An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it's official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
- Browse Titles
NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-.


StatPearls [Internet].
Breech presentation.
Caron J. Gray ; Meaghan M. Shanahan .
Affiliations
Last Update: November 6, 2022 .
- Continuing Education Activity
Breech presentation refers to the fetus in the longitudinal lie with the buttocks or lower extremity entering the pelvis first. The three types of breech presentation include frank breech, complete breech, and incomplete breech. In a frank breech, the fetus has flexion of both hips, and the legs are straight with the feet near the fetal face, in a pike position. This activity reviews the cause and pathophysiology of breech presentation and highlights the role of the interprofessional team in its management.
- Describe the pathophysiology of breech presentation.
- Review the physical exam of a patient with a breech presentation.
- Summarize the treatment options for breech presentation.
- Explain the importance of improving care coordination among interprofessional team members to improve outcomes for patients affected by breech presentation.
- Introduction
Breech presentation refers to the fetus in the longitudinal lie with the buttocks or lower extremity entering the pelvis first. The three types of breech presentation include frank breech, complete breech, and incomplete breech. In a frank breech, the fetus has flexion of both hips, and the legs are straight with the feet near the fetal face, in a pike position. The complete breech has the fetus sitting with flexion of both hips and both legs in a tuck position. Finally, the incomplete breech can have any combination of one or both hips extended, also known as footling (one leg extended) breech, or double footling breech (both legs extended). [1] [2] [3]
Clinical conditions associated with breech presentation include those that may increase or decrease fetal motility, or affect the vertical polarity of the uterine cavity. Prematurity, multiple gestations, aneuploidies, congenital anomalies, Mullerian anomalies, uterine leiomyoma, and placental polarity as in placenta previa are most commonly associated with a breech presentation. Also, a previous history of breech presentation at term increases the risk of repeat breech presentation at term in subsequent pregnancies. [4] [5] These are discussed in more detail in the pathophysiology section.
- Epidemiology
Breech presentation occurs in 3% to 4% of all term pregnancies. A higher percentage of breech presentations occurs with less advanced gestational age. At 32 weeks, 7% of fetuses are breech, and 28 weeks or less, 25% are breech.
Specifically, following one breech delivery, the recurrence rate for the second pregnancy was nearly 10%, and for a subsequent third pregnancy, it was 27%. Prior cesarean delivery has also been described by some to increase the incidence of breech presentation two-fold.
- Pathophysiology
As mentioned previously, the most common clinical conditions or disease processes that result in the breech presentation are those that affect fetal motility or the vertical polarity of the uterine cavity. [6] [7]
Conditions that change the vertical polarity or the uterine cavity, or affect the ease or ability of the fetus to turn into the vertex presentation in the third trimester include:
- Mullerian anomalies: Septate uterus, bicornuate uterus, and didelphys uterus
- Placentation: Placenta previa as the placenta is occupying the inferior portion of the uterine cavity. Therefore, the presenting part cannot engage
- Uterine leiomyoma: Mainly larger myomas located in the lower uterine segment, often intramural or submucosal, that prevent engagement of the presenting part.
- Prematurity
- Aneuploidies and fetal neuromuscular disorders commonly cause hypotonia of the fetus, inability to move effectively
- Congenital anomalies: Fetal sacrococcygeal teratoma, fetal thyroid goiter
- Polyhydramnios: Fetus is often in unstable lie, unable to engage
- Oligohydramnios: Fetus is unable to turn to vertex due to lack of fluid
- Laxity of the maternal abdominal wall: Uterus falls forward, the fetus is unable to engage in the pelvis.
The risk of cord prolapse varies depending on the type of breech. Incomplete or footling breech carries the highest risk of cord prolapse at 15% to 18%, while complete breech is lower at 4% to 6%, and frank breech is uncommon at 0.5%.
- History and Physical
During the physical exam, using the Leopold maneuvers, palpation of a hard, round, mobile structure at the fundus and the inability to palpate a presenting part in the lower abdomen superior to the pubic bone or the engaged breech in the same area, should raise suspicion of a breech presentation.
During a cervical exam, findings may include the lack of a palpable presenting part, palpation of a lower extremity, usually a foot, or for the engaged breech, palpation of the soft tissue of the fetal buttocks may be noted. If the patient has been laboring, caution is warranted as the soft tissue of the fetal buttocks may be interpreted as caput of the fetal vertex.
Any of these findings should raise suspicion and ultrasound should be performed.
Diagnosis of a breech presentation can be accomplished through abdominal exam using the Leopold maneuvers in combination with the cervical exam. Ultrasound should confirm the diagnosis.
On ultrasound, the fetal lie and presenting part should be visualized and documented. If breech presentation is diagnosed, specific information including the specific type of breech, the degree of flexion of the fetal head, estimated fetal weight, amniotic fluid volume, placental location, and fetal anatomy review (if not already done previously) should be documented.
- Treatment / Management
Expertise in the delivery of the vaginal breech baby is becoming less common due to fewer vaginal breech deliveries being offered throughout the United States and in most industrialized countries. The Term Breech Trial (TBT), a well-designed, multicenter, international, randomized controlled trial published in 2000 compared planned vaginal delivery to planned cesarean delivery for the term breech infant. The investigators reported that delivery by planned cesarean resulted in significantly lower perinatal mortality, neonatal mortality, and serious neonatal morbidity. Also, there was no significant difference in maternal morbidity or mortality between the two groups. Since that time, the rate of term breech infants delivered by planned cesarean has increased dramatically. Follow-up studies to the TBT have been published looking at maternal morbidity and outcomes of the children at two years. Although these reports did not show any significant difference in the risk of death and neurodevelopmental, these studies were felt to be underpowered. [8] [9] [10] [11]
Since the TBT, many authors since have argued that there are still some specific situations that vaginal breech delivery is a potential, safe alternative to planned cesarean. Many smaller retrospective studies have reported no difference in neonatal morbidity or mortality using these specific criteria.
The initial criteria used in these reports were similar: gestational age greater than 37 weeks, frank or complete breech presentation, no fetal anomalies on ultrasound examination, adequate maternal pelvis, and estimated fetal weight between 2500 g and 4000 g. In addition, the protocol presented by one report required documentation of fetal head flexion and adequate amniotic fluid volume, defined as a 3-cm vertical pocket. Oxytocin induction or augmentation was not offered, and strict criteria were established for normal labor progress. CT pelvimetry did determine an adequate maternal pelvis.
Despite debate on both sides, the current recommendation for the breech presentation at term includes offering external cephalic version (ECV) to those patients that meet criteria, and for those whom are not candidates or decline external cephalic version, a planned cesarean section for delivery sometime after 39 weeks.
Regarding the premature breech, gestational age will determine the mode of delivery. Before 26 weeks, there is a lack of quality clinical evidence to guide mode of delivery. One large retrospective cohort study recently concluded that from 28 to 31 6/7 weeks, there is a significant decrease in perinatal morbidity and mortality in a planned cesarean delivery versus intended vaginal delivery, while there is no difference in perinatal morbidity and mortality in gestational age 32 to 36 weeks. Of note, due to lack of recruitment, no prospective clinical trials are examining this issue.
- Differential Diagnosis
- Face and brow presentation
- Fetal anomalies
- Fetal death
- Grand multiparity
- Multiple pregnancies
- Oligohydramnios
- Pelvis Anatomy
- Preterm labor
- Primigravida
- Uterine anomalies
- Pearls and Other Issues
In light of the decrease in planned vaginal breech deliveries, thus the decrease in expertise in managing this clinical scenario, it is prudent that policies requiring simulation and instruction in the delivery technique for vaginal breech birth are established to care for the emergency breech vaginal delivery.
- Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
A breech delivery is usually managed by an obstetrician, labor and delivery nurse, anesthesiologist and a neonatologist. The ultimate decison rests on the obstetrician. To prevent complications, today cesarean sections are performed and experienced with vaginal deliveries of breech presentation is limited. For healthcare workers including the midwife who has no experience with a breech delivery, it is vital to communicate with an obstetrician, otherwise one risks litigation if complications arise during delivery. [12] [13] [14]
- Review Questions
- Access free multiple choice questions on this topic.
- Comment on this article.
Disclosure: Caron Gray declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies.
Disclosure: Meaghan Shanahan declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies.
This book is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0) ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/ ), which permits others to distribute the work, provided that the article is not altered or used commercially. You are not required to obtain permission to distribute this article, provided that you credit the author and journal.
- Cite this Page Gray CJ, Shanahan MM. Breech Presentation. [Updated 2022 Nov 6]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-.
In this Page
Bulk download.
- Bulk download StatPearls data from FTP
Related information
- PMC PubMed Central citations
- PubMed Links to PubMed
Similar articles in PubMed
- [What effect does leg position in breech presentation have on mode of delivery and early neonatal morbidity?]. [Z Geburtshilfe Neonatol. 1997] [What effect does leg position in breech presentation have on mode of delivery and early neonatal morbidity?]. Krause M, Fischer T, Feige A. Z Geburtshilfe Neonatol. 1997 Jul-Aug; 201(4):128-35.
- The effect of intra-uterine breech position on postnatal motor functions of the lower limbs. [Early Hum Dev. 1993] The effect of intra-uterine breech position on postnatal motor functions of the lower limbs. Sival DA, Prechtl HF, Sonder GH, Touwen BC. Early Hum Dev. 1993 Mar; 32(2-3):161-76.
- The influence of the fetal leg position on the outcome in vaginally intended deliveries out of breech presentation at term - A FRABAT prospective cohort study. [PLoS One. 2019] The influence of the fetal leg position on the outcome in vaginally intended deliveries out of breech presentation at term - A FRABAT prospective cohort study. Jennewein L, Allert R, Möllmann CJ, Paul B, Kielland-Kaisen U, Raimann FJ, Brüggmann D, Louwen F. PLoS One. 2019; 14(12):e0225546. Epub 2019 Dec 2.
- Review Breech vaginal delivery at or near term. [Semin Perinatol. 2003] Review Breech vaginal delivery at or near term. Tunde-Byass MO, Hannah ME. Semin Perinatol. 2003 Feb; 27(1):34-45.
- Review [Breech Presentation: CNGOF Guidelines for Clinical Practice - Epidemiology, Risk Factors and Complications]. [Gynecol Obstet Fertil Senol. 2...] Review [Breech Presentation: CNGOF Guidelines for Clinical Practice - Epidemiology, Risk Factors and Complications]. Mattuizzi A. Gynecol Obstet Fertil Senol. 2020 Jan; 48(1):70-80. Epub 2019 Nov 1.
Recent Activity
- Breech Presentation - StatPearls Breech Presentation - StatPearls
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
Turn recording back on
Connect with NLM
National Library of Medicine 8600 Rockville Pike Bethesda, MD 20894
Web Policies FOIA HHS Vulnerability Disclosure
Help Accessibility Careers

- Pregnancy Classes

Breech Births
In the last weeks of pregnancy, a baby usually moves so his or her head is positioned to come out of the vagina first during birth. This is called a vertex presentation. A breech presentation occurs when the baby’s buttocks, feet, or both are positioned to come out first during birth. This happens in 3–4% of full-term births.
What are the different types of breech birth presentations?
- Complete breech: Here, the buttocks are pointing downward with the legs folded at the knees and feet near the buttocks.
- Frank breech: In this position, the baby’s buttocks are aimed at the birth canal with its legs sticking straight up in front of his or her body and the feet near the head.
- Footling breech: In this position, one or both of the baby’s feet point downward and will deliver before the rest of the body.
What causes a breech presentation?
The causes of breech presentations are not fully understood. However, the data show that breech birth is more common when:
- You have been pregnant before
- In pregnancies of multiples
- When there is a history of premature delivery
- When the uterus has too much or too little amniotic fluid
- When there is an abnormally shaped uterus or a uterus with abnormal growths, such as fibroids
- The placenta covers all or part of the opening of the uterus placenta previa
How is a breech presentation diagnosed?
A few weeks prior to the due date, the health care provider will place her hands on the mother’s lower abdomen to locate the baby’s head, back, and buttocks. If it appears that the baby might be in a breech position, they can use ultrasound or pelvic exam to confirm the position. Special x-rays can also be used to determine the baby’s position and the size of the pelvis to determine if a vaginal delivery of a breech baby can be safely attempted.
Can a breech presentation mean something is wrong?
Even though most breech babies are born healthy, there is a slightly elevated risk for certain problems. Birth defects are slightly more common in breech babies and the defect might be the reason that the baby failed to move into the right position prior to delivery.
Can a breech presentation be changed?
It is preferable to try to turn a breech baby between the 32nd and 37th weeks of pregnancy . The methods of turning a baby will vary and the success rate for each method can also vary. It is best to discuss the options with the health care provider to see which method she recommends.
Medical Techniques
External Cephalic Version (EVC) is a non-surgical technique to move the baby in the uterus. In this procedure, a medication is given to help relax the uterus. There might also be the use of an ultrasound to determine the position of the baby, the location of the placenta and the amount of amniotic fluid in the uterus.
Gentle pushing on the lower abdomen can turn the baby into the head-down position. Throughout the external version the baby’s heartbeat will be closely monitored so that if a problem develops, the health care provider will immediately stop the procedure. ECV usually is done near a delivery room so if a problem occurs, a cesarean delivery can be performed quickly. The external version has a high success rate and can be considered if you have had a previous cesarean delivery.
ECV will not be tried if:
- You are carrying more than one fetus
- There are concerns about the health of the fetus
- You have certain abnormalities of the reproductive system
- The placenta is in the wrong place
- The placenta has come away from the wall of the uterus ( placental abruption )
Complications of EVC include:
- Prelabor rupture of membranes
- Changes in the fetus’s heart rate
- Placental abruption
- Preterm labor
Vaginal delivery versus cesarean for breech birth?
Most health care providers do not believe in attempting a vaginal delivery for a breech position. However, some will delay making a final decision until the woman is in labor. The following conditions are considered necessary in order to attempt a vaginal birth:
- The baby is full-term and in the frank breech presentation
- The baby does not show signs of distress while its heart rate is closely monitored.
- The process of labor is smooth and steady with the cervix widening as the baby descends.
- The health care provider estimates that the baby is not too big or the mother’s pelvis too narrow for the baby to pass safely through the birth canal.
- Anesthesia is available and a cesarean delivery possible on short notice
What are the risks and complications of a vaginal delivery?
In a breech birth, the baby’s head is the last part of its body to emerge making it more difficult to ease it through the birth canal. Sometimes forceps are used to guide the baby’s head out of the birth canal. Another potential problem is cord prolapse . In this situation the umbilical cord is squeezed as the baby moves toward the birth canal, thus slowing the baby’s supply of oxygen and blood. In a vaginal breech delivery, electronic fetal monitoring will be used to monitor the baby’s heartbeat throughout the course of labor. Cesarean delivery may be an option if signs develop that the baby may be in distress.
When is a cesarean delivery used with a breech presentation?
Most health care providers recommend a cesarean delivery for all babies in a breech position, especially babies that are premature. Since premature babies are small and more fragile, and because the head of a premature baby is relatively larger in proportion to its body, the baby is unlikely to stretch the cervix as much as a full-term baby. This means that there might be less room for the head to emerge.
Want to Know More?
- Creating Your Birth Plan
- Labor & Birth Terms to Know
- Cesarean Birth After Care
Compiled using information from the following sources:
- ACOG: If Your Baby is Breech
- William’s Obstetrics Twenty-Second Ed. Cunningham, F. Gary, et al, Ch. 24.
- Danforth’s Obstetrics and Gynecology Ninth Ed. Scott, James R., et al, Ch. 21.
BLOG CATEGORIES
- Can I get pregnant if… ? 3
- Child Adoption 19
- Fertility 54
- Pregnancy Loss 11
- Breastfeeding 29
- Changes In Your Body 5
- Cord Blood 4
- Genetic Disorders & Birth Defects 17
- Health & Nutrition 2
- Is it Safe While Pregnant 54
- Labor and Birth 65
- Multiple Births 10
- Planning and Preparing 24
- Pregnancy Complications 68
- Pregnancy Concerns 62
- Pregnancy Health and Wellness 149
- Pregnancy Products & Tests 8
- Pregnancy Supplements & Medications 14
- The First Year 41
- Week by Week Newsletter 40
- Your Developing Baby 16
- Options for Unplanned Pregnancy 18
- Paternity Tests 2
- Pregnancy Symptoms 5
- Prenatal Testing 16
- The Bumpy Truth Blog 7
- Uncategorized 4
- Abstinence 3
- Birth Control Pills, Patches & Devices 21
- Women's Health 34
- Thank You for Your Donation
- Unplanned Pregnancy
- Getting Pregnant
- Healthy Pregnancy
- Privacy Policy
Share this post:
Similar post.

Episiotomy: Advantages & Complications

Retained Placenta

What is Dilation in Pregnancy?
Track your baby’s development, subscribe to our week-by-week pregnancy newsletter.
- The Bumpy Truth Blog
- Fertility Products Resource Guide
Pregnancy Tools
- Ovulation Calendar
- Baby Names Directory
- Pregnancy Due Date Calculator
- Pregnancy Quiz
Pregnancy Journeys
- Partner With Us
- Corporate Sponsors
TYPES OF BREECH PRESENTATION
● Frank breech – Both hips are flexed and both knees are extended so that the feet are adjacent to the head ( figure 1 ); accounts for 50 to 70 percent of breech fetuses at term.
● Complete breech – Both hips and both knees are flexed ( figure 2 ); accounts for 5 to 10 percent of breech fetuses at term.
When viewing this topic in a different language, you may notice some differences in the way the content is structured, but it still reflects the latest evidence-based guidance.
Breech presentation
- Overview
- Theory
- Diagnosis
- Management
- Follow up
- Resources
Breech presentation refers to the baby presenting for delivery with the buttocks or feet first rather than head.
Associated with increased morbidity and mortality for the mother in terms of emergency cesarean section and placenta previa; and for the baby in terms of preterm birth, small fetal size, congenital anomalies, and perinatal mortality.
Incidence decreases as pregnancy progresses and by term occurs in 3% to 4% of singleton term pregnancies.
Treatment options include external cephalic version to increase the likelihood of vaginal birth or a planned cesarean section, the optimal gestation being 37 and 39 weeks, respectively.
Planned cesarean section is considered the safest form of delivery for infants with a persisting breech presentation at term.
Breech presentation in pregnancy occurs when a baby presents with the buttocks or feet rather than the head first (cephalic presentation) and is associated with increased morbidity and mortality for both the mother and the baby. [1] Cunningham F, Gant N, Leveno K, et al. Williams obstetrics. 21st ed. New York: McGraw-Hill; 1997. [2] Kish K, Collea JV. Malpresentation and cord prolapse. In: DeCherney AH, Nathan L, eds. Current obstetric and gynecologic diagnosis and treatment. New York: McGraw-Hill Professional; 2002. There is good current evidence regarding effective management of breech presentation in late pregnancy using external cephalic version and/or planned cesarean section.
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors.
- buttocks or feet as the presenting part
- fetal head under costal margin
- fetal heartbeat above the maternal umbilicus
Other diagnostic factors
- subcostal tenderness
- pelvic or bladder pain
Risk factors
- premature fetus
- small for gestational age fetus
- nulliparity
- fetal congenital anomalies
- previous breech delivery
- uterine abnormalities
- abnormal amniotic fluid volume
- placental abnormalities
- female fetus
Diagnostic investigations
1st investigations to order.
- transabdominal/transvaginal ultrasound
Treatment algorithm
<37 weeks' gestation, ≥37 weeks' gestation not in labor, ≥37 weeks' gestation in labor: no imminent delivery, ≥37 weeks' gestation in labor: imminent delivery, contributors, natasha nassar, phd.
Associate Professor
Menzies Centre for Health Policy
Sydney School of Public Health
University of Sydney
Disclosures
NN has received salary support from Australian National Health and a Medical Research Council Career Development Fellowship; she is an author of a number of references cited in this topic.
Christine L. Roberts, MBBS, FAFPHM, DrPH
Research Director
Clinical and Population Health Division
Perinatal Medicine Group
Kolling Institute of Medical Research
CLR declares that she has no competing interests.
Jonathan Morris, MBChB, FRANZCOG, PhD
Professor of Obstetrics and Gynaecology and Head of Department
JM declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewers
John w. bachman, md.
Consultant in Family Medicine
Department of Family Medicine
Mayo Clinic
JWB declares that he has no competing interests.
Rhona Hughes, MBChB
Lead Obstetrician
Lothian Simpson Centre for Reproductive Health
The Royal Infirmary
RH declares that she has no competing interests.
Brian Peat, MD
Director of Obstetrics
Women's and Children's Hospital
North Adelaide
South Australia
BP declares that he has no competing interests.
Lelia Duley, MBChB
Professor of Obstetric Epidemiology
University of Leeds
Bradford Institute of Health Research
Temple Bank House
Bradford Royal Infirmary
LD declares that she has no competing interests.
Justus Hofmeyr, MD
Head of the Department of Obstetrics and Gynaecology
East London Private Hospital
East London
South Africa
JH is an author of a number of references cited in this topic.
Differentials
- Transverse lie
- Antenatal corticosteroids to reduce neonatal morbidity and mortality
- Caesarean birth
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer
Help us improve BMJ Best Practice
Please complete all fields.
I have some feedback on:
We will respond to all feedback.
For any urgent enquiries please contact our customer services team who are ready to help with any problems.
Phone: +44 (0) 207 111 1105
Email: [email protected]
Your feedback has been submitted successfully.
- Type 2 Diabetes
- Heart Disease
- Digestive Health
- Multiple Sclerosis
- Diet & Nutrition
- Supplements
- Health Insurance
- Public Health
- Patient Rights
- Caregivers & Loved Ones
- End of Life Concerns
- Health News
- Thyroid Test Analyzer
- Doctor Discussion Guides
- Hemoglobin A1c Test Analyzer
- Lipid Test Analyzer
- Complete Blood Count (CBC) Analyzer
- What to Buy
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Medical Expert Board
What Is Breech?
When a fetus is delivered buttocks or feet first
- Types of Presentation
Risk Factors
Complications.
Breech concerns the position of the fetus before labor . Typically, the fetus comes out headfirst, but in a breech delivery, the buttocks or feet come out first. This type of delivery is risky for both the pregnant person and the fetus.
This article discusses the different types of breech presentations, risk factors that might make a breech presentation more likely, treatment options, and complications associated with a breech delivery.
Verywell / Jessica Olah
Types of Breech Presentation
During the last few weeks of pregnancy, a fetus usually rotates so that the head is positioned downward to come out of the vagina first. This is called the vertex position.
In a breech presentation, the fetus does not turn to lie in the correct position. Instead, the fetus’s buttocks or feet are positioned to come out of the vagina first.
At 28 weeks of gestation, approximately 20% of fetuses are in a breech position. However, the majority of these rotate to the proper vertex position. At full term, around 3%–4% of births are breech.
The different types of breech presentations include:
- Complete : The fetus’s knees are bent, and the buttocks are presenting first.
- Frank : The fetus’s legs are stretched upward toward the head, and the buttocks are presenting first.
- Footling : The fetus’s foot is showing first.
Signs of Breech
There are no specific symptoms associated with a breech presentation.
Diagnosing breech before the last few weeks of pregnancy is not helpful, since the fetus is likely to turn to the proper vertex position before 35 weeks gestation.
A healthcare provider may be able to tell which direction the fetus is facing by touching a pregnant person’s abdomen. However, an ultrasound examination is the best way to determine how the fetus is lying in the uterus.
Most breech presentations are not related to any specific risk factor. However, certain circumstances can increase the risk for breech presentation.
These can include:
- Previous pregnancies
- Multiple fetuses in the uterus
- An abnormally shaped uterus
- Uterine fibroids , which are noncancerous growths of the uterus that usually appear during the childbearing years
- Placenta previa, a condition in which the placenta covers the opening to the uterus
- Preterm labor or prematurity of the fetus
- Too much or too little amniotic fluid (the liquid that surrounds the fetus during pregnancy)
- Fetal congenital abnormalities
Most fetuses that are breech are born by cesarean delivery (cesarean section or C-section), a surgical procedure in which the baby is born through an incision in the pregnant person’s abdomen.
In rare instances, a healthcare provider may plan a vaginal birth of a breech fetus. However, there are more risks associated with this type of delivery than there are with cesarean delivery.
Before cesarean delivery, a healthcare provider might utilize the external cephalic version (ECV) procedure to turn the fetus so that the head is down and in the vertex position. This procedure involves pushing on the pregnant person’s belly to turn the fetus while viewing the maneuvers on an ultrasound. This can be an uncomfortable procedure, and it is usually done around 37 weeks gestation.
ECV reduces the risks associated with having a cesarean delivery. It is successful approximately 40%–60% of the time. The procedure cannot be done once a pregnant person is in active labor.
Complications related to ECV are low and include the placenta tearing away from the uterine lining, changes in the fetus’s heart rate, and preterm labor.
ECV is usually not recommended if the:
- Pregnant person is carrying more than one fetus
- Placenta is in the wrong place
- Healthcare provider has concerns about the health of the fetus
- Pregnant person has specific abnormalities of the reproductive system
Recommendations for Previous C-Sections
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) says that ECV can be considered if a person has had a previous cesarean delivery.
During a breech delivery, the umbilical cord might come out first and be pinched by the exiting fetus. This is called cord prolapse and puts the fetus at risk for decreased oxygen and blood flow. There’s also a risk that the fetus’s head or shoulders will get stuck inside the mother’s pelvis, leading to suffocation.
Complications associated with cesarean delivery include infection, bleeding, injury to other internal organs, and problems with future pregnancies.
A healthcare provider needs to weigh the risks and benefits of ECV, delivering a breech fetus vaginally, and cesarean delivery.
In a breech delivery, the fetus comes out buttocks or feet first rather than headfirst (vertex), the preferred and usual method. This type of delivery can be more dangerous than a vertex delivery and lead to complications. If your baby is in breech, your healthcare provider will likely recommend a C-section.
A Word From Verywell
Knowing that your baby is in the wrong position and that you may be facing a breech delivery can be extremely stressful. However, most fetuses turn to have their head down before a person goes into labor. It is not a cause for concern if your fetus is breech before 36 weeks. It is common for the fetus to move around in many different positions before that time.
At the end of your pregnancy, if your fetus is in a breech position, your healthcare provider can perform maneuvers to turn the fetus around. If these maneuvers are unsuccessful or not appropriate for your situation, cesarean delivery is most often recommended. Discussing all of these options in advance can help you feel prepared should you be faced with a breech delivery.
American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. If your baby is breech .
TeachMeObGyn. Breech presentation .
MedlinePlus. Breech birth .
Hofmeyr GJ, Kulier R, West HM. External cephalic version for breech presentation at term . Cochrane Database Syst Rev . 2015 Apr 1;2015(4):CD000083. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD000083.pub3
By Christine Zink, MD Dr. Zink is a board-certified emergency medicine physician with expertise in the wilderness and global medicine.
- Help & Feedback
- About epocrates
Breech presentation
Highlights & basics, diagnostic approach, risk factors, history & exam, differential diagnosis.
- Tx Approach
Emerging Tx
Complications.
PATIENT RESOURCES
Patient Instructions
Breech presentation refers to the baby presenting for delivery with the buttocks or feet first rather than head.
Associated with increased morbidity and mortality for the mother in terms of emergency cesarean section and placenta previa; and for the baby in terms of preterm birth, small fetal size, congenital anomalies, and perinatal mortality.
Incidence decreases as pregnancy progresses and by term occurs in 3% to 4% of singleton term pregnancies.
Treatment options include external cephalic version to increase the likelihood of vaginal birth or a planned cesarean section, the optimal gestation being 37 and 39 weeks, respectively.
Planned cesarean section is considered the safest form of delivery for infants with a persisting breech presentation at term.
Quick Reference
Key Factors
buttocks or feet as the presenting part
Fetal head under costal margin, fetal heartbeat above the maternal umbilicus.
Other Factors
subcostal tenderness
Pelvic or bladder pain.
Diagnostics Tests
1st Tests to Order
transabdominal/transvaginal ultrasound
Treatment options.
presumptive
<37 weeks' gestation
specialist evaluation
corticosteroid
magnesium sulfate
≥37 weeks' gestation not in labor
unsuccessful ECV with persistent breech
Classifications
Types of breech presentation
Baby's buttocks lead the way into the birth canal
Hips are flexed, knees are extended, and the feet are in close proximity to the head
65% to 70% of breech babies are in this position.
Baby presents with buttocks first
Both the hips and the knees are flexed; the baby may be sitting cross-legged.
One or both of the baby's feet lie below the breech so that the foot or knee is lowermost in the birth canal
This is rare at term but relatively common with premature fetuses.
Common Vignette
Other Presentations
Epidemiology
33% of births less than 28 weeks' gestation
14% of births at 29 to 32 weeks' gestation
9% of births at 33 to 36 weeks' gestation
6% of births at 37 to 40 weeks' gestation.
Pathophysiology
- Natasha Nassar, PhD
- Christine L. Roberts, MBBS, FAFPHM, DrPH
- Jonathan Morris, MBChB, FRANZCOG, PhD
- John W. Bachman, MD
- Rhona Hughes, MBChB
- Brian Peat, MD
- Lelia Duley, MBChB
- Justus Hofmeyr, MD

Clinical exam
Palpation of the abdomen to determine the position of the baby's head
Palpation of the abdomen to confirm the position of the fetal spine on one side and fetal extremities on the other
Palpation of the area above the symphysis pubis to locate the fetal presenting part
Palpation of the presenting part to confirm presentation, to determine how far the fetus has descended and whether the fetus is engaged.
Ultrasound examination
Premature fetus.
Prematurity is consistently associated with breech presentation. [ 6 ] [ 9 ] This may be due to the smaller size of preterm infants, who are more likely to change their in utero position.
Increasing duration of pregnancy may allow breech-presenting fetuses time to grow, turn spontaneously or by external cephalic version, and remain cephalic-presenting.
Larger fetuses may be forced into a cephalic presentation in late pregnancy due to space or alignment constraints within the uterus.
small for gestational age fetus
Low birth-weight is a risk factor for breech presentation. [ 9 ] [ 11 ] [ 12 ] [ 13 ] [ 14 ] Term breech births are associated with a smaller fetal size for gestational age, highlighting the association with low birth-weight rather than prematurity. [ 6 ]
nulliparity
Women having a first birth have increased rates of breech presentation, probably due to the increased likelihood of smaller fetal size. [ 6 ] [ 9 ]
Relaxation of the uterine wall in multiparous women may reduce the odds of breech birth and contribute to a higher spontaneous or external cephalic version rate. [ 10 ]
fetal congenital anomalies
Congenital anomalies in the fetus may result in a small fetal size or inappropriate fetal growth. [ 9 ] [ 12 ] [ 14 ] [ 15 ]
Anencephaly, hydrocephaly, Down syndrome, and fetal neuromuscular dysfunction are associated with breech presentation, the latter due to its effect on the quality of fetal movements. [ 9 ] [ 14 ]
previous breech delivery
The risk of recurrent breech delivery is 8%, the risk increasing from 4% after one breech delivery to 28% after three. [ 16 ]
The effects of recurrence may be due to recurring specific causal factors, either genetic or environmental in origin.
uterine abnormalities
Women with uterine abnormalities have a high incidence of breech presentation. [ 14 ] [ 17 ] [ 18 ] [ 19 ]
female fetus
Fifty-four percent of breech-presenting fetuses are female. [ 14 ]
abnormal amniotic fluid volume
Both oligohydramnios and polyhydramnios are associated with breech presentation. [ 1 ] [ 12 ] [ 14 ]
Low amniotic fluid volume decreases the likelihood of a fetus turning to a cephalic position; an increased amniotic fluid volume may facilitate frequent change in position.

placental abnormalities
An association between placental implantation in the cornual-fundal region and breech presentation has been reported, although some studies have not found it a risk factor. [ 8 ] [ 20 ] [ 21 ] [ 22 ] [ 10 ] [ 14 ]
The association with placenta previa is also inconsistent. [ 8 ] [ 9 ] [ 22 ] Placenta previa is associated with preterm birth and may be an indirect risk factor.
Pelvic or vaginal examination reveals the buttocks and/or feet, felt as a yielding, irregular mass, as the presenting part. [ 26 ] In cephalic presentation, a hard, round, regular fetal head can be palpated. [ 26 ]
The Leopold maneuver on examination suggests breech position by palpation of the fetal head under the costal margin. [ 26 ]
The baby's heartbeat should be auscultated using a Pinard stethoscope or a hand-held Doppler to indicate the position of the fetus. The fetal heartbeat lies above the maternal umbilicus in breech presentation. [ 1 ]
Tenderness under one or other costal margin as a result of pressure by the harder fetal head.
Pain due to fetal kicks in the maternal pelvis or bladder.
breech position
Visualizes the fetus and reveals its position.
Used to confirm a clinically suspected breech presentation. [ 28 ]
Should be performed by practitioners with appropriate skills in obstetric ultrasound.
Establishes the type of breech presentation by imaging the fetal femurs and their relationship to the distal bones.
Transverse lie
Differentiating Signs/Symptoms
Fetus lies horizontally across the uterus with the shoulder as the presenting part.
Similar predisposing factors such as placenta previa, abnormal amniotic fluid volume, and uterine anomalies, although more common in multiparity. [ 1 ] [ 2 ] [ 29 ]
Differentiating Tests
Clinical examination and fetal auscultation may be indicative.
Ultrasound confirms presentation.
Treatment Approach
Breech presentation <37 weeks' gestation.
The UK Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists (RCOG) recommends that corticosteroids should be offered to women between 24 and 34+6 weeks' gestation, in whom imminent preterm birth is anticipated. Corticosteroids should only be considered after discussion of risks/benefits at 35 to 36+6 weeks. Given within 7 days of preterm birth, corticosteroids may reduce perinatal and neonatal death and respiratory distress syndrome. [ 32 ] The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) recommends a single course of corticosteroids for pregnant women between 24 and 33+6 weeks' gestation who are at risk of preterm delivery within 7 days, including those with ruptured membranes and multiple gestations. It may also be considered for pregnant women starting at 23 weeks' gestation who are at risk of preterm delivery within 7 days. A single course of betamethasone is recommended for pregnant women between 34 and 36+6 weeks' gestation at risk of preterm birth within 7 days, and who have not received a previous course of prenatal corticosteroids. Regularly scheduled repeat courses or serial courses (more than two) are not currently recommended. A single repeat course of prenatal corticosteroids should be considered in women who are less than 34 weeks' gestation, who are at risk of preterm delivery within 7 days, and whose prior course of prenatal corticosteroids was administered more than 14 days previously. Rescue course corticosteroids could be provided as early as 7 days from the prior dose, if indicated by the clinical scenario. [ 33 ]
Magnesium sulfate given before anticipated early preterm birth reduces the risk of cerebral palsy in surviving infants. Physicians electing to use magnesium sulfate for fetal neuroprotection should develop specific guidelines regarding inclusion criteria, treatment regimens, and concurrent tocolysis. [ 34 ]
Breech presentation from 37 weeks' gestation, before labor
ECV is the initial treatment for a breech presentation at term when the patient is not in labor. It involves turning a fetus presenting by the breech to a cephalic (head-down) presentation to increase the likelihood of vaginal birth. [ 35 ] [ 36 ] Where available, it should be offered to all women in late pregnancy, by an experienced clinician, in hospitals with facilities for emergency delivery, and no contraindications to the procedure. [ 35 ] There is no upper time limit on the appropriate gestation for ECV, with success reported at 42 weeks.
There is no general consensus on contraindications to ECV. Contraindications include multiple pregnancy (except after delivery of a first twin), ruptured membranes, current or recent (<1 week) vaginal bleeding, rhesus isoimmunization, other indications for cesarean section (e.g., placenta previa or uterine malformation), or abnormal electronic fetal monitoring. [ 35 ] One systematic review of relative contraindications for ECV highlighted that most contraindications do not have clear empirical evidence. Exceptions include placental abruption, severe preeclampsia/HELLP syndrome, or signs of fetal distress (abnormal cardiotocography and/or Doppler flow). [ 36 ]
The procedure involves applying external pressure and firmly pushing or palpating the mother's abdomen to coerce the fetus to somersault (either forward or backward) into a cephalic position. [ 37 ]
The overall ECV success rate varies but, in a large series, 47% of women following an ECV attempt had a cephalic presentation at birth. [ 35 ] [ 38 ] Various factors influence the success rate. One systematic review found ECV success rates to be 68% overall, with the rate significantly higher for women from African countries (89%) compared with women from non-African countries (62%), and higher among multiparous (78%) than nulliparous women (48%). [ 39 ] Overall, the ECV success rates for nulliparous and multiparous non-African women were 43% and 73%, respectively, while for nulliparous and multiparous African women rates were 79% and 91%, respectively. Another study reported no difference in success rate or rate of cesarean section among women with previous cesarean section undergoing ECV compared with women with previous vaginal birth. However, numbers were small and further studies in this regard are required. [ 40 ]
Women's preference for vaginal delivery is a major contributing factor in their decision for ECV. However, studies suggest women with a breech presentation at term may not receive complete and/or evidence-based information about the benefits and risks of ECV. [ 41 ] [ 42 ] Although up to 60% of women reported ECV to be painful, the majority highlighted the benefits outweigh the risks (71%) and would recommend ECV to their friends or be willing to repeat for themselves (84%). [ 41 ] [ 42 ]
Cardiotocography and ultrasound should be performed before and after the procedure. Tocolysis should be used to facilitate the maneuver, and Rho(D) immune globulin should be administered to women who are Rhesus negative. [ 35 ] Tocolytic agents include adrenergic beta-2 receptor stimulants such as albuterol, terbutaline, or ritodrine (widely used with ECV in some countries, but not yet available in the US). One Cochrane review of tocolytic beta stimulants demonstrates that these are less likely to be associated with failed ECV, and are effective in increasing cephalic presentation and reducing cesarean section. [ 43 ] There is no current evidence to recommend one beta-2 adrenergic receptor agonist over another. Until these data are available, adherence to a local protocol for tocolysis is recommended. The Food and Drug Administration has issued a warning against using injectable terbutaline beyond 48 to 72 hours, or acute or prolonged treatment with oral terbutaline, in pregnant women for the prevention or prolonged treatment of preterm labor, due to potential serious maternal cardiac adverse effects and death. [ 44 ] Whether this warning applies to the subcutaneous administration of terbutaline in ECV is still unclear; however, studies currently support this use. The European Medicines Agency (EMA) recommends that injectable beta agonists should be used for up to 48 hours between the 22nd and 37th week of pregnancy only. They should be used under specialist supervision with continuous monitoring of the mother and unborn baby owing to the risk of adverse cardiovascular effects in both the mother and baby. The EMA no longer recommends oral or rectal formulations for obstetric indications. [ 45 ]
If ECV is successful, pregnancy care should continue as usual for any cephalic presentation. One systematic review assessing the mode of delivery after a successful ECV found that these women were at increased risk for cesarean section and instrumental vaginal delivery compared with women with spontaneous cephalic pregnancies. However, they still had a lower rate of cesarean section following ECV (i.e., 47%) compared with the cesarean section rate for those with a persisting breech (i.e., 85%). With a number needed to treat of three, ECV is still considered to be an effective means of preventing the need for cesarean section. [ 46 ]
Planned cesarean section should be offered as the safest mode of delivery for the baby, even though it carries a small increase in serious immediate maternal complications compared with vaginal birth. [ 24 ] [ 25 ] [ 31 ] In the US, most unsuccessful ECV with persistent breech will be delivered via cesarean section.
A vaginal mode of delivery may be considered by some clinicians as an option, particularly when maternal request is provided, senior and experienced staff are available, there is no absolute contraindication to vaginal birth (e.g., placenta previa, compromised fetal condition), and with optimal fetal growth (estimated weight above the tenth centile and up to 3800 g). Other factors that make planned vaginal birth higher risk include hyperextended neck on ultrasound and footling presentation. [ 24 ]
Breech presentation from 37 weeks' gestation, during labor
The first option should be a planned cesarean section.
There is a small increase in the risk of serious immediate maternal complications compared with vaginal birth (RR 1.29, 95% CI 1.03 to 1.61), including pulmonary embolism, infection, bleeding, damage to the bladder and bowel, slower recovery from the delivery, longer hospitalization, and delayed bonding and breast-feeding. [ 23 ] [ 31 ] [ 47 ] [ 48 ] [ 49 ] [ 50 ] [ 51 ] [ 52 ] [ 53 ] [ 54 ] [ 55 ] [ 56 ] [ 57 ] [ 58 ] Consider using antimicrobial triclosan-coated sutures for wound closure to reduce the risk of surgical site infection. [ 59 ]
The long-term risks include potential compromise of future obstetric performance, increased risk of repeat cesarean section, infertility, uterine rupture, placenta accreta, placental abruption, and emergency hysterectomy. [ 60 ] [ 61 ] [ 62 ] [ 63 ]
Planned cesarean section is safer for babies, but is associated with increased neonatal respiratory distress. The risk is reduced when the section is performed at 39 weeks' gestation. [ 64 ] [ 65 ] [ 66 ] For women undergoing a planned cesarean section, RCOG recommends an informed discussion about the potential risks and benefits of a course of prenatal corticosteroids between 37 and 38+6 weeks' gestation. Although prenatal corticosteroids may reduce admission to the neonatal unit for respiratory morbidity, it is uncertain if there is any reduction in respiratory distress syndrome, transient tachypnea of the newborn, or neonatal unit admission overall. In addition, prenatal corticosteroids may result in harm to the neonate, including hypoglycemia and potential developmental delay. [ 32 ] ACOG does not recommend corticosteroids in women >37 weeks' gestation. [ 33 ]
Undiagnosed breech in labor generally results in cesarean section after the onset of labor, higher rates of emergency cesarean section associated with the least favorable maternal outcomes, a greater likelihood of cord prolapse, and other poor infant outcomes. [ 23 ] [ 67 ] [ 49 ] [ 68 ] [ 69 ] [ 70 ] [ 71 ]
This mode of delivery may be considered by some clinicians as an option for women who are in labor, particularly when delivery is imminent. Vaginal breech delivery may also be considered, where suitable, when delivery is not imminent, maternal request is provided, senior and experienced staff are available, there is no absolute contraindication to vaginal birth (e.g., placenta previa, compromised fetal condition), and with optimal fetal growth (estimated weight above the tenth centile and up to 3800 g). Other factors that make planned vaginal birth higher risk include hyperextended neck on ultrasound and footling presentation. [ 24 ]
Findings from one systematic review of 27 observational studies revealed that the absolute risks of perinatal mortality, fetal neurologic morbidity, birth trauma, 5-minute Apgar score <7, and neonatal asphyxia in the planned vaginal delivery group were low at 0.3%, 0.7%, 0.7%, 2.4%, and 3.3%, respectively. However, the relative risks of perinatal mortality and morbidity were 2- to 5-fold higher in the planned vaginal than in the planned cesarean delivery group. Authors recommend ongoing judicious decision-making for vaginal breech delivery for selected singleton, term breech babies. [ 72 ]
ECV may also be considered an option for women with breech presentation in early labor, when delivery is not imminent, provided that the membranes are intact.
A woman presenting with a breech presentation <37 weeks is an area of clinical controversy. Optimal mode of delivery for preterm breech has not been fully evaluated in clinical trials, and the relative risks for the preterm infant and mother remain unclear. In the absence of good evidence, if diagnosis of breech presentation prior to 37 weeks' gestation is made, prematurity and clinical circumstances should determine management and mode of delivery.
Primary Options
12 mg intramuscularly every 24 hours for 2 doses
6 mg intramuscularly every 12 hours for 4 doses
The UK Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists recommends that corticosteroids should be offered to women between 24 and 34+6 weeks' gestation, in whom imminent preterm birth is anticipated. Corticosteroids should only be considered after discussion of risks/benefits at 35 to 36+6 weeks. Given within 7 days of preterm birth, corticosteroids may reduce perinatal and neonatal death and respiratory distress syndrome. [ 32 ]
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists recommends a single course of corticosteroids for pregnant women between 24 and 33+6 weeks' gestation who are at risk of preterm delivery within 7 days, including those with ruptured membranes and multiple gestations. It may also be considered for pregnant women starting at 23 weeks' gestation who are at risk of preterm delivery within 7 days. A single course of betamethasone is recommended for pregnant women between 34 and 36+6 weeks' gestation at risk of preterm birth within 7 days, and who have not received a previous course of prenatal corticosteroids. Regularly scheduled repeat courses or serial courses (more than two) are not currently recommended. A single repeat course of prenatal corticosteroids should be considered in women who are less than 34 weeks' gestation, who are at risk of preterm delivery within 7 days, and whose prior course of prenatal corticosteroids was administered more than 14 days previously. Rescue course corticosteroids could be provided as early as 7 days from the prior dose, if indicated by the clinical scenario. [ 33 ]
consult specialist for guidance on dose
external cephalic version (ECV)
There is no upper time limit on the appropriate gestation for ECV; it should be offered to all women in late pregnancy by an experienced clinician in hospitals with facilities for emergency delivery and no contraindications to the procedure. [ 35 ] [ 36 ]
ECV involves applying external pressure and firmly pushing or palpating the mother's abdomen to coerce the fetus to somersault (either forward or backward) into a cephalic position. [ 37 ]
There is no general consensus on contraindications to ECV. Contraindications include multiple pregnancy (except after delivery of a first twin), ruptured membranes, current or recent (<1 week) vaginal bleeding, rhesus isoimmunization, other indications for cesarean section (e.g., placenta previa or uterine malformation), or abnormal electronic fetal monitoring. [ 35 ] One systematic review of relative contraindications for ECV highlighted that most contraindications do not have clear empirical evidence. Exceptions include placental abruption, severe preeclampsia/HELLP syndrome, or signs of fetal distress (abnormal cardiotocography and/or Doppler flow). [ 36 ]
Cardiotocography and ultrasound should be performed before and after the procedure.
If ECV is successful, pregnancy care should continue as usual for any cephalic presentation. A systematic review assessing the mode of delivery after a successful ECV found that these women were at increased risk for cesarean section and instrumental vaginal delivery compared with women with spontaneous cephalic pregnancies. However, they still had a lower rate of cesarean section following ECV (i.e., 47%) compared with the cesarean section rate for those with a persisting breech (i.e., 85%). With a number needed to treat of 3, ECV is still considered to be an effective means of preventing the need for cesarean section. [ 46 ]
tocolytic agents
see local specialist protocol for dosing guidelines
Tocolytic agents include adrenergic beta-2 receptor stimulants such as albuterol, terbutaline, or ritodrine (widely used with external cephalic version [ECV] in some countries, but not yet available in the US). They are used to delay or inhibit labor and increase the success rate of ECV. There is no current evidence to recommend one beta-2 adrenergic receptor agonist over another. Until these data are available, adherence to a local protocol for tocolysis is recommended.
The Food and Drug Administration has issued a warning against using injectable terbutaline beyond 48-72 hours, or acute or prolonged treatment with oral terbutaline, in pregnant women for the prevention or prolonged treatment of preterm labor, due to potential serious maternal cardiac adverse effects and death. [ 44 ] Whether this warning applies to the subcutaneous administration of terbutaline in ECV is still unclear; however, studies currently support this use. The European Medicines Agency (EMA) recommends that injectable beta agonists should be used for up to 48 hours between the 22nd and 37th week of pregnancy only. They should be used under specialist supervision with continuous monitoring of the mother and unborn baby owing to the risk of adverse cardiovascular effects in both the mother and baby. The EMA no longer recommends oral or rectal formulations for obstetric indications. [ 45 ]
A systematic review found there was no evidence to support the use of nifedipine for tocolysis. [ 73 ]
There is insufficient evidence to evaluate other interventions to help ECV, such as fetal acoustic stimulation in midline fetal spine positions, or epidural or spinal analgesia. [ 43 ]
Rho(D) immune globulin
300 micrograms intramuscularly as a single dose
Nonsensitized Rh-negative women should receive Rho(D) immune globulin. [ 35 ]
The indication for its administration is to prevent rhesus isoimmunization, which may affect subsequent pregnancy outcomes.
Rho(D) immune globulin needs to be given at the time of external cephalic version and should be given again postpartum to those women who give birth to an Rh-positive baby. [ 74 ]
It is best administered as soon as possible after the procedure, usually within 72 hours.
Dose depends on brand used. Dose given below pertains to most commonly used brands. Consult specialist for further guidance on dose.
elective cesarean section/vaginal breech delivery
Mode of delivery (cesarean section or vaginal breech delivery) should be based on the experience of the attending clinician, hospital policies, maternal request, and the presence or absence of complicating factors. In the US, most unsuccessful external cephalic version (ECV) with persistent breech will be delivered via cesarean section.
Cesarean section, at 39 weeks or greater, has been shown to significantly reduce perinatal mortality and neonatal morbidity compared with vaginal breech delivery (RR 0.33, 95% CI 0.19 to 0.56). [ 31 ] Although safer for these babies, there is a small increase in serious immediate maternal complications compared with vaginal birth (RR 1.29, 95% CI 1.03 to 1.61), as well as long-term risks for future pregnancies, including pulmonary embolism, bleeding, infection, damage to the bladder and bowel, slower recovery from the delivery, longer hospitalization, and delayed bonding and breast-feeding. [ 23 ] [ 31 ] [ 47 ] [ 48 ] [ 49 ] [ 50 ] [ 51 ] [ 52 ] [ 53 ] [ 54 ] [ 55 ] [ 56 ] [ 57 ] [ 58 ] Consider using antimicrobial triclosan-coated sutures for wound closure to reduce the risk of surgical site infection. [ 59 ]
Vaginal delivery may be considered by some clinicians as an option, particularly when maternal request is provided, when senior and experienced staff are available, when there is no absolute contraindication to vaginal birth (e.g., placenta previa, compromised fetal condition), and with optimal fetal growth (estimated weight above the tenth centile and up to 3800 g). Other factors that make planned vaginal birth higher risk include hyperextended neck on ultrasound and footling presentation. [ 24 ]
For women undergoing a planned cesarean section, the UK Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists recommends an informed discussion about the potential risks and benefits of a course of prenatal corticosteroids between 37 and 38+6 weeks' gestation. Although prenatal corticosteroids may reduce admission to the neonatal unit for respiratory morbidity, it is uncertain if there is any reduction in respiratory distress syndrome, transient tachypnea of the newborn, or neonatal unit admission overall. In addition, prenatal corticosteroids may result in harm to the neonate, including hypoglycemia and potential developmental delay. [ 32 ] The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists does not recommend corticosteroids in women >37 weeks' gestation. [ 33 ]
It is best administered as soon as possible after delivery, usually within 72 hours.
Administration of postpartum Rho (D) immune globulin should not be affected by previous routine prenatal prophylaxis or previous administration for a potentially sensitizing event. [ 74 ]
≥37 weeks' gestation in labor: no imminent delivery
planned cesarean section
For women with breech presentation in labor, planned cesarean section at 39 weeks or greater has been shown to significantly reduce perinatal mortality and neonatal morbidity compared with vaginal breech delivery (RR 0.33, 95% CI 0.19 to 0.56). [ 31 ]
Although safer for these babies, there is a small increase in serious immediate maternal complications compared with vaginal birth (RR 1.29, 95% CI 1.03 to 1.61), as well as long-term risks for future pregnancies, including pulmonary embolism, infection, bleeding, damage to the bladder and bowel, slower recovery from the delivery, longer hospitalization, and delayed bonding and breast-feeding. [ 23 ] [ 31 ] [ 47 ] [ 48 ] [ 49 ] [ 50 ] [ 51 ] [ 52 ] [ 53 ] [ 54 ] [ 55 ] [ 56 ] [ 57 ] [ 58 ] Consider using antimicrobial triclosan-coated sutures for wound closure to reduce the risk of surgical site infection. [ 59 ]
Continuous cardiotocography monitoring should continue until delivery. [ 24 ] [ 25 ]
vaginal breech delivery
Mode of delivery (cesarean section or vaginal breech delivery) should be based on the experience of the attending clinician, hospital policies, maternal request, and the presence or absence of complicating factors.
This mode of delivery may be considered by some clinicians as an option, particularly when maternal request is provided, when senior and experienced staff are available, when there is no absolute contraindication to vaginal birth (e.g., placenta previa, compromised fetal condition), and with optimal fetal growth (estimated weight above the tenth centile and up to 3800 g). Other factors that make planned vaginal birth higher risk include hyperextended neck on ultrasound and footling presentation. [ 24 ]
For women with persisting breech presentation, planned cesarean section has, however, been shown to significantly reduce perinatal mortality and neonatal morbidity compared with vaginal breech delivery (RR 0.33, 95% CI 0.19 to 0.56). [ 31 ]
ECV may also be considered an option for women with breech presentation in early labor, provided that the membranes are intact.
There is no upper time limit on the appropriate gestation for ECV. [ 35 ]
Involves applying external pressure and firmly pushing or palpating the mother's abdomen to coerce the fetus to somersault (either forward or backward) into a cephalic position. [ 37 ]
Relative contraindications include placental abruption, severe preeclampsia/HELLP syndrome, and signs of fetal distress (abnormal cardiotocography and/or abnormal Doppler flow). [ 35 ] [ 36 ]
Rho(D) immune globulin needs to be given at the time of ECV and should be given again postpartum to those women who give birth to an Rh-positive baby. [ 74 ]
≥37 weeks' gestation in labor: imminent delivery
cesarean section
For women with persistent breech presentation, planned cesarean section has been shown to significantly reduce perinatal mortality and neonatal morbidity compared with vaginal breech delivery (RR 0.33, 95% CI 0.19 to 0.56). [ 31 ] Although safer for these babies, there is a small increase in serious immediate maternal complications compared with vaginal birth (RR 1.29, 95% CI 1.03 to 1.61), as well as long-term risks for future pregnancies, including pulmonary embolism, infection, bleeding, damage to the bladder and bowel, slower recovery from the delivery, longer hospitalization, and delayed bonding and breast-feeding. [ 23 ] [ 31 ] [ 47 ] [ 48 ] [ 49 ] [ 50 ] [ 51 ] [ 52 ] [ 53 ] [ 54 ] [ 55 ] [ 56 ] [ 57 ] [ 58 ] Consider using antimicrobial triclosan-coated sutures for wound closure to reduce the risk of surgical site infection. [ 59 ]
This mode of delivery may be considered by some clinicians as an option, particularly when delivery is imminent, maternal request is provided, when senior and experienced staff are available, when there is no absolute contraindication to vaginal birth (e.g., placenta previa, compromised fetal condition), and with optimal fetal growth (estimated weight above the tenth centile and up to 3800 g). Other factors that make planned vaginal birth higher risk include hyperextended neck on ultrasound and footling presentation. [ 24 ]
It is best administered as soon as possible after the delivery, usually within 72 hours.
External cephalic version before term
Moxibustion, postural management, follow-up overview, perinatal complications.
Compared with cephalic presentation, persistent breech presentation has increased frequency of cord prolapse, abruptio placentae, prelabor rupture of membranes, perinatal mortality, fetal distress (heart rate <100 bpm), preterm delivery, lower fetal weight. [ 10 ] [ 11 ] [ 67 ]
complications of cesarean section
There is a small increase in the risk of serious immediate maternal complications compared with vaginal birth (RR 1.29, 95% CI 1.03 to 1.61), including pulmonary embolism, infection, bleeding, damage to the bladder and bowel, slower recovery from the delivery, longer hospitalization, and delayed bonding and breast-feeding. [ 23 ] [ 31 ] [ 47 ] [ 48 ] [ 49 ] [ 50 ] [ 51 ] [ 52 ] [ 53 ] [ 54 ] [ 55 ] [ 56 ] [ 57 ] [ 58 ]
The long-term risks include potential compromise of future obstetric performance, increased risk of repeat cesarean section, infertility, uterine rupture, placenta accreta, placental abruption, and emergency hysterectomy. [ 60 ] [ 61 ] [ 62 ] [ 63 ] The evidence suggests that using sutures, rather than staples, for wound closure after cesarean section reduces the incidence of wound dehiscence. [ 59 ]
Emergency cesarean section, compared with planned cesarean section, has demonstrated a higher risk of severe obstetric morbidity, intra-operative complications, postoperative complications, infection, blood loss >1500 mL, fever, pain, tiredness, and breast-feeding problems. [ 23 ] [ 48 ] [ 50 ] [ 70 ] [ 81 ]
Key Articles
Impey LWM, Murphy DJ, Griffiths M, et al; Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists. Management of breech presentation: green-top guideline no. 20b. BJOG. 2017 Jun;124(7):e151-77. [Full Text]
Hofmeyr GJ, Hannah M, Lawrie TA. Planned caesarean section for term breech delivery. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Jul 21;(7):CD000166. [Abstract] [Full Text]
Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists. External cephalic version and reducing the incidence of term breech presentation. March 2017 [internet publication]. [Full Text]
Cluver C, Gyte GM, Sinclair M, et al. Interventions for helping to turn term breech babies to head first presentation when using external cephalic version. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Feb 9;(2):CD000184. [Abstract] [Full Text]
de Hundt M, Velzel J, de Groot CJ, et al. Mode of delivery after successful external cephalic version: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Obstet Gynecol. 2014 Jun;123(6):1327-34. [Abstract]
Referenced Articles
1. Cunningham F, Gant N, Leveno K, et al. Williams obstetrics. 21st ed. New York: McGraw-Hill; 1997.
2. Kish K, Collea JV. Malpresentation and cord prolapse. In: DeCherney AH, Nathan L, eds. Current obstetric and gynecologic diagnosis and treatment. New York: McGraw-Hill Professional; 2002.
3. Scheer K, Nubar J. Variation of fetal presentation with gestational age. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1976 May 15;125(2):269-70. [Abstract]
4. Nassar N, Roberts CL, Cameron CA, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of clinical examination for detection of non-cephalic presentation in late pregnancy: cross sectional analytic study. BMJ. 2006 Sep 16;333(7568):578-80. [Abstract] [Full Text]
5. Roberts CL, Peat B, Algert CS, et al. Term breech birth in New South Wales, 1990-1997. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol. 2000 Feb;40(1):23-9. [Abstract]
6. Roberts CL, Algert CS, Peat B, et al. Small fetal size: a risk factor for breech birth at term. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 1999 Oct;67(1):1-8. [Abstract]
7. Brar HS, Platt LD, DeVore GR, et al. Fetal umbilical velocimetry for the surveillance of pregnancies complicated by placenta previa. J Reprod Med. 1988 Sep;33(9):741-4. [Abstract]
8. Kian L. The role of the placental site in the aetiology of breech presentation. J Obstet Gynaecol Br Commonw. 1963 Oct;70:795-7. [Abstract]
9. Rayl J, Gibson PJ, Hickok DE. A population-based case-control study of risk factors for breech presentation. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1996 Jan;174(1 Pt 1):28-32. [Abstract]
10. Westgren M, Edvall H, Nordstrom L, et al. Spontaneous cephalic version of breech presentation in the last trimester. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1985 Jan;92(1):19-22. [Abstract]
11. Brenner WE, Bruce RD, Hendricks CH. The characteristics and perils of breech presentation. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1974 Mar 1;118(5):700-12. [Abstract]
12. Hall JE, Kohl S. Breech presentation. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1956 Nov;72(5):977-90. [Abstract]
13. Morgan HS, Kane SH. An analysis of 16,327 breech births. JAMA. 1964 Jan 25;187:262-4. [Abstract]
14. Luterkort M, Persson P, Weldner B. Maternal and fetal factors in breech presentation. Obstet Gynecol. 1984 Jul;64(1):55-9. [Abstract]
15. Braun FH, Jones KL, Smith DW. Breech presentation as an indicator of fetal abnormality. J Pediatr. 1975 Mar;86(3):419-21. [Abstract]
16. Albrechtsen S, Rasmussen S, Dalaker K, et al. Reproductive career after breech presentation: subsequent pregnancy rates, interpregnancy interval, and recurrence. Obstet Gynecol. 1998 Sep;92(3):345-50. [Abstract]
17. Zlopasa G, Skrablin S, Kalafatić D, et al. Uterine anomalies and pregnancy outcome following resectoscope metroplasty. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2007 Aug;98(2):129-33. [Abstract]
18. Acién P. Breech presentation in Spain, 1992: a collaborative study. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 1995 Sep;62(1):19-24. [Abstract]
19. Michalas SP. Outcome of pregnancy in women with uterine malformation: evaluation of 62 cases. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 1991 Jul;35(3):215-9. [Abstract]
20. Fianu S, Vaclavinkova V. The site of placental attachment as a factor in the aetiology of breech presentation. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 1978;57(4):371-2. [Abstract]
21. Haruyama Y. Placental implantation as the cause of breech presentation [in Japanese]. Nihon Sanka Fujinka Gakkai Zasshi. 1987 Jan;39(1):92-8. [Abstract]
22. Filipov E, Borisov I, Kolarov G. Placental location and its influence on the position of the fetus in the uterus [in Bulgarian]. Akush Ginekol (Sofiia). 2000;40(4):11-2. [Abstract]
23. Waterstone M, Bewley S, Wolfe C. Incidence and predictors of severe obstetric morbidity: case-control study. BMJ. 2001 May 5;322(7294):1089-93. [Abstract] [Full Text]
24. Impey LWM, Murphy DJ, Griffiths M, et al; Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists. Management of breech presentation: green-top guideline no. 20b. BJOG. 2017 Jun;124(7):e151-77. [Full Text]
25. American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists Committee on Obstetric Practice. ACOG committee opinion no. 745: mode of term singleton breech delivery. Obstet Gynecol. 2018 Aug;132(2):e60-3. [Abstract] [Full Text]
26. Beischer NA, Mackay EV, Colditz P, eds. Obstetrics and the newborn: an illustrated textbook. 3rd ed. London: W.B. Saunders; 1997.
27. Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists. Antepartum haemorrhage: green-top guideline no. 63. November 2011 [internet publication]. [Full Text]
28. American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Practice bulletin no. 175: ultrasound in pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol. 2016 Dec;128(6):e241-56. [Abstract]
29. Enkin M, Keirse MJNC, Neilson J, et al. Guide to effective care in pregnancy and childbirth. 3rd ed. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 2000.
30. Hofmeyr GJ, Kulier R, West HM. External cephalic version for breech presentation at term. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Oct 17;(10):CD000083. [Abstract] [Full Text]
31. Hofmeyr GJ, Hannah M, Lawrie TA. Planned caesarean section for term breech delivery. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Jul 21;(7):CD000166. [Abstract] [Full Text]
32. Stock SJ, Thomson AJ, Papworth S, et al. Antenatal corticosteroids to reduce neonatal morbidity and mortality: Green-top Guideline No. 74. BJOG. 2022 Jul;129(8):e35-60. [Abstract] [Full Text]
33. American College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists Committee on Obstetric Practice. Committee opinion no. 713: antenatal corticosteroid therapy for fetal maturation. August 2017 (reaffirmed 2020) [internet publication]. [Full Text]
34. American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists Committee on Obstetric Practice. Committee opinion no. 455: magnesium sulfate before anticipated preterm birth for neuroprotection. March 2010 (reaffirmed 2020) [internet publication]. [Full Text]
35. Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists. External cephalic version and reducing the incidence of term breech presentation. March 2017 [internet publication]. [Full Text]
36. Rosman AN, Guijt A, Vlemmix F, et al. Contraindications for external cephalic version in breech position at term: a systematic review. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2013 Feb;92(2):137-42. [Abstract]
37. Hofmeyr GJ. Effect of external cephalic version in late pregnancy on breech presentation and caesarean section rate: a controlled trial. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1983 May;90(5):392-9. [Abstract]
38. Beuckens A, Rijnders M, Verburgt-Doeleman GH, et al. An observational study of the success and complications of 2546 external cephalic versions in low-risk pregnant women performed by trained midwives. BJOG. 2016 Feb;123(3):415-23. [Abstract]
39. Nassar N, Roberts CL, Barratt A, et al. Systematic review of adverse outcomes of external cephalic version and persisting breech presentation at term. Paediatr Perinat Epidemiol. 2006 Mar;20(2):163-71. [Abstract]
40. Sela HY, Fiegenberg T, Ben-Meir A, et al. Safety and efficacy of external cephalic version for women with a previous cesarean delivery. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2009 Feb;142(2):111-4. [Abstract]
41. Pichon M, Guittier MJ, Irion O, et al. External cephalic version in case of persisting breech presentation at term: motivations and women's experience of the intervention [in French]. Gynecol Obstet Fertil. 2013 Jul-Aug;41(7-8):427-32. [Abstract]
42. Nassar N, Roberts CL, Raynes-Greenow CH, et al. Evaluation of a decision aid for women with breech presentation at term: a randomised controlled trial [ISRCTN14570598]. BJOG. 2007 Mar;114(3):325-33. [Abstract] [Full Text]
43. Cluver C, Gyte GM, Sinclair M, et al. Interventions for helping to turn term breech babies to head first presentation when using external cephalic version. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Feb 9;(2):CD000184. [Abstract] [Full Text]
44. US Food & Drug Administration. FDA Drug Safety Communication: new warnings against use of terbutaline to treat preterm labor. Feb 2011 [internet publication]. [Full Text]
45. European Medicines Agency. Restrictions on use of short-acting beta-agonists in obstetric indications - CMDh endorses PRAC recommendations. October 2013 [internet publication]. [Full Text]
46. de Hundt M, Velzel J, de Groot CJ, et al. Mode of delivery after successful external cephalic version: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Obstet Gynecol. 2014 Jun;123(6):1327-34. [Abstract]
47. Lydon-Rochelle M, Holt VL, Martin DP, et al. Association between method of delivery and maternal rehospitalisation. JAMA. 2000 May 10;283(18):2411-6. [Abstract]
48. Yokoe DS, Christiansen CL, Johnson R, et al. Epidemiology of and surveillance for postpartum infections. Emerg Infect Dis. 2001 Sep-Oct;7(5):837-41. [Abstract]
49. van Ham MA, van Dongen PW, Mulder J. Maternal consequences of caesarean section. A retrospective study of intra-operative and postoperative maternal complications of caesarean section during a 10-year period. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 1997 Jul;74(1):1-6. [Abstract]
50. Murphy DJ, Liebling RE, Verity L, et al. Early maternal and neonatal morbidity associated with operative delivery in second stage of labour: a cohort study. Lancet. 2001 Oct 13;358(9289):1203-7. [Abstract]
51. Lydon-Rochelle MT, Holt VL, Martin DP. Delivery method and self-reported postpartum general health status among primiparous women. Paediatr Perinat Epidemiol. 2001 Jul;15(3):232-40. [Abstract]
52. Wilson PD, Herbison RM, Herbison GP. Obstetric practice and the prevalence of urinary incontinence three months after delivery. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1996 Feb;103(2):154-61. [Abstract]
53. Persson J, Wolner-Hanssen P, Rydhstroem H. Obstetric risk factors for stress urinary incontinence: a population-based study. Obstet Gynecol. 2000 Sep;96(3):440-5. [Abstract]
54. MacLennan AH, Taylor AW, Wilson DH, et al. The prevalence of pelvic disorders and their relationship to gender, age, parity and mode of delivery. BJOG. 2000 Dec;107(12):1460-70. [Abstract]
55. Thompson JF, Roberts CL, Currie M, et al. Prevalence and persistence of health problems after childbirth: associations with parity and method of birth. Birth. 2002 Jun;29(2):83-94. [Abstract]
56. Australian Institute of Health and Welfare. Australia's mothers and babies 2015 - in brief. October 2017 [internet publication]. [Full Text]
57. Mutryn CS. Psychosocial impact of cesarean section on the family: a literature review. Soc Sci Med. 1993 Nov;37(10):1271-81. [Abstract]
58. DiMatteo MR, Morton SC, Lepper HS, et al. Cesarean childbirth and psychosocial outcomes: a meta-analysis. Health Psychol. 1996 Jul;15(4):303-14. [Abstract]
59. National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Caesarean birth. Mar 2021 [internet publication]. [Full Text]
60. Greene R, Gardeit F, Turner MJ. Long-term implications of cesarean section. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1997 Jan;176(1 Pt 1):254-5. [Abstract]
61. Coughlan C, Kearney R, Turner MJ. What are the implications for the next delivery in primigravidae who have an elective caesarean section for breech presentation? BJOG. 2002 Jun;109(6):624-6. [Abstract]
62. Hemminki E, Merilainen J. Long-term effects of cesarean sections: ectopic pregnancies and placental problems. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1996 May;174(5):1569-74. [Abstract]
63. Gilliam M, Rosenberg D, Davis F. The likelihood of placenta previa with greater number of cesarean deliveries and higher parity. Obstet Gynecol. 2002 Jun;99(6):976-80. [Abstract]
64. Morrison JJ, Rennie JM, Milton PJ. Neonatal respiratory morbidity and mode of delivery at term: influence of timing of elective caesarean section. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1995 Feb;102(2):101-6. [Abstract]
65. Annibale DJ, Hulsey TC, Wagner CL, et al. Comparative neonatal morbidity of abdominal and vaginal deliveries after uncomplicated pregnancies. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 1995 Aug;149(8):862-7. [Abstract]
66. Hook B, Kiwi R, Amini SB, et al. Neonatal morbidity after elective repeat cesarean section and trial of labor. Pediatrics. 1997 Sep;100(3 Pt 1):348-53. [Abstract]
67. Nassar N, Roberts CL, Cameron CA, et al. Outcomes of external cephalic version and breech presentation at term: an audit of deliveries at a Sydney tertiary obstetric hospital, 1997-2004. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2006;85(10):1231-8. [Abstract]
68. Nwosu EC, Walkinshaw S, Chia P, et al. Undiagnosed breech. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1993 Jun;100(6):531-5. [Abstract]
69. Flamm BL, Ruffini RM. Undetected breech presentation: impact on external version and cesarean rates. Am J Perinatol. 1998 May;15(5):287-9. [Abstract]
70. Cockburn J, Foong C, Cockburn P. Undiagnosed breech. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1994 Jul;101(7):648-9. [Abstract]
71. Leung WC, Pun TC, Wong WM. Undiagnosed breech revisited. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1999 Jul;106(7):638-41. [Abstract]
72. Berhan Y, Haileamlak A. The risks of planned vaginal breech delivery versus planned caesarean section for term breech birth: a meta-analysis including observational studies. BJOG. 2016 Jan;123(1):49-57. [Abstract] [Full Text]
73. Wilcox C, Nassar N, Roberts C. Effectiveness of nifedipine tocolysis to facilitate external cephalic version: a systematic review. BJOG. 2011 Mar;118(4):423-8. [Abstract]
74. Qureshi H, Massey E, Kirwan D, et al. BCSH guideline for the use of anti-D immunoglobulin for the prevention of haemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn. Transfus Med. 2014 Feb;24(1):8-20. [Abstract] [Full Text]
75. Hutton EK, Hofmeyr GJ, Dowswell T. External cephalic version for breech presentation before term. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Jul 29;(7):CD000084. [Abstract] [Full Text]
76. Coyle ME, Smith CA, Peat B. Cephalic version by moxibustion for breech presentation. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 May 16;(5):CD003928. [Abstract] [Full Text]
77. Hofmeyr GJ, Kulier R. Cephalic version by postural management for breech presentation. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Oct 17;(10):CD000051. [Abstract] [Full Text]
78. Hannah ME, Whyte H, Hannah WJ, et al. Maternal outcomes at 2 years after planned cesarean section versus planned vaginal birth for breech presentation at term: the International Randomized Term Breech Trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2004 Sep;191(3):917-27. [Abstract]
79. Eide MG, Oyen N, Skjaerven R, et al. Breech delivery and Intelligence: a population-based study of 8,738 breech infants. Obstet Gynecol. 2005 Jan;105(1):4-11. [Abstract]
80. Whyte H, Hannah ME, Saigal S, et al. Outcomes of children at 2 years after planned cesarean birth versus planned vaginal birth for breech presentation at term: the International Randomized Term Breech Trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2004 Sep;191(3):864-71. [Abstract]
81. Brown S, Lumley J. Maternal health after childbirth: results of an Australian population based survey. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1998 Feb;105(2):156-61. [Abstract]
Published by
American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists
2016 (reaffirmed 2022)
Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists (UK)
National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (UK)
Topic last updated: 2024-03-05
Natasha Nassar , PhD
Associate Professor
Menzies Centre for Health Policy
Sydney School of Public Health
University of Sydney
Christine L. Roberts , MBBS, FAFPHM, DrPH
Research Director
Clinical and Population Health Division
Perinatal Medicine Group
Kolling Institute of Medical Research
Jonathan Morris , MBChB, FRANZCOG, PhD
Professor of Obstetrics and Gynaecology and Head of Department
Peer Reviewers
John W. Bachman , MD
Consultant in Family Medicine
Department of Family Medicine
Mayo Clinic
Rhona Hughes , MBChB
Lead Obstetrician
Lothian Simpson Centre for Reproductive Health
The Royal Infirmary
Brian Peat , MD
Director of Obstetrics
Women's and Children's Hospital
North Adelaide
South Australia
Lelia Duley , MBChB
Professor of Obstetric Epidemiology
University of Leeds
Bradford Institute of Health Research
Temple Bank House
Bradford Royal Infirmary
Justus Hofmeyr , MD
Head of the Department of Obstetrics and Gynaecology
East London Private Hospital
East London
South Africa
Management of Breech Presentation (Green-top Guideline No. 20b)
Summary: The aim of this guideline is to aid decision making regarding the route of delivery and choice of various techniques used during delivery. It does not include antenatal or postnatal care. Information regarding external cephalic version is the topic of the separate Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists Green-top Guideline No. 20a, External Cephalic Version and Reducing the Incidence of Term Breech Presentation .
Breech presentation occurs in 3–4% of term deliveries and is more common in preterm deliveries and nulliparous women. Breech presentation is associated with uterine and congenital abnormalities, and has a significant recurrence risk. Term babies presenting by the breech have worse outcomes than cephalic presenting babies, irrespective of the mode of delivery.
A large reduction in the incidence of planned vaginal breech birth followed publication of the Term Breech Trial. Nevertheless, due to various circumstances vaginal breech births will continue. Lack of experience has led to a loss of skills essential for these deliveries. Conversely, caesarean section can has serious long-term consequences.
COVID disclaimer: This guideline was developed as part of the regular updates to programme of Green-top Guidelines, as outlined in our document Developing a Green-top Guideline: Guidance for developers , and prior to the emergence of COVID-19.
Version history: This is the fourth edition of this guideline.
Please note that the RCOG Guidelines Committee regularly assesses the need to update the information provided in this publication. Further information on this review is available on request.
Developer declaration of interests:
Mr M Griffiths is a member of Doctors for a Woman's right to Choose on Abortion. He is an unpaid member of a Quality Standards Advisory Committee at NICE, for which he does receive expenses for related travel, accommodation and meals.
Mr LWM Impey is Director of Oxford Fetal Medicine Ltd. and a member of the International Society of Ultrasound in Obstetrics and Gynecology. He also holds patents related to ultrasound processing, which are of no relevance to the Breech guidelines.
Professor DJ Murphy provides medicolegal expert opinions in Scotland and Ireland for which she is remunerated.
Dr LK Penna: None declared.
- Access the PDF version of this guideline on Wiley
- Access the web version of this guideline on Wiley
This page was last reviewed 16 March 2017.
We have a new app!
Take the Access library with you wherever you go—easy access to books, videos, images, podcasts, personalized features, and more.
Download the Access App here: iOS and Android . Learn more here!
- Remote Access
- Save figures into PowerPoint
- Download tables as PDFs

Chapter 25: Breech Presentation
Jessica Dy; Darine El-Chaar
- Download Chapter PDF
Disclaimer: These citations have been automatically generated based on the information we have and it may not be 100% accurate. Please consult the latest official manual style if you have any questions regarding the format accuracy.
Download citation file:
- Search Book
Jump to a Section
General considerations.
- CLASSIFICATION
- RIGHT SACRUM ANTERIOR
- MECHANISMS OF LABOR: BREECH PRESENTATIONS
- PROGNOSIS: BREECH PRESENTATIONS
- INVESTIGATION OF BREECH PRESENTATION AT TERM
- MANAGEMENT OF BREECH PRESENTATION DURING LATE PREGNANCY
- MANAGEMENT OF DELIVERY OF BREECH PRESENTATION
- ARREST IN BREECH PRESENTATION
- BREECH EXTRACTION
- HYPEREXTENSION OF THE FETAL HEAD
- SELECTED READING
- Full Chapter
- Supplementary Content
Breech presentation is a longitudinal lie with a variation in polarity. The fetal pelvis is the leading pole. The denominator is the sacrum. A right sacrum anterior (RSA) is a breech presentation where the fetal sacrum is in the right anterior quadrant of the mother's pelvis and the bitrochanteric diameter of the fetus is in the right oblique diameter of the pelvis ( Fig. 25-1 ).
FIGURE 25-1.
Positions of breech presentation. LSA, left sacrum anterior; LSP, left sacrum posterior; LST, left sacrum transverse; RSA, right sacrum anterior; RSP, right sacrum posterior; RST, right sacrum transverse.

Breech presentation at delivery occurs in 3 to 4 percent of pregnancies. However, before 28 weeks of gestation, the incidence is about 25 percent. As term gestation approaches, the incidence decreases. In most cases, the fetus converts to the cephalic presentation by 34 weeks of gestation.
As term approaches, the uterine cavity, in most cases, accommodates the fetus best in a longitudinal lie with a cephalic presentation. In many cases of breech presentation, no reason for the malpresentation can be found and, by exclusion, the cause is ascribed to chance. Some women deliver all their children as breeches, suggesting that the pelvis is so shaped that the breech fits better than the head.
Breech presentation is more common at the end of the second trimester than near term; hence, fetal prematurity is associated frequently with this presentation.
Maternal Factors
Factors that influence the occurrence of breech presentation include (1) the uterine relaxation associated with high parity; (2) polyhydramnios, in which the excessive amount of amniotic fluid makes it easier for the fetus to change position; (3) oligohydramnios, in which, because of the small amount of fluid, the fetus is trapped in the position assumed in the second trimester; (4) uterine anomalies; (5) neoplasms, such as leiomyomata of the myometrium; (6) while contracted pelvis is an uncommon cause of breech presentation, anything that interferes with the entry of the fetal head into the pelvis may play a part in the etiology of breech presentation.
Placental Factors
Placental site: There is some evidence that implantation of the placenta in either cornual-fundal region tends to promote breech presentation. There is a positive association of breech with placenta previa.
Fetal Factors
Fetal factors that influence the occurrence of breech presentation include multiple pregnancy, hydrocephaly, anencephaly, chromosomal anomalies, and intrauterine fetal death.
Notes and Comments
The patient commonly feels fetal movements in the lower abdomen and may complain of painful kicking against the rectum, vagina, and bladder
Pop-up div Successfully Displayed
This div only appears when the trigger link is hovered over. Otherwise it is hidden from view.
Please Wait
Breech presentation: diagnosis and management
Key messages.
- All women with a breech presentation should be offered an external cephalic version (ECV) from 37 weeks, if there are no contraindications.
- Elective caesarean section (ELCS) for a singleton breech at term has been shown to reduce perinatal and neonatal mortality rates.
- Planning for vaginal breech birth requires careful assessment of suitability criteria, contraindications and the ability of the service to provide experienced personnel.
In June 2023, we commenced a project to review and update the Maternity and Neonatal eHandbook guidelines, with a view to targeting completion in 2024. Please be aware that pending this review, some of the current guidelines may be out of date. In the meantime, we recommend that you also refer to more contemporaneous evidence.
Breech and external cephalic version
Breech presentation is when the fetus is lying longitudinally and its buttocks, foot or feet are presenting instead of its head.
Figure 1. Breech presentations
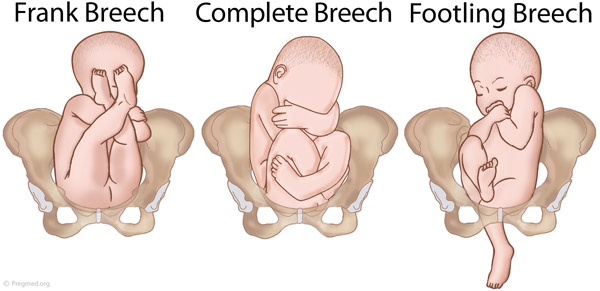
- Breech presentation occurs in three to four per cent of term deliveries and is more common in nulliparous women.
- External cephalic version (ECV) from 37 weeks has been shown to decrease the incidence of breech presentation at term and the subsequent elective caesarean section (ELCS) rate.
- Vaginal breech birth increases the risk of low Apgar scores and more serious short-term complications, but evidence has not shown an increase in long-term morbidity.
- Emergency caesarean section (EMCS) is needed in approximately 40 per cent of women planning a vaginal breech birth.
- 0.5/1000 with ELCS for breech >39 weeks gestation
- 2.0/1000 planned vaginal breech birth >39/40
- 1.0/1000 with planned cephalic birth.
- A reduction in planned vaginal breech birth followed publication of the Term Breech Trial (TBT) in 2001.
- Acquisition of skills necessary to manage breech presentation (for example, ECV) is important to optimise outcomes.
Clinical suspicion of breech presentation
- Abdominal palpation: if the presenting part is irregular and not ballotable or if the fetal head is ballotable at the fundus
- Pelvic examination: head not felt in the pelvis
- Cord prolapse
- Very thick meconium after rupture of membranes
- Fetal heart heard higher in the abdomen
In cases of extended breech, the breech may not be ballotable and the fetal heart may be heard in the same location as expected for a cephalic presentation.
If breech presentation is suspected, an ultrasound examination will confirm diagnosis.
Cord prolapse is an obstetric emergency. Urgent delivery is indicated after confirming gestation and fetal viability.
Diagnosis: preterm ≤36+6 weeks
- Breech presentation is a normal finding in preterm pregnancy.
- If diagnosed at the 35-36 week antenatal visit, refer the woman for ultrasound scan to enable assessment prior to ECV.
- Mode of birth in a breech preterm delivery depends on the clinical circumstances.
Diagnosis: ≥37+0 weeks
- determine type of breech presentation
- determine extension/flexion of fetal head
- locate position of placenta and exclude placenta praevia
- exclude fetal congenital abnormality
- calculate amniotic fluid index
- estimate fetal weight.
Practice points
- Offer ECV if there are no contraindications.
- If ECV is declined or unsuccessful, provide counselling on risks and benefits of a planned vaginal birth versus an ELCS.
- Inform the woman that there are fewer maternal complications with a successful vaginal birth, however the risk to the woman increases significantly if there is a need for an EMCS.
- Inform the woman that caesarean section increases the risk of complication in future pregnancies, including the risk of a repeat caesarean section and the risk of invasive placentation.
- If the woman chooses an ELCS, document consent and organise booking for 39 weeks gestation.
Information and decision making
Women with a breech presentation should have the opportunity to make informed decisions about their care and treatment, in partnership with the clinicians providing care.
Planning for birth requires careful assessment for risk of poor outcomes relating to planned vaginal breech birth. If any risk factors are identified, inform the woman that an ELCS is recommended due to increased perinatal risk.
Good communication between clinicians and women is essential. Treatment, care and information provided should:
- take into account women's individual needs and preferences
- be supported by evidence-based, written information tailored to the needs of the individual woman
- be culturally appropriate
- be accessible to women, their partners, support people and families
- take into account any specific needs, such as physical or cognitive disabilities or limitations to their ability to understand spoken or written English.
Documentation
The following should be documented in the woman's hospital medical record and (where applicable) in her hand-held medical record:
- discussion of risks and benefits of vaginal breech birth and ELCS
- discussion of the woman's questions about planned vaginal breech birth and ELCS
- discussion of ECV, if applicable
- consultation, referral and escalation
External cephalic version (ECV)
- ECV can be offered from 37 weeks gestation
- The woman must provide written consent prior to the procedure
- The success rate of ECV is 40-60 per cent
- Approximately one in 200 ECV attempts will lead to EMCS
- ECV should only be performed by a suitably trained, experienced clinician
- continuous electronic fetal monitoring (EFM)
- capability to perform an EMCS.
Contraindications
Table 1. Contraindications to ECV
Precautions
- Hypertension
- Oligohydramnios
- Nuchal cord
Escalate care to a consultant obstetrician if considering ECV in these circumstances.
- Perform a CTG prior to the procedure - continue until RANZCOG criteria for a normal antenatal CTG are met.
- 250 microg s/c, 30 minutes prior to the procedure.
- Administer Anti-D immunoglobulin if the woman is rhesus negative.
- Do not make more than four attempts at ECV, for a suggested maximum time of ten minutes in total.
- Undertake CTG monitoring post-procedure until RANZCOG criteria for a normal antenatal CTG are met.
Emergency management
Urgent delivery is indicated in the event of the following complications:
- abnormal CTG
- vaginal bleeding
- unexplained pain.
Initiate emergency response as per local guidelines.
Alternatives to ECV
There is a lack of evidence to support the use of moxibustion, acupuncture or postural techniques to achieve a vertex presentation after 35 weeks gestation.
Criteria for a planned vaginal breech birth
- Documented evidence of counselling regarding mode of birth
- Documentation of informed consent, including written consent from the woman
- Estimated fetal weight of 2500-4000g
- Flexed fetal head
- Emergency theatre facilities available on site
- Availability of suitably skilled healthcare professional
- Frank or complete breech presentation
- No previous caesarean section.
- Cord presentation
- Fetal growth restriction or macrosomia
- Any presentation other than a frank or complete breech
- Extension of the fetal head
- Fetal anomaly incompatible with vaginal delivery
- Clinically inadequate maternal pelvis
- Previous caesarean section
- Inability of the service to provide experienced personnel.
If an ELCS is booked
- Confirm presentation by ultrasound scan when a woman presents for ELCS.
- If fetal presentation is cephalic on admission for ELCS, plan ongoing management with the woman.
Intrapartum management
Fetal monitoring.
- Advise the woman that continuous EFM may lead to improved neonatal outcomes.
- Where continuous EFM is declined, perform intermittent EFM or intermittent auscultation, with conversion to EFM if an abnormality is detected.
- A fetal scalp electrode can be applied to the breech.
Position of the woman
- The optimal maternal position for birth is upright.
- Lithotomy may be appropriate, depending on the accoucheur's training and experience.
Pain relief
- Epidural analgesia may increase the risk of intervention with a vaginal breech birth.
- Epidural analgesia may impact on the woman's ability to push spontaneously in the second stage of labour.
Induction of labour (IOL)
See the IOL eHandbook page for more detail.
- IOL may be offered if clinical circumstances are favourable and the woman wishes to have a vaginal birth.
- Augmentation (in the absence of an epidural) should be avoided as adequate progress in the absence of augmentation may be the best indicator of feto-pelvic proportions.
The capacity to offer IOL will depend on clinician experience and availability and service capability.
First stage
- Manage with the same principles as a cephalic presentation.
- Labour should be expected to progress as for a cephalic presentation.
- If progress in the first stage is slow, consider a caesarean section.
- If an epidural is in situ and contractions are less than 4:10, consult with a senior obstetrician.
- Avoid routine amniotomy to avoid the risk of cord prolapse or cord compression.
Second stage
- Allow passive descent of the breech to the perineum prior to active pushing.
- If breech is not visible within one hour of passive descent, a caesarean section is normally recommended.
- Active second stage should be ½ hour for a multigravida and one hour for a primipara.
- All midwives and obstetricians should be familiar with the techniques and manoeuvres required to assist a vaginal breech birth.
- Ensure a consultant obstetrician is present for birth.
- Ensure a senior paediatric clinician is present for birth.
VIDEO: Maternity Training International - Vaginal Breech Birth
- Encouragement of maternal pushing (if at all) should not begin until the presenting part is visible.
- A hands-off approach is recommended.
- Significant cord compression is common once buttocks have passed the perineum.
- Timely intervention is recommended if there is slow progress once the umbilicus has delivered.
- Allow spontaneous birth of the trunk and limbs by maternal effort as breech extraction can cause extension of the arms and head.
- Grasp the fetus around the bony pelvic girdle, not soft tissue, to avoid trauma.
- Assist birth if there is a delay of more than five minutes from delivery of the buttocks to the head, or of more than three minutes from the umbilicus to the head.
- Signs that delivery should be expedited also include lack of tone or colour or sign of poor fetal condition.
- Ensure fetal back remains in the anterior position.
- Routine episiotomy not recommended.
- Lovset's manoeuvre for extended arms.
- Reverse Lovset's manoeuvre may be used to reduce nuchal arms.
- Supra-pubic pressure may aide flexion of the fetal head.
- Maricueau-Smellie-Veit manoeuvre or forceps may be used to deliver the after coming head.
Undiagnosed breech in labour
- This occurs in approximately 25 per cent of breech presentations.
- Management depends on the stage of labour when presenting.
- Assessment is required around increased complications, informed consent and suitability of skilled expertise.
- Do not routinely offer caesarean section to women in active second stage.
- If there is no senior obstetrician skilled in breech delivery, an EMCS is the preferred option.
- If time permits, a detailed ultrasound scan to estimate position of fetal neck and legs and estimated fetal weight should be made and the woman counselled.
Entrapment of the fetal head
This is an extreme emergency
This complication is often due to poor selection for vaginal breech birth.
- A vaginal examination (VE) should be performed to ensure that the cervix is fully dilated.
- If a lip of cervix is still evident try to push the cervix over the fetal head.
- If the fetal head has entered the pelvis, perform the Mauriceau-Smellie-Veit manoeuvre combined with suprapubic pressure from a second attendant in a direction that maintains flexion and descent of the fetal head.
- Rotate fetal body to a lateral position and apply suprapubic pressure to flex the fetal head; if unsuccessful consider alternative manoeuvres.
- Reassess cervical dilatation; if not fully dilated consider Duhrssen incision at 2, 10 and 6 o'clock.
- A caesarean section may be performed if the baby is still alive.
Neonatal management
- Paediatric review.
- Routine observations as per your local guidelines, recorded on a track and trigger chart.
- Observe for signs of jaundice.
- Observe for signs of tissue or nerve damage.
- Hip ultrasound scan to be performed at 6-12 weeks post birth to monitor for developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH). See Neonatal eHandbook - Developmental dysplasia of the hip .
More information
Audit and performance improvement.
All maternity services should have processes in place for:
- auditing clinical practice and outcomes
- providing feedback to clinicians on audit results
- addressing risks, if identified
- implementing change, if indicated.
Potential auditable standards are:
- number of women with a breech presentation offered ECV
- success rate of ECV
- ECV complications
- rate of planned vaginal breech birth
- breech birth outcomes for vaginal and caesarean birth.
For more information or assistance with auditing, please contact us via [email protected]
- Bue and Lauszus 2016, Moxibustion did not have an effect in a randomised clinical trial for version of breech position. Danish Medical Journal 63(2), A599
- Coulon et.al. 2014, Version of breech fetuses by moxibustion with acupuncture. Obstetrics and Gynecology 124(1), 32-39. DOI: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000000303
- Coyle ME, Smith CA, Peat B 2012, Cephalic version by moxibustion for breech presentation. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2012, Issue 5. Art. No.: CD003928. DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD003928.pub3
- Evans J 2012, Essentially MIDIRS Understanding Physiological Breech Birth Volume 3. Number 2. February 2012
- Hoffmann J, Thomassen K, Stumpp P, Grothoff M, Engel C, Kahn T, et al. 2016, New MRI Criteria for Successful Vaginal Breech Delivery in Primiparae. PLoS ONE 11(8): e0161028. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0161028
- Hofmeyr GJ, Kulier R 2012, Cephalic version by postural management for breech presentation. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2012, Issue 10. Art. No.: CD000051. DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD000051.pub2
- New South Wales Department of Health 2013, Maternity: Management of Breech Presentation HNELHD CG 13_01, NSW Government; 2013
- Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists 2017, External Cephalic Version and Reducing the Incidence of Term Breech Presentation. Green-top Guideline No. 20a . London: RCOG; 2017
- The Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists (RANZCOG) 2016, Management of breech presentation at term , July 2016 C-Obs-11:
- The Royal Women's Hospital 2015, Management of Breech - Clinical Guideline
- Women's and Newborn Health Service, King Edward Memorial Hospital 2015, Complications of Pregnancy Breech Presentation
Abbreviations
Get in touch, version history.
First published: November 2018 Due for review: November 2021
Uncontrolled when downloaded
Related links.

An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock Locked padlock icon ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.

- Health Topics
- Drugs & Supplements
- Medical Tests
- Medical Encyclopedia
- About MedlinePlus
- Customer Support
Breech - series—Types of breech presentation
- Go to slide 1 out of 7
- Go to slide 2 out of 7
- Go to slide 3 out of 7
- Go to slide 4 out of 7
- Go to slide 5 out of 7
- Go to slide 6 out of 7
- Go to slide 7 out of 7
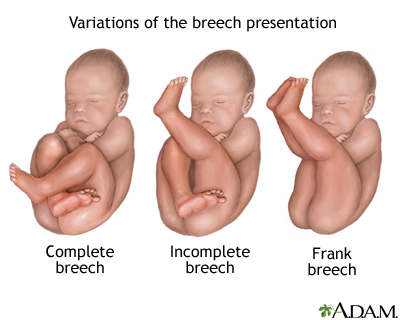
There are three types of breech presentation: complete, incomplete, and frank.
Complete breech is when both of the baby's knees are bent and his feet and bottom are closest to the birth canal.
Incomplete breech is when one of the baby's knees is bent and his foot and bottom are closest to the birth canal.
Frank breech is when the baby's legs are folded flat up against his head and his bottom is closest to the birth canal.
There is also footling breech where one or both feet are presenting.
Review Date 11/21/2022
Updated by: LaQuita Martinez, MD, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Emory Johns Creek Hospital, Alpharetta, GA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Related MedlinePlus Health Topics
- Childbirth Problems
- More from M-W
- To save this word, you'll need to log in. Log In
breech presentation
Definition of breech presentation
Examples of breech presentation in a sentence.
These examples are programmatically compiled from various online sources to illustrate current usage of the word 'breech presentation.' Any opinions expressed in the examples do not represent those of Merriam-Webster or its editors. Send us feedback about these examples.
Word History
1801, in the meaning defined above
Dictionary Entries Near breech presentation
breech plug
Cite this Entry
“Breech presentation.” Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary , Merriam-Webster, https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/breech%20presentation. Accessed 20 May. 2024.
Medical Definition
Medical definition of breech presentation, more from merriam-webster on breech presentation.
Britannica.com: Encyclopedia article about breech presentation
Subscribe to America's largest dictionary and get thousands more definitions and advanced search—ad free!

Can you solve 4 words at once?
Word of the day.
See Definitions and Examples »
Get Word of the Day daily email!
Popular in Grammar & Usage
More commonly misspelled words, your vs. you're: how to use them correctly, every letter is silent, sometimes: a-z list of examples, more commonly mispronounced words, how to use em dashes (—), en dashes (–) , and hyphens (-), popular in wordplay, the words of the week - may 17, birds say the darndest things, a great big list of bread words, 10 scrabble words without any vowels, 12 more bird names that sound like insults (and sometimes are), games & quizzes.


AI + Machine Learning , Announcements , Azure AI Content Safety , Azure AI Studio , Azure OpenAI Service , Partners
Introducing GPT-4o: OpenAI’s new flagship multimodal model now in preview on Azure
By Eric Boyd Corporate Vice President, Azure AI Platform, Microsoft
Posted on May 13, 2024 2 min read
- Tag: Copilot
- Tag: Generative AI
Microsoft is thrilled to announce the launch of GPT-4o, OpenAI’s new flagship model on Azure AI. This groundbreaking multimodal model integrates text, vision, and audio capabilities, setting a new standard for generative and conversational AI experiences. GPT-4o is available now in Azure OpenAI Service, to try in preview , with support for text and image.
Azure OpenAI Service

A step forward in generative AI for Azure OpenAI Service
GPT-4o offers a shift in how AI models interact with multimodal inputs. By seamlessly combining text, images, and audio, GPT-4o provides a richer, more engaging user experience.
Launch highlights: Immediate access and what you can expect
Azure OpenAI Service customers can explore GPT-4o’s extensive capabilities through a preview playground in Azure OpenAI Studio starting today in two regions in the US. This initial release focuses on text and vision inputs to provide a glimpse into the model’s potential, paving the way for further capabilities like audio and video.
Efficiency and cost-effectiveness
GPT-4o is engineered for speed and efficiency. Its advanced ability to handle complex queries with minimal resources can translate into cost savings and performance.
Potential use cases to explore with GPT-4o
The introduction of GPT-4o opens numerous possibilities for businesses in various sectors:
- Enhanced customer service : By integrating diverse data inputs, GPT-4o enables more dynamic and comprehensive customer support interactions.
- Advanced analytics : Leverage GPT-4o’s capability to process and analyze different types of data to enhance decision-making and uncover deeper insights.
- Content innovation : Use GPT-4o’s generative capabilities to create engaging and diverse content formats, catering to a broad range of consumer preferences.
Exciting future developments: GPT-4o at Microsoft Build 2024
We are eager to share more about GPT-4o and other Azure AI updates at Microsoft Build 2024 , to help developers further unlock the power of generative AI.
Get started with Azure OpenAI Service
Begin your journey with GPT-4o and Azure OpenAI Service by taking the following steps:
- Try out GPT-4o in Azure OpenAI Service Chat Playground (in preview).
- If you are not a current Azure OpenAI Service customer, apply for access by completing this form .
- Learn more about Azure OpenAI Service and the latest enhancements.
- Understand responsible AI tooling available in Azure with Azure AI Content Safety .
- Review the OpenAI blog on GPT-4o.
Let us know what you think of Azure and what you would like to see in the future.
Provide feedback
Build your cloud computing and Azure skills with free courses by Microsoft Learn.
Explore Azure learning
Related posts
AI + Machine Learning , Azure AI Studio , Customer stories
3 ways Microsoft Azure AI Studio helps accelerate the AI development journey chevron_right
AI + Machine Learning , Analyst Reports , Azure AI , Azure AI Content Safety , Azure AI Search , Azure AI Services , Azure AI Studio , Azure OpenAI Service , Partners
Microsoft is a Leader in the 2024 Gartner® Magic Quadrant™ for Cloud AI Developer Services chevron_right
AI + Machine Learning , Azure AI , Azure AI Content Safety , Azure Cognitive Search , Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) , Azure OpenAI Service , Customer stories
AI-powered dialogues: Global telecommunications with Azure OpenAI Service chevron_right
AI + Machine Learning , Azure AI , Azure AI Content Safety , Azure OpenAI Service , Customer stories
Generative AI and the path to personalized medicine with Microsoft Azure chevron_right
Join the conversation, leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
I understand by submitting this form Microsoft is collecting my name, email and comment as a means to track comments on this website. This information will also be processed by an outside service for Spam protection. For more information, please review our Privacy Policy and Terms of Use .
I agree to the above

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Breech presentation refers to the fetus in the longitudinal lie with the buttocks or lower extremity entering the pelvis first. The three types of breech presentation include frank breech, complete breech, and incomplete breech. In a frank breech, the fetus has flexion of both hips, and the legs are straight with the feet near the fetal face, in a pike position. The complete breech has the ...
Breech Births. In the last weeks of pregnancy, a baby usually moves so his or her head is positioned to come out of the vagina first during birth. This is called a vertex presentation. A breech presentation occurs when the baby's buttocks, feet, or both are positioned to come out first during birth. This happens in 3-4% of full-term births.
A breech baby (breech birth or breech presentation) is when a baby's feet or buttocks are positioned to come out of your vagina first. This means its head is up toward your chest and its lower body is closest to your vagina. Ideally, your baby is in a head down, or vertex presentation, at delivery. While most babies do eventually turn into this ...
The main types of breech presentation are: Frank breech - Both hips are flexed and both knees are extended so that the feet are adjacent to the head ( figure 1 ); accounts for 50 to 70 percent of breech fetuses at term. Complete breech - Both hips and both knees are flexed ( figure 2 ); accounts for 5 to 10 percent of breech fetuses at term.
In breech presentation, the presenting part is a poor dilating wedge, which can cause the head to be trapped during delivery, often compressing the umbilical cord. For breech presentation, usually do cesarean delivery at 39 weeks or during labor, but external cephalic version is sometimes successful before labor, usually at 37 or 38 weeks.
Overview. Breech presentation is defined as a fetus in a longitudinal lie with the buttocks or feet closest to the cervix. This occurs in 3-4% of all deliveries. The percentage of breech deliveries decreases with advancing gestational age from 22-25% of births prior to 28 weeks' gestation to 7-15% of births at 32 weeks' gestation to 3-4% of ...
Definition. Breech presentation in pregnancy occurs when a baby presents with the buttocks or feet rather than the head first (cephalic presentation) and is associated with increased morbidity and mortality for both the mother and the baby. Cunningham F, Gant N, Leveno K, et al. Williams obstetrics. 21st ed.
Breech presentation: clinical practice guideline from the French College of Gynaecologists and Obstetricians [2020] ... The lack of a standard definition of a footling breech is problematic because the term is open to interpretation and will invariably lead to a higher rate of C/S for breech in this setting, further limiting birth mode options ...
Labour with a preterm breech should be managed as with a term breech. C. Where there is head entrapment, incisions in the cervix (vaginal birth) or vertical uterine D incision extension (caesarean section) may be used, with or without tocolysis. Evidence concerning the management of preterm labour with a breech presentation is lacking.
At full term, around 3%-4% of births are breech. The different types of breech presentations include: Complete: The fetus's knees are bent, and the buttocks are presenting first. Frank: The fetus's legs are stretched upward toward the head, and the buttocks are presenting first. Footling: The fetus's foot is showing first.
Breech presentation is a type of malpresentation and occurs when the fetal head lies over the uterine fundus and fetal buttocks or feet present over the maternal pelvis (instead of cephalic/head presentation). The incidence in the United Kingdom of breech presentation is 3-4% of all fetuses. 1.
Definition. Breech presentation in pregnancy occurs when a baby presents with the buttocks or feet rather than the head first (cephalic presentation) and is associated with increased morbidity and mortality for both the mother and the baby. ... Breech presentation is a normal finding in preterm pregnancies, when the fetus is more mobile, and ...
In face presentation, the baby's neck arches back so that the face presents first rather than the top of the head.. In brow presentation, the neck is moderately arched so that the brow presents first.. Usually, fetuses do not stay in a face or brow presentation. These presentations often change to a vertex (top of the head) presentation before or during labor.
Women with a breech presentation at term should be offered external cephalic version (ECV) unless there is an absolute contraindication. ... The strict criteria included 'normal' (definition unstated) radiological pelvimetry which was performed in 82.5% of planned vaginal births, continuous EFM and routine ultrasound.
Breech presentation occurs in 3-4% of term deliveries and is more common in preterm deliveries and nulliparous women. Breech presentation is associated with uterine and congenital abnormalities, and has a significant recurrence risk. Term babies presenting by the breech have worse outcomes than cephalic presenting babies, irrespective of the ...
Definition + + Breech presentation is a longitudinal lie with a variation in polarity. The fetal pelvis is the leading pole. The denominator is the sacrum. ... Factors that influence the occurrence of breech presentation include (1) the uterine relaxation associated with high parity; (2) polyhydramnios, in which the excessive amount of amniotic ...
What Causes Breech Presentation? - Only about 15% of breech presentations have an identifiable etiology.5 - Established risks for breech presentation are: Previous breech presentation pregnancy,5,6,7,8 Late or lack of antenatal care,8,9 Prematurity (<37 weeks gestation),6,7,8 Comparatively lower birth weight,8,9 and Congenital anomalies.8,9,10
Breech and external cephalic version. Breech presentation is when the fetus is lying longitudinally and its buttocks, foot or feet are presenting instead of its head. Figure 1. Breech presentations. Breech presentation occurs in three to four per cent of term deliveries and is more common in nulliparous women.
1. Background. The management of breech presentation continues to cause academic and clinical contention globally [[1], [2], [3]].In recent years, research has shown that if certain criteria are met, and appropriately experienced and skilled clinicians are available, Vaginal Breech Birth (VBB) is a safe option [[4], [5], [6]].However, with Caesarean Section (C/S) rates for breech presentation ...
Overview. There are three types of breech presentation: complete, incomplete, and frank. Complete breech is when both of the baby's knees are bent and his feet and bottom are closest to the birth canal. Incomplete breech is when one of the baby's knees is bent and his foot and bottom are closest to the birth canal.
Complete breech presentation is the next most favorable position, but these babies sometimes shift and become footling breeches during labour. Footling and kneeling breeches have a higher risk of cord prolapse and head entrapment. Parity - Parity refers to the number of times a woman has given birth before. If a woman has given birth ...
The meaning of BREECH PRESENTATION is presentation of the fetus in which the breech is the first part to appear at the uterine cervix. ... Share the Definition of breech presentation on Twitter Twitter. Medical Definition. breech presentation. noun: ...
OpenAI, in partnership with Microsoft, announces GPT-4o, a groundbreaking multimodal model for text, vision, and audio capabilities. Learn more.