
Princeton Correspondents on Undergraduate Research

How to Make a Successful Research Presentation
Turning a research paper into a visual presentation is difficult; there are pitfalls, and navigating the path to a brief, informative presentation takes time and practice. As a TA for GEO/WRI 201: Methods in Data Analysis & Scientific Writing this past fall, I saw how this process works from an instructor’s standpoint. I’ve presented my own research before, but helping others present theirs taught me a bit more about the process. Here are some tips I learned that may help you with your next research presentation:
More is more
In general, your presentation will always benefit from more practice, more feedback, and more revision. By practicing in front of friends, you can get comfortable with presenting your work while receiving feedback. It is hard to know how to revise your presentation if you never practice. If you are presenting to a general audience, getting feedback from someone outside of your discipline is crucial. Terms and ideas that seem intuitive to you may be completely foreign to someone else, and your well-crafted presentation could fall flat.
Less is more
Limit the scope of your presentation, the number of slides, and the text on each slide. In my experience, text works well for organizing slides, orienting the audience to key terms, and annotating important figures–not for explaining complex ideas. Having fewer slides is usually better as well. In general, about one slide per minute of presentation is an appropriate budget. Too many slides is usually a sign that your topic is too broad.

Limit the scope of your presentation
Don’t present your paper. Presentations are usually around 10 min long. You will not have time to explain all of the research you did in a semester (or a year!) in such a short span of time. Instead, focus on the highlight(s). Identify a single compelling research question which your work addressed, and craft a succinct but complete narrative around it.
You will not have time to explain all of the research you did. Instead, focus on the highlights. Identify a single compelling research question which your work addressed, and craft a succinct but complete narrative around it.
Craft a compelling research narrative
After identifying the focused research question, walk your audience through your research as if it were a story. Presentations with strong narrative arcs are clear, captivating, and compelling.
- Introduction (exposition — rising action)
Orient the audience and draw them in by demonstrating the relevance and importance of your research story with strong global motive. Provide them with the necessary vocabulary and background knowledge to understand the plot of your story. Introduce the key studies (characters) relevant in your story and build tension and conflict with scholarly and data motive. By the end of your introduction, your audience should clearly understand your research question and be dying to know how you resolve the tension built through motive.
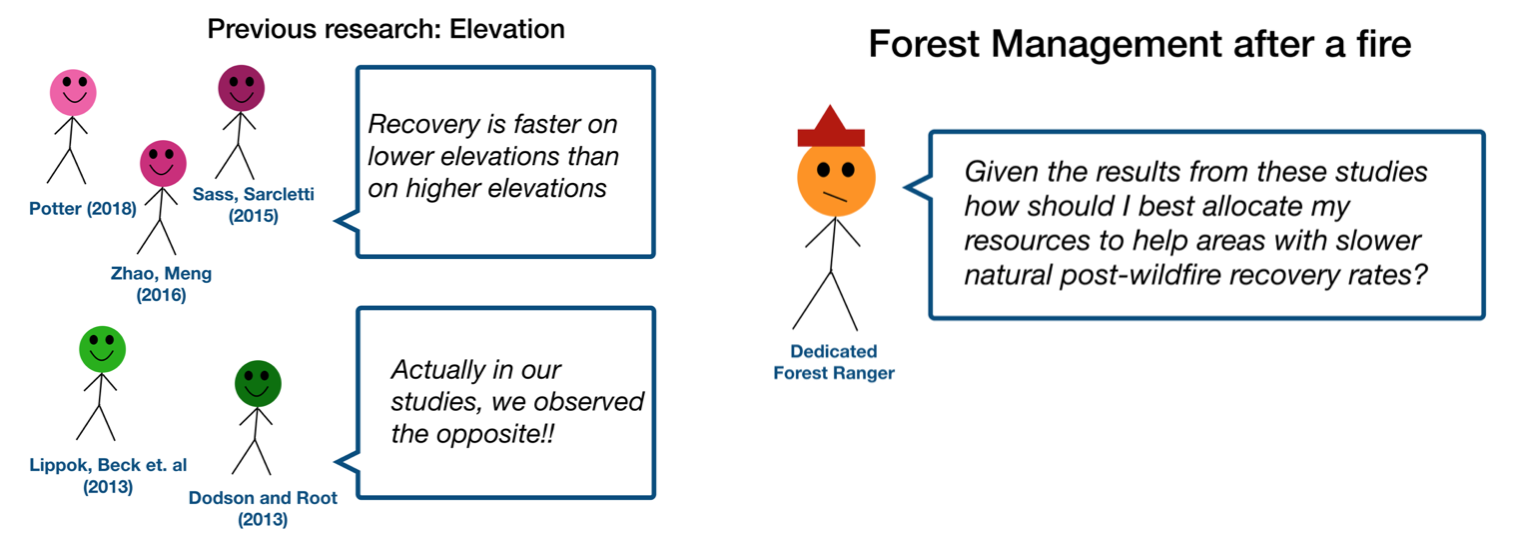
- Methods (rising action)
The methods section should transition smoothly and logically from the introduction. Beware of presenting your methods in a boring, arc-killing, ‘this is what I did.’ Focus on the details that set your story apart from the stories other people have already told. Keep the audience interested by clearly motivating your decisions based on your original research question or the tension built in your introduction.
- Results (climax)
Less is usually more here. Only present results which are clearly related to the focused research question you are presenting. Make sure you explain the results clearly so that your audience understands what your research found. This is the peak of tension in your narrative arc, so don’t undercut it by quickly clicking through to your discussion.
- Discussion (falling action)
By now your audience should be dying for a satisfying resolution. Here is where you contextualize your results and begin resolving the tension between past research. Be thorough. If you have too many conflicts left unresolved, or you don’t have enough time to present all of the resolutions, you probably need to further narrow the scope of your presentation.
- Conclusion (denouement)
Return back to your initial research question and motive, resolving any final conflicts and tying up loose ends. Leave the audience with a clear resolution of your focus research question, and use unresolved tension to set up potential sequels (i.e. further research).
Use your medium to enhance the narrative
Visual presentations should be dominated by clear, intentional graphics. Subtle animation in key moments (usually during the results or discussion) can add drama to the narrative arc and make conflict resolutions more satisfying. You are narrating a story written in images, videos, cartoons, and graphs. While your paper is mostly text, with graphics to highlight crucial points, your slides should be the opposite. Adapting to the new medium may require you to create or acquire far more graphics than you included in your paper, but it is necessary to create an engaging presentation.
The most important thing you can do for your presentation is to practice and revise. Bother your friends, your roommates, TAs–anybody who will sit down and listen to your work. Beyond that, think about presentations you have found compelling and try to incorporate some of those elements into your own. Remember you want your work to be comprehensible; you aren’t creating experts in 10 minutes. Above all, try to stay passionate about what you did and why. You put the time in, so show your audience that it’s worth it.
For more insight into research presentations, check out these past PCUR posts written by Emma and Ellie .
— Alec Getraer, Natural Sciences Correspondent
Share this:
- Share on Tumblr

Please log in to save materials. Log in
- Resource Library
- Research Methods
- VIVA Grant Recipients
- Vgr-social-work-research
Education Standards
Radford university.
Learning Domain: Social Work
Standard: Basic Research Methodology
Lesson 10: Sampling in Qualitative Research
Lesson 11: qualitative measurement & rigor, lesson 12: qualitative design & data gathering, lesson 1: introduction to research, lesson 2: getting started with your research project, lesson 3: critical information literacy, lesson 4: paradigm, theory, and causality, lesson 5: research questions, lesson 6: ethics, lesson 7: measurement in quantitative research, lesson 8: sampling in quantitative research, lesson 9: quantitative research designs, powerpoint slides: sowk 621.01: research i: basic research methodology.
The twelve lessons for SOWK 621.01: Research I: Basic Research Methodology as previously taught by Dr. Matthew DeCarlo at Radford University. Dr. DeCarlo and his team developed a complete package of materials that includes a textbook, ancillary materials, and a student workbook as part of a VIVA Open Course Grant.
The PowerPoint slides associated with the twelve lessons of the course, SOWK 621.01: Research I: Basic Research Methodology, as previously taught by Dr. Matthew DeCarlo at Radford University.
- Privacy Policy

Home » Research Report – Example, Writing Guide and Types
Research Report – Example, Writing Guide and Types
Table of Contents

Research Report
Definition:
Research Report is a written document that presents the results of a research project or study, including the research question, methodology, results, and conclusions, in a clear and objective manner.
The purpose of a research report is to communicate the findings of the research to the intended audience, which could be other researchers, stakeholders, or the general public.
Components of Research Report
Components of Research Report are as follows:
Introduction
The introduction sets the stage for the research report and provides a brief overview of the research question or problem being investigated. It should include a clear statement of the purpose of the study and its significance or relevance to the field of research. It may also provide background information or a literature review to help contextualize the research.
Literature Review
The literature review provides a critical analysis and synthesis of the existing research and scholarship relevant to the research question or problem. It should identify the gaps, inconsistencies, and contradictions in the literature and show how the current study addresses these issues. The literature review also establishes the theoretical framework or conceptual model that guides the research.
Methodology
The methodology section describes the research design, methods, and procedures used to collect and analyze data. It should include information on the sample or participants, data collection instruments, data collection procedures, and data analysis techniques. The methodology should be clear and detailed enough to allow other researchers to replicate the study.
The results section presents the findings of the study in a clear and objective manner. It should provide a detailed description of the data and statistics used to answer the research question or test the hypothesis. Tables, graphs, and figures may be included to help visualize the data and illustrate the key findings.
The discussion section interprets the results of the study and explains their significance or relevance to the research question or problem. It should also compare the current findings with those of previous studies and identify the implications for future research or practice. The discussion should be based on the results presented in the previous section and should avoid speculation or unfounded conclusions.
The conclusion summarizes the key findings of the study and restates the main argument or thesis presented in the introduction. It should also provide a brief overview of the contributions of the study to the field of research and the implications for practice or policy.
The references section lists all the sources cited in the research report, following a specific citation style, such as APA or MLA.
The appendices section includes any additional material, such as data tables, figures, or instruments used in the study, that could not be included in the main text due to space limitations.
Types of Research Report
Types of Research Report are as follows:
Thesis is a type of research report. A thesis is a long-form research document that presents the findings and conclusions of an original research study conducted by a student as part of a graduate or postgraduate program. It is typically written by a student pursuing a higher degree, such as a Master’s or Doctoral degree, although it can also be written by researchers or scholars in other fields.
Research Paper
Research paper is a type of research report. A research paper is a document that presents the results of a research study or investigation. Research papers can be written in a variety of fields, including science, social science, humanities, and business. They typically follow a standard format that includes an introduction, literature review, methodology, results, discussion, and conclusion sections.
Technical Report
A technical report is a detailed report that provides information about a specific technical or scientific problem or project. Technical reports are often used in engineering, science, and other technical fields to document research and development work.
Progress Report
A progress report provides an update on the progress of a research project or program over a specific period of time. Progress reports are typically used to communicate the status of a project to stakeholders, funders, or project managers.
Feasibility Report
A feasibility report assesses the feasibility of a proposed project or plan, providing an analysis of the potential risks, benefits, and costs associated with the project. Feasibility reports are often used in business, engineering, and other fields to determine the viability of a project before it is undertaken.
Field Report
A field report documents observations and findings from fieldwork, which is research conducted in the natural environment or setting. Field reports are often used in anthropology, ecology, and other social and natural sciences.
Experimental Report
An experimental report documents the results of a scientific experiment, including the hypothesis, methods, results, and conclusions. Experimental reports are often used in biology, chemistry, and other sciences to communicate the results of laboratory experiments.
Case Study Report
A case study report provides an in-depth analysis of a specific case or situation, often used in psychology, social work, and other fields to document and understand complex cases or phenomena.
Literature Review Report
A literature review report synthesizes and summarizes existing research on a specific topic, providing an overview of the current state of knowledge on the subject. Literature review reports are often used in social sciences, education, and other fields to identify gaps in the literature and guide future research.
Research Report Example
Following is a Research Report Example sample for Students:
Title: The Impact of Social Media on Academic Performance among High School Students
This study aims to investigate the relationship between social media use and academic performance among high school students. The study utilized a quantitative research design, which involved a survey questionnaire administered to a sample of 200 high school students. The findings indicate that there is a negative correlation between social media use and academic performance, suggesting that excessive social media use can lead to poor academic performance among high school students. The results of this study have important implications for educators, parents, and policymakers, as they highlight the need for strategies that can help students balance their social media use and academic responsibilities.
Introduction:
Social media has become an integral part of the lives of high school students. With the widespread use of social media platforms such as Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, and Snapchat, students can connect with friends, share photos and videos, and engage in discussions on a range of topics. While social media offers many benefits, concerns have been raised about its impact on academic performance. Many studies have found a negative correlation between social media use and academic performance among high school students (Kirschner & Karpinski, 2010; Paul, Baker, & Cochran, 2012).
Given the growing importance of social media in the lives of high school students, it is important to investigate its impact on academic performance. This study aims to address this gap by examining the relationship between social media use and academic performance among high school students.
Methodology:
The study utilized a quantitative research design, which involved a survey questionnaire administered to a sample of 200 high school students. The questionnaire was developed based on previous studies and was designed to measure the frequency and duration of social media use, as well as academic performance.
The participants were selected using a convenience sampling technique, and the survey questionnaire was distributed in the classroom during regular school hours. The data collected were analyzed using descriptive statistics and correlation analysis.
The findings indicate that the majority of high school students use social media platforms on a daily basis, with Facebook being the most popular platform. The results also show a negative correlation between social media use and academic performance, suggesting that excessive social media use can lead to poor academic performance among high school students.
Discussion:
The results of this study have important implications for educators, parents, and policymakers. The negative correlation between social media use and academic performance suggests that strategies should be put in place to help students balance their social media use and academic responsibilities. For example, educators could incorporate social media into their teaching strategies to engage students and enhance learning. Parents could limit their children’s social media use and encourage them to prioritize their academic responsibilities. Policymakers could develop guidelines and policies to regulate social media use among high school students.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, this study provides evidence of the negative impact of social media on academic performance among high school students. The findings highlight the need for strategies that can help students balance their social media use and academic responsibilities. Further research is needed to explore the specific mechanisms by which social media use affects academic performance and to develop effective strategies for addressing this issue.
Limitations:
One limitation of this study is the use of convenience sampling, which limits the generalizability of the findings to other populations. Future studies should use random sampling techniques to increase the representativeness of the sample. Another limitation is the use of self-reported measures, which may be subject to social desirability bias. Future studies could use objective measures of social media use and academic performance, such as tracking software and school records.
Implications:
The findings of this study have important implications for educators, parents, and policymakers. Educators could incorporate social media into their teaching strategies to engage students and enhance learning. For example, teachers could use social media platforms to share relevant educational resources and facilitate online discussions. Parents could limit their children’s social media use and encourage them to prioritize their academic responsibilities. They could also engage in open communication with their children to understand their social media use and its impact on their academic performance. Policymakers could develop guidelines and policies to regulate social media use among high school students. For example, schools could implement social media policies that restrict access during class time and encourage responsible use.
References:
- Kirschner, P. A., & Karpinski, A. C. (2010). Facebook® and academic performance. Computers in Human Behavior, 26(6), 1237-1245.
- Paul, J. A., Baker, H. M., & Cochran, J. D. (2012). Effect of online social networking on student academic performance. Journal of the Research Center for Educational Technology, 8(1), 1-19.
- Pantic, I. (2014). Online social networking and mental health. Cyberpsychology, Behavior, and Social Networking, 17(10), 652-657.
- Rosen, L. D., Carrier, L. M., & Cheever, N. A. (2013). Facebook and texting made me do it: Media-induced task-switching while studying. Computers in Human Behavior, 29(3), 948-958.
Note*: Above mention, Example is just a sample for the students’ guide. Do not directly copy and paste as your College or University assignment. Kindly do some research and Write your own.
Applications of Research Report
Research reports have many applications, including:
- Communicating research findings: The primary application of a research report is to communicate the results of a study to other researchers, stakeholders, or the general public. The report serves as a way to share new knowledge, insights, and discoveries with others in the field.
- Informing policy and practice : Research reports can inform policy and practice by providing evidence-based recommendations for decision-makers. For example, a research report on the effectiveness of a new drug could inform regulatory agencies in their decision-making process.
- Supporting further research: Research reports can provide a foundation for further research in a particular area. Other researchers may use the findings and methodology of a report to develop new research questions or to build on existing research.
- Evaluating programs and interventions : Research reports can be used to evaluate the effectiveness of programs and interventions in achieving their intended outcomes. For example, a research report on a new educational program could provide evidence of its impact on student performance.
- Demonstrating impact : Research reports can be used to demonstrate the impact of research funding or to evaluate the success of research projects. By presenting the findings and outcomes of a study, research reports can show the value of research to funders and stakeholders.
- Enhancing professional development : Research reports can be used to enhance professional development by providing a source of information and learning for researchers and practitioners in a particular field. For example, a research report on a new teaching methodology could provide insights and ideas for educators to incorporate into their own practice.
How to write Research Report
Here are some steps you can follow to write a research report:
- Identify the research question: The first step in writing a research report is to identify your research question. This will help you focus your research and organize your findings.
- Conduct research : Once you have identified your research question, you will need to conduct research to gather relevant data and information. This can involve conducting experiments, reviewing literature, or analyzing data.
- Organize your findings: Once you have gathered all of your data, you will need to organize your findings in a way that is clear and understandable. This can involve creating tables, graphs, or charts to illustrate your results.
- Write the report: Once you have organized your findings, you can begin writing the report. Start with an introduction that provides background information and explains the purpose of your research. Next, provide a detailed description of your research methods and findings. Finally, summarize your results and draw conclusions based on your findings.
- Proofread and edit: After you have written your report, be sure to proofread and edit it carefully. Check for grammar and spelling errors, and make sure that your report is well-organized and easy to read.
- Include a reference list: Be sure to include a list of references that you used in your research. This will give credit to your sources and allow readers to further explore the topic if they choose.
- Format your report: Finally, format your report according to the guidelines provided by your instructor or organization. This may include formatting requirements for headings, margins, fonts, and spacing.
Purpose of Research Report
The purpose of a research report is to communicate the results of a research study to a specific audience, such as peers in the same field, stakeholders, or the general public. The report provides a detailed description of the research methods, findings, and conclusions.
Some common purposes of a research report include:
- Sharing knowledge: A research report allows researchers to share their findings and knowledge with others in their field. This helps to advance the field and improve the understanding of a particular topic.
- Identifying trends: A research report can identify trends and patterns in data, which can help guide future research and inform decision-making.
- Addressing problems: A research report can provide insights into problems or issues and suggest solutions or recommendations for addressing them.
- Evaluating programs or interventions : A research report can evaluate the effectiveness of programs or interventions, which can inform decision-making about whether to continue, modify, or discontinue them.
- Meeting regulatory requirements: In some fields, research reports are required to meet regulatory requirements, such as in the case of drug trials or environmental impact studies.
When to Write Research Report
A research report should be written after completing the research study. This includes collecting data, analyzing the results, and drawing conclusions based on the findings. Once the research is complete, the report should be written in a timely manner while the information is still fresh in the researcher’s mind.
In academic settings, research reports are often required as part of coursework or as part of a thesis or dissertation. In this case, the report should be written according to the guidelines provided by the instructor or institution.
In other settings, such as in industry or government, research reports may be required to inform decision-making or to comply with regulatory requirements. In these cases, the report should be written as soon as possible after the research is completed in order to inform decision-making in a timely manner.
Overall, the timing of when to write a research report depends on the purpose of the research, the expectations of the audience, and any regulatory requirements that need to be met. However, it is important to complete the report in a timely manner while the information is still fresh in the researcher’s mind.
Characteristics of Research Report
There are several characteristics of a research report that distinguish it from other types of writing. These characteristics include:
- Objective: A research report should be written in an objective and unbiased manner. It should present the facts and findings of the research study without any personal opinions or biases.
- Systematic: A research report should be written in a systematic manner. It should follow a clear and logical structure, and the information should be presented in a way that is easy to understand and follow.
- Detailed: A research report should be detailed and comprehensive. It should provide a thorough description of the research methods, results, and conclusions.
- Accurate : A research report should be accurate and based on sound research methods. The findings and conclusions should be supported by data and evidence.
- Organized: A research report should be well-organized. It should include headings and subheadings to help the reader navigate the report and understand the main points.
- Clear and concise: A research report should be written in clear and concise language. The information should be presented in a way that is easy to understand, and unnecessary jargon should be avoided.
- Citations and references: A research report should include citations and references to support the findings and conclusions. This helps to give credit to other researchers and to provide readers with the opportunity to further explore the topic.
Advantages of Research Report
Research reports have several advantages, including:
- Communicating research findings: Research reports allow researchers to communicate their findings to a wider audience, including other researchers, stakeholders, and the general public. This helps to disseminate knowledge and advance the understanding of a particular topic.
- Providing evidence for decision-making : Research reports can provide evidence to inform decision-making, such as in the case of policy-making, program planning, or product development. The findings and conclusions can help guide decisions and improve outcomes.
- Supporting further research: Research reports can provide a foundation for further research on a particular topic. Other researchers can build on the findings and conclusions of the report, which can lead to further discoveries and advancements in the field.
- Demonstrating expertise: Research reports can demonstrate the expertise of the researchers and their ability to conduct rigorous and high-quality research. This can be important for securing funding, promotions, and other professional opportunities.
- Meeting regulatory requirements: In some fields, research reports are required to meet regulatory requirements, such as in the case of drug trials or environmental impact studies. Producing a high-quality research report can help ensure compliance with these requirements.
Limitations of Research Report
Despite their advantages, research reports also have some limitations, including:
- Time-consuming: Conducting research and writing a report can be a time-consuming process, particularly for large-scale studies. This can limit the frequency and speed of producing research reports.
- Expensive: Conducting research and producing a report can be expensive, particularly for studies that require specialized equipment, personnel, or data. This can limit the scope and feasibility of some research studies.
- Limited generalizability: Research studies often focus on a specific population or context, which can limit the generalizability of the findings to other populations or contexts.
- Potential bias : Researchers may have biases or conflicts of interest that can influence the findings and conclusions of the research study. Additionally, participants may also have biases or may not be representative of the larger population, which can limit the validity and reliability of the findings.
- Accessibility: Research reports may be written in technical or academic language, which can limit their accessibility to a wider audience. Additionally, some research may be behind paywalls or require specialized access, which can limit the ability of others to read and use the findings.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples

Institutional Review Board – Application Sample...

Evaluating Research – Process, Examples and...
- Google Slides Presentation Design
- Pitch Deck Design
- Powerpoint Redesign
- Other Design Services
- Guide & How to's
How to present a research paper in PPT: best practices
A research paper presentation is frequently used at conferences and other events where you have a chance to share the results of your research and receive feedback from colleagues. Although it may appear as simple as summarizing the findings, successful examples of research paper presentations show that there is a little bit more to it.
In this article, we’ll walk you through the basic outline and steps to create a good research paper presentation. We’ll also explain what to include and what not to include in your presentation of research paper and share some of the most effective tips you can use to take your slides to the next level.
Research paper PowerPoint presentation outline
Creating a PowerPoint presentation for a research paper involves organizing and summarizing your key findings, methodology, and conclusions in a way that encourages your audience to interact with your work and share their interest in it with others. Here’s a basic research paper outline PowerPoint you can follow:
1. Title (1 slide)
Typically, your title slide should contain the following information:
- Title of the research paper
- Affiliation or institution
- Date of presentation
2. Introduction (1-3 slides)
On this slide of your presentation, briefly introduce the research topic and its significance and state the research question or objective.
3. Research questions or hypothesis (1 slide)
This slide should emphasize the objectives of your research or present the hypothesis.
4. Literature review (1 slide)
Your literature review has to provide context for your research by summarizing relevant literature. Additionally, it should highlight gaps or areas where your research contributes.
5. Methodology and data collection (1-2 slides)
This slide of your research paper PowerPoint has to explain the research design, methods, and procedures. It must also Include details about participants, materials, and data collection and emphasize special equipment you have used in your work.
6. Results (3-5 slides)
On this slide, you must present the results of your data analysis and discuss any trends, patterns, or significant findings. Moreover, you should use charts, graphs, and tables to illustrate data and highlight something novel in your results (if applicable).
7. Conclusion (1 slide)
Your conclusion slide has to summarize the main findings and their implications, as well as discuss the broader impact of your research. Usually, a single statement is enough.
8. Recommendations (1 slide)
If applicable, provide recommendations for future research or actions on this slide.
9. References (1-2 slides)
The references slide is where you list all the sources cited in your research paper.
10. Acknowledgments (1 slide)
On this presentation slide, acknowledge any individuals, organizations, or funding sources that contributed to your research.
11. Appendix (1 slide)
If applicable, include any supplementary materials, such as additional data or detailed charts, in your appendix slide.
The above outline is just a general guideline, so make sure to adjust it based on your specific research paper and the time allotted for the presentation.
Steps to creating a memorable research paper presentation
Creating a PowerPoint presentation for a research paper involves several critical steps needed to convey your findings and engage your audience effectively, and these steps are as follows:
Step 1. Understand your audience:
- Identify the audience for your presentation.
- Tailor your content and level of detail to match the audience’s background and knowledge.
Step 2. Define your key messages:
- Clearly articulate the main messages or findings of your research.
- Identify the key points you want your audience to remember.
Step 3. Design your research paper PPT presentation:
- Use a clean and professional design that complements your research topic.
- Choose readable fonts, consistent formatting, and a limited color palette.
- Opt for PowerPoint presentation services if slide design is not your strong side.
Step 4. Put content on slides:
- Follow the outline above to structure your presentation effectively; include key sections and topics.
- Organize your content logically, following the flow of your research paper.
Step 5. Final check:
- Proofread your slides for typos, errors, and inconsistencies.
- Ensure all visuals are clear, high-quality, and properly labeled.
Step 6. Save and share:
- Save your presentation and ensure compatibility with the equipment you’ll be using.
- If necessary, share a copy of your presentation with the audience.
By following these steps, you can create a well-organized and visually appealing research paper presentation PowerPoint that effectively conveys your research findings to the audience.
What to include and what not to include in your presentation
In addition to the must-know PowerPoint presentation recommendations, which we’ll cover later in this article, consider the following do’s and don’ts when you’re putting together your research paper presentation:
- Focus on the topic.
- Be brief and to the point.
- Attract the audience’s attention and highlight interesting details.
- Use only relevant visuals (maps, charts, pictures, graphs, etc.).
- Use numbers and bullet points to structure the content.
- Make clear statements regarding the essence and results of your research.
Don’ts:
- Don’t write down the whole outline of your paper and nothing else.
- Don’t put long, full sentences on your slides; split them into smaller ones.
- Don’t use distracting patterns, colors, pictures, and other visuals on your slides; the simpler, the better.
- Don’t use too complicated graphs or charts; only the ones that are easy to understand.
- Now that we’ve discussed the basics, let’s move on to the top tips for making a powerful presentation of your research paper.
8 tips on how to make research paper presentation that achieves its goals
You’ve probably been to a presentation where the presenter reads word for word from their PowerPoint outline. Or where the presentation is cluttered, chaotic, or contains too much data. The simple tips below will help you summarize a 10 to 15-page paper for a 15 to 20-minute talk and succeed, so read on!
Tip #1: Less is more
You want to provide enough information to make your audience want to know more. Including details but not too many and avoiding technical jargon, formulas, and long sentences are always good ways to achieve this.
Tip #2: Be professional
Avoid using too many colors, font changes, distracting backgrounds, animations, etc. Bullet points with a few words to highlight the important information are preferable to lengthy paragraphs. Additionally, include slide numbers on all PowerPoint slides except for the title slide, and make sure it is followed by a table of contents, offering a brief overview of the entire research paper.
Tip #3: Strive for balance
PowerPoint slides have limited space, so use it carefully. Typically, one to two points per slide or 5 lines for 5 words in a sentence are enough to present your ideas.
Tip #4: Use proper fonts and text size
The font you use should be easy to read and consistent throughout the slides. You can go with Arial, Times New Roman, Calibri, or a combination of these three. An ideal text size is 32 points, while a heading size is 44.
Tip #5: Concentrate on the visual side
A PowerPoint presentation is one of the best tools for presenting information visually. Use graphs instead of tables and topic-relevant illustrations instead of walls of text. Keep your visuals as clean and professional as the content of your presentation.
Tip #6: Practice your delivery
Always go through your presentation when you’re done to ensure a smooth and confident delivery and time yourself to stay within the allotted limit.
Tip #7: Get ready for questions
Anticipate potential questions from your audience and prepare thoughtful responses. Also, be ready to engage in discussions about your research.
Tip #8: Don’t be afraid to utilize professional help
If the mere thought of designing a presentation overwhelms you or you’re pressed for time, consider leveraging professional PowerPoint redesign services . A dedicated design team can transform your content or old presentation into effective slides, ensuring your message is communicated clearly and captivates your audience. This way, you can focus on refining your delivery and preparing for the presentation.
Lastly, remember that even experienced presenters get nervous before delivering research paper PowerPoint presentations in front of the audience. You cannot know everything; some things can be beyond your control, which is completely fine. You are at the event not only to share what you know but also to learn from others. So, no matter what, dress appropriately, look straight into the audience’s eyes, try to speak and move naturally, present your information enthusiastically, and have fun!
If you need help with slide design, get in touch with our dedicated design team and let qualified professionals turn your research findings into a visually appealing, polished presentation that leaves a lasting impression on your audience. Our experienced designers specialize in creating engaging layouts, incorporating compelling graphics, and ensuring a cohesive visual narrative that complements content on any subject.
#ezw_tco-2 .ez-toc-widget-container ul.ez-toc-list li.active::before { background-color: #ededed; } Table of contents
- Presenting techniques
- 50 tips on how to improve PowerPoint presentations in 2022-2023 [Updated]
- Keynote VS PowerPoint
- Types of presentations
- Present financial information visually in PowerPoint to drive results

- Design Tips
8 rules of effective presentation

- Business Slides
Employee training and onboarding presentation: why and how

How to structure, design, write, and finally present executive summary presentation?

Researched by Consultants from Top-Tier Management Companies

Powerpoint Templates
Icon Bundle
Kpi Dashboard
Professional
Business Plans
Swot Analysis
Gantt Chart
Business Proposal
Marketing Plan
Project Management
Business Case
Business Model
Cyber Security
Business PPT
Digital Marketing
Digital Transformation
Human Resources
Product Management
Artificial Intelligence
Company Profile
Acknowledgement PPT
PPT Presentation
Reports Brochures
One Page Pitch
Interview PPT
All Categories
Top 10 Research Presentation Templates with Examples and Samples

Simran Shekhawat
Research organizes all your thoughts, suggestions, findings and innovations in one area that postulates to determining the future applicability. A crucial part of strategic planning is research. It aids organizations in goal setting, decision-making, and resource allocation. Research allows us to uncover and discover many segments of society by establishing facts and generating data that effectively determine future outcomes and progress.
Here's an ultimate guide to conduct market research! Click to know more!
Research primarily comprises gathering and analysing information about consumer behaviour, industry dynamics, economic conditions, and other elements that affect how markets and businesses behave in the context of understanding market trends. Understanding market trends requires market research, which is likely to be successful. Research can reveal prospective market dangers and difficulties, enabling organizations to create backup plans and decide on market entry or expansion with more excellent knowledge. By understanding market trends, businesses can create marketing and advertising efforts that resonate with their target audience.
Learn about product market research templates. Click here .
Additionally, it aids in determining the best customer-reach methods. Businesses can better satisfy market demands by customizing their products or services by studying consumer behaviours, preferences, and feedback. Assessing Market Size and Potential research can shed light on a market's size, potential for expansion, and competitive environment. Businesses aiming to expand or enter new markets need to know this information.
SlideTeam introduces you with their newly launch research templates that has been extensively built to enhance the quality of company’s research and development area by forging to bring answers related to every ‘how’ and ‘why’. The sole purpose of these is to inform, gather information and contributes towards the development and knowledge about the field of study. These templates are professionally design to disseminate knowledge to provide better judgements.
Template 1: Clinical Research Trial PowerPoint Template

Use this premium PPT template to captivate your audience. Download this well-created template to raise your presenting threshold. Establish your milestones with workflows designed to ease the overburdening of tasks. State clear-cut objectives to specify your aim and deliver a timeline. Use these 58-page PowerPoint slides to launch your product success and deliver a presentation that awakes the audience with your research performance and goals.
Click here!
Template 2: Company Stock Analysis and Equity Research Report Slide

Uncover impacts about the stock markets and analyze company-related specific and general equity design using this ready-made template. Understanding the technicality of maintenance and presentation of stocks and equity research, we at SlideTeam have designed an equity research PowerPoint slide to ease your presentation load. This presentation aims to analyze the target company's financial performance, ratios, and financial model to welcome investment in the company. Provide an extensive company summary, income statement, balance sheet, vertical and horizontal analysis, organization shareholding structure, SWOT analysis, and share price performance throughout history through this template.
Download Now!
Template 3: IT Services Research and Development Template

Showcase the power of your company's services, expertise achievement and future goals using this PPT template. This PPT slide provides you with a summary, key statistics, targets, and overview of your IT service Company. Allow this template to lay out values mission, categorize solutions, and enlist a range of services provided along with expenditure incurred on Research development. The deck also includes a business model canvas that depicts the company's historical development, global reach, management team, organizational structure, employee breakdown, and ownership structure.
Template 4: Research Proposal Steps PowerPoint Template

If you are looking to learn how to draft a research proposal, this slide is the ultimate fit for a newbie to comprehend about - 'what', 'where', and 'how' of research. Download this slide to learn about the format and structure of the research proposal. Use this template to illustrate the goal of the research proposal. Furthermore, our PPT sample file aids in instructing students on how to write a research proposal. Furthermore, you may quickly persuade the audience about the proposal's limitations, objectives, and research gap.
Template 5: Research Proposal for Thesis Template

Provide a clear idea and concise summary of your research with the help of this premium template. A well-written thesis statement frequently paves the way for discussion and debate. It can be the foundation for academic dialogue, enabling others to interact with and challenge your ideas—essential for developing knowledge across all disciplines. Your thesis statement will determine the depth of your study and conclusion while enabling you to attract your targeted audience.
Template 6: Market Research PowerPoint Template

To understand the trends and techniques of market structure, companies need to be aware of the trends and to enable that, and market research is one such profitable asset to invest in to allow numerous investments from companies across. Use this template to highlight the key drivers of growth that define the ultimate indicators of market trends. Use this PPT slide to solve marketing issues and make company decisions, incorporating polished business analysis PPT visuals. Get this template to connect business operations with your company's strategic goals.
Template 7: Establish Research Objective Template

For an effective and meaningful research, clarity is essential. Deploy this template to facilitate that research objectives should specify the precise goals and targets of the study to assist in limiting its scope. To ensure the study's readability and comprehensibility, SlideTeam has crafted a flowchart template design to help you elucidate the study's objective, providing a basis for measuring and evaluating the success of well-defined research. Define and design your research with the help of this four-stage design pattern.
Template 8: A Company Research Venn Chart Presentation
Establish relationships between the sets and groups of data while comparing and contrasting the company's research analysis. This template is helpful as it helps to understand the abstract, objectives, limitations, methodologies, research gap, etc., of the research effectively while focusing on postulating future recommendations and suggestions.
Template 9: Sample Research Paper Outline in a One-Pager Summary Presentation

How effortless it is to study a research paper without turning several pages? Grab this PPT template to research any topic and jot down your findings in a simple and concise format. Most importantly, a significant amount of their precious time can now be dedicated to critical tasks, aiding them in accelerating the research process. This incredibly well-curated one-pager template includes information about the introduction, problem, literature review, suggestions, and conclusions.
Template 10: Big Data Analytics Market Research Template
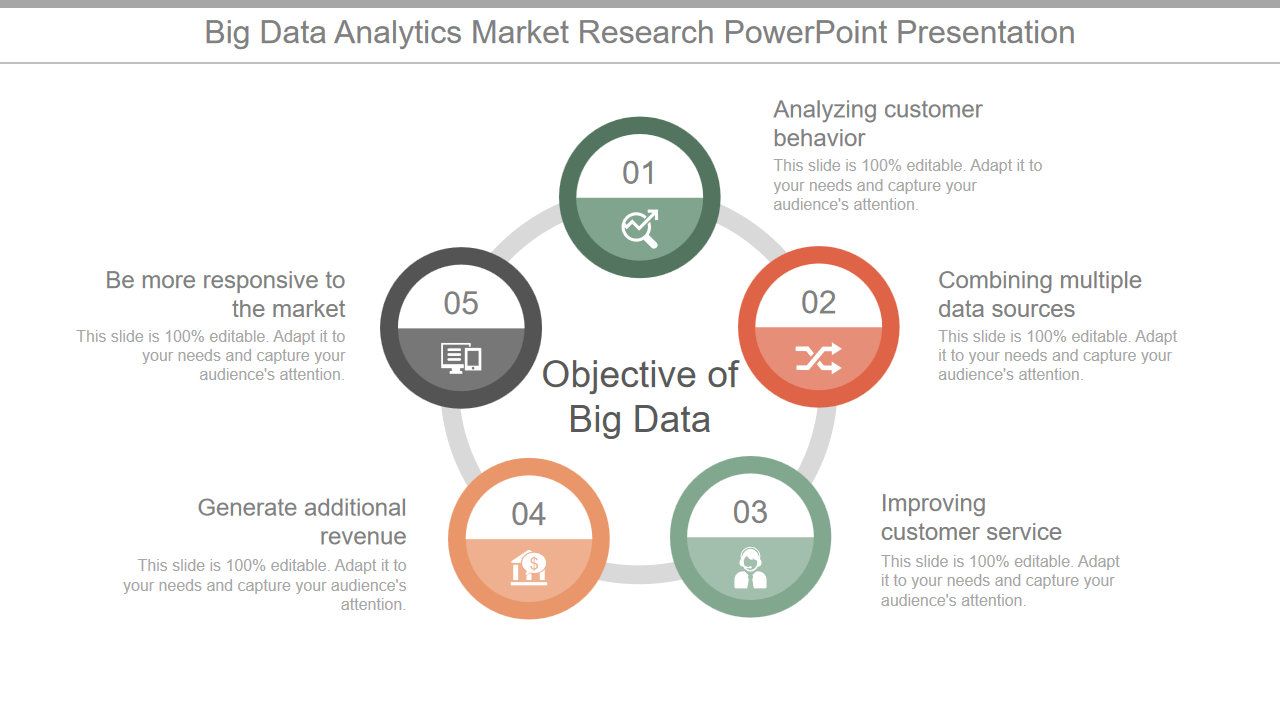
Deploy this template to introduce your company's extensive data analysis to understand the industry landscape, identify objectives, and make informed business decisions. Use this template slide to determine the current market size and growth rate. Consider the variables influencing this expansion, such as the rising volume of data produced and the demand for data-driven insights. Give information about the big data analysis market's prospects for the future. Over the coming few years, forecast growth trajectories, rising technologies, and market dynamics. Recognize the intended client base's demographics. Summarize your research and include suggestions for companies wishing to enter or grow in the big data analysis market.
PS: Provide an extensive statistical analysis for your research with this template. Check out now!
Refine your Research with SlideTeam.
SlideTeam introduces to its extensively built research templates that not only refines your search capability but also contributes towards the authenticity and development of your organization. It helps you to uncover veils of possibilities of growth while determining the bottlenecks and deriving appropriate solutions for future deliverables.
One of the attractive features about SlideTeam’s template are they are 100% customisable and editable as per the needs.
Download now!
PS: Provide an extensive statistical analysis for your research with this template . Check out now!
FAQs on Research Presentation
What is a research presentation.
Research Presentation is a visual representation of an individual or a team's observational findings or invocation in a particular subject.
What are the steps in research presentation?
To effectively convey your research findings to your audience, various phases are involved in creating a research presentation. Whether you're giving a presentation at a conference or a business meeting,
- Define your audience - Identify your audience's interests and level of knowledge. Make sure to adjust your presentation to fit their wants and needs.
- Outline What You Present - Create a clear structure with an introduction, three main ideas, and a conclusion. Choose the most essential points you want your audience to remember.
- Research and Data Collection - Gather and arrange the pertinent information, facts, and proof. Make sure your sources are reliable and current.
- Develop Visuals - To improve understanding, create visual aids like slides, charts, graphs, and photographs. Keep visuals straightforward, clutter-free, and with a distinct visual hierarchy.
- Get Your Audience Active - Take advantage of storytelling, anecdotes, or pertinent instances to draw in your audience. If appropriate, encourage audience participation and questions during the lecture.
- Present your argument - Start with a compelling introduction. Follow your outline while ensuring a logical and obvious flow.
- Keep an open line of communication, communicate clearly, and change your tone and pace. Improve your communication by making gestures and using body language. Respond to comments and questions as they come up or after the presentation.
- Recap and Draw a Conclusion - Summarize the core ideas and principal conclusions. Reiterate the importance of your study and its consequences.
How do you research a topic for a presentation?
To begin with, the idea of research presentation, choosing topics that align with your expertise and knowledge is the first and foremost. After understanding the topic, collect core factual and empirical data for proper understanding. After gauging information, it creates a place for every subtopic that must be introduced.
Related posts:
- Must-have Business Analyst Resume Templates with Examples and Samples
- Top 10 Data Processing Templates with Samples and Examples
- Must-have Data Mapping Document Templates with Samples and Examples
- Must-have Power BI Templates with Samples and Examples
Liked this blog? Please recommend us

Top 10 Business Model Templates with Samples and Examples
Top 7 Introduction Templates with Samples and Examples
This form is protected by reCAPTCHA - the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

Digital revolution powerpoint presentation slides

Sales funnel results presentation layouts
3d men joinning circular jigsaw puzzles ppt graphics icons

Business Strategic Planning Template For Organizations Powerpoint Presentation Slides

Future plan powerpoint template slide

Project Management Team Powerpoint Presentation Slides

Brand marketing powerpoint presentation slides

Launching a new service powerpoint presentation with slides go to market

Agenda powerpoint slide show

Four key metrics donut chart with percentage

Engineering and technology ppt inspiration example introduction continuous process improvement

Meet our team representing in circular format

Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

REPORT WRITING PRSENTATION
Related Papers
Presentation of e
ANGEL KRIS CADENAS
VIDYA - A JOURNAL OF GUJARAT UNIVERSITY
Alpesh Prajapati
The paper is designed to acquaint the researchers about how to write a research report. The paper intends to discuss the common format of research report. There can be several reasons for writing a research report. It can be written for publishing in scholarly journals, peer-reviewed journals, publications and books. The paper will improve our understanding of writing a good academic research report with example of our research topics on various issues. The examples are based on our research on HIV positive people, adolescent health and infertility issues. The primary source of data collection for the paper is our field work.
IJAR Indexing
Nowadays many University students in Tanzania are facing challenges in writing their research reports, be it in government or private Universities. Specifically, students encounter problems in writing and formulating background of the study, statement of the problem, study objectives, literature review and research methodology. Their failure in these preceding chapters, leads to failure in data analysis and presentation, hence shortfalls in discussion and conclusion chapters. Methodologically, the article reviewed some scholarly studies conducted in Tanzania to substantiate the problem and indicate examples on how best the research reports can be written. Apart from narrations given, the article indicates examples with the aim of helping both junior and senior researchers to organize well their research reports in a manner of aligning ideas and chapters within the report. The article will as well help both undergraduate and postgraduate students whose programmes require researches in fulfillment of the requirement, for the award of their particular degrees.
Kylie Dixon
Michael Evans
Richard Baskas, Ed.D. Candidate
dominic omondi
Introduction This report provides an in-depth analysis of the specific area of research that I intend to conduct. The report will clearly state the key research question that I have developedfor my study.It will be divided into two parts. The first section will succinctly describe how theresearch question for the research was developed. Here, the report will provide a detailed view of the entire process through which the research question has been derived, along with the tool that has been used for deriving the research question. In addition to this, this part of the report will also state how the research question aligns with my values. On the other hand, the second part of the report will provide a statement of the methodology that will be the best for the research. This objective will be realized through the provision of a detailed justification for the methodological selection of the study. The report will mention different methodological elements that the research will follow at the time of conducting the investigation with proper justification. It means this particular part will provide detailed information about the research design, research approach, data collection and data analysis techniques that will be used for the investigation.
British journal of community nursing
Keith Meadows
This last article of the series reviews some of the key issues that need to be considered when preparing your research findings for dissemination. Dissemination is an integral part of the research process and this article outlines some of the initial steps that need to be taken, including the establishment of agreements between authors. The importance of writing for a specific audience and how this determines the content of the report is then discussed. An overview together with guidelines on how to report qualitative and quantitative research is presented. General guidance on the choice of title, writing an abstract, listing references and acknowledgements are discussed. The article concludes with an outline of some of the key criteria editors use when reviewing a paper for publication.
mohan dissanayaka
RELATED PAPERS
Rhomeo Porto
santi susanti
Amir Hidayatullah
Journal of Abnormal Psychology
Carolyn Cutrona
Dinda Galannam
Journal of Biological Chemistry
Anthony Reginato
Applied Mathematics and Computation
Journal of South American Earth Sciences
Carlos Augusto Sommer
Journal of King Saud University - Science
Maria Helena Florencio
Remote Sensing
Tiejun Wang
Muhammad Razzaq
Journal of Cell Science
Research Square (Research Square)
Paloma Gil-Olarte
USYD研究生文凭 USYD毕业证悉尼大学
Nermin Yusuf
Francisca Daussy
SAGA: Journal of English Language Teaching and Applied Linguistics
Andreas Winardi
Acta Mechanica Slovaca
Janusz Sikora
Parasitology Research
Maxime Madder
Zenodo (CERN European Organization for Nuclear Research)
Lala Akhundova
Journal of Affective Disorders
Gabriella Palumbo
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024

Research Methodology
Aug 20, 2014
2.77k likes | 6.36k Views
Research Methodology. Introduction to Research Methodology. Stages of Research Project. Chapter 1: Introduction Chapter 2: Literature Review Chapter 3: Methodology Chapter 4: Data Analysis and Interpretation of Findings Chapter 5: Discussion and conclusion. Why do we research?.
Share Presentation
- highest contributor
- human resource managers
- data collection
- better employees job satisfaction
- direct relationship
- adequate solutions

Presentation Transcript
Research Methodology Introduction to Research Methodology
Stages of Research Project • Chapter 1: Introduction • Chapter 2: Literature Review • Chapter 3: Methodology • Chapter 4: Data Analysis and Interpretation of Findings • Chapter 5: Discussion and conclusion
Why do we research? • To acquire information/knowledge • Research – a particular way of knowing • Emphasis on systematic investigation • Scientific method- collecting observations in a systematic and objective manner • Identify problem • Generate Objectives/hypotheses/RQ • Collect data • Determine whether or not the hypotheses are supported. • Researches that use non-scientific method • Historical, etnography
Types of researches (by purpose) • Basic research (Fundamental Research) • Concerned with fundamental and theoretical questions. • A foundation upon which others can develop applications and solutions • while basic research may not appear to be helpful in the real world, it can direct us toward practical applications in the long run. • E.g. A study on job rotation impact (positive and negative impact) on employees.
Applied research • concerned with finding solutions to practical problems and putting these solutions to work in order to help others • E.g. Action Research on Best Job Rotation practices for Academic Institution
Chap.1: Introduction • Research Introduction and background • Problem statement • Objectives (main & specific objective) • Hypotheses or research questions • Theoretical/conceptual framework (quantitative only) • Variables definition (quantitative only) • Definition of terms (include operational definition) • Contribution/Significance/important of research • Limitation of research
Choosing a research topic • 2 things to be considered • Level of interest • Topic of interest will motivate one to do research on it • Choosing the wrong topic – you might end up or fail to discover some interesting value. • Feasibility • Your capability to complete a research conducted – e.g. data collection and analysis, report writing • Always take a research as you want to unveil a mystery
Getting ideas for researchers • Yourself (observation on a particular phenomena/experiences) • Discussion with expert in the field • Journal articles • Academic books (based on research work) • Proceeding and conference papers • Thesis, dissertation, final year project • Organizational Report (e.g statistic) • Others (Internet, Newspapers/magazines
Preparing a Problem Statement • A problem statement is a clear concise description of the issues (or problems) that need to be addressed by a researcher. • The primary purpose of a problem statement is to focus the attention of the researcher. • A research-worthy problem statement is the description of an active challenge (i.e. problem) faced by a researcher that does not have adequate solutions or theoretical foundation. • Should briefly address the question: What is the problem that the research will address?
More… • Define a problem or a gap that need to be researched to find a solution • Justify the need for a research • These gaps are discovered through journal articles (refer to limitations or suggestions in journal articles) • Sometimes a problem is discovered through: • personal experience of a researcher or a research sponsor • phenomena that happens around us.
Example of a problem statement • No known study that has looked into this specific topic. - exploratory research • There are only few studies that address this issue but most of the studies were done in Western countries especially in the United States(Mueller, 1998; Adruce, 2002; Adam, 2008) – Confirmatory research • There are several research works in this specific area but the findings are not consistent. Therefore, there is a need to do further research in this area – Confirmatory research
Continue … • There are several research works that have looked into a direct relationship between smoking habit and cancer; however, no known research has specifically looked into a mediator/moderator effect of a third variable (types of food consumed) • This incident (eg. Tsunami) has never happened in Malaysia, therefore, there is a need to study the post Tsunami effects in the affected region of Malaysia. • Most of the previous research in this area were done using qualitative method; therefore, there is a need to use quantitative/experimental method to test the preposition/ hypothesis.
Continue • Most of the previous research in this area were done using quantitative method; therefore, there is a need to use qualitative/experimental method to validate the findings.
How to prepare the Objective for the study • Based on the Problem Statement mentioned earlier • It is a statement that explains what the study will focus on • There are two types of objective • Main (This study is interested in studying the employees behavior related to job rotation amongst support staff) • Specific (to study the relation ship between job rotation and job satisfaction)
Hypothesis or research question • The purpose is to refine the objective of the study and make it easier to understand what we want to study • When to use Hypothesis or research question • Phenomena has been studied before and to test the findings we use hypotheses testing (e.g There is a relationship between job rotation and job satisfaction) • If no known study has been done in that specific area we should use research question instead (e.g Is there any relationship between job rotation and job satisfaction? • When can we use hypothesis even if there is no know research done in a specific area? • Experimental research
Theoretical/conceptual framework • Only to be used in quantitative study. • There is no need for theoretical/conceptual framework in a Qualitative study
Employees Satisfaction Based on Maslow Hierarchy of Needs Thory Basic Needs (Salary, Benefits) Job Satisfaction Job Security Peer Support
Hypothesis • There is a relationship between Basic Needs and Employees Job Satisfaction • Better Job Security will result in Better Employees Job Satisfaction • There is a relationship between work environment and employees job Satisfaction • RQ if there is no hypothesis • Which of the above factors rank the highest contributor to job satisfaction?
Successful Organization Based on Systems Theory Employees Performance External Environment Management Capability Organization Performance Services Provided
Definition of Terms used in your study • Dictionary definition • Defined by dictionary • Operational definition • An operational definition defines something (e.g. a variable, term, or object) in terms of the specific process or set of validation tests used to determine its presence and quantity.
Continue… • Theoretical Definition • A theoretical definition relies on the acceptance of theories and so it does not simply reduce to a set of observationsLike the theories that build them, theoretical definitions also improve as scientific understanding grows
Research Contribution • Contributions • theory/concept/model/hypothesis/proposition or knowledge in the field • Methodology • Research Framework (statement of problem, objective, hypothesis, research question) • Instrument (questionnaire, interview guide, observation guide etc.) • Data Collected • Data Analysis Framework • Practitioner and community
Contribution toward theory and knowledge • This study is expected to contribute toward a theory (e.g. diffusion of innovation) related to the use of technology in organization because findings from previous studies implicate lack of consistencies either in supporting or refuting the theory. • Use of ICT in organization is a developing area and not many studies have really studied Malaysian organizations pertaining to their employees usage of ICT
Contribution toward Methodology • Since not many research were done in this area before, the Research Framework (statement of problem, objective, Hypothesis and Research Questions) use in this study could be use by future researcher who wanted to replicate this study. • The Instrument (questionnaire, interview guide, observation guide etc.) used in this research could be used for future research in the same area.
Contribution toward Practitioner and community • Findings from this research especially on the office and environmental factors that ensure success in job rotation should be a good guide to Human Resource Managers. • Finding from this research should also inform the community of employees in the organization on the important of office and environmental factors to ensure success in job rotation practices.
Limitation of the Study • Topical/subject/field limitation (limited to study of HRD and not on Psychology or management aspect of human resource) • Methodological limitation (Data collection method) • Population and Sample • Time Frame • Area/place of research • Resources Limitation (for example Literature Review is limited to Emerald online database)
Chap. 2:Literature Review • Gather all related and relevant findings from previous studies. • Introduction to the Chapter • Discussion on Theories, models, concepts and philosophy related to the research • Discussion on previous studies related to the topics. Guided by the specific objectives in the study. • Summary of the chapter
What is a Lit Review • What it is not • Not an essay • Not just a mere summary or annotated bibliography or abstract • What it is • Reflection of previous studies • Improve understanding on topic of interest • Status of works done in similar area • Updating you on what have been done in the past
How to do a Literature Review • Locate all related Previous Works on same topic to update you on what have been done. • Highlight the status of Previous research and finding Gaps or opportunities (availability, strength, weaknesses) • Uncertainties and doubts in previous findings • Limitations of previous studies that need to be dealt with • Methodological limitation • Geographical location • Time factor
Chap. 3:Methodology • Research Framework (Qualitative, Quantitative or Experimental) • Place and time of study • Population under study • Unit of analysis • Sample/respondent/informant (qualitative) • Sampling method and sampling framework • Method of Data Collection • Survey using Questionnaire (quantitative) • Interview (qualitative) • Document Analysis • Observation Technique • Determining method of data collection for each objective/research question/hypothesis
Methodology… continue • Research Instrument • Pre-Test and pilot test (quantitative) • Validity and reliability issues • Equipments (video, audio recorder etc.) to be used during data collections • Consent Form • Research Schedules and Timelines
Research Framework • Quantitative (mostly using Deductive Reasoning) - Confirmatory • to research questions that are best answered by collecting and analyzing numerical data (using statistical) • Qualitative (mostly using inductive Reasoning) – Exploratory • Mixed Method – Qualitative and Quantitative • To research questions that are best answered by giving descriptions on how one understand and interpret various aspects in their surroundings • Experimental (mostly using Deductive Reasoning) – Looking at Cause & Effect
Place and Time of Study • To be determined – provide justification • Determined also time to conduct the study because both place and time could determine the outcome of the study
Population and Sample • Determine the population where the study will be conducted • Identify the unit of analysis (individual or group) • Determine the sampling method (simple random method, cluster, stratified, systematic, purposeful/convenient, snow balling etc.) to be used and design the sampling framework
Main types of research methodologies • Survey - Quantitative • Experimental – Quantitative, Qualitative • Correlation - Quantitative • Case study – Quantitative, Qualitative • Historical - Qualitative • Ethnography – Qualitative
Chap. 4 Data Analysis and Interpretation • Present your analysis of data – summarize the relevant findings that are crucial to your study.
Chap. 5 Discussion • Interpret your data to meaningful information that is understandable. • Discussion and comparison with previous studies (focusing on similarities or differences in term of result)
- More by User

RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY. (Business Research Methods). Week 3. Decision-Making. Decision-Making is the process of resolving a problem or choosing amongst alternative opportunities What is the problem or opportunity? How much Information is available? What Information is needed?. Absolute
728 views • 16 slides

RESEARCH METHODOLOGY. (Business Research Methods). Week 13. Editing and Coding Data. Editing is the process of checking data for errors such as omissions, illegibility and inconsistency, and correcting data where and when the need arises
1.03k views • 18 slides

RESEARCH METHODOLOGY. (Business Research Methods). Week 1. How This Course Will Be Conducted. Comprehensive introduction to Research Methodology (Business Research Methods) Knowledge acquisition and application of subject matter to real-life situations
1.17k views • 36 slides

Research Methodology. Basic Information. Research Methodology. Basic Information Your Instructors Program of the Lessons Goal of the Course Material Modalities of Examination. Your Instructor Fausto Giunchiglia (http://www.dit.unitn.it/~fausto). Program of the Lessons
866 views • 57 slides

Research Methodology. Lecture #3. Roadmap . Understand What is Research . Define Research Problem . How to solve it? Research methods Experiment Design . How to write and publish an IT paper?. How to solve the problem?. Understanding the problem
2.54k views • 66 slides

Research methodology
Research methodology. What is a resume??? "Resume CV" is a bit of a misnomer. A resume is a CV. They are two different expressions for the same thing. What is a CV?? CV stands for "Curriculum Vitae" which is Latin for "course of life" . The difference between them is:.
631 views • 44 slides

LITERATURE REVIEW. RESEARCH METHODOLOGY. PROFESSOR DR. MOHAMMAD ISMAIL UTM Construction Research Centre, Faculty of Civil Engineering UTM. CONTACT INFO. Room : C09–117-09 Tel : +60731757. Course Contents. Introduction Literature Review Research Design Result and Analysis
1.99k views • 46 slides

Research methodology. A plan and structure of the investigation in order to obtain evidence to answer the research questions. RM Involves a. choosing the subjects b. data collection techniques/tools c. procedures/steps for collecting data d. data analysis techniques/tools
2.11k views • 29 slides

Research Methodology. Group Members: April Tulloch Kerekia Walker Sashield Walker Daneik Wallace Juliann Wallace Nicole Wallace Lecturer: Dr. J. Lindo. PICO.
514 views • 24 slides

Research Methodology. Session 11 Research Design Sampling. Latest Schedule (1). Latest Schedule (2). Recap. Assignments Language feedback Language self-reflection Structural PS -> RO -> RQ Sub-problems => hypotheses / research questions Presentation Participation Feedback. Preview.
994 views • 25 slides

Research Methodology. SDLC MDLC Waterfall Model RAD. Introduction. A framework that describes the activities performed at each stage of a software development project.
1.29k views • 30 slides

Research Methodology*
Research Methodology*. Mian Ali Haider L.L.B., L.L.M ( Cum Laude) U.K. *(Contents of this PPT are not mine, infact, gathered from different electronic materials). What is Research ?.
1.36k views • 37 slides

Research Methodology. Aisha Hassan Abdalla Hashim (PhD) Professor Electrical & Computer Engineering Department Faculty of Engineering, IIUM. Report Writing. PROJECT II The Design Chapter The Evaluation chapter Evaluation Techniques Experimental Analytical Simulation
494 views • 3 slides

Research Methodology. Lecture No :24. Recap Lecture. In the last lecture we discussed about: Frequencies Bar charts and pie charts Histogram Stem and leaf display Pareto diagram Box plot SPSS cross tabulation. Lecture Objectives. Getting the feel for the data
459 views • 27 slides

CHP400: Community Health Program - lI. gy. What is Research ?. gy. Research Methodology. Mohamed M. B. Alnoor. Research Methodology. What is Research ?. gy. Content. Definition of Research. Steps in conducting Research. gy. Research Objectives. Hypotheses. Title of the study.
671 views • 16 slides

Research Methodology. EPH 7112 LECTURE 8: VALIDATION. Contents. Validation Compute Performance Draw Conclusions Peer Review. Scientific Method. Objectives. Objective of Validation phase is To decide whether the objective of the task has been achieved Based on formal conclusions
735 views • 9 slides
Research Methodology. Research Traditions What is research? Research is “the systematic approach to finding answers to questions.” “Questions” comes first – questions drive inquiry; questions will inform the kind of research we do. Quantitative and Qualitative research traditions
1.4k views • 41 slides

Research Methodology. Definition: Business Research. Systematic and Scientific inquiry aimed at providing information to solve managerial problems. Basic (Fundamental) Research. Generalization of natural phenomenon or human behavior
2.07k views • 83 slides

Research Methodology. 尚惠芳 教授兼系主任 義守大學應用英語學系. 98 學年度第一學期. 1. Outline. Qualitative vs. Quantitative Research Literature Review and Research Problems Survey Research Qualitative Methods Mixed-Methods and Mixed-Model Designs Sampling Data Collection
1.88k views • 144 slides

RESEARCH METHODOLOGY. Sampling. Introduction. Our Knowledge, Attitudes and Actions are based to a large extent on samples. This is equally true in every day life and scientific research. Introduction (Cont’d).
987 views • 38 slides

904 views • 37 slides

755 views • 37 slides

- My presentations
Auth with social network:
Download presentation
We think you have liked this presentation. If you wish to download it, please recommend it to your friends in any social system. Share buttons are a little bit lower. Thank you!
Presentation is loading. Please wait.
Lecture Notes on Research Methodology
Published by Eileen Garrison Modified over 6 years ago
Similar presentations
Presentation on theme: "Lecture Notes on Research Methodology"— Presentation transcript:

Introduction to Research Methodology

Sabine Mendes Lima Moura Issues in Research Methodology PUC – November 2014.

Today Concepts underlying inferential statistics

Richard M. Jacobs, OSA, Ph.D.

Research Methodology Lecture 1.

Chapter 12 Inferential Statistics Gay, Mills, and Airasian

Sample Design.

Copyright © 2008 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey All rights reserved. John W. Creswell Educational Research: Planning,

Magister of Electrical Engineering Udayana University September 2011

Chapter 1: Introduction to Statistics

RESEARCH A systematic quest for undiscovered truth A way of thinking

Research Methodology.

Educational Research: Competencies for Analysis and Application, 9 th edition. Gay, Mills, & Airasian © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.

Research Seminars in IT in Education (MIT6003) Quantitative Educational Research Design 2 Dr Jacky Pow.

PROCESSING OF DATA The collected data in research is processed and analyzed to come to some conclusions or to verify the hypothesis made. Processing of.

Academic Research Academic Research Dr Kishor Bhanushali M

Question paper 1997.

Chapter 6: Analyzing and Interpreting Quantitative Data

Module III Multivariate Analysis Techniques- Framework, Factor Analysis, Cluster Analysis and Conjoint Analysis Research Report.
Chapter 7 Measuring of data Reliability of measuring instruments The reliability* of instrument is the consistency with which it measures the target attribute.
About project
© 2024 SlidePlayer.com Inc. All rights reserved.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A research paper/report is a systematic write up on the findings of the study including methodologies, discussion, conclusions etc. following a definite style. 6. Purpose research report Present the results of a research. Allow research results to invariably enter the general store of knowledge. Provide a persuasive argument to readers of what ...
This ppt contains Types of Research Report Writing in which a technical report, a popular report, an article, a monograph or at times even in the form of Oral presentation. Difference between Oral & Written Report Types of Research Report Writing
Use the section headings (outlined above) to assist with your rough plan. Write a thesis statement that clarifies the overall purpose of your report. Jot down anything you already know about the topic in the relevant sections. 3 Do the Research. Steps 1 and 2 will guide your research for this report.
Turning a research paper into a visual presentation is difficult; there are pitfalls, and navigating the path to a brief, informative presentation takes time and practice. As a TA for GEO/WRI 201: Methods in Data Analysis & Scientific Writing this past fall, I saw how this process works from an instructor's standpoint.
Writing a Research Report: Presentation. Tables, Diagrams, Photos, and Maps. - Use when relevant and refer to them in the text. - Redraw diagrams rather than copying them directly. - Place at appropriate points in the text. - Select the most appropriate device. - List in contents at beginning of the report.
DeCarlo and his team developed a complete package of materials that includes a textbook, ancillary materials, and a student workbook as part of a VIVA Open Course Grant. The PowerPoint slides associated with the twelve lessons of the course, SOWK 621.01: Research I: Basic Research Methodology, as previously taught by Dr. Matthew DeCarlo at ...
The anatomy of a research report I use a slide deck to create a 'Slidedoc' . Tools like Keynote, Google slides, Pitch, or PowerPoint make it easy to combine detailed text and visuals in the ...
Writing a Research Report • A research report has seven components: • 1. Abstract or Summary—an example. Writing a Research Report • A research report has seven components: • Introduction • The introduction tells the reader: • what the topic of the paper is in general terms, • why the topic is important • what to expect in the ...
Thesis. Thesis is a type of research report. A thesis is a long-form research document that presents the findings and conclusions of an original research study conducted by a student as part of a graduate or postgraduate program. It is typically written by a student pursuing a higher degree, such as a Master's or Doctoral degree, although it ...
Step 4. Put content on slides: Follow the outline above to structure your presentation effectively; include key sections and topics. Organize your content logically, following the flow of your research paper. Step 5. Final check: Proofread your slides for typos, errors, and inconsistencies.
1. Your outline should be written before you start your paper and after you finish researching. It organizes your thoughts and creates a plan so you know how your paper will look. 2. Your introduction or thesis statement tells the audience what you will explain in your paper. It will let the audience know what to expect from reading your paper. 3.
Presentation Transcript. Components of the Research Report Session 4 C507 Scientific Writing. Research Report • Also called an original data report • Most frequent type of scientific paper. The Conventional Format • Readers expect to read about your research in the sequence in which the research developed: • What question you set out to ...
Template 10: Big Data Analytics Market Research Template. Deploy this template to introduce your company's extensive data analysis to understand the industry landscape, identify objectives, and make informed business decisions. Use this template slide to determine the current market size and growth rate.
The paper intends to discuss the common format of research report. There can be several reasons for writing a research report. It can be written for publishing in scholarly journals, peer-reviewed journals, publications and books. The paper will improve our understanding of writing a good academic research report with example of our research ...
Tips for research paper presentation in national conferences and international conferences with sample ppt examples. For Business Enquiries: https://bit.ly/3...
Research Methodology. Introduction to Research Methodology. Stages of Research Project. Chapter 1: Introduction Chapter 2: Literature Review Chapter 3: Methodology Chapter 4: Data Analysis and Interpretation of Findings Chapter 5: Discussion and conclusion. Why do we research?. Download Presentation. highest contributor. human resource managers.
New York: Prentice-Hall, 1960. Download ppt "Lecture Notes on Research Methodology". 1 Research Methodology: An Introduction: MEANING OF RESEARCH: Research in common parlance refers to a search for knowledge. Once can also define research as a scientific & systematic search for pertinent information on a specific topic.
Research Report Presentation. Number of slides: 10. Signup Free to download. Research provides valuable data and in-depth information to make the best decisions. Perhaps the sales manager wants to know what people think about the new product features or the marketing department needs to understand more about the market to craft better messages.
New research into B2B content marketing trends for 2024 reveals specifics of AI implementation, social media use, and budget forecasts, plus content success factors. ... Another 57% report moderate success and 15% feel minimally or not at all successful. ... The online survey was emailed to a sample of marketers using lists from CMI and ...