Open Access is an initiative that aims to make scientific research freely available to all. To date our community has made over 100 million downloads. It’s based on principles of collaboration, unobstructed discovery, and, most importantly, scientific progression. As PhD students, we found it difficult to access the research we needed, so we decided to create a new Open Access publisher that levels the playing field for scientists across the world. How? By making research easy to access, and puts the academic needs of the researchers before the business interests of publishers.
We are a community of more than 103,000 authors and editors from 3,291 institutions spanning 160 countries, including Nobel Prize winners and some of the world’s most-cited researchers. Publishing on IntechOpen allows authors to earn citations and find new collaborators, meaning more people see your work not only from your own field of study, but from other related fields too.
Brief introduction to this section that descibes Open Access especially from an IntechOpen perspective
Want to get in touch? Contact our London head office or media team here
Our team is growing all the time, so we’re always on the lookout for smart people who want to help us reshape the world of scientific publishing.
Home > Books > Organ Donation and Transplantation - Current Status and Future Challenges

Organ Donation and Transplantation: “Life after Death”
Submitted: 13 November 2017 Reviewed: 03 April 2018 Published: 25 July 2018
DOI: 10.5772/intechopen.76962
Cite this chapter
There are two ways to cite this chapter:
From the Edited Volume
Organ Donation and Transplantation - Current Status and Future Challenges
Edited by Georgios Tsoulfas
To purchase hard copies of this book, please contact the representative in India: CBS Publishers & Distributors Pvt. Ltd. www.cbspd.com | [email protected]
Chapter metrics overview
2,110 Chapter Downloads
Impact of this chapter
Total Chapter Downloads on intechopen.com
Total Chapter Views on intechopen.com
Organ donation is defined as giving an organ or part of an organ to be transplanted into another person. Organ transplantation is the only option to save lives in patients affected by terminal organ failures and improve their quality of life. However, there is a disparity exists between the supply and demand of donated organs, leads to a loss of many lives. The number of organ transplantation have gradually increased in the last two decades and provide excellent results in children and young adults, and are challenging by the growing proportion of elderly transplant patients with co morbidity. The results of organ transplantation continue to improve, as a consequence of the innovations and the improvements in peri-operative management. This chapter describes organ donation and transplantation and its trends and challenges.
- organ donation
- psychosocial
Author Information
Kanmani job *.
- Amrita College of Nursing, Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham, Kochi, India
Anooja Antony
*Address all correspondence to: [email protected]
1. Introduction
Organ donation is defined as giving an organ or part of an organ to be transplanted into another person. Organ transplantation is the only option to save lives in patients affected by terminal organ failures and improve their quality of life. However, there is a disparity exists between the supply and demand of donated organs, leads to a loss of many lives. The number of organ transplantation have gradually increased in the last two decades and provide excellent results in children and young adults, and are challenging by the growing proportion of elderly transplant patients with co morbidity. The results of organ transplantation continue to improve, as a consequence of the innovations and the improvements in peri-operative management.
Organ transplantation currently depends on the availability of human organs. Their scarcity means that there is a waiting list of almost 63,000 in the European Union, and over 100,000 people in the United States according to the recent survey. The process of obtaining organs for donation and transplantation purely depends on the resources of health services and by health professionals’ performance in potential donor identification and management tasks. However, in accordance with the current legislation it is mainly subjected to a personal or family decision, strongly mediated by psychosocial processes. Therefore, the need to analyze and intervene both in the practices of the professionals involved in the process of organ generation and in the attitudes of the general population need to stressed and addressed [ 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 ].
2. Organ transplantation and organ donation: an overview
Organ transplantation involves the surgical implantation of an organ or section of an organ into a person whose own organ is failing. The donor organ may come from both deceased individual as well as from a living donor. The patients psychological and behavior aspect as well their emotional response and mental health and adherence to medical regimen should be assessed before and after organ transplantation. The living donor’s psychological response towards organ donation (most commonly for kidney and liver segment transplantation) is an important aspect to consider in the transplantation process.
Organ donation is defined as “giving an organ or part of an organ to be transplanted into another person” (Organ procurement of Transplant Network (OPTN), 2015), organ donation has the potential to save lives. The organs donated from one single donor can save up to eight lives. Organ transplantation may be one of the options left to sustain someone’s life. However, the disparity that exists between the supply and demand of donated organs, leads to a loss of many lives. Based on recent OPTN data, approximately 21 people will die each day while waiting for a transplant in the United States (US). Currently, 123, 358 people are awaiting organs and on the transplant list in the US with this number growing and the number of donated organs declining.
Asian Indians are more likely to have higher rates of having obesity and diabetes when compared with other Asian subgroups which make them at an increased risk of needing a donated organ [ 35 ]. These conditions can lead one to develop coronary artery disease and hypertension which then can lead to chronic kidney disease and other chronic illnesses. Patients who suffer from chronic kidney disease need regular dialysis which can ultimately lead them to organ transplantation to improve one’s quality of life. Also, conditions such as diabetes and obesity can be detrimental to one’s life and can lead to fatty liver disease which can lead to chronic liver disease requiring liver transplantation if the liver decompensates.
The development of organ transplantation in the second half of the 20th century has been a remarkable achievement. Recently; organ transplantation is one of the most effective options for those with an end-stage organ failure. Its success has been basically dependent on public awareness, support and active participation. Without these factors, the efficiency of organ transplantation and the consequent saving or extension of lives would have undoubtedly suffered adversely.
The number of patients in need of organ transplantation has increased at a rapid pace; in contrast, the number of available organs has increased only slightly. Expanded criteria for donor selection, such as older age, have resulted in more people who meet the criteria for brain death becoming organ donors although fewer organs are transplanted from each donor. Improvements in automobile and highway safety, as well as increased enforcement of gun control laws, have also contributed to a plateau in the number of young, healthy donors. Public education efforts that encourage organ donation may be effective in getting more people to sign organ donor cards, but most individuals who do so will never be in a position to become organ donors.
Faced with increasing numbers of patients who need transplantation, deaths on the waiting list, and a fixed number of available organs, some transplant programs are working to increase the number of transplants from living donors. Although living donation has always been an option for some types of transplants, many programs have been reluctant to promote it, as living donation requires invasive surgery on a healthy person with associated risks of morbidity and mortality. For example, since dialysis is an option for patients with end-stage renal disease, surgery on a healthy donor may be difficult to justify, despite the dialysis patient’s diminished quality of life.
The most important in organ donation is to maximize the psychological status and well-being of the donors before and after transplantation has become the foremost goal of all transplantation centres. The psychological issues that mainly concern with the living organ donation includes prevention of psychological harm, ensuring the donors are fully informed and decide to donate without coercion, monitoring donor psychosocial outcomes are intimately linked to the factors that historically served as barriers to use of organs from living donors. These barriers can be overcome by the motivating of the public and creating awareness and responsibility among oneself.
Organs that can be transplanted from the living donor includes one kidney, part of intestine, pancreas, islets of Langerhans, bone, part of liver, one testis, bone marrow and blood. The organ that can be transplanted from the deceased donor are heart, kidney, pancreas, stomach, hand, skin, blood vessels, lungs, liver, intestine, testis, cornea and heart valve.
Autograft: Transplanting a person’s tissues from one site and use it in another site of his body and is called autograft. For example, removal of skin from the legs and using it for damaged skin face or other exposed part.
Allograft: Transplant of an organ between two genetically non identical individuals, it is called allograft. Due to the genetic difference, the donor’s organ will be treated as foreign by the recipient and will try to destroy it. This is called s rejection.
Isograft: Transplant of organ/tissue from a donor to genetically identical recipient is called isograft. There will not be any immune response hence no transplant rejection.
Xenograft: Transplantation of organ/tissues forms one species to another species. For example, the heart valve of pig is transplanted successfully to human.
Split transplant: An organ like liver retrieved from the deceased donor can be divided between two recipients, usually an adult and a child.
Domino transplant: When the lungs are to be transplanted, surgically it is easier to replace them along with the heart. If the recipient’s original heart is healthy, it can be transplanted into another recipient in the need of one.
ABO incompatible transplantation: The immune system of young children aged below 12 months might have developed fully. They can receive organs from incompatible donors.
Live donors: A living person, mentally and physically healthy can donate one of a paired organ, part of an organ or a tissue. The organs donated are kidneys, part of live, one of the lung, part of small intestine, skin, bone marrow, one of the testis and one of the ovaries. Live donor can either be related or unrelated.
Unrelated donors: For altruistic reasons, a person can donate one of his organs to an unrelated donor. According to TOHO act, the unrelated donor should be known to the recipient and have some obligation to him. It has to be established that there is no monetary transaction between them. But in many other countries, even a stranger can donate one of his organs to a needy person on altruistic grounds.
Deceased donors: Organs are harvested from brain dead person whose respiration and circulation are maintained artificially. Brain dead has to be certified by a team of doctors nominated by Government I every organ retrieval centers.
Paired exchange: When a living donor is not compatible with the related recipient, but may be compatible for another recipient. That second recipient related donor is compatible to the first recipient, then permission can be granted for transplantation. The surgery for all four donors and recipient are conducted simultaneously and anonymity is kept until after the transplant.
Spousal donation: A spouse can donate an organ to the partner. It has to be recorded that the couple is legally married.
3. Current scenario: trends

Despite advances in medicine and technology, and increased awareness of organ donation and transplantation, the gap between supply and demand continues to widen. Each year, the number of people in the waiting list is increasing in both donor and transplant. The donation statistics according to OPTN Annual report shows that in 2016, total of 41,335 organs were donated. It can be either deceased or living and four out of five donations came from deceased donors and four out of ten from living donors. According to the report by OTPN 2018, 115,033 people need life-saving organ transplant, of those 74,926 people are the active waiting list candidates.
The real reason behind a living person’s interest in donating one’s organ is important to determine but it is often difficult. Now days, money has become the motivation for donation. The relationships also have played a great role in increasing donation rates. The shortage of available organs can be reduced if; people choose to donate their organs after they die. If more people did that the issue regarding organ shortage can be minimized.
The trend is expected to accelerate each year. Many organ procurement and the Joint Commission on Accreditation of Healthcare Organizations actively participate to increase the donation rates. The organizations take various to steps against traditional social taboos.
The approach, known as “donation after cardiac death” (DCD), usually involves patients who have suffered brain damage, such as from a car accident or a stroke. After family members have made the difficult decision to discontinue a ventilator or other life-sustaining treatment, organ-bank representatives talk to them about donation. Sometimes, the donor is suffering from an incurable disease also end up with the decision of organ donation.
According to U.S Department of Health and Human Services, more than 1,23,000 men, women and children currently needed life-saving organ transplants every 10 minutes and another name is added to the national organ transplant waiting list. In 2014, more than 8500 deceased donors made possible approximately 24,000 organ transplants. In addition, there were nearly 6000 transplants from living donors. In India, nationally with a population of 1.2 billion people, the statistics stands 0.08 persons as organ donor populations. Mrithasanjeevani, Kerala network of organ sharing which began in 2012, also states that the need for organ transplantation is high as the patients in waiting list is increasing day by day who requires organ transplantation.
The need for organ has gone up substantially all over the world. India also suffers from acute organ shortage with little to no solution for this issue. It is estimated that every year 1.5 lakh people suffer from renal failure out of which only 3000 people get donors. Similarly, every year around 2 lakh people die of liver failure or cancer and rarely get any help in the form of organ donors. It is the same for heart patients, for every 50,000 heart attack patients there are only 15 hearts available for transplant. Therefore, there is an urgent need for widespread campaigns to spread awareness about organ donation in India and to bridge the gap between supply and demand. The numbers that are mentioned here are estimates and real numbers could be far more than this, it is scary because this means very few people get relief and get a second chance in life.
The main reasons for organ shortage in India are mainly ignorance and lack of knowledge. People are not well informed enough about the benefits of organ donation. Today social media and so many other forums can promote the positives of organ donation and how it will save so many lives if more people register themselves for organ donation. The reason for organ shortage is myth and superstition. Many people do not want to donate their organs even after death because of so many myths and superstition they are instilled with. People with existing medical condition or old people, who wish to donate, do not donate thinking they are not fit or eligible. Almost everyone can donate some part or the other unless you have any extreme medical condition.
The need for organ donation is necessary because out of the 1.5 lakh people who need kidney in India only 3000 people receive them, only 1 out of 30 people receive kidney and 90% of people in the waiting list die without getting any donor. Around 70% liver transplants are dependent on a live donor but 30% dependent on cadaver (corpse) donations. Hence, there is an urgent need to increase the organ donation rates and give a person a second chance in their life.
4. Challenges in organ donation
As far as the challenges concerned it includes mainly donor’s motives for donation, the predominant ways in which donors arrive at the decision to donate, and the donors’ psychological status and its relationship to their fitness as donors.
4.1. Pre-donation challenges
4.1.1. donor’s motives.
Most donors are likely to be motivated by multiple factors. These factors include intrinsic factors (e.g., desires to relieve the suffering of another or to act in according to the religious convictions) and extrinsic factors (e.g., the social pressures or perceived norms) that may operate simultaneously. The particular combination of motivational forces will also differ depending on whether and how the donor is related to the recipient.
Among living related donors, it has long been assumed that family members or emotional partners are motivated primarily for saving the lives of their loved ones. Such motives are indeed the most commonly expressed feelings, as noted in a variety of studies over the past 30 years. Among nondirected living donors (individuals donating to unrelated patients whom the donors did not select)(NDLDs), it was identified as the altruistic/humanitarian motives, along with beliefs that the donor’s self-worth would be improved, and feelings of moral and religious obligation or self- identity.
4.1.2. Donor’s decision-making
The motivation for the organ donation is purely on the donor’s decision of organ donation and it may be influenced by many factors including the relationship to the recipients. Decision-making swiftness may indicate the type of decision being made. There appear to be two decision-making approaches that include the moral decision making and the rational decision making. “Moral decision-making” involves awareness that one’s actions can affect another; ascription of responsibility to oneself; acceptance of the social/moral norm governing the behavior; and taking action consistent with that norm. Because moral decision-making does not involve the costs and benefits of a given behavior but, instead, is based on perceived norms governing that behavior, it is likely to lead to non- deliberative, instantaneous decisions. In contrast, “rational” decision-making includes various steps that focus on gathering relevant information, evaluating alternatives, selecting an alternative, and implementing the decision.
4.1.3. Support
It includes mainly the assessment of the donor’s available physical, financial and emotional support. It is necessary to identify whether the donor have someone to provide care in the recovery period, have sufficient financial support and so on. This important to avoid distress if the donor develops any complications. Finally, does the donor have the support of significant others for being a donor, or is he or she choosing to donate over the objections of persons who have a legitimate interest in the outcome of an autonomous decision.
4.1.4. Family attitudes toward donation
Spouse and family attitudes about donation should also be explored. Collateral interviews with significant others is necessary, especially those who will be providing tangible support to the donor during the recovery period, should be conducted whenever possible. Conflicts between potential donors and significant others should be addressed and, ideally, resolved prior to surgery itself in order to avoid conflicts later. Family members should provide a good understanding of the donor’s wishes and motives, even if they agree to disagree to the donor’s decision.
4.1.5. Behavioral and psychological health
The behavioral and psychological health of the donor should also be considered before donation. It is important to identify donor’s lifestyle is sufficiently healthy to reduce unnecessary risk for both donor and recipient. Many potential donors may have some unhealthy behaviors, such as moderate obesity or smoking. It is necessary to identify that there is sufficient time for the donor to reduce risks (e.g., lose weight, stop smoking). Moreover, it needs to be taken care of that the donor is emotionally stable to cope with stresses which may come up before, during, and after the donation. Hence it is important to identify psychological and behavioral status of the donor or else it may affect the quality of life.
4.1.6. Donor-recipient relationship
The relationship between the donor and recipient is a complex matter. Even when both parties are agree for donation and transplant, family dynamics may be complicated, and other family members may assertively involve themselves in the decision-making process. The donor may have unrealizable expectations that transplant will alter his or her relationship with the recipient. The health care team should not expect an ideal relationship in which all interactions between donor and recipient are harmonious. However, obvious tensions and overt psychological issues should be addressed. Joint interviews, involving both donor and recipient, should be avoided early in the evaluation process in order to preserve privacy and give the potential donor the opportunity to express reservations or “opt out” gracefully.
4.1.7. Diversity issues
Non directed donors may have diversity concerns that may affect the organ donation. The potential donors should be assessed for comfort with donation to recipients of different genders, races, religions, sexual orientations, nationalities, ages, underlying diseases, and lifestyles. Donors who express objections, fears, or concerns about who might receive their organ may need to be deferred until they can receive counseling.
4.1.8. Psychological status of potential donors
The potential donor’s psychological status is of greatest concern for donation and transplantation. Concerns have been particularly high in case of unrelated donation (either directed to a specific patient, or NDLD): the willingness or desire to donate to a stranger has been historically viewed with suspicion and as likely to reflect significant psychopathology. There is no doubt that some potential donors will be psychologically poor candidates to serve as donors.
4.1.9. Post-donation challenges
The donors’ perceptions of their physical functional, psychological, and social well-being were found to be either nonsignificantly different from or significantly better than levels reported in the general population. The post challenges mainly includes recipient death or graft loss, donor medical complications, donor history of mood or other psychiatric problems, and poor donor relationships with recipient or family. The other factor is that it may affect the donor’s quality of life if any complication arises.
The post transplantation challenges are many which include minimizing rejection risks, immunosuppression, organ shortage, handling of the stressors of transplantation, psychosocial adaptation and psychological disorders and so on.
4.1.10. Minimizing rejection risks
The twin conditions of antibody sensitization and antibody-mediated rejection remain challenging and frustrating to treat. The recent drugs which are used to desensitize patients or reverse antibody-mediated rejection, especially chronic antibody mediated rejection is totally unsatisfactory. Development of therapies those are more effective and less toxic should be made available. Recent regimens used for antibody desensitization and reversal of antibody-mediated rejection include plasmapheresis, immunoglobulin (IVIG), and rituximab, an anti-chimeric, anti-CD20 antibody. Recently, the proteasome inhibitor Velcade has also been reported to reverse refractory antibody rejection. Eculizumab, a humanized anti-C5 monoclonal antibody appears to protect the renal allograft despite the presence of donor-specific antibodies (DSA). None of these agents have been tested in rigorous studies.
4.1.11. Immunosuppression
This is one of the major challenges after organ transplantation. Many studies have suggested that most of the late graft loss occurs because of immunologic reasons, frequently antibody-mediated. So the approach of minimizing immunosuppression is necessary with the present drugs to reduce toxicities may actually be helpful in the long-term survival of the graft. The toxicities are minimized by allowing more grafts to be rejected by immune mechanisms. Hence, development of effective agents that lack long-term toxicities so that we can maintain optimum immunosuppression over the long-term.
4.1.12. Stressors after transplantation
In the perioperative period, the focus is on the patient’s physical recovery, with possible rejection episodes and other medical complications causing anxiety and emotional strain. Within the first days after transplantation, a postoperative delirium can occur. The patient can present with symptoms of mental confusion, language disturbances, and occasional hallucinations and delusions are often a frightening experience to patients and their families. Acute brain dysfunction can occur in intensive care patients and patients after surgery. The corticosteroids which are administered for immunosuppression cause these problems. Some of the patients experience problems in accepting the new organ from another individual and suffer with feeling of guilt towards the donor which, in turn, can increase psychological stress and nonadherence [ 6 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 , 11 ].
In the long-term postoperative period, medication side effects and associated comorbidities become central stressors impeding patient’s life quality. Most common comorbidities seen are infections, diabetes mellitus, hypertension, lipometabolic disorders, adipositas, cardiovascular diseases, oncological diseases, osteoporosis, and chronic kidney failure [ 12 , 13 ]. Furthermore, psychiatric symptoms (e.g., depression, anxiety, agitation, psychosis) and neurological symptoms (e.g., sleep disturbances, cognitive impairment, delirium) can occur as neurotoxic side effects in patients receiving immunosuppressive drugs.
Faced with the multiple health risks, patients often continue to experience anxiety and worries regarding possible retransplantation, serious comorbidities, and death. Even patients in good physical health are confronted with severe challenges, for example, regaining their previously lost or restricted social roles as family members and partners (including sexual activity) and returning to work or taking up other meaningful activities. Financial constraints and legal disputes with health or pension insurance agencies constitute other possible sources of psychological strain.
5. Psychosocial adaptation and psychological disorders
After the transplantation, the psychosocial burden more severe in preoperative period than postoperative period. Nevertheless, patients themselves have to demonstrate considerable coping skills. In the best case, transplant patients learn to adapt to their new situation, often by reevaluating life goals and by focusing on more positive consequences, for example, personal growth. On the other hand, unsuccessful readjustment can lower the quality of life and psychiatric morbidity. The most common psychological disorders among patients before and after transplantation are affective and anxiety disorders.
The literature review shows that prevalence of depression in 20–25% of cases before and after kidney transplantation. Less information is available concerning patients receiving other organs. Prior to and following lung transplantation, depression seems to be prevalent in approximately 30% of patients. Hence these show that the depression is a major challenge after transplantation. These issues can be reduced by personal and social resources (resilience factors), that is, favorable coping skills, self-efficacy, sense of coherence, optimism, and social support.
6. Factors affecting donor’s motivation
There are many factors affecting donor’s motivation which includes feelings of love and responsibility, spiritual motives, and greater success rate of organ donation.
6.1. Feelings of love and responsibility
Motives for donating organ to their relative patients were that they tended to do something for their loved ones. In fact, they feel responsible for their problems. They do not treat others’ problems with indifference and attempted to do whatever they could for resolving the problems experienced by transplant recipients. It is considered as their own responsibilities to help them to get rid of their problems. The feel like they are the ones who need to support their patients.
6.2. Close and constant companionship
Another factor affecting the participants’ feeling of responsibility for donation to their family members was close and constant companionship with recipients. This close and constant companionship made the participants to clearly understand the recipients’ conditions and hence, it had resulted in their decision on organ donation in order to alleviate recipients’ problems. This close and constant companionship with patients help family members understand patients’ problems well and increase their degree of commitment to do something for patient’s pain and discomfort. They also noted that this had made them experience deeper shared emotions with their patients and hence, required them to feel responsible for minimizing their patient’s problems.
6.3. Inability to tolerate recipient’s discomfort
Another motive for organ donation was one’s difficulty in tolerating recipient’s discomfort. Love for their sick family members had made the participants feel responsible and decide on doing something for solving their patient’s problems. Their patient’s pain, suffering and discomfort cause a great inconvenience and irritation which lead them to the decision of organ donation. They hoped that organ donation alleviate their patient’s problems [ 14 , 15 , 16 , 17 , 18 , 19 , 20 , 21 , 22 , 23 , 24 , 25 , 26 , 27 , 28 , 29 , 30 , 31 , 32 , 33 , 34 , 36 ].
6.4. Spiritual motives for donation
Religious beliefs played a significant role in motivating to organ donation. Some of them believed that donation was a way for expiating their past sins. They referred to faith in God, reliance on Him, and hope for a successful transplant as the important motives for organ donation. Some of them even accused themselves of causing their family members to develop organ failure and believed that donation was a way for alleviating their feelings of guilt. Such a practice was particularly common among the parents of sick children. Some of them considered donation as a God-approved practice, and noted that God has helped them donate their organs. They noted that they donated their organs for gratifying God and believed that he sees it and help them in all bad situations.
6.5. Greater success rate of organ transplantation
The category is the greater success of organ transplantation. In other words, obtaining information and realizing the greater benefits of organ transplantation had motivated the participants to opt for organ donation. Some of them reported that they had never thought about donation until obtaining information from their patient’s physicians. However, after obtaining adequate information, they had made an irreversible decision about organ donation. Accordingly, a major motive for organ donation was the lower likelihood of organ rejection.
7. Measures to overcome challenges for organ donation
The decisions regarding organ donation based on the personal beliefs (religious, cultural, family, social and body integrity) levels of knowledge about organ donation and previous interaction with the health care team. Many maintained positive attitudes to organ donation despite significant reservations about the organ donation process. Resistance to organ donation found to be less in the case of living donation for family.
There are some religious beliefs that can have both positive and negative influences, these often stemmed from uncertainty or misrepresentation of religious edicts. One solution would be to actively engage religious leaders in the transplant community, especially when it has been reported that, across the major religions, there are very few cases where organ donation can be seen to be inconsistent with religious beliefs. Religious leaders should be made available in hospitals and other transplantation setting to assist families in making decisions regarding organ donation and potentially to remove the misperceptions. Staff members who are involved in approaching families to request consent for donation should be part of the awareness programs and resources about religious concerns. Similarly, cultural sensitivity to issues such as apprehensiveness to discuss death among certain groups or individuals and the importance to many of death rituals may improve dialog regarding organ donation.
Studies have shown that engaging some minority groups in the health care system and creating a sense of belonging and ownership can improve compliance with organ donation. As a consequence, more efforts should be made to create positive interactions within the health care team members, especially for minority groups, to improve the organ donation rates. Although many of the studies have showed that higher socio-economic status and education were associated with a stronger willingness to be an organ donor. Some of the strong reservations held, even among those with generally positive views towards donation, such as concerns that agreeing to donation would discourage doctors from caring so much about saving their lives in case of an emergency or that it would result in the premature removal of their organs or indeed prevent them from having an open coffin at their funerals, are examples of very real barriers that can be readily addressed through information. Through a proper awareness and motivation the donation rates can be improved which can save many lives.
7.1. Psychological care
Psychological consultation is essential for all disease stages enabling patients to better cope with their extraordinarily stressful situation. A need for psychological care was found in up to 50% of transplant patients. Educational and supportive therapies are of utmost importance but also cognitive-behavioral interventions including relaxation techniques can also be considered. Less common methods like hypnotherapy and “Quality of Life Therapy” have also been utilized for overcoming the challenges.
Moreover, family members as well as caregivers of transplant patients show increased psychological strain before and after transplantation. Family counseling, and psychotherapeutic support, can help reduce psychological strain, thus also maintaining the valuable social support provided by care givers and family members of the transplant patient. Henceforth, the family and care givers should also be considered in psychosocial evaluation to overcome the problems.
7.2. Alternative methods to increase donation
In view of ethical, legal and political issues, it was deemed important to obtain some opinion about alternative methods to increase organ donation rates. Financial incentives were given to increase organ donation. Many in both donor and non-donor groups were given a reasonable incentive. Education and dissemination of information about donation and transplantation was important to increase organ donation rates. There was nearly universal agreement that implied consent (presumed consent) should not be tried. The use of financial incentives was not markedly opposed (some accepted the idea of funeral expense reimbursement), although there was not strong support either. In general, methods to increase organ donation had not been well thought out by either donors or nondonors indicating, perhaps, that the assumption of altruism or motivation is the best way to increase the donation rates.
8. Responsibilities of nurses in organ donation and transplantation
Organ and tissue transplant nurses need comprehensive and scientific knowledge. They include the evaluation and management of deceased donors, transplant recipients, potential donors or live donors, teaching and counseling of transplant recipients and live donors related to self-care management, healthy life and a peaceful death when this is imminent. This is important in order to improve the posttransplant quality of life.
Nurses have important role in the development of a successful transplantation program. They are key members of the team that works to deliver care to patients and relatives, through the use of technological, logistic and human resources, with a view to coordination, care, education and research on organ and tissue donation and transplantation. Therefore, the nurses need adequate knowledge on the principles of good ethical principles and should have resources available for them to assess patient’s risks and social issues related to organ transplants and donation. The researchers hope that the future studies will encourage further researches on the role and responsibilities of nurses.
9. Conclusion
The organ donation decision is a complex one, based strongly on personal beliefs. There are some factors, such as religious and cultural beliefs, that are seemingly intractable and are often cited as reasons for a refusal to donate. In this chapter, it is shown that these have often been found to be tied in with more complex issues such as a distrust of the medical system, misunderstandings about religious stances and ignorance about the donation process. Interventions to better engage the community, including disadvantaged and minority groups, to foster trust and provide information represent promising opportunities of promoting organ donation in the future.
Donor motives directly contribute to their decision to donate, is not uniform and is influenced by multiple factors. Majority of the donors were relationship oriented donor, whose major motives were desires to relieve the suffering & save the life of their loving ones. Creating awareness to the organ donation will directly influence the donor motives and willingness. By deriving the motives many more intervention to improve the willingness to be a living organ donor can be evolved. Recruitment of living donors represents a medical and moral responsibility. The possibility of organ removal from healthy donor to a recipient needs great inner motivation. Saving one’s life is divine.
The psycho social assessment must be made as a routine part of the nursing process. These assessments are meant to identify patients at risk for poor outcomes, provide guidelines for their management and improve the post-transplant quality of life [ 6 ]. “Because donated organs are a severely limited resource, the best potential, recipients should be identified. The probability of a good outcome must be highly emphasized to achieve the maximum benefit for all transplants” (OPTN/UNOS Ethics committee General Considerations in Assessment for Transplant Candidacy White paper-2010).
- 1. United Network for Organ Sharing. 1999 Annual Report of the U. S. Scientific Registry of Transplant Recipients and the Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network.: Transplant Data 1989–1998. Richmond, Va: US Department of Health and Human Services, Health Research Services Administration, Office of Sponsored Projects, Division of Transportation, and United Network for Organ Sharing; 2000
- 2. Alexander JW, Zola JC. Expanding the donor pool: Use of marginal donors for solid organ transplantation. Clinical Transplantation. 1996; 10 :1-19
- 3. Kumar A, Mandhani A, Verma BS, et al. Expanding the living related donor pool in renal transplantation: Use of marginal donors. Journal of Urology. 2000a; 163 :33-36
- 4. Mandal AK, Kalligonis AN, Ratner LE. Expanded criteria donors: Attempts to increase the renal donor transplant pool. Advances in Renal Replacement Therapy. 2000a; 7 :117-113
- 5. Simmons RG et al. Gift of Life: The Social and Psychological Impact of Organ Transplantation. NY: Wiley; 1977. Reprinted with additions, Brunswick, NJ: Transaction Books, 1987
- 6. Corley MC et al. Attitude, self-image, and quality of life of living kidney donors. Nephrology Nursing Journal. 2000; 27 (1):43-52
- 7. Goldman LS. Liver transplantation using living donors: Preliminary donor psychiatric outcomes. Psychsomatics. 1993; 34 (3):235-240
- 8. Pradel FG et al. Exploring donors’ and recipients’ attitudes about living donor kidney transplantation. Progress in Transplantation. 2003; 13 (3):203-210
- 9. Fellner CH. Renal transplantation and the living donor. Decision and consequences. Psychother Psychosomat. 1976/77; 27 :139-143
- 10. Toronyi E et al. Attitudes of donors towards organ transplantation in living related kidney transplantations. Transplant International. 1998; 11 (Suppl 1):S481-S483
- 11. Henderson AJZ et al. The living anonymous kidney donor: Lunatic or saint? American Journal of Transplantation. 2003; 3 :203-213
- 12. Jacobs CL et al. Twenty-two nondirected kidney donors: An update on a single center’s experience. American Journal of Transplantation. 2004; 4 :1110-1116
- 13. Matas AJ et al. Nondirected donation of kidneys from living donors. The New England Journal of Medicine. 2000; 343 (6):433-436
- 14. Olbrisch ME et al. Psychological, Social and Behavioral Characteristics of Living Donor Candidates for Adult Liver Transplantation. Biennial Meeting on Psychiatric, Psychosocial and Ethical Issues in Organ Transplantation. Santa Monica, CA; February, 2005
- 15. Crowley-Matoka M et al. Long-term quality of life issues among adult-to-pediatric living donors: A qualitative exploration. American Journal of Transplantation. 2004; 4 :744-750
- 16. Karliova M et al. Living-related liver transplantation from the view of the donor: A 1-year follow-up survey. Transplantation. 2002; 73 (11):1799-1804
- 17. De Graaf Olson W, Bogetti-Dumlao A. Living donors’ perception of their quality of health after donation. Progress in Transplantation. 2001; 11 (2):108-115
- 18. Beavers KL et al. The living donor experience: Donor health assessment and outcomes after living donor liver transplantation. Liver Transplant. 2001; 7 (11):943-947
- 19. Lennerling A et al. Becoming a living kidney donor. Transplantation. 2003; 76 :1243-1247
- 20. Pradel FG. Exploring donor’s and receipient’s attitudes about living door kidney transplantation. Progress in Transplantation. 2003; 13 (3):203-210
- 21. Smith MD. Living related kidney donors. A multicenter study of donor education, socioeconomic adjustment and rehabilitation. American Journal of Kidney Diseases. 1986; 8 (4):223-233
- 22. Jacobs CL. Expanding living donor options. Minnesota Medicine. 2001; 84 :46-48
- 23. Switzer GE. Understaning donor;s motivations. A study of unrelated bone arrow donors. Social Science & Medicine. 1999; 45 (1):137-147
- 24. Rosenthal JT. Expanded criteria for cadaver organ donation in renal transplant. The Urologic Clinics of North America. 1994; 21 :283-292
- 25. Shiel AGR. Transplantation and society. In: Ginns LC, Cosimi A, Morris PJ, editors. Transplantation. Malden, MA: Blackwell Science; 1999. pp. 897-913
- 26. Callender CO, Bay AS, Miles PV, Yeager CL. A national minority organ/tissue transplant education program: The first step in the evolution of a national minority strategy and minority transplant equity in the USA. Transplantation Proceedings. 1995; 27 :1441-1443
- 27. Surman OS et al. Live organ donation: Social context, clinical encounter, and the psychology of communication. Psychosomatics. 2005; 46 :1-6
- 28. Papachristou C et al. Motivation for living-donor liver transplantation from the donor’s perspective: An in-depth qualitative research study. Transplantation. 2004; 78 :1506-1514
- 29. Haljamäe U. Remaining experiences of living kidney donors more than 3 yr after early recipient graft loss. Clinical Transplantation. 2003; 17 :503-510
- 30. Hamburger J, Crosnier J. Moral and ethical problems in transplantation. Rapaport F, Daussert J. Human Transplantation. NY: Grune & Stratton; 1968. pp. 68
- 31. Sadler HH et al. The living, genetically unrelated, kidney donor. Seminars in Psychiatry. 1971; 3 :86-101
- 32. Walter M et al. Psychosocial outcome of living donors after living donor liver transplantation: A pilot study. Clinical Transplantation. 2002; 16 :339-344
- 33. Fukunishi I et al. Psychiatric disorders before and after living-related transplantation. Psychosomatics. 2001; 42 (4):337-343
- 34. Crowley-Matoka M, Switzer G. Nondirected living donation: A survey of current trends and practices. Transplantation. 2005; 79 (5):515-519
- 35. Boparai J, Davila H, Chandalia M. Cardiovascular disease in Asian Indians living in the United States. Current Cardiovascular Risk Reports. 2011; 5 :240-245
- 36. Ji WR, Frederick B, Hsin CY. Trends in prevalence of Type 2 diabetes in Asians Versus Whites results from the United States National Health Interview Survey 1997-2008. Diabetes Care. Feb 2011; 34 (2):353-357
© 2018 The Author(s). Licensee IntechOpen. This chapter is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Continue reading from the same book
Organ donation and transplantation.
Published: 25 July 2018
By Bulang He, Xiuwu Han and Michael A. Fink
2407 downloads
By Félix Cantarovich
1948 downloads
By Alyssa Green, Peter G. Thomas, Rebecca Wilde-Onia,...
1206 downloads
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
A ‘Preventable Tragedy’: Dying for Lack of an Organ Donor
More from our inbox:, a public misinformed about the federal budget, making bread by hand, foie gras ‘status’, against gambling.

To the Editor:
Re “ She Feared the Organ Donation System Would Kill Her. It Did ,” by Kendall Ciesemier (Opinion guest essay, Feb. 1):
I read this essay with great sadness. When we testified together before Congress, I was inspired by Tonya Ingram’s story and resonant voice to our legislators: “Please don’t make us wait.”
Tragically, she was one of 12,000 people last year on waiting lists who died or became too sick to receive a transplant.
As a transplant surgeon who studies organ donation, I believe that the organ shortage is due to ineffective regulation and failing contractors. High-quality research over 20 years demonstrates that for every donor used, even more potential donors are wasted — enough to end most deaths and dramatically reduce dialysis time.
Members of Congress agree on the solutions: Replace failing local organ contractors and break up the national organ monopoly.
Time matters in transplantation. For the thousands who face the prospect of death this year while waiting for an organ, I implore the Biden administration to move forward with common-sense reforms, and recall the words of Ms. Ingram: Please don’t make patients wait.
Seth Karp Nashville The writer is the surgeon in chief at Vanderbilt University Medical Center and director of its transplant center.
The Association of Organ Procurement Organizations is saddened by the news of Tonya Ingram’s death. Sadly, 17 people die each day waiting for a lifesaving transplant. There is no question that Americans, especially those suffering from acute kidney disease, deserve greater access to organs for transplant. However, Kendall Ciesemier placed the responsibility on organ procurement organizations (O.P.O.s) while ignoring critical facts about why more organs are not transplanted.
O.P.O.s, the nonprofit entities federally designated to facilitate the recovery of organs from deceased donors, have been working for decades to bridge the gap between the availability of organs and the growing need for organ transplants in the U.S. Recent data released by the Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network shows that since 2010, there has been an 87 percent increase overall in deceased organ donors.
However, the number of organs recovered by O.P.O.s that go to waste because they are refused by transplant centers is rising dramatically. In fact, 7,543 kidneys, 26 percent of all kidneys offered by O.P.O.s for transplantation in the U.S., were turned down by transplant centers last year.
This rise in rejection rates was called out by the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering and Medicine as a major concern. It is disheartening to the O.P.O.s that work each day to increase the number of organs they are recovering. But it is devastating to patients living — and often dying — on dialysis, waiting for an organ.
O.P.O.s have no control over whether organs are actually transplanted into patients. For the entire system to save more lives, we need to ensure that transplant centers have clear organ acceptance criteria, have the appropriate resources to process the influx of available organs and use organs from more medically complex donors.
Every American can help ensure that more organs are available for transplantation by registering as an organ, eye and tissue donor on the National Donate Life Registry: registerme.org .
Barry Massa McLean, Va. The writer is president of the Association of Organ Procurement Organizations.
Seven years ago, I donated my right kidney to a stranger. This year, I’m being evaluated by a transplant center to donate a lobe of my liver to another stranger.
I’m grateful that I have the good health, financial stability and social support to be a living organ donor. But as Kendall Ciesemier makes clear, the U.S. organ donation crisis is a systemic problem that will never be fixed equitably or effectively by individual solutions.
How many more people will die before the Biden administration steps up to its responsibility for making meaningful systemic reforms?
Jennifer Roberts San Francisco
There is an urgent need to reform the U.S. organ donation system. Americans are dying every day because too often organ contractors fail to do their jobs, and the federal government fails to hold them accountable.
That some 28,000 organs are going unrecovered each year is a wholly preventable tragedy. That this tragedy disproportionately harms patients of color who too often receive inequitable and inferior treatment from a taxpayer-funded system makes it even worse.
We support bipartisan calls from Congress to break up the national organ monopoly held by the United Network for Organ Sharing, to ensure that failing local organ procurement organizations are replaced by high performers, and to open data for evidence of effective and equitable performance.
Most health care policy issues are complex. This one is not.
Jennifer Erickson Abe Sutton Ms. Erickson served in the White House Office of Science and Technology Policy under President Barack Obama. Mr. Sutton served on the National Economic Council under President Donald Trump.
Kendall Ciesemier’s heartbreaking essay reveals the need for organ donation reform so that donated organs and tissue can be processed safely and efficiently. According to Donor Network West, 95 percent of Americans are in favor of organ donation, but only 58 percent are registered to be donors.
What is also needed are laws at the state level, and perhaps the national level, that would make organ donation the default choice in the absence of documented rejection to be an organ donor.
Robert A. Edelman Oakland, Calif. The writer is an ophthalmologist.
Re “ Biden Demands Details on Budget Cuts From McCarthy ” (nytimes.com, Jan. 31):
You write that in the debt limit fight, “Mr. Biden is seeking to force Mr. McCarthy to specify which programs he would cut — a list that most likely includes some spending that is popular with the public.”
That’s true — but, as Speaker Kevin McCarthy knows, unless media outlets start giving the public more actual information about what’s in the budget, the public won’t believe it.
Polls have shown that the average American thinks that over 50 percent of the federal budget is “wasted.” People have no idea that most of the budget goes to Social Security, Medicare, Medicaid and the military. That gives Republicans an enormous advantage in budget fights: People assume we can just “cut the waste.”
The news media is a huge part of the problem: You hardly ever see articles that recite simple facts about the budget. Until such articles become commonplace, Republicans will retain an enormous unfair advantage in budget fights.
Steve Novick Portland, Ore.
Re “ Bread Bakers, and the Machine They Love ” (Food, Feb. 1):
The joys of homemade bread go far beyond just the texture and taste. The tactile experience of creating a satiny supple dough with one’s own hands from a gloppy mess of flour and water defines satisfaction.
Also, experienced bread bakers assess the appropriate amounts of flour and hydration in a dough by feel, outside of the recipe’s parameters. Finally, shaping loaves is creative and fun.
Using a bread machine deprives the baker of all of these pleasures.
For those who really don’t have time or the physical ability to make bread by hand, a bread machine will deliver “homemade” bread, but it is a poor substitute for the handmade bread experience.
Barbara Giesser Pacific Palisades, Calif.
Re “ The War Over Foie Gras in New York City Rages On ” (news article, Jan. 28):
Given the current understanding that animals feel pain and suffering much like humans, it’s sad that the New York elite have to gain “status” through the torture of ducks and geese in the making of foie gras. Surely they can buy more expensive Champagne, watches, clothing and cars to show off.
Michael Fasman San Francisco
Re “ Developers Chasing a New York Casino ” (news article, Jan. 19):
Regarding gambling, there is one sure bet: Gambling has never done humanity any good, and never will.
Brant Thomas Cold Spring, N.Y.
Essay on Organ Donation for Students and Children
500+ words essay on organ donation.
Essay on Organ Donation – Organ donation is a process in which a person willingly donates an organ of his body to another person. Furthermore, it is the process of allowing the removal of one’s organ for its transplanting in another person. Moreover, organ donation can legally take place by the consent of the donor when he is alive. Also, organ donation can also take place by the assent of the next of kin of a dead person. There has been a significant increase in organ donations due to the advancement of medical science.

Organ Donation in Different Countries
First of all, India follows the opt-in system regarding organ donation. Furthermore, any person wishing to donate an organ must fill a compulsory form. Most noteworthy, this form is available on the website of the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare Government of India. Also, The Transplantation of Human Organs Act 1994, controls organ donation in India.
The need for organ donation in the United States is growing at a considerable rate. Furthermore, there has also been a significant rise in the number of organ donors in the United States. Most noteworthy, organ donation in the United States takes place only by the consent of the donor or their family. Nevertheless, plenty of organizations are pushing for opt-out organ donation
Within the European Union, the regulation of organ donation takes place by the member states. Furthermore, many European countries have some form of an opt-out system. Moreover, the most prominent opt-out systems are in Austria, Spain, and Belgium. In England, no consent is presumed and organ donation is a voluntary process.
Argentina is a country that has plenty of awareness regarding organ donation. Most noteworthy, the congress of Argentina introduced an opt-out organ donation policy. Moreover, this means that every person over 18 years of age will be a donor unless they or their family state their negative. However, in 2018, another law was passed by congress. Under the new law, the family requirement was removed. Consequently, this means that the organ donor is the only person who can state their negative.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas

Benefits of Organ Donation
First of all, organ donation is very helpful for the grieving process. Furthermore, many donor families take relief and consolation due to organ donation. This is because they understand that their loved one has helped save the life of other people. Most noteworthy, a single donor can save up to eight lives.
Organ donation can also improve the quality of life of many people. An eye transplant could mean the ability to see again for a blind person. Similarly, donating organs could mean removing the depression and pain of others. Most noteworthy, organ donation could also remove the dependency on costly routine treatments.
Organ donation is significantly beneficial for medical science research. Donated organs offer an excellent tool for conducting scientific researches and experiments. Furthermore, many medical students can greatly benefit from these organs. Most noteworthy, beneficial medical discoveries could result due to organ donation. Organ donation would also contribute to the field of Biotechnology.
To sum it up, organ donation is a noble deed. Furthermore, it shows the contribution of an individual even after death. Most noteworthy, organ donation can save plenty of lives. Extensive awareness regarding organ donation must certainly be spread among the people.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

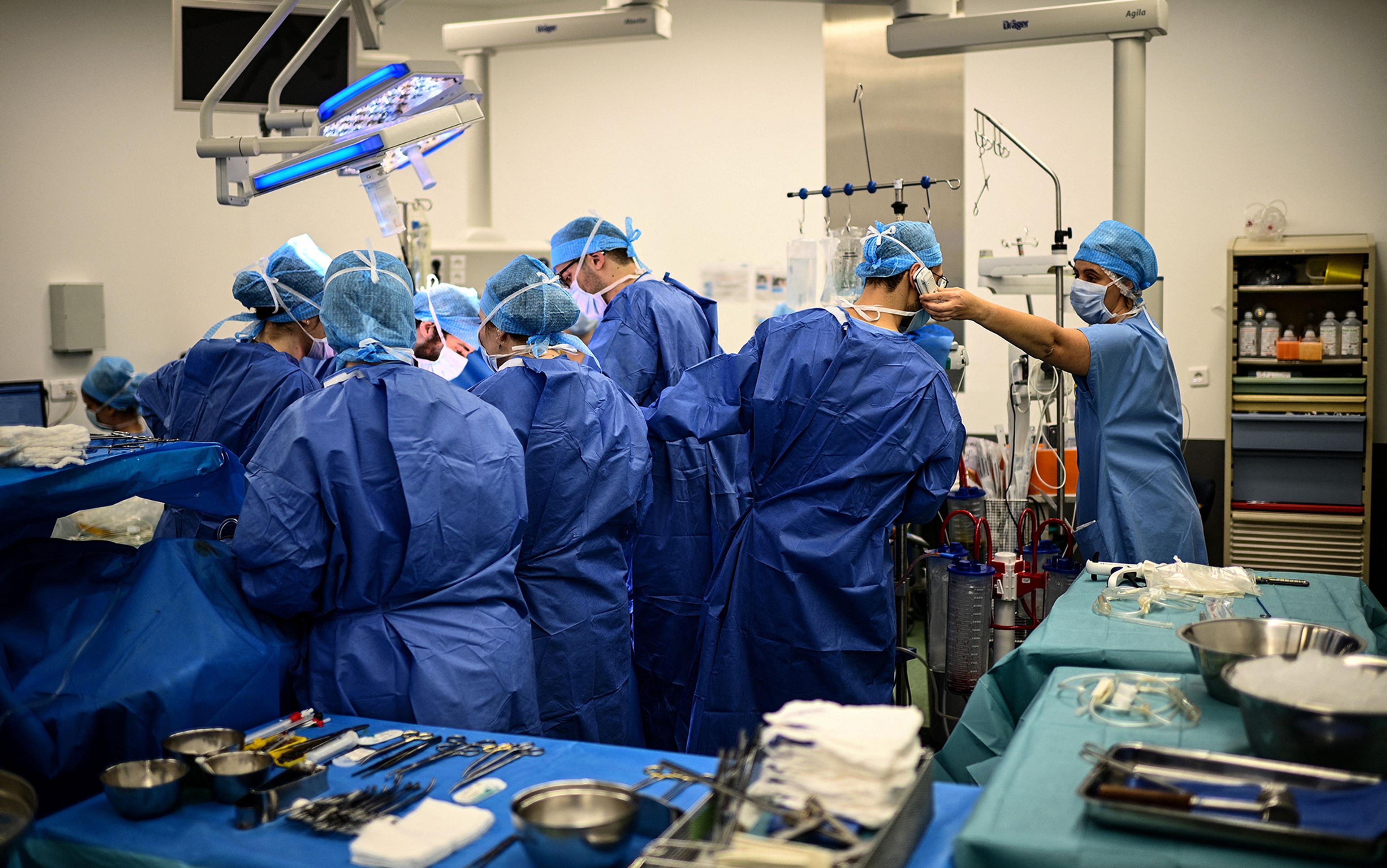
After assessing the lungs of a deceased patient, the thoracic surgeon Thomas Charrier (second from right) gives the green light for transplantation to his colleagues on the phone at the Foch hospital in Suresnes, Paris. This and all photos below taken on 9 December 2022 by Christophe Archambault/AFP. Courtesy Getty Images
Last hours of an organ donor
In the liminal time when the brain is dead but organs are kept alive, there is an urgent tenderness to medical care.
by Ronald W Dworkin + BIO
My patient was dead before I even saw her. She had been in a car accident. Now she was scheduled for organ donation.
She was called an ‘ASA 6’. To estimate operative risk, the American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) has a classification system built around how sick a patient is, ranging from a healthy ASA 1 to a moribund ASA 5, the latter meaning someone is not expected to live 24 hours. When the system was created in the mid-20th century, a sixth class for dead people seemed pointless. Death was known to the dead only, and life to the living only, and between the two there had been no bridge. When the definition of death changed in the late 1960s, making it possible for a person to be ‘brain dead’ but with organs still very much alive and available for donation, a bridge appeared and a sixth class was created in the early 1980s. Since 1988, when officials started collecting organ transplant data, almost a million organ transplants have been performed in the United States. Most of the organs have come from brain-dead donors. In 2021 alone, the US had almost 10,000 such donors.
When told of my upcoming case, I had mixed feelings. On the one hand, being in perfect health, unaccustomed to suffering and therefore easily disconcerted by the thought of death, I was horrified. My attitude toward death was like that of a young person standing blindfolded and tied to a post, awaiting a volley from a firing squad. The whole concept made my blood run cold. Yet the case also aroused in me a feeling of relief. Simply put, there was no risk of malpractice, as my patient was already dead. Many anaesthesiologists have such self-centred thoughts when taking care of ASA 6 patients.
I n her early 30s, she had a youthful face, without the traces of severe illness that ICU patients typically have. With her hair wrapped inside a bright, polka-dotted kerchief, she gave off an expression of almost pleasant, good-humoured cheeriness.
Who was this young person whose life had been tragically snuffed out? I jabbed into every crack of her medical record to find out. But little had been written down. Both her life and death seemed simple enough to be chronicled in a few lines. Something had happened inside her brain with the car accident, and the end came.
We wheeled her toward the operating room. Before departing, I pulled the sheet over her exposed feet. Why? I had an objection to her being dead, but I had an even more serious objection to her being undignified. With my patient still partly in the world of the living, I wanted to keep a place for her in the part that pretends to be genteel.
Six hours she had been officially dead. Now she had re-entered the world of the living
When we arrived in the operating room, something turned over inside me, sank, and went cold. After all, she was dead. The day before, she was as whole as me – and now look. She would never rise again.
After we moved her from the gurney to the operating table, the doctors and nurses, so used to taking care of living patients, stared at one another stupidly, as if not knowing why they had come together or why they stood around the table. For a brief moment, each one of us likely had the same supernatural vision, how for the past six hours, after being declared brain dead, this woman had lain under the measureless power of death. Six hours she had been officially dead. Six times had the hour hand on the clock moved – and she had lain dead. Now she had re-entered the world of the living. I would support her blood pressure and pulse. I would make her blood bright red with oxygen. Indeed, she might even wake up and look at us, I fantasised. She might be raised from the dead.
Ghoulish thinking, yet I do not write about this case to be ghoulish. Nor am I trying to stake out a new position in the bioethics debate. My purpose is more practical. Today, artificial intelligence (AI) looms over medical practice. Although unlikely to replace doctors completely, AI makes some medical activities especially ripe targets for takeover, including the harvesting of organs from brain-dead donors. And why not? Bedside manner and the common touch cease to be concerns. Using AI machines rather than doctors to harvest organs also promises to save money.
Yet this impersonal, nonhuman method of organ retrieval may discourage people from becoming organ donors , or from letting dead relatives become so, thereby exacerbating the current organ shortage. People will see pictures of organ retrieval being carried on all around by inanimate machinery in a room completely abandoned by human beings. Bodies will be brought in and sent out, while the invisible, sleepless work of the machines goes on. ‘Please, tell me this is not my end,’ people will fret privately. And they will resist consenting to organ donation.
O rgan retrieval can take place at odd hours because the time between retrieval and transplantation must be minimised. A donor heart or lungs can last only four to six hours outside the body. A kidney, liver or pancreas can last a bit longer. Because donation and transplantation must be synched perfectly, surgical teams must be allowed to work at any hour of the day.
Although donors are dead, managing their anaesthesia can be tricky. To keep their organs healthy, their physiology must be carefully attended to, yet brain death affects each organ system differently. High intracranial pressure can lead to an enormous outpouring of adrenaline, which can injure the heart and other organs as circulation fails. Brain death can cause pulmonary oedema (fluid in the lungs), making it hard to oxygenate the blood, thereby damaging the organs by a second route. Brain death also wreaks havoc on the body’s endocrine system, causing vital hormone levels to fall and damaging organs by a third route.
My patient lay stretched out on the table. The room was silent, as I had not yet placed any vital sign monitors on her body. It was a sinister silence. The monitors typically emit sounds that resemble the unconcerned twitter of birds. In an operating room, they symbolise life. Their absence suggests that a patient is not alive. In fact, mine wasn’t.
Nature will never permit anyone to know the exact point where brain death becomes real death
Ready to cut, the surgeon spoke through his headphones to surgeons in other cities waiting for the organs. The rest of us said nothing as he gave them an estimated time of arrival. The team had a real need for a stout word in these last few moments before the operation began. Sensing the mood, the surgeon said some dignified things about how our patient was giving other people a chance to live. Everyone nodded in agreement. He seemed thankful and sincere, yet he had to be that way for, at such a moment, anyone with even a modicum of intelligence would have felt anything else as an affront.
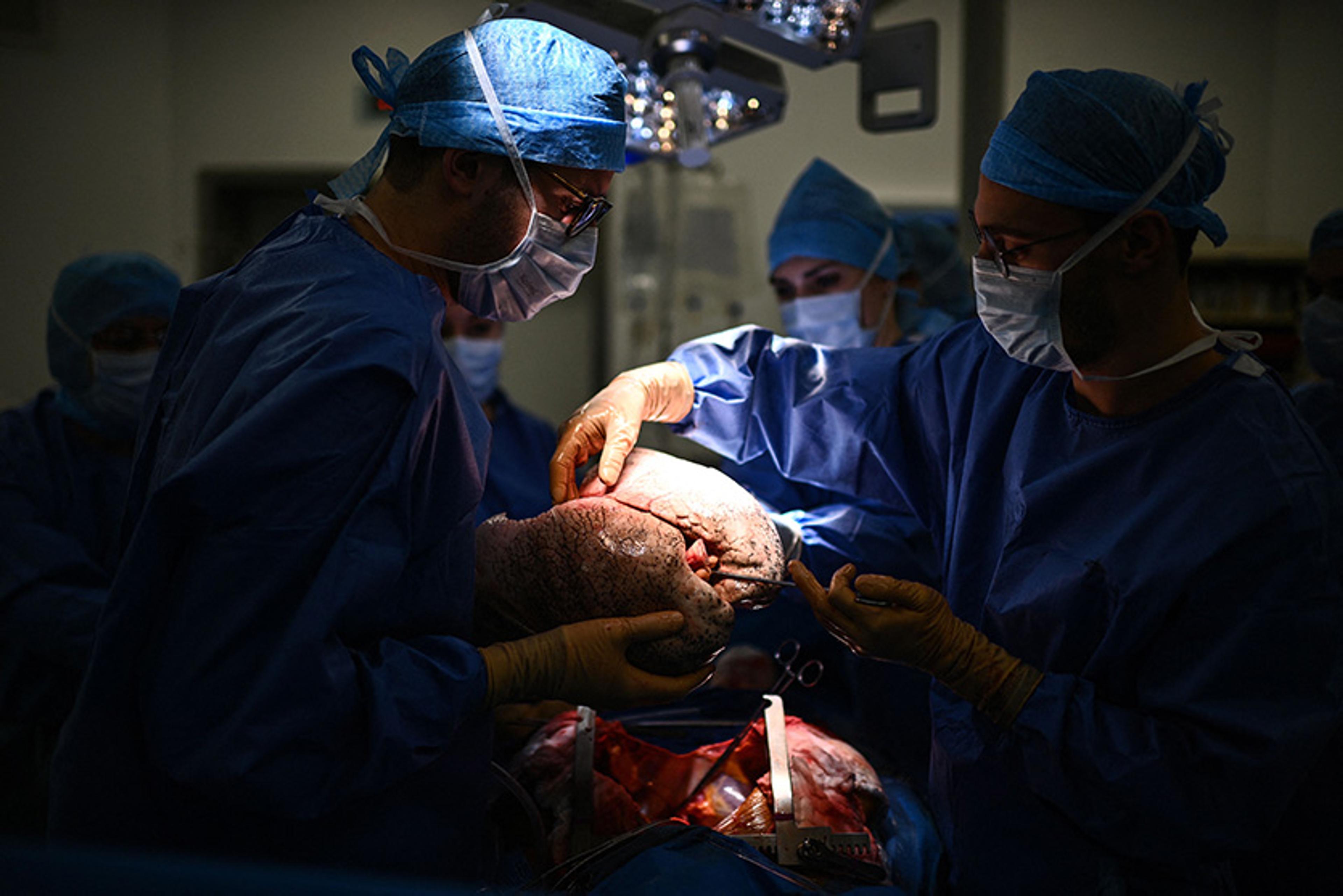
The surgeon cut into the patient’s chest. Almost immediately the patient’s heart rate and blood pressure jumped. It resembled the powerful surge of life that comes during a period when a person’s very existence and survival are at stake. The jump originated in a spinal reflex that stimulated the woman’s sympathetic nervous system below the level of the brain. Still, it seemed a manifestation of her will to live. Even more so when her hand moved – a sure sign of life! But that, too, was mediated through a spinal reflex.
I gave the patient some anaesthetic gas. I also gave her some opioids. Why the latter? After all, a dead patient doesn’t feel pain. In part because opioids help to lower heart rate and blood pressure directly, but also, I must admit, because I thought my patient might still be a ‘little alive’, whatever that means, and therefore in pain. Irrational on my part, yes, but the secret of life, including the definition of life, still remains the deepest and most mysterious one. Here Nature permits no eavesdroppers; never will she permit anyone to know the exact point where brain death becomes real death. At this, she draws a veil. I wanted to hedge my bets.
The woman’s blood pressure soon dropped too low. I poured fluid into her intravenous line. In the meantime, the surgeon moved hurriedly to extract her heart, clamping the large blood vessels leading both to and from it. Our fast pace betrayed another incongruence. Speed is thought to be a bit unrefined in an operating room. True, it is needed to save money, but ideally the operating room is an ordered world with calm transitions, a world without haste, except during an emergency to save a patient’s life. The visibly hasty fashion in which I and the surgeon worked made it seem like one of those urgent situations. In fact, I was trying to keep her circulation going long enough for the surgeon to tear her heart out.
I transfused a unit of blood, as excessive blood clotting, common after brain death, had made her dangerously anaemic. I turned on the warming mattress lying underneath her to keep her body temperature from dropping below 36 degrees Celsius. Brain death interferes with the body’s ability to regulate temperature, and the resulting hypothermia poses a risk to the organs. Finally, I gave her insulin to control her blood sugar level, as brain death often causes blood sugar to rise. All of these are routine lifesaving measures. In the past, I had used them to fight off death in my sickest patients, but here I had to remind myself that my patient was already dead.
T he surgeon removed her heart. The irrevocable instant had come. It was as when a train starts with a violent jerk, as if to overcome a disinclination to change its state of inertia. For many in the operating room, this was the moment when the woman’s life really ended.
A minute before, I had heard the melodies of the electrocardiogram (EKG) and pulse oximeter without really thinking about them. An anaesthesiologist’s ear is so capable of adapting itself that a continuous din, like the noise of a street or the rushing sound of a river, adjusts itself completely to their consciousness. But the unexpected halt in the sounds startled me into listening – and looking. I stared over the ether screen into the woman’s now-vacant chest cavity. It was shameful and terrible to gaze upon. Part of me felt as if I had abetted a murder around the corner.
I tried to make this last sigh worthy of the moment, a sigh that only another human being could replicate
The surgeon injected the heart with cold preservative and put it in a box. His next target was the lungs. He asked me to manually give the woman one last deep breath so that he could confirm that all parts of her lungs had been expanded before their removal. The breath I gave her was slow and gentle, like a sigh. Indeed, medically speaking, it was a sigh. On ventilators, there is a function labelled ‘sigh’ which, when pressed, gives a patient a single sustained deep breath to open up the lung’s small air sacs. Almost proudly, I imagined the sigh I gave this woman to be more human than what a machine could give. Compressing the anaesthesia bag with my hand, I imagined how she might have sighed in the past, on her own, in the face of some bitter reality, some trick or force of fate, crushing her heart but also uplifting her. I tried to make this last sigh worthy of the moment, a sigh that only another human being could replicate, a deep breath that begins with disappointment, passes into resignation, and ends in acceptance. I crafted that last sigh as if it were the epilogue to a tragedy.
When the woman exhaled her last bit of sigh, I removed her breathing tube. The surgeon took out her lungs and stapled her windpipe shut. At this point, there was little for me to do, and my inactivity plunged me into a sense of nothingness. I felt I was going to gag on my thoughts if I didn’t do something. I walked away from my patient to look inside a cupboard. I opened a few drawers. Then I felt badly for doing so. Although one of us was dead, still there seemed to be two of us here. It’s as if the woman and I were friends and I didn’t want to leave my friend. I went back and stood by her head.
The surgical team removed the rest of her organs and the case finished. Here the woman and I reached a parting of the ways. I stared at her face seriously and fixedly as though I wanted to look my fill and imprint forever on my memory her image. I cannot recall for how long I looked. Great moments are always outside of time.
Our relationship proved significant. Nothing is more characteristic of the total lack of spiritual connection between myself and other patients than the fact that I have forgotten most of their names and faces. But this woman’s name and face I remember. And when I speak of memory, I do not mean something akin to a register kept in a well-ordered office, a place in which documents are laid away in store. I mean something submerged in the rushing stream of my blood, memory as a living organ in which every feeling experienced that day retains its natural essence, its original intensity, its primary historical form.

M y patient lived longer than what her death certificate says. She lived in my mind during the organ retrieval and continues to live in my memory because I do not want to forget her, and because I cannot forget her. Although I know only her general outlines, our connection satisfies some deep law of harmony underlying all life, in which every person must enter into communion with another person in order fully to live. By that standard, my patient lived past her official time of death.
When AI replaces the anaesthesiologist during organ retrievals, you, the organ donor, will not live any longer than what’s listed on your death certificate. The air inside the operating room is already cold, dry and unpleasant. Various monitors will sit on the top shelf of the anaesthesia machine, regulated by AI. Their special melodic rings will no longer be necessary, as their data will be sent along to AI in silence. Care will be delivered without the mediation of human minds, senses or hands.
Before your lungs are removed, the machine’s ventilator bellows will go up, down, up, down. Capable only of whooshing and not ringing, the bellows will seem to call sadly through the cold air to the monitors sitting above, waiting fruitlessly for a response. What a simple, insignificant movement: up, down, up, down, never getting away from the same place. It will be the only activity surrounding your head amid the metal machines, with their cold, menacing gleam. Nobody will be sitting next to you to wonder about what you were like, or about the things that distinguished your personality and made it special. A vision of the future arises: similarly deserted operating rooms with AI machines all moving automatically, while the people who used to work in them have gone off somewhere to sit dreamily on the grass beneath the sky.
Medicine has tapped a new source of organs in the form of donation after circulatory death
It seems a decidedly unpleasant environment in which to meet one’s end, and enough to discourage those on the fence from becoming potential organ donors. Rather than live a bit longer in the mind of another person, rather than have that person think about you and wonder about you, entertain irrational imaginary concerns about you, slip a little extra narcotic into your intravenous line ‘just in case’, engage in metaphysical speculations about your breathing pattern, and imagine you a friend, you will be alone on the table, and your surgery will more closely resemble a bandit raid. The machines will be determined to take everything, every organ. Reduced to financial terms, it will be as if you were left penniless.
Worse, a new danger will come to overlie the chilling sense of emptiness, scaring even more people away from becoming organ donors. Because there are already too few brain-dead donors – each year, more than 8,000 people in the US die while on the waiting list for organs – medicine has tapped a new source of organs in the form of donation after circulatory death (DCD). These organ donors are not brain dead, although many of them are unconscious. Instead, they lack circulatory or respiratory activity after being disconnected from artificial life-support systems. Without such activity after a few minutes of so-called ‘no touch’, they are declared dead, and their organs become available for donation. Their numbers have been growing over the past two decades. Today, they account for about 10 per cent of transplanted organs in the US.
The problem is that certain medicines necessarily given to these donors before death, but in expectation of death, may hasten their death. The medicines are given for the sole purpose of making their organs more viable for transplantation. Heparin, for example, prevents blood clotting, while phentolamine dilates blood vessels and improves blood flow to the organs. Yet heparin also increases the chances of bleeding into the brain, while phentolamine may lower blood pressure to the degree that a person goes into shock. Although these patients are near death for other reasons, the medicines may become their actual cause of death. This makes doctors uneasy; hence the rule not to give these medicines to donors prone to bleeding or with low blood pressure.
Y et the rule risks driving away potential donors, who will naturally think: ‘Doctors won’t give you these medicines to kill you; on the other hand, they won’t give you these medicines to help you. At some point, doctors aren’t really on your side. But when?’ As the number of brain-dead donors drops, medicine will increasingly rely on DCD donors to compensate. Already sensitised by the image of surrendering their organs to machines in a metallic desert, potential donors will fear being herded into the ‘imminent death’ category to meet some organ quota, a fear only heightened when word gets out that doctors are not always their advocates.
Currently, doctors in the US must get consent before declaring people DCD donors, but another model, called the ‘presumed consent model’, already operates in other countries and allows the recovery of organs without prior authorisation. A cascade of events threatens to turn organ retrieval into a kind of science-fiction nightmare, where organ shortages lead to medicines being given to people to preserve their organs while possibly hastening their death, all without telling them the plan or asking for their permission.
My experience in the operating room serves as a warning to those eager to cut corners and replace doctors with AI machines
Whenever people start to think about becoming an organ donor, they immediately make a leap to their own precious person. Who am I, what am I, what am I without my organs, and so forth. It is part and parcel of being a human being. That some people are willing to surrender their organs after death suggests that, to feel oneself human, they need more than merely having a whole body; they also need an atmosphere of simple humanity. To feel human, people need to feel that they occupy space in the thoughts and feelings of others. It is why they consider becoming organ donors in the first place. They imagine helping others by giving up a part of themselves in the future. In exchange, they imagine the recipients thinking from time to time about what they, their donors, were like. In that way, the donors feel a connection with whomever those recipients might be, and feel somehow fulfilled.

I’d like to think that caring for my brain-dead patient satisfied some small part of this need to feel human, whether on the part of my patient before she died and who perhaps lived in expectation of becoming a donor one day, or on the part of her relatives who gave their consent to the procedure after she was declared brain dead. Either way, I connected with her or with her family.
My experience in the operating room serves as a warning to those eager to cut corners and replace doctors with AI machines willy-nilly. You don’t satisfy people’s urge to feel human by making the bridge to the next world a totally inhuman one.
The lesson extends far beyond organ donation. AI promises to make healthcare quicker, more precise, and error-free. To the degree that it replaces doctors and nurses, it portends a massive shift in medicine that seems to come every 30 years, when people are so overwhelmed by the burden of their own technological creations, they need every iota of their strength to adjust. Once again, with the advent of AI, advancements promise to put healthcare on an entirely new footing and, once again, the inevitable backlash will be there. So it was in the 1960s, when new medical technologies and procedures, such as home dialysis machines and coronary artery bypass surgery, improved life, and yet, during this same period, the medical profession’s reputation plummeted, as patients complained that doctors had grown cold and impersonal. So it was in the 1990s, when the rise of managed care promised greater efficiency at less cost, and a ‘win-win’ strategy anchored in preventive medicine, led to a patient rebellion against being treated like cattle, including their inability to choose their own doctor, and rushed visits to practitioners ‘on the plan’.
Now, in the 2020s, the stage is set for outrage, yet again. AI promises to elevate healthcare; but, to the degree that it replaces doctors and nurses, it also threatens to depersonalise patients and to wash off their distinctive colours until everyone has the same drab tint. In the crucible that looms, patients are going to rebel. And it is in the arena of organ donation, where they face death by machine, that they are likely to baulk loudest, and first.

The environment
We need to find a way for human societies to prosper while the planet heals. So far we can’t even think clearly about it
Ville Lähde

Stories and literature
Do liberal arts liberate?
In Jack London’s novel, Martin Eden personifies debates still raging over the role and purpose of education in American life

Alien life is no joke
Not long ago the search for extraterrestrials was considered laughable nonsense. Today, it’s serious and scientific

History of ideas
Reimagining balance
In the Middle Ages, a new sense of balance fundamentally altered our understanding of nature and society

What would Thucydides say?
In constantly reaching for past parallels to explain our peculiar times we miss the real lessons of the master historian
Mark Fisher

Emergency action
Could civil disobedience be morally obligatory in a society on a collision course with climate catastrophe?
Rupert Read

Presentations made painless
- Get Premium
117 Organ Donation Essay Topic Ideas & Examples
Inside This Article
Organ donation is a crucial and life-saving practice that can have a profound impact on the lives of individuals in need of organ transplants. However, many people are still hesitant to become organ donors due to various reasons such as lack of awareness, misconceptions, or personal beliefs. To address this issue and encourage more people to consider becoming organ donors, it is important to raise awareness about the benefits of organ donation and dispel any myths or misconceptions surrounding the topic.
To help facilitate discussions and promote awareness about organ donation, here are 117 organ donation essay topic ideas and examples that can serve as inspiration for students, writers, and advocates:
- The importance of organ donation in saving lives
- The process of organ donation and transplantation
- Myths and misconceptions about organ donation
- Religious perspectives on organ donation
- Ethical considerations in organ donation
- The impact of organ donation on the healthcare system
- Organ donation policies and regulations
- Organ donation in minority communities
- Organ donation in the LGBTQ+ community
- Organ donation and social justice
- Organ donation and mental health
- Organ donation and organ trafficking
- Organ donation and the black market
- Organ donation and medical tourism
- Organ donation and the role of media
- Organ donation and public education campaigns
- Organ donation and celebrity endorsements
- Organ donation and the role of healthcare providers
- Organ donation and cultural beliefs
- Organ donation and family dynamics
- Organ donation and the grieving process
- Organ donation and the donor registry
- Organ donation and organ allocation
- Organ donation and organ matching
- Organ donation and organ rejection
- Organ donation and organ preservation
- Organ donation and organ procurement
- Organ donation and organ storage
- Organ donation and organ transplantation success rates
- Organ donation and organ waitlists
- Organ donation and organ shortage
- Organ donation and organ trafficking laws
- Organ donation and organ trafficking prevention
- Organ donation and organ trafficking statistics
- Organ donation and organ trafficking victims
- Organ donation and organ trafficking organizations
- Organ donation and organ trafficking awareness campaigns
- Organ donation and organ trafficking survivor stories
- Organ donation and organ trafficking documentaries
- Organ donation and organ trafficking movies
- Organ donation and organ trafficking books
- Organ donation and organ trafficking research
- Organ donation and organ trafficking advocacy
- Organ donation and organ trafficking support groups
- Organ donation and organ trafficking fundraising
- Organ donation and organ trafficking volunteer opportunities
- Organ donation and organ trafficking partnerships
- Organ donation and organ trafficking collaborations
- Organ donation and organ trafficking initiatives
- Organ donation and organ trafficking events
- Organ donation and organ trafficking conferences
- Organ donation and organ trafficking workshops
- Organ donation and organ trafficking seminars
- Organ donation and organ trafficking webinars
- Organ donation and organ trafficking symposiums
- Organ donation and organ trafficking forums
- Organ donation and organ trafficking roundtables
- Organ donation and organ trafficking panels
- Organ donation and organ trafficking discussions
- Organ donation and organ trafficking debates
- Organ donation and organ trafficking dialogues
- Organ donation and organ trafficking interviews
- Organ donation and organ trafficking Q&A sessions
- Organ donation and organ trafficking surveys
- Organ donation and organ trafficking polls
- Organ donation and organ trafficking feedback
- Organ donation and organ trafficking testimonials
- Organ donation and organ trafficking success stories
- Organ donation and organ trafficking challenges
- Organ donation and organ trafficking obstacles
- Organ donation and organ trafficking setbacks
- Organ donation and organ trafficking failures
- Organ donation and organ trafficking lessons learned
- Organ donation and organ trafficking best practices
- Organ donation and organ trafficking tips
- Organ donation and organ trafficking strategies
- Organ donation and organ trafficking tactics
- Organ donation and organ trafficking tools
- Organ donation and organ trafficking resources
- Organ donation and organ trafficking guidelines
- Organ donation and organ trafficking policies
- Organ donation and organ trafficking procedures
- Organ donation and organ trafficking protocols
- Organ donation and organ trafficking standards
- Organ donation and organ trafficking regulations
- Organ donation and organ trafficking compliance
- Organ donation and organ trafficking enforcement
- Organ donation and organ trafficking monitoring
- Organ donation and organ trafficking evaluation
- Organ donation and organ trafficking assessment
- Organ donation and organ trafficking measurement
- Organ donation and organ trafficking analysis
- Organ donation and organ trafficking reporting
- Organ donation and organ trafficking tracking
- Organ donation and organ trafficking documentation
- Organ donation and organ trafficking records
- Organ donation and organ trafficking data
- Organ donation and organ trafficking trends
- Organ donation and organ trafficking forecasts
- Organ donation and organ trafficking projections
- Organ donation and organ trafficking models
- Organ donation and organ trafficking simulations
- Organ donation and organ trafficking experiments
- Organ donation and organ trafficking tests
- Organ donation and organ trafficking trials
- Organ donation and organ trafficking studies
- Organ donation and organ trafficking investigations
- Organ donation and organ trafficking inquiries
- Organ donation and organ trafficking assessments
- Organ donation and organ trafficking evaluations
- Organ donation and organ trafficking analyses
- Organ donation and organ trafficking reports
- Organ donation and organ trafficking recommendations
By exploring these organ donation essay topic ideas and examples, individuals can gain a deeper understanding of the importance of organ donation and the impact it can have on the lives of those in need. Through education, advocacy, and awareness, we can work together to promote organ donation and save lives.
Want to create a presentation now?
Instantly Create A Deck
Let PitchGrade do this for me
Hassle Free
We will create your text and designs for you. Sit back and relax while we do the work.
Explore More Content
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Service
© 2023 Pitchgrade
Home — Essay Samples — Nursing & Health — Organ Donation — Organ Donation: Analysis of Ethical Issues Involved
Organ Donation: Analysis of Ethical Issues Involved
- Categories: Organ Donation Organ Transplant
About this sample

Words: 1773 |
Published: Oct 2, 2020
Words: 1773 | Pages: 4 | 9 min read
Table of contents
Introduction, the ethics of organ procurement, the ethical implications for recipients and donors, emerging ethical issues and future considerations, works cited.
- Biotechnological Advancements
- Data Privacy and Equity
- Cultural and Religious Perspectives
- Patient Advocacy and Education
- Interdisciplinary Collaboration
- Abadie, A., & Gay, S. (2006). The impact of presumed consent legislation on cadaveric organ donation: A cross-country study. Journal of Health Economics, 25(4), 599-620.
- Boudjema, K. (2019). Opt-out organ donation: A public health policy that will save lives. Journal of Hepatology, 71(1), 184-186.
- Dewey, C., & Holecek, A. (2017). Organ transplantation and ethical dilemmas in nursing practice: An overview. Journal of Bioethical Inquiry, 14(3), 365-373.
- Gómez‐Lobo, A., & Topic, D. (2016). Organ donation: Presumed consent and compulsory rules. The Hastings Center Report, 46(2), 21-28.
- Grinyó, J. M. (2009). Why do we have a shortage of organs for transplantation? A Spanish point of view. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation, 24(3), 698-701.
- Jansen, N. E., Haase-Kromwijk, B. J., van Leiden, H. A., Hoitsma, A. J., & IJzermans, J. N. (2018). The implementation of opt-out systems instead of informed consent: A possible solution to organ donation shortages in the Netherlands. Nederlands Tijdschrift Voor Geneeskunde, 162, D2061.
- Kardamanidis, K., Russell, J., Prakash, V., Axelrad, J., & Ravindra, K. V. (2018). Opt-out system improves organ donation rates in the United States: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clinical Transplantation, 32(3), e13164.
- Moradi, S., Abbasi, M., & Hami, M. (2017). A systematic review of the effect of presumed consent systems on organ donation. Transplantation Proceedings, 49(7), 1405-1410.
- Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network. (2021). OPTN/SRTR 2020 annual data report: Transplantation. Health Resources and Services Administration, Healthcare Systems Bureau, Division of Transplantation. https://srtr.transplant.hrsa.gov/annual_reports/2020/Default.aspx
- Sadler, G., & Webb, C. (2018). The ethics of organ donation and transplantation: An overview. Journal of Nursing Ethics, 25(3), 265-274.

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Prof Ernest (PhD)
Verified writer
- Expert in: Nursing & Health

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
3 pages / 1215 words
6 pages / 2570 words
3 pages / 1236 words
1 pages / 673 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Organ Donation
The case of Baby Theresa, a newborn born with anencephaly in 1992, ignited a profound ethical debate regarding organ donation, the definition of death, and the boundaries of medical intervention. This essay delves into the [...]
The advent of the concept of organ transplantation came as an important breakthrough in the medical field, in the 20th century. The idea behind organ donation and transplant is simple. A healthy organ (such as heart, lungs, [...]
Organ donation is a pure act of kindness. However, it is often debated about whether it should be mandatory or not. Donating your organ is a social cause which is all together a decision of the person who is willing to donate [...]
Nowadays the number of people who need an organ because of a disease or maybe a medical condition. The time people need to wait for an organ is too long and most of them lose the faith. A big number of people may think that the [...]
Organ transplantation stands as a remarkable medical achievement, offering a lifeline to countless individuals whose organs have failed due to illness or injury. However, the global shortage of available organs has led to a [...]
Ionising radiation is a method of treatment that commonly used to treat cancer. Radiation therapy uses high-energy particles or waves, such as x-rays, gamma rays, electron beams, or protons, to destroy or damage cancer cells. [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
Organ Donation - Free Essay Samples And Topic Ideas
Organ Donation is the process of surgically removing an organ or tissue from one person (the organ donor) and placing it into another person (the recipient). Essays could explore the ethical, social, and medical aspects of organ donation, including the processes of organ transplantation, the importance of donor registries, and the debates surrounding consent and allocation policies. A substantial compilation of free essay instances related to Organ Donation you can find in Papersowl database. You can use our samples for inspiration to write your own essay, research paper, or just to explore a new topic for yourself.
Mandatory Organ Donation: Ethical or Unethical
The American Transplant Foundation reports that every 12 minutes, there is an additional member who joins 123,000 national organ transplant donors. Even though many people are aware of the advantages that come with organ donation, they may not comprehend all the benefits that come with organ donation, especially to the donor (Santivasi, Strand, Mueller & Beckman, 2017). The subject of organ donation is important because it improves the quality of life for the recipient of the organ transplant. For instance, […]
Should Organ Donation be Mandatory?
Organ donation is the gift of life. By donating organs you are literally saving thousands of adults and children. The number of patients whose organs are failing on a continuous bases. consequently , the more people who are on the list the less likely they are to get an organ which sadly results in their untimely death. But why would you want to see another human being die? Here in the united states, there is a shortage of organs. According […]
Should Organ Donors be Paid for Donations
There seems to be a great debate in this country about whether or not donors should be paid for organ donations. I honestly did not know that this debate was going on before I started doing research on this subject. It seems crazy to think that the state legislator should get involved in the question whether people should be paid for organ donations. I have read a few articles about"the gift of life" and it all sounds ridiculous to me. […]
We will write an essay sample crafted to your needs.
The Benefit of Organ Donation
If there is one thing that everyone in the world can agree on it is the fact that eventually we are all going to die. Death is going to happen to each and every one of us, and the thought of dying is usually very tragic to most people. It is not knowing what is going to happen that can cause the fear of dying in a person or a family. Diseases and tragic accidents are usually the cause for […]
Understanding of Organ Donation
Do we ever think about those patients who lay on bed 24 hours days a week in search of Organ ? There are many simpler ways in which patients can be cured, but it gets very difficult when only one way left which is by donating organ. In simpler words, Organ Donation is the removal process of Organ or tissue from one person through surgical process to be transplanted to another person for the purpose of replacing an Organ injured […]
3D Printing and Bioprinting Revolutionizing Healthcare
3D bioprinting is one of the most anticipating and promising technological advancements of all time. According to the US National Library of Medicine, 3D bioprinting is "a manufacturing method in which objects are made by fusing or depositing materials? such as plastic, metal, ceramics, powders, liquids, or even living cells? in layers to produce a 3D object" (Ventola, 2014, para 2). Is With the capability of using real cells, 3D bioprinting will make it possible to create living tissue. This […]
Why Organ Donation should be Compulsory?
Imagine this: you are diagnosed with severe heart failure and your only chance of survival is to receive a heart transplant. Although your loved ones would desperately like to help, they are unable to. Unlike a set of lungs or a pair of kidneys, you only have one heart, thus making it impossible to consider the idea of utilizing a living donor. You now are faced with the fact that in order to live, you need to rely on an […]
Definition of Organ Donation
Organ donation is defined as the process of transplanting human organs from one person to another ("Organ donation," 2017). As of November 2018, there are more than 114,600 people on the national waiting list for a donor organ, and a new person is added to the list every 10 minutes ("Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network," n.d.). So far in 2018, over 30,400 transplants have been performed from more than 14,500 donors ("Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network," n.d.). The most commonly […]
Reborn to be Alive : Critical Analysis of an Advertisement
“Becoming a donor is probably your only chance to get inside her.” Reborn to be Alive showcases their slogan proudly across their advertisement as a provocative half-naked woman entices the viewer with her gaze. Being an organ donor means being selfless, having compassion, and altruism; yet being an organ donor isn’t enough sufficiency for a good marketing campaign, thus the sexist direction of their advertisement. Reborn to be Alive meant to capture men’s attention by the use of such sexist […]
Role of the Default Bias in Organ Donation Rates
The first law of motion, also known as the law of inertia by Newton goes like this: A body in motion remains in motion or, if at rest, remains at rest at a constant velocity unless acted on by an external force. If one thought inertia was only confined to the walls of physics, behavioral economics asks them to think again. Here I'd like to introduce the reader to the concept of cognitive bias – an organized and consistent pattern […]
Organ Donation Programmes Across the World
Organ Donation Programmes Across the World China Till 2014, Chinese authorities permitted the harvesting of organs from executed prisoners without prior consent from them or their families. In fact, in December 2005, the country’s deputy health minister estimated that as many as 95 per cent of the organs used in China’s transplants came from such sources. Since then, China has banned the practice and is now trying to galvanize organ donations from regular civilians. Iran Iran is the as it […]
Organ Donation not being Accessible for all
Organ Donation: Not Accessible for All "Don't think of organ donation as giving up part of yourself to keep a total stranger alive. It's really a total stranger giving up almost all of themselves to keep part of you alive" (~Author Unknown). Organ donation is the process of surgically removing an organ or tissue from one person (the organ donor) and placing it into another person (the recipient). This is necessary when the recipient's organ has failed or has been […]
Additional Example Essays
- Poor Nutrition and Its Effects on Learning
- The Mental Health Stigma
- Psychiatric Nurse Practitioner
- Substance Abuse and Mental Illnesses
- The Extraordinary Science of Addictive Junk Food
- PTSD in Veterans
- Drunk Driving
- Arguments For and Against Euthanasia
- Effects of Childhood Trauma on Children Development
- Gender Inequality in the Medical Field
- Leadership in Nursing
- Causes of Teenage Pregnancy
1. Tell Us Your Requirements
2. Pick your perfect writer
3. Get Your Paper and Pay
Hi! I'm Amy, your personal assistant!
Don't know where to start? Give me your paper requirements and I connect you to an academic expert.
short deadlines
100% Plagiarism-Free
Certified writers
93 Organ Donation Essay Topic Ideas & Examples
🏆 best organ donation topic ideas & essay examples, ⭐ good research topics about organ donation, 👍 interesting topics to write about organ donation, ❓ organ donation research questions.
- Importance of Organ Donation Considering the huge number of people in need of different body organs today, and the many that are dying each day due to organ problems, a socially upright member of our society should not consider […]
- Organ Transplantation and Donation Since people donate organs to others regardless of their locations, nations need to be cautious in order to avoid spread of diseases in the process.
- Organ Donation: Willingness to Donate Organ Among Medical Students In conclusion, organ donation is a vital and life-changing procedure that can help save lives and improve the quality of life for those in need.
- The COVID-19 Impact on Organ Donation The official statistics of the United States government also support the idea that with the onset of the pandemic, the number of organ transplantation procedures has decreased. The pandemic appears to be the main cause […]
- The Organ Donation Legislation Critique She expresses outrage and condemnation of the current organ donation legislation and the politicians who drafted it. If the global majority accepts such a perspective, it will lead to a worldwide spike of violence and […]
- Researching of Xenograft and Organ Donation Doctors have been searching for methods to save lives all along, and xenograft has shown to be one of the most reliable, particularly when it comes to organ replacement. A xenograft is fraught with dangers, […]
- Organ Donation: Donor Prevalence in Saudi Arabia Donating organs does not pose a threat to the life of the donor; however, it can save the lives of many other people who need organ transplants.
- Organ Donation Registry Beginning 16th February 2010 through to the 18th the Ypsilanti Lions club organized the organ donation registry table whose main purpose was to invite people from all walks of life to literally give a piece […]
- Organ Donation: Postmortem Transplantation The ethicality of such actions has been questioned, as this procedure may be ambiguously perceived by the relatives of the deceased patient and the recipient of organs.
- The Issue of Compensation for Organ Donation Nevertheless, in spite of the fact that proponents of the compensation for the organ donation indicate obvious advantages of using this approach for the healthcare system, opponents emphasize the unethical character of such approaches.
- Organ Donation: Ethical and Legal Considerations The other approach is by requesting the family of the deceased to give consent for the donation in a case where the deceased did not permit earlier on.
- Organ Donation in Saudi Arabia: Survey Results A total of 27 participants answered the questions that were asked in the survey. The problems that are behind the ambiguity that people have over this issue are some of their limitations and perceptions.
- Organ Donation: Ethical Dilemmas An example of an ethical dilemma surrounding the procedure is the case of rich man vs.poor man, or rather, the case of a person who can afford to buy an organ on the black market […]
- Ethics of Organ Donation After Human Death In reference to this case, the ethical dilemma is related to the fact that the hospital administrator needs to disregard the necessity of informed consent for organ donation.
- Medical Ethics of Child’s Organ Donation Obviously, the parents are the only people who represent the wishes of the patient in the case. The above-mentioned position seems to be viable when it comes to the concept of the greatest good used […]
- Gene Patenting and Organ Donation Profitability is the key to violating the law, and that is the reason for the lack of transparency in the tissue market.
- Organ Donation and Transplantation Medicine Although money and financial support will be a major factor in the process of body transplant that Canavero expects to take two years, pegging human life on money is unethical.
- Organ Donation Myths: Critical Thought This essay is aimed at subverting three of the most common myths about the subject matter by considering the facts closely, relating them to the values concerning the organ donation, and isolating the issues related […]
- Organ Donation: Importance Information Because of the improved and advanced technology, the practice of organ transplant is becoming more popular and acceptable in the society.
- Ethical Issues in Organ Donation According to the authors of the study, death is defined as, “the irreversible loss of the integrated and coordinated life of the person as a single living organism”.
- The Ethics of Organ Donation in Modern World The patient is referred to a transplant center and is to their “dismay” put on a national waiting list, after a “series of interviews, physical and medical tests” to determine the suitability of the recipient […]
- Pros and Cons of Paying for Organ Donation: Arguments for Prohibition Although the potential of people to purchase organs might bring in profits to health care and increase supply and demand of transplanted organs, the fact of increased supply rates is doubtful because recent surveys prove […]
- The Nebraska Laws on Organ Donation in the United States
- Factors Influencing Organ Donation Among African Americans
- Pros and Cons of a New Opt-Out System of Organ Donation
- An Argument in Favor of Encouraging Organ Donation After Death for Transplantation Opportunities
- Beneficence Justice Malfeasance and Autonomy in Organ Donation
- The Cases of Brain Death and Organ Donation in Children and Adults
- Comparison of the Organ Donation in the U.S. and Sweden
- Compensation for Organ Donation: The Sale of Organs
- Could Death Row Inmates Be a Viable Source for Organ Donation
- Overview of the Dutch and Belgium Organ Donation Acts
- Donation of the Organs and Their Harmful Effects on the Society
- Knoweldge and Attitudes of Health Professionals on Organ Donation
- Financial Compensation for Organ Donation
- Analyzing the Importance of the Organ Donation
- The Benefits and Shotrcomes of Organ Donation
- Improving Organ Donation Through Clarification and Education
- Increasing Organ Donation via Changes in the Default Choice or Allocation Rule
- Organ Donation: Why Everyone Should Be a Donor
- Legal and Ethical Issues Regarding Organ Donation
- Mandatory Organ Donation: Ethical or Unethical
- Organ Donation: How Recipients Are Chosen and Should Donors Be Compensated
- The Discussion of the Legalization of Organ Donation
- Effects of the Organ Donation on the Lives of Thousands of Recipients
- Ethical Issues Surrounding Organ Donation
- Why Cash for Kidneys Is Better Than Organ Donation
- Organ Donation Issues and Laws: Federal and California State
- Social Madia Initiative May Help Increase Organ Donation
- Organ Donation: Life That You May Have the Power to Save
- The Best Ways to Decrease the Shortage of Organs for Transplantation
- Public Policies in the Question of Consent for Organ Donation
- Organ Donation: Keeping the Gift of Life Alive
- Description of the Commercial Market for Organ Donation
- The Controversy Associated With the Opt-Out Organ Donation
- The Life Saving Benefits of Organ Donation
- Comparing Organ Donation Programmes Across the World
- The Global Need for Organ Donations
- Why Organ Donation Should Be Encouraged
- Organ Donation: Two Deaths or One Life
- Neonatal and Pediatric Organ Donation: Ethical Perspectives and Implications
- Organ Donation and Forest Depletion Depicted in Fitzhugh’s “The Organ Grinders”
- Is There a Black Market for Organ Donation?
- What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Organ Donation?
- How Is Organ Donation a Lucrative Business?
- Why Do Muslims Disagree With Organ Donation?
- Is Organ Donation Against God and Nature?
- What Are the Ethical Issues in Organ Donation?
- Is the US Opt-in or Opt-Out for Organ Donation?
- Why Is Organ Donation a Moral Issue?
- How Does the Process of Organ Donation Work?
- What Ethical Theory Is Against Organ Donation?
- Does Islam Support the Concept of Organ Donation After Death?
- What Is the Most Complicated Organ Donation?
- Are Organ Donations Compulsory in China?
- Why Can’t Organ Donation Be Mandatory?
- Is There an Age Limit for Organ Donation?
- What Do Religions Think About Organ Donation?
- Why Is Organ Donation in Exchange for Money Illegal?
- Is an Opt-in or Opt-Out More Effective for Organ Donation?
- What Are the Disadvantages of Organ Donation After Death?
- Are Religious Beliefs Keeping Organ Donations From Going Mainstream?
- What Cultures Don’t Believe in Organ Donation?
- Why Is Organ Donation Uncommon in India?
- Should Presumed Consent for Organ Donation Be Used in the US?
- What Are the Laws Behind Organ Donation?
- How Does the Debate on Deontology vs. Consequentialism Stand When It Comes to Organ Donation?
- What Are the Emotional Tolls of Organ Donation for the Donor?
- How Do Living Organ Donations Compare to Deceased Organ Donations in the United States?
- What Are the Challenges of Organ Donation?
- Are There Barriers to Organ Donation in the US?
- Why Are Donated Organs Sometimes Rejected?
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, March 2). 93 Organ Donation Essay Topic Ideas & Examples. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/organ-donation-essay-topics/
"93 Organ Donation Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." IvyPanda , 2 Mar. 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/topic/organ-donation-essay-topics/.
IvyPanda . (2024) '93 Organ Donation Essay Topic Ideas & Examples'. 2 March.
IvyPanda . 2024. "93 Organ Donation Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." March 2, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/organ-donation-essay-topics/.
1. IvyPanda . "93 Organ Donation Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." March 2, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/organ-donation-essay-topics/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "93 Organ Donation Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." March 2, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/organ-donation-essay-topics/.
- Cardiovascular Diseases Titles
- Ethical Dilemma Titles
- Genetic Engineering Topics
- Healthcare Reform Essay Ideas
- Nursing Theory Questions
- Bureaucracy Paper Topics
- Fundraising Topics
- Stem Cell Essay Titles
Organ Donation Essay
500+ words essay on organ donation.
Organ donation is a noble cause, and by doing this, you can give life to many people. In the current scenario, organs like the small intestine, kidney, eyes, liver, heart, and skin tissues are in great demand.
Every year, thousands of people die due to accidents, and their organs give life to different people. Organs such as kidneys, lungs, livers, and intestines can be donated while we are alive. Most are transplanted within 6 to 72 hours. One donor can save at least eight people’s lives.
What is Organ Donation?
Organ donation is a procedure where healthy tissues and organs are extracted from human beings. Then these organs are transplanted to another needy person, legally, either by consent while the donor is alive or dead with the permission of the donor’s family. In this way, another person’s life can be saved with organ donation. World Organ Donation Day is observed every year on the 13th of August to create awareness about the importance of organ donation and encourage people to do the same.
Organ Donation in Various Countries
When we talk about organ donation in India, it follows an opt-in system. Our Indian Government framed a law to control organ commerce and encourage donation among people after brain death. As per the law, The Transplantation of Human Organs Act, 1994, any individual who wants to donate their organs needs to fill out a prescribed form on the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare of the Government of India’s website.
United States of America
In the United States, the need for organs is multiplying. The States has witnessed a rise in organ donors, but unfortunately, patients waiting for donors have increased rapidly. In the US, one can donate organs with the permission of a doctor or family member. However, various organisations are trying to follow the opt-out system for organ donation.
United Kingdom
In the United Kingdom, organ donation is voluntary. It means those who want to donate their organs voluntarily after death can register for the same.
Iran is the single country that has overcome the shortage of organ transplants. The country follows a proper legal payment system and has legalised organ trade.
In comparison to other countries, organ donation is relatively low in Japan because of cultural reasons, mistrust in western medicines and controversial organ transplants in 1968.
In August 2016, ‘Law 1805’ was passed in Columbia, and the opt-out policy for organ donation was introduced.
Under ‘Law 20,413’, Chile introduced the opt-out policy for organ donation. The Law stated that any individual above 18 years could donate organs unless and until they deny it before death.
Benefits of Organ Donation
Firstly, donating organs is helpful for the grieving process because many people feel relieved and satisfied by donating organs. They think so because they have helped save other people’s lives by donating organs. It also helps in uplifting the quality of life of various people. For example, an eye transplant will help a blind person see the world. Similarly, by organ donation, we can remove the pain and hardship of others. It also reduces the dependency on costly medical treatment.
Organ donation is beneficial in the process of medical science research. With the help of donated organs, researchers can work towards new developments in their respective fields. Not only researchers but medical students are also benefited, especially in fields like biotechnology.
Conclusion of Essay on Organ Donation
We can conclude the essay by saying that organ donation is a good cause. It also ensures the continued contribution of an individual towards society’s well-being even after death. We all should pledge to donate our organs to give life to different needy people. We should promote the importance of organ donation among people through various campaigns. By doing so, we can save the lives of many human beings.
From our BYJU’S website, students can learn CBSE Essays related to different topics. It will help students to get good marks in their upcoming exams.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

Counselling
Request Screening Information >

News & Events
Making an impact on the world: celebrating the 2024 mrh essay contest winners.

The Vaccine Education Center at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia (VEC), in collaboration with our partners, the Public Health Association of British Columbia, Kids Boost Immunity, Immunize Canada and the National Association of Biology Teachers (NABT), are pleased to announce the winners of the 2024 Maurice R. Hilleman Essay Contest. Eight winners were celebrated during a virtual event hosted by Dr. Paul Offit, VEC Director and Dr. Hilleman biographer. The students composed their essays in response to the writing prompt, “Dr. Hilleman made his impact on the world through the development of vaccines. What scientific issue would you take on if given the chance and why?” Entries were diverse in the topics they described, including essays about medical research for conditions including Alzheimer’s and dementia, cancers, diabetes, rare genetic disorders, addiction, and mental health. Some students wrote about engineering solutions for fusion energy, improved medical equipment, vehicle engines, Artificial Intelligence, and nanotechnology. Others focused on the intersection of science and society, considering topics such as climate change, women’s health equity, health insurance, the ethics of human experimentation and organ donation, and misinformation and distrust in science, among others.
The winners from Canada are:
Middle School Pramathas Paul (1st Place) Kai Salgado (2nd Place)
High School Jade Amberg (1st Place) Hayden Wu (2nd Place)
The winners from the Unites States are:
Middle School Jacob Rogers (1st Place) Esther Schonberger (2nd Place)
High School Mara McClellan (1st Place) Lexi Gordon (2nd Place)
In their consideration of the impact they would make on the world, the student winners addressed a variety of issues:
- Jade Amberg wrote her original essay in French and spoke about her desire to “join the fight against dementia.” She shared a personal tragedy of losing a loved one to the affliction and noted its growing threat, observing: “It's only a matter of time before we have neither the infrastructure, resources or personnel needed to accommodate this colossal wave of people living with dementia.” But she also urged hope because “the positive side of dementia is that it is partly preventable,” saying, “Let's act right now, for the next generation.”
- Lexie Gordon wrote that she would “take on the scientific issue of creating reliable BCI [Brain Computer Interface] technology that is accessible to all who need it.” She highlighted existing research, noting that, “These successes demonstrate the potential this technology possesses to change the lives of those with neurological disorders and provides faces for why this research is so important.” She also reflected on the current situation, stating that although there are cost and access concerns, “this scientific issue is the perfect avenue to create a better world and advance understanding of the brain.”
- Mara McClellan asked, “How can we develop cancer treatments that harm the cancer, not the person?” By sharing a personal story about a family member’s cancer, Mara illustrated the challenges of cancer treatment today, writing “Each option was an effective weapon in the battle against her cancer, but each treatment would inflict collateral damage on her entire body.” In her essay, Mara explored ways in which reality can match her “dream of a future where such treatments exist, do not cause major side effects, and are affordable and accessible for all cancer patients.”
- Pramathas Paul examined mechanisms and potential treatments of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) “because the disease does not have a therapeutic cure.” Although the disease can be severe, he noted that prevention is possible and considered the benefits of “researching the disease’s weakness and using that to create a cure.” Pramathas cited a quote from Alice Morse Earle to end on a positive note, pointing out that, “To have a fulfilling life, it takes determination, but we also need to look at the positive side. ‘Every day may not be good, but there is something good in every day. Focus on the good, no matter how diminutive it is.’”
- Jacob Rogers spoke of his desire to "study how neuroplasticity can help children with ADD or Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) overcome their symptoms without taking medication.” He discussed how human brains heal through the lens of his family and noted that “Medications come with side effects.” With this understanding, Jacob wrote of his hope that research in neuroplasticity “could lead to a low cost and accessible treatment option for children with attention disorders worldwide.”
- Kai Salgado wondered, “What if the problem doesn’t look like a problem at all?” He imagined taking on the challenge of regulating technology “in a more balanced way,” expressing that it “has many benefits that, if used properly, could be very beneficial for learning, connecting, and innovating.” In considering the risks of technology use, Kai wrote that he, hopes for “more honesty about the dangers so that parents can make healthier choices for their children.”
- Esther Schonberger would "work on solving the problem of clean drinking water for all.” She compared the relative ease of finding safe water near her home to the difficulties of others around the world, reflecting that, “Knowing that people struggle with this when I live so close to what appears to be all of the water in the world is powerful.” She looked to Dr. Hilleman as a role model in this crisis, saying “When Dr. Hilleman observed a catastrophe spiraling downhill around him, that of children dying from illnesses, he did something about it.”
- Hayden Wu aspired to “to contribute to the treatment of neurological diseases and propel the progress of artificial intelligence through discovering the brain.” He pointed out that, “Despite rapid medical advancements in the past decade, the human brain remains an intricate puzzle waiting to be solved,” and considered how such knowledge could be applied to “push the limits of scientific knowledge and improve health outcomes.”
The celebratory event, held virtually on May 3, 2024, marked the sixth year of the contest and included a keynote address from Dr. Andrew Steenhoff, Medical Director at the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia’s Global Health Center. Dr. Kirstin J. Milks, President-Elect of the National Association of Biology Teachers (NABT), Craig Thompson from the Public Health Association of British Columbia, and Lorraine Hilleman, Dr. Hilleman’s wife, also offered remarks. Along with presenting their winning essays during the event, the students attended an informal virtual gathering with the event speakers prior to the celebration.
Teachers named in each student’s winning entry received a signed copy of a book written by Paul A. Offit, MD, and a 1-year, complimentary membership to the National Association of Biology Teachers, graciously provided by NABT.
Read the 2024 winning essays here.
Learn more about Dr. Hilleman’s life and work.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Organ donation provides a life-giving, life-enhancing opportunity to those who are at the end of the line for hope. And the need for organ donors is growing. When Donna Lee died in 1992, there were 27,000 people on the transplant wait list. When Vikki died just four years later, that number had grown to 47,000 (Unpublished data, OPTN, January ...
organ donation, the act of giving one or more organs (or parts thereof), without compensation, for transplantation into someone else. Organ donation is a very personal yet complex decision, intertwined with medical, legal, religious, cultural, and ethical issues. Today organ donation, strictly defined, encompasses the donation and transplantation of the heart, intestines, kidneys, liver, lungs ...
To those that have in one way or the other received or given their body organs, they portray a good heroic example of human acts since, for example, one organ from one person can save up to 50 people (MedlinePlus, 2009). This can lead to saving many lives that would otherwise have been lost. In Michigan, a positive attitude towards organ ...
Organ donation essay topics are on verge of medicine and ethics and may take the form of a range of discursive questions: 1. What is the best way to decrease the shortage of organs for transplantation? 2. Should the legislature concerning organ transplantation be changed? 3.
Organ donation is defined as giving an organ or part of an organ to be transplanted into another person. Organ transplantation is the only option to save lives in patients affected by terminal organ failures and improve their quality of life. However, there is a disparity exists between the supply and demand of donated organs, leads to a loss of many lives. The number of organ transplantation ...
However, despite its critical importance, there persists a significant gap in awareness and understanding surrounding organ donation. This essay embarks on a journey to shed light on the multifaceted dimensions of organ donation, encompassing its types, benefits, and the misconceptions that often shroud this life-saving practice. ...
Although kidney donation is not practiced in the United States, it has been found to be effective in other nations. For example, Iran pays its residents up to $1,200 for kidney donations, but the recipients must be Iranian nationals and get long-term medical attention (Monday & Ogugua, 2020). There should be discussions regarding possible ...
To the Editor: Re "She Feared the Organ Donation System Would Kill Her.It Did," by Kendall Ciesemier (Opinion guest essay, Feb. 1):. I read this essay with great sadness. When we testified ...
The Ethics of Organ Donation: First, Do No Harm? 2 Part I. Context Cape Town, South Africa On December 3rd, 1967 Dr. Christiaan Barnard performed the world's first successful heart transplant. The New York Times heralded it as "one of the peaks of modern scientific achievement" (Editorial Board 1967).
500+ Words Essay on Organ Donation. Essay on Organ Donation - Organ donation is a process in which a person willingly donates an organ of his body to another person. Furthermore, it is the process of allowing the removal of one's organ for its transplanting in another person. Moreover, organ donation can legally take place by the consent of ...
Organ donation is the act of physically removing an organ or a tissue from donor and placing it into the recipient. The organs that can be transplanted are many including heart, intestine, kidney, liver, skin and bone marrow amongst others. Made-to-order essay as fast as... Organ Donation Organ Transplant.
And they will resist consenting to organ donation. Organ retrieval can take place at odd hours because the time between retrieval and transplantation must be minimised. A donor heart or lungs can last only four to six hours outside the body. A kidney, liver or pancreas can last a bit longer.
Organ Donation in Contemporary UK. PAGES 8 WORDS 2693. 2009). The susceptibility is highest is the first month of the transplantation and decreases afterwards. it, however, remains high even after 12 following. Susceptibility is highest among kidney recipients who are more likely to develop the infection 12 months after the transplantation.
Conclusion. Organ transplantation is among the latest development in the field of medicine. Doctors have been able to save people's lives in the recent past whereby people donate body organs to institutions. However, a lot of activities have emerged involving organ donations leading to situations where people sell their organs.
To help facilitate discussions and promote awareness about organ donation, here are 117 organ donation essay topic ideas and examples that can serve as inspiration for students, writers, and advocates: The importance of organ donation in saving lives. The process of organ donation and transplantation. Myths and misconceptions about organ donation.
In conclusion, organ donation is a beacon of hope for individuals in dire need of life-saving transplants. However, the ethical issues surrounding organ donation are complex and multifaceted. Balancing the principles of autonomy, justice, and beneficence while safeguarding the well-being of donors and recipients remains a formidable task.
12 essay samples found. Organ Donation is the process of surgically removing an organ or tissue from one person (the organ donor) and placing it into another person (the recipient). Essays could explore the ethical, social, and medical aspects of organ donation, including the processes of organ transplantation, the importance of donor ...
Organ and Blood Donation. However, ethical and legal issues, and unwillingness of many potential donors to provide consents have slowed down the rate of organ and blood donation in the county. We will write. a custom essay specifically for you by our professional experts. 809 writers online.
500+ Words Essay on Organ Donation. Organ donation is a noble cause, and by doing this, you can give life to many people. In the current scenario, organs like the small intestine, kidney, eyes, liver, heart, and skin tissues are in great demand. Every year, thousands of people die due to accidents, and their organs give life to different people ...
Organ donation is the medical process of voluntarily giving one or more of your organs to someone in need, whether it be someone you know or a stranger. It is strictly voluntary, no payment for the organ/s will be given from the hospital, the recipient or the recipients family. In organ donation, there are two types of donations, living organ ...
Cause and Effect Argument Essay. Joseph Hicks Department of English, Grand Canyon University ENG- Dr. Amy Green July 2021. Organ donation in itself can be a very beautiful and fulfilling process.
Organ Donation. Ruben D. Gomez Grand Canyon University PHI-105; 21st Century Skills: Critical Thinking and Problem Solving Christal Abron 18 September 2022. Organ Donation Organ donations are critical to keeping family and friends alive. The need for organ donation is rising, and the demand has significantly increased over the years.
The winners from the Unites States are: Middle School. Jacob Rogers (1st Place) Esther Schonberger (2nd Place) High School. Mara McClellan (1st Place) Lexi Gordon (2nd Place) In their consideration of the impact they would make on the world, the student winners addressed a variety of issues: Jade Amberg wrote her original essay in French and ...