

How to Write a Book Report College Level – Guide & Template
- Fred Waititu
- June 9, 2022
- How To's
Here's What We'll Cover
Back in high school, book reports probably consisted of writing a book summary and then giving your opinion. As a college student, you’re expected to do more than that. Professors want to see that you’ve engaged with the material, analyzed it critically, and thought about it deeply. So, how do you write a book report that meets those expectations? This post will give you a complete guide on how to write a book report college level. But if you still feel inadequate writing a college-level book report after reading this guide, we would be delighted to offer our expert writing services at affordable prices.
Let’s get started!
What is a Book Report?
A book report is a summary of a book that you have read. It includes your thoughts and analysis of the story and presents your reaction to the reader.
When you are assigned a book report in college, your professor will usually give you specific guidelines on what they are looking for and expecting. It is essential to make sure that you understand the assignment before beginning.
Types of Book Reports
Three book reports are commonly assigned in college: plot summary, character analysis , and theme analysis. Below is a clear definition of each.
Plot Summary
A plot is a summary of the story. In summary, you’ll need to explain your opinion of the story. What is so compelling about the story? Analyzing the story makes a good plot summary, and a good plot summary makes an excellent book report. It should include the story’s leading events, the conflict, and the resolution.
Character Analysis
A character analysis is an in-depth look at a particular character. Take your time to explore and analyze the character’s physical appearance, personality traits, and the roles of each character in the story. Describe their motivations, actions, and thoughts. Compile all your observations together and explain the correlation of each character with the story.
Theme Analysis
Books/stories provide different themes. A book report features the examination of underlying themes in a book. Give observation as a reader into your report to show the power of a theme. Throughout the character’s journey, they will experience different motifs. It could be anything from love to loss to betrayal.
What is the Difference Between a Book Report and Book Review?
Below are clear descriptions and differences between the two;
Simple Book Report Format
Before you begin your journey of how to write a book report college level, you must identify and understand the format you need to follow.
A simple book report format that you can use is;
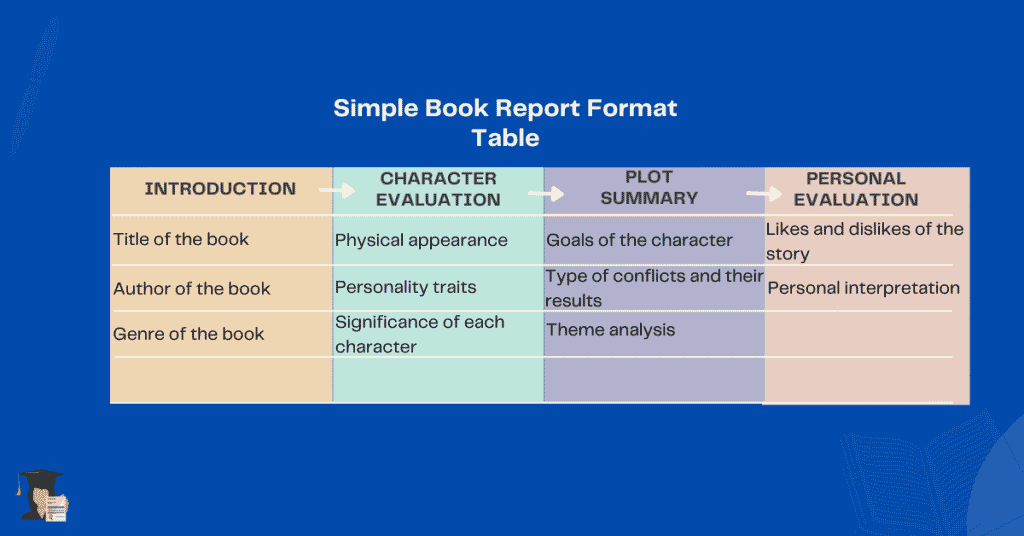
Introduction
Lay out all the necessary information about the book.
Introduce the following;
- Title of the book .
- Author of the book.
- Type/Genre of the book.
Character Evaluation.
Giving a vivid description of the book’s character to create an imagery illusion is critical.
Highlight the following;
- Physical appearance- When writing about a character’s physical appearance in your book report, it’s essential to pay attention to their overall look and the specific details of their clothing, hair, etc. How does the character dress? Do they have any distinguishing features? How do they carry themselves? All of these details can give you clues about them.
- Personality traits- One of the most important aspects of a character’s personality trait is their motivation, actions, behaviours, and attitude. Furthermore, another aspect of the book report is their relationship with other characters. By taking the time to consider these aspects of a character’s personality, you can write a well-rounded and engaging book report.
- Significance of each character in the story- describe the character’s role and how they correlate throughout the story.
Plot Summary (Briefly Describe the Story)
Here is where you focus on the main sequence of events within the book. You mention any use of literary devices the authors may have used. You can discuss these key events;
- Goals of the character- In a story, the characters carry a specific goal they desire to achieve. In your book report, take your reader through the character’s journey.
- Type of conflict and their results- A critical aspect of writing a summary book report is understanding the different types of conflict present in a text. There are four main types of conflict: man vs self, man vs man, man vs society, and man vs nature. Each type of conflict can offer different insights into the message of a book.
For example, if the book you are reading is about a character struggling with addiction, the conflict would likely be classified as man vs self. This conflict can provide insight into the character’s internal struggle and motivations.
Alternatively, if the book is about two characters competing against each other, the conflict would likely be classified as man vs man. This type of conflict can offer insight into the characters’ relationships with each other and their individual goals. Understanding the different types of conflict present in a book can help you write a more engaging and insightful book report.
Theme Analysis (Examine One or More Themes)
The story’s theme is one of the biggest highlights that many students ignore. It provides the reader with significant contexts of place, time, and mood of the story. The theme plays a huge role in the story, allowing a connection between the reader and the book’s characters.
Personal Evaluation
Personal evaluation is where you chyme in your take on the book and give your honest opinions of the book. What did you learn from the book? Balance out your thoughts and support your statement.
Likes and Dislikes Of the Story.
You are allowed to emphasize your likes and dislikes of the book.
Personal Interpretation
Take time and give your understanding of the book to support your thesis.
How to Start a Book Report
If you desire to get your professor’s attention, give them something to look forward to when reading your report.
The following will you a great way to create excitement and write an excellent book report:
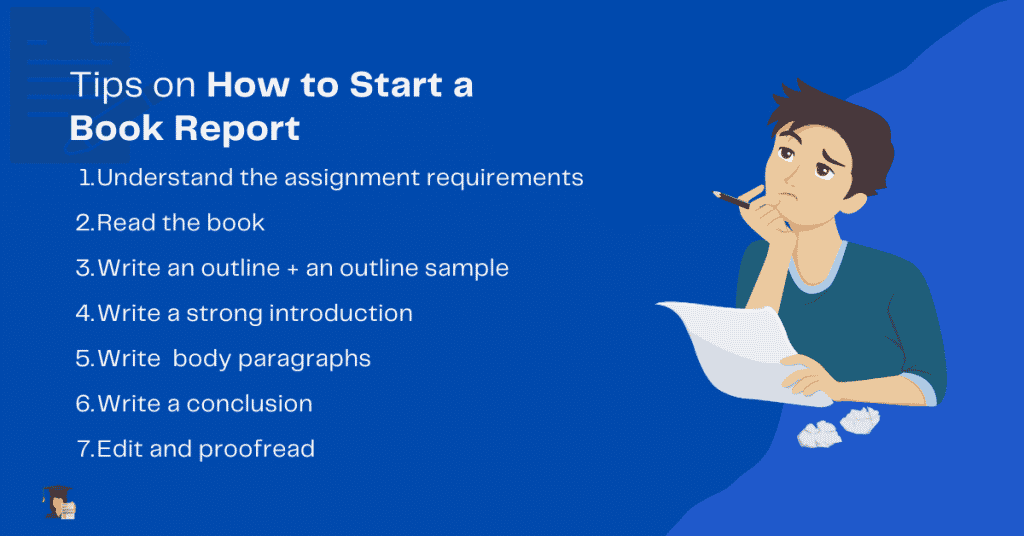
Understand the Assignment Requirements
When you are assigned a book report, you must make sure that you understand the assignment requirements. Look into and research; What type of book report are you supposed to write? How long should it be? What format should you use? These are all important questions that you need to ask yourself before you begin how to write a book report college level.
If you are unsure about anything, ask your professor for clarification.
Read the Book
Once you understand the assignment’s requirements, you can start reading the book. Take note of any significant events or characters that stand out to you as you read. These will be important to include in your book report.
Write an Outline + an Outline Sample.
Once you have finished reading the book, it is time to start writing your report. Begin by creating an outline of what you are going to write. It will help you organize your thoughts and ensure you include all the vital information.
Here is a simple outline that you can follow:
- Introduction.
- Plot Summary (Briefly describe the story).
- Character Analysis (Analyze one or more of the characters).
- Theme Analysis (Examine one or more of the themes).
- Conclusion (Briefly summarize your thoughts on the book).
Book Report Template

Write a Strong Introduction
There are a couple of things to consider. First, you must ensure that you introduce the book in a way that will grab the reader’s attention. i.e. giving a summary of the plot.
It would help if you also tried to incorporate fascinating facts about the book or the author. Secondly, you need to make sure that your introduction is well-organized. You should clearly state the purpose of your paper and what points you will be discussing. Lastly, you want to ensure that your introduction is concise, as you should not include any unnecessary information.
Write Body Paragraphs
The body paragraphs are where you will include your analysis of the story. These include a plot summary, character analysis, and theme analysis.
When writing a body paragraph, start by introducing the paragraph’s main idea in a topic sentence. Several sentences of evidence or examples then follow it to support the main idea. Be sure to choose evidence that is relevant and persuasive. Finally, conclude the paragraph with a sentence that ties back to the overall thesis of the book report.
Remember, each body paragraph should focus on a different aspect of the book, such as the characters, plot, or theme.
Write a Conclusion
The conclusion is where you will sum up your thoughts on the book. It can include; What did you think of it? Would you recommend it to others? It is also an excellent place to mention any unanswered questions or issues.
The next section of your book report should be the plot summary. Here, you will briefly summarise the story, including the main events, conflict, and resolution.
Edit and Proofread
How you edit and proofread your book report can make the difference between a good and bad grade. Here are some helpful tips:
- Use active voice when possible; it is more concise and easier to read.
- Check for grammar, punctuation, and spelling errors. Use a spell-checker if necessary or when feeling doubtful.
- Make sure all information in the report is accurate.
- Check for clarity and conciseness. Make sure the book report flows well and is easy to read.
- Ask someone else to read the book report before you turn it in to check for errors and get opinions from a third person’s point of view.
How to Write a Book Report Without Reading the Book
When presented with an assignment on how to write a book report college level and you have no time to read the entire book, here are some dependable ways to write one without reading it;

Read the Book Summary.
One of the best ways to write a book report without reading the book itself is to read its summary instead. It provides you with all the critical information you need about the story.
You can find summaries online or in the back of many books. But take note to be sure that you are getting your information from a reliable source.
Focus on Significant Details Only.
You don’t need to include every detail from the story. Instead, focus on the essential information that will help to support your claims.
For example, if you are doing character analysis, you might want to focus on their actions and thoughts rather than every little detail about them.
Get Help From a Professional.
If you have trouble understanding the book, try looking up a summary online or ask a friend for help. You can also hire a professional book report writer to help you with your assignment.
Try to Discuss Different Angle
Another way to write a book report without reading it is to discuss it from a different angle. For example, focus on their motivations or actions when discussing the characters. If you examine the plot, focus on the conflict or resolution as this will help you better understand the story without reading it yourself.
We hope this blog post has helped you know what is expected of you on how to write a book report college level. Reading a novel and writing a comprehensive report on it can be daunting, but if you follow our outline and example, we believe you will produce an A+ paper. If you need help along the way, don’t hesitate to reach out to us. We are here to help students achieve their academic goals!

What are the parts of a book report?
A book report includes the introduction, body paragraphs, and conclusion. In the introduction, you should provide basic information about the book, including the title, author, and type of book. The body paragraphs are where you will include your analysis of the story.
While at the conclusion, you will summarize your thoughts on the book.
Is a report a summary?
No, a report is not a summary. It is a brief story overview, including the main events, characters, and themes. A report is a more in-depth book analysis that includes your thoughts and opinions.
How many paragraphs should be included in a book report?
You should include no set number of paragraphs in a book report. However, it is recommended to have at least three body paragraphs. It gives you enough space to discuss the different aspects of the story in detail.
How long is a book report?
A book report can be as long or as short as you want it to be. However, most college-level book reports are at least five pages in length. It gives you enough space to provide a thorough analysis of the story.
Let Us Help You Get Better Grades
Achieve academic success with Bright Writers
Unlocking A+ Essays
Insider Tips Your Professor Won't Share
Don't leave before you grab this deal!!
Get 20% OFF your first order. Professional essays at $10 a page
Do you need better
Let us handle your essays today
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Writing a Book Report

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
Book reports are informative reports that discuss a book from an objective stance. They are similar to book reviews but focus more on a summary of the work than an evaluation of it. Book reports commonly describe what happens in a work; their focus is primarily on giving an account of the major plot, characters, thesis, and/or main idea of the work. Most often, book reports are a K-12 assignment and range from 250 to 500 words.
Book reviews are most often a college assignment, but they also appear in many professional works: magazines, newspapers, and academic journals. If you are looking to write a book review instead of a book report, please see the OWL resource, Writing a Book Review .
Before You Read
Before you begin to read, consider what types of things you will need to write your book report. First, you will need to get some basic information from the book:
- Publisher location, name of publisher, year published
- Number of Pages
You can either begin your report with some sort of citation, or you can incorporate some of these items into the report itself.
Next, try to answer the following questions to get you started thinking about the book:
- Author: Who is the author? Have you read any other works by this author?
- Genre: What type of book is this: fiction, nonfiction, biography, etc.? What types of people would like to read this kind of book? Do you typically read these kinds of books? Do you like them?
- Title: What does the title do for you? Does it spark your interest? Does it fit well with the text of the book?
- Pictures/Book Jacket/Cover/Printing: What does the book jacket or book cover say? Is it accurate? Were you excited to read this book because of it? Are there pictures? What kinds are there? Are they interesting?
As You Read
While reading a work of fiction, keep track of the major characters. You can also do the same with biographies. When reading nonfiction works, however, look for the main ideas and be ready to talk about them.
- Characters: Who are the main characters? What happens to them? Did you like them? Were there good and bad characters?
- Main Ideas: What is the main idea of the book? What happens? What did you learn that you did not know before?
- Quotes: What parts did you like best? Are there parts that you could quote to make your report more enjoyable?
When You Are Ready to Write
Announce the book and author. Then, summarize what you have learned from the book. Explain what happens in the book, and discuss the elements you liked, did not like, would have changed, or if you would recommend this book to others and why. Consider the following items as well:
- Principles/characters: What elements did you like best? Which characters did you like best and why? How does the author unfold the story or the main idea of the book?
- Organize: Make sure that most of your paper summarizes the work. Then you may analyze the characters or themes of the work.
- Your Evaluation: Choose one or a few points to discuss about the book. What worked well for you? How does this work compare with others by the same author or other books in the same genre? What major themes, motifs, or terms does the book introduce, and how effective are they? Did the book appeal to you on an emotional or logical way?
- Recommend: Would you recommend this book to others? Why? What would you tell them before they read it? What would you talk about after you read it?
Revising/Final Copy
Do a quick double check of your paper:
- Double-check the spelling of the author name(s), character names, special terms, and publisher.
- Check the punctuation and grammar slowly.
- Make sure you provide enough summary so that your reader or instructor can tell you read the book.
- Consider adding some interesting quotes from the reading.
- Translators
- Graphic Designers
Please enter the email address you used for your account. Your sign in information will be sent to your email address after it has been verified.
How to Write Outstanding College Level Book Reports

There's nothing quite like enjoying a really solid piece of literature. Hours can pass while you're diving into a new world that the author has created. Your enjoyment of your novel may dissipate slightly when you are trying to figure out how to write a college level book report about it—but it doesn't have to be that way. Analyzing (and maybe even critiquing) novels is a useful skill that will help you both in and outside of the classroom. In this post we will outline the best strategies of painlessly writing a book report. It's important to note that there is no one generic book report assignment. This isn't necessarily a step-by-step guide, but it can help get you started thinking about the specific requirements that your instructor has for you.
Know the assignment
When you start out your book report assignment, it's important that you know exactly what your instructor is requiring. Does your instructor want you to explore the book's theme and write a five-paragraph essay on it, or are you supposed to be writing an essay about a particular character? Read through the assignment sheet very carefully and make sure that you understand all of the instructions. If you have questions or are uncertain about something, be sure to ask your instructor.
Actually read the book
Even though it may be tempting to take a shortcut and watch a movie adaptation of your book or even to read the Sparknotes , definitely resist that urge. Not only will your report be more thorough if you read the book the whole way through, but reading and understanding themes and outlining a novel plot is an invaluable experience. You'll be able to understand books on a completely new and more appreciative level. When you are reading the novel for your book report, write down page numbers or passages that pertain to the assignment or that you think might be interesting to mention.
Try to really sink into what the author is trying to say by asking yourself the following questions:
- What is the main theme of the book? The theme is the meaning or the entire reason behind writing the book. An author doesn't typically write just to write something down. What motivated them to pen this novel?
- What is happening to the characters? Typically novels are told from the perspective (either in the first or third person) of the main character, though some novels have multiple perspectives. Is this character a good character or are they flawed? What kinds of obstacles is the character going through? What did they learn during the course of the story?
- What is the plot of the book? There are several different kinds of plots, and it's helpful to know what kind your chosen novel has in order to help you analyze it better. Some stories are quests: that is, the main character is on a journey to accomplish a goal (think Lord of the Rings). Some stories are overcoming obstacles—whether that's internal or external. What kind of plot does your novel have and why do you think the author chose that particular type?
Write a good introduction
After you've read your book thoroughly and you've thought about the characters, themes, plot, and some good quotes, you'll be ready to start writing the book report. Like any other paper, a good book report needs an explanatory introduction that is easy to understand. When writing the introduction, be sure to include the title of the work, the author, and a sentence or two on what you will be overviewing in the report. Even though it may not be required to have a thesis statement in your book report, writing one in your paper might keep it more focused and help you narrow down what you will be writing in the body paragraphs.

For example, if we were writing an introduction about a book report over Harper Lee's To Kill a Mockingbird , we might write something like this:
In Harper Lee's iconic coming of age novel, To Kill a Mockingbird, Lee confronts the audience with the idea that systemic racism was rampant in the U.S. court system in the early 20th century in the South. She illustrates this idea with the unfair trial of convicted rapist Tom Robinson, whose lawyer Atticus Finch handily proves is innocent, yet is still sentenced with a crime he did not commit. Through the eyes of the young main character, Scout Finch, the audience is able to learn about these injustices with the innocent eyes of a child.
As you can see, we mentioned the name of the book, the author, and we also outlined what we would be discussing throughout the body paragraphs in the book report. Not only will this let the reader know what this report is about, but it'll also help you stay organized when you are writing the paper. Note that nowhere in this paragraph does it say that we really liked the book. Whether or not we liked the book is irrelevant in the report. What the book report is trying to do is to objectively understand a book's relevance and importance wit themes, characters, motifs, etc. (Though of course it's perfectly okay and encouraged to like the book that you are reviewing.)
Implement the ideas in the body paragraphs
The meat of your book report will be in the body paragraphs. These paragraphs will expand on the ideas that you brought up in your introduction paragraph and allow you to introduce the novel in depth to your reader.
Though no two book report assignments are the same, it's likely that your instructor is going to want to see some summarization in your book report. Your summary of the novel shouldn't be too lengthy (this is a report after all, so it's typically quite short). If your instructor has assigned a five-page book report, don't summarize the book in four and a half pages. As a general rule, commit about 1/3 of the paper to a summary just so you can make sure the reader understands your analysis of it without having read it.
Once you are done writing the summary of the novel, then you can get into your actual analysis of it. You may remember that we brought up systemic racism in the U.S. court system in the South in our essay on To Kill a Mockingbird. In our summary, we would then explore those ideas that we brought forth to the reader. How does Lee illustrate this idea throughout the novel? A good way to show how the author is making this point is through direct quotations from the book that you believe are a good showcase.
In your analysis, you should also be discussing theme (or what was the author's purpose behind writing this book) and character. No two analyses are the same, which is what makes book reports and literary criticism so interesting. Everyone will read the novel through their own personal lenses and experiences and come up with a completely different interpretation of what the author intended for us to come away with.
Again, it's crucial to keep looking at your instructions for your book report so that you know exactly what you need to be discussing. Even if you write a brilliant report over the theme of systemic racism in the court system in To Kill a Mockingbird, it won't do you any good when you were actually supposed to write about the relationship between Scout and Atticus Finch and why it mattered. Paying attention to instructions is one of the biggest keys to success in writing a book report.
As with all other conclusions, focus on wrapping things up neatly. Though you may be tempted to just say in the conclusion that you either loved or hated the book, this doesn't make for a very interesting paragraph. When you are writing your conclusion on your book report, think about why this novel matters. If you didn't like it, think about why you didn't like it. Think about how well the author gets his or her point across. Should this book be read widely to gain a critical understanding of a subject? Why or why not? Would you recommend this book to others? The genre of book reports generally seeks out the opinion of the writer, so make sure that you let your voice be heard.

Like any other paper that you write, it's crucial to go back through and revise if you are turning in the final copy. It's extremely rare that you'll write something that doesn't have any mistakes or reworking to do. Once you have written the first draft, take a short break to get your eyes off the paper for just a bit. Come back to the paper after the break with a set of fresh eyes and try to read through it for grammar and spelling mistakes (spell check doesn't get everything!) and then once again for content. Make sure that everything makes sense and is very explanatory. After all—you have to assume that your audience hasn't read your book yet so you want to make sure that you are explaining it well enough to someone who has never read a sentence of it and still be able to understand.
If you are uncertain about sentences or even entire passages of your book report, ask a friend or your instructor to take a look at your work. Sometimes it helps to get an outside opinion since you've been closely working with the text.
Book reports teach us more than just how to write a report
Though we do a lot of research and studying about subjects that may not be applicable after college, book reports may be one of the only exceptions to that. Novels, no matter how abstract the concept, teach us about human behavior and life through plots and characters. Understanding how to break down an author's intent on their stories will absolutely be relevant to your life. Having the curiosity and the skills to understand a novel with a more complex understanding will undoubtedly enrich your reading experience.
Remember than an effective book report will have an introduction that mentions the book title, author, and include the points you will be making throughout the body paragraphs. Your body paragraphs will expand on those ideas that you brought up in the introduction, using quotes from the book, analysis, and summary to aide you.
Finally, be sure that once the book report has been written that you are carefully looking at spelling, grammar, and the content of your paragraphs. Get a friend, your instructor, or even a professional editor to look at your book report to make sure you are on the right track.
Related Posts

Understanding the Different Types of Research Methods

The Concluding Paragraph: How to End Your Essay
- Academic Writing Advice
- All Blog Posts
- Writing Advice
- Admissions Writing Advice
- Book Writing Advice
- Short Story Advice
- Employment Writing Advice
- Business Writing Advice
- Web Content Advice
- Article Writing Advice
- Magazine Writing Advice
- Grammar Advice
- Dialect Advice
- Editing Advice
- Freelance Advice
- Legal Writing Advice
- Poetry Advice
- Graphic Design Advice
- Logo Design Advice
- Translation Advice
- Blog Reviews
- Short Story Award Winners
- Scholarship Winners

Need an academic editor before submitting your work?

How to Write a Book Report
Use the links below to jump directly to any section of this guide:
Book Report Fundamentals
Preparing to write, an overview of the book report format, how to write the main body of a book report, how to write a conclusion to a book report, reading comprehension and book reports, book report resources for teachers .
Book reports remain a key educational assessment tool from elementary school through college. Sitting down to close read and critique texts for their content and form is a lifelong skill, one that benefits all of us well beyond our school years. With the help of this guide, you’ll develop your reading comprehension and note-taking skills. You’ll also find resources to guide you through the process of writing a book report, step-by-step, from choosing a book and reading actively to revising your work. Resources for teachers are also included, from creative assignment ideas to sample rubrics.
Book reports follow general rules for composition, yet are distinct from other types of writing assignments. Central to book reports are plot summaries, analyses of characters and themes, and concluding opinions. This format differs from an argumentative essay or critical research paper, in which impartiality and objectivity is encouraged. Differences also exist between book reports and book reviews, who do not share the same intent and audience. Here, you’ll learn the basics of what a book report is and is not.
What Is a Book Report?
"Book Report" ( ThoughtCo )
This article, written by a professor emeritus of rhetoric and English, describes the defining characteristics of book reports and offers observations on how they are composed.
"Writing a Book Report" (Purdue OWL)
Purdue’s Online Writing Lab outlines the steps in writing a book report, from keeping track of major characters as you read to providing adequate summary material.
"How to Write a Book Report" ( Your Dictionary )
This article provides another helpful guide to writing a book report, offering suggestions on taking notes and writing an outline before drafting.
"How to Write a Successful Book Report" ( ThoughtCo )
Another post from ThoughtCo., this article highlights the ten steps for book report success. It was written by an academic advisor and college enrollment counselor.
What’s the Difference Between a Book Report and an Essay?
"Differences Between a Book Report & Essay Writing" ( Classroom)
In this article from the education resource Classroom, you'll learn the differences and similarities between book reports and essay writing.
"Differences Between a Book Report and Essay Writing" (SeattlePi.com)
In this post from a Seattle newspaper's website, memoirist Christopher Cascio highlights how book report and essay writing differ.
"The Difference Between Essays and Reports" (Solent Online Learning)
This PDF from Southampton Solent University includes a chart demonstrating the differences between essays and reports. Though it is geared toward university students, it will help students of all levels understand the differing purposes of reports and analytical essays.
What’s the Difference Between a Book Report and a Book Review?
"How to Write a Book Review and a Book Report" (Concordia Univ.)
The library at Concordia University offers this helpful guide to writing book report and book reviews. It defines differences between the two, then presents components that both forms share.
"Book Reviews" (Univ. of North Carolina)
The University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill’s writing guide shows the step-by-step process of writing book reviews, offering a contrast to the composition of book reports.
Active reading and thoughtful preparation before you begin your book report are necessary components of crafting a successful piece of writing. Here, you’ll find tips and resources to help you learn how to select the right book, decide which format is best for your report, and outline your main points.
Selecting and Finding a Book
"30 Best Books for Elementary Readers" (Education.com)
This article from Education.com lists 30 engaging books for students from kindergarten through fifth grade. It was written by Esme Raji Codell, a teacher, author, and children's literature specialist.
"How to Choose a Good Book for a Report (Middle School)" (WikiHow)
This WikiHow article offers suggestions for middle schoolers on how to choose the right book for a report, from getting started early on the search process to making sure you understand the assignment's requirements.
"Best Book-Report Books for Middle Schoolers" (Common Sense Media)
Common Sense Media has compiled this list of 25 of the best books for middle school book reports. For younger students, the article suggests you check out the site's "50 Books All Kids Should Read Before They're 12."
"50 Books to Read in High School" (Lexington Public Library)
The Lexington, Kentucky Public Library has prepared this list to inspire high school students to choose the right book. It includes both classics and more modern favorites.
The Online Computer Library Center's catalogue helps you locate books in libraries near you, having itemized the collections of 72,000 libraries in 170 countries.
Formats of Book Reports
"Format for Writing a Book Report" ( Your Dictionary )
Here, Your Dictionary supplies guidelines for the basic book report format. It describes what you'll want to include in the heading, and what information to include in the introductory paragraph. Be sure to check these guidelines against your teacher's requirements.
"The Good Old Book Report" (Scholastic)
Nancy Barile’s blog post for Scholastic lists the questions students from middle through high school should address in their book reports.
How to Write an Outline
"Writer’s Web: Creating Outlines" (Univ. of Richmond)
The University of Richmond’s Writing Center shows how you can make use of micro and macro outlines to organize your argument.
"Why and How to Create a Useful Outline" (Purdue OWL)
Purdue’s Online Writing Lab demonstrates how outlines can help you organize your report, then teaches you how to create outlines.
"Creating an Outline" (EasyBib)
EasyBib, a website that generates bibliographies, offers sample outlines and tips for creating your own. The article encourages you to think about transitions and grouping your notes.
"How to Write an Outline: 4 Ways to Organize Your Thoughts" (Grammarly)
This blog post from a professional writer explains the advantages of using an outline, and presents different ways to gather your thoughts before writing.
In this section, you’ll find resources that offer an overview of how to write a book report, including first steps in preparing the introduction. A good book report's introduction hooks the reader with strong opening sentences and provides a preview of where the report is going.
"Step-by-Step Outline for a Book Report" ( Classroom )
This article from Classroom furnishes students with a guide to the stages of writing a book report, from writing the rough draft to revising.
"Your Roadmap to a Better Book Report" ( Time4Writing )
Time4Writing offers tips for outlining your book report, and describes all of the information that the introduction, body, and conclusion should include.
"How to Start a Book Report" ( ThoughtCo)
This ThoughtCo. post, another by academic advisor and college enrollment counselor Grace Fleming, demonstrates how to write a pithy introduction to your book report.
"How to Write an Introduction for a Book Report" ( Classroom )
This brief but helpful post from Classroom details what makes a good book report introduction, down to the level of individual sentences.
The body paragraphs of your book report accomplish several goals: they describe the plot, delve more deeply into the characters and themes that make the book unique, and include quotations and examples from the book. Below are some resources to help you succeed in summarizing and analyzing your chosen text.
Plot Summary and Description
"How Do You Write a Plot Summary?" ( Reference )
This short article presents the goals of writing a plot summary, and suggests a word limit. It emphasizes that you should stick to the main points and avoid including too many specific details, such as what a particular character wears.
"How to Write a Plot for a Book Report" ( The Pen & The Pad )
In this article from a resource website for writers, Patricia Harrelson outlines what information to include in a plot summary for a book report.
"How to Write a Book Summary" (WikiHow)
Using Harry Potter and the Sorcerer’s Stone as an example, this WikiHow article demonstrates how to write a plot summary one step at a time.
Analyzing Characters and Themes
"How to Write a Character Analysis Book Report" ( The Pen & The Pad )
Kristine Tucker shows how to write a book report focusing on character. You can take her suggestions as they are, or consider incorporating them into the more traditional book report format.
"How to Write a Character Analysis" (YouTube)
The SixMinuteScholar Channel utilizes analysis of the film Finding Nemo to show you how to delve deeply into character, prioritizing inference over judgment.
"How to Define Theme" ( The Editor's Blog )
Fiction editor Beth Hill contributes an extended definition of theme. She also provides examples of common themes, such as "life is fragile."
"How to Find the Theme of a Book or Short Story" ( ThoughtCo )
This blog post from ThoughtCo. clarifies the definition of theme in relation to symbolism, plot, and moral. It also offers examples of themes in literature, such as love, death, and good vs. evil.
Selecting and Integrating Quotations
"How to Choose and Use Quotations" (Santa Barbara City College)
This guide from a college writing center will help you choose which quotations to use in your book report, and how to blend quotations with your own words.
"Guidelines for Incorporating Quotes" (Ashford Univ.)
This PDF from Ashford University's Writing Center introduces the ICE method for incorporating quotations: introduce, cite, explain.
"Quote Integration" (YouTube)
This video from The Write Way YouTube channel illustrates how to integrate quotations into writing, and also explains how to cite those quotations.
"Using Literary Quotations" (Univ. of Wisconsin-Madison)
This guide from the University of Wisconsin-Madison’s Writing Center helps you emphasize your analysis of a quotation, and explains how to incorporate quotations into your text.
Conclusions to any type of paper are notoriously tricky to write. Here, you’ll learn some creative ways to tie up loose ends in your report and express your own opinion of the book you read. This open space for sharing opinions that are not grounded in critical research is an element that often distinguishes book reports from other types of writing.
"How to Write a Conclusion for a Book Report" ( Classroom )
This brief article from the education resource Classroom illustrates the essential points you should make in a book report conclusion.
"Conclusions" (Univ. of North Carolina)
The University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill’s Writing Center lays out strategies for writing effective conclusions. Though the article is geared toward analytical essay conclusions, the tips offered here will also help you write a strong book report.
"Ending the Essay: Conclusions" (Harvard College Writing Center)
Pat Bellanca’s article for Harvard University’s Writing Center presents ways to conclude essays, along with tips. Again, these are suggestions for concluding analytical essays that can also be used to tie up a book report's loose ends.
Reading closely and in an engaged manner is the strong foundation upon which all good book reports are built. The resources below will give you a picture of what active reading looks like, and offer strategies to assess and improve your reading comprehension. Further, you’ll learn how to take notes—or “annotate” your text—making it easier to find important information as you write.
How to Be an Active Reader
"Active Reading Strategies: Remember and Analyze What You Read" (Princeton Univ.)
Princeton University’s McGraw Center for Teaching and Learning recommends ten strategies for active reading, and includes sample diagrams.
"Active Reading" (Open Univ.)
The Open University offers these techniques for reading actively alongside video examples. The author emphasizes that you should read for comprehension—not simply to finish the book as quickly as possible.
"7 Active Reading Strategies for Students" ( ThoughtCo )
In this post, Grace Fleming outlines seven methods for active reading. Her suggestions include identifying unfamiliar words and finding the main idea.
"5 Active Reading Strategies for Textbook Assignments" (YouTube)
Thomas Frank’s seven-minute video demonstrates how you can retain the most important information from long and dense reading material.
Assessing Your Reading Comprehension
"Macmillan Readers Level Test" (MacMillan)
Take this online, interactive test from a publishing company to find out your reading level. You'll be asked a number of questions related to grammar and vocabulary.
"Reading Comprehension Practice Test" (ACCUPLACER)
ACCUPLACER is a placement test from The College Board. This 20-question practice test will help you see what information you retain after reading short passages.
"Reading Comprehension" ( English Maven )
The English Maven site has aggregated exercises and tests at various reading levels so you can quiz your reading comprehension skills.
How to Improve Your Reading Comprehension
"5 Tips for Improving Reading Comprehension" ( ThoughtCo )
ThoughtCo. recommends five tips to increase your reading comprehension ability, including reading with tools such as highlighters, and developing new vocabulary.
"How to Improve Reading Comprehension: 8 Expert Tips" (PrepScholar)
This blog post from PrepScholar provides ideas for improving your reading comprehension, from expanding your vocabulary to discussing texts with friends.
CrashCourse video: "Reading Assignments" (YouTube)
This CrashCourse video equips you with tools to read more effectively. It will help you determine how much material you need to read, and what strategies you can use to absorb what you read.
"Improving Reading Comprehension" ( Education Corner )
From a pre-reading survey through post-reading review, Education Corner walks you through steps to improve reading comprehension.
Methods of In-text Annotation
"The Writing Process: Annotating a Text" (Hunter College)
This article from Hunter College’s Rockowitz Writing Center outlines how to take notes on a text and provides samples of annotation.
"How To Annotate Text While Reading" (YouTube)
This video from the SchoolHabits YouTube channel presents eleven annotation techniques you can use for better reading comprehension.
"5 Ways To Annotate Your Books" ( Book Riot )
This article from the Book Riot blog highlights five efficient annotation methods that will save you time and protect your books from becoming cluttered with unnecessary markings.
"How Do You Annotate Your Books?" ( Epic Reads )
This post from Epic Reads highlights how different annotation methods work for different people, and showcases classic methods from sticky notes to keeping a reading notebook.
Students at every grade level can benefit from writing book reports, which sharpen critical reading skills. Here, we've aggregated sources to help you plan book report assignments and develop rubrics for written and oral book reports. You’ll also find alternative book report assessment ideas that move beyond the traditional formats.
Teaching Elementary School Students How to Write Book Reports
"Book Reports" ( Unique Teaching Resources )
These reading templates courtesy of Unique Teaching Resources make great visual aids for elementary school students writing their first book reports.
"Elementary Level Book Report Template" ( Teach Beside Me )
This printable book report template from a teacher-turned-homeschooler is simple, classic, and effective. It asks basic questions, such as "who are the main characters?" and "how did you feel about the main characters?"
"Book Reports" ( ABC Teach )
ABC Teach ’s resource directory includes printables for book reports on various subjects at different grade levels, such as a middle school biography book report form and a "retelling a story" elementary book report template.
"Reading Worksheets" ( Busy Teacher's Cafe )
This page from Busy Teachers’ Cafe contains book report templates alongside reading comprehension and other language arts worksheets.
Teaching Middle School and High School Students How to Write Book Reports
"How to Write a Book Report: Middle and High School Level" ( Fact Monster)
Fact Monster ’s Homework Center discusses each section of a book report, and explains how to evaluate and analyze books based on genre for students in middle and high school.
"Middle School Outline Template for Book Report" (Trinity Catholic School)
This PDF outline template breaks the book report down into manageable sections for seventh and eighth graders by asking for specific information in each paragraph.
"Forms for Writing a Book Report for High School" ( Classroom )
In this article for Classroom, Elizabeth Thomas describes what content high schoolers should focus on when writing their book reports.
"Forms for Writing a Book Report for High School" ( The Pen & The Pad )
Kori Morgan outlines techniques for adapting the book report assignment to the high school level in this post for The Pen & The Pad .
"High School Book Lists and Report Guidelines" (Highland Hall Waldorf School)
These sample report formats, grading paradigms, and tips are collected by Highland Hall Waldorf School. Attached are book lists by high school grade level.
Sample Rubrics
"Book Review Rubric Editable" (Teachers Pay Teachers)
This free resource from Teachers Pay Teachers allows you to edit your book report rubric to the specifications of your assignment and the grade level you teach.
"Book Review Rubric" (Winton Woods)
This PDF rubric from a city school district includes directions to take the assignment long-term, with follow-up exercises through school quarters.
"Multimedia Book Report Rubric" ( Midlink Magazine )
Perfect for oral book reports, this PDF rubric from North Carolina State University's Midlink Magazine will help you evaluate your students’ spoken presentations.
Creative Book Report Assignments
"25 Book Report Alternatives" (Scholastic)
This article from the Scholastic website lists creative alternatives to the standard book report for pre-kindergarteners through high schoolers.
"Fresh Ideas for Creative Book Reports" ( Education World )
Education World offers nearly 50 alternative book report ideas in this article, from a book report sandwich to a character trait diagram.
"A Dozen Ways to Make Amazingly Creative Book Reports" ( We Are Teachers )
This post from We Are Teachers puts the spotlight on integrating visual arts into literary study through multimedia book report ideas.
"More Ideas Than You’ll Ever Use for Book Reports" (Teachnet.com)
This list from Teachnet.com includes over 300 ideas for book report assignments, from "interviewing" a character to preparing a travel brochure to the location in which the book is set.
"Fifty Alternatives to the Book Report" (National Council of Teachers of English)
In this PDF resource from the NCTE's English Journal, Diana Mitchell offers assignment ideas ranging from character astrology signs to a character alphabet.
- PDFs for all 136 Lit Terms we cover
- Downloads of 1929 LitCharts Lit Guides
- Teacher Editions for every Lit Guide
- Explanations and citation info for 40,694 quotes across 1929 books
- Downloadable (PDF) line-by-line translations of every Shakespeare play
Need something? Request a new guide .
How can we improve? Share feedback .
LitCharts is hiring!

Book Report

What is a Book Report & How to Write a Perfect One
Published on: Jan 26, 2022
Last updated on: Jan 31, 2024

Share this article
Writing a book report is a terrifying experience for many students. The terror begins with reading and understanding what you're reading but then continues as your thoughts become paper in front of you.
Have you ever been assigned a book report and thought, ‘Ugh! This is going to be terrible?’ Well, we're here to help.
Below you can find a helpful guide to understand how to write a perfect report. Here we have also provided some sample book reports and a free book report template for your help.
On This Page On This Page -->
What is a Book Report?
A book report is an informative piece of writing that summarizes the novel and presents some brief analysis on its main elements like plot, setting, characters.
This could either be a work of fiction or nonfiction with a tone covering everything from serious to humorous.
A book review is not the same as a book report.
Although they may look similar, one requires in-depth analysis and an objective point of view while the other is more descriptive and subjective.
Some course instructors may ask students to add relevant themes of the book and plot elements into their book reports. But, on a very basic level, a book report is an extremely simple form of review for any given text - no matter what its genre or author.
How does a book report writing benefit you?
Writing a good report will help students to improve their analytical and communication skills. They also get the opportunity to practice expressing themselves through creative or critical thought about the different aspects of books they read.
Assessing the Book Before Writing the Review
Before delving into the content of a book, it's essential to gather some key information. Begin by noting the following details:
- Author: Who authored the book? Are you familiar with any other works by this author?
- Genre: What category does the book fall intoâfiction, nonfiction, biography, etc.?
- Which audience would find this type of book appealing? Is this your typical genre preference? Do you enjoy reading books within this genre?
- Title: How does the title impact you? Does it pique your interest? Does it align well with the book's content?
- Pictures/Book Jacket/Cover/Printing: Analyze the book jacket or cover. What does it convey? Is it an accurate representation of the book? Did it generate excitement for you to read it? Are there any illustrations or images within the book? If so, what type are they, and do they captivate your interest?

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
Book Report Outline
Writing a book report becomes more manageable when you follow a structured outline. Here's an outline you can use as a guideline for your book report:
How to Write a Book Report? - H2
Writing a book report involves several key steps that can help you effectively communicate your understanding and analysis of a book. Here's a guide on how to write a book report:
Introduction
- Begin with an engaging introductory paragraph that includes the book's title, author, and publication information.
- Provide a brief overview of the book's genre and main theme.
- Include any initial reactions or expectations you had before reading the book.
- Summarize the main plot or central idea of the book without giving away major spoilers.
- Highlight key events, conflicts, and characters that drive the narrative.
- Focus on the most significant aspects of the story and avoid excessive details.
Analysis and Evaluation
- Analyze the author's writing style, storytelling techniques, and use of literary devices.
- Discuss the book's strengths and weaknesses, supporting your statements with examples from the text.
- Evaluate how effectively the author conveys their message and engages the reader.
- Consider the book's impact on you personally and its relevance to broader themes or issues.
Themes and Messages
- Identify the main themes or messages explored in the book.
- Discuss how these themes are developed throughout the narrative.
- Provide specific examples or quotes to support your analysis.
Character Analysis
- Analyze the main characters in the book, their development, and their relationships.
- Discuss their motivations, personalities, and how they contribute to the story.
- Use examples and quotes to illustrate your points.
- Summarize your main points and overall assessment of the book.
- Offer your personal opinion on the book, highlighting its strengths and weaknesses.
- Reflect on the impact the book had on you and who you would recommend it to.
Formatting and Proofreading
- Structure your book report into paragraphs with clear topic sentences.
- Check for spelling, grammar, and punctuation errors.
- Ensure your report is well-organized and follows a logical flow.
- Citations may be required if you quote or reference specific passages from the book.
Remember, a book report is not just a summary; it also involves critical analysis and interpretation.
By following these steps, you can create a comprehensive and insightful book report that effectively conveys your understanding.
Book Report Examples
Before you head into the writing process of your book report, it's a great idea to take some time and look at examples of other people's book reports.
In this way, you'll see how others have written their own work in an engaging manner that will inspire creativity on your part as well.
Book Report Sample
Book Report on Harry Potter
Book Report on Matilda
Book Report on Pride and Prejudice
Book Report for Kids
Book Report MLA Format
Book Report Worksheet
High School Book Report Template
Non-Fiction Book Report Template
Book Report Template 4th Grade
3rd Grade Book Report Template
Book Report Ideas
Picking a book for your report can be an intimidating task. You don't have any idea which books to read or what the professor will prefer, but there are some ideas of different subjects you could write about:
- To Kill a Mockingbird by Harper Lee
- The Catcher in the Rye by J.D. Salinger
- The Fault in Our Stars book report
- Animal Farm by George Orwell
- The Great Gatsby by F. Scott Fitzgerald
- Brave New World by Aldous Huxley
- Hunger Games book report
- A Tale of Two Cities by Charles Dickens
- Kite Runner by Khaled Hosseini
- Charlotte's webbook report
If you are still not sure about how to write a book report that will help you earn an A, then our essay writer AI is the perfect solution for you. Consider taking professional essay writing assistance from one of our experienced writers who specialize in this area.
No matter if you need help with your college essay, book review, book report, or full-length research paper, we provide essay writing service for students . Contact our expert essay writing service today to get the best assistance with all your academic tasks!
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main parts of a book report.
The main parts of a book report are the bibliography, characters, setting, themes, and plot. These four elements form a descriptive book report. However, most reports that you will read in high school or college are expository-based, meaning they explore an idea rather than discuss it.
Are book reports essays?
A book report is, quite simply, an essay about a book. A book report is a type of essay that students are asked to write by their teachers. Different formats for this writing assignment may be used, but the most common one is expository style (i.e., telling about something).
How long should a book report be?
Your book report should not exceed two double-spaced pages, and it should be somewhere between 600 and 800 words in length.
What is a thesis in a book report?
After a brief introduction of your topic, you state your point of view on the topic. This sentence is the thesis statement and serves as an overview of what will be discussed in this paper.
Caleb S. (Literature, Marketing)
Caleb S. has extensive experience in writing and holds a Masters from Oxford University. He takes great satisfaction in helping students exceed their academic goals. Caleb always puts the needs of his clients first and is dedicated to providing quality service.
Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!

Legal & Policies
- Privacy Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Terms of Use
- Refunds & Cancellations
- Our Writers
- Success Stories
- Our Guarantees
- Affiliate Program
- Referral Program
- AI Essay Writer
Disclaimer: All client orders are completed by our team of highly qualified human writers. The essays and papers provided by us are not to be used for submission but rather as learning models only.
- Try for free
How to Write a Book Report (+ Book Report Example)
Download for free, specific tips for writing effective book reports..
Write better book reports using the tips, examples, and outlines presented here. This resource covers three types of effective book reports: plot summaries, character analyses, and theme analyses. It also features a specific book report example for students.

How to write a book report (+ book report example)
Whether you're a student looking to show your comprehension of a novel, or simply a book lover wanting to share your thoughts, writing a book report can be a rewarding experience. This guide, filled with tips, tricks, and a book report example, will help you craft a report that effectively communicates your understanding and analysis of your chosen book.
Looking for a printable resource on book reports? See our Printable Book Report Outlines and Examples
What is a book report?
Book reports can take on many different forms. Writing a book review helps you practice giving your opinion about different aspects of a book, such as an author's use of description or dialogue.
You can write book reports of any type, from fiction to non-fiction research papers, or essay writing; however, there are a few basic elements you need to include to convey why the book you read was interesting when writing a good book report.

Types of book reports
Three types of effective book reports are plot summaries, character analyses, and theme analyses. Each type focuses on different aspects of the book and requires a unique approach. These three types of book reports will help you demonstrate your understanding of the book in different ways.
Plot summary
When you are writing a plot summary for your book report you don't want to simply summarize the story. You need to explain what your opinion is of the story and why you feel the plot is so compelling, unrealistic, or sappy. It is the way you analyze the plot that will make this a good report. Make sure that you use plenty of examples from the book to support your opinions.
Try starting the report with a sentence similar to the following:
The plot of I Married a Sea Captain , by Monica Hubbard, is interesting because it gives the reader a realistic sense of what it was like to be the wife of a whaling captain and live on Nantucket during the 19th century.
Character analysis
If you choose to write a character analysis, you can explore the physical and personality traits of different characters and the way their actions affect the plot of the book.
- Explore the way a character dresses and what impression that leaves with the reader.
- What positive characteristics does the character possess?
- Does the character have a "fatal flaw" that gets him/her into trouble frequently?
- Try taking examples of dialogue and analyzing the way a character speaks. Discuss the words he/she chooses and the way his/her words affect other characters.
- Finally, tie all of your observations together by explaining the way the characters make the plot move forward.
In the novel Charlotte's Web , by E. B. White, Templeton the rat may seem like an unnecessary character but his constant quest for food moves the plot forward in many ways.
Theme analyses
Exploring the themes (or big ideas that run throughout the story) in a book can be a great way to write a book report because picking a theme that you care about can make the report easier to write. Try bringing some of your thoughts and feelings as a reader into the report as a way to show the power of a theme. Before you discuss your own thoughts, however, be sure to establish what the theme is and how it appears in the story.
- Explain exactly what theme you will be exploring in your book report.
- Use as many examples and quotations from the book as possible to prove that the theme is important to the story.
- Make sure that you talk about each example or quotation you've included. Make a direct connection between the theme and the example from the book.
- After you have established the theme and thoroughly examined the way it affects the book, include a few sentences about the impact the theme had upon you and why it made the book more or less enjoyable to read.
In the novel Roll of Thunder Hear My Cry , by Mildred Taylor, the theme of racial prejudice is a major catalyst in the story.
How to write a book report

1. Thoroughly read the book
Immerse yourself in the book, taking the time to read it in its entirety. As you read, jot down notes on important aspects such as key points, themes, and character developments.
2. Identify the main elements of the book
Scrutinize the book's primary components, including its main themes, characters, setting, and plot. These elements will form the basis of your report.
3. Formulate a thesis statement
Compose a thesis statement that encapsulates your personal perspective about the book. This should be a concise statement that will guide your analysis and give your report a clear focus.
4. Create a detailed outline
Plan the structure of your book report. This outline should include an introduction, body paragraphs each focusing on a different aspect of the book, and a conclusion.
5. Craft the introduction
The introduction should provide basic information such as the book's title and author, and present your thesis statement. It should engage the reader and make them interested in your analysis.
6. Write the body of the report
In the body of your report, discuss in detail the book's main elements that you identified in step 3. Use specific examples from the text to support your analysis and to prove your thesis statement.
7. Write a strong conclusion
Your conclusion should summarize your analysis, reaffirm your thesis, and provide a closing thought or reflection on the overall book.
8. Review and edit your report
After writing, take the time to revise your report for clarity and coherence. Check for and correct any grammar or spelling errors. Ensure that your report clearly communicates your understanding and analysis of the book.
9. Include citations
If you have used direct quotes or specific ideas from the book, make sure to include proper citations . This is crucial in academic writing and helps avoid plagiarism.
10. Proofread
Finally, proofread your work. Look for any missed errors and make sure that the report is the best it can be before submitting it.

Book report example
Below is a book report example on the novel To Kill a Mockingbird by Harper Lee.
In To Kill a Mockingbird , Harper Lee presents a thoughtful exploration of racial prejudice, morality, and the loss of innocence. Set in the small, fictional town of Maycomb, Alabama, during the Great Depression, the book centers around the Finch family - young Scout, her older brother Jem, and their widowed father, Atticus. Scout's character provides a fresh perspective as she narrates her experiences and observations of the unjust racial prejudice in her town. Her honesty and curiosity, coupled with her father's teachings, allow her to grow from innocence to a more profound understanding of her society's inequalities. The plot revolves around Atticus Finch, a respected lawyer, defending a black man, Tom Robinson, unjustly accused of raping a white woman. As the trial progresses, it becomes clear that Robinson is innocent, and the accusation was a product of racial prejudice. Despite compelling evidence in Robinson's favor, he is convicted, symbolizing the power of bias over truth. The theme of racial prejudice is a significant part of the book. Lee uses the trial and its unjust outcome to critique the racial prejudice prevalent in society. For example, despite Atticus's solid defense, the jury's racial bias leads them to find Robinson guilty. This instance highlights how deeply ingrained prejudice can subvert justice. The book also explores the theme of the loss of innocence. Scout and Jem's experiences with prejudice and injustice lead to their loss of innocence and a better understanding of the world's complexities. For example, Scout's realization of her town's unfair treatment of Robinson demonstrates her loss of innocence and her understanding of societal biases. Overall, To Kill a Mockingbird is a compelling exploration of the harsh realities of prejudice and the loss of innocence. Harper Lee's intricate characters and vivid storytelling have made this book a classic.
The above is an excellent book report example for several reasons. First, it provides a clear, concise summary of the plot without giving away the entire story. Second, it analyzes the main characters, their roles, and their impacts on the story. Third, it discusses the major themes of the book - racial prejudice and loss of innocence - and supports these themes with evidence from the text. Finally, it presents a personal perspective on the book's impact and overall message, demonstrating a deep understanding of the book's significance.
Book report checklist
Always include the following elements in any book report:
- The type of book report you are writing
- The book's title
- The author of the book
- The time when the story takes place
- The location where the story takes place
- The names and a brief description of each of the characters you will be discussing
- Many quotations and examples from the book to support your opinions
- A thesis statement
- The point of view of the narrator
- Summary of the book
- The main points or themes discussed in the work of fiction or non-fiction
- The first paragraph (introductory paragraph), body paragraphs, and final paragraph
- The writing styles of the author
- A critical analysis of the fiction or non-fiction book
Don't forget!
No matter what type of book report you decide to write, ensure it includes basic information about the main characters, and make sure that your writing is clear and expressive so that it’s easy for audiences in middle school, high school, college-level, or any grade level to understand. Also, include examples from the book to support your opinions. Afterward, conduct thorough proofreading to complete the writing process. Book reports may seem disconnected from your other schoolwork, but they help you learn to summarize, compare and contrast, make predictions and connections, and consider different perspectives & skills you'll need throughout your life.
Looking for more writing resources? You can find them in our creative writing center .
Featured Middle School Resources
Related Resources

- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Arts and Entertainment
A Beginner's Guide to Writing a Book Report (with Examples)
Last Updated: March 13, 2024 Fact Checked
- Researching
- Drafting the Report
- Reviewing & Revising
Sample Book Reports & Summaries
Expert q&a.
This article was co-authored by Jake Adams and by wikiHow staff writer, Raven Minyard, BA . Jake Adams is an academic tutor and the owner of Simplifi EDU, a Santa Monica, California based online tutoring business offering learning resources and online tutors for academic subjects K-College, SAT & ACT prep, and college admissions applications. With over 14 years of professional tutoring experience, Jake is dedicated to providing his clients the very best online tutoring experience and access to a network of excellent undergraduate and graduate-level tutors from top colleges all over the nation. Jake holds a BS in International Business and Marketing from Pepperdine University. There are 9 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 1,416,233 times.
A book report is a short essay that summarizes and analyzes a work of fiction or nonfiction. Writing a book report may not seem fun at first, but it gives you a great chance to fully understand a work and its author. In this article, we’ll teach you everything you need to know about how to write a book report, from choosing a book and outlining to drafting and editing your final paper.
Things You Should Know
- Read the entire book and take notes on important themes, characters, and events. Use your notes to create an outline with evidence that supports your analysis.
- Include the title and author in your intro, then summarize the plot, main characters, and setting of the book.
- Analyze the author’s writing style, as well as the main themes and arguments of the book. Include quotes and examples to support your statements.
Researching Your Book Report

- For example, find out if your teacher wants you to include citations, such as page numbers from the book, in your report.
- Ask your teacher how much of your paper to devote to summary versus analysis. Most book reports are direct summaries with objective analysis rather than your personal opinions. In contrast, a book review or commentary is more opinion-driven.
- Some popular books for book reports include To Kill a Mockingbird by Harper Lee, Animal Farm by George Orwell, and The Hunger Games by Suzanne Collins. Choose a book at your grade level.

- Author: Who wrote the book? Do you know any other works by this author?
- Genre: Is the book fiction or nonfiction? If it’s fiction, is it historical, fantasy, horror, etc.? If it’s nonfiction, is it a biography, memoir, science, etc.?
- Audience: Who would find this book appealing? Is it intended for a specific age range or gender? Do you typically enjoy books like this?
- Title: Does the title catch your interest? Does it fit well with the book’s content?
- Book Cover/Illustrations: What does the book cover convey and does it accurately represent the book? How do you feel when you look at it? If the book has illustrations, what are they and do they hold your interest?

- Take breaks while reading to keep your attention sharp. Try to find a pace that is comfortable for you. If you get distracted after 15 minutes, read in 15-minute intervals. If you can go an hour, read for an hour at a time.
- Give yourself enough time to read the entire book. It’s very difficult to write a book report if you’ve just skimmed over everything. Don’t procrastinate!
- Don’t trust online book summaries. You can’t guarantee that they are accurate or true to the text.

- For example, look for a sentence that clearly describes a main setting in the book, such as “The castle was gloomy and made out of large black stones.”
Outlining Your Book Report

- Introduction: Introduce the title, author, and publication information. Include a brief overview of the book’s genre and main theme, and state your purpose for writing the report.
- Summary: Concisely summarize the plot or central idea, highlighting main events, characters, and conflicts. Focus on important aspects while avoiding spoilers.
- Analysis and Evaluation: Evaluate the author’s writing style and use of literary devices, like foreshadowing, metaphors, imagery, etc. Discuss the strengths and weaknesses of the book and use quotes and examples from the text.
- Themes and Messages: Identify the book’s main themes or messages and how they develop through the course of the book. Provide specific quotes and examples.
- Character Analysis: Analyze the main characters in the book, their development, and their relationships. Explain their motivations, personalities, and significance to the story. Provide examples and quotes to support your analysis.
- Personal Reflection: Depending on your teacher’s instructions, you might share your personal opinions and discuss what you liked and disliked about the book. Reflect on how the book relates to broader themes or issues.
- Conclusion: Summarize your main points and conclude with your final thoughts or reflections on the book.
- Bibliography: If required, include a works cited page or bibliography listing all the sources you used to write your book report.
- Outlining takes time, but it saves you more time once you reach the editing stage.
- Some people prefer to outline with pen and paper, while others just type up a list on the computer. Choose the method that works best for you.

- Be careful not to overuse quotes. If it seems like every other line is a quote, try to dial back. Aim to include a maximum of one quotation per paragraph. Quotes and examples should still take a backseat to your summary.

- For example, you’ll likely need to focus primarily on discussing the most important characters or the characters that appear most frequently in the text.
- When you are finished with your outline, go back through it to see if it makes sense. If the paragraphs don’t flow into one another, move them around or add/delete new ones until they do.
- Also, check to see if your outline covers all of the major elements of the book, such as the plot, characters, and setting.
Writing Your Book Report

- For example, a sentence summary might state, “This book is about the main character’s journey to Africa and what she learns on her travels.”
- Don’t take up too much space with your introduction. In general, an introduction should be 3-6 sentences long, though in rare cases, they may be longer or shorter.

- Use vivid language when you can and include plenty of details. For example, you might write, “The farm was surrounded by rolling hills.”

- For instance, if the main character moves to Africa, you might describe what happens before the move, how the move goes, and how they settle in once they arrive.

- For example, you might write that the main character is “a middle-aged woman who enjoys the finer things in life, such as designer clothes.” Then, connect this description to the plot summary by describing how her views change after her travels, if they do.
- Expect to introduce the characters in the same sentences and paragraphs as the plot introduction.

- You might write, “The author argues that travel gives you a new perspective. That is why her main characters all seem happier and more grounded after visiting new places.”
- For fiction, determine if the author is using the story to pass along a certain moral or lesson. For example, a book about an underdog athlete could encourage readers to take chances to pursue their dreams.

- For example, an author who uses lots of slang terms is probably going for a hip, approachable style.

- Some teachers require, or strongly suggest, that you include the author’s name and the book title in your concluding paragraph.
- When writing a conclusion , don’t introduce any new thoughts. Any important points should be made in your body paragraphs. Save the space for your recap.

Reviewing and Revising Your Book Report

- Before you submit your paper, make sure that you’ve spelled the author’s name and any character names correctly.
- Don’t trust your computer’s spell check to catch all the errors for you. Spell check can be helpful, but it isn’t perfect and can make mistakes.

- If you’re nervous about asking, try saying something like “It would be great if you could go over my book report and make sure that it reads smoothly.”
- Remember, no one’s first draft is perfect, so don’t get upset if someone suggests you do something differently. They want to help make your report the best it can be, so don’t take constructive criticism personally.

- For example, double-check that you are using the correct font, font size, and margins.
- Once you've finished proofreading, revising, and checking that you've addressed all the requirements, you're ready to submit your book report!

- Even though your book report is your own work, avoid using “I” too much. It can make your writing feel choppy. Thanks Helpful 1 Not Helpful 0
- It might be tempting to watch the movie or read the online notes instead of reading the book. Resist this urge! Your teacher will be able to tell the difference. Thanks Helpful 2 Not Helpful 0
Tips from our Readers
- Calm down and walk around if you get too frustrated while writing. If you write a book report while angry, you're more likely to misspell things!
- Choose a unique book. Harry Potter or Percy Jackson is an absolute no. Everyone chooses those. Try something different!
- Write when anything comes to mind! You don't want to lose your ideas!

- Give yourself plenty of time to write your report. Don’t wait until the last minute or you may feel rushed. Thanks Helpful 2 Not Helpful 0
- Stealing or using another person’s work is considered plagiarism and academic dishonesty. Make sure that the work you submit is all your own. Thanks Helpful 1 Not Helpful 0
You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://www.aresearchguide.com/write-book-report.html
- ↑ Jake Adams. Academic Tutor & Test Prep Specialist. Expert Interview. 24 July 2020.
- ↑ https://grammark.org/how-to-write-a-book-report/
- ↑ https://library.valleycollege.edu/elements_of_book_report.pdf
- ↑ https://takelessons.com/blog/steps-to-writing-a-book-report
- ↑ https://www.infoplease.com/homework-help/homework-center-writing-book-report
- ↑ https://liberalarts.oregonstate.edu/wlf/what-setting
- ↑ https://www.tcc.edu/wp-content/uploads/archive/writing-center-handouts/essay-types-plot-summary.pdf
- ↑ https://www.cornerstone.edu/blog-post/six-steps-to-really-edit-your-paper/
About This Article

To write a book report, start by introducing the author and the name of the book and then briefly summarizing the story. Next, discuss the main themes and point out what you think the author is trying to suggest to the reader. Finally, write about the author’s style of writing, paying particular attention to word choice and the overall tone of the book. For tips on editing and polishing your paper before turning it in, keep reading! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Louise Pena
May 17, 2016
Did this article help you?

Ashley Egerage
Nov 13, 2017
Aug 20, 2016
Charlotte Arney
Mar 10, 2023
Nov 16, 2017

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Don’t miss out! Sign up for
wikiHow’s newsletter
How To E-D-U
How to write a college book report.
So you’ve been assigned your first college book report…are you at a loss as to how to complete it? Don’t worry; you aren’t alone. Many students enter college not really knowing where to start when it comes to book reports. College professors expect a much higher level of work than high school teachers expect. Step by step, here’s how to write a book report that’s on that higher level :
Read the book. Yes, every word. You can’t just skim over the book when you’re going to be writing about it. As you read, use a highlighter or sticky notes to mark the most important passages. You can also take notes if it will help you remember the book’s plot.
Read what others have written about the book. If you have a popular selection, narrow down your research to read about the research that interests you most. Don’t worry about the topic of your own paper just yet; read the research that interest you. Draw research from scholarly sources, not popular magazines, and if you do research online, find credible sources.
Narrow your topic. Start by reading the guidelines for the report given to you by your professor so that you stay within the parameters of the project. Think about the topics and debates you enjoyed the most when reading through research on the book.
Write a thesis statement. In one or two sentences, you should be able to describe the argument of your paper. In college, a book report isn’t expected to just describe the book and your personal opinion of it. You need to have an arguable point, which could be as simple as “this book is one of the most important pieces of literature for young adults” to something much more specific about the author’s theme, characters, setting, writing style, or plot. Avoid a thesis statement that is extremely similar to any research you’ve read.
Outline your report. You should start with an introductory paragraph (or few paragraphs if your report is extremely long) that includes your thesis statement and can include a very brief summary of the book. Your final paragraph should restate your thesis statement. Between, focus on at least three points that support your thesis statement’s argument.
Narrow down the resources you’ll use from your research. Your professor likely has a requirement for the number of resources you’ll have to use; stick to it carefully. Highlight specific quotes you want to use from your resources.
Write! If you’ve done your research and created a good outline, this part should be easier than you think. Remember, this is your first draft, so it doesn’t have to be too refined.
Edit and proofread. This is a crucial step, and one that many students avoid. Some professors give you time to review work in class or will give you feedback on your first draft, but if yours doesn’t, make sure you edit and proofread on your own.
Cite your sources. This should be your final step and is one of the most important. Ethical writing is your key to success in college, at least when it comes to papers. Plagiarism and inappropriate paraphrasing will not just destroy you academically – it is also illegal. Follow your professor’s preferred citation method carefully.
Subscribe to RSS
Follow us on Twitter
Subscribe to Email
How-To Guides
- Applying to College
- College Facts
- Financial Aid / Paying for College
- Online Education
- SAT / ACT / College Prep
- Student Tips

Book Reviews
What this handout is about.
This handout will help you write a book review, a report or essay that offers a critical perspective on a text. It offers a process and suggests some strategies for writing book reviews.
What is a review?
A review is a critical evaluation of a text, event, object, or phenomenon. Reviews can consider books, articles, entire genres or fields of literature, architecture, art, fashion, restaurants, policies, exhibitions, performances, and many other forms. This handout will focus on book reviews. For a similar assignment, see our handout on literature reviews .
Above all, a review makes an argument. The most important element of a review is that it is a commentary, not merely a summary. It allows you to enter into dialogue and discussion with the work’s creator and with other audiences. You can offer agreement or disagreement and identify where you find the work exemplary or deficient in its knowledge, judgments, or organization. You should clearly state your opinion of the work in question, and that statement will probably resemble other types of academic writing, with a thesis statement, supporting body paragraphs, and a conclusion.
Typically, reviews are brief. In newspapers and academic journals, they rarely exceed 1000 words, although you may encounter lengthier assignments and extended commentaries. In either case, reviews need to be succinct. While they vary in tone, subject, and style, they share some common features:
- First, a review gives the reader a concise summary of the content. This includes a relevant description of the topic as well as its overall perspective, argument, or purpose.
- Second, and more importantly, a review offers a critical assessment of the content. This involves your reactions to the work under review: what strikes you as noteworthy, whether or not it was effective or persuasive, and how it enhanced your understanding of the issues at hand.
- Finally, in addition to analyzing the work, a review often suggests whether or not the audience would appreciate it.
Becoming an expert reviewer: three short examples
Reviewing can be a daunting task. Someone has asked for your opinion about something that you may feel unqualified to evaluate. Who are you to criticize Toni Morrison’s new book if you’ve never written a novel yourself, much less won a Nobel Prize? The point is that someone—a professor, a journal editor, peers in a study group—wants to know what you think about a particular work. You may not be (or feel like) an expert, but you need to pretend to be one for your particular audience. Nobody expects you to be the intellectual equal of the work’s creator, but your careful observations can provide you with the raw material to make reasoned judgments. Tactfully voicing agreement and disagreement, praise and criticism, is a valuable, challenging skill, and like many forms of writing, reviews require you to provide concrete evidence for your assertions.
Consider the following brief book review written for a history course on medieval Europe by a student who is fascinated with beer:
Judith Bennett’s Ale, Beer, and Brewsters in England: Women’s Work in a Changing World, 1300-1600, investigates how women used to brew and sell the majority of ale drunk in England. Historically, ale and beer (not milk, wine, or water) were important elements of the English diet. Ale brewing was low-skill and low status labor that was complimentary to women’s domestic responsibilities. In the early fifteenth century, brewers began to make ale with hops, and they called this new drink “beer.” This technique allowed brewers to produce their beverages at a lower cost and to sell it more easily, although women generally stopped brewing once the business became more profitable.
The student describes the subject of the book and provides an accurate summary of its contents. But the reader does not learn some key information expected from a review: the author’s argument, the student’s appraisal of the book and its argument, and whether or not the student would recommend the book. As a critical assessment, a book review should focus on opinions, not facts and details. Summary should be kept to a minimum, and specific details should serve to illustrate arguments.
Now consider a review of the same book written by a slightly more opinionated student:
Judith Bennett’s Ale, Beer, and Brewsters in England: Women’s Work in a Changing World, 1300-1600 was a colossal disappointment. I wanted to know about the rituals surrounding drinking in medieval England: the songs, the games, the parties. Bennett provided none of that information. I liked how the book showed ale and beer brewing as an economic activity, but the reader gets lost in the details of prices and wages. I was more interested in the private lives of the women brewsters. The book was divided into eight long chapters, and I can’t imagine why anyone would ever want to read it.
There’s no shortage of judgments in this review! But the student does not display a working knowledge of the book’s argument. The reader has a sense of what the student expected of the book, but no sense of what the author herself set out to prove. Although the student gives several reasons for the negative review, those examples do not clearly relate to each other as part of an overall evaluation—in other words, in support of a specific thesis. This review is indeed an assessment, but not a critical one.
Here is one final review of the same book:
One of feminism’s paradoxes—one that challenges many of its optimistic histories—is how patriarchy remains persistent over time. While Judith Bennett’s Ale, Beer, and Brewsters in England: Women’s Work in a Changing World, 1300-1600 recognizes medieval women as historical actors through their ale brewing, it also shows that female agency had its limits with the advent of beer. I had assumed that those limits were religious and political, but Bennett shows how a “patriarchal equilibrium” shut women out of economic life as well. Her analysis of women’s wages in ale and beer production proves that a change in women’s work does not equate to a change in working women’s status. Contemporary feminists and historians alike should read Bennett’s book and think twice when they crack open their next brewsky.
This student’s review avoids the problems of the previous two examples. It combines balanced opinion and concrete example, a critical assessment based on an explicitly stated rationale, and a recommendation to a potential audience. The reader gets a sense of what the book’s author intended to demonstrate. Moreover, the student refers to an argument about feminist history in general that places the book in a specific genre and that reaches out to a general audience. The example of analyzing wages illustrates an argument, the analysis engages significant intellectual debates, and the reasons for the overall positive review are plainly visible. The review offers criteria, opinions, and support with which the reader can agree or disagree.
Developing an assessment: before you write
There is no definitive method to writing a review, although some critical thinking about the work at hand is necessary before you actually begin writing. Thus, writing a review is a two-step process: developing an argument about the work under consideration, and making that argument as you write an organized and well-supported draft. See our handout on argument .
What follows is a series of questions to focus your thinking as you dig into the work at hand. While the questions specifically consider book reviews, you can easily transpose them to an analysis of performances, exhibitions, and other review subjects. Don’t feel obligated to address each of the questions; some will be more relevant than others to the book in question.
- What is the thesis—or main argument—of the book? If the author wanted you to get one idea from the book, what would it be? How does it compare or contrast to the world you know? What has the book accomplished?
- What exactly is the subject or topic of the book? Does the author cover the subject adequately? Does the author cover all aspects of the subject in a balanced fashion? What is the approach to the subject (topical, analytical, chronological, descriptive)?
- How does the author support their argument? What evidence do they use to prove their point? Do you find that evidence convincing? Why or why not? Does any of the author’s information (or conclusions) conflict with other books you’ve read, courses you’ve taken or just previous assumptions you had of the subject?
- How does the author structure their argument? What are the parts that make up the whole? Does the argument make sense? Does it persuade you? Why or why not?
- How has this book helped you understand the subject? Would you recommend the book to your reader?
Beyond the internal workings of the book, you may also consider some information about the author and the circumstances of the text’s production:
- Who is the author? Nationality, political persuasion, training, intellectual interests, personal history, and historical context may provide crucial details about how a work takes shape. Does it matter, for example, that the biographer was the subject’s best friend? What difference would it make if the author participated in the events they write about?
- What is the book’s genre? Out of what field does it emerge? Does it conform to or depart from the conventions of its genre? These questions can provide a historical or literary standard on which to base your evaluations. If you are reviewing the first book ever written on the subject, it will be important for your readers to know. Keep in mind, though, that naming “firsts”—alongside naming “bests” and “onlys”—can be a risky business unless you’re absolutely certain.
Writing the review
Once you have made your observations and assessments of the work under review, carefully survey your notes and attempt to unify your impressions into a statement that will describe the purpose or thesis of your review. Check out our handout on thesis statements . Then, outline the arguments that support your thesis.
Your arguments should develop the thesis in a logical manner. That logic, unlike more standard academic writing, may initially emphasize the author’s argument while you develop your own in the course of the review. The relative emphasis depends on the nature of the review: if readers may be more interested in the work itself, you may want to make the work and the author more prominent; if you want the review to be about your perspective and opinions, then you may structure the review to privilege your observations over (but never separate from) those of the work under review. What follows is just one of many ways to organize a review.
Introduction
Since most reviews are brief, many writers begin with a catchy quip or anecdote that succinctly delivers their argument. But you can introduce your review differently depending on the argument and audience. The Writing Center’s handout on introductions can help you find an approach that works. In general, you should include:
- The name of the author and the book title and the main theme.
- Relevant details about who the author is and where they stand in the genre or field of inquiry. You could also link the title to the subject to show how the title explains the subject matter.
- The context of the book and/or your review. Placing your review in a framework that makes sense to your audience alerts readers to your “take” on the book. Perhaps you want to situate a book about the Cuban revolution in the context of Cold War rivalries between the United States and the Soviet Union. Another reviewer might want to consider the book in the framework of Latin American social movements. Your choice of context informs your argument.
- The thesis of the book. If you are reviewing fiction, this may be difficult since novels, plays, and short stories rarely have explicit arguments. But identifying the book’s particular novelty, angle, or originality allows you to show what specific contribution the piece is trying to make.
- Your thesis about the book.
Summary of content
This should be brief, as analysis takes priority. In the course of making your assessment, you’ll hopefully be backing up your assertions with concrete evidence from the book, so some summary will be dispersed throughout other parts of the review.
The necessary amount of summary also depends on your audience. Graduate students, beware! If you are writing book reviews for colleagues—to prepare for comprehensive exams, for example—you may want to devote more attention to summarizing the book’s contents. If, on the other hand, your audience has already read the book—such as a class assignment on the same work—you may have more liberty to explore more subtle points and to emphasize your own argument. See our handout on summary for more tips.
Analysis and evaluation of the book
Your analysis and evaluation should be organized into paragraphs that deal with single aspects of your argument. This arrangement can be challenging when your purpose is to consider the book as a whole, but it can help you differentiate elements of your criticism and pair assertions with evidence more clearly. You do not necessarily need to work chronologically through the book as you discuss it. Given the argument you want to make, you can organize your paragraphs more usefully by themes, methods, or other elements of the book. If you find it useful to include comparisons to other books, keep them brief so that the book under review remains in the spotlight. Avoid excessive quotation and give a specific page reference in parentheses when you do quote. Remember that you can state many of the author’s points in your own words.
Sum up or restate your thesis or make the final judgment regarding the book. You should not introduce new evidence for your argument in the conclusion. You can, however, introduce new ideas that go beyond the book if they extend the logic of your own thesis. This paragraph needs to balance the book’s strengths and weaknesses in order to unify your evaluation. Did the body of your review have three negative paragraphs and one favorable one? What do they all add up to? The Writing Center’s handout on conclusions can help you make a final assessment.
Finally, a few general considerations:
- Review the book in front of you, not the book you wish the author had written. You can and should point out shortcomings or failures, but don’t criticize the book for not being something it was never intended to be.
- With any luck, the author of the book worked hard to find the right words to express her ideas. You should attempt to do the same. Precise language allows you to control the tone of your review.
- Never hesitate to challenge an assumption, approach, or argument. Be sure, however, to cite specific examples to back up your assertions carefully.
- Try to present a balanced argument about the value of the book for its audience. You’re entitled—and sometimes obligated—to voice strong agreement or disagreement. But keep in mind that a bad book takes as long to write as a good one, and every author deserves fair treatment. Harsh judgments are difficult to prove and can give readers the sense that you were unfair in your assessment.
- A great place to learn about book reviews is to look at examples. The New York Times Sunday Book Review and The New York Review of Books can show you how professional writers review books.
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
Drewry, John. 1974. Writing Book Reviews. Boston: Greenwood Press.
Hoge, James. 1987. Literary Reviewing. Charlottesville: University Virginia of Press.
Sova, Dawn, and Harry Teitelbaum. 2002. How to Write Book Reports , 4th ed. Lawrenceville, NY: Thomson/Arco.
Walford, A.J. 1986. Reviews and Reviewing: A Guide. Phoenix: Oryx Press.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift

How to write outstanding college level book reports

Many generations of students from completely different areas have been facing the same common assignment: writing a book report. Book reports are very popular because professors like them, and they are not going to disappear anytime soon. However, students are rarely excited when they get a book report assigned. Book reports require you to not only read a book and understand its key concepts but also to provide a detailed analysis.
First, your book report must address the most important aspects, such as the title, information about the author, key information about the characters, and plot summary. These are the details that you would also provide in a book review, as well. However, a book report is different because you should also provide your personal opinion. The author’s point is usually presented in the form of a thesis statement and then supported with examples from the book. We decided to help you write an outstanding book report. Here are some useful tips.
Understand your assignment
First of all, you should know exactly what you’ve been asked to do. Make sure to clarify all the requirements, deadlines, and the necessary format. For example, if you’re being asked to write an essay, it can be an essay about the main theme of the book or about a particular character. Read your prompt carefully and don’t hesitate to talk to your instructor if you have any questions.
Read the book
Obviously, you need to read the book before writing anything about it. Many students prefer to skim through a book, looking for certain keywords and trying to select the most important passages. This is a very bad practice because, this way, you may miss something important. Make sure to dedicate enough time to reading.
Nathan Stewart, writer at LegitWritingServices advises: “Don’t copy information from book reports. On the one hand, it may seem that using reports written by professionals is a good idea, however you work will suffer from plagiarism issues.”
When reading a fiction book, make sure to write notes and focus on the following details:
- the setting;
- characters and connections between them;
- themes addressed in the book;
- literary symbols and metaphors;
- the author’s viewpoint.
When reading a nonfiction book, focus on the chapter titles to have a better understanding of the structure. Here are important things to consider:
- the general topic of the book;
- the most important events;
- the key characters and the way they impact the topic;
- new information that you’ve learned from the book.
Write an outline
We recommend that you write an outline before you start to write the book report itself. This way, it will be easier for you to create a proper report with a clear structure. Plan your report and think of what information you’re going to write first, and how you’re going to connect different sections so that your report will be logical and easy to read. Plan the introduction, body, and conclusion. Review your notes and select the best pieces of evidence to support your thesis statement.
Write a strong introduction
The introduction is one of the most important sections of a book report because it’s the first thing that your readers will see. Grammarly recommends writing a hook that will immediately grab the reader’s attention. A hook is basically one or two sentences that are aimed at capturing your reader’s attention. Write an explanatory introduction, mentioning the title of the book and the author. You should also explain what your report will be about. Even if you haven’t been asked to include a thesis statement in your report, having one will give you a certain advantage because your report will be more focused and specific.
Write body paragraphs
Use your outline and notes to write the main body of the report. Provide a brief plot summary and add your own thoughts, considering the themes of the book in the context of your topic and thesis statement. If it’s a nonfiction book, you should also explain the author’s thesis. Explain why the author uses a particular tone and style. Pay your attention to any symbols. Address the most important moments in the storyline, and use evidence from the book to support your own claims.
Write the conclusion
In the last paragraph of your book report, sum up your key points and the most important evidence. Some instructors may also ask you to restate the author’s name and the title of the book. The conclusion also gives you an opportunity to leave your readers with something to think about. For example, you can ask them a question related to the topic of your report, or consider the book in a broader context, drawing analogies between the events described in the book and important issues from real life.
Edit and proofread
Last but not least, you must edit and proofread your report, writing the final draft. Even the most talented writers need to write several drafts before their paper becomes perfect. We recommend that you never skip this important step. Take a break and then come back to your paper. Make sure that the structure is logically correct and all the sections are formatted according to the required style. Edit sentences that sound awkward or are hard to read. After this, proofread your report and fix any grammar or spelling mistakes. Also, don’t forget about the formatting of your paper. Use the standard MLA format in case your teacher hasn’t provided a specific format to follow.
Although writing a book report may seem to be a difficult task, you can make it much easier if you follow our step-by-step guide. Book reports allow you to demonstrate your understanding of various books and complex topics, as well as your analytical skills. We hope that our tips will help you write a book report that will impress everyone.
The editorial unit
More in Feature of the week

Exploring Bishkek, Kyrgyzstan: A gateway to Central Asian adventure

Zematopic®: The SOS treatment against eczema

How do winter tyres actually work?

Preparing for the first tantric massage: What to expect and how to get ready

Five ways couples’ sensual massages improve the relationship

Ten strategies to save money on everyday expenses

How to build an emergency fund while managing debts?

How to choose a car for the family

London and beyond: A shopper’s guide to the best shopping centres
- Page Content
- Sidebar Content
- Main Navigation
- Quick links
- All TIP Sheets
- Writing a Summary
- Writing Paragraphs
- Writing an Analogy
- Writing a Descriptive Essay
- Writing a Persuasive Essay
- Writing a Compare/Contrast Paper
- Writing Cause and Effect Papers
- Writing a Process Paper
- Writing a Classification Paper
- Definitions of Writing Terms
- How to Write Clearly
- Active and Passive Voice
- Developing a Thesis and Supporting Arguments
- Writing Introductions & Conclusions
- How to Structure an Essay: Avoiding Six Weaknesses in Papers
Writing Book Reports
- Writing about Literature
- Writing about Non-Fiction Books
- Poetry: Meter and Related Topics
- Revising and Editing
- Proofreading
TIP Sheet WRITING BOOK REPORTS
It's likely that, whatever your educational goals, you will eventually write a book report. Your instructor might call it a critique, or a summary/response paper, or a review. The two components these assignments have in common are summary and evaluation.
Other TIP Sheets on related topics that might prove helpful in developing a book report, depending on the type of book and the specifics of your assignment, include the following:
- How to Write a Summary
- Writing About Non-Fiction Books
- Writing About Literature
Summary AND evaluation Typically, a book report begins with a paragraph to a page of simple information-author, title, genre (for example, science fiction, historical fiction, biography), summary of the central problem and solution, and description of the main character(s) and what they learned or how they changed.
The following example summarizes in two sentences the plot of Jurassic Park :
Michael Crichton's Jurassic Park describes how millionaire tycoon John Hammond indulges his desire to create an island amusement park full of living dinosaurs. In spite of elaborate precautions to make the park safe, his animals run wild, killing and maiming his employees, endangering the lives of his two visiting grandchildren, and finally escaping to mainland Costa Rica.
On the other hand, a thesis statement for a book report reflects your evaluation of the work; "I really, really liked it" is inadequate. Students sometimes hesitate to make judgments about literature, because they are uncertain what standards apply. It's not so difficult to evaluate a book in terms of story elements: character, setting, problem/solution, even organization. (See TIP Sheet Writing About Literature for ideas on how to handle these standard story elements.) Nevertheless, a good thesis statement should include your reflection on the ideas, purpose, and attitudes of the author as well.
To develop an informed judgment about the work, start by asking yourself lots of questions (for more ideas, see "Evaluation" on the TIP Sheet Writing About Literature). Then choose your most promising area, the one about which you have something clear to say and can easily find evidence from the book to illustrate. Develop this into a thesis statement.
For example, here is what one thesis statement might look like for Jurassic Park (notice how this thesis statement differs from the simple summary above):
In Jurassic Park , Crichton seems to warn us chillingly that, in bioengineering as in chaos theory, the moment we most appear to be in control of events is the exact moment control is already irredeemably lost to us.
To develop an informed judgment and a corresponding thesis statement about a book, brainstorm by answering questions such as the following:
- For what purpose did the author write this, and did he fulfill that purpose?
- What did the main character learn? Does this lesson reflect reality as you know it?
- Were the characters complex and believable? What do they reveal of the author? of human nature?
- How well did the setting contribute to the mood? How did setting affect character and plot development?
The invisible author One common mistake students make is failing to step back far enough from the story to evaluate it as a piece of work produced by someone . Evaluation–you may be surprised to learn it!–is as much about the author as about the story itself. It is about making informed guesses about the author's purpose, ideas, and attitudes based on his use of language, organization, plot, and character development.
Usually the author does not figure prominently in the story unless the book is autobiographical. More often he is the invisible persona–invisible, yet not absent. The author leaves traces of himself throughout. Paradoxically, your understanding of the author depends on your deliberate detachment from the story itself to discover those traces.
Imagine standing very, very close to a large painting–inches away. Your focus is on blobs of color, but you are unable to identify the object represented. When you move back a few steps and alter your focus, the blobs take on a recognizable form. In the same way, you have to draw back from the story to discern the purpose, ideas , and attitudes of the author.
Author's purpose No one goes to the trouble to write something without purpose. Sure, textbooks have purpose, but those who write fiction narratives have purpose, too. Even fantasy writers have purpose. A book report should include your evaluation of whether the author succeeded in his purpose.
The following writer has made a statement about the author's purpose:
Crichton seems not so much to be warning us of the evils of scientific inquiry as begging us, in a very convincing way, to exercise collective moral restraint on scientific research.
This writer would then go on to use quotations, examples, and evidence from the book to show why she believes this is Crichton's purpose.
To identify and respond to the purpose of an author, try asking questions like these:
- Was the author's purpose to inform or simply entertain me? Did I learn something? Was I entertained? Did I lose interest? If I lost interest, was this author, perhaps, writing to a different audience?
- Is the author trying to persuade me to think or act in a particular way? About what issue? What point of view would he or she have me adopt? Was I convinced?
Author's ideas The author's ideas may be stated by the author himself in a foreword, or they may show up in the words of a narrator or a principal character. The character Ian Malcolm, for example, is a primary spokesman for Crichton's criticism of post-modern science. Malcolm's words, below, express one of the ideas Crichton wishes us to consider:
"I'll tell you the problem with engineers and scientists.... They are focused on whether they can do something. They never stop to ask if they should do something."
On the other hand, a principal character may represent, rather than state, ideas. Hammond's visiting grandchildren, for example, might represent the oblivious, yet threatened, human populations of the mainland and the planet itself. When ideas are implied rather than stated, they are called themes.
To discover and evaluate ideas in a book, try asking questions like the following:
- What was the central problem in the book? Was it a personal, social, or moral problem? Does it relate to life as you know it?
- What ideas(s) about life and society does the author seem to hold?
- What did the principal character(s) learn? How did they change? What does this seem to say about people? About society? About morality?
Author's attitudes Once you have identified what ideas an author is trying to examine, you must still determine what the author's attitude is toward those ideas. An author's attitudes are revealed in part by the tone, or overall mood, of the work. In writing, as in conversation, tone is not so much stated as implied. In reading we depend solely on the emotional overtones of the words to infer the attitudes of the author.
For example, suppose you have determined that Crichton wishes to explore the idea of how private industry exploits scientific research. You must then determine, as well, what Crichton's attitude is toward this situation. Does he think this is a positive development, or a negative one, or a little of both? Does he think it is inevitable, or preventable? One way to figure out Crichton's attitude about this is to identify the tone he uses to tell the story. We describe the tone of a book with adjectives, and more than one if necessary: straightforward, complex, ironic, creepy, pathetic, bitter, comic, tragic.
For example, here is a statement using three different adjectives to describe Crichton's attitude toward one of the central problems in Jurassic Park :
Crichton strikes an ominous tone in Jurassic Park. Even though this is a cautionary tale, the author nevertheless is optimistic that the mainstream scientific community, represented in this story by Alan Grant, can learn restraint and respect for nature.
(When identifying the tone of a book, make the effort to distinguish an individual character's attitude from the author's overall attitude-they may differ.)
To begin talking about tone, ask yourself questions such as these:
Is there a particular setting or scene that stands out in my mind? What was the mood of that scene? Is this mood indicative of the entire book? Is the author an optimist, a pessimist, or a realist? How does he show it? Does a principal character experience one persistent state of mind or emotion? What would I call it? Is it indicative of the work overall? Did the mood of the work help or hinder my understanding of the author's ideas?
"In conclusion..." Clearly it is important to be able to make intelligent inferences about the author, because a book evaluation evaluates how well the author has done her job, not just how much you liked the story. After you have asked and answered that question, then you may add, "I really, really liked it."
Home | Calendars | Library | Bookstore | Directory | Apply Now | Search for Classes | Register | Online Classes | MyBC Portal MyBC -->
Butte College | 3536 Butte Campus Drive, Oroville CA 95965 | General Information (530) 895-2511
How To Write a College Level Book Report
- Haley Drucker
- Categories : College , Education
- Tags : Education college topics studying
College Book Reports
Chances are, you’ve written more than one book report during your school career. And if you’re taking any English classes in college, you’ll likely be required to do a few more. In college, though, book reports are a little different than the kind most high school teachers expect. This type of assignment also goes by a couple different names, including “ book review ” and “critical review.”
High school book reports are mostly about summarizing the book, proving you’ve actually read it. A college level book report is a little more complex. Instead of just explaining what happened in the book, you’ll be required to provide a critical analysis of its contents. This isn’t as hard as it sounds, and it isn’t much different from the other essays you’re used to writing in English class. Follow the advice below, and you’ll be well prepared to turn out a thoughtful and college-worthy report.
The Summary
The first and most important thing to do when writing a college level book report is to actually read the book. It might be tempting to use something like Spark Notes , but that won’t give you the knowledge you need to write an effective critique. So read the book carefully, and if possible give yourself some time to reflect on it before starting your paper.
When you’re ready to write the book review, the first you’ll need (after the introduction and thesis) is a short summary. Notice the word “short.” The summarization should take up no more than a third of your paper, and a forth would probably be better. You don’t have to explain every plot twist and every chapter—just give the reader an overview of what happens in the book and what it’s about.
Before you start writing this part of the book report, you might want to figure out what you’ll be covering in the analysis section (see below). That way, you can summarize with an eye towards what you’ll be discussing later on. If you spend most of the paper talking about how the theme of greed plays out in the book, your summary should focus on those parts of the book that illustrate greed and its consequences.
It’s possible you might not need to include a summary in your critical review. Some professors want you to assume your reader has already read the book. In that case, you could omit this first part altogether. So read the assignment carefully, and check with your teacher to make sure you know what he or she is expecting.
The Analysis
The bulk of your paper should be an analysis of the book. Instead of just repeating what you read, you’ll be asked to go beyond the obvious and show your understanding of what the text by providing a critique. You won’t be able to critique everything about the book, of course. So again, be sure to read the assignment carefully because your teacher might tell you what to focus on.
If not, choose a specific aspect of the book to build your paper around. Narrowing your focus to a particular character, theme, relationship, or plot point keeps your book report from rambling and your thoughts from becoming disorganized. When in doubt, go with a theme since that approach proves you’ve thought carefully about the novel. Explain the theme’s role in the book, and how it relates to the various characters and events. Use plenty of concrete examples and a few quotes (not too many—no more than one or two per paragraph).
In any critique, you’ll want to draw from your personal opinions and reactions to the book. But if your teacher is calling the assignment a “book review” you might be expected to actually evaluate the book. In this case, expand on your analysis by including your own (reasoned and supported) opinion on how well the novel is written and whether it does a good job with its stories and themes. Read a few book reviews online or in the newspaper if you’re not sure how to do that.
Going Outside the Book
This part is optional—some teachers expect it and some don’t. But it can really improve your analysis to go beyond the text and analyze the novel as it relates to the outside world. Learn something about the author, and the time and culture in which the book was written. Consider the author’s intentions and influences. In what ways does this outside knowledge inform your reading of the book, help you understand why it was written the way it was? Professors love it when you treat a book as part of the real world, rather than just an isolated text. Don’t be afraid to use a little research here—just be sure to cite your sources.
In Conclusion
A few final things to consider:
- It can’t be stressed too much—make sure you know what your professor is looking for. A college book report can be written in a variety of ways, and you don’t want to find out too late that you’ve chosen the wrong approach.
- It can be a good idea to read the book more than once. This takes extra time, of course, but you’ll pick up on things during the second read that you didn’t notice the first time around. A second read also lets you reflect on the deeper aspects and themes of the book, since you already know the plot. And you can keep an eye out for good examples and quotes to include in your critical review.
- Write about something that’s interesting to you. Book reports and especially book reviews are all about engaging with the text on a personal level. Even in the most boring novel there’s likely one idea or character that grabs your interest. Focus on that—the writing will go more smoothly and the paper’s quality will be higher.
These are the basics of how to write a college or university level book report. For more help and information, you can check out the following resources. Also, here’s a short, sample book report that is not about a college-level novel, but does a good job of illustrating the mix of summary and critical analysis that should go into a college level book report or review. And don’t be afraid to ask for help during the writing process. Professors love to chat with you about papers in progress, and librarians and writing centers are also valuable resources.
- “ How to Write a Critical Book Review ” by Carleton College
- “ How to Write a Book Review ” by Los Angeles Valley College Library
- “ Writing Book Reviews ” by Writing Tutorial Services at Indiana University (PDF file)

Tips on How to Write Your College Book Review
Table of contents
- 1.1 Read the Book
- 1.2 Understand the Genre and Audience
- 1.3 Figure Out Book Review Structure
- 2.1 Provide a Brief Summary
- 2.2 Discuss the Author's Writing Style
- 2.3 Evaluate the Book's Strengths and Weaknesses
- 2.4 Share Personal Reflections
- 3 Tips for an Effective Review
- 4 Book Reviews Have Never Been So Easy with Papersowl
A book review is, without exaggeration, one of the most interesting writing assignments in a university curriculum. This type of literary criticism allows the reviewer to express his own opinion regarding the material read. Yet, like other types of scientific writing, book reviews involve a certain list of requirements for design and structure. In the following sections, we will look at the following book review guidelines and tips:
- You will know important tips that a reviewer should consider when preparing to write a book review.
- Practical tips and guidelines to help you craft a high-quality book review that effectively conveys your insights and analysis, making your review informative and engaging.
- The factors and techniques that can take your book review from ordinary to memorable, leaving a lasting impact on your readers and fellow book enthusiasts.
Preparing to Write the Review
Before we dive into the process of crafting an effective book review, let's first explore the crucial steps involved in preparing to write a review that truly captures the essence of the book.
Read the Book
No matter how trivial it may sound, the key factor to writing a good book review is to read the original in full. Authors of brief description works often try to convey only key events important to the plot. In turn, the reviewer can look at the work from a fresh angle, highlighting his favorite moments and coming to unusual conclusions to write book reviews.
To improve the efficiency of book reviews, use active reading techniques . This strategy involves highlighting the key points of the book, taking notes, and creating a visualization. These techniques are used to increase awareness and facilitate further analysis of what you read to create outstanding book reviews.
Understand the Genre and Audience
After reading the book, you are ready to start a book review. First of all, indicate who the author of the book is and what its title is. It is also necessary to determine the book's genre, main theme, and message . Finally, figure out who the target audience for this book is, whether it is written for children or adults, and whether it is aimed at specific people or people of a certain profession.
Figure Out Book Review Structur e
The last part of the preparatory stage to write a book review essay is to become familiar with the structure. Before writing book reviews, make sure to compose a book review outline. PapersOwl’s pro writers of academic essay papers have identified a list of five key components to structure a book review:
- Introduction
- Body or Summary
- Analysis and evaluation
As with other types of essays, book reviews usually follow the basic 5-paragraph structure : introduction, three body paragraphs and the conclusion. Each body paragraph of your book review for school should be logically connected to the previous one and begin with a topic sentence. It provides the general idea disclosed in the paragraph.
How to Write the Review of a Book
Now when you know the basic structural elements of a book review, we can move forward and answer the main question. How to write a book review? Let's start with general criteria for a book report and then go on to more detailed ones. Each fragment will contain basic questions to give you a hint on what to write about in a review of a book.
- First, describe your overall impression of the book. What emotions did the reading evoke in you, and what thoughts did you have?
- Then, smoothly go on writing a book review by describing the main plot of the book. This step doesn't require much creativity on your part and is more about stating the facts.
- It is also important to clarify whether events occur linearly or chaotically. Don’t forget to mention the number of storylines and their direction. See whether the author uses unusual narrative techniques such as flashbacks or multiple perspectives to attract the reader's attention.
Provide a Brief Summary
It's time to write a brief summary for your book review. To do this, list the main characters, the setting, and the main point of the plot:
- What is the basic plot or main argument of the book?
- How is the book structured? Are there chapters, sections, or parts?
Pay special attention to the characters in the book. Authors often put special meaning into the set of character traits of individual characters. Also, note whether there were any changes in the behaviour of the characters during events.
- Who are the main characters, and what are their primary traits?
- Are the characters well-developed and multi-dimensional?
- Do the characters undergo any significant changes or growth throughout the story?
Discuss the Author's Writing Style
One of the key factors when writing about books is determining the writer's style. Each author tries to bring something new to stand out from other writers. Each article review writer at PapersOwl is ready to advise you on how to distinguish the writer’s outstanding features, as they are experts in writing a book review for students. With the help of certain syntax and vocabulary, the author can influence how the audience perceives what is written.
- How would you describe the author's writing style? (e.g., descriptive, succinct, humorous, serious)
- Are there any distinctive elements of the author's prose that stood out?
- Did the writing style enhance or detract from the book's themes or messages?
Evaluate the Book's Strengths and Weaknesses
When writing a book review, a comparative analysis of the strengths and weaknesses of the work is very important. Highlight the most impressive aspects of the book for yourself, and pay attention to explaining why exactly they hooked you. If certain fragments of the story seemed unnecessary to the reviewer and did not carry much significance, it’s necessary to mention this in the book review.
- What are the strongest aspects of the book?
- Were there any parts of the book that felt unnecessary or redundant?
- Did you feel engaged and connected throughout, or were there parts where your interest waned?
It is not obligatory to compare an author with other writers in your review of the book. You can also make a comparative description of the works of one author in different periods of his creation. If you are familiar with other works by the author of the book you have chosen, do not be afraid to show off your erudition. Try to notice the similarities and divergences of books from different periods, concluding the hidden messages.
- How does this book compare to other works by the same author (if you've read any)?
- Are there other books in the same genre that you'd compare it to?
- What sets this book apart from others in its genre?
Share Personal Reflections
A good book review strikes the perfect balance between analyzing objective and subjective factors. Therefore, the reviewer‘s personal opinions must be included in the structure of the essay. Share your emotions in your own words. Tell about the changes that occurred in your worldview as a result of reading the book. If the book did not cause you a strong response, analyze what exactly caused the lack of reaction.
- What was your initial reaction upon finishing the book?
- Which parts of the book resonated most with you?
- Were there moments that provoked strong emotions, such as joy, sadness, anger, or excitement?
If there were quotes that particularly resonated with you, be sure to share them with other readers. Briefly tell why this or that author’s thought is special for you.
- Were there any notable quotes or passages that you'd like to highlight?
When writing a book review, highlight the main educational message of the book and share your experience, whether the book motivated you to learn more about this book’s argument.
- Did the book inspire you to read more about a particular subject or theme?
- Would you be interested in reading a sequel or another book by the same author?
Tips for an Effective Review
You already know what is a book review, how to write a book review, and the importance of following the structure.. We’ve also reminded about reading the book in its entirety, and you have an idea of what exactly you need to include in a book review. Now, we will share with you actual tips on writing an exceptional book review and get an A+.
- Stay objective
Remember, the reviewer needs to strike a balance between expressing own opinions and being objective. For example, you are not a fan of romance novels, and you are reviewing fiction. Even if you don’t like the kind, try to abstract yourself and professionally evaluate this literary work.
- Provide an example
Any argument must be supported by evidence. Think about what real-life or an example from other literary works you can support your point.
- Criticize the work, not the author
Always keep in mind that your constructive criticism concerns the author’s book, not the author himself. A professional reviewer knows how to separate a writer’s personal characteristics from his writing talent when they review a book.
The golden rule of any descriptive essay , including a book review, is to check the spelling several times before submitting the work. Even the most profound essay with a non-trivial meaning can be spoiled by grammatical errors and wrong structure. Make sure all body paragraphs contain a thesis statement.
Book Reviews Have Never Been So Easy with Papersowl
Writing book reviews is an interesting assignment that tests students' creativity and analytical skills. When you have an idea of what is a book review, what it includes, and what factors you should pay attention to when you do a book review, you can easily cope with writing such an essay. Remember to be creative while following our book review tips, and the process will be easy and enjoyable. We also advise you to study an example of a book review. Our experienced team is always ready to help you out writing a review for a book of any complexity.
Readers also enjoyed

WHY WAIT? PLACE AN ORDER RIGHT NOW!
Just fill out the form, press the button, and have no worries!
We use cookies to give you the best experience possible. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy.
Book Review Writing
Book Review Examples
Book Review Examples to Help You Get Started

People also read
How to Write a Book Review - A Step By Step Guide
A Complete Book Review Format Guide For Students
Are you in desperate need of some assistance to up your book review writing game?
We know that penning down a review can come off as a tricky challenge, but do not worry!
To help you write book reviews that carry the essence of the book and engage readers, we have collected a handful of book review examples in this blog.
The included examples will enable you to understand different writing styles and approaches taken toward book review writing . So, you can use your words effectively to craft the perfect book review.
Let’s kickstart things off!
- 1. Good Book Review Examples for Students
- 2. Short Book Review Examples for Fiction Books
- 3. Non-Fiction Book Review Examples
Good Book Review Examples for Students
You might be a professional writer, or you may not have any experience in writing book reviews. Rest assured, we’ll show you how to write perfect book reviews with the help of a sample template and great examples.
See this template to know what you should include in your book review:
Book Review Template
Here is a good book review example for 4th-grade students:

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
Book Review Examples for Middle School Students
Reading reviews written by others can help you get a feel and flavor of good book reviews. Learning how to write a perfect book review can help students to:
- Critically analyze a text
- Give a personal opinion on the text
- Improve analyzing and critical thinking skills
Here are some interesting book review examples suitable for middle school students.
Book Review Example for Middle School Students
Book Review Example for Kids
Book Review of Any Book in 300 Words
Science Book Review Example
Book Review Examples For High School Students
Below, you can also find some good book review examples for high school students. These real-life examples can help you get a clear understanding of the standard book review format that you should follow.
Book Review Example for High School Students
Book Review Examples for Class 9
Book Review Example for Grade 10
Book Review Examples for College Students
As a college student, you are required to demonstrate that you have examined the book from different angles. The points you raise in your book review need to be supported with clear facts and evidence.
The following are some interesting critical book review examples for college students to learn how to write a perfect review.
Book Review Example for Class 12
Short Book Review for Students
Conclusion of Book Review Example
Short Book Review Examples for Fiction Books
Fiction book reviews follow the same basic formula as writing book reviews of any other genre. For your help, we have compiled exciting examples of fiction book reviews that you can get valuable assistance from.
Short Book Review Example for Fiction Books
Book Review of Hazel Wood by Melissa Albert
“The Hazel Wood” by Melissa Albert is a work of fiction and falls into fantasy and young adult fiction genres. The novel revolves around fantastical fairy tales, and magical realism, blurring the lines between reality and fantasy.
Here is an example of a comprehensive review of the book Hazel Wood:
Tough Essay Due? Hire Tough Writers!
Non-Fiction Book Review Examples
For reviewing a non-fiction book, you are required to describe the book and summarize major points of interest. You should evaluate the author’s contribution to a subject that you may know very little about.
Here is a great non-fiction book review example to help you come up with a critical perspective on a text.
Non-Fiction Book Review Example
Hopefully, with the help of the above examples, you get a better idea of how to write a perfect book review.
To wrap it up, Writing a great book review is a tricky task, no matter if you are a high school, college, or university student. Book review writing might seem like a simple task, but it requires excellent analyzing and critical thinking skills.
But, not everyone can crack this task easily. They might need additional help from expert book review writers. That’s why our professional essay writing service offers book review writing help whenever you need it.
Professional essay writers at MyPerfectWords.com can help you with all your academic requests within your specified timeline. Just contact our customer service and we’ll handle all your queries promptly.
Keep the words flowing!

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Cathy has been been working as an author on our platform for over five years now. She has a Masters degree in mass communication and is well-versed in the art of writing. Cathy is a professional who takes her work seriously and is widely appreciated by clients for her excellent writing skills.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A book review is a critical analysis of the book. It is where you can share your reaction to the book. It is a guidebook for potential readers a book. It is an objective summary of the main ideas and arguments in the book. It is a descriptive and critical evaluation of the book. It ranges from 200 to 250 words.
Book reports commonly describe what happens in a work; their focus is primarily on giving an account of the major plot, characters, thesis, and/or main idea of the work. Most often, book reports are a K-12 assignment and range from 250 to 500 words. Book reviews are most often a college assignment, but they also appear in many professional ...
Step #1: Understanding the Assignment. A top-notch book report starts with fully understanding your assignment, a step that shapes your entire approach. First, determine the required length and format, like APA or MLA, as this sets the stage for the depth of your analysis and presentation.
For example, if we were writing an introduction about a book report over Harper Lee's To Kill a Mockingbird, we might write something like this:. In Harper Lee's iconic coming of age novel, To Kill a Mockingbird, Lee confronts the audience with the idea that systemic racism was rampant in the U.S. court system in the early 20th century in the South.
The body paragraphs of your book report accomplish several goals: they describe the plot, delve more deeply into the characters and themes that make the book unique, and include quotations and examples from the book. Below are some resources to help you succeed in summarizing and analyzing your chosen text.
Here's an outline you can use as a guideline for your book report: I. Introduction. A. Introduce the book with the title, author, and publication information. B. Provide a brief overview of the book's genre and main theme. C. State your purpose for writing the report and any initial expectations you had. II.
2. Identify the main elements of the book. Scrutinize the book's primary components, including its main themes, characters, setting, and plot. These elements will form the basis of your report. 3. Formulate a thesis statement. Compose a thesis statement that encapsulates your personal perspective about the book.
Include the title and author in your intro, then summarize the plot, main characters, and setting of the book. Analyze the author's writing style, as well as the main themes and arguments of the book. Include quotes and examples to support your statements. Part 1.
Avoid a thesis statement that is extremely similar to any research you've read. Outline your report. You should start with an introductory paragraph (or few paragraphs if your report is extremely long) that includes your thesis statement and can include a very brief summary of the book. Your final paragraph should restate your thesis statement.
3. Organize your notes and create an outline. Gather your notes and arrange them into categories. Once you've completed this, write an outline and organize the categories to become the paragraphs of your book report. Jot down bullet points on what each paragraph will include and what part of the book can support it.
This handout will help you write a book review, a report or essay that offers a critical perspective on a text. It offers a process and suggests some strategies for writing book reviews. ... A great place to learn about book reviews is to look at examples. The New York Times Sunday Book Review and The New York Review of Books can show you how ...
Write body paragraphs. Use your outline and notes to write the main body of the report. Provide a brief plot summary and add your own thoughts, considering the themes of the book in the context of ...
TIP Sheet. WRITING BOOK REPORTS. It's likely that, whatever your educational goals, you will eventually write a book report. Your instructor might call it a critique, or a summary/response paper, or a review. The two components these assignments have in common are summary and evaluation. Other TIP Sheets on related topics that might prove ...
Make notes for quick reference. Gather important and relevant information: Relevant and strong quotations from the book add weightage to your book report and help you give your point of view in a better manner. Gather the quotes that are relevant to your report's theme and idea. After you've gathered enough information and understood the ...
You probably wrote book reports in high school, and maybe you've mastered the form. In college, however, you'll need to get used to writing a different kind of paper. A college level book report, also known as a book review or critical review, is less about summary and more about analysis and critique. You have to show that you understand the novel on a deeper-than-surface level, and ...
Here are quick steps to create a book report: Consult Summary Websites: Visit websites providing book summaries and analyses. For instance, SparkNotes or CliffsNotes offer concise overviews. Focus on Key Details: Select 2-3 crucial aspects of the book, like major themes or character development. Discuss these in-depth.
An academic book review provides the main ideas, and since published book reviews typically have a limited word count, the summary should remain brief. Analysis and Significance. Compare the book and its argument with the other literature on the topic. Discuss its contribution to past and current research and literature.
Keep in mind that a good book report example should always include the five elements: the title, the introduction, the setting, a summary of the tale, and the conclusion. ... When writing a college level book report, it is important to do an excellent job so as to get an excellent grade. The article explained how to review the character in the ...
The college book report template provided below gives good sense of what content should be included in report, how outline should be completed. You can use this outline as a structure for your own report, or just read it for inspiration before completing your essay: 1. Introduction. Here, bibliography elements should be listed (author's name ...
When writing a book report, provide your own perspective and understanding. Meanwhile, stay away from confrontational or dismissive language. Use evidence and moderate emotion, neutral tone. don't just get away with an evaluation of how good/bad, relevant/irrelevant is it.
1.1 Read the Book. 1.2 Understand the Genre and Audience. 1.3 Figure Out Book Review Structure. 2 How to Write the Review of a Book. 2.1 Provide a Brief Summary. 2.2 Discuss the Author's Writing Style. 2.3 Evaluate the Book's Strengths and Weaknesses. 2.4 Share Personal Reflections. 3 Tips for an Effective Review.
Book Review Template. Here is a good book review example for 4th-grade students: "Charlotte's Web" by E.B. White — A Heartwarming Tale of Friendship. "Charlotte's Web" by E.B. White is a heartwarming tale of friendship that takes us to Zuckerman's farm, where a special pig named Wilbur forms an unlikely bond with Charlotte, a clever ...