- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences

Where Financial Reporting Still Falls Short
- H. David Sherman
- S. David Young

For financial statements to be useful, they must be accurate. Unfortunately, these reports often depend on subjective judgement calls, offer misleading comparisons, and fall prey to manipulation due to misaligned incentives. The authors examine several examples of poor accounting from recent history and discuss what went wrong in each of these cases. They then go on to suggest several strategies to help leaders improve accuracy in financial reporting, including techniques to detect fraudulent numbers and recognize verbal cues that indicate unscrupulous behavior.
Even after a raft of reforms, corporate accounting remains murky. Here’s what you need to know to evaluate a company accurately.
Idea in Brief
The problem.
Despite tightening financial regulations, such as Sarbanes-Oxley and Dodd-Frank, investors, board members, and executives are still unable to rely on financial statements in order to make wise decisions about whether to invest in or acquire a company, for several reasons.
Why It Happens
First, flawed estimates creep in to financial statements, even when made in good faith. Second, standard metrics often don’t capture the true value of companies, especially for innovative firms in new markets. And third, executives continue to face strong incentives to manipulate the numbers.
What to Do About It
In this article, the authors examine the impact of recent financial regulations and consider new techniques to combat the gaming of performance numbers.
In a perfect world, investors, board members, and executives would have full confidence in companies’ financial statements. They could rely on the numbers to make intelligent estimates of the magnitude, timing, and uncertainty of future cash flows and to judge whether the resulting estimate of value was fairly represented in the current stock price. And they could make wise decisions about whether to invest in or acquire a company, thus promoting the efficient allocation of capital.
- H. David Sherman ( [email protected] ) is a professor of accounting at Northeastern University’s D’Amore-McKim School of Business and a former fellow at the SEC Division of Corporate Finance. He is a coauthor of “Tread Lightly Through These Accounting Minefields” (HBR July–August 2001).
- S. David Young ( [email protected] ) is a professor of accounting and control at INSEAD. He is a coauthor of “Tread Lightly Through These Accounting Minefields” (HBR July–August 2001).
Partner Center
- Browse All Articles
- Newsletter Sign-Up

- 22 Apr 2024
- Research & Ideas
When Does Impact Investing Make the Biggest Impact?
More investors want to back businesses that contribute to social change, but are impact funds the only approach? Research by Shawn Cole, Leslie Jeng, Josh Lerner, Natalia Rigol, and Benjamin Roth challenges long-held assumptions about impact investing and reveals where such funds make the biggest difference.

- 23 Jan 2024
More Than Memes: NFTs Could Be the Next Gen Deed for a Digital World
Non-fungible tokens might seem like a fad approach to selling memes, but the concept could help companies open new markets and build communities. Scott Duke Kominers and Steve Kaczynski go beyond the NFT hype in their book, The Everything Token.

- 12 Sep 2023
How Can Financial Advisors Thrive in Shifting Markets? Diversify, Diversify, Diversify
Financial planners must find new ways to market to tech-savvy millennials and gen Z investors or risk irrelevancy. Research by Marco Di Maggio probes the generational challenges that advisory firms face as baby boomers retire. What will it take to compete in a fintech and crypto world?

- 17 Aug 2023
‘Not a Bunch of Weirdos’: Why Mainstream Investors Buy Crypto
Bitcoin might seem like the preferred tender of conspiracy theorists and criminals, but everyday investors are increasingly embracing crypto. A study of 59 million consumers by Marco Di Maggio and colleagues paints a shockingly ordinary picture of today's cryptocurrency buyer. What do they stand to gain?

- 17 Jul 2023
Money Isn’t Everything: The Dos and Don’ts of Motivating Employees
Dangling bonuses to checked-out employees might only be a Band-Aid solution. Brian Hall shares four research-based incentive strategies—and three perils to avoid—for leaders trying to engage the post-pandemic workforce.

- 20 Jun 2023
- Cold Call Podcast
Elon Musk’s Twitter Takeover: Lessons in Strategic Change
In late October 2022, Elon Musk officially took Twitter private and became the company’s majority shareholder, finally ending a months-long acquisition saga. He appointed himself CEO and brought in his own team to clean house. Musk needed to take decisive steps to succeed against the major opposition to his leadership from both inside and outside the company. Twitter employees circulated an open letter protesting expected layoffs, advertising agencies advised their clients to pause spending on Twitter, and EU officials considered a broader Twitter ban. What short-term actions should Musk take to stabilize the situation, and how should he approach long-term strategy to turn around Twitter? Harvard Business School assistant professor Andy Wu and co-author Goran Calic, associate professor at McMaster University’s DeGroote School of Business, discuss Twitter as a microcosm for the future of media and information in their case, “Twitter Turnaround and Elon Musk.”

- 06 Jun 2023
The Opioid Crisis, CEO Pay, and Shareholder Activism
In 2020, AmerisourceBergen Corporation, a Fortune 50 company in the drug distribution industry, agreed to settle thousands of lawsuits filed nationwide against the company for its opioid distribution practices, which critics alleged had contributed to the opioid crisis in the US. The $6.6 billion global settlement caused a net loss larger than the cumulative net income earned during the tenure of the company’s CEO, which began in 2011. In addition, AmerisourceBergen’s legal and financial troubles were accompanied by shareholder demands aimed at driving corporate governance changes in companies in the opioid supply chain. Determined to hold the company’s leadership accountable, the shareholders launched a campaign in early 2021 to reject the pay packages of executives. Should the board reduce the executives’ pay, as of means of improving accountability? Or does punishing the AmerisourceBergen executives for paying the settlement ignore the larger issue of a business’s responsibility to society? Harvard Business School professor Suraj Srinivasan discusses executive compensation and shareholder activism in the context of the US opioid crisis in his case, “The Opioid Settlement and Controversy Over CEO Pay at AmerisourceBergen.”

- 16 May 2023
- In Practice
After Silicon Valley Bank's Flameout, What's Next for Entrepreneurs?
Silicon Valley Bank's failure in the face of rising interest rates shook founders and funders across the country. Julia Austin, Jeffrey Bussgang, and Rembrand Koning share key insights for rattled entrepreneurs trying to make sense of the financing landscape.

- 27 Apr 2023
Equity Bank CEO James Mwangi: Transforming Lives with Access to Credit
James Mwangi, CEO of Equity Bank, has transformed lives and livelihoods throughout East and Central Africa by giving impoverished people access to banking accounts and micro loans. He’s been so successful that in 2020 Forbes coined the term “the Mwangi Model.” But can we really have both purpose and profit in a firm? Harvard Business School professor Caroline Elkins, who has spent decades studying Africa, explores how this model has become one that business leaders are seeking to replicate throughout the world in her case, “A Marshall Plan for Africa': James Mwangi and Equity Group Holdings.” As part of a new first-year MBA course at Harvard Business School, this case examines the central question: what is the social purpose of the firm?

- 25 Apr 2023
Using Design Thinking to Invent a Low-Cost Prosthesis for Land Mine Victims
Bhagwan Mahaveer Viklang Sahayata Samiti (BMVSS) is an Indian nonprofit famous for creating low-cost prosthetics, like the Jaipur Foot and the Stanford-Jaipur Knee. Known for its patient-centric culture and its focus on innovation, BMVSS has assisted more than one million people, including many land mine survivors. How can founder D.R. Mehta devise a strategy that will ensure the financial sustainability of BMVSS while sustaining its human impact well into the future? Harvard Business School Dean Srikant Datar discusses the importance of design thinking in ensuring a culture of innovation in his case, “BMVSS: Changing Lives, One Jaipur Limb at a Time.”

- 18 Apr 2023
What Happens When Banks Ditch Coal: The Impact Is 'More Than Anyone Thought'
Bank divestment policies that target coal reduced carbon dioxide emissions, says research by Boris Vallée and Daniel Green. Could the finance industry do even more to confront climate change?

The Best Person to Lead Your Company Doesn't Work There—Yet
Recruiting new executive talent to revive portfolio companies has helped private equity funds outperform major stock indexes, says research by Paul Gompers. Why don't more public companies go beyond their senior executives when looking for top leaders?

- 11 Apr 2023
A Rose by Any Other Name: Supply Chains and Carbon Emissions in the Flower Industry
Headquartered in Kitengela, Kenya, Sian Flowers exports roses to Europe. Because cut flowers have a limited shelf life and consumers want them to retain their appearance for as long as possible, Sian and its distributors used international air cargo to transport them to Amsterdam, where they were sold at auction and trucked to markets across Europe. But when the Covid-19 pandemic caused huge increases in shipping costs, Sian launched experiments to ship roses by ocean using refrigerated containers. The company reduced its costs and cut its carbon emissions, but is a flower that travels halfway around the world truly a “low-carbon rose”? Harvard Business School professors Willy Shih and Mike Toffel debate these questions and more in their case, “Sian Flowers: Fresher by Sea?”

Is Amazon a Retailer, a Tech Firm, or a Media Company? How AI Can Help Investors Decide
More companies are bringing seemingly unrelated businesses together in new ways, challenging traditional stock categories. MarcAntonio Awada and Suraj Srinivasan discuss how applying machine learning to regulatory data could reveal new opportunities for investors.

- 07 Apr 2023
When Celebrity ‘Crypto-Influencers’ Rake in Cash, Investors Lose Big
Kim Kardashian, Lindsay Lohan, and other entertainers have been accused of promoting crypto products on social media without disclosing conflicts. Research by Joseph Pacelli shows what can happen to eager investors who follow them.

- 31 Mar 2023
Can a ‘Basic Bundle’ of Health Insurance Cure Coverage Gaps and Spur Innovation?
One in 10 people in America lack health insurance, resulting in $40 billion of care that goes unpaid each year. Amitabh Chandra and colleagues say ensuring basic coverage for all residents, as other wealthy nations do, could address the most acute needs and unlock efficiency.

- 23 Mar 2023
As Climate Fears Mount, More Investors Turn to 'ESG' Funds Despite Few Rules
Regulations and ratings remain murky, but that's not deterring climate-conscious investors from paying more for funds with an ESG label. Research by Mark Egan and Malcolm Baker sizes up the premium these funds command. Is it time for more standards in impact investing?
- 14 Mar 2023
What Does the Failure of Silicon Valley Bank Say About the State of Finance?
Silicon Valley Bank wasn't ready for the Fed's interest rate hikes, but that's only part of the story. Victoria Ivashina and Erik Stafford probe the complex factors that led to the second-biggest bank failure ever.

- 13 Mar 2023
What Would It Take to Unlock Microfinance's Full Potential?
Microfinance has been seen as a vehicle for economic mobility in developing countries, but the results have been mixed. Research by Natalia Rigol and Ben Roth probes how different lending approaches might serve entrepreneurs better.

- 16 Feb 2023
ESG Activists Met the Moment at ExxonMobil, But Did They Succeed?
Engine No. 1, a small hedge fund on a mission to confront climate change, managed to do the impossible: Get dissident members on ExxonMobil's board. But lasting social impact has proved more elusive. Case studies by Mark Kramer, Shawn Cole, and Vikram Gandhi look at the complexities of shareholder activism.
Demand-side and Supply-side Constraints in the Market for Financial Advice
In this review, we argue that access to financial advice and the quality of this advice is shaped by a broad array of demand-side and supply-side constraints. While the literature has predominantly focused on conflicts of interest between advisors and clients, we highlight that the transaction costs of providing advice, mistaken beliefs on the demand side or supply side, and other factors can have equally detrimental effects on the quality and access to advice. Moreover, these factors affect how researchers should assess the impact of financial advice across heterogeneous groups of households. While households with low levels of financial literacy are more likely to benefit from advice—potentially including conflicted advice—they are also the least likely to detect misconduct, and perhaps the least likely to understand the value of paying for advice. Regulators should consider not only how regulation changes the quality of advice, but also the fraction of households who are able to receive it and how different groups would have invested without any advice. Financial innovation has the potential to provide customized advice at low cost, but also to embed conflicts of interest in algorithms that are opaque to households and regulators.
Jonathan Reuter is affiliated with Boston College and NBER. Antoinette Schoar is affiliated with MIT Sloan, ideas42 and NBER. The authors thank Roman Inderst (editor) for helpful comments and Xin Xiong for helpful research assistance. Neither author has any funding or material and relevant financial relationships to disclose. The views expressed herein are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of the National Bureau of Economic Research.
MARC RIS BibTeΧ
Download Citation Data
Working Groups
More from nber.
In addition to working papers , the NBER disseminates affiliates’ latest findings through a range of free periodicals — the NBER Reporter , the NBER Digest , the Bulletin on Retirement and Disability , the Bulletin on Health , and the Bulletin on Entrepreneurship — as well as online conference reports , video lectures , and interviews .

McKinsey Global Private Markets Review 2024: Private markets in a slower era
At a glance, macroeconomic challenges continued.

McKinsey Global Private Markets Review 2024: Private markets: A slower era
If 2022 was a tale of two halves, with robust fundraising and deal activity in the first six months followed by a slowdown in the second half, then 2023 might be considered a tale of one whole. Macroeconomic headwinds persisted throughout the year, with rising financing costs, and an uncertain growth outlook taking a toll on private markets. Full-year fundraising continued to decline from 2021’s lofty peak, weighed down by the “denominator effect” that persisted in part due to a less active deal market. Managers largely held onto assets to avoid selling in a lower-multiple environment, fueling an activity-dampening cycle in which distribution-starved limited partners (LPs) reined in new commitments.
About the authors
This article is a summary of a larger report, available as a PDF, that is a collaborative effort by Fredrik Dahlqvist , Alastair Green , Paul Maia, Alexandra Nee , David Quigley , Aditya Sanghvi , Connor Mangan, John Spivey, Rahel Schneider, and Brian Vickery , representing views from McKinsey’s Private Equity & Principal Investors Practice.
Performance in most private asset classes remained below historical averages for a second consecutive year. Decade-long tailwinds from low and falling interest rates and consistently expanding multiples seem to be things of the past. As private market managers look to boost performance in this new era of investing, a deeper focus on revenue growth and margin expansion will be needed now more than ever.

Perspectives on a slower era in private markets
Global fundraising contracted.
Fundraising fell 22 percent across private market asset classes globally to just over $1 trillion, as of year-end reported data—the lowest total since 2017. Fundraising in North America, a rare bright spot in 2022, declined in line with global totals, while in Europe, fundraising proved most resilient, falling just 3 percent. In Asia, fundraising fell precipitously and now sits 72 percent below the region’s 2018 peak.
Despite difficult fundraising conditions, headwinds did not affect all strategies or managers equally. Private equity (PE) buyout strategies posted their best fundraising year ever, and larger managers and vehicles also fared well, continuing the prior year’s trend toward greater fundraising concentration.
The numerator effect persisted
Despite a marked recovery in the denominator—the 1,000 largest US retirement funds grew 7 percent in the year ending September 2023, after falling 14 percent the prior year, for example 1 “U.S. retirement plans recover half of 2022 losses amid no-show recession,” Pensions and Investments , February 12, 2024. —many LPs remain overexposed to private markets relative to their target allocations. LPs started 2023 overweight: according to analysis from CEM Benchmarking, average allocations across PE, infrastructure, and real estate were at or above target allocations as of the beginning of the year. And the numerator grew throughout the year, as a lack of exits and rebounding valuations drove net asset values (NAVs) higher. While not all LPs strictly follow asset allocation targets, our analysis in partnership with global private markets firm StepStone Group suggests that an overallocation of just one percentage point can reduce planned commitments by as much as 10 to 12 percent per year for five years or more.
Despite these headwinds, recent surveys indicate that LPs remain broadly committed to private markets. In fact, the majority plan to maintain or increase allocations over the medium to long term.

Investors fled to known names and larger funds
Fundraising concentration reached its highest level in over a decade, as investors continued to shift new commitments in favor of the largest fund managers. The 25 most successful fundraisers collected 41 percent of aggregate commitments to closed-end funds (with the top five managers accounting for nearly half that total). Closed-end fundraising totals may understate the extent of concentration in the industry overall, as the largest managers also tend to be more successful in raising non-institutional capital.
While the largest funds grew even larger—the largest vehicles on record were raised in buyout, real estate, infrastructure, and private debt in 2023—smaller and newer funds struggled. Fewer than 1,700 funds of less than $1 billion were closed during the year, half as many as closed in 2022 and the fewest of any year since 2012. New manager formation also fell to the lowest level since 2012, with just 651 new firms launched in 2023.
Whether recent fundraising concentration and a spate of M&A activity signals the beginning of oft-rumored consolidation in the private markets remains uncertain, as a similar pattern developed in each of the last two fundraising downturns before giving way to renewed entrepreneurialism among general partners (GPs) and commitment diversification among LPs. Compared with how things played out in the last two downturns, perhaps this movie really is different, or perhaps we’re watching a trilogy reusing a familiar plotline.
Dry powder inventory spiked (again)
Private markets assets under management totaled $13.1 trillion as of June 30, 2023, and have grown nearly 20 percent per annum since 2018. Dry powder reserves—the amount of capital committed but not yet deployed—increased to $3.7 trillion, marking the ninth consecutive year of growth. Dry powder inventory—the amount of capital available to GPs expressed as a multiple of annual deployment—increased for the second consecutive year in PE, as new commitments continued to outpace deal activity. Inventory sat at 1.6 years in 2023, up markedly from the 0.9 years recorded at the end of 2021 but still within the historical range. NAV grew as well, largely driven by the reluctance of managers to exit positions and crystallize returns in a depressed multiple environment.
Private equity strategies diverged
Buyout and venture capital, the two largest PE sub-asset classes, charted wildly different courses over the past 18 months. Buyout notched its highest fundraising year ever in 2023, and its performance improved, with funds posting a (still paltry) 5 percent net internal rate of return through September 30. And although buyout deal volumes declined by 19 percent, 2023 was still the third-most-active year on record. In contrast, venture capital (VC) fundraising declined by nearly 60 percent, equaling its lowest total since 2015, and deal volume fell by 36 percent to the lowest level since 2019. VC funds returned –3 percent through September, posting negative returns for seven consecutive quarters. VC was the fastest-growing—as well as the highest-performing—PE strategy by a significant margin from 2010 to 2022, but investors appear to be reevaluating their approach in the current environment.
Private equity entry multiples contracted
PE buyout entry multiples declined by roughly one turn from 11.9 to 11.0 times EBITDA, slightly outpacing the decline in public market multiples (down from 12.1 to 11.3 times EBITDA), through the first nine months of 2023. For nearly a decade leading up to 2022, managers consistently sold assets into a higher-multiple environment than that in which they had bought those assets, providing a substantial performance tailwind for the industry. Nowhere has this been truer than in technology. After experiencing more than eight turns of multiple expansion from 2009 to 2021 (the most of any sector), technology multiples have declined by nearly three turns in the past two years, 50 percent more than in any other sector. Overall, roughly two-thirds of the total return for buyout deals that were entered in 2010 or later and exited in 2021 or before can be attributed to market multiple expansion and leverage. Now, with falling multiples and higher financing costs, revenue growth and margin expansion are taking center stage for GPs.
Real estate receded
Demand uncertainty, slowing rent growth, and elevated financing costs drove cap rates higher and made price discovery challenging, all of which weighed on deal volume, fundraising, and investment performance. Global closed-end fundraising declined 34 percent year over year, and funds returned −4 percent in the first nine months of the year, losing money for the first time since the 2007–08 global financial crisis. Capital shifted away from core and core-plus strategies as investors sought liquidity via redemptions in open-end vehicles, from which net outflows reached their highest level in at least two decades. Opportunistic strategies benefited from this shift, with investors focusing on capital appreciation over income generation in a market where alternative sources of yield have grown more attractive. Rising interest rates widened bid–ask spreads and impaired deal volume across food groups, including in what were formerly hot sectors: multifamily and industrial.
Private debt pays dividends
Debt again proved to be the most resilient private asset class against a turbulent market backdrop. Fundraising declined just 13 percent, largely driven by lower commitments to direct lending strategies, for which a slower PE deal environment has made capital deployment challenging. The asset class also posted the highest returns among all private asset classes through September 30. Many private debt securities are tied to floating rates, which enhance returns in a rising-rate environment. Thus far, managers appear to have successfully navigated the rising incidence of default and distress exhibited across the broader leveraged-lending market. Although direct lending deal volume declined from 2022, private lenders financed an all-time high 59 percent of leveraged buyout transactions last year and are now expanding into additional strategies to drive the next era of growth.
Infrastructure took a detour
After several years of robust growth and strong performance, infrastructure and natural resources fundraising declined by 53 percent to the lowest total since 2013. Supply-side timing is partially to blame: five of the seven largest infrastructure managers closed a flagship vehicle in 2021 or 2022, and none of those five held a final close last year. As in real estate, investors shied away from core and core-plus investments in a higher-yield environment. Yet there are reasons to believe infrastructure’s growth will bounce back. Limited partners (LPs) surveyed by McKinsey remain bullish on their deployment to the asset class, and at least a dozen vehicles targeting more than $10 billion were actively fundraising as of the end of 2023. Multiple recent acquisitions of large infrastructure GPs by global multi-asset-class managers also indicate marketwide conviction in the asset class’s potential.
Private markets still have work to do on diversity
Private markets firms are slowly improving their representation of females (up two percentage points over the prior year) and ethnic and racial minorities (up one percentage point). On some diversity metrics, including entry-level representation of women, private markets now compare favorably with corporate America. Yet broad-based parity remains elusive and too slow in the making. Ethnic, racial, and gender imbalances are particularly stark across more influential investing roles and senior positions. In fact, McKinsey’s research reveals that at the current pace, it would take several decades for private markets firms to reach gender parity at senior levels. Increasing representation across all levels will require managers to take fresh approaches to hiring, retention, and promotion.
Artificial intelligence generating excitement
The transformative potential of generative AI was perhaps 2023’s hottest topic (beyond Taylor Swift). Private markets players are excited about the potential for the technology to optimize their approach to thesis generation, deal sourcing, investment due diligence, and portfolio performance, among other areas. While the technology is still nascent and few GPs can boast scaled implementations, pilot programs are already in flight across the industry, particularly within portfolio companies. Adoption seems nearly certain to accelerate throughout 2024.
Private markets in a slower era
If private markets investors entered 2023 hoping for a return to the heady days of 2021, they likely left the year disappointed. Many of the headwinds that emerged in the latter half of 2022 persisted throughout the year, pressuring fundraising, dealmaking, and performance. Inflation moderated somewhat over the course of the year but remained stubbornly elevated by recent historical standards. Interest rates started high and rose higher, increasing the cost of financing. A reinvigorated public equity market recovered most of 2022’s losses but did little to resolve the valuation uncertainty private market investors have faced for the past 18 months.
Within private markets, the denominator effect remained in play, despite the public market recovery, as the numerator continued to expand. An activity-dampening cycle emerged: higher cost of capital and lower multiples limited the ability or willingness of general partners (GPs) to exit positions; fewer exits, coupled with continuing capital calls, pushed LP allocations higher, thereby limiting their ability or willingness to make new commitments. These conditions weighed on managers’ ability to fundraise. Based on data reported as of year-end 2023, private markets fundraising fell 22 percent from the prior year to just over $1 trillion, the largest such drop since 2009 (Exhibit 1).
The impact of the fundraising environment was not felt equally among GPs. Continuing a trend that emerged in 2022, and consistent with prior downturns in fundraising, LPs favored larger vehicles and the scaled GPs that typically manage them. Smaller and newer managers struggled, and the number of sub–$1 billion vehicles and new firm launches each declined to its lowest level in more than a decade.
Despite the decline in fundraising, private markets assets under management (AUM) continued to grow, increasing 12 percent to $13.1 trillion as of June 30, 2023. 2023 fundraising was still the sixth-highest annual haul on record, pushing dry powder higher, while the slowdown in deal making limited distributions.
Investment performance across private market asset classes fell short of historical averages. Private equity (PE) got back in the black but generated the lowest annual performance in the past 15 years, excluding 2022. Closed-end real estate produced negative returns for the first time since 2009, as capitalization (cap) rates expanded across sectors and rent growth dissipated in formerly hot sectors, including multifamily and industrial. The performance of infrastructure funds was less than half of its long-term average and even further below the double-digit returns generated in 2021 and 2022. Private debt was the standout performer (if there was one), outperforming all other private asset classes and illustrating the asset class’s countercyclical appeal.
Private equity down but not out
Higher financing costs, lower multiples, and an uncertain macroeconomic environment created a challenging backdrop for private equity managers in 2023. Fundraising declined for the second year in a row, falling 15 percent to $649 billion, as LPs grappled with the denominator effect and a slowdown in distributions. Managers were on the fundraising trail longer to raise this capital: funds that closed in 2023 were open for a record-high average of 20.1 months, notably longer than 18.7 months in 2022 and 14.1 months in 2018. VC and growth equity strategies led the decline, dropping to their lowest level of cumulative capital raised since 2015. Fundraising in Asia fell for the fourth year of the last five, with the greatest decline in China.
Despite the difficult fundraising context, a subset of strategies and managers prevailed. Buyout managers collectively had their best fundraising year on record, raising more than $400 billion. Fundraising in Europe surged by more than 50 percent, resulting in the region’s biggest haul ever. The largest managers raised an outsized share of the total for a second consecutive year, making 2023 the most concentrated fundraising year of the last decade (Exhibit 2).
Despite the drop in aggregate fundraising, PE assets under management increased 8 percent to $8.2 trillion. Only a small part of this growth was performance driven: PE funds produced a net IRR of just 2.5 percent through September 30, 2023. Buyouts and growth equity generated positive returns, while VC lost money. PE performance, dating back to the beginning of 2022, remains negative, highlighting the difficulty of generating attractive investment returns in a higher interest rate and lower multiple environment. As PE managers devise value creation strategies to improve performance, their focus includes ensuring operating efficiency and profitability of their portfolio companies.
Deal activity volume and count fell sharply, by 21 percent and 24 percent, respectively, which continued the slower pace set in the second half of 2022. Sponsors largely opted to hold assets longer rather than lock in underwhelming returns. While higher financing costs and valuation mismatches weighed on overall deal activity, certain types of M&A gained share. Add-on deals, for example, accounted for a record 46 percent of total buyout deal volume last year.
Real estate recedes
For real estate, 2023 was a year of transition, characterized by a litany of new and familiar challenges. Pandemic-driven demand issues continued, while elevated financing costs, expanding cap rates, and valuation uncertainty weighed on commercial real estate deal volumes, fundraising, and investment performance.
Managers faced one of the toughest fundraising environments in many years. Global closed-end fundraising declined 34 percent to $125 billion. While fundraising challenges were widespread, they were not ubiquitous across strategies. Dollars continued to shift to large, multi-asset class platforms, with the top five managers accounting for 37 percent of aggregate closed-end real estate fundraising. In April, the largest real estate fund ever raised closed on a record $30 billion.
Capital shifted away from core and core-plus strategies as investors sought liquidity through redemptions in open-end vehicles and reduced gross contributions to the lowest level since 2009. Opportunistic strategies benefited from this shift, as investors turned their attention toward capital appreciation over income generation in a market where alternative sources of yield have grown more attractive.
In the United States, for instance, open-end funds, as represented by the National Council of Real Estate Investment Fiduciaries Fund Index—Open-End Equity (NFI-OE), recorded $13 billion in net outflows in 2023, reversing the trend of positive net inflows throughout the 2010s. The negative flows mainly reflected $9 billion in core outflows, with core-plus funds accounting for the remaining outflows, which reversed a 20-year run of net inflows.
As a result, the NAV in US open-end funds fell roughly 16 percent year over year. Meanwhile, global assets under management in closed-end funds reached a new peak of $1.7 trillion as of June 2023, growing 14 percent between June 2022 and June 2023.
Real estate underperformed historical averages in 2023, as previously high-performing multifamily and industrial sectors joined office in producing negative returns caused by slowing demand growth and cap rate expansion. Closed-end funds generated a pooled net IRR of −3.5 percent in the first nine months of 2023, losing money for the first time since the global financial crisis. The lone bright spot among major sectors was hospitality, which—thanks to a rush of postpandemic travel—returned 10.3 percent in 2023. 2 Based on NCREIFs NPI index. Hotels represent 1 percent of total properties in the index. As a whole, the average pooled lifetime net IRRs for closed-end real estate funds from 2011–20 vintages remained around historical levels (9.8 percent).
Global deal volume declined 47 percent in 2023 to reach a ten-year low of $650 billion, driven by widening bid–ask spreads amid valuation uncertainty and higher costs of financing (Exhibit 3). 3 CBRE, Real Capital Analytics Deal flow in the office sector remained depressed, partly as a result of continued uncertainty in the demand for space in a hybrid working world.
During a turbulent year for private markets, private debt was a relative bright spot, topping private markets asset classes in terms of fundraising growth, AUM growth, and performance.
Fundraising for private debt declined just 13 percent year over year, nearly ten percentage points less than the private markets overall. Despite the decline in fundraising, AUM surged 27 percent to $1.7 trillion. And private debt posted the highest investment returns of any private asset class through the first three quarters of 2023.
Private debt’s risk/return characteristics are well suited to the current environment. With interest rates at their highest in more than a decade, current yields in the asset class have grown more attractive on both an absolute and relative basis, particularly if higher rates sustain and put downward pressure on equity returns (Exhibit 4). The built-in security derived from debt’s privileged position in the capital structure, moreover, appeals to investors that are wary of market volatility and valuation uncertainty.
Direct lending continued to be the largest strategy in 2023, with fundraising for the mostly-senior-debt strategy accounting for almost half of the asset class’s total haul (despite declining from the previous year). Separately, mezzanine debt fundraising hit a new high, thanks to the closings of three of the largest funds ever raised in the strategy.
Over the longer term, growth in private debt has largely been driven by institutional investors rotating out of traditional fixed income in favor of private alternatives. Despite this growth in commitments, LPs remain underweight in this asset class relative to their targets. In fact, the allocation gap has only grown wider in recent years, a sharp contrast to other private asset classes, for which LPs’ current allocations exceed their targets on average. According to data from CEM Benchmarking, the private debt allocation gap now stands at 1.4 percent, which means that, in aggregate, investors must commit hundreds of billions in net new capital to the asset class just to reach current targets.
Private debt was not completely immune to the macroeconomic conditions last year, however. Fundraising declined for the second consecutive year and now sits 23 percent below 2021’s peak. Furthermore, though private lenders took share in 2023 from other capital sources, overall deal volumes also declined for the second year in a row. The drop was largely driven by a less active PE deal environment: private debt is predominantly used to finance PE-backed companies, though managers are increasingly diversifying their origination capabilities to include a broad new range of companies and asset types.
Infrastructure and natural resources take a detour
For infrastructure and natural resources fundraising, 2023 was an exceptionally challenging year. Aggregate capital raised declined 53 percent year over year to $82 billion, the lowest annual total since 2013. The size of the drop is particularly surprising in light of infrastructure’s recent momentum. The asset class had set fundraising records in four of the previous five years, and infrastructure is often considered an attractive investment in uncertain markets.
While there is little doubt that the broader fundraising headwinds discussed elsewhere in this report affected infrastructure and natural resources fundraising last year, dynamics specific to the asset class were at play as well. One issue was supply-side timing: nine of the ten largest infrastructure GPs did not close a flagship fund in 2023. Second was the migration of investor dollars away from core and core-plus investments, which have historically accounted for the bulk of infrastructure fundraising, in a higher rate environment.
The asset class had some notable bright spots last year. Fundraising for higher-returning opportunistic strategies more than doubled the prior year’s total (Exhibit 5). AUM grew 18 percent, reaching a new high of $1.5 trillion. Infrastructure funds returned a net IRR of 3.4 percent in 2023; this was below historical averages but still the second-best return among private asset classes. And as was the case in other asset classes, investors concentrated commitments in larger funds and managers in 2023, including in the largest infrastructure fund ever raised.
The outlook for the asset class, moreover, remains positive. Funds targeting a record amount of capital were in the market at year-end, providing a robust foundation for fundraising in 2024 and 2025. A recent spate of infrastructure GP acquisitions signal multi-asset managers’ long-term conviction in the asset class, despite short-term headwinds. Global megatrends like decarbonization and digitization, as well as revolutions in energy and mobility, have spurred new infrastructure investment opportunities around the world, particularly for value-oriented investors that are willing to take on more risk.
Private markets make measured progress in DEI
Diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) has become an important part of the fundraising, talent, and investing landscape for private market participants. Encouragingly, incremental progress has been made in recent years, including more diverse talent being brought to entry-level positions, investing roles, and investment committees. The scope of DEI metrics provided to institutional investors during fundraising has also increased in recent years: more than half of PE firms now provide data across investing teams, portfolio company boards, and portfolio company management (versus investment team data only). 4 “ The state of diversity in global private markets: 2023 ,” McKinsey, August 22, 2023.
In 2023, McKinsey surveyed 66 global private markets firms that collectively employ more than 60,000 people for the second annual State of diversity in global private markets report. 5 “ The state of diversity in global private markets: 2023 ,” McKinsey, August 22, 2023. The research offers insight into the representation of women and ethnic and racial minorities in private investing as of year-end 2022. In this chapter, we discuss where the numbers stand and how firms can bring a more diverse set of perspectives to the table.
The statistics indicate signs of modest advancement. Overall representation of women in private markets increased two percentage points to 35 percent, and ethnic and racial minorities increased one percentage point to 30 percent (Exhibit 6). Entry-level positions have nearly reached gender parity, with female representation at 48 percent. The share of women holding C-suite roles globally increased 3 percentage points, while the share of people from ethnic and racial minorities in investment committees increased 9 percentage points. There is growing evidence that external hiring is gradually helping close the diversity gap, especially at senior levels. For example, 33 percent of external hires at the managing director level were ethnic or racial minorities, higher than their existing representation level (19 percent).
Yet, the scope of the challenge remains substantial. Women and minorities continue to be underrepresented in senior positions and investing roles. They also experience uneven rates of progress due to lower promotion and higher attrition rates, particularly at smaller firms. Firms are also navigating an increasingly polarized workplace today, with additional scrutiny and a growing number of lawsuits against corporate diversity and inclusion programs, particularly in the US, which threatens to impact the industry’s pace of progress.
Fredrik Dahlqvist is a senior partner in McKinsey’s Stockholm office; Alastair Green is a senior partner in the Washington, DC, office, where Paul Maia and Alexandra Nee are partners; David Quigley is a senior partner in the New York office, where Connor Mangan is an associate partner and Aditya Sanghvi is a senior partner; Rahel Schneider is an associate partner in the Bay Area office; John Spivey is a partner in the Charlotte office; and Brian Vickery is a partner in the Boston office.
The authors wish to thank Jonathan Christy, Louis Dufau, Vaibhav Gujral, Graham Healy-Day, Laura Johnson, Ryan Luby, Tripp Norton, Alastair Rami, Henri Torbey, and Alex Wolkomir for their contributions
The authors would also like to thank CEM Benchmarking and the StepStone Group for their partnership in this year's report.
This article was edited by Arshiya Khullar, an editor in the Gurugram office.
Explore a career with us
Related articles.

CEO alpha: A new approach to generating private equity outperformance

Private equity turns to resiliency strategies for software investments

The state of diversity in global private markets: 2022
- About the New York Fed
- Bank Leadership
- Diversity and Inclusion
- Communities We Serve
- Board of Directors
- Disclosures
- Ethics and Conflicts of Interest
- Annual Financial Statements
- News & Events
- Advisory Groups
- Vendor Information
- Holiday Schedule
At the New York Fed, our mission is to make the U.S. economy stronger and the financial system more stable for all segments of society. We do this by executing monetary policy, providing financial services, supervising banks and conducting research and providing expertise on issues that impact the nation and communities we serve.

The New York Innovation Center bridges the worlds of finance, technology, and innovation and generates insights into high-value central bank-related opportunities.

Do you have a request for information and records? Learn how to submit it.

Learn about the history of the New York Fed and central banking in the United States through articles, speeches, photos and video.
- Markets & Policy Implementation
- Reference Rates
- Effective Federal Funds Rate
- Overnight Bank Funding Rate
- Secured Overnight Financing Rate
- SOFR Averages & Index
- Broad General Collateral Rate
- Tri-Party General Collateral Rate
- Desk Operations
- Treasury Securities
- Agency Mortgage-Backed Securities
- Reverse Repos
- Securities Lending
- Central Bank Liquidity Swaps
- System Open Market Account Holdings
- Primary Dealer Statistics
- Historical Transaction Data
- Monetary Policy Implementation
- Agency Commercial Mortgage-Backed Securities
- Agency Debt Securities
- Repos & Reverse Repos
- Discount Window
- Treasury Debt Auctions & Buybacks as Fiscal Agent
- INTERNATIONAL MARKET OPERATIONS
- Foreign Exchange
- Foreign Reserves Management
- Central Bank Swap Arrangements
- Statements & Operating Policies
- Survey of Primary Dealers
- Survey of Market Participants
- Annual Reports
- Primary Dealers
- Standing Repo Facility Counterparties
- Reverse Repo Counterparties
- Foreign Exchange Counterparties
- Foreign Reserves Management Counterparties
- Operational Readiness
- Central Bank & International Account Services
- Programs Archive
- Economic Research
- Consumer Expectations & Behavior
- Survey of Consumer Expectations
- Household Debt & Credit Report
- Home Price Changes
- Growth & Inflation
- Equitable Growth Indicators
- Multivariate Core Trend Inflation
- New York Fed DSGE Model
- New York Fed Staff Nowcast
- R-star: Natural Rate of Interest
- Labor Market
- Labor Market for Recent College Graduates
- Financial Stability
- Corporate Bond Market Distress Index
- Outlook-at-Risk
- Treasury Term Premia
- Yield Curve as a Leading Indicator
- Banking Research Data Sets
- Quarterly Trends for Consolidated U.S. Banking Organizations
- Empire State Manufacturing Survey
- Business Leaders Survey
- Supplemental Survey Report
- Regional Employment Trends
- Early Benchmarked Employment Data
- INTERNATIONAL ECONOMY
- Global Supply Chain Pressure Index
- Staff Economists
- Visiting Scholars
- Resident Scholars
- PUBLICATIONS
- Liberty Street Economics
- Staff Reports
- Economic Policy Review
- RESEARCH CENTERS
- Applied Macroeconomics & Econometrics Center (AMEC)
- Center for Microeconomic Data (CMD)
- Economic Indicators Calendar
- Financial Institution Supervision
- Regulations
- Reporting Forms
- Correspondence
- Bank Applications
- Community Reinvestment Act Exams
- Frauds and Scams
As part of our core mission, we supervise and regulate financial institutions in the Second District. Our primary objective is to maintain a safe and competitive U.S. and global banking system.

The Governance & Culture Reform hub is designed to foster discussion about corporate governance and the reform of culture and behavior in the financial services industry.

Need to file a report with the New York Fed? Here are all of the forms, instructions and other information related to regulatory and statistical reporting in one spot.

The New York Fed works to protect consumers as well as provides information and resources on how to avoid and report specific scams.
- Financial Services & Infrastructure
- Services For Financial Institutions
- Payment Services
- Payment System Oversight
- International Services, Seminars & Training
- Tri-Party Repo Infrastructure Reform
- Managing Foreign Exchange
- Money Market Funds
- Over-The-Counter Derivatives
The Federal Reserve Bank of New York works to promote sound and well-functioning financial systems and markets through its provision of industry and payment services, advancement of infrastructure reform in key markets and training and educational support to international institutions.

The New York Fed offers the Central Banking Seminar and several specialized courses for central bankers and financial supervisors.

The New York Fed has been working with tri-party repo market participants to make changes to improve the resiliency of the market to financial stress.
- Community Development & Education
- Household Financial Well-being
- Fed Communities
- Fed Listens
- Fed Small Business
- Workforce Development
- Other Community Development Work
- High School Fed Challenge
- College Fed Challenge
- Teacher Professional Development
- Classroom Visits
- Museum & Learning Center Visits
- Educational Comic Books
- Economist Spotlight Series
- Lesson Plans and Resources
- Economic Education Calendar

We are connecting emerging solutions with funding in three areas—health, household financial stability, and climate—to improve life for underserved communities. Learn more by reading our strategy.

The Economic Inequality & Equitable Growth hub is a collection of research, analysis and convenings to help better understand economic inequality.

Household Debt Rose by $184 Billion in Q1 2024; Delinquency Transition Rates Increased Across All Debt Types
NEW YORK — The Federal Reserve Bank of New York’s Center for Microeconomic Data today issued its Quarterly Report on Household Debt and Credit . The report shows total household debt increased by $184 billion (1.1%) in the first quarter of 2024, to $17.69 trillion. The report is based on data from the New York Fed’s nationally representative Consumer Credit Panel .
The New York Fed also issued an accompanying Liberty Street Economics blog post examining credit card utilization and its relationship with delinquency. The Quarterly Report also includes a one-page summary of key takeaways and their supporting data points.
“In the first quarter of 2024, credit card and auto loan transition rates into serious delinquency continued to rise across all age groups,” said Joelle Scally, Regional Economic Principal within the Household and Public Policy Research Division at the New York Fed. “An increasing number of borrowers missed credit card payments, revealing worsening financial distress among some households.”
Mortgage balances rose by $190 billion from the previous quarter and was $12.44 trillion at the end of March. Balances on home equity lines of credit (HELOC) increased by $16 billion, representing the eighth consecutive quarterly increase since Q1 2022, and now stand at $376 billion. Credit card balances decreased by $14 billion to $1.12 trillion. Other balances, which include retail cards and consumer loans, also decreased by $11 billion. Auto loan balances increased by $9 billion, continuing the upward trajectory seen since 2020, and now stand at $1.62 trillion.
Mortgage originations continued increasing at the same pace seen in the previous three quarters, and now stand at $403 billion. Aggregate limits on credit card accounts increased modestly by $63 billion, representing a 1.3% increase from the previous quarter. Limits on HELOC grew by $30 billion and have grown by 14% over the past two years, after 10 years of observed declines.
Aggregate delinquency rates increased in Q1 2024, with 3.2% of outstanding debt in some stage of delinquency at the end of March. Delinquency transition rates increased for all debt types. Annualized, approximately 8.9% of credit card balances and 7.9% of auto loans transitioned into delinquency. Delinquency transition rates for mortgages increased by 0.3 percentage points yet remain low by historic standards.
Household Debt and Credit Developments as of Q1 2024
*Change from Q4 2023 to Q1 2024 ** Change from Q1 2023 to Q1 2024
Flow into Serious Delinquency (90 days or more delinquent)
About the Report
The Federal Reserve Bank of New York’s Household Debt and Credit Report provides unique data and insight into the credit conditions and activity of U.S. consumers. Based on data from the New York Fed’s Consumer Credit Panel , a nationally representative sample drawn from anonymized Equifax credit data, the report provides a quarterly snapshot of household trends in borrowing and indebtedness, including data about mortgages, student loans, credit cards, auto loans and delinquencies. The report aims to help community groups, small businesses, state and local governments and the public to better understand, monitor, and respond to trends in borrowing and indebtedness at the household level. Sections of the report are presented as interactive graphs on the New York Fed’s Household Debt and Credit Report web page and the full report is available for download.

- Request a Speaker
- International Seminars & Training
- Governance & Culture Reform
- Data Visualization
- Economic Research Tracker
- Markets Data APIs
- Terms of Use

Shredding Inefficiency: A Blueprint for Eliminating Paper Checks
- Date: May 20, 2024
- Albert Bodine
- Report Details: 9 pages, 1 graphics
- Research Topic(s):
- Commercial & Enterprise
- PAID CONTENT
In the midst of our rapidly advancing digital era, the persistence of paper checks in commercial payments is a glaring testament to outdated financial practices. These checks, with their slow delivery, susceptibility to fraud, environmental harm, high processing costs, and negative impact on payee liquidity, are relics that should have been phased out long ago. Yet they persist, with a staggering 92% of organizations accepting checks for incoming payments and 86% using them for outgoing payments. This is a clear indication that old, inefficient habits die hard.
Despite advancements in electronic payment systems and the widespread adoption of digital alternatives, checks are still very much around. Check volumes have decreased, but checks constitute 33% of all global commercial payments. The per-item average value of checks has increased steadily for the past 10 years, outpacing inflation, so we can’t conclude that the increase is solely due to more expensive goods and services. Something else is afoot. Over the past year, the Javelin Commercial & Enterprise Payments group has written extensively about the world’s lingering check problem. Rather than further dissecting the issue, this research paper will focus on the solution. It will provide specific recommendations on eradicating paper checks from the commercial payments spectrum, including suggestions on structuring environmental, social, and governance (ESG) initiatives, approaches for effective government policy, and guidance on how large corporates can be change leaders. It will also delve into commercial success stories and provide key cost-benefit analysis components that enterprises should include when building their digital-only initiatives.
Learn More About This Report & Javelin
Related content, movements in global commercial payments and banking: 2024 edition.
Global commercial banking and payments are evolving swiftly, driven by technological progress, evolving corporate habits, and emerging market dynamics. This puts businesses on the ...
Fleet Cards 2024: Small Fleets Are an Opportunity
Nothing stays the same for fuel card providers, or for the fleet operators that rely on them. Declining fuel costs in 2023 cut into fuel card companies’ revenues, sending them off ...
Understanding Commercial Card ePayables: An Abridged Guide for Commercial Buyers
In the world of commercial card payments instruments, ePayables—a virtual type of card payment—is the fastest growing segment, bringing operational efficiency for buyers and their ...
Make informed decisions in a digital financial world
- Election 2024
- Entertainment
- Newsletters
- Photography
- Personal Finance
- AP Investigations
- AP Buyline Personal Finance
- AP Buyline Shopping
- Press Releases
- Israel-Hamas War
- Russia-Ukraine War
- Global elections
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East
- Election Results
- Delegate Tracker
- AP & Elections
- Auto Racing
- 2024 Paris Olympic Games
- Movie reviews
- Book reviews
- Personal finance
- Financial Markets
- Business Highlights
- Financial wellness
- Artificial Intelligence
- Social Media
The larger the nonprofit, the more likely it is run by a white man, says new Candid diversity report
Candid CEO Ann Mei Chang poses for a photo at the nonprofit’s headquarters on Wednesday, Jan. 31, 2024, in New York. Chang, CEO since 2021, believes her organization can help the philanthropic sector work more efficiently by making more data from donors and grantees available to the public.(AP Photo/Peter K. Afriyie)
Candid CEO Ann Mei Chang poses for a photo at the nonprofits’s headquarters on Wednesday, Jan. 31, 2024, in New York. Chang, CEO since 2021, believes her organization can help the philanthropic sector work more efficiently by making more data from donors and grantees available to the public. (AP Photo/Peter K. Afriyie)
- Copy Link copied

NEW YORK (AP) — White men are most likely to lead the largest, best-funded nonprofits, while women of color tend to lead the organizations with the fewest financial resources, according to a study from the nonprofit data research organization Candid.
“ The State of Diversity in the U.S. Nonprofit Sector ” report released by Candid on Thursday is the largest demographic study of the nonprofit sector, based on diversity information provided by nearly 60,000 public charities.
According to the study, white CEOs lead 74% of organizations with more than $25 million in annual revenue, with white men heading 41% of those nonprofits, despite being only about 30% of the population. Women of color, who make up about 20% of the U.S. population, lead 14% of the organizations with more than $25 million in revenue and 28% of the smallest nonprofits — those with less than $50,000 in revenue.
The Candid report provides data for nonprofits who have complained for years that minority-led nonprofits attract fewer donations, government resources and sales, even after the racial reckoning following the murder of George Floyd and promises from funders of all sizes seeking change. Many groups argue that when the leadership of a charity comes from the community it is serving, its needs are met more effectively. According to a report from the Ms. Foundation for Women and the consulting group Strength in Numbers, less than 1% of the $67 billion that foundations donated in 2017 was earmarked specifically for minority women and girls.
“Our mission is to use data to help make the whole sector more efficient, effective and equitable,” Candid CEO Ann Mei Chang told The Associated Press. “We think that data is a force for good and can help everybody trying to do good, to do good better.”
The report’s findings are based on data gathered from the Demographics via Candid initiative, where nonprofits voluntarily report the diversity numbers of their organizations. Cathleen Clerkin, Candid’s associate vice president of research, said authors of the report compared its findings to other sector-wide data and found them to be consistent.
Because the diversity information was self-reported, Clerkin said Candid studied whether nonprofits would be more likely to share their information because they were more diverse, but found that was not the case. What was more likely to determine whether a nonprofit reported its diversity information was how much they depended on outside donations, said Clerkin, adding that Candid hopes the report will encourage more charities to provide its organization’s information.
The report found that environmental and animal welfare groups were least likely to have diverse leadership, with 88% having a white CEO. Nearly three-quarters of religious nonprofits had white CEOs, according to the report.
Portia Allen-Kyle, chief of staff and interim head of external affairs at the racial justice nonprofit Color of Change, said the report’s findings were not surprising. “The backsliding of Black leadership and other underrepresented populations is exactly what we unfortunately expect to see in an era of attacks on the tools of Black power like affirmative action, like DEI (diversity, equity and inclusion), et cetera,” she said. ”It’s a nonprofit space where disproportionately white leaders disproportionately receive resources from these white, ultrawealthy donors, while Black leaders from the most impacted communities are expected to often turn water into wine, using nothing but pennies on the dollar.”
Allen-Kyle said the fact that the report also finds that women of color are overrepresented as leaders of the smallest charities is also not a surprise. “With these small nonprofits, especially with advocacy, Black women are going to be doing this work regardless and they’re doing it on nothing and whether or not they get paid because they believe in it,” she said.
The report also found that Latinos were underrepresented as nonprofit CEOs in nearly every state.
“We have been talking about that for decades,” said Frankie Miranda, president and CEO of the Hispanic Federation, which supports Latino communities and nonprofits. “It’s the reason the Hispanic Federation was created in 1990 — to advocate for Latino-led, Latino-serving providers because we were not part of the conversation when decision-making around funding and support was happening.”
That has led to Hispanic Federation becoming one of the nation’s largest grantmakers for Latino nonprofits. However, even though its findings are not unexpected, the Candid study is still extraordinarily valuable, Miranda said.
“This study will validate our argument,” he said. “This is critically important for us to be able to say, ‘Here’s the proof.’ It’s proof for major donors that you need to do better when it comes to diversity within your organization. Your institution needs to have the cultural competency to understand the importance of investing in our organizations, the importance of getting to know these organizations. They know how to serve these communities.”
Associated Press coverage of philanthropy and nonprofits receives support through the AP’s collaboration with The Conversation US, with funding from Lilly Endowment Inc. The AP is solely responsible for this content. For all of AP’s philanthropy coverage, visit https://apnews.com/hub/philanthropy .

- Kreyòl Ayisyen

Early impacts of removing low-balance medical collections
The three nationwide credit reporting companies removed a large share of medical collections items—tradelines, in industry parlance—from consumers’ credit reports in 2022 and 2023. Specifically, the companies committed to removing medical collections tradelines that were paid, less than one year past due (up from six months previously) or with initial balance less than $500. Medical collections tradelines of less than $500 were removed in April 2023, while the others were removed in July 2022. In a recent report we documented that the share of consumers with a least one medical collections tradeline on their credit report dropped from around 14 percent in March 2022, prior to the changes, to around 5 percent in June 2023, after all the changes went into effect. The vast majority of the removed tradelines were those with initial balances of less than $500. This is on top of a longer-running decline in all collections tradelines on consumer credit reports . Although many medical collections tradelines were removed, the majority of medical collections balances still remain on credit records . In this Spotlight, we take an early look at how the changes to the reporting of medical collections tradelines have affected the financial health of consumers who had medical collections tradelines on their credit records prior to the changes.
We find that:
- There continues to be significant churn in the reporting of medical collections tradelines. About 10 percent of consumers who we expected should have had all medical collections removed due to the changes had acquired new medical collections above $500 by the end of the period studied. At the same time, about a third of consumers who we expected would continue to have medical collections tradelines actually had all medical collections removed during the same period.
- Consumers who had all their medical collections removed saw significant improvements in credit scores . The presence of medical collections on a consumer’s credit report can lower their credit score. Compared to similar consumers who did not have all their medical collections removed, credit scores rose by an average of 20 points. Many consumers saw their credit scores rise enough to put them in a higher credit score tier .
- Removing medical collections has not yet led consumers to seek more credit. While many consumers with medical collections made inquiries for new accounts between April 2023 and August 2023, there was no difference between consumers for whom we would expect all medical collections removed, and those who we would expect to continue to have medical collections reported.
Data and Methodology
We use data from the CFPB Consumer Credit Panel (CCP), a sample of approximately five million de-identified credit records from one of the three nationwide consumer reporting agencies. We focus specifically on consumers who had medical collections on their credit records in December 2022 before the majority of medical collections tradelines were removed, and examine those consumers’ credit records in August 2023, (8 months later) after all the reporting changes were complete. This sample includes about 650,000 consumers in the CCP, corresponding to roughly 31 million consumers in the U.S. as a whole.
Simply looking at changes in credit scores or other outcomes for these consumers would not necessarily capture the effect of the reporting changes. Consumers’ credit scores can change for many reasons, and medical collections tradelines are frequently removed from consumers’ credit records independent of any broader changes by the credit reporting companies . Moreover, CFPB research has shown a general downward trend in the prevalence of medical collections tradelines going back several years prior to the recent reporting changes. To disentangle the effect of the reporting changes from reasons that consumer outcomes may change, we focus in on consumers whose largest medical collections tradeline in December 2022 was just under $500 (and thus we would expect all their medical collections tradelines to be removed) and on consumers whose largest medical collections tradeline was just above $500 (and thus we would expect some of their medical collections tradelines to remain on their credit records). This does not capture the entire effect of the reporting changes, but instead captures one aspect of the changes: The effect of having all medical collections tradelines removed compared to having some or none removed.
We use December 2022 as the baseline because prior CFPB research indicates that medical collections tradelines under $500 began being removed in March 2023, and moreover credit score information in the CCP is only available quarterly (such that there is no score information for February 2023). Just under half our sample of consumers with medical collections tradelines on their credit record in December 2022 had an initial balance of less than $500 on their largest medical collection tradeline.
Most, but not all, consumers with all medical collections tradelines below $500 in December 2022 had no medical collections tradelines in August 2023.
In the figure below, we plot the share of consumers who still had a medical collections tradeline in August 2023, grouped by the value of their largest medical collections tradeline in December 2022. We also plot a flexible best-fit line showing the smoothed average relationship above and below the $500 threshold. Unsurprisingly, there is a clear split that occurs at $500. The vast majority of the consumers whose largest medical collections tradeline had a balance just below this amount did not have any medical collections tradelines on their credit records in August 2023. However, it is also notable that the split is not absolute: Around 10 percent of consumers whose largest December 2022 medical collections tradeline was just under $500 still had at least one medical collections tradeline in August 2023 (necessarily a new medical collection for more than $500). At the same time, while we would expect most consumers whose largest medical collection tradeline was over $500 to continue having at least one medical collection tradeline, in fact only around two-thirds of consumers whose largest medical collections tradeline was greater than $500 still had at least one medical collections tradeline on their credit records in August 2023.
This is consistent with previous CFPB research showing that medical collections tradeline reporting is characterized by a huge amount of churn, with these collections tradelines rapidly falling off of consumers’ credit reports but being replaced by other medical collections tradelines. Sometimes this churn is due to the same debt being re-assigned to another debt collector, and furnishers can vary in how long they continue reporting . However, even when following the same original medical debt across collectors, prior to the reporting changes it was common for as much as a quarter of all medical collections tradelines to be removed from consumers’ credit reports within 6 months of first being added, and medical collections tradelines with an initial balance above $500 were removed faster than those with an initial balance below $500. For context, the Fair Credit Reporting Act generally imposes a limit of seven years from the date of delinquency for negative information like collections to be reported. Even prior to the reporting changes, the majority of medical collections tradelines were typically removed much sooner than seven years.
Figure 1: Share of consumers with at least one medical collections tradeline on their credit records in August 2023, by amount of largest initial reported medical collections tradeline in December 2022.
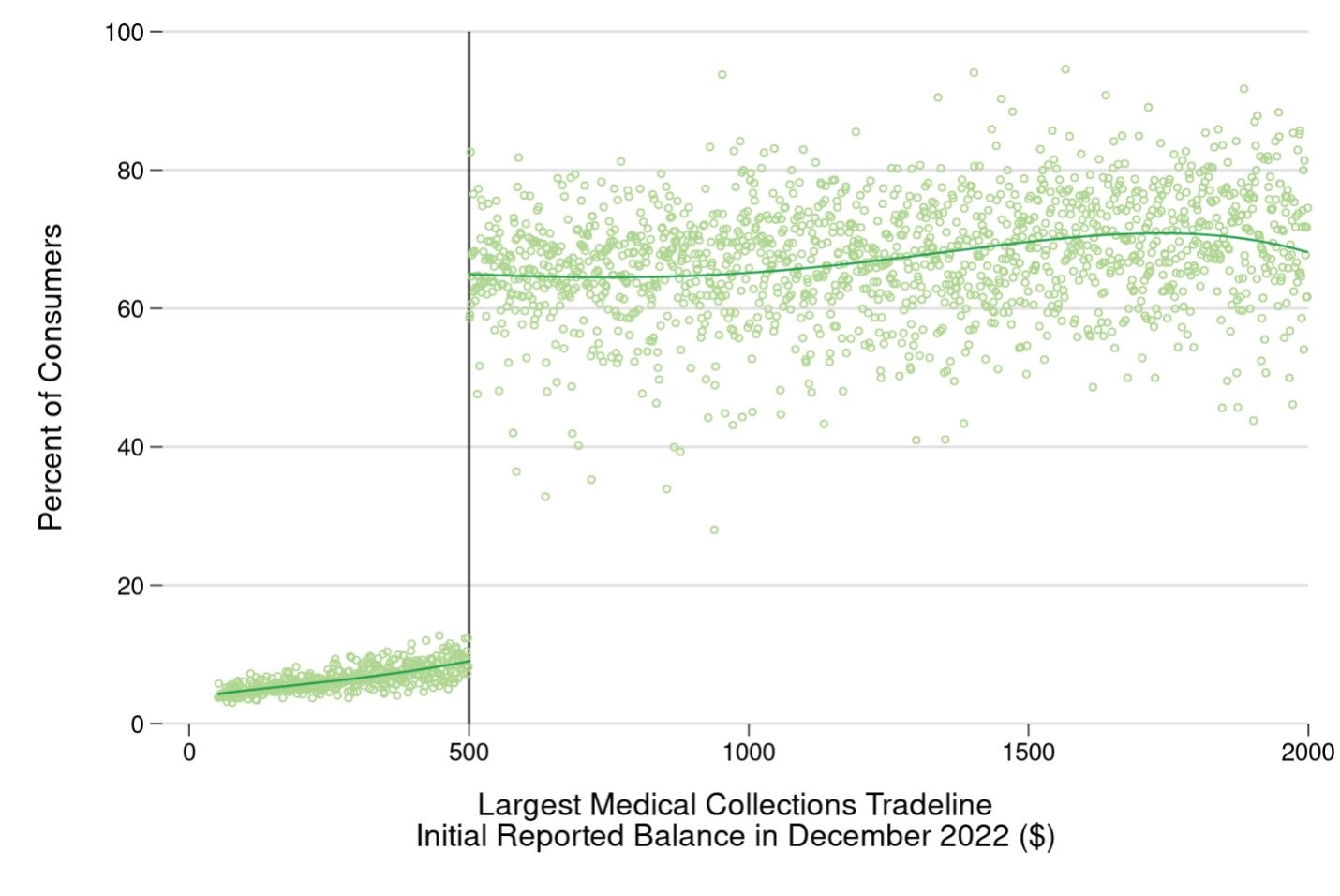
Source: CFPB Consumer Credit Panel
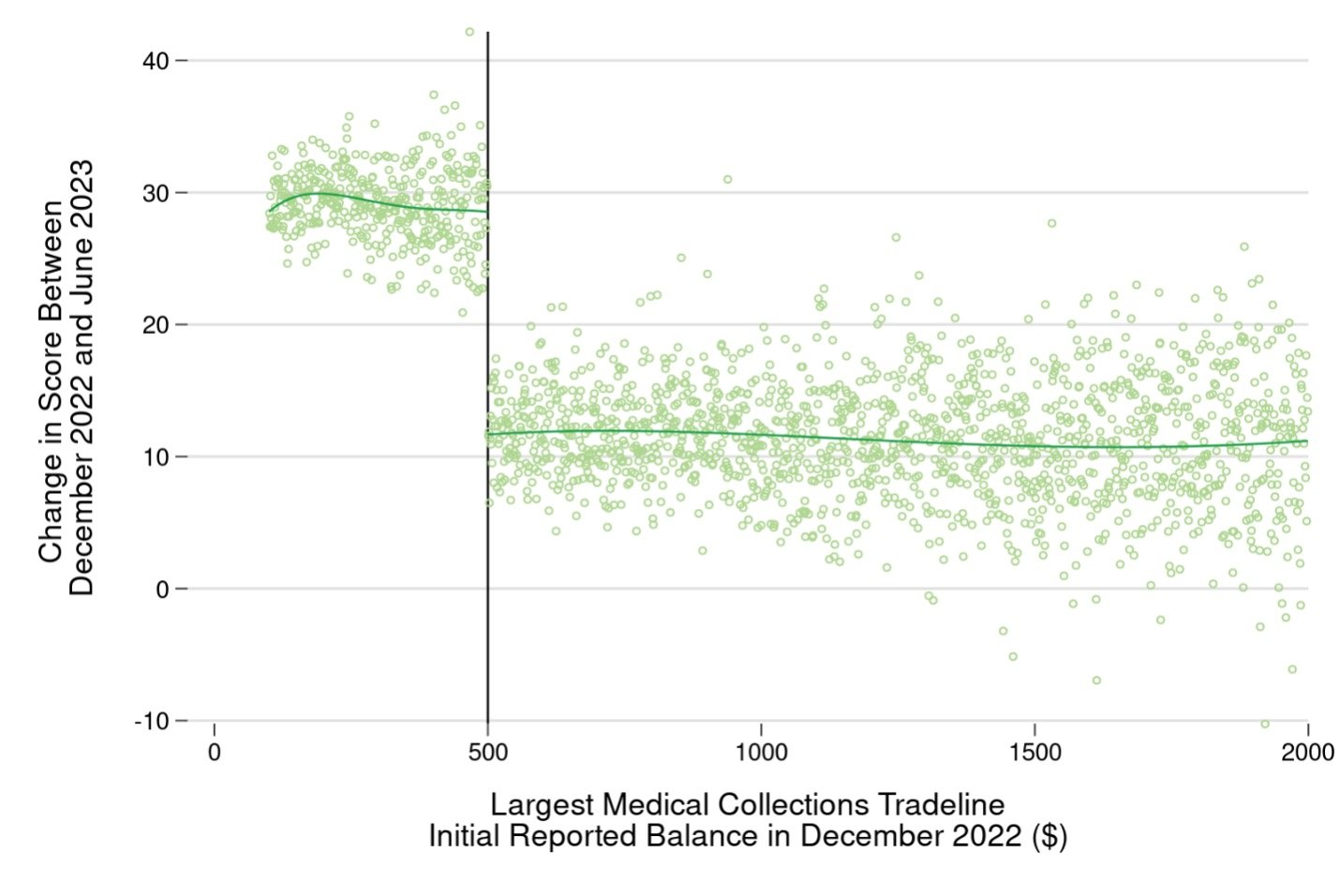
Credit scores improved for consumers who were likely to have all medical collections tradelines removed
Turning now to consumer outcomes, the next figure plots the average change in credit score (specifically the FICO® Score 8 credit score) between December 2022 and June 2023 for consumers who had medical collections tradelines on their credit records in December2022 (credit scores in the CCP are only available quarterly). Again, each point represents a group of consumers with the same largest medical collections tradeline balance in December 2022. Because, like other recent FICO Score models, the FICO® Score 8 model disregards collections tradelines below $100 , the figure is limited to consumers whose largest medical collections tradeline balance was at least $100 in December 2022.
All consumers with medical collections in December saw improved credit scores on average over the 6 months from December 2022 to June 2023, but credit scores rose about 20 points more for consumers whose largest medical collections tradeline was just under $500, compared to those whose largest medical collections tradeline was just over $500. About 37 percent of consumers whose largest medical collection tradeline in December 2022 had an initial balance less than $500 had their FICO Score increase enough to put them in a higher score tier , compared to about 24 percent of consumers whose largest medical collections tradeline in December 2022 had initial balance greater than $500.
To some extent these results are specific to the credit score used here, and we might expect different changes using other credit scoring models . The credit score that financial institutions use for credit decisions may differ from the FICO Score used here, which in turn may also differ from the scores provided to consumers through their banks or financial management apps.
Figure 2: Average change in FICO Score between December 2022 and June 2023, by amount of largest initial reported medical collections tradeline in December 2022.
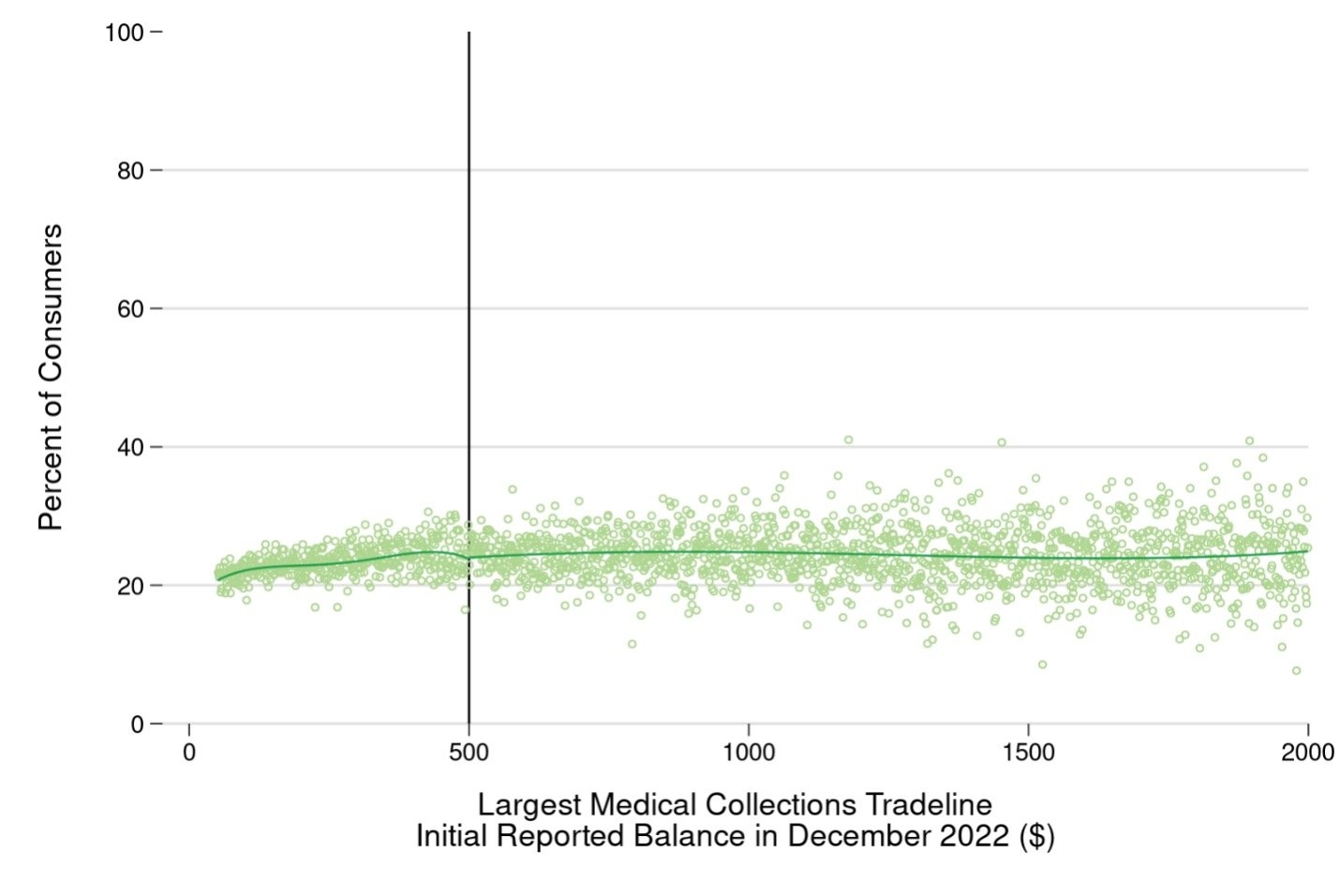
Credit-seeking behavior hasn’t changed
We also examine whether consumers whose credit scores have improved due to the reporting changes are seeking more credit. The CCP contains records of “hard” credit inquiries, generated when a consumer applies for a new credit account. To the extent that consumers realize that their FICO Scores have improved and think they are more likely to be approved for credit than before, we might expect them to be more likely to apply for credit, and for more inquiries to appear in the CCP data. The figure below plots the share of consumers with at least one credit-related inquiry at the national consumer reporting agency our data come from between April 2023 (the month after all the reporting changes went into effect) through August 2023 (the latest month we have data for). Again, each point represents a group of consumers with the same largest initial balance amount on their medical collections tradelines in December 2022. About 25 percent of consumers with a medical collections tradeline in December 2022 had an inquiry for a new account between April 2023 and August 2023, but there is no meaningful difference between consumers whose largest medical collection was just below or just above $500.
Figure 3: Share of consumers who had at least one hard inquiry for credit between April 2023 and August 2023, by amount of largest initial reported medical collections tradeline in December 2022.
The recent move by the credit reporting companies to remove certain medical collections information from consumers’ credit records has improved the credit scores of a number of consumers. A majority of medical collections balances still remain on credit records. This analysis shows that the effect on scores was notably larger for those who had all medical collections removed compared to consumers with at least one collection with a balance greater than $500, the threshold for one of the removal criteria. At the same time, the reporting of medical collections tradelines on consumer credit reports remains inconsistent, with medical collections frequently being removed shortly after they are first added, independent of the reporting changes. Given how many consumers had an unpaid medical collections tradeline above $500 prior to the changes and nonetheless had no medical collections after the changes, a large share of consumers who had medical collections prior to the reporting changes would likely have had those medical collections removed without the changes. Conversely, many consumers whose medical collections tradelines prior to the changes met the credit reporting companies’ criteria for removal continued to have new medical collections tradelines added that do not meet the criteria for removal. However, given prior trends showing that medical collections tradelines often drop off quickly for no obvious reason, we anticipate that many of those new collections tradelines will likely drop off before long. Prior CFPB work concluded that medical collections tradelines are less predictive of future default than other types of collections tradelines. However, the inconsistency in whether and how long medical collections tradelines are reported makes it unclear whether medical collections tradelines, or the lack thereof, provide any clear signal to creditors about which consumers have medical debts, much less whether a consumer has the ability to repay future obligations on time.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
In this paper, I provide an overview of the research on the real effects of financial reporting on investing and financing decisions made by firms. Accounting can improve investment efficiency and affect nearly every aspect of the financing decision by reducing information asymmetry and improving monitoring.
Financial analysis is a study of the company's finan cial statements by analyzing the reports. Report. analysis is a tool that easily calculates and interprets reports that are used by investors ...
We identify the consequences. of financial reporting for 1) the reporting firm, 2) its peer firms, and 3) the input and output. market s. We also highlight the effects of firms' internal ...
This article systematically reviews 94 accounting and finance studies that address the real effects of financial reporting. Whereas the effects of financial reporting on capital suppliers' decisions traditionally have received much attention, recent research has generated important new insights into the feedback effects of financial reporting on the reporting firms' real activities (e.g ...
223 James P Brawley Drive. Atlanta GA 30314 SW, USA. Abstract. The purpose of this paper is to review current articles and research papers with regard to influences on and. measures of the quality ...
The Journal of Finance publishes leading research across all the major fields of financial research. It is the most widely cited academic journal on finance and one of the most widely cited journals in economics as well. Each issue of the journal reaches over 8,000 academics, finance professionals, libraries, government and financial ...
The Journal of Finance publishes leading research across all the major fields of financial research. It is the most widely cited academic journal on finance. Each issue of the journal reaches over 8,000 academics, finance professionals, libraries, government and financial institutions around the world. Published six times a year, the journal is the official publication of The American Finance ...
Financial statements (FSs) provide information to investors, regulators, financial analysts, and other users in a standardized and reliable format for use in making economic decisions regarding the financial condition ... Table 1a provides a review summary of various research papers, including their problem type, the model used, and the Dataset ...
3. The financial reporting system: three perspectives. Despite the increased prevalence of the idea of a financial reporting and auditing eco-system, there are relatively few academic studies which directly focus on systems issues (Ball Citation 2001, Bushman and Smith Citation 2001, Mennicken Citation 2010, Knechel et al. Citation 2020), although more which focus on comparative institutional ...
Given the volume of research on the complete annual report texts, that is, 18 papers, 63% of the total, the integral annual reports are the major source of language data. In terms of the financial data, they are collected from 18 databases, including Compustat and Center for Research of Security Prices (CRSP), among others.
In this paper, I review the extant research on financial statement analysis. I then provide some preliminary evidence using Chinese data and offer suggestions for future research, with a focus on utilising unique features of the Chinese business environment as motivation.
Where Financial Reporting Still Falls Short. Even after a raft of reforms, corporate accounting remains murky. Here's what you need to know to evaluate a company accurately. by. H. David Sherman ...
There are three main financial statements that need to be understood to evaluate the financial condition, profitability, and cash flows of any organization: the balance sheet, the income statement, and the cash flow statement. This publication covers the fundamental concepts to construct and analyze these critical financial statements. 2.
We examine research that has developed financial ratio models to: (a) predict significant corporate events; and (b) predict future performance after significant corporate events. The events we analyze include financial distress and bankruptcy, downsizing, raising equity capital, and material earnings misstatements.
included in financial statements of an organization. Financial statement analysis can be used to determine an organization's liquidity position, long-term solvency, financial viability, and profitability. Therefore, this research paper explains in detail why financial statements are important and their uses for an organization.
New research on finance from Harvard Business School faculty on issues and topics including corporate investment, governance, and accounting management. ... In addition, AmerisourceBergen's legal and financial troubles were accompanied by shareholder demands aimed at driving corporate governance changes in companies in the opioid supply chain ...
ISSN 2222-1697 (Paper) ISSN 2222-2847 (Online) Vol.5, No.19, 2014 ... This research is to analyze the financial statements of these banks using liquidity ratios, activity ratios, leverage ratios, profitability ratios, and market value ratios. ... Financial statements are the medium by which a company discloses information concerning its
presents tools and techniques for analysis of financial statements. This research paper will helpful to understand the throw knowledge of analysis and interpretation through analysis of financial statements. 1.Financial statements analysis: Concept and Meaning Financial statements are not prepared to satisfy the requirements of all stakeholders ...
In addition to working papers, the NBER disseminates affiliates' latest findings through a range of free periodicals — the NBER Reporter, the NBER Digest, the Bulletin on Retirement and Disability, the Bulletin on Health, and the Bulletin on Entrepreneurship — as well as online conference reports, video lectures, and interviews.
Quick Analysis Financial Reports. The collection of reports included in this document is based on the sample client data that has been transferred from CSA for the FACS01 Sample Client, with FACS02 and FACS03 set up as industry peers, as outlined in the Financial Analysis CS Getting Started guide.
This article is a summary of a larger report, available as a PDF, that is a collaborative effort by Fredrik Dahlqvist, ... losing money for the first time since the 2007-08 global financial crisis. Capital shifted away from core and core-plus strategies as investors sought liquidity via redemptions in open-end vehicles, from which net ...
9 The Compustat database, which is commonly used in accounting and finance research and is based on firms' financial statements, shows no R&D expenditures for 50% of firms. Of course, many of these firms do not actually engage in R&D activities, but at least 5% (10.5% of 50%) of them do, according to Koh and Reeb (Citation 2015).
Financial concerns, and family welfare are major stressors, alongside job related factors such as long working hours and lack of recognition. Many respondents believe that their employers are taking mental health seriously. ... Download the 2024 Gen Z and Millennial Report 5 MB PDF To learn more about the mental health findings, read the Mental ...
At the New York Fed, our mission is to make the U.S. economy stronger and the financial system more stable for all segments of society. We do this by executing monetary policy, providing financial services, supervising banks and conducting research and providing expertise on issues that impact the nation and communities we serve.
Rather than further dissecting the issue, this research paper will focus on the solution. It will provide specific recommendations on eradicating paper checks from the commercial payments spectrum, including suggestions on structuring environmental, social, and governance (ESG) initiatives, approaches for effective government policy, and ...
The report's findings are based on data gathered from the Demographics via Candid initiative, where nonprofits voluntarily report the diversity numbers of their organizations. Cathleen Clerkin, Candid's associate vice president of research, said authors of the report compared its findings to other sector-wide data and found them to be ...
In a recent report we documented that the share of consumers with a least one medical collections tradeline on their credit report dropped from around 14 percent in March 2022, prior to the changes, to around 5 percent in June 2023, after all the changes went into effect. The vast majority of the removed tradelines were those with initial ...
In brief, financial analysis is the process of selection, relation and evaluation. (Khan, M Y, 2007). Financial performance analysis is, therefore, the process of identifying the financial ...
Goldman Sachs Research economists continue to see consumer spending as a source of strength and forecast above-consensus real spending growth of 2.6% in 2024 in Q4/Q4 terms. Income Personal income increased by 0.5% in March, in line with consensus expectations, reflecting a 0.7% increase in nominal wage and salary income.