- History Classics
- Your Profile
- Find History on Facebook (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on Twitter (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on YouTube (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on Instagram (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on TikTok (Opens in a new window)
- This Day In History
- History Podcasts
- History Vault

Mahatma Gandhi
By: History.com Editors
Updated: June 6, 2019 | Original: July 30, 2010

Revered the world over for his nonviolent philosophy of passive resistance, Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi was known to his many followers as Mahatma, or “the great-souled one.” He began his activism as an Indian immigrant in South Africa in the early 1900s, and in the years following World War I became the leading figure in India’s struggle to gain independence from Great Britain. Known for his ascetic lifestyle–he often dressed only in a loincloth and shawl–and devout Hindu faith, Gandhi was imprisoned several times during his pursuit of non-cooperation, and undertook a number of hunger strikes to protest the oppression of India’s poorest classes, among other injustices. After Partition in 1947, he continued to work toward peace between Hindus and Muslims. Gandhi was shot to death in Delhi in January 1948 by a Hindu fundamentalist.
Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi was born on October 2, 1869, at Porbandar, in the present-day Indian state of Gujarat. His father was the dewan (chief minister) of Porbandar; his deeply religious mother was a devoted practitioner of Vaishnavism (worship of the Hindu god Vishnu), influenced by Jainism, an ascetic religion governed by tenets of self-discipline and nonviolence. At the age of 19, Mohandas left home to study law in London at the Inner Temple, one of the city’s four law colleges. Upon returning to India in mid-1891, he set up a law practice in Bombay, but met with little success. He soon accepted a position with an Indian firm that sent him to its office in South Africa. Along with his wife, Kasturbai, and their children, Gandhi remained in South Africa for nearly 20 years.
Did you know? In the famous Salt March of April-May 1930, thousands of Indians followed Gandhi from Ahmadabad to the Arabian Sea. The march resulted in the arrest of nearly 60,000 people, including Gandhi himself.
Gandhi was appalled by the discrimination he experienced as an Indian immigrant in South Africa. When a European magistrate in Durban asked him to take off his turban, he refused and left the courtroom. On a train voyage to Pretoria, he was thrown out of a first-class railway compartment and beaten up by a white stagecoach driver after refusing to give up his seat for a European passenger. That train journey served as a turning point for Gandhi, and he soon began developing and teaching the concept of satyagraha (“truth and firmness”), or passive resistance, as a way of non-cooperation with authorities.
The Birth of Passive Resistance
In 1906, after the Transvaal government passed an ordinance regarding the registration of its Indian population, Gandhi led a campaign of civil disobedience that would last for the next eight years. During its final phase in 1913, hundreds of Indians living in South Africa, including women, went to jail, and thousands of striking Indian miners were imprisoned, flogged and even shot. Finally, under pressure from the British and Indian governments, the government of South Africa accepted a compromise negotiated by Gandhi and General Jan Christian Smuts, which included important concessions such as the recognition of Indian marriages and the abolition of the existing poll tax for Indians.
In July 1914, Gandhi left South Africa to return to India. He supported the British war effort in World War I but remained critical of colonial authorities for measures he felt were unjust. In 1919, Gandhi launched an organized campaign of passive resistance in response to Parliament’s passage of the Rowlatt Acts, which gave colonial authorities emergency powers to suppress subversive activities. He backed off after violence broke out–including the massacre by British-led soldiers of some 400 Indians attending a meeting at Amritsar–but only temporarily, and by 1920 he was the most visible figure in the movement for Indian independence.
Leader of a Movement
As part of his nonviolent non-cooperation campaign for home rule, Gandhi stressed the importance of economic independence for India. He particularly advocated the manufacture of khaddar, or homespun cloth, in order to replace imported textiles from Britain. Gandhi’s eloquence and embrace of an ascetic lifestyle based on prayer, fasting and meditation earned him the reverence of his followers, who called him Mahatma (Sanskrit for “the great-souled one”). Invested with all the authority of the Indian National Congress (INC or Congress Party), Gandhi turned the independence movement into a massive organization, leading boycotts of British manufacturers and institutions representing British influence in India, including legislatures and schools.
After sporadic violence broke out, Gandhi announced the end of the resistance movement, to the dismay of his followers. British authorities arrested Gandhi in March 1922 and tried him for sedition; he was sentenced to six years in prison but was released in 1924 after undergoing an operation for appendicitis. He refrained from active participation in politics for the next several years, but in 1930 launched a new civil disobedience campaign against the colonial government’s tax on salt, which greatly affected Indian’s poorest citizens.
A Divided Movement
In 1931, after British authorities made some concessions, Gandhi again called off the resistance movement and agreed to represent the Congress Party at the Round Table Conference in London. Meanwhile, some of his party colleagues–particularly Mohammed Ali Jinnah, a leading voice for India’s Muslim minority–grew frustrated with Gandhi’s methods, and what they saw as a lack of concrete gains. Arrested upon his return by a newly aggressive colonial government, Gandhi began a series of hunger strikes in protest of the treatment of India’s so-called “untouchables” (the poorer classes), whom he renamed Harijans, or “children of God.” The fasting caused an uproar among his followers and resulted in swift reforms by the Hindu community and the government.
In 1934, Gandhi announced his retirement from politics in, as well as his resignation from the Congress Party, in order to concentrate his efforts on working within rural communities. Drawn back into the political fray by the outbreak of World War II , Gandhi again took control of the INC, demanding a British withdrawal from India in return for Indian cooperation with the war effort. Instead, British forces imprisoned the entire Congress leadership, bringing Anglo-Indian relations to a new low point.
Partition and Death of Gandhi
After the Labor Party took power in Britain in 1947, negotiations over Indian home rule began between the British, the Congress Party and the Muslim League (now led by Jinnah). Later that year, Britain granted India its independence but split the country into two dominions: India and Pakistan. Gandhi strongly opposed Partition, but he agreed to it in hopes that after independence Hindus and Muslims could achieve peace internally. Amid the massive riots that followed Partition, Gandhi urged Hindus and Muslims to live peacefully together, and undertook a hunger strike until riots in Calcutta ceased.
In January 1948, Gandhi carried out yet another fast, this time to bring about peace in the city of Delhi. On January 30, 12 days after that fast ended, Gandhi was on his way to an evening prayer meeting in Delhi when he was shot to death by Nathuram Godse, a Hindu fanatic enraged by Mahatma’s efforts to negotiate with Jinnah and other Muslims. The next day, roughly 1 million people followed the procession as Gandhi’s body was carried in state through the streets of the city and cremated on the banks of the holy Jumna River.

Sign up for Inside History
Get HISTORY’s most fascinating stories delivered to your inbox three times a week.
By submitting your information, you agree to receive emails from HISTORY and A+E Networks. You can opt out at any time. You must be 16 years or older and a resident of the United States.
More details : Privacy Notice | Terms of Use | Contact Us

15 Great Leaders of Modern India Who Changed History
- Share On Facebook
- Share On Twitter
- Share On WhatsApp
- shares
India is an extremely diverse country which houses different communities and a rich history, and we have had some incredible leaders who have inspired us through the decades. They all have contributed to the foundation of the nation through their different roles, and continue to be sources of inspiration for many. Here are 15 of the great leaders of India we think you should always remember.
1. Dr B.R. Ambedkar
Bhimrao Ramji Ambedkar was an Indian jurist, economist, social reformer, and political figure who served as the chairman of the committee that drafted the Constitution of India from the discussions in the Constituent Assembly. He also held the position of Law and Justice Minister in Jawaharlal Nehru’s first cabinet and, after renunciating Hinduism, served as an inspiration for the Dalit Buddhist movement. Ambedkar received the Bharat Ratna, the highest civilian honour in India, posthumously in 1990. Followers honour him with the salutation Jai Bhim. Additionally, he goes by the title Babasaheb. He is an unforgettable name when it comes to mentioning the great leaders of India.
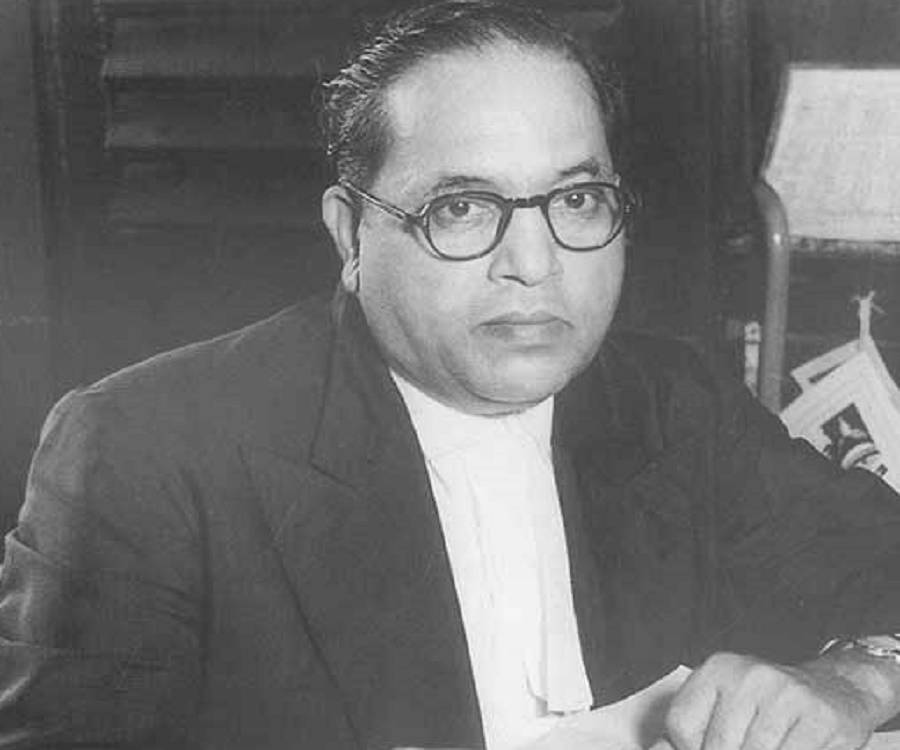

2. APJ Abdul Kalam
Scientist in aerospace and statesman Avul Pakir Jainulabdeen Abdul Kalam led India as its 11th president from 2002 to 2007. He studied physics and aeronautical engineering and was nurtured in Rameswaram, Tamil Nadu. He worked as a scientist and science administrator for the following four decades, primarily at the Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) and the Defence Research and Development Organization (DRDO). He was heavily involved in both India’s efforts to develop military missiles and its civilian space programme. As a result of his contributions to the advancement of ballistic missile and launch vehicle technology, he earned the moniker “Missile Man of India.” He also had a significant organisational, technical, and political involvement in India’s 1998 Pokhran-II nuclear tests, which were the country’s first since its initial test in 1974.

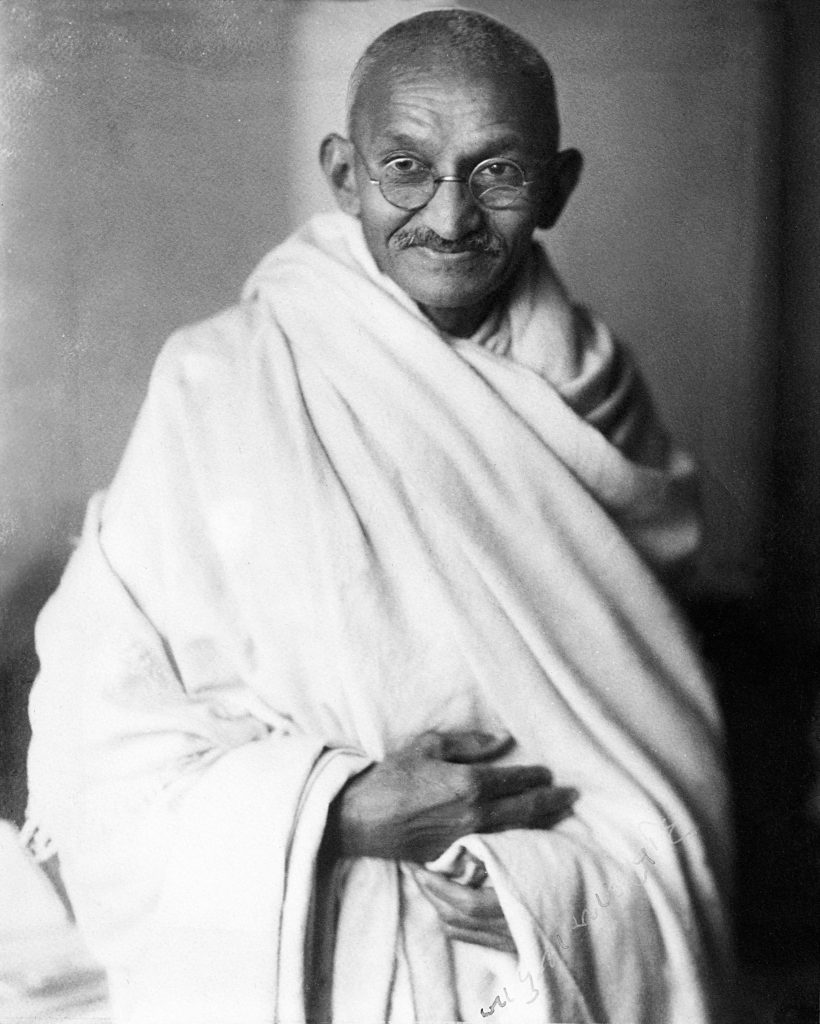
3. Mahatma Gandhi
The victorious struggle for India’s independence from British control was led by Indian lawyer, anti-colonial nationalist, and political ethicist Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi, who later served as an inspiration for movements for civil rights and freedom around the globe. In 1914, in South Africa, the title Mahtm (Sanskrit: “great-souled,” “venerable”) was first used to refer to him. Gandhi’s birthday, 2 October, is observed as an international day of nonviolence and as Gandhi Jayanti, a national holiday in India. Gandhi was known as Bapu and is regarded as the Father of the Nation in India, though not formally. It would be remiss to not mention Gandhi when compiling a list of the great leaders of India.

4. C. Rajagopalachari
Chakravarti Rajagopalachari was a statesman, author, lawyer, and champion for Indian independence. Rajagopalachari served as India’s final governor general before it became a republic in 1950. Additionally, he was the first governor-general who was born in India; all previous occupants of the position were British nationals. Aside from leading the Indian National Congress, he also held the positions of premier of the Madras Presidency, governor of West Bengal, minister of home affairs for the Indian Union, and chief minister of the state of Madras. Rajagopalachari was one of the first individuals to receive the Bharat Ratna, India’s highest civilian honour. He also created the Swatantra Party. He was a strong supporter of world peace and disarmament and fiercely opposed the use of nuclear weapons. Throughout his life, he also picked up the moniker “Mango of Salem.”

5. Sardar Vallabhai Patel
The first Deputy Prime Minister of India and the country’s first Home Minister, Vallabhbhai Jhaverbhai Patel, also known as Sardar, was an Indian lawyer, prominent political figure, lawyer, and statesman who served from 1947 to 1950. He is sometimes referred to as “Unifying India.” At a cost of USD 420 million, the Indian government built the Statue of Unity, the tallest statue in the world, which was dedicated to him on October 31, 2018. Its height is roughly 182 metres (597 feet). He was a lawyer and a prominent member of the Indian National Congress who led the country’s independence movement and oversaw its fusion into a single, sovereign state.
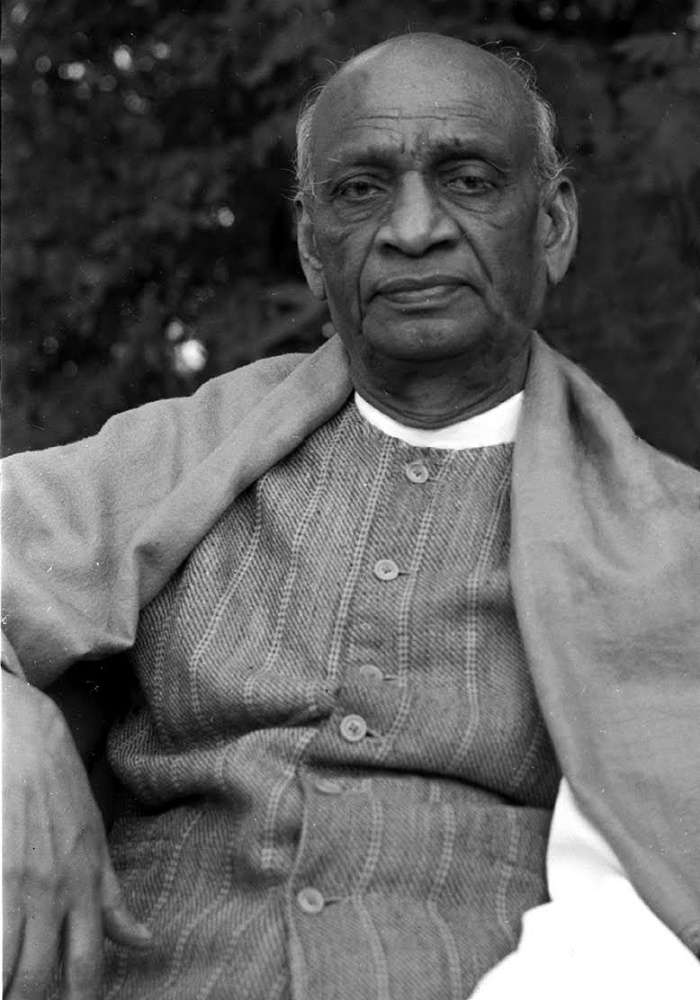

6. Jawaharlal Nehru
A major personality in India throughout the middle of the 20th century, Jawaharlal Nehru was an anti-colonial patriot, secular humanist, social democrat, and author. In the 1930s and 1940s, Nehru was a key figure in the Indian nationalist movement. He presided over India for 16 years after the country gained its independence in 1947. Nehru greatly influenced India’s development into a modern nation in the 1950s by promoting parliamentary democracy, secularism, science, and technology. He kept India out of the Cold War’s two blocs in foreign affairs. He was a respected novelist who wrote several works while incarcerated, including The Discovery of India (1946), An Autobiography, and Letters from a Father to His Daughter (1929).
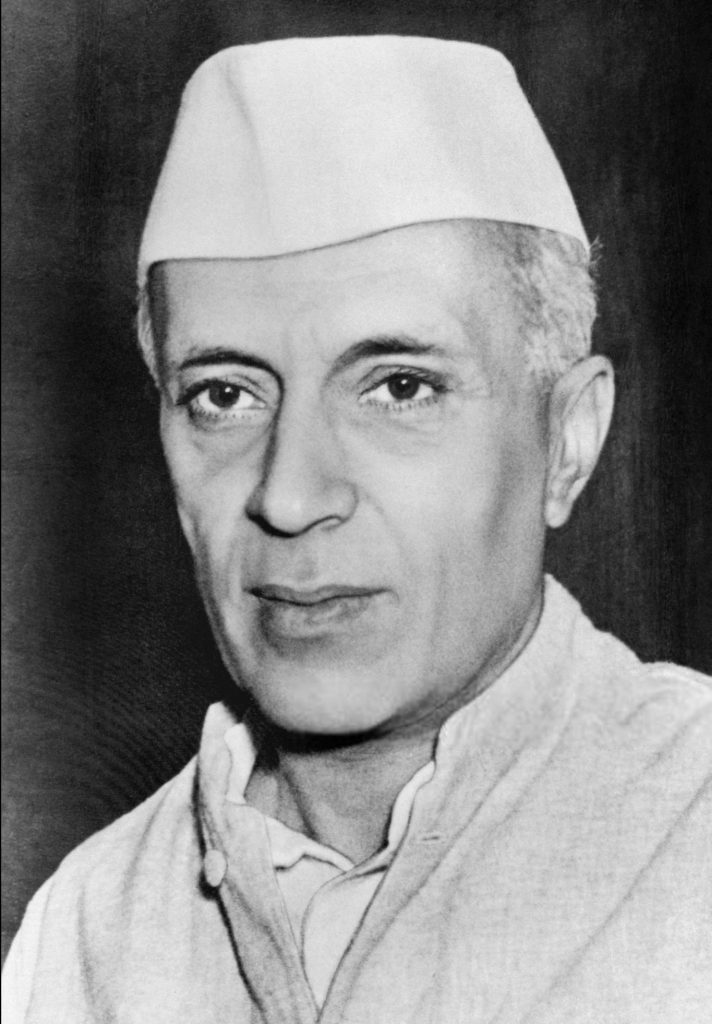

7. Mother Teresa
Mother Teresa, commonly referred to as Saint Teresa of Calcutta, and a foremost name among the great leaders of India, was an Albanian-Indian Roman Catholic nun who founded the Missionaries of Charity in 1950 and was a prominent member of the order. Despite having the name Mary Teresa Bojaxhiu on her passport, she was actually born Anjez Gonxhe Bojaxhiu in the North Macedonian city of Üsküb (now Skopje). She migrated to Ireland and subsequently India after spending eighteen years there in Skopje, where she spent the majority of her life.
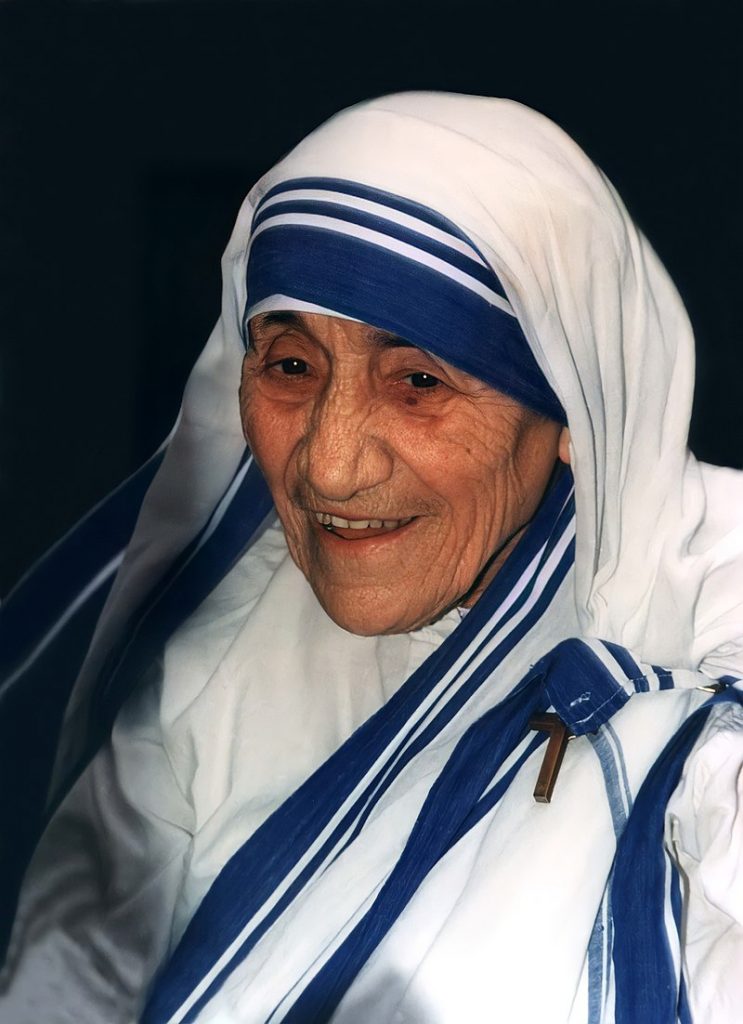

8. Atal Bihari Vajpayee
As India’s 10th prime minister, Atal Bihari Vajpayee was an Indian politician and diplomat who held office for three terms: for 13 days in 1996, for 13 months from 1998 to 1999, and then for a full term from 1999 to 2004. One of the Bharat Janata Party’s co-founders and a prominent figure, Vajpayee (BJP). He belonged to the Rashtriya Swayamsevak Sangh, a group of volunteers with Hindu nationalist views. He was the first Indian prime minister to hold office for the whole duration who was not a member of the Indian National Congress. He was also a well-known writer and poet.

9. R.K. Laxman
Indian cartoonist, artist, and humorist Rasipuram Krishnaswami Laxman created these works. His best-known works are The Common Man, which he created, and You Said It, a daily cartoon that he began publishing in The Times of India in 1951. R. K. Laxman began his career as a part-time cartoonist, primarily for regional publications and newspapers. He drew his older brother R. K. Narayan’s stories for The Hindu while still a college student. Political cartoonist for The Free Press Journal in Mumbai, that was his first full-time position. Later, he joined The Times of India, where he rose to fame as the fictional character known as The Common Man. This proved to be the turning point in Laxman’s life.

10. Baba Amte
Indian social worker and activist Murlidhar Devidas Amte, better known by his stage name Baba Amte, is well renowned for his work in the rehabilitation and empowerment of leprosy patients. He has won various honours and accolades, including the Padma Vibhushan, the Templeton Prize, the Ramon Magsaysay Award, the Gandhi Peace Prize, the Dr. Ambedkar International Award, and the Jamnalal Bajaj Award. He is frequently referred to be India’s contemporary Gandhi, and an unforgettable mention among the great leaders of India.

11. Homi J Bhabha
Homi Jehangir Bhabha, FRS, was an Indian nuclear physicist who founded the Tata Institute of Fundamental Research and served as its founding director and professor of physics (TIFR). Bhabha was the founding director of the Atomic Energy Establishment, Trombay (AEET), which is now known as the Bhabha Atomic Research Centre in his honour. He is also known colloquially as the “Father of the Indian Nuclear Program.” The cornerstones of Indian nuclear weapon development, which Bhabha also oversaw as director, were TIFR and AEET. The Adams Prize (1942) and the Padma Bhushan were given to Homi Bhabha (1954). In 1951 and 1953–1956, he was again a candidate for the Nobel Prize in Physics.

12. Aruna Asaf Ali
Aruna Asaf Ali was a publisher, political activist, and educator from India. She was an ardent member of the fight for Indian independence, and she is well known for raising the Indian National flag at the Gowalia Tank Maidan in Bombay in 1942, during the Quit India Movement. She continued involved in politics after independence and was elected as Delhi’s first Mayor.

13. Asima Chatterjee
Asima Chatterjee was an Indian organic chemist known for her contributions to phytomedicine and organic chemistry. Her study on vinca alkaloids, invention of anti-epileptic medications, and creation of anti-malarial medications are some of her most well-known accomplishments. She also wrote a sizable amount of material about Indian subcontinental medicinal plants. She was the first female to be awarded a doctorate in science by a university in India.

14. Mahashweta Devi
An activist and Bengali writer from India, Mahasweta Devi. Rudali, Aranyer Adhikar, and Hajar Churashir Maa are some of her best-known literary works. She was a socialist who fought for the liberation and empowerment of the Lodha and Shabar tribespeople in the Indian states of West Bengal, Bihar, Madhya Pradesh, and Chhattisgarh. She received numerous literary honours, including the Padma Shri and Padma Vibhushan, India’s civilian honours, the Jnanpith Award, and the Sahitya Akademi Award (in Bengali). She has been hailed among the great leaders of India for decades.

15. Ela Bhatt
Ela Ramesh Bhatt founded the Self-Employed Women’s Association of India (SEWA) in 1972 and held the position of general secretary for the organisation from 1972 until 1996. She is an Indian cooperative organiser, activist, and supporter of Gandhi. She is the Gujarat Vidyapith’s current chancellor. Bhatt, a lawyer by profession, has received numerous national and international honours, including the Padma Bhushan, the Right Livelihood Award, the Ramon Magsaysay Award, and the Right Livelihood Award for “assisting home-based producers to organise for their welfare and self-respect” (1986).

We hope we reminded you of these great names who have led our nation’s progress through their own journeys. They will continue to be extremely inspiring for all of us throughout the decades that have gone by and the decades to come.

Saptaparna likes movies and cats, and is socially awkward. She also likes giving random recommendations to uninterested people.
15 Mesmerizing Krishna Temples In India
All You Need To Know About Aditya L1: India’s First Mission To The Sun
8-year-old Boy From Shivamogga Becomes Inspector For One Day
15 Lesser Known Freedom Fighters Of India Who Died For The Nation
Gauri Sawant- The Transgender Activist on Whom Sushmita Sen’s Latest Web Series…
India Rising: Stories From The Last Month That’ll Inspire You (July 2023)
10 Famous People, Hollywood Stars & Celebs Who Follow Hinduism and Hindu…
India Rising: Stories From The Last Month That’ll Inspire You (June 2023)
14 Kargil War Heroes Whose Stories Will Make Your Heart Swell in Pride!
The 1992 Ajmer Rape Case: The True Story Behind the Movie Ajmer 92

Essay on Greatness of India
Students are often asked to write an essay on Greatness of India in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on Greatness of India
The land of diversity.
India, a country rich in its diverse culture and heritage, is known for its unique identity. It’s a land where numerous religions, languages, and traditions coexist harmoniously.
Historical Significance
India’s history is a testament to its greatness. From the ancient Indus Valley Civilization to the mighty Mughal Empire, India’s past is filled with stories of grandeur and glory.
Contributions to Science
India has made significant contributions to science. The concept of zero, Ayurveda, and Yoga originated from India, showcasing its intellectual prowess.
Rich Natural Beauty
India’s natural beauty, from the Himalayan peaks to the Indian Ocean’s shores, is breathtaking and diverse, reflecting the country’s greatness.
India’s greatness lies in its diversity, historical richness, scientific contributions, and natural beauty. It truly is a land of wonders.
250 Words Essay on Greatness of India
The historical eminence of india.
India, a country with an ancient civilization, has been a beacon of knowledge and wisdom throughout history. Home to the world’s oldest urban civilization, the Indus Valley, and the birthplace of four major religions, India’s cultural richness and diversity are unparalleled.
India’s Scientific Prowess
India’s contributions to science and technology are noteworthy. Ancient Indian mathematicians introduced the concept of zero and the decimal system. The field of astronomy also flourished in India with Aryabhata’s accurate calculations of celestial bodies. Today, India’s prowess is evident in space technology, with successful missions like Mangalyaan and Chandrayaan.
Cultural Richness and Diversity
India’s cultural heritage is a melting pot of various customs, traditions, and languages. With over 2000 distinct ethnic groups and more than 1600 spoken languages, India stands as a testament to multicultural coexistence. Its literature, music, dance, and visual arts are a reflection of its societal mosaic.
Economic Potential
India’s economic potential is vast. It’s the world’s fifth-largest economy by nominal GDP and is projected to be the third-largest by 2030. India’s IT sector is a global powerhouse, and its manufacturing and services sectors are rapidly growing, contributing to its economic strength.
India’s Global Influence
India’s influence on the global stage is increasing. As the world’s largest democracy, it plays a crucial role in global politics. India’s philosophy of Vasudhaiva Kutumbakam, meaning ‘the world is one family’, is a guiding principle in its foreign policy, promoting global peace and cooperation.
In conclusion, India’s greatness lies in its historical eminence, scientific contributions, cultural diversity, economic potential, and increasing global influence. Its journey from an ancient civilization to a modern nation-state is a testament to its resilience and adaptability.
500 Words Essay on Greatness of India
The cultural mosaic.
India, a country known for its vibrant cultural diversity, is a land where numerous ethnic groups coexist, each contributing to the rich tapestry of the nation’s heritage. The cultural plurality of India is reflected in a multitude of languages, religions, traditions, and festivals that are celebrated with great fervor. The country’s cultural richness is not only a testament to its historical legacy but also a reflection of its capacity to adapt and evolve over time.
Ancient Knowledge Systems
India’s greatness is also evident in its ancient knowledge systems. The country is the birthplace of many scientific and mathematical concepts, including the decimal system, zero, and advanced astronomy. The ancient texts of Ayurveda, Yoga, and Naturopathy are still relevant today, providing alternative healing methods to modern medicine.
Architectural Marvels
The architectural grandeur of India is another aspect that contributes to its greatness. From the meticulously carved temples of the south to the majestic forts of the north, from the intricate stepwells of the west to the grand monasteries of the east, every region boasts architectural marvels that reflect the country’s artistic brilliance and technological prowess. These structures not only stand as a testament to India’s rich history but also contribute to the country’s cultural identity.
India’s economic potential is another facet of its greatness. With one of the largest and youngest populations in the world, India is poised to become a significant player in the global economy. The country’s tech industry is a global powerhouse, and its manufacturing sector is rapidly expanding. Despite the challenges, India’s economic resilience and potential for growth make it a key player in the global economic landscape.
Spiritual Legacy
India’s spiritual legacy is a significant aspect of its greatness. The country is the birthplace of religions like Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism, and Sikhism. It has welcomed and assimilated various other beliefs, making it a global spiritual hub. The teachings of peace, tolerance, and non-violence, propagated by Indian spiritual leaders, have left an indelible mark on the world.
The greatness of India lies not in its size or wealth but in its diversity, history, and culture. Its vibrant cultural mosaic, ancient knowledge systems, architectural marvels, economic potential, and spiritual legacy collectively contribute to its greatness. Despite the challenges it faces, India’s resilience and adaptability make it a country of immense potential and enduring greatness. The richness of its heritage and the promise of its future are what truly define the greatness of India.
That’s it! I hope the essay helped you.
If you’re looking for more, here are essays on other interesting topics:
- Essay on Glory of India
- Essay on Globalisation and Indian Economy
- Essay on Freedom of Speech in India
Apart from these, you can look at all the essays by clicking here .
Happy studying!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.


10 Lines Essay On Great Leaders Of India In English For Students
- India is a land of great political leaders who ruled the country for years.
- They played a great role in changing the perspective of the world towards India.
- They framed the Constitution of India by including the best possible clauses of the world.
- Their selfless contribution towards the nation deserves a great honor and respect.
- Bhagat singh, Tilak, Pandit Jawaharlal Nehru, Subhash chander bose, Lal Bahadur Shastri, Mahatma Gandhi and Indira Gandhi are some of the important leaders.
- They devoted their life for the pride and honor of the country.
- We are living in democratic and Independent country due to these great leaders.
- They sacrificed their whole life for the betterment and sake of the country.
- We should respect their contribution and should remember them with dignity.
- Its our duty to not let their names fade in darkness.
Related Posts:
- Short Essay on Freedom Fighters in English
- Future of Democracy in India Essay
- Howl Poem By Allen Ginsberg Summary, Notes and Line by Line Explanation in English
- A Grammarian's Funeral by Robert Browning Summary
- 2 Minute Speech On Jawaharlal Nehru In English
- 3 Minute Speech On Bhagat Singh In English


Gandhi : A Leader Of Indian Nationalism Essay
Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi, commonly known as Mohatma Gandhi, was the preeminent leader of Indian nationalism in British ruled India. He led India to independence by a nonviolent movement. He is widely considered as the most powerful and successful leader in the history of India. He believed in nonviolence. Many people believe that Mohatma Gandhi has abrupt contribution in the history of India . But it is a matter of sorrow that this leader had some problems that led the country towards an unknown future. He launched nonviolent movement as he had no arms. He never wanted to launch nonviolent movement. He said, ‘’ I have no arms. If I had arms, I would give arms to the people against British. As I have no arms, I have chosen this way. ’After the battle of Palashi, the Indian subcontinent went under the rule of East Indian company. The company ruled India from 1757 to 157. From 157 to 1947 Indian subcontinent was ruled by the British Government. Then India won freedom. To get freedom, India had to sacrifice a lot of lives of her brave sons. Many legends do not consider Mohatma Gandhi as the preeminent leader of India. Such as a)Suzanna Arundhati Roy b)AlokkrisnoChakroborti c)Subhas Chandra Bose d)AbulKalam Azad e)Michael Edwards f)Leonard Mosley g)M.M. Kothari h)NiharenduDuttMazumder and others. He had an intention behind this nonviolent movement Mohatma Gandhi wanted to be the most powerful leader of India. He Wanted to be a Hitler of
Disobedience Essay
Mahatma Gandhi changed India’s history forever through disobedience. Even though he disobeyed the law he had a good reason to. India was under the British rule and the people were doing as british were telling them to do because they had no other option. Gandhi was the one who didn’t do as the british said, but instead stood against it because he knew that what they were doing was unfair. As he have said, “A man who was completely innocent, offered himself as a sacrifice for the good of others, including his enemies, and became the ransom of the world. It was a perfect act”. He disobeyed the british laws to free
Mahatma Gandhi: The Crucible Martyr
In conclusion, Mahatma Gandhi was the primary leader of India’s independence movement and also the architect of a form of non-violent civil disobedience that would influence the world. He died sadly in 1948 when. Around one million people followed the precision as Gandhi’s body was carried in state through the streets of the
Gandhi Speech Outline
Thesis: A true leader, an anti-war activist, and the leader of India’s independence movement, Mohandas Gandhi was a man of great significance.
Mahatma Gandhi Dbq Essay
British rule was tough on many Indians. Gandhi, an Indian born lawyer, believed in freedom and peace for his people. He once experienced racism when he was kicked out of a train in Europe. He changed people’s point of view without breaking the law, which was tough for him. Gandhi made his nonviolent movement work through the use of determination, peaceful civil disobedience, and being a powerful leader.
Rhetorical Analysis Of Gandhi Speech
Mahatma Gandhi was the leader of the Indian independence movement against British rule. He proposed a speech to all of his followers explaining what his resolution was to gain independence, without using violence. Mahatma Gandhi adopts a subtle and affirmative tone while revealing that non violence and the spreading of love is the way to approach this movement for independence. He also portrays his outline for the movement by appealing to the audience's emotions.
Nonviolence And Its Absolute Moral
Mahatma Gandhi pioneered the philosophy and practice of nonviolence. On the vast subcontinent of India he led a colonial people to freedom through Satyagraha, defeating what was at the time the greatest empire on earth, the
Mahatma Gandhi Research Paper
Aroused by the massacre of Amritsar in 1919, Gandhi devoted his life to gaining India’s independence from Great Britain. As the dominant figure used his persuasive philosophy of non-violent confrontation, he inspired political activists with many persuasions throughout the world (Andrews 23). Not only was Mahatma Gandhi a great peacemaker, but also his work to achieve freedom and equality for all people was greatly acknowledged. Gandhi’s unconventional style of leadership gained him the love of a country and eventually enabled him to lead the independence movement in India.
Osama Gandhi Research Paper
Gandhi was a civil rights leader who passively fought for equality in British ruled India. His full name is, Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi. He used non-aggressive tactics to gain rights from the British. Gandhi led India to independence, and inspired people to form civil rights movements across his birth country. His most famous march was the Dandi Salt March, in which Gandhi led Indians 250 miles to challenge the British’s tax on salt, this caused Britain to stop residing and controlling India.
Analysis Of Mahatma Gandhi, Robby Novak, And Farah Ahmedi
Mahatma Gandhi was a man who fought for India to be free from the British domination and equality for all. Gandhi was a shy lawyer who did not like
Gandhi's Civil Disobedience Movement
Mohandas Gandhi was known all over the world for his nonviolent philosophy of passive resistance. He returned to India from South Africa in 1914 and within years he emerged as a key figure in the Indian struggle for independence. Gandhi had the mindset that he was prepared to die in order to achieve this goal. Throughout…...Gandhi positively affected human society when completing his lifetime goals which were ending untouchability, uniting Hindus and Muslims in India and gaining independence from the British.
Research Paper On Gandhi The Great
Mahatma Gandhi led one of the biggest movements in the world and inspired others, therefore many people might not have the privileges that they have today if it weren't for him.
The Virtue Of Civil Disobedience
Mahatma Gandhi taught us what Christ and Buddha had longed to teach long ago. He became an immortal spirit who guides us through the path of peace and non-violence. Gandhi demonstrated acts of truth and non-violence in South Africa. The non-violent protest of Gandhi got huge popularity. It was here that he cultivated in him the idea of ‘Satyagraha’, which he was to put into practice afterwards, both in South Africa and India. In South Africa, Gandhi endeavored hard to secure for the colored people, including Indians who were domiciled there, equal rights with the White People. In this context he had to court imprisonment several times. After arriving in India, Mahatma Gandhi joined the Indian National congress, which was at that time more or less a social institution. He made Congress an organization, which was to play its vital role in the winning of the country’s independence. Before he joined the Congress and took its reins in his hands, it was predominantly an organization of the Upper Middle Class people. Mahatma Gandhi changed it into a mass-organization, in which the peasants began to take an active part. He firmly believed that freedom can be achieved in a peaceful manner. He wanted all his followers to always maintain truth and integrity. The principles of Ahimsa were practiced in all of the independence
Research Paper On Gandhi
Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi, better known as Mahatma Gandhi, was a prominent Indian leader who was influential in India’s struggle to gain independence from Great Britain. Gandhi led India to independence through non-violent methods of protesting. Gandhi’s peaceful approaches were later copied by great leaders such as Martin Luther King Jr. retaught by peace experts like Sissela Bok, and followed by ordinary people like Madeline Slade, which attested how powerful his legacy was. Mahatma Gandhi’s leadership and non-violent methods in India’s fight for independence influenced many great leaders after him, proving that Gandhi’s legacy lives on.
I - Gandhi led peaceful demonstrations against the British in order help gain independence for
How Did Mahatma Gandhi Use Of Nonviolence
Violence and war has been used throughout the existence of mankind to assert dominance, gain wealth, or to maintain one’s gained power. Mahatma Gandhi was an Indian man who fought for justice and equality in India by leading protests through peaceful means. He also openly advocated against the British’s rule in India. What made Gandhi so powerful was that he fought his adversaries using the unique technique of nonviolence. Nonviolence introduces the idea of “cowardice vs true strength” many leaders face today. Gandhi focused on these ideals mainly because of his early childhood and teachings from his mother. Gandhi was an influential
Related Topics
- Indian independence movement
- Indian National Congress
- British Raj
- Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi
- Jawaharlal Nehru

Essay on Mahatma Gandhi

Freedom is the need of every living thing on this earth. However, this freedom does not come free of cost. We feel proud to say that our country India is an independent country but when we say this, we also remember the story behind this freedom. This freedom cost us millions lives and thousands of struggles. Many people fought tirelessly to make India an independent country. Moreover, when we talk about India’s independence movement, the first name that strikes our mind is “Mahatma Gandhi”. Every child of India is well aware of this name. So, to discover more about this famous personality, let us discuss Mahatma Gandhi in detail.
Mahatma Gandhi Essay in English
Here, we are presenting long and short essays on Mahatma Gandhi in English for students under word limits of 100 – 150 Words, 200 – 250 words, and 500 – 600 words. This topic is useful for students of classes 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, and 12 in English. These provided essays will also be helpful for students to write essay, speech, or paragraphs on this topic.
10 Lines Essay on Mahatma Gandhi (100 – 120 Words)
1) Mahatma Gandhi, born on October 2, 1869, was an Indian political leader.
2) His mother was Putlibai and father was Karamchand Gandhi.
3) He played a vital role in India’s struggle for independence against British rule.
4) He led several peaceful protests and movements, including the famous Salt March.
5) His beliefs and teachings inspired many other civil rights leaders around the world.
6) He was imprisoned numerous times for his protests against violence and injustice.
7) Gandhi was against the British rule and he worked hard to get India’s freedom.
8) Gandhi is widely known for his philosophy of nonviolence and civil disobedience.
9) He was shot on 30 January 1948 at 5:17 pm by Nathuram Godse.
10) Gandhi inspires people worldwide to fight for peace, justice, and equality.
Essay on Mahatma Gandhi (250 – 300 Words)
Introduction
Mahatma Gandhi is one of the most important people in India’s movement for independence. Mahatma Gandhi, Gandhi ji, father of the nation, bapu, etc are the various names of our beloved freedom fighter Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi.
Mahatma Gandhi: The Father of the Nation
Mahatma Gandhi was born in Porbandar, Gujarat on 2 nd October 1869 to Karamchand Gandhi and Putlibai. Mahatma Gandhi was an Indian writer, politician, lawyer, and social worker. Gandhi is often called the “Father of the Nation” in India, because his tireless efforts and selfless fight for freedom made him an advocate of the oppressed people. He supported civil resistance that didn’t involve violence and promoted the idea of Satyagraha, which means “the force of truth.”
Role of Gandhi in Independence Movement
Gandhi’s contribution to the Indian independence movement cannot be overstated. He believed that India could only achieve true freedom through non-violence and civil disobedience. In 1919, Gandhi called for a nationwide strike in protest against the Rowlatt Act. This led to widespread protests and marked the beginning of Gandhi’s mass civil disobedience campaigns. Gandhi organized several significant movements such as the Salt March in 1930. These movements got the attention and support of most Indians and were a key part of getting the country independence.
Gandhi’s ability to lead and his unwavering dedication to his cause have made him a true freedom fighter. His strategy of using nonviolence and civil disobedience to win freedom is still a great example of how peaceful resistance can change politics. As we remember and honor the “Father of the Nation,” let’s try to live by his values of truth, nonviolence, and social justice to make the world a better place for everyone.
Long Essay on Mahatma Gandhi (500 Words)
Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi, who was also known as Mahatma Gandhi, was an important leader in India’s fight for freedom. Gandhi was not only a political leader but also a great thinker and philosopher. His nonviolent approach to fighting injustice inspired individuals and movements around the world and continues to be remembered as a symbol of peace and resistance.
Mahatma Gandhi: Early Life
Gandhi was born on October 2, 1869, in Porbandar, Gujarat to Karamchand Gandhi and Putlibai. In May 1883, Mohandas, who was 13 at the time, got married to Kasturba devi, who was 14. He received his formal education in India and later studied law in London. Gandhi faced discrimination during his time in South Africa, which became a turning point in his life. This experience prompted him to fight for justice and equality, not only for Indians but for all oppressed people. When he got back to India, he became a well-known leader of the Indian National Congress.
Principles or Ideology of Gandhi Ji
Gandhi’s thought was based on the ideas of nonviolence, truth, and not caring about yourself. He thought that Satyagraha, a movement of nonviolent protest, could bring about social and political change. Gandhi was sure that violence leads to more violence and that kindness and understanding are the only ways to solve problems without violence. His ideas highlighted the value of being kind, forgiving, and loving to one’s enemies.
Contributions of Mahatma Gandhi
Gandhi’s contributions to the Indian independence movement were immense. He played a pivotal role in organizing mass protests, strikes, and boycotts against British rule. The Salt March, which he led in 1930, is widely regarded as one of his most significant accomplishments. This act of civil disobedience sparked international attention and brought the Indian independence movement to the forefront. Other than this, Gandhi ji also led Champaran and Kheda Agitations, Non-cooperation Movement, Quit India Movement, etc. He was also an advocate for women’s rights. He believed in gender equality and fought against social norms that oppressed women.
Legacy of Mahatma Gandhi
Gandhi’s idea of nonviolent resistance inspired leaders like Martin Luther King Jr. and Nelson Mandela to fight for human rights and equality. Truth and sincerity are still seen as important values for people who want to live in a fair and peaceful society. However, we lost this gem on 30 January 1948. Nathuram Godse, an extremist Hindu, shot and killed Mahatma Gandhi. The news of his death was felt all throughout the world. In India, 2 nd October is seen as Gandhi Jayanti and is a national holiday.
Mahatma Gandhi’s effect on the world cannot be overestimated. His peaceful way of fighting for freedom not only led to India’s independence but also changed the course of history for oppressed people all over the world. Gandhi’s ideas and teachings continue to inspire people and groups that work for peace, justice, and equality. Mahatma Gandhi will always be remembered as a sign of hope and courage in the face of hardship.
I hope the above provided essay on Mahatma Gandhi will be helpful in understanding his contribution for this country.
FAQs: Frequently Asked Questions on Mahatma Gandhi
Ans. Nathuram Godse killed Mahatma Gandhi, a spiritual leader known as the “Great Soul of India,” when he was 78 years old. “Hey Ram” were the last words Mahatma Gandhi spoke before he died from the gunshot.
Ans. On January 30, 1948, after a prayer gathering in New Delhi, Mahatma Gandhi was killed, he was 78 years old. At point-blank range, three bullets were shot into his chest and stomach.
Ans. Satyagraha was the most important tool Mahatma Gandhi used to fight the British and free India. The concept of Satyagraha was created by Mahatma Gandhi. It is a form of civil protest that doesn’t use violence.
Ans. “Mahatma,” which means “great soul,” was a name that people used to call Gandhi. Rabindranath Tagore, a poet and philosopher from Bengal, gave him this title.
Ans. Mahatma Gandhi hasn’t won either the Bharat Ratna or the Nobel Prize, but he was named 5 times for the Nobel Peace Prize between 1937 and 1948. The Court said that Gandhi Ji and the things he did will live on forever. Any award, including the Bharat Ratna, will hurt his reputation.
Related Posts
Essay on digital india, cashless india essay, essay on child is father of the man, essay on causes, effects and prevention of corona virus, essay on dr. sarvepalli radhakrishnan, durga puja essay, essay on summer vacation, essay on my plans for summer vacation, essay on holiday.
As a rising global power, what is India’s vision for the world?

India has the opportunity to put in place a new framework for its own security and growth, and that of developing countries around the world. Image: REUTERS
.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo{-webkit-transition:all 0.15s ease-out;transition:all 0.15s ease-out;cursor:pointer;-webkit-text-decoration:none;text-decoration:none;outline:none;color:inherit;}.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo:hover,.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo[data-hover]{-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;}.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo:focus,.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo[data-focus]{box-shadow:0 0 0 3px rgba(168,203,251,0.5);} Samir Saran
.chakra .wef-9dduvl{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-size:1.25rem;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-9dduvl{font-size:1.125rem;}} Explore and monitor how .chakra .wef-15eoq1r{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-size:1.25rem;color:#F7DB5E;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-15eoq1r{font-size:1.125rem;}} India is affecting economies, industries and global issues

.chakra .wef-1nk5u5d{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;color:#2846F8;font-size:1.25rem;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-1nk5u5d{font-size:1.125rem;}} Get involved with our crowdsourced digital platform to deliver impact at scale
Stay up to date:.
Seventy-one years ago – on 15 August 1947 – India gained independence. Over the subsequent decades, the country has managed its evolution in an international system largely created and guided by the United States and its partners. While it was not easy for India to pursue independent domestic and foreign policies within this system, the American-led order was preferable to the British Empire from which New Delhi had liberated itself.
Today, this global system is under serious threat. Washington, along with capital cities across the European Union, finds itself caught in a polarizing debate on the social contracts of its society – questions of domestic inequality and identity have left the US and its allies incapable of effectively championing the values of the international order. Simultaneously, the balance of global economic power has once again tipped in favour of Asia.
Within this shifting global landscape, India has the opportunity to put in place a new framework for its own security, growth and development, and that of developing countries around the world. As a rising global power, this must be India’s principle endeavor in the coming decades.
The changing international order
The extraordinary rise of countries in Asia has spawned at least two new dynamics. First, political boundaries – many of them colonial legacies – are steadily becoming more porous through economic cooperation. Markets are converging across the Eurasian landmass as well as facilitating the geo-economic “union” of the Indian and Pacific oceans. This has resulted in new integrative dynamics; as cultures, markets and communities aspire for development and new opportunities. Second, even though territorial considerations acknowledge economic linkages, political differences are still being reasserted – not just to contest the consensus of the past, but to shape a new order altogether.
Asia is coming together economically but is also threatening to grow apart politically; market-driven growth in the region sits uneasily with a diverse array of political systems.
China is, in large part, responsible for both. While offering a political vision that stands in sharp contrast to the “liberal international order”, China has been equally assertive about advancing free trade, raising new development finance, and offering a new model for development and global governance. The prospect of China using its economic clout to advance its own norms is worrying for India.

A consensus to shape a new order
Given the velocity of change underway, the challenge for India on its Independence Day is to shape an inclusive and equitable international order by the centenary of its independence. To achieve this, India must prepare to act according to its capabilities: by mid-century it must build the necessary state capacity, industrial and economic heft and strategic culture that would befit its status as a leading power. The country could present this as a model for much of the developing world to emulate, and anchor faith in the liberalism and internationalism of the world order.
India, then, requires a “consensus” – a new proposition that will not only guide its own trajectory for the better part of the 21st century, but one that appeals to communities around the world.
What then are the tenets of a “New Delhi Consensus”?
First, India must sustain and strengthen its own trajectory of rapid economic growth, and show to the world that it is capable of realizing its development goals within the rubric of liberal democracy. No argument for the New Delhi Consensus can be more powerful and alluring than the economic success of India. By IMF estimates, India already accounts for 15% of global growth. Even though nearly 40% of its population live in various shades of poverty and barely a third are connected to the internet, India is still able to proportionately shoulder the world’s economic burden. Imagine the possibilities for global growth if India can meet, and even exceed, the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
States in the developing world yearn for replicable templates of growth, yet they find themselves with a binary choice between Western democracy, which is ill suited for deeply plural and socially stratified societies, and autocratic systems that have little room for individual freedom.
India, on the other hand has “emerged as a bridge between the many extremes of the world”, as former Prime Minister Manmohan Singh once remarked . India’s plural and composite culture, he said, was “living proof of the possibility of a confluence of civilizations”. The global 2030 development agenda, for the most part, may as well be a story of India’s domestic economic transformation and of its defence of diversity and democracy.
Second and flowing from the above, Delhi must claim leadership over the global development agenda. It is worth pointing out that India sits at the intersection of the world’s two most dynamics regions, Eurasia and the Indo-Pacific. The largest bulk of development finance will emerge from, and be invested in, these regions. It is incumbent on India to ensure that this is not a new means to maximize political interference, but a moment to offer unfettered opportunities.
In his recent address to the Ugandan Parliament, Prime Minister Narendra Modi affirmed that “India’s development partnership will be guided by [African] priorities” – a position that contrasts sharply with the West’s evangelical focus on governance reforms and China’s economic policies in the region. India’s recipient-led partnership framework will allow states to secure development pathways that are economically sustainable and politically acceptable. India now needs to articulate its intentions and the principles that will shape international development cooperation in the days ahead.
Third, Delhi must create and protect the space for equitable and inclusive global governance. For too long, leadership in the international system was considered a free pass to monopolize the global commons. India has always bucked this trend, emerging as a leading power that has never tempered its idealism of “having an interest in peace, and a tradition of friendliness to all”, as one official put it. Whether it is on free trade, climate change or international security, India’s non-interventionist and multilateral approach is well suited to support and sustain global governance in a multipolar world: the new reality of this century.
Finally, India must incubate a new social contract between its own state, industry and civil society. At the turn of the century, former Prime Minister Atal Bihari Vajpayee lamented that India’s democratic growth was held back by three failures: of the government to heed industry voices, of industry to appreciate the objectives of government, and of both in their commitment to the common individual.
Nearly two decades later, the imperative for India to correct these failures is even greater. The spread of information communication technologies and global supply chains implies that businesses and civil society must be made equal stakeholders if India is to develop its own unique consensus. Not only will this add greater legitimacy to India’s proposition, it will also create natural and grassroots champions for the country around the world.
For the first time since the end of the Second World War, a nation state that is wary of hegemonic tendencies and identifies itself with the equitable governance of the global commons is in a position to shape the international order. India is home to one-sixth of the global population and has sustained a unique democratic ethos and a foreign policy that is defined not only by national interest but also by solidarity with the developing world.
As a leading power, India must look beyond raw indexes of economic, political and military might, and craft a consensus that is consistent with its ancient and historic view of the world.
Have you read?
Narendra modi: these are the 3 greatest threats to civilization , this is how much the global economy will grow in 2018, according to the imf, where will future economic growth come from, don't miss any update on this topic.
Create a free account and access your personalized content collection with our latest publications and analyses.
License and Republishing
World Economic Forum articles may be republished in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International Public License, and in accordance with our Terms of Use.
The views expressed in this article are those of the author alone and not the World Economic Forum.
The Agenda .chakra .wef-n7bacu{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-weight:400;} Weekly
A weekly update of the most important issues driving the global agenda
.chakra .wef-1dtnjt5{display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;-webkit-flex-wrap:wrap;-ms-flex-wrap:wrap;flex-wrap:wrap;} More on Geographies in Depth .chakra .wef-17xejub{-webkit-flex:1;-ms-flex:1;flex:1;justify-self:stretch;-webkit-align-self:stretch;-ms-flex-item-align:stretch;align-self:stretch;} .chakra .wef-nr1rr4{display:-webkit-inline-box;display:-webkit-inline-flex;display:-ms-inline-flexbox;display:inline-flex;white-space:normal;vertical-align:middle;text-transform:uppercase;font-size:0.75rem;border-radius:0.25rem;font-weight:700;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;line-height:1.2;-webkit-letter-spacing:1.25px;-moz-letter-spacing:1.25px;-ms-letter-spacing:1.25px;letter-spacing:1.25px;background:none;padding:0px;color:#B3B3B3;-webkit-box-decoration-break:clone;box-decoration-break:clone;-webkit-box-decoration-break:clone;}@media screen and (min-width:37.5rem){.chakra .wef-nr1rr4{font-size:0.875rem;}}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-nr1rr4{font-size:1rem;}} See all

How MENA’s biggest actors can help the region’s suppliers and SMEs to decarbonize
Akram Alami and Kelsey Goodman
May 27, 2024

The Horn of Africa's deep groundwater could be a game-changer for drought resilience
Bradley Hiller, Jude Cobbing and Andrew Harper
May 16, 2024

Scale matters more than ever for European competitiveness. Here's why
Sven Smit and Jan Mischke
May 15, 2024

Funding the green technology innovation pipeline: Lessons from China
May 8, 2024

These are the top ranking universities in Asia for 2024

Global South leaders: 'It’s time for the Global North to walk the talk and collaborate'
Pooja Chhabria
April 29, 2024

Incredible India Essay for Students and Children
500+ words essay on incredible india.
India represents “Unity in Diversity” . Our country is a mixture of cultures, regions, traditions, diversity in food, languages, etc. Our people of India are so polite, understanding and helping in nature. The national bird of India is Peacock and is very beautiful. India is so incredible and is full of colors and has the tiger as its national animal, hockey as its national game, etc. the national language or mother tongue of our country is Hindi. Indians are also so talented and have shown very high growth. The I.T. sector of our country shows accelerating growth due to intelligent software engineers.

India As a Country
India is the seventh-largest country by its geographical area and is located in South Asia. The beauty surrounds our country from each and every aspect. India is also known by two other names Bharat and Hindustan and the people of India are known as Indians. The national anthem of our country is “ Jan Gan Man ” and the national song of our country is “Sare Jahan Se Achcha”.
India is a Democratic country where people themselves choose their leader and live with freedom i.e. they can do anything they wish to within the limits of the law. If any citizen of India tries to harm any other person, there are also rules and regulations to punish him in order to make him realize his mistake.
Our country is also incredible because of its beautiful mountains, lakes, forests , seas, oceans, etc. Many foreigners each year visit India to see the beauty of our country that is its rich historical temples, its traditions, its language, its heritage, etc.
Different Regions of India
North region.
North Region consists of the most incredible thing in the world that is The Himalayas which is the highest mountain in the world. This region also consists of the beautiful Kashmir covered with mountains. It consists of Uttar Pradesh which is mainly known as the land of Krishna, land of Rama, etc. This region also consists of one of the wonders of the world i.e. Taj Mahal which people come to visit across the world.
Southern Region
This is the “Land of Nawabs”. It is famous for its festivals, food, and languages. The place is famous for its rice dishes. This region consists of cities like Kerala, Tamil Nadu, and Karnataka, etc.
East Region
East part of India consists of West Bengal, Jharkhand, Bihar, Odisha, etc. The capital of West Bengal, Kolkata is the largest city of this section and is the metropolitan city and is the third’s largest city in the country. Kolkata is known for its sweetness and festival.
West Region
The West part of the country is really incredible as it is covered with sands and deserts. Rajasthan, Gujarat, and Maharashtra are the three most amazing places in this region. The culture, the language, the traditions and the clothes of this region are incredible and you will love to visit this region.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
Indian Culture and Religion
India’s culture is among the world’s oldest; civilization in India began about 4,500 years ago. India has 29 states with different culture and civilizations and one of the most populated countries in the world. The Indian culture, often labeled as a mixture of several various cultures.
India gave birth to Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism, Sikhism, and other religions. They are now collectively known as Indian religions. Today, Hinduism and Buddhism are the third and fourth-largest religions respectively of the world. Although India is a secular Hindu-majority country, it has a large Muslim population.
India, being a multi-cultural, multi-ethnic and multi-religious society, celebrates holidays and festivals of various religions. Major festivals include Diwali, Durga puja, Holi, Ganesh puja, Navratri, Rath yatra, etc are there round the year.
Indian food is a cosmopolitan cuisine that has so many ingredients. It is as diverse as India. Indian recipes use numerous ingredients, deploy a wide range of food preparation styles, cooking techniques, and culinary presentation. Thus the tastes of same food like salads, sauces, vegetables, meat, desserts vary from region to region.
We are proud of our cultural distinctiveness. We are proud to be the inhabitants of India. It is our duty to maintain its unique feature. We have to think beyond the petty interests and work for the broader goals of bringing prosperity and progress in society.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

143 Words Essay on my Favorite Leader or a Great Indian Leader
Mahatma Gandhi is my favourite leader. He is called the Father of the Nation. He raised his voice against the British rulers. India got freedom under his leadership.
He was born on October 2, 1869 at Porbandar in Gujarat. His father was the Diwan of Rajkot. His mother’s name was Putlibai. He got his early education at Rajkot. After passing his matriculation, he went to England for higher studies.
He returned from England as a lawyer. He then went to South Africa. In South Africa he worked to improve the condition of Indians living there. He returned to India and took part in the Indian Freedom Movement.
Truth and non-violence were his great weapons. He worked to remove poverty, economic inequality and untouchability. After Independence, he worked for Hindu- Muslim unity. On 30th January 1948, he was shot dead by Nathu Ram Godse.
Related Articles:
- Short Paragraph for kids on my Favourite Leader
- 206 Words Short Essay on My Favourite Leader
- 142 Words Short Paragraph for kids on Mahatma Gandhi
- 224 Words Essay for Kids on Mahatma Gandhi
What to Know About India’s Enormous Election: How It Works and What’s at Stake
What’s set to be the largest election in history is wrapping up in the world’s largest democracy, with Prime Minister Narendra Modi vying for a third term. Here’s what you need to know.
India's Massive Election, Explained

Altaf Qadri | AP
People gather to vote during the first round of polling in India's national elections in Chennai, in the southern state of Tamil Nadu, on April 19. Voting for more than 500 seats in the country's lower house of Parliament wraps up on June 1.
It’s expected to be the largest democratic vote in human history, and it takes place over a full six weeks: In April, nearly a billion eligible voters in India began casting ballots in the country’s general election, which will determine both its next prime minister and the makeup of its larger legislative body.
Did You Know?
There’s a lot at stake. For the past 10 years, India – which is roughly 80% Hindu but also home to some 200 million Muslims as well as Christians, Sikhs, Buddhists and other religious minorities – has been ruled by the Bharatiya Janata Party , a generally right-wing, socially conservative party that advocates for Hindu nationalism .
It’s a vision of India in which “Hinduism and Indian national identity are more or less synonymous,” as one South Asia scholar put it, and for years the BJP has been growing more forceful in rhetoric and policy, leading to criticism that it’s eroding democracy, persecuting minorities and violating human rights . In January, marking one of the country’s biggest religious controversies in recent memory, party leaders celebrated the opening of a new Hindu temple built atop the ruins of a historic mosque. Weeks later, the government implemented a new migrant citizenship law designed to exclude Muslims.
The World’s Most Populous Countries

The moves fall in line with a yearslong charge led by Narendra Modi , India’s popular – and populist – prime minister who is seeking a third term in this year’s election. Modi and his BJP are up against a coalition called the Indian National Developmental Inclusive Alliance, or INDIA, which is led by the Indian National Congress – the onetime party of Mohandes Gandhi and Pandit Nehru that held power for much of the 20th century. The coalition’s leaders say they’re running to save Indian democracy .
The final day of voting is Saturday, June 1, with results slated for counting on Tuesday, June 4. Here’s what else you need to know about the massive election in the world’s most populous country .
Who Is on the Ballot?

Manish Swarup | AP
K. Datta, 91, reviews a ballot paper before casting his vote from his home in New Delhi on May 17. To encourage and assist the elderly to vote, Indian authorities put in place a home voting program for the general elections.
Modi, of course, is by far the biggest name. The 73-year-old prime minister, who was born in the western state of Gujarat and formerly served as that state’s chief minister, now represents a parliamentary region that includes Varanasi – a northern city on the Ganges River that’s deeply important to Indian Hindus. Modi’s opponents for the Varanasi seat include Ajay Rai, a former BJP member who now represents the Congress party, and Athar Jamal Lari, a political veteran from the Bahujan Samaj Party, which aims to represent religious and other minorities.
But that’s just one race out of 543 to decide members of the Lok Sabha, the country’s lower and larger house of Parliament. (The country uses a “first past the post” system, where the candidate with the most votes wins the seat.)
In Uttar Pradesh – the country’s most populous state, which accounts for 80 Lok Sabha seats – one key race pits Akhilesh Yadav, leader of the socialist Samajwadi Party, against an incumbent from the BJP.
In Maharashtra, the heavily populated state that includes Mumbai, 48 seats are up for grabs, with candidates representing a mix of allegiances tied to major national parties as well as more regional parties like Shiv Sena, a far-right party founded in the 1960s as a reaction against migrants who were coming to the region from other Indian states.
In West Bengal, which includes Kolkata, a party called the All India Trinamool Congress – a breakaway from the Congress party – previously dominated but has been forced to grapple with the ascension of the BJP.
How Does Voting Work?

Polling officials carry electronic voting machines on the eve of the sixth phase of national elections in New Delhi on May 24.
India has broken the massive voting operation into seven different phases of one day each. The process kicked off on April 19, and various constituencies are allotted to each phase: Phase 4, for example, took place on May 13 and included races to represent more than 90 constituencies in nine of India’s 28 states, plus one territory. The election is poised to be India’s second-longest ever, following its first elections in the early 1950s, which lasted close to four months .
Voting is carried out with the help of millions of election workers and is generally electronic , though alternative postal ballots are available for some , including people with disabilities and older voters . The process is intensely local: Because India mandates that citizens not have to travel more than 2 kilometers – or 1.2 miles – to vote, workers sometimes trudge through rough or vast terrain to reach rural voters. That includes getting to the remote village of Malogam, near the country’s border with China, where a team of officials reportedly hiked roughly 40 kilometers to reach a single 44-year-old voter named Sokela Tayang .
India reportedly deployed hundreds of thousands of members of its federal security forces to keep the peace during voting and to help transport voting machines around the country.
What Major Issues Are at Play?

Muslims offer prayers at a mosque in New Delhi on April 11. Violence against Muslims, who account for 14% of the population, is common in India. The Associated Press reports Muslims have been lynched by Hindu mobs over allegations of eating beef or smuggling cows, an animal considered holy to Hindus. Their homes and businesses have been bulldozed , and their places of worship set on fire .
The issue of Hindu nationalism is central. So is what’s widely viewed as Modi’s increasing authoritarianism: Ahead of the election, the opposition Congress party had its bank accounts frozen by the Modi-led government, though the BJP countered the move was made due to tax evasion. Opposition leader Arvind Kejriwal , the chief minister of New Delhi, also was arrested on corruption charges and later released on bail. His stint in custody included a strange dispute involving mangoes and blood sugar levels.
Modi opponents claim the actions were politically motivated, and concerns persist that another Modi victory is likely to bring still more anti-democratic shifts for the world’s largest democracy, even as he boasts of helping the poor and wins followers with a savvy populism message.
Power has been centered “around the cult of the leader’s personality,” policy analyst Yamini Aiyar told The New York Times . And “the deep centralization of power has significantly undermined institutional checks and balances baked into India’s democratic structure.”
Another big issue is jobs and the economy: While the country’s gross domestic product and stock market have seen strong growth over the years, benefiting corporations and ushering many Indians into a better life, inequality remains stark, and many others are underemployed and destitute. The Congress party ahead of the election unveiled a platform that includes plans to create manufacturing jobs and implement a new cash transfer program for poor families. Modi, meanwhile, has sought to benefit in the election from his government’s expansion of welfare programs .
How Has Voting Gone So Far?

A woman checks the ink mark on her index finger after casting her vote in the general election in Agra, in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh, on May 7.
In late April, voting in Manipur, a northeastern state that’s been wracked by Hindu-Christian ethnic tensions, was marred when armed men raided polling stations and damaged voting machines, prompting authorities to order a revote at 11 stations. Indian media also have reported violence in West Bengal, a state with a history of election clashes , as well as several violent incidents, including stone pelting, in Andhra Pradesh .
But much of the surrounding season has been peaceful and even exuberant, with supporters of various parties attending political rallies and roadshows . There’s a reason the weekslong vote has been called “a festival of democracy.”
India currently has around 970 million eligible voters. In 2019, the last year the country held Lok Sabha elections, it saw a figure closer to 900 million, and a record 67% ended up casting ballots.
This year’s turnout was on track to be at least a bit lower: As reported by The Times of India , the first three phases saw turnouts of around 66%, while the fourth phase reached a mark over 69%. Turnout then fell to 62% and 63% for the fifth and sixth phases, respectively, averaging out to about 65.5%. Voters notably have had to grapple with extreme heat amid the process.
An overall turnout of 66% this year, however, still would mean more voters overall than in 2019, making this the largest election in history.
Who’s Favored to Win?

Mahesh Kumar A. | AP
Bharatiya Janata Party supporters carry portraits of Prime Minister Narendra Modi as they attend a rally in Hyderabad, India, on May 10.
Modi and the BJP – potentially by a landslide. After securing a majority in the Lok Sabha in 2014 by winning 282 seats, Modi’s party improved on that total in 2019, winning 303 seats and securing dozens more through its allies.
This time around, the party has set its sights on securing 400 seats, which would allow it to further cement its grip on power and has been tied to speculation that it might try to change the country’s constitution .
Analysts expect Modi and the BJP to indeed secure another victory, though lower turnout, potential apathy and stronger-than-expected opposition could make such a supermajority less likely.
Join the Conversation
Tags: India , elections , world news , politics , Best Countries
Recent Articles
Best countries.

World Report

Best Countries Rankings
- # 1 Switzerland
- # 5 Australia
- # 5 United States
Health News Bulletin
Stay informed on the latest news on health and COVID-19 from the editors at U.S. News & World Report.
Sign in to manage your newsletters »
Sign up to receive the latest updates from U.S News & World Report and our trusted partners and sponsors. By clicking submit, you are agreeing to our Terms and Conditions & Privacy Policy .
You May Also Like
Switzerland is world's best country.
Julia Haines Sept. 6, 2023

Photos: Best Countries Around the World
Sept. 6, 2023

The 25 Best Countries in the World
Elliott Davis Jr. Sept. 6, 2023

Security Tight in China and Hong Kong on Tiananmen Crackdown Anniversary
Reuters June 3, 2024

Taiwan President Says Tiananmen Crackdown Will Never Be Forgotten

- Today's news
- Reviews and deals
- Climate change
- 2024 election
- Fall allergies
- Health news
- Mental health
- Sexual health
- Family health
- So mini ways
- Unapologetically
- Buying guides
Entertainment
- How to Watch
- My watchlist
- Stock market
- Biden economy
- Personal finance
- Stocks: most active
- Stocks: gainers
- Stocks: losers
- Trending tickers
- World indices
- US Treasury bonds
- Top mutual funds
- Highest open interest
- Highest implied volatility
- Currency converter
- Basic materials
- Communication services
- Consumer cyclical
- Consumer defensive
- Financial services
- Industrials
- Real estate
- Mutual funds
- Credit cards
- Balance transfer cards
- Cash back cards
- Rewards cards
- Travel cards
- Online checking
- High-yield savings
- Money market
- Home equity loan
- Personal loans
- Student loans
- Options pit
- Fantasy football
- Pro Pick 'Em
- College Pick 'Em
- Fantasy baseball
- Fantasy hockey
- Fantasy basketball
- Download the app
- Daily fantasy
- Scores and schedules
- GameChannel
- World Baseball Classic
- Premier League
- CONCACAF League
- Champions League
- Motorsports
- Horse racing
- Newsletters
New on Yahoo
- Privacy Dashboard
Who will lead India? World’s largest nation begins a mammoth day of vote counting after weeks-long election
Hundreds of millions of votes cast, more than six weeks of polling, and billions of dollars spent: India on Tuesday will declare a new leader after a mammoth nationwide election that has become a referendum on the last decade of leadership by Prime Minister Narendra Modi.
His powerful right-wing Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) is seeking a supermajority in the lower house of parliament – or Lok Sabha – a goal which, if successful, would give it an unstoppable mandate to further enshrine its Hindu-nationalist agenda, deepening India’s move away from its secular foundations .
Given India’s strategic position in Asia and its booming economy, the election result will reverberate far beyond its borders, capturing the attention of the United States, China and Russia in particular.
Some 642 million people cast their vote in the world’s largest election, as swathes of the country was blanketed in searing heat, making people sick and killing dozens.
Hoping to unseat India’s charismatic but divisive leader is an alliance of more than two dozen parties, including the country’s main opposition, the Indian National Congress, which is running on a platform of reducing inequality and upholding democratic institutions which it argues are at risk.
Since assuming power in 2014, Modi has attained levels of popularity not seen in decades, owing to a raft of development and welfare programs, mixed with a strident brand of Hindu nationalism in a country where about 80% of the population are followers of the polytheistic faith.
Under Modi’s leadership, the country of 1.4 billion people has become the world’s fastest-growing major economy and a modern global power, making strides in technology and space. Yet, despite these successes, poverty and youth unemployment persist – particularly in rural areas – and the wealth gap has widened.
Critics also say a decade of Modi’s governance has led to growing religious polarization, with Islamophobia marginalizing much of the country’s more than 200 million Muslims, and religious violence flaring up in a nation with a long history of communal tensions.
Polling began on April 19 and ended on June 1. Nearly 1 billion Indians were eligible to vote for 543 seats in the lower house of parliament. The leader of the party that wins a majority will become prime minister and form a ruling government.
Modi has set an ambitious target of securing a 400-seat supermajority, with 370 directly controlled by his BJP – up from 303 in 2019 – and the others from its National Democratic Alliance.
His BJP centered its manifesto on job creation and anti-poverty programs, with a focus on women, the poor and farmers. He’s promised to turn India into a developed nation by 2047 and transform the country into a global manufacturing hub.
Yet, on the campaign trail, he has been accused of deploying openly divisive rhetoric that has been condemned as Islamophobic, while casting himself as an instrument chosen by God.
Modi sparked a row over hate speech when he accused Muslims – who have been part of India for centuries – of being “infiltrators,” and echoing a false conspiracy voiced by some Hindu nationalists that Muslims are displacing the country’s Hindu population by deliberately having large families. His BJP released several political videos targeting Muslims, one of which is under investigation by police.
Congress has governed India for much of its independent history, having been instrumental in ending nearly 200 years of British colonial rule. But over the last decade, it has struggled to find relevance – partly due to a series of corruption scandals and infighting – unable to break through Modi’s popularity.
Rahul Gandhi, the son of the famed Gandhi dynasty, is the face of the party but lost the past two elections to Modi. He is contending once again from the southern state of Kerala and the crucial state of Uttar Pradesh in the north, also India’s most populous.
Opposition leaders and parties have faced a slew of legal and financial challenges in the run-up to this year’s election, with many accusing the BJP of using state agencies to stifle opponents.
The arrest in March of the popular Aam Aadmi Party leader, chief minister of Delhi and staunch Modi critic Arvind Kejriwal sparked protests in the capital and prompted claims of a political “conspiracy” by his party – claims the BJP has denied.
Kejriwal’s release on interim bail last month galvanized the opposition to put up a tough fight against the BJP, uniting a group of political leaders who were once divided over ideological differences.
The Congress’ manifesto has also been dubbed one of India’s most progressive, pledging “freedom from fear” and vowing to protect freedom of speech, expression and religious belief espoused in the constitution.
Turnout across all seven phases has slightly dipped from the record highs of 2019, yet India’s general election remains the largest exercise in democracy, with hundreds of millions showing up to determine who will lead the world’s most populous country.
For more CNN news and newsletters create an account at CNN.com
Recommended Stories
Texans wr tank dell opens up for first time about being shot: 'wrong place, wrong time'.
C.J. Stroud joined Dell on a podcast appearance and described the moment he heard that Dell had been shot.
How the Supreme Court could upend the other criminal cases against Trump
The United States Supreme Court is expected to issue a ruling at any time on whether the principle of presidential immunity protects former President Donald Trump from prosecution in the federal election interference case brought by special counsel Jack Smith.
TechCrunch Space: China's victory
Unfortunately, Boeing's Starliner launch was delayed yet again, this time due to issues with one of the three redundant computers used by United Launch Alliance, the rocket provider, to initiate the launch sequence. According to some other space CEOs, the answer is yes.
Report: Astros pitcher Jose Urquidy expected to undergo Tommy John surgery
Houston Astros pitcher Jose Urquidy is expected to undergo Tommy John surgery after he receives a second opinion on MRI results for forearm tightness.
How to transfer Apple Cash to your bank account
If you have a positive Apple Cash balance, you may want to transfer funds to your bank account. Here are the steps for transferring Apple Cash, plus the costs and timeline.
Don't miss StrictlyVC in DC next week
Coming off of sold-out events in London, Los Angeles, and San Francisco, we're heading to Washington, D.C. for a cozy-vc-packed, evening at the Woolly Mammoth Theatre on Tuesday, June 11 in partnership with Revolution. Attendees can look forward to thought-provoking discussions, insightful perspectives, and plenty of chances to network—all while enjoying complimentary drinks and hors d'oeuvres.
French Open 2024: How to watch the Carlos Alcaraz vs. Stefanos Tsitsipas match
It's time for the clay court Grand Slam at Roland Garros. Here's how to tune into Alcaraz vs. Tsitsipas.
25 best gifts for your father-in-law for Father's Day and beyond
June 16 is right around the corner, and you don't want to forget about your 'other' dad!
French Open 2024: How to watch the Iga Swiatek vs. Markéta Vondroušová match
It's time for the clay court Grand Slam at Roland Garros. Here's how to tune into Swiatek vs. Vondroušová.
Conor McGregor issues statement after UFC press conference with Michael Chandler is postponed
A press conference to promote the UFC 303 match between Conor McGregor and Michael Chandler was postponed, fueling speculation as to how the fight might be affected.
'Looks pristine': This robot pool cleaner is a crystal-clear steal at 40% off
According to one fan, it took five days of clouds and rain before this snazzy swimmer ran out of juice.
You can now customize your For You feed on Threads using swipes
Threads, Meta's Twitter/X competitor and the company's first bet on decentralized social media, is now making it easier for users to control their Threads experience. After launching a customizable dashboard interface last week, Instagram head Adam Mosseri announced Monday that the app is now rolling out the ability for users to signal which sort of posts they wanted to see more or less of. Users would "swipe right on a post to like it, or swipe left to show you're not interested," Mosseri explained in a post on Threads.
The GameStop trade remains frothy and risky as retail investors flock back to meme stocks
Retail investor favorite Keith Gill is back, and so is the meme frenzy. But Wall Street pros caution investors to think twice before buying.
GameStop stock soars after 'Roaring Kitty' reveals $175 million bet on the retailer
GameStop stock surged as a Reddit user linked with its biggest booster appeared to reveal a new bold bet on the video game retailer late Sunday.
Stock market today: Nasdaq rises, Dow slumps in bumpy trading day as GameStop rallies
US stocks are looking to build on their strong performance in May as hopes for rate cuts revive and the meme stock mania roars back.
Father's Day gift ideas for any budget at Dick's Sporting Goods
Save on Father's Day gifts from Yeti, adidias, Callaway, Under Armour, Nike, and more - including up to 43% off Nike clothing while supplies last.
Fauci testifies before Congress for first time since leaving government: 5 takeaways from the hearing
The 83-year-old former director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases sought to debunk conservative conspiracy theories about his response to COVID-19.
What to expect from Apple's AI-powered iOS 18 at WWDC
Apple's Worldwide Developers Conference next week promises to be a pivotal moment in the iPhone maker's history. Among the changes, Apple is said to be powering some of its new AI features with its Ajax LLM. Other reports indicate that Apple plans to process data from AI in a way that even employees won't be able to access, which would help Apple continue to deliver on its promise of data privacy for its users.
After raising $100M, AI fintech LoanSnap is being sued, fined, evicted
AI mortgage startup LoanSnap is facing an avalanche of lawsuits from creditors and has been evicted from its headquarters in Southern California, leaving employees worried about the company’s future, TechCrunch has learned. LoanSnap, founded by serial entrepreneurs Karl Jacob (pictured above) and Allan Carroll, has raised around $100 million in funding since its 2017 seed round, $90 million of which was raised between 2021 and 2023, according to PitchBook. Investors include Richard Branson's Virgin Group, the Chainsmokers’ Mantis Ventures, Baseline Ventures, and Reid Hoffman, LoanSnap says.
Cadillac's 'No Perfect Formula' is a brutal, beautiful look at Le Mans program
The documentary 'No Perfect Formula' is a hard look at what Cadillac is putting into its Le Mans program. In five tries, the brand hasn't made the podium.
- Share full article
For more audio journalism and storytelling, download New York Times Audio , a new iOS app available for news subscribers.
The Government Takes On Ticketmaster
Explaining a case that could reshape the multibillion-dollar live entertainment industry..
This transcript was created using speech recognition software. While it has been reviewed by human transcribers, it may contain errors. Please review the episode audio before quoting from this transcript and email [email protected] with any questions.
Hi, everybody, it’s Sabrina. Before we start today, we wanted to invite you to something special. The Tribeca Festival is starting a brand new annual gala to celebrate excellence in audio. For this, the inaugural year, they’ve chosen to celebrate “The Daily.” We know you, our incredible audience, live all over the world, but we’d like to invite you to join us.
The gala is in New York, on June 9, at 5:00 pm. You can get all the details and buy tickets at tribecafil.com/thedaily. That’s tribecafilm.com/thedaily. I’ll be there, Michael too, along with a bunch of us from the show. Mo Rocca is going to host it. So if you’re in the area or you’re visiting, we’d love to see you there. OK, on with today’s show. From “The New York Times,” I’m Sabrina Tavernise. And this is “The Daily.”
I have got a bone to pick, as usual, with Ticketmaster.
The biggest problem that I have right now is not getting tickets to the Era Tour.
Loading, loading, loading. Want them so bad. Want them so bad. Want them so bad. Nope.
I looked at my account and the tickets are gone.
Over the past few years, few companies have provoked as much anger —
I cannot afford $1,500 tickets.
— among music fans.
Oh, my god.
— as Ticketmaster.
I literally hate Ticketmaster. Like, there is no company I think I hate more than Ticketmaster.
Ticketmaster ought to look in the mirror and say, I’m the problem. It’s me.
Last week, the Department of Justice announced it was taking the company to court. Today, my colleague David McCabe, on how the government’s case could reshape America’s multi-billion dollar live music industry.
It’s Thursday, May 30.
So, David, good to have you back. You have become a beloved guest at “The Daily,” because the government keeps bringing these huge antitrust cases and we keep turning to you to explain them.
Well, it’s a pleasure to be back. And today I have a question for you, which is, what was the first concert you ever went to?
Oh, my gosh. The first concert I ever went to? Oh, my god, I think it was Van Halen in the 1980s, which maybe is before you were born.
You know, no comment, but that’s a pretty good first concert.
And the case that we’re here to talk about today is actually all about shows like a Van Halen concert in 1980.
OK, I’m ready. So let’s get into it. This case, as you and I both know, is about Ticketmaster. So tell us about this case.
So anyone who attends concerts regularly or even irregularly probably knows about Ticketmaster. It’s kind of the ubiquitous digital box office. And those people are probably also familiar with the ubiquitous fan complaints about Ticketmaster — that the company puts high fees that they don’t entirely explain onto tickets, that tickets will sell out really fast during these sort of frantic pre-sales for tours, and that the website doesn’t always work very well.
And probably the most infamous Ticketmaster incident in recent memory was a couple of years ago when the pre-sale began for Taylor Swift’s massive Eras Tour. And fans got locked out, couldn’t get tickets and were absolutely furious. And it really put in the spotlight the power of this company over the ability to buy a ticket to a live music event.
So the DOJ is pointing the finger at this company for all this consumer angst at Ticketmaster.
Well, and when you say this company, it’s not just Ticketmaster. It’s the company that owns Ticketmaster, a company called Live Nation Entertainment. We’ll say Live Nation for short. And it’s a giant company. And to think about just how gigantic and how expansive Live Nation is, I think it’s helpful to think about the fan experience of going to a concert.
[MUSIC PLAYING]
It starts with buying a ticket. And maybe you buy a group of tickets for you and your friends. And then one of your friends can’t make it. They’ve got other plans. You resell their tickets so you can make your money back. And then the day of the show you go, it’s this big production. It’s at a venue. Someone has booked the artist to appear. You go, you buy a beer, you have a good time.
Live Nation is involved in many parts of that process, and that starts with being a major concert promoter. They’re the one putting it on, arranging the event. They’re also selling the tickets through Ticketmaster. Sometimes they’re also involved in reselling the tickets when your friend can’t make it.
And not only that, they actually sometimes manage the artists. And they own or operate the venues where the show is happening. So even down to that beer you’re drinking to enjoy with the show, they might be involved in picking the person who sells that beer to you.
So, basically, they’re everywhere.
They’re everywhere. And the Justice Department says that’s a big part of the problem, that its power is bad for fans.
Good morning. Earlier today, the Department of Justice —
And we really heard that come through at the press conference last week that the Justice Department held to announce this case —
People always remember the first time that they were transformed by live music.
— where Merrick Garland, the Attorney General, really personalized this issue.
I still remember, as a senior in college, going to a Bonnie Raitt concert and seeing a —
He told this story about going to a Bonnie Raitt concert in college.
Merrick Garland did?
Yeah, Merrick Garland did.
I don’t think of Merrick Garland and Bonnie Raitt together in the same sentence.
Well, apparently, in college he attended a Bonnie Raitt show. And the thing he highlighted was that the opener was a young Bruce Springsteen.
We all knew that we had just seen the future of rock and roll.
And in that story, the attorney general seems to be getting at two important threads of this case. The first is that concerts are formative for the people who attend them. And the second is that concerts are an important way that artists reach their fans. That young Bruce Springsteen went on to now be one of the biggest touring artists in the world.
The Justice Department filed this lawsuit on behalf of fans who should be able to go to concerts without a monopoly standing in their way. We have filed this lawsuit on behalf of artists who should be able —
And so the Justice Department is responding here to a feeling that Live Nation, this giant company, has become a gatekeeper for both artists and fans. And that has allowed it to pay artists less sometimes, but also charge fans those fees that they’re so mad about.
It is time for fans and artists to stop paying the price for Live Nation’s monopoly. Thank you.
So help us understand how things have gotten to this point, where Live Nation is so powerful that the DOJ feels the need to sue them.
Well, this company has a long history of tangling with the Justice Department. And that really starts in 2009, when Live Nation and Ticketmaster announced that they were going to merge. And this merger, this big corporate deal, will marry Live Nation’s concert promotion business, the business of putting on shows, with Ticketmaster’s experience as an online ticketing platform.
And the Justice Department — a big part of its job is looking at corporate mergers to figure out if they will substantially lessen competition in the economy. So the Justice Department reviews this merger, and in 2010 decides we will let this merger go through. But we do have some concerns that it might reduce competition in the industry of ticketing. And so we’re going to reach a legal settlement with Live Nation and Ticketmaster that puts conditions on the deal, that requires the company to sell some assets to kind of lessen its footprint. And so the merger goes through. And that creates the sort of modern day Live Nation, Ticketmaster combination.
So the government ultimately actually just lets it happen.
That’s right. They put conditions on the merger, but ultimately they let it go through. And the company continues to tangle with the Justice Department over the next 15 or so years. But mostly they keep getting bigger. They keep growing their footprint across this ecosystem that creates some of the biggest concert tours in the country.
So just how big has the company actually become? Give me some numbers.
Well, let’s start here. Every year, they sell about 600 million tickets.
600 million tickets? That’s more than the number of people in the United States of America.
Yeah. And that is a global number, but it’s a lot of tickets. Right? The Department of Justice estimates that in the United states, Live Nation controls about percent of ticketing to major venue concerts.
So that’s a big percentage. They also own or control, like, in excess of 250 venues, including a big percentage, the Justice Department says, of major amphitheaters, the kind of big outdoor concert venues that are ultimately kind of in between a nightclub and the size of a big football stadium. And they manage hundreds of artists. They have this direct relationship with artists. And so this company is wide and it is deep into this industry.
So ultimately, the Justice Department says that — and I’m going to quote here — it’s the, quote, “gatekeeper for delivery of nearly all live music in America today.”
OK, it’s big. But as we know from other DOJ cases — and this is something that you have taught me, David — the cases against Apple and Google, just being big is not in and of itself a problem.
That’s right. Where companies run afoul of the law is when they use their power as a monopoly against their competitors in order to stay powerful or get more powerful.
And the Justice Department says that Live Nation has built a complex machine to do just that.
We’ll be right back.
So what does the DOJ say that Live Nation is able to do because it is so big? How does it use its bigness?
So the most prominent allegation is that Live Nation uses its power as a concert promoter to entrench its power in ticketing. As a reminder, when you put together a concert, a promoter works with an artist to book the show. They book the show at a venue. And that venue, for all of its shows, has to choose a ticketing provider, a digital box office where people can buy their way into the shows.
And what the Justice Department is arguing here is that Live Nation is able to wield its big artists, the tours that it promotes, as a cudgel to force venues to use Ticketmaster, its ticketing service. So the Justice Department says that in an instance in which a venue switched away from using Ticketmaster, that Live Nation routed tours around that venue, which of course means less money for that venue and a problem for their business.
Interesting. So basically, Live Nation is saying, look, if you want Taylor Swift in your little amphitheater over there, you’re going to have to use Ticketmaster. It’s Ticketmaster or no Taylor Swift.
That is effectively the behavior the Justice Department is arguing has happened here. They’re saying that Live Nation does this in veiled ways and that, more importantly, it’s really understood by venues throughout the industry that if you don’t use Ticketmaster, that you really risk out on losing important Live Nation managed tours. And then once these venues do choose Ticketmaster, Live Nation locks them into these long, exclusive ticketing contracts, which can last for as long as 14 years.
14 years? That’s pretty long. What else is DOJ alleging that Live Nation has done?
Another thing the Justice Department says that Live Nation does is use its power as an owner of venues to get away with paying artists less money for their tours.
So how does that work?
Basically, the argument is that because Live Nation controls so many of certain types of venues, that there are instances in which an artist’s tour might largely be dominated by Live Nation owned venues. And the Justice Department is saying that Live Nation knows that artists don’t have a lot of other options for where to play their concerts and, as a result, is able to pay those artists less. Because there’s not competitive pressure when they’re booking those tours.
That seems pretty unfair to artists who would really benefit from other venues owned by other people competing for them.
And that’s exactly what the Justice Department is saying, that artists lose out, not just fans. And there’s a striking story in the complaint that I think crystallizes how the Justice Department sees these streams of power coming together.
And it concerns a concert, which the lawsuit doesn’t name, in 2021. My colleague Ben Sisario has reported that it was a Kanye West concert featuring Drake. It was a benefit show, and it was taking place at the LA Coliseum in Los Angeles.
One of the companies involved in putting on this show was a firm called TEG. They do promotion and ticketing of the kind that Live Nation does. And the government says that Live Nation saw this as a threat, that they saw this company TEG involved in this show, and they were worried about what it would mean for them, and that they then undertook steps to put pressure on TEG and make their life difficult in a couple of ways.
The first was that TEG had reached a deal to sell some tickets, according to the complaint, through StubHub. StubHub is a secondary resale market. You can buy tickets to shows when people aren’t going to use them.
Right, and competitor to Ticketmaster, right?
And competitor to Ticketmaster. And the Justice Department says that Live Nation found out about that and said, well, we have the exclusive ticketing contract for this venue. And so we will make sure that if you bought your ticket on StubHub, you won’t be allowed to come in to this show.
Really? Like, they couldn’t come into the concert?
Well, and ultimately, the complaint says that StubHub had to work with Ticketmaster to fulfill the tickets that had already been sold, that they stopped selling new tickets, and that hundreds of people who bought their tickets on StubHub didn’t get into the show.
That seems very unfair. Like, they bought a ticket.
Well, and according to the Justice Department, it didn’t stop there, that Live Nation used its industry connections to pressure an investor in TEG, this company that it viewed as a threat, and that it pushed that investor to pull back from its relationship with TEG, which obviously would have weakened this potential competitor.
So these are very strong armed tactics. What is the DOJ saying is the result of all of this? What does all of this amount to?
It says that all of this adds up to higher fees for consumers and a worse product, a worse quality ticketing experience when fans go to buy. Because Live Nation doesn’t have to compete with anyone. It doesn’t have to innovate in response to competitors. So, among other things, the Justice Department wants to break this company up, at the very least by separating Ticketmaster, the ticketing unit, the box office unit, from the rest of Live Nation that does all these other things — promotes concerts, owns venues, et cetera.
So in other words, go back to the way it was in the beginning.
Yeah, or as much as you can.
And why does that fix the problem?
Well, the Justice Department doesn’t say a lot on this point. But it’s clear that what they want to do with this lawsuit is disrupt this cycle where Live Nation’s power reinforces itself again, and again, and again.
And what does Live Nation say in response? I imagine they disagree with all of this.
They do. They’ve said a lot. And they start out by saying something that will be familiar to you, because other companies that have been accused of antitrust violations say it as well, which is that they don’t fit the profile of a monopoly, that their overall profit margins are lower than those of companies like Meta, or Apple, or Google, and that even if you look at Ticketmaster specifically, they take a smaller percentage of every sale than a lot of other digital platforms. So they say basically the numbers show that we don’t have the kind of power you would normally associate with a monopoly.
And then they say, listen, we know that there are things that fans don’t like about the ticketing experience. There may be fixes to those. But largely, it’s not Live Nation’s fault, they say. They say that artists generally set the prices they want people to pay for tickets.
Really? So artists themselves do it.
Right, that artists sign off on how much a ticket will cost to their shows.
And they also say that demand sometimes drives ticket prices up. If there are more people who want to see a show than there are seats or standing room to see that show, the prices will be higher. And finally, they say that there’s this kind of pernicious outside force of scalpers, people who resell tickets, that use bots to hoover up way more tickets than they could possibly use and then resell them at a higher price. And so they say that all of these things may contribute to a fan experience that people don’t like, but that it’s not necessarily Live Nation’s fault.
I mean, to me, this makes certain sense. I guess if you think of a Taylor Swift show and lots of people trying to buy tickets, one reason why those tickets are expensive is not necessarily because there’s something nefarious going on, but because lots of people want to buy tickets. And there’s a market, and supply and demand has a role here.
Well, and a clear question here that I have, that other people have asked, is how much does the Justice Department think ticket prices have gone up because of this alleged Live Nation monopoly? And the Justice Department hasn’t answered that question.
They haven’t disentangled it with all of the other stuff that’s around — market forces, everything?
That’s right. And there’s another element of Live Nation’s response that we should mention, which is that the company basically says this lawsuit is politically motivated, that this administration, the Biden administration, is bringing lawsuits that don’t hold a lot of water but are anti-business. That’s what Live Nation is saying.
I mean, it does sort of ring true in some sense. Right? This has been the tilt of this administration toward cracking down on big companies. The DOJ has changed in this respect. They’re filing a lawsuit to break up a merger that a previous DOJ had actually approved.
Well, you’re right. This Department of Justice, this administration more broadly, has a different view about antitrust. They think that antitrust law can be a more expansive tool to address problems in the economy. And they’ve put that into practice. They’ve sued Google for violating anti-monopoly laws. They’ve sued Apple for violating anti-monopoly laws.
But I think ultimately what they believe is that they’re responding to a change in the economy, that these companies have gotten much bigger, that they have gotten more powerful. And they are responding to the way the companies broke the law on their way to becoming that big.
So, David, when you and I talked about Google and Apple — you referenced them here — you know, we talked about how there were broad repercussions for the future on American society. What would you say the implications are in this case?
This case ultimately, for the Justice Department, is about the market for culture and creativity. You know, a few years ago, the Justice Department successfully blocked Penguin Random House, a big publisher, from buying Simon and Schuster, another publisher. And they said that one problem with this merger was that it would reduce how much authors got paid, and that it would create a market where fewer books and fewer types of stories broke through.
This Justice Department is embracing an idea that the more concentrated the economy gets, the more it stifles creative expression, the ability of artists to make art and get it to the public and the ability of the public to consume it. And that, they say, is a central question of democracy. Because things like music are how we talk about big social issues or big political issues. So that is, they say, what’s at the heart of this case, that it is not just about the fees, it’s not just about how much an artist gets paid. But it’s about whether or not there is a fair marketplace for ideas, and whether or not consumers are able to access it.
David, thank you.
Thank you. [MUSIC PLAYING]
Here’s what else you should know today. On Wednesday, Supreme Court Justice Samuel Alito declined to recuse himself from two cases arising from the January 6, 2021, attack on the Capitol after “The Times” reported that flags displayed outside his houses appeared to support the Stop the Steal movement. In letters to Democratic members of Congress who had demanded his recusal, Justice Alito said that the flags, at his home in Virginia and a beach house in New Jersey, were flown by his wife, Martha Ann, and that he had had nothing to do with it.
And a group of 12 New York jurors deliberated for more than four hours in the final stretch of the criminal trial of Donald Trump, in which the former president is accused of falsifying business records. The jurors asked for portions of the testimony from two witnesses to be read back to them, as well as the judge’s instructions. They were then dismissed for the day and will resume deliberations today.
Today’s episode was produced by Will Reid, Rob Szypko and Rachelle Bonja. It was edited by Michael Benoit and Brendan Klinkenberg, contains original music by Marion Lozano, Dan Powell, and Will Reid, and was engineered by Alyssa Moxley. Our theme music is by Jim Brunberg and Ben Landsverk of Wonderly.
That’s it for “The Daily.” I’m Sabrina Tavernise. See you tomorrow.

- June 3, 2024 • 32:07 How Trump’s Conviction Could Reshape the Election
- May 31, 2024 • 31:29 Guilty
- May 30, 2024 • 25:21 The Government Takes On Ticketmaster
- May 29, 2024 • 29:46 The Closing Arguments in the Trump Trial
- May 28, 2024 • 25:56 The Alitos and Their Flags
- May 24, 2024 • 25:18 Whales Have an Alphabet
- May 23, 2024 • 34:24 I.C.C. Prosecutor Requests Warrants for Israeli and Hamas Leaders
- May 22, 2024 • 23:20 Biden’s Open War on Hidden Fees
- May 21, 2024 • 24:14 The Crypto Comeback
- May 20, 2024 • 31:51 Was the 401(k) a Mistake?
- May 19, 2024 • 33:23 The Sunday Read: ‘Why Did This Guy Put a Song About Me on Spotify?’
- May 17, 2024 • 51:10 The Campus Protesters Explain Themselves
Hosted by Sabrina Tavernise
Featuring David McCabe
Produced by Will Reid , Rob Szypko and Rachelle Bonja
Edited by Brendan Klinkenberg and Michael Benoist
Original music by Marion Lozano , Dan Powell and Will Reid
Engineered by Alyssa Moxley
Listen and follow The Daily Apple Podcasts | Spotify | Amazon Music | YouTube
Over recent years, few companies have provoked more anger among music fans than Ticketmaster. Last week, the Department of Justice announced it was taking the business to court.
David McCabe, who covers technology policy for The Times, explains how the case could reshape America’s multibillion-dollar live music industry.
On today’s episode

David McCabe , a technology policy correspondent for The New York Times.

Background reading
The government is accusing Ticketmaster’s corporate parent, Live Nation Entertainment, of violating antitrust laws .
Here’s a guide to the emails at the heart of the government’s case .
There are a lot of ways to listen to The Daily. Here’s how.
We aim to make transcripts available the next workday after an episode’s publication. You can find them at the top of the page.
The Daily is made by Rachel Quester, Lynsea Garrison, Clare Toeniskoetter, Paige Cowett, Michael Simon Johnson, Brad Fisher, Chris Wood, Jessica Cheung, Stella Tan, Alexandra Leigh Young, Lisa Chow, Eric Krupke, Marc Georges, Luke Vander Ploeg, M.J. Davis Lin, Dan Powell, Sydney Harper, Mike Benoist, Liz O. Baylen, Asthaa Chaturvedi, Rachelle Bonja, Diana Nguyen, Marion Lozano, Corey Schreppel, Rob Szypko, Elisheba Ittoop, Mooj Zadie, Patricia Willens, Rowan Niemisto, Jody Becker, Rikki Novetsky, John Ketchum, Nina Feldman, Will Reid, Carlos Prieto, Ben Calhoun, Susan Lee, Lexie Diao, Mary Wilson, Alex Stern, Sophia Lanman, Shannon Lin, Diane Wong, Devon Taylor, Alyssa Moxley, Summer Thomad, Olivia Natt, Daniel Ramirez and Brendan Klinkenberg.
Our theme music is by Jim Brunberg and Ben Landsverk of Wonderly. Special thanks to Sam Dolnick, Paula Szuchman, Lisa Tobin, Larissa Anderson, Julia Simon, Sofia Milan, Mahima Chablani, Elizabeth Davis-Moorer, Jeffrey Miranda, Renan Borelli, Maddy Masiello, Isabella Anderson, Nina Lassam and Nick Pitman.
David McCabe covers tech policy. He joined The Times from Axios in 2019. More about David McCabe
Advertisement

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The first essay is a long essay on the Great Leader of 400-500 words. This long essay about Great Leader is suitable for students of class 7, 8, 9 and 10, and also for competitive exam aspirants. The second essay is a short essay on Great Leader of 150-200 words. These are suitable for students and children in class 6 and below.
India is a land of great political leaders who ruled the country effectively and also by protecting its national interest. It was not an easy task to accomplish, keeping in view the changes taking place in the world political scenario. Leaders like Pandit Jawaharlal Nehru, Lal Bahadur Shastri and Indira Gandhi Bose played an indispensable role in changing the perspective of world towards India ...
Mahatma Gandhi, the revered Indian leader and advocate of nonviolent resistance, inspired a nation to fight for independence from British rule through peaceful means, leaving an enduring legacy in history.
Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi was leader of India's nonviolent independence movement against British rule. He was revered the world over for his philosophy of passive resistance and was known to his ...
Click to read about 15 of the great leaders of India who continue to inspire us through the passing times greatly.
Assuming leadership of the Indian National Congress in 1921, Gandhi led nationwide campaigns for easing poverty, expanding women's rights, building religious and ethnic amity, ending untouchability, and, above all, achieving swaraj or self-rule. Gandhi adopted the short dhoti woven with hand-spun yarn as a mark of identification with India's rural poor. He began to live in a self-sufficient ...
Mahatma Gandhi was a great patriotic Indian. He was a man of an unbelievably great personality. Furthermore, his efforts for Indian independence are unparalleled. Consequently, the British because of his pressure left India in 1947. Click the link and read the full essay on Mahatma Gandhi
Mahatma Gandhi was one of the greatest national and civil rights leaders of the 20th century. He served as a lawyer, politician, and activist in the struggle for social justice and for India's independence from British rule. Gandhi is internationally esteemed for his doctrine of nonviolent protest (satyagraha) to achieve political and social progress.
Jawaharlal Nehru, first prime minister of independent India (1947-64), who established parliamentary government and became noted for his neutralist (nonaligned) policies in foreign affairs. He was also one of the principal leaders of India's independence movement of the 1930s and '40s.
Arguably, Gandhi's greatest leadership trait was his ability to visualize the qualities of a successful, post-Independence Indian nation, and maintain a life-long focus on the four intertwined ...
High-quality essay on the topic of "Greatness of India" for students in schools and colleges.
Learn about India's history, culture, diversity, and achievements in this 500-word essay. Find out why India is a great country for students and children.
Bhagat singh, Tilak, Pandit Jawaharlal Nehru, Subhash chander bose, Lal Bahadur Shastri, Mahatma Gandhi and Indira Gandhi are some of the important leaders. They devoted their life for the pride and honor of the country. We are living in democratic and Independent country due to these great leaders. They sacrificed their whole life for the ...
5 Pages. Open Document. Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi, commonly known as Mohatma Gandhi, was the preeminent leader of Indian nationalism in British ruled India. He led India to independence by a nonviolent movement. He is widely considered as the most powerful and successful leader in the history of India. He believed in nonviolence.
10 Lines Essay on Mahatma Gandhi (100 - 120 Words) 1) Mahatma Gandhi, born on October 2, 1869, was an Indian political leader. 2) His mother was Putlibai and father was Karamchand Gandhi. 3) He played a vital role in India's struggle for independence against British rule. 4) He led several peaceful protests and movements, including the ...
Discover FREE essays on Great Indian Leaders to understand writing styles, structures, and find new ideas. Explore the largest database of free samples on StudyMoose.
Essay on Freedom Fighters of India in English: Freedom Fighters were those great leaders who sacrificed their lives with fearless courage to bring freedom to the Nation. They faced pains, exploitation, immense torture, and hardships to bring freedom. So, people considered them the epitome of patriotic people. British ruled over India for more than 200 years. Many Freedom Fighters adopted ...
Within this shifting global landscape, India has the opportunity to put in place a new framework for its own security, growth and development, and that of developing countries around the world. As a rising global power, this must be India's principle endeavor in the coming decades. The changing international order.
Our country is a mixture of cultures, regions, traditions, diversity in food, languages, etc. In this Essay on Incredible India will discuss about Indian Culture, Religions, and Regions.
143 Words Essay on my Favorite Leader or a Great Indian Leader. Article shared by: Mahatma Gandhi is my favourite leader. He is called the Father of the Nation. He raised his voice against the British rulers. India got freedom under his leadership. He was born on October 2, 1869 at Porbandar in Gujarat. His father was the Diwan of Rajkot.
The national leaders lead their nations. But the best of them give their lives for the good of their nations. They dedicate themselves in the interest of their nations. So, if they die they become martyrs and if they live they become heroes. Gandhiji was the greatest national leader of India. He is a martyr. He died for his country.
What's set to be the largest election in history is wrapping up in the world's largest democracy, with Prime Minister Narendra Modi vying for a third term. Here's what you need to know.
Hundreds of millions of votes cast, more than six weeks of polling, and billions of dollars spent: India on Tuesday will declare a new leader after a mammoth nationwide election that has become a ...
Already braced for uncertainty about the U.S. election, countries in Europe and Asia are now even more unclear about the future of American diplomacy.
BJP and RSS leaders are going to great lengths to send out the message that the RSS is a cultural organization and uninvolved in the BJP's political activity.
GENEVA - Health leaders from countries and areas of the World Health Organization (WHO) South-East Asia and Western Pacific Regions today sounded the alarm and committed to work together to more effectively tackle antimicrobial resistance (AMR). They endorsed a joint position paper on AMR in the human health sector in the Asia-Pacific region at an event held on the sidelines of the World ...
Explaining a case that could reshape the multibillion-dollar live entertainment industry.