Essay on India
Here we have shared the Essay on India in detail so you can use it in your exam or assignment of 150, 250, 400, 500, or 1000 words.
You can use this Essay on India in any assignment or project whether you are in school (class 10th or 12th), college, or preparing for answer writing in competitive exams.
Topics covered in this article.

Essay on India in 150 words
Essay on india in 200-300 words, essay on india in 500-1000 words.
India, a diverse and culturally rich country located in South Asia, is renowned for its vibrant festivals, ancient heritage sites, and diverse landscapes. With a population of over 1.3 billion people, India is a melting pot of religions, languages, and ethnicities. It is a secular nation that upholds democracy and freedom. India has made significant contributions to art, literature, science, and philosophy. Despite challenges, it has achieved progress in various fields, including technology and economic growth. As the world’s largest democracy, India’s cultural richness, traditions, and hospitality attract tourists from around the world. With a young and dynamic workforce, India is emerging as a global player in innovation and entrepreneurship. India’s resilience, cultural heritage, and growing influence continue to captivate the world, making it an important player on the global stage.
India, known as the land of diversity, is a country of rich culture, history, and traditions. It is located in South Asia and is the seventh-largest country by land area. India is renowned for its vibrant festivals, ancient heritage sites, and diverse landscapes, ranging from the majestic Himalayas to the serene backwaters of Kerala.
With a population of over 1.3 billion people, India is a melting pot of different religions, languages, and ethnicities. It is a secular country that upholds the principles of democracy and freedom. India has made significant contributions to art, literature, science, and philosophy throughout history.
Despite its challenges, India has achieved notable progress in various fields, including technology, space exploration, and economic growth. It is the world’s largest democracy and has a parliamentary system of government. India’s cultural richness, traditions, and hospitality attract millions of tourists from around the world each year.
In recent years, India has emerged as a global player, contributing to the world economy, science, and technology. It is home to a young and dynamic workforce that is driving innovation and entrepreneurship.
In conclusion, India is a country that embraces diversity, celebrates its rich cultural heritage, and strives for progress. With its vast landscapes, ancient history, and vibrant culture, India continues to captivate the world. The resilience and spirit of its people, coupled with its growing influence, make India a significant player on the global stage.
Title: India – A Tapestry of Diversity, Heritage, and Progress
Introduction :
India, a nation located in South Asia, is a land of rich cultural heritage, diverse traditions, and breathtaking landscapes. With a population of over 1.3 billion people, India is known for its vibrant festivals, ancient history, and varied cuisines. This essay explores the multifaceted aspects of India, including its rich cultural tapestry, historical significance, economic growth, and contributions to the world. From the majestic Himalayas in the north to the serene backwaters of Kerala in the south, India’s beauty and diversity captivate the hearts of millions. Let us embark on a journey through the vibrant and enchanting land of India.
Cultural Heritage
India’s cultural heritage is as vast and diverse as its geographical expanse. It is a melting pot of religions, languages, and customs. The country is home to numerous religions, including Hinduism, Islam, Christianity, Sikhism, Buddhism, and Jainism. Each religion has its own unique rituals, traditions, and festivals, contributing to the colorful tapestry of Indian culture. Festivals like Diwali, Eid, Holi, Christmas, and Durga Puja are celebrated with great enthusiasm and are a reflection of India’s religious diversity.
Historical Significance
India boasts a rich history that spans thousands of years. It has been the birthplace of several ancient civilizations, including the Indus Valley Civilization and the Maurya and Gupta Empires. The country has been the center of learning and trade for centuries, attracting scholars, explorers, and traders from around the world. The Mughal Empire, known for its architectural marvels like the Taj Mahal, left a lasting legacy on India’s history. The British colonial rule in India and the subsequent struggle for independence led by Mahatma Gandhi shaped the modern history of the nation.
Economic Growth
India has experienced significant economic growth in recent years. It is one of the world’s fastest-growing major economies and has become a prominent player on the global stage. The country has embraced economic liberalization, attracting foreign investments and fostering entrepreneurship. India’s information technology industry, pharmaceutical sector, and service industries have flourished, contributing to its economic prosperity. However, challenges such as poverty, income inequality, and unemployment persist, highlighting the need for inclusive growth and sustainable development.
Contributions to the World
India has made remarkable contributions to various fields, including science, literature, arts, and spirituality. Ancient Indian scholars made significant advancements in mathematics, astronomy, and medicine. Indian literature, such as the Vedas, Ramayana, and Mahabharata, continues to inspire and influence people worldwide. Indian art forms like classical music, dance, and cinema have gained international recognition for their richness and beauty. Spiritual traditions like yoga and meditation have transcended borders, offering tools for holistic well-being.
Unity in Diversity
India’s strength lies in its unity amidst diversity. Despite its linguistic, religious, and cultural differences, the people of India have come together as a nation. The Constitution of India, adopted in 1950, upholds the principles of democracy, secularism, and unity. The diverse fabric of Indian society is reflected in its official languages, Hindi and English, and the recognition of regional languages. India’s unity in diversity is celebrated through cultural exchange, interfaith dialogue, and the promotion of national integration.
Future Challenges and Opportunities
India faces a range of challenges, including poverty, environmental degradation, healthcare disparities, and social inequality. Addressing these challenges requires concerted efforts in education, healthcare, sustainable development, and social welfare. However, India also presents immense opportunities for progress. With a young and dynamic workforce, a vibrant entrepreneurial spirit, and a growing middle class, India has the potential to achieve inclusive growth, technological advancements, and social transformation.
Conclusion :
India, with its diverse cultures, historical significance, economic growth, and contributions to the world, stands as a shining example of unity in diversity. The nation’s cultural heritage, ancient history, and rapid development reflect its resilience and potential. As India continues its journey toward progress and prosperity, it must embrace sustainable development, address societal challenges, and build an inclusive and equitable society. India’s beauty, traditions, and people leave an indelible mark on the hearts and minds of those who explore its captivating tapestry.
Related Posts

Essential Elements of Valid Contract (Explained With Examples)

What is World Population? Main Causes, Effects, Top 20 Countries

Essay on Incredible India
Students are often asked to write an essay on Incredible India in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on Incredible India
Land of diversity.
India, often known as “Incredible India,” is a land of rich culture, history, and diversity. It is famous for its colorful festivals, diverse languages, and varied landscapes.
Historical Significance
India’s history spans over five millennia, with significant contributions to art, science, and philosophy. It is home to ancient civilizations and world-famous monuments.
Cultural Richness
The Indian culture, with its myriad traditions, music, dance forms, and cuisines, is a true reflection of its diversity. Each region has a unique cultural identity.
Natural Beauty
From snow-capped mountains to sun-kissed beaches, India’s natural beauty is breathtaking. It has numerous national parks and wildlife sanctuaries.
Incredible India is a treasure trove of experiences, offering a fascinating mix of tradition and modernity. It truly symbolizes unity in diversity.
Also check:
- 10 Lines on Incredible India
- Speech on Incredible India
250 Words Essay on Incredible India
Introduction.
India, often referred to as ‘Incredible India’, is a nation that boasts of rich cultural heritage, diverse traditions, and historical landmarks. This unique amalgamation of cultures, religions, and languages makes India a truly incredible country to explore.
Cultural Diversity
India’s cultural diversity is its most remarkable feature. Home to a multitude of religions, India thrives on harmonious co-existence, tolerance, and respect for all faiths. With over 2,000 distinct ethnic groups and more than 1,600 spoken languages, the country exemplifies unity in diversity.
India’s historical significance is another aspect that contributes to its incredibility. From the architectural grandeur of Mughal monuments like the Taj Mahal to the spiritual allure of ancient Hindu temples, India’s historical sites are a testament to its rich past.
Natural Wonders
India’s geographical diversity is equally fascinating. From the snow-capped Himalayan peaks to the tropical beaches of Goa, from the arid Thar Desert to the lush Sundarbans, India offers an array of natural wonders that captivate the senses.
In conclusion, the term ‘Incredible India’ perfectly encapsulates the essence of this vibrant nation. Its cultural diversity, historical significance, and natural beauty make it a country like no other. The uniqueness of India lies in its ability to maintain its cultural essence while embracing modernity, making it truly incredible.
500 Words Essay on Incredible India
The land of diversity and harmony.
India, often known as “Incredible India,” is a country that stands out for its diverse culture, rich history, and fascinating traditions. It is a land where 1.3 billion people live in harmony, speaking over 2000 dialects, practicing various religions, and celebrating numerous festivals. This diversity is not a weakness but a strength that adds to the incredible nature of India.
The Cultural Mosaic
India’s culture is a colorful mosaic of different traditions, religions, and languages that have evolved over thousands of years. Each state has its unique culture, food, dance, music, and art forms, contributing to the country’s rich cultural heritage. This diversity in culture is a testament to India’s tolerance and acceptance, where every festival, be it Diwali, Eid, Christmas, or Pongal, is celebrated with equal fervor.
The Architectural Marvels
India is home to numerous architectural wonders that reflect its glorious past. From the intricate carvings of Ajanta and Ellora caves to the majestic Mughal architecture of Taj Mahal, from the grand palaces of Rajasthan to the serene monasteries of Ladakh, India’s architecture is a blend of various styles, each narrating a unique story of its time.
The Land of Spirituality
India is known as the birthplace of many religions like Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism, and Sikhism. It is a spiritual sanctuary where seekers from around the world come to find peace and enlightenment. The sacred Ganges, the tranquil Himalayas, the serene temples, and the vibrant ashrams all contribute to India’s spiritual allure.
India’s Natural Splendour
India’s natural beauty is as diverse as its culture. From the snow-capped Himalayan peaks to the sun-kissed beaches of Goa, from the dense forests of Sundarbans to the arid Thar Desert, India offers a wide range of landscapes. The country is also rich in biodiversity, hosting a variety of flora and fauna, some of which are endemic to the region.
Economic Growth and Challenges
India is a rapidly developing economy, with significant advancements in technology, healthcare, and education. However, it still grapples with challenges such as poverty, illiteracy, and corruption. Addressing these issues is crucial for India to fully realize its potential and continue its journey towards becoming a global superpower.
The essence of India lies in its diversity, its rich cultural heritage, its architectural grandeur, its spiritual ethos, and its natural beauty. Despite the challenges it faces, India continues to inspire and amaze the world with its resilience, tolerance, and unity in diversity. The journey through India is indeed incredible, filled with awe-inspiring sights, enriching experiences, and profound learnings. It is not just a country but a feeling that leaves an indelible mark on the hearts of those who experience it. In the words of Mark Twain, “India is the cradle of the human race, the birthplace of human speech, the mother of history, the grandmother of legend, and the great grandmother of tradition. Our most valuable and most instructive materials in the history of man are treasured up in India only.”
That’s it! I hope the essay helped you.
If you’re looking for more, here are essays on other interesting topics:
- Essay on Indian Economy
- Essay on Development of India
- Essay on Agriculture in India
Apart from these, you can look at all the essays by clicking here .
Happy studying!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.


Unity in Diversity: The Essence of India’s Composite Culture | Essay Writing for UPSC by Vikash Ranjan Sir | Triumph ias
Table of Contents
India’s Mosaic: A Celebration of Unity in Diversity
(relevant for essay writing for upsc civil services examination).

India’s vibrant landscape is dotted with myriad cultures, traditions, and histories. Dive into the mesmerizing mosaic of India’s composite culture and discover how it epitomizes unity in diversity.
The Threads of Time
From the ancient Indus Valley Civilization to modern-day India, the country has imbibed, evolved, and celebrated a myriad of influences, giving birth to its unique identity.
A Symphony of Cultures
Whether it’s the resonating chants from temples, the melodic calls for prayer from mosques, or the harmonious carols from churches, India embraces them all with open arms. Languages, festivals, art – every facet of Indian life reflects its harmonious blend.
Conclusion: A Lesson for the World
In times of global divisiveness, India’s composite culture stands tall as a testament to the strength and beauty of unity in diversity.
To master these intricacies and fare well in the Sociology Optional Syllabus , aspiring sociologists might benefit from guidance by the Best Sociology Optional Teacher and participation in the Best Sociology Optional Coaching . These avenues provide comprehensive assistance, ensuring a solid understanding of sociology’s diverse methodologies and techniques
India, Composite Culture, Unity in Diversity, Religions, Languages, Festivals, Art, Architecture, Historical Evolution.

Sociology Optional Syllabus Course Commencement Information
- Enrolment is limited to a maximum of 250 Seats.
- Course Timings: Evening Batch
- Course Duration: 4.5 Months
- Class Schedule: Monday to Saturday
- Batch Starts from: Admission open for online batch
Book Your Seat Fast Book Your Seat Fast
We would like to hear from you. Please send us a message by filling out the form below and we will get back with you shortly.
Instructional Format:
- Each class session is scheduled for a duration of two hours.
- At the conclusion of each lecture, an assignment will be distributed by Vikash Ranjan Sir for Paper-I & Paper-II coverage.
Study Material:
- A set of printed booklets will be provided for each topic. These materials are succinct, thoroughly updated, and tailored for examination preparation.
- A compilation of previous years’ question papers (spanning the last 27 years) will be supplied for answer writing practice.
- Access to PDF versions of toppers’ answer booklets will be available on our website.
- Post-course, you will receive two practice workbooks containing a total of 10 sets of mock test papers based on the UPSC format for self-assessment.
Additional Provisions:
- In the event of missed classes, video lectures will be temporarily available on the online portal for reference.
- Daily one-on-one doubt resolution sessions with Vikash Ranjan Sir will be organized post-class.
Syllabus of Sociology Optional
FUNDAMENTALS OF SOCIOLOGY
- Modernity and social changes in Europe and emergence of sociology.
- Scope of the subject and comparison with other social sciences.
- Sociology and common sense.
- Science, scientific method and critique.
- Major theoretical strands of research methodology.
- Positivism and its critique.
- Fact value and objectivity.
- Non- positivist methodologies.
- Qualitative and quantitative methods.
- Techniques of data collection.
- Variables, sampling, hypothesis, reliability and validity.
- Karl Marx- Historical materialism, mode of production, alienation, class struggle.
- Emile Durkheim- Division of labour, social fact, suicide, religion and society.
- Max Weber- Social action, ideal types, authority, bureaucracy, protestant ethic and the spirit of capitalism.
- Talcott Parsons- Social system, pattern variables.
- Robert K. Merton- Latent and manifest functions, conformity and deviance, reference groups.
- Mead – Self and identity.
- Concepts- equality, inequality, hierarchy, exclusion, poverty and deprivation.
- Theories of social stratification- Structural functionalist theory, Marxist theory, Weberian theory.
- Dimensions – Social stratification of class, status groups, gender, ethnicity and race.
- Social mobility- open and closed systems, types of mobility, sources and causes of mobility.
- Social organization of work in different types of society- slave society, feudal society, industrial /capitalist society
- Formal and informal organization of work.
- Labour and society.
- Sociological theories of power.
- Power elite, bureaucracy, pressure groups, and political parties.
- Nation, state, citizenship, democracy, civil society, ideology.
- Protest, agitation, social movements, collective action, revolution.
- Sociological theories of religion.
- Types of religious practices: animism, monism, pluralism, sects, cults.
- Religion in modern society: religion and science, secularization, religious revivalism, fundamentalism.
- Family, household, marriage.
- Types and forms of family.
- Lineage and descent.
- Patriarchy and sexual division of labour.
- Contemporary trends.
- Sociological theories of social change.
- Development and dependency.
- Agents of social change.
- Education and social change.
- Science, technology and social change.
INDIAN SOCIETY: STRUCTURE AND CHANGE
Introducing indian society.
- Indology (GS. Ghurye).
- Structural functionalism (M N Srinivas).
- Marxist sociology (A R Desai).
- Social background of Indian nationalism.
- Modernization of Indian tradition.
- Protests and movements during the colonial period.
- Social reforms.
SOCIAL STRUCTURE
- The idea of Indian village and village studies.
- Agrarian social structure – evolution of land tenure system, land reforms.
- Perspectives on the study of caste systems: GS Ghurye, M N Srinivas, Louis Dumont, Andre Beteille.
- Features of caste system.
- Untouchability – forms and perspectives.
- Definitional problems.
- Geographical spread.
- Colonial policies and tribes.
- Issues of integration and autonomy.
- Social Classes in India:
- Agrarian class structure.
- Industrial class structure.
- Middle classes in India.
- Lineage and descent in India.
- Types of kinship systems.
- Family and marriage in India.
- Household dimensions of the family.
- Patriarchy, entitlements and sexual division of labour
- Religious communities in India.
- Problems of religious minorities.
SOCIAL CHANGES IN INDIA
- Idea of development planning and mixed economy
- Constitution, law and social change.
- Programmes of rural development, Community Development Programme, cooperatives,poverty alleviation schemes
- Green revolution and social change.
- Changing modes of production in Indian agriculture.
- Problems of rural labour, bondage, migration.
3. Industrialization and Urbanisation in India:
- Evolution of modern industry in India.
- Growth of urban settlements in India.
- Working class: structure, growth, class mobilization.
- Informal sector, child labour
- Slums and deprivation in urban areas.
4. Politics and Society:
- Nation, democracy and citizenship.
- Political parties, pressure groups , social and political elite
- Regionalism and decentralization of power.
- Secularization
5. Social Movements in Modern India:
- Peasants and farmers movements.
- Women’s movement.
- Backward classes & Dalit movement.
- Environmental movements.
- Ethnicity and Identity movements.
6. Population Dynamics:
- Population size, growth, composition and distribution
- Components of population growth: birth, death, migration.
- Population policy and family planning.
- Emerging issues: ageing, sex ratios, child and infant mortality, reproductive health.
7. Challenges of Social Transformation:
- Crisis of development: displacement, environmental problems and sustainability
- Poverty, deprivation and inequalities.
- Violence against women.
- Caste conflicts.
- Ethnic conflicts, communalism, religious revivalism.
- Illiteracy and disparities in education.

Mr. Vikash Ranjan, arguably the Best Sociology Optional Teacher , has emerged as a versatile genius in teaching and writing books on Sociology & General Studies. His approach to the Sociology Optional Syllabus / Sociology Syllabus is remarkable, and his Sociological Themes and Perspectives are excellent. His teaching aptitude is Simple, Easy and Exam Focused. He is often chosen as the Best Sociology Teacher for Sociology Optional UPSC aspirants.
About Triumph IAS
Innovating Knowledge, Inspiring Success We, at Triumph IAS , pride ourselves on being the best sociology optional coaching platform. We believe that each Individual Aspirant is unique and requires Individual Guidance and Care, hence the need for the Best Sociology Teacher . We prepare students keeping in mind his or her strength and weakness, paying particular attention to the Sociology Optional Syllabus / Sociology Syllabus , which forms a significant part of our Sociology Foundation Course .
Course Features
Every day, the Best Sociology Optional Teacher spends 2 hours with the students, covering each aspect of the Sociology Optional Syllabus / Sociology Syllabus and the Sociology Course . Students are given assignments related to the Topic based on Previous Year Question to ensure they’re ready for the Sociology Optional UPSC examination.
Regular one-on-one interaction & individual counseling for stress management and refinement of strategy for Exam by Vikash Ranjan Sir , the Best Sociology Teacher , is part of the package. We specialize in sociology optional coaching and are hence fully equipped to guide you to your dream space in the civil service final list.
Specialist Guidance of Vikash Ranjan Sir

The Best Sociology Teacher helps students to get a complete conceptual understanding of each and every topic of the Sociology Optional Syllabus / Sociology Syllabus , enabling them to attempt any of the questions, be direct or applied, ensuring 300+ Marks in Sociology Optional .
Classrooms Interaction & Participatory Discussion
The Best Sociology Teacher, Vikash Sir , ensures that there’s explanation & DISCUSSION on every topic of the Sociology Optional Syllabus / Sociology Syllabus in the class. The emphasis is not just on teaching but also on understanding, which is why we are known as the Best Sociology Optional Coaching institution.
Preparatory-Study Support

Online Support System (Oss)
Get access to an online forum for value addition study material, journals, and articles relevant to Sociology on www.triumphias.com . Ask preparation related queries directly to the Best Sociology Teacher , Vikash Sir, via mail or WhatsApp.
Strategic Classroom Preparation

Comprehensive Study Material
We provide printed booklets of concise, well-researched, exam-ready study material for every unit of the Sociology Optional Syllabus / Sociology Syllabus , making us the Best Sociology Optional Coaching platform.
Why Vikash Ranjan’s Classes for Sociology?
Proper guidance and assistance are required to learn the skill of interlinking current happenings with the conventional topics. VIKASH RANJAN SIR at TRIUMPH IAS guides students according to the Recent Trends of UPSC, making him the Best Sociology Teacher for Sociology Optional UPSC.
At Triumph IAS, the Best Sociology Optional Coaching platform, we not only provide the best study material and applied classes for Sociology for IAS but also conduct regular assignments and class tests to assess candidates’ writing skills and understanding of the subject.
Choose T he Best Sociology Optional Teacher for IAS Preparation?
At the beginning of the journey for Civil Services Examination preparation, many students face a pivotal decision – selecting their optional subject. Questions such as “ which optional subject is the best? ” and “ which optional subject is the most scoring? ” frequently come to mind. Choosing the right optional subject, like choosing the best sociology optional teacher , is a subjective yet vital step that requires a thoughtful decision based on facts. A misstep in this crucial decision can indeed prove disastrous.
Ever since the exam pattern was revamped in 2013, the UPSC has eliminated the need for a second optional subject. Now, candidates have to choose only one optional subject for the UPSC Mains , which has two papers of 250 marks each. One of the compelling choices for many has been the sociology optional. However, it’s strongly advised to decide on your optional subject for mains well ahead of time to get sufficient time to complete the syllabus. After all, most students score similarly in General Studies Papers; it’s the score in the optional subject & essay that contributes significantly to the final selection.
“ A sound strategy does not rely solely on the popular Opinion of toppers or famous YouTubers cum teachers. ”
It requires understanding one’s ability, interest, and the relevance of the subject, not just for the exam but also for life in general. Hence, when selecting the best sociology teacher, one must consider the usefulness of sociology optional coaching in General Studies, Essay, and Personality Test.
The choice of the optional subject should be based on objective criteria, such as the nature, scope, and size of the syllabus, uniformity and stability in the question pattern, relevance of the syllabic content in daily life in society, and the availability of study material and guidance. For example, choosing the best sociology optional coaching can ensure access to top-quality study materials and experienced teachers. Always remember, the approach of the UPSC optional subject differs from your academic studies of subjects. Therefore, before settling for sociology optional , you need to analyze the syllabus, previous years’ pattern, subject requirements (be it ideal, visionary, numerical, conceptual theoretical), and your comfort level with the subject.
This decision marks a critical point in your UPSC – CSE journey , potentially determining your success in a career in IAS/Civil Services. Therefore, it’s crucial to choose wisely, whether it’s the optional subject or the best sociology optional teacher . Always base your decision on accurate facts, and never let your emotional biases guide your choices. After all, the search for the best sociology optional coaching is about finding the perfect fit for your unique academic needs and aspirations.
To master these intricacies and fare well in the Sociology Optional Syllabus , aspiring sociologists might benefit from guidance by the Best Sociology Optional Teacher and participation in the Best Sociology Optional Coaching . These avenues provide comprehensive assistance, ensuring a solid understanding of sociology’s diverse methodologies and techniques. Sociology, Social theory, Best Sociology Optional Teacher, Best Sociology Optional Coaching, Sociology Optional Syllabus. Best Sociology Optional Teacher, Sociology Syllabus, Sociology Optional, Sociology Optional Coaching, Best Sociology Optional Coaching, Best Sociology Teacher, Sociology Course, Sociology Teacher, Sociology Foundation, Sociology Foundation Course, Sociology Optional UPSC, Sociology for IAS,
Follow us :
🔎 https://www.instagram.com/triumphias
🔎 www.triumphias.com
🔎https://www.youtube.com/c/TriumphIAS
https://t.me/VikashRanjanSociology
Find More Blogs
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Incredible India Essay for Students and Children
500+ words essay on incredible india.
India represents “Unity in Diversity” . Our country is a mixture of cultures, regions, traditions, diversity in food, languages, etc. Our people of India are so polite, understanding and helping in nature. The national bird of India is Peacock and is very beautiful. India is so incredible and is full of colors and has the tiger as its national animal, hockey as its national game, etc. the national language or mother tongue of our country is Hindi. Indians are also so talented and have shown very high growth. The I.T. sector of our country shows accelerating growth due to intelligent software engineers.

India As a Country
India is the seventh-largest country by its geographical area and is located in South Asia. The beauty surrounds our country from each and every aspect. India is also known by two other names Bharat and Hindustan and the people of India are known as Indians. The national anthem of our country is “ Jan Gan Man ” and the national song of our country is “Sare Jahan Se Achcha”.
India is a Democratic country where people themselves choose their leader and live with freedom i.e. they can do anything they wish to within the limits of the law. If any citizen of India tries to harm any other person, there are also rules and regulations to punish him in order to make him realize his mistake.
Our country is also incredible because of its beautiful mountains, lakes, forests , seas, oceans, etc. Many foreigners each year visit India to see the beauty of our country that is its rich historical temples, its traditions, its language, its heritage, etc.
Different Regions of India
North region.
North Region consists of the most incredible thing in the world that is The Himalayas which is the highest mountain in the world. This region also consists of the beautiful Kashmir covered with mountains. It consists of Uttar Pradesh which is mainly known as the land of Krishna, land of Rama, etc. This region also consists of one of the wonders of the world i.e. Taj Mahal which people come to visit across the world.
Southern Region
This is the “Land of Nawabs”. It is famous for its festivals, food, and languages. The place is famous for its rice dishes. This region consists of cities like Kerala, Tamil Nadu, and Karnataka, etc.
East Region
East part of India consists of West Bengal, Jharkhand, Bihar, Odisha, etc. The capital of West Bengal, Kolkata is the largest city of this section and is the metropolitan city and is the third’s largest city in the country. Kolkata is known for its sweetness and festival.
West Region
The West part of the country is really incredible as it is covered with sands and deserts. Rajasthan, Gujarat, and Maharashtra are the three most amazing places in this region. The culture, the language, the traditions and the clothes of this region are incredible and you will love to visit this region.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
Indian Culture and Religion
India’s culture is among the world’s oldest; civilization in India began about 4,500 years ago. India has 29 states with different culture and civilizations and one of the most populated countries in the world. The Indian culture, often labeled as a mixture of several various cultures.
India gave birth to Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism, Sikhism, and other religions. They are now collectively known as Indian religions. Today, Hinduism and Buddhism are the third and fourth-largest religions respectively of the world. Although India is a secular Hindu-majority country, it has a large Muslim population.
India, being a multi-cultural, multi-ethnic and multi-religious society, celebrates holidays and festivals of various religions. Major festivals include Diwali, Durga puja, Holi, Ganesh puja, Navratri, Rath yatra, etc are there round the year.
Indian food is a cosmopolitan cuisine that has so many ingredients. It is as diverse as India. Indian recipes use numerous ingredients, deploy a wide range of food preparation styles, cooking techniques, and culinary presentation. Thus the tastes of same food like salads, sauces, vegetables, meat, desserts vary from region to region.
We are proud of our cultural distinctiveness. We are proud to be the inhabitants of India. It is our duty to maintain its unique feature. We have to think beyond the petty interests and work for the broader goals of bringing prosperity and progress in society.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
Religion in India: Tolerance and Segregation
Indians say it is important to respect all religions, but major religious groups see little in common and want to live separately, table of contents.
- The dimensions of Hindu nationalism in India
- India’s Muslims express pride in being Indian while identifying communal tensions, desiring segregation
- Muslims, Hindus diverge over legacy of Partition
- Religious conversion in India
- Religion very important across India’s religious groups
- Near-universal belief in God, but wide variation in how God is perceived
- Across India’s religious groups, widespread sharing of beliefs, practices, values
- Religious identity in India: Hindus divided on whether belief in God is required to be a Hindu, but most say eating beef is disqualifying
- Sikhs are proud to be Punjabi and Indian
- 1. Religious freedom, discrimination and communal relations
- 2. Diversity and pluralism
- 3. Religious segregation
- 4. Attitudes about caste
- 5. Religious identity
- 6. Nationalism and politics
- 7. Religious practices
- 8. Religion, family and children
- 9. Religious clothing and personal appearance
- 10. Religion and food
- 11. Religious beliefs
- 12. Beliefs about God
- Acknowledgments
- Appendix A: Methodology
- Appendix B: Index of religious segregation

This study is Pew Research Center’s most comprehensive, in-depth exploration of India to date. For this report, we surveyed 29,999 Indian adults (including 22,975 who identify as Hindu, 3,336 who identify as Muslim, 1,782 who identify as Sikh, 1,011 who identify as Christian, 719 who identify as Buddhist, 109 who identify as Jain and 67 who identify as belonging to another religion or as religiously unaffiliated). Interviews for this nationally representative survey were conducted face-to-face under the direction of RTI International from Nov. 17, 2019, to March 23, 2020.
To improve respondent comprehension of survey questions and to ensure all questions were culturally appropriate, Pew Research Center followed a multi-phase questionnaire development process that included expert review, focus groups, cognitive interviews, a pretest and a regional pilot survey before the national survey. The questionnaire was developed in English and translated into 16 languages, independently verified by professional linguists with native proficiency in regional dialects.
Respondents were selected using a probability-based sample design that would allow for robust analysis of all major religious groups in India – Hindus, Muslims, Christians, Sikhs, Buddhists and Jains – as well as all major regional zones. Data was weighted to account for the different probabilities of selection among respondents and to align with demographic benchmarks for the Indian adult population from the 2011 census. The survey is calculated to have covered 98% of Indians ages 18 and older and had an 86% national response rate.
For more information, see the Methodology for this report. The questions used in this analysis can be found here .
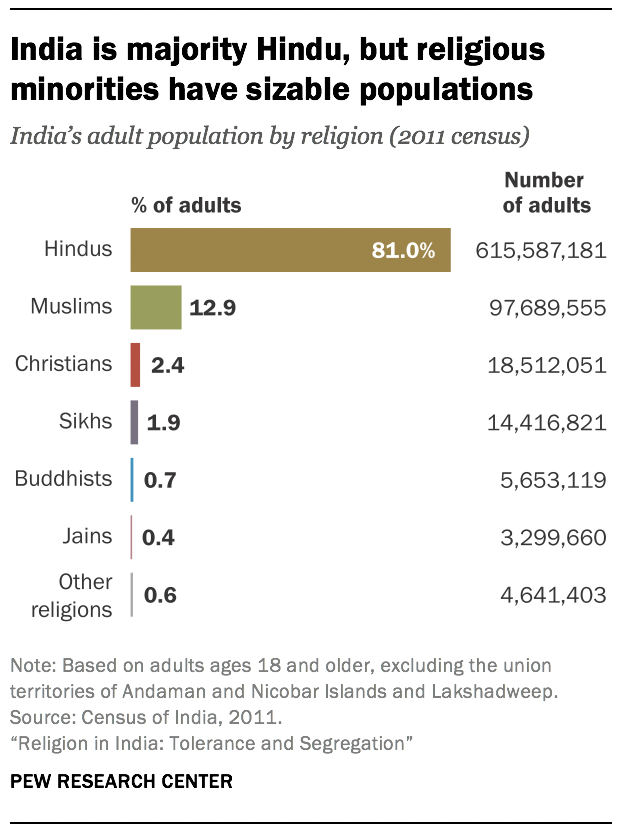
More than 70 years after India became free from colonial rule, Indians generally feel their country has lived up to one of its post-independence ideals: a society where followers of many religions can live and practice freely.
India’s massive population is diverse as well as devout. Not only do most of the world’s Hindus, Jains and Sikhs live in India, but it also is home to one of the world’s largest Muslim populations and to millions of Christians and Buddhists.
A major new Pew Research Center survey of religion across India, based on nearly 30,000 face-to-face interviews of adults conducted in 17 languages between late 2019 and early 2020 (before the COVID-19 pandemic ), finds that Indians of all these religious backgrounds overwhelmingly say they are very free to practice their faiths.
Related India research
This is one in a series of Pew Research Center reports on India based on a survey of 29,999 Indian adults conducted Nov. 17, 2019, to March 23, 2020, as well as demographic data from the Indian Census and other government sources. Other reports can be found here:
- How Indians View Gender Roles in Families and Society
- Religious Composition of India
- India’s Sex Ratio at Birth Begins To Normalize
Indians see religious tolerance as a central part of who they are as a nation. Across the major religious groups, most people say it is very important to respect all religions to be “truly Indian.” And tolerance is a religious as well as civic value: Indians are united in the view that respecting other religions is a very important part of what it means to be a member of their own religious community.
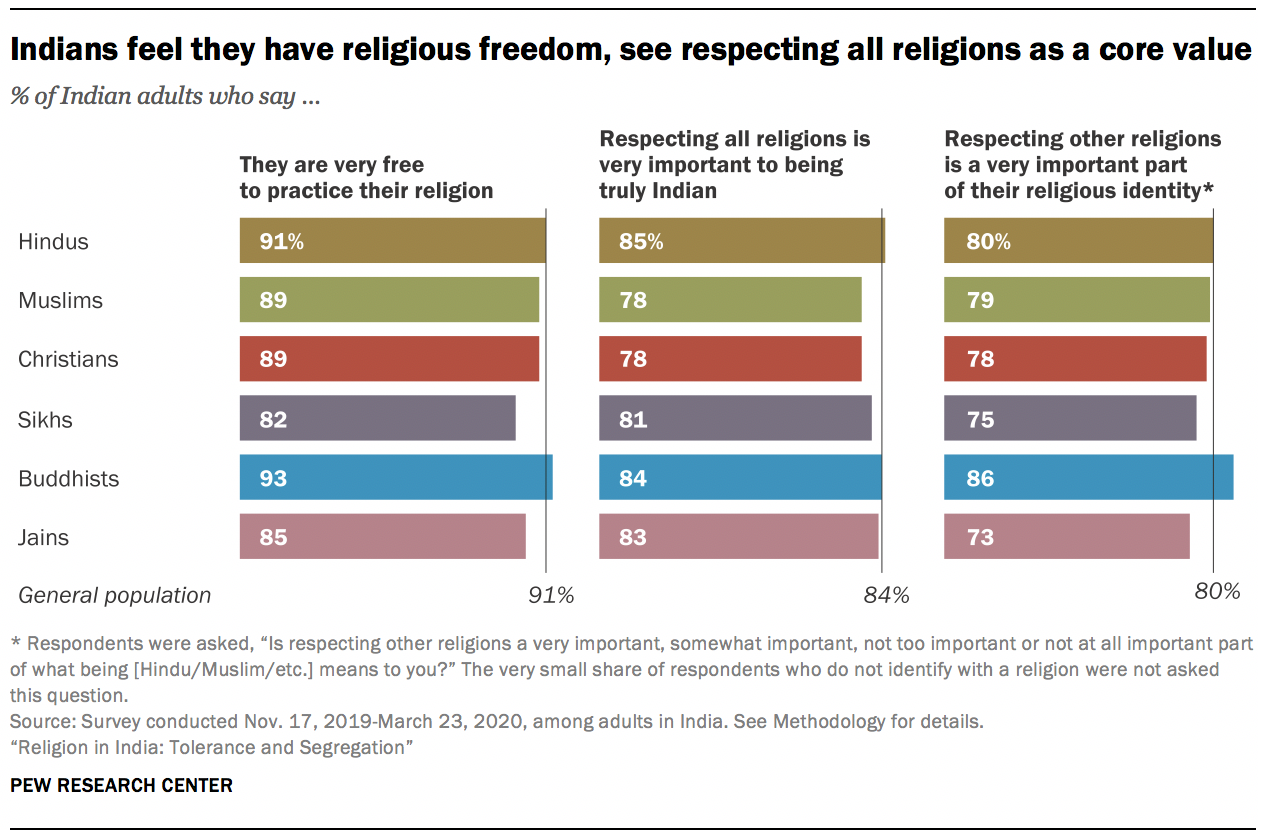
These shared values are accompanied by a number of beliefs that cross religious lines. Not only do a majority of Hindus in India (77%) believe in karma, but an identical percentage of Muslims do, too. A third of Christians in India (32%) – together with 81% of Hindus – say they believe in the purifying power of the Ganges River, a central belief in Hinduism. In Northern India, 12% of Hindus and 10% of Sikhs, along with 37% of Muslims, identity with Sufism, a mystical tradition most closely associated with Islam. And the vast majority of Indians of all major religious backgrounds say that respecting elders is very important to their faith.
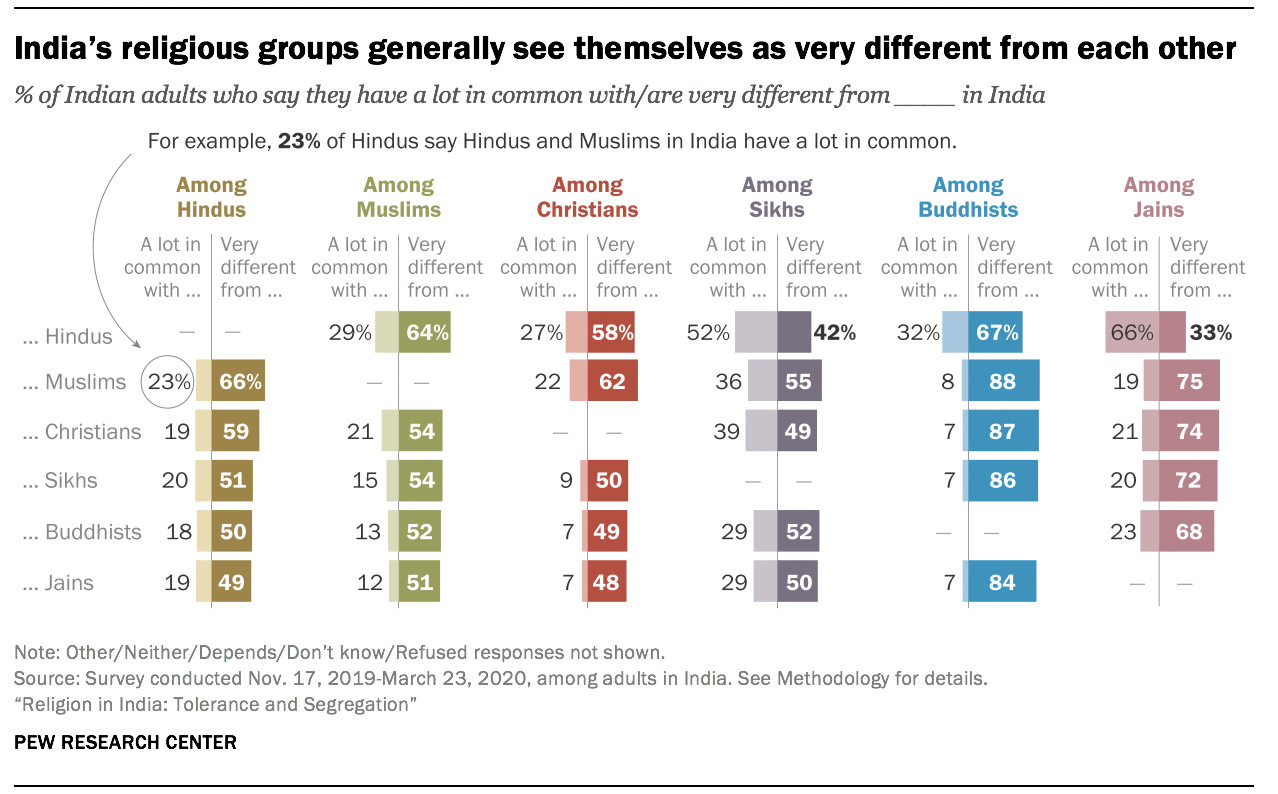
Yet, despite sharing certain values and religious beliefs – as well as living in the same country, under the same constitution – members of India’s major religious communities often don’t feel they have much in common with one another. The majority of Hindus see themselves as very different from Muslims (66%), and most Muslims return the sentiment, saying they are very different from Hindus (64%). There are a few exceptions: Two-thirds of Jains and about half of Sikhs say they have a lot in common with Hindus. But generally, people in India’s major religious communities tend to see themselves as very different from others.
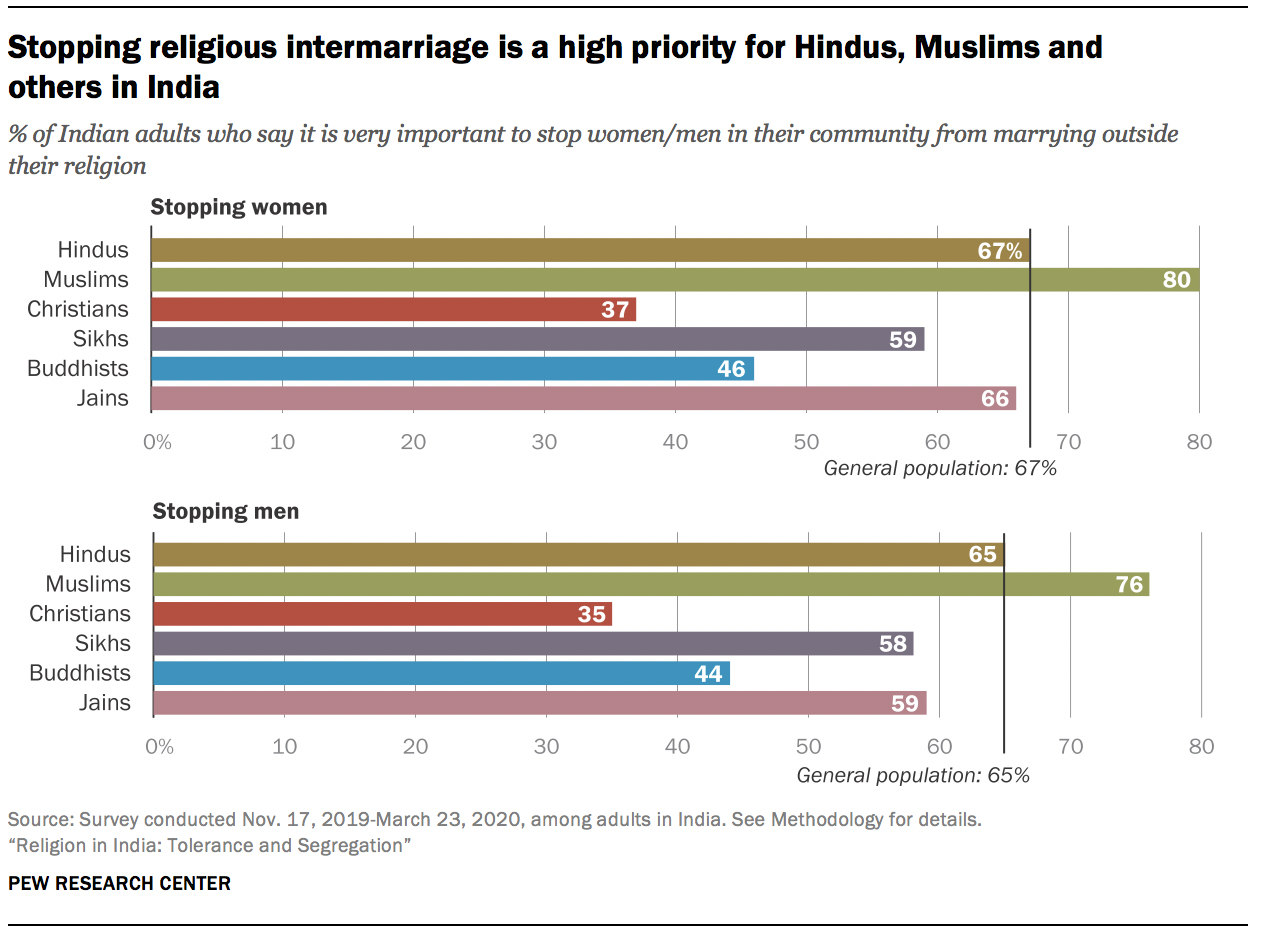
This perception of difference is reflected in traditions and habits that maintain the separation of India’s religious groups. For example, marriages across religious lines – and, relatedly, religious conversions – are exceedingly rare (see Chapter 3 ). Many Indians, across a range of religious groups, say it is very important to stop people in their community from marrying into other religious groups. Roughly two-thirds of Hindus in India want to prevent interreligious marriages of Hindu women (67%) or Hindu men (65%). Even larger shares of Muslims feel similarly: 80% say it is very important to stop Muslim women from marrying outside their religion, and 76% say it is very important to stop Muslim men from doing so.
Moreover, Indians generally stick to their own religious group when it comes to their friends. Hindus overwhelmingly say that most or all of their close friends are also Hindu. Of course, Hindus make up the majority of the population, and as a result of sheer numbers, may be more likely to interact with fellow Hindus than with people of other religions. But even among Sikhs and Jains, who each form a sliver of the national population, a large majority say their friends come mainly or entirely from their small religious community.
Fewer Indians go so far as to say that their neighborhoods should consist only of people from their own religious group. Still, many would prefer to keep people of certain religions out of their residential areas or villages. For example, many Hindus (45%) say they are fine with having neighbors of all other religions – be they Muslim, Christian, Sikh, Buddhist or Jain – but an identical share (45%) say they would not be willing to accept followers of at least one of these groups, including more than one-in-three Hindus (36%) who do not want a Muslim as a neighbor. Among Jains, a majority (61%) say they are unwilling to have neighbors from at least one of these groups, including 54% who would not accept a Muslim neighbor, although nearly all Jains (92%) say they would be willing to accept a Hindu neighbor.
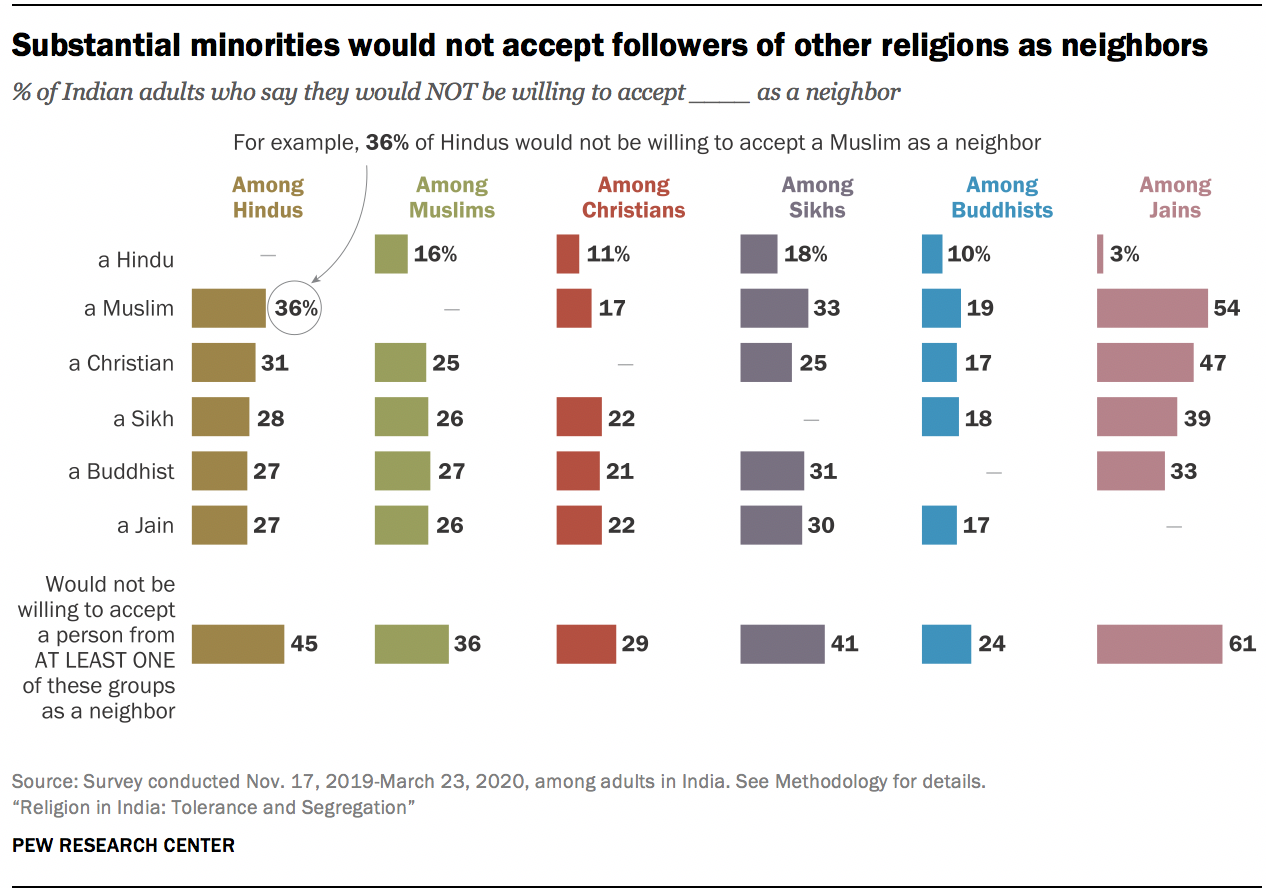
Indians, then, simultaneously express enthusiasm for religious tolerance and a consistent preference for keeping their religious communities in segregated spheres – they live together separately . These two sentiments may seem paradoxical, but for many Indians they are not.
Indeed, many take both positions, saying it is important to be tolerant of others and expressing a desire to limit personal connections across religious lines. Indians who favor a religiously segregated society also overwhelmingly emphasize religious tolerance as a core value. For example, among Hindus who say it is very important to stop the interreligious marriage of Hindu women, 82% also say that respecting other religions is very important to what it means to be Hindu. This figure is nearly identical to the 85% who strongly value religious tolerance among those who are not at all concerned with stopping interreligious marriage.
In other words, Indians’ concept of religious tolerance does not necessarily involve the mixing of religious communities. While people in some countries may aspire to create a “melting pot” of different religious identities, many Indians seem to prefer a country more like a patchwork fabric, with clear lines between groups.
One of these religious fault lines – the relationship between India’s Hindu majority and the country’s smaller religious communities – has particular relevance in public life, especially in recent years under the ruling Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP). Led by Prime Minister Narendra Modi, the BJP is often described as promoting a Hindu nationalist ideology .
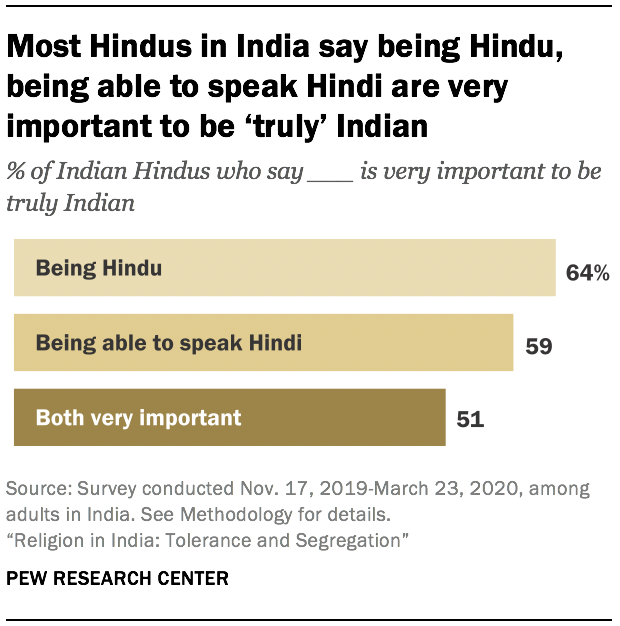
The survey finds that Hindus tend to see their religious identity and Indian national identity as closely intertwined: Nearly two-thirds of Hindus (64%) say it is very important to be Hindu to be “truly” Indian.
Most Hindus (59%) also link Indian identity with being able to speak Hindi – one of dozens of languages that are widely spoken in India. And these two dimensions of national identity – being able to speak Hindi and being a Hindu – are closely connected. Among Hindus who say it is very important to be Hindu to be truly Indian, fully 80% also say it is very important to speak Hindi to be truly Indian.
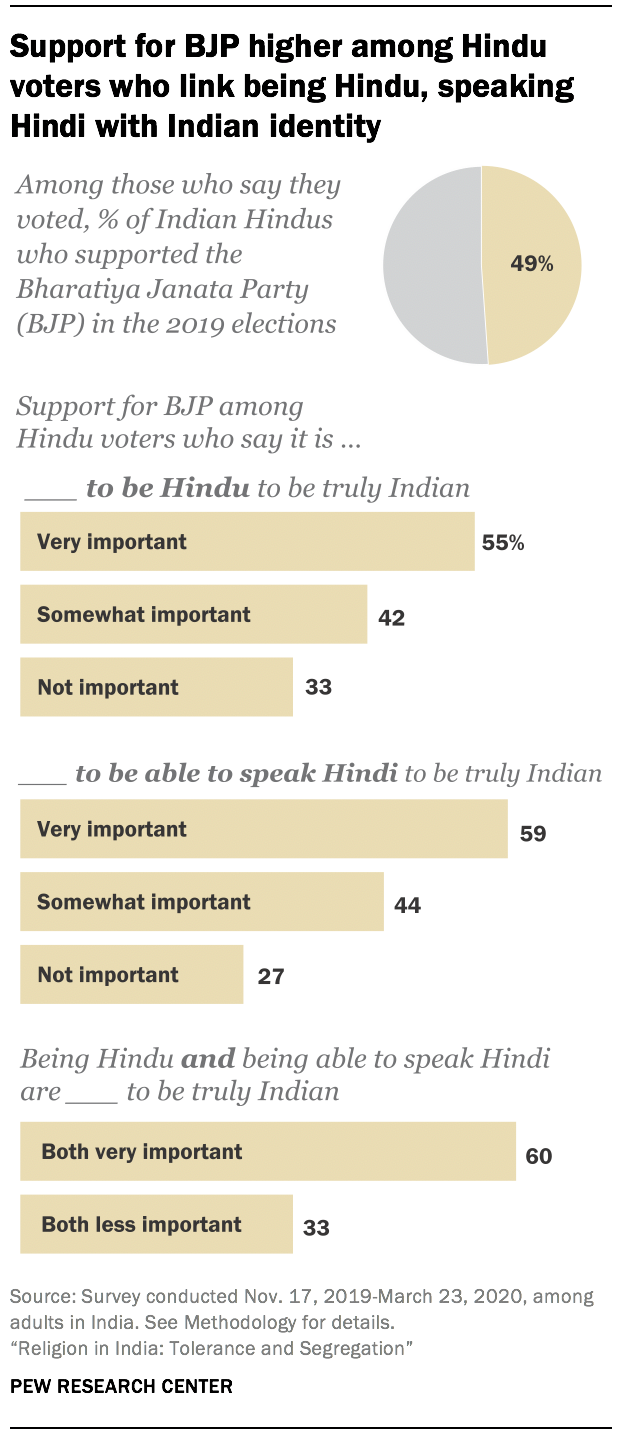
The BJP’s appeal is greater among Hindus who closely associate their religious identity and the Hindi language with being “truly Indian.” In the 2019 national elections, 60% of Hindu voters who think it is very important to be Hindu and to speak Hindi to be truly Indian cast their vote for the BJP, compared with only a third among Hindu voters who feel less strongly about both these aspects of national identity.
Overall, among those who voted in the 2019 elections, three-in-ten Hindus take all three positions: saying it is very important to be Hindu to be truly Indian; saying the same about speaking Hindi; and casting their ballot for the BJP.
These views are considerably more common among Hindus in the largely Hindi-speaking Northern and Central regions of the country, where roughly half of all Hindu voters fall into this category, compared with just 5% in the South.
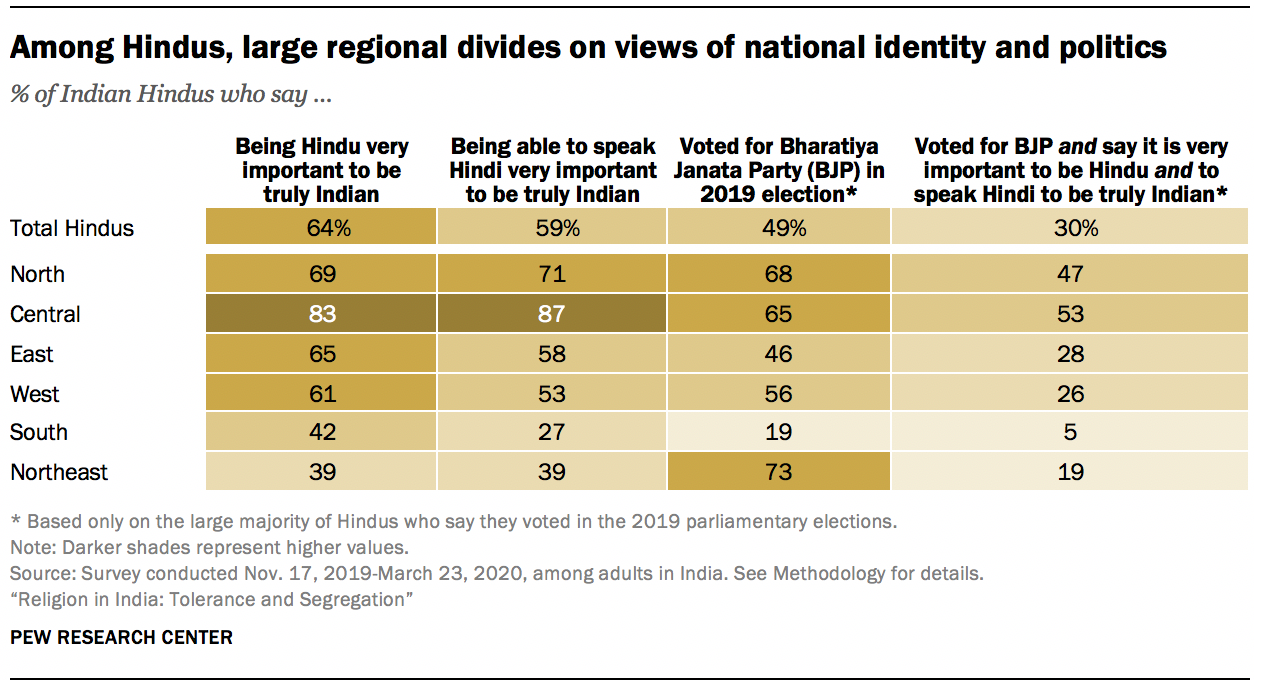
Whether Hindus who meet all three of these criteria qualify as “Hindu nationalists” may be debated, but they do express a heightened desire for maintaining clear lines between Hindus and other religious groups when it comes to whom they marry, who their friends are and whom they live among. For example, among Hindu BJP voters who link national identity with both religion and language, 83% say it is very important to stop Hindu women from marrying into another religion, compared with 61% among other Hindu voters.
This group also tends to be more religiously observant: 95% say religion is very important in their lives, and roughly three-quarters say they pray daily (73%). By comparison, among other Hindu voters, a smaller majority (80%) say religion is very important in their lives, and about half (53%) pray daily.
Even though Hindu BJP voters who link national identity with religion and language are more inclined to support a religiously segregated India, they also are more likely than other Hindu voters to express positive opinions about India’s religious diversity. Nearly two-thirds (65%) of this group – Hindus who say that being a Hindu and being able to speak Hindi are very important to be truly Indian and who voted for the BJP in 2019 – say religious diversity benefits India, compared with about half (47%) of other Hindu voters.
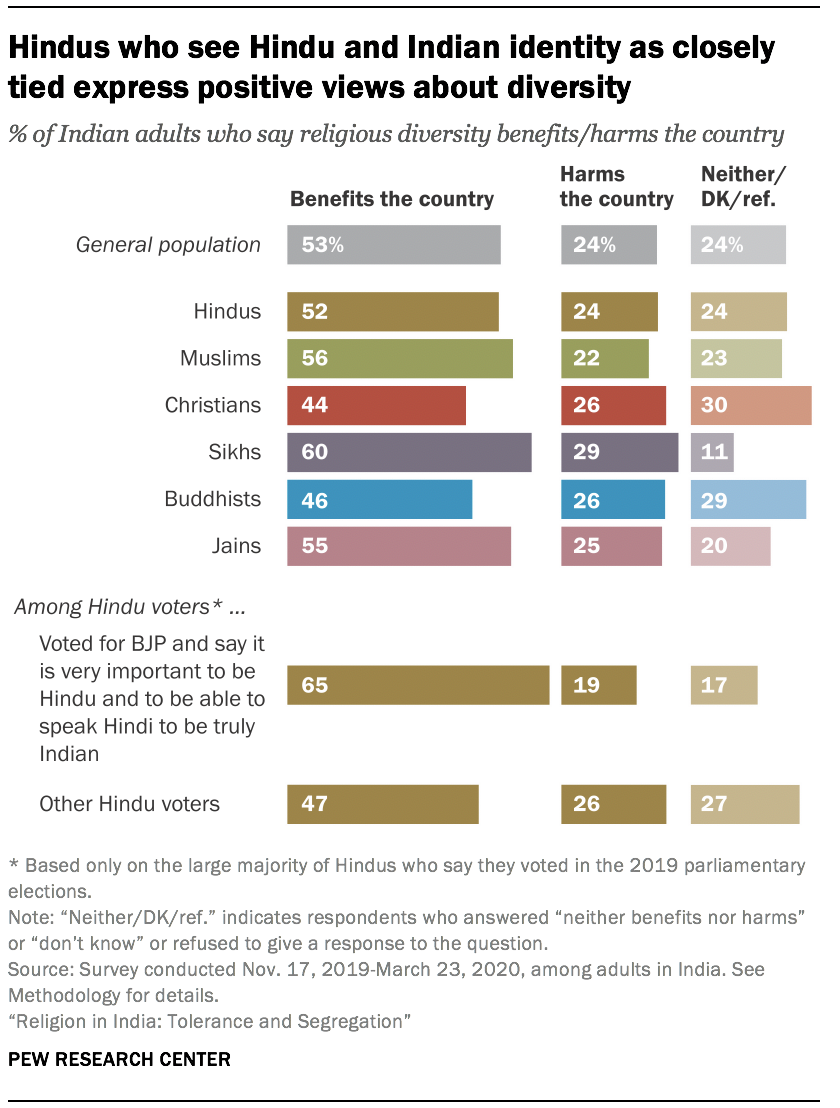
This finding suggests that for many Hindus, there is no contradiction between valuing religious diversity (at least in principle) and feeling that Hindus are somehow more authentically Indian than fellow citizens who follow other religions.
Among Indians overall, there is no overwhelming consensus on the benefits of religious diversity. On balance, more Indians see diversity as a benefit than view it as a liability for their country: Roughly half (53%) of Indian adults say India’s religious diversity benefits the country, while about a quarter (24%) see diversity as harmful, with similar figures among both Hindus and Muslims. But 24% of Indians do not take a clear position either way – they say diversity neither benefits nor harms the country, or they decline to answer the question. (See Chapter 2 for a discussion of attitudes toward diversity.)
India’s Muslim community, the second-largest religious group in the country, historically has had a complicated relationship with the Hindu majority. The two communities generally have lived peacefully side by side for centuries, but their shared history also is checkered by civil unrest and violence. Most recently, while the survey was being conducted, demonstrations broke out in parts of New Delhi and elsewhere over the government’s new citizenship law , which creates an expedited path to citizenship for immigrants from some neighboring countries – but not Muslims.
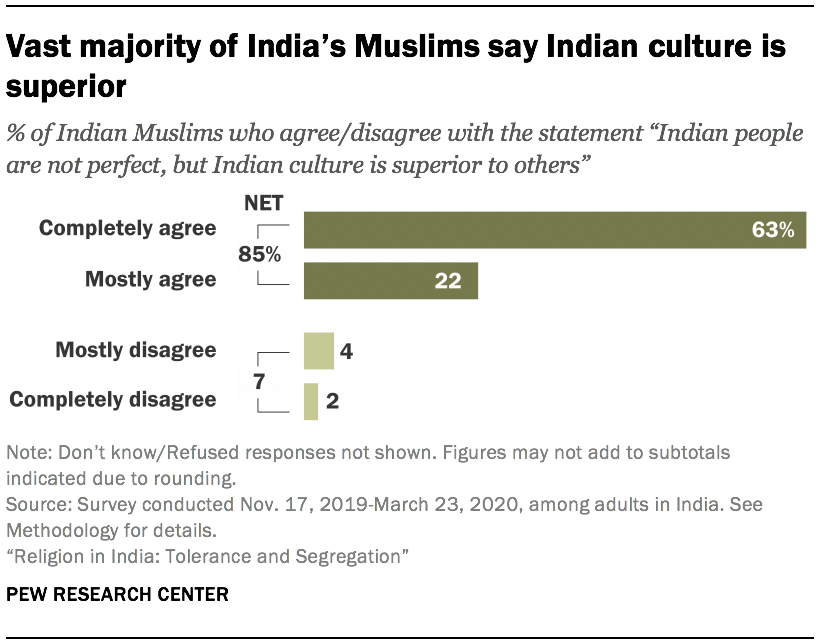
Today, India’s Muslims almost unanimously say they are very proud to be Indian (95%), and they express great enthusiasm for Indian culture: 85% agree with the statement that “Indian people are not perfect, but Indian culture is superior to others.”
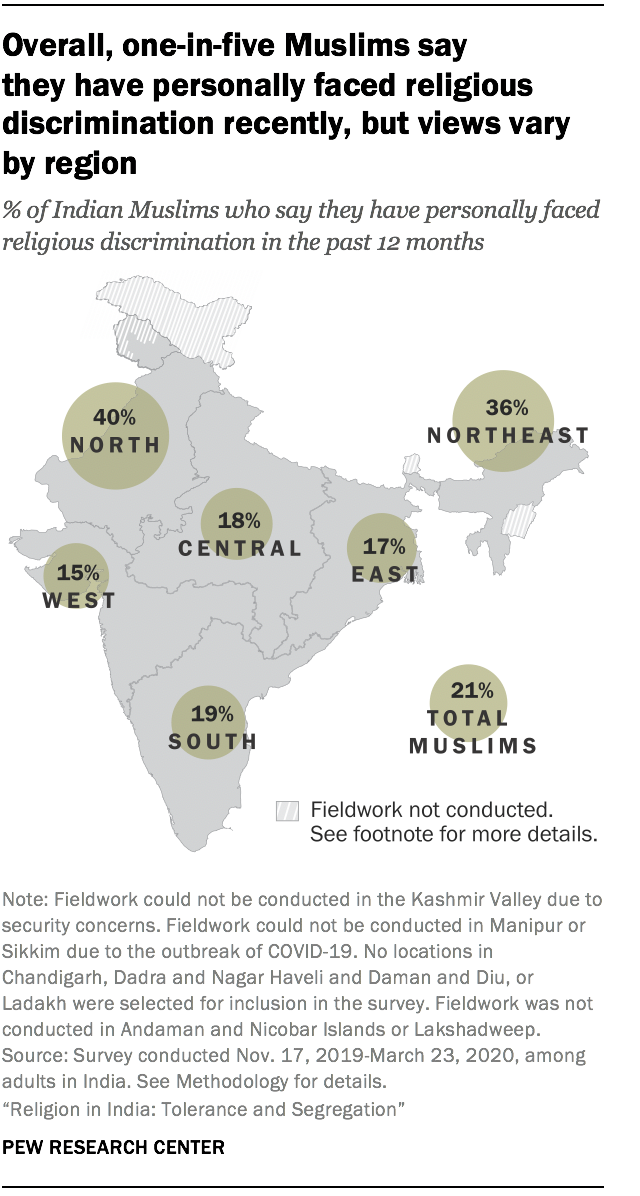
Relatively few Muslims say their community faces “a lot” of discrimination in India (24%). In fact, the share of Muslims who see widespread discrimination against their community is similar to the share of Hindus who say Hindus face widespread religious discrimination in India (21%). (See Chapter 1 for a discussion of attitudes on religious discrimination.)
But personal experiences with discrimination among Muslims vary quite a bit regionally. Among Muslims in the North, 40% say they personally have faced religious discrimination in the last 12 months – much higher levels than reported in most other regions.
In addition, most Muslims across the country (65%), along with an identical share of Hindus (65%), see communal violence as a very big national problem. (See Chapter 1 for a discussion of Indians’ attitudes toward national problems.)
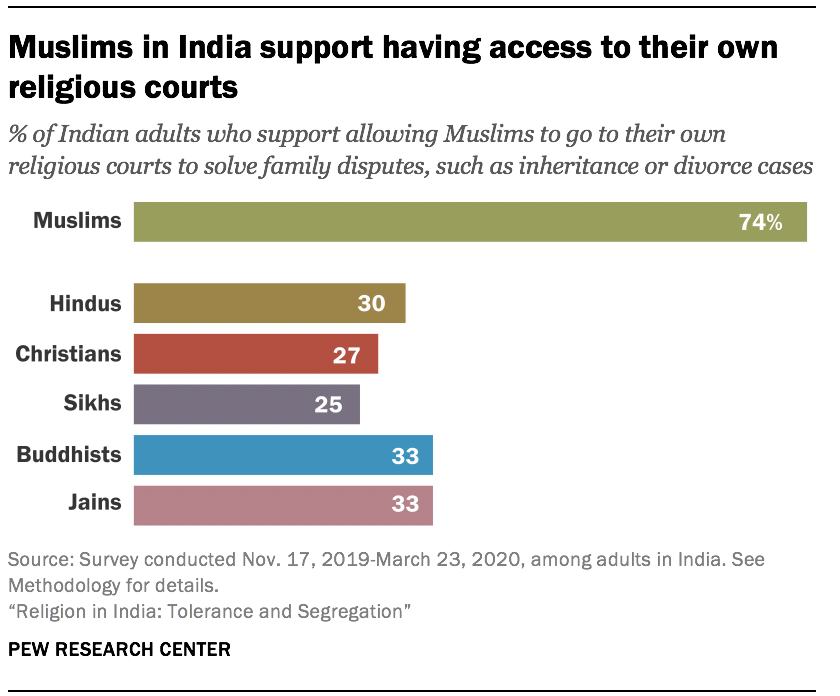
Like Hindus, Muslims prefer to live religiously segregated lives – not just when it comes to marriage and friendships, but also in some elements of public life. In particular, three-quarters of Muslims in India (74%) support having access to the existing system of Islamic courts, which handle family disputes (such as inheritance or divorce cases), in addition to the secular court system.
Muslims’ desire for religious segregation does not preclude tolerance of other groups – again similar to the pattern seen among Hindus. Indeed, a majority of Muslims who favor separate religious courts for their community say religious diversity benefits India (59%), compared with somewhat fewer of those who oppose religious courts for Muslims (50%).
Sidebar: Islamic courts in India
Since 1937, India’s Muslims have had the option of resolving family and inheritance-related cases in officially recognized Islamic courts, known as dar-ul-qaza. These courts are overseen by religious magistrates known as qazi and operate under Shariah principles . For example, while the rules of inheritance for most Indians are governed by the Indian Succession Act of 1925 and the Hindu Succession Act of 1956 (amended in 2005), Islamic inheritance practices differ in some ways, including who can be considered an heir and how much of the deceased person’s property they can inherit. India’s inheritance laws also take into account the differing traditions of other religious communities, such as Hindus and Christians, but their cases are handled in secular courts. Only the Muslim community has the option of having cases tried by a separate system of family courts. The decisions of the religious courts, however, are not legally binding , and the parties involved have the option of taking their case to secular courts if they are not satisfied with the decision of the religious court.
As of 2021, there are roughly 70 dar-ul-qaza in India. Most are in the states of Maharashtra and Uttar Pradesh. Goa is the only state that does not recognize rulings by these courts, enforcing its own uniform civil code instead. Dar-ul-qaza are overseen by the All India Muslim Personal Law Board .
While these courts can grant divorces among Muslims, they are prohibited from approving divorces initiated through the practice known as triple talaq, in which a Muslim man instantly divorces his wife by saying the Arabic/Urdu word “talaq” (meaning “divorce”) three times. This practice was deemed unconstitutional by the Indian Supreme Court in 2017 and formally outlawed by the Lok Sabha, the lower house of India’s Parliament, in 2019. 1
Recent debates have emerged around Islamic courts. Some Indians have expressed concern that the rise of dar-ul-qaza could undermine the Indian judiciary, because a subset of the population is not bound to the same laws as everyone else. Others have argued that the rulings of Islamic courts are particularly unfair to women, although the prohibition of triple talaq may temper some of these criticisms. In its 2019 political manifesto , the BJP proclaimed a desire to create a national Uniform Civil Code, saying it would increase gender equality.
Some Indian commentators have voiced opposition to Islamic courts along with more broadly negative sentiments against Muslims, describing the rising numbers of dar-ul-qaza as the “Talibanization” of India , for example.
On the other hand, Muslim scholars have defended the dar-ul-qaza, saying they expedite justice because family disputes that would otherwise clog India’s courts can be handled separately, allowing the secular courts to focus their attention on other concerns.
Since 2018, the Hindu nationalist party Hindu Mahasabha (which does not hold any seats in Parliament) has tried to set up Hindu religious courts , known as Hindutva courts, aiming to play a role similar to dar-ul-qaza, only for the majority Hindu community. None of these courts have been recognized by the Indian government, and their rulings are not considered legally binding.
The seminal event in the modern history of Hindu-Muslim relations in the region was the partition of the subcontinent into Hindu-majority India and Muslim-majority Pakistan at the end of the British colonial period in 1947. Partition remains one of the largest movements of people across borders in recorded history, and in both countries the carving of new borders was accompanied by violence, rioting and looting .
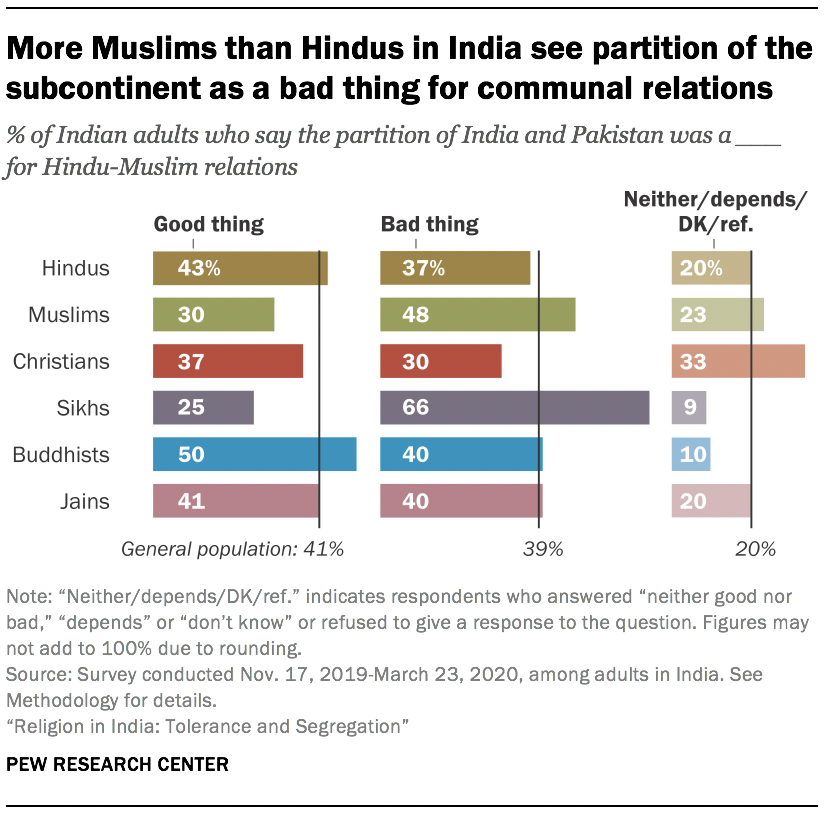
More than seven decades later, the predominant view among Indian Muslims is that the partition of the subcontinent was “a bad thing” for Hindu-Muslim relations. Nearly half of Muslims say Partition hurt communal relations with Hindus (48%), while fewer say it was a good thing for Hindu-Muslim relations (30%). Among Muslims who prefer more religious segregation – that is, who say they would not accept a person of a different faith as a neighbor – an even higher share (60%) say Partition was a bad thing for Hindu-Muslim relations.
Sikhs, whose homeland of Punjab was split by Partition, are even more likely than Muslims to say Partition was a bad thing for Hindu-Muslim relations: Two-thirds of Sikhs (66%) take this position. And Sikhs ages 60 and older, whose parents most likely lived through Partition, are more inclined than younger Sikhs to say the partition of the country was bad for communal relations (74% vs. 64%).
While Sikhs and Muslims are more likely to say Partition was a bad thing than a good thing, Hindus lean in the opposite direction: 43% of Hindus say Partition was beneficial for Hindu-Muslim relations, while 37% see it as a bad thing.
Context for the survey
Interviews were conducted after the conclusion of the 2019 national parliamentary elections and after the revocation of Jammu and Kashmir’s special status under the Indian Constitution. In December 2019, protests against the country’s new citizenship law broke out in several regions.
Fieldwork could not be conducted in the Kashmir Valley and a few districts elsewhere due to security concerns. These locations include some heavily Muslim areas, which is part of the reason why Muslims make up 11% of the survey’s total sample, while India’s adult population is roughly 13% Muslim, according to the most recent census data that is publicly available, from 2011. In addition, it is possible that in some other parts of the country, interreligious tensions over the new citizenship law may have slightly depressed participation in the survey by potential Muslim respondents.
Nevertheless, the survey’s estimates of religious beliefs, behaviors and attitudes can be reported with a high degree of confidence for India’s total population, because the number of people living in the excluded areas (Manipur, Sikkim, the Kashmir Valley and a few other districts) is not large enough to affect the overall results at the national level. About 98% of India’s total population had a chance of being selected for this survey.
Greater caution is warranted when looking at India’s Muslims separately, as a distinct population. The survey cannot speak to the experiences and views of Kashmiri Muslims. Still, the survey does represent the beliefs, behaviors and attitudes of around 95% of India’s overall Muslim population.
These are among the key findings of a Pew Research Center survey conducted face-to-face nationally among 29,999 Indian adults. Local interviewers administered the survey between Nov. 17, 2019, and March 23, 2020, in 17 languages. The survey covered all states and union territories of India, with the exceptions of Manipur and Sikkim, where the rapidly developing COVID-19 situation prevented fieldwork from starting in the spring of 2020, and the remote territories of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands and Lakshadweep; these areas are home to about a quarter of 1% of the Indian population. The union territory of Jammu and Kashmir was covered by the survey, though no fieldwork was conducted in the Kashmir region itself due to security concerns.
This study, funded by The Pew Charitable Trusts and the John Templeton Foundation, is part of a larger effort by Pew Research Center to understand religious change and its impact on societies around the world. The Center previously has conducted religion-focused surveys across sub-Saharan Africa ; the Middle East-North Africa region and many other countries with large Muslim populations ; Latin America ; Israel ; Central and Eastern Europe ; Western Europe ; and the United States .
The rest of this Overview covers attitudes on five broad topics: caste and discrimination; religious conversion; religious observances and beliefs; how people define their religious identity, including what kind of behavior is considered acceptable to be a Hindu or a Muslim; and the connection between economic development and religious observance.
Caste is another dividing line in Indian society, and not just among Hindus
Religion is not the only fault line in Indian society. In some regions of the country, significant shares of people perceive widespread, caste-based discrimination.
The caste system is an ancient social hierarchy based on occupation and economic status. People are born into a particular caste and tend to keep many aspects of their social life within its boundaries, including whom they marry. Even though the system’s origins are in historical Hindu writings , today Indians nearly universally identify with a caste, regardless of whether they are Hindu, Muslim, Christian, Sikh, Buddhist or Jain.
Overall, the majority of Indian adults say they are a member of a Scheduled Caste (SC) – often referred to as Dalits (25%) – Scheduled Tribe (ST) (9%) or Other Backward Class (OBC) (35%). 2
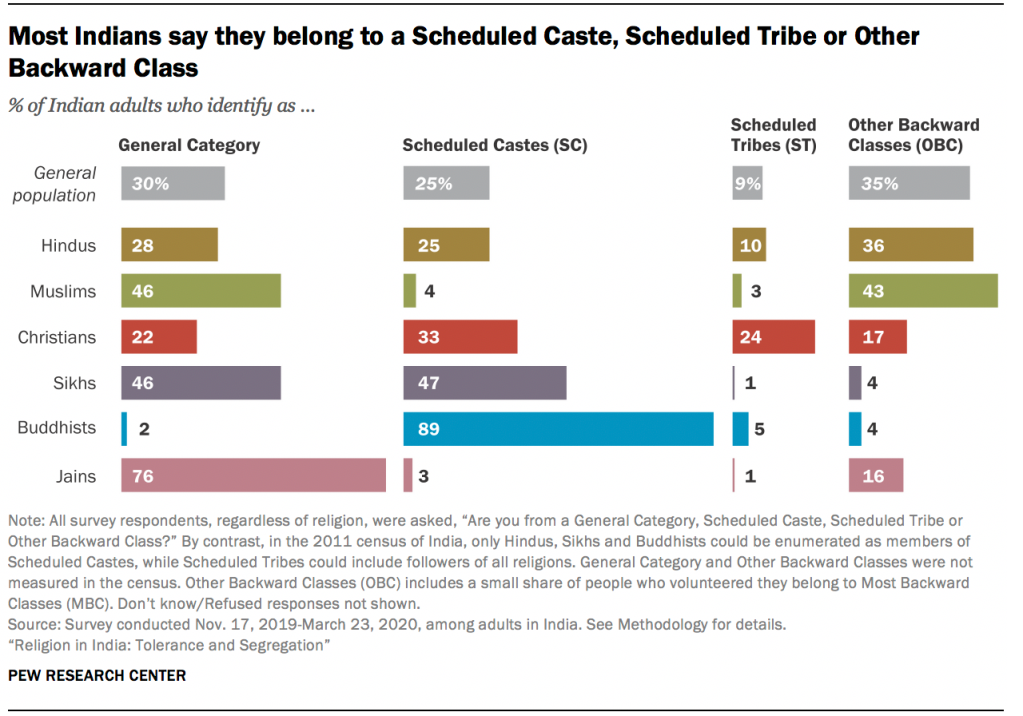
Buddhists in India nearly universally identify themselves in these categories, including 89% who are Dalits (sometimes referred to by the pejorative term “untouchables”).
Members of SC/ST/OBC groups traditionally formed the lower social and economic rungs of Indian society, and historically they have faced discrimination and unequal economic opportunities . The practice of untouchability in India ostracizes members of many of these communities, especially Dalits, although the Indian Constitution prohibits caste-based discrimination, including untouchability, and in recent decades the government has enacted economic advancement policies like reserved seats in universities and government jobs for Dalits, Scheduled Tribes and OBC communities.
Roughly 30% of Indians do not belong to these protected groups and are classified as “General Category.” This includes higher castes such as Brahmins (4%), traditionally the priestly caste. Indeed, each broad category includes several sub-castes – sometimes hundreds – with their own social and economic hierarchies.
Three-quarters of Jains (76%) identify with General Category castes, as do 46% of both Muslims and Sikhs.
Caste-based discrimination, as well as the government’s efforts to compensate for past discrimination, are politically charged topics in India . But the survey finds that most Indians do not perceive widespread caste-based discrimination. Just one-in-five Indians say there is a lot of discrimination against members of SCs, while 19% say there is a lot of discrimination against STs and somewhat fewer (16%) see high levels of discrimination against OBCs. Members of Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes are slightly more likely than others to perceive widespread discrimination against their two groups. Still, large majorities of people in these categories do not think they face a lot of discrimination.
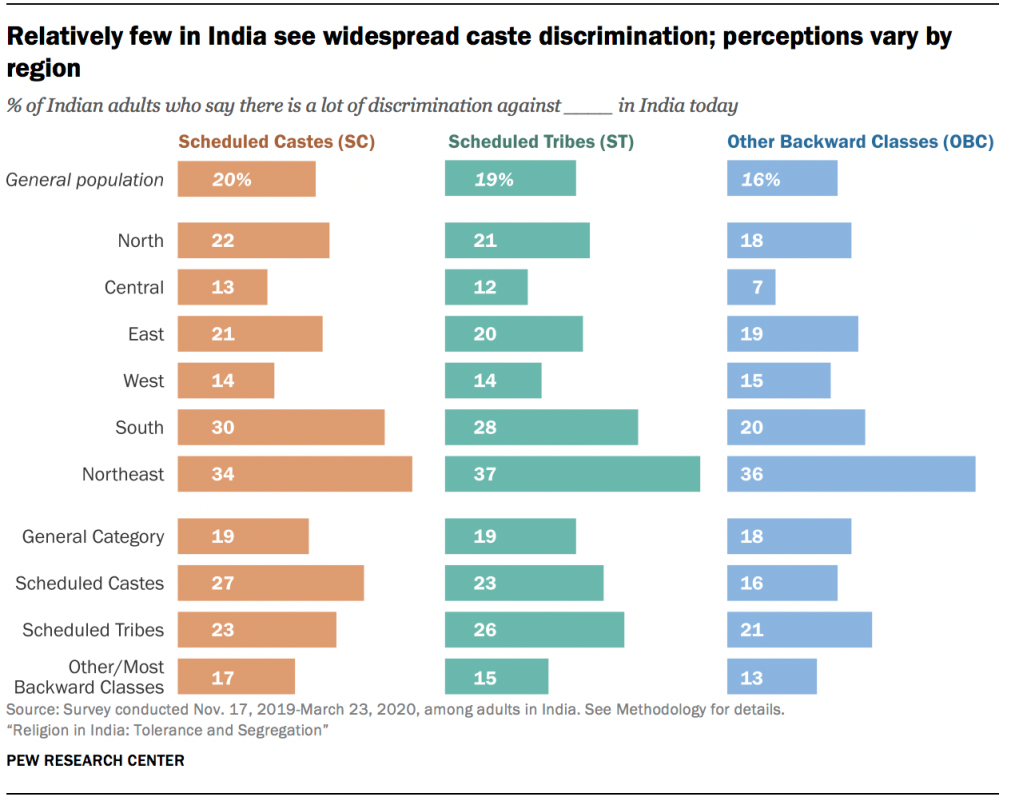
These attitudes vary by region, however. Among Southern Indians, for example, 30% see widespread discrimination against Dalits, compared with 13% in the Central part of the country. And among the Dalit community in the South, even more (43%) say their community faces a lot of discrimination, compared with 27% among Southern Indians in the General Category who say the Dalit community faces widespread discrimination in India.
A higher share of Dalits in the South and Northeast than elsewhere in the country say they, personally, have faced discrimination in the last 12 months because of their caste: 30% of Dalits in the South say this, as do 38% in the Northeast.
Although caste discrimination may not be perceived as widespread nationally, caste remains a potent factor in Indian society. Most Indians from other castes say they would be willing to have someone belonging to a Scheduled Caste as a neighbor (72%). But a similarly large majority of Indians overall (70%) say that most or all of their close friends share their caste. And Indians tend to object to marriages across caste lines, much as they object to interreligious marriages. 3
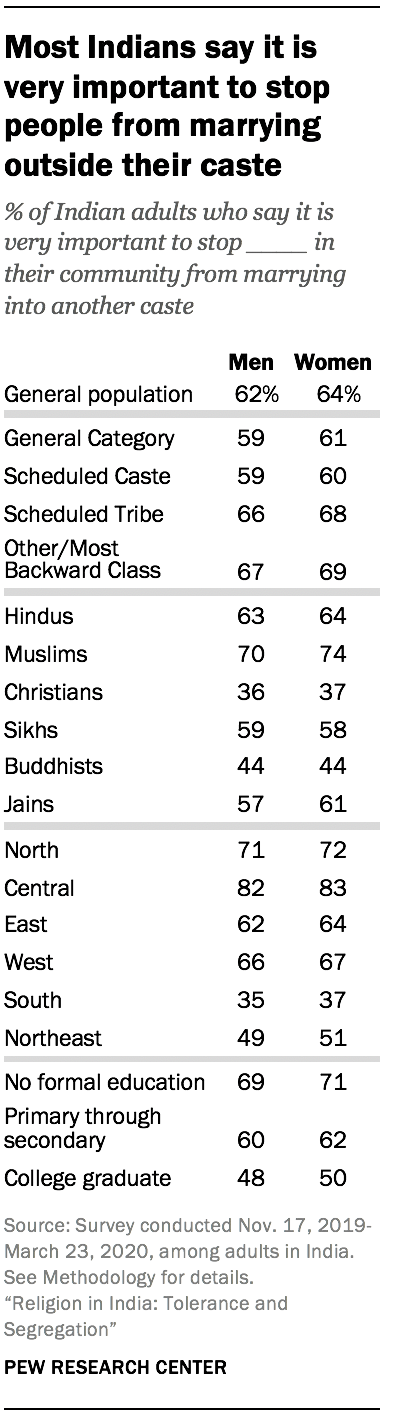
Overall, 64% of Indians say it is very important to stop women in their community from marrying into other castes, and about the same share (62%) say it is very important to stop men in their community from marrying into other castes. These figures vary only modestly across members of different castes. For example, nearly identical shares of Dalits and members of General Category castes say stopping inter-caste marriages is very important.
Majorities of Hindus, Muslims, Sikhs and Jains consider stopping inter-caste marriage of both men and women a high priority. By comparison, fewer Buddhists and Christians say it is very important to stop such marriages – although for majorities of both groups, stopping people from marrying outside their caste is at least “somewhat” important.
People surveyed in India’s South and Northeast see greater caste discrimination in their communities, and they also raise fewer objections to inter-caste marriages than do Indians overall. Meanwhile, college-educated Indians are less likely than those with less education to say stopping inter-caste marriages is a high priority. But, even within the most highly educated group, roughly half say preventing such marriages is very important. (See Chapter 4 for more analysis of Indians’ views on caste.)
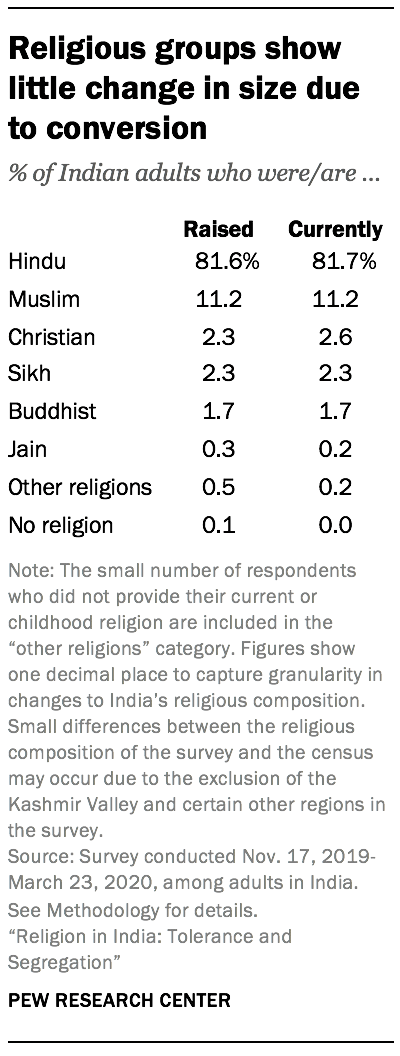
In recent years, conversion of people belonging to lower castes (including Dalits) away from Hinduism – a traditionally non-proselytizing religion – to proselytizing religions, especially Christianity, has been a contentious political issue in India. As of early 2021, nine states have enacted laws against proselytism , and some previous surveys have shown that half of Indians support legal bans on religious conversions. 4
This survey, though, finds that religious switching, or conversion, has a minimal impact on the overall size of India’s religious groups. For example, according to the survey, 82% of Indians say they were raised Hindu, and a nearly identical share say they are currently Hindu, showing no net losses for the group through conversion to other religions. Other groups display similar levels of stability.
Changes in India’s religious landscape over time are largely a result of differences in fertility rates among religious groups, not conversion.
Respondents were asked two separate questions to measure religious switching: “What is your present religion, if any?” and, later in the survey, “In what religion were you raised, if any?” Overall, 98% of respondents give the same answer to both these questions.
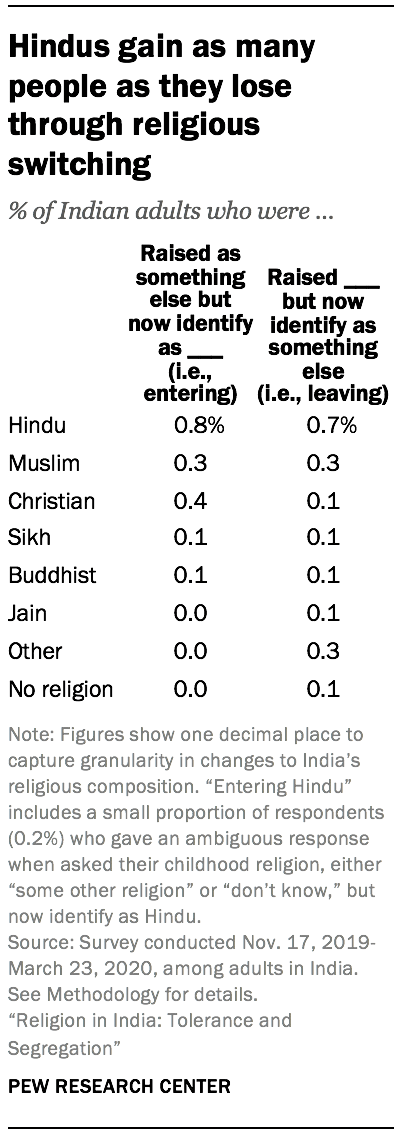
An overall pattern of stability in the share of religious groups is accompanied by little net gain from movement into, or out of, most religious groups. Among Hindus, for instance, any conversion out of the group is matched by conversion into the group: 0.7% of respondents say they were raised Hindu but now identify as something else, and although Hindu texts and traditions do not agree on any formal process for conversion into the religion, roughly the same share (0.8%) say they were not raised Hindu but now identify as Hindu. 5 Most of these new followers of Hinduism are married to Hindus.
Similarly, 0.3% of respondents have left Islam since childhood, matched by an identical share who say they were raised in other religions (or had no childhood religion) and have since become Muslim.
For Christians, however, there are some net gains from conversion: 0.4% of survey respondents are former Hindus who now identify as Christian, while 0.1% are former Christians.
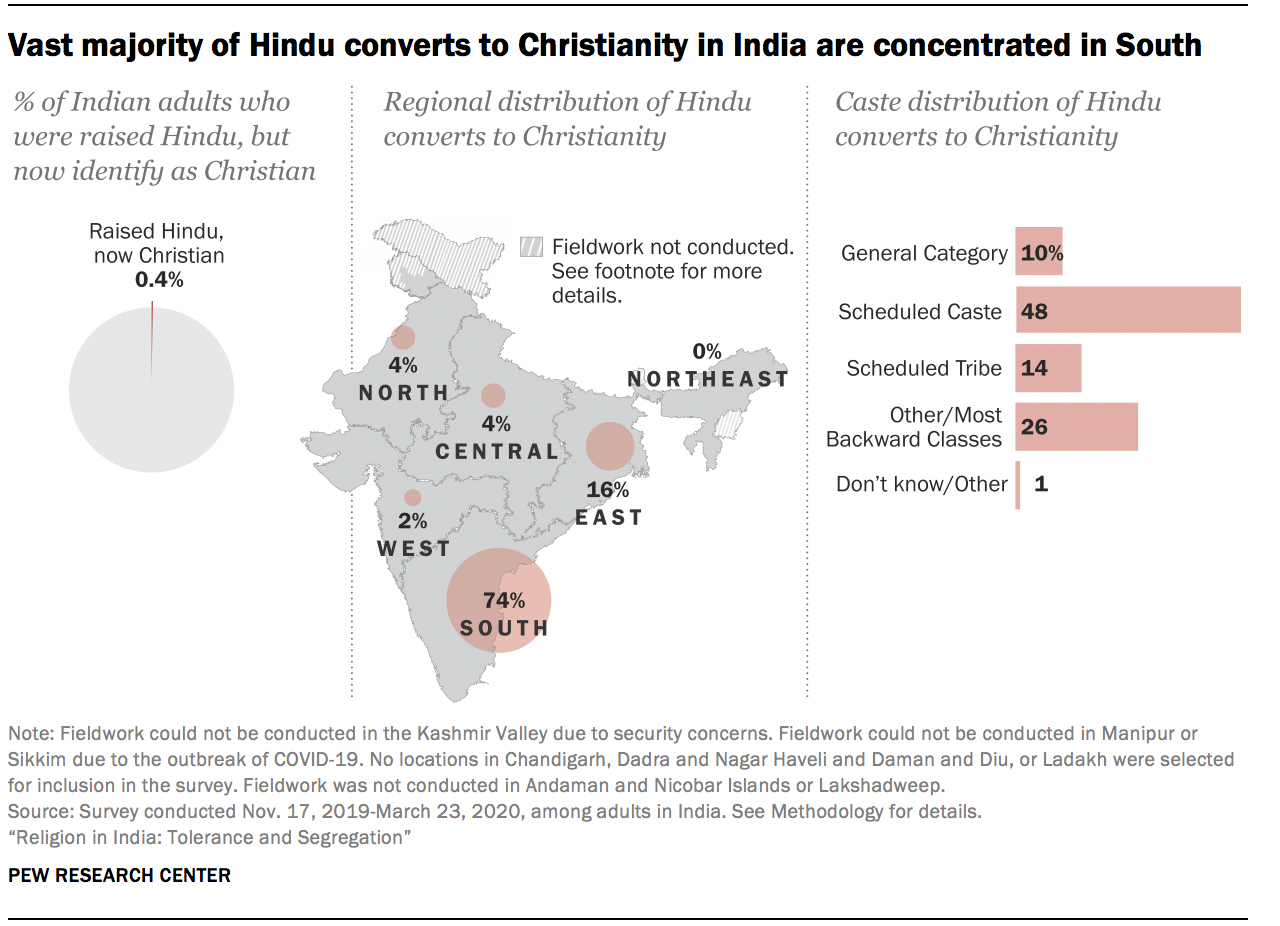
Three-quarters of India’s Hindu converts to Christianity (74%) are concentrated in the Southern part of the country – the region with the largest Christian population. As a result, the Christian population of the South shows a slight increase within the lifetime of survey respondents: 6% of Southern Indians say they were raised Christian, while 7% say they are currently Christian.
Some Christian converts (16%) reside in the East as well (the states of Bihar, Jharkhand, Odisha and West Bengal); about two-thirds of all Christians in the East (64%) belong to Scheduled Tribes.
Nationally, the vast majority of former Hindus who are now Christian belong to Scheduled Castes (48%), Scheduled Tribes (14%) or Other Backward Classes (26%). And former Hindus are much more likely than the Indian population overall to say there is a lot of discrimination against lower castes in India. For example, nearly half of converts to Christianity (47%) say there is a lot of discrimination against Scheduled Castes in India, compared with 20% of the overall population who perceive this level of discrimination against Scheduled Castes. Still, relatively few converts say they, personally, have faced discrimination due to their caste in the last 12 months (12%).
Though their specific practices and beliefs may vary, all of India’s major religious communities are highly observant by standard measures. For instance, the vast majority of Indians, across all major faiths, say that religion is very important in their lives. And at least three-quarters of each major religion’s followers say they know a great deal about their own religion and its practices. For example, 81% of Indian Buddhists claim a great deal of knowledge about the Buddhist religion and its practices.
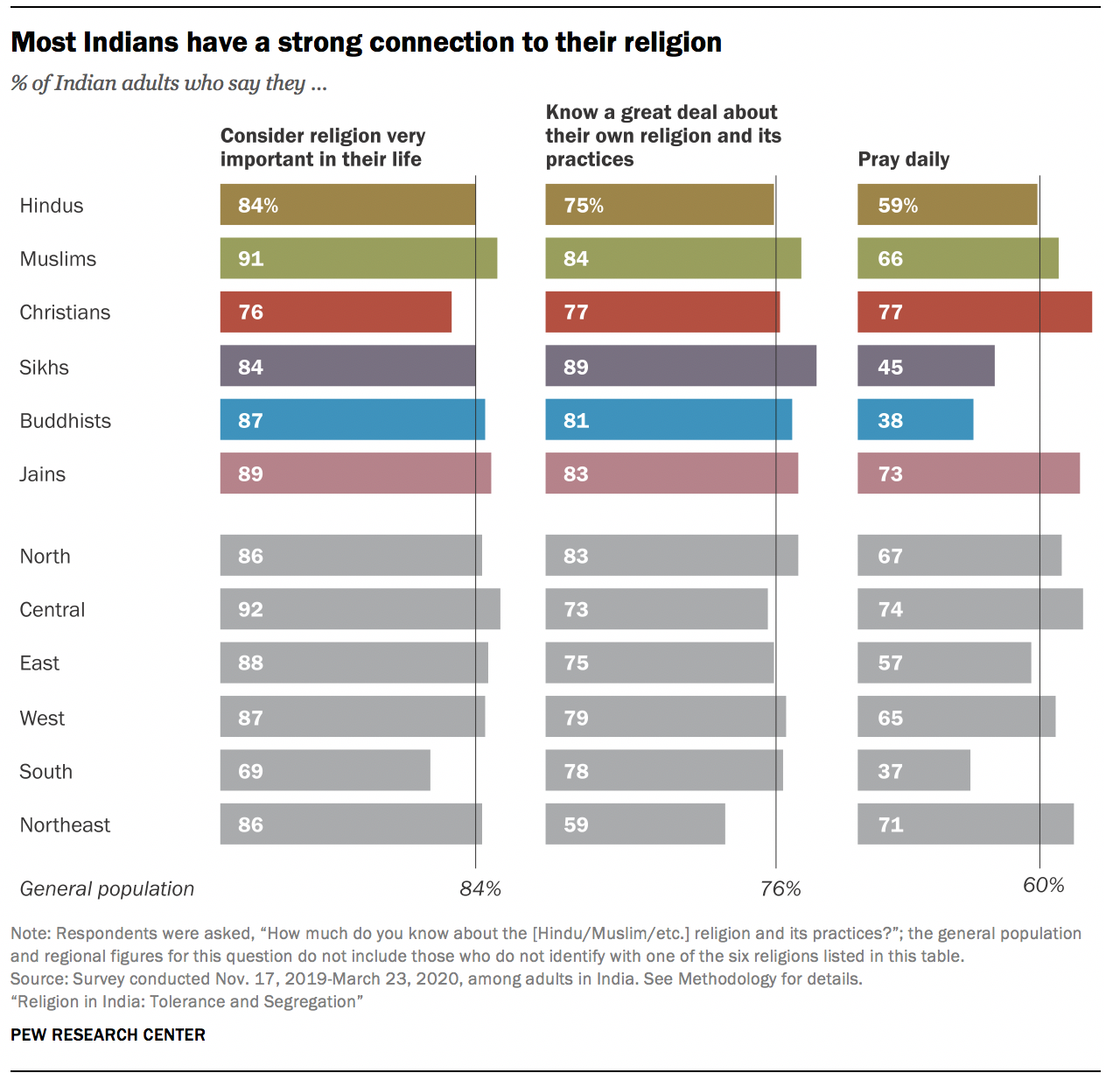
Indian Muslims are slightly more likely than Hindus to consider religion very important in their lives (91% vs. 84%). Muslims also are modestly more likely than Hindus to say they know a great deal about their own religion (84% vs. 75%).
Significant portions of each religious group also pray daily, with Christians among the most likely to do so (77%) – even though Christians are the least likely of the six groups to say religion is very important in their lives (76%). Most Hindus and Jains also pray daily (59% and 73%, respectively) and say they perform puja daily (57% and 81%), either at home or at a temple. 6
Generally, younger and older Indians, those with different educational backgrounds, and men and women are similar in their levels of religious observance. South Indians are the least likely to say religion is very important in their lives (69%), and the South is the only region where fewer than half of people report praying daily (37%). While Hindus, Muslims and Christians in the South are all less likely than their counterparts elsewhere in India to say religion is very important to them, the lower rate of prayer in the South is driven mainly by Hindus: Three-in-ten Southern Hindus report that they pray daily (30%), compared with roughly two-thirds (68%) of Hindus in the rest of the country (see “ People in the South differ from rest of the country in their views of religion, national identity ” below for further discussion of religious differences in Southern India).
The survey also asked about three rites of passage: religious ceremonies for birth (or infancy), marriage and death. Members of all of India’s major religious communities tend to see these rites as highly important. For example, the vast majority of Muslims (92%), Christians (86%) and Hindus (85%) say it is very important to have a religious burial or cremation for their loved ones.
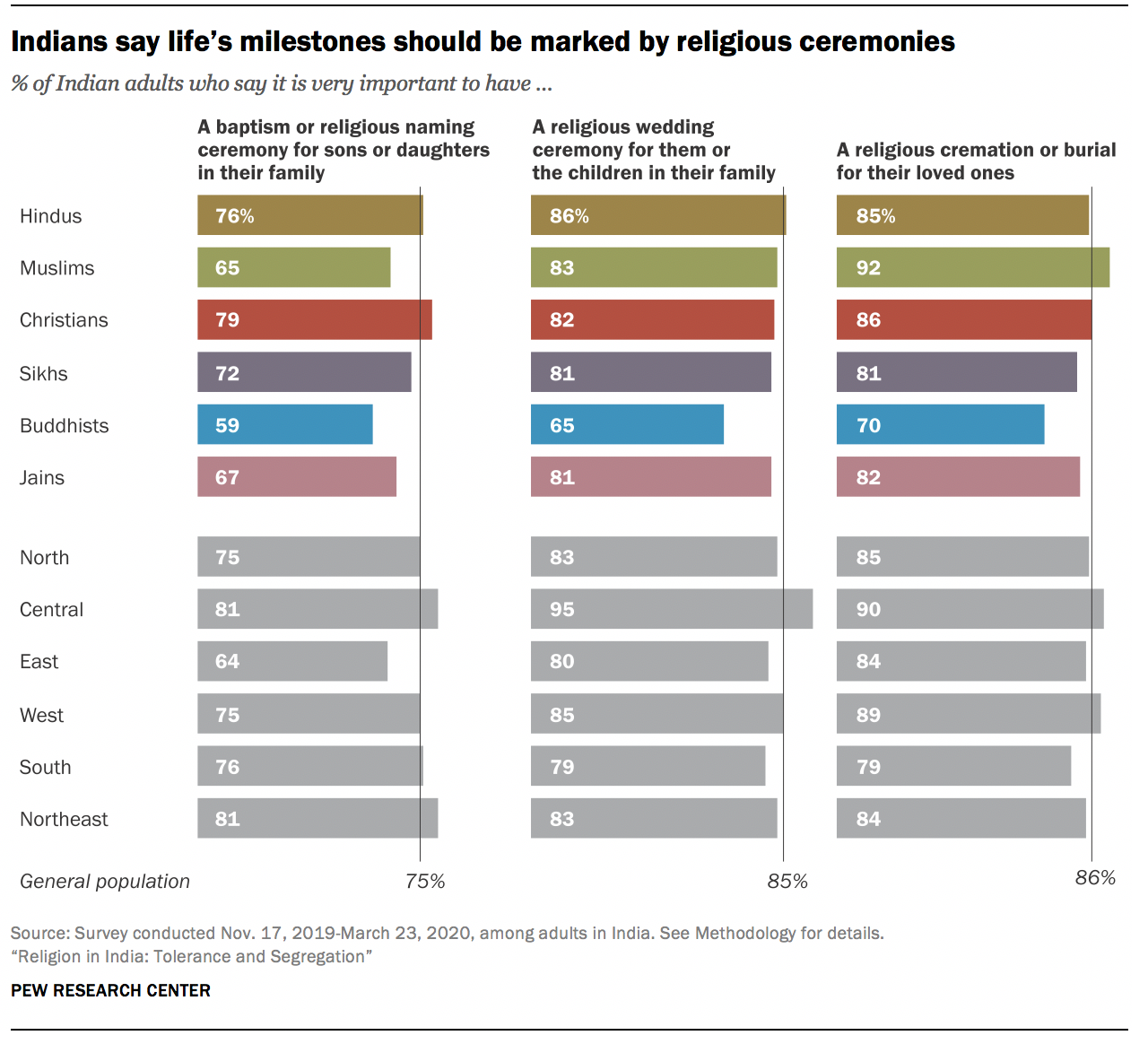
The survey also asked about practices specific to particular religions, such as whether people have received purification by bathing in holy bodies of water, like the Ganges River, a rite closely associated with Hinduism. About two-thirds of Hindus have done this (65%). Most Hindus also have holy basil (the tulsi plant) in their homes, as do most Jains (72% and 62%, respectively). And about three-quarters of Sikhs follow the Sikh practice of keeping their hair long (76%).
For more on religious practices across India’s religious groups, see Chapter 7 .
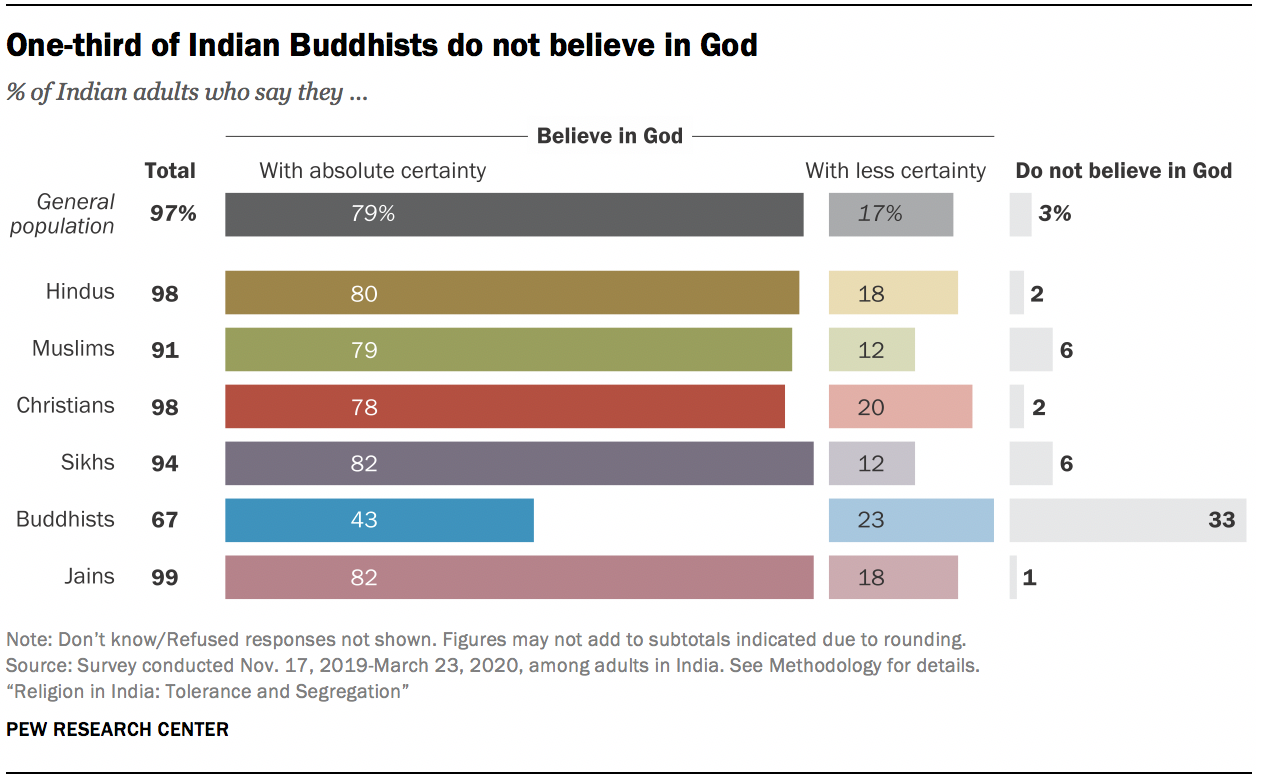
Nearly all Indians say they believe in God (97%), and roughly 80% of people in most religious groups say they are absolutely certain that God exists. The main exception is Buddhists, one-third of whom say they do not believe in God. Still, among Buddhists who do think there is a God, most say they are absolutely certain in this belief.
While belief in God is close to universal in India, the survey finds a wide range of views about the type of deity or deities that Indians believe in. The prevailing view is that there is one God “with many manifestations” (54%). But about one-third of the public says simply: “There is only one God” (35%). Far fewer say there are many gods (6%).
Even though Hinduism is sometimes referred to as a polytheistic religion , very few Hindus (7%) take the position that there are multiple gods. Instead, the most common position among Hindus (as well as among Jains) is that there is “only one God with many manifestations” (61% among Hindus and 54% among Jains).
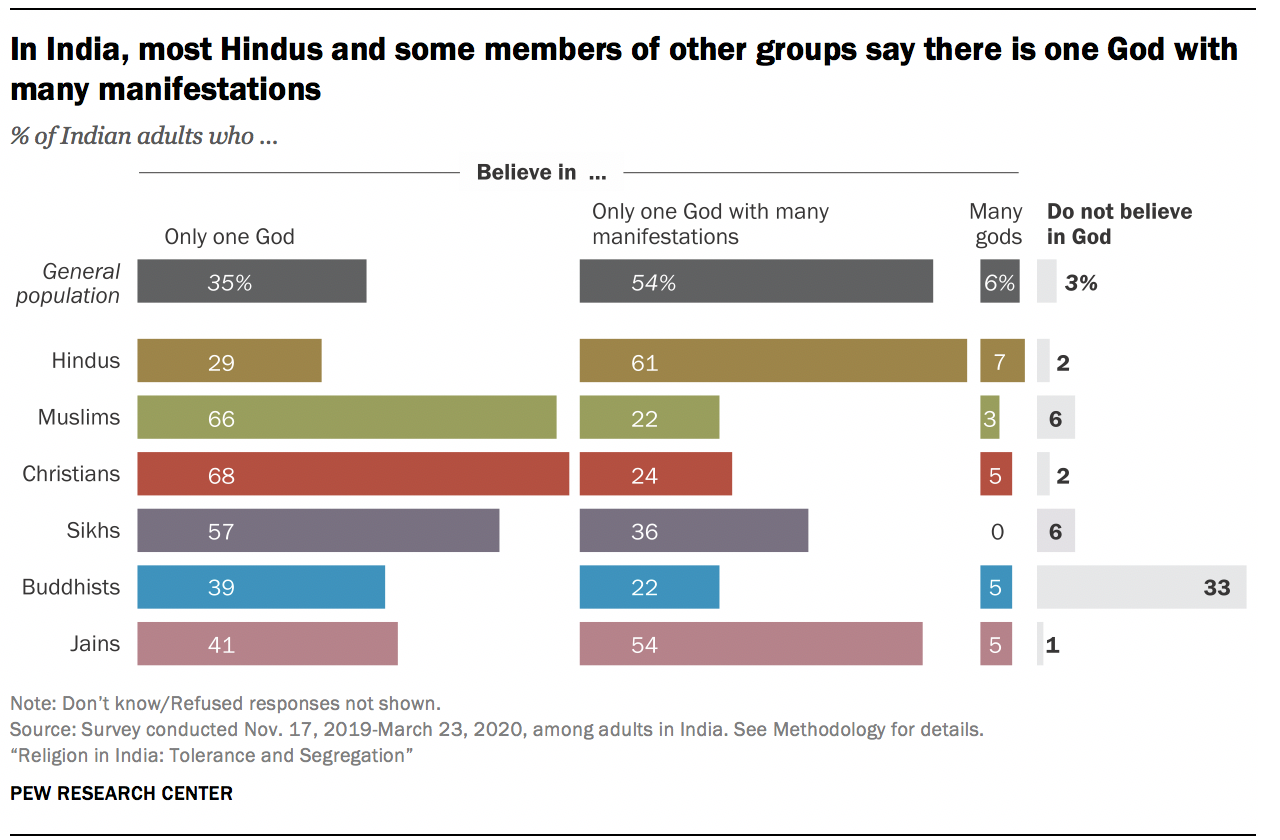
Among Hindus, those who say religion is very important in their lives are more likely than other Hindus to believe in one God with many manifestations (63% vs. 50%) and less likely to say there are many gods (6% vs. 12%).
By contrast, majorities of Muslims, Christians and Sikhs say there is only one God. And among Buddhists, the most common response is also a belief in one God. Among all these groups, however, about one-in-five or more say God has many manifestations, a position closer to their Hindu compatriots’ concept of God.
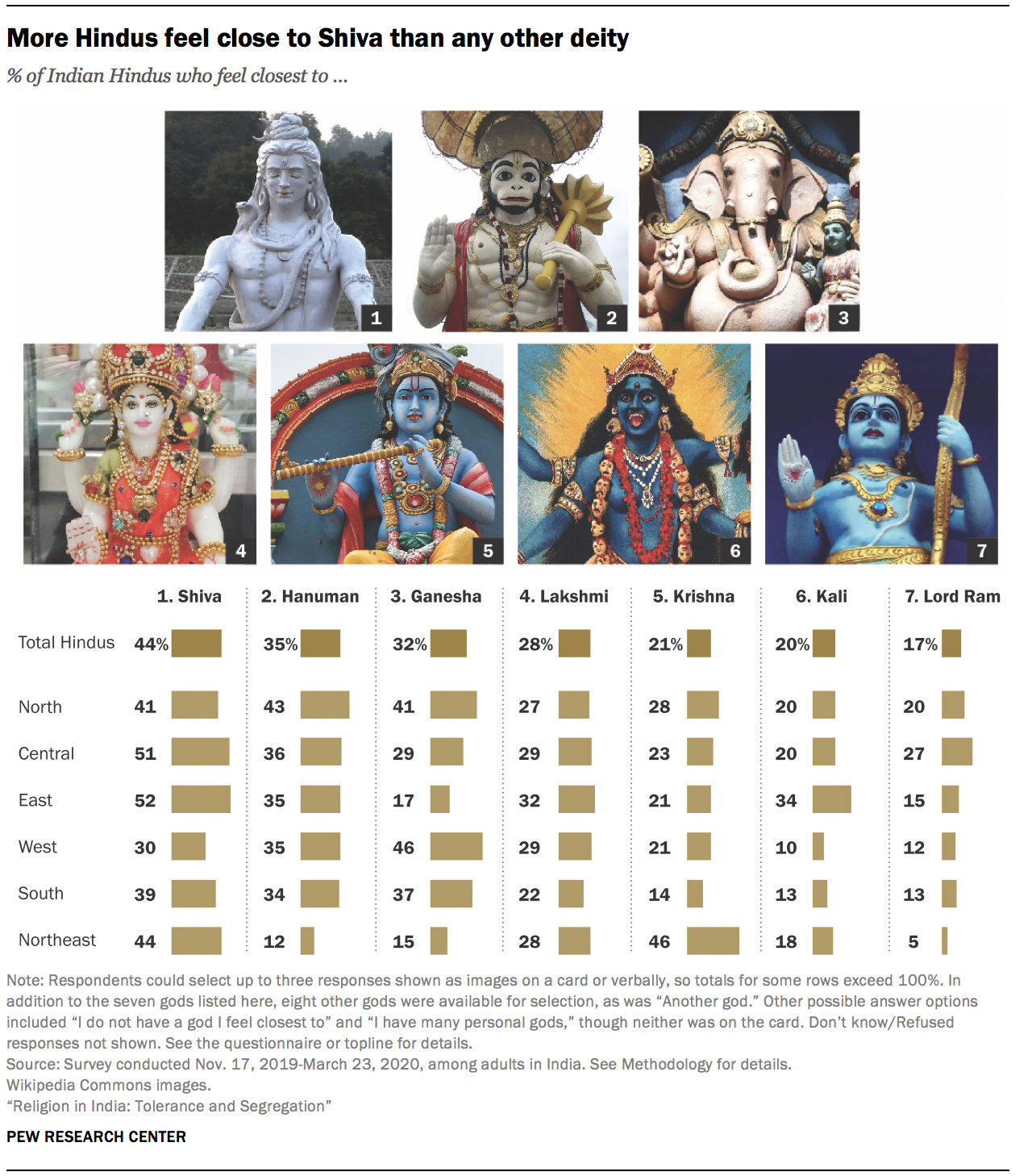
Most Hindus feel close to multiple gods, but Shiva, Hanuman and Ganesha are most popular
Traditionally, many Hindus have a “personal god,” or ishta devata: A particular god or goddess with whom they feel a personal connection. The survey asked all Indian Hindus who say they believe in God which god they feel closest to – showing them 15 images of gods on a card as possible options – and the vast majority of Hindus selected more than one god or indicated that they have many personal gods (84%). 7 This is true not only among Hindus who say they believe in many gods (90%) or in one God with many manifestations (87%), but also among those who say there is only one God (82%).
The god that Hindus most commonly feel close to is Shiva (44%). In addition, about one-third of Hindus feel close to Hanuman or Ganesha (35% and 32%, respectively).
There is great regional variation in how close India’s Hindus feel to some gods. For example, 46% of Hindus in India’s West feel close to Ganesha, but only 15% feel this way in the Northeast. And 46% of Hindus in the Northeast feel close to Krishna, while just 14% in the South say the same.
Feelings of closeness for Lord Ram are especially strong in the Central region (27%), which includes what Hindus claim is his ancient birthplace , Ayodhya. The location in Ayodhya where many Hindus believe Ram was born has been a source of controversy: Hindu mobs demolished a mosque on the site in 1992, claiming that a Hindu temple originally existed there. In 2019, the Indian Supreme Court ruled that the demolished mosque had been built on top of a preexisting non-Islamic structure and that the land should be given to Hindus to build a temple, with another location in the area given to the Muslim community to build a new mosque. (For additional findings on belief in God, see Chapter 12 .)
Sidebar: Despite economic advancement, few signs that importance of religion is declining
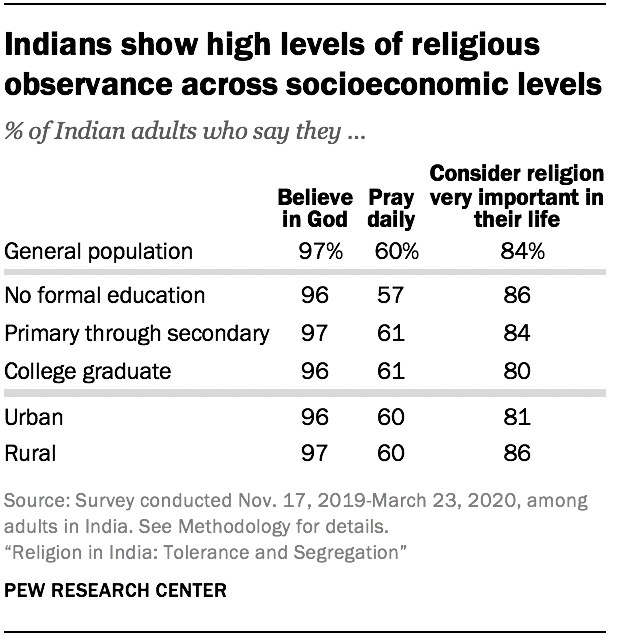
A prominent theory in the social sciences hypothesizes that as countries advance economically, their populations tend to become less religious, often leading to wider social change. Known as “secularization theory,” it particularly reflects the experience of Western European countries from the end of World War II to the present.
Despite rapid economic growth, India’s population so far shows few, if any, signs of losing its religion. For instance, both the Indian census and the new survey find virtually no growth in the minuscule share of people who claim no religious identity. And religion is prominent in the lives of Indians regardless of their socioeconomic status. Generally, across the country, there is little difference in personal religious observance between urban and rural residents or between those who are college educated versus those who are not. Overwhelming shares among all these groups say that religion is very important in their lives, that they pray regularly and that they believe in God.
Nearly all religious groups show the same patterns. The biggest exception is Christians, among whom those with higher education and those who reside in urban areas show somewhat lower levels of observance. For example, among Christians who have a college degree, 59% say religion is very important in their life, compared with 78% among those who have less education.
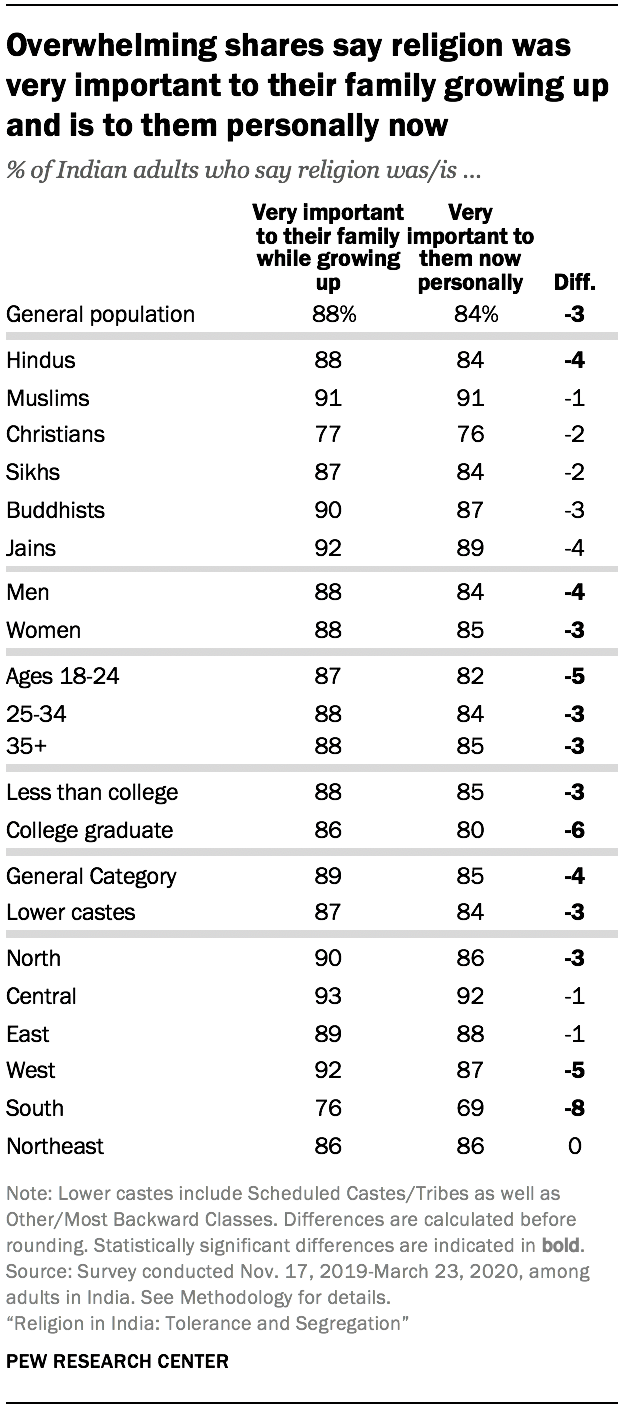
The survey does show a slight decline in the perceived importance of religion during the lifetime of respondents, though the vast majority of Indians indicate that religion remains central to their lives, and this is true among both younger and older adults.
Nearly nine-in-ten Indian adults say religion was very important to their family when they were growing up (88%), while a slightly lower share say religion is very important to them now (84%). The pattern is identical when looking only at India’s majority Hindu population. Among Muslims in India, the same shares say religion was very important to their family growing up and is very important to them now (91% each).
The states of Southern India (Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala, Puducherry, Tamil Nadu and Telangana) show the biggest downward trend in the perceived importance of religion over respondents’ lifetimes: 76% of Indians who live in the South say religion was very important to their family growing up, compared with 69% who say religion is personally very important to them now. Slight declines in the importance of religion, by this measure, also are seen in the Western part of the country (Goa, Gujarat and Maharashtra) and in the North, although large majorities in all regions of the country say religion is very important in their lives today.
Despite a strong desire for religious segregation, India’s religious groups share patriotic feelings, cultural values and some religious beliefs. For instance, overwhelming shares across India’s religious communities say they are very proud to be Indian, and most agree that Indian culture is superior to others.
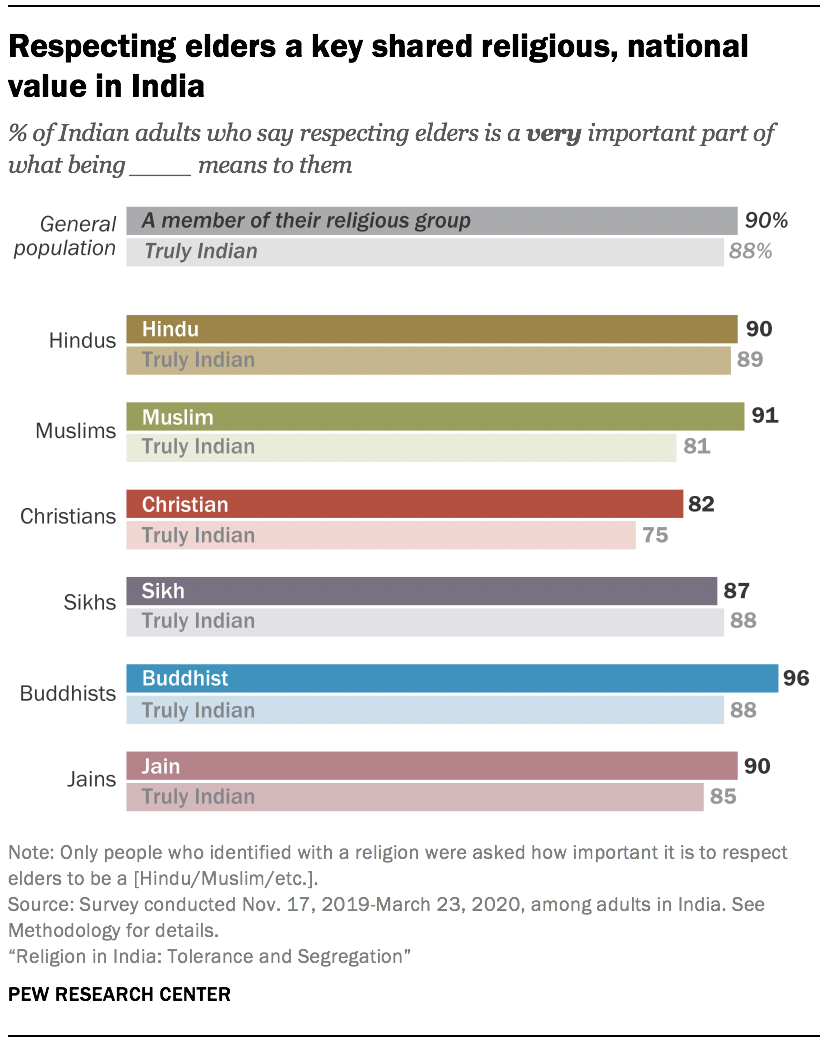
Similarly, Indians of different religious backgrounds hold elders in high respect. For instance, nine-in-ten or more Hindus, Muslims, Buddhists and Jains say that respecting elders is very important to what being a member of their religious group means to them (e.g., for Hindus, it’s a very important part of their Hindu identity). Christians and Sikhs also overwhelmingly share this sentiment. And among all people surveyed in all six groups, three-quarters or more say that respecting elders is very important to being truly Indian.
Within all six religious groups, eight-in-ten or more also say that helping the poor and needy is a crucial part of their religious identity.
Beyond cultural parallels, many people mix traditions from multiple religions into their practices: As a result of living side by side for generations, India’s minority groups often engage in practices that are more closely associated with Hindu traditions than their own. For instance, many Muslim, Sikh and Christian women in India say they wear a bindi (a forehead marking, often worn by married women), even though putting on a bindi has Hindu origins.
Similarly, many people embrace beliefs not traditionally associated with their faith: Muslims in India are just as likely as Hindus to say they believe in karma (77% each), and 54% of Indian Christians share this view. 8 Nearly three-in-ten Muslims and Christians say they believe in reincarnation (27% and 29%, respectively). While these may seem like theological contradictions, for many Indians, calling oneself a Muslim or a Christian does not preclude believing in karma or reincarnation – beliefs that do not have a traditional, doctrinal basis in Islam or Christianity.
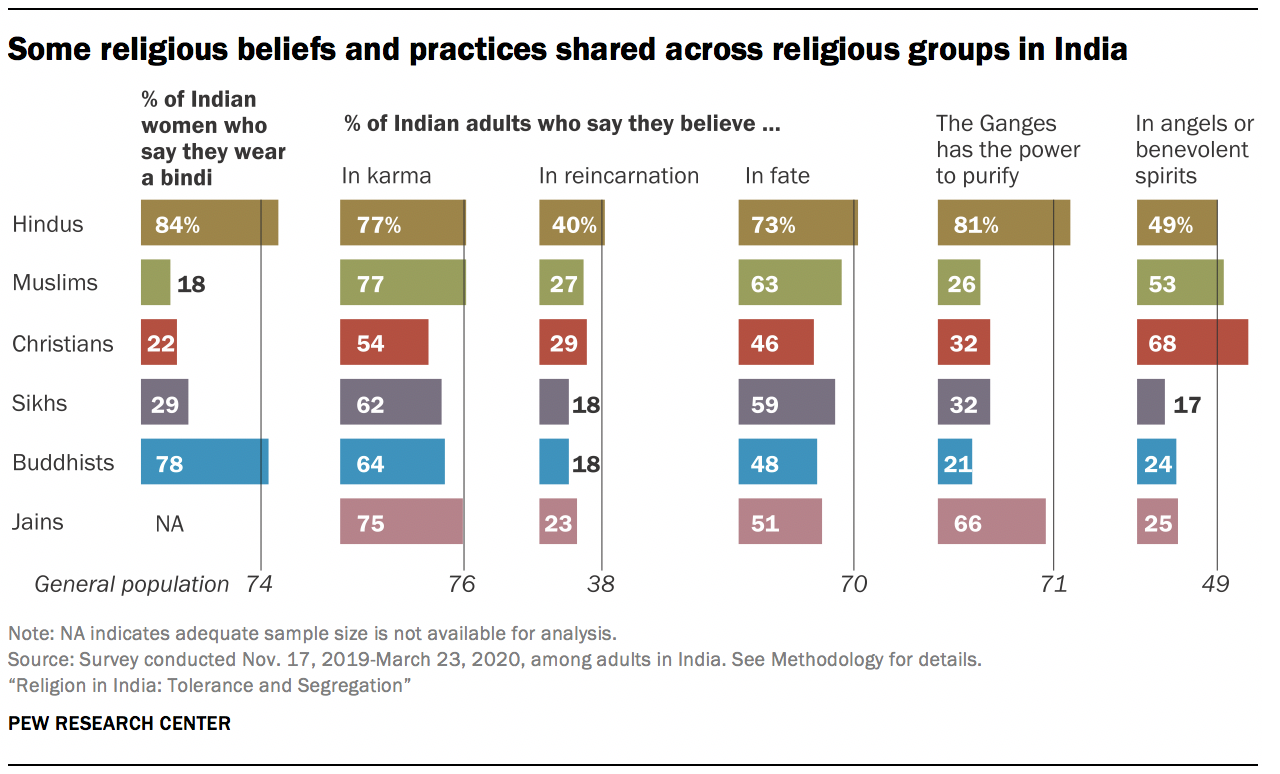
Most Muslims and Christians say they don’t participate in celebrations of Diwali, the Indian festival of lights that is traditionally celebrated by Hindus, Sikhs, Jains and Buddhists. But substantial minorities of Christians (31%) and Muslims (20%) report that they do celebrate Diwali. Celebrating Diwali is especially common among Muslims in the West, where 39% say they participate in the festival, and in the South (33%).
Not only do some followers of all these religions participate in a celebration (Diwali) that consumes most of the country once a year, but some members of the majority Hindu community celebrate Muslim and Christian festivals, too: 7% of Indian Hindus say they celebrate the Muslim festival of Eid, and 17% celebrate Christmas.
While there is some mixing of religious celebrations and traditions within India’s diverse population, many Hindus do not approve of this. In fact, while 17% of the nation’s Hindus say they participate in Christmas celebrations, about half of Hindus (52%) say that doing so disqualifies a person from being Hindu (compared with 35% who say a person can be Hindu if they celebrate Christmas). An even greater share of Hindus (63%) say a person cannot be Hindu if they celebrate the Islamic festival of Eid – a view that is more widely held in Northern, Central, Eastern and Northeastern India than the South or West.
Hindus are divided on whether beliefs and practices such as believing in God, praying and going to the temple are necessary to be a Hindu. But one behavior that a clear majority of Indian Hindus feel is incompatible with Hinduism is eating beef: 72% of Hindus in India say a person who eats beef cannot be a Hindu. That is even higher than the percentages of Hindus who say a person cannot be Hindu if they reject belief in God (49%), never go to a temple (48%) or never perform prayers (48%).
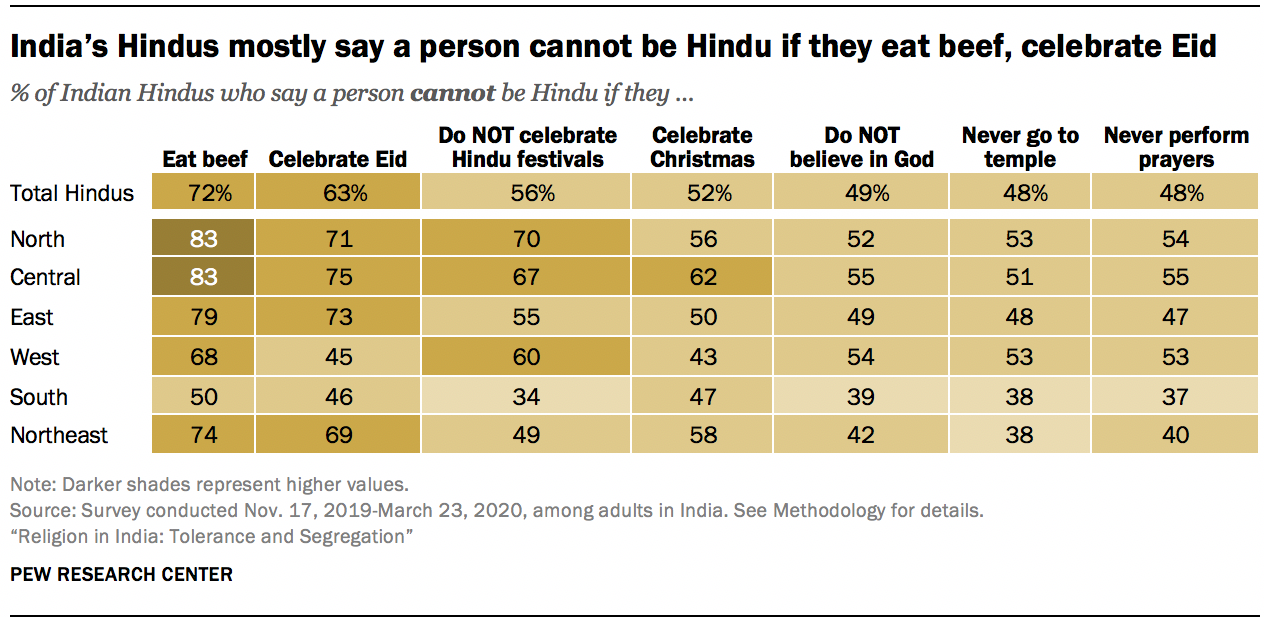
Attitudes toward beef appear to be part of a regional and cultural divide among Hindus: Southern Indian Hindus are considerably less likely than others to disqualify beef eaters from being Hindu (50% vs. 83% in the Northern and Central parts of the country). And, at least in part, Hindus’ views on beef and Hindu identity are linked with a preference for religious segregation and elements of Hindu nationalism. For example, Hindus who take a strong position against eating beef are more likely than others to say they would not accept followers of other religions as their neighbors (49% vs. 30%) and to say it is very important to be Hindu to be truly Indian (68% vs. 51%).
Relatedly, 44% of Hindus say they are vegetarians, and an additional 33% say they abstain from eating certain meats. Hindus traditionally view cows as sacred, and laws pertaining to cow slaughter have been a recent flashpoint in India . At the same time, Hindus are not alone in linking beef consumption with religious identity: 82% of Sikhs and 85% of Jains surveyed say that a person who eats beef cannot be a member of their religious groups, either. A majority of Sikhs (59%) and fully 92% of Jains say they are vegetarians, including 67% of Jains who do not eat root vegetables . 9 (For more data on religion and dietary habits, see Chapter 10 .)

Sidebar: People in the South differ from rest of the country in their views of religion, national identity
The survey consistently finds that people in the South (the states of Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu and Telangana, and the union territory of Puducherry) differ from Indians elsewhere in the country in their views on religion, politics and identity.
For example, by a variety of measures, people in the South are somewhat less religious than those in other regions – 69% say religion is very important in their lives, versus 92% in the Central part of the country. And 37% say they pray every day, compared with more than half of Indians in other regions. People in the South also are less segregated by religion or caste – whether that involves their friendship circles, the kind of neighbors they prefer or how they feel about intermarriage. (See Chapter 3 .)
Hindu nationalist sentiments also appear to have less of a foothold in the South. Among Hindus, those in the South (42%) are far less likely than those in Central states (83%) or the North (69%) to say being Hindu is very important to be truly Indian. And in the 2019 parliamentary elections, the BJP’s lowest vote share came in the South. In the survey, just 19% of Hindus in the region say they voted for the BJP, compared with roughly two-thirds in the Northern (68%) and Central (65%) parts of the country who say they voted for the ruling party.
Culturally and politically, people in the South have pushed back against the BJP’s restrictions on cow slaughter and efforts to nationalize the Hindi language . These factors may contribute to the BJP’s lower popularity in the South, where more people prefer regional parties or the Indian National Congress party.
These differences in attitudes and practices exist in a wider context of economic disparities between the South and other regions of the country. Over time, Southern states have seen stronger economic growth than the Northern and Central parts of the country. And women and people belonging to lower castes in the South have fared better economically than their counterparts elsewhere in the country. Even though three-in-ten people in the South say there is widespread caste discrimination in India, the region also has a history of anti-caste movements . Indeed, one author has attributed the economic growth of the South largely to the flattening of caste hierarchies.
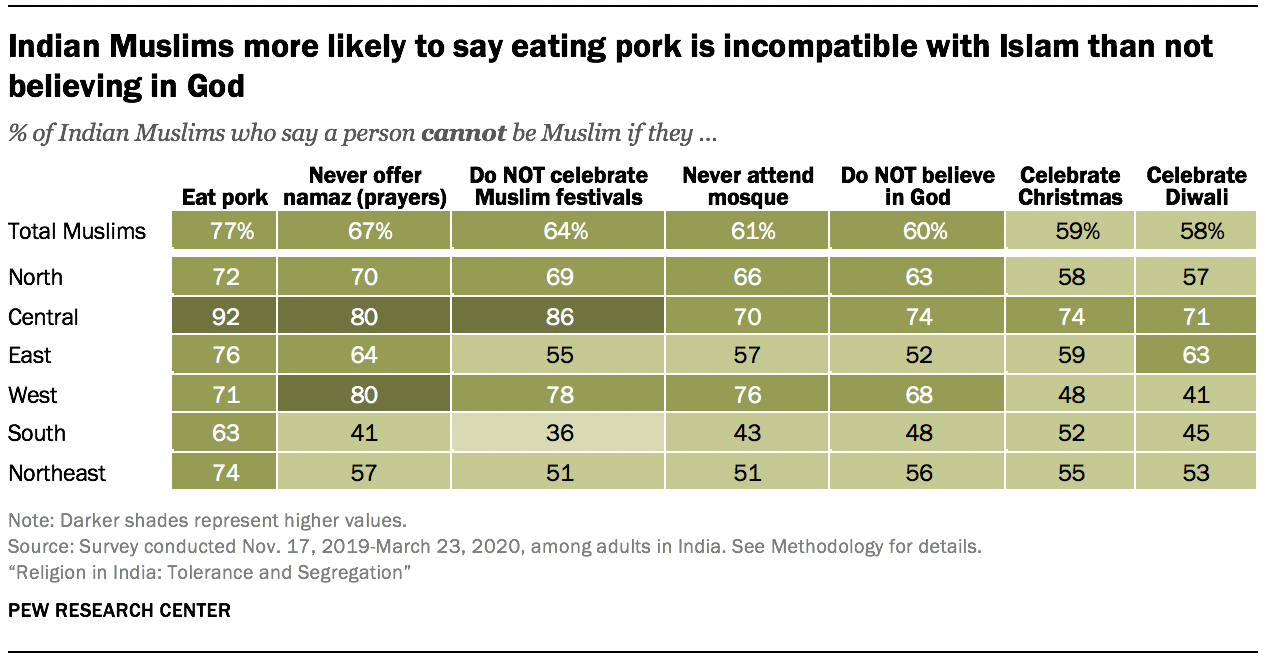
Muslim identity in India
Most Muslims in India say a person cannot be Muslim if they never pray or attend a mosque. Similarly, about six-in-ten say that celebrating Diwali or Christmas is incompatible with being a member of the Muslim community. At the same time, a substantial minority express a degree of open-mindedness on who can be a Muslim, with fully one-third (34%) saying a person can be Muslim even if they don’t believe in God. (The survey finds that 6% of self-described Muslims in India say they do not believe in God; see “ Near-universal belief in God, but wide variation in how God is perceived ” above.)
Like Hindus, Muslims have dietary restrictions that resonate as powerful markers of identity. Three-quarters of Indian Muslims (77%) say that a person cannot be Muslim if they eat pork, which is even higher than the share who say a person cannot be Muslim if they do not believe in God (60%) or never attend mosque (61%).
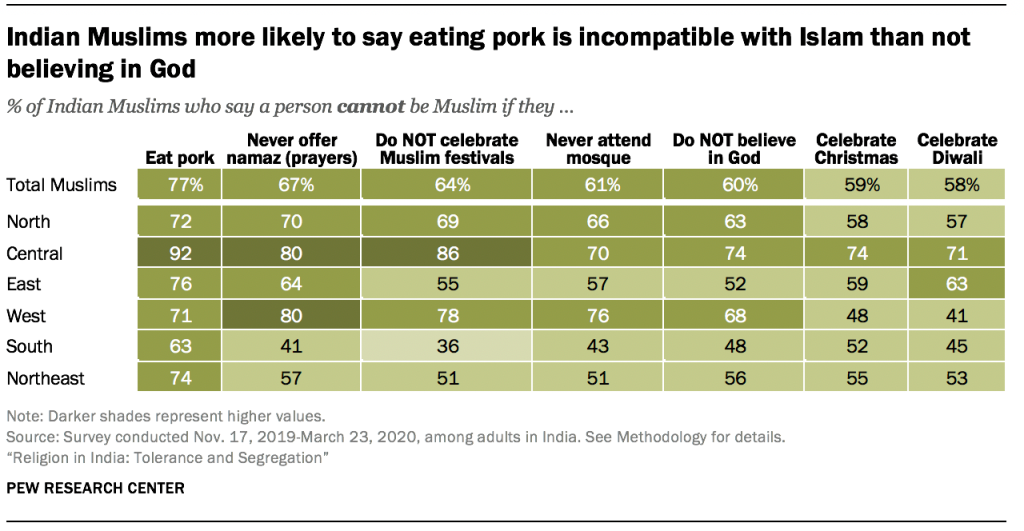
Indian Muslims also report high levels of religious commitment by a host of conventional measures: 91% say religion is very important in their lives, two-thirds (66%) say they pray at least once a day, and seven-in-ten say they attend mosque at least once a week – with even higher attendance among Muslim men (93%).
By all these measures, Indian Muslims are broadly comparable to Muslims in the neighboring Muslim-majority countries of Pakistan and Bangladesh, according to a Pew Research Center survey conducted in those countries in late 2011 and early 2012. In Pakistan, for example, 94% of Muslims said religion is very important in their lives , while 81% of Bangladeshi Muslims said the same. Muslims in India are somewhat more likely than those elsewhere in South Asia to say they regularly worship at a mosque (70% in India vs. 59% in Pakistan and 53% in Bangladesh), with the difference mainly driven by the share of women who attend.
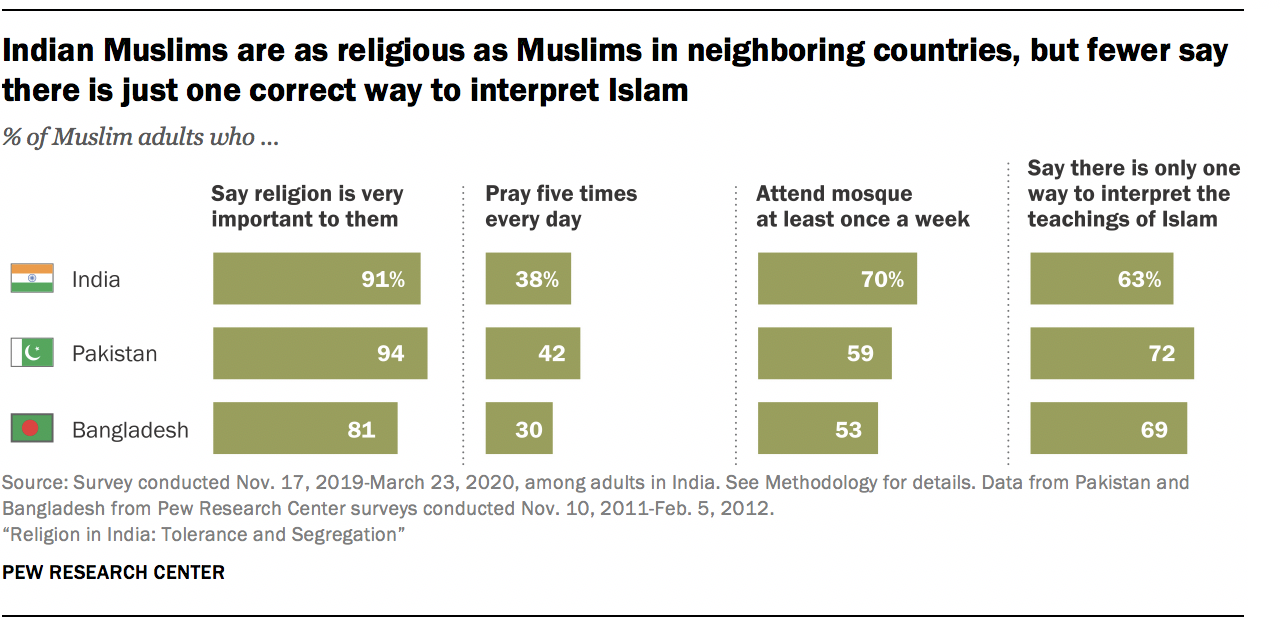
At the same time, Muslims in India are slightly less likely to say there is “only one true” interpretation of Islam (72% in Pakistan, 69% in Bangladesh, 63% in India), as opposed to multiple interpretations.
When it comes to their religious beliefs, Indian Muslims in some ways resemble Indian Hindus more than they resemble Muslims in neighboring countries. For example, Muslims in Pakistan and Bangladesh almost universally say they believe in heaven and angels, but Indian Muslims seem more skeptical: 58% say they believe in heaven and 53% express belief in angels. Among Indian Hindus, similarly, 56% believe in heaven and 49% believe in angels.
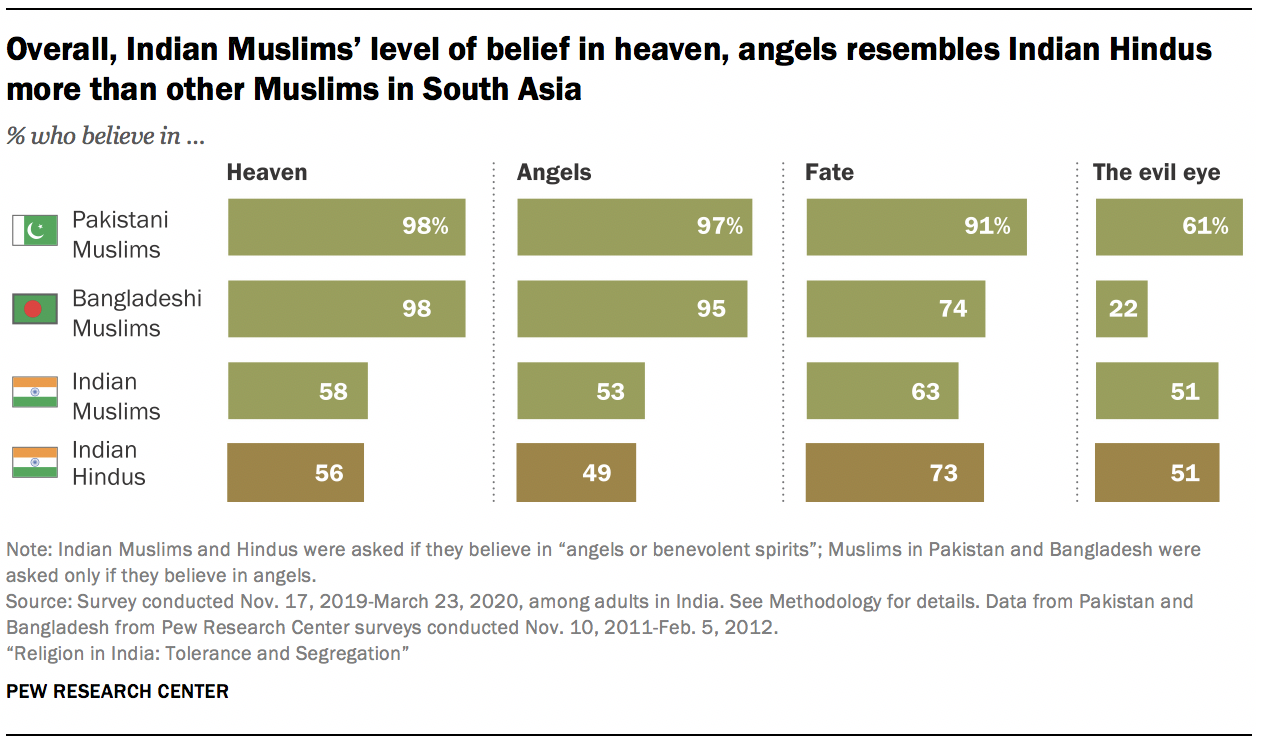
Majority of Muslim women in India oppose ‘triple talaq’ (Islamic divorce)
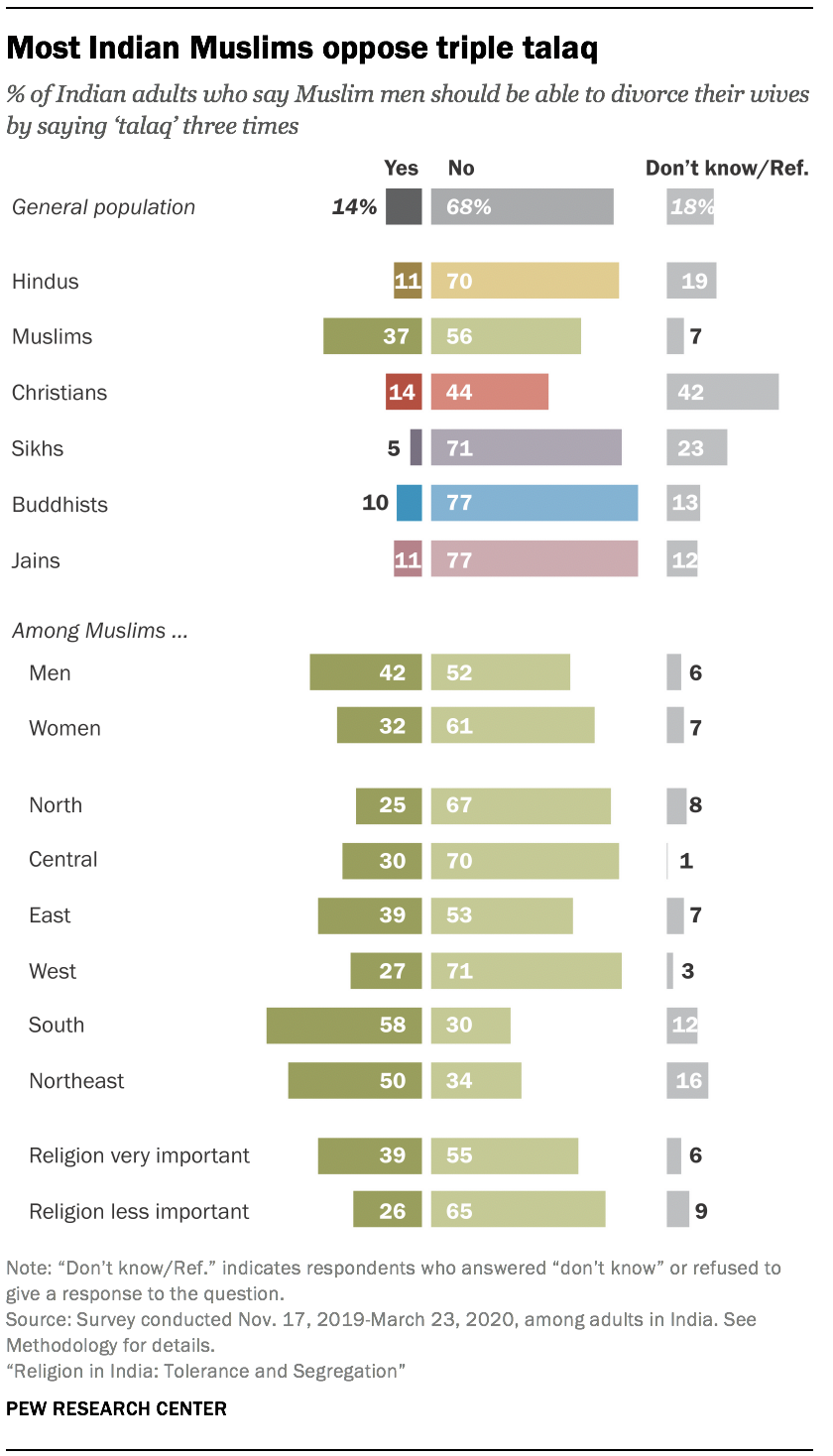
Many Indian Muslims historically have followed the Hanafi school of thought, which for centuries allowed men to divorce their wives by saying “talaq” (which translates as “divorce” in Arabic and Urdu) three times. Traditionally, there was supposed to be a waiting period and attempts at reconciliation in between each use of the word, and it was deeply frowned upon (though technically permissible) for a man to pronounce “talaq” three times quickly in a row. India’s Supreme Court ruled triple talaq unconstitutional in 2017, and it was banned by legislation in 2019 .
Most Indian Muslims (56%) say Muslim men should not be allowed to divorce this way. Still, 37% of Indian Muslims say they support triple talaq, with Muslim men (42%) more likely than Muslim women (32%) to take this position. A majority of Muslim women (61%) oppose triple talaq.
Highly religious Muslims – i.e., those who say religion is very important in their lives – also are more likely than other Muslims to say Muslim men should be able to divorce their wives simply by saying “talaq” three times (39% vs. 26%).
Triple talaq seems to have the most support among Muslims in the Southern and Northeastern regions of India, where half or more of Muslims say it should be legal (58% and 50%, respectively), although 12% of Muslims in the South and 16% in the Northeast do not take a position on the issue either way.
Sikhism is one of four major religions – along with Hinduism, Buddhism and Jainism – that originated on the Indian subcontinent. The Sikh religion emerged in Punjab in the 15th century, when Guru Nanak, who is revered as the founder of Sikhism, became the first in a succession of 10 gurus (teachers) in the religion.
Today, India’s Sikhs remain concentrated in the state of Punjab. One feature of the Sikh religion is a distinctive sense of community, also known as “Khalsa” (which translates as “ones who are pure”). Observant Sikhs differentiate themselves from others in several ways, including keeping their hair uncut. Today, about three-quarters of Sikh men and women in India say they keep their hair long (76%), and two-thirds say it is very important to them that children in their families also keep their hair long (67%). (For more analysis of Sikhs’ views on passing religious traditions on to their children, see Chapter 8 .)
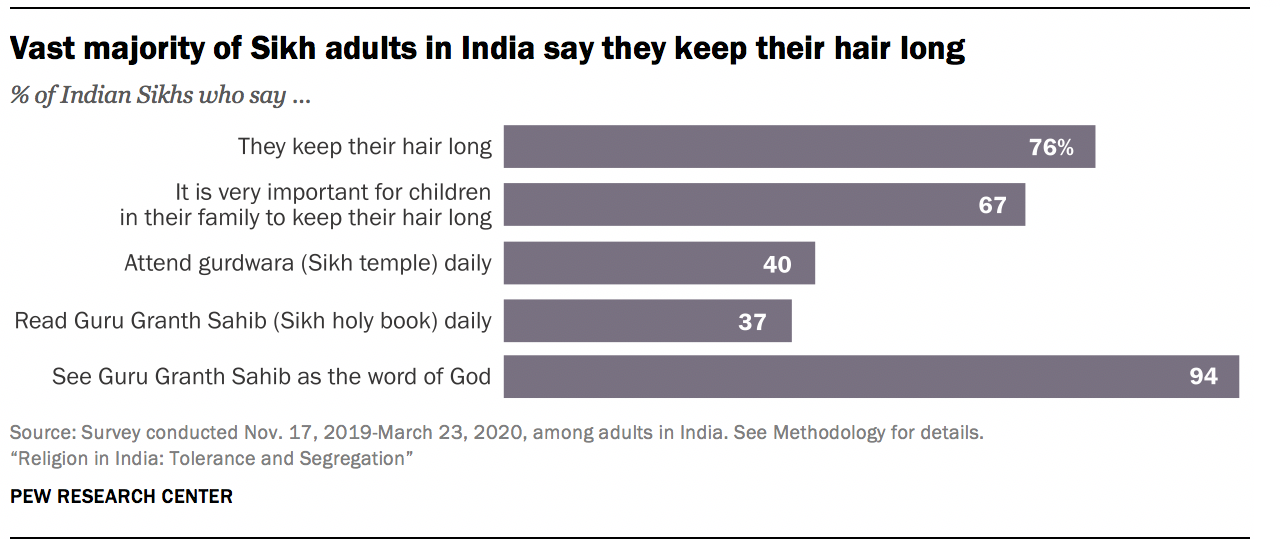
Sikhs are more likely than Indian adults overall to say they attend religious services every day – 40% of Sikhs say they go to the gurdwara (Sikh house of worship) daily. By comparison, 14% of Hindus say they go to a Hindu temple every day. Moreover, the vast majority of Sikhs (94%) regard their holy book, the Guru Granth Sahib, as the word of God, and many (37%) say they read it, or listen to recitations of it, every day.
Sikhs in India also incorporate other religious traditions into their practice. Some Sikhs (9%) say they follow Sufi orders, which are linked with Islam, and about half (52%) say they have a lot in common with Hindus. Roughly one-in-five Indian Sikhs say they have prayed, meditated or performed a ritual at a Hindu temple.
Sikh-Hindu relations were marked by violence in the 1970s and 1980s, when demands for a separate Sikh state covering the Punjab regions in both India and Pakistan (also known as the Khalistan movement) reached their apex. In 1984, Prime Minister Indira Gandhi was assassinated by her Sikh bodyguards as revenge for Indian paramilitary forces storming the Sikh Golden Temple in pursuit of Sikh militants. Anti-Sikh riots ensued in Northern India, especially in the state of Punjab.

According to the Indian census, the vast majority of Sikhs in India (77%) still live in Punjab, where Sikhs make up 58% of the adult population. And 93% of Punjabi Sikhs say they are very proud to live in the state.
Sikhs also are overwhelmingly proud of their Indian identity. A near-universal share of Sikhs say they are very proud to be Indian (95%), and the vast majority (70%) say a person who disrespects India cannot be a Sikh. And like India’s other religious groups, most Sikhs do not see evidence of widespread discrimination against their community – just 14% say Sikhs face a lot of discrimination in India, and 18% say they personally have faced religious discrimination in the last year.
At the same time, Sikhs are more likely than other religious communities to see communal violence as a very big problem in the country. Nearly eight-in-ten Sikhs (78%) rate communal violence as a major issue, compared with 65% of Hindus and Muslims.
The BJP has attempted to financially compensate Sikhs for some of the violence that occurred in 1984 after Indira Gandhi’s assassination, but relatively few Sikh voters (19%) report having voted for the BJP in the 2019 parliamentary elections. The survey finds that 33% of Sikhs preferred the Indian National Congress Party – Gandhi’s party.
- Ahmed, Hilal. 2019. “ Siyasi Muslims: A story of political Islams in India .” ↩
- All survey respondents, regardless of religion, were asked, “Are you from a General Category, Scheduled Caste, Scheduled Tribe or Other Backward Class?” By contrast, in the 2011 census of India, only Hindus, Sikhs and Buddhists could be enumerated as members of Scheduled Castes, while Scheduled Tribes could include followers of all religions. General Category and Other Backward Classes were not measured in the census. A detailed analysis of differences between 2011 census data on caste and survey data can be found here . ↩
- According to the 2004 and 2009 National Election Studies by the Centre for the Study of Developing Societies (CSDS), roughly half of Indians or more said that marriages of boys and girls from different castes should be banned . In 2004, a majority also said this about people from different religions. ↩
- In both the 2004 and 2009 National Election Studies (organized by CSDS), roughly half of Indians said that “There should be a legal ban on religious conversions.” ↩
- This includes 0.2% of all Indian adults who now identify as Hindu but give an ambiguous response on how they were raised – either saying “some other religion” or saying they don’t know their childhood religion. ↩
- Puja is a specific worship ritual that involves prayer along with rites like offering flowers and food, using vermillion, singing and chanting. ↩
- Fifteen named deities were available for selection, though no answer options were read aloud. Respondents could select up to three of those 15 deities by naming them or selecting the corresponding image shown on a card. The answer option “another god” was available on the card or if any other deity name was volunteered by the respondent. Other possible answer options included “I do not have a god I feel closest to” and “I have many personal gods,” though neither was on the card. See the questionnaire or topline for the full list of gods offered. ↩
- The religious origins of karma are debated by scholars, but the concept has deep roots in Hinduism, Buddhism, Sikhism and Jainism. ↩
- For an analysis of Jain theology on the concept of jiva (soul) see Chapple, Christopher K. 2014. “Life All Around: Soul in Jainism.” In Biernacki, Loriliai and Philip Clayton, eds. “ Panentheism Across the World’s Traditions .” ↩
Sign up for our weekly newsletter
Fresh data delivery Saturday mornings
Sign up for The Briefing
Weekly updates on the world of news & information
- Beliefs & Practices
- Christianity
- International Political Values
- International Religious Freedom & Restrictions
- Interreligious Relations
- Other Religions
- Pew-Templeton Global Religious Futures Project
- Religious Characteristics of Demographic Groups
- Religious Identity & Affiliation
- Religiously Unaffiliated
- Size & Demographic Characteristics of Religious Groups
How common is religious fasting in the United States?
8 facts about atheists, spirituality among americans, how people in south and southeast asia view religious diversity and pluralism, religion among asian americans, most popular, report materials.
- Questionnaire
- இந்தியாவில் மதம்: சகிப்புத்தன்மையும், தனிமைப்படுத்துதலும்
- भारत में धर्म: सहिष्णुता और अलगाव
- ভারতে ধর্ম: সহনশীলতা এবং পৃথকীকরণ
- भारतातील धर्म : सहिष्णुता आणि विलग्नता
- Related: Religious Composition of India
- How Pew Research Center Conducted Its India Survey
- Questionnaire: Show Cards
- India Survey Dataset
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Age & Generations
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Economy & Work
- Family & Relationships
- Gender & LGBTQ
- Immigration & Migration
- International Affairs
- Internet & Technology
- Methodological Research
- News Habits & Media
- Non-U.S. Governments
- Other Topics
- Politics & Policy
- Race & Ethnicity
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
Copyright 2024 Pew Research Center
- AsianStudies.org
- Annual Conference
- EAA Articles
- 2025 Annual Conference March 13-16, 2025
- AAS Community Forum Log In and Participate
Education About Asia: Online Archives
Multilingualism in india.

With a growing population of just over 1.3 billion people, India is an incredibly diverse country in many ways. This article will focus specifically on contemporary linguistic diversity in India, first with an overview of India as a multilingual country just before and after Independence in 1947 and then through a brief outline of impacts of multilingualism on business and schools, as well as digital, visual, and print media.
India is home to many native languages, and it is also common that people speak and understand more than one language or dialect, which can entail the use of different scripts as well. India’s 2011 census documents that 121 languages are spoken as mother tongues, which is defined as the first language a person learns and uses.1 Of these languages, the Constitution of India recognizes twenty-two of them as official or “scheduled” languages. Articles 344(1) and 351 of the Constitution of India, titled the Eighth Schedule, recognizes the following languages as official languages of states of India: Assamese, Bengali, Bodo, Dogri, Gujarati, Hindi, Kannada, Kashmiri, Konkani, Maithili, Malayalam, Manipuri, Marathi, Nepali, Oriya, Punjabi, Sanskrit, Santhali, Sindhi, Tamil, Telugu, and Urdu.2
Six languages also hold the title of classical languages (Kannada, Malayalam, Odia, Sanskrit, Tamil, and Telugu), which are determined to have a history of recorded use for more than 1,500 years and a rich body of literature. Furthermore, for a contemporary language to also be a classical language, it must be an original language and cannot be a variety, such as a dialect, stemming from another language. Just as there are many people who wish for their mother tongues to be recognized as official, scheduled languages, there are also efforts to add Indian languages to the list of classical languages. Once a language has the official status of a classical language, the Ministry of Education organizes international awards for scholars of those languages, sets up language studies centers, and grants funding to universities to promote the study of the language. Interestingly, the Constitution of India lists no national language for the country as a whole.
Of the official, scheduled languages, Modern Standard Hindi—as an umbrella term for a family of languages—has the most mother tongue speakers, with around 528 million speakers, or 44 percent of India’s population, followed by Bengali with around 97 million speakers, or 8 percent of the population. Marathi has around 83 million speakers, or 7 percent of the population, and Telugu speakers number around 81 million, or almost 6 percent of the population. Speakers who list the remaining official languages as their mother tongues also number between 2 and 4 percent of the population, as recorded in the 2011 census. It is interesting to note that due to India’s large population, native speakers of these regional Indian languages often outnumber native speakers of other major world languages such as Korean—with 77.2 million native speakers—and Italian—with 67 million native speakers—as of 2020.3
Languages in India are categorized into language families based on their different linguistic origins, which often include different scripts as well. The main language families include Dravidian, Indo–Aryan, and Sino–Tibetan. Bodo is the Sino–Tibetan language spoken in northeastern Indian states with the most speakers (1.4 million). Languages considered to be mother tongues or regional languages in the south of India have grammatical structures and scripts with Dravidian roots, and languages used in the central and northern regions of India are part of the Indo–Aryan family of languages. Many central and northern Indian languages use scripts derived from the Nagari script. Contemporary variations of Hindi use the Devanagari script, and scripts used in Gujarati, Punjabi, and Marathi use Nagari-derived scripts or versions of Devanagari that include some differences in their alphabets.
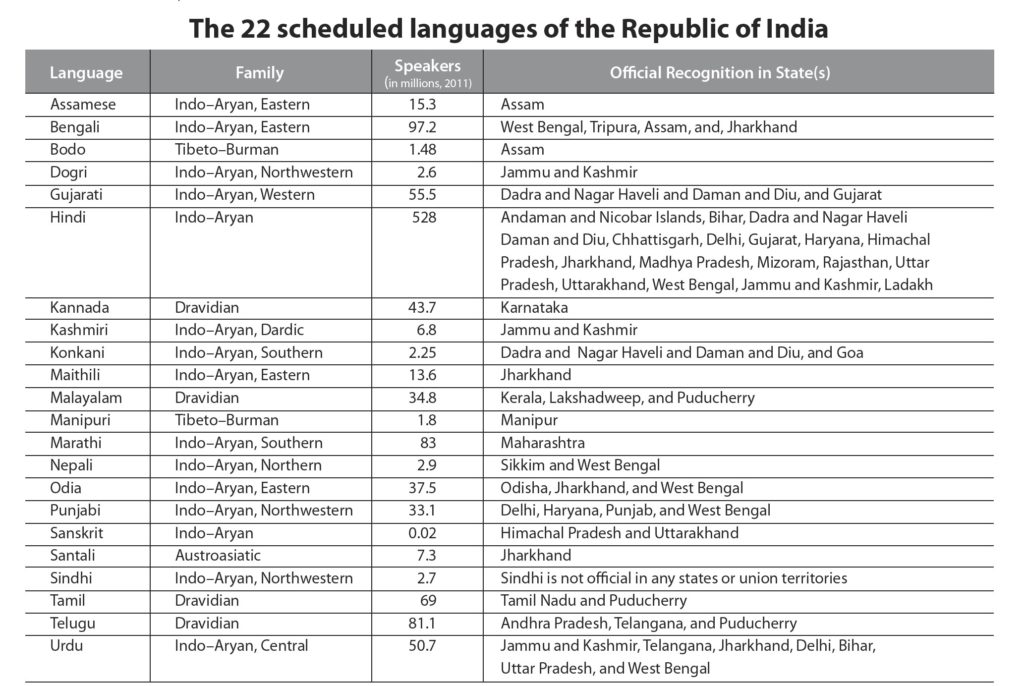
Similarly, Modern Standard Hindi and Urdu are grammatically identical, though they often differ in some vocabulary and their use of scripts, as Urdu uses a modified form of the Perso–Arabic script. As Hindi and Urdu are often considered to be one language with two scripts, a common belief is that the distinction among speaking and writing Hindi and Urdu falls along a religious divide between Hindus and Muslims, where Hindus are listed as Hindi speakers and Muslims as Urdu speakers in government documents such as the census.4 However, in practice, the distinction between Hindi and Urdu speakers is much more fluid and complex, as linguistic boundaries rely more on geographic location and speech community.
Another aspect of India’s multilingualism is that each mother tongue, or regional language, roughly belongs to one or more states. India’s twenty-eight states have been largely organized along linguistic lines since the 1950s, just after Independence, with the formation of the southeastern state of Andhra Pradesh in 1953 for Telugu speakers. Andhra Pradesh was created after prolonged protests and strikes by Telugu speakers, which included the prominent activist Potti Sreeramulu fasting for the creation of a Telugu state until his death in 1952.5 A new state was finally created in 1953 by dividing the Tamil- and Telugu-speaking regions in what, under the British, was called the Madras Presidency. Immediately after Independence, the country retained similar political divisions it had under colonial rule, which newly independent Indians felt did not accurately represent them in the new government. The state reorganization movement for Andhra Pradesh culminated in the government-organized Dhar commission, which was ordered to investigate reordering additional Indian state borders along the lines of linguistic communities, or groups of people who speak the same language. The commission produced the State Reorganization Act of 1956, which called for states to be formed to represent linguistic groups rather than to stay the way the country was divided over the course of British rule.
Following the division of the state of Andhra Pradesh and the orders of the State Reorganization Act of 1956, the states of Kerala, Mysore, and Madras were formed. (In 1969, Madras was renamed Tamil Nadu, and in 1973, Mysore was renamed Karnataka.) In 1956 as well, the princely state of Hyderabad was divided between Andhra Pradesh, Maharashtra, and Madhya Pradesh. Just as the state of Andhra Pradesh was formed after prolonged protests for the rights of Telugu speakers, the Province of Bombay was also divided between Marathi and Gujarati speakers in 1960 into the states of Gujarat and Maharashtra. The bustling port city of Bombay, later renamed Mumbai in 1995, became part of the state of Maharashtra. Large reorganization efforts along the lines of language and religious communities continued with the 1966 reorganization of Patiala and East Punjab States Union (PEPSU) and Punjab into three new states, Punjab, Haryana, and Himachal Pradesh; and India’s northeastern region also underwent a linguistic and communal reorganization into different states between the years of 1963 and 1987.
Multilingualism in India has therefore played a key role in the country’s contemporary politics. State boundaries were drawn along the lines of language groups, even though regions remain linguistically diverse, because languages in India can be an important way of defining one’s identity. Many people in different Indian regions in cultural and religious groups retain distinct identities that set them apart from other communities through language. As India is culturally, ethnically, and religiously diverse, language is one way people maintain group identities. Identity politics have also made mother tongues an object and mode of political struggle. Authors of the State Reorganization Act felt that democratic participation would grow if local populaces could access information and participate in government programs in their mother tongues. Language is a basis of identity and is why, when state boundaries were being redrawn after Independence in 1947, languages and the areas in which they were spoken were utmost factors of importance in where the boundaries of new Indian states would be.
Today, there are twenty-eight states in India and eight union territories, or areas directly governed by the federal government, and each state has at least one official language and many have two, in addition to English. In this way, with unique languages and scripts attributed to each state, India often seems like a collection of distinct countries due to the cultural and linguistic differences between states. Due to this vast diversity in languages and the way language is closely tied to identity, sometimes there are also struggles along religious and political lines that play out through language. Hindu nationalists engage in movements to spread the use of Hindi and Sanskrit as a means to spread the Hindu religion as well. Some have also felt that the distinct regional languages of states should indicate that people who do not speak those languages from birth should not be allowed to reside and work in states where they do not belong to the linguistic community. This was the message of the conservative party, the Shiv Sena, in Maharashtra.
English as an Indian Language
Adding to the complexity of the history of languages in South Asia, the English language was also integrated into the social fabric of the region insofar as it played a key role as a unifying language in the Constitution among north and south India at the time of Independence in 1947. Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi (1869–1948), also known by the name Mahatma, which means “Great Soul,” was a famous activist who led many Indians in peaceful protests against British rule. Gandhi and his supporters made concessions for the English language to remain in use in the new nation. They found English incredibly useful for unifying the country despite their support for Hindustani, the name for the mix of Hindi and Urdu commonly used in the northern regions of India, as the national language.
Paradoxically for Gandhi and his supporters, English represented a dividing force that emphasized the distance between educated Indian elites, who were more aligned with British colonizers, and non-English-speaking, often-uneducated masses. Gandhi maintained that to have a successful Independence movement was to govern through Indian ways, including through Indian regional languages. During the late colonial period, Gandhi addressed audiences from 1916 to 1928 over English linguistic colonization in education. He called for education in regional languages, stating, “The question of vernaculars as media of instruction is of national importance,” and he criticized how “English-educated Indians are the sole custodians of public and patriotic work”; he also said the “neglect of the vernaculars means national suicide.”6 However, the question of a national unifying language at Independence was a complicated one, as Gandhi’s call for Hindustani to wholly replace English was also rejected. Hindustani, later known as a variety of Hindi and Urdu, is not commonly spoken across all of India, and it is considered a northern Indian regional language since it is distinct from the language families and scripts used in south India. English, therefore, served as a utilitarian language to connect disparate and diverse areas of the newly unified country, as it still does today. Now, Indian English, with a unique vocabulary and accent, is a recognized variety of English in the world.
Ultimately, the English language was written into India’s new Constitution as a language to help with the new country’s transition from a British colonial subject to independent governance. Specifically, the 1949 original Constitution of India states that “business in Parliament shall be transacted in Hindi or in English” in Article 210, Article 343 states that “the official language of the Union shall be Hindi in Devanagari script” and “for a period of fifteen years from the commencement of this Constitution, the English language shall continue to be used for all the official purposes of the Union for which it was being used immediately before such commencement: provided that the president may, during the said period, by order authorize the use of the Hindi language in addition to the English language.”7 The intention of including English as a language for official government purposes along with Hindi was that English would be shed as the new nation matured.
In 1963, the impending transition away from English brought about similar concerns over the need for a unifying language, which were voiced at the time of Independence. Parliament enacted the Official Languages Act of 1963 to continue the use of English and section 3 of the act extended the implementation of English for official purposes along with Hindi.8 India decided to keep English as a unifying language to connect parts of the country where Modern Standard Hindi is not commonly spoken, such as in the southern Indian states with different scripts and language roots. While English is also a legacy of the British in India, it remains a tool and window through which to gain wider knowledge and understanding of the country. English also connects India with other English-speaking regions of the world.
Multilingualism in Daily Life
As there are many languages in India, many Indians can speak, read, and/or write in multiple languages, and multilingualism therefore is a part of daily life. Challenges and advantages of linguistic diversity affect the everyday lives of Indians in terms of businesses, educational institutions, and media. Due to the widespread use of English in India, the country is home to many international companies where English is commonly used for work. As English fluency often means higher socioeconomic status in India, middle- and upper-class Indians who have greater access to English have relative ease when working, studying, traveling, and immigrating to areas of the world where English is a lingua franca, or common language.

English is used in many office settings, especially in the international businesses and multinational corporations housed in India. Businesses in Indian cities hire employees from all over the country, and English is a common language among people with different mother tongues. In shops and supermarkets, many labels are written in English in the Roman script.
Other than English in business and commerce, many people also use Modern Standard Hindi as a common language, especially in the northern regions of India. In many of these places, mixing two or more languages or language varieties together when speaking is a prevalent practice known as “code-switching.”
Example of code-switching in conversation:
Waiter: Aur chahiye ? (Do you want anything else?) [Hindi] Man: Don coffee pahije (We want two coffees) [Marathi]
Code-switching as a practice is distinct from commonly used English words that have been subsumed into other Indian languages, which are called “loan” or “borrowed” words.9 While English and forms of code-switching are incorporated into Indian corporate culture, many people find themselves facing barriers to communication in these settings if they are not fluent in English or Hindi.
Example of loan words:
Teacher to the class: OK, all of you, open like this. Saglyana asa ghya aani, first page ogu-da, first page war kay lihile ? (Everyone take it like this and open to the first page. On the first page, what is written?) [English and Marathi]
The merits of multilingual education have dominated the field of education policy since the colonial period in India. Education in India is delivered in many different languages, but two languages are the most popular: English and Hindi. Additionally, many schools have instruction in students’ mother tongues or the regional state language as well. A plan for trilingual learning, called the three-language formula (TLF), was adopted into education policy by the Ministry of Education in 1968 and has been in discussion in parliament since 1948, just after Independence. The three-language formula requires schoolchildren to “(a) study and to receive content area instruction for twelve years in their mother tongue or the regional (state) language (which for some children will be one and the same); (b) study Hindi or English for ten to twelve years; and (c) study a modern Indian language (i.e., any one of the “scheduled” languages) or a foreign language for three to five years.” However, implementation of the TLF varies widely across the country today, with many English-language schools teaching limited English or only using English books and classroom materials. The idealized linguistic model presented in the 1968 TLF policy is meant to prepare students to be trilingual should students choose to enter the predominantly English-language higher education system and/or a globalized workforce. Proponents of multilingual education in India call attention to the importance of the three-language formula in adequately preparing primary and secondary school students for the linguistic demands of higher education, while also maintaining the rich linguistic heritage of India.
Even outside of education and business, Indians encounter English and multiple other Indian regional languages in media every day. They are especially likely to speak or read English in their daily lives if they are among the middle and upper socioeconomic classes, as increased English fluency aligns closely with socioeconomic class. There are many print media publications such as newspapers and magazines in English. Each city has at least one local English-language publication, and major print and online national publications can be found in Hindi and English. Each state’s news media publications are most commonly consumed in regional languages.
Visual media as well caters to regional language-speaking audiences, where local news broadcasts will be in the regional language and national news segments or specific programs will take place in Hindi. It is also becoming increasingly common for English to be used as part of code-switching practices in visual media, though English-only Indian broadcasts may be available at certain times or through special subscriptions or satellite television programming. In India, many regions have local film industries as well, where movies and television shows are produced in regional languages. Bollywood, the largest film industry in India, is located in Mumbai in the state of Maharashtra and produces films in Hindi. Bollywood movies are popular all over the world and can be viewed with subtitles for non-Hindi-speaking audiences. Interestingly, as of yet, no mainstream visual entertainment media industry in India makes English-only film or television productions, unlike in news and online digital media. It cannot be emphasized enough that as access and proliferation of English varies substantially along socioeconomic class lines, access to English in business, education, and media is linked to international capital and has a great capacity to increases one’s economic and social position.
As a multilingual country, India’s diversity has proven to be both a strength and a challenge to unifying the nation. Hopefully, this essay illustrates how multiple languages have shaped policies from education to the political boundaries of states, and, stemming from a colonial footprint and global pressures for greater use of English in international networks, the high demand for the use of English in India.
One can see there is a careful balance to multilingualism in India. English and languages like Hindi are deemed necessary for interaction in national and international communities beyond state and national borders, while mother tongues or regional languages are also made relevant through local state governments, institutions, and cultural identity. In this way, the cultivation and practices of multilingualism in India lends itself to more than just a preservation of unique, regional identities but has great impact on how Indians interact with fellow Indians and much of the world. Multilingualism in India defines the nation within global and national networks and communities for business, education, and media. As language plays an important part in our daily interactions, multilingualism and linguistic diversity in India have shaped the country and unique cultural practices and policies within it.
Share this:
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)
- “2011 Census Data,” Ministry of Home Affairs, Government of India, https://tinyurl.com/y66egqfl .
- See the Eighth Schedule of The Constitution of India, 1949
- Ethnologue, Languages of the World . Web archive (1992) at the Library of Congress at https://tinyurl.com/y6s2yjd3 .
- Christopher Rolland King, One Language, Two Scripts: The Hindi Movement in the Nineteenth Century North India (Bombay: Oxford University Press, 1994).
- Lisa Mitchell, Language, Emotion, and Politics in South India: The Making of a Mother Tongue (Bloomington: Indiana University Press, 2009).
- M. K. Gandhi 1917 as cited in Speeches and Writings of M. K. Gandhi 1922, https://tinyurl.com/ybxaft9e , 307.
- Articles 210 and 243 of The Constitution of India, 1949
- Official Languages Act, 1963, section 3
- Harold F. Schiffman and Michael C. Shapiro, Language and Society in South Asia (Delhi: Motilal Banarsidass, 1981).
- Latest News
- Join or Renew
- Education About Asia
- Education About Asia Articles
- Asia Shorts Book Series
- Asia Past & Present
- Key Issues in Asian Studies
- Journal of Asian Studies
- The Bibliography of Asian Studies
- AAS-Gale Fellowship
- Council Grants
- Book Prizes
- Graduate Student Paper Prizes
- Distinguished Contributions to Asian Studies Award
- First Book Subvention Program
- External Grants & Fellowships
- AAS Career Center
- Asian Studies Programs & Centers
- Study Abroad Programs
- Language Database
- Conferences & Events
- #AsiaNow Blog
Throughout May, AAS is celebrating Asian American and Native Hawaiian/Pacific Islander Heritage Month. Read more
Incredible India Essay
India is a country with vast culture and heritage. It has almost all types of landforms, climatic conditions, different languages, and religions, which represents unity in diversity. There are famous heritage sites and monuments in India which make anyone breathless. It has ice-covered Himalayan mountains in the north, the Thar Desert in Rajasthan, the rain forest in Assam and Meghalaya, the sea coast in Gujarat etc., which enhances its beauty. In India, guests are treated as God because they believe in “Atithi Devo Bhava”. With the help of this essay on Incredible India, students will get an overview of India, its culture and tradition.
Students can also check out the list of CBSE Essays to practise more essays on different topics to improve their writing skills. By boosting their writing section, they can participate in various writing competitions as well.
500+ Words Essay on Incredible India
India is the seventh largest country in the world. It lies to the north of the equator, between 804’ and 3706’ North Latitude and 6807’ and 97025’ East Longitude. India is spread over 3 million square kilometres of area and accounts for 20% of the world’s population. It is the fourth-largest economy and the fastest-growing free-market democracy. India shares its border with seven countries, which are Afghanistan, Pakistan, China, Bhutan, Nepal, Myanmar and Bangladesh. Sri Lanka and the Maldives are two countries that share water borders.
India is connected to the world with a vast network of 334 airports. It has the world’s second-largest rail network, which includes the most expensive trains like Maharajas’ Express, Palace on Wheels, The Golden Chariot, and The Deccan Odyssey. The road network of India is also well connected with the cities, towns and rural areas by expressways and highways.
India gained independence on 15 August 1947. Its National Bird is the peacock, while the National Animal is the tiger. The National Anthem is “Jana-gana-mana”, and the National Song is “Vande Mataram”. There are a lot of festivals celebrated in India. Some of the famous festivals are Diwali, Holi, Durga Puja, and Raksha Bandhan.
India’s Political and Administrative Divisions
India is a democratic country where all rights are given to its citizens. The government is formed by polling the election. For administrative purposes, the country is divided into 28 States and 8 Union Territories. Delhi is the national capital. The states are formed on the basis of languages.
Physical Features of India
India is marked by a diversity of physical features. It has many mountains, plains, plateaus, coasts and islands. In the north, it has beautiful Kashmir, which has the snow-capped Himalayas. It is a famous tourist place, and popular hill stations are situated here.
The Northern Indian plains lie to the south of the Himalayas, which are flat. These are formed by the alluvial deposits laid down by the Indus, the Ganga, and Brahmaputra rivers and their tributaries. These plains are fertile areas and are best for cultivation. Due to this reason, the population of this area is denser.
In the western part of India lies the Great Indian desert. This place is a hot, dry and sandy stretch of land. It has very little vegetation. To the south of the Northern plains lies the Peninsular plateau. This region has numerous hill ranges and valleys. The rivers Narmada and Tapi flow through these ranges. These are west-flowing rivers that drain into the Arabian Sea.
To the west of the Western Ghats and the east of the Eastern Ghats lie the Coastal plains. The rivers Mahanadi, Godavari, Krishna and Kaveri drain into the Bay of Bengal. These rivers have formed fertile deltas at their mouths. The Sunderban Delta is formed where the Ganga and Brahmaputra flow into the Bay of Bengal.
Two groups of islands also form part of India. Lakshadweep Islands are located in the Arabian Sea. These are coral islands located off the coast of Kerala. The Andaman and the Nicobar Islands lie to the southeast of the Indian mainland in the Bay of Bengal.
Incredible India Campaign
The Government of India started off a marketing campaign, “Incredible India”, in 2002 to boost tourism in the country and project India as a credible tourist destination. The incredible diversity exists in India with varied people, customs, topography, culture, and language, which itself perfectly suits the slogan ‘Incredible India’. The campaign was launched by the Ministry of Tourism to promote India as a world-class tourist destination.
Students must have found this essay on Incredible India useful for improving their essay writing skills. They can get the study material and the latest update on CBSE/ICSE/State Board/Competitive Exams at BYJU’S.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

Counselling
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- India Essay

Essay on India
India is the largest democratic country. It is a big country divided into 29 states and 7 union territories. These states and union territories have been created so that the government can run the country more easily. India also has many different kinds of physical features in different parts of the country that are spread over its states and union territories. India is a very diverse country as well, which means that the people around the country are different in many ways. Even though India is such a diverse place, it is united as one country.
Political Divisions
India is the seventh-largest country and has the second-largest population in the world. Here is the map of India showing 29 states and 7 union territories. These political divisions are made so that the government can run the country more easily. Though we live in different states, everyone is an Indian first.
[Image will be uploaded soon]
Physical Features
The Indian subcontinent has many different physical features shared with its neighbours that are also in the subcontinent – Pakistan, Nepal, Bhutan and Bangladesh. The physical features of India form six different natural regions.
The Northern Mountains
The Northern Plains
The Great Indian Desert
The Southern Plateau
The Coastal Plains
The Island Regions
The Northern Mountains: These are the Himalayas, the highest mountain range in the world. They form a natural boundary between India and a large part of Asia. Two neighbouring countries, Nepal and Bhutan are situated in these mountains.
The Northern Plains: They are located to the south of the Himalayas. They extend into Pakistan in the west. Bangladesh is situated on the eastern part of the plains.
The Great Indian Desert: The western part of India is a desert with less rainfall. This desert is called the Thar Desert.
The Southern Plateau: This plateau region lies to the south of the Great Northern Plains and is called the Deccan Plateau. The Vindhya and Satpura ranges in the north, the Western Ghats and the Eastern Ghats surround the Deccan Plateau.
The Coastal Plains: The Eastern coastal plain lies between the Bay of Bengal and the Eastern Ghats. The western coastal plain lies between the Arabian Sea and the Western Ghats.
The Island Regions: The island regions of India are two archipelagos on either side of Peninsula India. The Lakshadweep Islands are in the Arabian Sea and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands are in the Bay of Bengal.
The Rivers of India
The Indian subcontinent has many rivers. Some important rivers are the Indus, Ganga, Yamuna, Brahmaputra, Sutlej, the Narmada and Tapi rivers.
These physical features and rivers link the people of India.
National Symbols
The National Flag of India is in the tricolour of deep saffron at the top, white in the middle and dark green at the bottom in equal proportions. The saffron stands for courage, sacrifice and the spirit of renunciation, the white for purity and the truth and the green for faith and fertility. In the centre of the white band, there is a wheel of law in the Sarnath Lion Capital.
The National Emblem of India is a replica of the Lion of Sarnath and symbolizes India’s reaffirmation of its ancient commitment to world peace and goodwill.
The National Anthem of India is Jana Gana Mana and the National song is Vande Mataram.
The National Animal of India is Tiger, which symbolizes grace, strength and power.
The National Bird of India is Peacock, which symbolizes beauty, majesty and pride.
The National Flower of India is Lotus, which symbolizes purity, wealth, richness, knowledge and serenity.
The National Tree of India is the Great Banyan Tree and because of its characteristics and longevity, the tree is considered immortal and sacred. It is an integral part of the myths and legends in India.
The National Fruit is Mango and it is the most cultivated fruit of the tropical world.
Indian food is diverse. The geography of a region influences the food that people eat. The staple food of people is what grows in their regions. In North India, the staple food is Wheat. In East and South India, the staple food is Rice. In West India, the staple food is Millet. Daals are eaten in almost the entire country and prepared in different ways.
Indians speak different languages. The Constitution of India mentions 22 languages. However, India has around 800 languages. Hindi is the official language of India.
India is a country of many different religions and each has different festivals. Some important festivals are Baisakhi, Diwali, Eid, Ganesh Chaturthi, Dussehra and Christmas.
Unity in Diversity
The people of India, their foods, festivals and languages – all these make India a very diverse country. However, there are also things that unite the people of India:
The National symbols like the Indian flag and the National Anthem.
The Constitution of India, which was written in the early years of our Independence. It unites the Indians because it has rules and laws that are the same for all people.
The Constitution says that all Indians are equal in the eyes of the law.
All Indians who are over the age of 18 and have registered as voters can vote in elections.

FAQs on India Essay
Q1. Describe the National Flag of India.
Ans. The National Flag of India is in the tricolour of deep saffron at the top, white in the middle and dark green at the bottom in equal proportions. The saffron stands for courage, sacrifice and the spirit of renunciation, the white, for purity and the truth and the green for faith and fertility. In the centre of the white band, there is a wheel of law in the Sarnath Lion Capital.
Q2. What is the population of India?
Ans. The population of India is 1 billion 325 million. India has the second-largest population in the world.
Q3. What are the important Festivals Celebrated in India?
Ans. Some of the important festivals celebrated in India are Diwali, Dussehra, Eid and Christmas.
Q4. Why is India called the largest Democratic Country?
Ans. India is the largest democratic country because the citizens of India have the right to elect their representatives who form and run the government.
- CBSE Class 10th
- CBSE Class 12th
- UP Board 10th
- UP Board 12th
- Bihar Board 10th
- Bihar Board 12th
- Top Schools in India
- Top Schools in Delhi
- Top Schools in Mumbai
- Top Schools in Chennai
- Top Schools in Hyderabad
- Top Schools in Kolkata
- Top Schools in Pune
- Top Schools in Bangalore
Products & Resources
- JEE Main Knockout April
- Free Sample Papers
- Free Ebooks
- NCERT Notes
- NCERT Syllabus
- NCERT Books
- RD Sharma Solutions
- Navodaya Vidyalaya Admission 2024-25
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11
- NCERT solutions for Class 10
- NCERT solutions for Class 9
- NCERT solutions for Class 8
- NCERT Solutions for Class 7
- JEE Main 2024
- MHT CET 2024
- JEE Advanced 2024
- BITSAT 2024
- View All Engineering Exams
- Colleges Accepting B.Tech Applications
- Top Engineering Colleges in India
- Engineering Colleges in India
- Engineering Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- Engineering Colleges Accepting JEE Main
- Top IITs in India
- Top NITs in India
- Top IIITs in India
- JEE Main College Predictor
- JEE Main Rank Predictor
- MHT CET College Predictor
- AP EAMCET College Predictor
- GATE College Predictor
- KCET College Predictor
- JEE Advanced College Predictor
- View All College Predictors
- JEE Main Question Paper
- JEE Main Cutoff
- JEE Main Advanced Admit Card
- JEE Advanced Admit Card 2024
- Download E-Books and Sample Papers
- Compare Colleges
- B.Tech College Applications
- KCET Result
- MAH MBA CET Exam
- View All Management Exams
Colleges & Courses
- MBA College Admissions
- MBA Colleges in India
- Top IIMs Colleges in India
- Top Online MBA Colleges in India
- MBA Colleges Accepting XAT Score
- BBA Colleges in India
- XAT College Predictor 2024
- SNAP College Predictor
- NMAT College Predictor
- MAT College Predictor 2024
- CMAT College Predictor 2024
- CAT Percentile Predictor 2023
- CAT 2023 College Predictor
- CMAT 2024 Admit Card
- TS ICET 2024 Hall Ticket
- CMAT Result 2024
- MAH MBA CET Cutoff 2024
- Download Helpful Ebooks
- List of Popular Branches
- QnA - Get answers to your doubts
- IIM Fees Structure
- AIIMS Nursing
- Top Medical Colleges in India
- Top Medical Colleges in India accepting NEET Score
- Medical Colleges accepting NEET
- List of Medical Colleges in India
- List of AIIMS Colleges In India
- Medical Colleges in Maharashtra
- Medical Colleges in India Accepting NEET PG
- NEET College Predictor
- NEET PG College Predictor
- NEET MDS College Predictor
- NEET Rank Predictor
- DNB PDCET College Predictor
- NEET Admit Card 2024
- NEET PG Application Form 2024
- NEET Cut off
- NEET Online Preparation
- Download Helpful E-books
- Colleges Accepting Admissions
- Top Law Colleges in India
- Law College Accepting CLAT Score
- List of Law Colleges in India
- Top Law Colleges in Delhi
- Top NLUs Colleges in India
- Top Law Colleges in Chandigarh
- Top Law Collages in Lucknow
Predictors & E-Books
- CLAT College Predictor
- MHCET Law ( 5 Year L.L.B) College Predictor
- AILET College Predictor
- Sample Papers
- Compare Law Collages
- Careers360 Youtube Channel
- CLAT Syllabus 2025
- CLAT Previous Year Question Paper
- NID DAT Exam
- Pearl Academy Exam
Predictors & Articles
- NIFT College Predictor
- UCEED College Predictor
- NID DAT College Predictor
- NID DAT Syllabus 2025
- NID DAT 2025
- Design Colleges in India
- Top NIFT Colleges in India
- Fashion Design Colleges in India
- Top Interior Design Colleges in India
- Top Graphic Designing Colleges in India
- Fashion Design Colleges in Delhi
- Fashion Design Colleges in Mumbai
- Top Interior Design Colleges in Bangalore
- NIFT Result 2024
- NIFT Fees Structure
- NIFT Syllabus 2025
- Free Design E-books
- List of Branches
- Careers360 Youtube channel
- IPU CET BJMC
- JMI Mass Communication Entrance Exam
- IIMC Entrance Exam
- Media & Journalism colleges in Delhi
- Media & Journalism colleges in Bangalore
- Media & Journalism colleges in Mumbai
- List of Media & Journalism Colleges in India
- CA Intermediate
- CA Foundation
- CS Executive
- CS Professional
- Difference between CA and CS
- Difference between CA and CMA
- CA Full form
- CMA Full form
- CS Full form
- CA Salary In India
Top Courses & Careers
- Bachelor of Commerce (B.Com)
- Master of Commerce (M.Com)
- Company Secretary
- Cost Accountant
- Charted Accountant
- Credit Manager
- Financial Advisor
- Top Commerce Colleges in India
- Top Government Commerce Colleges in India
- Top Private Commerce Colleges in India
- Top M.Com Colleges in Mumbai
- Top B.Com Colleges in India
- IT Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- IT Colleges in Uttar Pradesh
- MCA Colleges in India
- BCA Colleges in India
Quick Links
- Information Technology Courses
- Programming Courses
- Web Development Courses
- Data Analytics Courses
- Big Data Analytics Courses
- RUHS Pharmacy Admission Test
- Top Pharmacy Colleges in India
- Pharmacy Colleges in Pune
- Pharmacy Colleges in Mumbai
- Colleges Accepting GPAT Score
- Pharmacy Colleges in Lucknow
- List of Pharmacy Colleges in Nagpur
- GPAT Result
- GPAT 2024 Admit Card
- GPAT Question Papers
- NCHMCT JEE 2024
- Mah BHMCT CET
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Delhi
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Hyderabad
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Mumbai
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Maharashtra
- B.Sc Hotel Management
- Hotel Management
- Diploma in Hotel Management and Catering Technology
Diploma Colleges
- Top Diploma Colleges in Maharashtra
- UPSC IAS 2024
- SSC CGL 2024
- IBPS RRB 2024
- Previous Year Sample Papers
- Free Competition E-books
- Sarkari Result
- QnA- Get your doubts answered
- UPSC Previous Year Sample Papers
- CTET Previous Year Sample Papers
- SBI Clerk Previous Year Sample Papers
- NDA Previous Year Sample Papers
Upcoming Events
- NDA Application Form 2024
- UPSC IAS Application Form 2024
- CDS Application Form 2024
- CTET Admit card 2024
- HP TET Result 2023
- SSC GD Constable Admit Card 2024
- UPTET Notification 2024
- SBI Clerk Result 2024
Other Exams
- SSC CHSL 2024
- UP PCS 2024
- UGC NET 2024
- RRB NTPC 2024
- IBPS PO 2024
- IBPS Clerk 2024
- IBPS SO 2024
- Top University in USA
- Top University in Canada
- Top University in Ireland
- Top Universities in UK
- Top Universities in Australia
- Best MBA Colleges in Abroad
- Business Management Studies Colleges
Top Countries
- Study in USA
- Study in UK
- Study in Canada
- Study in Australia
- Study in Ireland
- Study in Germany
- Study in China
- Study in Europe
Student Visas
- Student Visa Canada
- Student Visa UK
- Student Visa USA
- Student Visa Australia
- Student Visa Germany
- Student Visa New Zealand
- Student Visa Ireland
- CUET PG 2024
- IGNOU B.Ed Admission 2024
- DU Admission 2024
- UP B.Ed JEE 2024
- LPU NEST 2024
- IIT JAM 2024
- IGNOU Online Admission 2024
- Universities in India
- Top Universities in India 2024
- Top Colleges in India
- Top Universities in Uttar Pradesh 2024
- Top Universities in Bihar
- Top Universities in Madhya Pradesh 2024
- Top Universities in Tamil Nadu 2024
- Central Universities in India
- CUET Exam City Intimation Slip 2024
- IGNOU Date Sheet
- CUET Mock Test 2024
- CUET Admit card 2024
- CUET PG Syllabus 2024
- CUET Participating Universities 2024
- CUET Previous Year Question Paper
- CUET Syllabus 2024 for Science Students
- E-Books and Sample Papers
- CUET Exam Pattern 2024
- CUET Exam Date 2024
- CUET Cut Off 2024
- CUET Exam Analysis 2024
- IGNOU Exam Form 2024
- CUET 2024 Exam Live
- CUET Answer Key 2024
Engineering Preparation
- Knockout JEE Main 2024
- Test Series JEE Main 2024
- JEE Main 2024 Rank Booster
Medical Preparation
- Knockout NEET 2024
- Test Series NEET 2024
- Rank Booster NEET 2024
Online Courses
- JEE Main One Month Course
- NEET One Month Course
- IBSAT Free Mock Tests
- IIT JEE Foundation Course
- Knockout BITSAT 2024
- Career Guidance Tool
Top Streams
- IT & Software Certification Courses
- Engineering and Architecture Certification Courses
- Programming And Development Certification Courses
- Business and Management Certification Courses
- Marketing Certification Courses
- Health and Fitness Certification Courses
- Design Certification Courses
Specializations
- Digital Marketing Certification Courses
- Cyber Security Certification Courses
- Artificial Intelligence Certification Courses
- Business Analytics Certification Courses
- Data Science Certification Courses
- Cloud Computing Certification Courses
- Machine Learning Certification Courses
- View All Certification Courses
- UG Degree Courses
- PG Degree Courses
- Short Term Courses
- Free Courses
- Online Degrees and Diplomas
- Compare Courses
Top Providers
- Coursera Courses
- Udemy Courses
- Edx Courses
- Swayam Courses
- upGrad Courses
- Simplilearn Courses
- Great Learning Courses
Indian Culture Essay
India is renowned throughout the world for its tradition and culture. It is a country with many different cultures and traditions. The world's ancient civilisations can be found in this country. Good manners, etiquette, civilised dialogue, customs, beliefs, values, etc., are essential elements of Indian culture . India is a special country because of the ability of its citizens from many cultures and traditions to live together in harmony. Here are a few sample essays on ‘Indian culture’.

100 Words Essay on Indian Culture
India's culture is the oldest in the world and dates back over 5,000 years. The first and greatest cultures in the world are regarded as being those of India. The phrase "Unity in Diversity" refers to India as a diverse nation where people of many religions coexist while maintaining their distinct customs. People of different religions have different languages, culinary customs, ceremonies, etc and yet they all live in harmony.
Hindi is India's official language. However, there are 400 other languages regularly spoken in India's many states and territories, in addition to the country's nearly 22 recognised languages. History has established India as the country where religions like Buddhism and Hinduism first emerged.
200 Words Essay on Indian Culture
India is a land of diverse cultures, religions, languages, and traditions. The rich cultural heritage of India is a result of its long history and the various invasions and settlements that have occurred in the country. Indian culture is a melting pot of various customs and traditions, which have been passed down from generation to generation.
Religion | Religion plays a significant role in Indian culture. The major religions practiced in India are Hinduism, Islam, Buddhism, Sikhism, and Jainism. Each religion has its own set of beliefs, customs, and practices. Hinduism, the oldest religion in India, is the dominant religion and has a vast array of gods and goddesses. Islam, Buddhism, Sikhism, and Jainism are also widely practiced and have a significant number of followers in the country.
Food | Indian cuisine is known for its diverse range of flavors and spices. Each region in India has its own unique style of cooking and distinct dishes. Indian cuisine is known for its use of spices, herbs, and a variety of cooking techniques. Some of the most famous Indian dishes include biryani, curry, tandoori chicken, and dal makhani. Indian cuisine is also famous for its street food, which is a popular and affordable way to experience the diverse range of flavors that Indian food has to offer.
500 Words Essay on Indian Culture
Indian culture is known for its rich art and architecture. The ancient Indus Valley Civilization, which existed around 2500 BCE, had a sophisticated system of town planning and impressive architectural structures. Indian art is diverse and includes painting, sculpture, and architecture. The most famous form of Indian art is the cave paintings of Ajanta and Ellora, which date back to the 2nd century BCE. Indian architecture is also famous for its temples, palaces, and forts, which are a reflection of the rich cultural heritage of the country.
Music and dance are an integral part of Indian culture . Indian music is diverse and ranges from classical to folk to modern. The classical music of India is known for its use of ragas, which are a set of musical notes that are used to create a melody. The traditional Indian dance forms include Kathak, Bharatanatyam, and Kathakali. These dance forms are known for their elaborate costumes, expressive gestures, and intricate footwork.
My Experience
I had always been fascinated by the rich culture and history of India. So, when I finally got the opportunity to visit the country, I was beyond excited. I had heard so much about the diverse customs and traditions of India, and I couldn't wait to experience them firsthand. The moment I stepped off the plane and hit the streets, I was greeted by the overwhelming smell of spices and the hustle and bustle of the streets. I knew right away that I was in for an unforgettable journey.
My first stop was the ancient city of Varanasi, also known as Banaras. As I walked through the streets, I was struck by the vibrant colors and the sound of temple bells and chants. I visited the famous Kashi Vishwanath Temple and was amazed by the intricate architecture and the devotion of the devotees.
From Varanasi, I traveled to Jaipur, also known as the Pink City . Here, I visited the famous Amber Fort, which was built in the 16th century. The fort was a perfect example of the rich architecture of India and the level of craftsmanship that existed in ancient India.
As I continued my journey, I also had the opportunity to experience the food of India. From the spicy curries of the south to the tandoori dishes of the north, I was blown away by the range of flavors and the use of spices.
I also had the chance to experience the music and dance of India. I attended a Kathak dance performance and was mesmerized by the intricate footwork and the expressiveness of the dancers. I also had the opportunity to attend a classical music concert and was struck by the beauty of the ragas and the skill of the musicians.
My journey through India was truly an unforgettable experience. I had the chance to experience the diverse customs and traditions of India and was struck by the richness of the culture. From the ancient temples to the vibrant street markets, India is a treasure trove of history and culture. I knew that this would not be my last trip to India, as there is so much more to explore and experience.
Applications for Admissions are open.

Aakash iACST Scholarship Test 2024
Get up to 90% scholarship on NEET, JEE & Foundation courses

ALLEN Digital Scholarship Admission Test (ADSAT)
Register FREE for ALLEN Digital Scholarship Admission Test (ADSAT)

JEE Main Important Physics formulas
As per latest 2024 syllabus. Physics formulas, equations, & laws of class 11 & 12th chapters

PW JEE Coaching
Enrol in PW Vidyapeeth center for JEE coaching

PW NEET Coaching
Enrol in PW Vidyapeeth center for NEET coaching

JEE Main Important Chemistry formulas
As per latest 2024 syllabus. Chemistry formulas, equations, & laws of class 11 & 12th chapters
Download Careers360 App's
Regular exam updates, QnA, Predictors, College Applications & E-books now on your Mobile
Certifications
We Appeared in
- Art & Culture
- Offbeat Travel
- Volunteering
- Nostalgiphilia
- Culture Directory
- Collaborate
Indian Cultural diversity: The True Essence and Beauty of India
- Indian Culture
- Indian Heritage
Table of contents
India the land of diversity, diversity in architecture , diversity in indian clothing, diversity in indian food, diversity in religion, diversity in indian customs and tradition, diversity of indian languages, diversity in indian art forms, diversity in indian festivals, diversity in indian music, diversity in indian cinema, diversity in indian litrature, diversity in indian celebration.

Indian culture is one of the most ancient cultures present in the world. The country is quite diverse and is home to several communities, each of whom has their own culture and traditions. It is this combination of various splendid cultures that make India one of a kind. The Indian cultural diversity is what makes India unique and beautiful.

Situated in the continent of Asia and enclosed by the Arabian sea, the Indian Ocean, and the Bay of Bengal, the nation, is divided into twenty-nine states and seven union territories. Pakistan, China, Bangladesh, Myanmar, Bhutan , and Nepal form the neighbouring countries of India.

India is a land of diversity each state in the country is home to several communities who live in harmony with each other while preserving and upholding their own distinct culture and traditions. From Delhi , the capital of India, to Tamil Nadu , the southernmost state of India, the land, is blessed with amazing scenic beauty. The country is also home to several historical monuments which add to the varied heritage of India.
Recommended Read – Understanding the Culture of Indian States [Infographic]

India is a country that is incredibly diversified and that of Indian architecture . India’s architecture spans from ancient caves to contemporary skyscrapers. As India grows, India’s architecture continues to diversify through continuously reverting to its roots while maintaining current trends.
India is also classified by the Dravidian and the Nagara architectural styles as the focal focus of Hindu architecture. In the empires, in the South of India, the Dravidian style prospered, whilst in the North of India, the Nagara style predominately appeared. India’s history, culture and religion are ingrained in its architecture.

India’s vast and boundless array of traditional dress is full of aesthetic beauty. Made from many states of the country are fabrics, weaving processes, embellishments, styles and accessories of multiple sorts. A compelling epic about craftsmanship, culture or legacy tells a story in each piece. The land is a centre of heritage mode. Its diversity was a muse for a number of notable connoisseurs of fashion. In addition to the western clothing, Indians have their own ethnic attire like dhoti, kurta, sari, sherwani, turban etc. Dhoti is a piece of cloth draped around the waist by men. Dhoti is sometimes called Laacha or Dhuti. Kurta is one of India’s famous men’s ethnic clothing. It is usually worn on holidays today by folks. Likewise, the saree is the favourite choice for Indian women. A saree is a long robe, gracefully drawn by women around their bodies. Saree is Indian women’s most trendy clothing worldwide. Indian women are mostly seen in lovely sarees during religious and cultural events. However, due to their convenience, the sarees are substituted by salwar suits for the preferred daily wear.

Indian food is one of the world’s most tasteful and nuanced. There is no flavour homogeneity between North and South or East and West but rather an incredible richness of tastes. One of India’s assets is its culinary diversity.
Indian food contains so much that one ought to discuss more than just “Indian cuisines.” Each region offers a number of traditional meals and its own culinary features.
Each area is specialised in cuisine, not solely at regional, but also at the provincial level. The diversity in cuisine stem from diverse local cultures, geography (whether the region is near the sea, desert or mountains), and the economy. Indigenous kitchen likewise relies heavily on fresh local products and is seasonal.
Indian cuisine tends generally to seek a balance between spices and herbs that offers delicious dishes with surprising therapeutic and medicinal benefits.

Indian religions have influenced and shaped the Indian culture

The vast differences in the customs, traditional beliefs and rituals can be witnessed if one analyses the differences in the culture prevalent in the northern and southern part of India. The festivals, the art forms, and to an extent, even the dressing style of the people are quite different in Northern India when compared to those in Southern India . While most of the Indian women wear the saree, the style of draping the saree varies in different parts of India. This difference can be seen, not only among different states but also among the various communities within the same state.

Though Hindi is the most commonly used language in India, there exist many other languages too. As diverse the country is, each state has its distinct language, such as Kannada, (which, is spoken in Karnataka), Malayalam, (which, is spoken in Kerala), Tamil , is spoken in Tamil Nadu, etc. Apart from the fact that each state has its own language, it is also worth mentioning that some states in India have more than one and sometimes more than three prevalent languages. Due to this, it would not come as a surprise that most Indians are bilingual (or sometimes Multilingual), and can effortlessly handle more than one or two languages.

The family has always been an integral part of Indian society. In an Indian family, all the members share a close-knit connection. Joint families are also common in the country. In joint families, all the members of the family live under the same roof. However, in present times, nuclear families are becoming more common. In India, arranged marriages are relatively more common. The concept of an arranged marriage might seem a bit confusing to people from the western part of the world. However, in India, arranged marriages are more encouraged and are still very much prevalent in the country.

The unique and splendid art forms of India have a significant position in the culture of India. Each state is blessed with its unique art form and differs considerably from that of its neighbour. Though, it is worthwhile to note that many art forms of India are in some ways the amalgamation of other art forms borrowed from the neighbouring states. From the elegant Mohiniyattam , which focuses on the elegant and graceful movements of the dancer to the Ghoomar , a folk dance in Rajasthan, the art forms vary from each other but are equally beautiful and magical.

The festivals of India , too, are worth mentioning. As said earlier, each state has its own festivals, from the fragrant Onam, the festival of Kerala , which is characterized by the making of a floral carpet to the Pôhela Boishakh, (the onset New Year according to the Bengali calendar), the festivals are both colourful and equally incredible.

Music plays a significant role in the culture of any country, and India, too, is not an exception. Carnatic music , Hindustani music are the most popular in India. These are usually accompanied by the tune of the traditional musical instruments such as the tabla and the veena. Indian music is quite soothing and pleasing to the ear.

The movies produced in India, too, reflect the culture of the society. Each state in India has its own movie industry, though Bollywood is the most popular among them. The movie industries in India are known by different terms such as Mollywood (Malayalam movie industry), Tollywood, etc. Owing to the number of movies produced each year in different languages across India, adding to the fact that Indians love movies, India has now become one of the greatest producers of films.

India has also been blessed with many intellectuals and legendary writers and poets who are renowned worldwide for their contributions to humanity. Prominent among them is Rabindranath Tagore , the first Asian and Indian to win the Nobel Prize . His work Gitanjali continues to spread its message and inspires all those who read it. Other prominent writers of India include Sarojini Naidu, Aurobindo Ghosh, among others. Artists such as Raja Ravi Varma, Rabindranath Tagore, and M F Hussain have helped in changing the face of Indian art.

Festivals and celebrations are a common occurrence in India as they occur almost every other day; however, the grandeur and pomp of these festivals are quite impressive. The country is also home to many heritage sites and monuments , including the Taj Mahal. It is all these facts combined that makes the Indian culture unique and distinct from others.

The seventh-largest country in the world, India has set itself a unique and distinct place among the other countries of the world. The host of a culture that has been prevalent for a long time, India is perhaps one of the most diverse countries in the world. From the attire worn by the people belonging to different communities to the languages spoken and even in the food habits, the country both reflects its diversity and varied heritage.
Cover Photo by Tom Chen on Unsplash
Image credits: The copyright for the images used in this article belong to their respective owners. Best known credits are given under the image. For changing the image credit or to get the image removed from Caleidoscope, please contact us.
very good knowledge
Very good guys
It’s very helpful for my science homework theme page: celebrating cultural diversity
Thanks Aarradhya, all the best for your class project!
LEAVE A REPLY Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
INSPIRING READS
Sonepur cattle fair: a celebration of tradition and trade, temples of orissa – illustrious architectural wonders of india, sita kund: the heartbeat of bihar’s cultural legacy, traditional indian summer dishes to beat the heat and be healthy, the celebration of indian new year in various cultures of india, usher in a new ugadi festival by saving water , trending topics.
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
Affiliate disclosure: As an Amazon Associate, we may earn commissions from qualifying purchases from Amazon. Learn more
© caleidoscope - 2024.

"Need to tell stories of a new India": British journalist praises country's diversity and growth journey
N ew Delhi [India], May 19 (ANI): Lauding the "new India", Sam Stevenson , Assistant Editor of the UK -based newspaper Daily Express, emphasised on Sunday that it is time to start telling the positive stories of this new India on its epic trajectory to become a USD 5 trillion economy in the future.
On his visit to India to cover the general elections , Sam Stevenson said that there are a lot of positive stories that can be told from India.
"It's time to start telling the positive stories of new India and of this great nation on its epic trajectory to becoming a USD 5 trillion economy in the future. And look, there's loads and loads of positive stories that we can be telling from India, and that's what we're here to do," Stevenson told ANI.
Responding to a question about whether India in real life is different from the picture painted by the West, the journalist stressed that enough with India bashing down.
"I think it's time to say, enough with India bashing down with the anti-India 'Bakwas'. We need to come here and tell the true, positive stories of New India on the ground reporting," he told ANI.
Stevenson further highlighted that people have been hearing things like religious divisions, but that's not what is on the ground.
"Unfortunately, a lot of the narratives that exist in London and across Europe are negative stories about India. We're hearing things like religious divisions, but that's not what we've witnessed on the ground," he said.
Calling India a "great and wonderful nation," he said that he is here to level up the British media's coverage of this nation.
"We have seen Muslim women in full burqas attending Narendra Modi's rally. We've seen examples of the pluralism of this great and wonderful nation. We're here to level up the British media's coverage of this nation. And we're here to get to the truth, find some real facts and bring them home to London," he said.
Stevenson continued that the perceptions of India across Europe and the West are not good.
"This is because we are being fed negative stories from the press," he stressed, adding that "it is a shame because, actually, people need to come here, see it with their own eyes, live it, breathe it, meet the people, speak to people on the ground, and you will be seeing that, new India, global Britain, we can be a force for good," he said.
The British journalist emphasised that the two countries have shared culture, language, heritage, and history.
"The British media are attempting to simplify something that's very complicated. They're saying Modi is anti-Islam. But actually, when you get on the ground and speak to real Muslims, when you speak to Hindus, Sikhs, you will see that India is accepting of all cultures or religions," he stressed.
"And that is the absolutely fantastic thing about this place," he added. (ANI)

- Ground Reports
- 50-Word Edit
- National Interest
- Campus Voice
- Security Code
- Off The Cuff
- Democracy Wall
- Around Town
- PastForward
- In Pictures
- Last Laughs
- ThePrint Essential


New Delhi [India], May 19 (ANI): Lauding the “new India”, Sam Stevenson, Assistant Editor of the UK-based newspaper Daily Express, emphasised on Sunday that it is time to start telling the positive stories of this new India on its epic trajectory to become a USD 5 trillion economy in the future.
On his visit to India to cover the general elections, Sam Stevenson said that there are a lot of positive stories that can be told from India.
“It’s time to start telling the positive stories of new India and of this great nation on its epic trajectory to becoming a USD 5 trillion economy in the future. And look, there’s loads and loads of positive stories that we can be telling from India, and that’s what we’re here to do,” Stevenson told ANI.
Responding to a question about whether India in real life is different from the picture painted by the West, the journalist stressed that enough with India bashing down.
“I think it’s time to say, enough with India bashing down with the anti-India ‘Bakwas’. We need to come here and tell the true, positive stories of New India on the ground reporting,” he told ANI.
Stevenson further highlighted that people have been hearing things like religious divisions, but that’s not what is on the ground.
“Unfortunately, a lot of the narratives that exist in London and across Europe are negative stories about India. We’re hearing things like religious divisions, but that’s not what we’ve witnessed on the ground,” he said.
Calling India a “great and wonderful nation,” he said that he is here to level up the British media’s coverage of this nation.
“We have seen Muslim women in full burqas attending Narendra Modi’s rally. We’ve seen examples of the pluralism of this great and wonderful nation. We’re here to level up the British media’s coverage of this nation. And we’re here to get to the truth, find some real facts and bring them home to London,” he said.
Stevenson continued that the perceptions of India across Europe and the West are not good.
“This is because we are being fed negative stories from the press,” he stressed, adding that “it is a shame because, actually, people need to come here, see it with their own eyes, live it, breathe it, meet the people, speak to people on the ground, and you will be seeing that, new India, global Britain, we can be a force for good,” he said.
The British journalist emphasised that the two countries have shared culture, language, heritage, and history.
“The British media are attempting to simplify something that’s very complicated. They’re saying Modi is anti-Islam. But actually, when you get on the ground and speak to real Muslims, when you speak to Hindus, Sikhs, you will see that India is accepting of all cultures or religions,” he stressed.
“And that is the absolutely fantastic thing about this place,” he added. (ANI)
This report is auto-generated from ANI news service. ThePrint holds no responsibility for its content.
Subscribe to our channels on YouTube , Telegram & WhatsApp
Support Our Journalism
India needs fair, non-hyphenated and questioning journalism, packed with on-ground reporting. ThePrint – with exceptional reporters, columnists and editors – is doing just that.
Sustaining this needs support from wonderful readers like you.
Whether you live in India or overseas, you can take a paid subscription by clicking here .
LEAVE A REPLY Cancel
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Most Popular
With defence push, india looks to capture markets in africa beyond western indian ocean, ‘jobs on merit, no bribery’ — in karnal, khattar makes a poll pitch based on 9-yr record as cm, you have heard the common myths about retinol. here’s what you need to know.
Required fields are marked *
Copyright © 2024 Printline Media Pvt. Ltd. All rights reserved.
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
BREAKING: DC police officer shot in Northwest DC

Iranian President Ebrahim Raisi, supreme leader’s protege, dies at 63 in helicopter crash
The Associated Press
May 20, 2024, 9:52 AM
- Share This:
- share on facebook
- share on threads
- share on linkedin
- share on email
DUBAI, United Arab Emirates (AP) — Iranian President Ebrahim Raisi, a hard-line protege of the country’s supreme leader who helped oversee the mass executions of thousands in 1988 and later led the country as it enriched uranium near weapons-grade levels, launched a major attack on Israel and experienced mass protests, has died . He was 63.
Raisi’s death, along with the foreign minister and other officials in a helicopter crash Sunday in northwestern Iran, came as Iran struggles with internal dissent and its relations with the wider world. A cleric first, Raisi once kissed the Quran, the Islamic holy book, before the United Nations and spoke more like a preacher than a statesman when addressing the world.
Raisi , who lost a presidential election to the relatively moderate incumbent Hassan Rouhani in 2017, came to power four years later in a vote carefully managed by Supreme Leader Ayatollah Ali Khamenei to clear any major opposition candidate.
His election came at a time when relations between Tehran and Washington were particularly tense following U.S. President Donald Trump’s 2018 decision to unilaterally withdraw America from a nuclear deal aimed at limiting Iran’s uranium enrichment in exchange for sanctions relief.
While Raisi said he wanted to rejoin the deal with world powers, his new administration instead pushed back against international inspections of nuclear facilities, in part over an alleged sabotage campaign that Tehran blamed on Israel. Talks to restore the accord remained stalled in his government’s first months.
“Sanctions are the U.S.’ new way of war with the nations of the world,” Raisi told the United Nations in September 2021. “The policy of ‘maximum oppression’ is still on. We want nothing more than what is rightfully ours.”
Mass protests swept the country in 2022 after the death of Mahsa Amini , a woman who had been detained over her allegedly loose headscarf, or hijab. The monthslong security crackdown that followed the demonstrations killed more than 500 people and more than 22,000 others were detained.
In March, a United Nations investigative panel found that Iran was responsible for the “physical violence” that led to Amini’s death.
Then came the current Israel-Hamas war , in which Iran-backed militants targeted Israel. Tehran launched an extraordinary attack itself on Israel in April that used hundreds of drones, cruise missiles and ballistic missiles . Israel, the U.S. and its allies shot down the incoming fire, but it showed just how intense the yearslong shadow war between Iran and Israel was.
Born in Mashhad on Dec. 14, 1960, Raisi came from a family that traces its lineage to Islam’s Prophet Muhammad, as signaled by the black turban he would later wear. His father died when he was 5. He went on to the seminary in the Shiite holy city of Qom and later described himself as an ayatollah, a high-ranking Shiite cleric.
On Monday, state-run media referred to Raisi as being “martyred while serving the nation.” Khamenei said Raisi “did not believe in tiredness.” Others cited the detente reached last year with Saudi Arabia as a major milestone.
But activists abroad, like the New York-based Center for Human Rights in Iran, described his presidency as seeing “a stunning escalation of state repression and violence against peaceful dissent in Iran.”
“Raisi presided over a country suffocated by a regime that fears its own people,” said Hadi Ghaemi, the center’s executive director. “He was merely one boot on the necks of the Iranian people; others can easily take his place.”
In 1988, at the end of Iran’s long war with Iraq, Raisi served on what would become known as “death commissions,” which handed down death sentences for political prisoners, militants and others. International rights groups estimate that as many as 5,000 people were executed.
After Iran’s then-Supreme Leader Ruhollah Khomeini accepted a U.N.-brokered cease-fire, members of the Iranian opposition group Mujahedeen-e-Khalq, heavily armed by Iraq’s Saddam Hussein, stormed across the Iranian border in a surprise attack. Iran ultimately blunted their assault, but the attack set the stage for the sham retrials .
Some who appeared were asked to identify themselves. Those who responded “mujahedeen” were sent to their deaths .
Raisi was defiant when asked at a news conference after his election about the executions.
“I am proud of being a defender of human rights and of people’s security and comfort as a prosecutor wherever I was,” said Raisi, who also served as Iran’s attorney general for a time.
In 2016, Khamenei appointed Raisi to run the Imam Reza charity foundation, which manages a conglomerate of businesses and endowments in Iran. It is one of many bonyads, or charitable foundations, fueled by donations or assets seized after Iran’s 1979 Islamic Revolution.
These foundations offer no public accounting of their spending and answer only to Iran’s supreme leader. The Imam Reza charity, known as “Astan-e Quds-e Razavi” in Farsi, is believed to be one of the biggest. Analysts estimate its worth at tens of billions of dollars as it owns almost half the land in Mashhad, Iran’s second-largest city.
At Raisi’s appointment to the foundation, Khamenei called him a “trustworthy person with high-profile experience.” That led to analyst speculation that Khamenei could be grooming Raisi as a possible candidate to be Iran’s third-ever supreme leader, a Shiite cleric who has final say on all state matters and serves as the country’s commander-in-chief.
Though Raisi lost his 2017 campaign, he still garnered nearly 16 million votes. Khamenei installed him as the head of Iran’s internationally criticized judiciary, long known for its closed-door trials of human rights activists and those with Western ties. The U.S. Treasury in 2019 sanctioned Raisi “for his administrative oversight over the executions of individuals who were juveniles at the time of their crime and the torture and other cruel, inhuman, or degrading treatment or punishment of prisoners in Iran, including amputations.”
By 2021, Raisi became the dominant figure in the election after a panel under Khamenei disqualified candidates who posed the greatest challenge to his protege. He swept nearly 62% of the 28.9 million votes in that election. Millions stayed home and others voided ballots, resulting in the lowest turnout by percentage in the Islamic Republic’s history.
Raisi is survived by his wife and two daughters.
Copyright © 2024 The Associated Press. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, written or redistributed.
Related News

Stock market today: Wall Street ticks higher as S&P 500 and Nasdaq composite head for more records

‘The Apprentice,’ about a young Donald Trump, premieres in Cannes

WikiLeaks founder Assange wins right to appeal against an extradition order to the US
Recommended.

WATCH: Tugboats escort ship that caused deadly Baltimore bridge collapse back to port

Is a move to a 6-day workweek 'tone-deaf'? Survey says some companies may try it

The buffet is back and why it’s ‘the best place’ to hold a party
Related categories:.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
500 Words Essay on India the Land of Diversity Introduction. India, a country known for its rich cultural heritage and diverse ethnicity, is often referred to as the "Land of Diversity". This diversity is evident in its geography, culture, languages, religions, and traditions, making it a unique blend of unity in diversity. Geographical ...
Diversity In India Essay. Diversity in India is a remarkable phenomenon, one that has been celebrated since ancient times. It is a country where different cultures, religions, languages, and traditions coexist in harmony, reflecting its traditional adage of 'unity in diversity'. India is home to a plethora of different ethnicities ...
Essay on India in 150 words. India, a diverse and culturally rich country located in South Asia, is renowned for its vibrant festivals, ancient heritage sites, and diverse landscapes. With a population of over 1.3 billion people, India is a melting pot of religions, languages, and ethnicities.
Essay on Diversity in India: "Unity in diversity is India's strength. There is simplicity in every Indian. There is unity in every corner of India.". As India celebrates 77 years of independence, it's crucial to explore the vast diversity that defines this nation. Despite the colonial past, which attempted to diminish the rich tapestry ...
You can also find more Essay Writing articles on events, persons, sports, technology and many more. India - A Land Of Diversity Essay India is a kaleidoscope of cultures that includes umpteen variations in food, clothing, language, music and religious beliefs. This colourful spread has been shaped by the long history and unique geography of […]
India's least populous territory, the southern archipelago of Lakshadweep, had about 60,000 people in 2011. That was on par with Greenland and Bermuda, and equaled roughly a tenth of Wyoming's residents at that time. Hindus were a majority in 28 of India's 35 states in 2011. Around 94% of the world's Hindus (966 million) lived in India ...
500+ Words Essay on India. India is a great country where people speak different languages but the national language is Hindi. India is full of different castes, creeds, religion, and cultures but they live together. That's the reasons India is famous for the common saying of " unity in diversity ". India is the seventh-largest country in ...
The Land of Diversity and Harmony. India, often known as "Incredible India," is a country that stands out for its diverse culture, rich history, and fascinating traditions. It is a land where 1.3 billion people live in harmony, speaking over 2000 dialects, practicing various religions, and celebrating numerous festivals.
About half of Indians (53%) say religious diversity benefits the country, while 24% say it is harmful. The remainder (24%) don't take a position either way. At the same time, Indians of different religious backgrounds don't see much in common with each other. For example, most Muslims say members of their religious community are very ...
In times of global divisiveness, India's composite culture stands tall as a testament to the strength and beauty of unity in diversity. Why Sociology for Success in CSE. To master these intricacies and fare well in the Sociology Optional Syllabus, aspiring sociologists might benefit from guidance by the Best Sociology Optional Teacher and ...
500+ Words Essay on Incredible India. India represents "Unity in Diversity" . Our country is a mixture of cultures, regions, traditions, diversity in food, languages, etc. Our people of India are so polite, understanding and helping in nature. The national bird of India is Peacock and is very beautiful.
A major new Pew Research Center survey of religion across India, based on nearly 30,000 face-to-face interviews of adults conducted in 17 languages between late 2019 and early 2020 (before the COVID-19 pandemic ), finds that Indians of all these religious backgrounds overwhelmingly say they are very free to practice their faiths.
As a multilingual country, India's diversity has proven to be both a strength and a challenge to unifying the nation. Hopefully, this essay illustrates how multiple languages have shaped policies from education to the political boundaries of states, and, stemming from a colonial footprint and global pressures for greater use of English in ...
Incredible India Essay. India is a country with vast culture and heritage. It has almost all types of landforms, climatic conditions, different languages, and religions, which represents unity in diversity. There are famous heritage sites and monuments in India which make anyone breathless. It has ice-covered Himalayan mountains in the north ...
200 Words Essay on Unity in Diversity in India. Harmony and unity among various disparate people are called "Unity in Diversity.". These differences might result from cultural norms, political views, religious perspectives, or political beliefs. The idea is known by several other names, including "diversity without fragmentation" and "unity ...
Even though India is such a diverse place, it is united as one country. Political Divisions. India is the seventh-largest country and has the second-largest population in the world. Here is the map of India showing 29 states and 7 union territories. These political divisions are made so that the government can run the country more easily.
200 Words Essay on Indian Culture. India is a land of diverse cultures, religions, languages, and traditions. The rich cultural heritage of India is a result of its long history and the various invasions and settlements that have occurred in the country. Indian culture is a melting pot of various customs and traditions, which have been passed ...
India Essay. India is a vibrant and diverse country located in South Asia and is home to a population of over 1.3 billion people. India is a land of many cultures, religions, and languages of its, rich history, varied landscapes, and unique cuisine. India is also one of the world's fastest-growing economies and has one of the most significant ...
Diversity in Indian Music Image - Prabhu B Doss via Flickr. Music plays a significant role in the culture of any country, and India, too, is not an exception. Carnatic music, Hindustani music are the most popular in India. These are usually accompanied by the tune of the traditional musical instruments such as the tabla and the veena. Indian ...
All in all, India's vast diversity is matched by its geographical features and shows the strength of the country. India is a vast country and is considered as a Sub-Continent for its vastness. This sub-continent extending from the Himalayas to the sea is called Bharata-Varsha or the land of Bharata, a famous king of the Puranic tradition.
India, country that occupies the greater part of South Asia.It is made up of 28 states and eight union territories, and its national capital is New Delhi, built in the 20th century just south of the historic hub of Old Delhi to serve as India's administrative center.Its government is a constitutional republic that represents a highly diverse population consisting of thousands of ethnic ...
New Delhi [India], May 19 (ANI): Lauding the "new India", Sam Stevenson, Assistant Editor of the UK-based newspaper Daily Express, emphasised on Sunday that it is time to start telling the ...
New Delhi [India], May 19 (ANI): Lauding the "new India", Sam Stevenson, Assistant Editor of the UK-based newspaper Daily Express, emphasised on Sunday that it is time to start telling the positive stories of this new India on its epic trajectory to become a USD 5 trillion economy in the future. On his visit to […]
DUBAI, United Arab Emirates (AP) — Iranian President Ebrahim Raisi, a hard-line protégé of the country's supreme leader who helped oversee the mass executions of thousands in 1988 and later ...