
Gurukul of Excellence
Classes for Physics, Chemistry and Mathematics by IITians
Join our Telegram Channel for Free PDF Download

Case Study Questions for Class 6 Science Chapter 5 Separation of Substances
- Last modified on: 3 months ago
- Reading Time: 8 Minutes

Table of Contents
[Download] Case Study Questions for Class 6 Science Chapter 5 Separation of Substances
Here we are providing case study or passage-based questions for class 6 science chapter 5 Separation of Substances.
Case Study/Passage Based Questions
You are asked to add two spoons of solid salt to some liquid water taken in a beaker. On stirring it you find that whole of the salt has disappeared and only liquid can be seen in beaker. 1. After stirring the salt completely disappears and you can see only liquid in the beaker. The liquid in beaker is (a) water (b) solution (c) solute (d) solvent 2 . Which of the following processes will be useful to get salt from this solution? (a) Condensation (b) Evaporation (c) Filtration (d) Sedimentation 3. Which process can you use to get liquid water from the water vapours if you collect them in another container? (a) Sedimentation (b) Condensation (c) Evaporation (d) Filtration
Related Posts
What is case study question for class 6 science.
Case study or passage-based questions in class 6 Science typically require students to read a given scenario or passage and answer questions based on the information provided. These questions assess students’ comprehension, analytical thinking, and application of scientific concepts. Here is an example of case study or passage-based questions for class 6 Science:
Passage: Rahul conducted an experiment to investigate how different liquids affect the rusting of iron nails. He placed four iron nails in four separate beakers containing water, vinegar, oil, and saltwater. After one week, he observed the nails and recorded his observations.
a) What is the purpose of Rahul’s experiment?
b) Compare and contrast the appearance of the iron nails in each beaker after one week.
Best Ways to Prepare for Case Study Questions
To develop a strong command on class 6 Science case study questions, you can follow these steps:
- Read the textbook and study materials: Familiarize yourself with the concepts and topics covered in your class 6 Science curriculum. Read the textbook thoroughly and take notes on important information.
- Practice analyzing case studies: Look for case studies or passages related to class 6 Science topics. Analyze the given information, identify key details, and understand the context of the situation.
- Develop comprehension skills: Focus on improving your reading comprehension skills. Practice reading passages or articles and try to summarize the main points or extract relevant information. Pay attention to details, vocabulary, and the overall structure of the passage.
- Understand scientific concepts: Ensure that you have a solid understanding of the scientific concepts discussed in class. Review the fundamental principles and theories related to each topic.
- Make connections: Try to connect the information provided in the case study to the concepts you have learned in class. Identify any cause-effect relationships, patterns, or relevant scientific principles that apply to the situation.
- Practice critical thinking: Develop your critical thinking skills by analyzing and evaluating the information given in the case study. Think logically, consider multiple perspectives, and draw conclusions based on the evidence provided.
- Solve practice questions: Look for practice questions or sample case study questions specifically designed for class 6 Science. Solve these questions to apply your knowledge, practice your analytical skills, and familiarize yourself with the format of case study questions.
- Seek clarification: If you come across any challenging concepts or have doubts, don’t hesitate to ask your teacher for clarification. Understanding the underlying principles will help you tackle case study questions effectively.
Download CBSE Books
Exam Special Series:
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Science (for 2024)
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Maths (for 2024)
- CBSE Most Repeated Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important Diagram Based Questions Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Practical Based Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important “Differentiate Between” Based Questions Class 10 Social Science
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Physics (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Chemistry (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Maths (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Biology (for 2024)
- CBSE Important Diagrams & Graphs Asked in Board Exams Class 12 Physics
- Master Organic Conversions CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Definitions Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Laws & Principles Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Physics Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Maths Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Biology Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- ICSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (215 Numericals)
- ICSE Important Figure Based Questions Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (230 Questions)
- ICSE Mole Concept and Stoichiometry Numericals Class 10 Chemistry (65 Numericals)
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Chemistry BOARD Exams (150 Qs)
- ICSE Important Functions and Locations Based Questions Class 10 Biology
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Biology BOARD Exams (100 Qs)
✨ Join our Online JEE Test Series for 499/- Only (Web + App) for 1 Year
✨ Join our Online NEET Test Series for 499/- Only for 1 Year
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Join our Online Test Series for CBSE, ICSE, JEE, NEET and Other Exams

Editable Study Materials for Your Institute - CBSE, ICSE, State Boards (Maharashtra & Karnataka), JEE, NEET, FOUNDATION, OLYMPIADS, PPTs
Discover more from Gurukul of Excellence
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading

- Book Solutions
- State Boards
Class 6 Science Case Study Question
Case study question class 6 science (cbse / ncert board).
Class 6 Science Case Study Question and Answer: CBSE / NCERT Board Class 6 Science Case Study Question prepared by expert Science Teacher. Students can learn Case Based Question / Paragraph Type Question for NCERT Class 6 Science.
There are total 16 chapter Food Where Does It Come From, Components of Food, Fibre to Fabric, Sorting Materials Into Groups, Separation of Substances, Changes Around Us, Getting to Know Plants, Body Movements, The Living Organisms and Their Surroundings, Motion and Measurement of Distances, Light Shadows and Reflection, Electricity and Circuits, Fun with Magnets, Water, Air Around Us, Garbage In Garbage Out.
For any problem during learning any Case or any doubts please comment us. We are always ready to help You.
CBSE Class 6 Science Case Study Question
Chapter 1 Food Where Does It come From Case Study Question
Chapter 2 Components of Food Case Study Question
Chapter 3 Fibre to Fabric Case Study Question
Chapter 4 Sorting Materials Into Groups Case Study Question
Chapter 5 Separation of Substances Case Study Question
Chapter 6 Changes Around Us Case Study Question
Chapter 7 Getting to Know Plants Case Study Question
Chapter 8 Body Movements Case Study Question
Chapter 9 The Living Organisms – Characteristics and Habitats Case Study Question
Chapter 10 Motion and Measurement of Distances Case Study Question
Chapter 11 Light Shadows and Reflection Case Study Question
Chapter 12 Electricity and Circuits Case Study Question
Chapter 13 Fun with Magnets Case Study Question
Chapter 14 Water Case Study Question
Chapter 15 Air Around Us Case Study Question
Chapter 16 Garbage In Garbage Out Case Study Question
What is Case Study Question?
Ans. At case Study there will one paragraph and on the basis of that concept some question will made. Students have to solve that question.
How many marks will have at case based question?
Most of time 5 questions will made from each case. There will 1 or 2 marks for each question.
Important links:
- Lakhmir Singh Class 6 Book Solution
- NCERT Solution Class 6 Science
Sign in to your account
Username or Email Address
Remember Me
Class 6 Science Chapter 3 Case Based Questions - Separation of Substances
Case 1: separation of substances in agriculture.
Mr. Patel is a farmer in India, and he's been using traditional methods for separating grains from harvested stalks. He's curious about modern farming equipment. Answer the following questions:
Q1: Explain the traditional method Mr. Patel uses for threshing. What are the advantages and disadvantages of this method? Ans: Mr. Patel uses manual threshing, where small bundles of harvested stalks are thrashed on a hard surface to separate the grains. The advantage is that it's simple and doesn't require machinery. The disadvantage is that it's labor-intensive. Q2: Describe the modern farming equipment called a combine harvester. How does it work, and what are its benefits over traditional methods? Ans: A combine harvester is a modern farming machine that can harvest, thresh, and winnow in a single operation. It works by cutting and collecting crops, separating grains from stalks, and removing husks. Benefits include increased efficiency and reduced labor. Q3: What is the main purpose of threshing in agriculture? (a) Separating grains from harvested stalks (b) Separating stones from rice (c) Separating sand from gravel (d) Separating bran from flour Ans: (a) Q4: What is the purpose of winnowing in agriculture? (a) Separating grains from husk (b) Separating stones from rice (c) Separating sand from gravel (d) Separating bran from flour Ans: (a)
Case 2: Separation of Substances in Filtration
Sophia is a chemistry student conducting an experiment to separate fine insoluble solid particles from a liquid. Answer the following questions:
Q5: Explain the process of filtration that Sophia is using in her experiment. What equipment does she need, and how does it work? Ans: Filtration is a process where a mixture is passed through a filter paper or sieve to separate solid particles from the liquid. Sophia needs a funnel, filter paper, and a container. The liquid passes through the filter paper, leaving solid particles behind. Q6: What are the common applications of filtration in daily life? Provide at least three examples. Ans: Common applications of filtration include purifying drinking water, filtering coffee grounds, and separating impurities from cooking oil. Q7: What does filtration help separate? (a) Soluble solids from liquids (b) Insoluble solids from liquids (c) Gases from liquids (d) Liquids from solids Ans: (b) Q8: In which of the following scenarios would filtration be most suitable? (a) Separating sugar from tea (b) Separating salt from water (c) Separating oxygen from air (d) Separating oil from vinegar Ans: (a)
Case 3: Separation of Substances in Evaporation and Condensation
Lisa wants to separate salt from a solution of salt and water. She decides to use evaporation and condensation. Answer the following questions:
Q9: Explain how Lisa can separate salt from the saltwater solution using evaporation and condensation. What are the steps involved? Ans: Lisa can separate salt from the saltwater solution by evaporating the water, leaving behind salt crystals. Then, she can use condensation to collect the evaporated water vapor and convert it back into liquid water. Q10: Why is it important to use both evaporation and condensation in this process? Ans: Using both evaporation and condensation ensures that only the water is separated from the solution, leaving the salt behind. Q11: What is a saturated solution? (a) A solution with too much solid dissolved in it (b) A solution with too little solid dissolved in it (c) A solution with an equal amount of solid and liquid (d) A solution with no solid dissolved in it Ans: (a) Q12: What is the purpose of condensation in the separation of salt from a saltwater solution? (a) To convert liquid water into vapor (b) To convert water vapor into liquid water (c) To separate salt from water (d) To dissolve salt in water Ans: (b)
Case 4: Separation of Substances in Handpicking and Sieving
John is helping his mother in the kitchen, and she asks him to separate stones from a bowl of rice. Answer the following questions:
Q13: Describe how John can use handpicking to separate stones from rice. What conditions make handpicking suitable for this task? Ans: John can use handpicking to separate stones from rice because the stones have different sizes and colors than the rice. He can simply pick out the stones by hand. Q14: Explain the process of sieving and how it can be used to separate substances. What type of materials can be separated effectively through sieving? Ans: Sieving involves using a sieve with appropriately sized holes to separate substances. It is effective for separating materials like bran from flour, sand from gravel, and pearls of different sizes. Q15: What is the primary condition that makes handpicking effective for separating substances? (a) Differences in size and color (b) Differences in taste (c) Differences in temperature (d) Differences in shape and smell Ans: (a) Q16: What can be effectively separated using sieving? (a) Salt from water (b) Bran from flour (c) Air from gases (d) Liquid from solids Ans: (d)
Case 5: Separation of Substances in Sedimentation and Decantation
Sara is conducting an experiment with muddy water. She wants to separate soil and sand from the water. Answer the following questions:
Q17: Explain the process of sedimentation and how it can be used to separate soil and sand from muddy water. What happens during sedimentation? Ans: Sedimentation involves allowing insoluble particles (soil and sand) to settle at the bottom of the container over time. Sara can use this process to separate soil and sand from muddy water. Q18: What is the purpose of decantation, and when is it used in conjunction with sedimentation? Ans: Decantation is used after sedimentation to carefully pour out the upper layer (water) while leaving the sediment (soil and sand) behind. Q19: What is the outcome of sedimentation in the separation of soil and sand from water? (a) Soil and sand remain suspended in water. (b) Soil and sand settle at the bottom of the container. (c) Water evaporates completely. (d) Soil and sand turn into gas. Ans: (b) Q20: When is decantation typically used in the separation of substances? (a) Before sedimentation (b) After sedimentation (c) Instead of sedimentation (d) During filtration Ans: (b)
Top Courses for Class 6
Faqs on class 6 science chapter 3 case based questions - separation of substances, past year papers, important questions, viva questions, video lectures, sample paper, shortcuts and tricks, mock tests for examination, extra questions, previous year questions with solutions, study material, objective type questions, semester notes, practice quizzes.

Case Based Questions: Separation of Substances Free PDF Download
Importance of case based questions: separation of substances, case based questions: separation of substances notes, case based questions: separation of substances class 6, study case based questions: separation of substances on the app, welcome back, create your account for free.
Forgot Password
Unattempted tests, change country, practice & revise.
The Site is down as we are performing important server maintenance, during which time the server will be unavailable for approximately 24 hours. Please hold off on any critical actions until we are finished. As always your feedback is appreciated.

- Study Packages
- NCERT Solutions
- Sample Papers
- Online Test

- Questions Bank
- Separation of Substances
- Test Series
- Ncert Solutions
- Solved Papers
- Current Affairs
- JEE Main & Advanced
- Pre-Primary
- MP State Exams
- UP State Exams
- Rajasthan State Exams
- Jharkhand State Exams
- Chhattisgarh State Exams
- Bihar State Exams
- Haryana State Exams
- Gujarat State Exams
- MH State Exams
- Himachal State Exams
- Delhi State Exams
- Uttarakhand State Exams
- Punjab State Exams
- J&K State Exams
6th Class Science Separation of Substances Question Bank
Done separation of substances total questions - 45.

question_answer 1) X is a separation technique based on the difference in weights of the solids in a solid-solid mixture. What is X?
A) Sieving done clear
B) Handpicking done clear
C) Threshing done clear
D) Winnowing done clear
question_answer 2) What type of a substance is steel?
A) A solid - liquid heterogeneous mixture done clear
B) A solid - solid heterogeneous mixture done clear
C) A solid - solid homogeneous mixture done clear
D) A pure substance done clear
question_answer 3) Vinegar is a solution of acetic acid in water. What kind of mixture is vinegar?
A) A homogeneous mixture of solid and liquid done clear
B) A heterogeneous mixture of liquid and liquid done clear
C) A homogeneous mixture of liquid and liquid done clear
D) A heterogeneous mixture of solid and liquid done clear
question_answer 4) Which of the following separation techniques is used for separating a mixture of two or more gases?
A) Sedimentation done clear
B) Liquification done clear
C) Hand picking done clear
D) Decantation done clear
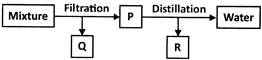
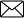
A) Water + sand + glass done clear
B) Oxygen + hydrogen + salt done clear
C) Stones + rice + water done clear
D) Chalk powder + sugar + water done clear
A) Sugar done clear
B) Chalk powder done clear
C) Glass done clear
D) Oxygen done clear
C) Alcohol done clear
D) Oxygen done clear
question_answer 8) How are grain seeds removed from their stalks?
A) Sieving done clear
B) Winnowing done clear
C) Threshing done clear
D) All of the above done clear
question_answer 9) A compound has
A) only one kind of mixture. done clear
B) only one kind of element. done clear
C) a mixture of elements and molecules. done clear
D) only one kind of molecules. done clear
question_answer 10) A Identify the mixture from the following.
A) Oxygen done clear
B) Carbon dioxide done clear
C) Hydrogen done clear
D) Air done clear
question_answer 11) Identify the compound from the following.
question_answer 12) Identify the element from the following.
C) Water done clear
question_answer 13) Which of the following is an example of a solid-in-gas mixture?
A) Soil done clear
B) Smoke done clear
C) Moisture done clear
D) Dew done clear
question_answer 14) Which of the following does NOT belong to the group formed by the others?
A) Brass done clear
B) Water done clear
C) Butter-milk done clear
D) Steel done clear
question_answer 15) A pure substance is made of
A) only one kind of atoms or molecules. done clear
B) two or more kinds of molecules. done clear
C) mixture of homogeneous substances done clear
D) all of the above done clear
question_answer 16) Which of the following statements about a mixture is TRUE?
A) It is a pure substance. done clear
B) Its constituents are not combined chemically. done clear
C) Its constituents do not retain their individual properties. done clear
D) It is always homogeneous. done clear
question_answer 17) In a mixture, constituents exhibit
A) similar properties. done clear
B) only those properties which are characteristic to the mixture. done clear
C) their own properties. done clear
D) no properties. done clear
question_answer 18) What is the process by which a gas changes into a liquid?
A) Decantation done clear
B) Sublimation done clear
C) Condensation done clear
D) Sedimentation done clear
question_answer 19) What kind of mixtures are alloys?
A) Solid-Gas done clear
B) Liquid-Liquid done clear
C) Gas-Gas done clear
D) Solid-Solid done clear
question_answer 20) What kind of mixtures are aerated drinks?
A) Solid-Solid done clear
B) Liquid-Solid done clear
C) Gas-Liquid done clear
D) Liquid-Liquid done clear
question_answer 21) Identify the liquid-in-gas type of mixture from the following.
A) Dissolved carbon dioxide in water done clear
B) Droplets of water in air done clear
C) Dissolved oxygen in water done clear
question_answer 22) A homogeneous mixture
A) is made up of one type of molecules. done clear
B) is the one in which the components can be distinguished. done clear
C) is the one in which the components cannot be distinguished. done clear
D) can be separated into its constituents physically. done clear
question_answer 23) A mixture contains three different substances X, Y and Z. They are of the same size, cubical in shape and yellow in colour. X particles are very heavy, insoluble, non-magnetic and contribute 50% of the mixture. Y particles are very light, insoluble, non-magnetic and contribute 40% of the mixture. And Z particles are iron pieces. Which of the following methods can separate X, Y and Z?
A) Winnowing, Magnetic separation done clear
B) Magnetic separation, Winnowing done clear
C) Sieving, Magnetic separation. Filtration done clear
D) Handpicking, Sublimation, Sieving done clear
question_answer 24) The sky looks clearer and brighter after the rain due to loading by rain drops. Which of the following is similar to the process mentioned above?
A) Separation of butter from curd. done clear
B) Separation of salt from sea water. done clear
C) Sprinkling water on a dusty street before sweeping. done clear
D) Separation of grain seeds from their stalks. done clear
question_answer 25) X is a separation technique used only when the components of a solid-solid mixture have different sizes. Identify X.
A) Winnowing done clear
B) Sieving done clear
C) Threshing done clear
D) Magnetic separation done clear
A) Only X done clear
B) Only Y, Z done clear
C) Only Z, X done clear
D) X, Y and Z done clear
question_answer 27) How is scrap-iron separated from other wastes in the scrap yard?
A) Sublimation done clear
B) Magnetic separation done clear
C) Handpicking done clear
D) Winnowing done clear
A) \[a-2,\text{ }b-3,\text{ }c-4,\text{ }d-1\] done clear
B) \[a-1,\text{ }b-4,\text{ }c-2,\text{ }d-3\] done clear
C) \[a-2,\text{ }b-4,\text{ }c-3,\text{ }d-1\] done clear
D) \[a-2,\text{ }b-4,\text{ }c-1,\text{ }d-3\] done clear
question_answer 29) Which of the following mixtures can be separated by using a filter paper?
A) Vinegar done clear
B) Saltwater done clear
C) Sand and water done clear
D) Sugar water done clear
question_answer 31) Which process is used to separate a pure solid from a solid-liquid solution?
A) Simple distillation done clear
B) Crystallization done clear
C) Filtration done clear
D) Sedimentation and decantation done clear
A) Only (i) and (ii) done clear
B) Only (ii) and (iii) done clear
C) Only (i) and (iii) done clear
D) (i), (ii) and (iii) done clear
question_answer 33) What happens when distilled water is evaporated?
A) Some salt is left behind. done clear
B) Some sand is left behind. done clear
C) Some sugar is left behind. done clear
D) Nothing is left behind. done clear
question_answer 34) Which process is used for separating a mixture of water and sulphur?
A) Filtration done clear
C) Evaporation done clear
D) Distillation done clear
question_answer 35) Which of the following are involved in filtration technique?
A) Hair in our nostrils done clear
B) Oil and air filters in cars done clear
C) Air filters in air conditioners done clear
question_answer 36) What process is used for separating heterogeneous mixtures of insoluble solid-in-liquid?
A) Filtration done clear
C) Sublimation done clear
D) Fractional distillation done clear

A) Salt done clear
B) Flour done clear
C) Sand done clear
D) Iron filings done clear
A) Iodine done clear
B) Calcium done clear
C) Air done clear
D) Sugar done clear
question_answer 39) Which process takes place in a washing machine while clothes are being dried.
A) Magnetic separation done clear
B) Filtration done clear
C) Evaporation done clear
D) Centrifugation done clear
question_answer 41) Which of the following statements is NOT true?
A) No more salt can be dissolved in a saturated solution of salt water without heating. done clear
B) Water dissolves different amounts of soluble substances in it. done clear
C) A mixture of milk and water can be separated by filtration. done clear
D) Salt is separated from sea water by evaporation. done clear
question_answer 42) By which method is wheat flour separated from wheat bran?
A) Handpicking done clear
C) Winnowing done clear
D) Filtration done clear
question_answer 43) Which of the following is NOT a pure substance?
A) Argon done clear
B) Helium done clear
C) Water done clear
D) Air done clear
Study Package

Question - Separation of Substances
Related question.

Reset Password.
OTP has been sent to your mobile number and is valid for one hour

Mobile Number Verified
Your mobile number is verified.
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.
Unit 3: Separation of substances
Elements, compounds and mixtures.
- No videos or articles available in this lesson
- Elements, Compounds and mixtures Get 4 of 5 questions to level up!
Types of mixtures
- Types of mixtures (Opens a modal)
- Types of mixtures: Homogeneous and Heterogeneous mixtures Get 6 of 8 questions to level up!
Common methods of separation
- Sedimentation and Decantation (Opens a modal)
- Filtration (Opens a modal)
- Sublimation (Opens a modal)
- Vaporisation (Opens a modal)
- Condensation (Opens a modal)
- Distillation (Opens a modal)
- Chromatography (Opens a modal)
- Methods of separation Get 7 of 10 questions to level up!
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- CBSE Class 6 Science Separation of Substances Worksheets

CBSE Class 6 Science Separation of Substances Worksheets with Answers - Chapter 5 - PDF
Contrary to what people may believe, the preparation for the mighty class 10 board exams does not begin a year after the student appears for the test, but actually multiple years before that. It’s from classes 5 and 6 that the students must develop certain habits that will shape their strong foundation and help them in the latter years of their school life. Put simply, it is crucial that every student takes these exams seriously and leaves no stone unturned in an attempt to get a good score in the exam.
To help you with your preparation of the CBSE Class 6 Science Separation of Substances Worksheets with Answers for Chapter 5 in PDF format to download prepared by expert Science teachers from the latest edition of CBSE(NCERT) books. Register Online for NCERT Class 6 Science tuition on Vedantu to score more marks in CBSE board examination.
Vedantu is a platform that provides free CBSE Solutions (NCERT) and other study materials for students. Maths Students who are looking for the better solutions ,can download Class 6 Maths NCERT Solutions to help you to revise the complete syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Features of Worksheets Available on Vedantu
Some cool features of Class 6 Science Separation of Substances Worksheets:
Available for free
Prepared by highly experienced teachers
Strictly adhering to the guidelines set by CBSE
Based completely on the textbook
Provide solutions for self-analysis
Can be downloaded and used later on without the need for an internet connection.

FAQs on CBSE Class 6 Science Separation of Substances Worksheets
1. How shall the student strategize a plan to score well in the Class 6 Science exam?
Today, for any student, it is important that he or she makes a proper plan on what the approach is going to be while appearing for the paper. Before even beginning the preparation a proper strategy must be designed, customized according to the student’s strengths and weaknesses. Go through the entire syllabus once and try to get a gist of what you are about to learn throughout the year. Note down the subjects that you think you can perform well and others that you will need to put more effort into. Engage them accordingly.
2. What is the topic Separation of Substances all about and what type of questions can be asked on it for Class 6?
The students in the chapter have learned about how many of the things that we encounter daily are nothing but materials, those consisting of different types of mixtures. In many cases, what we are interested in is not the mixture but what the constituents are made up of. This chapter deals with exactly that and gives us information and different techniques as to how it is possible to separate the individual components from the mixture that they come together to make. Students can expect different types of questions such as the techniques for separation like handpicking, winnowing, threshing, sieving, etc or even the differences between some of them.
3. What are the important things to remember while preparing for the Science paper in Class 6?
The Science paper usually consists of a lot of complex nomenclature as well as various diagrams and reactions that the student must be very well aware of in ordetowell. This is not as easy as it sounds because remembering tons of reactions along with the little details is a tedious task and won't come by easily without proper preparation or a revision. A few important things to take care of while studying the subject are as follows:
Practising the diagrams by actually drawing them and not just looking at them
Labelling of diagrams is ordered medical reactions along with the detailed coefficients and the conditions under which they occur.
Supporting your answer with examples is always recommended.
4. What are the pros and cons of referring to various sources for the same topic of Separation of Substances?
There is a lot of study material available on the Internet, for free, covering different types of questions and also providing their solutions. It is only natural that most of the content in many of the reference materials overlaps and it can be quite confusing for students to understand which one is better for them. Some students also choose to refer to more than one book for proper guidance. We have listed down below a few pros and cons of the same:
Get to know all possible ways to solve a problem
Make sure you don’t miss any important point
Solving questions of various difficulty levels
Time-consuming
Might create confusion in the mind of the student.
5. How many worksheets should students solve for a particular topic in Science?
Different chapters are allotted a different type of weightage in the exam and also have different areas of the subject that they cover. Some chapters extend above 20 pages while others are limited to only 10. Thus a specific number as to how many worksheets a student must solve for a particular topic cannot be obtained, since it is variable. As long as the student has made sure that the worksheet covers every important subtopic mentioned in the chapter, he shall not worry about finding and solving more worksheets.
Question and Answer forum for K12 Students

MCQ Questions for Class 6 Science Chapter 5 Separation of Substances with Answers
We have compiled the NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 6 Science Chapter 5 Separation of Substances with Answers Pdf free download covering the entire syllabus. Practice MCQ Questions for Class 6 Science with Answers on a daily basis and score well in exams. Refer to the Separation of Substances Class 6 MCQs Questions with Answers here along with a detailed explanation.
Separation of Substances Class 6 MCQs Questions with Answers
Choose the correct option.
Question 1. Mixtures need to be separated because (a) to remove undesirable substances (b) to get desirable substances (c) to obtain highly pure substances (d) all of the above
Answer: (d) all of the above

Question 2. The method of separation used to separate stones from rice is (a) handpicking (b) threshing (c) winnowing (d) all of these
Answer: (a) handpicking

Question 3. Butter is separated from milk by (a) sedimentation (b) filtration (c) churning (d) decantation
Answer: (c) churning
Question 4. The separation of grains from husk is done by the process of (a) handpicking (b) sieving (c) winnowing (d) threshing
Answer: (c) winnowing
Question 5. Threshing is done by (a) beating (b) animals (c) machines (d) all of these
Answer: (d) all of these
Question 6. Filtration is a method to separate the components of a (a) solution (b) mixture of a liquid and an insoluble substance (c) both (a) & (b) (d) pure substance
Answer: (b) mixture of a liquid and an insoluble substance
Question 7. A solid is dissolved in water. Which one of the following methods can be used to separate it? (a) Filtration (b) Decantation (c) Distillation (d) Evaporation
Answer: (d) Evaporation
Question 8. Petroleum contains (a) petrol (b) methanol (c) oil (d) water
Answer: (a) petrol
Question 9. Which of the following method is used when there is a difference in size and colour of desirable and undesirable constituents? (a) Handpicking (b) Threshing (c) Filtration (d) Decantation
Answer: (a) Handpicking
Question 10. The components of a solution of sugar in water can be separated by (a) filtration (b) crystallisation (c) decantation (d) sedimentation
Answer: (b) crystallisation
Question 11. At water treatment plants, the river water is filtered by using (a) filter paper (b) porcelain filters (c) cloth filters (d) sand filters
Answer: (d) sand filters
Question 12. The process of separating grains from the stalks is called (a) handpicking (b) threshing (c) decantation (d) evaporation
Answer: (b) threshing
Question 13. Iodine can be recovered from tincture of iodine by the process of (a) filtration (b) distillation (c) evaporation (d) decantation
Answer: (c) evaporation
Question 14. A mesh which is used to separate things on the basis of their difference in size (a) sieve (b) thresher (c) filter paper (d) none of these
Answer: (a) sieve
Question 15. The process of conversion of water into vapour is called (a) condensation (b) evaporation (c) sedimentation (d) decantation
Answer: (b) evaporation
Question 16. The process of separation of tea leaves by strainer is called (a) filtration (b) sedimentation (c) evaporation (d) condensation
Answer: (a) filtration
Question 17. Which of the following mixtures cannot be separated by using water as solvent followed by filtration and evaporation? (a) Sand and sugar (b) Salt and chalk powder (c) Sand and sulphur (d) Blue vitriol and sand
Answer: (c) Sand and sulphur
Question 18. The property which forms the basis of sieving is (a) difference in weight (b) difference in colour (c) difference in shape (d) difference in size
Answer: (d) difference in size
Question 19. When no more salt dissolves in water at a particular temperature, then the solution at that temperature is called (a) unsaturated (b) saturated (c) supersaturated (d) none of these
Answer: (b) saturated
Question 20. The separation of insoluble solids from liquids can be done by (a) sedimentation (b) decantation (c) loading (d) all of these
Answer: (a) sedimentation
Question 21. An example of a heterogeneous mixture is (a) fresh air (b) fresh water (c) sugar solution (d) dirty water
Answer: (d) dirty water
Question 22. ………….. is a convenient method of separation. (a) Handpicking (b) Threshing (c) Winnowing (d) Sieving
Question 23. Thresher machines are also used to thresh large quantities of …………….. (a) grain (b) sugar (c) salt (d) sand
Answer: (a) grain
Question 24. A separation funnel is a ……….. bulb to the stem of which is fitted a stopcock. (a) wooden (b) copper (c) glass (d) steel
Answer: (c) glass
Question 25. Distillation is a method of obtaining pure …………….. from a solution. (a) liquid (b) solid (c) gas (d) all of them
Answer: (a) liquid
Question 26. Water present in …………… is in the form of water vapour. (a) soil (b) moist (c) air (d) dry
Answer: (c) air
Question 27. Common salt is recovered from sea water by the process of (a) filtration (b) evaporation (c) sublimation (d) decantation
Question 28. When no more salt dissolves in water at a particular temperature, then the solution at that temperature is called (a) unsaturated (b) saturated (c) super saturated (d) none of the above
Question 29. The process of conversion of water into vapour is called (a) evaporation (b) condensation (c) sedimentation (d) decantation
Answer: (a) evaporation
Question 30. Tincture of iodine is a weak solution of iodine in alcohol. Iodine can be recovered from tincture of iodine by the process of (a) filtration (b) distillation (c) evaporation (d) decantation
Answer: (b) distillation
Fill in the Blanks
Question 1. Milk is a mixture of ……………., ……………. and …………….
Answer: milk-proteins, water, cream
Question 2. ……………. substance contains particles of only one type.
Answer: Pure
Question 3. ……………. and ……………. are the types of mixtures.
Answer: Heterogeneous, homogeneous
Question 4. Pebbles can be separated from wheat by …………….
Answer: handpicking
Question 5. ……………. is used to separate husk from wheat.
Answer: Winnowing
Question 6. Glass is a …………….
Answer: mixture
Question 7. Common salt is obtained from sea water by …………….
Answer: evaporation
Question 8. Compounds have ……………. melting points.
Answer: fixed
Question 9. Cream is separated from milk by the process of …………….
Answer: churning
Question 10. The method used to separate the components of different sizes in a mixture using a sieve is called …………….
Answer: sieving
Question 11. The process of separating grains from the stalks is called …………….
Answer: Threshing
Question 12. Fine sand can be separated from larger particles by …………….
Question 13. Breaking of stalks from grains is done by a machine called …………….
Answer: threshers
Question 14. Butter is a component of …………….
Answer: buttermilk
Question 15. Mixture may be solid, liquid or …………….
Answer: gas
Question 16. ……………. is used for separating insoluble substances from a liquid.
Answer: Filtration
Question 17. Sedimentation can be done more quickly by adding ……………. into it.
Answer: alum
Question 18. The used tea-leaves are separated from tea by the method of …………….
Answer: filtration
Question 19. The changing of liquid into vapours is called …………….
Question 20. Components retain their properties in a …………….
Question 21. Peanuts can be separated from a mixture of wheat and peanuts by ………………
Question 22. Fine sand can be separated from larger particles by ………………
Question 23. Compounds have ……………… melting points.
Question 24. Mixture may be solid, liquid or ………………
Question 25. Butter is a component of ………………
Answer: milk
Question 26. Sugarcane juice is a mixture of ……………… water and many other substances.
Answer: sugar
Question 27. Separation of components is done to obtain a ……………… substance.
Answer: pure
Question 28. Components retain their properties in a ………………
Question 29. The solid left behind after filtration is called ………………
Answer: residue
Question 30. The component dissolved in a solvent is called ………………
Answer: solute
True or False
Question 1. Milk is a pure substance.
Answer: False
Question 2. Evaporation is a continuous process.
Answer: True
Question 3. Air is a mixture of gases.
Question 4. Filtration can remove any solid substance which are dissolved in a liquid.
Question 5. A mixture of chalk powder and water is separated by sieving.
Question 6. A mixture of oil and water can be separated by decantation.
Question 7. Rocks are pure substances.
Question 8. Ink loses its properties when mixed in water.
Question 9. Common salt is a pure substance.
Question 10. Loading helps the suspended clay particles to settle down.
Question 11. Separating a mixture of two solids by winnowing is based on the difference in their weights.
Question 12. When no more solute can be dissolved in a given amount of solvent at a particular temperature, the solution is said to be unsaturated.
Question 13. Grain and husk can be separated by decantation.
Question 14. Handpicking can be used to separate pulses from a mixture of pulsed and pebbles in a plate.
Question 15. Lemonade is a homogeneous mixture.
Question 16. There are a number of useful minerals present in sea water.
Question 17. The tap water is completely pure and fit for drinking.
Question 18. When a mixture consists of heavier and lighter particles, the lighter particles are separated using winnowing.
Question 19. Winnowing and threshing are same processes.
Question 20. Decantation is generally preceded by sedimentation.
Match the following
Hope the information shed above regarding NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 6 Science Chapter 5 Separation of Substances with Answers Pdf free download has been useful to an extent. If you have any other queries of CBSE Class 6 Science Separation of Substances MCQs Multiple Choice Questions with Answers, feel free to reach us so that we can revert back to us at the earliest possible.
- Important Questions
- Important Questions Class 6 Chemistry
- Important Questions Class 6 Chemistry Chapter 5 Separation of Substances
Class 6 Chemistry Chapter 5 – Separation of Substances Important Questions with Answers
Class 6 chemistry important questions with answers are provided here for Chapter 5 – Separation of Substances. These important questions are based on the CBSE board curriculum and correspond to the most recent Class 6 chemistry syllabus. By practising these Class 6 important questions, students will be able to quickly review all of the ideas covered in the chapter and prepare for the Class 6 annual examinations.
Download Class 6 Chemistry Chapter 5 – Separation of Substances Important Questions with Answers PDF by clicking on the button below. Download PDF
Recommended Videos
Separation of substances – complete chapter – mindmap with explanation.

Class 6 Chapter 5 – Separation of Substances Important Questions with Answers
Fill in the blanks.
i.) When a heavier component of a mixture settles after adding water to it, this process is called ____.
ii.) The two liquids that do not mix with each other are called ____ liquids.
iii.) ____ is the opposite of evaporation.
iv.) Chalk powder can be separated from water by ____.
v.) ____ is the essential condition for winnowing.
i.) When a heavier component of a mixture settles after adding water to it, this process is called sedimentation.
ii.) The two liquids that do not mix with each other are called immiscible liquids.
iii.) Condensation is the opposite of evaporation.
iv.) Chalk powder can be separated from water by filtration.
v.) Wind is the essential condition for winnowing.
State True or False
i.) Handpicking should be used only when the quantity of impurities is small.
ii.) At a given temperature, a saturated solution can dissolve more of the solute.
iii.) The sieving method can be used to separate wheat flour from bran.
iv.) Winnowing can separate the heavier and lighter components of a mixture.
v.) Common salt is separated from its solution by decantation.
Match the Following
Very short answer questions.
Q1. What is the use of a strainer in separating substances?
Answer. A strainer is a type of sieve used to separate liquid from solid.
Q2. Which process is used to separate cream from curd?
Answer. Centrifugation.
Q3. List some of the materials that are used as filters.
Answer. Cotton, ceramic, filter cloth, and filter paper are some materials used as filters.
Q4. Which method can be used to separate salt from seawater?
Answer. Evaporation.
Q5. Which process is considered the opposite of evaporation?
Answer. Condensation.
Q6. How can husk be removed from wheat?
Answer. By winnowing.
Q7. Which method is used to separate stones from grains?
Answer. Handpicking.
Q8. Which method is used to separate two liquids that do not mix with each other?
Answer. Separating funnel.
Q9. Name the liquid that is known as the universal solvent.
Answer. Water.
Q10. What is the process for separating the heavier and lighter components of a mixture?
Answer. Winnowing.
Short Answer Questions
Q1. Define winnowing.
Answer. Winnowing is the process of separating heavier components of a mixture from lighter components using wind. This method is used to separate grains from the husk after the threshing process.
Q2. Define sedimentation.
Answer. Sedimentation is the separation of solids from liquids. This process is carried out when the heavier component of a mixture settles after water is added to it.
Q3. Define decantation.
Answer. Decantation is the process of separating liquid from solid and other immiscible non-mixing) liquids by removing the liquid layer on top of the solid or liquid layer just below it. The process can be carried out by tilting the mixture after pouring out the top layer.
Q4. What are evaporation and condensation?
Answer. Evaporation is the conversion of a liquid state (water) into a gaseous state (vapour). Condensation is the opposite process that converts gaseous state water (vapour) to a liquid state (water).
Q5. What is a saturated and unsaturated solution?
Answer. A saturated solution is one that cannot dissolve any more solute at that temperature.
An unsaturated solution is one in which the solute can be dissolved at any fixed temperature.
Q6. When is the handpicking method used?
Answer. Handpicking method is used for separating undesirable components that differ in shape, size, and colour and are present in small quantities.
Q7. Define threshing.
Answer. The process of separating grains from the stalk by beating is known as threshing. Since the grains are weakly attached to the stalk, they separate when the stalks are beaten on the ground.
Q8. What is a mixture?
Answer. A mixture is a mixture of two or more substances that do not react with one another. Examples include sugar and water, sugar and sand, and so on.
Q9. Why is it necessary to separate substances from mixtures?
Answer. It is necessary to separate substances from mixtures in order to obtain pure substances for various purposes.
Q10. What are the five methods for separating substances from their mixtures?
Answer. The following are five methods for separating substances:
- Handpicking
- Decantation
Q11. Define handpicking.
Answer. Handpicking is a method of separation in which impurities in a mixture that differ from the useful material are hand-picked and removed.
For example, stone pieces can be separated from wheat or rice by handpicking.
Q12. How will you separate a mixture of oil and water?
Answer. Since oil is lighter than water, it will float on it. Two distinct layers form, and oil is slowly allowed to flow into another container, where it is separated from the water. This method to separate oil and water is called a separating funnel.
Long Answer Questions
Q1 . Differentiate between sedimentation and decantation with a suitable example.
Answer. Sedimentation is the process by which the heavier components of a mixture settle down. For example, when a sand-water mixture is allowed to stand undisturbed for some time and sand settles at the bottom.
Decantation is the process of separating the liquid portion of a mixture when the heavier component settles as sediments at the bottom. In other words, it is the process of moving a liquid from one container to another while leaving the sediments at the bottom alone.
For example, sand settles at the bottom of a container when a mixture of sand and water is allowed to stand. The upper portion of the container contains water. This can be separated from the sand at the bottom simply by pouring it into another container without the use of any other separating device. This is referred to as decantation.
Q2. Describe the process of separating salt from seawater.
Answer. Many salts are present in seawater. When seawater is allowed to stand in shallow pits, sunlight evaporates the water, which slowly turns into water vapour. The water evaporates completely in a few days, leaving behind the solid salts. After further purification, common salt is obtained from this salt mixture.
Q3. Explain how to separate the following mixture:
i.) Sand and husk
ii.) Wheat, sugar and stalk
iii.) Water and petrol
iv.) Rice and salt
v.) Sand and salt
i.) Sand and husk mixture: Sand and husk can be separated using the winnowing method.
ii.) Wheat, sugar, and stalk mixture: The winnowing method can be used to separate the stalk from the mixture because it is lighter than the other two components and separates easily. Because wheat and sugar have different sizes, sieving can be used to separate them.
iii.) Water-petroleum mixture: Water does not dissolve in petrol. As a result, it can be separated using a separating funnel.
iv.) Rice and salt mixture: Rice and salt can be separated by sieving.
v.) Sand and salt mixture: When sand and salt are mixed with water, salt dissolves in water, and sand solution can be separated by sedimentation, decantation, and filtration. The common salt is then separated using evaporation.
Q4. Explain the method of separation of solid-liquid mixtures.
Answer. Filtration is used to separate solid and liquid mixtures when the solid particles are too large to pass through a filter paper.
Solid particles in a liquid can sometimes be so small that they can pass through filter paper. The filtration technique cannot be used to separate such particles. Centrifugation is used to separate such mixtures. Centrifugation is the process of separating insoluble materials from a liquid when filtration does not work well. The centrifugation is determined by the particle size, shape, and density.
Sedimentation and decantation can be used to separate heavy solid particles. If the mixture is left undisturbed for an extended period of time, the solid particles settle to the bottom. They can then be separated from the liquid by decantation.
Q5. What is sieving? Explain how it is done.
Answer. Sieving is a separation method used to separate substances of varying sizes that cannot be separated by handpicking.
The difference in the size of the solid particles is the basis for the principle.
Separation Technique – By passing the mixture through a sieve, large particles are separated from small or finer particles. The sieve is made of wood and has a metal mesh at the bottom. When the sieve is shaken, the mixture is added from the top as the larger particles remain above and the finer particles collect below.
For example, Impurities such as husk and stones are removed from wheat before it is ground in a flour mill.
- Separation of Substances
- Methods of Separation
- Class 6 Chemistry Worksheet on Chapter 5 Separation of Substances – Set 1
- Class 6 Chemistry Worksheet on Chapter 5 Separation of Substances – Set 2
- Class 6 Chemistry Worksheet on Chapter 5 Separation of Substances – Set 3
- Class 6 Chemistry Chapter 5 Separation of Substances MCQs
- Separation Techniques Questions
- Separation Questions
- Chemistry Concept Questions and Answers
Sieving – Separation of Mixture

Decantation and The Separation Process

- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
A lock ( ) or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
- About Mild TBI and Concussion
- After a Mild TBI or Concussion
- Health Disparities in TBI
- Comparing Head Impacts
- Clinical Guidance
- Mild Traumatic Brain Injury Management Guideline
- Resources for Health Care Providers
Traumatic Brain Injury & Concussion
About Moderate and Severe TBI

Preventing TBI
Symptoms of Mild TBI and Concussion

Where to Get Help

Facts About TBI
For Medical Professionals

Clinical Guidance for Pediatric mTBI

Health Care Provider Resources
CDC Programs

HEADS UP Online Training Courses
National Concussion Surveillance System
Core State Injury Prevention Program (Core SIPP)
A traumatic brain injury, or TBI, is an injury that affects how the brain works. TBI is a major cause of death and disability in the United States.
For Everyone
Health care providers.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
[Download] Case Study Questions for Class 6 Science Chapter 5 Separation of Substances Here we are providing case study or passage-based questions for class 6 science chapter 5 Separation of Substances. Case Study/Passage Based Questions Passage-1 You are asked to add two spoons of solid salt to some liquid water taken in a beaker. On … Continue reading Case Study Questions for Class 6 ...
CBSE Class 6 Science Case Study Question and Answer for all Chapter 1 to 16. Class 6 Students can learn Case Type Question from here. 100% FREE Exercise & Practice for CBSE, NCERT and ICSE ... Chapter 5 Separation of Substances Case Study Question. Chapter 6 Changes Around Us Case Study Question.
Give one example of sieving used in everyday life. Separation of barn (choker) from flour. Question 5. Name some materials that are used as filters. Cotton, ceramic, filter cloth, filter paper. Question 6. Name the process of separating two immiscible liquids. By using separating funnel or by decantation.
Download Most Important Questions for Class 6 Science Chapter - 5 Separation of Substances. Download Important Questions PDF. The NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science are crucial study sources that will help learners clear all the doubts that occur while studying the CBSE syllabus Chapter 5 of Class 6 Science. Fill in the blanks, true or false ...
Case 3: Separation of Substances in Evaporation and Condensation. Lisa wants to separate salt from a solution of salt and water. She decides to use evaporation and condensation. Answer the following questions: Q9: Explain how Lisa can separate salt from the saltwater solution using evaporation and condensation.
Chapter 5 - Separation of Substances present on this page provides answers to the questions related to each and every topic discussed in this chapter. Students can refer to and easily download the PDF of NCERT Exemplar Class 6 Science solutions for free from the link given below.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science - All Chapters. Chapter 1 Food Where Does It Come From. Chapter 2 Components of Food. Chapter 3 Fibre to Fabric. Chapter 4 Sorting Materials Into Groups. Chapter 5 Separation of Substances. Chapter 6 Changes Around Us. Chapter 7 Getting to Know Plants. Chapter 8 Body Movements.
Free PDF download of Important Questions with solutions for CBSE Class 6 Science Chapter 5 - Separation of Substances prepared by expert Science teachers from latest edition of CBSE(NCERT) books.Register Online for NCERT Class 6 Science tuition on Vedantu.com to score more marks in CBSE board examination. Vedantu is a platform that provides free CBSE Solutions (NCERT) and other study materials ...
5.1 Methods of Separation. The different separation methods of substances Class 6 chapter are simplified in NCERT solution for Class 6 Science Chapter 5. Some of the methods include hand-picking, winnowing, threshing, sieving, evaporation, sedimentation, filtration, etc. Let us discuss each of these methods in detail.
CBSE Class 6 Science Notes Chapter 5 are now available online with Vedantu in PDF format to ensure complete exam preparation. Our standard Class 6 Notes in Science on Separation of Substances are compiled by subject experts having years of experience in this field. Such Separation of Substances Class 6 Notes consists of step-by-step chapter ...
Answer: The materials having different size and colour can be separated by handpicking. 8. Name the other methods used to separate solid materials of different size. Answer: Sieving. 9. Name the process used to separate heavier and lighter components of a mixture. Answer: Winnowing.
Free Question Bank for 6th Class Science Separation of Substances Separation of Substances. Customer Care : 6267349244. Toggle navigation ... Study the information given below. Some substances are made up of two or more elements combined together chemically.
Separation of Substances - Competency Based Questions. Select the number of questions for the test: Strengthen your understanding of Separation of Substances in CBSE Class 6 Science through competency based questions. Acquire in-depth knowledge and improve problem-solving abilities with comprehensive solutions.
Question 1. VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTION. (i)List few methods of separations. (ii)which method will you prefer to separate a solid dissolved in liquid? (iii)Name the process used to separate butter from curd. (iv)Which method is used to obtain a pure liquid from a solution? (v)What property is used to separate water from bigger soil particles?
CBSE important Questions for Class 6 Science will help to score more marks in your CBSE Board Exams. Very Short Answer Type Questions. 1. What is strainer?Answer: Strainer is a kind of sieve which is used to separate a liquid from solid. 2. Name the method used to separate cream from curd.Answer: Centrifugation. 3.
Write the steps involved for the separation of salt, sand and oil from the mixture by giving an activity along with the diagram. Solution: A mixture of salt, sand, oil and water can be separated by following steps. Decant the oil from the mixture which is floating - oil is separated. Filter the mixture.
Separation of Substances Class 6 Notes - Chapter 5. According to the CBSE Syllabus 2023-24, this chapter has been renumbered as Chapter 3. We all have seen our parents and grandparents separating small stones or pebbles from the rice grains and pulses, filtering tea leaves before serving tea and a lot more.
Steps for the separation of salt, sand, oil and water. First we will use decantation method to separate oil and water. Water being heavier, forms the lower layer and oil being lighter, forms the upper layer in the beaker. We can decant off the upper layer of oil into another beaker carefully.
UP Class 6th Science. 17 units · 61 skills. Unit 1. Science in daily life. Unit 2. Substances and groups of substances ... Separation of substances: Unit test; Elements, Compounds and Mixtures ... Practice. Types of mixtures: Homogeneous and Heterogeneous mixtures Get 6 of 8 questions to level up! Common methods of separation. Learn ...
Some cool features of Class 6 Science Separation of Substances Worksheets: Available for free. Prepared by highly experienced teachers. Strictly adhering to the guidelines set by CBSE. Based completely on the textbook. Provide solutions for self-analysis. Can be downloaded and used later on without the need for an internet connection.
Separation of Substances Class 6 MCQs Questions with Answers. Choose the correct option. Question 1. Mixtures need to be separated because. (a) to remove undesirable substances. (b) to get desirable substances. (c) to obtain highly pure substances. (d) all of the above. Answer.
Answer: (a) Shopkeepers add these undesirable substances to increase the quantity of the food materials and thus their profit. (b) Through handpicking. (c) Shopkeepers observing such practices are greedy, self-centred, criminal-minded and soulless. Question 2.
Class 6 Chapter 5 - Separation of Substances Important Questions with Answers Fill in the Blanks. i.) When a heavier component of a mixture settles after adding water to it, this process is called ____. ii.) The two liquids that do not mix with each other are called ____ liquids. iii.) ____ is the opposite of evaporation. iv.)
Overview. E. coli are germs called bacteria.They are found in many places, including in the environment, foods, water, and the intestines of people and animals. Most E. coli are harmless and are part of a healthy intestinal tract.E. coli help us digest food, produce vitamins, and protect us from harmful germs. But some E. coli can make people sick with diarrhea, urinary tract infections ...
Nov. 6, 2023. Core State Injury Prevention Program (Core SIPP) Learn about CDC's Core State Injury Prevention Program (CoreSIPP) Feb. 6, 2024. Traumatic Brain Injury & Concussion A traumatic brain injury, or TBI, is an injury that affects how the brain works. TBI is a major cause of death and disability in the United States.