
Presentations made painless
- Get Premium

107 Video Game Essay Topic Ideas & Examples
Inside This Article
Video games have become a popular form of entertainment for people of all ages. From action-packed shooters to immersive role-playing games, there is a video game out there for everyone. With such a wide variety of games to choose from, it can be overwhelming to decide on a topic for an essay about video games. To help you get started, here are 107 video game essay topic ideas and examples to inspire your writing:
- The impact of violent video games on children's behavior
- The evolution of video game graphics over the years
- The rise of esports and its influence on the gaming industry
- The benefits of playing video games for cognitive development
- The representation of gender and race in video games
- The history of virtual reality gaming
- The psychology of loot boxes in video games
- The role of music in enhancing the gaming experience
- The ethics of video game journalism
- The impact of video game addiction on mental health
- The cultural significance of video game franchises like Mario and Pokemon
- The future of cloud gaming and streaming services
- The role of storytelling in video games
- The influence of video games on popular culture
- The relationship between video games and education
- The impact of video game censorship on creative expression
- The portrayal of mental health issues in video games
- The role of social media in video game marketing
- The history of video game consoles
- The impact of online multiplayer games on social interaction
- The evolution of game mechanics in the survival horror genre
- The representation of LGBTQ+ characters in video games
- The influence of Japanese culture on video game aesthetics
- The role of nostalgia in the popularity of retro gaming
- The impact of microtransactions on player experience
- The relationship between video games and violence in society
- The role of artificial intelligence in game development
- The impact of video game streaming platforms like Twitch
- The representation of disability in video games
- The influence of game design on player engagement
- The evolution of mobile gaming
- The role of virtual economies in online multiplayer games
- The impact of video game sound design on immersion
- The portrayal of mental illness in video games
- The influence of Eastern philosophy on game narratives
- The role of user-generated content in game communities
- The impact of fan culture on video game development
- The representation of indigenous cultures in video games
- The influence of literature on game storytelling
- The role of game difficulty in player satisfaction
- The impact of video game piracy on the industry
- The portrayal of war in military shooter games
- The relationship between video games and sports
- The influence of board games on video game design
- The role of player choice in game narratives
- The impact of virtual reality on therapy and rehabilitation
- The representation of historical events in video games
- The influence of film on game aesthetics
- The role of gender stereotypes in video game marketing
- The impact of game mods on player creativity
- The portrayal of mental health professionals in video games
- The influence of tabletop role-playing games on video game mechanics
- The role of game mechanics in promoting teamwork and cooperation
- The impact of game development crunch on industry workers
- The representation of animals in video games
- The influence of science fiction on game narratives
- The role of player agency in game storytelling
- The impact of game difficulty on player motivation
- The portrayal of addiction in video games
- The influence of mythology on game aesthetics
- The role of puzzles in game design
- The impact of game reviews on player purchasing decisions
- The representation of mental illness in horror games
- The influence of architecture on game environments
- The role of game soundtracks in enhancing the player experience
- The impact of game tutorials on player learning
- The portrayal of robots and AI in video games
- The influence of fashion on character design in games
- The role of humor in game narratives
- The impact of game localization on cultural representation
- The representation of environmental issues in video games
- The influence of psychology on game design
- The role of game narratives in exploring complex themes
- The impact of game communities on player engagement
- The portrayal of mental health struggles in indie games
- The influence of mythology on game storytelling
- The role of player feedback in game development
- The impact of game accessibility on player inclusivity
- The representation of gender identity in video games
- The influence of surrealism on game aesthetics
- The role of morality systems in game narratives
- The impact of game tutorials on player retention
- The portrayal of mental health professionals in horror games
- The influence of psychology on game narratives
- The role of player choice in shaping game outcomes
- The impact of game aesthetics on player immersion
- The representation of LGBTQ+ relationships in video games
- The role of environmental storytelling in game design
- The impact of game streaming on player engagement
- The portrayal of mental illness in puzzle games
- The role of player feedback in shaping game development
- The impact of game aesthetics on player perception
- The representation of LGBTQ+ characters in horror games
- The influence of film noir on game narratives
- The role of environmental storytelling in shaping game worlds
- The impact of game tutorials on player skill progression
- The portrayal of mental illness in narrative-driven games
- The influence of science fiction on game aesthetics
- The role of player choice in determining game endings
- The impact of game aesthetics on player emotional response
- The representation of LGBTQ+ relationships in indie games
- The influence of literature on game design
- The role of environmental storytelling in immersive game worlds
- The impact of game streaming on player community building
- The portrayal of mental health struggles in interactive fiction games
Whether you are writing a research paper, a critical analysis, or a personal reflection on video games, these topics provide a diverse range of ideas to explore. From examining the psychological effects of gaming to analyzing the cultural significance of game narratives, there is no shortage of fascinating topics to delve into. So, pick a topic that interests you and start exploring the world of video games through the lens of your essay. Happy writing!
Want to create a presentation now?
Instantly Create A Deck
Let PitchGrade do this for me
Hassle Free
We will create your text and designs for you. Sit back and relax while we do the work.
Explore More Content
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Service
© 2023 Pitchgrade
Home — Essay Samples — Entertainment — Video Games — Video Games and Their Impact
Video Games and Their Impact
- Categories: Cognitive Development Video Games
About this sample

Words: 433 |
Published: Feb 12, 2024
Words: 433 | Page: 1 | 3 min read
References:
- Barr, Matthew. “Video Games Can Turn University Graduates into Better Employees.” The Guardian, Guardian News and Media, 2019.
- Etchells, Pete. “Five Damaging Myths about Video Games – Let’s Shoot ‘Em Up.” The Guardian, 2019.

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Prof Ernest (PhD)
Verified writer
- Expert in: Psychology Entertainment

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
2 pages / 789 words
5 pages / 2475 words
1 pages / 505 words
1 pages / 490 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Video Games
The commentary is a theoretical framework that builds on the concept that eSports should be considered a sport. The first part of the paper analyzes the definition of a sport and determines that competitive video games should [...]
Video games have often been criticized for promoting violence, addiction, and social isolation. However, Jane McGonigal, a game designer and author, presents a different perspective in her book "Reality is Broken: Why Games Make [...]
Blomberg, R. (2019). Video Games Can Never Be Sport. Huffpost. Retrieved from
Video games have become an integral part of modern society, with millions of people around the world playing games on various devices. From consoles to mobile phones, video games have become ubiquitous and enjoyed by individuals [...]
In the realm of online video games, narrative refers to the story and characters that drive the gameplay. It encompasses the plot, character development, and world-building elements that immerse players in the game's universe. [...]
Mobile gaming is quite popular and it started with the first ever mobile game Tetris, this game was launched on the Hagenuk MT – 2000 phone in 1994. Although this was the first ever game it wasn’t as popular as Snake, this was [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free

Essay on Importance of Games
Students are often asked to write an essay on Importance of Games in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on Importance of Games
Introduction.
Games are a crucial part of our lives. They instill values, promote health, and provide entertainment.
Health Benefits
Games improve our physical health. They promote strength, agility, and endurance, keeping us fit and active.
Developing Skills
They also develop our skills. Team games teach us cooperation, while strategy games improve our problem-solving abilities.
Social Interaction
Games encourage social interaction. They help us make friends and learn to work as a team.
In conclusion, games are essential for our overall development. They offer fun while teaching us valuable life skills.
Also check:
- Paragraph on Importance of Games
250 Words Essay on Importance of Games
The essence of games.
Games, both physical and digital, play a pivotal role in the holistic development of individuals. They serve as a powerful tool, fostering psychological growth, enhancing physical fitness, and nurturing social skills.
Psychological Development
Games stimulate cognitive abilities, promoting analytical thinking, decision-making, and problem-solving skills. For example, strategy-based games, such as chess or Risk, demand players to anticipate opponents’ moves and plan their own. This helps in improving critical thinking and strategic planning skills.
Physical Fitness
Physical games like football, basketball, or tennis, contribute significantly to maintaining health and fitness. They enhance stamina, agility, and coordination, and teach the importance of discipline and teamwork. In an era where sedentary lifestyle diseases are on the rise, games act as a countermeasure, promoting a healthy lifestyle.
Social Skills
Games are social constructs that encourage interaction and cooperation. They instill a sense of camaraderie, helping individuals to develop empathy, communication skills, and a spirit of healthy competition. Multiplayer games, for instance, require players to strategize and communicate effectively with their teammates.
In conclusion, games are not merely a source of entertainment but a medium that fosters physical, mental, and social development. They equip individuals with essential life skills, making them more resilient, adaptable, and capable of facing real-world challenges. Therefore, the importance of games should not be underestimated, and they should be integrated more into educational and professional environments.
500 Words Essay on Importance of Games
Games, in their many forms, have been a central part of human culture throughout history. They are a universal language that transcends age, culture, and geography, uniting people through shared experiences. The importance of games cannot be overstated, as they play a pivotal role in physical, mental, and social development. They are not just a source of fun and entertainment, but also a means of learning and personal growth.
Physical and Mental Health Benefits
Physically engaging games, such as sports, are a vital part of maintaining a healthy lifestyle. They promote physical fitness, improve coordination, and enhance motor skills. Participating in games can also help in managing weight, reducing the risk of obesity, and promoting cardiovascular health.
Moreover, games also have significant mental health benefits. They stimulate mental agility and improve cognitive functions. Complex board games, for instance, require strategic thinking, problem-solving, and decision-making skills. Video games, often criticized for promoting sedentary behavior, have been found to enhance spatial navigation, memory, and perception when played in moderation.
Social and Emotional Development
Games are also instrumental in social and emotional development. They foster a sense of community and teamwork, as players often need to collaborate to achieve a common goal. This interaction helps in developing communication skills, understanding social cues, and building empathy.
Additionally, games provide a safe space to experience and manage emotions. Winning and losing are part of every game, teaching players to handle success with humility and defeat with grace. This emotional resilience is a crucial life skill that extends beyond the game.
Educational Value
The educational value of games is often overlooked. They can be effective learning tools, promoting critical thinking, creativity, and innovation. Many educational institutions are incorporating game-based learning to make education more engaging and effective. Games have the potential to transform traditional learning methods, making them more interactive and enjoyable.
In conclusion, games are an integral part of human life. They are not just pastimes, but platforms for learning, growth, and development. They contribute to physical and mental health, foster social and emotional development, and have significant educational value. As society evolves, so do games, reflecting our changing interests, values, and technologies. The importance of games, therefore, lies not only in their inherent entertainment value but also in their ability to promote well-rounded development and foster a sense of community.
That’s it! I hope the essay helped you.
If you’re looking for more, here are essays on other interesting topics:
- Essay on Chess Game
- Essay on Importance of Outdoor Games
- Essay on My Favourite Game Kho Kho
Apart from these, you can look at all the essays by clicking here .
Happy studying!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- My Account Login
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Open access
- Published: 24 April 2020
The role of game genres and gamers’ communication networks in perceived learning
- Chang Won Jung ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-4376-2200 1
Palgrave Communications volume 6 , Article number: 69 ( 2020 ) Cite this article
11k Accesses
4 Citations
2 Altmetric
Metrics details
- Cultural and media studies
The present study examined the educational roles of games that were not designed for pedagogical purposes. With respect to the roles of gamers’ communication—communication networks, network diversity, and heterogenous discussion—three specific sub-objectives of the present work include: (1) to examine the extent to which games can be social learning environments, (2) to examine how gamers’ communication contributes to perceived learning, and (3) to evaluate the relationship between game genre’s unique characteristics and learning effects. This work statistically tested a series of research hypotheses using empirical data obtained from a national survey of Korean gamers ( N = 1392). The results from hierarchical multiple regression analysis indicate that game genres and gamers’ communicative networks were significant predictors of perceived game learning. Importantly, game genres that are considered by policymakers to be violent and addictive were found to contribute to learning. Additionally, gamers’ communication variables that are not closely related to education and politics significantly predicted their learning. Based on the results, this study suggests that game coplaying or gamers’ social networks should be considered important for socio-cultural learning. Moreover, the current study provides empirical evidence that exposure to diverse perspectives during game playing contributes significantly to not only tolerance and deliberative democracy but also the socio-political learning of gamers. In this regard, the present study expands the literature on pedagogy (learning effects), political communication (benefits of heterogeneous/deliberative discussions), and game studies (game addiction/gaming disorder). Thus, this study provides new insights for current research on the educational roles of games.
Similar content being viewed by others

Virtual tree, real impact: how simulated worlds associate with the perception of limited resources

The effects of children’s participation and co-creation in science

A bibliometric analysis of the use of the Gamification Octalysis Framework in training: evidence from Web of Science
Introduction.
There has been a significant body of research to suggest that playing games explicitly designed for educational purposes provides an alternative means of teaching (Ninaus et al., 2019 ). For example, a recent work by Chen et al. ( 2019 ) insisted that game-based negotiation learning can promote students’ goal setting. Game-based learning is characterised by balancing gaming play with subject matter or knowledge and the ability of student players to maintain the motivation of participants. It has been regarded as an educational tool of a learner-driven environment that can apply the principles or guidelines of game design to learning processes to enable student engagement in learning and their participation (Gaydos and Squire, 2012 ; Gee, 2003 ; Gee and Hayes, 2012 ; Jabbar and Felicia, 2015 ; Shapiro and Squire, 2011 ; Yeh and Lan, 2018 ).
Importantly, there is a potential to promote learning by playing games that are not designed for a pedagogical purpose. Stufft ( 2018 ) argued that the use of games that are not intrinsically designed to convey a specific concept may promote students’ engagement in an interest-driven pursuit of learning knowledge. It is noteworthy to state that past literature suggests a possible positive linkage of playing games and learning in political science through the formation of network ties (Pathak et al., 2008 ; Freeman, 2017 ). The main tenet behind the educational strategy is that playing games may act as a social simulator that helps people connect with each other ( building social capital ), share ideas, and teach each other ( collective intelligence ). Moreover, literature on political communication asserts that communication or discussion significantly contributes to increasing political knowledge (Jung et al., 2011 ; Loy et al., 2019 ). While intrinsically designed game-based learning has been well recognised to be beneficial to student learning, there is no empirical documentation for the extrinsic role of game playing in the promotion of learning, particularly in the field of socio-political issues.
The current study discusses (1) to what extent games can be a learning environment, (2) how gamers’ communication contributes to perceived learning of social issues, and (3) how game genre’s unique characteristics relate to learning effects. As the theoretical basis, this study applies the notion of gamification on perceived game learning as discussed in pedagogical studies on game playing (Nietfeld, 2020 ; Park et al., 2019 ). In addition, the present study suggests that gamers who play certain genres (e.g. role playing or augmented reality (AR) games involving multiple players and interaction among them) are more likely to form their communication networks and discuss various political issues with others through diverse channels, as well as participate in discourse more often than other players of other game genres.
According to the results of political communication studies, communication or discussion significantly contributes to increasing political knowledge (Bennett et al., 2011 ; Eveland et al., 2005 ; Eveland and Thomson, 2006 ; Eveland and Hively, 2009 ), and thus, gamers’ communication may also demonstrate learning effects. Additionally, to expand the literature on heterogeneous discussion (Mutz, 2006 ; Huckfeldt et al., 2004 ; Wojcieszak and Rojas, 2011 ; Kim and Hyun, 2017 ; Yoo and De Zuniga, 2019 ) and the deliberative aspect of gamers’ communication, this study explores the role played by heterogeneous discussion in learning. Taken together, this study analyses the effects of three aspects of gamers’ communication—communication networks, network diversity, and heterogeneous discussion—on learning of political issues. This work further validates the conceptual framework and tests a series of research hypotheses using empirical data obtained from a national survey of Korean gamers ( N = 1392).
Games as a tool for collective learning
What is the relationship between game genres and perceived learning via game playing.
Regarding the relationship between game playing and learning, or gaming as a learning tool, the literature on game learning (gamification) provides evidence of the learning effects of game playing. Moreover, as a social consequence of game playing, Squire ( 2010 ) suggested that ‘prolonged participation in game cultures may lead to a more active, problem-solving orientation to learning’ (p. 2572) along with increased confidence in one’s ability to foster feelings of concern. Furthermore, participation in gaming also catalyses collaborative decision-making in gamers, as reported by Beck and Wade ( 2004 ). Moreover, Halverson ( 2012 ) introduced the notion of participatory media spaces in which participants learn by performing, and proposed that such spaces serve as environments in which people can express ideas. Halverson ( 2012 ) analysed the art-creation space, whereas this study argues that gaming can be considered to provide participatory media spaces that promote teamwork and continuous interaction between players of different ages, social statuses, and other characteristics.
Kahne et al. ( 2013 ) found that online participatory activities for youth, including gaming, are increasing and creating communities, and that such activities promote understanding of the norms of membership and potentially foster collective activities. In addition, Thomas and Brown ( 2011 ) stated that ‘gam[ing] does not just teach programming; it cultivates citizenship’ (p. 22), and examined the collective nature of the game environment as a collection of people, skills, and talents. This collectivity is characterised by an active engagement in the process of learning or designing, with the aim of mutual learning.
With culture defined as a ‘system of meaning that is shared by a social group’ (Goncu and Katsarou, 2000 , p. 223), Boellstorff ( 2008 ) indicated that language and other semiotic mediation in an online space serve as cultural tools that crystallise learning and development. Participating in online spaces also engages people in socialisation (Martin and Steinkuehler, 2010 ; Steinkuehler et al., 2012 ). Using this logic, people who play games acquire not only the knowledge and information required for a game, but also the behaviour patterns and communication tools that help them interact with other gamers in the community. Thus, gamers in the collective environment view each other as resources and engage in peer-to-peer learning with all members considered to be at equal positions within the community.
In fact, gamers can learn about political systems, citizenships, and real-life relationships not only by playing games that are specifically designed for this purpose as the pedagogical objective, but also by playing massively multiplayer online games (MMOGs) (Williams et al., 2006 ; Martin and Steinkuehler, 2010 ); this is because participation in gaming creates a unique culture in which the members rely on each other for completing various tasks. Williams and his colleagues ( 2006 ) analysed the guilds in World of Warcraft and found out that ‘as guild size increased, guilds were also more likely to engage in more formal management and organisational practices’ (p. 346), similar to real-life structures and organisations—such as political systems, hierarchies and power structures; this may be because these structures reflect not only the social constructs of organisation, but also natural human tendencies (i.e. instincts) in forming organisations. Due to these complex and formal structures in games, gamers experience opportunities for socialisation while interacting with other gamers. Moreover, by their nature, MMOGs are socially constructed worlds in which meanings are collaboratively achieved (Martin and Steinkuehler, 2010 ). While playing games, gamers share a social context, acquire opportunities for learning how to socialise with other gamers, and build a community aimed at learning.
The current study examined six game genres: role playing games (including massively multiplayer online role-playing games ([MMOGs]), multiplayer online battle arena ([MOBA]) (including Aeon of Strife), action/first person shooter (FPS)/third person shooter (TPS) (e.g. Grand Theft Auto, Overwatch, Sudden Attack, Call of Duty), strategy games, AR games (e.g. Pokémon GO), social network games and puzzles, and web board games ([SPW]) (Schroeder Publishing and Wargames). For each game genre, the top 10 games were listed based on their sales and subscriptions.
Based on the characteristics of the game genre, this study proposes the following hypotheses regarding the relationship between a specific game genre and perceived learning via gaming. As previous studies only examined the learning effects of collective-oriented game genres (role playing, MOBA, and AR games) the current study hypothesises the following relationships (see Fig. 1 ):
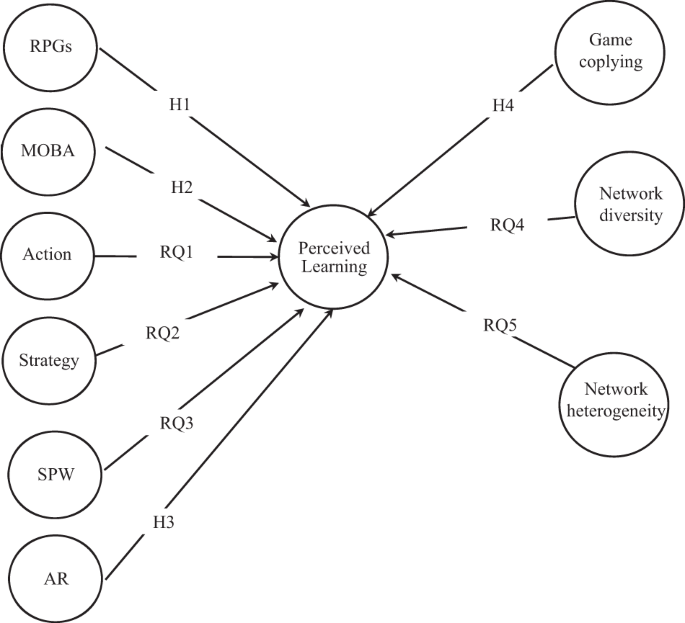
Conceptual model of game genre, game copying, network diversity and network heterogeneity predicting the effect of perceived learning by playing games.
H1: Playing role playing games is positively related to perceived learning via playing games .
H2: Playing MOBA games is positively related to perceived learning via playing games .
H3: Playing AR games is positively related to perceived learning via playing games .
Because the relationships between action genre, strategy, and social network games and puzzles, and web board games ([SPW]) and learning have not been examined in previous studies, the current study examines the above associations as the research objective.
RQ1: What is the relationship between playing action games and perceived learning?
RQ2: What is the relationship between playing strategy games and perceived learning?
RQ3: What is the relationship between social network games and puzzles, and web board games ([SPW]) and perceived learning?
Gamers’ communication
What is the relationship between gamers’ communication and perceived learning via game playing.
According to Squire ( 2010 ), gamers’ communities function as spaces for communication, which creates a learning culture for gamers. As discussed above, the collective or participatory aspects of game playing or gaming culture plays a crucial role in learning, more specifically, this study argues that communication/discussion among members has an important role in the process of learning by playing games.
Political communication studies discussed the role of communication or discussion in acquiring knowledge (Eveland et al., 2005 ; Eveland and Thomson, 2006 ; Eveland and Hively, 2009 ). These studies found that individuals who engage in discussions with others are more likely to acquire knowledge, which ultimately contributes to political participation. Although these studies analysed the political aspects of communication/discussion and their role in gaining political knowledge or participatory behaviour, the current study attempts to expand the relationship between communication and learning; gamers’ discussion that is not thoroughly related to politics may significantly connect knowledge/learning.
Game coplaying
Apart from communication, it is also important to examine the role of communication partner/encounters. This study explores the gamers’ communication networks and sources of interactions between guild members or game friends (game co-players/ coplaying ). According to Yee ( 2006 ), gamer interactions are closely related to the major motivation of achievement in game playing. In other words, the social nature of engaging in the gaming culture contributes to acquiring game friendships and discussions, among others. Thus, this study argues that communication among game members through various channels of communication may contribute to building communities based on collective intelligence, and this communication is positively related to learning. Based on the previous literature, this study offers the following fourth hypothesis:
H4: Game coplaying is positively related to perceived learning via game playing .
Network diversity and heterogeneous discussion
With the large number of social networking services (SNS) available today, members of online social networks have more communication networks as well as opportunities to encounter diverse opinions that differ from their own. In social networks, likes talk to likes, ultimately leading to polarisation resulting from the reinforcement of existing views (Mutz, 2006 ). As such, people tend to converse with others whom they share close connections with than those who are only acquaintances, and are less likely to discuss opposing views. Moreover, according to Mutz ( 2006 ), a large network size does not guarantee diversity; people are less likely to engage in cross-cutting or heterogeneous discussions, which results in highly partisan communication while isolating individuals and significantly increasing the potential for segregation and polarisation (Sunstein, 2001 , 2002 ).
However, this study argues that democratic citizenship requires tolerance and understanding of others’ viewpoints (Bohman, 2003 ). Mutz ( 2006 ) suggested heterogeneous discussion as a potential solution for such segregation or polarisation. Furthermore, as a positive impact of heterogeneous discussion, Mutz ( 2006 ) found that individuals with heterogeneous discussions were aware of both the rationales for oppositional opinions and those for their own viewpoints, while demonstrating tolerance. Thus, investigating the role of heterogeneous networks in political discussions has important implications for deliberation and democratic citizenship. To expand the literature on game studies and the role of heterogeneous discussion among gamers on learning, this study raises empirical questions regarding whether the deliberative interactions (heterogeneous discussion) among discussion networks affect the perceived learning of gamers.
As no previous study has discussed the relationship between gamers’ communication networks and perceived learning via game playing, the current study offers the following research questions:
RQ4: What is the relationship between network diversity and perceived learning?
RQ5: What is the relationship between network heterogeneity and perceived learning?
The present study was conducted in compliance with the ethical guidelines of the author’s university institutional review board. All participants provided written informed consent prior to the online survey.
To test the perceived learning effects of game playing, an online survey was administered to Korean adults between October 26 and November 2, 2016. The study participants were selected randomly to receive the survey URL in an online invitation. Among the 2162 responses received, 403 were removed due to short response time, quitting midway, or insincere answers. The response rate was determined to be 30% by the AAPOR method version 4.0 (web). As the main study subjects, the current study focuses on gamers ( N = 1362) who play games at present.
Participants
A total of 1362 adult Korea gamers (male = 768, female = 594, age range = 20–59) were selected. The participants provided information regarding their highest educational levels (1 = Elementary school; 2 = Middle school; 3 = High sschool; 4 = University; 5 = Graduate: M = 3.88; SD = 3.88), household annual incomes (1 = <10,000,000 won [~$8900]; 2 = 10,000,000–20,000,000 won; 3 = 20,000,000—40,000,000 won; 4 = 40,000,000–60,000,000 won; 5 = 60,000,000–80,000,000 won; 6 = 80,000,000–100,000,000 won; 7 = More than 100,000,000 won; M = 3.22; SD = 3.22). The average time spent playing games by participants was between 2 and 3 h a day (0 = I do not play games; 1 = <1 h; 2 = between 1 and 2 h; 3 = between 2 and 3 h; 4 = more than 3 h; M = 2.96; SD = 0.96).
Measurement
Data for the RPG genre (e.g. Lineage, World of Warcraft, Maple Story) were obtained by a single item regarding the frequency of game play, ranging from 0 = never to 5 = very frequently ( M = 1.64, SD = 1.67). Data for the MOBA game genre (e.g. League of Legends, Heroes of the Storm) were obtained by a single item regarding the frequency of game play (0 = never to 5 = very frequently; M = 1.14, SD = 1.56). Data for the strategy game genre (e.g. Civilization, SimCity, Football Manager) were acquired using a single item regarding the frequency of game play (0 = never to 5 = very frequently; M = 1.51, SD = 1.71). For the AR genre (e.g. Pokémon GO), data were obtained by a single item regarding the frequency of game play (0 = never to 5 = very frequently; M = 2.09, SD = 1.80). Similarly, data for the SNG/Puzzle/Web board genre (e.g. Clash of Clans, Kakao Mahjong, Net Marble, Baduk) were measured through a single item regarding the frequency of game play (0 = never to 5 = very frequently; M = 0.59, SD = 1.14).
Game coplaying was considered as the combined size of game friends and guild memberships. The number of game friends was measured by an additive index of the following three items regarding the number of people that participants play with: ‘Random encounters (in quest)’, ‘Online friends’, and ‘Offline friends’. An index was divided into four groups: ‘0’ (41.4%), ‘1–3’ (18.2%), ‘4–10’ (21.2%), and ‘11–410’ (19.3%) ( M = 1.16, SD = 1.16). The number of guild members was measured using a single item on the average number of guild members with whom the respondents play. An index was divided into four groups: ‘0’ (60.4%), ‘1–6’ (12.4%), ‘17–20’ (15.2%), and ‘23–200’ (12.0%). ( M = 0.78, SD = 1.08). These two variables were averaged into a single index ( M = 1.19, SD = 0.96, r = 0.48) (Table 1 ).
Discussion network diversity
This study used five items to measure the discussion network diversity. The questions enquired respondents regarding their frequency of discussions during the past year with (a) guild members ( M = 0.84, SD = 1.22), (b) coworkers ( M = 1.07, SD = 1.28), (c) family members ( M = 1.30, SD = 1.41), (d) random encounters (in-quest/game; M = 0.90, SD = 1.26), (e) online friends (including bloggers or community members; M = 1.00, SD = 1.35), and (f) offline friends (e.g. friends from their neighbourhoods, schools, or workplaces) ( M = 1.30, SD = 1.40). These six variables were averaged into a single index ( M = 1.07, SD = 1.07, Cronbach’s α = 0.89).
Discussion network heterogeneity
Respondents were asked how frequently they commented on news or discussions about politics, including game regulation with (a) people with very different ideas from your own ( M = 0.96, SD = 1.3), (b) people with leftist views ( M = 1.2, SD = 1.3), (c) people with rightist views ( M = 1.0, SD = 1.2), (d) people of a different social status ( M = 1.0, SD = 1.2), and (e) people of different ages ( M = 1.0, SD = 1.2) on a 6-point scale. The final scale was calculated using the approach used by Scheufele et al. ( 2004 ). Respondents’ self-placement on the ideological range was used to recalculate the frequency of political discussions with ideologically like-minded individuals to 0. In other words, a left-leaning person who discussed politics with other leftists were given a score of 0, and similarly for right-leaning respondents. The items regarding the frequency of discussion with an individual of different social status and different political viewpoints remained unchanged because their heterogeneity was measured directly (Wojcieszak and Rojas, 2011 ). The final variable was calculated by averaging the mean of the five items ( M = 1.1, SD = 1.13, Cronbach’s α = 0.66), with higher values indicating greater heterogeneity of discussion networks.
Perceived learning by playing games was measured by asking respondents whether they agreed or disagreed with the following three statements: ‘Through games, I have a chance to learn about socio-political systems/structures’, ‘Through games, I am exposed to a new world that I have not seen before’, and ‘Through games, I meet new people/friends to trust and share emotions with’. A 6-point Likert scale was used for each item, ranging from 0 = totally disagree to 5 = totally agree. An index of socio-political learning by playing games was created by averaging the scores across all measures ( M = 1.43, SD = 1.33, Cronbach’s α = 0.84).
A multiple hierarchical regression was performed to examine whether certain game genres and gamers’ communication (networks, network diversity, and heterogeneous discussion) contribute to perceived learning. For the analysis, the demographic variables (gender, age, education, income) and game play hours of respondents were included in the first block of the equation. In the second block, the game genre variables including RPGs, MOBA, Strategy, AR, and SNG/Puzzle/Web board (SPW). In the third block, gamers’ communication variables—such as game coplaying (gamers’ discussion networks), discussion network diversity, and discussion heterogeneous discussion—were included.
Demographics and game play hour
The model for perceived learning by game playing explained 42.7% of the variance (Table 2 ). In the first block, only game play hours ( β = 0.369, p < 0.001) were significant for predicting learning via game playing (13.1% of incremental variance). The model and the R 2 change were statistically significant ( F (5, 1356) = 41.947, p = 0.00). The game play hours remained significant when other variables were entered into the equation. Those who play games for longer durations tend to perceive that they acquire knowledge about socio-political issues by playing games. The age ( β = 0.094, t (1361) = 3.57, p < 0.001) became significant when the game genre variables were introduced. This suggests that the effect of age is mediated by game genres and gamers’ communication.
The game genre accounted for 19% of the incremental variance. The model and the R 2 change were statistically significant ( F (6, 1350) = 59.390, p = 0.00). Except for the action game genre, all game genres were significantly related to perceived learning via game playing. Nonetheless, when gamers’ communicative network variables were entered into the model, role playing games ( β = 0.081, t (1361) = 3.06, p < 0.01), MOBA ( β = 0.103, t (1361) = 3.62, p < 0.001), and AR ( β = 0.071, t (1361) = 2.61, p < 0.01) game genres contributed significantly to learning via game playing. The findings in Table 2 suggest that while the RPG, MOBA, and AR genres have a direct and indirect effect, the effect of strategy and SPW games was indirect through gamers’ communication when predicting learning via game playing. Those who play RPG, MOBA, and AR genre games tend to acquire knowledge about socio-political issues via game playing. The effect of game learning was stronger in MOBA than in the RPG and AR genre.
Gamers’ communicative networks
The contribution of gamers’ communicative networks accounted for 10.6% of the incremental variance. The model and the R 2 change were statistically significant ( F (3, 1347) = 73.324, p = 0.00). Communication variables played a significant role in predicting perceived learning. Game coplaying ( β = 0.193, t (1361) = 7.42, p < 0.001), discussion network diversity ( β = 0.217, t (1361) = 6.78, p < 0.001), and discussion network heterogeneity ( β = 0.138, t (1361) = 4.70, p < 0.001) were significant indicators for learning via game playing. These results indicate that those who have larger and diverse networks and engaged in discussions with others who have different viewpoints are more likely to learn via playing games. While all gamers’ communicative networks were important, the effect of game learning was stronger in network diversity and game coplaying than in discussion network heterogeneity (see Figs. 2 and 3 ).
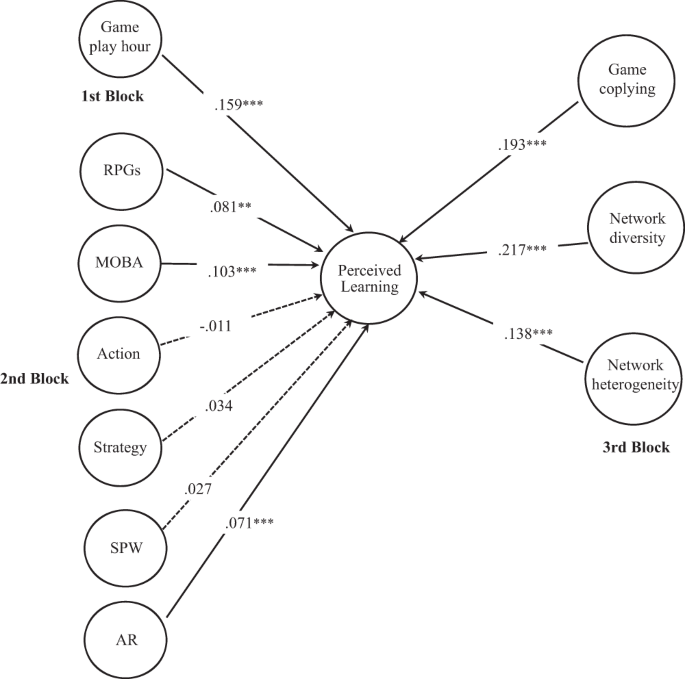
Standardized regression coefficients for the relationship between game play hour, game genre, game copying, network diversity, network heterogeneity and perceived learning by playing games. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001; N = 1362.
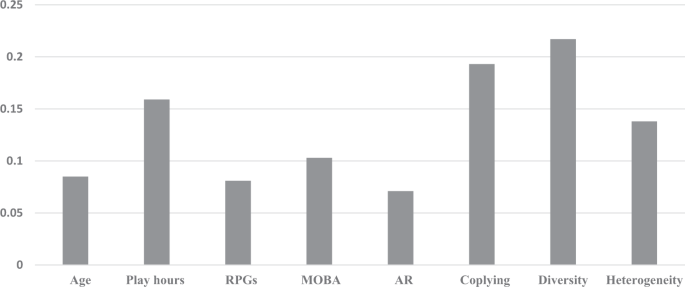
Standardized regression coefficients for the relationship between age, game play hour, RPGs, MOBA, AR, game copying, network diversity, network heterogeneity and perceived learning by playing games.
This study examined whether playing a specific game genre and gamers’ communication networks contribute to perceived learning via playing games. The findings of this study provide empirical evidence that game genres and gamers’ communicative networks are significant predictors of perceived game learning. It is noteworthy that game genres that policymakers are concerned about due to their violent content and tendency for addiction, such as RPG and MOBA games, were in reality found to contribute to learning. Moreover, the results of this study expand the literature on pedagogy, political communication, and game studies, and the variables that were not closely related to education and politics significantly predicted learning via game playing. Similar to previous studies on the new/emerging media’s roles (especially SNSs usage and discussions) in participatory behaviour, the present study’s findings indicate that gamers’ communication networks play a significant role in game learning.
Regarding the demographic characteristics and how they predict perceived game learning, older people were found to be more likely to perceive that they learn about socio-political systems through playing games. Although the current study only sampled an adult population, one had expected a negative or insignificant relationship between age and learning (i.e. younger people would learn more or at least perceive themselves as learning more about socio-political systems via gaming). This result suggests that there are no age restrictions for learning about society and politics through playing games.
Game playing was found to be significantly related with perceived game learning. The present study’s results suggest that playing RPG, MOBA, and AR game genres has social learning effects, as these genres both directly and indirectly affected learning, further implying that playing these genres encompasses a socio-political learning process. As argued in previous studies, RPGs (including MMORPGs) play a socialising role for gamers (Steinkuehler, 2006 ; Williams et al., 2006 ; Martin and Steinkuehler, 2010 ), and playing MMORPGs also has a critical role in learning. More specifically, Steinkuehler ( 2006 , 2008 ) claimed that MMOGs provided naturally occurring learning environments that involve cognitive/participatory learning communities, which are associated with ‘reciprocal forms of teaching and learning that occur in all directions throughout the social network’ (p. 43). Furthermore, Steinkuehler ( 2006 ) argued that ‘MMOGs are social simulations’ (p. 44); in other words, MMOGs promote social communities that involve building relationships among individuals and groups.
The MOBA and AR game genres share similar characteristics, such as requiring cooperativeness and teamwork among game players. Therefore, it is possible that such collective or party-oriented characteristics of gaming communities offer gamers a culture of learning (Boellstorff, 2008 ) and encourage the learning effect. Thus, RPG, MOBA, and AR game quests can be considered to provide learning environments in which shared meanings are collaboratively achieved (Martin and Steinkuehler, 2010 ), gamers socialise with others, and build a community for learning.
Most importantly, this study found out that communication among gamers facilitates the perceived learning effects, as examined by political communication scholars (Eveland et al., 2005 ; Eveland and Thomson, 2006 ; Eveland and Hively, 2009 ). Game coplaying as significant gamers’ social network amplified learning. While some studies argued that peer groups or gaming friends influence gaming disorder/addiction or excessive game playing (e.g. Amialchuk and Kotalik, 2016 ; Gunuc, 2017 ), the current study suggests that game coplaying or gamers’ social networks should be considered one of the key conditions for socio-cultural learning.
Gamers who engage in diverse discussion networks and discussion involving various views tend to learn more by playing games. This idea implies that heterogeneous network discussion does not only positively influence tolerance as indicated by Mutz ( 2006 ), but also positively influences socio-political learning. Based on this empirical finding, the notion of the benefits of heterogeneous/deliberative discussions can be expanded and re-conceptualised by analysing the over-normative argument as an important factor for gamers’ learning. Thus, if modern communication media offer new channels for discussion and education in democratic processes, then the newly emerging media of games also play a critical role in this dynamic.
While many communication studies have highlighted the negative aspects of game playing, the present study provides meaningful findings regarding the positive effects of gaming. Moreover, the present study’s findings clarify the importance of gamers’ communication networks for learning. Guild members, online friends, and people who play games together can all be considered important resources for learning. Additionally, the current study provides empirical evidence that exposing diverse viewpoints greatly contributes to not only tolerance, but also perceived learning. It is believed that heterogeneous network discussion is an important element of social integration in a polarised society as well as for perceived learning via playing games. In this regard, the results of this study provide new insights for academia and scholars who study games in the context of violence or addiction.
While the present study mainly focused on positive aspects of game playing, the researchers also realise that game playing may have negative impacts for a vulnerable group of young children. For a small percentage, excessive game playing is detrimental to psychological status (e.g. depression, anxiety, stress) or mental health (Frölich et al., 2016 ; Lee and Morgan, 2018 ; Oskenbay et al., 2016 ). Some studies found that self-control or parents’ support are key mediators/moderators to prevent game addiction or gaming disorder (Şahin et al., 2019 ; Soh et al., 2018 ; Zhu et al., 2015 ). Further research into all aspects of gaming would provide meaningful information to assist parents, schools, policymakers, and government health agencies in creating guidelines that promote prosocial gaming while allowing for intervention when gaming has become a negative issue for a particular group.
Regarding policy campaigns to prevent excessive game playing, this study offers in-depth insights into characteristics of a specific game genre. For instance, compared to the other gaming genres, RPG and MOBA gamers are multifaceted gamers who tend to consider various aspects both inside and outside of game play. Policymakers should consider the unique characteristics of the game genre and game players. In addition, as this study suggests, policymakers or those who design campaigns should understand that players of each genre have unique characteristics and gamers’ interpersonal communication networks play positive roles. An identical campaign or policy may not work in a complex gaming world. Thus, policymakers should deeply understand the nature of games and gamers’ communicative networks to effectively prevent negative gaming disorder.
Several previous studies on game learning explored the positive impacts of educationally predesigned games on learning. However, this study found that playing games of artificially violent and hypothetically addictive genres has educational effects. The current study provides new insights for current research on the educational roles of games. In addition, the findings of present study indicate that contrary to certain governments (e.g. those of China, Korea, or Vietnam) and media scholars who consider games to be violent or addictive, several critical aspects of games facilitate learning among gamers.
Data availability
The datasets analysed during the current study are available in the Dataverse repository: https://doi.org/10.7910/DVN/KPD8UN , Harvard Dataverse.
Amialchuk A, Kotalik A (2016) Do your school mates influence how long you game? Evidence from the US. PLoS ONE 11(8):1–16
Article CAS Google Scholar
Beck JC, Wade M (2004) Got game. Harvard Business School Press, Boston
Google Scholar
Bennett WL, Wells C, Freelon D (2011) Communicating civic engagement: contrasting models of citizenship in the youth web sphere. J Commun 61(5):835–856
Article Google Scholar
Boellstorff T (2008) Coming of age in Second Life: an anthropologist explores the virtually human. Princeton University Press
Bohman J (2003) Deliberative toleration. Polit Theory 31(6):757–779
Chen ZH, Lu HD, Chou CY (2019) Using game-based negotiation mechanism to enhance students’ goal setting and regulation. Comput Educ 129:71–81
Eveland WP Jr, Hayes AF, Shah DV et al (2005) Understanding the relationship between communication and political knowledge: a model comparison approach using panel data Polit Commun 22(4):423–446
Eveland WP Jr, Hively MH (2009) Political discussion frequency, network size, and ‘heterogeneity’ of discussion as predictors of political knowledge and participation J Commun 59(2):205–224
Eveland WP Jr, Thomson T (2006) Is it talking, thinking, or both? A lagged dependent variable model of discussion effects on political knowledge J Commun 56(3):523–542
Freeman ME (2017) Pushing the envelope of pedagogical gaming: dark networks. PS Polit Sci Polit 50(4):1083–1088
Frölich J, Lehmkuhl G, Orawa H, Bromba M, Wolf K, Görtz-Dorten A (2016) Computer game misuse and addiction of adolescents in a clinically referred study sample. Comput Hum Behav 55:9–15
Gaydos MJ, Squire KD (2012) Role playing games for scientific citizenship. Cult Stud Sci Educ 7(4):821–844
Gee JP (2003) What video games have to teach us about learning and literacy. Edu Train 46(4):175–178
Gee JP, Hayes E (2012) Nurturing affinity spaces and game-based learning. In: Miller C, Doering A (eds) The new landscape of mobile learning: redesigning education in an app-based world. Routledge, New York
Goncu A, Katsarou E (2000) Constructing sociocultural approaches to literacy education. Play and literacy in early childhood. Lawrence Erlbaum, Mahwah
Gunuc S (2017) Peer influence in internet and digital game addicted adolescents: Is Internet/Digital Game Addiction Contagious? Int J High Risk Behav Addict 6:e33681
Halverson ER (2012) Participatory media spaces: a design perspective on learning with media and technology in the twenty-first century. In Steinkuehler C, Squire K, Barab S (eds) Games, learning, and society: learning and meaning in the digital age. Cambridge University Press
Huckfeldt R, Mendez JM, Osborn T (2004) Disagreement, ambivalence, and engagement: the political consequences of heterogeneous networks. Polit Psychol 25(1):65–95
Jabbar AIA, Felicia P (2015) Gameplay engagement and learning in game-based learning a systematic review. Rev Educ Res 85(4):740–779
Jung N, Kim Y, De Zúñiga HG (2011) The mediating role of knowledge and efficacy in the effects of communication on political participation. Mass Commun Soc 14(4):407–430
Kahne J, Lee NJ, Feezell JT (2013) The civic and political significance of online participatory cultures among youth transitioning to adulthood. J Inf Technol 10(1):1–20
Kim J, Hyun KD (2017) Political disagreement and ambivalence in new information environment: exploring conditional indirect effects of partisan news use and heterogeneous discussion networks on SNSs on political participation. Telemat Inform 34(8):1586–1596
Lee GL, Morgan H (2018) Understanding children’s attraction toward digital games and preventing their gaming addiction. US–China Educ Rev A 8:11–17
Loy LS, Masur PK, Schmitt JB, Mothes C (2019) Psychological predictors of political Internet use and political knowledge in light of the perceived complexity of political issues. Inf Commun Soc 22(12):1733–1750
Martin C, Steinkuehler C (2010) Collective information literacy in massively multiplayer online games. E-learn Digit Media 7(4):355–365
Mutz DC (2006) Hearing the other side: deliberative versus participatory democracy. Cambridge University Press
Nietfeld JL (2020) Predicting transfer from a game-based learning environment. Comput Educ 146, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2019.103780
Ninaus M, Greipl S, Kiili K et al. (2019) Increased emotional engagement in game-based learning – A machine learning approach on facial emotion detection data. Comput Educ 142:103641
Oskenbay F, Tolegenova A, Kalymbetova E, Chung MC, Faizullina A, Jakupov M (2016) Psychological trauma as a reason for computer game addiction among adolescents. Int J Environ Sci Educ 11:2343–2353
Park J, Kim S., Kim A, Yi M Y (2019) Learning to be better at the game: Performance vs. completion contingent reward for game-based learning. Comput Educ 139:1–15
Pathak N, Mane S, Srivastava J et al. (2008) Analysis of social networks & group dynamics from electronic communication. Next generation of data mining, Taylor and Francis
Şahin M, Keskin S, Yurdugül H (2019) Impact of family support and perception of loneliness on game addiction analysis of a mediation and moderation. Int J Game-Based Learn 9:15–30
Scheufele DA, Nisbet MC, Brossard D, Nisbet EC (2004) Social structure and citizenship: Examining the impacts of social setting, network heterogeneity, and informational variables on political participation. Polit Commun 21:315–338
Shapiro RB, Squire KD (2011) Games for participatory science: a paradigm for game-based learning for promoting science literacy. Educ Technol 51(6):34–43
Soh PC, Chew KW, Koay KY, Ang PH (2018) Parents vs peers’ influence on teenagers’ Internet addiction and risky online activities. Telemat Inf 35:225–236
Squire K (2010) From information to experience: place-based augmented reality games as a model for learning in a globally networked society. Teach Coll Rec 112(10):2565–2602
Squire K (2011) Video games and learning: teaching and participatory culture in the digital age. Teachers College Press, New York
Steinkuehler CA (2006) Massively multiplayer online video gaming as participation in a discourse. Mind Cult Act 13(1):38–52
Steinkuehler CA (2008) Cognition and literacy in massively multiplayer online games. In: Coiro J, Knobel M, Lankshear C, Leu DJ (eds). Handbook of research on new literacies. Routledge, pp. 611–634
Steinkuehler CA, Squire K, Barab S (eds) (2012) Games, learning, and society: learning and meaning in the digital age. Cambridge University Press
Stufft CJ (2018) Engaging students in literacy practices through video game book groups. LR:TMP 67:195–210
Sunstein CR (2001) The daily we. Boston Rev 26(3):1–13
Sunstein CR (2002) Republic.com 2.0. Princeton University Press, Princeton, NJ
Thomas D, Brown JS (2011) A new culture of learning: cultivating the imagination for a world of constant change. CreateSpace, Lexington
Williams D, Ducheneaut N, Xiong L et al. (2006) From tree house to barracks: the social life of guilds in World of Warcraft. Games Cult 1(4):338–361
Wojcieszak M, Rojas H (2011) Hostile public effect: communication diversity and the projection of personal opinions onto others. J Broadcast Electron 55(4):543–562
Yee N (2006) The demographics, motivations, and derived experiences of users of massively multi-user online graphical environments. Presence—Teleop Virt 15(3):309–329
Yeh YL, Lan YJ (2018) Fostering student autonomy in English learning through creations in a 3D virtual world. ETRD 66(3):693–708
Yoo SW, De Zuniga HG (2019) The role of heterogeneous political discussion and partisanship on the effects of incidental news exposure online. J Inf Technol Politics 16(1):203–235
Zhu J, Zhang W, Yu C, Bao Z (2015) Early adolescent Internet game addiction in context: how parents, school, and peers impact youth. Comput Hum Behav 50:159–168
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Yonsei University Institute for Communication Research, Seoul, South Korea
Chang Won Jung
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Chang Won Jung .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The author declares no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Jung, C.W. The role of game genres and gamers’ communication networks in perceived learning. Palgrave Commun 6 , 69 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-020-0439-y
Download citation
Received : 18 December 2019
Accepted : 18 March 2020
Published : 24 April 2020
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-020-0439-y
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
This article is cited by
Online gaming as a double-edged sword: an analysis of game community receptiveness, in-game vitality, and player well-being.
- Enrico Gandolfi
- Richard E. Ferdig
- Sk Rezwan Shihab
Education and Information Technologies (2024)
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Impact of Videogames on Children Essay
- To find inspiration for your paper and overcome writer’s block
- As a source of information (ensure proper referencing)
- As a template for you assignment
Introduction
Modern children live in an extremely digitalized environment characterized by the availability of information and specific ways to spend free time. Today, most young people prefer to spend time in front of the computer, either doing their homework or socializing by using social networks. Another trend of contemporary society is the high popularity of video games that become more complex, similar to reality, and demanding much time. The constantly updating content along with the ability to play with friends online attract children. In such a way, videogames replace other activities such as running, walking, or socializing in the street. The given change of priorities triggers vigorous debates about the possible effects of games on children, their physical and mental development, and long-term consequences. For this reason, the given research is devoted to the issue of videogames and how they influence children. To investigate the problem, the following thesis is offered:
The adverse effects of videogames on children might include the development of anxiety, depression, changes in brain functioning, problems with weight, socialization, and trigger the evolution of chronic diseases; however, they can also positively influence children increasing visuospatial cognition, attention, creativity, and reducing aggression levels.
The development of the videogames industry resulted in the emergence of complex games that create attractive images and exciting tasks to engage players and hold their attention. Statistics show that 66% of children aged 8 to 12 years play video games about 2 hours per day, while teens aged 13 to 17 play about 2,5 hours per day (Halbrook et al. 1097). However, in real life, the numbers can be even higher because of the inability to trace the amount of time spent on such activities. It means, for children, videogames become the main type of activity practiced every day.
Addiction and Accessibility
Another problem linked to videogames is their ability to precondition addiction. They affect the brain similarly to drugs as they stimulate the pleasure center and trigger the release of dopamine responsible for the emergence of specific behaviors (Paturel). In such a way, playing videogames, children feel the need to spend more time. The problem is complicated by the fact that today, games are spread globally, and there is hardly an area, excluding the poorest ones with no Internet or computers, where children are deprived of a chance to play (Paturel). The combination of addiction and accessibility contributes to the spread of videogames and the growing topicality of the question of how they impact the physical and mental health of a child.
Mental Development of a Child
One of the main problems linked to videogames is their influence on the mental development of a child. Childhood is the period fundamental for the mental development of a child, and numerous factors might have either a positive or negative effects on their brain and behaviors (Lobel et al. 885). In such a way, the fact that videogames become the central way to spend free time, replacing the previous activities, attracts the attention of researchers as it has a direct impact on the psyche and health of an individual. However, there is still no consensus on whether videogames have only negative or positive effects.
Brain Functioning
One of the popular fears is that videogames can affect brain functioning. Some researchers assume that excessive gaming in childhood can physically rewire the brain and introduce irreversible changes into its work (Paturel). The recent Chinese research presupposing two control groups showed that gamers (individuals spending about 10 hours a day online) have less gray matter if to compare with people who spend less than two hours online (Paturel). In such a way, gaming can be dangerous as it affects various brain areas, depending on the type of game and reaction it cultivates.
Depression and Anxiety
There is also a belief that games might precondition the development of depression and anxiety in children. The given states are mainly associated with failures in online games, the inability to get some achievement, or bullying, one of the common practices on the Internet. The research shows that excessive gaming might precondition dopamine exhaustion, emotional suppression, and the lack of motivation to achieve various real-life goals (Paturel). Moreover, people with depression might suffer from the deterioration of their states caused by addictive playing (Video Games and Children: Playing with Violence”). Analyzing the impact of videogames on anxiety, researchers also offer various assumptions. First of all, gaming can be a normal and healthy way to relieve stress and decrease anxiety levels by engaging in online activities (Pellissier). However, for children with gaming disorder, using gaming as the anxiety coping mechanism can be dangerous and contribute to the accumulation of negative effects and increased risks (Pellissier). In such a way, video games have diverse effects on depression and anxiety, including the positive and negative ones.
Lack of Socialization
The lack of socialization and contact with peers in real life is one of the most popular fears among parents. Today, most games demand much time; moreover, they are focused on cooperation online by using the Internet, which means that children do not have to leave their houses to communicate with other people. It preconditions the increased time they spend at home. The recent research states that there is a direct correlation between the time spent online and social skills, or the higher the gaming addiction, the less the social skills (Lobel et al. 885). Children might demonstrate the inability to communicate in real life because of the absence of the demanded experience.
Weight Management and Chronic Diseases
Excessive gaming can also result in poor weight management. Gamers usually have snacks consisting of unhealthy food such as sweets, chips, or soda (Halbrook et al. 1100). The given dietary patterns create the basis for the emergence of several problems. First, they might acquire extra weight and suffer from obesity. At the same time, spending much time in front of the computer with decreased physical activity and wrong posture might result in the development of scoliosis and other problems with the locomotor system (Lobel et al. 885). Moreover, there is an increased risk of acquiring chronic diseases such as gastritis. From this perspective, videogames can be dangerous for children.
Nature-Deficit Disorder
Spending much time at home and playing videogames, children devote less attention to real life and the world surrounding them. Thus, Louv states that the threatening tendency towards the decreased exposure of children to nature can be observed in Western countries today (23). The given nature-deficit disorder has a negative impact on children and society as for health development, they need to interact with the environment and acquire all benefits from this cooperation (Louv 45). The inability to remain in contact with the world affects all systems of the child body and prevents them from healthy evolution. For this reason, videogames should be viewed as the factor limiting children’s access to nature and triggering the growth of the nature-deficit disorder.
Enhancement of Brain Capabilities
However, it is critical to mention the fact that there are also positive effects linked to videogames. For instance, studies show that by playing action games, players improve their visual capabilities, including tracking multiple objects, reaction, storing, and manipulating them in specific memory centers in the brain (Paturel). Because of the need to consider several factors at the same time, players have to perform multiple tasks simultaneously and make immediate decisions, which affects their brains and makes them more flexible (Paturel). These positive effects differentiate gamers from other children and help them to cope with diverse tasks while visiting their educational establishments.
Playing action games is also directly correlated with reaction speed. Investigations show that gamers who spend much time in this sort of activities have a lower speed of reaction (Paturel). It is explained by the fact that their gaming sessions can be viewed as training, which results in the formation of bonds in the brain and the development of skills (Pellissier). Because multiple repetitions of the same actions are an effective form of learning, gamers acquire new capabilities linked to similar situations (Paturel).
Imagination
There are also different opinions on how videogames affect the imagination. Thus, most studies conclude that modern role-playing games (RPG) contribute to the development of creative and imaginary qualities of the child brain (Halbrook et al. 1100). They offer a person a unique world, and a player should use his/her imagination to dive into it and associate his/her hero with himself/herself. Additionally, quests and strategies might precondition the rise of strategic thinking and the ability to resolve problematic puzzles or questions (Halbrook et al. 1100). For this reason, videogames can be viewed as a factor stimulating the development of this aspect of the brain’s functioning.
Recommendation
In such a way, there is no unified opinion about whether videogames should be viewed as a positive or negative factor impacting the mental development of a child. This complexity comes from the fact that there are both positive and negative effects associated with gaming. However, all sources emphasize the dangerous nature of excessive gaming and addiction. It means that parents are recommended to control their children playing patterns to avoid spending too much time in the virtual world and guarantee that they interact with the world and their peers in real life.
Altogether, videogames have both positive and negative effects on children. They might precondition the development of chronic diseases and extra weight, high anxiety, and depression levels, along with the changes in brain functioning. The highly-addictive nature increases the risks of spending too much time in games. However, there are also positive effects, such as better reaction, motor skills, visuospatial cognition, and creativity, which are trained during gaming sessions. For this reason, it is vital to continue the further investigation of the problem to outline more effects and conclude whether children’s brains suffer critical damage from games or they can be a tool to stimulate its development and optimal functioning.
Works Cited
Halbrook, Yemaya J., et al. “When and How Video Games Can Be Good: A Review of the Positive Effects of Video Games on Well-Being.” Perspectives on Psychological Science , vol. 14, no. 6, Nov. 2019, pp. 1096–1104.
Lobel, Adam, et al. “Video Gaming and Children’s Psychosocial Wellbeing: A Longitudinal Study.” Journal of Youth and Adolescence , vol. 46, no. 4, 2017, pp. 884-897. doi:10.1007/s10964-017-0646-z.
Louv, Richard. Last Child in the Woods: Saving Our Children from Nature-Deficit Disorder . Algonquin Books, 2008.
Paturel, Amy. “ Game Theory: The Effects of Video Games on the Brain .” Brain & Life , Web.
Pellissier, Hank. “ Your child’s Brain on Technology: Video Games .” Great Schools , 2014, Web.
“Video Games and Children: Playing with Violence.” American Academy of Child & Adolescents Psychiatry , 2015, Web.
- Pokémon Go as a Pop Culture Phenomenon
- Simulations, Visual Worlds, and Game Mechanics in Nursing Education
- Discord Server as Online Public Space
- Maintaining a Balance of Upbringing
- Teens Talking With Their Partners About Sex: The Role of Parent Communication
- The Value of Children’s Playing
- Parent Interview: Through the Generations
- Florida Child Custody Laws: Child Well-Being
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2022, February 27). Impact of Videogames on Children. https://ivypanda.com/essays/impact-of-videogames-on-children/
"Impact of Videogames on Children." IvyPanda , 27 Feb. 2022, ivypanda.com/essays/impact-of-videogames-on-children/.
IvyPanda . (2022) 'Impact of Videogames on Children'. 27 February.
IvyPanda . 2022. "Impact of Videogames on Children." February 27, 2022. https://ivypanda.com/essays/impact-of-videogames-on-children/.
1. IvyPanda . "Impact of Videogames on Children." February 27, 2022. https://ivypanda.com/essays/impact-of-videogames-on-children/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Impact of Videogames on Children." February 27, 2022. https://ivypanda.com/essays/impact-of-videogames-on-children/.
- Search Menu
Sign in through your institution
- Browse content in Arts and Humanities
- Browse content in Archaeology
- Anglo-Saxon and Medieval Archaeology
- Archaeological Methodology and Techniques
- Archaeology by Region
- Archaeology of Religion
- Archaeology of Trade and Exchange
- Biblical Archaeology
- Contemporary and Public Archaeology
- Environmental Archaeology
- Historical Archaeology
- History and Theory of Archaeology
- Industrial Archaeology
- Landscape Archaeology
- Mortuary Archaeology
- Prehistoric Archaeology
- Underwater Archaeology
- Zooarchaeology
- Browse content in Architecture
- Architectural Structure and Design
- History of Architecture
- Residential and Domestic Buildings
- Theory of Architecture
- Browse content in Art
- Art Subjects and Themes
- History of Art
- Industrial and Commercial Art
- Theory of Art
- Biographical Studies
- Byzantine Studies
- Browse content in Classical Studies
- Classical Literature
- Classical Reception
- Classical History
- Classical Philosophy
- Classical Mythology
- Classical Art and Architecture
- Classical Oratory and Rhetoric
- Greek and Roman Archaeology
- Greek and Roman Papyrology
- Greek and Roman Epigraphy
- Greek and Roman Law
- Late Antiquity
- Religion in the Ancient World
- Digital Humanities
- Browse content in History
- Colonialism and Imperialism
- Diplomatic History
- Environmental History
- Genealogy, Heraldry, Names, and Honours
- Genocide and Ethnic Cleansing
- Historical Geography
- History by Period
- History of Agriculture
- History of Education
- History of Emotions
- History of Gender and Sexuality
- Industrial History
- Intellectual History
- International History
- Labour History
- Legal and Constitutional History
- Local and Family History
- Maritime History
- Military History
- National Liberation and Post-Colonialism
- Oral History
- Political History
- Public History
- Regional and National History
- Revolutions and Rebellions
- Slavery and Abolition of Slavery
- Social and Cultural History
- Theory, Methods, and Historiography
- Urban History
- World History
- Browse content in Language Teaching and Learning
- Language Learning (Specific Skills)
- Language Teaching Theory and Methods
- Browse content in Linguistics
- Applied Linguistics
- Cognitive Linguistics
- Computational Linguistics
- Forensic Linguistics
- Grammar, Syntax and Morphology
- Historical and Diachronic Linguistics
- History of English
- Language Variation
- Language Families
- Language Evolution
- Language Reference
- Language Acquisition
- Lexicography
- Linguistic Theories
- Linguistic Typology
- Linguistic Anthropology
- Phonetics and Phonology
- Psycholinguistics
- Sociolinguistics
- Translation and Interpretation
- Writing Systems
- Browse content in Literature
- Bibliography
- Children's Literature Studies
- Literary Studies (Modernism)
- Literary Studies (Romanticism)
- Literary Studies (American)
- Literary Studies (Asian)
- Literary Studies (European)
- Literary Studies (Eco-criticism)
- Literary Studies - World
- Literary Studies (1500 to 1800)
- Literary Studies (19th Century)
- Literary Studies (20th Century onwards)
- Literary Studies (African American Literature)
- Literary Studies (British and Irish)
- Literary Studies (Early and Medieval)
- Literary Studies (Fiction, Novelists, and Prose Writers)
- Literary Studies (Gender Studies)
- Literary Studies (Graphic Novels)
- Literary Studies (History of the Book)
- Literary Studies (Plays and Playwrights)
- Literary Studies (Poetry and Poets)
- Literary Studies (Postcolonial Literature)
- Literary Studies (Queer Studies)
- Literary Studies (Science Fiction)
- Literary Studies (Travel Literature)
- Literary Studies (War Literature)
- Literary Studies (Women's Writing)
- Literary Theory and Cultural Studies
- Mythology and Folklore
- Shakespeare Studies and Criticism
- Browse content in Media Studies
- Browse content in Music
- Applied Music
- Dance and Music
- Ethics in Music
- Ethnomusicology
- Gender and Sexuality in Music
- Medicine and Music
- Music Cultures
- Music and Culture
- Music and Media
- Music and Religion
- Music Education and Pedagogy
- Music Theory and Analysis
- Musical Scores, Lyrics, and Libretti
- Musical Structures, Styles, and Techniques
- Musicology and Music History
- Performance Practice and Studies
- Race and Ethnicity in Music
- Sound Studies
- Browse content in Performing Arts
- Browse content in Philosophy
- Aesthetics and Philosophy of Art
- Epistemology
- Feminist Philosophy
- History of Western Philosophy
- Metaphysics
- Moral Philosophy
- Non-Western Philosophy
- Philosophy of Action
- Philosophy of Law
- Philosophy of Religion
- Philosophy of Language
- Philosophy of Mind
- Philosophy of Perception
- Philosophy of Science
- Philosophy of Mathematics and Logic
- Practical Ethics
- Social and Political Philosophy
- Browse content in Religion
- Biblical Studies
- Christianity
- East Asian Religions
- History of Religion
- Judaism and Jewish Studies
- Qumran Studies
- Religion and Education
- Religion and Health
- Religion and Politics
- Religion and Science
- Religion and Law
- Religion and Art, Literature, and Music
- Religious Studies
- Browse content in Society and Culture
- Cookery, Food, and Drink
- Cultural Studies
- Customs and Traditions
- Ethical Issues and Debates
- Hobbies, Games, Arts and Crafts
- Natural world, Country Life, and Pets
- Popular Beliefs and Controversial Knowledge
- Sports and Outdoor Recreation
- Technology and Society
- Travel and Holiday
- Visual Culture
- Browse content in Law
- Arbitration
- Browse content in Company and Commercial Law
- Commercial Law
- Company Law
- Browse content in Comparative Law
- Systems of Law
- Competition Law
- Browse content in Constitutional and Administrative Law
- Government Powers
- Judicial Review
- Local Government Law
- Military and Defence Law
- Parliamentary and Legislative Practice
- Construction Law
- Contract Law
- Browse content in Criminal Law
- Criminal Procedure
- Criminal Evidence Law
- Sentencing and Punishment
- Employment and Labour Law
- Environment and Energy Law
- Browse content in Financial Law
- Banking Law
- Insolvency Law
- History of Law
- Human Rights and Immigration
- Intellectual Property Law
- Browse content in International Law
- Private International Law and Conflict of Laws
- Public International Law
- IT and Communications Law
- Jurisprudence and Philosophy of Law
- Law and Society
- Law and Politics
- Browse content in Legal System and Practice
- Courts and Procedure
- Legal Skills and Practice
- Primary Sources of Law
- Regulation of Legal Profession
- Medical and Healthcare Law
- Browse content in Policing
- Criminal Investigation and Detection
- Police and Security Services
- Police Procedure and Law
- Police Regional Planning
- Browse content in Property Law
- Personal Property Law
- Study and Revision
- Terrorism and National Security Law
- Browse content in Trusts Law
- Wills and Probate or Succession
- Browse content in Medicine and Health
- Browse content in Allied Health Professions
- Arts Therapies
- Clinical Science
- Dietetics and Nutrition
- Occupational Therapy
- Operating Department Practice
- Physiotherapy
- Radiography
- Speech and Language Therapy
- Browse content in Anaesthetics
- General Anaesthesia
- Neuroanaesthesia
- Clinical Neuroscience
- Browse content in Clinical Medicine
- Acute Medicine
- Cardiovascular Medicine
- Clinical Genetics
- Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics
- Dermatology
- Endocrinology and Diabetes
- Gastroenterology
- Genito-urinary Medicine
- Geriatric Medicine
- Infectious Diseases
- Medical Oncology
- Medical Toxicology
- Pain Medicine
- Palliative Medicine
- Rehabilitation Medicine
- Respiratory Medicine and Pulmonology
- Rheumatology
- Sleep Medicine
- Sports and Exercise Medicine
- Community Medical Services
- Critical Care
- Emergency Medicine
- Forensic Medicine
- Haematology
- History of Medicine
- Medical Ethics
- Browse content in Medical Skills
- Clinical Skills
- Communication Skills
- Nursing Skills
- Surgical Skills
- Browse content in Medical Dentistry
- Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery
- Paediatric Dentistry
- Restorative Dentistry and Orthodontics
- Surgical Dentistry
- Medical Statistics and Methodology
- Browse content in Neurology
- Clinical Neurophysiology
- Neuropathology
- Nursing Studies
- Browse content in Obstetrics and Gynaecology
- Gynaecology
- Occupational Medicine
- Ophthalmology
- Otolaryngology (ENT)
- Browse content in Paediatrics
- Neonatology
- Browse content in Pathology
- Chemical Pathology
- Clinical Cytogenetics and Molecular Genetics
- Histopathology
- Medical Microbiology and Virology
- Patient Education and Information
- Browse content in Pharmacology
- Psychopharmacology
- Browse content in Popular Health
- Caring for Others
- Complementary and Alternative Medicine
- Self-help and Personal Development
- Browse content in Preclinical Medicine
- Cell Biology
- Molecular Biology and Genetics
- Reproduction, Growth and Development
- Primary Care
- Professional Development in Medicine
- Browse content in Psychiatry
- Addiction Medicine
- Child and Adolescent Psychiatry
- Forensic Psychiatry
- Learning Disabilities
- Old Age Psychiatry
- Psychotherapy
- Browse content in Public Health and Epidemiology
- Epidemiology
- Public Health
- Browse content in Radiology
- Clinical Radiology
- Interventional Radiology
- Nuclear Medicine
- Radiation Oncology
- Reproductive Medicine
- Browse content in Surgery
- Cardiothoracic Surgery
- Gastro-intestinal and Colorectal Surgery
- General Surgery
- Neurosurgery
- Paediatric Surgery
- Peri-operative Care
- Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
- Surgical Oncology
- Transplant Surgery
- Trauma and Orthopaedic Surgery
- Vascular Surgery
- Browse content in Science and Mathematics
- Browse content in Biological Sciences
- Aquatic Biology
- Biochemistry
- Bioinformatics and Computational Biology
- Developmental Biology
- Ecology and Conservation
- Evolutionary Biology
- Genetics and Genomics
- Microbiology
- Molecular and Cell Biology
- Natural History
- Plant Sciences and Forestry
- Research Methods in Life Sciences
- Structural Biology
- Systems Biology
- Zoology and Animal Sciences
- Browse content in Chemistry
- Analytical Chemistry
- Computational Chemistry
- Crystallography
- Environmental Chemistry
- Industrial Chemistry
- Inorganic Chemistry
- Materials Chemistry
- Medicinal Chemistry
- Mineralogy and Gems
- Organic Chemistry
- Physical Chemistry
- Polymer Chemistry
- Study and Communication Skills in Chemistry
- Theoretical Chemistry
- Browse content in Computer Science
- Artificial Intelligence
- Computer Architecture and Logic Design
- Game Studies
- Human-Computer Interaction
- Mathematical Theory of Computation
- Programming Languages
- Software Engineering
- Systems Analysis and Design
- Virtual Reality
- Browse content in Computing
- Business Applications
- Computer Games
- Computer Security
- Computer Networking and Communications
- Digital Lifestyle
- Graphical and Digital Media Applications
- Operating Systems
- Browse content in Earth Sciences and Geography
- Atmospheric Sciences
- Environmental Geography
- Geology and the Lithosphere
- Maps and Map-making
- Meteorology and Climatology
- Oceanography and Hydrology
- Palaeontology
- Physical Geography and Topography
- Regional Geography
- Soil Science
- Urban Geography
- Browse content in Engineering and Technology
- Agriculture and Farming
- Biological Engineering
- Civil Engineering, Surveying, and Building
- Electronics and Communications Engineering
- Energy Technology
- Engineering (General)
- Environmental Science, Engineering, and Technology
- History of Engineering and Technology
- Mechanical Engineering and Materials
- Technology of Industrial Chemistry
- Transport Technology and Trades
- Browse content in Environmental Science
- Applied Ecology (Environmental Science)
- Conservation of the Environment (Environmental Science)
- Environmental Sustainability
- Environmentalist Thought and Ideology (Environmental Science)
- Management of Land and Natural Resources (Environmental Science)
- Natural Disasters (Environmental Science)
- Nuclear Issues (Environmental Science)
- Pollution and Threats to the Environment (Environmental Science)
- Social Impact of Environmental Issues (Environmental Science)
- History of Science and Technology
- Browse content in Materials Science
- Ceramics and Glasses
- Composite Materials
- Metals, Alloying, and Corrosion
- Nanotechnology
- Browse content in Mathematics
- Applied Mathematics
- Biomathematics and Statistics
- History of Mathematics
- Mathematical Education
- Mathematical Finance
- Mathematical Analysis
- Numerical and Computational Mathematics
- Probability and Statistics
- Pure Mathematics
- Browse content in Neuroscience
- Cognition and Behavioural Neuroscience
- Development of the Nervous System
- Disorders of the Nervous System
- History of Neuroscience
- Invertebrate Neurobiology
- Molecular and Cellular Systems
- Neuroendocrinology and Autonomic Nervous System
- Neuroscientific Techniques
- Sensory and Motor Systems
- Browse content in Physics
- Astronomy and Astrophysics
- Atomic, Molecular, and Optical Physics
- Biological and Medical Physics
- Classical Mechanics
- Computational Physics
- Condensed Matter Physics
- Electromagnetism, Optics, and Acoustics
- History of Physics
- Mathematical and Statistical Physics
- Measurement Science
- Nuclear Physics
- Particles and Fields
- Plasma Physics
- Quantum Physics
- Relativity and Gravitation
- Semiconductor and Mesoscopic Physics
- Browse content in Psychology
- Affective Sciences
- Clinical Psychology
- Cognitive Neuroscience
- Cognitive Psychology
- Criminal and Forensic Psychology
- Developmental Psychology
- Educational Psychology
- Evolutionary Psychology
- Health Psychology
- History and Systems in Psychology
- Music Psychology
- Neuropsychology
- Organizational Psychology
- Psychological Assessment and Testing
- Psychology of Human-Technology Interaction
- Psychology Professional Development and Training
- Research Methods in Psychology
- Social Psychology
- Browse content in Social Sciences
- Browse content in Anthropology
- Anthropology of Religion
- Human Evolution
- Medical Anthropology
- Physical Anthropology
- Regional Anthropology
- Social and Cultural Anthropology
- Theory and Practice of Anthropology
- Browse content in Business and Management
- Business History
- Business Ethics
- Business Strategy
- Business and Technology
- Business and Government
- Business and the Environment
- Comparative Management
- Corporate Governance
- Corporate Social Responsibility
- Entrepreneurship
- Health Management
- Human Resource Management
- Industrial and Employment Relations
- Industry Studies
- Information and Communication Technologies
- International Business
- Knowledge Management
- Management and Management Techniques
- Operations Management
- Organizational Theory and Behaviour
- Pensions and Pension Management
- Public and Nonprofit Management
- Strategic Management
- Supply Chain Management
- Browse content in Criminology and Criminal Justice
- Criminal Justice
- Criminology
- Forms of Crime
- International and Comparative Criminology
- Youth Violence and Juvenile Justice
- Development Studies
- Browse content in Economics
- Agricultural, Environmental, and Natural Resource Economics
- Asian Economics
- Behavioural Finance
- Behavioural Economics and Neuroeconomics
- Econometrics and Mathematical Economics
- Economic Methodology
- Economic History
- Economic Systems
- Economic Development and Growth
- Financial Markets
- Financial Institutions and Services
- General Economics and Teaching
- Health, Education, and Welfare
- History of Economic Thought
- International Economics
- Labour and Demographic Economics
- Law and Economics
- Macroeconomics and Monetary Economics
- Microeconomics
- Public Economics
- Urban, Rural, and Regional Economics
- Welfare Economics
- Browse content in Education
- Adult Education and Continuous Learning
- Care and Counselling of Students
- Early Childhood and Elementary Education
- Educational Equipment and Technology
- Educational Strategies and Policy
- Higher and Further Education
- Organization and Management of Education
- Philosophy and Theory of Education
- Schools Studies
- Secondary Education
- Teaching of a Specific Subject
- Teaching of Specific Groups and Special Educational Needs
- Teaching Skills and Techniques
- Browse content in Environment
- Applied Ecology (Social Science)
- Climate Change
- Conservation of the Environment (Social Science)
- Environmentalist Thought and Ideology (Social Science)
- Natural Disasters (Environment)
- Social Impact of Environmental Issues (Social Science)
- Browse content in Human Geography
- Cultural Geography
- Economic Geography
- Political Geography
- Browse content in Interdisciplinary Studies
- Communication Studies
- Museums, Libraries, and Information Sciences
- Browse content in Politics
- African Politics
- Asian Politics
- Chinese Politics
- Comparative Politics
- Conflict Politics
- Elections and Electoral Studies
- Environmental Politics
- European Union
- Foreign Policy
- Gender and Politics
- Human Rights and Politics
- Indian Politics
- International Relations
- International Organization (Politics)
- International Political Economy
- Irish Politics
- Latin American Politics
- Middle Eastern Politics
- Political Theory
- Political Behaviour
- Political Economy
- Political Institutions
- Political Methodology
- Political Communication
- Political Philosophy
- Political Sociology
- Politics and Law
- Politics of Development
- Public Policy
- Public Administration
- Quantitative Political Methodology
- Regional Political Studies
- Russian Politics
- Security Studies
- State and Local Government
- UK Politics
- US Politics
- Browse content in Regional and Area Studies
- African Studies
- Asian Studies
- East Asian Studies
- Japanese Studies
- Latin American Studies
- Middle Eastern Studies
- Native American Studies
- Scottish Studies
- Browse content in Research and Information
- Research Methods
- Browse content in Social Work
- Addictions and Substance Misuse
- Adoption and Fostering
- Care of the Elderly
- Child and Adolescent Social Work
- Couple and Family Social Work
- Direct Practice and Clinical Social Work
- Emergency Services
- Human Behaviour and the Social Environment
- International and Global Issues in Social Work
- Mental and Behavioural Health
- Social Justice and Human Rights
- Social Policy and Advocacy
- Social Work and Crime and Justice
- Social Work Macro Practice
- Social Work Practice Settings
- Social Work Research and Evidence-based Practice
- Welfare and Benefit Systems
- Browse content in Sociology
- Childhood Studies
- Community Development
- Comparative and Historical Sociology
- Economic Sociology
- Gender and Sexuality
- Gerontology and Ageing
- Health, Illness, and Medicine
- Marriage and the Family
- Migration Studies
- Occupations, Professions, and Work
- Organizations
- Population and Demography
- Race and Ethnicity
- Social Theory
- Social Movements and Social Change
- Social Research and Statistics
- Social Stratification, Inequality, and Mobility
- Sociology of Religion
- Sociology of Education
- Sport and Leisure
- Urban and Rural Studies
- Browse content in Warfare and Defence
- Defence Strategy, Planning, and Research
- Land Forces and Warfare
- Military Administration
- Military Life and Institutions
- Naval Forces and Warfare
- Other Warfare and Defence Issues
- Peace Studies and Conflict Resolution
- Weapons and Equipment

- < Previous chapter
- Next chapter >
11 The Role of Games
- Published: October 2009
- Cite Icon Cite
- Permissions Icon Permissions
This chapter considers the realm of children's and adolescents' games. As noted, this area is incredibly under-researched. That games are so under-studied yet so interesting and important to children, adolescents, and adults should be a message to the research community: this is an important topic. If there is doubt, consider the billions of dollars spent in the “gaming” (i.e. gambling) industry, state and national lotteries, and sport at both professional and college levels. From this perspective it is imperative to study games, and indeed sport, in order to understand the contexts in which individuals actually develop.
Signed in as
Institutional accounts.
- GoogleCrawler [DO NOT DELETE]
- Google Scholar Indexing
Personal account
- Sign in with email/username & password
- Get email alerts
- Save searches
- Purchase content
- Activate your purchase/trial code
- Add your ORCID iD
Institutional access
Sign in with a library card.
- Sign in with username/password
- Recommend to your librarian
- Institutional account management
- Get help with access
Access to content on Oxford Academic is often provided through institutional subscriptions and purchases. If you are a member of an institution with an active account, you may be able to access content in one of the following ways:
IP based access
Typically, access is provided across an institutional network to a range of IP addresses. This authentication occurs automatically, and it is not possible to sign out of an IP authenticated account.
Choose this option to get remote access when outside your institution. Shibboleth/Open Athens technology is used to provide single sign-on between your institution’s website and Oxford Academic.
- Click Sign in through your institution.
- Select your institution from the list provided, which will take you to your institution's website to sign in.
- When on the institution site, please use the credentials provided by your institution. Do not use an Oxford Academic personal account.
- Following successful sign in, you will be returned to Oxford Academic.
If your institution is not listed or you cannot sign in to your institution’s website, please contact your librarian or administrator.
Enter your library card number to sign in. If you cannot sign in, please contact your librarian.

Society Members
Society member access to a journal is achieved in one of the following ways:
Sign in through society site
Many societies offer single sign-on between the society website and Oxford Academic. If you see ‘Sign in through society site’ in the sign in pane within a journal:
- Click Sign in through society site.
- When on the society site, please use the credentials provided by that society. Do not use an Oxford Academic personal account.
If you do not have a society account or have forgotten your username or password, please contact your society.
Sign in using a personal account
Some societies use Oxford Academic personal accounts to provide access to their members. See below.
A personal account can be used to get email alerts, save searches, purchase content, and activate subscriptions.
Some societies use Oxford Academic personal accounts to provide access to their members.
Viewing your signed in accounts
Click the account icon in the top right to:
- View your signed in personal account and access account management features.
- View the institutional accounts that are providing access.
Signed in but can't access content
Oxford Academic is home to a wide variety of products. The institutional subscription may not cover the content that you are trying to access. If you believe you should have access to that content, please contact your librarian.
For librarians and administrators, your personal account also provides access to institutional account management. Here you will find options to view and activate subscriptions, manage institutional settings and access options, access usage statistics, and more.
Our books are available by subscription or purchase to libraries and institutions.
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Rights and permissions
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.

Exploring the Cognitive Benefits of Video Games: How Gaming Can Improve Learning
by Katrine B
September 10, 2023
Video games have become a popular form of entertainment for people of all ages. While there has been much debate about the potential negative effects of gaming, more recent research has focused on the positive impact of video games on cognitive development and learning. In this narrative essay , we will explore the cognitive benefits of video games and discuss how gaming can improve learning.
Understanding the Cognitive Benefits of Video Games
Before delving into the specific cognitive benefits of video games, it is important to define what cognitive benefits are. Cognitive benefits refer to improvements in cognitive functions such as attention, memory, problem-solving, and decision-making that can result from engaging in certain activities or experiences.
Defining Cognitive Benefits
When we talk about cognitive benefits, we are referring to positive changes in cognitive abilities as a result of playing video games. These changes can include enhanced attention span, improved memory retention, better problem-solving skills, and increased cognitive flexibility.
The Connection Between Gaming and Cognitive Function
Research has shown that video games can have a positive impact on various aspects of cognitive function. One study conducted by researchers at the University of California, Irvine, found that playing certain video games can lead to improvements in attention and multitasking abilities.
The researchers found that video game players were better at ignoring irrelevant information and were more efficient at switching between different tasks compared to non-gamers. They suggested that the fast-paced and immersive nature of video games may contribute to these cognitive improvements.
The Impact of Video Games on Learning
In addition to the cognitive benefits, video games have also been found to have a positive impact on learning. In particular, they can enhance memory and improve problem-solving skills.
Video Games and Memory Enhancement
Several studies have shown that playing video games can enhance memory function. In a study published in the journal Nature, researchers found that participants who played a 3D video game had better memory performance compared to those who played a 2D game or did not play any game at all.
The researchers suggested that the immersive and interactive nature of 3D video games may stimulate the hippocampus, a region of the brain associated with memory formation, leading to improved memory function.
Improving Problem-Solving Skills Through Gaming
Video games often require players to think critically and solve puzzles or challenges to progress in the game. This constant engagement with problem-solving tasks can enhance players' abilities to think critically and creatively, and to approach problems from different angles.
Furthermore, research has shown that video games can improve players' ability to transfer problem-solving skills to real-world scenarios. A study conducted by researchers at the University of Wisconsin-Madison found that individuals who played strategy-based video games showed better problem-solving skills and an increased ability to think strategically in real-world situations.
The Psychological Perspective of Gaming
Another aspect to consider when exploring the cognitive benefits of video games is the psychological perspective. Video games have been found to have an impact on attention span and emotional regulation.
Gaming and Attention Span
Contrary to popular belief, research suggests that playing video games in moderation can actually improve attention span. A study published in the journal Current Biology found that action video game players had better attentional control and were able to sustain their attention for longer periods compared to non-players.
This improved attention span may be attributed to the fast-paced nature of video games, which require players to quickly process and react to various stimuli within the game environment.
The Role of Video Games in Emotional Regulation
Video games can also play a role in emotional regulation. Studies have shown that playing video games can provide an outlet for emotional expression and serve as a means of stress relief.
Furthermore, multiplayer online games can provide opportunities for social interaction and can help individuals develop social skills and emotional intelligence. Engaging in cooperative gameplay can foster teamwork and collaboration, which can be beneficial in both virtual and real-world settings.
The Social Benefits of Multiplayer Games
Multiplayer games, in particular, offer a unique opportunity for social interaction and the development of important skills.
Developing Communication Skills Through Gaming
Multiplayer games often require players to communicate and cooperate with others to achieve shared objectives. This can help individuals develop effective communication skills, as they learn to coordinate actions, share information, and work together as a team.
Teamwork and Collaboration in Multiplayer Games
Playing multiplayer games can also cultivate teamwork and collaboration skills. By working together towards a common goal, players learn to delegate tasks, strategize, and make decisions as a team.
Research has shown that individuals who regularly engage in multiplayer gaming tend to have enhanced teamwork and collaboration skills, which can be transferable to various real-life situations, such as group projects or work environments.
Debunking Myths About Video Games
Despite the growing evidence of the cognitive and social benefits of video games, there are still misconceptions and concerns surrounding their use.
Addressing Concerns About Gaming Addiction
Gaming addiction is a controversial topic that has attracted much attention in recent years. While it is true that excessive gaming can have negative consequences, it is important to note that moderate and responsible gaming can bring about positive effects.
Individuals who engage in gaming as a recreational activity, in balance with other aspects of their lives, are unlikely to develop addiction problems. It is important to establish healthy gaming habits and recognize when it starts to interfere with other important areas of life, such as school or work.
The Truth About Video Games and Violence
Another major concern associated with video games is the belief that they promote aggression and violent behavior. However, research conducted in this area has not found a causal link between video games and real-life violence.
Studies have shown that while video games may temporarily increase aggression levels immediately after playing, this effect is short-lived and does not lead to long-term changes in behavior. It is important to consider other factors, such as pre-existing aggression or a lack of parental involvement, when examining the relationship between video games and aggression.
In conclusion, video games have the potential to offer various cognitive benefits and contribute to learning. They can improve attention, memory, problem-solving skills, and emotional regulation. Additionally, multiplayer games can enhance communication, teamwork, and collaboration skills. It is crucial to approach gaming in a responsible and balanced manner, recognizing the positive aspects while addressing concerns about addiction and violence. By understanding and harnessing the cognitive benefits of video games, we can explore their potential as tools for learning and personal development.
Essays About Video Games: Top 12 Examples and Prompts
Video games have revolutionized the way we have fun today. If you are writing essays about video games, check out our guide to inspire your writing.
Few can contest the fact that video games have taken over the world. From the basic, almost “primitive” games of the 1970s like Pong to the mind-bending virtual reality games of the 2020s, they have been a source of entertainment for all. Moreover, they have proven quite profitable; countries like Japan and the United States have made tens of billions of dollars solely from the video game market.
Despite their popularity, much has been debated over the potentially harmful side effects that video games may have, particularly on children. One side argues that playing certain video games can lead to people exhibiting violence in the future, while others believe that video games teach players essential life skills. Regardless, they will continue to be a part of our lives for the foreseeable future.
For engaging essays about video games, read the essay examples featured below for inspiration.
1. What electronic games can teach us by Kendall Powell
2. designers are imagining video games without guns by keith stuart, 3. playing video games all summer won’t make you feel worse by nicole wetsman, 4. violent video games bad by andrea newman.
- 5. The health effects of too much gaming by Peter Grinspoon
Writing Prompts For Essays About Video Games
1. video games: good or bad, 2. the benefits of video games, 3. what is your favorite video game, 4. do video games cause people to become violent, 5. video games in your life, 6. video games vs. traditional games, 7. is the video game rating system enough.
“In other studies, researchers found that gamers who trained on Tetris were better at mentally rotating two-dimensional shapes than those who played a control game. Students who played two hours of All You Can E.T., an educational game designed to enhance the executive function of switching between tasks, improved their focus-shifting skills compared with students who played a word search game.”
Powell explains a few possibilities of applying video games to education. As it turns out, certain video games can improve players’ skills, depending on the mechanics. Researchers are inspired by this and hope to take advantage of the competitive, motivational nature of gaming to encourage children to learn. New games are designed to help kids improve their focus, coordination, and resilience, and game designers hope they will succeed.
“Imagine a game where you’re a war reporter seeking to capture the most iconic, representative images in a battle environment: You’d still get the sense of peril that audiences expect from action adventures, but your relationship with the environment would be more profound. It would be Call of Duty from the perspective of a creative participant rather than a violent interloper.”
The graphic nature of some video games is said to make kids violent, so it is only natural that some creators try to change this. Stuart writes that it is possible to maintain the fun that shooter-type games induce without using guns. He gives examples of games where you do not kill your enemy, simply stunning or capturing them instead. He also suggests photography as an alternative to killing in a “shooting” game. Finally, he suggests basing video games around helping others, making friends, and doing more peaceful, creative tasks.
“Any role video games play in skewing well-being that did pop up in the study was too small to have a real-world impact on how people feel, the authors said. People would have to play games for 10 more hours per day than their baseline to notice changes in their well-being, the study found.”
Wetsman counters the widespread belief that video games “destroy your brain.” Research done with a sample of 39,000 players over six weeks has shown that whether one plays video games for long or short periods, their mental health is not impacted much. There are some exceptions; however, there are not enough to conclude that video games are, in fact, harmful.
“Some people believe that the connection between violent games, and real violence is also fairly intuitive. In playing the games kids are likely to become desensitized to gory images;which could make them less disturbing, and perhaps easier to deal with in real life. While video games aren’t about violence their capacity to teach can be a good thing.”
In her essay, Newman writes about the supposed promotion of violence in some video games. However, she believes this violence does not cause people to be more aggressive later. Instead, she believes these games expose children to certain atrocities so they will not be traumatized if they see them in real life. In addition, these games supposedly promote connections and friendships. Finally, Newman believes that these “harmful” can make you a better person.
5. The health effects of too much gaming by Peter Grinspoon
“Gamers need to be educated on how to protect their thumbs, wrists, and elbows, their waistlines, their emotional state, their sleep, and their eyes. Simple education around taking breaks, stretching, eating healthy snacks, and resting and icing your thumb, wrist, or elbow when it starts hurting can address injuries early, before they become significant. For the eyes, gamers can try the 20-20-20 rule: every 20 minutes, try to look at something 20 feet away for 20 seconds.”
Grinspoon discusses both the benefits and the health risks of gaming. Video games allow people to interact with each other remotely and bond over specific missions or tasks, and some research shows that they have cognitive benefits. However, some gamers may develop vision problems and hand and wrist injuries. Gaming and “staring in front of a screen the whole day” is also associated with obesity. Overall, Grinspoon believes that gaming is best done in moderation.
Looking for more? Check out these essays about hobbies .
Many parents believe that their children’s “bad behavior” is because of video games. Based on your experience and others, decide: are video games good or bad for you? Make sure to read viewpoints from both sides and write an essay based on your position. Would you encourage others to play video games? Discuss these pros and cons for an interesting argumentative essay.
Like anything else, video games have both positive and negative aspects. Explain the good that video games can do for you: the skills they can equip you with, the lessons they can teach, and anything else. Also, include whether you believe their benefits outweigh the disadvantages they may pose.
For your essay, write about your favorite video game and why you chose it. What is its meaning to you, and how has it affected your life? Describe the gameplay mechanics, characters, storyline, and general impact on the gaming community or society. You can write about any game you want, even if you have not played it; just ensure the content is sufficient.
Many claim that playing violent video games can make you violent in the future. Research this phenomenon and conclude whether it is true or not. Is the evidence sufficient? There are many resources on this topic; support your argument by citing credible sources, such as news articles, statistics, and scientific research.
Video games have been a part of almost all our lives. Recall a treasured experience with video games and explain why it is significant. How old were you? Why do you remember it fondly? How did this experience make you feel? Answer these questions in your own words for an exciting essay.

There are stark differences between video and traditional games, such as board games and card games. For an engaging essay, compare and contrast them and write about which is more entertaining, in your opinion. Be creative; this should be based on your own opinions and ideas.
The video game content rating system is used to classify video games based on their appropriateness for specific ages. However, parents complain that they are not strict enough and allow the display of violent content to children. Explore the criteria behind the rating system, decide whether it needs to be changed or not, and give examples to support your argument.
If you are interested in learning more, check out our essay writing tips !
Tip: If writing an essay sounds like a lot of work, simplify it. Write a simple 5 paragraph essay instead.

Martin is an avid writer specializing in editing and proofreading. He also enjoys literary analysis and writing about food and travel.
View all posts
Video Games and Their Impact on Teens’ Mental Health
- First Online: 02 March 2018
Cite this chapter

- Melissa E. DeRosier Ph.D. 3 &
- James M. Thomas Ph.D. 3
7967 Accesses
3 Citations
The role that video games play in the lives of teenagers has grown dramatically and without pause for the past generation or two. Between computers, smart phones, and dedicated game consoles, not only are individual adolescents spending more of their days playing video games, but the percentage of teens whose daily lives include video games is quickly approaching universality. In this chapter, we first review recent trends in video gaming and explore the various and myriad video games that teens tend to play as well as their motivations to play video games. Then, we review the literature regarding the influence of playing different types of commercial video games on mental health. And last, we explore recent innovations in game development whereby video games are specifically developed to improve mental health symptoms or psychosocial adjustment, including a review of the research supporting use of these “impactful video games.” It is hoped that the information presented in this chapter will provide practitioners with greater understanding of the diversity and breadth of experiences that fall under the umbrella term “video gaming” in order to help foster more open and productive conversations with teens about their video gaming behavior. We also hope the research evidence presented in this chapter will encourage practitioners to integrate the use of video games into their treatment of teen patients, both as a means of fostering the therapeutic alliance and as an innovative accompaniment to traditional therapeutic methods to enhance teens’ mental and behavioral health.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Yi M. They got game: stacks of new releases for hungry video game enthusiasts mean it’s boom time for an industry now even bigger than Hollywood. San Francisco Chronicle [Internet]; 2004 Dec [cited 2017 Apr 26]. http://www.sfgate.com/news/article/THEY-GOT-GAME-Stacks-of-new-releases-for-hungry-2663371.php
Lenhart A, Kahne J, Middaugh E, MacGill A, Evans C, Vitak J. Teens, video games, and civics. Pew Research Center [Internet]; 2008 Sep [cited 2017 Apr 26]. http://www.pewinternet.org/2008/09/16/teens-video-games-and-civics/ #.
Statista: The Statistics Portal. Statistics and facts on mobile gaming [Internet]. Hamburg, Germany: Statista; [cited 2017 Apr 26]. https://www.statista.com/topics/1906/mobile-gaming/
NPD Group. Average time spent playing games on mobile devices has increased 57 percent since 2012 [Internet]; 2014 [cited] 2017 Apr 27. https://www.npd.com/wps/portal/npd/us/news/press-releases/2015/average-time-spent-playing-games-on-mobile-devices-has-increased-57-percent-since-2012/
Entertainment Software Association. Essential facts about the computer and video game industry [Internet]. Washington, DC: ESA; 2015 Apr [cited 2017 Apr 27]. 20 p. http://www.theesa.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/04/ESA-Essential-Facts-2015.pdf
Bartle R. Hearts, clubs, diamonds, spades: players who suit MUDS. J MUD Res [Internet]. 1996 [cited 2017 Apr 26];1(1). http://mud.co.uk/richard/hcds.htm .
Bartle RA. Designing virtual worlds. New Riders: Berkely; 2004.
Google Scholar
Yee N. Motivations for play in online games. Cyberpsychol Behav. 2006;9(6):772–5.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Sherry JL, Lucas K, Greenberg BS, Lachlan K. Video game uses and gratifications as predictors of use and game preference. In: Bryant J, Vorderer P, editors. Playing video games: motives, responses, and consequences. Mahwah: Lawrence Erlbaum; 2006. p. 213–24.
Boyan A, Sherry JL. The challenge in creating games for education: aligning mental models with game models. Child Dev Perspect. 2011;5(2):82–7.
Article Google Scholar
Csikszentmihalyi M. Flow: the psychology of optimal experience. New York: Harper & Row; 1990.
Ryan RM, Rigby CS, Przybylski AK. The motivational pull of video games: a self-determination theory approach. Motiv Emot. 2006;30:347–64.
Przybylski AK, Rigby CS, Ryan RMA. motivational model of video game engagement. Rev Gen Psychol. 2010;14(2):154–66.
American Academy of Pediatrics [Internet]. Elk Grove Village, IL: AAP; 2017 [cited 2017 Apr 27]. https://www.aap.org/en-us/advocacy-and-policy/aap-health-initiatives/Pages/Media-and-Children.aspx
APA Task Force on Violent Media. Technical report on the review of the violent video game literature [Internet]. Washington, DC: American Psychological Association; 2015 [cited 2017 Apr 27]. 31 p. http://www.apa.org/pi/families/review-video-games.pdf
Gee JP. What video games have to teach us about learning and literacy. New York: St. Martin’s Press; 2003.
Smyth JM. Beyond self-selection in video game play: an experimental examination of the consequences of Massively Multiplayer Online Role-Playing Game play. Cyberpsychol Behav. 2007;10(5):717–21.
Gallup J, Serianni B, Duff C, Gallup A. An exploration of friendships and socialization for adolescents with autism engaged in Massively Multiplayer Online Role-Playing Games (MMORPG). Educ Train Autism Dev Disabil. 2016;51(3):223–37.
Olson CK, Kutner LA, Warner DE. The role of violent video game content in adolescent development. J Adolesc Res. 2008;23(1):55–75.
Yee N. The demographics, motivations, and derived experiences of users of massively multi-user online graphical environments. Presence. 2006;15(3):309–29.
Zhong Z. The effects of collective MMORPG (Massively Multiplayer Online Role-Playing Games) play on gamers’ online and offline social capital. Comput Human Behav. 2011;27(6):2352–63.
Gentile DA, Anderson CA, Yukawa S, Ihori N, Saleem M, Ming LK, et al. The effects of prosocial video games on prosocial behaviors: international evidence from correlational, longitudinal, and experimental studies. Pers Soc Psychol Bull. 2009;35:752–63.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Cole H, Griffiths MD. Social interactions in massively multiplayer online role-playing gamers. Cyberpsychol Behav. 2007;10(4):575–83.
Belozerov SA. Virtual worlds of MMORPG. Part II. Remedy for social and psychological ill-being. Psychology: Journal of Higher School of Economics. 2015;12(1):71–89.
LaRose R. Eastin MS, Gregg J. Reformulating the Internet paradox: social cognitive explanations of Internet use and depression. J Online Behav. 2001;1(2).
Shaw LH, Grant LM. defense of the internet: the relationship between internet communication and depression, loneliness, self-esteem, and perceived social support. Cyberpsychol Behav. 2002;5(2):157–71.
Snodgrass JG, Lacy MG, Francois Dengah HJ 2nd, Fagan J. Enhancing one life rather than living two: playing MMOs with offline friends. Comput Human Behav. 2011;27(3):1211–22.
Russoniello CV, Fish M, O’Brien K. The efficacy of casual video game play in reducing clinical depression: a randomized controlled study. Games Health J. 2013;2(6):341–6.
Russoniello CV, O’Brien K, Parks JM. The effectiveness of casual video games in improving mood and decreasing stress. J Cyber Ther Rehabil. 2009;2(1):53–66.
Fish MT, Russoniello CV, O’Brien K. The efficacy of prescribed casual videogame play in reducing symptoms of anxiety: a randomized controlled study. Games Health J. 2014;3(5):291–5.
Patel A, Schieble T, Davidson M, Tran MC, Schoenberg C, Delphin E, et al. Distraction with a hand-held video game reduces pediatric preoperative anxiety. Paediatr Anaesth. 2006;16(10):1019–27.
Colwell J. Needs met through computer game play among adolescents. Personal Individ Differ. 2007;43:2072–82.
Snodgrass JG, Lacy M, Francois Dengah HJ 2nd, Fagan J, Most D. Magical flight and monstrous stress: technologies of absorption and mental wellness in Azeroth. Cult Med Psychiatry 2011;35(1):26–62.
Holmes EA, James EL, Coode-Bate T, Deeprose C. Can playing the computer game “Tetris” reduce the build-up of flashbacks for trauma? A proposal from cognitive science. PLoS One. 2009;4(1):e4153.
Holmes EA, James EL, Kilford EJ, Deeprose C. Key steps in developing a cognitive vaccine against traumatic flashbacks: visuospatial Tetris versus Verbal Pub Quiz. PLoS One. 2010;5(11):e13706.
Moisala M, Salmela V, Hietajarvi L, Carlson S, Vuontela V, Lonka K, et al. Gaming is related to enhanced working memory performance and task-related cortical activity. Brain Res. 2017;1655:204–15.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Chan PA, Rabinowitz TA. cross-sectional analysis of video games and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder symptoms in adolescents. Ann Gen Psychiatry. 2006;5(16):5–16.
Barlett CP, Anderson CA, Swing EL. Video game effects—confirmed, suspected, and speculative. Simul Gaming. 2009;40(3):377–403.
Subrahmanyam K, Greenfield PM. Effect of video game practice on spatial skills in girls and boys. J Appl Dev Psychol. 1994;15(1):13–32.
Middleton KK, Hamilton T, Tsai PC, Middleton DB, Falcone JL, Hamad G. Improved nondominant hand performance on a laparoscopic virtual reality simulator after playing the Nintendo Wii. Surg Endosc. 2013;27(11):4224–31.
Li J, Theng Y, Foo S. Game-based digital interventions for depression therapy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cyberpsychol Behav Soc Netw. 2014;17(8):519–27.
Merry SN, Stasiak K, Shepherd M, Frampton C, Fleming T, Lucassen MF. The effectiveness of SPARX, a computerised self help intervention for adolescents seeking help for depression: randomised controlled non-inferiority trial. BMJ. 2012;344:e2598.
Carrasco AE. Acceptability of an adventure video game in the treatment of female adolescents with symptoms of depression. Res Psychother. 2016;19(1):10–8.
Sharry J, McDermott M, Condron J. ‘Relax To Win’—treating children with anxiety problems with a biofeedback video game. Eistach. 2003;2:22–6.
Knox M, Lentini J, Cummings TS, McGrady A, Whearty K, Sancrant L. Game-based biofeedback for paediatric anxiety and depression. Ment Health Fam Med. 2011;8(3):195–203.
CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Scholten H, Malmberg M, Lobel A, Engels A, Granic IA. randomized controlled trial to test the effectiveness of an immersive 3D video game for anxiety prevention among adolescents. PLoS One. 2016;11(1):e0147763.
Pope AT, Bogart EH. Extended attention span training system: video game neurotherapy for attention deficit disorder. Child Study Journal. 1996;26(1):39–50.
Butnik SM. Neurofeedback in adolescents and adults with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder. J Clin Psychol. 2005;61(5):621–5.
Nodell B. Game your brain to treat depression, studies suggest. News Beat: UW Health Sciences [Internet]. 03 Jan 2017 [cited 28 Apr 2017]; Research [about 3 screens]. http://hsnewsbeat.uw.edu/story/studies-suggest-gaming-your-brain-treat-depression
Anguera JA, Gunning FM, Arean PA. Improving late life depression and cognitive control through the use of therapeutic video game technology: a proof-of-concept randomized trial. Depress Anxiety. 2016 Dec [cited 28 Apr 2017]. https://doi.org/10.1002/da.22588
Rabiner DL, Murray DW, Skinner AT, Malone PSA. randomized trial of two promising computer-based interventions for students with attention difficulties. J Abnorm Child Psychol. 2010;38(1):131–42.
Weerdmeester J, Cima M, Granic I, Hashemian Y, Gotsis M. A feasibility study on the effectiveness of a full-body videogame intervention for decreasing attention deficit hyperactivity disorder symptoms. Games for Health. 2016;5(4):258–69.
Bellack AS, Dickinson D, Morris SE, Tenhula WN. The development of a computer-assisted cognitive remediation program for patients with schizophrenia. Isr J Psychiatry Relat Sci. 2005;42(1):5–14.
PubMed Google Scholar
Shrimpton B, Hurworth R. Adventures in evaluation: reviewing a CD-ROM based adventure game designed for young people recovering from psychosis. J Educ Multimed Hypermedia. 2005;14(3):273–90.
Tanaka JW, Wolf JM, Klaiman C, Koenig K, Cockburn J, Herlihy L, et al. Using computerized games to teach face recognition skills to children with autism spectrum disorder: the Let’s Face It! program. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2010;51(8):944–52.
Brown ER, Craig AB, DeRosier ME. Hall of Heroes: a social skills training game to prepare students for the transition to middle school. Forthcoming: J Early Adolesc; 2017.
Corrigan PW, Druss BG, Perlick DA. The impact of mental illness stigma on seeking and participating in mental health care. Psychol Sci Public Interest. 2014;15(2):37–70.
Shandley K, Austin D, Klein B, Kyrios M. An evaluation of ‘Reach Out Central’: an online gaming program for supporting the mental health of young people. Health Educ Res. 2010;25(4):563–74.
Download references
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank their three sons—Jefferson Thomas, Benjamin Thomas, and Lincoln Thomas—who provided considerable input (and fact-checking) for this chapter regarding popular commercial video games, video game genres, and video gaming experiences. Their feedback and sharing were integral in helping the authors conceptualize teens’ gameplay experiences when writing the first section of this chapter. The authors would also like to thank Mary Whatley who aided considerably in conducting a literature search and compiling the citations included in this chapter.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
3C Institute, Durham, NC, USA
Melissa E. DeRosier Ph.D. & James M. Thomas Ph.D.
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Melissa E. DeRosier Ph.D. .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Department of Pediatrics, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, Wisconsin, USA
Megan A. Moreno
Department of Pediatrics, University of Pittsburgh Children’s Hospital of Pittsburgh of UPMC, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, USA
Ana Radovic
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer International Publishing AG
About this chapter
DeRosier, M.E., Thomas, J.M. (2018). Video Games and Their Impact on Teens’ Mental Health. In: Moreno, M., Radovic, A. (eds) Technology and Adolescent Mental Health . Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-69638-6_17
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-69638-6_17
Published : 02 March 2018
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-319-69637-9
Online ISBN : 978-3-319-69638-6
eBook Packages : Medicine Medicine (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
Essay on Importance of Games and Sports: 200, 300, 400, 500, 600 Words
Today we are providing 5 different types and formats of Essay on the Importance of Games and Sports for you. This is a really important topic for school and college students. Even the graduation level students can use these essays for them. You will find a suitable one for you.
In This Blog We Will Discuss
Short Essay on Importance of Games and Sports: 200 Words for Class 1, 2, 3

Sports and games are really important in human life. We should play games and sports regularly to build better physical and mental health. It helps us in several ways to get a better body. Especially the students should play more and more games and sports. Sports increase stamina and self-confidence. When you are playing a competitive game, you will learn lots of things in real. That will help you to grow your self-confidence. At the same time, your body will get lots of stamina. Both physical fitness and mental health become better by playing games. It teaches you lots of rules that help you to become a more disciplined person in the future. Games like chess are really effective to increase your mental health. Sometimes sports like football or rugby could be a bit dangerous for unprofessional players. But if everyone is friendly, then there is not a problem. Anybody should play football or games like this without proper training because that could fall you in an injury. Overall sports and games are really important in our life. We should play and let our kids play sports regularly.
Essay on Importance of Games and Sports: 300 Words for Class 4, 5

Introduction: Sports are really important for the youth. An entire young generation should be involved with sports and games. There are lots of advantages to that. In this essay, we will talk about sports and games’ importance in our regular life. Sports and games help people to grow physically and mentally faster. Even it helps to get interesting characteristics. And several games and sports competition makes people really competitive that are important for regular life.
Teamwork: Sports are the best option to learn teamwork. We know it’s easy to achieve something with a good team. Teamwork is not easy always if you don’t have the proper knowledge to handle your team. If you play sports regularly, you have to be with a team. You will get a proper guide from the leader and once you become the leader, you need to guide them properly. In that process, you will learn how a team works and it will be great for your future teamwork. If a team can perform properly together, then anything is possible.
Release Stress: Stress could be a reason for suicide in some cases. We all look for a way to release stress. Sport is an amazing way to release stress. When you are playing a game, your complete concentration will be on the game. In that case, you will forget other things that were happening with you. That will help you to get out of hard times.
Conclusion: We all need to get some time for sports from our busy schedule because it’s important for our physical and mental health both. And it teaches us so many real things. So from now, we should let our kids play more.
Importance of Games and Sports Essay: 400 Words for Class 6, 7, 8

Introduction: Games and sports are part and parcel of our regular life. We should play more sports every day to keep ourselves healthy and fit. There are lots of researches and experts said that playing sports could be a really great option to be fit and keep our heart and organs healthy. Participating in sports reduces your stress and make your mood better. It is the best option to become healthy, fit, improves sleeps and improves self-confidence.
Sports to Keep You Fit: Fitness is important in our life. If you don’t remain fit and healthy, your normal life will be hampered. Most of the time, you don’t need to do extra exercise if you are a regular sports lover.
Sports for Kids: Kids should play regularly, first of all, it improves their immune system. It is a little bit hard to control the kids and their health. When a kid sleeps properly, it makes him fit for the next day. We need to let our kids play outside. It is a way of entertainment for them too.
Improving Mental Strength: It is proved by the experts that sports can make your inner power stronger. It is important for mental growth too. The brain of a sportsman become so much fast and they become clever in their regular life. When the kids play games regularly, they learn several tricks to survive and it helps them to be mature in real life.
Sports as Profession: There are lots of sportsmen we see and we follow as influencers and celebrities. All of them came from a really simple family. They did hard work and they understood their talent. As like this, there are lots of students are really good at cricket or football. The school should pick them and arrange special training for them. These students are future Virat Kohli or MS Dhoni. If you look back, all these legends came from the really normal area and normal family. Their parents and they cared about their talent. Even ordinary students also should get the opportunity to practice and make them strong physically. Physical strength is important for everyone. Without enough physical strength, you won’t be able to perform better in your life.
Conclusion: As you can understand, the importance of sports and games is very much in our life. We should be involved in sports.
Essay on Importance of Games and Sports: 500 Words for Class 9, 10

Introduction: Sports and games are a really important part of our life. It helps us to become strong physically and mentally. A good sportsman is a good human too. A sport teaches us so many real-life lessons that help us to understand the meaning of life. There is a huge importance of games and sports for students, ordinary people and almost everyone.
Importance of Sports in Life: There are so many benefits of sports in life. First of all, let’s consider the physical side. It is proved that regular sportsperson has a good heart. That’s means, if you play games and sports regularly, it will improve your heart condition. Doctors say that sport is a strong option to prevent heart diseases. You won’t find any people facing heart problem who is a regular player in cricket, football or another game. It makes our physics really strong, the blood vessels become cleaner. Even you can consider this as your regular exercise too. It reduces fats and cholesterol from the body that makes people really healthy. Overall sport is really important for good health. If you want to learn discipline, you can learn it from sports. Because there are some specific rules and regulations that you must need to follow in every game. You can’t commit any action out of rules. If you are good in a specific sport, that could be your career too. Lots of people are getting connected with sports permanently and there is a bright career ahead. Even they are making a fair amount of money with their skill and entertaining characteristics.
Never Give Up Mentality: Sports build a never give up mentality in your brain. You will face lots of a hard time and under pressure moments in the game. If you can overcome these moments and get a win, you will gain lots of self-confidence. That will teach you not to lose hope in your life. This mentality or mental strength is really important for everyone. If you are really strong inside, you will be able to make hard things easy in your life.
Makes More Competitive: Competition is the core thing in a game or sport. There are usually two teams that compete with each other. In some games, there could be more than two teams. But the main thing is to compete with each other. End of the competition the best performer becomes the winner. So if you play games and sports regularly, you will get a competitiveness mind setup for your future. That will assist you to compete with bad moments of your life.
No Need to Do Extra Exercise: You don’t need to do any extra physical exercise to keep yourself healthy if you are a regular sportsman. It will keep you fit and healthy. There is no better option than playing sports to stay healthy.
Conclusion: There is a lot of importance to sports in our life. We need to play and promote sports among the young generation.
Importance of Games and Sports Essay: 600 Words for Class 11, 12

Introduction: We all play games and sports in our life. But nowadays, the time for sports and games are really limited for the students. They have to follow a tight study schedule or they don’t have proper facilities for playing sports. The biggest problem is enough space or playground. In big cities, there are really fewer playgrounds for the students. That’s a really threatening thing for the future generation. Sports are really important in many ways in our life. We are going to talk about this in that essay. I hope you will enjoy it.
Sports in My School: In my school , sport is mandatory. We have a really big playground in front of our school. The field is really amazing for playing both football and cricket. Most of the time, students play cricket, but there is a specific season for football too. We have a really strong football and cricket team. Last year, we won the interschool cricket championship in our district. Our teachers are also really conscious of sports. They want every student to participate in different games. Not only cricket and football, but there are also some other sports too that we play. Our cricket coach is Mahmudul Hasan sir. He is a great person and really experienced sports coach. He is conscious of our fitness. We need to do proper exercise, before any cricket tournament. We play three main tournaments in a year. I got selected in the main team when I was in class nine. And then became a captain in class ten, and stills serving the school team as a captain. We have won lots of trophies under my captaincy. So overall, there is an amazing sports environment in my school . I wish every school to become a sport-loving place like my school .
Importance of Sports in Student Life: A student’s main duty is to study. But to keep balance in mental and physical health, we need to come out and do some physical exercise. And as a young boy or girl, there not other better option to do physical exercise than playing games and sports. It makes us really happy when we do something good in the game. Even if we lose, it teaches us to accept lose and walk ahead. Sometimes, we face hard times in the cricket pitch or football field. We learn how to control the pressure in a hard time. So the sport is full of lessons. We can learn lots of real-life lessons from it. There is no hesitation that the importance of sports is really high in student life. You must need to participate in lots of sports at that age.
Sports to Spread Social Awareness: The youth is facing lots of problems these days. A big number of them are being connected with drugs and eve-teasing. In that case, sports can change the entire scenario. When a young boy gets free time, he wants to use it on a thing that he can make fun of. So it’s not really surprising that they start taking drugs with bad company. But if that boy is connected with cricket or football, he will love the game automatically. He always will try to keep himself fit for the game. In that case, he will use his spare time to practice and will do physical exercise. Overall, it’s a matter to enjoy the game. We know we all love playing and watching sports and games. We just need proper facilities to play that. So we need to promote games and sports with some social messages and spreading some social awareness to save our youth from the drugs and other crimes.
Conclusion: We need to give our kids enough opportunity to play sports and games so that they can prepare themselves mentally and physically.
Similar Search Terms:
• importance of games and sports essay for 12th class
• essay on the importance of games and sports in 500 words
• essay writing on the value of games and sports
• importance of games and sports essay in English with headings
• essay on the importance of games and sports with headings
• importance of games and sports essay for 10th class
• importance of games and sports essay for class 9
• importance of games and sports essay in points
More Essays
- Environment Pollution Essay Writing for Students
- Essay on Aim in Life | 100, 150, 300, 500 Words Paragraphs and Essays
- Essay on Railway Station | Short and Long Essays for Students
- Essay on Female Education: For All Students
- Essay on My Mother: 200, 300, 400, 500, 600 Words Essays
- Rainy Season Essay and Paragraph for School Students
- Essay on Winter Vacation for All Class Students
- My Grandmother Essay in 100, 150, 250, 300, 400 Words for Students
- Essay on Social Media for School and College Students
- Essay on Myself: For All Classes Students and Children
- Essay on Travelling in English for All Class
- Essay on Save Water in 200, 300, 400, 500 and 600 Words for All Classes
- Essay on My Best Friend in 200, 300, 400, 500 and 600 Words
- Essay on My Parents: 100, 200, 300, 400, 500 Words
- My Sister Essay in 100, 200, 300, 400, 500 Words for All Students
- Visit to a Historical Place Essay for All Class
- Essay on How I Spent My Holidays at Home
- Essay on My Dad My Hero for All Classes
- Essay on My School for All Class Students
- Essay on Importance of Computer for All Students
- A Rainy Day Essay: 100, 200, 300, 400, 500 Words
Related posts:
- Essay on Childhood Memories in 200, 300, 400, 500, 600 Words
- Essay on Early Rising in 300, 400, 500, 600 Words for Class 1-10
- Essay on Good Manners in 300, 400, 500, 600 Words for Class 1-10

Essay on Sports and Games for Students and Children
500+ words essay on sports and games.
sports and games are essential for both physical and mental of the students. Moreover, it increases the immunity of the person. As it increases the blood flow in the body and makes it adaptable for exertion. The main difference between a sport and a game is, we can play games both indoors and outdoors. But we can only play sports outdoors. Furthermore, there are various advantages to sports and games. Some of them are below:

Advantages of sports
Physical Fitness- Sports and games play a major rule in keeping a person fit and fine. Furthermore, it increases the blood flow in the entire body. So this helps in keeping the heart in the best condition. Moreover, the immunity of the body increases by playing outdoor sports. Also, it helps in keeping your body fat percentage low. This makes the appearance of the body better and makes a person good-looking.
Increase mental health- Games like chess , card games increase the mental health of a person . As it develops Spontaneity and the response time of a person. As a result, a person’s mind can make a decision under pressure. Thus this helps in increasing the IQ of a person and its’ presence of mind.
Increase Stamina- Outdoor Sports like Football , cricket, basketball, swimming builds the stamina of a person. As all these sports require a lot of running, the stamina of a person automatically increases. Therefore a person can work for a longer period of time without getting tired.
Builds a sense of teamwork- Some sports need individual participation, while some require teamwork. Thus sports enlists teamwork in a person. Which is essential in every fieldwork. A company can only run by working together and not individually. So it is important for a person to know how to work together in a team. Only then you can achieve the desired goal .
Stress-relieving- Sports can bring a change to your day to day routine. Moreover, it can relieve you from stress as your body will experience a change. It gives your mind a boost of enthusiasm and happiness. As a result, it will fill you with energy for the next day.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
Disadvantages of sport and games
Dangerous- Some sports like football, cricket , basketball, swimming can be dangerous. Because any injury can occur while playing these sports. Therefore you should wear proper safety gear before playing it. Moreover, it can be harmful if you are playing it while you are sick.
Exhausting- Sports require energy, so a person needs to have proper meals. Moreover, the body needs rest to recover from the exertion. Therefore you need proper sleep every day if you are indulging in any sport.
Takes time- In order to play any sport, you have to take out time from your busy schedule. This may be very difficult for some people. As they work day and night to fulfill the needs of their family. So a person needs to cut off some things from their busy schedule to take out time to play a sport.
FAQ On the essay on sports and games
Q1. What is the main difference between sports and games?
A1. The main difference between sports and games is, we can play sports only outdoors. But games can take place both indoors and outdoors.
Q2. Write any two advantages and disadvantages of sports.
A2. The advantages of sports are it keeps a person fit and is a stress buster. The disadvantages of sports are it can be dangerous to play, injury can occur while playing and it is can be exhausting.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

The Role and Importance of Body Farms in Forensic Science
This essay about body farms explains their role and importance in forensic science. Body farms are research facilities where scientists study the decomposition of human remains under various conditions. The information gathered helps forensic experts determine the time of death and identify human remains in criminal investigations. Established by Dr. William Bass in 1981, these facilities simulate real-world scenarios to understand how environmental factors affect decomposition. The research also aids in educational training and has broader applications in fields like environmental science and archaeology. Despite public discomfort, body farms make significant contributions to science and justice.
How it works
A body farm, more formally termed as a forensic osteology research enclave, denotes a specialized open-air laboratory where scholars scrutinize the necrosis of human cadavers. These facilities assume a pivotal function in legal medicine by furnishing invaluable data that facilitates forensic osteologists, pathologists, and law enforcement entities in comprehending the phases of human necrosis under diverse circumstances. This erudition is imperative for accurately ascertaining the chronology of demise and other medico-legal intricacies in criminal inquiries.
The notion of a body farm was pioneered by Dr.
William Bass in 1981 with the inauguration of the University of Tennessee Anthropological Research Facility in Knoxville. Since then, several other necrotariums have been established in disparate regions of the United States, each augmenting the burgeoning repository of knowledge in forensic osteology.
At a body farm, donated human cadavers are situated in myriad environs to observe their decomposition. These environs encompass interment, surface exposure, submersion in aqueous habitats, or emplacement within diverse receptacles. Researchers meticulously chronicle the necrotic process, documenting parameters such as ambient temperature, humidity, arthropod activity, and the ramifications of scavenging fauna. By scrutinizing these variables, scholars can devise more precise methodologies for gauging post-mortem intervals, i.e., the duration that has elapsed since decease.
A fundamental facet of necrotariums is their capability to emulate real-world scenarios that forensic connoisseurs might confront. For instance, cadavers may be positioned in shaded locales, exposed to direct solar irradiation, or interred at varying depths. These scenarios facilitate researchers in discerning how sundry environmental factors influence the pace of decomposition. This intel is pivotal when investigators need to approximate the time of demise in instances where cadavers are unearthed in divergent conditions, such as arboreal regions, arid hinterlands, or urban milieus.
In tandem with aiding in the estimation of the time of demise, research conducted at necrotariums also assists in the identification of human remains. By scrutinizing the repercussions of decomposition on osseous and corporeal tissues, forensic osteologists can contrive methodologies for identifying individuals predicated on skeletal remains. This is markedly consequential in instances of mass catastrophes, unmarked sepulchers, or circumstances where cadavers are exceedingly decomposed.
The research conducted at necrotariums also proffers broader applications beyond criminal investigations. For instance, it contributes to our comprehension of the ecologic repercussions of human necrosis, which can inform domains such as environmental science and biology. Additionally, the amassed data can ameliorate practices in fields like archaeology, where discerning how antiquated remains have decomposed over epochs can yield insights into historical and prehistorical events.
Necrotariums also discharge an educational function, affording tutelage for scholars and professionals in legal medicine. They provide a hands-on learning milieu where individuals can acquire pragmatic proficiency in forensic methodologies and techniques. This pedagogy is invaluable for those embarking on vocations in forensic osteology, law enforcement, and kindred domains, as it primes them for the intricacies and vicissitudes they will encounter in real-world scenarios.
Despite their scientific and pedagogical merit, necrotariums are occasionally perceived with discomposure by the populace. The notion of scrutinizing decomposing cadavers can appear somber or disquieting. However, it is imperative to acknowledge the substantive contributions these facilities render to legal medicine and the broader comprehension of human necrosis. The insights gleaned from necrotariums bear a direct impact on resolving crimes, identifying missing persons, and advancing scientific erudition.
In summation, body farms are indispensable research enclaves that furnish crucial data for legal medicine. By scrutinizing the decomposition of human remains under diverse conditions, these facilities aid forensic connoisseurs in devising more precise methodologies for ascertaining the time of demise and identifying human remains. The research conducted at necrotariums harbors far-reaching ramifications, benefitting criminal inquiries, environmental science, and educational initiatives. While they may elicit mixed reactions, the contributions of necrotariums to science and jurisprudence are invaluable, rendering them an integral component of contemporary forensic osteology.
Cite this page
The Role and Importance of Body Farms in Forensic Science. (2024, Jun 01). Retrieved from https://papersowl.com/examples/the-role-and-importance-of-body-farms-in-forensic-science/
"The Role and Importance of Body Farms in Forensic Science." PapersOwl.com , 1 Jun 2024, https://papersowl.com/examples/the-role-and-importance-of-body-farms-in-forensic-science/
PapersOwl.com. (2024). The Role and Importance of Body Farms in Forensic Science . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/the-role-and-importance-of-body-farms-in-forensic-science/ [Accessed: 3 Jun. 2024]
"The Role and Importance of Body Farms in Forensic Science." PapersOwl.com, Jun 01, 2024. Accessed June 3, 2024. https://papersowl.com/examples/the-role-and-importance-of-body-farms-in-forensic-science/
"The Role and Importance of Body Farms in Forensic Science," PapersOwl.com , 01-Jun-2024. [Online]. Available: https://papersowl.com/examples/the-role-and-importance-of-body-farms-in-forensic-science/. [Accessed: 3-Jun-2024]
PapersOwl.com. (2024). The Role and Importance of Body Farms in Forensic Science . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/the-role-and-importance-of-body-farms-in-forensic-science/ [Accessed: 3-Jun-2024]
Don't let plagiarism ruin your grade
Hire a writer to get a unique paper crafted to your needs.

Our writers will help you fix any mistakes and get an A+!
Please check your inbox.
You can order an original essay written according to your instructions.
Trusted by over 1 million students worldwide
1. Tell Us Your Requirements
2. Pick your perfect writer
3. Get Your Paper and Pay
Hi! I'm Amy, your personal assistant!
Don't know where to start? Give me your paper requirements and I connect you to an academic expert.
short deadlines
100% Plagiarism-Free
Certified writers
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player

Author Interviews
- LISTEN & FOLLOW
- Apple Podcasts
- Google Podcasts
- Amazon Music
Your support helps make our show possible and unlocks access to our sponsor-free feed.
For 'Such Kindness' novelist Andre Dubus III, chronic pain is a fact of life

Terry Gross
Dubus talks about the injuries he faced as a carpenter and his relationship with his dad. His a new collection of personal essays is Ghost Dogs: On Killers and Kin. Originally broadcast in 2023.
Hear the Original Interivew
Copyright © 2024 NPR. All rights reserved. Visit our website terms of use and permissions pages at www.npr.org for further information.
NPR transcripts are created on a rush deadline by an NPR contractor. This text may not be in its final form and may be updated or revised in the future. Accuracy and availability may vary. The authoritative record of NPR’s programming is the audio record.

Sign in to add this item to your wishlist, follow it, or mark it as ignored
Online interactivity, In-game chat
Coming soon
About this game, system requirements.
- Requires a 64-bit processor and operating system
- OS: Windows 10/11 64-bit
- Processor: Intel® Core i5 (Quad Core or better)
- Memory: 8 GB RAM
- Graphics: NVIDIA® GeForce® GTX 1060
- DirectX: Version 12
- Network: Broadband Internet connection
- Storage: 20 GB available space
- Additional Notes: SSD Recommended
- Processor: Intel® Core™ i7 (6 Core or better)
- Memory: 16 GB RAM
- Graphics: NVIDIA® GeForce® RTX 2060
©2024 Middle-earth Enterprises. All rights reserved. "Moria", "Middle-Earth" and "The Lord of the Rings" and the names of the characters, events, items, and places therein are trademarks or registered trademarks of Middle-earth Enterprises, LLC under license to Open Door Entertainment, LLC dba North Beach Games. ©2024 Free Range Games. All rights reserved. Free Range Games and the Free Range Games logo are trademarks or service marks of Free Range Games. ©2024 North Beach Games and associated logos and names are trademarks of Open Door Entertainment, LLC
More like this
What curators say.
You can write your own review for this product to share your experience with the community. Use the area above the purchase buttons on this page to write your review.

You can use this widget-maker to generate a bit of HTML that can be embedded in your website to easily allow customers to purchase this game on Steam.
Enter up to 375 characters to add a description to your widget:
Copy and paste the HTML below into your website to make the above widget appear

Popular user-defined tags for this product: (?)
Sign in to add your own tags to this product.


Sky's Chennedy Carter has 'no regrets' about foul on Caitlin Clark; Angel Reese will 'take the bad guy role'
I t's been two days since the Chicago Sky lost 71-70 to the Indiana Fever , and the Sky have finally broken their silence about the most talked-about play from that game: Chennedy Carter's upgraded flagrant foul on Fever rookie Caitlin Clark .
Head coach Teresa Weatherspoon was the first to speak about it on Monday, releasing a statement about how she addressed the play with Carter.
"Physical play, intensity, and a competitive spirit are hallmarks of Chicago Sky basketball. Chennedy got caught up in the heat of the moment in an effort to win the game. She and I have discussed what happened and that it was not appropriate, nor is it what we do or who we are. Chennedy understands that there are better ways to handle situations on the court, and she will learn from this as we all will.
"As a team, we will grow together and continue to work hard to display strong leadership and set a positive example for our competitors, fans, and partners."
Carter gave Clark a hard shove at the end of the third quarter without the ball in play. Clark landed on the floor and Carter was called for a personal foul. The WNBA upgraded the foul to a flagrant-1 after further review on Sunday. No one on the Sky commented about Clark or the foul following the game.
Angel Reese skipped her postgame media commitments completely, which is against WNBA media policy. The league announced Sunday that Reese had been fined $1,000 for skipping interviews and the Sky had been fined $5,000 for allowing her to violate the WNBA's media policy.
But both Reese and Carter were front and center on Monday afternoon, addressing the media together and speaking their minds about what happened Saturday. Carter began by saying she had "no regrets."
Carter followed that up by saying she has "no complaints" even though the Sky have been the subject of a lot of negative talk over the past few days.
Reese, who was seen cheering on the sideline when Carter fouled Clark, then said she's willing to play whatever role the game needs her to play. If she needs to be the villain, then that's exactly what she'll do.
The Sky's next game is against the New York Liberty on Tuesday night.
Edmonton Oilers reach Stanley Cup Final with Game 6 victory against Dallas Stars

The Edmonton Oilers are heading to the Stanley Cup Final for the first time in the Connor McDavid era, and the team captain played a huge role in making it happen in clinching Game 6.
McDavid had a highlight-reel goal and an assist in a 2-1 victory against the Dallas Stars on Sunday night that earned the Oilers their first trip to the championship round since 2006.
They will face the Florida Panthers in the best-of-seven series, starting Saturday night in Sunrise, Florida. The Panthers, back in the Final for the second consecutive season, are seeking their first Stanley Cup title. The Oilers have five championships and last won in 1990.
"It feels great to be in this position," McDavid told reporters. "This was always part of the plan, and it feels good to be here today."
McDavid has been the NHL's best player since being drafted No. 1 overall in 2015 and is a three-time winner of the Hart Trophy. But the farthest he has reached in the playoffs previously was the Oilers being swept in the 2022 conference final.
The Oilers broke through during a season in which they started 3-9-1, fired coach Jay Woodcroft and hired Kris Knoblauch. They turned their season around with a 16-game winning streak , and McDavid joined rare company with an 100-assist season . McDavid leads all playoff scorers with 31 points.
Here's how the Oilers won Game 6 and what's next for them and the Stars:
How the Edmonton Oilers beat the Dallas Stars in Game 6
McDavid gave the Oilers a 1-0 lead at 4:17 of the first period with a spectacular goal. He took a pass on the power play, stickhandled between Sam Steel and Miro Heiskanen and roofed a shot past Stars goalie Jake Oettinger.
"There's only one player in the world that can make things like that happen," teammate Leon Draisaitl said.
McDavid helped add to the lead when he fed Zach Hyman on the power play. Hyman scored his league-leading 14th goal of the playoffs.
The Oilers emerged from the first period with a 2-0 lead despite being outshot 12-3.
The Stars continued to press in the second period with Roope Hintz hitting the post.
The Oilers killed a delay of game penalty to Draisaitl in the third period, but Dallas' Mason Marchment soon after cut the Stars' deficit to 2-1 at 9:18.
Oilers goalie Stuart Skinner finished with 34 saves for the victory in a game in which Edmonton was outshot 35-10.
"We're on a plane to Dallas if not for Stu," McDavid said.
The Oilers didn't touch the Clarence S. Campbell Bowl awarded to the Western Conference champion. The Panthers didn't touch the Prince of Wales Trophy on Saturday, either.
What's next for the Edmonton Oilers?
They will open on the road against the Panthers in the Stanley Cup Final. But they have won the past two rounds without having home-ice advantage and won Game 7 against the Vancouver Canucks on the road.
The Panthers won the season series 2-0.
The Oilers have four power-play goals in their last two games after none in the first four games against the Stars. That will be a plus against a Panthers team that allowed only one power-play goal against the New York Rangers. But Edmonton also has been excellent at penalty killing, perfect in its last 10 games.
The matchup of Selke Trophy winner Aleksander Barkov and McDavid should be fun to watch.
What's next for the Dallas Stars?
They have fallen in the Western Conference final for the second consecutive season.
"You could probably argue that it was our best game of the series," captain Jamie Benn said. "It just didn't go our way."
Trade deadline acquisition Chris Tanev played a big role in their playoff run and is an unrestricted free agent.
So is Joe Pavelski, 39. Does the all-time leading U.S.-born playoff goal scorer return for another season or retire?
"I don't know if it will be Joe's last game or not, but an absolute privilege of my coaching career to coach a guy like that," Stars coach Peter DeBoer said.
The UFA list also includes Matt Duchene, who scored 25 goals this season after being bought out by the Nashville Predators , backup goalie Scott Wedgewood and defenseman Jani Hakanpaa.
Defenseman Thomas Harley is their key restricted free agent.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Given this vast diversity in video games, a single definition may not be useful. In fact, top scholars in the field have declared, "One can no more say what the effects of video games are, than one can say what the effects of food are" (Bavelier et al., 2011, p. 763). Thus, rather than define video games according to a convenient generality,
From action-packed shooters to immersive role-playing games, there is a video game out there for everyone. With such a wide variety of games to choose from, it can be overwhelming to decide on a topic for an essay about video games. To help you get started, here are 107 video game essay topic ideas and examples to inspire your writing:
This included AAA games, indie games, games on personal computers, on various consoles, old and new , on mobile devices, on web-bro wsers, online, offline, alone, with others, and much more.
In conclusion, video games can be a valuable tool for the cognitive and intellectual development of individuals. They require players to exercise various skills such as attentiveness, fast reaction times, logical thinking, and problem-solving. Additionally, video games can also benefit adults by improving communication, resourcefulness, and ...
250 Words Essay on Importance of Games The Essence of Games. Games, both physical and digital, play a pivotal role in the holistic development of individuals. They serve as a powerful tool, fostering psychological growth, enhancing physical fitness, and nurturing social skills. Psychological Development
The present study examined the educational roles of games that were not designed for pedagogical purposes. With respect to the roles of gamers' communication—communication networks, network ...
Conclusion. Altogether, videogames have both positive and negative effects on children. They might precondition the development of chronic diseases and extra weight, high anxiety, and depression levels, along with the changes in brain functioning. The highly-addictive nature increases the risks of spending too much time in games.
Design. The evolution of video games as a storytelling medium, and the role of narrative in modern games. This essay aims to investigate the topic of narrative in video games. Specifically, the evolution of narratives in games, and the role of narrative in today's story-based games.
Participation in games varies from simple turn-taking games, such as tag and chase, to typically more complex games with a variety of roles and rules, such as ball games and verbal games (Borman & Kurdek, 1987; Sutton-Smith, 1973; 1975 ). Though chase games can be complicated (Finnan, 1982 ), most are relatively simple.
Video games can also play a role in emotional regulation. Studies have shown that playing video games can provide an outlet for emotional expression and serve as a means of stress relief. Furthermore, multiplayer online games can provide opportunities for social interaction and can help individuals develop social skills and emotional intelligence.
For engaging essays about video games, read the essay examples featured below for inspiration. Quick Summary: ... "Any role video games play in skewing well-being that did pop up in the study was too small to have a real-world impact on how people feel, the authors said. People would have to play games for 10 more hours per day than their ...
video games have a direct impact on the transmission of culture. Patterns and agents of cultural. representation, transmission and communication were identified, allowing researchers to evaluate ...
Sports and games are crucial for promoting the overall health and well-being of an individual. Playing sports and games helps keep the human body in shape and develop strength, endurance, and patience. All medical professionals advise regular exercise as a disease prevention strategy. Exercising regularly or participating in any outdoor sport ...
Role-playing games (RPGs) typically combine action, adventure, and/or strategy elements into gameplay, but what differentiates RPGs is that the player assumes a particular role and acts out that role within the story world's narrative. Each role (or class) has a defined set of abilities, skills, and characteristics, and a primary focus of ...
Games focused pertain to some recurrent genres, notably massively multiplayer online games or MMO (n = 57), role-playing games or RPG (n = 34), and, at the intersection of these two, massively multiplayer online role-playing games or MMORPG (n = 28). MMOs and MMORPGs are usually highlighted for their social outcomes and many of these works aim ...
Advantages of Games in Life. Competition Factor: It generates a healthy, fair and strong spirit of competition. It also conducts that positive competition is the best and active way of competition in the student's life. Discipline Factor: It makes the child more active, patient and disciplined. Unity Factor: It teaches us about teamwork, sense ...
Every phase has played a crucial role in shaping the VGI, influencing both players and consumers, and weaving a rich tapestry of experiences. The nascent era of the Video Game Industry traces its origins back to the 1950s and 1960s, when trailblazers like William Higinbotham and Ralph Baer laid the foundation for interactive electronic games ...
Game -Based Teaching (GBT): Refers to the teacher practices involved in selecting, facilitating, and validating the use of games for educational purposes. The term is also used in contrast to the ...
Short Essay on Importance of Games and Sports: 200 Words for Class 1, 2, 3. Essay on Importance of Games and Sports: 300 Words for Class 4, 5. Importance of Games and Sports Essay: 400 Words for Class 6, 7, 8. Essay on Importance of Games and Sports: 500 Words for Class 9, 10. Importance of Games and Sports Essay: 600 Words for Class 11, 12.
500+ Words Essay on Sports and Games. sports and games are essential for both physical and mental of the students. Moreover, it increases the immunity of the person. As it increases the blood flow in the body and makes it adaptable for exertion. The main difference between a sport and a game is, we can play games both indoors and outdoors.
This essay about body farms explains their role and importance in forensic science. Body farms are research facilities where scientists study the decomposition of human remains under various conditions. The information gathered helps forensic experts determine the time of death and identify human remains in criminal investigations.
Wishlist Call of Duty®: Black Ops 6 now! Get Ready for the Worldwide Reveal on June 9. All Reviews: No user reviews. Release Date: Coming soon. Developer: Treyarch, Raven Software, Beenox, High Moon Studios, Activision Shanghai, Sledgehammer Games, Infinity Ward, Demonware. Publisher:
At a time when Americans are divided by race and class and age, pickup basketball cuts across those lines. On the court, it doesn't matter what you look like or what you do for a living, and the ...
Dubus talks about the injuries he faced as a carpenter and his relationship with his dad. His a new collection of personal essays is Ghost Dogs: On Killers and Kin. Originally broadcast in 2023.
About This Game. The Lord of the Rings: Return to Moria™ follows the Dwarves as they embark on a new adventure to reclaim their legendary home of Moria beneath the Misty Mountains. Players will join forces to survive, craft, build and explore the iconic, sprawling mines. Courageous expeditioners will need to be vigilant as mysterious dangers ...
Reese, who was seen cheering on the sideline when Carter fouled Clark, then said she's willing to play whatever role the game needs her to play. If she needs to be the villain, then that's exactly ...
In this paper, we study the vital role of artificial intelligence (AI) in the development of video games, with a focus on various aspects of AI application in this industry. In the introduction ...
That's according to DanielRPK (thanks, The Game Awards), an industry insider behind repeated leaks. Sanada already boasts an impressive list of IMDB credits , but his role as Yoshii Toranaga ...
100 Words Essay On Games. Games are an essential and effective way for children to learn life skills like team spirit, leadership, relationship-building, as well as hone mental skills like problem-solving and decision-making. Kids who spend a lot of time indoors need indoor games. Playing these activities has various advantages, including ...
The Edmonton Oilers are heading to the Stanley Cup Final for the first time in the Connor McDavid era, and the team captain played a huge role in making it happen in clinching Game 6.. McDavid had ...