Java Tutorial
Java methods, java classes, java file handling, java how to, java reference, java examples, java operators.
Operators are used to perform operations on variables and values.
In the example below, we use the + operator to add together two values:
Try it Yourself »
Although the + operator is often used to add together two values, like in the example above, it can also be used to add together a variable and a value, or a variable and another variable:
Java divides the operators into the following groups:
- Arithmetic operators
- Assignment operators
- Comparison operators
- Logical operators
- Bitwise operators

Arithmetic Operators
Arithmetic operators are used to perform common mathematical operations.
Advertisement
Java Assignment Operators
Assignment operators are used to assign values to variables.
In the example below, we use the assignment operator ( = ) to assign the value 10 to a variable called x :
The addition assignment operator ( += ) adds a value to a variable:
A list of all assignment operators:
Java Comparison Operators
Comparison operators are used to compare two values (or variables). This is important in programming, because it helps us to find answers and make decisions.
The return value of a comparison is either true or false . These values are known as Boolean values , and you will learn more about them in the Booleans and If..Else chapter.
In the following example, we use the greater than operator ( > ) to find out if 5 is greater than 3:
Java Logical Operators
You can also test for true or false values with logical operators.
Logical operators are used to determine the logic between variables or values:
Java Bitwise Operators
Bitwise operators are used to perform binary logic with the bits of an integer or long integer.
Note: The Bitwise examples above use 4-bit unsigned examples, but Java uses 32-bit signed integers and 64-bit signed long integers. Because of this, in Java, ~5 will not return 10. It will return -6. ~00000000000000000000000000000101 will return 11111111111111111111111111111010
In Java, 9 >> 1 will not return 12. It will return 4. 00000000000000000000000000001001 >> 1 will return 00000000000000000000000000000100
Test Yourself With Exercises
Multiply 10 with 5 , and print the result.
Start the Exercise

COLOR PICKER

Contact Sales
If you want to use W3Schools services as an educational institution, team or enterprise, send us an e-mail: [email protected]
Report Error
If you want to report an error, or if you want to make a suggestion, send us an e-mail: [email protected]
Top Tutorials
Top references, top examples, get certified.

Java Tutorial
Control statements, java object class, java inheritance, java polymorphism, java abstraction, java encapsulation, java oops misc.
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share

Learn Latest Tutorials
Transact-SQL
Reinforcement Learning
R Programming
React Native
Python Design Patterns
Python Pillow
Python Turtle
Preparation

Verbal Ability

Interview Questions

Company Questions
Trending Technologies
Artificial Intelligence
Cloud Computing
Data Science
Machine Learning
B.Tech / MCA
Data Structures
Operating System
Computer Network
Compiler Design
Computer Organization
Discrete Mathematics
Ethical Hacking
Computer Graphics
Software Engineering
Web Technology
Cyber Security
C Programming
Control System
Data Mining
Data Warehouse

- Enterprise Java
- Web-based Java
- Data & Java
- Project Management
- Visual Basic
- Ruby / Rails
- Java Mobile
- Architecture & Design
- Open Source
- Web Services

Developer.com content and product recommendations are editorially independent. We may make money when you click on links to our partners. Learn More .

Java provides many types of operators to perform a variety of calculations and functions, such as logical , arithmetic , relational , and others. With so many operators to choose from, it helps to group them based on the type of functionality they provide. This programming tutorial will focus on Java’s numerous a ssignment operators.
Before we begin, however, you may want to bookmark our other tutorials on Java operators, which include:
- Arithmetic Operators
- Comparison Operators
- Conditional Operators
- Logical Operators
- Bitwise and Shift Operators
Assignment Operators in Java
As the name conveys, assignment operators are used to assign values to a variable using the following syntax:
The left side operand of the assignment operator must be a variable, whereas the right side operand of the assignment operator may be a literal value or another variable. Moreover, the value or variable on the right side must be of the same data type of the operand on the left side. Otherwise, the compiler will raise an error. Assignment operators have a right to left associativity in that the value given on the right-hand side of the operator is assigned to the variable on the left. Therefore, the right-hand side variable must be declared before assignment.
You can learn more about variables in our programming tutorial: Working with Java Variables .
Types of Assignment Operators in Java
Java assignment operators are classified into two types: simple and compound .
The Simple assignment operator is the equals ( = ) sign, which is the most straightforward of the bunch. It simply assigns the value or variable on the right to the variable on the left.
Compound operators are comprised of both an arithmetic, bitwise, or shift operator in addition to the equals ( = ) sign.
Equals Operator (=) Java Example
First, let’s learn to use the one-and-only simple assignment operator – the Equals ( = ) operator – with the help of a Java program. It includes two assignments: a literal value to num1 and the num1 variable to num2 , after which both are printed to the console to show that the values have been assigned to the numbers:
The += Operator Java Example
A compound of the + and = operators, the += adds the current value of the variable on the left to the value on the right before assigning the result to the operand on the left. Here is some sample code to demonstrate how to use the += operator in Java:
The -= Operator Java Example
Made up of the – and = operators, the -= first subtracts the variable’s value on the right from the current value of the variable on the left before assigning the result to the operand on the left. We can see it at work below in the following code example showing how to decrement in Java using the -= operator:
The *= Operator Java Example
This Java operator is comprised of the * and = operators. It operates by multiplying the current value of the variable on the left to the value on the right and then assigning the result to the operand on the left. Here’s a program that shows the *= operator in action:
The /= Operator Java Example
A combination of the / and = operators, the /= Operator divides the current value of the variable on the left by the value on the right and then assigns the quotient to the operand on the left. Here is some example code showing how to use the /= operator in Java:
%= Operator Java Example
The %= operator includes both the % and = operators. As seen in the program below, it divides the current value of the variable on the left by the value on the right and then assigns the remainder to the operand on the left:
Compound Bitwise and Shift Operators in Java
The Bitwise and Shift Operators that we just recently covered can also be utilized in compound form as seen in the list below:
- &= – Compound bitwise Assignment operator.
- ^= – Compound bitwise ^ assignment operator.
- >>= – Compound right shift assignment operator.
- >>>= – Compound right shift filled 0 assignment operator.
- <<= – Compound left shift assignment operator.
The following program demonstrates the working of all the Compound Bitwise and Shift Operators :
Final Thoughts on Java Assignment Operators
This programming tutorial presented an overview of Java’s simple and compound assignment Operators. An essential building block to any programming language, developers would be unable to store any data in their programs without them. Though not quite as indispensable as the equals operator, compound operators are great time savers, allowing you to perform arithmetic and bitwise operations and assignment in a single line of code.
Read more Java programming tutorials and guides to software development .
Get the Free Newsletter!
Subscribe to Developer Insider for top news, trends & analysis
Latest Posts
What is the role of a project manager in software development, how to use optional in java, overview of the jad methodology, microsoft project tips and tricks, how to become a project manager in 2023, related stories, understanding types of thread synchronization errors in java, understanding memory consistency in java threads.

01 Career Opportunities
- Top 50 Java Interview Questions and Answers
- Java Developer Salary Guide in India – For Freshers & Experienced
02 Beginner
- What are Copy Constructors In Java? Explore Types,Examples & Use
- Single Inheritance in Java
- Ternary Operator in Java - (With Example)
- Top 50 Java Full Stack Developer Interview Questions and Answers
- Hierarchical Inheritance in Java
- Arithmetic operators in Java
- Unary operator in Java
- Relational operators in Java
Assignment operator in Java
- Logical operators in Java
- Primitive Data Types in Java
- Parameterized Constructor in Java
- What is a Bitwise Operator in Java? Type, Example and More
- Constructor Overloading in Java
- Best Java Developer Roadmap 2024
- Constructor Chaining in Java
- Multiple Inheritance in Java
- do...while Loop in Java
- for Loop in Java: Its Types and Examples
- Java Full Stack Developer Salary
- while Loop in Java
- Hybrid Inheritance in Java
- Data Structures in Java
- Top 10 Reasons to know why Java is Important?
- What is Java? A Beginners Guide to Java
- Differences between JDK, JRE, and JVM: Java Toolkit
- Variables in Java: Local, Instance and Static Variables
- Data Types in Java - Primitive and Non-Primitive Data Types
- Conditional Statements in Java: If, If-Else and Switch Statement
- What are Operators in Java - Types of Operators in Java ( With Examples )
- Java VS Python
- Looping Statements in Java - For, While, Do-While Loop in Java
- Jump Statements in JAVA - Types of Statements in JAVA (With Examples)
- Java Arrays: Single Dimensional and Multi-Dimensional Arrays
- What is String in Java - Java String Types and Methods (With Examples)
03 Intermediate
- OOPs Concepts in Java: Encapsulation, Abstraction, Inheritance, Polymorphism
- What is Class in Java? - Objects and Classes in Java {Explained}
- Access Modifiers in Java: Default, Private, Public, Protected
- Constructors in Java: Types of Constructors with Examples
- Polymorphism in Java: Compile time and Runtime Polymorphism
- Abstract Class in Java: Concepts, Examples, and Usage
- What is Inheritance in Java: Types of Inheritance in Java
- What is Exception Handling in Java? Types, Handling, and Common Scenarios
04 Questions
- Top 50 Java MCQ Questions
- Top 50 Java 8 Interview Questions and Answers
- Java Multithreading Interview Questions and Answers 2024
05 Training Programs
- Java Programming Course
- C++ Programming Course
- MERN: Full-Stack Web Developer Certification Training
- Data Structures and Algorithms Training
- Assignment Operator In Ja..

Java Programming For Beginners Free Course
Assignment operators in java: an overview.
We already discussed the Types of Operators in the previous tutorial Java. In this Java tutorial , we will delve into the different types of assignment operators in Java, and their syntax, and provide examples for better understanding. Because Java is a flexible and widely used programming language. Assignment operators play a crucial role in manipulating and assigning values to variables. To further enhance your understanding and application of Java assignment operator's concepts, consider enrolling in the best Java Certification Course .
What are the Assignment Operators in Java?
Assignment operators in Java are used to assign values to variables . They are classified into two main types: simple assignment operator and compound assignment operator.
The general syntax for a simple assignment statement is:
And for a compound assignment statement:
Read More - Advanced Java Interview Questions
Read More - Mostly Asked Java Multithreading Interview Questions
Types of Assignment Operators in Java
- Simple Assignment Operator: The Simple Assignment Operator is used with the "=" sign, where the operand is on the left side and the value is on the right. The right-side value must be of the same data type as that defined on the left side.
- Compound Assignment Operator: Compound assignment operators combine arithmetic operations with assignments. They provide a concise way to perform an operation and assign the result to the variable in one step. The Compound Operator is utilized when +,-,*, and / are used in conjunction with the = operator.
1. Simple Assignment Operator (=):
The equal sign (=) is the basic assignment operator in Java. It is used to assign the value on the right-hand side to the variable on the left-hand side.
Explanation
2. addition assignment operator (+=) :, 3. subtraction operator (-=):, 4. multiplication operator (*=):.
Read More - Java Developer Salary
5. Division Operator (/=):
6. modulus assignment operator (%=):, example of assignment operator in java.
Let's look at a few examples in our Java Playground to illustrate the usage of assignment operators in Java:
- Unary Operator in Java
- Arithmetic Operators in Java
- Relational Operators in Java
- Logical Operators in Java
- Ternary Operator in Java
Q1. Can I use multiple assignment operators in a single statement?
Q2. are there any other compound assignment operators in java, q3. how many types of assignment operators.
- 1. (=) operator
- 1. (+=) operator
- 2. (-=) operator
- 3. (*=) operator
- 4. (/=) operator
- 5. (%=) operator
About Author

We use cookies to make interactions with our websites and services easy and meaningful. Please read our Privacy Policy for more details.
Java Assignment Operators
Java programming tutorial index.
The Java Assignment Operators are used when you want to assign a value to the expression. The assignment operator denoted by the single equal sign = .
In a Java assignment statement, any expression can be on the right side and the left side must be a variable name. For example, this does not mean that "a" is equal to "b", instead, it means assigning the value of 'b' to 'a'. It is as follows:
Java also has the facility of chain assignment operators, where we can specify a single value for multiple variables.

- Basics of Java
- ➤ Java Introduction
- ➤ History of Java
- ➤ Getting started with Java
- ➤ What is Path and Classpath
- ➤ Checking Java installation and Version
- ➤ Syntax in Java
- ➤ My First Java Program
- ➤ Basic terms in Java Program
- ➤ Runtime and Compile time
- ➤ What is Bytecode
- ➤ Features of Java
- ➤ What is JDK JRE and JVM
- ➤ Basic Program Examples
- Variables and Data Types
- ➤ What is Variable
- ➤ Types of Java Variables
- ➤ Naming conventions for Identifiers
- ➤ Data Type in Java
- ➤ Mathematical operators in Java
- ➤ Assignment operator in Java
- ➤ Arithmetic operators in Java
- ➤ Unary operators in Java
- ➤ Conditional and Relational Operators
- ➤ Bitwise and Bit Shift Operators
- ➤ Operator Precedence
- ➤ Overflow Underflow Widening Narrowing
- ➤ Variable and Data Type Programs
- Control flow Statements
- ➤ Java if and if else Statement
- ➤ else if and nested if else Statement
- ➤ Java for Loop
- ➤ Java while and do-while Loop
- ➤ Nested loops
- ➤ Java break Statement
- ➤ Java continue and return Statement
- ➤ Java switch Statement
- ➤ Control Flow Program Examples
- Array and String in Java
- ➤ Array in Java
- ➤ Multi-Dimensional Arrays
- ➤ for-each loop in java
- ➤ Java String
- ➤ Useful Methods of String Class
- ➤ StringBuffer and StringBuilder
- ➤ Array and String Program Examples
- Classes and Objects
- ➤ Classes in Java
- ➤ Objects in Java
- ➤ Methods in Java
- ➤ Constructors in Java
- ➤ static keyword in Java
- ➤ Call By Value
- ➤ Inner/nested classes in Java
- ➤ Wrapper Classes
- ➤ Enum in Java
- ➤ Initializer blocks
- ➤ Method Chaining and Recursion
- Packages and Interfaces
- ➤ What is package
- ➤ Sub packages in java
- ➤ built-in packages in java
- ➤ Import packages
- ➤ Access modifiers
- ➤ Interfaces in Java
- ➤ Key points about Interfaces
- ➤ New features in Interfaces
- ➤ Nested Interfaces
- ➤ Structure of Java Program
- OOPS Concepts
- ➤ What is OOPS
- ➤ Inheritance in Java
- ➤ Inheritance types in Java
- ➤ Abstraction in Java
- ➤ Encapsulation in Java
- ➤ Polymorphism in Java
- ➤ Runtime and Compile-time Polymorphism
- ➤ Method Overloading
- ➤ Method Overriding
- ➤ Overloading and Overriding Differences
- ➤ Overriding using Covariant Return Type
- ➤ this keyword in Java
- ➤ super keyword in Java
- ➤ final keyword in Java
Assignment Operator in Java with Example
Assignment operator is one of the simplest and most used operator in java programming language. As the name itself suggests, the assignment operator is used to assign value inside a variable. In java we can divide assignment operator in two types :
- Assignment operator or simple assignment operator
- Compound assignment operators
What is assignment operator in java
The = operator in java is known as assignment or simple assignment operator. It assigns the value on its right side to the operand(variable) on its left side. For example :
The left-hand side of an assignment operator must be a variable while the right side of it should be a value which can be in the form of a constant value, a variable name, an expression, a method call returning a compatible value or a combination of these.
The value at right side of assignment operator must be compatible with the data type of left side variable, otherwise compiler will throw compilation error. Following are incorrect assignment :
Another important thing about assignment operator is that, it is evaluated from right to left . If there is an expression at right side of assignment operator, it is evaluated first then the resulted value is assigned in left side variable.
Here in statement int x = a + b + c; the expression a + b + c is evaluated first, then the resulted value( 60 ) is assigned into x . Similarly in statement a = b = c , first the value of c which is 30 is assigned into b and then the value of b which is now 30 is assigned into a .
The variable at left side of an assignment operator can also be a non-primitive variable. For example if we have a class MyFirstProgram , we can assign object of MyFirstProgram class using = operator in MyFirstProgram type variable.
Is == an assignment operator ?
No , it's not an assignment operator, it's a relational operator used to compare two values.
Is assignment operator a binary operator
Yes , as it requires two operands.
Assignment operator program in Java
a = 2 b = 2 c = 4 d = 4 e = false
Java compound assignment operators
The assignment operator can be mixed or compound with other operators like addition, subtraction, multiplication etc. We call such assignment operators as compound assignment operator. For example :
Here the statement a += 10; is the short version of a = a + 10; the operator += is basically addition compound assignment operator. Similarly b *= 5; is short version of b = b * 5; the operator *= is multiplication compound assignment operator. The compound assignment can be in more complex form as well, like below :
List of all assignment operators in Java
The table below shows the list of all possible assignment(simple and compound) operators in java. Consider a is an integer variable for this table.
How many assignment operators are there in Java ?
Including simple and compound assignment we have total 12 assignment operators in java as given in above table.
What is shorthand operator in Java ?
Shorthand operators are nothing new they are just a shorter way to write something that is already available in java language. For example the code a += 5 is shorter way to write a = a + 5 , so += is a shorthand operator. In java all the compound assignment operator(given above) and the increment/decrement operators are basically shorthand operators.
Compound assignment operator program in Java
a = 20 b = 80 c = 30 s = 64 s2 = 110 b2 = 15
What is the difference between += and =+ in Java?
An expression a += 1 will result as a = a + 1 while the expression a =+ 1 will result as a = +1 . The correct compound statement is += , not =+ , so do not use the later one.

JavaScript disabled. A lot of the features of the site won't work. Find out how to turn on JavaScript HERE .
- Fundamentals
- Objects & Classes
- OO Concepts
- API Contents
- Input & Output
- Collections
- Concurrency
- Swing & RMI
- Certification
Assignment Operators J8 Home « Assignment Operators
- << Relational & Logical Operators
- Bitwise Logical Operators >>
Symbols used for mathematical and logical manipulation that are recognized by the compiler are commonly known as operators in Java. In the third of five lessons on operators we look at the assignment operators available in Java.
Assignment Operators Overview Top
The single equal sign = is used for assignment in Java and we have been using this throughout the lessons so far. This operator is fairly self explanatory and takes the form variable = expression; . A point to note here is that the type of variable must be compatible with the type of expression .
Shorthand Assignment Operators
The shorthand assignment operators allow us to write compact code that is implemented more efficiently.
Automatic Type Conversion, Assignment Rules Top
The following table shows which types can be assigned to which other types, of course we can assign to the same type so these boxes are greyed out.
When using the table use a row for the left assignment and a column for the right assignment. So in the highlighted permutations byte = int won't convert and int = byte will convert.
Casting Incompatible Types Top
The above table isn't the end of the story though as Java allows us to cast incompatible types. A cast instructs the compiler to convert one type to another enforcing an explicit type conversion.
A cast takes the form target = (target-type) expression .
There are a couple of things to consider when casting incompatible types:
- With narrowing conversions such as an int to a short there may be a loss of precision if the range of the int exceeds the range of a short as the high order bits will be removed.
- When casting a floating-point type to an integer type the fractional component is lost through truncation.
- The target-type can be the same type as the target or a narrowing conversion type.
- The boolean type is not only incompatible but also inconvertible with other types.
Lets look at some code to see how casting works and the affect it has on values:
Running the Casting class produces the following output:
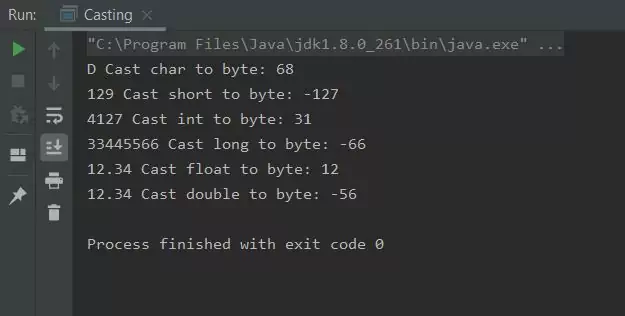
The first thing to note is we got a clean compile because of the casts, all the type conversions would fail otherwise. You might be suprised by some of the results shown in the screenshot above, for instance some of the values have become negative. Because we are truncating everything to a byte we are losing not only any fractional components and bits outside the range of a byte , but in some cases the signed bit as well. Casting can be very useful but just be aware of the implications to values when you enforce explicit type conversion.
Related Quiz
Fundamentals Quiz 8 - Assignment Operators Quiz
Lesson 9 Complete
In this lesson we looked at the assignment operators used in Java.
What's Next?
In the next lesson we look at the bitwise logical operators used in Java.
Getting Started
Code structure & syntax, java variables, primitives - boolean & char data types, primitives - numeric data types, method scope, arithmetic operators, relational & logical operators, assignment operators, assignment operators overview, automatic type conversion, casting incompatible types, bitwise logical operators, bitwise shift operators, if construct, switch construct, for construct, while construct.
Java 8 Tutorials
Learn Java practically and Get Certified .
Popular Tutorials
Popular examples, reference materials, learn java interactively, java introduction.
- Get Started With Java
- Your First Java Program
- Java Comments
Java Fundamentals
- Java Variables and Literals
- Java Data Types (Primitive)
Java Operators
- Java Basic Input and Output
- Java Expressions, Statements and Blocks
Java Flow Control
- Java if...else Statement
Java Ternary Operator
- Java for Loop
- Java for-each Loop
- Java while and do...while Loop
- Java break Statement
- Java continue Statement
- Java switch Statement
- Java Arrays
- Java Multidimensional Arrays
- Java Copy Arrays
Java OOP(I)
- Java Class and Objects
- Java Methods
- Java Method Overloading
- Java Constructors
- Java Static Keyword
- Java Strings
- Java Access Modifiers
- Java this Keyword
- Java final keyword
- Java Recursion
Java instanceof Operator
Java OOP(II)
- Java Inheritance
- Java Method Overriding
- Java Abstract Class and Abstract Methods
- Java Interface
- Java Polymorphism
- Java Encapsulation
Java OOP(III)
- Java Nested and Inner Class
- Java Nested Static Class
- Java Anonymous Class
- Java Singleton Class
- Java enum Constructor
- Java enum Strings
- Java Reflection
- Java Package
- Java Exception Handling
- Java Exceptions
- Java try...catch
- Java throw and throws
- Java catch Multiple Exceptions
- Java try-with-resources
- Java Annotations
- Java Annotation Types
- Java Logging
- Java Assertions
- Java Collections Framework
- Java Collection Interface
- Java ArrayList
- Java Vector
- Java Stack Class
- Java Queue Interface
- Java PriorityQueue
- Java Deque Interface
- Java LinkedList
- Java ArrayDeque
- Java BlockingQueue
- Java ArrayBlockingQueue
- Java LinkedBlockingQueue
- Java Map Interface
- Java HashMap
- Java LinkedHashMap
- Java WeakHashMap
- Java EnumMap
- Java SortedMap Interface
- Java NavigableMap Interface
- Java TreeMap
- Java ConcurrentMap Interface
- Java ConcurrentHashMap
- Java Set Interface
- Java HashSet Class
- Java EnumSet
- Java LinkedHashSet
- Java SortedSet Interface
- Java NavigableSet Interface
- Java TreeSet
- Java Algorithms
- Java Iterator Interface
- Java ListIterator Interface

Java I/o Streams
- Java I/O Streams
- Java InputStream Class
- Java OutputStream Class
- Java FileInputStream Class
- Java FileOutputStream Class
- Java ByteArrayInputStream Class
- Java ByteArrayOutputStream Class
- Java ObjectInputStream Class
- Java ObjectOutputStream Class
- Java BufferedInputStream Class
- Java BufferedOutputStream Class
- Java PrintStream Class
Java Reader/Writer
- Java File Class
- Java Reader Class
- Java Writer Class
- Java InputStreamReader Class
- Java OutputStreamWriter Class
- Java FileReader Class
- Java FileWriter Class
- Java BufferedReader
- Java BufferedWriter Class
- Java StringReader Class
- Java StringWriter Class
- Java PrintWriter Class
Additional Topics
- Java Keywords and Identifiers
Java Operator Precedence
Java Bitwise and Shift Operators
- Java Scanner Class
- Java Type Casting
- Java Wrapper Class
- Java autoboxing and unboxing
- Java Lambda Expressions
- Java Generics
- Nested Loop in Java
- Java Command-Line Arguments
Java Tutorials
- Java Math IEEEremainder()
Operators are symbols that perform operations on variables and values. For example, + is an operator used for addition, while * is also an operator used for multiplication.
Operators in Java can be classified into 5 types:
- Arithmetic Operators
- Assignment Operators
- Relational Operators
- Logical Operators
- Unary Operators
- Bitwise Operators
1. Java Arithmetic Operators
Arithmetic operators are used to perform arithmetic operations on variables and data. For example,
Here, the + operator is used to add two variables a and b . Similarly, there are various other arithmetic operators in Java.
Example 1: Arithmetic Operators
In the above example, we have used + , - , and * operators to compute addition, subtraction, and multiplication operations.
/ Division Operator
Note the operation, a / b in our program. The / operator is the division operator.
If we use the division operator with two integers, then the resulting quotient will also be an integer. And, if one of the operands is a floating-point number, we will get the result will also be in floating-point.
% Modulo Operator
The modulo operator % computes the remainder. When a = 7 is divided by b = 4 , the remainder is 3 .
Note : The % operator is mainly used with integers.
2. Java Assignment Operators
Assignment operators are used in Java to assign values to variables. For example,
Here, = is the assignment operator. It assigns the value on its right to the variable on its left. That is, 5 is assigned to the variable age .
Let's see some more assignment operators available in Java.
Example 2: Assignment Operators
3. java relational operators.
Relational operators are used to check the relationship between two operands. For example,
Here, < operator is the relational operator. It checks if a is less than b or not.
It returns either true or false .
Example 3: Relational Operators
Note : Relational operators are used in decision making and loops.
4. Java Logical Operators
Logical operators are used to check whether an expression is true or false . They are used in decision making.
Example 4: Logical Operators
Working of Program
- (5 > 3) && (8 > 5) returns true because both (5 > 3) and (8 > 5) are true .
- (5 > 3) && (8 < 5) returns false because the expression (8 < 5) is false .
- (5 < 3) || (8 > 5) returns true because the expression (8 > 5) is true .
- (5 > 3) || (8 < 5) returns true because the expression (5 > 3) is true .
- (5 < 3) || (8 < 5) returns false because both (5 < 3) and (8 < 5) are false .
- !(5 == 3) returns true because 5 == 3 is false .
- !(5 > 3) returns false because 5 > 3 is true .
5. Java Unary Operators
Unary operators are used with only one operand. For example, ++ is a unary operator that increases the value of a variable by 1 . That is, ++5 will return 6 .
Different types of unary operators are:
- Increment and Decrement Operators
Java also provides increment and decrement operators: ++ and -- respectively. ++ increases the value of the operand by 1 , while -- decrease it by 1 . For example,
Here, the value of num gets increased to 6 from its initial value of 5 .
Example 5: Increment and Decrement Operators
In the above program, we have used the ++ and -- operator as prefixes (++a, --b) . We can also use these operators as postfix (a++, b++) .
There is a slight difference when these operators are used as prefix versus when they are used as a postfix.
To learn more about these operators, visit increment and decrement operators .
6. Java Bitwise Operators
Bitwise operators in Java are used to perform operations on individual bits. For example,
Here, ~ is a bitwise operator. It inverts the value of each bit ( 0 to 1 and 1 to 0 ).
The various bitwise operators present in Java are:
These operators are not generally used in Java. To learn more, visit Java Bitwise and Bit Shift Operators .
Other operators
Besides these operators, there are other additional operators in Java.
The instanceof operator checks whether an object is an instanceof a particular class. For example,
Here, str is an instance of the String class. Hence, the instanceof operator returns true . To learn more, visit Java instanceof .
The ternary operator (conditional operator) is shorthand for the if-then-else statement. For example,
Here's how it works.
- If the Expression is true , expression1 is assigned to the variable .
- If the Expression is false , expression2 is assigned to the variable .
Let's see an example of a ternary operator.
In the above example, we have used the ternary operator to check if the year is a leap year or not. To learn more, visit the Java ternary operator .
Now that you know about Java operators, it's time to know about the order in which operators are evaluated. To learn more, visit Java Operator Precedence .
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Java Arithmetic Operators
- Java Assignment Operators
- Java Relational Operators
- Java Logical Operators
- Java Unary Operators
- Java Bitwise Operators
Sorry about that.
Related Tutorials
Java Tutorial
The Java Tutorials have been written for JDK 8. Examples and practices described in this page don't take advantage of improvements introduced in later releases and might use technology no longer available. See Java Language Changes for a summary of updated language features in Java SE 9 and subsequent releases. See JDK Release Notes for information about new features, enhancements, and removed or deprecated options for all JDK releases.
Now that you've learned how to declare and initialize variables, you probably want to know how to do something with them. Learning the operators of the Java programming language is a good place to start. Operators are special symbols that perform specific operations on one, two, or three operands , and then return a result.
As we explore the operators of the Java programming language, it may be helpful for you to know ahead of time which operators have the highest precedence. The operators in the following table are listed according to precedence order. The closer to the top of the table an operator appears, the higher its precedence. Operators with higher precedence are evaluated before operators with relatively lower precedence. Operators on the same line have equal precedence. When operators of equal precedence appear in the same expression, a rule must govern which is evaluated first. All binary operators except for the assignment operators are evaluated from left to right; assignment operators are evaluated right to left.
In general-purpose programming, certain operators tend to appear more frequently than others; for example, the assignment operator " = " is far more common than the unsigned right shift operator " >>> ". With that in mind, the following discussion focuses first on the operators that you're most likely to use on a regular basis, and ends focusing on those that are less common. Each discussion is accompanied by sample code that you can compile and run. Studying its output will help reinforce what you've just learned.
About Oracle | Contact Us | Legal Notices | Terms of Use | Your Privacy Rights
Copyright © 1995, 2022 Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
We Love Servers.
- WHY IOFLOOD?
- BARE METAL CLOUD
- DEDICATED SERVERS
Understanding the Java += (Addition Assignment) Operator

Stumped by the ‘+=’ operator in Java? You’re not alone. Many developers find this operator a bit puzzling, but it’s actually a handy tool that can simplify your code and make your programming tasks easier.
Think of the ‘+=’ operator in Java as a mathematical shortcut – a bridge that connects your variables and values in a more efficient way. It’s a powerful tool that can streamline your code, making it more readable and maintainable.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through the process of understanding and using the ‘+=’ operator in Java , from the basics to more advanced techniques. We’ll cover everything from simple assignments and calculations to its use with strings and arrays, and even discuss alternative approaches.
So, let’s dive in and start mastering the ‘+=’ operator in Java!
TL;DR: What Does ‘+=’ Mean in Java?
In Java, the ‘+=’ represents the additional assignment operator and is used to add the right operand to the left operand and assign the result back to the left operand, with the syntax, operandA += operandB . It’s a shorthand for a common operation that can make your code more concise and easier to read.
Here’s a simple example:
In this example, we declare an integer a and assign it a value of 5. Then, we use the ‘+=’ operator to add 3 to a and assign the result back to a . When we print out a , the output is 8.
This is just a basic use of the ‘+=’ operator in Java, but there’s much more to learn about this operator and how it can simplify your code. Continue reading for more detailed information and advanced usage scenarios.
Table of Contents
The Basics of ‘+=’ in Java
Advanced uses of ‘+=’ in java, exploring alternatives to ‘+=’ in java, troubleshooting java ‘+=’ operator issues, digging into java operators, applying ‘+=’ operator in larger java projects, wrapping up: additional assignment ‘+=’ operator.
The ‘+=’ operator in Java is a compound assignment operator. It’s a shorthand that combines the addition and assignment operations into a single operation. This operator adds the right operand to the left operand and then assigns the result back to the left operand.
Let’s look at a simple example:
In this example, we declare an integer b and assign it a value of 10. Then, we use the ‘+=’ operator to add 5 to b and assign the result back to b . When we print out b , the output is 15.
Advantages of Using ‘+=’
One of the main advantages of using the ‘+=’ operator is that it can make your code more concise and easier to read. Instead of writing b = b + 5; , you can simply write b += 5; .
Pitfalls to Avoid
While the ‘+=’ operator can simplify your code, it’s important to be aware of potential pitfalls. For example, if you use the ‘+=’ operator with a null value, you’ll get a NullPointerException. It’s also important to remember that the ‘+=’ operator performs an implicit cast, which can lead to unexpected results if you’re not careful.
Here’s an example:
In this example, the ‘+=’ operator performs an implicit cast from int (the type of the right operand) to byte (the type of the left operand). The result is -116, which might not be what you expected.
While the ‘+=’ operator is commonly used with numeric types, it can also be used with other types in Java, such as strings and arrays. This versatility can lead to more complex and interesting use cases.
‘+=’ with Strings
In Java, the ‘+=’ operator can be used to concatenate strings. Here’s an example:
In this example, we declare a string s and assign it a value of “Java”. Then, we use the ‘+=’ operator to append ” programming” to s . When we print out s , the output is “Java programming”.
‘+=’ with Arrays
The ‘+=’ operator can also be used with arrays in Java. However, it’s important to note that this usage is not as straightforward as with numeric types or strings. Here’s an example:
In this example, we declare an array and use a for loop to iterate through each element. We use the ‘+=’ operator to add 5 to each element in the array. When we print out the elements of the array, the output is 6, 7, 8.
These advanced uses of the ‘+=’ operator can help you write more efficient and concise code in Java, especially when working with strings and arrays.
While the ‘+=’ operator is a powerful tool in Java, there are other related operators that you can use depending on the specific needs of your code. Understanding these alternatives can give you more flexibility and control over your code.
The ‘+’ Operator
The ‘+’ operator in Java is the most basic form of addition. It adds the right operand to the left operand.
In this example, we’re doing the same thing as c += 3; , but we’re writing it out in a longer form. The ‘+’ operator is straightforward and easy to understand, but it can make your code more verbose.
The ‘++’ Operator
The ‘++’ operator in Java is an increment operator. It increases the value of the variable by 1.
In this example, we’re increasing the value of d by 1. The ‘++’ operator is a concise way to increment a variable, but it’s limited to increasing the value by 1.
Decision-Making Considerations
When deciding which operator to use, consider the needs of your code and the readability of your code. The ‘+=’ operator can make your code more concise, but it might be less clear to someone who isn’t familiar with this operator. The ‘+’ and ‘++’ operators are more explicit, but they can make your code more verbose.
Understanding these alternatives to the ‘+=’ operator can help you write more efficient and readable code in Java.
While the ‘+=’ operator in Java is a powerful tool, it’s not without its potential pitfalls. Understanding these common issues and how to address them can save you time and frustration.
Dealing with Null Values
One common issue is attempting to use the ‘+=’ operator with a null value. This will result in a NullPointerException.
In this example, we attempt to use the ‘+=’ operator to append ” programming” to a null string. This results in a NullPointerException. To avoid this, always ensure that your variables are initialized before using them with the ‘+=’ operator.
Implicit Casting
Another common issue is the implicit casting that occurs when using the ‘+=’ operator. This can lead to unexpected results.
In this example, the ‘+=’ operator performs an implicit cast from int (the type of the right operand) to byte (the type of the left operand), resulting in an unexpected value. To avoid this, be mindful of the types of your variables and the potential for implicit casting.
Optimization Tips
While the ‘+=’ operator can make your code more concise, it’s not always the most efficient choice. For example, if you’re performing a large number of additions, it might be more efficient to use a StringBuilder when working with strings, or to use a loop or a built-in method when working with arrays.
Understanding these common issues and best practices can help you use the ‘+=’ operator more effectively in Java.
Operators in Java are special symbols that perform specific operations on one, two, or three operands, and then return a result. They are the building blocks of any Java program, allowing us to perform calculations, manipulate bits, compare values, and more.
The Role of Operators in Java
Operators play a pivotal role in Java programming. They allow us to perform basic mathematical operations like addition ( + ), subtraction ( - ), multiplication ( * ), and division ( / ). They also let us compare values and determine logic ( == , != , > , < , && , || ), manipulate bits ( <> , & , | ), and more.
The Importance of ‘+=’ Operator
Among these operators, ‘+=’ holds a special place due to its dual functionality. It’s a compound assignment operator that performs both addition and assignment in a single step. This not only makes our code more concise but also can lead to performance improvements in certain situations.
In this example, we use the ‘+=’ operator to add 5 to x and assign the result back to x in a single step. This is more efficient than performing the addition and assignment in two separate steps.
The ‘+=’ Operator in the Broader Context of Java
The ‘+=’ operator is part of a family of compound assignment operators in Java, which also includes ‘-=’, ‘*=’, ‘/=’, and more. These operators all combine an arithmetic operation with an assignment, making our code more concise and potentially more efficient.
Understanding the ‘+=’ operator and its role in Java programming is key to mastering Java and writing efficient, readable code.
The ‘+=’ operator is not just for small programs or quick scripts. It can be a valuable tool in larger Java projects, where code efficiency and readability become critical.
In large codebases, the ‘+=’ operator can help simplify complex calculations and assignments, making the code easier to understand and maintain. It can also reduce the chance of errors, as it reduces the need to repeat variable names.
Related Topics to Explore
The ‘+=’ operator often accompanies several related topics in typical use cases. Understanding these related concepts can provide a more holistic view of Java programming. These include other compound assignment operators like ‘-=’, ‘*=’, ‘/=’, and ‘%=’, as well as the broader topic of operator precedence in Java.
Further Resources for Mastering Java Operators
To further your understanding of the ‘+=’ operator and related concepts, here are some resources that offer more in-depth information:
- Java Operator Tutorial: Getting Started – Discover Java’s bitwise operators for manipulating binary data.
.equals Method in Java – Learn to compare the contents of objects for equality with the “.equals()” method in Java.
Exploring ! Operator Usage – Understand how the “!” operator performs logical negation, flipping true to false and vice versa.
Java Operators: Oracle Docs provides a comprehensive overview of all operators in Java, including the ‘+=’ operator.
Java Compound Assignment Operators discusses the usage of compound assignment operators in Java.
Java Operator Precedence explains operator precedence in Java, which determines how expressions involving the ‘+=’ operator are evaluated.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ve demystified the ‘+=’ operator in Java, a handy tool that can simplify your code and streamline your programming tasks.
We began with the basics, examining how the ‘+=’ operator functions as a mathematical shortcut in Java. We then delved into more advanced usage scenarios, such as using the ‘+=’ operator with strings and arrays. We also explored alternative approaches and related operators in Java, giving you a broader understanding of the Java operator landscape.
Throughout our exploration, we tackled common issues and pitfalls associated with the ‘+=’ operator, such as dealing with null values and understanding implicit casting. We provided solutions and best practices to help you overcome these challenges.
Here’s a quick comparison of the methods we’ve discussed:
Whether you’re a beginner just starting out with Java or an experienced developer looking to brush up on your skills, we hope this guide has shed light on the ‘+=’ operator in Java and its usage.
The ‘+=’ operator is a powerful tool in your Java toolkit, offering a combination of simplicity, efficiency, and versatility. Now, you’re well equipped to use it in your Java projects. Happy coding!
About Author
Gabriel Ramuglia
Gabriel is the owner and founder of IOFLOOD.com , an unmanaged dedicated server hosting company operating since 2010.Gabriel loves all things servers, bandwidth, and computer programming and enjoys sharing his experience on these topics with readers of the IOFLOOD blog.
Related Posts

- TutorialKart
- SAP Tutorials
- Salesforce Admin
- Salesforce Developer
- Visualforce
- Informatica
- Kafka Tutorial
- Spark Tutorial
- Tomcat Tutorial
- Python Tkinter
Programming
- Bash Script
- Julia Tutorial
- CouchDB Tutorial
- MongoDB Tutorial
- PostgreSQL Tutorial
- Android Compose
- Flutter Tutorial
- Kotlin Android
Web & Server
- Selenium Java
- Java Basics
- Java Tutorial
- Java HelloWorld Program
- Java Program Structure
- Java Datatypes
- Java Variable Types
- Java Access Modifiers
- Java Operators
- Java Decision Making
- Print array
- Initialize array
- Array of integers
- Array of strings
- Array of objects
- Array of arrays
- Iterate over array
- Array For loop
- Array while loop
- Append element to array
- Check if array is empty
- Array average
- Check if array contains
- Array ForEach
- Array - Find Index of Item
- Concatenate arrays
- Find smallest number in array
- Find largest number in array
- Array reverse
- Classes and Objects
- Inheritance
- Polymorphism
- Method Overloading
- Method Overriding/
- Abstraction
- Abstract methods and classes
- Encapsulation
- Print string
- Read string from console
- Create string from Char array
- Create string from Byte array
- Concatenate two strings
- Get index of the first Occurrence of substring
- Get index of nth occurrence of substring
- Check if two strings are equal
- Check if string ends with specific suffix
- Check if string starts with specific prefix
- Check if string is blank
- Check if string is empty
- Check if string contains search substring
- Validate if string is a Phone Number
- Character Level
- Get character at specific index in string
- Get first character in string
- Get last character from string
- Transformations
- Replace first occurrence of string
- Replace all occurrences of a string
- Join strings
- Join strings in string array
- Join strings in ArrayList
- Reverse a string
- Trim string
- Split string
- Remove whitespaces in string
- Replace multiple spaces with single space
- Comparisons
- Compare strings lexicographically
- Compare String and CharSequence
- Compare String and StringBuffer
- Java Exception Handling StringIndexOutOfBoundsException
- Convert string to int
- Convert string to float
- Convert string to double
- Convert string to long
- Convert string to boolean
- Convert int to string
- Convert int to float
- Convert int to double
- Convert int to long
- Convert int to char
- Convert float to string
- Convert float to int
- Convert float to double
- Convert float to long
- Convert long to string
- Convert long to float
- Convert long to double
- Convert long to int
- Convert double to string
- Convert double to float
- Convert double to int
- Convert double to long
- Convert char to int
- Convert boolean to string
- Create a file
- Read file as string
- Write string to file
- Delete File
- Rename File
- Download File from URL
- Replace a String in File
- Filter list of files or directories
- Check if file is readable
- Check if file is writable
- Check if file is executable
- Read contents of a file line by line using BufferedReader
- Read contents of a File line by line using Stream
- Check if n is positive or negative
- Read integer from console
- Add two integers
- Count digits in number
- Largest of three numbers
- Smallest of three numbers
- Even numbers
- Odd numbers
- Reverse a number
- Prime Number
- Print All Prime Numbers
- Factors of a Number
- Check Palindrome number
- Check Palindrome string
- Swap two numbers
- Even or Odd number
- Java Classes
- ArrayList add()
- ArrayList addAll()
- ArrayList clear()
- ArrayList clone()
- ArrayList contains()
- ArrayList ensureCapacity()
- ArrayList forEach()
- ArrayList get()
- ArrayList indexOf()
- ArrayList isEmpty()
- ArrayList iterator()
- ArrayList lastIndexOf()
- ArrayList listIterator()
- ArrayList remove()
- ArrayList removeAll()
- ArrayList removeIf()
- ArrayList removeRange()
- ArrayList retainAll()
- ArrayList set()
- ArrayList size()
- ArrayList spliterator()
- ArrayList subList()
- ArrayList toArray()
- ArrayList trimToSize()
- HashMap clear()
- HashMap clone()
- HashMap compute()
- HashMap computeIfAbsent()
- HashMap computeIfPresent()
- HashMap containsKey()
- HashMap containsValue()
- HashMap entrySet()
- HashMap get()
- HashMap isEmpty()
- HashMap keySet()
- HashMap merge()
- HashMap put()
- HashMap putAll()
- HashMap remove()
- HashMap size()
- HashMap values()
- HashSet add()
- HashSet clear()
- HashSet clone()
- HashSet contains()
- HashSet isEmpty()
- HashSet iterator()
- HashSet remove()
- HashSet size()
- HashSet spliterator()
- Integer bitCount()
- Integer byteValue()
- Integer compare()
- Integer compareTo()
- Integer compareUnsigned()
- Integer decode()
- Integer divideUnsigned()
- Integer doubleValue()
- Integer equals()
- Integer floatValue()
- Integer getInteger()
- Integer hashCode()
- Integer highestOneBit()
- Integer intValue()
- Integer longValue()
- Integer lowestOneBit()
- Integer max()
- Integer min()
- Integer numberOfLeadingZeros()
- Integer numberOfTrailingZeros()
- Integer parseInt()
- Integer parseUnsignedInt()
- Integer remainderUnsigned()
- Integer reverse()
- Integer reverseBytes()
- Integer rotateLeft()
- Integer rotateRight()
- Integer shortValue()
- Integer signum()
- Integer sum()
- Integer toBinaryString()
- Integer toHexString()
- Integer toOctalString()
- Integer toString()
- Integer toUnsignedLong()
- Integer toUnsignedString()
- Integer valueOf()
- StringBuilder append()
- StringBuilder appendCodePoint()
- StringBuilder capacity()
- StringBuilder charAt()
- StringBuilder chars()
- StringBuilder codePointAt()
- StringBuilder codePointBefore()
- StringBuilder codePointCount()
- StringBuilder codePoints()
- StringBuilder delete()
- StringBuilder deleteCharAt()
- StringBuilder ensureCapacity()
- StringBuilder getChars()
- StringBuilder indexOf()
- StringBuilder insert()
- StringBuilder lastIndexOf()
- StringBuilder length()
- StringBuilder offsetByCodePoints()
- StringBuilder replace()
- StringBuilder reverse()
- StringBuilder setCharAt()
- StringBuilder setLength()
- StringBuilder subSequence()
- StringBuilder substring()
- StringBuilder toString()
- StringBuilder trimToSize()
- Arrays.asList()
- Arrays.binarySearch()
- Arrays.copyOf()
- Arrays.copyOfRange()
- Arrays.deepEquals()
- Arrays.deepToString()
- Arrays.equals()
- Arrays.fill()
- Arrays.hashCode()
- Arrays.sort()
- Arrays.toString()
- Random doubles()
- Random ints()
- Random longs()
- Random next()
- Random nextBoolean()
- Random nextBytes()
- Random nextDouble()
- Random nextFloat()
- Random nextGaussian()
- Random nextInt()
- Random nextLong()
- Random setSeed()
- Math random
- Math signum
- Math toDegrees
- Math toRadians
- Java Date & Time
- ❯ Java Tutorial
Java Bitwise AND Assignment (&=) Operator
Java bitwise and assignment.
In Java, Bitwise AND Assignment Operator is used to compute the Bitwise AND operation of left and right operands, and assign the result back to left operand. In this tutorial, we will learn how to use Bitwise AND Assignment operator in Java, with examples.
The syntax to compute bitwise AND a value of 2 and value in variable x , and assign the result back to x using Bitwise AND Assignment Operator is
In the following example, we take a variable x with an initial value of 9 , add bitwise AND it with value of 2 , and assign the result to x , using Bitwise AND Assignment Operator.
In this Java Tutorial , we learned about Bitwise AND Assignment Operator in Java, with examples.
Popular Courses by TutorialKart
App developement, web development, online tools.
- Python Basics
- Interview Questions
- Python Quiz
- Popular Packages
- Python Projects
- Practice Python
- AI With Python
- Learn Python3
- Python Automation
- Python Web Dev
- DSA with Python
- Python OOPs
- Dictionaries
Python Operators
Precedence and associativity of operators in python.
- Python Arithmetic Operators
- Difference between / vs. // operator in Python
- Python - Star or Asterisk operator ( * )
- What does the Double Star operator mean in Python?
- Division Operators in Python
- Modulo operator (%) in Python
- Python Logical Operators
- Python OR Operator
- Difference between 'and' and '&' in Python
- not Operator in Python | Boolean Logic
Ternary Operator in Python
- Python Bitwise Operators
Python Assignment Operators
Assignment operators in python.
- Walrus Operator in Python 3.8
- Increment += and Decrement -= Assignment Operators in Python
- Merging and Updating Dictionary Operators in Python 3.9
- New '=' Operator in Python3.8 f-string
Python Relational Operators
- Comparison Operators in Python
- Python NOT EQUAL operator
- Difference between == and is operator in Python
- Chaining comparison operators in Python
- Python Membership and Identity Operators
- Difference between != and is not operator in Python
In Python programming, Operators in general are used to perform operations on values and variables. These are standard symbols used for logical and arithmetic operations. In this article, we will look into different types of Python operators.
- OPERATORS: These are the special symbols. Eg- + , * , /, etc.
- OPERAND: It is the value on which the operator is applied.
Types of Operators in Python
- Arithmetic Operators
- Comparison Operators
- Logical Operators
- Bitwise Operators
- Assignment Operators
- Identity Operators and Membership Operators
Arithmetic Operators in Python
Python Arithmetic operators are used to perform basic mathematical operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication , and division .
In Python 3.x the result of division is a floating-point while in Python 2.x division of 2 integers was an integer. To obtain an integer result in Python 3.x floored (// integer) is used.
Example of Arithmetic Operators in Python
Division operators.
In Python programming language Division Operators allow you to divide two numbers and return a quotient, i.e., the first number or number at the left is divided by the second number or number at the right and returns the quotient.
There are two types of division operators:
Float division
- Floor division
The quotient returned by this operator is always a float number, no matter if two numbers are integers. For example:
Example: The code performs division operations and prints the results. It demonstrates that both integer and floating-point divisions return accurate results. For example, ’10/2′ results in ‘5.0’ , and ‘-10/2’ results in ‘-5.0’ .
Integer division( Floor division)
The quotient returned by this operator is dependent on the argument being passed. If any of the numbers is float, it returns output in float. It is also known as Floor division because, if any number is negative, then the output will be floored. For example:
Example: The code demonstrates integer (floor) division operations using the // in Python operators . It provides results as follows: ’10//3′ equals ‘3’ , ‘-5//2’ equals ‘-3’ , ‘ 5.0//2′ equals ‘2.0’ , and ‘-5.0//2’ equals ‘-3.0’ . Integer division returns the largest integer less than or equal to the division result.
Precedence of Arithmetic Operators in Python
The precedence of Arithmetic Operators in Python is as follows:
- P – Parentheses
- E – Exponentiation
- M – Multiplication (Multiplication and division have the same precedence)
- D – Division
- A – Addition (Addition and subtraction have the same precedence)
- S – Subtraction
The modulus of Python operators helps us extract the last digit/s of a number. For example:
- x % 10 -> yields the last digit
- x % 100 -> yield last two digits
Arithmetic Operators With Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication, Modulo and Power
Here is an example showing how different Arithmetic Operators in Python work:
Example: The code performs basic arithmetic operations with the values of ‘a’ and ‘b’ . It adds (‘+’) , subtracts (‘-‘) , multiplies (‘*’) , computes the remainder (‘%’) , and raises a to the power of ‘b (**)’ . The results of these operations are printed.
Note: Refer to Differences between / and // for some interesting facts about these two Python operators.
Comparison of Python Operators
In Python Comparison of Relational operators compares the values. It either returns True or False according to the condition.
= is an assignment operator and == comparison operator.
Precedence of Comparison Operators in Python
In Python, the comparison operators have lower precedence than the arithmetic operators. All the operators within comparison operators have the same precedence order.
Example of Comparison Operators in Python
Let’s see an example of Comparison Operators in Python.
Example: The code compares the values of ‘a’ and ‘b’ using various comparison Python operators and prints the results. It checks if ‘a’ is greater than, less than, equal to, not equal to, greater than, or equal to, and less than or equal to ‘b’ .
Logical Operators in Python
Python Logical operators perform Logical AND , Logical OR , and Logical NOT operations. It is used to combine conditional statements.
Precedence of Logical Operators in Python
The precedence of Logical Operators in Python is as follows:
- Logical not
- logical and
Example of Logical Operators in Python
The following code shows how to implement Logical Operators in Python:
Example: The code performs logical operations with Boolean values. It checks if both ‘a’ and ‘b’ are true ( ‘and’ ), if at least one of them is true ( ‘or’ ), and negates the value of ‘a’ using ‘not’ . The results are printed accordingly.
Bitwise Operators in Python
Python Bitwise operators act on bits and perform bit-by-bit operations. These are used to operate on binary numbers.
Precedence of Bitwise Operators in Python
The precedence of Bitwise Operators in Python is as follows:
- Bitwise NOT
- Bitwise Shift
- Bitwise AND
- Bitwise XOR
Here is an example showing how Bitwise Operators in Python work:
Example: The code demonstrates various bitwise operations with the values of ‘a’ and ‘b’ . It performs bitwise AND (&) , OR (|) , NOT (~) , XOR (^) , right shift (>>) , and left shift (<<) operations and prints the results. These operations manipulate the binary representations of the numbers.
Python Assignment operators are used to assign values to the variables.
Let’s see an example of Assignment Operators in Python.
Example: The code starts with ‘a’ and ‘b’ both having the value 10. It then performs a series of operations: addition, subtraction, multiplication, and a left shift operation on ‘b’ . The results of each operation are printed, showing the impact of these operations on the value of ‘b’ .
Identity Operators in Python
In Python, is and is not are the identity operators both are used to check if two values are located on the same part of the memory. Two variables that are equal do not imply that they are identical.
Example Identity Operators in Python
Let’s see an example of Identity Operators in Python.
Example: The code uses identity operators to compare variables in Python. It checks if ‘a’ is not the same object as ‘b’ (which is true because they have different values) and if ‘a’ is the same object as ‘c’ (which is true because ‘c’ was assigned the value of ‘a’ ).
Membership Operators in Python
In Python, in and not in are the membership operators that are used to test whether a value or variable is in a sequence.
Examples of Membership Operators in Python
The following code shows how to implement Membership Operators in Python:
Example: The code checks for the presence of values ‘x’ and ‘y’ in the list. It prints whether or not each value is present in the list. ‘x’ is not in the list, and ‘y’ is present, as indicated by the printed messages. The code uses the ‘in’ and ‘not in’ Python operators to perform these checks.
in Python, Ternary operators also known as conditional expressions are operators that evaluate something based on a condition being true or false. It was added to Python in version 2.5.
It simply allows testing a condition in a single line replacing the multiline if-else making the code compact.
Syntax : [on_true] if [expression] else [on_false]
Examples of Ternary Operator in Python
The code assigns values to variables ‘a’ and ‘b’ (10 and 20, respectively). It then uses a conditional assignment to determine the smaller of the two values and assigns it to the variable ‘min’ . Finally, it prints the value of ‘min’ , which is 10 in this case.
In Python, Operator precedence and associativity determine the priorities of the operator.
Operator Precedence in Python
This is used in an expression with more than one operator with different precedence to determine which operation to perform first.
Let’s see an example of how Operator Precedence in Python works:
Example: The code first calculates and prints the value of the expression 10 + 20 * 30 , which is 610. Then, it checks a condition based on the values of the ‘name’ and ‘age’ variables. Since the name is “ Alex” and the condition is satisfied using the or operator, it prints “Hello! Welcome.”
Operator Associativity in Python
If an expression contains two or more operators with the same precedence then Operator Associativity is used to determine. It can either be Left to Right or from Right to Left.
The following code shows how Operator Associativity in Python works:
Example: The code showcases various mathematical operations. It calculates and prints the results of division and multiplication, addition and subtraction, subtraction within parentheses, and exponentiation. The code illustrates different mathematical calculations and their outcomes.
To try your knowledge of Python Operators, you can take out the quiz on Operators in Python .
Python Operator Exercise Questions
Below are two Exercise Questions on Python Operators. We have covered arithmetic operators and comparison operators in these exercise questions. For more exercises on Python Operators visit the page mentioned below.
Q1. Code to implement basic arithmetic operations on integers
Q2. Code to implement Comparison operations on integers
Explore more Exercises: Practice Exercise on Operators in Python
Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.
- python-basics
- Python-Operators
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
variable operator value; Types of Assignment Operators in Java. The Assignment Operator is generally of two types. They are: 1. Simple Assignment Operator: The Simple Assignment Operator is used with the "=" sign where the left side consists of the operand and the right side consists of a value. The value of the right side must be of the same data type that has been defined on the left side.
Java Comparison Operators. Comparison operators are used to compare two values (or variables). This is important in programming, because it helps us to find answers and make decisions. The return value of a comparison is either true or false. These values are known as Boolean values, and you will learn more about them in the Booleans and If ...
The Simple Assignment Operator. One of the most common operators that you'll encounter is the simple assignment operator "=". You saw this operator in the Bicycle class; it assigns the value on its right to the operand on its left: ... The Java programming language provides operators that perform addition, subtraction, multiplication, and ...
There are mainly two types of assignment operators in Java, which are as follows: Simple Assignment Operator ; We use the simple assignment operator with the "=" sign, where the left side consists of an operand and the right side is a value. The value of the operand on the right side must be of the same data type defined on the left side.
To assign a value to a variable, use the basic assignment operator (=). It is the most fundamental assignment operator in Java. It assigns the value on the right side of the operator to the variable on the left side. Example: int x = 10; int x = 10; In the above example, the variable x is assigned the value 10.
Java assignment operators are classified into two types: simple and compound. The Simple assignment operator is the equals ( =) sign, which is the most straightforward of the bunch. It simply assigns the value or variable on the right to the variable on the left. Compound operators are comprised of both an arithmetic, bitwise, or shift operator ...
Assignment Operators in Java: An Overview. We already discussed the Types of Operators in the previous tutorial Java. In this Java tutorial, we will delve into the different types of assignment operators in Java, and their syntax, and provide examples for better understanding.Because Java is a flexible and widely used programming language. Assignment operators play a crucial role in ...
Java Assignment Operators. The Java Assignment Operators are used when you want to assign a value to the expression. The assignment operator denoted by the single equal sign =. In a Java assignment statement, any expression can be on the right side and the left side must be a variable name. For example, this does not mean that "a" is equal to ...
positive without this, however) - Unary minus operator; negates. an expression. ++ Increment operator; increments. a value by 1. -- Decrement operator; decrements. a value by 1. Logical complement operator; inverts the value of a boolean.
The = operator in java is known as assignment or simple assignment operator. It assigns the value on its right side to the operand (variable) on its left side. For example : int a = 10; // value 10 is assigned in variable a double d = 20.25; // value 20.25 is assigned in variable d char c = 'A'; // Character A is assigned in variable c. a = 20 ...
Assignment Operators Overview Top. The single equal sign = is used for assignment in Java and we have been using this throughout the lessons so far. This operator is fairly self explanatory and takes the form variable = expression; . A point to note here is that the type of variable must be compatible with the type of expression.
2. Java Assignment Operators. Assignment operators are used in Java to assign values to variables. For example, int age; age = 5; Here, = is the assignment operator. It assigns the value on its right to the variable on its left. That is, 5 is assigned to the variable age. Let's see some more assignment operators available in Java.
The Java Assignment operators are used to assign the values to the declared variables. The equals ( = ) operator is the most commonly used Java assignment operator. For example: int i = 25; The table below displays all the assignment operators in the Java programming language. Operators.
Compound Assignment Operators. Sometime we need to modify the same variable value and reassigned it to a same reference variable. Java allows you to combine assignment and addition operators using a shorthand operator. For example, the preceding statement can be written as: i +=8; //This is same as i = i+8; The += is called the addition ...
It's the Addition assignment operator. Let's understand the += operator in Java and learn to use it for our day to day programming. x += y in Java is the same as x = x + y. It is a compound assignment operator. Most commonly used for incrementing the value of a variable since x++ only increments the value by one.
Learning the operators of the Java programming language is a good place to start. Operators are special symbols that perform specific operations on one, two, or three operands, and then return a result. As we explore the operators of the Java programming language, it may be helpful for you to know ahead of time which operators have the highest ...
2. These are examples of assignment operators. Essentially, they both perform the arithmetic operation on a variable, and assign its result to that variable, in a single operation. They're equivalent to doing it in two steps, for the most part: int a = 23; int b = 2; a += b; // addition - same as `a = a + b`.
The '+=' operator in Java is a compound assignment operator. It's a shorthand that combines the addition and assignment operations into a single operation. This operator adds the right operand to the left operand and then assigns the result back to the left operand. Let's look at a simple example:
The |= is a compound assignment operator ( JLS 15.26.2) for the boolean logical operator | ( JLS 15.22.2 ); not to be confused with the conditional-or || ( JLS 15.24 ). There are also &= and ^= corresponding to the compound assignment version of the boolean logical & and ^ respectively. In other words, for boolean b1, b2, these two are ...
In Java, Bitwise AND Assignment Operator is used to compute the Bitwise AND operation of left and right operands, and assign the result back to left operand. In this tutorial, we will learn how to use Bitwise AND Assignment operator in Java, with examples. The syntax to compute bitwise AND a value of 2 and value in variable x, and assign the ...
a |= b; is the same as. a = (a | b); It calculates the bitwise OR of the two operands, and assigns the result to the left operand. To explain your example code: for (String search : textSearch.getValue()) matches |= field.contains(search); I presume matches is a boolean; this means that the bitwise operators behave the same as logical operators.
Assignment Operators in Python. Let's see an example of Assignment Operators in Python. Example: The code starts with 'a' and 'b' both having the value 10. It then performs a series of operations: addition, subtraction, multiplication, and a left shift operation on 'b'.