
Along with Stanford news and stories, show me:
- Student information
- Faculty/Staff information
We want to provide announcements, events, leadership messages and resources that are relevant to you. Your selection is stored in a browser cookie which you can remove at any time using “Clear all personalization” below.

Education scholar Denise Pope has found that too much homework has negative effects on student well-being and behavioral engagement. (Image credit: L.A. Cicero)
A Stanford researcher found that too much homework can negatively affect kids, especially their lives away from school, where family, friends and activities matter.
“Our findings on the effects of homework challenge the traditional assumption that homework is inherently good,” wrote Denise Pope , a senior lecturer at the Stanford Graduate School of Education and a co-author of a study published in the Journal of Experimental Education .
The researchers used survey data to examine perceptions about homework, student well-being and behavioral engagement in a sample of 4,317 students from 10 high-performing high schools in upper-middle-class California communities. Along with the survey data, Pope and her colleagues used open-ended answers to explore the students’ views on homework.
Median household income exceeded $90,000 in these communities, and 93 percent of the students went on to college, either two-year or four-year.
Students in these schools average about 3.1 hours of homework each night.
“The findings address how current homework practices in privileged, high-performing schools sustain students’ advantage in competitive climates yet hinder learning, full engagement and well-being,” Pope wrote.
Pope and her colleagues found that too much homework can diminish its effectiveness and even be counterproductive. They cite prior research indicating that homework benefits plateau at about two hours per night, and that 90 minutes to two and a half hours is optimal for high school.
Their study found that too much homework is associated with:
* Greater stress: 56 percent of the students considered homework a primary source of stress, according to the survey data. Forty-three percent viewed tests as a primary stressor, while 33 percent put the pressure to get good grades in that category. Less than 1 percent of the students said homework was not a stressor.
* Reductions in health: In their open-ended answers, many students said their homework load led to sleep deprivation and other health problems. The researchers asked students whether they experienced health issues such as headaches, exhaustion, sleep deprivation, weight loss and stomach problems.
* Less time for friends, family and extracurricular pursuits: Both the survey data and student responses indicate that spending too much time on homework meant that students were “not meeting their developmental needs or cultivating other critical life skills,” according to the researchers. Students were more likely to drop activities, not see friends or family, and not pursue hobbies they enjoy.
A balancing act
The results offer empirical evidence that many students struggle to find balance between homework, extracurricular activities and social time, the researchers said. Many students felt forced or obligated to choose homework over developing other talents or skills.
Also, there was no relationship between the time spent on homework and how much the student enjoyed it. The research quoted students as saying they often do homework they see as “pointless” or “mindless” in order to keep their grades up.
“This kind of busy work, by its very nature, discourages learning and instead promotes doing homework simply to get points,” Pope said.
She said the research calls into question the value of assigning large amounts of homework in high-performing schools. Homework should not be simply assigned as a routine practice, she said.
“Rather, any homework assigned should have a purpose and benefit, and it should be designed to cultivate learning and development,” wrote Pope.
High-performing paradox
In places where students attend high-performing schools, too much homework can reduce their time to foster skills in the area of personal responsibility, the researchers concluded. “Young people are spending more time alone,” they wrote, “which means less time for family and fewer opportunities to engage in their communities.”
Student perspectives
The researchers say that while their open-ended or “self-reporting” methodology to gauge student concerns about homework may have limitations – some might regard it as an opportunity for “typical adolescent complaining” – it was important to learn firsthand what the students believe.
The paper was co-authored by Mollie Galloway from Lewis and Clark College and Jerusha Conner from Villanova University.
Media Contacts
Denise Pope, Stanford Graduate School of Education: (650) 725-7412, [email protected] Clifton B. Parker, Stanford News Service: (650) 725-0224, [email protected]

Home » Tips for Teachers » 7 Research-Based Reasons Why Students Should Not Have Homework: Academic Insights, Opposing Perspectives & Alternatives
7 Research-Based Reasons Why Students Should Not Have Homework: Academic Insights, Opposing Perspectives & Alternatives
In recent years, the question of why students should not have homework has become a topic of intense debate among educators, parents, and students themselves. This discussion stems from a growing body of research that challenges the traditional view of homework as an essential component of academic success. The notion that homework is an integral part of learning is being reevaluated in light of new findings about its effectiveness and impact on students’ overall well-being.

The push against homework is not just about the hours spent on completing assignments; it’s about rethinking the role of education in fostering the well-rounded development of young individuals. Critics argue that homework, particularly in excessive amounts, can lead to negative outcomes such as stress, burnout, and a diminished love for learning. Moreover, it often disproportionately affects students from disadvantaged backgrounds, exacerbating educational inequities. The debate also highlights the importance of allowing children to have enough free time for play, exploration, and family interaction, which are crucial for their social and emotional development.
Checking 13yo’s math homework & I have just one question. I can catch mistakes & help her correct. But what do kids do when their parent isn’t an Algebra teacher? Answer: They get frustrated. Quit. Get a bad grade. Think they aren’t good at math. How is homework fair??? — Jay Wamsted (@JayWamsted) March 24, 2022
As we delve into this discussion, we explore various facets of why reducing or even eliminating homework could be beneficial. We consider the research, weigh the pros and cons, and examine alternative approaches to traditional homework that can enhance learning without overburdening students.
Once you’ve finished this article, you’ll know:
- Insights from Teachers and Education Industry Experts →
- 7 Reasons Why Students Should Not Have Homework →
- Opposing Views on Homework Practices →
- Exploring Alternatives to Homework →
Insights from Teachers and Education Industry Experts: Diverse Perspectives on Homework
In the ongoing conversation about the role and impact of homework in education, the perspectives of those directly involved in the teaching process are invaluable. Teachers and education industry experts bring a wealth of experience and insights from the front lines of learning. Their viewpoints, shaped by years of interaction with students and a deep understanding of educational methodologies, offer a critical lens through which we can evaluate the effectiveness and necessity of homework in our current educational paradigm.
Check out this video featuring Courtney White, a high school language arts teacher who gained widespread attention for her explanation of why she chooses not to assign homework.
Here are the insights and opinions from various experts in the educational field on this topic:
“I teach 1st grade. I had parents ask for homework. I explained that I don’t give homework. Home time is family time. Time to play, cook, explore and spend time together. I do send books home, but there is no requirement or checklist for reading them. Read them, enjoy them, and return them when your child is ready for more. I explained that as a parent myself, I know they are busy—and what a waste of energy it is to sit and force their kids to do work at home—when they could use that time to form relationships and build a loving home. Something kids need more than a few math problems a week.” — Colleen S. , 1st grade teacher
“The lasting educational value of homework at that age is not proven. A kid says the times tables [at school] because he studied the times tables last night. But over a long period of time, a kid who is drilled on the times tables at school, rather than as homework, will also memorize their times tables. We are worried about young children and their social emotional learning. And that has to do with physical activity, it has to do with playing with peers, it has to do with family time. All of those are very important and can be removed by too much homework.” — David Bloomfield , education professor at Brooklyn College and the City University of New York graduate center
“Homework in primary school has an effect of around zero. In high school it’s larger. (…) Which is why we need to get it right. Not why we need to get rid of it. It’s one of those lower hanging fruit that we should be looking in our primary schools to say, ‘Is it really making a difference?’” — John Hattie , professor
”Many kids are working as many hours as their overscheduled parents and it is taking a toll – psychologically and in many other ways too. We see kids getting up hours before school starts just to get their homework done from the night before… While homework may give kids one more responsibility, it ignores the fact that kids do not need to grow up and become adults at ages 10 or 12. With schools cutting recess time or eliminating playgrounds, kids absorb every single stress there is, only on an even higher level. Their brains and bodies need time to be curious, have fun, be creative and just be a kid.” — Pat Wayman, teacher and CEO of HowtoLearn.com
7 Reasons Why Students Should Not Have Homework
Let’s delve into the reasons against assigning homework to students. Examining these arguments offers important perspectives on the wider educational and developmental consequences of homework practices.
1. Elevated Stress and Health Consequences

The ongoing debate about homework often focuses on its educational value, but a vital aspect that cannot be overlooked is the significant stress and health consequences it brings to students. In the context of American life, where approximately 70% of people report moderate or extreme stress due to various factors like mass shootings, healthcare affordability, discrimination, racism, sexual harassment, climate change, presidential elections, and the need to stay informed, the additional burden of homework further exacerbates this stress, particularly among students.
Key findings and statistics reveal a worrying trend:
- Overwhelming Student Stress: A staggering 72% of students report being often or always stressed over schoolwork, with a concerning 82% experiencing physical symptoms due to this stress.
- Serious Health Issues: Symptoms linked to homework stress include sleep deprivation, headaches, exhaustion, weight loss, and stomach problems.
- Sleep Deprivation: Despite the National Sleep Foundation recommending 8.5 to 9.25 hours of sleep for healthy adolescent development, students average just 6.80 hours of sleep on school nights. About 68% of students stated that schoolwork often or always prevented them from getting enough sleep, which is critical for their physical and mental health.
- Turning to Unhealthy Coping Mechanisms: Alarmingly, the pressure from excessive homework has led some students to turn to alcohol and drugs as a way to cope with stress.
This data paints a concerning picture. Students, already navigating a world filled with various stressors, find themselves further burdened by homework demands. The direct correlation between excessive homework and health issues indicates a need for reevaluation. The goal should be to ensure that homework if assigned, adds value to students’ learning experiences without compromising their health and well-being.
By addressing the issue of homework-related stress and health consequences, we can take a significant step toward creating a more nurturing and effective educational environment. This environment would not only prioritize academic achievement but also the overall well-being and happiness of students, preparing them for a balanced and healthy life both inside and outside the classroom.
2. Inequitable Impact and Socioeconomic Disparities
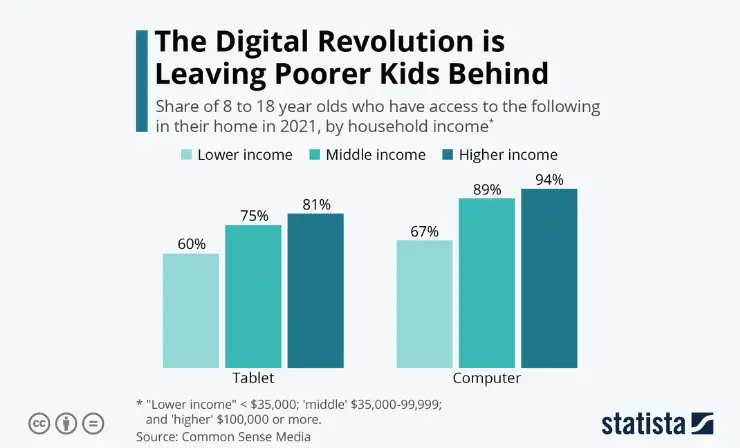
In the discourse surrounding educational equity, homework emerges as a factor exacerbating socioeconomic disparities, particularly affecting students from lower-income families and those with less supportive home environments. While homework is often justified as a means to raise academic standards and promote equity, its real-world impact tells a different story.
The inequitable burden of homework becomes starkly evident when considering the resources required to complete it, especially in the digital age. Homework today often necessitates a computer and internet access – resources not readily available to all students. This digital divide significantly disadvantages students from lower-income backgrounds, deepening the chasm between them and their more affluent peers.
Key points highlighting the disparities:
- Digital Inequity: Many students lack access to necessary technology for homework, with low-income families disproportionately affected.
- Impact of COVID-19: The pandemic exacerbated these disparities as education shifted online, revealing the extent of the digital divide.
- Educational Outcomes Tied to Income: A critical indicator of college success is linked more to family income levels than to rigorous academic preparation. Research indicates that while 77% of students from high-income families graduate from highly competitive colleges, only 9% from low-income families achieve the same . This disparity suggests that the pressure of heavy homework loads, rather than leveling the playing field, may actually hinder the chances of success for less affluent students.
Moreover, the approach to homework varies significantly across different types of schools. While some rigorous private and preparatory schools in both marginalized and affluent communities assign extreme levels of homework, many progressive schools focusing on holistic learning and self-actualization opt for no homework, yet achieve similar levels of college and career success. This contrast raises questions about the efficacy and necessity of heavy homework loads in achieving educational outcomes.
The issue of homework and its inequitable impact is not just an academic concern; it is a reflection of broader societal inequalities. By continuing practices that disproportionately burden students from less privileged backgrounds, the educational system inadvertently perpetuates the very disparities it seeks to overcome.
3. Negative Impact on Family Dynamics

Homework, a staple of the educational system, is often perceived as a necessary tool for academic reinforcement. However, its impact extends beyond the realm of academics, significantly affecting family dynamics. The negative repercussions of homework on the home environment have become increasingly evident, revealing a troubling pattern that can lead to conflict, mental health issues, and domestic friction.
A study conducted in 2015 involving 1,100 parents sheds light on the strain homework places on family relationships. The findings are telling:
- Increased Likelihood of Conflicts: Families where parents did not have a college degree were 200% more likely to experience fights over homework.
- Misinterpretations and Misunderstandings: Parents often misinterpret their children’s difficulties with homework as a lack of attention in school, leading to feelings of frustration and mistrust on both sides.
- Discriminatory Impact: The research concluded that the current approach to homework disproportionately affects children whose parents have lower educational backgrounds, speak English as a second language, or belong to lower-income groups.
The issue is not confined to specific demographics but is a widespread concern. Samantha Hulsman, a teacher featured in Education Week Teacher , shared her personal experience with the toll that homework can take on family time. She observed that a seemingly simple 30-minute assignment could escalate into a three-hour ordeal, causing stress and strife between parents and children. Hulsman’s insights challenge the traditional mindset about homework, highlighting a shift towards the need for skills such as collaboration and problem-solving over rote memorization of facts.
The need of the hour is to reassess the role and amount of homework assigned to students. It’s imperative to find a balance that facilitates learning and growth without compromising the well-being of the family unit. Such a reassessment would not only aid in reducing domestic conflicts but also contribute to a more supportive and nurturing environment for children’s overall development.
4. Consumption of Free Time

In recent years, a growing chorus of voices has raised concerns about the excessive burden of homework on students, emphasizing how it consumes their free time and impedes their overall well-being. The issue is not just the quantity of homework, but its encroachment on time that could be used for personal growth, relaxation, and family bonding.
Authors Sara Bennett and Nancy Kalish , in their book “The Case Against Homework,” offer an insightful window into the lives of families grappling with the demands of excessive homework. They share stories from numerous interviews conducted in the mid-2000s, highlighting the universal struggle faced by families across different demographics. A poignant account from a parent in Menlo Park, California, describes nightly sessions extending until 11 p.m., filled with stress and frustration, leading to a soured attitude towards school in both the child and the parent. This narrative is not isolated, as about one-third of the families interviewed expressed feeling crushed by the overwhelming workload.
Key points of concern:
- Excessive Time Commitment: Students, on average, spend over 6 hours in school each day, and homework adds significantly to this time, leaving little room for other activities.
- Impact on Extracurricular Activities: Homework infringes upon time for sports, music, art, and other enriching experiences, which are as crucial as academic courses.
- Stifling Creativity and Self-Discovery: The constant pressure of homework limits opportunities for students to explore their interests and learn new skills independently.
The National Education Association (NEA) and the National PTA (NPTA) recommend a “10 minutes of homework per grade level” standard, suggesting a more balanced approach. However, the reality often far exceeds this guideline, particularly for older students. The impact of this overreach is profound, affecting not just academic performance but also students’ attitudes toward school, their self-confidence, social skills, and overall quality of life.
Furthermore, the intense homework routine’s effectiveness is doubtful, as it can overwhelm students and detract from the joy of learning. Effective learning builds on prior knowledge in an engaging way, but excessive homework in a home setting may be irrelevant and uninteresting. The key challenge is balancing homework to enhance learning without overburdening students, allowing time for holistic growth and activities beyond academics. It’s crucial to reassess homework policies to support well-rounded development.
5. Challenges for Students with Learning Disabilities
Homework, a standard educational tool, poses unique challenges for students with learning disabilities, often leading to a frustrating and disheartening experience. These challenges go beyond the typical struggles faced by most students and can significantly impede their educational progress and emotional well-being.
Child psychologist Kenneth Barish’s insights in Psychology Today shed light on the complex relationship between homework and students with learning disabilities:
- Homework as a Painful Endeavor: For students with learning disabilities, completing homework can be likened to “running with a sprained ankle.” It’s a task that, while doable, is fraught with difficulty and discomfort.
- Misconceptions about Laziness: Often, children who struggle with homework are perceived as lazy. However, Barish emphasizes that these students are more likely to be frustrated, discouraged, or anxious rather than unmotivated.
- Limited Improvement in School Performance: The battles over homework rarely translate into significant improvement in school for these children, challenging the conventional notion of homework as universally beneficial.
These points highlight the need for a tailored approach to homework for students with learning disabilities. It’s crucial to recognize that the traditional homework model may not be the most effective or appropriate method for facilitating their learning. Instead, alternative strategies that accommodate their unique needs and learning styles should be considered.
In conclusion, the conventional homework paradigm needs reevaluation, particularly concerning students with learning disabilities. By understanding and addressing their unique challenges, educators can create a more inclusive and supportive educational environment. This approach not only aids in their academic growth but also nurtures their confidence and overall development, ensuring that they receive an equitable and empathetic educational experience.
6. Critique of Underlying Assumptions about Learning
The longstanding belief in the educational sphere that more homework automatically translates to more learning is increasingly being challenged. Critics argue that this assumption is not only flawed but also unsupported by solid evidence, questioning the efficacy of homework as an effective learning tool.
Alfie Kohn , a prominent critic of homework, aptly compares students to vending machines in this context, suggesting that the expectation of inserting an assignment and automatically getting out of learning is misguided. Kohn goes further, labeling homework as the “greatest single extinguisher of children’s curiosity.” This critique highlights a fundamental issue: the potential of homework to stifle the natural inquisitiveness and love for learning in children.
The lack of concrete evidence supporting the effectiveness of homework is evident in various studies:
- Marginal Effectiveness of Homework: A study involving 28,051 high school seniors found that the effectiveness of homework was marginal, and in some cases, it was counterproductive, leading to more academic problems than solutions.
- No Correlation with Academic Achievement: Research in “ National Differences, Global Similarities ” showed no correlation between homework and academic achievement in elementary students, and any positive correlation in middle or high school diminished with increasing homework loads.
- Increased Academic Pressure: The Teachers College Record published findings that homework adds to academic pressure and societal stress, exacerbating performance gaps between students from different socioeconomic backgrounds.
These findings bring to light several critical points:
- Quality Over Quantity: According to a recent article in Monitor on Psychology , experts concur that the quality of homework assignments, along with the quality of instruction, student motivation, and inherent ability, is more crucial for academic success than the quantity of homework.
- Counterproductive Nature of Excessive Homework: Excessive homework can lead to more academic challenges, particularly for students already facing pressures from other aspects of their lives.
- Societal Stress and Performance Gaps: Homework can intensify societal stress and widen the academic performance divide.
The emerging consensus from these studies suggests that the traditional approach to homework needs rethinking. Rather than focusing on the quantity of assignments, educators should consider the quality and relevance of homework, ensuring it truly contributes to learning and development. This reassessment is crucial for fostering an educational environment that nurtures curiosity and a love for learning, rather than extinguishing it.
7. Issues with Homework Enforcement, Reliability, and Temptation to Cheat
In the academic realm, the enforcement of homework is a subject of ongoing debate, primarily due to its implications on student integrity and the true value of assignments. The challenges associated with homework enforcement often lead to unintended yet significant issues, such as cheating, copying, and a general undermining of educational values.
Key points highlighting enforcement challenges:
- Difficulty in Enforcing Completion: Ensuring that students complete their homework can be a complex task, and not completing homework does not always correlate with poor grades.
- Reliability of Homework Practice: The reliability of homework as a practice tool is undermined when students, either out of desperation or lack of understanding, choose shortcuts over genuine learning. This approach can lead to the opposite of the intended effect, especially when assignments are not well-aligned with the students’ learning levels or interests.
- Temptation to Cheat: The issue of cheating is particularly troubling. According to a report by The Chronicle of Higher Education , under the pressure of at-home assignments, many students turn to copying others’ work, plagiarizing, or using creative technological “hacks.” This tendency not only questions the integrity of the learning process but also reflects the extreme stress that homework can induce.
- Parental Involvement in Completion: As noted in The American Journal of Family Therapy , this raises concerns about the authenticity of the work submitted. When parents complete assignments for their children, it not only deprives the students of the opportunity to learn but also distorts the purpose of homework as a learning aid.
In conclusion, the challenges of homework enforcement present a complex problem that requires careful consideration. The focus should shift towards creating meaningful, manageable, and quality-driven assignments that encourage genuine learning and integrity, rather than overwhelming students and prompting counterproductive behaviors.
Addressing Opposing Views on Homework Practices
While opinions on homework policies are diverse, understanding different viewpoints is crucial. In the following sections, we will examine common arguments supporting homework assignments, along with counterarguments that offer alternative perspectives on this educational practice.
1. Improvement of Academic Performance

Homework is commonly perceived as a means to enhance academic performance, with the belief that it directly contributes to better grades and test scores. This view posits that through homework, students reinforce what they learn in class, leading to improved understanding and retention, which ultimately translates into higher academic achievement.
However, the question of why students should not have homework becomes pertinent when considering the complex relationship between homework and academic performance. Studies have indicated that excessive homework doesn’t necessarily equate to higher grades or test scores. Instead, too much homework can backfire, leading to stress and fatigue that adversely affect a student’s performance. Reuters highlights an intriguing correlation suggesting that physical activity may be more conducive to academic success than additional homework, underscoring the importance of a holistic approach to education that prioritizes both physical and mental well-being for enhanced academic outcomes.
2. Reinforcement of Learning

Homework is traditionally viewed as a tool to reinforce classroom learning, enabling students to practice and retain material. However, research suggests its effectiveness is ambiguous. In instances where homework is well-aligned with students’ abilities and classroom teachings, it can indeed be beneficial. Particularly for younger students , excessive homework can cause burnout and a loss of interest in learning, counteracting its intended purpose.
Furthermore, when homework surpasses a student’s capability, it may induce frustration and confusion rather than aid in learning. This challenges the notion that more homework invariably leads to better understanding and retention of educational content.
3. Development of Time Management Skills

Homework is often considered a crucial tool in helping students develop important life skills such as time management and organization. The idea is that by regularly completing assignments, students learn to allocate their time efficiently and organize their tasks effectively, skills that are invaluable in both academic and personal life.
However, the impact of homework on developing these skills is not always positive. For younger students, especially, an overwhelming amount of homework can be more of a hindrance than a help. Instead of fostering time management and organizational skills, an excessive workload often leads to stress and anxiety . These negative effects can impede the learning process and make it difficult for students to manage their time and tasks effectively, contradicting the original purpose of homework.
4. Preparation for Future Academic Challenges

Homework is often touted as a preparatory tool for future academic challenges that students will encounter in higher education and their professional lives. The argument is that by tackling homework, students build a foundation of knowledge and skills necessary for success in more advanced studies and in the workforce, fostering a sense of readiness and confidence.
Contrarily, an excessive homework load, especially from a young age, can have the opposite effect . It can instill a negative attitude towards education, dampening students’ enthusiasm and willingness to embrace future academic challenges. Overburdening students with homework risks disengagement and loss of interest, thereby defeating the purpose of preparing them for future challenges. Striking a balance in the amount and complexity of homework is crucial to maintaining student engagement and fostering a positive attitude towards ongoing learning.
5. Parental Involvement in Education

Homework often acts as a vital link connecting parents to their child’s educational journey, offering insights into the school’s curriculum and their child’s learning process. This involvement is key in fostering a supportive home environment and encouraging a collaborative relationship between parents and the school. When parents understand and engage with what their children are learning, it can significantly enhance the educational experience for the child.
However, the line between involvement and over-involvement is thin. When parents excessively intervene by completing their child’s homework, it can have adverse effects . Such actions not only diminish the educational value of homework but also rob children of the opportunity to develop problem-solving skills and independence. This over-involvement, coupled with disparities in parental ability to assist due to variations in time, knowledge, or resources, may lead to unequal educational outcomes, underlining the importance of a balanced approach to parental participation in homework.
Exploring Alternatives to Homework and Finding a Middle Ground

In the ongoing debate about the role of homework in education, it’s essential to consider viable alternatives and strategies to minimize its burden. While completely eliminating homework may not be feasible for all educators, there are several effective methods to reduce its impact and offer more engaging, student-friendly approaches to learning.
Alternatives to Traditional Homework
- Project-Based Learning: This method focuses on hands-on, long-term projects where students explore real-world problems. It encourages creativity, critical thinking, and collaborative skills, offering a more engaging and practical learning experience than traditional homework. For creative ideas on school projects, especially related to the solar system, be sure to explore our dedicated article on solar system projects .
- Flipped Classrooms: Here, students are introduced to new content through videos or reading materials at home and then use class time for interactive activities. This approach allows for more personalized and active learning during school hours.
- Reading for Pleasure: Encouraging students to read books of their choice can foster a love for reading and improve literacy skills without the pressure of traditional homework assignments. This approach is exemplified by Marion County, Florida , where public schools implemented a no-homework policy for elementary students. Instead, they are encouraged to read nightly for 20 minutes . Superintendent Heidi Maier’s decision was influenced by research showing that while homework offers minimal benefit to young students, regular reading significantly boosts their learning. For book recommendations tailored to middle school students, take a look at our specially curated article .
Ideas for Minimizing Homework
- Limiting Homework Quantity: Adhering to guidelines like the “ 10-minute rule ” (10 minutes of homework per grade level per night) can help ensure that homework does not become overwhelming.
- Quality Over Quantity: Focus on assigning meaningful homework that is directly relevant to what is being taught in class, ensuring it adds value to students’ learning.
- Homework Menus: Offering students a choice of assignments can cater to diverse learning styles and interests, making homework more engaging and personalized.
- Integrating Technology: Utilizing educational apps and online platforms can make homework more interactive and enjoyable, while also providing immediate feedback to students. To gain deeper insights into the role of technology in learning environments, explore our articles discussing the benefits of incorporating technology in classrooms and a comprehensive list of educational VR apps . These resources will provide you with valuable information on how technology can enhance the educational experience.
For teachers who are not ready to fully eliminate homework, these strategies offer a compromise, ensuring that homework supports rather than hinders student learning. By focusing on quality, relevance, and student engagement, educators can transform homework from a chore into a meaningful component of education that genuinely contributes to students’ academic growth and personal development. In this way, we can move towards a more balanced and student-centric approach to learning, both in and out of the classroom.
Useful Resources
- Is homework a good idea or not? by BBC
- The Great Homework Debate: What’s Getting Lost in the Hype
- Alternative Homework Ideas
The evidence and arguments presented in the discussion of why students should not have homework call for a significant shift in homework practices. It’s time for educators and policymakers to rethink and reformulate homework strategies, focusing on enhancing the quality, relevance, and balance of assignments. By doing so, we can create a more equitable, effective, and student-friendly educational environment that fosters learning, well-being, and holistic development.
- “Here’s what an education expert says about that viral ‘no-homework’ policy”, Insider
- “John Hattie on BBC Radio 4: Homework in primary school has an effect of zero”, Visible Learning
- HowtoLearn.com
- “Time Spent On Homework Statistics [Fresh Research]”, Gitnux
- “Stress in America”, American Psychological Association (APA)
- “Homework hurts high-achieving students, study says”, The Washington Post
- “National Sleep Foundation’s updated sleep duration recommendations: final report”, National Library of Medicine
- “A multi-method exploratory study of stress, coping, and substance use among high school youth in private schools”, Frontiers
- “The Digital Revolution is Leaving Poorer Kids Behind”, Statista
- “The digital divide has left millions of school kids behind”, CNET
- “The Digital Divide: What It Is, and What’s Being Done to Close It”, Investopedia
- “COVID-19 exposed the digital divide. Here’s how we can close it”, World Economic Forum
- “PBS NewsHour: Biggest Predictor of College Success is Family Income”, America’s Promise Alliance
- “Homework and Family Stress: With Consideration of Parents’ Self Confidence, Educational Level, and Cultural Background”, Taylor & Francis Online
- “What Do You Mean My Kid Doesn’t Have Homework?”, EducationWeek
- “Excerpt From The Case Against Homework”, Penguin Random House Canada
- “How much homework is too much?”, neaToday
- “The Nation’s Report Card: A First Look: 2013 Mathematics and Reading”, National Center for Education Statistics
- “Battles Over Homework: Advice For Parents”, Psychology Today
- “How Homework Is Destroying Teens’ Health”, The Lion’s Roar
- “ Breaking the Homework Habit”, Education World
- “Testing a model of school learning: Direct and indirect effects on academic achievement”, ScienceDirect
- “National Differences, Global Similarities: World Culture and the Future of Schooling”, Stanford University Press
- “When school goes home: Some problems in the organization of homework”, APA PsycNet
- “Is homework a necessary evil?”, APA PsycNet
- “Epidemic of copying homework catalyzed by technology”, Redwood Bark
- “High-Tech Cheating Abounds, and Professors Bear Some Blame”, The Chronicle of Higher Education
- “Homework and Family Stress: With Consideration of Parents’ Self Confidence, Educational Level, and Cultural Background”, ResearchGate
- “Kids who get moving may also get better grades”, Reuters
- “Does Homework Improve Academic Achievement? A Synthesis of Research, 1987–2003”, SageJournals
- “Is it time to get rid of homework?”, USAToday
- “Stanford research shows pitfalls of homework”, Stanford
- “Florida school district bans homework, replaces it with daily reading”, USAToday
- “Encouraging Students to Read: Tips for High School Teachers”, wgu.edu
- Recent Posts

Simona Johnes is the visionary being the creation of our project. Johnes spent much of her career in the classroom working with students. And, after many years in the classroom, Johnes became a principal.
- 28 Exciting Yarn Crafts for Preschool Kids: Igniting Creativity and Fine Motor Skills - April 29, 2024
- 16 Engaging and Educational Cause and Effect Activities for Preschoolers to Boost Cognitive Development - April 24, 2024
- 25 Innovative and Engaging Parts of Speech Activities for Middle School: Fun Grammar Games to Enhance Learning - April 14, 2024
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

- About the Hub
- Announcements
- Faculty Experts Guide
- Subscribe to the newsletter
Explore by Topic
- Arts+Culture
- Politics+Society
- Science+Technology
- Student Life
- University News
- Voices+Opinion
- About Hub at Work
- Gazette Archive
- Benefits+Perks
- Health+Well-Being
- Current Issue
- About the Magazine
- Past Issues
- Support Johns Hopkins Magazine
- Subscribe to the Magazine
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser to improve your experience.

Credit: August de Richelieu
Does homework still have value? A Johns Hopkins education expert weighs in
Joyce epstein, co-director of the center on school, family, and community partnerships, discusses why homework is essential, how to maximize its benefit to learners, and what the 'no-homework' approach gets wrong.
By Vicky Hallett
The necessity of homework has been a subject of debate since at least as far back as the 1890s, according to Joyce L. Epstein , co-director of the Center on School, Family, and Community Partnerships at Johns Hopkins University. "It's always been the case that parents, kids—and sometimes teachers, too—wonder if this is just busy work," Epstein says.
But after decades of researching how to improve schools, the professor in the Johns Hopkins School of Education remains certain that homework is essential—as long as the teachers have done their homework, too. The National Network of Partnership Schools , which she founded in 1995 to advise schools and districts on ways to improve comprehensive programs of family engagement, has developed hundreds of improved homework ideas through its Teachers Involve Parents in Schoolwork program. For an English class, a student might interview a parent on popular hairstyles from their youth and write about the differences between then and now. Or for science class, a family could identify forms of matter over the dinner table, labeling foods as liquids or solids. These innovative and interactive assignments not only reinforce concepts from the classroom but also foster creativity, spark discussions, and boost student motivation.
"We're not trying to eliminate homework procedures, but expand and enrich them," says Epstein, who is packing this research into a forthcoming book on the purposes and designs of homework. In the meantime, the Hub couldn't wait to ask her some questions:
What kind of homework training do teachers typically get?
Future teachers and administrators really have little formal training on how to design homework before they assign it. This means that most just repeat what their teachers did, or they follow textbook suggestions at the end of units. For example, future teachers are well prepared to teach reading and literacy skills at each grade level, and they continue to learn to improve their teaching of reading in ongoing in-service education. By contrast, most receive little or no training on the purposes and designs of homework in reading or other subjects. It is really important for future teachers to receive systematic training to understand that they have the power, opportunity, and obligation to design homework with a purpose.
Why do students need more interactive homework?
If homework assignments are always the same—10 math problems, six sentences with spelling words—homework can get boring and some kids just stop doing their assignments, especially in the middle and high school years. When we've asked teachers what's the best homework you've ever had or designed, invariably we hear examples of talking with a parent or grandparent or peer to share ideas. To be clear, parents should never be asked to "teach" seventh grade science or any other subject. Rather, teachers set up the homework assignments so that the student is in charge. It's always the student's homework. But a good activity can engage parents in a fun, collaborative way. Our data show that with "good" assignments, more kids finish their work, more kids interact with a family partner, and more parents say, "I learned what's happening in the curriculum." It all works around what the youngsters are learning.
Is family engagement really that important?
At Hopkins, I am part of the Center for Social Organization of Schools , a research center that studies how to improve many aspects of education to help all students do their best in school. One thing my colleagues and I realized was that we needed to look deeply into family and community engagement. There were so few references to this topic when we started that we had to build the field of study. When children go to school, their families "attend" with them whether a teacher can "see" the parents or not. So, family engagement is ever-present in the life of a school.
My daughter's elementary school doesn't assign homework until third grade. What's your take on "no homework" policies?
There are some parents, writers, and commentators who have argued against homework, especially for very young children. They suggest that children should have time to play after school. This, of course is true, but many kindergarten kids are excited to have homework like their older siblings. If they give homework, most teachers of young children make assignments very short—often following an informal rule of 10 minutes per grade level. "No homework" does not guarantee that all students will spend their free time in productive and imaginative play.
Some researchers and critics have consistently misinterpreted research findings. They have argued that homework should be assigned only at the high school level where data point to a strong connection of doing assignments with higher student achievement . However, as we discussed, some students stop doing homework. This leads, statistically, to results showing that doing homework or spending more minutes on homework is linked to higher student achievement. If slow or struggling students are not doing their assignments, they contribute to—or cause—this "result."
Teachers need to design homework that even struggling students want to do because it is interesting. Just about all students at any age level react positively to good assignments and will tell you so.
Did COVID change how schools and parents view homework?
Within 24 hours of the day school doors closed in March 2020, just about every school and district in the country figured out that teachers had to talk to and work with students' parents. This was not the same as homeschooling—teachers were still working hard to provide daily lessons. But if a child was learning at home in the living room, parents were more aware of what they were doing in school. One of the silver linings of COVID was that teachers reported that they gained a better understanding of their students' families. We collected wonderfully creative examples of activities from members of the National Network of Partnership Schools. I'm thinking of one art activity where every child talked with a parent about something that made their family unique. Then they drew their finding on a snowflake and returned it to share in class. In math, students talked with a parent about something the family liked so much that they could represent it 100 times. Conversations about schoolwork at home was the point.
How did you create so many homework activities via the Teachers Involve Parents in Schoolwork program?
We had several projects with educators to help them design interactive assignments, not just "do the next three examples on page 38." Teachers worked in teams to create TIPS activities, and then we turned their work into a standard TIPS format in math, reading/language arts, and science for grades K-8. Any teacher can use or adapt our prototypes to match their curricula.
Overall, we know that if future teachers and practicing educators were prepared to design homework assignments to meet specific purposes—including but not limited to interactive activities—more students would benefit from the important experience of doing their homework. And more parents would, indeed, be partners in education.
Posted in Voices+Opinion
You might also like
News network.
- Johns Hopkins Magazine
- Get Email Updates
- Submit an Announcement
- Submit an Event
- Privacy Statement
- Accessibility
Discover JHU
- About the University
- Schools & Divisions
- Academic Programs
- Plan a Visit
- my.JohnsHopkins.edu
- © 2024 Johns Hopkins University . All rights reserved.
- University Communications
- 3910 Keswick Rd., Suite N2600, Baltimore, MD
- X Facebook LinkedIn YouTube Instagram
11 Surprising Homework Statistics, Facts & Data

The age-old question of whether homework is good or bad for students is unanswerable because there are so many “ it depends ” factors.
For example, it depends on the age of the child, the type of homework being assigned, and even the child’s needs.
There are also many conflicting reports on whether homework is good or bad. This is a topic that largely relies on data interpretation for the researcher to come to their conclusions.
To cut through some of the fog, below I’ve outlined some great homework statistics that can help us understand the effects of homework on children.
Homework Statistics List
1. 45% of parents think homework is too easy for their children.
A study by the Center for American Progress found that parents are almost twice as likely to believe their children’s homework is too easy than to disagree with that statement.
Here are the figures for math homework:
- 46% of parents think their child’s math homework is too easy.
- 25% of parents think their child’s math homework is not too easy.
- 29% of parents offered no opinion.
Here are the figures for language arts homework:
- 44% of parents think their child’s language arts homework is too easy.
- 28% of parents think their child’s language arts homework is not too easy.
- 28% of parents offered no opinion.
These findings are based on online surveys of 372 parents of school-aged children conducted in 2018.
2. 93% of Fourth Grade Children Worldwide are Assigned Homework
The prestigious worldwide math assessment Trends in International Maths and Science Study (TIMSS) took a survey of worldwide homework trends in 2007. Their study concluded that 93% of fourth-grade children are regularly assigned homework, while just 7% never or rarely have homework assigned.

3. 17% of Teens Regularly Miss Homework due to Lack of High-Speed Internet Access
A 2018 Pew Research poll of 743 US teens found that 17%, or almost 2 in every 5 students, regularly struggled to complete homework because they didn’t have reliable access to the internet.
This figure rose to 25% of Black American teens and 24% of teens whose families have an income of less than $30,000 per year.
4. Parents Spend 6.7 Hours Per Week on their Children’s Homework
A 2018 study of 27,500 parents around the world found that the average amount of time parents spend on homework with their child is 6.7 hours per week. Furthermore, 25% of parents spend more than 7 hours per week on their child’s homework.
American parents spend slightly below average at 6.2 hours per week, while Indian parents spend 12 hours per week and Japanese parents spend 2.6 hours per week.
5. Students in High-Performing High Schools Spend on Average 3.1 Hours per night Doing Homework
A study by Galloway, Conner & Pope (2013) conducted a sample of 4,317 students from 10 high-performing high schools in upper-middle-class California.
Across these high-performing schools, students self-reported that they did 3.1 hours per night of homework.
Graduates from those schools also ended up going on to college 93% of the time.
6. One to Two Hours is the Optimal Duration for Homework
A 2012 peer-reviewed study in the High School Journal found that students who conducted between one and two hours achieved higher results in tests than any other group.
However, the authors were quick to highlight that this “t is an oversimplification of a much more complex problem.” I’m inclined to agree. The greater variable is likely the quality of the homework than time spent on it.
Nevertheless, one result was unequivocal: that some homework is better than none at all : “students who complete any amount of homework earn higher test scores than their peers who do not complete homework.”
7. 74% of Teens cite Homework as a Source of Stress
A study by the Better Sleep Council found that homework is a source of stress for 74% of students. Only school grades, at 75%, rated higher in the study.
That figure rises for girls, with 80% of girls citing homework as a source of stress.
Similarly, the study by Galloway, Conner & Pope (2013) found that 56% of students cite homework as a “primary stressor” in their lives.
8. US Teens Spend more than 15 Hours per Week on Homework
The same study by the Better Sleep Council also found that US teens spend over 2 hours per school night on homework, and overall this added up to over 15 hours per week.
Surprisingly, 4% of US teens say they do more than 6 hours of homework per night. That’s almost as much homework as there are hours in the school day.
The only activity that teens self-reported as doing more than homework was engaging in electronics, which included using phones, playing video games, and watching TV.
9. The 10-Minute Rule
The National Education Association (USA) endorses the concept of doing 10 minutes of homework per night per grade.
For example, if you are in 3rd grade, you should do 30 minutes of homework per night. If you are in 4th grade, you should do 40 minutes of homework per night.
However, this ‘rule’ appears not to be based in sound research. Nevertheless, it is true that homework benefits (no matter the quality of the homework) will likely wane after 2 hours (120 minutes) per night, which would be the NEA guidelines’ peak in grade 12.
10. 21.9% of Parents are Too Busy for their Children’s Homework
An online poll of nearly 300 parents found that 21.9% are too busy to review their children’s homework. On top of this, 31.6% of parents do not look at their children’s homework because their children do not want their help. For these parents, their children’s unwillingness to accept their support is a key source of frustration.
11. 46.5% of Parents find Homework too Hard
The same online poll of parents of children from grades 1 to 12 also found that many parents struggle to help their children with homework because parents find it confusing themselves. Unfortunately, the study did not ask the age of the students so more data is required here to get a full picture of the issue.
Get a Pdf of this article for class
Enjoy subscriber-only access to this article’s pdf
Interpreting the Data
Unfortunately, homework is one of those topics that can be interpreted by different people pursuing differing agendas. All studies of homework have a wide range of variables, such as:
- What age were the children in the study?
- What was the homework they were assigned?
- What tools were available to them?
- What were the cultural attitudes to homework and how did they impact the study?
- Is the study replicable?
The more questions we ask about the data, the more we realize that it’s hard to come to firm conclusions about the pros and cons of homework .
Furthermore, questions about the opportunity cost of homework remain. Even if homework is good for children’s test scores, is it worthwhile if the children consequently do less exercise or experience more stress?
Thus, this ends up becoming a largely qualitative exercise. If parents and teachers zoom in on an individual child’s needs, they’ll be able to more effectively understand how much homework a child needs as well as the type of homework they should be assigned.
Related: Funny Homework Excuses
The debate over whether homework should be banned will not be resolved with these homework statistics. But, these facts and figures can help you to pursue a position in a school debate on the topic – and with that, I hope your debate goes well and you develop some great debating skills!

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ Social-Emotional Learning (Definition, Examples, Pros & Cons)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ What is Educational Psychology?
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ What is IQ? (Intelligence Quotient)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 5 Top Tips for Succeeding at University
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Is it time to get rid of homework? Mental health experts weigh in.

It's no secret that kids hate homework. And as students grapple with an ongoing pandemic that has had a wide range of mental health impacts, is it time schools start listening to their pleas about workloads?
Some teachers are turning to social media to take a stand against homework.
Tiktok user @misguided.teacher says he doesn't assign it because the "whole premise of homework is flawed."
For starters, he says, he can't grade work on "even playing fields" when students' home environments can be vastly different.
"Even students who go home to a peaceful house, do they really want to spend their time on busy work? Because typically that's what a lot of homework is, it's busy work," he says in the video that has garnered 1.6 million likes. "You only get one year to be 7, you only got one year to be 10, you only get one year to be 16, 18."
Mental health experts agree heavy workloads have the potential do more harm than good for students, especially when taking into account the impacts of the pandemic. But they also say the answer may not be to eliminate homework altogether.
Emmy Kang, mental health counselor at Humantold , says studies have shown heavy workloads can be "detrimental" for students and cause a "big impact on their mental, physical and emotional health."
"More than half of students say that homework is their primary source of stress, and we know what stress can do on our bodies," she says, adding that staying up late to finish assignments also leads to disrupted sleep and exhaustion.
Cynthia Catchings, a licensed clinical social worker and therapist at Talkspace , says heavy workloads can also cause serious mental health problems in the long run, like anxiety and depression.
And for all the distress homework can cause, it's not as useful as many may think, says Dr. Nicholas Kardaras, a psychologist and CEO of Omega Recovery treatment center.
"The research shows that there's really limited benefit of homework for elementary age students, that really the school work should be contained in the classroom," he says.
For older students, Kang says, homework benefits plateau at about two hours per night.
"Most students, especially at these high achieving schools, they're doing a minimum of three hours, and it's taking away time from their friends, from their families, their extracurricular activities. And these are all very important things for a person's mental and emotional health."
Catchings, who also taught third to 12th graders for 12 years, says she's seen the positive effects of a no-homework policy while working with students abroad.
"Not having homework was something that I always admired from the French students (and) the French schools, because that was helping the students to really have the time off and really disconnect from school," she says.
The answer may not be to eliminate homework completely but to be more mindful of the type of work students take home, suggests Kang, who was a high school teacher for 10 years.
"I don't think (we) should scrap homework; I think we should scrap meaningless, purposeless busy work-type homework. That's something that needs to be scrapped entirely," she says, encouraging teachers to be thoughtful and consider the amount of time it would take for students to complete assignments.
The pandemic made the conversation around homework more crucial
Mindfulness surrounding homework is especially important in the context of the past two years. Many students will be struggling with mental health issues that were brought on or worsened by the pandemic , making heavy workloads even harder to balance.
"COVID was just a disaster in terms of the lack of structure. Everything just deteriorated," Kardaras says, pointing to an increase in cognitive issues and decrease in attention spans among students. "School acts as an anchor for a lot of children, as a stabilizing force, and that disappeared."
But even if students transition back to the structure of in-person classes, Kardaras suspects students may still struggle after two school years of shifted schedules and disrupted sleeping habits.
"We've seen adults struggling to go back to in-person work environments from remote work environments. That effect is amplified with children because children have less resources to be able to cope with those transitions than adults do," he explains.
'Get organized' ahead of back-to-school
In order to make the transition back to in-person school easier, Kang encourages students to "get good sleep, exercise regularly (and) eat a healthy diet."
To help manage workloads, she suggests students "get organized."
"There's so much mental clutter up there when you're disorganized. ... Sitting down and planning out their study schedules can really help manage their time," she says.
Breaking up assignments can also make things easier to tackle.
"I know that heavy workloads can be stressful, but if you sit down and you break down that studying into smaller chunks, they're much more manageable."
If workloads are still too much, Kang encourages students to advocate for themselves.
"They should tell their teachers when a homework assignment just took too much time or if it was too difficult for them to do on their own," she says. "It's good to speak up and ask those questions. Respectfully, of course, because these are your teachers. But still, I think sometimes teachers themselves need this feedback from their students."
More: Some teachers let their students sleep in class. Here's what mental health experts say.
More: Some parents are slipping young kids in for the COVID-19 vaccine, but doctors discourage the move as 'risky'
Request More Info
Fill out the form below and a member of our team will reach out right away!
" * " indicates required fields
Is Homework Necessary? Education Inequity and Its Impact on Students

The Problem with Homework: It Highlights Inequalities
How much homework is too much homework, when does homework actually help, negative effects of homework for students, how teachers can help.
Schools are getting rid of homework from Essex, Mass., to Los Angeles, Calif. Although the no-homework trend may sound alarming, especially to parents dreaming of their child’s acceptance to Harvard, Stanford or Yale, there is mounting evidence that eliminating homework in grade school may actually have great benefits , especially with regard to educational equity.
In fact, while the push to eliminate homework may come as a surprise to many adults, the debate is not new . Parents and educators have been talking about this subject for the last century, so that the educational pendulum continues to swing back and forth between the need for homework and the need to eliminate homework.
One of the most pressing talking points around homework is how it disproportionately affects students from less affluent families. The American Psychological Association (APA) explained:
“Kids from wealthier homes are more likely to have resources such as computers, internet connections, dedicated areas to do schoolwork and parents who tend to be more educated and more available to help them with tricky assignments. Kids from disadvantaged homes are more likely to work at afterschool jobs, or to be home without supervision in the evenings while their parents work multiple jobs.”
[RELATED] How to Advance Your Career: A Guide for Educators >>
While students growing up in more affluent areas are likely playing sports, participating in other recreational activities after school, or receiving additional tutoring, children in disadvantaged areas are more likely headed to work after school, taking care of siblings while their parents work or dealing with an unstable home life. Adding homework into the mix is one more thing to deal with — and if the student is struggling, the task of completing homework can be too much to consider at the end of an already long school day.
While all students may groan at the mention of homework, it may be more than just a nuisance for poor and disadvantaged children, instead becoming another burden to carry and contend with.
Beyond the logistical issues, homework can negatively impact physical health and stress — and once again this may be a more significant problem among economically disadvantaged youth who typically already have a higher stress level than peers from more financially stable families .
Yet, today, it is not just the disadvantaged who suffer from the stressors that homework inflicts. A 2014 CNN article, “Is Homework Making Your Child Sick?” , covered the issue of extreme pressure placed on children of the affluent. The article looked at the results of a study surveying more than 4,300 students from 10 high-performing public and private high schools in upper-middle-class California communities.
“Their findings were troubling: Research showed that excessive homework is associated with high stress levels, physical health problems and lack of balance in children’s lives; 56% of the students in the study cited homework as a primary stressor in their lives,” according to the CNN story. “That children growing up in poverty are at-risk for a number of ailments is both intuitive and well-supported by research. More difficult to believe is the growing consensus that children on the other end of the spectrum, children raised in affluence, may also be at risk.”
When it comes to health and stress it is clear that excessive homework, for children at both ends of the spectrum, can be damaging. Which begs the question, how much homework is too much?
The National Education Association and the National Parent Teacher Association recommend that students spend 10 minutes per grade level per night on homework . That means that first graders should spend 10 minutes on homework, second graders 20 minutes and so on. But a study published by The American Journal of Family Therapy found that students are getting much more than that.
While 10 minutes per day doesn’t sound like much, that quickly adds up to an hour per night by sixth grade. The National Center for Education Statistics found that high school students get an average of 6.8 hours of homework per week, a figure that is much too high according to the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD). It is also to be noted that this figure does not take into consideration the needs of underprivileged student populations.
In a study conducted by the OECD it was found that “after around four hours of homework per week, the additional time invested in homework has a negligible impact on performance .” That means that by asking our children to put in an hour or more per day of dedicated homework time, we are not only not helping them, but — according to the aforementioned studies — we are hurting them, both physically and emotionally.
What’s more is that homework is, as the name implies, to be completed at home, after a full day of learning that is typically six to seven hours long with breaks and lunch included. However, a study by the APA on how people develop expertise found that elite musicians, scientists and athletes do their most productive work for about only four hours per day. Similarly, companies like Tower Paddle Boards are experimenting with a five-hour workday, under the assumption that people are not able to be truly productive for much longer than that. CEO Stephan Aarstol told CNBC that he believes most Americans only get about two to three hours of work done in an eight-hour day.
In the scope of world history, homework is a fairly new construct in the U.S. Students of all ages have been receiving work to complete at home for centuries, but it was educational reformer Horace Mann who first brought the concept to America from Prussia.
Since then, homework’s popularity has ebbed and flowed in the court of public opinion. In the 1930s, it was considered child labor (as, ironically, it compromised children’s ability to do chores at home). Then, in the 1950s, implementing mandatory homework was hailed as a way to ensure America’s youth were always one step ahead of Soviet children during the Cold War. Homework was formally mandated as a tool for boosting educational quality in 1986 by the U.S. Department of Education, and has remained in common practice ever since.
School work assigned and completed outside of school hours is not without its benefits. Numerous studies have shown that regular homework has a hand in improving student performance and connecting students to their learning. When reviewing these studies, take them with a grain of salt; there are strong arguments for both sides, and only you will know which solution is best for your students or school.
Homework improves student achievement.
- Source: The High School Journal, “ When is Homework Worth the Time?: Evaluating the Association between Homework and Achievement in High School Science and Math ,” 2012.
- Source: IZA.org, “ Does High School Homework Increase Academic Achievement? ,” 2014. **Note: Study sample comprised only high school boys.
Homework helps reinforce classroom learning.
- Source: “ Debunk This: People Remember 10 Percent of What They Read ,” 2015.
Homework helps students develop good study habits and life skills.
- Sources: The Repository @ St. Cloud State, “ Types of Homework and Their Effect on Student Achievement ,” 2017; Journal of Advanced Academics, “ Developing Self-Regulation Skills: The Important Role of Homework ,” 2011.
- Source: Journal of Advanced Academics, “ Developing Self-Regulation Skills: The Important Role of Homework ,” 2011.
Homework allows parents to be involved with their children’s learning.
- Parents can see what their children are learning and working on in school every day.
- Parents can participate in their children’s learning by guiding them through homework assignments and reinforcing positive study and research habits.
- Homework observation and participation can help parents understand their children’s academic strengths and weaknesses, and even identify possible learning difficulties.
- Source: Phys.org, “ Sociologist Upends Notions about Parental Help with Homework ,” 2018.
While some amount of homework may help students connect to their learning and enhance their in-class performance, too much homework can have damaging effects.
Students with too much homework have elevated stress levels.
- Source: USA Today, “ Is It Time to Get Rid of Homework? Mental Health Experts Weigh In ,” 2021.
- Source: Stanford University, “ Stanford Research Shows Pitfalls of Homework ,” 2014.
Students with too much homework may be tempted to cheat.
- Source: The Chronicle of Higher Education, “ High-Tech Cheating Abounds, and Professors Bear Some Blame ,” 2010.
- Source: The American Journal of Family Therapy, “ Homework and Family Stress: With Consideration of Parents’ Self Confidence, Educational Level, and Cultural Background ,” 2015.
Homework highlights digital inequity.
- Sources: NEAToday.org, “ The Homework Gap: The ‘Cruelest Part of the Digital Divide’ ,” 2016; CNET.com, “ The Digital Divide Has Left Millions of School Kids Behind ,” 2021.
- Source: Investopedia, “ Digital Divide ,” 2022; International Journal of Education and Social Science, “ Getting the Homework Done: Social Class and Parents’ Relationship to Homework ,” 2015.
- Source: World Economic Forum, “ COVID-19 exposed the digital divide. Here’s how we can close it ,” 2021.
Homework does not help younger students.
- Source: Review of Educational Research, “ Does Homework Improve Academic Achievement? A Synthesis of Researcher, 1987-2003 ,” 2006.
To help students find the right balance and succeed, teachers and educators must start the homework conversation, both internally at their school and with parents. But in order to successfully advocate on behalf of students, teachers must be well educated on the subject, fully understanding the research and the outcomes that can be achieved by eliminating or reducing the homework burden. There is a plethora of research and writing on the subject for those interested in self-study.
For teachers looking for a more in-depth approach or for educators with a keen interest in educational equity, formal education may be the best route. If this latter option sounds appealing, there are now many reputable schools offering online master of education degree programs to help educators balance the demands of work and family life while furthering their education in the quest to help others.
YOU’RE INVITED! Watch Free Webinar on USD’s Online MEd Program >>
Be Sure To Share This Article
- Share on Twitter
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Top 11 Reasons to get Your Master of Education Degree
Free 22-page Book

- Master of Education
Related Posts


School Life Balance , Tips for Online Students
The Pros and Cons of Homework
Updated: December 7, 2023
Published: January 23, 2020

Homework is a word that most students dread hearing. After hours upon hours of sitting in class , the last thing we want is more schoolwork over our precious weekends. While it’s known to be a staple of traditional schooling, homework has also become a rather divise topic. Some feel as though homework is a necessary part of school, while others believe that the time could be better invested. Should students have homework? Have a closer look into the arguments on both sides to decide for yourself.

Photo by energepic.com from Pexels
Why should students have homework, 1. homework encourages practice.
Many people believe that one of the positive effects of homework is that it encourages the discipline of practice. While it may be time consuming and boring compared to other activities, repetition is needed to get better at skills. Homework helps make concepts more clear, and gives students more opportunities when starting their career .
2. Homework Gets Parents Involved
Homework can be something that gets parents involved in their children’s lives if the environment is a healthy one. A parent helping their child with homework makes them take part in their academic success, and allows for the parent to keep up with what the child is doing in school. It can also be a chance to connect together.
3. Homework Teaches Time Management
Homework is much more than just completing the assigned tasks. Homework can develop time management skills , forcing students to plan their time and make sure that all of their homework assignments are done on time. By learning to manage their time, students also practice their problem-solving skills and independent thinking. One of the positive effects of homework is that it forces decision making and compromises to be made.
4. Homework Opens A Bridge Of Communication
Homework creates a connection between the student, the teacher, the school, and the parents. It allows everyone to get to know each other better, and parents can see where their children are struggling. In the same sense, parents can also see where their children are excelling. Homework in turn can allow for a better, more targeted educational plan for the student.
5. Homework Allows For More Learning Time
Homework allows for more time to complete the learning process. School hours are not always enough time for students to really understand core concepts, and homework can counter the effects of time shortages, benefiting students in the long run, even if they can’t see it in the moment.
6. Homework Reduces Screen Time
Many students in North America spend far too many hours watching TV. If they weren’t in school, these numbers would likely increase even more. Although homework is usually undesired, it encourages better study habits and discourages spending time in front of the TV. Homework can be seen as another extracurricular activity, and many families already invest a lot of time and money in different clubs and lessons to fill up their children’s extra time. Just like extracurricular activities, homework can be fit into one’s schedule.

The Other Side: Why Homework Is Bad
1. homework encourages a sedentary lifestyle.
Should students have homework? Well, that depends on where you stand. There are arguments both for the advantages and the disadvantages of homework.
While classroom time is important, playground time is just as important. If children are given too much homework, they won’t have enough playtime, which can impact their social development and learning. Studies have found that those who get more play get better grades in school , as it can help them pay closer attention in the classroom.
Children are already sitting long hours in the classroom, and homework assignments only add to these hours. Sedentary lifestyles can be dangerous and can cause health problems such as obesity. Homework takes away from time that could be spent investing in physical activity.
2. Homework Isn’t Healthy In Every Home
While many people that think homes are a beneficial environment for children to learn, not all homes provide a healthy environment, and there may be very little investment from parents. Some parents do not provide any kind of support or homework help, and even if they would like to, due to personal barriers, they sometimes cannot. Homework can create friction between children and their parents, which is one of the reasons why homework is bad .
3. Homework Adds To An Already Full-Time Job
School is already a full-time job for students, as they generally spend over 6 hours each day in class. Students also often have extracurricular activities such as sports, music, or art that are just as important as their traditional courses. Adding on extra hours to all of these demands is a lot for children to manage, and prevents students from having extra time to themselves for a variety of creative endeavors. Homework prevents self discovery and having the time to learn new skills outside of the school system. This is one of the main disadvantages of homework.
4. Homework Has Not Been Proven To Provide Results
Endless surveys have found that homework creates a negative attitude towards school, and homework has not been found to be linked to a higher level of academic success.
The positive effects of homework have not been backed up enough. While homework may help some students improve in specific subjects, if they have outside help there is no real proof that homework makes for improvements.
It can be a challenge to really enforce the completion of homework, and students can still get decent grades without doing their homework. Extra school time does not necessarily mean better grades — quality must always come before quantity.
Accurate practice when it comes to homework simply isn’t reliable. Homework could even cause opposite effects if misunderstood, especially since the reliance is placed on the student and their parents — one of the major reasons as to why homework is bad. Many students would rather cheat in class to avoid doing their homework at home, and children often just copy off of each other or from what they read on the internet.
5. Homework Assignments Are Overdone
The general agreement is that students should not be given more than 10 minutes a day per grade level. What this means is that a first grader should be given a maximum of 10 minutes of homework, while a second grader receives 20 minutes, etc. Many students are given a lot more homework than the recommended amount, however.
On average, college students spend as much as 3 hours per night on homework . By giving too much homework, it can increase stress levels and lead to burn out. This in turn provides an opposite effect when it comes to academic success.
The pros and cons of homework are both valid, and it seems as though the question of ‘‘should students have homework?’ is not a simple, straightforward one. Parents and teachers often are found to be clashing heads, while the student is left in the middle without much say.
It’s important to understand all the advantages and disadvantages of homework, taking both perspectives into conversation to find a common ground. At the end of the day, everyone’s goal is the success of the student.
Related Articles
Negative Effects of Homework
Experts say that students should have no more than 10 minutes of homework per grade, starting in the 1st grade. Many students have much more homework than this, though, and it could be detrimental.
Just what does too much homework do? Keep reading to find out more.
Too Much Homework Can be Harmful
What are the negative effects of too much homework? Too much homework can cause students to experience stress, anxiety, depression, physical ailments, and even cause lower test scores.
How much homework is too much? The National PTA and the National Education Association agree that homework that takes longer than 10 minutes per grade period is excessive. For example, a third-grader should have no more than 30 minutes of homework. Any homework beyond the 30 minutes is too much.
The problem lies in determining how long a homework assignment will take each child. As we all know, each child is different. One child may speed through the assignment while another may spend hours on it. At that point, it's up to the individual parents to discuss the issues with the teacher to come up with a plan appropriate for that child.
How much homework is appropriate for high schoolers? High school aged students can handle more homework. Going with the 10-minute rule per grade, freshman should have no more than 90 minutes and seniors no more than 2 hours of homework.
Does homework affect family time? Excessive homework can cut down on productive family time. This is especially true in families where the parents are incapable of assisting with the homework. As the stress levels increase, fights begin, which takes away from any quality family time students can spend on school nights.
Too much homework can also take time away from teens trying to save up for a big purchase or even college. If you're a teen looking to earn some extra cash, don't miss this list on all the best online jobs for teens.
Does homework affect test scores in high school? Studies show that a certain amount of homework can help test scores increase, but the benefits begin to fall off after doing about an hour of homework on any given subject. According to the Journal of Educational Psychology , students who did more than 90 to 100 minutes of homework per night actually performed worse on tests than those with less than 90 minutes of homework.
Does homework affect test scores in elementary school? Studies show that increased homework at the elementary school level actually has a negative effect on students' test scores. Increased homework often means it's a remedial attempt to catch a child up on what the teacher couldn't teach in the classroom. Because of the lack of teaching, children often do worse on tests as a result.
When did you first start to feel genuinely stressed by schoolwork?
The Health Effects of Homework
Are teens sleep deprived? The Journal of Adolescent Health states that 8% of high schoolers in the US get the recommended 9 hours of sleep each night. They also state that 23% of high school students get 6 hours or less of sleep and 10% get 5 hours or less.
Does Homework Cause Anxiety? A study conducted by Stanford University determined that students who feel that they spend "too much time" on homework experience stress and physical ailments that can be tied to anxiety. Students also cited having difficulty balancing everything in their life, including family time and extracurricular activities in addition to homework, which can contribute to the anxiety.
What health problems can homework cause? Excessive homework, which exceeds the 10-minute per grade rule, has been known to cause digestive issues, sleeping problems, headaches, weight loss, and generalized stress.
Can homework cause depression? Homework itself might not be the direct cause of depression, but it could have an indirect relationship. Students who feel overwhelmed with homework have a harder time balancing their family life, extracurricular activities, and social life. This can lead them to isolation and depression.
Does homework take away from a person's childhood? If a child has excessive amounts of homework and they have trouble balancing their life outside of school, it may take away from their childhood. Not having time to go outside, play with friends, or just "chill" could take away from the milestone experiences of childhood.
What type of homework was most stressful for you?
Does Homework Ever Make Sense?
What is the point of homework? According to the Review of Educational Research , homework should serve a purpose and that purpose is to practice, prepare, or extend a student's learning. The homework should be age appropriate and either engage a child's interest or help him/her learn good study habits.
Does homework help in any subject? This is a question of quality versus quantity. We've established that an overabundance of homework is detrimental. A study in the Economics of Education Review determined that homework in subjects like English, history, and science didn't affect a student's test scores. The one subject that does show benefits from homework is math, though.
Does more homework mean better grades? A Penn State and the Curry School of Education study claims that a relationship does not exist between homework and better grades. In fact, it can actually hurt a child if it causes unnecessary stress or anxiety.
Can homework be damaging to kids who don't understand a topic? According to a study conducted by Lee Bartel , a University of Toronto professor, homework is useless for students who know the topic and anxiety-provoking for students who don't understand the topic. This anxiety can lead to breakdowns, a dislike for school, and even begin to damage a family's well-being.
Does excessive homework encourage cheating? Students who find that they can't do the homework but know it's a large part of their grade often turn to cheating. Whether they cheat off peers or find other ways to do it, the point of the homework is lost.
According to NoCheating.org , 9 out of 10 middle schoolers copy someone else's homework, and 75% to 98% of college students admit to cheating at some point during their school career. The homework most copied is in math and science.
Does homework cause loneliness or social isolation? Handling homework as well as life's demands outside of school can prove to be too much for many students. This can leave them feeling lonely or isolated as they do their homework as they were told, but have less time to cultivate relationships outside of school.
Study on Homework Effects Outside of School
Does homework promote personal responsibility? Some researchers do believe that homework helps students develop a sense of responsibility at a young age. It can also help them develop the ability to multi-task, which is another important life skill that is best taught through doing.
Can homework take away from the chance to learn about personal responsibilities? Other researchers argue that homework takes away from the chance to learn about personal responsibilities. Because homework can be so daunting and take up so much time, it doesn't leave much time for learning about responsibilities outside of school.
Understanding How to Cope with Homework
Why is homework so stressful? Homework isn't just stressful for the students—the stress can often carry over to the family as well. This is especially true in families where the parents don't feel capable of helping their child after being out of school themselves for a decade or two. This can increase family fights and stress throughout the family unit.
How can you stay calm during homework? Homework can seem overwhelming and stressful, but there are ways to stay calm:
How should you handle homework that is too hard? It's inevitable that some homework will be harder than others. Rather than letting it stress you out, consider the following tips:
How should you cope with too much homework? If you find that you just have too much homework, try talking to your teacher about it. If it's overwhelming you and making you stressed out, your teacher may have ways to help you.
Write to Kim P at [email protected] . Follow us on Twitter and Facebook for our latest posts.
Note: This website is made possible through financial relationships with some of the products and services mentioned on this site. We may receive compensation if you shop through links in our content. You do not have to use our links, but you help support CreditDonkey if you do.
Student Credit Cards
How to choose a student credit card.
- Benefits of a Credit Card for College Students
About CreditDonkey CreditDonkey is a credit card comparison website. We publish data-driven analysis to help you save money & make savvy decisions.
Editorial Note: Any opinions, analyses, reviews or recommendations expressed on this page are those of the author's alone, and have not been reviewed, approved or otherwise endorsed by any card issuer.
†Advertiser Disclosure: Many of the offers that appear on this site are from companies from which CreditDonkey receives compensation. This compensation may impact how and where products appear on this site (including, for example, the order in which they appear). CreditDonkey does not include all companies or all offers that may be available in the marketplace.
*See the card issuer's online application for details about terms and conditions. Reasonable efforts are made to maintain accurate information. However, all information is presented without warranty. When you click on the "Apply Now" button you can review the terms and conditions on the card issuer's website.
CreditDonkey does not know your individual circumstances and provides information for general educational purposes only. CreditDonkey is not a substitute for, and should not be used as, professional legal, credit or financial advice. You should consult your own professional advisors for such advice.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Education scholar Denise Pope has found that too much homework has negative effects on student well-being and behavioral engagement. (Image credit: L.A. Cicero)
Examining these arguments offers important perspectives on the wider educational and developmental consequences of homework practices. 1. Elevated Stress and Health Consequences. According to Gitnux, U.S. high school students who have over 20 hours of homework per week are 27% more likely to encounter health issues.
Beyond that point, kids don't absorb much useful information, Cooper says. In fact, too much homework can do more harm than good. Researchers have cited drawbacks, including boredom and burnout toward academic material, less time for family and extracurricular activities, lack of sleep and increased stress.
In the early 1900s, progressive education theorists, championed by the magazine Ladies' Home Journal, decried homework's negative impact on children's physical and mental health, leading California to ban homework for students under 15 from 1901 until 1917. In the 1930s, homework was portrayed as child labor, which was newly illegal, but ...
A Stanford education researcher found that too much homework can negatively affect kids, especially their lives away from school, where family, friends and activities matter. "Our findings on the effects of homework challenge the traditional assumption that homework is inherently good," wrote Denise Pope, a senior lecturer at the Stanford Graduate School of Education and a
Emmy Kang, mental health counselor at Humantold, says studies have shown heavy workloads can be "detrimental" for students and cause a "big impact on their mental, physical and emotional health ...
The necessity of homework has been a subject of debate since at least as far back as the 1890s, according to Joyce L. Epstein, co-director of the Center on School, Family, and Community Partnerships at Johns Hopkins University. "It's always been the case that parents, kids—and sometimes teachers, too—wonder if this is just busy work ...
The authors believe this meritocratic narrative is a myth and that homework — math homework in particular — further entrenches the myth in the minds of teachers and their students.
Some studies show positive effects of homework under certain conditions and for certain students, some show no effects, and some suggest negative effects (Kohn 2006; Trautwein and Koller 2003). Homework appears to have more positive effects for certain groups of students. Older students benefit more from homework than younger students.
A 2018 Pew Research poll of 743 US teens found that 17%, or almost 2 in every 5 students, regularly struggled to complete homework because they didn't have reliable access to the internet. This figure rose to 25% of Black American teens and 24% of teens whose families have an income of less than $30,000 per year. 4.
For older students, Kang says, homework benefits plateau at about two hours per night. "Most students, especially at these high achieving schools, they're doing a minimum of three hours, and it's ...
Elementary school kids are dealing with large amounts of homework. Howard County Library System, CC BY-NC-ND. One in 10 children report spending multiple hours on homework. There are no benefits ...
Homework can affect both students' physical and mental health. According to a study by Stanford University, 56 per cent of students considered homework a primary source of stress. Too much homework can result in lack of sleep, headaches, exhaustion and weight loss. Excessive homework can also result in poor eating habits, with families ...
This is a rather curious fact when you stop to think about it, but not as curious as the fact that few people ever stop to think about it. 1. The negative effects of homework are well known. They include children's frustration and exhaustion, lack of time for other activities, and possible loss of interest in learning.
The homework wars are back. By Jacob Sweet Updated Feb 23, 2023, 6:04am EST. As the Covid-19 pandemic began and students logged into their remote classrooms, all work, in effect, became homework ...
A big report for the Department for Education, published in 2014, concluded that students in Year 9 who spent between two and three hours on homework on an average week night were almost 10 times ...
Negative Effects of Homework for Students. While some amount of homework may help students connect to their learning and enhance their in-class performance, too much homework can have damaging effects. Students with too much homework have elevated stress levels. Students regularly report that homework is their primary source of stress.
Homework allows for more time to complete the learning process. School hours are not always enough time for students to really understand core concepts, and homework can counter the effects of time shortages, benefiting students in the long run, even if they can't see it in the moment. 6. Homework Reduces Screen Time.
Excessive homework, which exceeds the 10-minute per grade rule, has been known to cause digestive issues, sleeping problems, headaches, weight loss, and generalized stress. Can homework cause depression? Homework itself might not be the direct cause of depression, but it could have an indirect relationship.
Probing Question: Is homework bad for kids? | Penn State University. Ask an eleven-year-old whether homework is a bad thing, and you'll likely be greeted with vigorous nodding and not a hint of ambiguity. But do grown-up experts agree? As with so many things, the answer is mixed.
Is homework a huge topic for stress and disappointment in your household? Sadly, you're not alone. ... Students who struggle with homework or who get a large volume of homework each night can experience negative effects in their family and social relationships. Explore this article. Time Constraints; Family Stress; Less Active Learning;
Homework refers to academic work assigned by teachers to be completed outside of class. let's look at some interesting facts about homework that you don't know. ... Negative Effects of Homework. While homework has many benefits, it can also have some negative effects, particularly if students are overloaded with too much work. ...
Experts are closely watching KP.2, now the leading variant. By Dani Blum For most of this year, the JN.1 variant of the coronavirus accounted for an overwhelming majority of Covid cases. But now ...