

Understanding Assignments
What this handout is about.
The first step in any successful college writing venture is reading the assignment. While this sounds like a simple task, it can be a tough one. This handout will help you unravel your assignment and begin to craft an effective response. Much of the following advice will involve translating typical assignment terms and practices into meaningful clues to the type of writing your instructor expects. See our short video for more tips.
Basic beginnings
Regardless of the assignment, department, or instructor, adopting these two habits will serve you well :
- Read the assignment carefully as soon as you receive it. Do not put this task off—reading the assignment at the beginning will save you time, stress, and problems later. An assignment can look pretty straightforward at first, particularly if the instructor has provided lots of information. That does not mean it will not take time and effort to complete; you may even have to learn a new skill to complete the assignment.
- Ask the instructor about anything you do not understand. Do not hesitate to approach your instructor. Instructors would prefer to set you straight before you hand the paper in. That’s also when you will find their feedback most useful.
Assignment formats
Many assignments follow a basic format. Assignments often begin with an overview of the topic, include a central verb or verbs that describe the task, and offer some additional suggestions, questions, or prompts to get you started.
An Overview of Some Kind
The instructor might set the stage with some general discussion of the subject of the assignment, introduce the topic, or remind you of something pertinent that you have discussed in class. For example:
“Throughout history, gerbils have played a key role in politics,” or “In the last few weeks of class, we have focused on the evening wear of the housefly …”
The Task of the Assignment
Pay attention; this part tells you what to do when you write the paper. Look for the key verb or verbs in the sentence. Words like analyze, summarize, or compare direct you to think about your topic in a certain way. Also pay attention to words such as how, what, when, where, and why; these words guide your attention toward specific information. (See the section in this handout titled “Key Terms” for more information.)
“Analyze the effect that gerbils had on the Russian Revolution”, or “Suggest an interpretation of housefly undergarments that differs from Darwin’s.”
Additional Material to Think about
Here you will find some questions to use as springboards as you begin to think about the topic. Instructors usually include these questions as suggestions rather than requirements. Do not feel compelled to answer every question unless the instructor asks you to do so. Pay attention to the order of the questions. Sometimes they suggest the thinking process your instructor imagines you will need to follow to begin thinking about the topic.
“You may wish to consider the differing views held by Communist gerbils vs. Monarchist gerbils, or Can there be such a thing as ‘the housefly garment industry’ or is it just a home-based craft?”
These are the instructor’s comments about writing expectations:
“Be concise”, “Write effectively”, or “Argue furiously.”
Technical Details
These instructions usually indicate format rules or guidelines.
“Your paper must be typed in Palatino font on gray paper and must not exceed 600 pages. It is due on the anniversary of Mao Tse-tung’s death.”
The assignment’s parts may not appear in exactly this order, and each part may be very long or really short. Nonetheless, being aware of this standard pattern can help you understand what your instructor wants you to do.
Interpreting the assignment
Ask yourself a few basic questions as you read and jot down the answers on the assignment sheet:
Why did your instructor ask you to do this particular task?
Who is your audience.
- What kind of evidence do you need to support your ideas?
What kind of writing style is acceptable?
- What are the absolute rules of the paper?
Try to look at the question from the point of view of the instructor. Recognize that your instructor has a reason for giving you this assignment and for giving it to you at a particular point in the semester. In every assignment, the instructor has a challenge for you. This challenge could be anything from demonstrating an ability to think clearly to demonstrating an ability to use the library. See the assignment not as a vague suggestion of what to do but as an opportunity to show that you can handle the course material as directed. Paper assignments give you more than a topic to discuss—they ask you to do something with the topic. Keep reminding yourself of that. Be careful to avoid the other extreme as well: do not read more into the assignment than what is there.
Of course, your instructor has given you an assignment so that they will be able to assess your understanding of the course material and give you an appropriate grade. But there is more to it than that. Your instructor has tried to design a learning experience of some kind. Your instructor wants you to think about something in a particular way for a particular reason. If you read the course description at the beginning of your syllabus, review the assigned readings, and consider the assignment itself, you may begin to see the plan, purpose, or approach to the subject matter that your instructor has created for you. If you still aren’t sure of the assignment’s goals, try asking the instructor. For help with this, see our handout on getting feedback .
Given your instructor’s efforts, it helps to answer the question: What is my purpose in completing this assignment? Is it to gather research from a variety of outside sources and present a coherent picture? Is it to take material I have been learning in class and apply it to a new situation? Is it to prove a point one way or another? Key words from the assignment can help you figure this out. Look for key terms in the form of active verbs that tell you what to do.
Key Terms: Finding Those Active Verbs
Here are some common key words and definitions to help you think about assignment terms:
Information words Ask you to demonstrate what you know about the subject, such as who, what, when, where, how, and why.
- define —give the subject’s meaning (according to someone or something). Sometimes you have to give more than one view on the subject’s meaning
- describe —provide details about the subject by answering question words (such as who, what, when, where, how, and why); you might also give details related to the five senses (what you see, hear, feel, taste, and smell)
- explain —give reasons why or examples of how something happened
- illustrate —give descriptive examples of the subject and show how each is connected with the subject
- summarize —briefly list the important ideas you learned about the subject
- trace —outline how something has changed or developed from an earlier time to its current form
- research —gather material from outside sources about the subject, often with the implication or requirement that you will analyze what you have found
Relation words Ask you to demonstrate how things are connected.
- compare —show how two or more things are similar (and, sometimes, different)
- contrast —show how two or more things are dissimilar
- apply—use details that you’ve been given to demonstrate how an idea, theory, or concept works in a particular situation
- cause —show how one event or series of events made something else happen
- relate —show or describe the connections between things
Interpretation words Ask you to defend ideas of your own about the subject. Do not see these words as requesting opinion alone (unless the assignment specifically says so), but as requiring opinion that is supported by concrete evidence. Remember examples, principles, definitions, or concepts from class or research and use them in your interpretation.
- assess —summarize your opinion of the subject and measure it against something
- prove, justify —give reasons or examples to demonstrate how or why something is the truth
- evaluate, respond —state your opinion of the subject as good, bad, or some combination of the two, with examples and reasons
- support —give reasons or evidence for something you believe (be sure to state clearly what it is that you believe)
- synthesize —put two or more things together that have not been put together in class or in your readings before; do not just summarize one and then the other and say that they are similar or different—you must provide a reason for putting them together that runs all the way through the paper
- analyze —determine how individual parts create or relate to the whole, figure out how something works, what it might mean, or why it is important
- argue —take a side and defend it with evidence against the other side
More Clues to Your Purpose As you read the assignment, think about what the teacher does in class:
- What kinds of textbooks or coursepack did your instructor choose for the course—ones that provide background information, explain theories or perspectives, or argue a point of view?
- In lecture, does your instructor ask your opinion, try to prove their point of view, or use keywords that show up again in the assignment?
- What kinds of assignments are typical in this discipline? Social science classes often expect more research. Humanities classes thrive on interpretation and analysis.
- How do the assignments, readings, and lectures work together in the course? Instructors spend time designing courses, sometimes even arguing with their peers about the most effective course materials. Figuring out the overall design to the course will help you understand what each assignment is meant to achieve.
Now, what about your reader? Most undergraduates think of their audience as the instructor. True, your instructor is a good person to keep in mind as you write. But for the purposes of a good paper, think of your audience as someone like your roommate: smart enough to understand a clear, logical argument, but not someone who already knows exactly what is going on in your particular paper. Remember, even if the instructor knows everything there is to know about your paper topic, they still have to read your paper and assess your understanding. In other words, teach the material to your reader.
Aiming a paper at your audience happens in two ways: you make decisions about the tone and the level of information you want to convey.
- Tone means the “voice” of your paper. Should you be chatty, formal, or objective? Usually you will find some happy medium—you do not want to alienate your reader by sounding condescending or superior, but you do not want to, um, like, totally wig on the man, you know? Eschew ostentatious erudition: some students think the way to sound academic is to use big words. Be careful—you can sound ridiculous, especially if you use the wrong big words.
- The level of information you use depends on who you think your audience is. If you imagine your audience as your instructor and they already know everything you have to say, you may find yourself leaving out key information that can cause your argument to be unconvincing and illogical. But you do not have to explain every single word or issue. If you are telling your roommate what happened on your favorite science fiction TV show last night, you do not say, “First a dark-haired white man of average height, wearing a suit and carrying a flashlight, walked into the room. Then a purple alien with fifteen arms and at least three eyes turned around. Then the man smiled slightly. In the background, you could hear a clock ticking. The room was fairly dark and had at least two windows that I saw.” You also do not say, “This guy found some aliens. The end.” Find some balance of useful details that support your main point.
You’ll find a much more detailed discussion of these concepts in our handout on audience .
The Grim Truth
With a few exceptions (including some lab and ethnography reports), you are probably being asked to make an argument. You must convince your audience. It is easy to forget this aim when you are researching and writing; as you become involved in your subject matter, you may become enmeshed in the details and focus on learning or simply telling the information you have found. You need to do more than just repeat what you have read. Your writing should have a point, and you should be able to say it in a sentence. Sometimes instructors call this sentence a “thesis” or a “claim.”
So, if your instructor tells you to write about some aspect of oral hygiene, you do not want to just list: “First, you brush your teeth with a soft brush and some peanut butter. Then, you floss with unwaxed, bologna-flavored string. Finally, gargle with bourbon.” Instead, you could say, “Of all the oral cleaning methods, sandblasting removes the most plaque. Therefore it should be recommended by the American Dental Association.” Or, “From an aesthetic perspective, moldy teeth can be quite charming. However, their joys are short-lived.”
Convincing the reader of your argument is the goal of academic writing. It doesn’t have to say “argument” anywhere in the assignment for you to need one. Look at the assignment and think about what kind of argument you could make about it instead of just seeing it as a checklist of information you have to present. For help with understanding the role of argument in academic writing, see our handout on argument .
What kind of evidence do you need?
There are many kinds of evidence, and what type of evidence will work for your assignment can depend on several factors–the discipline, the parameters of the assignment, and your instructor’s preference. Should you use statistics? Historical examples? Do you need to conduct your own experiment? Can you rely on personal experience? See our handout on evidence for suggestions on how to use evidence appropriately.
Make sure you are clear about this part of the assignment, because your use of evidence will be crucial in writing a successful paper. You are not just learning how to argue; you are learning how to argue with specific types of materials and ideas. Ask your instructor what counts as acceptable evidence. You can also ask a librarian for help. No matter what kind of evidence you use, be sure to cite it correctly—see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial .
You cannot always tell from the assignment just what sort of writing style your instructor expects. The instructor may be really laid back in class but still expect you to sound formal in writing. Or the instructor may be fairly formal in class and ask you to write a reflection paper where you need to use “I” and speak from your own experience.
Try to avoid false associations of a particular field with a style (“art historians like wacky creativity,” or “political scientists are boring and just give facts”) and look instead to the types of readings you have been given in class. No one expects you to write like Plato—just use the readings as a guide for what is standard or preferable to your instructor. When in doubt, ask your instructor about the level of formality they expect.
No matter what field you are writing for or what facts you are including, if you do not write so that your reader can understand your main idea, you have wasted your time. So make clarity your main goal. For specific help with style, see our handout on style .
Technical details about the assignment
The technical information you are given in an assignment always seems like the easy part. This section can actually give you lots of little hints about approaching the task. Find out if elements such as page length and citation format (see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial ) are negotiable. Some professors do not have strong preferences as long as you are consistent and fully answer the assignment. Some professors are very specific and will deduct big points for deviations.
Usually, the page length tells you something important: The instructor thinks the size of the paper is appropriate to the assignment’s parameters. In plain English, your instructor is telling you how many pages it should take for you to answer the question as fully as you are expected to. So if an assignment is two pages long, you cannot pad your paper with examples or reword your main idea several times. Hit your one point early, defend it with the clearest example, and finish quickly. If an assignment is ten pages long, you can be more complex in your main points and examples—and if you can only produce five pages for that assignment, you need to see someone for help—as soon as possible.
Tricks that don’t work
Your instructors are not fooled when you:
- spend more time on the cover page than the essay —graphics, cool binders, and cute titles are no replacement for a well-written paper.
- use huge fonts, wide margins, or extra spacing to pad the page length —these tricks are immediately obvious to the eye. Most instructors use the same word processor you do. They know what’s possible. Such tactics are especially damning when the instructor has a stack of 60 papers to grade and yours is the only one that low-flying airplane pilots could read.
- use a paper from another class that covered “sort of similar” material . Again, the instructor has a particular task for you to fulfill in the assignment that usually relates to course material and lectures. Your other paper may not cover this material, and turning in the same paper for more than one course may constitute an Honor Code violation . Ask the instructor—it can’t hurt.
- get all wacky and “creative” before you answer the question . Showing that you are able to think beyond the boundaries of a simple assignment can be good, but you must do what the assignment calls for first. Again, check with your instructor. A humorous tone can be refreshing for someone grading a stack of papers, but it will not get you a good grade if you have not fulfilled the task.
Critical reading of assignments leads to skills in other types of reading and writing. If you get good at figuring out what the real goals of assignments are, you are going to be better at understanding the goals of all of your classes and fields of study.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift
- Conjunctions
- Prepositions
ASSIGNMENT in a Sentence Examples: 21 Ways to Use Assignment

Are you struggling to understand the concept of an assignment? An assignment is a task or piece of work that has been assigned to someone as part of their job or studies. It requires them to complete a specific set of actions or deliverables within a defined timeframe.
In an academic setting, assignments often involve research, analysis, and the presentation of findings in various formats. Understanding the requirements of an assignment is crucial for students to produce high-quality work and meet the expectations of their instructors.
Table of Contents
7 Examples Of Assignment Used In a Sentence For Kids
- Please complete your assignment by coloring the picture.
- Your assignment is to count how many animals you see.
- Draw a circle around the smallest object in this assignment .
- Can you find the letter “A” in your assignment ?
- Remember to write your name on the top of your assignment .
- Let’s work on this assignment together, okay?
- Practice tracing the numbers in your assignment .
14 Sentences with Assignment Examples
- The professor’s surprise assignment caught many students off guard.
- Completing the group assignment required effective communication and collaboration.
- I spent all night working on my assignment due tomorrow.
- The guidelines for the assignment were clearly outlined in the syllabus.
- I need to visit the library to conduct research for my assignment .
- The deadline for the assignment has been extended by a week.
- My assignment score was negatively impacted by late submission.
- The professor announced a pop assignment to test our understanding of the topic.
- I received positive feedback from the professor on my assignment .
- The assignment requires a minimum of 1000 words and proper citations.
- Submitting a plagiarized assignment will result in severe consequences.
- The assignment is a key component of our overall grade in the course.
- I struggled to grasp the concept, which made completing the assignment challenging.
- Working on the assignment together with classmates helped clarify confusing concepts.
How To Use Assignment in Sentences?
Assignment is a task or piece of work that someone is given to do. It can also refer to the allocation of a particular task or job to someone. To use the word assignment in a sentence, simply place it in the context of giving or receiving a task. For example, “The teacher handed out the math assignment to the students” or “I have a new assignment at work that I need to complete by Friday.”
When using assignment in a sentence, it is important to ensure that it fits naturally within the sentence structure. Make sure the context in which you use the word is appropriate and clear for the reader to understand.
You can also use assignment in a broader sense, such as “The assignment of duties within the team was well-organized.” In this case, assignment refers to the distribution of tasks among team members.
Remember that assignment can be used in various contexts, not just limited to academic settings. It can be applied to work projects, volunteer tasks, or even household chores. By understanding the versatility of the word assignment , you can effectively communicate tasks and responsibilities in different situations.
In conclusion, the examples of sentences with the keyword “assignment” demonstrate its role in conveying the idea of a task or duty that needs to be completed. Whether referring to a school assignment, work task, or project, the keyword is versatile in indicating a specific job that requires attention and effort. These sentences show how assignments can vary in complexity and nature, from academic exercises to professional responsibilities.
By examining the usage of the keyword “assignment” in different contexts, it is clear that assignments play a crucial role in education, work, and daily life. They serve as a way to allocate tasks, assess knowledge or skills, and facilitate learning and growth. Understanding the significance of assignments can help individuals prioritize and manage their responsibilities effectively, leading to successful completion of tasks and achievements of goals.
Related Posts

In Front or Infront: Which Is the Correct Spelling?
As an expert blogger with years of experience, I’ve delved… Read More » In Front or Infront: Which Is the Correct Spelling?
Targeted vs. Targetted: Correct Spelling Explained in English (US) Usage
Are you unsure about whether to use “targetted” or “targeted”?… Read More » Targeted vs. Targetted: Correct Spelling Explained in English (US) Usage
As per Request or As per Requested: Understanding the Correct Usage
Having worked in various office environments, I’ve often pondered the… Read More » As per Request or As per Requested: Understanding the Correct Usage

- More from M-W
- To save this word, you'll need to log in. Log In
Definition of assignment
task , duty , job , chore , stint , assignment mean a piece of work to be done.
task implies work imposed by a person in authority or an employer or by circumstance.
duty implies an obligation to perform or responsibility for performance.
job applies to a piece of work voluntarily performed; it may sometimes suggest difficulty or importance.
chore implies a minor routine activity necessary for maintaining a household or farm.
stint implies a carefully allotted or measured quantity of assigned work or service.
assignment implies a definite limited task assigned by one in authority.
Examples of assignment in a Sentence
These examples are programmatically compiled from various online sources to illustrate current usage of the word 'assignment.' Any opinions expressed in the examples do not represent those of Merriam-Webster or its editors. Send us feedback about these examples.
Word History
see assign entry 1
14th century, in the meaning defined at sense 1
Phrases Containing assignment
- self - assignment
Dictionary Entries Near assignment
Cite this entry.
“Assignment.” Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary , Merriam-Webster, https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/assignment. Accessed 30 May. 2024.
Legal Definition
Legal definition of assignment, more from merriam-webster on assignment.
Nglish: Translation of assignment for Spanish Speakers
Britannica English: Translation of assignment for Arabic Speakers
Subscribe to America's largest dictionary and get thousands more definitions and advanced search—ad free!

Can you solve 4 words at once?
Word of the day.
See Definitions and Examples »
Get Word of the Day daily email!
Popular in Grammar & Usage
More commonly misspelled words, commonly misspelled words, how to use em dashes (—), en dashes (–) , and hyphens (-), absent letters that are heard anyway, how to use accents and diacritical marks, popular in wordplay, pilfer: how to play and win, the words of the week - may 24, 9 superb owl words, 10 words for lesser-known games and sports, your favorite band is in the dictionary, games & quizzes.

- U.S. Locations
- UMGC Europe
- Learn Online
- Find Answers
- 855-655-8682
- Current Students
UMGC Effective Writing Center Assignment Analysis & Sentence Outline
Explore more of umgc.
- Writing Resources
In the Effective Writing Center, we sometimes have to tell students, "Your paper is well written and interesting, but it doesn't fulfill the assignment. You've done good work, but it's not what your professor is looking for. Let's analyze this assignment closely . . . ."
Now, whose fault is this? Nobody's. Learning how to analyze academic assignments is a skill that requires practice and experience. They call it "education" for a reason--students come to college to learn things. One of the things you learn is how to use the thought patterns of academic disciplines you study before earning that coveted degree.
So in the EWC we recommend that whenever you receive a writing assignment from a professor your first step should be to analyze it--preferably with input from us at the Effective Writing Center . In other words, let us help you break down the assignment and determine what the professor really wants so that you can be successful in the experience. In some situations like timed essay exams, you must perform this step quickly. But with formal writing assignments like this one, you have the opportunity to:
- break down the assignment into its required parts
- check your understanding of the assignment with your professor
- create an assignment map or outline before you start writing
This practice of planning out a task before starting it--and receiving feedback on that plan--is common practice in the professional workplace. Whether you share the plan with coworkers or a supervisor, your professor or an EWC advisor , the purpose is the same: For everyone to be "on the same page."
The Basic Question
Here is the basic question that you are trying to answer in this thread or whenever you analyze a writing assignment:
What must my paper contain in order to meet all of my professor's expectations?
Let's say that in another course you received this assignment:
Topic: "The Influence of Television Violence on Children."
What do you think is the overall effect of televised violence on children? Research this question to determine the amount of violence that the average child watches on American television, the concerns of parents and parent groups, what experts in psychology and medicine say about the effects, and what changes, if any, need to be made to safeguard our children.
You might want to limit your definition of a child to a certain age group. At the end of your paper, be sure to give your position on this issue and what actions you would take as a parent.
If you study it closely, you will see that the assignment above provides a clear indication of what your outline must contain:
- Title: Effects of Televised Violence on Children
- Introduction: Statistics on televised violence and age group for this paper
- Body section: Concerns of parents/parent groups
- Body section: Studies by experts
- Body section: Recommended changes
- Conclusion: My views as a parent
- Works Cited
See how a preliminary outline can ensure that you understand all assignment requirements before writing? For us at the EWC, it does not matter if your outline is formal or informal. All that matters is that you pre-plan what your paper should contain so that you provide everything the professor is expecting.
Your Assignment:
After reading your teacher's directions closely, write a starter outline and get feedback on it. When writing this outline, focus on the categories of information required in the paper and the examples provided.
The purpose of this outline is to demonstrate that you have an organized way to answer the assignment description with relevant, persuasive points.
Assignment Analysis
When a teacher writes an assignment, the teacher has in mind a correct way for students to respond. View the Effective Writing Center's Video on Assignment Analysis.
Sentence Outline
Click through to view the Effective Writing Center's video on sentence outlines and how to use them.
Our helpful admissions advisors can help you choose an academic program to fit your career goals, estimate your transfer credits, and develop a plan for your education costs that fits your budget. If you’re a current UMGC student, please visit the Help Center .
Personal Information
Contact information, additional information.
By submitting this form, you acknowledge that you intend to sign this form electronically and that your electronic signature is the equivalent of a handwritten signature, with all the same legal and binding effect. You are giving your express written consent without obligation for UMGC to contact you regarding our educational programs and services using e-mail, phone, or text, including automated technology for calls and/or texts to the mobile number(s) provided. For more details, including how to opt out, read our privacy policy or contact an admissions advisor .
Please wait, your form is being submitted.
By using our website you agree to our use of cookies. Learn more about how we use cookies by reading our Privacy Policy .
Simple Sentences in English: 50 Examples
What is a simple sentence.
A simple sentence contains one independent clause.
What’s an “independent clause”?
It’s one subject followed by one verb or verb phrase . It expresses a single idea.
- Learn more about simple, compound, complex, and compound-complex sentences.
- Learn Basic & Intermediate English Grammar
Let’s look at 50 simple sentence examples in different English verb tenses.

Download the PDF of this lesson
Simple sentences in the Present Simple Tense
The subject of the sentence is in blue .
The verb of the sentence is in red .
- I ‘m happy.
- She exercises every morning.
- His dog barks loudly.
- My school starts at 8:00.
- We always eat dinner together.
- They take the bus to work.
- He doesn’t like vegetables.
- I don’t want anything to drink.
- This little black dress isn’t expensive.
- Those kids don’t speak English.
You can see that simple sentences can contain other words, such as:
- a direct object (“eat dinner” – dinner is the direct object)
- a prepositional phrase (“at 8:00”)
- adjectives (“little black dress” – little and black are adjectives)
- adverbs (“loudly”)
The important thing is that there’s only ONE subject and ONE verb or verb phrase (this could be a helping verb + main verb, for example “don’t speak” and “doesn’t like”).

Simple sentences in the Past Simple Tense
- I went to the store.
- She took the test last Friday.
- We talked for hours.
- The little girl played at the playground.
- He had a great time yesterday.
- I didn’t know about the meeting.
- He didn’t take a shower.
- My friend and I didn’t buy anything on our trip.
- We didn’t have enough food for everyone.
- Rachel didn’t tell anyone the secret.

We talked for hours. (We = subject, talked = verb)
Simple sentences in the Future Simple Tense
- I will visit my parents next weekend.
- She ‘ll finish her project by tomorrow.
- They will go on vacation next month.
- We ‘ll have dinner at a fancy restaurant tonight.
- He will start his new job next week.
- I won’t attend the party tomorrow.
- She won’t buy a new car this year.
- They will not complete the assignment on time.
- We won’t go to the concert on Saturday.
- He will not pass the exam without studying.

He won’t pass the exam without studying.
Simple sentences in the Present Continuous Tense
- I am currently working on a new project.
- She is dancing gracefully on stage.
- They are enjoying their vacation in Hawaii.
- We are learning to play the guitar.
- He is studying for his upcoming exams.
- I ‘ m not feeling well today.
- She isn’t attending the party tonight.
- They ‘ re not participating in the competition.
- We aren’t going out for dinner this evening.
- He ‘ s not wearing a jacket despite the cold weather.

He’s not wearing a jacket despite the cold weather.
Simple sentences in the Past Continuous Tense
I was watching a movie last night.
- She was singing loudly during the concert.
- They were playing soccer yesterday.
- We were having dinner at a fancy restaurant.
- He was studying hard for his final exams.
- I wasn’t paying attention to the lecture.
- She was not watching her kids at the park.
- They were not listening to the teacher’s instructions.
- We weren’t traveling over spring break.
- He was not feeling well yesterday.

Simple sentences in the Future Continuous Tense
- I ‘ll be giving a presentation at the conference.
- She will be traveling to Europe next month.
- They ‘ll be celebrating their anniversary on a cruise.
- We will be taking our son to college in September.
- He ‘ll be working on a new project next week.
- I will not be attending the party tonight.
- She will not be participating in the competition.
- They won’t be going on a vacation this summer.
- We won’t be looking for new jobs anytime soon.
- He won’t be taking so many classes next semester.

They’ll be celebrating their anniversary on a cruise.
Simple sentences in the Present Perfect Tense
- I ‘ ve finished reading the book.
- She has traveled to many countries.
- They ‘ ve won the championship.
- We have completed the project on time.
- He ‘ s learned to play the piano.
- I haven’t visited that museum yet.
- She has not received the package.
- They have not finished their homework.
- We haven’t seen that movie.
- He hasn’t achieved his goal.

They’ve won the championship
Now you know how to form simple sentences in various verb tenses! Try writing your own simple sentence examples to help you remember this sentence structure. Next, learn about compound sentences and complex sentences.

English Grammar E-Books
More Espresso English Lessons:
About the author.
Shayna Oliveira
Shayna Oliveira is the founder of Espresso English, where you can improve your English fast - even if you don’t have much time to study. Millions of students are learning English from her clear, friendly, and practical lessons! Shayna is a CELTA-certified teacher with 10+ years of experience helping English learners become more fluent in her English courses.

Simple Sentences: Definition, Examples, & Exercises
- The Albert Team
- Last Updated On: March 1, 2022
Do you remember the first time you learned how to write a sentence? Most of us are taught how to put three words together to make sentences in kindergarten: I like dogs. She eats cookies. Games are fun! Sound familiar? These three-word sentences are one of the most basic types of simple sentences , and they serve as a foundation to forming more complex sentences. However, simple sentences are not always as simple as three-word sentences.
In this post we’ll review what simple sentences are, the parts of a simple sentence, and different ways to create simple sentences.
Once you’re feeling confident, test yourself with a post-assessment quiz and practice with our high quality, standards-aligned questions here .
What We Review
The Basics of Simple Sentences
What are Simple Sentences?
A simple sentence is a sentence containing only one clause, or more specifically, an independent clause, with a subject and a predicate.
A simple sentence is typically made up of a subject , verb , and object , or SVO , and creates a complete thought; however, since a simple predicate is a verb or verb phrase only, a simple sentence can also be made up of only a subject and verb (SV).
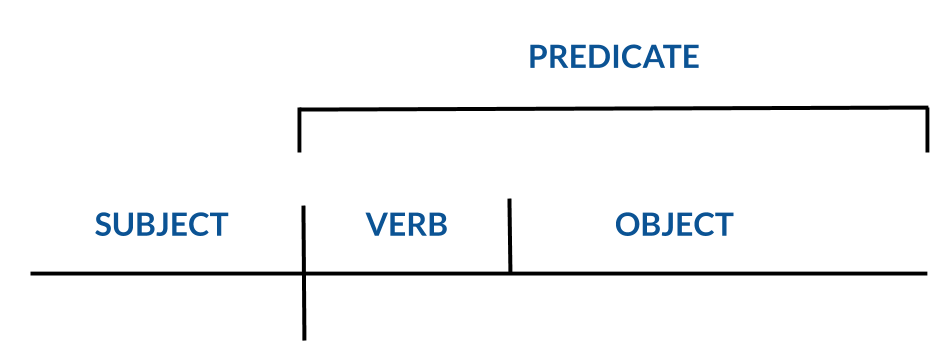
Subject + Verb + Object (SVO)
- Jessie ate dinner.
Subject + Verb (SV)
- Jessie ate.
Both of these examples are grammatically correct simple sentences, but including an object helps to clarify the full idea of the sentence.
Despite their name, simple sentences can include things that are not so simple. Let’s review the use of modifiers , compound subjects , and compound verbs/predicates in simple sentences.
Modifiers in Simple Sentences

Modifiers are words or phrases that can be included in simple sentences to add more detail. Let’s see how we can modify the simple sentence used above:
Adding Articles/Adjectives
- The hungry Jessie ate a large dinner.
Adding Adverbs
- The hungry Jessie quickly ate a very large dinner.
Adding a Prepositional Phrase
- The hungry Jessie quickly ate a very large dinner after a long day at work .
All of these examples still qualify as simple sentences, because they are all independent clauses that convey a complete thought.
Pro Tip: Ask yourself how the sentence is changed as a result of a modifier.
Compound Subjects in Simple Sentences
Compound subjects are two or more nouns or pronouns sharing the same verb. They are joined using coordinate or correlative conjunctions.
Compound Subjects Using Coordinate Conjunctions
- Jessie and Jade ate dinner.
- Jessie or Jade ate dinner.
- Jessie, Jade, and Titus ate dinner.
Compound Subjects Using Correlative Conjunctions
- Both Jessie and Jade ate dinner.
- Neither Jessie nor Jade ate dinner.
Even with two or more simple subjects, these examples are independent clauses conveying a complete thought, so they are still simple sentences.
Compound Verbs/Predicates in Simple Sentences

Compound verbs, or compound predicates, are two or more verbs/predicates that share the same subject. This may be written as simply as a subject performing multiple verbs (simple predicates) or, more elaborately, as a subject performing multiple complete predicates. The compound verbs/predicates are joined by a conjunction.
Compound Verbs/Simple Predicates
- Jessie cooked and ate dinner.
- Jessie rinsed and washed the dishes.
Compound Predicates
- Jessie ate dinner and washed the dishes .
- Jessie cooked dinner and rinsed the dishes
Again, these examples are all independent clauses conveying a complete thought. So even with multiple verbs, a sentence can be a simple sentence.
Return to the Table of Contents
Tips for Using and Identifying Simple Sentences

Tip #1: Subject + Verb + Object (SVO) Simple Sentences Can be Arranged in Different Ways.
While a simple sentence is typically expected to contain a subject, verb, and object, this does not always mean that the subject will be the first thing we see in a sentence. When we place parts of the predicate at the beginning of the sentence or ask a question, the standard SVO arrangement of a simple sentence will vary.
Placing a Part of the Predicate Before the Subject
When the predicate, or verb + object portion of the sentence contains a prepositional phrase or adverb, they can appear at the beginning of the sentence followed by a comma. Check out the following examples to see sentences in both their standard forms and rearranged forms:
Prepositional Phrase:
- We completed our homework after school .
- After school , we completed our homework.
- I ran quickly to the store.
- Quickly , I ran to the store.
Asking a Question
Sentences that ask a question are called interrogative sentences, and they are often simple sentences. Some questions start with the main verb or part of the verb phrase. Look at the examples below to see the placement of the verb in both a question and the statement form of the question:
- Will it rain tomorrow?
- It will rain tomorrow.
- Has the race been postponed?
- The race has been postponed.
- Were you sick today?
- You were sick today.
Tip #2: Avoid using too many basic simple sentences in your writing.
Remember, basic simple sentences are the first type of sentence we learn how to write. So it’s probably safe to assume that filling our writing with three or four word sentences is not the best idea. Too many simple sentences close together can sound choppy and disconnected. Always revise your work to see where simple sentences can be edited to create more sophisticated writing.
Combine Simple Sentences
If you have a string of very basic simple sentences in your writing, you can probably combine some of those sentences into compound sentences.
- He loves baseball. He first played little league baseball. He joined the baseball team in middle school.
- He loves baseball and played little league before joining the baseball team in middle school.
Tip #3: Add more detail.
There’s nothing wrong with using simple sentences in your writing, but you can (and should) use modifiers to enhance simple sentences when possible.
Basic Simple Sentence:
- I visited Chichén Itzá.
- On my vacation to Mexico, I visited the ancient Mayan ruins of Chichén Itzá.
Applying the Basics: Simple Sentences Review & Practice
Now that you understand what simple sentences are, and how to use them properly in your writing, let’s practice identifying them. Remember, a simple sentence is a sentence that contains one independent clause, or one complete thought.
Simple Sentences Exercises & Review
Complete the quick exercise below to assess your mastery of simple sentences.
Determine if the sentence is a simple sentence or not.
1. I finally received my passport for our trip overseas.
- Simple Sentence
2. Last week, she told the funniest joke in the middle of the meeting.
3. Tim went to the store, and he bought a new laptop for school.
- Not a Simple Sentence
4. Julie and Paige went to the amusement park and rode a rollercoaster.
5. I was exhausted after working all day.
For additional practice, check out the Simple Sentences content on Albert.
Try for Yourself: Simple Sentences Quiz

Feeling confident in your understanding of Simple Sentences?
Take this short quiz to see what you’ve learned:
1. Can a simple sentence have more than one subject?
- Answer: Yes
- Correct Explanation: That’s right! A simple sentence can have more than one subject, or a compound subject, if they are sharing the same verb. The subjects are joined using coordinate or correlative conjunctions.
- Incorrect Explanation: Sorry, that’s not right. A simple sentence can have more than one subject, or a compound subject, if they are sharing the same verb. The subjects are joined using coordinate or correlative conjunctions.
2. Can a simple sentence be a single dependent clause?
- Correct Explanation: That’s right! A simple sentence must be a single independent clause in order to be a simple sentence. It is a complete thought and can stand alone. A dependent clause cannot stand alone as a complete thought.
- Incorrect Explanation: Sorry, that’s not right. A dependent clause cannot stand alone as a complete thought. A simple sentence must be a single independent clause in order to be a simple sentence. It is a complete thought and can stand alone.
3. Can a simple sentence have more than one verb?
- Correct Explanation: That’s right! A simple sentence can have more than one verb ( compound verb/simple predicate ) or more than one complete predicate ( compound predicate ) if they share the same subject. They are combined using a conjunction.
- Incorrect Explanation: Sorry, that’s not right. A simple sentence can have more than one verb ( compound verb/simple predicate ) or more than one complete predicate ( compound predicate ) if they share the same subject. They are combined using a conjunction.
4. Does a simple sentence always start with the subject?
- Correct Explanation: That’s right! A simple sentence can start with part of the predicate. This might be a prepositional phrase, and adverb, or a question.
- Incorrect Explanation: Sorry, that’s not right. A simple sentence can start with part of the predicate. This might be a prepositional phrase, and adverb, or a question.
5. Is the following example a simple sentence?
After eating breakfast, Hayley went to dance practice, and she prepared for her performance.
- Correct Explanation: That’s right! A simple sentence can have more than one predicate when that predicate shares the same subject. In this sentence, there are two independent clauses: After eating breakfast, Hayley went to dance practice. She prepared for her performance.
- Incorrect Explanation: Sorry, that’s not right. A simple sentence can have more than one predicate when that predicate shares the same subject. In this sentence, there are two independent clauses: After eating breakfast, Hayley went to dance practice. She prepared for her performance.
6. Is the following example a simple sentence?
Jim and Amy thoroughly cleared out the basement and hired contractors for a remodel.
- Correct Explanation: That’s right! A simple sentence can have compound subjects and compound predicates as long as they form one complete thought. The subjects share the predicates, and the predicates share the subjects . In this case, the compound subject “Jim and Amy” share the compound predicates “thoroughly cleared out the basement” and “hired contractors for a remodel.”
- Incorrect Explanation: Sorry, that’s not right. A simple sentence can have compound subjects and compound predicates as long as they form one complete thought. The subjects share the predicates, and the predicates share the subjects . In this case, the compound subject “Jim and Amy” share the compound predicates “thoroughly cleared out the basement” and “hired contractors for a remodel.”
For additional practice with simple sentences, check out our completely free practice on Albert.io: Simple Sentences .
Teacher’s Corner for Simple Sentences
While it’s true that simple sentences are a foundational grammar skill, the Common Core English Language Progressive Skills Chart shows that even elementary-level skills “require continued attention in higher grades as they are applied to increasingly sophisticated writing and speaking.”
For specific standards addressing simple sentences, check out the Common Core State Standards site!
Albert’s grammar course is 100% free, and the Simple Sentences practices can be used for much more than homework!
Our assessments can be used as pre-and post-tests to measure student progress. Our pre-made quizzes can be used as bell-ringers, exit tickets, and more!
In addition to our pre-made assessments, you can also use our assignments feature to create your own quizzes and assessments.

Summary on Simple Sentences
Simple sentences are sentences containing one independent clause, with a subject and a predicate.
Modifiers, compound subjects, and compound verbs/predicates can be used in simple sentences.
The standard arrangement of a simple sentence is subject + verb + object, or SVO order. This can vary by arranging parts of the predicate before the subject.
Practice makes perfect! Use our Simple Sentences practice on Albert’s completely free grammar course !
Need help preparing for your Grammar exam?
Albert has hundreds of grammar practice questions with detailed explanations to help you master concepts.
Interested in a school license?
Popular posts.

AP® Score Calculators
Simulate how different MCQ and FRQ scores translate into AP® scores

AP® Review Guides
The ultimate review guides for AP® subjects to help you plan and structure your prep.

Core Subject Review Guides
Review the most important topics in Physics and Algebra 1 .

SAT® Score Calculator
See how scores on each section impacts your overall SAT® score

ACT® Score Calculator
See how scores on each section impacts your overall ACT® score

Grammar Review Hub
Comprehensive review of grammar skills

AP® Posters
Download updated posters summarizing the main topics and structure for each AP® exam.

- Walden University
- Faculty Portal
Grammar: Sentence Structure and Types of Sentences
Definitions and examples of basic sentence elements.
The Mastering the Mechanics webinar series also describes required sentence elements and varying sentence types. Please see these archived webinars for more information.
Key: Yellow, bold = subject; green underline = verb, blue, italics = object, pink, regular font = prepositional phrase
Independent clause : An independent clause can stand alone as a sentence. It contains a subject and a verb and is a complete idea.
- I like spaghetti .
- He reads many books .
Dependent clause : A dependent clause is not a complete sentence. It must be attached to an independent clause to become complete. This is also known as a subordinate clause.
- Although I like spaghetti,…
- Because he reads many books,…
Subject : A person, animal, place, thing, or concept that does an action. Determine the subject in a sentence by asking the question “Who or what?”
- I like spaghetti.
- He reads many books.
Verb : Expresses what the person, animal, place, thing, or concept does. Determine the verb in a sentence by asking the question “What was the action or what happened?”
- The movie is good. (The be verb is also sometimes referred to as a copula or a linking verb. It links the subject, in this case "the movie," to the complement or the predicate of the sentence, in this case, "good.")
Object : A person, animal, place, thing, or concept that receives the action. Determine the object in a sentence by asking the question “The subject did what?” or “To whom?/For whom?”
Prepositional Phrase : A phrase that begins with a preposition (i.e., in, at for, behind, until, after, of, during) and modifies a word in the sentence. A prepositional phrase answers one of many questions. Here are a few examples: “Where? When? In what way?”
- I like spaghetti for dinner .
- He reads many books in the library .
English Sentence Structure
The following statements are true about sentences in English:
- H e obtained his degree.
- He obtained his degree .
- Smith he obtained his degree.
- He obtained his degree.
- He (subject) obtained (verb) his degree (object).
Simple Sentences
A simple sentence contains a subject and a verb, and it may also have an object and modifiers. However, it contains only one independent clause.
Key: Yellow, bold = subject; green underline = verb, blue, italics = object, pink, regular font =prepositional phrase
Here are a few examples:
- She wrote .
- She completed her literature review .
- He organized his sources by theme .
- They studied APA rules for many hours .
Compound Sentences
A compound sentence contains at least two independent clauses. These two independent clauses can be combined with a comma and a coordinating conjunction or with a semicolon .
Key: independent clause = yellow, bold ; comma or semicolon = pink, regular font ; coordinating conjunction = green, underlined
- She completed her literature review , and she created her reference list .
- He organized his sources by theme ; then, he updated his reference list .
- They studied APA rules for many hours , but they realized there was still much to learn .
Using some compound sentences in writing allows for more sentence variety .
Complex Sentences
A complex sentence contains at least one independent clause and at least one dependent clause. Dependent clauses can refer to the subject (who, which) the sequence/time (since, while), or the causal elements (because, if) of the independent clause.
If a sentence begins with a dependent clause, note the comma after this clause. If, on the other hand, the sentence begins with an independent clause, there is not a comma separating the two clauses.
Key: independent clause = yellow, bold ; comma = pink, regular font ; dependent clause = blue, italics
- Note the comma in this sentence because it begins with a dependent clause.
- Note that there is no comma in this sentence because it begins with an independent clause.
- Using some complex sentences in writing allows for more sentence variety .
Compound-Complex Sentences
Sentence types can also be combined. A compound-complex sentence contains at least two independent clauses and at least one dependent clause.
Key: independent clause = yellow, bold ; comma or semicolon = pink, regular font ; coordinating conjunction = green, underlined ; dependent clause = blue, italics
- She completed her literature review , but she still needs to work on her methods section even though she finished her methods course last semester .
- Although he organized his sources by theme , he decided to arrange them chronologically , and he carefully followed the MEAL plan for organization .
- T hey studied APA rules for many hours , and they decided that writing in APA made sense because it was clear, concise, and objective .
- Using some complex-compound sentences in writing allows for more sentence variety .
- Pay close attention to comma usage in complex-compound sentences so that the reader is easily able to follow the intended meaning.
Sentence Structure Video Playlist
Note that these videos were created while APA 6 was the style guide edition in use. There may be some examples of writing that have not been updated to APA 7 guidelines.
- Structuring Sentences: Types of Sentences (video transcript)
- Structuring Sentences: Simple Sentences (video transcript)
- Structuring Sentences: Compound Sentences (video transcript)
- Structuring Sentences: Complex Sentences (video transcript)
- Structuring Sentences: Combining Sentences (video transcript)
- Common Error: Unclear Subjects (video transcript)
- Mastering the Mechanics: Punctuation as Symbols (video transcript)
- Mastering the Mechanics: Commas (video transcript)
- Mastering the Mechanics: Periods (video transcript)
- Mastering the Mechanics: Semicolons (video transcript)
Related Resources
Knowledge Check: Sentence Structure and Types of Sentences
Didn't find what you need? Email us at [email protected] .
- Previous Page: Main Parts of Speech
- Next Page: Run-On Sentences and Sentence Fragments
- Office of Student Disability Services
Walden Resources
Departments.
- Academic Residencies
- Academic Skills
- Career Planning and Development
- Customer Care Team
- Field Experience
- Military Services
- Student Success Advising
- Writing Skills
Centers and Offices
- Center for Social Change
- Office of Academic Support and Instructional Services
- Office of Degree Acceleration
- Office of Research and Doctoral Services
- Office of Student Affairs
Student Resources
- Doctoral Writing Assessment
- Form & Style Review
- Quick Answers
- ScholarWorks
- SKIL Courses and Workshops
- Walden Bookstore
- Walden Catalog & Student Handbook
- Student Safety/Title IX
- Legal & Consumer Information
- Website Terms and Conditions
- Cookie Policy
- Accessibility
- Accreditation
- State Authorization
- Net Price Calculator
- Contact Walden
Walden University is a member of Adtalem Global Education, Inc. www.adtalem.com Walden University is certified to operate by SCHEV © 2024 Walden University LLC. All rights reserved.
- Cambridge Dictionary +Plus
Examples of assign

Word of the Day
Your browser doesn't support HTML5 audio
height above sea level

Keeping up appearances (Talking about how things seem)

Learn more with +Plus
- Recent and Recommended {{#preferredDictionaries}} {{name}} {{/preferredDictionaries}}
- Definitions Clear explanations of natural written and spoken English English Learner’s Dictionary Essential British English Essential American English
- Grammar and thesaurus Usage explanations of natural written and spoken English Grammar Thesaurus
- Pronunciation British and American pronunciations with audio English Pronunciation
- English–Chinese (Simplified) Chinese (Simplified)–English
- English–Chinese (Traditional) Chinese (Traditional)–English
- English–Dutch Dutch–English
- English–French French–English
- English–German German–English
- English–Indonesian Indonesian–English
- English–Italian Italian–English
- English–Japanese Japanese–English
- English–Norwegian Norwegian–English
- English–Polish Polish–English
- English–Portuguese Portuguese–English
- English–Spanish Spanish–English
- English–Swedish Swedish–English
- Dictionary +Plus Word Lists
{{message}}
There was a problem sending your report.
Definition of 'assignment'

assignment in American English
Assignment in british english, examples of 'assignment' in a sentence assignment, related word partners assignment, trends of assignment.
View usage over: Since Exist Last 10 years Last 50 years Last 100 years Last 300 years
Browse alphabetically assignment
- assigned randomly
- assigned risk
- assimilability
- assimilable
- All ENGLISH words that begin with 'A'
Related terms of assignment
- seat assignment
- tough assignment
- writing assignment
- challenging assignment
- difficult assignment
- View more related words
Quick word challenge
Quiz Review
Score: 0 / 5
Wordle Helper

Scrabble Tools


Sentence Structure: A Complete Guide (With Examples & Tasks)
This article is part of the ultimate guide to language for teachers and students. Click the buttons below to view these.
A TEACHER’S GUIDE TO SENTENCE STRUCTURE
This article aims to inform teachers and students about writing great sentences for all text types and genres. I would also recommend reading our complete guide to writing a great paragraph here. Both articles will find great advice, teaching ideas, and resources.
WHAT IS SENTENCE STRUCTURE?
When we talk about ‘sentence structure’, we are discussing the various elements of a sentence and how these elements are organized on the page to convey the desired effect of the author.
Writing well in terms of sentence structure requires our students to become familiar with various elements of grammar and the various types of sentences that exist in English.
In this article, we will explore these areas and discuss various ideas and activities you can use in the classroom to help your students on the road to mastering these different sentence structures. This will help make their writing more precise and interesting in the process.

TYPES OF SENTENCE STRUCTURE
In English, students need to get their heads around four types of sentences. They are:
Mastering these four types of sentences will enable students to articulate themselves effectively and with personality and style.
Achieving this necessarily takes plenty of practice, but the process begins with ensuring that each student has a firm grasp on how each type of sentence structure works.
But, before we examine these different types of structures, we must ensure our students understand the difference between independent and dependent clauses. Understanding clauses and how they work will make it much easier for students to grasp the following types of sentences.
A COMPLETE UNIT ON TEACHING SENTENCE STRUCTURE

This complete SENTENCE STRUCTURE UNIT is designed to take students from zero to hero over FIVE STRATEGIC LESSONS to improve SENTENCE WRITING SKILLS through PROVEN TEACHING STRATEGIES covering:
SENTENCE CLAUSES
Teaching sentence clauses requires a deep understanding of the topic and an ability to explain it in an engaging and easy way for students to understand. In this article, we’ll discuss the basics of sentence clauses and provide some tips for teaching them to students.
What are Sentence Clauses?
A sentence clause is a group of words that contains a subject and a verb. It can be a complete sentence on its own or a part of a larger sentence. There are two types of sentence clauses: independent and dependent.
Independent Clauses
Put simply; clauses are parts of a sentence containing a verb. An independent clause can stand by itself as a complete sentence. It expresses a complete thought or idea and includes a subject and a verb – more on this shortly!
Here’s an example of an independent clause in a sentence:
“I went to the store.”
In this sentence, “I went to the store” is an independent clause because it can stand alone as a complete sentence and expresses a complete thought. It has a subject (“I”) and a verb (“went”), and it can be punctuated with a period.
Dependent Clauses / Subordinate Clauses
Dependent clauses, on the other hand, are not complete sentences and cannot stand by themselves. They do not express a complete idea. To become complete, they must be attached to an independent clause. Dependent clauses are also known as subordinate clauses .
An excellent way to illustrate the difference between the two is by providing an example that contains both.
For example:
Even though I am tired, I am going to work tonight.
The non-underlined portion of the sentence doesn’t work as a sentence on its own, so it is a dependent clause. The underlined portion of the sentence could operate as a sentence in its own right, and it is, therefore, an independent clause.
Now we’ve got clauses out of the way, we’re ready to look at each type of sentence in turn.
Teaching sentence clauses to students is essential because it helps them understand sentence structure. Understanding the structure of sentences is essential for effective writing and communication. It also helps students to identify and correct common errors in their writing, such as sentence fragments and run-on sentences.

Simple Sentences
Simple sentences are, unsurprisingly, the easiest type of sentence for students to grasp and construct for themselves. Often these types of sentences will be the first sentences that children write by themselves, following the well-known Subject – Verb – Object or SVO pattern.
The subject of the sentence will be the noun that begins the sentence. This may be a person, place, or thing, but most importantly, it is the doer of the action in the sentence.
The action itself will be encapsulated by the verb, which is the action word that describes what the doer does.
The object of the sentence follows the verb and describes that which receives the action.
This is again best illustrated by an example. Take a look at the simple sentence below:
Tom ate many cookies.
In this easy example, the doer of the action is Tom , the action is ate , and the receiver of the action is the many cookies .
Subject = Tom
Object = many cookies
After some practice, students will become adept at recognizing SVO sentences and forming their own. It’s also important to point out that simple sentences don’t necessarily have to be short.
This research reveals that an active lifestyle can have a great impact for the good on the life expectancy of the average person.
Despite this sentence looking more sophisticated (and longer!), this is still a simple sentence as it follows the SVO structure:
Subject = research
Verb = reveals
Object = that an active lifestyle can have a great impact for the good on the life expectancy of the average person.
Though basic in construction, it is essential to note that a simple sentence is often the perfect structure for dealing with complex ideas. Simple sentences can effectively provide clarity and efficiency of expression, breaking down complex concepts into manageable chunks.
MORE SIMPLE SENTENCE EXAMPLES
- She ran to the store.
- The sun is shining.
- He likes to read books.
- The cat is sleeping.
- I am happy.
Simple Sentence Reinforcement Activity
To ensure your students grasp the simple sentence structure, have them read a photocopied text pitched at a language level suited to their age and ability.
On the first run-through, have students identify and highlight simple sentences in the text. Then, students should use various colors of pens to pick out and underline the subject, the verb, and the object in each sentence.
This activity helps ensure a clear understanding of how this structure works and helps to internalize it. This will reap rich rewards for students when they come to the next stage, and it’s time for them to write their own sentences using this basic pattern.
After students have mastered combining subjects, verbs, and objects into both long and short sentences, they will be ready to move on to the other three types of sentences, the next of which is the compound sentence .

EXAMPLES OF SIMPLE, COMPLEX AND COMPOUND SENTENCES
Compound sentence s.
While simple sentences consist of one clause with a subject and a verb, compound sentences combine at least two independent clauses that are joined together with a coordinating conjunction .
There’s a helpful acronym to help students remember these coordinating conjunctions; FANBOYS .

Some conjunctions will be more frequently used than others, with the most commonly used being and , but , or , and so .
Whichever of the conjunctions the student chooses, it will connect the two halves of the compound sentence – each of which could stand alone as a complete sentence.
Compound sentences are an essential way of bringing variety and rhythm to a piece of writing. The decision to join two sentences together into one longer compound sentence is made because there is a strong relationship between the two. Still, it is important to remind students that they need not necessarily be joined as they can remain as separate sentences.
The decision to join or not is often a stylistic one.
For example, the two simple sentences:
1. She ran to the school.
2. The school was closed.
It can be easily joined together with a coordinating conjunction that reveals an essential relationship between the two:
She ran to the school, but the school was closed.
As a bonus, while working on compound sentences, a convenient opportunity arises to introduce the correct usage of the semicolon. Often, where two clauses are joined with a conjunction, that conjunction can be replaced with a semicolon when the two parts of the sentence are related, for example:
She ran to the school; the school was closed.
While you may not wish to muddy the waters by introducing the semicolon while dealing with compound sentences, more advanced students may benefit from making the link here.
MORE COMPOUND SENTENCE EXAMPLES
- I want to go to the beach this weekend, but I also need to finish my homework.
- She loves to sing and dance, so she decided to audition for the school musical.
- I enjoy reading books, and my brother prefers to watch movies.
- The dog barked at the mailman, and the mailman quickly walked away.
- He ate his breakfast, and then he went for a run in the park.
Reinforcement Activity:

A good way for students to practice forming compound sentences is to provide them with copies of simple books from early on in a reading scheme. Books for emergent readers are often written in simple sentences that form repetitive patterns that help children internalize various language patterns.
Challenge your students to rewrite some of these texts using compound sentences where appropriate. This will provide valuable practice in spotting such opportunities in their writing and experience in selecting the appropriate conjunction.
COMPLEX SENTENCES
There are various ways to construct complex sentences, but essentially any complex sentence will contain at least one independent and one dependent clause. However, these clauses are not joined by coordinating conjunctions. Instead, subordinating conjunctions are used.
Here are some examples of subordinating conjunctions:
● after
● although
● as
● as long as
● because
● before
● even if
● if
● in order to
● in case
● once
● that
● though
● until
● when
● whenever
● wherever
● while
Subordinating conjunctions join dependent and independent clauses together. They provide a transition between the two ideas in the sentence. This transition will involve a time, place, or a cause and effect relationship. The more important idea is contained in the sentence’s main clause, while the less important idea is introduced by the subordinating conjunction.
Although Catherine ran to school , she didn’t get there in time.
We can see that the first part of this complex sentence (in bold ) is a dependent clause that cannot stand alone. This fragment begins with the subordinating conjunction ‘although’ which joins it to, and expresses the relationship with, the independent clause which follows.
When complex sentences are organized this way (with the dependent clause first), you’ll note the comma separates the dependent clause from the independent clause. If the structure is reorganized to place the independent clause first, with the dependent clause following, then there is no need for this comma.
You will not do well if you refuse to study.
Complex sentences can be great tools for students to not only bring variety to their writing but to explore complex ideas, set up comparisons and contrasts, and convey cause and effect.
MORE COMPLEX SENTENCE EXAMPLES
- Despite feeling exhausted from a long day at work, she still managed to summon the energy to cook a delicious dinner for her family.
- In order to fully appreciate the beauty of the artwork, one must take the time to examine it closely and consider the artist’s intentions.
- The new student, who had just moved to the city from a small town, felt overwhelmed by the size and complexity of her new school.
- Although he had studied diligently for weeks, he was still nervous about the upcoming exam, knowing that his entire future depended on his performance.
- As the sun began to set, the birds flew back to their nests, signalling the end of another day and the beginning of a peaceful evening.
Reinforcement Activity

A helpful way to practice writing complex sentences is to provide students with a subordinating conjunction and dependent clause and challenge them to provide a suitable independent clause to finish out the sentence.
After returning home for work,…
Although it was late,…
You may also flip this and provide the independent clause first before challenging them to come up with a suitable dependent clause and subordinating conjunction to finish out the sentence.
Daily Quick Writes For All Text Types

Our FUN DAILY QUICK WRITE TASKS will teach your students the fundamentals of CREATIVE WRITING across all text types. Packed with 52 ENGAGING ACTIVITIES
COMPOUND-COMPLEX SENTENCES
Compound-complex sentences are, not surprisingly, the most difficult for students to write well. If, however, your students have put the work in to gain a firm grasp of the preceding three sentence types, then they should manage these competently with a bit of practice.
Before teaching compound-complex sentences, it’ll be worth asking your students if they can make an educated guess at a definition of this type of sentence based on its title alone.
The more astute among your students may well be able to work out that a compound-complex sentence refers to joining a compound sentence with a complex one. More accurately, a compound-complex sentence combines at least two independent clauses and one dependent clause.
Since the school was closed, Sarah ran home and her mum made her some breakfast.
We can see here the sentence begins with a dependent clause followed by a compound sentence. We can also see a complex sentence nestled there if we look at the bracketed content in the version below.
( Since the school was closed, Sarah ran home ) and her mum made her some breakfast.
This is a fairly straightforward example of complex sentences, but they can come in lots of guises, containing lots more information while still conforming to the compound-complex structure.
Because most visitors to the city regularly miss out on the great bargains available here, local companies endeavor to attract tourists to their businesses and help them understand how to access the best deals the capital has to offer.
A lot is going on in this sentence, but it follows the same structure as the previous one on closer examination. That is, it opens with a dependent clause (that starts with subordinating conjunction) and is then followed by a compound sentence.
With practice, your students will soon be able to quickly identify these more sophisticated types of sentences and produce their own examples.
Compound-complex sentences can bring variety to a piece of writing and help articulate complex things. However, it is essential to encourage students to pay particular attention to the placement of commas in these sentences to ensure readers do not get confused. Encourage students to proofread all their writing, especially when writing longer, more structurally sophisticated sentences such as these.
MORE COMPOUND-COMPLEX SENTENCE EXAMPLES
- Despite the fact that he was exhausted from his long day at work, he went to the gym and completed a gruelling hour-long workout, but he still managed to make it home in time for dinner with his family.
- The orchestra played beautifully, filling the concert hall with their harmonious melodies, yet the soloist stole the show with her hauntingly beautiful rendition of the final movement.
- Although the road was treacherous and steep, the hiker persevered through the difficult terrain, and after several hours, she reached the summit and was rewarded with a breathtaking view of the valley below.
- The chef prepared a mouth-watering feast, consisting of a savory roast beef, a colorful array of fresh vegetables, and a decadent chocolate cake for dessert, yet the dinner party was still overshadowed by the heated political debate.
- After a long and tiring day, the student sat down to study for her final exam, but she couldn’t concentrate because her mind was consumed with worries about her future, so she decided to take a break and go for a run to clear her head.
Regenerate response
You could begin reinforcing student understanding of compound-complex sentences by providing them with a handout featuring several examples of this type of sentence.
Working in pairs or small groups, have the students identify and mark the independent clauses (more than 1) and dependent clauses (at least 1) in each sentence. When students can do this confidently, they can then begin to attempt to compose their own sentences.
Another good activity that works well as a summary of sentence structure work is to provide the students with a collection of jumbled sentences of each of the four types.

Challenge the students to sort the sentences into each of the four types. In a plenary, compare each group’s findings and examine those sentences where the groups disagreed on their categorization.
In teaching sentence structure, it is essential to emphasize to our students that though the terminology may seem quite daunting at first, they will quickly come to understand how each structure works and recognize them when they come across them in a text.
Much of this is often done by feel, especially for native English speakers. Just as someone may be a competent cyclist and struggle to explain the process verbally, grammar can sometimes feel like a barrier to doing.
Be sure to make lots of time for students to bridge the gap between the theoretical and the practical by offering opportunities to engage in activities that allow students to get creative in producing their own sentences.
WRITING CHECKLISTS FOR ALL TEXT TYPES

⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ (92 Reviews)
WHAT IS A SENTENCE FRAGMENT?
A sentence fragment is a collection of words that looks similar to a sentence but actually isn’t a complete sentence. Sentence fragments usually lack a subject or verb or don’t express a complete thought. Whilst a fragmented sentence can be punctuated to appear similar to a complete sentence; it is no substitute for a sentence.
Sentence fragment features:
These are the distinguishing features of a sentence fragment:
- Example: Jumped further than a Kangaroo. (Who jumped?)
- Example: My favorite math teacher. (What did the teacher do or say?)
- Example: For better or worse. (What is better or worse? What is it modifying?)
- Example: When my mother married my father. (What happened when “my mother married my father?”)
- Example: Such as, my brother was practising martial arts. (It is unclear; did something happen when my brother was practising martial arts?)
The methods for correcting a sentence fragment are varied, but essentially it will boil down to three options. Either attach it to a nearby sentence, revise and add the missing elements or rewrite the entire passage or fragment until they are operating in sync with each other.
Let’s explore some of these methods to fix a fragmented sentence. Firstly, one must identify the subject and verb to ensure that the fragment contains the necessary components of a complete sentence. For instance, in the sentence “Running down the street, I saw a dog,” the subject (“I”) and verb (“saw”) are present, making it a complete sentence.
Furthermore, it is important to check for a complete thought within the sentence fragment. In other words, the fragment should express a complete idea; if it doesn’t, it should be revised accordingly. An example of a sentence fragment with a complete thought is “Running down the street, I saw a dog chasing a cat.”
Lastly, combining sentence fragments with independent clauses can help create complete sentences. For instance, “Running down the street, I saw a dog. It was chasing a cat” can be combined into one sentence: “Running down the street, I saw a dog chasing a cat.” This not only creates a complete sentence but also enhances the overall coherence and readability of the text.
In summary, sentence fragments can hinder effective communication and must be avoided in writing. To fix a sentence fragment, one must identify the subject and verb, ensure a complete thought is expressed, and consider combining it with an independent clause. By doing so, writers can create clear, concise, and meaningful sentences that easily convey their intended message.
TOP TIPS FOR TEACHING SENTENCE STRUCTURE
- Start with the basics: Begin by teaching students about the different parts of a sentence, such as subject, verb, and object. Use examples and visual aids to help them understand the function of each part.
- Use varied sentence structures: Show students examples of different sentence structures, such as simple, compound, and complex sentences. Please encourage them to use varied sentence structures in their writing.
- Practice with sentence combining: Give students several short, simple sentences and ask them to combine them into a longer sentence using conjunctions or other connecting words. This exercise will help them understand how to construct complex sentences.
- Use real-life examples: Incorporate examples from everyday life to help students understand how sentence structure affects meaning. For example, “I saw the man with the telescope” and “I saw the man, with the telescope” have different meanings due to the placement of the comma.
- Provide feedback: Give students feedback on their writing, focusing on the structure of their sentences. Encourage them to revise and improve their writing by experimenting with different sentence structures. Please provide specific examples of how they can improve their sentence structure.
SENTENCE STRUCTURE VIDEO TUTORIALS
OTHER GREAT ARTICLES RELATED TO SENTENCE STRUCTURE

Glossary of literary terms

The Writing Process

Perfect Paragraph Writing: The Ultimate Guide

Teaching Proofreading and Editing Skills

How to write a perfect 5 Paragraph Essay
- Letter Writing
- Acknowledgement For Assignment
Acknowledgement for Assignment │How to Write with Samples
If you are a student, you will have to do a lot of assignments. An acknowledgement is a write-up that expresses gratitude to all the people who are directly or indirectly involved in helping you complete your assignment. Read through the article to learn how to write an acknowledgement for your assignment.
Table of Contents
How to write acknowledgement for assignment, acknowledgement for college assignment – individual assignment, acknowledgement sample for assignment – group assignment, acknowledgement for assignment example – individual school assignment, frequently asked questions on acknowledgement for assignment.
An acknowledgement is an essential part of every assignment or project. An acknowledgement is a short write-up that is written with the motive of thanking all of the people who played an instrumental role in helping you or your group overcome the difficulties and complete the assignment. It is always considered an act of good manners to express your gratitude to the people who have directly or indirectly been involved in the process of your assignment.
Before you start writing the acknowledgement for your assignment, you have to make sure that you have the following details in hand.
- Have a list of all the names of the people who have extended their support directly or indirectly and offered suggestions to help you finish the assignment.
- See that you mention the names of the people in a logical order by putting the names of the most important people in the beginning of the acknowledgement.
- Explain briefly how their support and encouragement have aided the completion of the assignment.
- Try not to use many high sounding words in the acknowledgement. Keep it as simple as possible so that it is easy to understand.
- Take care not to miss out on anyone who has been an integral part of the process, no matter how small a role they have played in helping you with the assignment. In case the list is long, you can thank all of them collectively.
- Most importantly, make sure the acknowledgement sounds formal and professional.
Check out Letter Writing for different types of letter writing, including formal letters and informal letters .
Sample Acknowledgements for Assignment
Have a look at the sample acknowledgements for the assignment to have an idea of how you can write an acknowledgement for your assignment.
I would like to thank my Professor-in-charge, Dr. Neelaveni for guiding me throughout the course of this assignment. She was there to help me every step of the way, and her motivation is what helped me complete this assignment successfully. I thank all the teachers who helped me by providing the equipment that was necessary and vital, without which I would not have been able to work effectively on this assignment.
I would also like to express my sincere gratitude to my friends and parents, who stood by me and encouraged me to work on this assignment.
First of all, we would like to thank our Class Teacher, Mrs. Lorraine, who was a constant source of inspiration. She encouraged us to think creatively and motivated us to work on this assignment without giving it a second thought. She expressed full support and provided us with the different teaching aids that were required to complete this assignment. She believed in us even when we could not believe that we could do it. We are also thankful to every member of this group. It was each and every individual’s contribution that made this assignment a success. We were always there to lift each other up, and that was what helped us stay together till the end.
We thank our parents for always trusting in us and teaching us to believe in our abilities and strengths and never give up until the goal is achieved. We are thankful to all our friends who extended their moral support, and above all, we are thankful to God for being with us and giving us the wisdom and ability to do this assignment.
First of all, I would like to thank God, who has always been my guidance and support all these years. I would like to thank my Class Teacher, Mrs. Sindhu Krishna, for giving me the opportunity to work on this assignment and for believing in me. I would like to thank my Science Teachers, Mrs. Agnes, Mrs. Antonette, Mrs. Usha and Ms. Latha, for helping me with the planning and working of this assignment. All of them were ever ready to clear my doubts and help me with all the necessary information and equipment. I would also like to thank my classmates who have extended their moral support throughout the course of this assignment.
My parents never ceased to believe in me. I thank them for encouraging me, guiding me and being there to strengthen me with confidence every time I felt weak or discouraged. I would also like to express my gratitude to all those who played a role directly and indirectly in the completion of this assignment.
What is an acknowledgement for an assignment?
An acknowledgement is usually a short or detailed write up that is written with the motive of expressing the individual’s/group’s gratitude to all those who played a part directly or indirectly in the completion of the said assignment. It is considered an essential and foremost part of an assignment.
What is an acknowledgement for an individual assignment?
I would like to thank my Professor-in-charge, Dr. Neelaveni for guiding me throughout the course of this assignment. She was there to help me every step of the way, and her motivation is what helped me complete this assignment successfully. I thank all the teachers who helped me by providing the equipment when necessary. I would also like to express my sincere gratitude to my friends and parents, who stood by me and encouraged me to work on this assignment.
How long should an acknowledgement for an assignment be?
The length of an acknowledgement for an assignment can be decided in accordance with the type of assignment. An acknowledgement for a simple school assignment can be anywhere between 200-400 words. For a more complex assignment, like a college project, the acknowledgement can be between 500-1000 words, and for a thesis, the acknowledgement can go on even for two pages.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
- Top1000 word
- Top5000 word
- Conjunction
- Sentence into pic
Assign in a sentence

- 某某 2016-01-13 联网相关的政策
- pleasure (225+47)
- sensibility (163+4)
- shipment (201+12)
- for a time (225+6)
- lend (215+20)
- borrow (205+22)
- quorum (47)
- rather (230+68)
- abrogate (32)
- blasphemy (39+1)
- harangue (21+1)
- labyrinth (99+3)
- tangible (163+6)
- replete (51+3)
- private (158+75)
- ton (208+8)
- crowd (163+78)
- dare (250+11)
- shyness (104+5)
- indulge (186+11)
How To Write an Email For Submission Of Assignment
Welcome to this informative article that will guide you on how to write an effective email for the submission of your assignment. If you’re unsure about how to draft an email for submitting your assignment, this article is here to help you!
Table of Contents
What To Do Before Writing the Email
Before you start writing the actual email, it’s important to take a few preparatory steps to ensure that your email is clear, concise, and professional:
- Gather all necessary information related to your assignment, such as the due date, submission guidelines, and any specific instructions given by your instructor.
- Review your assignment to ensure it meets the requirements and makes sense.
- If your instructor has provided a specific email address or subject line to use, make note of it.
- Consider attaching your assignment in the appropriate format if required.
What to Include In the Email
When composing your email for assignment submission, it’s important to include the following parts:
Subject Line
Choose a subject line that clearly indicates the purpose of your email. For example, “Assignment Submission – [Course Name]”. This helps the recipient identify the email’s content quickly.
Begin your email with a polite and professional greeting, such as “Dear Professor [Last Name],” or “Hi [Instructor’s Name],”. Use the appropriate salutation based on your relationship with the recipient.
Introduction
Introduce yourself briefly and mention the course or assignment you are submitting. This provides context for the recipient.
In the body of the email, mention any relevant details or specific instructions provided by your instructor. Clearly state that you are submitting your assignment and acknowledge the due date. If there are any additional comments or questions related to the assignment, include them here.
End your email with a courteous closing, such as “Thank you,” or “Best regards,” followed by your full name and contact information. This shows professionalism and makes it easy for the recipient to respond if necessary.
Email Template – Assignment Submission
Subject: Assignment Submission – [Course Name] Dear Professor/Instructor [Last Name], I hope this email finds you well. I am writing to submit my assignment for the [Course Name]. The assignment is attached in the required format. I have completed the assignment as per the given guidelines and it is ready for submission. The due date for the assignment is [Due Date]. If you have any further instructions or clarifications, please let me know. Thank you for your time and consideration. I look forward to hearing from you soon. Best regards, [Your Full Name] [Your Contact Information]
Writing an effective email for the submission of an assignment is essential to ensure clarity and professionalism. By following the steps outlined in this article, you can confidently compose your email and increase the likelihood of a positive response. Remember to always be polite, concise, and include all necessary information. Good luck with your assignment!
Additional tips:
- Double-check all the information before sending the email to avoid any errors or omissions.
- Use a professional email address and avoid using casual or inappropriate language.
- If there is a specific email format recommended by your institution, consult it for guidance.

Donald Trump found guilty in historic New York hush money case
A New York jury on Thursday found Donald Trump guilty on all 34 felony counts of falsifying business records — the first time a former U.S. president has been convicted of a crime.
The jury reached its verdict in the historic case after 9½ hours of deliberations, which began Wednesday.
He'll be sentenced on July 11, four days before the Republican National Convention. He faces penalties from a fine to four years in prison on each count, although it's expected he would be sentenced for the offenses concurrently, not consecutively.
Follow live updates here.
"This was a disgrace. This was a rigged trial by a conflicted judge who was corrupt,” Trump fumed to reporters afterward.
The verdict was read in the Manhattan courtroom where Trump has been on trial since April 15. He had pleaded not guilty to 34 counts of falsifying business records related to a hush money payment his former lawyer Michael Cohen made to adult film star Stormy Daniels in the final weeks of the 2016 presidential election.
Trump looked down with his eyes narrowed as the jury foreperson read the word "guilty" to each count.
The judge thanked the jurors for their service in the weekslong trial. “You gave this matter the attention it deserved, and I want to thank you for that,” Judge Juan Merchan told them. Trump appeared to be scowling at the jurors as they walked by him on their way out of the courtroom.
Trump's attorney Todd Blanche made a motion for acquittal after the jury left the room, which the judge denied.
Manhattan District Attorney Alvin Bragg would not comment on what type of sentence he might seek, saying his office would do its talking in court papers.
"While this defendant may be unlike any other in American history, we arrived at this trial and ultimately today at this verdict in the same manner as every other case that comes to the courtroom doors — by following the facts and the law in doing so, without fear or favor," Bragg said. Asked for his reaction to the verdict, Bragg, who was inundated with threats from Trump supporters during the probe, said, "I did my job. We did our job."
Trump, the presumptive Republican nominee for president, immediately set out fundraising off the news, posting on his website that he's "a political prisoner" and urging his followers to give money.
Legal experts have told NBC News that even if Trump is sentenced to time behind bars, he'd most likely be allowed to remain out of jail while he appeals the verdict, a process that could take months or more. That means the sentence would most likely not interfere with his ability to accept the Republican nomination for president at the July convention.
And it likely wouldn't impact his ability to be elected. "There are no other qualifications other than those in the Constitution,” Chuck Rosenberg, a former U.S. attorney and NBC News & MSNBC Legal Analyst said following Thursday’s verdict.
President Joe Biden's campaign praised the verdict in a statement but stressed that Trump needs to be defeated in November.
“In New York today, we saw that no one is above the law," said the campaign's communications director, Michael Tyler, but the "verdict does not change the fact that the American people face a simple reality. There is still only one way to keep Donald Trump out of the Oval Office: at the ballot box."
In his closing argument this week, prosecutor Joshua Steinglass told the jury that “the law is the law, and it applies to everyone equally. There is no special standard for this defendant.”
“You, the jury, have the ability to hold the defendant accountable,” Steinglass said.
Trump had maintained that the DA’s office had no case and that there had been no crime. “President Trump is innocent. He did not commit any crimes,” Blanche said in his closing statement, arguing the payments to Cohen were legitimate.
Prosecutors said the disguised payment to Cohen was part of a “planned, coordinated long-running conspiracy to influence the 2016 election, to help Donald Trump get elected through illegal expenditures, to silence people who had something bad to say about his behavior, using doctored corporate records and bank forms to conceal those payments along the way.”
“It was election fraud. Pure and simple,” prosecutor Matthew Colangelo said in his opening statement.
While Trump wasn’t charged with conspiracy, prosecutors argued he caused the records to be falsified because he was trying to cover up a violation of state election law — and falsifying business records with the intent to cover another crime raises the offense from a misdemeanor to a felony.
Trump was convicted after a sensational weekslong trial that included combative testimony from Cohen, Trump’s self-described former fixer, and Daniels, who testified that she had a sexual encounter with Trump in 2006 after she met him at a celebrity golf tournament. Trump has denied her claim, and his attorney had suggested that Cohen acted on his own because he thought it would make “the boss” happy.
Other witnesses included former White House staffers, among them adviser Hope Hicks, former Trump Organization executives and former National Enquirer publisher David Pecker.
Trump didn’t take the witness stand to offer his own account of what happened, even though he proclaimed before the trial began that he would “absolutely” testify. The defense’s main witness was Robert Costello, a lawyer whom Cohen considered retaining in 2018. Costello, who testified that Cohen had told him Trump had nothing to do with the Daniels’ payment, enraged Merchan by making disrespectful comments and faces on the stand. At one point, the judge cleared the courtroom during Costello’s testimony and threatened to hold him in contempt.
Cohen testified that he lied to Costello because he didn’t trust him and that he’d lied to others about Trump’s involvement at the time because he wanted to protect his former boss.
Cohen was the lone witness to testify to Trump’s direct involvement in the $130,000 payment and the subsequent reimbursement plan. Blanche spent days challenging his credibility, getting Cohen to acknowledge he has a history of lying, including under oath.
Cohen said he was paid the Daniels cash in a series of payments from Trump throughout 2017 that the Trump Organization characterized as payments pursuant to a retainer agreement “for legal services rendered.”
Prosecutors said there was no such agreement, and Cohen’s version of events was supported by documentary evidence and witness testimony.
Blanche contended that the series of checks then-President Trump paid Cohen in 2017 “was not a payback to Mr. Cohen for the money that he gave to Ms. Daniels” and that he was being paid for his legal work as Trump’s personal lawyer.
Testimony from Jeff McConney, a former senior vice president at Trump’s company, challenged that position. McConney said the company’s chief financial officer, Allen Weisselberg, told him that Cohen was being reimbursed for a $130,000 payment, and prosecutors entered Weisselberg’s handwritten notes about the payment formula as evidence. Cohen said Trump agreed to the arrangement in a meeting with him and Weisselberg just days before he was inaugurated as the 45th president.
Weisselberg didn't testify. He’s in jail on a perjury charge related to his testimony in New York Attorney General Letitia James’ civil fraud case against Trump and his company. Cohen, McConney and other witnesses said Weisselberg, who spent decades working for Trump, always sought his approval for large expenditures.
In all, the prosecution called 20 witnesses, while the defense called two.
Trump had frequently claimed, falsely, that the charges against him were a political concoction orchestrated by Biden to keep him off the campaign trail. But Trump eventually managed to bring the campaign to the courtroom, hosting top Republicans, including House Speaker Mike Johnson of Louisiana and Sens. JD Vance of Ohio and Rick Scott of Florida, as his guests in court. Trump also used court breaks to tout political messages to his supporters, while his surrogates sidestepped Merchan’s gag order by attacking witnesses, individual prosecutors and Merchan’s daughter.
Merchan fined Trump $10,000 during the trial for violating his order, including attacks on Cohen and Daniels, and warned he could have him locked up if he continued violating the order.
Cohen celebrated the verdict in a post on X. "Today is an important day for accountability and the rule of law. While it has been a difficult journey for me and my family, the truth always matters," Cohen wrote.
Trump was indicted in March of last year after a yearslong investigation by Bragg and his predecessor, Cyrus Vance. The charges were the first ever brought against a former president, although Trump has since been charged and pleaded not guilty in three other cases. None of the three — a federal election interference case in Washington, D.C., a state election interference case in Georgia and a federal case alleging he mishandled classified documents and national security information — appear likely to go to trial before the Nov. 5 presidential election.
Adam Reiss is a reporter and producer for NBC and MSNBC.
Gary Grumbach produces and reports for NBC News, based in Washington, D.C.
Dareh Gregorian is a politics reporter for NBC News.
Tom Winter is a New York-based correspondent covering crime, courts, terrorism and financial fraud on the East Coast for the NBC News Investigative Unit.
Jillian Frankel is a 2024 NBC News campaign embed.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
For example, if you have an interest in photography, you may find an assignment asking for an explanation of the differences between digital and film lens focal lengths. 0. 1. The animals were to race across a river, and the order of assignment would be based on the order of the animals reaching the opposite riverbank.
What this handout is about. The first step in any successful college writing venture is reading the assignment. While this sounds like a simple task, it can be a tough one. This handout will help you unravel your assignment and begin to craft an effective response. Much of the following advice will involve translating typical assignment terms ...
noun. Definition of assignment. Synonyms for assignment. The reporter is here on assignment. The reporter is here on an assignment. She asked if she could change her seating assignment. The students were given a homework assignment. The reporter's assignment is to interview the candidate.
Assignment is a task or piece of work that someone is given to do. It can also refer to the allocation of a particular task or job to someone. To use the word assignment in a sentence, simply place it in the context of giving or receiving a task. For example, "The teacher handed out the math assignment to the students" or "I have a new ...
Examples Of Using Assignment In A Sentence. When it comes to incorporating the word "assignment" into a sentence, it is crucial to showcase its versatility and various contexts. By utilizing a combination of simple and complex sentences, we can shed light on the different nuances associated with this term. Let's explore some examples: 1.
The meaning of ASSIGNMENT is the act of assigning something. How to use assignment in a sentence. Synonym Discussion of Assignment.
I settled for a short hop across the Channel on a work assignment. Times, Sunday Times. ( 2016) His first assignment was to write a program for an insurance broker in Dorset, using assembly code. Times, Sunday Times. ( 2016) They must be capable of being converted into specific targets and specific assignments. Peter F. Drucker.
Assignment Analysis & Sentence Outline. In the Effective Writing Center, we sometimes have to tell students, "Your paper is well written and interesting, but it doesn't fulfill the assignment. You've done good work, but it's not what your professor is looking for. Let's analyze this assignment closely . . . ."
Examples of assignment in a sentence, how to use it. 98 examples: Apart from that, there is a suspicion that programming without assignments or…
Simple sentences in the Future Simple Tense. I will visit my parents next weekend. She'll finish her project by tomorrow. They will go on vacation next month. We'll have dinner at a fancy restaurant tonight. He will start his new job next week. I won't attend the party tomorrow. She won't buy a new car this year.
A simple sentence is a sentence containing only one clause, or more specifically, an independent clause, with a subject and a predicate. A simple sentence is typically made up of a subject, verb, and object, or SVO, and creates a complete thought; however, since a simple predicate is a verb or verb phrase only, a simple sentence can also be ...
A simple sentence contains a subject and a verb, and it may also have an object and modifiers. However, it contains only one independent clause. Key: Yellow, bold = subject; green underline = verb, blue, italics = object, pink, regular font =prepositional phrase. Here are a few examples: She wrote.
Examples of ASSIGN in a sentence, how to use it. 23 examples: Works that were centrally planned and assigned, moreover, had a better chance…
assignment in American English. (əˈsainmənt) noun. 1. something assigned, as a particular task or duty. She completed the assignment and went on to other jobs. 2. a position of responsibility, post of duty, or the like, to which one is appointed. He left for his assignment in the Middle East.
Simple Sentences. Simple sentences are, unsurprisingly, the easiest type of sentence for students to grasp and construct for themselves. Often these types of sentences will be the first sentences that children write by themselves, following the well-known Subject - Verb - Object or SVO pattern.. The subject of the sentence will be the noun that begins the sentence.
Use these 37 simple sentence examples and the accompanying worksheet to help you understand this type of sentence, which has only one independent clause.
An acknowledgement for a simple school assignment can be anywhere between 200-400 words. For a more complex assignment, like a college project, the acknowledgement can be between 500-1000 words, and for a thesis, the acknowledgement can go on even for two pages.
Present simple vs. present continuous. While the present simple is typically used to refer to habits, states, and facts, the present continuous is used to describe a temporary action that is currently taking place.. Examples: Present simple vs. present continuous Justin eats. dinner at 6 p.m. every day.. [describing a habit] Justin is eating dinner right now. . [describing a temporary action ...
Meaning: [ə'saɪn] v. 1. give an assignment to (a person) to a post, or assign a task to (a person) 2. give out or allot 3. attribute or credit to 4. select something or someone for a specific purpose 5. attribute or give 6. make undue claims to having 7. transfer one's right to 8. decide as to where something belongs in a scheme. Random good ...
Dear Professor/Instructor [Last Name], I hope this email finds you well. I am writing to submit my assignment for the [Course Name]. The assignment is attached in the required format. I have completed the assignment as per the given guidelines and it is ready for submission. The due date for the assignment is [Due Date].
Simple Sentence. One independent clause. Independent clause. Group of words that: Can stand alone Has a subject and a verb Makes a complete statement. Subject. What the sentence is about. What kind of words do we use as subjects? Nouns. Nouns. Person, place, thing, quality, or idea. Compound subject.
A New York jury on Thursday found Donald Trump guilty on all 34 felony counts of falsifying business records — the first time a former U.S. president has been convicted of a crime. The jury ...
Link Copied! U.S. President Joe Biden looks on during a campaign event at Girard College in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, U.S., May 29, 2024. After dozens of Palestinian civilians were killed ...