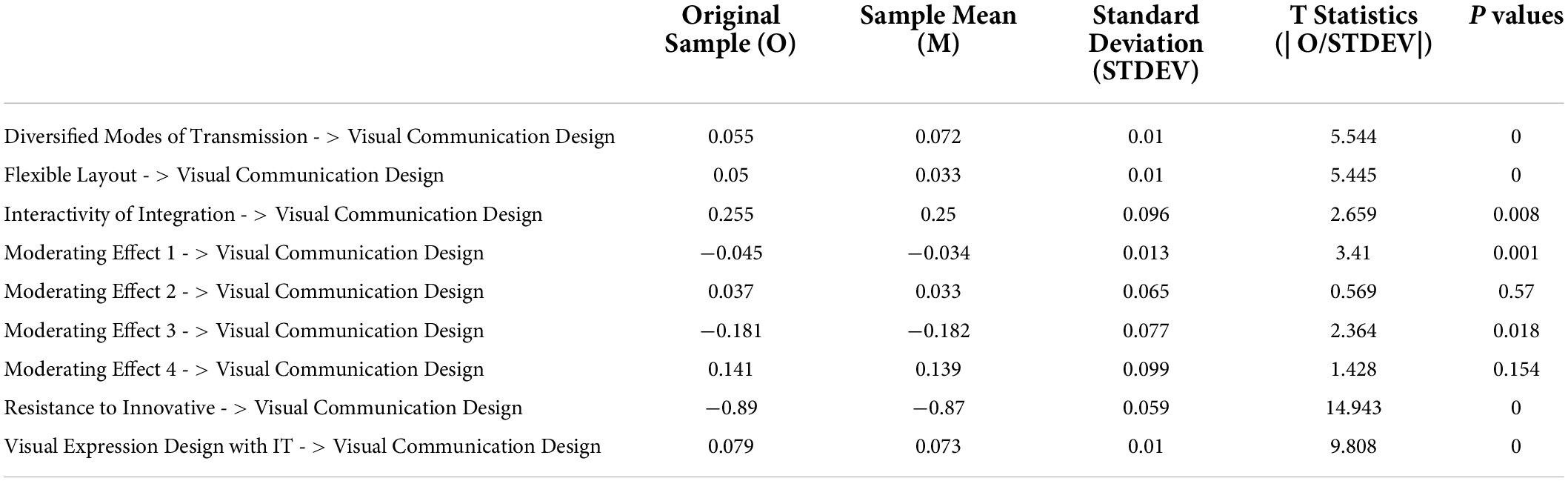
Table 5. Results.
Furthermore, diversified transmission modes also positively affect visual communication design with a t-value of 5.544. Similarly, interactivity of integration positively affects visual communication design with a t-value of 2.659. However, resistance to innovative change harms visual communication design, with a t-value of 14.943.
Moreover, this study examined the moderating role of resistance to innovative change. The moderating role of resistance to innovative change between visual expression design with IT and visual communication design is significant, with a t-value of 3.41. However, the moderating role of resistance to innovative change between flexible layout and visual communication design is insignificant. The moderating role of resistance to innovative change between diversified modes of transmission and visual communication design is significant, with a t-value of 2.364. Finally, the moderating role of resistance to innovative change between interactivity of integration and visual communication design is insignificant. The moderating effect of resistance to innovative change weakens the relationship between visual expression design with IT and visual communication design, as shown in Figure 5 . Additionally, the moderating effect of resistance to innovative change weakens the relationship between diversified modes of transmission and visual communication design, as shown in Figure 6 .
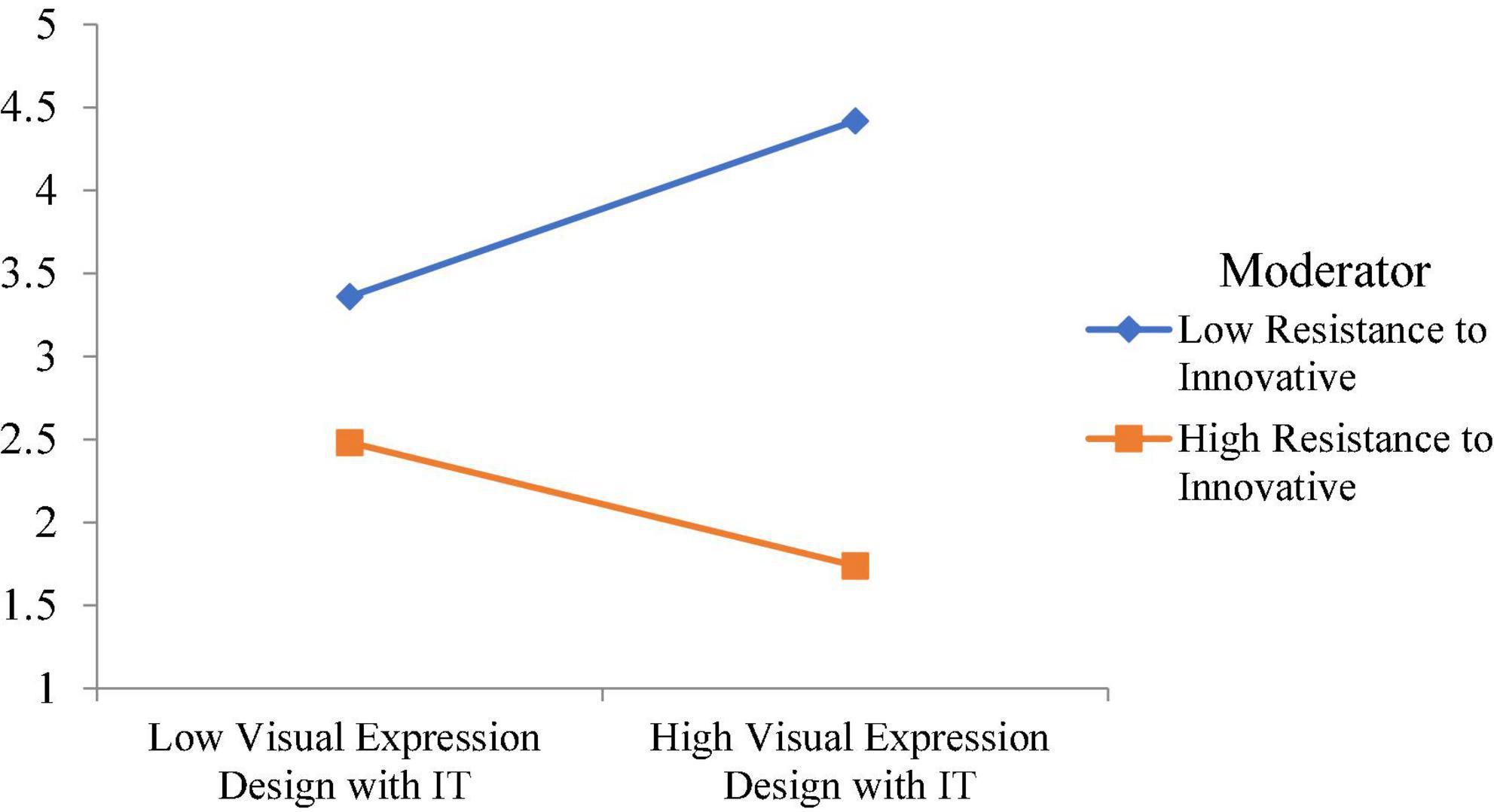
Figure 5. Moderating effect of resistance to innovative change weakens the relationship between visual expression design with IT and visual communication design.
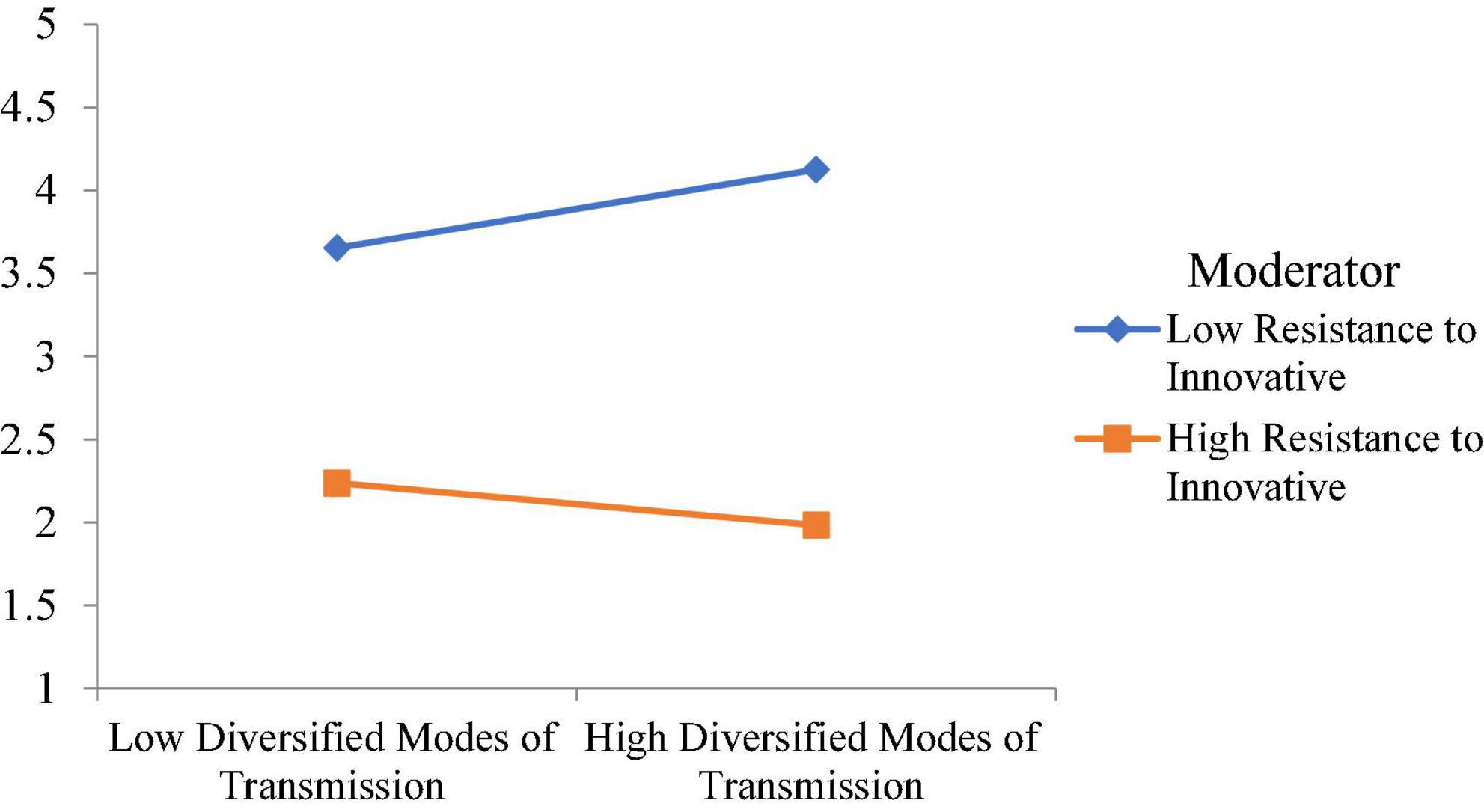
Figure 6. Moderating effect of resistance to innovative change weakens the relationship between diversified modes of transmission and visual communication design.
Discussion and conclusion
The current study examined the relationship between visual expression design with IT, flexible layout, diversified modes of transmission, interactivity of integration, visual communication design, and resistance to innovative change. Nine hypotheses are proposed, including the five direct and four moderating effect hypotheses. After collecting data by using a questionnaire survey, PLS-SEM is employed to examine the relationship between variables.
Hypothesis 1 highlighted the significant and positive relationship between visual expression design with IT and visual communication design. It shows that introducing visual expression design with IT among the educational intuitions can improve the visual communication design. In line with these results, previous studies also highlighted that IT is essential in visual communication design ( Andriyan and Anesti, 2020 ; Wu and Li, 2020 ; Guan and Wang, 2022 ). Hypothesis 2 considered the relationship between flexible layout and visual communication design. A positive and significant relationship was found between flexible layout and visual communication design. A better flexible layout has the potential to promote visual communication design.
Along with the current study, Yue (2020) highlighted the central role of layout in visual communication. According to Yue (2020) , innovation in layout can promote visual communication design. Hypothesis 3 investigated the relationship between diversified modes of transmission and visual communication design. Similar to other hypotheses, this hypothesis is significant and positive, showing that diversified transmission modes have a positive role in influencing visual communication in educational institutions in China. Hypothesis 4 is also significant and positive, highlighting the positive role of interactivity of integration in visual communication. Thus, the adoption of innovative applications related to the interactivity of integration and diversified modes of transmission in visual communication design is influential among institutions, also supported by Yue (2020) . Finally, while examining direct effect, hypothesis 5 indicated a relationship between resistance to innovative change and visual communication design. According to the results, resistance by individuals toward adopting innovative change has a negative role in visual communication.
Furthermore, the current study proposed five hypotheses regarding the moderating role of resistance to innovative change. Hypothesis 6 shows the moderating role of resistance to innovative change between visual expression design with IT and visual communication design. The moderating effect of resistance to innovative change weakens the relationship between visual expression design with IT and visual communication design. It shows that the increase in the level of resistance by the employees, teachers, and students in the educational institutions of China can lead to a decrease in the effect of innovative application of new media. Hypothesis 7 is not supported. However, hypothesis 8 shows the moderating role of resistance to innovative change between diversified modes of transmission and visual communication design. Results show that moderating effect of resistance to innovative change weakens the relationship between diversified modes of transmission and visual communication design. Therefore, the innovative application of new media cannot lead to visual communication in the presence of resistance to innovative change. Hypothesis 9 is not supported. Finally, the study results show that innovative applications of new media such as visual expression design with IT, flexible layout, diversified modes of transmission, interactivity of integration, and visual communication design can expedite visual communication among Chinese educational institutions. However, resistance from the employees, teachers, and students to adopt innovative change may decrease the effectiveness of new media applications.
Theoretical implications
The current study addressed the vital part of the literature gap by considering the role of innovative applications of new media in visual communication design. Therefore, this study has important theoretical implications. First, this study addressed the visual communication design of the new media rather than traditional media, which is not addressed by earlier studies. Second, this study focused on the innovative applications of media, which are rarely studied in the literature. Third, although few studies addressed visual expression design with IT, flexible layout, diversified modes of transmission, and interactivity of integration, earlier studies have not considered these elements of the educational institutions. Mainly, the educational institutions of China are ignored by the previous studies. Four, several studies investigated visual communication design through different dimensions. However, previous studies have not employed PLS-SEM. Therefore, this study contributed methodologically to the field of visual communication design by using a new data analysis tool. Five, this study introduced resistance to innovative change as moderating variable, which is not considered by previous studies.
Practical implications
The results of this study provided several insights for the practitioners to promote communication methods among educational institutions. This study highlighted the ignored part of the literature, therefore, this study has vital practical implications. First, as traditional media in visual communication design is lacking in performance, this study proposed innovative applications of new media that can foster visual communication performance. Second, the study results are helpful for the educational institutions of China to enhance communication methods which may strengthen the relationship between teachers and students, leading to better learning. Third, the study outcomes provided several insights for the practitioners to enhance visual communication by focusing on visual expression design with IT, flexible layout, diversified modes of transmission, and interactivity of integration. Four, the management of educational institutions must reduce the resistance to adopting innovation to foster visual communication among educational institutions in China. Educational institutions’ employees, teachers, and students should adopt innovative visual communication changes.
Limitations and recommendations
The study’s shortcomings are due to the small sample size, which may make it difficult to generalize the results. Future research may thus evaluate the findings using a bigger sample size. Employees and educators from Chinese educational institutions were included in the research. In comparison to the 500 surveys issued, only 225 were returned. It demonstrates that respondents had little interest in taking part in the study. Therefore, metrics that can entice respondents to participate in the study can be included in subsequent research. Additionally, this study might be conducted among staff members at institutions of higher learning that do not provide instruction. As predictive factors for visual communication design, flexible layout, transmission methods, and interactivity of integration have been employed. To get more understanding findings on the aspects that might influence the visual communication design, this model can be modified with additional variables. Future research might also examine how visual communication designs relate to mobile APP interfaces. Future research might also look at how user behavior and technology adoption play a mediating effect. A language barrier may be a moderator in a future study on visual communication designs.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author/s.
Author contributions
GY conceived the concept. SA designed the concept. GO collected the data. TK wrote the manuscript. KS read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Andriyan, W., and Anesti, V. (2020). Visual audio communication design on the role of information technology on student life style of universitas raharja. ADI J. Recent Innov. 2, 15–24.
Google Scholar
Arsyadi, R. (2019). “Innovation in classroom–application of design thinking in visual communication design class at higher education,” in Proceeding of the International Conference on Visual Culture and Urban Life , Jakarta.
Bezruk, V. M., Bukhanko, A. N., Chebotaryova, D., and Varich, V. V. (2012). “Multicriteria optimization in telecommunication networks planning, designing and controlling,” in Telecommunications networks , ed. J. H. Ortiz (London: IntechOpen), 251–274.
Blin, F., and Munro, M. (2008). Why hasn’t technology disrupted academics’ teaching practices? Understanding resistance to change through the lens of activity theory. Comput. Educ. 50, 475–490.
Cebollada, S. (2021). A state-of-the-art review on mobile robotics tasks using artificial intelligence and visual data. Expert Syst. Appl. 167:114195.
Chen, H., and Zheng, X. (2021). Application of traditional culture based on computer technology in modern visual communication design. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1744:032094.
Cheng, L. (2019). Convolutive blind source separation in frequency domain with kurtosis maximization by modified conjugate gradient. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 134:106331.
Demuyakor, J. (2020). Coronavirus (COVID-19) and online learning in higher institutions of education: a survey of the perceptions of Ghanaian international students in China. Online J. Commun. Media Technol. 10:e202018.
Duan, B. (2022). Refining the application of construal level theory: egocentric and nonegocentric psychological distances in climate change visual communication. Environ. Commun. 16, 92–107.
Emans, D., and Murdoch-Kitt, K. M. (2018). “Connective methodologies: visual communication design and sustainability in higher education,” in Handbook of Sustainability and Social Science Research , eds W. L. Filho, R. W. Marans, and J. Callewaert (Berlin: Springer), 83–105. doi: 10.1186/s12868-016-0283-6
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Erickson, A. (2020). “A review of visual perception research in optical see-through augmented reality,” in International Conference on Artificial Reality and Telexistence Eurographics Symposium on Virtual Environments , eds F. Argelaguet, M. Sugimoto, and R. McMahan (Orlando, FL: University of Central Florida), 27–35.
Flückiger, Y. (2021). The conditions for higher education institutions to meet the social challenges ahead. J. High. Educ. Policy Leadersh. Stud. 2, 120–129.
Friedman, N., and Ormiston, J. (2022). Blockchain as a sustainability-oriented innovation?: opportunities for and resistance to Blockchain technology as a driver of sustainability in global food supply chains. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 175:121403.
Frost, R. (2019). Progress in public health risk communication in China: lessons learned from SARS to H7N9. BMC Public Health 19(Suppl. 3):475. doi: 10.1186/s12889-019-6778-1
Gao, J. (2015). Multi-frequency optical unidirectional transmission based on one-way guided mode resonance in an extremely simple dielectric grating. Opt. Commun. 355, 137–142.
Goransson, K., and Fagerholm, A.-S. (2018). Towards visual strategic communications: an innovative interdisciplinary perspective on visual dimensions within the strategic communications field. J. Commun. Manag. 22, 46–66.
Guan, X., and Wang, K. (2022). Visual communication design using machine vision and digital media communication technology. Wirel. Commun. Mobile Comput. 2022:6235913.
Guan-Chen, L., and Ko, C.-H. (2022). Visual communication design and wireless data transmission technology for blockchain big data information presentation. Wirel. Commun. Mobile Comput. 2022:138 0387.
Haapala, K. (2022). Utilizing Different Design Principles for Hard-Surface 3D Art: a Study about Achieving Realistic 3D Mechanical designs. Tampere: Tampere University of Applied Sciences.
Haddou, H., and Benyoucef, L. (2019). Machine layout design problem under product family evolution in reconfigurable manufacturing environment: a two-phase-based AMOSA approach. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 104, 375–389.
Hair, C. (2020). Assessing measurement model quality in PLS-SEM using confirmatory composite analysis. J. Bus. Res. 109, 101–110.
Hair, J. F., Astrachan, C. B., Moisescu, O. I., Radomir, L., Sarstedt, M., Vaithilingam, S., et al. (2021). Executing and interpreting applications of PLS-SEM: updates for family business researchers. J. Fam. Bus. Strategy 12:100392.
Hameed, H.-C. (2021). Relationships between external knowledge, internal innovation, firms’ open innovation performance, service innovation and business performance in the Pakistani hotel industry. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 92:102745.
Hameed, K. (2020). Determinants of micro-enterprise success through microfinance institutions: a capital mix and previous work experience. Int. J. Bus. Soc. 21, 803–823.
Haotian, L. (2020). Visual communication design elements of Internet of Things based on cloud computing applied in graffiti art schema. Soft Comput. 24, 8077–8086.
Huang, L. (2020). Guidance on Flexible Learning during Campus Closures: Ensuring Course Quality of Higher Education in COVID-19 Outbreak. Beijing: Smart Learning Institute of Beijing Normal University.
Huang, M. (2021). “Research on the application strategy of mixed teaching mode of visual communication design specialty in colleges and universities based on multidimensional interaction,” in Paper Presented at the 2021 International Conference on Tourism, Economy and Environmental Sustainability , (Guangzhou: South China Normal University).
Huang, W. (2020). Handbook on Facilitating Flexible Learning During Educational Disruption: The Chinese Experience in Maintaining Undisrupted Learning in COVID-19 Outbreak. Beijing: Smart Learning Institute of Beijing Normal University, 46.
Huang, Z., and Zhou, W. (2022). Study on the construction of integrating regional characteristics into the talent training program of universities–taking the visual communication design major of jingdezhen ceramic university as an example. Int. J. Soc. Sci. Educ. Res. 5, 37–43.
Ji, S., and Lin, P.-S. (2022). Aesthetics of sustainability: research on the design strategies for emotionally durable visual communication design. Sustainability 14:4649.
Jia, C. (2017). “Study on the ways of cultivating information design consciousness in visual communication design education,” in Proceedings of the 2017 2nd International Conference on Education and Education Research (EDUER2017) (London: Francis Academic Press).
Kaur, A. (2020). An innovation resistance theory perspective on mobile payment solutions. J. Retail. Consum. Serv. 55:102059.
Kim, J., and Lee, K. H. (2019). Influence of integration on interactivity in social media luxury brand communities. J. Bus. Res. 99, 422–429.
King, M. (2007). How innovation can alleviate negative consequences of demanding work contexts: the influence of climate for innovation on organizational outcomes. J. Occup. Organ. Psychol. 80, 631–645.
Koch, S. (2021). Exploring passive innovation resistance—an empirical examination of predictors and consequences at the cognitive and situational level. Int. J. Innov. Manag. 25:2150012.
Kostis, P. (2018). Cultural change and innovation performance. J. Bus. Res. 88, 306–313.
Kujur, F., and Singh, S. (2020). Visual communication and consumer-brand relationship on social networking sites-uses & gratifications theory perspective. J. Theo. Appl. Electron. Commer. Res. 15, 30–47.
Lari, M., and Gandomani, Z. K. (2022). Effective capacity maximization of two-way full-duplex and half-duplex relays with finite block length packets transmission. arXiv [Preprint] doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2201.02774
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Liang, S. (2021). Research on emotional factors and emotional experience of information graphic design in visual communication design. Acad. J. Comput. Inf. Sci. 4, 7–10.
Liu, C. (2020). The development trend of visual communication design. Front. Art Res. 2, 83–87. doi: 10.25236/FAR.2020.020915
Liu, R. (2017). Hybrid half-duplex/full-duplex cooperative non-orthogonal multiple access with transmit power adaptation. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 17, 506–519.
Liu, Y. (2018). “Research on the innovative development of multimedia technology and visual communication design teaching,” in Proceedings of the 2018 2nd International Conference on Economic Development and Education Management (ICEDEM 2018) , Dalian. doi: 10.1002/bmb.21034
Matusitz, J. M. (2005). The current condition of visual communication in colleges and universities of the United States. J. Vis. Lit. 25, 97–112.
Naveed, K. (2022). Do organizations really evolve? The critical link between organizational culture and organizational innovation toward organizational effectiveness: pivotal role of organizational resistance. J. Innov. Knowl. 7:100178.
Ozkan, J. (2021). Movement and engagement in flexible, technology-enhanced classrooms: investigating cognitive and emotional engagement from the faculty perspective. Learn. Environ. Res. 25, 359–377.
Phoon, S. Y. (2018). Modelling and Simulation of Spine Layout Design for Flexible Manufacturing System in Digital Factory Platform/Phoon Sin Ye. Lumpur: University of Malaya.
Pourvaziri, H., Salimpour, S., Niaki, S. T. A., and Azab, A. (2021). Robust facility layout design for flexible manufacturing: a doe-based heuristic. Int. J. Prod. Res. 59, 1–22. doi: 10.1080/00207543.2021.1967500
Raposo, D. (2018). Communicating Visually: the Graphic Design of the Brand. Newcastle upon Tyne: Cambridge Scholars Publishing.
Russmann, A. O. (2019). “Political parties and their pictures: visual communication on Instagram in Swedish and Norwegian election campaigns,” in Visual Political Communication , eds A. Veneti, D. Jackson, and D. Lilleker (Cham: Springer), 119–144.
Saris, B. (2020). A review of engagement with creativity and creative design processes for Visual Communication Design (VCD) learning in China. Int. J. Art Des. Educ. 39, 306–318.
Shahbaz, Y. (2019). Investigating the adoption of big data analytics in healthcare: the moderating role of resistance to change. J. Big Data 6, 1–20.
Sumual, G. J. (2021). GUI application to setup simple graph on the plane using tkinter of python. d’CARTESIAN 10, 8–14.
Talidong, K. J. B., and Toquero, C. M. D. (2021). Facing COVID-19 through emergency online education anchored in Khan’s framework: case of Philippine teachers in Xi’an, China. Eur. J. Interact. Multimed. Educ. 2:e02104.
Talwar, A. (2020). Consumers’ resistance to digital innovations: a systematic review and framework development. Australas. Mark. J. 28, 286–299.
Turnbull, L. (2021). Transitioning to E-learning during the COVID-19 pandemic: how have Higher Education Institutions responded to the challenge? Educ. Inf. Technol. 26, 6401–6419. doi: 10.1007/s10639-021-10633-w
Vakulenko, A. (2021). The first step in removing communication and organizational barriers to stakeholders’ interaction in smart grids: a theoretical approach. E3S Web Conf. 234:00020.
Vasylevska, K. (2013). “Flexible spaces: dynamic layout generation for infinite walking in virtual environments,” in Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Symposium on 3D User Interfaces (3DUI) , (Orlando, FL: IEEE).
Wang, J., and Hsu, Y. (2020). The relationship of symmetry, complexity, and shape in mobile interface aesthetics, from an emotional perspective—a case study of the smartwatch. Symmetry 12:1403.
Wang, P. (2021). Research on the application of artificial intelligence in the innovative development of visual communication design education. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1744:032196. doi: 10.3390/s20072093
Wu, H., and Li, G. (2020). Innovation and improvement of visual communication design of mobile app based on social network interaction interface design. Multimed. Tools Appl. 79, 1–16.
Wu, Y. (2019). “Research on the training model of innovative talents in visual communication design specialty,” in Proceedings of the 2nd International Workshop on Education Reform and Social Sciences (ERSS 2019) , Chengdu.
Wu, Z.-N. (2021). The impact of internet development on the health of Chinese residents: transmission mechanisms and empirical tests. Socioecon. Plann. Sci. 81:101178.
Xiangwei, B. (2022). Research on the path of integrating regional culture into the ideological and political education of visual communication design curriculum from the perspective of core literacy. High. Educ. Soc. Sci. 22, 47–51.
Xie, J. (2022). “Research on the talent training mode for visual communication design—based on intelligent computing via project in studio project,” in Innovative Computing. Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering , Vol. 791, eds J. C. Hung, J. W. Chang, Y. Pei, and W. C. Wu (Berlin: Springer), 597–604.
Yadav, A., and Prakash, A. (2022). Factors influencing sustainable development integration in management education: an Empirical Assessment of management education institutions in India. Int. J. Manag. Educ. 20:100604.
Yan, C. (2012). ‘We can only change in a small way’: a study of secondary English teachers’ implementation of curriculum reform in China. J. Educ. Change 13, 431–447.
Yanarates, C., and Zhou, Z. (2021). Symmetrical pole placement method-based unity proportional gain resonant and gain scheduled proportional (PR-P) controller with harmonic compensator for single phase grid-connected PV inverters. IEEE Access 9, 93165–93181.
Yang, C.-M., and Hsu, T.-F. (2017). New perspective on visual communication design education: an empirical study of applying narrative theory to graphic design courses. Int. J. High. Educ. 6, 188–198.
Yue, W. (2020). Research on innovative application of new media in visual communication design. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1550:032146.
Zahlbruckner, M. A. (2021). Lntegrating Production Layout Planning into Structural Design for Flexible Lndustrial Buildings. Vienna: Technische Universität Wien.
Zhang, H., and Wu, C. (2021). An analysis of computer-aided design software course teaching in visual communication design major by integrating grey variable weight clustering evaluation model. Adv. Multimed. 2021:6588734.
Zhou, Y., Zheng, Y., Pan, J., Sui, L., Xing, F., Sun, H., et al. (2019). Experimental investigations on corrosion resistance of innovative steel-FRP composite bars using X-ray microcomputed tomography. Compos. B Eng. 161, 272–284.
Keywords : visual expression design with IT, flexible layout, diversified modes of transmission, interactivity of integration, resistance to innovative change, visual communication design
Citation: Yu G, Akhter S, Kumar T, Ortiz GGR and Saddhono K (2022) Innovative application of new media in visual communication design and resistance to innovation. Front. Psychol. 13:940899. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.940899
Received: 10 May 2022; Accepted: 28 June 2022; Published: 03 August 2022.
Reviewed by:
Copyright © 2022 Yu, Akhter, Kumar, Ortiz and Saddhono. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY) . The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ge Yu, [email protected] ; Shamim Akhter, [email protected]
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Visual Representation of Design Process: Research Projects in Communication Design
- Conference paper
- First Online: 23 October 2020
- Cite this conference paper

- Daniela Oliveira 10 ,
- Daniel Raposo 9 , 10 ,
- José Silva 9 , 10 &
- João Neves 9 , 10
Part of the book series: Springer Series in Design and Innovation ((SSDI,volume 12))
Included in the following conference series:
- International Conference on Design and Digital Communication
1594 Accesses
1 Citations
This study results of the application of the visual thinking methods through a non-interventionist methodology divided in two steps: exploratory interviews and exploratory descriptive diagrams. The research in this field has as main objectives to demonstrate that using visual thinking methods can help in a holistic comprehension of the methods and work processes of the projects, to simplify the complex information of each project and find key concepts common to all of the case studies. This research emerges because of the struggle in assess a detailed holistic perspective about the projects and his components, as the structure and organization of information during the project, since that the designer works in several projects at the same time. In this way, the study intends to evidence the importance that the organization of the information and his visual representation assumes in the development of the new knowledge, in the establishment of relations through the holistic view that visual thinking methods provides.
Furthermore, this study demonstrate that visual thinking is fundamental to a better comprehension of the structure and organization of the design process, as well as powerful tool to achieve findings in design and project methodology fields.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
- Durable hardcover edition
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Cash, P., Stanković, T., Štorga, M.: Using visual information analysis to explore complex patterns in the activity of designers. Des. Stud. 35 , 1–28 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.destud.2013.06.001
Article Google Scholar
Edkins, A.J., Kurul, E., Maytorena-Sanchez, E., Rintala, K.: The application of cognitive mapping methodologies in project management research. Int. J. Proj. Manag. 25 , 762–772 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijproman.2007.04.003
Eppler, M.J.: A comparison between concept maps, mind maps, conceptual diagrams, and visual metaphors as complementary tools for knowledge construction and sharing. Inf. Vis. 5 , 202–210 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1057/palgrave.ivs.9500131
Papanek, V.: Design for the Real World: Human Ecology and Social Change. Thames & Hudson, London (1985)
Google Scholar
Rodríguez Estrada, F.C., Davis, L.S.: Improving visual communication of science through the incorporation of graphic design theories and practices into science communication. Sci. Commun. 37 , 140–148 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1177/1075547014562914
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
CIAUD, Lisbon School of Architecture, Universidade de Lisboa, Rua Sá Nogueira, 1349-063, Lisbon, Portugal
Daniel Raposo, José Silva & João Neves
Instituto Politécnico de Castelo Branco, Av. Pedro Álvares Cabral, nº 12, 6000-084, Castelo Branco, Portugal
Daniela Oliveira, Daniel Raposo, José Silva & João Neves
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Daniela Oliveira .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
ID+/School of Design, Polytechnic Institute of Cavado and Ave, Barcelos, Portugal
Nuno Martins
CECS/Institute of Social Sciences, University of Minho, Braga, Portugal
Daniel Brandão
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 The Editor(s) (if applicable) and The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper.
Oliveira, D., Raposo, D., Silva, J., Neves, J. (2021). Visual Representation of Design Process: Research Projects in Communication Design. In: Martins, N., Brandão, D. (eds) Advances in Design and Digital Communication . Digicom 2020. Springer Series in Design and Innovation , vol 12. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-61671-7_56
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-61671-7_56
Published : 23 October 2020
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-030-61670-0
Online ISBN : 978-3-030-61671-7
eBook Packages : Engineering Engineering (R0)
Share this paper
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research

Graduate Overview
Visual communication design graduate overview.
Led by faculty who are actively engaged in design thinking and practice, Visual Communication Design students are challenged to think critically about what they create, take risks in their work, and experience the value and transformative ability of design.
Renowned Visual Communication Design faculty represent the diversity of contemporary design practice, research, and pedagogy with thriving practices both self-initiated and client-associated, physical and virtual, and individual and collaborative. Students are presented with a rich array of tools and ideas and work with faculty to broaden and deepen their understanding of the field, acquire new skills and approaches, and develop an innovative and mature body of work. Faculty guide students in self-initiated work that explores issues of personal interest and cultural/social significance.
Methodologies and Interdisciplinary Experimentation
Graduate students begin their coursework with critique seminars designed to encourage experimentation with new methodologies to further develop their individual work and exploration. Subsequent semesters are less structured—allowing students to work with individual advisors, generate individualized content, and experiment with other related disciplines—eventually culminating in fully realized theses. Students take part in advanced study of the history and interpretation of visual communication design through curricula that explore how the discipline has been influenced by, and in turn influences, cultural, social, political, industrial, and technological forces.
Design at the Intersection of Artistic Disciplines
Striking a balance between guidance and self-direction, the Visual Communication Design program offers both rigorous coursework and individualized attention in an open and interdisciplinary environment. Students are encouraged to explore other related departments at SAIC—Printmedia; Writing; Photography; Architecture, Interior Architecture, and Designed Objects; and Film, Video, New Media, and Animation—to extend their design work into new territories. Experiences with like-minded artists and designers working in various media allow students to make inventive, poetic, informative, expansive, and often unexpected connections in their own creative work.
MFA and Post-Baccalaureate Certificate Programs
Students are either admitted into the Master of Fine Arts (MFA) program, a two-year, 60-credit program, or the Post-Baccalaureate Certificate in Studio , a one-year, 30-credit program that can serve as a track into the MFA program. This path creates a three-year experience for students who often have little design experience and will benefit from additional education in preparation for continuation into the MFA program. The programs are highly competitive and bring together a talented group of students of diverse backgrounds, experiences, and research interests.
Graduate Projects
At the core of the MFA program are Graduate Projects . Taken every semester, Graduate Projects allow students to focus on their work in one-on-one meetings with a faculty member. In addition to meeting biweekly with a Visual Communication Design graduate faculty member, students may sign up for Graduate Projects with writers, artists, and academics from other departments at SAIC. Ultimately, it is the student’s work that drives the choice of advisor, and both disciplinary and interdisciplinary work is supported and advanced.
MFA Graduate Seminars
In the fall semester, several graduate seminar courses are offered. First-year MFA students are required to take a seminar. These courses explore a range of methodologies that lead to self-directed work and thesis development.
The primary issues these seminars address include: contemporary design practice, cultural and literary criticism, and cognitive, linguistic, structuralist, and other theories.
- MFA 5310 MFA Form-Configuration-Content
- MFA 5320 MFA Narrative A rchitectures
Critique Week
Critique Week, one of the principal means of assessment each semester, is a week-long schedule of critiques during which classes are suspended and the entire faculty and invited artists and designers assemble into panels that conduct intensive studio critiques with all studio and writing graduate students.
Fall semester critiques are organized by each department, with panels representing the discipline.
Spring semester critiques are interdisciplinary, with panel members of faculty, visiting artists, and peers from across SAIC departments. Interdisciplinary critiques in the spring semesters allow for a broader range of responses to the work, and are intended to assess the success of your work for a more general, yet highly informed, audience.
Studio critiques are required of every full-time graduate student pursuing an MFA in Studio or Writing degree. Typically, SAIC graduate students have at least four critique panels throughout their studies at SAIC, augmenting biweekly tutorials with their graduate advisors.
Interested in Learning More About the Program?
Continue to explore the SAIC Visual Communication Design department website to learn about our curricular offerings, faculty, students, and alumni, visit the Master of Fine Arts in Studio degree program for more detailed information, or schedule a tour.
Take the Next Step
Accepting applications.
Apply to SAIC's graduate Visual Communication Design programs for fall 2024 admission. APPLY
MFA in Studio Admissions Information
Curriculum & courses.
Visit the graduate admissions website or contact the graduate admissions office at 312.629.6100, 800.232.7242 or [email protected].

MA Visual Communication Design Program Brochure
Jill Gao (MFA 2022)

REQUEST INFO ON OUR GRADUATE DEGREE PROGRAMS
Exploring the Boundaries Between Visual Anthropology and Visual Communication Design Research
- Ann Bessemans
- María Pérez Mena
Researchers and/or designers in visual anthropology and visual communication share the visual aspect or visual study as a common interest. However, their views are different. Visual anthropologists consider the social impact and/or meaning of the visual communication within a culture. They are also interested in ways to present anthropological data by means of visual techniques.
Visual communication design researchers create visual communication, and are interested in how participants respond to visual matter in order to enhance the human experience. In a way, they are (partly) producing the visual culture visual anthropologists are reflecting upon.
In order to find out how and whether such disciplinary exploration might be fruitful, we were assigned three articles from Visual Anthropology Review within the category “Deaf Visual Culture.” As typographic legibility researchers within READSEARCH this felt familiar, since we have conducted several design studies (published and in preparation)—more specifically, practical legibility research—for the deaf and hard of hearing community.
As design researchers in legibility studies, we do see possibilities to build bridges among the disciplines of visual anthropology and visual communication. A remarkable resemblance between the different fields of study within a deaf culture, in our eyes, is the approach of trying to capture legibility/illegibility within language (spoken, signed, and/or written) by means of visual properties. Therefore, we would like to highlight differences and similarities between anthropology versus visual communication, drawing conclusions about why both disciplines should keep a close eye on each other. Implementing insights into their research practices and/or visual communication design artifacts may open horizons within innovative or even collaborative research projects. Both fields, visual anthropology and visual communication, are trying to contribute to a specific common concern in deaf education—namely, the educational context of language practice.
- Requires Subscription PDF
Back Issues
Because Visible Language is the oldest design journal, we support scholars by making PDFs of all back issues available. The full catalog of back issues is now available!
Make a Submission
Subscription.
Login to access subscriber-only resources.

An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Front Psychol
Innovative application of new media in visual communication design and resistance to innovation
1 College of Fine Arts, Shanxi University, Taiyuan, China
Shamim Akhter
2 School of Languages, Civilization and Philosophy, Universiti Utara Malaysia, Changlun, Kedah, Malaysia
Tribhuwan Kumar
3 Prince Sattam Bin Abdulaziz University, Al-Kharj, Saudi Arabia
Geovanny Genaro Reivan Ortiz
4 Catholic University of Cuenca, Cuenca, Ecuador
Kundharu Saddhono
5 Indonesia Language Education Study Program, Universitas Sebelas Maret, Surakarta, Indonesia
Associated Data
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author/s.
It has become essential to create and apply new media in visual communication design due to social media existence. This study aims to investigate the role of innovative applications of new media in visual communication design in educational institutions. Traditional media design in visual communication lacks to disseminate information more effectively, which requires innovative change. Therefore, this study attempts to highlight the role of innovative application of new media in visual communication by considering visual expression design with information technology (IT), flexible layout, diversified modes of transmission, and interactivity of integration. For this purpose, this study adopted a quantitative research approach in which a cross-sectional research design is followed. A questionnaire survey is carried out to collect data from educational institutions in China. Partial Least Square-Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM) is used for data analysis. Results of the study indicated that innovative applications of new media have central importance in visual communication. However, resistance to innovative change has a negative role in the relationship between innovative applications of new media and visual communication design. Results of the study highlighted that visual expression design with IT, flexible layout, diversified modes of transmission, and interactivity of integration have a positive effect on visual communication design. Therefore, among the educational intuitions of China, implementing innovative applications related to the new media can lead to visual communication design. The results of this study provided several insights for the practitioners to promote communication methods among educational institutions.
Introduction
Visual communication is the conveyance of ideas and information by using a broad range of forms that can be visually observed. These include different signs, diagrams, graphic designs, illustrations, animations, colors, and electronic resources ( Kujur and Singh, 2020 ; Ji and Lin, 2022 ). Visual communication is a powerful communication tool that is central to communication ( Ji and Lin, 2022 ; Xiangwei, 2022 ). It is based on animated Graphics Interchange Formats (GIFs), screenshots, different types of videos, pie charts, and infographics, along with slide deck presentations. All these types of visual communication have a vital role in the communication process through different methods. Along with other institutions, visual communication is standard in educational institutions as it provides different ways for teachers to teach effectively and lead to effective learning. Visual communication is an effective tool in educational institutions ( Matusitz, 2005 ), but it is lacking in Chinese institutions.
Visual communication requires innovative applications ( Goransson and Fagerholm, 2018 ; Liu, 2018 ). Mainly, new media applications in visual communication design are most important to introduce in Chinese educational institutions. Traditional communication design lacks different elements, which may lead to a lack of communication. The problems in traditional communication design can be well managed with the help of innovative applications of new media. New and traditional media complement each other and develop together ( Yue, 2020 ). However, new media has the potential to create a better communication environment which can lead to the accuracy of communication. The innovative applications in new media can cover a broader range than traditional media. Advance technology in new media has several forms which can perform better than traditional media in different ways ( Yue, 2020 ).
Earlier studies investigated visual communication through different aspects ( Russmann, 2019 ; Duan, 2022 ). However, the element of innovation is rarely addressed. Different studies on visual communication design, such as Guan-Chen and Ko (2022) , discussed the wireless data transmission technology about the Blockchain big data information presentation. Wang (2021) highlights visual communication design with the help of artificial intelligence and innovation development. Arsyadi (2019) discussed visual communication design in classrooms to facilitate instructors teaching at educational institutions. Huang and Zhou (2022) conducted a research study on visual communication design by considering the training program of universities. All these studies highlighted the essential findings and provided several implications.
However, the role of innovative applications of new media is not investigated. To get maximum benefits from visual communication, the role of innovative applications is required. Previously, research has investigated the impact of narrative theory on perspective development in graphic designing courses ( Yang and Hsu, 2017 ). The study did not find the impact of the application of new media on visual communication design. Therefore, based on narrative theory, the current research examines the impact of the application of new media on visual communication design. This study attempts to highlight the role of the innovative application of new media in visual communication. Thus, to address the role of new media on visual communication, this study addressed four significant elements; visual expression design with information technology (IT), flexible layout, diversified modes of transmission, and interactivity of integration.
The innovative application of new media faces resistance to innovative ideas. The implementation of innovative ideas faces resistance to innovative change. The employees working in educational institutions resist innovative change. Previous studies also mentioned that resistance to innovation causes a decrease in the implementation of innovative ideas among institutions ( Koch, 2021 ; Friedman and Ormiston, 2022 ; Naveed, 2022 ). Similarly, in visual communication design, resistance to innovative change is one of the significant problems. Hence, this study is one of the attempts to address the effect of resistance to innovative change in visual communication design. Finally, this study aims to investigate the role of innovative applications of new media in visual communication design in educational institutions. This study has vital theoretical contributions, which further lead to several practical implications for fostering visual communication design through the innovative application of new media.
Literature review
Visual expression design with information technology.
IT (information technology) is the use of networking among storage, computers, and other physical infrastructures, devices, and processes that create, secure, store, exchange, and process all forms of electronic data. IT intended for financial gain encompasses both telecommunication and computer technology. As a past study conducted by Cebollada (2021) , the visual form of data has a significant role in all forms of electronic data. It is because visual expressions are based on values, ideas, and feelings that are visually presented. In addition, Erickson (2020) described that visual expression design is something perceptible that is perceived on a screen.
According to the present study, visual expression design with IT refers to acceptable, tolerable, standard, and decent designs in every aspect of IT, mainly to depict the actual meaning of the cause behind the creation of the design. Raposo (2018) says that visual communication is an art that combines words, thoughts, images, and ideas to express a message or to convey information aiming to produce a particular effect. Visual expression design with IT is more effective, persuasive, convincing, and result-oriented because IT adds significant meaning to the growth of the business and commerce sector by generating the maximum possible outcome.
Flexible layout
To create consistency, avoidance of unnecessary items is necessary. However, a container must be able to hold all the items that are specified and unspecified. Sumual (2021) represented that a potent layout is always invisible to users and provides more comfort to get things done more quickly. A user-friendly and flexible layout is one of the primary purposes of any developer. A study on creating a dynamic layout for a virtual environment for walking conducted by Vasylevska (2013) says that a dynamically practical layout is called a flexible layout. It provides adequate methods to distribute, align, and space among items in a container or stack even when the size of the items is dynamic or unknown. Hence, a flexible layout is an art to fit the requirements of a system. Phoon (2018) presented that a flexible layout helps expand items to cover free space or shrinks the items to avoid overflow.
Moreover, Pourvaziri et al. (2021) described that regular layouts are limited which are vertically or horizontally based. While the flexible layout is direction-agnostic, it allows the automatic position of items by wrapping. In addition, Haddou and Benyoucef (2019) described that a flexible layout is always ready to accept products of uncertain sizes. Therefore, a flexible layout is crucial for accomplishing dynamic manufacturing cells, particularly in an environment with dynamic production.
Diversified modes of transmission
In telecommunication, transmission refers to the spreading or broadcasting of information. A transmission system sends a signal from place A to place B. Figure 1 shows a telecommunication network representing the current transmission mode. Figure 2 show the complete networking of telecommunication.

Research model.

Telecommunication network. Source: https://www.conceptdraw.com/How-To-Guide/picture/Computer-and-Networks-Telecommunication-Network-Diagrams-GPRS-network-scheme.png . VED-IT, Visual Expression Design with IT; FL, Flexible Layout; DMT, Diversified Modes of Transmission; II, Interactivity of Integration; VCD, Visual Communication Design; RI, Resistance to Innovative Change.
The transmission system sends information consisting of video or audio or some other type of data, in digital or analog form using optical or electromagnetic signals between various sites. Bezruk et al. (2012) researched multi-criteria optimization in telecommunication network planning, designing, and controlling. They described the following four types of telecommunication networks: (a) public-switched telephone networks, (b) radio networks, (c) packet-switched networks, and (d) computer networks.
The traditional modes of transmission are relatively simple. However, in computers, transmission modes are comparatively complex and more efficient ( Cheng, 2019 ). Furthermore, according to Liu (2017) , in computers, simple mode, half-duplex mode, and full-duplex mode are the three primary modes of transmission. Gao (2015) also determined that communication in simple mode is unidirectional, which means that between two devices, one will transmit while the other will receive. Lari and Gandomani (2022) explored that in a half-duplex mode of transmission, both the devices can transmit and receive data but not simultaneously. While in full-duplex, both the devices can simultaneously transmit and receive data.
Interactivity of integration
Innovation in visual communication design is necessary to use modern technologies because the innovative designs of products have become hot items produced by professional designers. Moreover, Chen and Zheng (2021) concluded that visual communication design’s professionally designed items are integrated with modern technologies. A previous study by Yue (2020) explored that interactivity of integration in visual communication design helps bring unique information that can be linked to design requiring more innovative creations. The interactivity of integration also refers to the process of designing in which a designer can display his/her work in a customized way; hence, viewers’ attention is increased to see more exciting content generated by the designer. In addition, Kim and Lee (2019) proved that interactivity of integration attracts viewers to participate in the designing process. Sometimes using advanced technologies that help achieve a higher sense of integration and incorporation aims to achieve higher quality and ensure that more decadent designs promote audiences.
Resistance to innovative change
Like any change, innovation is also a change that requires intention, effort, and motive; it needs leadership and vision. Furthermore, it generates resistance. In several cases, an increase is the primary goal, meaning innovation is mandatory in these cases. Kostis (2018) described that innovative changes have consequences that influence the performance in either positive or negative ways. According to Zhou et al. (2019) , resistance to innovative change refers to the limitation that decreases or stops increasing the performance volume. In other words, resistance to innovation change is a factor that spectacle the progressive boundaries of an institution. King (2007) determined that resistance to innovative change decreases the demanding work contexts that ultimately result in organizational outcomes. In addition, resistance to innovation change is defined as the act toward the acceptance and usage of any modernization that results in continuing the current situation and resisting any abnormality from prevailing beliefs. However, resistance to innovative change is categorized based on various factors such as rational, logical, emotional, psychological, and sociological resistance. According to Talwar (2020) , lack of trust, poor communication, emotional response, fear of failure, surprises, constant change, and listening to employees are the common reasons for resistance to innovative change.
Visual communication design
Scholars have long been concerned about the design principles such as unity, proportion, complexity, and symmetry ( Wang and Hsu, 2020 ; Yanarates and Zhou, 2021 ; Haapala, 2022 ). According to Liang (2021) , visual communication design is a process that combines technology and visual arts to communicate thoughts and creative ideas. Typically, every visual communication design begins with a message transformed into visual communication that goes beyond complete pictures and words. Zhang and Wu (2021) presented that broadcast, film, advertising, web, publishing, television, and industry are the visual channels and formats for creative visual material. Modern means of communication such as social media platforms and websites keep bringing current visual communications design to attract their audience.
Furthermore, typography and art also significantly positively affect visual communication design. Hence the fundamental purpose of visual communication design is to convey information. However, there is a difference between graphic design and visual communication design. According to Emans and Murdoch-Kitt (2018) , every image that people see is graphic design. Only the images that convey a message are visual communication design, while the images that do not convey a message are graphic design.
Development of hypotheses
Visual expression design with information technology and visual communication design.
A study by Jia (2017) explored that visual expression design plays a significant role in educational institutions. Educational institutions, especially in China, without visual expression design, fail to meet their targets, particularly concerning learning and teaching methods. In addition, Saris (2020) determined that learning becomes more compelling and persuasive for students through clear, attractive, engaging, and appropriate visual expression design. Several previous studies are also evident that increasing the value of visual expression design, especially in educational institutions, increases the value of the institutions ( Wu, 2019 ; Huang, 2021 ). Furthermore, visual expression design with IT adds significant meaning to the visual communication design. Prior literature also revealed that visual expression design with IT adds significant meaning to educational materials such as videos, infographics, animated GIFs, and slide presentations that make the massage or information clear, concise, and succinct; hence, learners easily understand. Previous literature shows that an increase in the value of visual expression design with IT also increases the value of visual communication design. Hence, it is enclosed.
- H1: Visual expression design with IT positively correlates with visual communication design.
Flexible layout and visual communication design
A flexible layout helps to design a visual communication design. According to the present study, the flexible layout has a significant favorable influence on the teaching methods, especially for teachers in China. It is observed that innovation in teaching and education increases the performance of the teachers and the educational institutions. Furthermore, Huang L. (2020) determined that during the COVID-19 outbreak, the flexible learning process was entirely ensuring for quality of education and increased the value of visual communication design by adding significant positive meaning to the online learning process. Ozkan (2021) explored that the faculty of an educational institution feel more comfortable with movement in the flexibility and engagement in technology-enhanced classrooms. In addition, Zahlbruckner (2021) determined that flexible layout significantly affects visual communication design. Results of the previous study show that increasing the value of flexible layouts also increases the value of visual communication design. Hence, it is enclosed.
- H2: Flexible layout has a positive relationship with visual communication design.
Diversified modes of transmission and visual communication design
For higher education institutions, diversified modes of transmission play a crucial role ( Flückiger, 2021 ). In countries like China, educational institutions are responsible for students’ behavior, personality building, career orientation, and socio-economic values. Therefore, diversified modes of transmission in educational institutions in the country are more significant. Previous literature shows that educational institutions in China having good value for diversified modes of transmission remain successful in building visual communication designs that are advantageous both for the teaching methods and learning process ( Talidong and Toquero, 2021 ). Furthermore, Wu (2021) determined that diversified modes of transmission have positive effects on the health of teachers and students. During the COVID-19 outbreak, the value for visual communication design increased due to the variety of diversified modes of transmission. Hence, it is clear from the results of the previous study that increasing the value of diversified modes of transmission also increases the value of visual communication design. Therefore, it is enclosed that:
- H3: Diversified modes of transmission have a positive relationship with visual communication design.
The interactivity of integration and visual communication design
Yadav and Prakash (2022) determined that interactivity of integration plays a significant role, especially in the sustainable development of educational institutions. Furthermore, interactivity of integration helps assess the management of educational institutions in countries like China and India. Turnbull (2021) also agreed that interactivity of integration helps to deal with the challenges such as communication gaps. The present study concluded from the previous literature that several kinds of barriers, such as physical, emotional, cultural, perceptual, language, and interpersonal barriers, are the real reasons that ultimately lead to communication gaps. However, decreased value of interactivity of integration is the real cause behind these barriers ( Vakulenko, 2021 ). Studies also determined that the value of the visual communication design increases with the increase in the interactivity of integration. Furthermore, the educational institutions in China have better versions of visual communication design that increased value for interactivity of integration. Therefore, it is enclosed that:
- H4: Interactivity of integration has a positive relationship with visual communication design.
Resistance to innovative change and visual communication design
Kujur and Singh (2020) investigated that effective visual communication design, especially in an educational institution, particularly in a country like China, helps students and learners to understand their lessons and other information. Faculty often need visual communication designs that can convey their message correctly to their pupils. Moreover, the faculty also demands innovation in visual communication design. However, Frost (2019) determined that resistance to innovative change in the learning process and teaching methods eventually results in a communication gap. In addition, Demuyakor (2020) also explored that during the COVID-19 outbreak, the learning process in higher institutions of education in China was diminished. It was due to resistance to innovative change because of COVID-19. Outcomes of the previous literature result in a decrease in the value of resistance to innovative change and a decrease in the value of visual communication design. Hence, it is enclosed:
- H5: Resistance to innovative change has a negative relationship with visual communication design.
Moderation relationship
Educational institutions in China having increased value of resistance to innovative change have adverse effects on the relationship between visual expression design with IT and visual communication design. Huang W. (2020) determined that resistance to innovative change results in reduced performance in educational institutions. Moreover, the moderation role of resistance to innovative change decreases the value of the visual expression design with IT and visual communication design. Xie (2022) concluded that resistance to innovative change decreases the value of talent in learners; hence, the value of intelligent computing decreases. Hence, it is enclosed:
- H6: Resistance to innovative change moderates the relationship between visual expression design with IT and visual communication design
Resistance to innovative change in the educational institutions in China results in adverse effects on the relationship between flexible layout and visual communication design. Liu (2020) investigated that a flexible classroom layout pattern adds significant meaning to students’ learning process in educational institutions. Moreover, the moderating role of resistance to innovative change decreases the value of flexible layout, eventually decreasing the value of visual communication design. Prior literature on the educational system also shows that resistance to innovative change decreases the value of educational institutions ( Yan, 2012 ). Hence, it is enclosed:
- H7: Resistance to innovative change moderates the relationship between flexible layout and visual communication design
Educational institutions in China having increased value of resistance to innovative change have adverse effects on the relationship between diversified modes of transmission and visual communication design. According to Kaur (2020) , resistance to innovative change always creates boundaries between the target and the current performance of an educational institution. Furthermore, the moderating role of resistance to innovative change decreases the value of diversified modes of transmission, ultimately resulting in a decrease in the value of visual communication design. Results of the previous study show that resistance to innovative change has sufficient influence on diversified modes of transmission and visual communication design ( Haotian, 2020 ). Hence, it is enclosed:
- H8: Resistance to innovative change moderates the relationship between diversified modes of transmission and visual communication design
In China, educational institutions that carry resistance to innovative change show adverse effects on the relationship between interactivity of integration and visual communication design. Shahbaz (2019) determined that needless interference with selective perception, loss of freedom, security, threats to the power of influence, skill obsolescence, need fulfillment, habit, and economic implications are the reasons behind resistance to innovative change. In addition, Blin and Munro (2008) explored that the moderation role of the resistance to innovative change decreases the value of interactivity of integration, ultimately resulting in a decrease in the value of visual communication design. Hence, it is enclosed:
- H9: Resistance to innovative change moderates the relationship between interactivity of integration and visual communication design
Research methodology
The current study examined the relationship among visual expression design with IT, flexible layout, diversified modes of transmission, interactivity of integration, visual communication design, and resistance to innovative change. The nature of this relationship is supported by a cross-sectional research design. Therefore, the current study followed a cross-sectional research design by following the quantitative research approach. While using a cross-sectional research design, this study carried out a questionnaire survey to collect data from respondents.
The population of the study is based on the educational institutions in China. The teachers and employees working in these institutions were considered the study’s respondents. Few previous studies investigated visual expression design with IT, flexible layout, diversified modes of transmission, interactivity of integration, visual communication design, and resistance to innovative change. However, these elements are rarely discussed among Chinese educational institutions. Therefore, this study conducted a questionnaire survey to collect data from Chinese educational institutions. The questionnaires were distributed by using simple random sampling among the educational institutions. This study distributed 500 questionnaires and 225 questionnaires were returned; 10 questionnaires were missing by a significant part, therefore, excluded from the survey; and 215 valid responses were used in the data analysis.
Visual communication design is measured by considering the effectiveness in educational institutions. Five items are used to measure visual communication design. Visual expression design with IT is measured by using the role of IT in visual expression design. Flexible layout is measured by using the different layouts and their effectiveness in visual communication among the educational institutions. Visual expression design with IT and flexible layout are measured using five items each.
Furthermore, four items are used to measure diversified modes of transmission, and these items are designed using different transmission modes. The interactivity of integration is also measured using four scale items based on the interactivity, which are regarding time and technology. Finally, four items are used to measure resistance to innovative change. These items are developed by considering the resistance to innovative change by the employees. After the development of the questionnaire, face validity and content validity are confirmed by reviewing the questionnaire from experts in a related field. After that, a pilot study is carried out by using 100 questionnaires. Additionally, exploratory factor analysis (EFA) is also employed.
Data analysis
The current study analyzed data using Partial Least Square-Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM). PLS-SEM is the most well-known data analysis technique recommended by several previous studies ( Hair, 2020 ; Hair et al., 2021 ). PLS-SEM is based on two significant steps: (1) measurement model assessment and (2) structural model assessment. However, before data analysis, the current study performed initial data screening in which missing values and outliers are examined. After data screening, the data statistics are given in Table 1 .
Data statistics.
VED-IT, Visual Expression Design with IT; FL, Flexible Layout; DMT, Diversified Modes of Transmission; II, Interactivity of Integration; VCD, Visual Communication Design; RI, Resistance to Innovative Change.
Measurement model assessment
The PLS measurement model is highlighted in Figure 3 . In this step of data analysis, reliability and validity are considered. While considering the reliability, this study preferred to examine factor loadings and composite reliability (CR). According to the literature, factor loadings must not be less than 0.7 ( Hameed, 2020 , 2021 ; Hair et al., 2021 ). Results shown in Table 2 highlighted that all the scale items have factor loading higher than 0.7.

Measurement model. VED-IT, Visual Expression Design with IT; FL, Flexible Layout; DMT, Diversified Modes of Transmission; II, Interactivity of Integration; VCD, Visual Communication Design; RI, Resistance to Innovative Change.
Factor loadings, reliability, and convergent validity.
Furthermore, composite reliability (CR) is reported in Table 2 . It must be higher than 0.7 for all variables. This study achieved the minimum level of CR, as shown in Table 2 . Additionally, to check the convergent validity, this study preferred the average variance extracted (AVE), which must be higher than 0.5. AVE higher than 0.5 confirmed the convergent validity, as shown in Table 2 .
Finally, in the measurement model, this study considered discriminant validity, which is essential before examining the relationship between variables. Two methods are used to confirm the discriminant validity. First, the heterotrait-monotrait ratio of correlations (HTMT) 0.9 is considered because all the values must not be higher than 0.9. HTMT is highlighted in Table 3 . AVE square root is considered, which is highlighted in Table 4 .
Discriminant validity (HTMT).
Discriminant validity (AVE Square Root).
Structural model assessment
The structural model examines the relationship between visual expression design with IT, flexible layout, diversified modes of transmission, interactivity of integration, visual communication design, and resistance to innovative change. Figure 4 shows the structural model assessment, and the results are reported in Table 5 . This study considered a t-value of 1.96 to accept the hypotheses. Results show that visual expression design with IT positively affects visual communication design with a t-value of 9.808. A flexible layout positively affects visual communication design with a t-value of 5.445.

Structural model.
Furthermore, diversified transmission modes also positively affect visual communication design with a t-value of 5.544. Similarly, interactivity of integration positively affects visual communication design with a t-value of 2.659. However, resistance to innovative change harms visual communication design, with a t-value of 14.943.
Moreover, this study examined the moderating role of resistance to innovative change. The moderating role of resistance to innovative change between visual expression design with IT and visual communication design is significant, with a t-value of 3.41. However, the moderating role of resistance to innovative change between flexible layout and visual communication design is insignificant. The moderating role of resistance to innovative change between diversified modes of transmission and visual communication design is significant, with a t-value of 2.364. Finally, the moderating role of resistance to innovative change between interactivity of integration and visual communication design is insignificant. The moderating effect of resistance to innovative change weakens the relationship between visual expression design with IT and visual communication design, as shown in Figure 5 . Additionally, the moderating effect of resistance to innovative change weakens the relationship between diversified modes of transmission and visual communication design, as shown in Figure 6 .

Moderating effect of resistance to innovative change weakens the relationship between visual expression design with IT and visual communication design.

Moderating effect of resistance to innovative change weakens the relationship between diversified modes of transmission and visual communication design.
Discussion and conclusion
The current study examined the relationship between visual expression design with IT, flexible layout, diversified modes of transmission, interactivity of integration, visual communication design, and resistance to innovative change. Nine hypotheses are proposed, including the five direct and four moderating effect hypotheses. After collecting data by using a questionnaire survey, PLS-SEM is employed to examine the relationship between variables.
Hypothesis 1 highlighted the significant and positive relationship between visual expression design with IT and visual communication design. It shows that introducing visual expression design with IT among the educational intuitions can improve the visual communication design. In line with these results, previous studies also highlighted that IT is essential in visual communication design ( Andriyan and Anesti, 2020 ; Wu and Li, 2020 ; Guan and Wang, 2022 ). Hypothesis 2 considered the relationship between flexible layout and visual communication design. A positive and significant relationship was found between flexible layout and visual communication design. A better flexible layout has the potential to promote visual communication design.
Along with the current study, Yue (2020) highlighted the central role of layout in visual communication. According to Yue (2020) , innovation in layout can promote visual communication design. Hypothesis 3 investigated the relationship between diversified modes of transmission and visual communication design. Similar to other hypotheses, this hypothesis is significant and positive, showing that diversified transmission modes have a positive role in influencing visual communication in educational institutions in China. Hypothesis 4 is also significant and positive, highlighting the positive role of interactivity of integration in visual communication. Thus, the adoption of innovative applications related to the interactivity of integration and diversified modes of transmission in visual communication design is influential among institutions, also supported by Yue (2020) . Finally, while examining direct effect, hypothesis 5 indicated a relationship between resistance to innovative change and visual communication design. According to the results, resistance by individuals toward adopting innovative change has a negative role in visual communication.
Furthermore, the current study proposed five hypotheses regarding the moderating role of resistance to innovative change. Hypothesis 6 shows the moderating role of resistance to innovative change between visual expression design with IT and visual communication design. The moderating effect of resistance to innovative change weakens the relationship between visual expression design with IT and visual communication design. It shows that the increase in the level of resistance by the employees, teachers, and students in the educational institutions of China can lead to a decrease in the effect of innovative application of new media. Hypothesis 7 is not supported. However, hypothesis 8 shows the moderating role of resistance to innovative change between diversified modes of transmission and visual communication design. Results show that moderating effect of resistance to innovative change weakens the relationship between diversified modes of transmission and visual communication design. Therefore, the innovative application of new media cannot lead to visual communication in the presence of resistance to innovative change. Hypothesis 9 is not supported. Finally, the study results show that innovative applications of new media such as visual expression design with IT, flexible layout, diversified modes of transmission, interactivity of integration, and visual communication design can expedite visual communication among Chinese educational institutions. However, resistance from the employees, teachers, and students to adopt innovative change may decrease the effectiveness of new media applications.
Theoretical implications
The current study addressed the vital part of the literature gap by considering the role of innovative applications of new media in visual communication design. Therefore, this study has important theoretical implications. First, this study addressed the visual communication design of the new media rather than traditional media, which is not addressed by earlier studies. Second, this study focused on the innovative applications of media, which are rarely studied in the literature. Third, although few studies addressed visual expression design with IT, flexible layout, diversified modes of transmission, and interactivity of integration, earlier studies have not considered these elements of the educational institutions. Mainly, the educational institutions of China are ignored by the previous studies. Four, several studies investigated visual communication design through different dimensions. However, previous studies have not employed PLS-SEM. Therefore, this study contributed methodologically to the field of visual communication design by using a new data analysis tool. Five, this study introduced resistance to innovative change as moderating variable, which is not considered by previous studies.
Practical implications
The results of this study provided several insights for the practitioners to promote communication methods among educational institutions. This study highlighted the ignored part of the literature, therefore, this study has vital practical implications. First, as traditional media in visual communication design is lacking in performance, this study proposed innovative applications of new media that can foster visual communication performance. Second, the study results are helpful for the educational institutions of China to enhance communication methods which may strengthen the relationship between teachers and students, leading to better learning. Third, the study outcomes provided several insights for the practitioners to enhance visual communication by focusing on visual expression design with IT, flexible layout, diversified modes of transmission, and interactivity of integration. Four, the management of educational institutions must reduce the resistance to adopting innovation to foster visual communication among educational institutions in China. Educational institutions’ employees, teachers, and students should adopt innovative visual communication changes.
Limitations and recommendations
The study’s shortcomings are due to the small sample size, which may make it difficult to generalize the results. Future research may thus evaluate the findings using a bigger sample size. Employees and educators from Chinese educational institutions were included in the research. In comparison to the 500 surveys issued, only 225 were returned. It demonstrates that respondents had little interest in taking part in the study. Therefore, metrics that can entice respondents to participate in the study can be included in subsequent research. Additionally, this study might be conducted among staff members at institutions of higher learning that do not provide instruction. As predictive factors for visual communication design, flexible layout, transmission methods, and interactivity of integration have been employed. To get more understanding findings on the aspects that might influence the visual communication design, this model can be modified with additional variables. Future research might also examine how visual communication designs relate to mobile APP interfaces. Future research might also look at how user behavior and technology adoption play a mediating effect. A language barrier may be a moderator in a future study on visual communication designs.
Data availability statement
Author contributions.
GY conceived the concept. SA designed the concept. GO collected the data. TK wrote the manuscript. KS read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
- Andriyan W., Anesti V. (2020). Visual audio communication design on the role of information technology on student life style of universitas raharja. ADI J. Recent Innov. 2 15–24. [ Google Scholar ]
- Arsyadi R. (2019). “ Innovation in classroom–application of design thinking in visual communication design class at higher education ,” in Proceeding of the International Conference on Visual Culture and Urban Life , Jakarta. [ Google Scholar ]
- Bezruk V. M., Bukhanko A. N., Chebotaryova D., Varich V. V. (2012). “ Multicriteria optimization in telecommunication networks planning, designing and controlling ,” in Telecommunications networks , ed. Ortiz J. H. (London: IntechOpen; ), 251–274. [ Google Scholar ]
- Blin F., Munro M. (2008). Why hasn’t technology disrupted academics’ teaching practices? Understanding resistance to change through the lens of activity theory. Comput. Educ. 50 475–490. [ Google Scholar ]
- Cebollada S. (2021). A state-of-the-art review on mobile robotics tasks using artificial intelligence and visual data. Expert Syst. Appl. 167 : 114195 . [ Google Scholar ]
- Chen H., Zheng X. (2021). Application of traditional culture based on computer technology in modern visual communication design. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1744 : 032094 . [ Google Scholar ]
- Cheng L. (2019). Convolutive blind source separation in frequency domain with kurtosis maximization by modified conjugate gradient. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 134 : 106331 . [ Google Scholar ]
- Demuyakor J. (2020). Coronavirus (COVID-19) and online learning in higher institutions of education: a survey of the perceptions of Ghanaian international students in China. Online J. Commun. Media Technol. 10 : e202018 . [ Google Scholar ]
- Duan B. (2022). Refining the application of construal level theory: egocentric and nonegocentric psychological distances in climate change visual communication. Environ. Commun. 16 92–107. [ Google Scholar ]
- Emans D., Murdoch-Kitt K. M. (2018). “ Connective methodologies: visual communication design and sustainability in higher education ,” in Handbook of Sustainability and Social Science Research , eds Filho W. L., Marans R. W., Callewaert J. (Berlin: Springer; ), 83–105. 10.1186/s12868-016-0283-6 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Erickson A. (2020). “ A review of visual perception research in optical see-through augmented reality ,” in International Conference on Artificial Reality and Telexistence Eurographics Symposium on Virtual Environments , eds Argelaguet F., Sugimoto M., McMahan R. (Orlando, FL: University of Central Florida; ), 27–35. [ Google Scholar ]
- Flückiger Y. (2021). The conditions for higher education institutions to meet the social challenges ahead. J. High. Educ. Policy Leadersh. Stud. 2 120–129. [ Google Scholar ]
- Friedman N., Ormiston J. (2022). Blockchain as a sustainability-oriented innovation?: opportunities for and resistance to Blockchain technology as a driver of sustainability in global food supply chains. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 175 : 121403 . [ Google Scholar ]
- Frost R. (2019). Progress in public health risk communication in China: lessons learned from SARS to H7N9. BMC Public Health 19 ( Suppl. 3 ):475. 10.1186/s12889-019-6778-1 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gao J. (2015). Multi-frequency optical unidirectional transmission based on one-way guided mode resonance in an extremely simple dielectric grating. Opt. Commun. 355 137–142. [ Google Scholar ]
- Goransson K., Fagerholm A.-S. (2018). Towards visual strategic communications: an innovative interdisciplinary perspective on visual dimensions within the strategic communications field. J. Commun. Manag. 22 46–66. [ Google Scholar ]
- Guan X., Wang K. (2022). Visual communication design using machine vision and digital media communication technology. Wirel. Commun. Mobile Comput. 2022 : 6235913 . [ Google Scholar ]
- Guan-Chen L., Ko C.-H. (2022). Visual communication design and wireless data transmission technology for blockchain big data information presentation. Wirel. Commun. Mobile Comput. 2022 : 138 0387 . [ Google Scholar ]
- Haapala K. (2022). Utilizing Different Design Principles for Hard-Surface 3D Art: a Study about Achieving Realistic 3D Mechanical designs. Tampere: Tampere University of Applied Sciences. [ Google Scholar ]
- Haddou H., Benyoucef L. (2019). Machine layout design problem under product family evolution in reconfigurable manufacturing environment: a two-phase-based AMOSA approach. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 104 375–389. [ Google Scholar ]
- Hair C. (2020). Assessing measurement model quality in PLS-SEM using confirmatory composite analysis. J. Bus. Res. 109 101–110. [ Google Scholar ]
- Hair J. F., Astrachan C. B., Moisescu O. I., Radomir L., Sarstedt M., Vaithilingam S., et al. (2021). Executing and interpreting applications of PLS-SEM: updates for family business researchers. J. Fam. Bus. Strategy 12 : 100392 . [ Google Scholar ]
- Hameed H.-C. (2021). Relationships between external knowledge, internal innovation, firms’ open innovation performance, service innovation and business performance in the Pakistani hotel industry. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 92 : 102745 . [ Google Scholar ]
- Hameed K. (2020). Determinants of micro-enterprise success through microfinance institutions: a capital mix and previous work experience. Int. J. Bus. Soc. 21 803–823. [ Google Scholar ]
- Haotian L. (2020). Visual communication design elements of Internet of Things based on cloud computing applied in graffiti art schema. Soft Comput. 24 8077–8086. [ Google Scholar ]
- Huang L. (2020). Guidance on Flexible Learning during Campus Closures: Ensuring Course Quality of Higher Education in COVID-19 Outbreak. Beijing: Smart Learning Institute of Beijing Normal University. [ Google Scholar ]
- Huang M. (2021). “ Research on the application strategy of mixed teaching mode of visual communication design specialty in colleges and universities based on multidimensional interaction ,” in Paper Presented at the 2021 International Conference on Tourism, Economy and Environmental Sustainability , (Guangzhou: South China Normal University; ). [ Google Scholar ]
- Huang W. (2020). Handbook on Facilitating Flexible Learning During Educational Disruption: The Chinese Experience in Maintaining Undisrupted Learning in COVID-19 Outbreak. Beijing: Smart Learning Institute of Beijing Normal University, 46. [ Google Scholar ]
- Huang Z., Zhou W. (2022). Study on the construction of integrating regional characteristics into the talent training program of universities–taking the visual communication design major of jingdezhen ceramic university as an example. Int. J. Soc. Sci. Educ. Res. 5 37–43. [ Google Scholar ]
- Ji S., Lin P.-S. (2022). Aesthetics of sustainability: research on the design strategies for emotionally durable visual communication design. Sustainability 14 : 4649 . [ Google Scholar ]
- Jia C. (2017). “ Study on the ways of cultivating information design consciousness in visual communication design education ,” in Proceedings of the 2017 2nd International Conference on Education and Education Research (EDUER2017) (London: Francis Academic Press; ). [ Google Scholar ]
- Kaur A. (2020). An innovation resistance theory perspective on mobile payment solutions. J. Retail. Consum. Serv. 55 : 102059 . [ Google Scholar ]
- Kim J., Lee K. H. (2019). Influence of integration on interactivity in social media luxury brand communities. J. Bus. Res. 99 422–429. [ Google Scholar ]
- King M. (2007). How innovation can alleviate negative consequences of demanding work contexts: the influence of climate for innovation on organizational outcomes. J. Occup. Organ. Psychol. 80 631–645. [ Google Scholar ]
- Koch S. (2021). Exploring passive innovation resistance—an empirical examination of predictors and consequences at the cognitive and situational level. Int. J. Innov. Manag. 25 : 2150012 . [ Google Scholar ]
- Kostis P. (2018). Cultural change and innovation performance. J. Bus. Res. 88 306–313. [ Google Scholar ]
- Kujur F., Singh S. (2020). Visual communication and consumer-brand relationship on social networking sites-uses & gratifications theory perspective. J. Theo. Appl. Electron. Commer. Res. 15 30–47. [ Google Scholar ]
- Lari M., Gandomani Z. K. (2022). Effective capacity maximization of two-way full-duplex and half-duplex relays with finite block length packets transmission. arXiv [Preprint] 10.48550/arXiv.2201.02774 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Liang S. (2021). Research on emotional factors and emotional experience of information graphic design in visual communication design. Acad. J. Comput. Inf. Sci. 4 7–10. [ Google Scholar ]
- Liu C. (2020). The development trend of visual communication design. Front. Art Res. 2 83–87. 10.25236/FAR.2020.020915 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Liu R. (2017). Hybrid half-duplex/full-duplex cooperative non-orthogonal multiple access with transmit power adaptation. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 17 506–519. [ Google Scholar ]
- Liu Y. (2018). “ Research on the innovative development of multimedia technology and visual communication design teaching ,” in Proceedings of the 2018 2nd International Conference on Economic Development and Education Management (ICEDEM 2018) , Dalian. 10.1002/bmb.21034 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Matusitz J. M. (2005). The current condition of visual communication in colleges and universities of the United States. J. Vis. Lit. 25 97–112. [ Google Scholar ]
- Naveed K. (2022). Do organizations really evolve? The critical link between organizational culture and organizational innovation toward organizational effectiveness: pivotal role of organizational resistance. J. Innov. Knowl. 7 : 100178 . [ Google Scholar ]
- Ozkan J. (2021). Movement and engagement in flexible, technology-enhanced classrooms: investigating cognitive and emotional engagement from the faculty perspective. Learn. Environ. Res. 25 359–377. [ Google Scholar ]
- Phoon S. Y. (2018). Modelling and Simulation of Spine Layout Design for Flexible Manufacturing System in Digital Factory Platform/Phoon Sin Ye. Lumpur: University of Malaya. [ Google Scholar ]
- Pourvaziri H., Salimpour S., Niaki S. T. A., Azab A. (2021). Robust facility layout design for flexible manufacturing: a doe-based heuristic . Int. J. Prod. Res. 59 , 1–22. 10.1080/00207543.2021.1967500 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Raposo D. (2018). Communicating Visually: the Graphic Design of the Brand. Newcastle upon Tyne: Cambridge Scholars Publishing. [ Google Scholar ]
- Russmann A. O. (2019). “ Political parties and their pictures: visual communication on Instagram in Swedish and Norwegian election campaigns ,” in Visual Political Communication , eds Veneti A., Jackson D., Lilleker D. (Cham: Springer; ), 119–144. [ Google Scholar ]
- Saris B. (2020). A review of engagement with creativity and creative design processes for Visual Communication Design (VCD) learning in China. Int. J. Art Des. Educ. 39 306–318. [ Google Scholar ]
- Shahbaz Y. (2019). Investigating the adoption of big data analytics in healthcare: the moderating role of resistance to change. J. Big Data 6 1–20. [ Google Scholar ]
- Sumual G. J. (2021). GUI application to setup simple graph on the plane using tkinter of python. d’CARTESIAN 10 8–14. [ Google Scholar ]
- Talidong K. J. B., Toquero C. M. D. (2021). Facing COVID-19 through emergency online education anchored in Khan’s framework: case of Philippine teachers in Xi’an, China. Eur. J. Interact. Multimed. Educ. 2 : e02104 . [ Google Scholar ]
- Talwar A. (2020). Consumers’ resistance to digital innovations: a systematic review and framework development. Australas. Mark. J. 28 286–299. [ Google Scholar ]
- Turnbull L. (2021). Transitioning to E-learning during the COVID-19 pandemic: how have Higher Education Institutions responded to the challenge? Educ. Inf. Technol. 26 6401–6419. 10.1007/s10639-021-10633-w [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Vakulenko A. (2021). The first step in removing communication and organizational barriers to stakeholders’ interaction in smart grids: a theoretical approach. E3S Web Conf. 234 : 00020 . [ Google Scholar ]
- Vasylevska K. (2013). “ Flexible spaces: dynamic layout generation for infinite walking in virtual environments ,” in Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Symposium on 3D User Interfaces (3DUI) , (Orlando, FL: IEEE; ). [ Google Scholar ]
- Wang J., Hsu Y. (2020). The relationship of symmetry, complexity, and shape in mobile interface aesthetics, from an emotional perspective—a case study of the smartwatch. Symmetry 12 : 1403 . [ Google Scholar ]
- Wang P. (2021). Research on the application of artificial intelligence in the innovative development of visual communication design education. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1744 : 032196 . 10.3390/s20072093 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wu H., Li G. (2020). Innovation and improvement of visual communication design of mobile app based on social network interaction interface design. Multimed. Tools Appl. 79 1–16. [ Google Scholar ]
- Wu Y. (2019). “ Research on the training model of innovative talents in visual communication design specialty ,” in Proceedings of the 2nd International Workshop on Education Reform and Social Sciences (ERSS 2019) , Chengdu. [ Google Scholar ]
- Wu Z.-N. (2021). The impact of internet development on the health of Chinese residents: transmission mechanisms and empirical tests. Socioecon. Plann. Sci. 81 : 101178 . [ Google Scholar ]
- Xiangwei B. (2022). Research on the path of integrating regional culture into the ideological and political education of visual communication design curriculum from the perspective of core literacy. High. Educ. Soc. Sci. 22 47–51. [ Google Scholar ]
- Xie J. (2022). “ Research on the talent training mode for visual communication design—based on intelligent computing via project in studio project ,” in Innovative Computing. Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering , Vol. 791 eds Hung J. C., Chang J. W., Pei Y., Wu W. C. (Berlin: Springer; ), 597–604. [ Google Scholar ]
- Yadav A., Prakash A. (2022). Factors influencing sustainable development integration in management education: an Empirical Assessment of management education institutions in India. Int. J. Manag. Educ. 20 : 100604 . [ Google Scholar ]
- Yan C. (2012). ‘We can only change in a small way’: a study of secondary English teachers’ implementation of curriculum reform in China. J. Educ. Change 13 431–447. [ Google Scholar ]
- Yanarates C., Zhou Z. (2021). Symmetrical pole placement method-based unity proportional gain resonant and gain scheduled proportional (PR-P) controller with harmonic compensator for single phase grid-connected PV inverters. IEEE Access 9 93165–93181. [ Google Scholar ]
- Yang C.-M., Hsu T.-F. (2017). New perspective on visual communication design education: an empirical study of applying narrative theory to graphic design courses. Int. J. High. Educ. 6 188–198. [ Google Scholar ]
- Yue W. (2020). Research on innovative application of new media in visual communication design. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1550 : 032146 . [ Google Scholar ]
- Zahlbruckner M. A. (2021). Lntegrating Production Layout Planning into Structural Design for Flexible Lndustrial Buildings. Vienna: Technische Universität Wien. [ Google Scholar ]
- Zhang H., Wu C. (2021). An analysis of computer-aided design software course teaching in visual communication design major by integrating grey variable weight clustering evaluation model. Adv. Multimed. 2021 : 6588734 . [ Google Scholar ]
- Zhou Y., Zheng Y., Pan J., Sui L., Xing F., Sun H., et al. (2019). Experimental investigations on corrosion resistance of innovative steel-FRP composite bars using X-ray microcomputed tomography. Compos. B Eng. 161 272–284. [ Google Scholar ]
Ohio State nav bar
Ohio state navigation bar.
- BuckeyeLink
- Search Ohio State
Visual Communication Design

The practice of visual communication design at The Ohio State University includes exposure to the many areas of specialization offered by this complex and dynamic profession. Students learn to employ human-centered research approaches to inform development of brand identity, environmental way-finding, publication, packaging, interactive, web/mobile, and data visualization systems. Courses integrate a variety of advanced computing and digital media tools that enable students to develop highly-refined visual communications that meet or exceed professional standards. The program culminates in final projects that demonstrate students' abilities to develop solutions that address four design themes: education and learning; health and wellness; history, culture, and technology; and social impact. Projects are displayed in our annual spring exhibit that includes events to acknowledge the achievements of our graduating students.
Curriculum and Course Sequence
All required 2100 and 2300 series courses in the Design Foundations Program must be taken in an exact sequence, as they are offered only once per academic year and each course is a required prerequisite for the following courses. Any student failing a required course will be removed from the foundations program and be required to stop the course sequence.
DESIGN 2110: Design Fundamentals I
DESIGN 2310: Visual Principles and Techniques I
DESIGN 2700: Introduction to Design Practice OR DESIGN 2750: Design History
DESIGN 2130: Design Fundamentals II
DESIGN 2330: Visual Principles and Techniques II
This Design Foundations sequence begins with a competitive selection process to become a design foundations student and concludes with a portfolio-based major admissions review process.
Apply the Design Foundations Program!
DESIGN 3103: Introduction to Visual Communication Design I
DESIGN 3200: Design Research I
DESIGN 3403: Design Media I for Visual Communication Design
DESIGN 3503: Typographic Design
DESIGN 3153: Introduction to Visual Communication Design II
DESIGN 3453: Design Media II for Visual Communication Design
DESIGN 3553: Materials, Process, and Production for Visual Communication Design
DESIGN 4103: Intermediate Visual Communication Design I
DESIGN 4200: Design Research II
DESIGN 4403: Design Media III for Visual Communication Design
DESIGN 4153: Intermediate Visual Communication Design II
DESIGN 4650: Collaborative Design
DESIGN 4750: Professional Practices
DESIGN 5103: Advanced Visual Communication Design I
DESIGN 5203: Design Research III for Visual Communication Design
DESIGN 5803: Design Seminar for Visual Communication Design
DESIGN 5453: Design Media IV for Visual Communication Design
DESIGN 5650: Advanced Collaborative Design
Technology Requirements
Students in the Department of Design at The Ohio State University are required to have their own laptop computers after being admitted into one of our major programs. We do not make recommendations of specific computers, but students pursuing a major in Visual Communication Design will need a machine that is capable of meeting the technology specifications of the following softwares:
- Microsoft Office 365
- Adobe Creative Cloud

Students should check with The Office of the CIO prior to purchasing software for site licensed software that is available at discounted prices for students.
Students should check Tech Hub for prices.
Tech Hub is the Ohio State campus computer store. Get software and hardware at or below academic discounted pricing. They work with students, faculty and staff for personal and departmental orders. A variety of Apple, Dell and HP hardware is available including laptops, iPads, tablets, desktops, accessories and add-ons. A variety of software is available including Microsoft, Adobe, EndNote/Reference Manager and more. Tech Hub prices extended to students, faculty and staff with a valid Ohio State BuckID.
Student Portfolios
This voluntary listing of digital portfolios represents our current students' professional preparation at varying levels of experience. It also provides insight into some of the learning experiences provided by courses in our program.
Looking to hire a Design student?
Prospective employers may reach out to students directly about freelance employment opportunities. Employers seeking to hire for internships and/or full-time opportunities are encouraged to work with the Center for Career and Professional Success to post openings via Handshake.
Allie Rhule Christian Robinson Ellie Armstrong Emma Peters Jane Zucker Kathryn Keverkamp Keyah Madaris Mackie Herrlinger Mary Gibson McKenzy Connelly Nola Valerian Olivia Knight Philip Cress Ran Ren Shaylee Shepherd
Abby Giesecke Alex Horton Bekka Ranalli Brianna Gallagher Ciera Yamarick Dana Richardson Dawson Estep Giulia Blake Kayla Eastman Keyah Madaris Levi Gaidos Lilyana Bryan Lucy Vidmar Mekayla Gladman Melina Oliver
Athira Vasudevan Bryce Patterson Carter Teal Dawson Estep Delaney Brown Elaine Smith Liann Trahey Megan Feeney
Ananya Muddappa Anastasia Allison Elizabeth Howes Isabel Nixon Jada Davis Phillip Biondo Suyeon Chae
Gain Experiences & Discover Your Passion
Opportunities to become fully engaged in an experience are instrumental to discovering your passion. Internships will give you the experience you need to differentiate yourself from other candidates, support your career goals, contribute to your skill set and determine how your career exploration process and focus may need to be modified to support your long-term goals. Employers are looking for graduates that have already taken the next step to becoming professionals in their field.

Internship Spotlight
Lucy Vidmar
Lucy joined Verint as the Sales Enablement Content Marketing Intern and experienced working for a global company and leader of innovative technologies.

- Chute Gerdeman
Lydia spent the summer as a Brand Communication Intern at Chute Gerdeman, a strategic design firm based in Westerville, OH.

Nola Valerian
Nola spent her summer on the team at Outbrain, a web recommendation platform based in Ljubljana, Slovenia.
Career Prospects in Visual Communication Design
Students graduating with a Bachelor of Science in Design take positions with design consulting offices, corporate design departments, and government design agencies.
The work of design occurs in either the context of consultant design, where independent design firms provide services to clients, or in the context of corporate, governmental, or non-governmental/not-for-profit design, where design services are provided within an organization.
Consultant design offices can be as small as one person -- an office of 15-20 people is considered relatively large -- and the largest might employ 100 or more. Consultant offices may specialize in one design discipline, or even a subcategory of that specialty. Consultant offices can also be multidisciplinary, and employ designers from all categories, as well as engineers, researchers, marketing and human factors experts, etc.
Corporate design groups exist in all major industries, and employ designers of all disciplines. Organizations that place emphasis on public communications typically maintain a visual communication design department.
Design offers many opportunities for a challenging career. Many designers begin with project work, and advance to research, coordination and management. Planning activities often place designers in the role of analyzing business trends, and establishing strategic goals for design activities. Many organizations value the contributions designers make to their businesses, and provide good opportunities for advancement.
Who hired our graduates?
- Bits and Bops
- OSU Office of Student Life
- The Ohio State University Department of Athletics
- Augment Therapy
- Sketch Blue
- GM Industrial LLC
- Pratt Institute
- Mountain TOP
- McDougald Research
- Push Digital
- Moen Incorporated
- Esports Foundry
- JPMorgan Chase & Co.
- The Ohio State University Engineering Career Services
- Publicis Sapient
- Holden Ellis
- wearesad.co
- The Pivot Group
- ZoCo Design
- Kinopicz American
- Crown Equipment Corporation
- Owens Corning
- ERM: Environmental Resources Management
- Self-Employed Freelance
- Wildflower Press + Paper
- Become Known
- Continental Office
- The Ohio State University College of Nursing
- The New Jersey Digest
- Next Day Signs
- ArtCenter College of Design
- Destination Pet, LLC
- National Low Income Housing Coalition
- Corporate One Federal Credit Union
- WD Partners
- Financial Cornerstone Inc.
- Involve, LLC
- American Electric Power
- Gilbane Building Company
- Rocky Brands, Inc.
- Kolar Design
- Creative Spot
- Chepri, LLC
- Impact Communications
- The Walt Disney Company
- T-CETRA, LLC
- Ikove Capital
- Profashion Hair Styling Tools
- Ohio REALTORS
- Influenster
- Esse Soap Co.
- King Business Interiors
- Walt Disney Imagineering
- Inst Study of Race & Ethnicity, The Ohio State University
- Revolution Experiment
- College of Arts and Sciences Marketing & Communications
- Design Central
- Make You, LLC
- Scotts Miracle-Gro
- Jump Goat Media
- McGraw-Hill Education

Professional Organizations
Professional organizations play an important role in the development of design disciplines and provide valuable resources to their student and professional members. The following organizations are all relevant to Visual Communication Design.
American Institute of Graphic Arts (AIGA) Columbus Society of Communicating Arts (CSCA) Interaction Design Association (IxDA) Society for Environmental Graphic Design (SEGD) Usability Professionals Association (UPA)
Learn more in the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics Occupational Outlook Handbook

Alumni Spotlight: Amanda Buck
BSD - Visual Communication Design, 2008
- Senior Designer at Ashton Design
- Adjunct Professor at Maryland Institute College of Art
- Designer at Studio of Amanda Buck
Amanda Buck is a designer and educator based in Baltimore, MD. She shapes brands and visually communicates stories through digital designs and printed matter. She strives to create timeless work with strong visual order, effective typographic details, and a forward-looking point of view. Whether it’s a web site or a book, she loves taking complex ideas and distilling them into intelligent, approachable, and straight-forward solutions. She believes in a human-centered approach to her work and enjoys collaborating with organizations with purpose to create positive social impact.

COMMENTS
Visual Communication provides an international forum for the growing body of work in numerous interrelated disciplines. Its broad coverage includes: still and moving images; graphic design and typography; visual phenomena such as fashion, professional vision, posture and interaction; the built and landscaped environment; the role of the visual in relation to language, music, sound and action.
1 An overview of research methods 2 in visual communication design education. 3 The article presents a review of studies done on research in visual 4 communication design education. It examines the use of research in 5 postgraduate and undergraduate programmes, and evaluates the debate over 6 research methods applicable to the field. The article includes an overview of
About the Journal. The journal of visual communication research. Visible Language supports the community of communication design scholars, researchers, and practitioners through the publication of rigorous, relevant communication design research. Visible Language is published three times a year: April, August, and December.
research methods applicable to the field. The article includ es an overview of. 6. commonly-used methods for visual comm unication design education such as. 7. Action Research and Reflective ...
Abstract. The article presents a review of studies done on research in visual communication design education. According to reviews, the design practice in visual communication design education has shifted from an emphasis on training in traditional vocational courses to a focus on research being integral to the course; this prompted this article to examine the use of research in postgraduate ...
The new media technological advent has changed the ways of communication by changing the life aspect, day to day living, study and work. This paper aims at study of dynamic visual communication design applications in digital media environment. This work analyzes the basic design elements application form of text in dynamic visual communication, to provide a research reference in other dynamic ...
Photojournalism and Design academic tracks are common at universities around the world. Several factors have led to the expansion of visual communication ... tity and quality of visual communication research. While much research continues to be descriptive, many new scholars are conduct-ing studies involving rigorous research methods.
Arsyadi (2019) discussed visual communication design in classrooms to facilitate instructors teaching at educational institutions. Huang and Zhou (2022) conducted a research study on visual communication design by considering the training program of universities. All these studies highlighted the essential findings and provided several ...
ABSTRACT. Visual Communication Research Designs provides a step-by-step guide for designing research involving visuals relevant to communications media. This volume explains the process from conceptualization to research questions, instrumentation, analysis, and reliability and validity checks. It also addresses the lack of sufficient methods ...
Visual Communication Research Designs provides a step-by-step guide for designing research involving visuals relevant to communications media. This volume explains the process from conceptualization to research questions, instrumentation, analysis, and reliability and validity checks. It also addresses the lack of sufficient methods to answer theoretical questions attending visual ...
The Journal of Visual Communication and Image Representation publishes papers on state-of-the-art visual communication and image representation, with emphasis on novel technologies and theoretical work in this multidisciplinary area of pure and applied research. The field of visual communication and image representation is considered in its broadest sense and covers both digital and analog ...
Research in communication design; Visual thinking; 1 Introduction. The present article corresponds to a component of a research project about design and project methodologies in communication design research field. This research emerges because of the struggle in assess a detailed holistic view about the projects and his components, namely the ...
Introduction. For a scientist, the ability to communicate science is crucial 1.Recently, a proliferation of science communication training opportunities has appeared in the USA, the UK, and beyond 2-4.These opportunities are usually for professional science communicators; however, "communication" has now become well accepted as a desired component of tertiary science education.
This article examines the use of research in postgraduate and undergraduate programs and evaluates the debate over research methods applicable to the field and provides a brief overview on the nature of problem in undergraduate studies. The article presents a review of studies done on research in visual communication design education. According to reviews, the design practice in visual ...
Abstract. Visual Communication Research Designs provides a step-by-step guide for designing research involving visuals relevant to communications media. This volume explains the process from ...
Renowned Visual Communication Design faculty represent the diversity of contemporary design practice, research, and pedagogy with thriving practices both self-initiated and client-associated, physical and virtual, and individual and collaborative. Students are presented with a rich array of tools and ideas and work with faculty to broaden and ...
Visual communication is defined as the action of delivering a message using images and involves the role of images in influencing people (Günay, 2021). Based on psychological ideology, the ...
Implementing insights into their research practices and/or visual communication design artifacts may open horizons within innovative or even collaborative research projects. Both fields, visual anthropology and visual communication, are trying to contribute to a specific common concern in deaf education-namely, the educational context of ...
The maturity of digital technology makes the digital expression of visual communication design a new trend in the field of visual communication design. The digitalization of visual communication design has prompted designers to design through multidisciplinary cross-thinking and multiple design methods, and design strategies and thinking are ...
Researchers and/or designers in visual anthropology and visual communication share the visual aspect or visual study as a common interest. However, their views are different. Visual anthropologists consider the social impact and/or meaning of the visual communication within a culture. They are also interested in ways to present anthropological data by means of visual techniques.
Arsyadi (2019) discussed visual communication design in classrooms to facilitate instructors teaching at educational institutions. Huang and Zhou (2022) conducted a research study on visual communication design by considering the training program of universities. All these studies highlighted the essential findings and provided several ...
The purpose of visual communication design is t o. ensure the effective transmission of information through. aesthetics. With the transformation of information. dissemination methods to the ...
The practice of visual communication design at The Ohio State University includes exposure to the many areas of specialization offered by this complex and dynamic profession. Students learn to employ human-centered research approaches to inform development of brand identity, environmental way-finding, publication, packaging, interactive, web/mobile, and data visualization systems.
Visual communication design is an integral part of art design, and image is one of the most important topics in art design research. Visual communication design is primarily defined as an artistic creation that employs visual symbols to convey various types of information using words, images, and colors as the primary components.