
Get science-backed answers as you write with Paperpal's Research feature

What is Research Methodology? Definition, Types, and Examples

Research methodology 1,2 is a structured and scientific approach used to collect, analyze, and interpret quantitative or qualitative data to answer research questions or test hypotheses. A research methodology is like a plan for carrying out research and helps keep researchers on track by limiting the scope of the research. Several aspects must be considered before selecting an appropriate research methodology, such as research limitations and ethical concerns that may affect your research.
The research methodology section in a scientific paper describes the different methodological choices made, such as the data collection and analysis methods, and why these choices were selected. The reasons should explain why the methods chosen are the most appropriate to answer the research question. A good research methodology also helps ensure the reliability and validity of the research findings. There are three types of research methodology—quantitative, qualitative, and mixed-method, which can be chosen based on the research objectives.
What is research methodology ?
A research methodology describes the techniques and procedures used to identify and analyze information regarding a specific research topic. It is a process by which researchers design their study so that they can achieve their objectives using the selected research instruments. It includes all the important aspects of research, including research design, data collection methods, data analysis methods, and the overall framework within which the research is conducted. While these points can help you understand what is research methodology, you also need to know why it is important to pick the right methodology.
Why is research methodology important?
Having a good research methodology in place has the following advantages: 3
- Helps other researchers who may want to replicate your research; the explanations will be of benefit to them.
- You can easily answer any questions about your research if they arise at a later stage.
- A research methodology provides a framework and guidelines for researchers to clearly define research questions, hypotheses, and objectives.
- It helps researchers identify the most appropriate research design, sampling technique, and data collection and analysis methods.
- A sound research methodology helps researchers ensure that their findings are valid and reliable and free from biases and errors.
- It also helps ensure that ethical guidelines are followed while conducting research.
- A good research methodology helps researchers in planning their research efficiently, by ensuring optimum usage of their time and resources.
Writing the methods section of a research paper? Let Paperpal help you achieve perfection
Types of research methodology.
There are three types of research methodology based on the type of research and the data required. 1
- Quantitative research methodology focuses on measuring and testing numerical data. This approach is good for reaching a large number of people in a short amount of time. This type of research helps in testing the causal relationships between variables, making predictions, and generalizing results to wider populations.
- Qualitative research methodology examines the opinions, behaviors, and experiences of people. It collects and analyzes words and textual data. This research methodology requires fewer participants but is still more time consuming because the time spent per participant is quite large. This method is used in exploratory research where the research problem being investigated is not clearly defined.
- Mixed-method research methodology uses the characteristics of both quantitative and qualitative research methodologies in the same study. This method allows researchers to validate their findings, verify if the results observed using both methods are complementary, and explain any unexpected results obtained from one method by using the other method.
What are the types of sampling designs in research methodology?
Sampling 4 is an important part of a research methodology and involves selecting a representative sample of the population to conduct the study, making statistical inferences about them, and estimating the characteristics of the whole population based on these inferences. There are two types of sampling designs in research methodology—probability and nonprobability.
- Probability sampling
In this type of sampling design, a sample is chosen from a larger population using some form of random selection, that is, every member of the population has an equal chance of being selected. The different types of probability sampling are:
- Systematic —sample members are chosen at regular intervals. It requires selecting a starting point for the sample and sample size determination that can be repeated at regular intervals. This type of sampling method has a predefined range; hence, it is the least time consuming.
- Stratified —researchers divide the population into smaller groups that don’t overlap but represent the entire population. While sampling, these groups can be organized, and then a sample can be drawn from each group separately.
- Cluster —the population is divided into clusters based on demographic parameters like age, sex, location, etc.
- Convenience —selects participants who are most easily accessible to researchers due to geographical proximity, availability at a particular time, etc.
- Purposive —participants are selected at the researcher’s discretion. Researchers consider the purpose of the study and the understanding of the target audience.
- Snowball —already selected participants use their social networks to refer the researcher to other potential participants.
- Quota —while designing the study, the researchers decide how many people with which characteristics to include as participants. The characteristics help in choosing people most likely to provide insights into the subject.
What are data collection methods?
During research, data are collected using various methods depending on the research methodology being followed and the research methods being undertaken. Both qualitative and quantitative research have different data collection methods, as listed below.
Qualitative research 5
- One-on-one interviews: Helps the interviewers understand a respondent’s subjective opinion and experience pertaining to a specific topic or event
- Document study/literature review/record keeping: Researchers’ review of already existing written materials such as archives, annual reports, research articles, guidelines, policy documents, etc.
- Focus groups: Constructive discussions that usually include a small sample of about 6-10 people and a moderator, to understand the participants’ opinion on a given topic.
- Qualitative observation : Researchers collect data using their five senses (sight, smell, touch, taste, and hearing).
Quantitative research 6
- Sampling: The most common type is probability sampling.
- Interviews: Commonly telephonic or done in-person.
- Observations: Structured observations are most commonly used in quantitative research. In this method, researchers make observations about specific behaviors of individuals in a structured setting.
- Document review: Reviewing existing research or documents to collect evidence for supporting the research.
- Surveys and questionnaires. Surveys can be administered both online and offline depending on the requirement and sample size.
Let Paperpal help you write the perfect research methods section. Start now!
What are data analysis methods.
The data collected using the various methods for qualitative and quantitative research need to be analyzed to generate meaningful conclusions. These data analysis methods 7 also differ between quantitative and qualitative research.
Quantitative research involves a deductive method for data analysis where hypotheses are developed at the beginning of the research and precise measurement is required. The methods include statistical analysis applications to analyze numerical data and are grouped into two categories—descriptive and inferential.
Descriptive analysis is used to describe the basic features of different types of data to present it in a way that ensures the patterns become meaningful. The different types of descriptive analysis methods are:
- Measures of frequency (count, percent, frequency)
- Measures of central tendency (mean, median, mode)
- Measures of dispersion or variation (range, variance, standard deviation)
- Measure of position (percentile ranks, quartile ranks)
Inferential analysis is used to make predictions about a larger population based on the analysis of the data collected from a smaller population. This analysis is used to study the relationships between different variables. Some commonly used inferential data analysis methods are:
- Correlation: To understand the relationship between two or more variables.
- Cross-tabulation: Analyze the relationship between multiple variables.
- Regression analysis: Study the impact of independent variables on the dependent variable.
- Frequency tables: To understand the frequency of data.
- Analysis of variance: To test the degree to which two or more variables differ in an experiment.
Qualitative research involves an inductive method for data analysis where hypotheses are developed after data collection. The methods include:
- Content analysis: For analyzing documented information from text and images by determining the presence of certain words or concepts in texts.
- Narrative analysis: For analyzing content obtained from sources such as interviews, field observations, and surveys. The stories and opinions shared by people are used to answer research questions.
- Discourse analysis: For analyzing interactions with people considering the social context, that is, the lifestyle and environment, under which the interaction occurs.
- Grounded theory: Involves hypothesis creation by data collection and analysis to explain why a phenomenon occurred.
- Thematic analysis: To identify important themes or patterns in data and use these to address an issue.
How to choose a research methodology?
Here are some important factors to consider when choosing a research methodology: 8
- Research objectives, aims, and questions —these would help structure the research design.
- Review existing literature to identify any gaps in knowledge.
- Check the statistical requirements —if data-driven or statistical results are needed then quantitative research is the best. If the research questions can be answered based on people’s opinions and perceptions, then qualitative research is most suitable.
- Sample size —sample size can often determine the feasibility of a research methodology. For a large sample, less effort- and time-intensive methods are appropriate.
- Constraints —constraints of time, geography, and resources can help define the appropriate methodology.
Got writer’s block? Kickstart your research paper writing with Paperpal now!
How to write a research methodology .
A research methodology should include the following components: 3,9
- Research design —should be selected based on the research question and the data required. Common research designs include experimental, quasi-experimental, correlational, descriptive, and exploratory.
- Research method —this can be quantitative, qualitative, or mixed-method.
- Reason for selecting a specific methodology —explain why this methodology is the most suitable to answer your research problem.
- Research instruments —explain the research instruments you plan to use, mainly referring to the data collection methods such as interviews, surveys, etc. Here as well, a reason should be mentioned for selecting the particular instrument.
- Sampling —this involves selecting a representative subset of the population being studied.
- Data collection —involves gathering data using several data collection methods, such as surveys, interviews, etc.
- Data analysis —describe the data analysis methods you will use once you’ve collected the data.
- Research limitations —mention any limitations you foresee while conducting your research.
- Validity and reliability —validity helps identify the accuracy and truthfulness of the findings; reliability refers to the consistency and stability of the results over time and across different conditions.
- Ethical considerations —research should be conducted ethically. The considerations include obtaining consent from participants, maintaining confidentiality, and addressing conflicts of interest.
Streamline Your Research Paper Writing Process with Paperpal
The methods section is a critical part of the research papers, allowing researchers to use this to understand your findings and replicate your work when pursuing their own research. However, it is usually also the most difficult section to write. This is where Paperpal can help you overcome the writer’s block and create the first draft in minutes with Paperpal Copilot, its secure generative AI feature suite.
With Paperpal you can get research advice, write and refine your work, rephrase and verify the writing, and ensure submission readiness, all in one place. Here’s how you can use Paperpal to develop the first draft of your methods section.
- Generate an outline: Input some details about your research to instantly generate an outline for your methods section
- Develop the section: Use the outline and suggested sentence templates to expand your ideas and develop the first draft.
- P araph ras e and trim : Get clear, concise academic text with paraphrasing that conveys your work effectively and word reduction to fix redundancies.
- Choose the right words: Enhance text by choosing contextual synonyms based on how the words have been used in previously published work.
- Check and verify text : Make sure the generated text showcases your methods correctly, has all the right citations, and is original and authentic. .
You can repeat this process to develop each section of your research manuscript, including the title, abstract and keywords. Ready to write your research papers faster, better, and without the stress? Sign up for Paperpal and start writing today!
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What are the key components of research methodology?
A1. A good research methodology has the following key components:
- Research design
- Data collection procedures
- Data analysis methods
- Ethical considerations
Q2. Why is ethical consideration important in research methodology?
A2. Ethical consideration is important in research methodology to ensure the readers of the reliability and validity of the study. Researchers must clearly mention the ethical norms and standards followed during the conduct of the research and also mention if the research has been cleared by any institutional board. The following 10 points are the important principles related to ethical considerations: 10
- Participants should not be subjected to harm.
- Respect for the dignity of participants should be prioritized.
- Full consent should be obtained from participants before the study.
- Participants’ privacy should be ensured.
- Confidentiality of the research data should be ensured.
- Anonymity of individuals and organizations participating in the research should be maintained.
- The aims and objectives of the research should not be exaggerated.
- Affiliations, sources of funding, and any possible conflicts of interest should be declared.
- Communication in relation to the research should be honest and transparent.
- Misleading information and biased representation of primary data findings should be avoided.
Q3. What is the difference between methodology and method?
A3. Research methodology is different from a research method, although both terms are often confused. Research methods are the tools used to gather data, while the research methodology provides a framework for how research is planned, conducted, and analyzed. The latter guides researchers in making decisions about the most appropriate methods for their research. Research methods refer to the specific techniques, procedures, and tools used by researchers to collect, analyze, and interpret data, for instance surveys, questionnaires, interviews, etc.
Research methodology is, thus, an integral part of a research study. It helps ensure that you stay on track to meet your research objectives and answer your research questions using the most appropriate data collection and analysis tools based on your research design.
Accelerate your research paper writing with Paperpal. Try for free now!
- Research methodologies. Pfeiffer Library website. Accessed August 15, 2023. https://library.tiffin.edu/researchmethodologies/whatareresearchmethodologies
- Types of research methodology. Eduvoice website. Accessed August 16, 2023. https://eduvoice.in/types-research-methodology/
- The basics of research methodology: A key to quality research. Voxco. Accessed August 16, 2023. https://www.voxco.com/blog/what-is-research-methodology/
- Sampling methods: Types with examples. QuestionPro website. Accessed August 16, 2023. https://www.questionpro.com/blog/types-of-sampling-for-social-research/
- What is qualitative research? Methods, types, approaches, examples. Researcher.Life blog. Accessed August 15, 2023. https://researcher.life/blog/article/what-is-qualitative-research-methods-types-examples/
- What is quantitative research? Definition, methods, types, and examples. Researcher.Life blog. Accessed August 15, 2023. https://researcher.life/blog/article/what-is-quantitative-research-types-and-examples/
- Data analysis in research: Types & methods. QuestionPro website. Accessed August 16, 2023. https://www.questionpro.com/blog/data-analysis-in-research/#Data_analysis_in_qualitative_research
- Factors to consider while choosing the right research methodology. PhD Monster website. Accessed August 17, 2023. https://www.phdmonster.com/factors-to-consider-while-choosing-the-right-research-methodology/
- What is research methodology? Research and writing guides. Accessed August 14, 2023. https://paperpile.com/g/what-is-research-methodology/
- Ethical considerations. Business research methodology website. Accessed August 17, 2023. https://research-methodology.net/research-methodology/ethical-considerations/
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
- Dangling Modifiers and How to Avoid Them in Your Writing
- Webinar: How to Use Generative AI Tools Ethically in Your Academic Writing
- Research Outlines: How to Write An Introduction Section in Minutes with Paperpal Copilot
- How to Paraphrase Research Papers Effectively
Language and Grammar Rules for Academic Writing
Climatic vs. climactic: difference and examples, you may also like, mla works cited page: format, template & examples, how to ace grant writing for research funding..., powerful academic phrases to improve your essay writing , how to write a high-quality conference paper, how paperpal is enhancing academic productivity and accelerating..., academic editing: how to self-edit academic text with..., 4 ways paperpal encourages responsible writing with ai, what are scholarly sources and where can you..., how to write a hypothesis types and examples , what is academic writing: tips for students.
What Is Research Methodology? A Plain-Language Explanation & Definition (With Examples)
By Derek Jansen (MBA) and Kerryn Warren (PhD) | June 2020 (Last updated April 2023)
If you’re new to formal academic research, it’s quite likely that you’re feeling a little overwhelmed by all the technical lingo that gets thrown around. And who could blame you – “research methodology”, “research methods”, “sampling strategies”… it all seems never-ending!
In this post, we’ll demystify the landscape with plain-language explanations and loads of examples (including easy-to-follow videos), so that you can approach your dissertation, thesis or research project with confidence. Let’s get started.
Research Methodology 101
- What exactly research methodology means
- What qualitative , quantitative and mixed methods are
- What sampling strategy is
- What data collection methods are
- What data analysis methods are
- How to choose your research methodology
- Example of a research methodology

What is research methodology?
Research methodology simply refers to the practical “how” of a research study. More specifically, it’s about how a researcher systematically designs a study to ensure valid and reliable results that address the research aims, objectives and research questions . Specifically, how the researcher went about deciding:
- What type of data to collect (e.g., qualitative or quantitative data )
- Who to collect it from (i.e., the sampling strategy )
- How to collect it (i.e., the data collection method )
- How to analyse it (i.e., the data analysis methods )
Within any formal piece of academic research (be it a dissertation, thesis or journal article), you’ll find a research methodology chapter or section which covers the aspects mentioned above. Importantly, a good methodology chapter explains not just what methodological choices were made, but also explains why they were made. In other words, the methodology chapter should justify the design choices, by showing that the chosen methods and techniques are the best fit for the research aims, objectives and research questions.
So, it’s the same as research design?
Not quite. As we mentioned, research methodology refers to the collection of practical decisions regarding what data you’ll collect, from who, how you’ll collect it and how you’ll analyse it. Research design, on the other hand, is more about the overall strategy you’ll adopt in your study. For example, whether you’ll use an experimental design in which you manipulate one variable while controlling others. You can learn more about research design and the various design types here .
Need a helping hand?
What are qualitative, quantitative and mixed-methods?
Qualitative, quantitative and mixed-methods are different types of methodological approaches, distinguished by their focus on words , numbers or both . This is a bit of an oversimplification, but its a good starting point for understanding.
Let’s take a closer look.
Qualitative research refers to research which focuses on collecting and analysing words (written or spoken) and textual or visual data, whereas quantitative research focuses on measurement and testing using numerical data . Qualitative analysis can also focus on other “softer” data points, such as body language or visual elements.
It’s quite common for a qualitative methodology to be used when the research aims and research questions are exploratory in nature. For example, a qualitative methodology might be used to understand peoples’ perceptions about an event that took place, or a political candidate running for president.
Contrasted to this, a quantitative methodology is typically used when the research aims and research questions are confirmatory in nature. For example, a quantitative methodology might be used to measure the relationship between two variables (e.g. personality type and likelihood to commit a crime) or to test a set of hypotheses .
As you’ve probably guessed, the mixed-method methodology attempts to combine the best of both qualitative and quantitative methodologies to integrate perspectives and create a rich picture. If you’d like to learn more about these three methodological approaches, be sure to watch our explainer video below.
What is sampling strategy?
Simply put, sampling is about deciding who (or where) you’re going to collect your data from . Why does this matter? Well, generally it’s not possible to collect data from every single person in your group of interest (this is called the “population”), so you’ll need to engage a smaller portion of that group that’s accessible and manageable (this is called the “sample”).
How you go about selecting the sample (i.e., your sampling strategy) will have a major impact on your study. There are many different sampling methods you can choose from, but the two overarching categories are probability sampling and non-probability sampling .
Probability sampling involves using a completely random sample from the group of people you’re interested in. This is comparable to throwing the names all potential participants into a hat, shaking it up, and picking out the “winners”. By using a completely random sample, you’ll minimise the risk of selection bias and the results of your study will be more generalisable to the entire population.
Non-probability sampling , on the other hand, doesn’t use a random sample . For example, it might involve using a convenience sample, which means you’d only interview or survey people that you have access to (perhaps your friends, family or work colleagues), rather than a truly random sample. With non-probability sampling, the results are typically not generalisable .
To learn more about sampling methods, be sure to check out the video below.
What are data collection methods?
As the name suggests, data collection methods simply refers to the way in which you go about collecting the data for your study. Some of the most common data collection methods include:
- Interviews (which can be unstructured, semi-structured or structured)
- Focus groups and group interviews
- Surveys (online or physical surveys)
- Observations (watching and recording activities)
- Biophysical measurements (e.g., blood pressure, heart rate, etc.)
- Documents and records (e.g., financial reports, court records, etc.)
The choice of which data collection method to use depends on your overall research aims and research questions , as well as practicalities and resource constraints. For example, if your research is exploratory in nature, qualitative methods such as interviews and focus groups would likely be a good fit. Conversely, if your research aims to measure specific variables or test hypotheses, large-scale surveys that produce large volumes of numerical data would likely be a better fit.
What are data analysis methods?
Data analysis methods refer to the methods and techniques that you’ll use to make sense of your data. These can be grouped according to whether the research is qualitative (words-based) or quantitative (numbers-based).
Popular data analysis methods in qualitative research include:
- Qualitative content analysis
- Thematic analysis
- Discourse analysis
- Narrative analysis
- Interpretative phenomenological analysis (IPA)
- Visual analysis (of photographs, videos, art, etc.)
Qualitative data analysis all begins with data coding , after which an analysis method is applied. In some cases, more than one analysis method is used, depending on the research aims and research questions . In the video below, we explore some common qualitative analysis methods, along with practical examples.
Moving on to the quantitative side of things, popular data analysis methods in this type of research include:
- Descriptive statistics (e.g. means, medians, modes )
- Inferential statistics (e.g. correlation, regression, structural equation modelling)
Again, the choice of which data collection method to use depends on your overall research aims and objectives , as well as practicalities and resource constraints. In the video below, we explain some core concepts central to quantitative analysis.
How do I choose a research methodology?
As you’ve probably picked up by now, your research aims and objectives have a major influence on the research methodology . So, the starting point for developing your research methodology is to take a step back and look at the big picture of your research, before you make methodology decisions. The first question you need to ask yourself is whether your research is exploratory or confirmatory in nature.
If your research aims and objectives are primarily exploratory in nature, your research will likely be qualitative and therefore you might consider qualitative data collection methods (e.g. interviews) and analysis methods (e.g. qualitative content analysis).
Conversely, if your research aims and objective are looking to measure or test something (i.e. they’re confirmatory), then your research will quite likely be quantitative in nature, and you might consider quantitative data collection methods (e.g. surveys) and analyses (e.g. statistical analysis).
Designing your research and working out your methodology is a large topic, which we cover extensively on the blog . For now, however, the key takeaway is that you should always start with your research aims, objectives and research questions (the golden thread). Every methodological choice you make needs align with those three components.
Example of a research methodology chapter
In the video below, we provide a detailed walkthrough of a research methodology from an actual dissertation, as well as an overview of our free methodology template .

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
You Might Also Like:

199 Comments
Thank you for this simple yet comprehensive and easy to digest presentation. God Bless!
You’re most welcome, Leo. Best of luck with your research!
I found it very useful. many thanks
This is really directional. A make-easy research knowledge.
Thank you for this, I think will help my research proposal
Thanks for good interpretation,well understood.
Good morning sorry I want to the search topic
Thank u more
Thank you, your explanation is simple and very helpful.
Very educative a.nd exciting platform. A bigger thank you and I’ll like to always be with you
That’s the best analysis
So simple yet so insightful. Thank you.
This really easy to read as it is self-explanatory. Very much appreciated…
Thanks for this. It’s so helpful and explicit. For those elements highlighted in orange, they were good sources of referrals for concepts I didn’t understand. A million thanks for this.
Good morning, I have been reading your research lessons through out a period of times. They are important, impressive and clear. Want to subscribe and be and be active with you.
Thankyou So much Sir Derek…
Good morning thanks so much for the on line lectures am a student of university of Makeni.select a research topic and deliberate on it so that we’ll continue to understand more.sorry that’s a suggestion.
Beautiful presentation. I love it.
please provide a research mehodology example for zoology
It’s very educative and well explained
Thanks for the concise and informative data.
This is really good for students to be safe and well understand that research is all about
Thank you so much Derek sir🖤🙏🤗
Very simple and reliable
This is really helpful. Thanks alot. God bless you.
very useful, Thank you very much..
thanks a lot its really useful
in a nutshell..thank you!
Thanks for updating my understanding on this aspect of my Thesis writing.
thank you so much my through this video am competently going to do a good job my thesis
Thanks a lot. Very simple to understand. I appreciate 🙏
Very simple but yet insightful Thank you
This has been an eye opening experience. Thank you grad coach team.
Very useful message for research scholars
Really very helpful thank you
yes you are right and i’m left
Research methodology with a simplest way i have never seen before this article.
wow thank u so much
Good morning thanks so much for the on line lectures am a student of university of Makeni.select a research topic and deliberate on is so that we will continue to understand more.sorry that’s a suggestion.
Very precise and informative.
Thanks for simplifying these terms for us, really appreciate it.
Thanks this has really helped me. It is very easy to understand.
I found the notes and the presentation assisting and opening my understanding on research methodology
Good presentation
Im so glad you clarified my misconceptions. Im now ready to fry my onions. Thank you so much. God bless
Thank you a lot.
thanks for the easy way of learning and desirable presentation.
Thanks a lot. I am inspired
Well written
I am writing a APA Format paper . I using questionnaire with 120 STDs teacher for my participant. Can you write me mthology for this research. Send it through email sent. Just need a sample as an example please. My topic is ” impacts of overcrowding on students learning
Thanks for your comment.
We can’t write your methodology for you. If you’re looking for samples, you should be able to find some sample methodologies on Google. Alternatively, you can download some previous dissertations from a dissertation directory and have a look at the methodology chapters therein.
All the best with your research.
Thank you so much for this!! God Bless
Thank you. Explicit explanation
Thank you, Derek and Kerryn, for making this simple to understand. I’m currently at the inception stage of my research.
Thnks a lot , this was very usefull on my assignment
excellent explanation
I’m currently working on my master’s thesis, thanks for this! I’m certain that I will use Qualitative methodology.
Thanks a lot for this concise piece, it was quite relieving and helpful. God bless you BIG…
I am currently doing my dissertation proposal and I am sure that I will do quantitative research. Thank you very much it was extremely helpful.
Very interesting and informative yet I would like to know about examples of Research Questions as well, if possible.
I’m about to submit a research presentation, I have come to understand from your simplification on understanding research methodology. My research will be mixed methodology, qualitative as well as quantitative. So aim and objective of mixed method would be both exploratory and confirmatory. Thanks you very much for your guidance.
OMG thanks for that, you’re a life saver. You covered all the points I needed. Thank you so much ❤️ ❤️ ❤️
Thank you immensely for this simple, easy to comprehend explanation of data collection methods. I have been stuck here for months 😩. Glad I found your piece. Super insightful.
I’m going to write synopsis which will be quantitative research method and I don’t know how to frame my topic, can I kindly get some ideas..
Thanks for this, I was really struggling.
This was really informative I was struggling but this helped me.
Thanks a lot for this information, simple and straightforward. I’m a last year student from the University of South Africa UNISA South Africa.
its very much informative and understandable. I have enlightened.
An interesting nice exploration of a topic.
Thank you. Accurate and simple🥰
This article was really helpful, it helped me understanding the basic concepts of the topic Research Methodology. The examples were very clear, and easy to understand. I would like to visit this website again. Thank you so much for such a great explanation of the subject.
Thanks dude
Thank you Doctor Derek for this wonderful piece, please help to provide your details for reference purpose. God bless.
Many compliments to you
Great work , thank you very much for the simple explanation
Thank you. I had to give a presentation on this topic. I have looked everywhere on the internet but this is the best and simple explanation.
thank you, its very informative.
Well explained. Now I know my research methodology will be qualitative and exploratory. Thank you so much, keep up the good work
Well explained, thank you very much.
This is good explanation, I have understood the different methods of research. Thanks a lot.
Great work…very well explanation
Thanks Derek. Kerryn was just fantastic!
Great to hear that, Hyacinth. Best of luck with your research!
Its a good templates very attractive and important to PhD students and lectuter
Thanks for the feedback, Matobela. Good luck with your research methodology.
Thank you. This is really helpful.
You’re very welcome, Elie. Good luck with your research methodology.
Well explained thanks
This is a very helpful site especially for young researchers at college. It provides sufficient information to guide students and equip them with the necessary foundation to ask any other questions aimed at deepening their understanding.
Thanks for the kind words, Edward. Good luck with your research!
Thank you. I have learned a lot.
Great to hear that, Ngwisa. Good luck with your research methodology!
Thank you for keeping your presentation simples and short and covering key information for research methodology. My key takeaway: Start with defining your research objective the other will depend on the aims of your research question.
My name is Zanele I would like to be assisted with my research , and the topic is shortage of nursing staff globally want are the causes , effects on health, patients and community and also globally
Thanks for making it simple and clear. It greatly helped in understanding research methodology. Regards.
This is well simplified and straight to the point
Thank you Dr
I was given an assignment to research 2 publications and describe their research methodology? I don’t know how to start this task can someone help me?
Sure. You’re welcome to book an initial consultation with one of our Research Coaches to discuss how we can assist – https://gradcoach.com/book/new/ .
Thanks a lot I am relieved of a heavy burden.keep up with the good work
I’m very much grateful Dr Derek. I’m planning to pursue one of the careers that really needs one to be very much eager to know. There’s a lot of research to do and everything, but since I’ve gotten this information I will use it to the best of my potential.
Thank you so much, words are not enough to explain how helpful this session has been for me!
Thanks this has thought me alot.
Very concise and helpful. Thanks a lot
Thank Derek. This is very helpful. Your step by step explanation has made it easier for me to understand different concepts. Now i can get on with my research.
I wish i had come across this sooner. So simple but yet insightful
really nice explanation thank you so much
I’m so grateful finding this site, it’s really helpful…….every term well explained and provide accurate understanding especially to student going into an in-depth research for the very first time, even though my lecturer already explained this topic to the class, I think I got the clear and efficient explanation here, much thanks to the author.
It is very helpful material
I would like to be assisted with my research topic : Literature Review and research methodologies. My topic is : what is the relationship between unemployment and economic growth?
Its really nice and good for us.
THANKS SO MUCH FOR EXPLANATION, ITS VERY CLEAR TO ME WHAT I WILL BE DOING FROM NOW .GREAT READS.
Short but sweet.Thank you
Informative article. Thanks for your detailed information.
I’m currently working on my Ph.D. thesis. Thanks a lot, Derek and Kerryn, Well-organized sequences, facilitate the readers’ following.
great article for someone who does not have any background can even understand
I am a bit confused about research design and methodology. Are they the same? If not, what are the differences and how are they related?
Thanks in advance.
concise and informative.
Thank you very much
How can we site this article is Harvard style?
Very well written piece that afforded better understanding of the concept. Thank you!
Am a new researcher trying to learn how best to write a research proposal. I find your article spot on and want to download the free template but finding difficulties. Can u kindly send it to my email, the free download entitled, “Free Download: Research Proposal Template (with Examples)”.
Thank too much
Thank you very much for your comprehensive explanation about research methodology so I like to thank you again for giving us such great things.
Good very well explained.Thanks for sharing it.
Thank u sir, it is really a good guideline.
so helpful thank you very much.
Thanks for the video it was very explanatory and detailed, easy to comprehend and follow up. please, keep it up the good work
It was very helpful, a well-written document with precise information.
how do i reference this?
MLA Jansen, Derek, and Kerryn Warren. “What (Exactly) Is Research Methodology?” Grad Coach, June 2021, gradcoach.com/what-is-research-methodology/.
APA Jansen, D., & Warren, K. (2021, June). What (Exactly) Is Research Methodology? Grad Coach. https://gradcoach.com/what-is-research-methodology/
Your explanation is easily understood. Thank you
Very help article. Now I can go my methodology chapter in my thesis with ease
I feel guided ,Thank you
This simplification is very helpful. It is simple but very educative, thanks ever so much
The write up is informative and educative. It is an academic intellectual representation that every good researcher can find useful. Thanks
Wow, this is wonderful long live.
Nice initiative
thank you the video was helpful to me.
Thank you very much for your simple and clear explanations I’m really satisfied by the way you did it By now, I think I can realize a very good article by following your fastidious indications May God bless you
Thanks very much, it was very concise and informational for a beginner like me to gain an insight into what i am about to undertake. I really appreciate.
very informative sir, it is amazing to understand the meaning of question hidden behind that, and simple language is used other than legislature to understand easily. stay happy.
This one is really amazing. All content in your youtube channel is a very helpful guide for doing research. Thanks, GradCoach.
research methodologies
Please send me more information concerning dissertation research.
Nice piece of knowledge shared….. #Thump_UP
This is amazing, it has said it all. Thanks to Gradcoach
This is wonderful,very elaborate and clear.I hope to reach out for your assistance in my research very soon.
This is the answer I am searching about…
realy thanks a lot
Thank you very much for this awesome, to the point and inclusive article.
Thank you very much I need validity and reliability explanation I have exams
Thank you for a well explained piece. This will help me going forward.
Very simple and well detailed Many thanks
This is so very simple yet so very effective and comprehensive. An Excellent piece of work.
I wish I saw this earlier on! Great insights for a beginner(researcher) like me. Thanks a mil!
Thank you very much, for such a simplified, clear and practical step by step both for academic students and general research work. Holistic, effective to use and easy to read step by step. One can easily apply the steps in practical terms and produce a quality document/up-to standard
Thanks for simplifying these terms for us, really appreciated.
Thanks for a great work. well understood .
This was very helpful. It was simple but profound and very easy to understand. Thank you so much!
Great and amazing research guidelines. Best site for learning research
hello sir/ma’am, i didn’t find yet that what type of research methodology i am using. because i am writing my report on CSR and collect all my data from websites and articles so which type of methodology i should write in dissertation report. please help me. i am from India.
how does this really work?
perfect content, thanks a lot
As a researcher, I commend you for the detailed and simplified information on the topic in question. I would like to remain in touch for the sharing of research ideas on other topics. Thank you
Impressive. Thank you, Grad Coach 😍
Thank you Grad Coach for this piece of information. I have at least learned about the different types of research methodologies.
Very useful content with easy way
Thank you very much for the presentation. I am an MPH student with the Adventist University of Africa. I have successfully completed my theory and starting on my research this July. My topic is “Factors associated with Dental Caries in (one District) in Botswana. I need help on how to go about this quantitative research
I am so grateful to run across something that was sooo helpful. I have been on my doctorate journey for quite some time. Your breakdown on methodology helped me to refresh my intent. Thank you.
thanks so much for this good lecture. student from university of science and technology, Wudil. Kano Nigeria.
It’s profound easy to understand I appreciate
Thanks a lot for sharing superb information in a detailed but concise manner. It was really helpful and helped a lot in getting into my own research methodology.
Comment * thanks very much
This was sooo helpful for me thank you so much i didn’t even know what i had to write thank you!
You’re most welcome 🙂
Simple and good. Very much helpful. Thank you so much.
This is very good work. I have benefited.
Thank you so much for sharing
This is powerful thank you so much guys
I am nkasa lizwi doing my research proposal on honors with the university of Walter Sisulu Komani I m on part 3 now can you assist me.my topic is: transitional challenges faced by educators in intermediate phase in the Alfred Nzo District.
Appreciate the presentation. Very useful step-by-step guidelines to follow.
I appreciate sir
wow! This is super insightful for me. Thank you!
Indeed this material is very helpful! Kudos writers/authors.
I want to say thank you very much, I got a lot of info and knowledge. Be blessed.
I want present a seminar paper on Optimisation of Deep learning-based models on vulnerability detection in digital transactions.
Need assistance
Dear Sir, I want to be assisted on my research on Sanitation and Water management in emergencies areas.
I am deeply grateful for the knowledge gained. I will be getting in touch shortly as I want to be assisted in my ongoing research.
The information shared is informative, crisp and clear. Kudos Team! And thanks a lot!
hello i want to study
Hello!! Grad coach teams. I am extremely happy in your tutorial or consultation. i am really benefited all material and briefing. Thank you very much for your generous helps. Please keep it up. If you add in your briefing, references for further reading, it will be very nice.
All I have to say is, thank u gyz.
Good, l thanks
thank you, it is very useful
Trackbacks/Pingbacks
- What Is A Literature Review (In A Dissertation Or Thesis) - Grad Coach - […] the literature review is to inform the choice of methodology for your own research. As we’ve discussed on the Grad Coach blog,…
- Free Download: Research Proposal Template (With Examples) - Grad Coach - […] Research design (methodology) […]
- Dissertation vs Thesis: What's the difference? - Grad Coach - […] and thesis writing on a daily basis – everything from how to find a good research topic to which…
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
Reference management. Clean and simple.
What is research methodology?

The basics of research methodology
Why do you need a research methodology, what needs to be included, why do you need to document your research method, what are the different types of research instruments, qualitative / quantitative / mixed research methodologies, how do you choose the best research methodology for you, frequently asked questions about research methodology, related articles.
When you’re working on your first piece of academic research, there are many different things to focus on, and it can be overwhelming to stay on top of everything. This is especially true of budding or inexperienced researchers.
If you’ve never put together a research proposal before or find yourself in a position where you need to explain your research methodology decisions, there are a few things you need to be aware of.
Once you understand the ins and outs, handling academic research in the future will be less intimidating. We break down the basics below:
A research methodology encompasses the way in which you intend to carry out your research. This includes how you plan to tackle things like collection methods, statistical analysis, participant observations, and more.
You can think of your research methodology as being a formula. One part will be how you plan on putting your research into practice, and another will be why you feel this is the best way to approach it. Your research methodology is ultimately a methodological and systematic plan to resolve your research problem.
In short, you are explaining how you will take your idea and turn it into a study, which in turn will produce valid and reliable results that are in accordance with the aims and objectives of your research. This is true whether your paper plans to make use of qualitative methods or quantitative methods.
The purpose of a research methodology is to explain the reasoning behind your approach to your research - you'll need to support your collection methods, methods of analysis, and other key points of your work.
Think of it like writing a plan or an outline for you what you intend to do.
When carrying out research, it can be easy to go off-track or depart from your standard methodology.
Tip: Having a methodology keeps you accountable and on track with your original aims and objectives, and gives you a suitable and sound plan to keep your project manageable, smooth, and effective.
With all that said, how do you write out your standard approach to a research methodology?
As a general plan, your methodology should include the following information:
- Your research method. You need to state whether you plan to use quantitative analysis, qualitative analysis, or mixed-method research methods. This will often be determined by what you hope to achieve with your research.
- Explain your reasoning. Why are you taking this methodological approach? Why is this particular methodology the best way to answer your research problem and achieve your objectives?
- Explain your instruments. This will mainly be about your collection methods. There are varying instruments to use such as interviews, physical surveys, questionnaires, for example. Your methodology will need to detail your reasoning in choosing a particular instrument for your research.
- What will you do with your results? How are you going to analyze the data once you have gathered it?
- Advise your reader. If there is anything in your research methodology that your reader might be unfamiliar with, you should explain it in more detail. For example, you should give any background information to your methods that might be relevant or provide your reasoning if you are conducting your research in a non-standard way.
- How will your sampling process go? What will your sampling procedure be and why? For example, if you will collect data by carrying out semi-structured or unstructured interviews, how will you choose your interviewees and how will you conduct the interviews themselves?
- Any practical limitations? You should discuss any limitations you foresee being an issue when you’re carrying out your research.
In any dissertation, thesis, or academic journal, you will always find a chapter dedicated to explaining the research methodology of the person who carried out the study, also referred to as the methodology section of the work.
A good research methodology will explain what you are going to do and why, while a poor methodology will lead to a messy or disorganized approach.
You should also be able to justify in this section your reasoning for why you intend to carry out your research in a particular way, especially if it might be a particularly unique method.
Having a sound methodology in place can also help you with the following:
- When another researcher at a later date wishes to try and replicate your research, they will need your explanations and guidelines.
- In the event that you receive any criticism or questioning on the research you carried out at a later point, you will be able to refer back to it and succinctly explain the how and why of your approach.
- It provides you with a plan to follow throughout your research. When you are drafting your methodology approach, you need to be sure that the method you are using is the right one for your goal. This will help you with both explaining and understanding your method.
- It affords you the opportunity to document from the outset what you intend to achieve with your research, from start to finish.
A research instrument is a tool you will use to help you collect, measure and analyze the data you use as part of your research.
The choice of research instrument will usually be yours to make as the researcher and will be whichever best suits your methodology.
There are many different research instruments you can use in collecting data for your research.
Generally, they can be grouped as follows:
- Interviews (either as a group or one-on-one). You can carry out interviews in many different ways. For example, your interview can be structured, semi-structured, or unstructured. The difference between them is how formal the set of questions is that is asked of the interviewee. In a group interview, you may choose to ask the interviewees to give you their opinions or perceptions on certain topics.
- Surveys (online or in-person). In survey research, you are posing questions in which you ask for a response from the person taking the survey. You may wish to have either free-answer questions such as essay-style questions, or you may wish to use closed questions such as multiple choice. You may even wish to make the survey a mixture of both.
- Focus Groups. Similar to the group interview above, you may wish to ask a focus group to discuss a particular topic or opinion while you make a note of the answers given.
- Observations. This is a good research instrument to use if you are looking into human behaviors. Different ways of researching this include studying the spontaneous behavior of participants in their everyday life, or something more structured. A structured observation is research conducted at a set time and place where researchers observe behavior as planned and agreed upon with participants.
These are the most common ways of carrying out research, but it is really dependent on your needs as a researcher and what approach you think is best to take.
It is also possible to combine a number of research instruments if this is necessary and appropriate in answering your research problem.
There are three different types of methodologies, and they are distinguished by whether they focus on words, numbers, or both.
➡️ Want to learn more about the differences between qualitative and quantitative research, and how to use both methods? Check out our guide for that!
If you've done your due diligence, you'll have an idea of which methodology approach is best suited to your research.
It’s likely that you will have carried out considerable reading and homework before you reach this point and you may have taken inspiration from other similar studies that have yielded good results.
Still, it is important to consider different options before setting your research in stone. Exploring different options available will help you to explain why the choice you ultimately make is preferable to other methods.
If proving your research problem requires you to gather large volumes of numerical data to test hypotheses, a quantitative research method is likely to provide you with the most usable results.
If instead you’re looking to try and learn more about people, and their perception of events, your methodology is more exploratory in nature and would therefore probably be better served using a qualitative research methodology.
It helps to always bring things back to the question: what do I want to achieve with my research?
Once you have conducted your research, you need to analyze it. Here are some helpful guides for qualitative data analysis:
➡️ How to do a content analysis
➡️ How to do a thematic analysis
➡️ How to do a rhetorical analysis
Research methodology refers to the techniques used to find and analyze information for a study, ensuring that the results are valid, reliable and that they address the research objective.
Data can typically be organized into four different categories or methods: observational, experimental, simulation, and derived.
Writing a methodology section is a process of introducing your methods and instruments, discussing your analysis, providing more background information, addressing your research limitations, and more.
Your research methodology section will need a clear research question and proposed research approach. You'll need to add a background, introduce your research question, write your methodology and add the works you cited during your data collecting phase.
The research methodology section of your study will indicate how valid your findings are and how well-informed your paper is. It also assists future researchers planning to use the same methodology, who want to cite your study or replicate it.

- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- 6. The Methodology
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Applying Critical Thinking
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
The methods section describes actions taken to investigate a research problem and the rationale for the application of specific procedures or techniques used to identify, select, process, and analyze information applied to understanding the problem, thereby, allowing the reader to critically evaluate a study’s overall validity and reliability. The methodology section of a research paper answers two main questions: How was the data collected or generated? And, how was it analyzed? The writing should be direct and precise and always written in the past tense.
Kallet, Richard H. "How to Write the Methods Section of a Research Paper." Respiratory Care 49 (October 2004): 1229-1232.
Importance of a Good Methodology Section
You must explain how you obtained and analyzed your results for the following reasons:
- Readers need to know how the data was obtained because the method you chose affects the results and, by extension, how you interpreted their significance in the discussion section of your paper.
- Methodology is crucial for any branch of scholarship because an unreliable method produces unreliable results and, as a consequence, undermines the value of your analysis of the findings.
- In most cases, there are a variety of different methods you can choose to investigate a research problem. The methodology section of your paper should clearly articulate the reasons why you have chosen a particular procedure or technique.
- The reader wants to know that the data was collected or generated in a way that is consistent with accepted practice in the field of study. For example, if you are using a multiple choice questionnaire, readers need to know that it offered your respondents a reasonable range of answers to choose from.
- The method must be appropriate to fulfilling the overall aims of the study. For example, you need to ensure that you have a large enough sample size to be able to generalize and make recommendations based upon the findings.
- The methodology should discuss the problems that were anticipated and the steps you took to prevent them from occurring. For any problems that do arise, you must describe the ways in which they were minimized or why these problems do not impact in any meaningful way your interpretation of the findings.
- In the social and behavioral sciences, it is important to always provide sufficient information to allow other researchers to adopt or replicate your methodology. This information is particularly important when a new method has been developed or an innovative use of an existing method is utilized.
Bem, Daryl J. Writing the Empirical Journal Article. Psychology Writing Center. University of Washington; Denscombe, Martyn. The Good Research Guide: For Small-Scale Social Research Projects . 5th edition. Buckingham, UK: Open University Press, 2014; Lunenburg, Frederick C. Writing a Successful Thesis or Dissertation: Tips and Strategies for Students in the Social and Behavioral Sciences . Thousand Oaks, CA: Corwin Press, 2008.
Structure and Writing Style
I. Groups of Research Methods
There are two main groups of research methods in the social sciences:
- The e mpirical-analytical group approaches the study of social sciences in a similar manner that researchers study the natural sciences . This type of research focuses on objective knowledge, research questions that can be answered yes or no, and operational definitions of variables to be measured. The empirical-analytical group employs deductive reasoning that uses existing theory as a foundation for formulating hypotheses that need to be tested. This approach is focused on explanation.
- The i nterpretative group of methods is focused on understanding phenomenon in a comprehensive, holistic way . Interpretive methods focus on analytically disclosing the meaning-making practices of human subjects [the why, how, or by what means people do what they do], while showing how those practices arrange so that it can be used to generate observable outcomes. Interpretive methods allow you to recognize your connection to the phenomena under investigation. However, the interpretative group requires careful examination of variables because it focuses more on subjective knowledge.
II. Content
The introduction to your methodology section should begin by restating the research problem and underlying assumptions underpinning your study. This is followed by situating the methods you used to gather, analyze, and process information within the overall “tradition” of your field of study and within the particular research design you have chosen to study the problem. If the method you choose lies outside of the tradition of your field [i.e., your review of the literature demonstrates that the method is not commonly used], provide a justification for how your choice of methods specifically addresses the research problem in ways that have not been utilized in prior studies.
The remainder of your methodology section should describe the following:
- Decisions made in selecting the data you have analyzed or, in the case of qualitative research, the subjects and research setting you have examined,
- Tools and methods used to identify and collect information, and how you identified relevant variables,
- The ways in which you processed the data and the procedures you used to analyze that data, and
- The specific research tools or strategies that you utilized to study the underlying hypothesis and research questions.
In addition, an effectively written methodology section should:
- Introduce the overall methodological approach for investigating your research problem . Is your study qualitative or quantitative or a combination of both (mixed method)? Are you going to take a special approach, such as action research, or a more neutral stance?
- Indicate how the approach fits the overall research design . Your methods for gathering data should have a clear connection to your research problem. In other words, make sure that your methods will actually address the problem. One of the most common deficiencies found in research papers is that the proposed methodology is not suitable to achieving the stated objective of your paper.
- Describe the specific methods of data collection you are going to use , such as, surveys, interviews, questionnaires, observation, archival research. If you are analyzing existing data, such as a data set or archival documents, describe how it was originally created or gathered and by whom. Also be sure to explain how older data is still relevant to investigating the current research problem.
- Explain how you intend to analyze your results . Will you use statistical analysis? Will you use specific theoretical perspectives to help you analyze a text or explain observed behaviors? Describe how you plan to obtain an accurate assessment of relationships, patterns, trends, distributions, and possible contradictions found in the data.
- Provide background and a rationale for methodologies that are unfamiliar for your readers . Very often in the social sciences, research problems and the methods for investigating them require more explanation/rationale than widely accepted rules governing the natural and physical sciences. Be clear and concise in your explanation.
- Provide a justification for subject selection and sampling procedure . For instance, if you propose to conduct interviews, how do you intend to select the sample population? If you are analyzing texts, which texts have you chosen, and why? If you are using statistics, why is this set of data being used? If other data sources exist, explain why the data you chose is most appropriate to addressing the research problem.
- Provide a justification for case study selection . A common method of analyzing research problems in the social sciences is to analyze specific cases. These can be a person, place, event, phenomenon, or other type of subject of analysis that are either examined as a singular topic of in-depth investigation or multiple topics of investigation studied for the purpose of comparing or contrasting findings. In either method, you should explain why a case or cases were chosen and how they specifically relate to the research problem.
- Describe potential limitations . Are there any practical limitations that could affect your data collection? How will you attempt to control for potential confounding variables and errors? If your methodology may lead to problems you can anticipate, state this openly and show why pursuing this methodology outweighs the risk of these problems cropping up.
NOTE: Once you have written all of the elements of the methods section, subsequent revisions should focus on how to present those elements as clearly and as logically as possibly. The description of how you prepared to study the research problem, how you gathered the data, and the protocol for analyzing the data should be organized chronologically. For clarity, when a large amount of detail must be presented, information should be presented in sub-sections according to topic. If necessary, consider using appendices for raw data.
ANOTHER NOTE: If you are conducting a qualitative analysis of a research problem , the methodology section generally requires a more elaborate description of the methods used as well as an explanation of the processes applied to gathering and analyzing of data than is generally required for studies using quantitative methods. Because you are the primary instrument for generating the data [e.g., through interviews or observations], the process for collecting that data has a significantly greater impact on producing the findings. Therefore, qualitative research requires a more detailed description of the methods used.
YET ANOTHER NOTE: If your study involves interviews, observations, or other qualitative techniques involving human subjects , you may be required to obtain approval from the university's Office for the Protection of Research Subjects before beginning your research. This is not a common procedure for most undergraduate level student research assignments. However, i f your professor states you need approval, you must include a statement in your methods section that you received official endorsement and adequate informed consent from the office and that there was a clear assessment and minimization of risks to participants and to the university. This statement informs the reader that your study was conducted in an ethical and responsible manner. In some cases, the approval notice is included as an appendix to your paper.
III. Problems to Avoid
Irrelevant Detail The methodology section of your paper should be thorough but concise. Do not provide any background information that does not directly help the reader understand why a particular method was chosen, how the data was gathered or obtained, and how the data was analyzed in relation to the research problem [note: analyzed, not interpreted! Save how you interpreted the findings for the discussion section]. With this in mind, the page length of your methods section will generally be less than any other section of your paper except the conclusion.
Unnecessary Explanation of Basic Procedures Remember that you are not writing a how-to guide about a particular method. You should make the assumption that readers possess a basic understanding of how to investigate the research problem on their own and, therefore, you do not have to go into great detail about specific methodological procedures. The focus should be on how you applied a method , not on the mechanics of doing a method. An exception to this rule is if you select an unconventional methodological approach; if this is the case, be sure to explain why this approach was chosen and how it enhances the overall process of discovery.
Problem Blindness It is almost a given that you will encounter problems when collecting or generating your data, or, gaps will exist in existing data or archival materials. Do not ignore these problems or pretend they did not occur. Often, documenting how you overcame obstacles can form an interesting part of the methodology. It demonstrates to the reader that you can provide a cogent rationale for the decisions you made to minimize the impact of any problems that arose.
Literature Review Just as the literature review section of your paper provides an overview of sources you have examined while researching a particular topic, the methodology section should cite any sources that informed your choice and application of a particular method [i.e., the choice of a survey should include any citations to the works you used to help construct the survey].
It’s More than Sources of Information! A description of a research study's method should not be confused with a description of the sources of information. Such a list of sources is useful in and of itself, especially if it is accompanied by an explanation about the selection and use of the sources. The description of the project's methodology complements a list of sources in that it sets forth the organization and interpretation of information emanating from those sources.
Azevedo, L.F. et al. "How to Write a Scientific Paper: Writing the Methods Section." Revista Portuguesa de Pneumologia 17 (2011): 232-238; Blair Lorrie. “Choosing a Methodology.” In Writing a Graduate Thesis or Dissertation , Teaching Writing Series. (Rotterdam: Sense Publishers 2016), pp. 49-72; Butin, Dan W. The Education Dissertation A Guide for Practitioner Scholars . Thousand Oaks, CA: Corwin, 2010; Carter, Susan. Structuring Your Research Thesis . New York: Palgrave Macmillan, 2012; Kallet, Richard H. “How to Write the Methods Section of a Research Paper.” Respiratory Care 49 (October 2004):1229-1232; Lunenburg, Frederick C. Writing a Successful Thesis or Dissertation: Tips and Strategies for Students in the Social and Behavioral Sciences . Thousand Oaks, CA: Corwin Press, 2008. Methods Section. The Writer’s Handbook. Writing Center. University of Wisconsin, Madison; Rudestam, Kjell Erik and Rae R. Newton. “The Method Chapter: Describing Your Research Plan.” In Surviving Your Dissertation: A Comprehensive Guide to Content and Process . (Thousand Oaks, Sage Publications, 2015), pp. 87-115; What is Interpretive Research. Institute of Public and International Affairs, University of Utah; Writing the Experimental Report: Methods, Results, and Discussion. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Methods and Materials. The Structure, Format, Content, and Style of a Journal-Style Scientific Paper. Department of Biology. Bates College.
Writing Tip
Statistical Designs and Tests? Do Not Fear Them!
Don't avoid using a quantitative approach to analyzing your research problem just because you fear the idea of applying statistical designs and tests. A qualitative approach, such as conducting interviews or content analysis of archival texts, can yield exciting new insights about a research problem, but it should not be undertaken simply because you have a disdain for running a simple regression. A well designed quantitative research study can often be accomplished in very clear and direct ways, whereas, a similar study of a qualitative nature usually requires considerable time to analyze large volumes of data and a tremendous burden to create new paths for analysis where previously no path associated with your research problem had existed.
To locate data and statistics, GO HERE .
Another Writing Tip
Knowing the Relationship Between Theories and Methods
There can be multiple meaning associated with the term "theories" and the term "methods" in social sciences research. A helpful way to delineate between them is to understand "theories" as representing different ways of characterizing the social world when you research it and "methods" as representing different ways of generating and analyzing data about that social world. Framed in this way, all empirical social sciences research involves theories and methods, whether they are stated explicitly or not. However, while theories and methods are often related, it is important that, as a researcher, you deliberately separate them in order to avoid your theories playing a disproportionate role in shaping what outcomes your chosen methods produce.
Introspectively engage in an ongoing dialectic between the application of theories and methods to help enable you to use the outcomes from your methods to interrogate and develop new theories, or ways of framing conceptually the research problem. This is how scholarship grows and branches out into new intellectual territory.
Reynolds, R. Larry. Ways of Knowing. Alternative Microeconomics . Part 1, Chapter 3. Boise State University; The Theory-Method Relationship. S-Cool Revision. United Kingdom.
Yet Another Writing Tip
Methods and the Methodology
Do not confuse the terms "methods" and "methodology." As Schneider notes, a method refers to the technical steps taken to do research . Descriptions of methods usually include defining and stating why you have chosen specific techniques to investigate a research problem, followed by an outline of the procedures you used to systematically select, gather, and process the data [remember to always save the interpretation of data for the discussion section of your paper].
The methodology refers to a discussion of the underlying reasoning why particular methods were used . This discussion includes describing the theoretical concepts that inform the choice of methods to be applied, placing the choice of methods within the more general nature of academic work, and reviewing its relevance to examining the research problem. The methodology section also includes a thorough review of the methods other scholars have used to study the topic.
Bryman, Alan. "Of Methods and Methodology." Qualitative Research in Organizations and Management: An International Journal 3 (2008): 159-168; Schneider, Florian. “What's in a Methodology: The Difference between Method, Methodology, and Theory…and How to Get the Balance Right?” PoliticsEastAsia.com. Chinese Department, University of Leiden, Netherlands.
- << Previous: Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Next: Qualitative Methods >>
- Last Updated: May 30, 2024 9:38 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide
- How it works
Published by Nicolas at March 21st, 2024 , Revised On March 12, 2024
The Ultimate Guide To Research Methodology
Research methodology is a crucial aspect of any investigative process, serving as the blueprint for the entire research journey. If you are stuck in the methodology section of your research paper , then this blog will guide you on what is a research methodology, its types and how to successfully conduct one.
Table of Contents
What Is Research Methodology?
Research methodology can be defined as the systematic framework that guides researchers in designing, conducting, and analyzing their investigations. It encompasses a structured set of processes, techniques, and tools employed to gather and interpret data, ensuring the reliability and validity of the research findings.
Research methodology is not confined to a singular approach; rather, it encapsulates a diverse range of methods tailored to the specific requirements of the research objectives.
Here is why Research methodology is important in academic and professional settings.
Facilitating Rigorous Inquiry
Research methodology forms the backbone of rigorous inquiry. It provides a structured approach that aids researchers in formulating precise thesis statements , selecting appropriate methodologies, and executing systematic investigations. This, in turn, enhances the quality and credibility of the research outcomes.
Ensuring Reproducibility And Reliability
In both academic and professional contexts, the ability to reproduce research outcomes is paramount. A well-defined research methodology establishes clear procedures, making it possible for others to replicate the study. This not only validates the findings but also contributes to the cumulative nature of knowledge.
Guiding Decision-Making Processes
In professional settings, decisions often hinge on reliable data and insights. Research methodology equips professionals with the tools to gather pertinent information, analyze it rigorously, and derive meaningful conclusions.
This informed decision-making is instrumental in achieving organizational goals and staying ahead in competitive environments.
Contributing To Academic Excellence
For academic researchers, adherence to robust research methodology is a hallmark of excellence. Institutions value research that adheres to high standards of methodology, fostering a culture of academic rigour and intellectual integrity. Furthermore, it prepares students with critical skills applicable beyond academia.
Enhancing Problem-Solving Abilities
Research methodology instills a problem-solving mindset by encouraging researchers to approach challenges systematically. It equips individuals with the skills to dissect complex issues, formulate hypotheses , and devise effective strategies for investigation.
Understanding Research Methodology
In the pursuit of knowledge and discovery, understanding the fundamentals of research methodology is paramount.
Basics Of Research
Research, in its essence, is a systematic and organized process of inquiry aimed at expanding our understanding of a particular subject or phenomenon. It involves the exploration of existing knowledge, the formulation of hypotheses, and the collection and analysis of data to draw meaningful conclusions.
Research is a dynamic and iterative process that contributes to the continuous evolution of knowledge in various disciplines.
Types of Research
Research takes on various forms, each tailored to the nature of the inquiry. Broadly classified, research can be categorized into two main types:
- Quantitative Research: This type involves the collection and analysis of numerical data to identify patterns, relationships, and statistical significance. It is particularly useful for testing hypotheses and making predictions.
- Qualitative Research: Qualitative research focuses on understanding the depth and details of a phenomenon through non-numerical data. It often involves methods such as interviews, focus groups, and content analysis, providing rich insights into complex issues.
Components Of Research Methodology
To conduct effective research, one must go through the different components of research methodology. These components form the scaffolding that supports the entire research process, ensuring its coherence and validity.
Research Design
Research design serves as the blueprint for the entire research project. It outlines the overall structure and strategy for conducting the study. The three primary types of research design are:
- Exploratory Research: Aimed at gaining insights and familiarity with the topic, often used in the early stages of research.
- Descriptive Research: Involves portraying an accurate profile of a situation or phenomenon, answering the ‘what,’ ‘who,’ ‘where,’ and ‘when’ questions.
- Explanatory Research: Seeks to identify the causes and effects of a phenomenon, explaining the ‘why’ and ‘how.’
Data Collection Methods
Choosing the right data collection methods is crucial for obtaining reliable and relevant information. Common methods include:
- Surveys and Questionnaires: Employed to gather information from a large number of respondents through standardized questions.
- Interviews: In-depth conversations with participants, offering qualitative insights.
- Observation: Systematic watching and recording of behaviour, events, or processes in their natural setting.
Data Analysis Techniques
Once data is collected, analysis becomes imperative to derive meaningful conclusions. Different methodologies exist for quantitative and qualitative data:
- Quantitative Data Analysis: Involves statistical techniques such as descriptive statistics, inferential statistics, and regression analysis to interpret numerical data.
- Qualitative Data Analysis: Methods like content analysis, thematic analysis, and grounded theory are employed to extract patterns, themes, and meanings from non-numerical data.
The research paper we write have:
- Precision and Clarity
- Zero Plagiarism
- High-level Encryption
- Authentic Sources
Choosing a Research Method
Selecting an appropriate research method is a critical decision in the research process. It determines the approach, tools, and techniques that will be used to answer the research questions.
Quantitative Research Methods
Quantitative research involves the collection and analysis of numerical data, providing a structured and objective approach to understanding and explaining phenomena.
Experimental Research
Experimental research involves manipulating variables to observe the effect on another variable under controlled conditions. It aims to establish cause-and-effect relationships.
Key Characteristics:
- Controlled Environment: Experiments are conducted in a controlled setting to minimize external influences.
- Random Assignment: Participants are randomly assigned to different experimental conditions.
- Quantitative Data: Data collected is numerical, allowing for statistical analysis.
Applications: Commonly used in scientific studies and psychology to test hypotheses and identify causal relationships.
Survey Research
Survey research gathers information from a sample of individuals through standardized questionnaires or interviews. It aims to collect data on opinions, attitudes, and behaviours.
- Structured Instruments: Surveys use structured instruments, such as questionnaires, to collect data.
- Large Sample Size: Surveys often target a large and diverse group of participants.
- Quantitative Data Analysis: Responses are quantified for statistical analysis.
Applications: Widely employed in social sciences, marketing, and public opinion research to understand trends and preferences.
Descriptive Research
Descriptive research seeks to portray an accurate profile of a situation or phenomenon. It focuses on answering the ‘what,’ ‘who,’ ‘where,’ and ‘when’ questions.
- Observation and Data Collection: This involves observing and documenting without manipulating variables.
- Objective Description: Aim to provide an unbiased and factual account of the subject.
- Quantitative or Qualitative Data: T his can include both types of data, depending on the research focus.
Applications: Useful in situations where researchers want to understand and describe a phenomenon without altering it, common in social sciences and education.
Qualitative Research Methods
Qualitative research emphasizes exploring and understanding the depth and complexity of phenomena through non-numerical data.
A case study is an in-depth exploration of a particular person, group, event, or situation. It involves detailed, context-rich analysis.
- Rich Data Collection: Uses various data sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents.
- Contextual Understanding: Aims to understand the context and unique characteristics of the case.
- Holistic Approach: Examines the case in its entirety.
Applications: Common in social sciences, psychology, and business to investigate complex and specific instances.
Ethnography
Ethnography involves immersing the researcher in the culture or community being studied to gain a deep understanding of their behaviours, beliefs, and practices.
- Participant Observation: Researchers actively participate in the community or setting.
- Holistic Perspective: Focuses on the interconnectedness of cultural elements.
- Qualitative Data: In-depth narratives and descriptions are central to ethnographic studies.
Applications: Widely used in anthropology, sociology, and cultural studies to explore and document cultural practices.
Grounded Theory
Grounded theory aims to develop theories grounded in the data itself. It involves systematic data collection and analysis to construct theories from the ground up.
- Constant Comparison: Data is continually compared and analyzed during the research process.
- Inductive Reasoning: Theories emerge from the data rather than being imposed on it.
- Iterative Process: The research design evolves as the study progresses.
Applications: Commonly applied in sociology, nursing, and management studies to generate theories from empirical data.
Research design is the structural framework that outlines the systematic process and plan for conducting a study. It serves as the blueprint, guiding researchers on how to collect, analyze, and interpret data.
Exploratory, Descriptive, And Explanatory Designs
Exploratory design.
Exploratory research design is employed when a researcher aims to explore a relatively unknown subject or gain insights into a complex phenomenon.
- Flexibility: Allows for flexibility in data collection and analysis.
- Open-Ended Questions: Uses open-ended questions to gather a broad range of information.
- Preliminary Nature: Often used in the initial stages of research to formulate hypotheses.
Applications: Valuable in the early stages of investigation, especially when the researcher seeks a deeper understanding of a subject before formalizing research questions.
Descriptive Design
Descriptive research design focuses on portraying an accurate profile of a situation, group, or phenomenon.
- Structured Data Collection: Involves systematic and structured data collection methods.
- Objective Presentation: Aims to provide an unbiased and factual account of the subject.
- Quantitative or Qualitative Data: Can incorporate both types of data, depending on the research objectives.
Applications: Widely used in social sciences, marketing, and educational research to provide detailed and objective descriptions.
Explanatory Design
Explanatory research design aims to identify the causes and effects of a phenomenon, explaining the ‘why’ and ‘how’ behind observed relationships.
- Causal Relationships: Seeks to establish causal relationships between variables.
- Controlled Variables : Often involves controlling certain variables to isolate causal factors.
- Quantitative Analysis: Primarily relies on quantitative data analysis techniques.
Applications: Commonly employed in scientific studies and social sciences to delve into the underlying reasons behind observed patterns.
Cross-Sectional Vs. Longitudinal Designs
Cross-sectional design.
Cross-sectional designs collect data from participants at a single point in time.
- Snapshot View: Provides a snapshot of a population at a specific moment.
- Efficiency: More efficient in terms of time and resources.
- Limited Temporal Insights: Offers limited insights into changes over time.
Applications: Suitable for studying characteristics or behaviours that are stable or not expected to change rapidly.
Longitudinal Design
Longitudinal designs involve the collection of data from the same participants over an extended period.
- Temporal Sequence: Allows for the examination of changes over time.
- Causality Assessment: Facilitates the assessment of cause-and-effect relationships.
- Resource-Intensive: Requires more time and resources compared to cross-sectional designs.
Applications: Ideal for studying developmental processes, trends, or the impact of interventions over time.
Experimental Vs Non-experimental Designs
Experimental design.
Experimental designs involve manipulating variables under controlled conditions to observe the effect on another variable.
- Causality Inference: Enables the inference of cause-and-effect relationships.
- Quantitative Data: Primarily involves the collection and analysis of numerical data.
Applications: Commonly used in scientific studies, psychology, and medical research to establish causal relationships.
Non-Experimental Design
Non-experimental designs observe and describe phenomena without manipulating variables.
- Natural Settings: Data is often collected in natural settings without intervention.
- Descriptive or Correlational: Focuses on describing relationships or correlations between variables.
- Quantitative or Qualitative Data: This can involve either type of data, depending on the research approach.
Applications: Suitable for studying complex phenomena in real-world settings where manipulation may not be ethical or feasible.
Effective data collection is fundamental to the success of any research endeavour.
Designing Effective Surveys
Objective Design:
- Clearly define the research objectives to guide the survey design.
- Craft questions that align with the study’s goals and avoid ambiguity.
Structured Format:
- Use a structured format with standardized questions for consistency.
- Include a mix of closed-ended and open-ended questions for detailed insights.
Pilot Testing:
- Conduct pilot tests to identify and rectify potential issues with survey design.
- Ensure clarity, relevance, and appropriateness of questions.
Sampling Strategy:
- Develop a robust sampling strategy to ensure a representative participant group.
- Consider random sampling or stratified sampling based on the research goals.
Conducting Interviews
Establishing Rapport:
- Build rapport with participants to create a comfortable and open environment.
- Clearly communicate the purpose of the interview and the value of participants’ input.
Open-Ended Questions:
- Frame open-ended questions to encourage detailed responses.
- Allow participants to express their thoughts and perspectives freely.
Active Listening:
- Practice active listening to understand areas and gather rich data.
- Avoid interrupting and maintain a non-judgmental stance during the interview.
Ethical Considerations:
- Obtain informed consent and assure participants of confidentiality.
- Be transparent about the study’s purpose and potential implications.
Observation
1. participant observation.
Immersive Participation:
- Actively immerse yourself in the setting or group being observed.
- Develop a deep understanding of behaviours, interactions, and context.
Field Notes:
- Maintain detailed and reflective field notes during observations.
- Document observed patterns, unexpected events, and participant reactions.
Ethical Awareness:
- Be conscious of ethical considerations, ensuring respect for participants.
- Balance the role of observer and participant to minimize bias.
2. Non-participant Observation
Objective Observation:
- Maintain a more detached and objective stance during non-participant observation.
- Focus on recording behaviours, events, and patterns without direct involvement.
Data Reliability:
- Enhance the reliability of data by reducing observer bias.
- Develop clear observation protocols and guidelines.
Contextual Understanding:
- Strive for a thorough understanding of the observed context.
- Consider combining non-participant observation with other methods for triangulation.
Archival Research
1. using existing data.
Identifying Relevant Archives:
- Locate and access archives relevant to the research topic.
- Collaborate with institutions or repositories holding valuable data.
Data Verification:
- Verify the accuracy and reliability of archived data.
- Cross-reference with other sources to ensure data integrity.
Ethical Use:
- Adhere to ethical guidelines when using existing data.
- Respect copyright and intellectual property rights.
2. Challenges and Considerations
Incomplete or Inaccurate Archives:
- Address the possibility of incomplete or inaccurate archival records.
- Acknowledge limitations and uncertainties in the data.
Temporal Bias:
- Recognize potential temporal biases in archived data.
- Consider the historical context and changes that may impact interpretation.
Access Limitations:
- Address potential limitations in accessing certain archives.
- Seek alternative sources or collaborate with institutions to overcome barriers.
Common Challenges in Research Methodology
Conducting research is a complex and dynamic process, often accompanied by a myriad of challenges. Addressing these challenges is crucial to ensure the reliability and validity of research findings.
Sampling Issues
Sampling bias:.
- The presence of sampling bias can lead to an unrepresentative sample, affecting the generalizability of findings.
- Employ random sampling methods and ensure the inclusion of diverse participants to reduce bias.
Sample Size Determination:
- Determining an appropriate sample size is a delicate balance. Too small a sample may lack statistical power, while an excessively large sample may strain resources.
- Conduct a power analysis to determine the optimal sample size based on the research objectives and expected effect size.
Data Quality And Validity
Measurement error:.
- Inaccuracies in measurement tools or data collection methods can introduce measurement errors, impacting the validity of results.
- Pilot test instruments, calibrate equipment, and use standardized measures to enhance the reliability of data.
Construct Validity:
- Ensuring that the chosen measures accurately capture the intended constructs is a persistent challenge.
- Use established measurement instruments and employ multiple measures to assess the same construct for triangulation.
Time And Resource Constraints
Timeline pressures:.
- Limited timeframes can compromise the depth and thoroughness of the research process.
- Develop a realistic timeline, prioritize tasks, and communicate expectations with stakeholders to manage time constraints effectively.
Resource Availability:
- Inadequate resources, whether financial or human, can impede the execution of research activities.
- Seek external funding, collaborate with other researchers, and explore alternative methods that require fewer resources.
Managing Bias in Research
Selection bias:.
- Selecting participants in a way that systematically skews the sample can introduce selection bias.
- Employ randomization techniques, use stratified sampling, and transparently report participant recruitment methods.
Confirmation Bias:
- Researchers may unintentionally favour information that confirms their preconceived beliefs or hypotheses.
- Adopt a systematic and open-minded approach, use blinded study designs, and engage in peer review to mitigate confirmation bias.
Tips On How To Write A Research Methodology
Conducting successful research relies not only on the application of sound methodologies but also on strategic planning and effective collaboration. Here are some tips to enhance the success of your research methodology:
Tip 1. Clear Research Objectives
Well-defined research objectives guide the entire research process. Clearly articulate the purpose of your study, outlining specific research questions or hypotheses.
Tip 2. Comprehensive Literature Review
A thorough literature review provides a foundation for understanding existing knowledge and identifying gaps. Invest time in reviewing relevant literature to inform your research design and methodology.
Tip 3. Detailed Research Plan
A detailed plan serves as a roadmap, ensuring all aspects of the research are systematically addressed. Develop a detailed research plan outlining timelines, milestones, and tasks.
Tip 4. Ethical Considerations
Ethical practices are fundamental to maintaining the integrity of research. Address ethical considerations early, obtain necessary approvals, and ensure participant rights are safeguarded.
Tip 5. Stay Updated On Methodologies
Research methodologies evolve, and staying updated is essential for employing the most effective techniques. Engage in continuous learning by attending workshops, conferences, and reading recent publications.
Tip 6. Adaptability In Methods
Unforeseen challenges may arise during research, necessitating adaptability in methods. Be flexible and willing to modify your approach when needed, ensuring the integrity of the study.
Tip 7. Iterative Approach
Research is often an iterative process, and refining methods based on ongoing findings enhance the study’s robustness. Regularly review and refine your research design and methods as the study progresses.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the research methodology.
Research methodology is the systematic process of planning, executing, and evaluating scientific investigation. It encompasses the techniques, tools, and procedures used to collect, analyze, and interpret data, ensuring the reliability and validity of research findings.
What are the methodologies in research?
Research methodologies include qualitative and quantitative approaches. Qualitative methods involve in-depth exploration of non-numerical data, while quantitative methods use statistical analysis to examine numerical data. Mixed methods combine both approaches for a comprehensive understanding of research questions.
How to write research methodology?
To write a research methodology, clearly outline the study’s design, data collection, and analysis procedures. Specify research tools, participants, and sampling methods. Justify choices and discuss limitations. Ensure clarity, coherence, and alignment with research objectives for a robust methodology section.
How to write the methodology section of a research paper?
In the methodology section of a research paper, describe the study’s design, data collection, and analysis methods. Detail procedures, tools, participants, and sampling. Justify choices, address ethical considerations, and explain how the methodology aligns with research objectives, ensuring clarity and rigour.
What is mixed research methodology?
Mixed research methodology combines both qualitative and quantitative research approaches within a single study. This approach aims to enhance the details and depth of research findings by providing a more comprehensive understanding of the research problem or question.
You May Also Like
Discover Canadian doctoral dissertation format: structure, formatting, and word limits. Check your university guidelines.
What is a manuscript? A manuscript is a written or typed document, often the original draft of a book or article, before publication, undergoing editing and revisions.
Academic integrity: a commitment to honesty and ethical conduct in learning. Upholding originality and proper citation are its cornerstones.
Ready to place an order?
USEFUL LINKS
Learning resources, company details.
- How It Works
Automated page speed optimizations for fast site performance
When you choose to publish with PLOS, your research makes an impact. Make your work accessible to all, without restrictions, and accelerate scientific discovery with options like preprints and published peer review that make your work more Open.
- PLOS Biology
- PLOS Climate
- PLOS Complex Systems
- PLOS Computational Biology
- PLOS Digital Health
- PLOS Genetics
- PLOS Global Public Health
- PLOS Medicine
- PLOS Mental Health
- PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases
- PLOS Pathogens
- PLOS Sustainability and Transformation
- PLOS Collections
- How to Write Your Methods

Ensure understanding, reproducibility and replicability
What should you include in your methods section, and how much detail is appropriate?
Why Methods Matter
The methods section was once the most likely part of a paper to be unfairly abbreviated, overly summarized, or even relegated to hard-to-find sections of a publisher’s website. While some journals may responsibly include more detailed elements of methods in supplementary sections, the movement for increased reproducibility and rigor in science has reinstated the importance of the methods section. Methods are now viewed as a key element in establishing the credibility of the research being reported, alongside the open availability of data and results.
A clear methods section impacts editorial evaluation and readers’ understanding, and is also the backbone of transparency and replicability.
For example, the Reproducibility Project: Cancer Biology project set out in 2013 to replicate experiments from 50 high profile cancer papers, but revised their target to 18 papers once they understood how much methodological detail was not contained in the original papers.
What to include in your methods section
What you include in your methods sections depends on what field you are in and what experiments you are performing. However, the general principle in place at the majority of journals is summarized well by the guidelines at PLOS ONE : “The Materials and Methods section should provide enough detail to allow suitably skilled investigators to fully replicate your study. ” The emphases here are deliberate: the methods should enable readers to understand your paper, and replicate your study. However, there is no need to go into the level of detail that a lay-person would require—the focus is on the reader who is also trained in your field, with the suitable skills and knowledge to attempt a replication.
A constant principle of rigorous science
A methods section that enables other researchers to understand and replicate your results is a constant principle of rigorous, transparent, and Open Science. Aim to be thorough, even if a particular journal doesn’t require the same level of detail . Reproducibility is all of our responsibility. You cannot create any problems by exceeding a minimum standard of information. If a journal still has word-limits—either for the overall article or specific sections—and requires some methodological details to be in a supplemental section, that is OK as long as the extra details are searchable and findable .
Imagine replicating your own work, years in the future
As part of PLOS’ presentation on Reproducibility and Open Publishing (part of UCSF’s Reproducibility Series ) we recommend planning the level of detail in your methods section by imagining you are writing for your future self, replicating your own work. When you consider that you might be at a different institution, with different account logins, applications, resources, and access levels—you can help yourself imagine the level of specificity that you yourself would require to redo the exact experiment. Consider:
- Which details would you need to be reminded of?
- Which cell line, or antibody, or software, or reagent did you use, and does it have a Research Resource ID (RRID) that you can cite?
- Which version of a questionnaire did you use in your survey?
- Exactly which visual stimulus did you show participants, and is it publicly available?
- What participants did you decide to exclude?
- What process did you adjust, during your work?
Tip: Be sure to capture any changes to your protocols
You yourself would want to know about any adjustments, if you ever replicate the work, so you can surmise that anyone else would want to as well. Even if a necessary adjustment you made was not ideal, transparency is the key to ensuring this is not regarded as an issue in the future. It is far better to transparently convey any non-optimal methods, or methodological constraints, than to conceal them, which could result in reproducibility or ethical issues downstream.
Visual aids for methods help when reading the whole paper
Consider whether a visual representation of your methods could be appropriate or aid understanding your process. A visual reference readers can easily return to, like a flow-diagram, decision-tree, or checklist, can help readers to better understand the complete article, not just the methods section.
Ethical Considerations
In addition to describing what you did, it is just as important to assure readers that you also followed all relevant ethical guidelines when conducting your research. While ethical standards and reporting guidelines are often presented in a separate section of a paper, ensure that your methods and protocols actually follow these guidelines. Read more about ethics .
Existing standards, checklists, guidelines, partners
While the level of detail contained in a methods section should be guided by the universal principles of rigorous science outlined above, various disciplines, fields, and projects have worked hard to design and develop consistent standards, guidelines, and tools to help with reporting all types of experiment. Below, you’ll find some of the key initiatives. Ensure you read the submission guidelines for the specific journal you are submitting to, in order to discover any further journal- or field-specific policies to follow, or initiatives/tools to utilize.
Tip: Keep your paper moving forward by providing the proper paperwork up front
Be sure to check the journal guidelines and provide the necessary documents with your manuscript submission. Collecting the necessary documentation can greatly slow the first round of peer review, or cause delays when you submit your revision.
Randomized Controlled Trials – CONSORT The Consolidated Standards of Reporting Trials (CONSORT) project covers various initiatives intended to prevent the problems of inadequate reporting of randomized controlled trials. The primary initiative is an evidence-based minimum set of recommendations for reporting randomized trials known as the CONSORT Statement .
Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses – PRISMA The Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses ( PRISMA ) is an evidence-based minimum set of items focusing on the reporting of reviews evaluating randomized trials and other types of research.
Research using Animals – ARRIVE The Animal Research: Reporting of In Vivo Experiments ( ARRIVE ) guidelines encourage maximizing the information reported in research using animals thereby minimizing unnecessary studies. (Original study and proposal , and updated guidelines , in PLOS Biology .)
Laboratory Protocols Protocols.io has developed a platform specifically for the sharing and updating of laboratory protocols , which are assigned their own DOI and can be linked from methods sections of papers to enhance reproducibility. Contextualize your protocol and improve discovery with an accompanying Lab Protocol article in PLOS ONE .
Consistent reporting of Materials, Design, and Analysis – the MDAR checklist A cross-publisher group of editors and experts have developed, tested, and rolled out a checklist to help establish and harmonize reporting standards in the Life Sciences . The checklist , which is available for use by authors to compile their methods, and editors/reviewers to check methods, establishes a minimum set of requirements in transparent reporting and is adaptable to any discipline within the Life Sciences, by covering a breadth of potentially relevant methodological items and considerations. If you are in the Life Sciences and writing up your methods section, try working through the MDAR checklist and see whether it helps you include all relevant details into your methods, and whether it reminded you of anything you might have missed otherwise.
Summary Writing tips
The main challenge you may find when writing your methods is keeping it readable AND covering all the details needed for reproducibility and replicability. While this is difficult, do not compromise on rigorous standards for credibility!

- Keep in mind future replicability, alongside understanding and readability.
- Follow checklists, and field- and journal-specific guidelines.
- Consider a commitment to rigorous and transparent science a personal responsibility, and not just adhering to journal guidelines.
- Establish whether there are persistent identifiers for any research resources you use that can be specifically cited in your methods section.
- Deposit your laboratory protocols in Protocols.io, establishing a permanent link to them. You can update your protocols later if you improve on them, as can future scientists who follow your protocols.
- Consider visual aids like flow-diagrams, lists, to help with reading other sections of the paper.
- Be specific about all decisions made during the experiments that someone reproducing your work would need to know.

Don’t
- Summarize or abbreviate methods without giving full details in a discoverable supplemental section.
- Presume you will always be able to remember how you performed the experiments, or have access to private or institutional notebooks and resources.
- Attempt to hide constraints or non-optimal decisions you had to make–transparency is the key to ensuring the credibility of your research.
- How to Write a Great Title
- How to Write an Abstract
- How to Report Statistics
- How to Write Discussions and Conclusions
- How to Edit Your Work
The contents of the Peer Review Center are also available as a live, interactive training session, complete with slides, talking points, and activities. …
The contents of the Writing Center are also available as a live, interactive training session, complete with slides, talking points, and activities. …
There’s a lot to consider when deciding where to submit your work. Learn how to choose a journal that will help your study reach its audience, while reflecting your values as a researcher…
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Methodology
Research Methods | Definition, Types, Examples
Research methods are specific procedures for collecting and analysing data. Developing your research methods is an integral part of your research design . When planning your methods, there are two key decisions you will make.
First, decide how you will collect data . Your methods depend on what type of data you need to answer your research question :
- Qualitative vs quantitative : Will your data take the form of words or numbers?
- Primary vs secondary : Will you collect original data yourself, or will you use data that have already been collected by someone else?
- Descriptive vs experimental : Will you take measurements of something as it is, or will you perform an experiment?
Second, decide how you will analyse the data .
- For quantitative data, you can use statistical analysis methods to test relationships between variables.
- For qualitative data, you can use methods such as thematic analysis to interpret patterns and meanings in the data.
Table of contents
Methods for collecting data, examples of data collection methods, methods for analysing data, examples of data analysis methods, frequently asked questions about methodology.
Data are the information that you collect for the purposes of answering your research question . The type of data you need depends on the aims of your research.
Qualitative vs quantitative data
Your choice of qualitative or quantitative data collection depends on the type of knowledge you want to develop.
For questions about ideas, experiences and meanings, or to study something that can’t be described numerically, collect qualitative data .
If you want to develop a more mechanistic understanding of a topic, or your research involves hypothesis testing , collect quantitative data .
You can also take a mixed methods approach, where you use both qualitative and quantitative research methods.
Primary vs secondary data
Primary data are any original information that you collect for the purposes of answering your research question (e.g. through surveys , observations and experiments ). Secondary data are information that has already been collected by other researchers (e.g. in a government census or previous scientific studies).
If you are exploring a novel research question, you’ll probably need to collect primary data. But if you want to synthesise existing knowledge, analyse historical trends, or identify patterns on a large scale, secondary data might be a better choice.
Descriptive vs experimental data
In descriptive research , you collect data about your study subject without intervening. The validity of your research will depend on your sampling method .
In experimental research , you systematically intervene in a process and measure the outcome. The validity of your research will depend on your experimental design .
To conduct an experiment, you need to be able to vary your independent variable , precisely measure your dependent variable, and control for confounding variables . If it’s practically and ethically possible, this method is the best choice for answering questions about cause and effect.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Your data analysis methods will depend on the type of data you collect and how you prepare them for analysis.
Data can often be analysed both quantitatively and qualitatively. For example, survey responses could be analysed qualitatively by studying the meanings of responses or quantitatively by studying the frequencies of responses.
Qualitative analysis methods
Qualitative analysis is used to understand words, ideas, and experiences. You can use it to interpret data that were collected:
- From open-ended survey and interview questions, literature reviews, case studies, and other sources that use text rather than numbers.
- Using non-probability sampling methods .
Qualitative analysis tends to be quite flexible and relies on the researcher’s judgement, so you have to reflect carefully on your choices and assumptions.
Quantitative analysis methods
Quantitative analysis uses numbers and statistics to understand frequencies, averages and correlations (in descriptive studies) or cause-and-effect relationships (in experiments).
You can use quantitative analysis to interpret data that were collected either:
- During an experiment.
- Using probability sampling methods .
Because the data are collected and analysed in a statistically valid way, the results of quantitative analysis can be easily standardised and shared among researchers.
Quantitative research deals with numbers and statistics, while qualitative research deals with words and meanings.
Quantitative methods allow you to test a hypothesis by systematically collecting and analysing data, while qualitative methods allow you to explore ideas and experiences in depth.
In mixed methods research , you use both qualitative and quantitative data collection and analysis methods to answer your research question .
A sample is a subset of individuals from a larger population. Sampling means selecting the group that you will actually collect data from in your research.
For example, if you are researching the opinions of students in your university, you could survey a sample of 100 students.
Statistical sampling allows you to test a hypothesis about the characteristics of a population. There are various sampling methods you can use to ensure that your sample is representative of the population as a whole.
The research methods you use depend on the type of data you need to answer your research question .
- If you want to measure something or test a hypothesis , use quantitative methods . If you want to explore ideas, thoughts, and meanings, use qualitative methods .
- If you want to analyse a large amount of readily available data, use secondary data. If you want data specific to your purposes with control over how they are generated, collect primary data.
- If you want to establish cause-and-effect relationships between variables , use experimental methods. If you want to understand the characteristics of a research subject, use descriptive methods.
Methodology refers to the overarching strategy and rationale of your research project . It involves studying the methods used in your field and the theories or principles behind them, in order to develop an approach that matches your objectives.
Methods are the specific tools and procedures you use to collect and analyse data (e.g. experiments, surveys , and statistical tests ).
In shorter scientific papers, where the aim is to report the findings of a specific study, you might simply describe what you did in a methods section .
In a longer or more complex research project, such as a thesis or dissertation , you will probably include a methodology section , where you explain your approach to answering the research questions and cite relevant sources to support your choice of methods.
Is this article helpful?
More interesting articles.
- A Quick Guide to Experimental Design | 5 Steps & Examples
- Between-Subjects Design | Examples, Pros & Cons
- Case Study | Definition, Examples & Methods
- Cluster Sampling | A Simple Step-by-Step Guide with Examples
- Confounding Variables | Definition, Examples & Controls
- Construct Validity | Definition, Types, & Examples
- Content Analysis | A Step-by-Step Guide with Examples
- Control Groups and Treatment Groups | Uses & Examples
- Controlled Experiments | Methods & Examples of Control
- Correlation vs Causation | Differences, Designs & Examples
- Correlational Research | Guide, Design & Examples
- Critical Discourse Analysis | Definition, Guide & Examples
- Cross-Sectional Study | Definitions, Uses & Examples
- Data Cleaning | A Guide with Examples & Steps
- Data Collection Methods | Step-by-Step Guide & Examples
- Descriptive Research Design | Definition, Methods & Examples
- Doing Survey Research | A Step-by-Step Guide & Examples
- Ethical Considerations in Research | Types & Examples
- Explanatory Research | Definition, Guide, & Examples
- Explanatory vs Response Variables | Definitions & Examples
- Exploratory Research | Definition, Guide, & Examples
- External Validity | Types, Threats & Examples
- Extraneous Variables | Examples, Types, Controls
- Face Validity | Guide with Definition & Examples
- How to Do Thematic Analysis | Guide & Examples
- How to Write a Strong Hypothesis | Guide & Examples
- Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria | Examples & Definition
- Independent vs Dependent Variables | Definition & Examples
- Inductive Reasoning | Types, Examples, Explanation
- Inductive vs Deductive Research Approach (with Examples)
- Internal Validity | Definition, Threats & Examples
- Internal vs External Validity | Understanding Differences & Examples
- Longitudinal Study | Definition, Approaches & Examples
- Mediator vs Moderator Variables | Differences & Examples
- Mixed Methods Research | Definition, Guide, & Examples
- Multistage Sampling | An Introductory Guide with Examples
- Naturalistic Observation | Definition, Guide & Examples
- Operationalisation | A Guide with Examples, Pros & Cons
- Population vs Sample | Definitions, Differences & Examples
- Primary Research | Definition, Types, & Examples
- Qualitative vs Quantitative Research | Examples & Methods
- Quasi-Experimental Design | Definition, Types & Examples
- Questionnaire Design | Methods, Question Types & Examples
- Random Assignment in Experiments | Introduction & Examples
- Reliability vs Validity in Research | Differences, Types & Examples
- Reproducibility vs Replicability | Difference & Examples
- Research Design | Step-by-Step Guide with Examples
- Sampling Methods | Types, Techniques, & Examples
- Semi-Structured Interview | Definition, Guide & Examples
- Simple Random Sampling | Definition, Steps & Examples
- Stratified Sampling | A Step-by-Step Guide with Examples
- Structured Interview | Definition, Guide & Examples
- Systematic Review | Definition, Examples & Guide
- Systematic Sampling | A Step-by-Step Guide with Examples
- Textual Analysis | Guide, 3 Approaches & Examples
- The 4 Types of Reliability in Research | Definitions & Examples
- The 4 Types of Validity | Types, Definitions & Examples
- Transcribing an Interview | 5 Steps & Transcription Software
- Triangulation in Research | Guide, Types, Examples
- Types of Interviews in Research | Guide & Examples
- Types of Research Designs Compared | Examples
- Types of Variables in Research | Definitions & Examples
- Unstructured Interview | Definition, Guide & Examples
- What Are Control Variables | Definition & Examples
- What Is a Case-Control Study? | Definition & Examples
- What Is a Cohort Study? | Definition & Examples
- What Is a Conceptual Framework? | Tips & Examples
- What Is a Double-Barrelled Question?
- What Is a Double-Blind Study? | Introduction & Examples
- What Is a Focus Group? | Step-by-Step Guide & Examples
- What Is a Likert Scale? | Guide & Examples
- What is a Literature Review? | Guide, Template, & Examples
- What Is a Prospective Cohort Study? | Definition & Examples
- What Is a Retrospective Cohort Study? | Definition & Examples
- What Is Action Research? | Definition & Examples
- What Is an Observational Study? | Guide & Examples
- What Is Concurrent Validity? | Definition & Examples
- What Is Content Validity? | Definition & Examples
- What Is Convenience Sampling? | Definition & Examples
- What Is Convergent Validity? | Definition & Examples
- What Is Criterion Validity? | Definition & Examples
- What Is Deductive Reasoning? | Explanation & Examples
- What Is Discriminant Validity? | Definition & Example
- What Is Ecological Validity? | Definition & Examples
- What Is Ethnography? | Meaning, Guide & Examples
- What Is Non-Probability Sampling? | Types & Examples
- What Is Participant Observation? | Definition & Examples
- What Is Peer Review? | Types & Examples
- What Is Predictive Validity? | Examples & Definition
- What Is Probability Sampling? | Types & Examples
- What Is Purposive Sampling? | Definition & Examples
- What Is Qualitative Observation? | Definition & Examples
- What Is Qualitative Research? | Methods & Examples
- What Is Quantitative Observation? | Definition & Examples
- What Is Quantitative Research? | Definition & Methods
- What Is Quota Sampling? | Definition & Examples
- What is Secondary Research? | Definition, Types, & Examples
- What Is Snowball Sampling? | Definition & Examples
- Within-Subjects Design | Explanation, Approaches, Examples
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- BMC Med Res Methodol

A tutorial on methodological studies: the what, when, how and why
Lawrence mbuagbaw.
1 Department of Health Research Methods, Evidence and Impact, McMaster University, Hamilton, ON Canada
2 Biostatistics Unit/FSORC, 50 Charlton Avenue East, St Joseph’s Healthcare—Hamilton, 3rd Floor Martha Wing, Room H321, Hamilton, Ontario L8N 4A6 Canada
3 Centre for the Development of Best Practices in Health, Yaoundé, Cameroon
Daeria O. Lawson
Livia puljak.
4 Center for Evidence-Based Medicine and Health Care, Catholic University of Croatia, Ilica 242, 10000 Zagreb, Croatia
David B. Allison
5 Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, School of Public Health – Bloomington, Indiana University, Bloomington, IN 47405 USA
Lehana Thabane
6 Departments of Paediatrics and Anaesthesia, McMaster University, Hamilton, ON Canada
7 Centre for Evaluation of Medicine, St. Joseph’s Healthcare-Hamilton, Hamilton, ON Canada
8 Population Health Research Institute, Hamilton Health Sciences, Hamilton, ON Canada
Associated Data
Data sharing is not applicable to this article as no new data were created or analyzed in this study.
Methodological studies – studies that evaluate the design, analysis or reporting of other research-related reports – play an important role in health research. They help to highlight issues in the conduct of research with the aim of improving health research methodology, and ultimately reducing research waste.
We provide an overview of some of the key aspects of methodological studies such as what they are, and when, how and why they are done. We adopt a “frequently asked questions” format to facilitate reading this paper and provide multiple examples to help guide researchers interested in conducting methodological studies. Some of the topics addressed include: is it necessary to publish a study protocol? How to select relevant research reports and databases for a methodological study? What approaches to data extraction and statistical analysis should be considered when conducting a methodological study? What are potential threats to validity and is there a way to appraise the quality of methodological studies?
Appropriate reflection and application of basic principles of epidemiology and biostatistics are required in the design and analysis of methodological studies. This paper provides an introduction for further discussion about the conduct of methodological studies.
The field of meta-research (or research-on-research) has proliferated in recent years in response to issues with research quality and conduct [ 1 – 3 ]. As the name suggests, this field targets issues with research design, conduct, analysis and reporting. Various types of research reports are often examined as the unit of analysis in these studies (e.g. abstracts, full manuscripts, trial registry entries). Like many other novel fields of research, meta-research has seen a proliferation of use before the development of reporting guidance. For example, this was the case with randomized trials for which risk of bias tools and reporting guidelines were only developed much later – after many trials had been published and noted to have limitations [ 4 , 5 ]; and for systematic reviews as well [ 6 – 8 ]. However, in the absence of formal guidance, studies that report on research differ substantially in how they are named, conducted and reported [ 9 , 10 ]. This creates challenges in identifying, summarizing and comparing them. In this tutorial paper, we will use the term methodological study to refer to any study that reports on the design, conduct, analysis or reporting of primary or secondary research-related reports (such as trial registry entries and conference abstracts).
In the past 10 years, there has been an increase in the use of terms related to methodological studies (based on records retrieved with a keyword search [in the title and abstract] for “methodological review” and “meta-epidemiological study” in PubMed up to December 2019), suggesting that these studies may be appearing more frequently in the literature. See Fig. 1 .

Trends in the number studies that mention “methodological review” or “meta-
epidemiological study” in PubMed.
The methods used in many methodological studies have been borrowed from systematic and scoping reviews. This practice has influenced the direction of the field, with many methodological studies including searches of electronic databases, screening of records, duplicate data extraction and assessments of risk of bias in the included studies. However, the research questions posed in methodological studies do not always require the approaches listed above, and guidance is needed on when and how to apply these methods to a methodological study. Even though methodological studies can be conducted on qualitative or mixed methods research, this paper focuses on and draws examples exclusively from quantitative research.
The objectives of this paper are to provide some insights on how to conduct methodological studies so that there is greater consistency between the research questions posed, and the design, analysis and reporting of findings. We provide multiple examples to illustrate concepts and a proposed framework for categorizing methodological studies in quantitative research.
What is a methodological study?
Any study that describes or analyzes methods (design, conduct, analysis or reporting) in published (or unpublished) literature is a methodological study. Consequently, the scope of methodological studies is quite extensive and includes, but is not limited to, topics as diverse as: research question formulation [ 11 ]; adherence to reporting guidelines [ 12 – 14 ] and consistency in reporting [ 15 ]; approaches to study analysis [ 16 ]; investigating the credibility of analyses [ 17 ]; and studies that synthesize these methodological studies [ 18 ]. While the nomenclature of methodological studies is not uniform, the intents and purposes of these studies remain fairly consistent – to describe or analyze methods in primary or secondary studies. As such, methodological studies may also be classified as a subtype of observational studies.
Parallel to this are experimental studies that compare different methods. Even though they play an important role in informing optimal research methods, experimental methodological studies are beyond the scope of this paper. Examples of such studies include the randomized trials by Buscemi et al., comparing single data extraction to double data extraction [ 19 ], and Carrasco-Labra et al., comparing approaches to presenting findings in Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development and Evaluations (GRADE) summary of findings tables [ 20 ]. In these studies, the unit of analysis is the person or groups of individuals applying the methods. We also direct readers to the Studies Within a Trial (SWAT) and Studies Within a Review (SWAR) programme operated through the Hub for Trials Methodology Research, for further reading as a potential useful resource for these types of experimental studies [ 21 ]. Lastly, this paper is not meant to inform the conduct of research using computational simulation and mathematical modeling for which some guidance already exists [ 22 ], or studies on the development of methods using consensus-based approaches.
When should we conduct a methodological study?
Methodological studies occupy a unique niche in health research that allows them to inform methodological advances. Methodological studies should also be conducted as pre-cursors to reporting guideline development, as they provide an opportunity to understand current practices, and help to identify the need for guidance and gaps in methodological or reporting quality. For example, the development of the popular Preferred Reporting Items of Systematic reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines were preceded by methodological studies identifying poor reporting practices [ 23 , 24 ]. In these instances, after the reporting guidelines are published, methodological studies can also be used to monitor uptake of the guidelines.
These studies can also be conducted to inform the state of the art for design, analysis and reporting practices across different types of health research fields, with the aim of improving research practices, and preventing or reducing research waste. For example, Samaan et al. conducted a scoping review of adherence to different reporting guidelines in health care literature [ 18 ]. Methodological studies can also be used to determine the factors associated with reporting practices. For example, Abbade et al. investigated journal characteristics associated with the use of the Participants, Intervention, Comparison, Outcome, Timeframe (PICOT) format in framing research questions in trials of venous ulcer disease [ 11 ].

How often are methodological studies conducted?
There is no clear answer to this question. Based on a search of PubMed, the use of related terms (“methodological review” and “meta-epidemiological study”) – and therefore, the number of methodological studies – is on the rise. However, many other terms are used to describe methodological studies. There are also many studies that explore design, conduct, analysis or reporting of research reports, but that do not use any specific terms to describe or label their study design in terms of “methodology”. This diversity in nomenclature makes a census of methodological studies elusive. Appropriate terminology and key words for methodological studies are needed to facilitate improved accessibility for end-users.
Why do we conduct methodological studies?
Methodological studies provide information on the design, conduct, analysis or reporting of primary and secondary research and can be used to appraise quality, quantity, completeness, accuracy and consistency of health research. These issues can be explored in specific fields, journals, databases, geographical regions and time periods. For example, Areia et al. explored the quality of reporting of endoscopic diagnostic studies in gastroenterology [ 25 ]; Knol et al. investigated the reporting of p -values in baseline tables in randomized trial published in high impact journals [ 26 ]; Chen et al. describe adherence to the Consolidated Standards of Reporting Trials (CONSORT) statement in Chinese Journals [ 27 ]; and Hopewell et al. describe the effect of editors’ implementation of CONSORT guidelines on reporting of abstracts over time [ 28 ]. Methodological studies provide useful information to researchers, clinicians, editors, publishers and users of health literature. As a result, these studies have been at the cornerstone of important methodological developments in the past two decades and have informed the development of many health research guidelines including the highly cited CONSORT statement [ 5 ].
Where can we find methodological studies?
Methodological studies can be found in most common biomedical bibliographic databases (e.g. Embase, MEDLINE, PubMed, Web of Science). However, the biggest caveat is that methodological studies are hard to identify in the literature due to the wide variety of names used and the lack of comprehensive databases dedicated to them. A handful can be found in the Cochrane Library as “Cochrane Methodology Reviews”, but these studies only cover methodological issues related to systematic reviews. Previous attempts to catalogue all empirical studies of methods used in reviews were abandoned 10 years ago [ 29 ]. In other databases, a variety of search terms may be applied with different levels of sensitivity and specificity.
Some frequently asked questions about methodological studies
In this section, we have outlined responses to questions that might help inform the conduct of methodological studies.
Q: How should I select research reports for my methodological study?
A: Selection of research reports for a methodological study depends on the research question and eligibility criteria. Once a clear research question is set and the nature of literature one desires to review is known, one can then begin the selection process. Selection may begin with a broad search, especially if the eligibility criteria are not apparent. For example, a methodological study of Cochrane Reviews of HIV would not require a complex search as all eligible studies can easily be retrieved from the Cochrane Library after checking a few boxes [ 30 ]. On the other hand, a methodological study of subgroup analyses in trials of gastrointestinal oncology would require a search to find such trials, and further screening to identify trials that conducted a subgroup analysis [ 31 ].
The strategies used for identifying participants in observational studies can apply here. One may use a systematic search to identify all eligible studies. If the number of eligible studies is unmanageable, a random sample of articles can be expected to provide comparable results if it is sufficiently large [ 32 ]. For example, Wilson et al. used a random sample of trials from the Cochrane Stroke Group’s Trial Register to investigate completeness of reporting [ 33 ]. It is possible that a simple random sample would lead to underrepresentation of units (i.e. research reports) that are smaller in number. This is relevant if the investigators wish to compare multiple groups but have too few units in one group. In this case a stratified sample would help to create equal groups. For example, in a methodological study comparing Cochrane and non-Cochrane reviews, Kahale et al. drew random samples from both groups [ 34 ]. Alternatively, systematic or purposeful sampling strategies can be used and we encourage researchers to justify their selected approaches based on the study objective.
Q: How many databases should I search?
A: The number of databases one should search would depend on the approach to sampling, which can include targeting the entire “population” of interest or a sample of that population. If you are interested in including the entire target population for your research question, or drawing a random or systematic sample from it, then a comprehensive and exhaustive search for relevant articles is required. In this case, we recommend using systematic approaches for searching electronic databases (i.e. at least 2 databases with a replicable and time stamped search strategy). The results of your search will constitute a sampling frame from which eligible studies can be drawn.
Alternatively, if your approach to sampling is purposeful, then we recommend targeting the database(s) or data sources (e.g. journals, registries) that include the information you need. For example, if you are conducting a methodological study of high impact journals in plastic surgery and they are all indexed in PubMed, you likely do not need to search any other databases. You may also have a comprehensive list of all journals of interest and can approach your search using the journal names in your database search (or by accessing the journal archives directly from the journal’s website). Even though one could also search journals’ web pages directly, using a database such as PubMed has multiple advantages, such as the use of filters, so the search can be narrowed down to a certain period, or study types of interest. Furthermore, individual journals’ web sites may have different search functionalities, which do not necessarily yield a consistent output.
Q: Should I publish a protocol for my methodological study?
A: A protocol is a description of intended research methods. Currently, only protocols for clinical trials require registration [ 35 ]. Protocols for systematic reviews are encouraged but no formal recommendation exists. The scientific community welcomes the publication of protocols because they help protect against selective outcome reporting, the use of post hoc methodologies to embellish results, and to help avoid duplication of efforts [ 36 ]. While the latter two risks exist in methodological research, the negative consequences may be substantially less than for clinical outcomes. In a sample of 31 methodological studies, 7 (22.6%) referenced a published protocol [ 9 ]. In the Cochrane Library, there are 15 protocols for methodological reviews (21 July 2020). This suggests that publishing protocols for methodological studies is not uncommon.
Authors can consider publishing their study protocol in a scholarly journal as a manuscript. Advantages of such publication include obtaining peer-review feedback about the planned study, and easy retrieval by searching databases such as PubMed. The disadvantages in trying to publish protocols includes delays associated with manuscript handling and peer review, as well as costs, as few journals publish study protocols, and those journals mostly charge article-processing fees [ 37 ]. Authors who would like to make their protocol publicly available without publishing it in scholarly journals, could deposit their study protocols in publicly available repositories, such as the Open Science Framework ( https://osf.io/ ).
Q: How to appraise the quality of a methodological study?
A: To date, there is no published tool for appraising the risk of bias in a methodological study, but in principle, a methodological study could be considered as a type of observational study. Therefore, during conduct or appraisal, care should be taken to avoid the biases common in observational studies [ 38 ]. These biases include selection bias, comparability of groups, and ascertainment of exposure or outcome. In other words, to generate a representative sample, a comprehensive reproducible search may be necessary to build a sampling frame. Additionally, random sampling may be necessary to ensure that all the included research reports have the same probability of being selected, and the screening and selection processes should be transparent and reproducible. To ensure that the groups compared are similar in all characteristics, matching, random sampling or stratified sampling can be used. Statistical adjustments for between-group differences can also be applied at the analysis stage. Finally, duplicate data extraction can reduce errors in assessment of exposures or outcomes.
Q: Should I justify a sample size?
A: In all instances where one is not using the target population (i.e. the group to which inferences from the research report are directed) [ 39 ], a sample size justification is good practice. The sample size justification may take the form of a description of what is expected to be achieved with the number of articles selected, or a formal sample size estimation that outlines the number of articles required to answer the research question with a certain precision and power. Sample size justifications in methodological studies are reasonable in the following instances:
- Comparing two groups
- Determining a proportion, mean or another quantifier
- Determining factors associated with an outcome using regression-based analyses
For example, El Dib et al. computed a sample size requirement for a methodological study of diagnostic strategies in randomized trials, based on a confidence interval approach [ 40 ].
Q: What should I call my study?
A: Other terms which have been used to describe/label methodological studies include “ methodological review ”, “methodological survey” , “meta-epidemiological study” , “systematic review” , “systematic survey”, “meta-research”, “research-on-research” and many others. We recommend that the study nomenclature be clear, unambiguous, informative and allow for appropriate indexing. Methodological study nomenclature that should be avoided includes “ systematic review” – as this will likely be confused with a systematic review of a clinical question. “ Systematic survey” may also lead to confusion about whether the survey was systematic (i.e. using a preplanned methodology) or a survey using “ systematic” sampling (i.e. a sampling approach using specific intervals to determine who is selected) [ 32 ]. Any of the above meanings of the words “ systematic” may be true for methodological studies and could be potentially misleading. “ Meta-epidemiological study” is ideal for indexing, but not very informative as it describes an entire field. The term “ review ” may point towards an appraisal or “review” of the design, conduct, analysis or reporting (or methodological components) of the targeted research reports, yet it has also been used to describe narrative reviews [ 41 , 42 ]. The term “ survey ” is also in line with the approaches used in many methodological studies [ 9 ], and would be indicative of the sampling procedures of this study design. However, in the absence of guidelines on nomenclature, the term “ methodological study ” is broad enough to capture most of the scenarios of such studies.
Q: Should I account for clustering in my methodological study?
A: Data from methodological studies are often clustered. For example, articles coming from a specific source may have different reporting standards (e.g. the Cochrane Library). Articles within the same journal may be similar due to editorial practices and policies, reporting requirements and endorsement of guidelines. There is emerging evidence that these are real concerns that should be accounted for in analyses [ 43 ]. Some cluster variables are described in the section: “ What variables are relevant to methodological studies?”
A variety of modelling approaches can be used to account for correlated data, including the use of marginal, fixed or mixed effects regression models with appropriate computation of standard errors [ 44 ]. For example, Kosa et al. used generalized estimation equations to account for correlation of articles within journals [ 15 ]. Not accounting for clustering could lead to incorrect p -values, unduly narrow confidence intervals, and biased estimates [ 45 ].
Q: Should I extract data in duplicate?
A: Yes. Duplicate data extraction takes more time but results in less errors [ 19 ]. Data extraction errors in turn affect the effect estimate [ 46 ], and therefore should be mitigated. Duplicate data extraction should be considered in the absence of other approaches to minimize extraction errors. However, much like systematic reviews, this area will likely see rapid new advances with machine learning and natural language processing technologies to support researchers with screening and data extraction [ 47 , 48 ]. However, experience plays an important role in the quality of extracted data and inexperienced extractors should be paired with experienced extractors [ 46 , 49 ].
Q: Should I assess the risk of bias of research reports included in my methodological study?
A : Risk of bias is most useful in determining the certainty that can be placed in the effect measure from a study. In methodological studies, risk of bias may not serve the purpose of determining the trustworthiness of results, as effect measures are often not the primary goal of methodological studies. Determining risk of bias in methodological studies is likely a practice borrowed from systematic review methodology, but whose intrinsic value is not obvious in methodological studies. When it is part of the research question, investigators often focus on one aspect of risk of bias. For example, Speich investigated how blinding was reported in surgical trials [ 50 ], and Abraha et al., investigated the application of intention-to-treat analyses in systematic reviews and trials [ 51 ].
Q: What variables are relevant to methodological studies?
A: There is empirical evidence that certain variables may inform the findings in a methodological study. We outline some of these and provide a brief overview below:
- Country: Countries and regions differ in their research cultures, and the resources available to conduct research. Therefore, it is reasonable to believe that there may be differences in methodological features across countries. Methodological studies have reported loco-regional differences in reporting quality [ 52 , 53 ]. This may also be related to challenges non-English speakers face in publishing papers in English.
- Authors’ expertise: The inclusion of authors with expertise in research methodology, biostatistics, and scientific writing is likely to influence the end-product. Oltean et al. found that among randomized trials in orthopaedic surgery, the use of analyses that accounted for clustering was more likely when specialists (e.g. statistician, epidemiologist or clinical trials methodologist) were included on the study team [ 54 ]. Fleming et al. found that including methodologists in the review team was associated with appropriate use of reporting guidelines [ 55 ].
- Source of funding and conflicts of interest: Some studies have found that funded studies report better [ 56 , 57 ], while others do not [ 53 , 58 ]. The presence of funding would indicate the availability of resources deployed to ensure optimal design, conduct, analysis and reporting. However, the source of funding may introduce conflicts of interest and warrant assessment. For example, Kaiser et al. investigated the effect of industry funding on obesity or nutrition randomized trials and found that reporting quality was similar [ 59 ]. Thomas et al. looked at reporting quality of long-term weight loss trials and found that industry funded studies were better [ 60 ]. Kan et al. examined the association between industry funding and “positive trials” (trials reporting a significant intervention effect) and found that industry funding was highly predictive of a positive trial [ 61 ]. This finding is similar to that of a recent Cochrane Methodology Review by Hansen et al. [ 62 ]
- Journal characteristics: Certain journals’ characteristics may influence the study design, analysis or reporting. Characteristics such as journal endorsement of guidelines [ 63 , 64 ], and Journal Impact Factor (JIF) have been shown to be associated with reporting [ 63 , 65 – 67 ].
- Study size (sample size/number of sites): Some studies have shown that reporting is better in larger studies [ 53 , 56 , 58 ].
- Year of publication: It is reasonable to assume that design, conduct, analysis and reporting of research will change over time. Many studies have demonstrated improvements in reporting over time or after the publication of reporting guidelines [ 68 , 69 ].
- Type of intervention: In a methodological study of reporting quality of weight loss intervention studies, Thabane et al. found that trials of pharmacologic interventions were reported better than trials of non-pharmacologic interventions [ 70 ].
- Interactions between variables: Complex interactions between the previously listed variables are possible. High income countries with more resources may be more likely to conduct larger studies and incorporate a variety of experts. Authors in certain countries may prefer certain journals, and journal endorsement of guidelines and editorial policies may change over time.
Q: Should I focus only on high impact journals?
A: Investigators may choose to investigate only high impact journals because they are more likely to influence practice and policy, or because they assume that methodological standards would be higher. However, the JIF may severely limit the scope of articles included and may skew the sample towards articles with positive findings. The generalizability and applicability of findings from a handful of journals must be examined carefully, especially since the JIF varies over time. Even among journals that are all “high impact”, variations exist in methodological standards.
Q: Can I conduct a methodological study of qualitative research?
A: Yes. Even though a lot of methodological research has been conducted in the quantitative research field, methodological studies of qualitative studies are feasible. Certain databases that catalogue qualitative research including the Cumulative Index to Nursing & Allied Health Literature (CINAHL) have defined subject headings that are specific to methodological research (e.g. “research methodology”). Alternatively, one could also conduct a qualitative methodological review; that is, use qualitative approaches to synthesize methodological issues in qualitative studies.
Q: What reporting guidelines should I use for my methodological study?
A: There is no guideline that covers the entire scope of methodological studies. One adaptation of the PRISMA guidelines has been published, which works well for studies that aim to use the entire target population of research reports [ 71 ]. However, it is not widely used (40 citations in 2 years as of 09 December 2019), and methodological studies that are designed as cross-sectional or before-after studies require a more fit-for purpose guideline. A more encompassing reporting guideline for a broad range of methodological studies is currently under development [ 72 ]. However, in the absence of formal guidance, the requirements for scientific reporting should be respected, and authors of methodological studies should focus on transparency and reproducibility.
Q: What are the potential threats to validity and how can I avoid them?
A: Methodological studies may be compromised by a lack of internal or external validity. The main threats to internal validity in methodological studies are selection and confounding bias. Investigators must ensure that the methods used to select articles does not make them differ systematically from the set of articles to which they would like to make inferences. For example, attempting to make extrapolations to all journals after analyzing high-impact journals would be misleading.
Many factors (confounders) may distort the association between the exposure and outcome if the included research reports differ with respect to these factors [ 73 ]. For example, when examining the association between source of funding and completeness of reporting, it may be necessary to account for journals that endorse the guidelines. Confounding bias can be addressed by restriction, matching and statistical adjustment [ 73 ]. Restriction appears to be the method of choice for many investigators who choose to include only high impact journals or articles in a specific field. For example, Knol et al. examined the reporting of p -values in baseline tables of high impact journals [ 26 ]. Matching is also sometimes used. In the methodological study of non-randomized interventional studies of elective ventral hernia repair, Parker et al. matched prospective studies with retrospective studies and compared reporting standards [ 74 ]. Some other methodological studies use statistical adjustments. For example, Zhang et al. used regression techniques to determine the factors associated with missing participant data in trials [ 16 ].
With regard to external validity, researchers interested in conducting methodological studies must consider how generalizable or applicable their findings are. This should tie in closely with the research question and should be explicit. For example. Findings from methodological studies on trials published in high impact cardiology journals cannot be assumed to be applicable to trials in other fields. However, investigators must ensure that their sample truly represents the target sample either by a) conducting a comprehensive and exhaustive search, or b) using an appropriate and justified, randomly selected sample of research reports.
Even applicability to high impact journals may vary based on the investigators’ definition, and over time. For example, for high impact journals in the field of general medicine, Bouwmeester et al. included the Annals of Internal Medicine (AIM), BMJ, the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA), Lancet, the New England Journal of Medicine (NEJM), and PLoS Medicine ( n = 6) [ 75 ]. In contrast, the high impact journals selected in the methodological study by Schiller et al. were BMJ, JAMA, Lancet, and NEJM ( n = 4) [ 76 ]. Another methodological study by Kosa et al. included AIM, BMJ, JAMA, Lancet and NEJM ( n = 5). In the methodological study by Thabut et al., journals with a JIF greater than 5 were considered to be high impact. Riado Minguez et al. used first quartile journals in the Journal Citation Reports (JCR) for a specific year to determine “high impact” [ 77 ]. Ultimately, the definition of high impact will be based on the number of journals the investigators are willing to include, the year of impact and the JIF cut-off [ 78 ]. We acknowledge that the term “generalizability” may apply differently for methodological studies, especially when in many instances it is possible to include the entire target population in the sample studied.
Finally, methodological studies are not exempt from information bias which may stem from discrepancies in the included research reports [ 79 ], errors in data extraction, or inappropriate interpretation of the information extracted. Likewise, publication bias may also be a concern in methodological studies, but such concepts have not yet been explored.
A proposed framework
In order to inform discussions about methodological studies, the development of guidance for what should be reported, we have outlined some key features of methodological studies that can be used to classify them. For each of the categories outlined below, we provide an example. In our experience, the choice of approach to completing a methodological study can be informed by asking the following four questions:
- What is the aim?
A methodological study may be focused on exploring sources of bias in primary or secondary studies (meta-bias), or how bias is analyzed. We have taken care to distinguish bias (i.e. systematic deviations from the truth irrespective of the source) from reporting quality or completeness (i.e. not adhering to a specific reporting guideline or norm). An example of where this distinction would be important is in the case of a randomized trial with no blinding. This study (depending on the nature of the intervention) would be at risk of performance bias. However, if the authors report that their study was not blinded, they would have reported adequately. In fact, some methodological studies attempt to capture both “quality of conduct” and “quality of reporting”, such as Richie et al., who reported on the risk of bias in randomized trials of pharmacy practice interventions [ 80 ]. Babic et al. investigated how risk of bias was used to inform sensitivity analyses in Cochrane reviews [ 81 ]. Further, biases related to choice of outcomes can also be explored. For example, Tan et al investigated differences in treatment effect size based on the outcome reported [ 82 ].
Methodological studies may report quality of reporting against a reporting checklist (i.e. adherence to guidelines) or against expected norms. For example, Croituro et al. report on the quality of reporting in systematic reviews published in dermatology journals based on their adherence to the PRISMA statement [ 83 ], and Khan et al. described the quality of reporting of harms in randomized controlled trials published in high impact cardiovascular journals based on the CONSORT extension for harms [ 84 ]. Other methodological studies investigate reporting of certain features of interest that may not be part of formally published checklists or guidelines. For example, Mbuagbaw et al. described how often the implications for research are elaborated using the Evidence, Participants, Intervention, Comparison, Outcome, Timeframe (EPICOT) format [ 30 ].
Sometimes investigators may be interested in how consistent reports of the same research are, as it is expected that there should be consistency between: conference abstracts and published manuscripts; manuscript abstracts and manuscript main text; and trial registration and published manuscript. For example, Rosmarakis et al. investigated consistency between conference abstracts and full text manuscripts [ 85 ].
In addition to identifying issues with reporting in primary and secondary studies, authors of methodological studies may be interested in determining the factors that are associated with certain reporting practices. Many methodological studies incorporate this, albeit as a secondary outcome. For example, Farrokhyar et al. investigated the factors associated with reporting quality in randomized trials of coronary artery bypass grafting surgery [ 53 ].
Methodological studies may also be used to describe methods or compare methods, and the factors associated with methods. Muller et al. described the methods used for systematic reviews and meta-analyses of observational studies [ 86 ].
Some methodological studies synthesize results from other methodological studies. For example, Li et al. conducted a scoping review of methodological reviews that investigated consistency between full text and abstracts in primary biomedical research [ 87 ].
Some methodological studies may investigate the use of names and terms in health research. For example, Martinic et al. investigated the definitions of systematic reviews used in overviews of systematic reviews (OSRs), meta-epidemiological studies and epidemiology textbooks [ 88 ].
In addition to the previously mentioned experimental methodological studies, there may exist other types of methodological studies not captured here.
- 2. What is the design?
Most methodological studies are purely descriptive and report their findings as counts (percent) and means (standard deviation) or medians (interquartile range). For example, Mbuagbaw et al. described the reporting of research recommendations in Cochrane HIV systematic reviews [ 30 ]. Gohari et al. described the quality of reporting of randomized trials in diabetes in Iran [ 12 ].
Some methodological studies are analytical wherein “analytical studies identify and quantify associations, test hypotheses, identify causes and determine whether an association exists between variables, such as between an exposure and a disease.” [ 89 ] In the case of methodological studies all these investigations are possible. For example, Kosa et al. investigated the association between agreement in primary outcome from trial registry to published manuscript and study covariates. They found that larger and more recent studies were more likely to have agreement [ 15 ]. Tricco et al. compared the conclusion statements from Cochrane and non-Cochrane systematic reviews with a meta-analysis of the primary outcome and found that non-Cochrane reviews were more likely to report positive findings. These results are a test of the null hypothesis that the proportions of Cochrane and non-Cochrane reviews that report positive results are equal [ 90 ].
- 3. What is the sampling strategy?
Methodological reviews with narrow research questions may be able to include the entire target population. For example, in the methodological study of Cochrane HIV systematic reviews, Mbuagbaw et al. included all of the available studies ( n = 103) [ 30 ].
Many methodological studies use random samples of the target population [ 33 , 91 , 92 ]. Alternatively, purposeful sampling may be used, limiting the sample to a subset of research-related reports published within a certain time period, or in journals with a certain ranking or on a topic. Systematic sampling can also be used when random sampling may be challenging to implement.
- 4. What is the unit of analysis?
Many methodological studies use a research report (e.g. full manuscript of study, abstract portion of the study) as the unit of analysis, and inferences can be made at the study-level. However, both published and unpublished research-related reports can be studied. These may include articles, conference abstracts, registry entries etc.
Some methodological studies report on items which may occur more than once per article. For example, Paquette et al. report on subgroup analyses in Cochrane reviews of atrial fibrillation in which 17 systematic reviews planned 56 subgroup analyses [ 93 ].
This framework is outlined in Fig. 2 .

A proposed framework for methodological studies
Conclusions
Methodological studies have examined different aspects of reporting such as quality, completeness, consistency and adherence to reporting guidelines. As such, many of the methodological study examples cited in this tutorial are related to reporting. However, as an evolving field, the scope of research questions that can be addressed by methodological studies is expected to increase.
In this paper we have outlined the scope and purpose of methodological studies, along with examples of instances in which various approaches have been used. In the absence of formal guidance on the design, conduct, analysis and reporting of methodological studies, we have provided some advice to help make methodological studies consistent. This advice is grounded in good contemporary scientific practice. Generally, the research question should tie in with the sampling approach and planned analysis. We have also highlighted the variables that may inform findings from methodological studies. Lastly, we have provided suggestions for ways in which authors can categorize their methodological studies to inform their design and analysis.
Acknowledgements
Abbreviations, authors’ contributions.
LM conceived the idea and drafted the outline and paper. DOL and LT commented on the idea and draft outline. LM, LP and DOL performed literature searches and data extraction. All authors (LM, DOL, LT, LP, DBA) reviewed several draft versions of the manuscript and approved the final manuscript.
This work did not receive any dedicated funding.
Availability of data and materials
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
DOL, DBA, LM, LP and LT are involved in the development of a reporting guideline for methodological studies.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
- Privacy Policy

Home » Research Paper – Structure, Examples and Writing Guide
Research Paper – Structure, Examples and Writing Guide
Table of Contents

Research Paper
Definition:
Research Paper is a written document that presents the author’s original research, analysis, and interpretation of a specific topic or issue.
It is typically based on Empirical Evidence, and may involve qualitative or quantitative research methods, or a combination of both. The purpose of a research paper is to contribute new knowledge or insights to a particular field of study, and to demonstrate the author’s understanding of the existing literature and theories related to the topic.
Structure of Research Paper
The structure of a research paper typically follows a standard format, consisting of several sections that convey specific information about the research study. The following is a detailed explanation of the structure of a research paper:
The title page contains the title of the paper, the name(s) of the author(s), and the affiliation(s) of the author(s). It also includes the date of submission and possibly, the name of the journal or conference where the paper is to be published.
The abstract is a brief summary of the research paper, typically ranging from 100 to 250 words. It should include the research question, the methods used, the key findings, and the implications of the results. The abstract should be written in a concise and clear manner to allow readers to quickly grasp the essence of the research.
Introduction
The introduction section of a research paper provides background information about the research problem, the research question, and the research objectives. It also outlines the significance of the research, the research gap that it aims to fill, and the approach taken to address the research question. Finally, the introduction section ends with a clear statement of the research hypothesis or research question.
Literature Review
The literature review section of a research paper provides an overview of the existing literature on the topic of study. It includes a critical analysis and synthesis of the literature, highlighting the key concepts, themes, and debates. The literature review should also demonstrate the research gap and how the current study seeks to address it.
The methods section of a research paper describes the research design, the sample selection, the data collection and analysis procedures, and the statistical methods used to analyze the data. This section should provide sufficient detail for other researchers to replicate the study.
The results section presents the findings of the research, using tables, graphs, and figures to illustrate the data. The findings should be presented in a clear and concise manner, with reference to the research question and hypothesis.
The discussion section of a research paper interprets the findings and discusses their implications for the research question, the literature review, and the field of study. It should also address the limitations of the study and suggest future research directions.
The conclusion section summarizes the main findings of the study, restates the research question and hypothesis, and provides a final reflection on the significance of the research.
The references section provides a list of all the sources cited in the paper, following a specific citation style such as APA, MLA or Chicago.
How to Write Research Paper
You can write Research Paper by the following guide:
- Choose a Topic: The first step is to select a topic that interests you and is relevant to your field of study. Brainstorm ideas and narrow down to a research question that is specific and researchable.
- Conduct a Literature Review: The literature review helps you identify the gap in the existing research and provides a basis for your research question. It also helps you to develop a theoretical framework and research hypothesis.
- Develop a Thesis Statement : The thesis statement is the main argument of your research paper. It should be clear, concise and specific to your research question.
- Plan your Research: Develop a research plan that outlines the methods, data sources, and data analysis procedures. This will help you to collect and analyze data effectively.
- Collect and Analyze Data: Collect data using various methods such as surveys, interviews, observations, or experiments. Analyze data using statistical tools or other qualitative methods.
- Organize your Paper : Organize your paper into sections such as Introduction, Literature Review, Methods, Results, Discussion, and Conclusion. Ensure that each section is coherent and follows a logical flow.
- Write your Paper : Start by writing the introduction, followed by the literature review, methods, results, discussion, and conclusion. Ensure that your writing is clear, concise, and follows the required formatting and citation styles.
- Edit and Proofread your Paper: Review your paper for grammar and spelling errors, and ensure that it is well-structured and easy to read. Ask someone else to review your paper to get feedback and suggestions for improvement.
- Cite your Sources: Ensure that you properly cite all sources used in your research paper. This is essential for giving credit to the original authors and avoiding plagiarism.
Research Paper Example
Note : The below example research paper is for illustrative purposes only and is not an actual research paper. Actual research papers may have different structures, contents, and formats depending on the field of study, research question, data collection and analysis methods, and other factors. Students should always consult with their professors or supervisors for specific guidelines and expectations for their research papers.
Research Paper Example sample for Students:
Title: The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health among Young Adults
Abstract: This study aims to investigate the impact of social media use on the mental health of young adults. A literature review was conducted to examine the existing research on the topic. A survey was then administered to 200 university students to collect data on their social media use, mental health status, and perceived impact of social media on their mental health. The results showed that social media use is positively associated with depression, anxiety, and stress. The study also found that social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO (Fear of Missing Out) are significant predictors of mental health problems among young adults.
Introduction: Social media has become an integral part of modern life, particularly among young adults. While social media has many benefits, including increased communication and social connectivity, it has also been associated with negative outcomes, such as addiction, cyberbullying, and mental health problems. This study aims to investigate the impact of social media use on the mental health of young adults.
Literature Review: The literature review highlights the existing research on the impact of social media use on mental health. The review shows that social media use is associated with depression, anxiety, stress, and other mental health problems. The review also identifies the factors that contribute to the negative impact of social media, including social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO.
Methods : A survey was administered to 200 university students to collect data on their social media use, mental health status, and perceived impact of social media on their mental health. The survey included questions on social media use, mental health status (measured using the DASS-21), and perceived impact of social media on their mental health. Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics and regression analysis.
Results : The results showed that social media use is positively associated with depression, anxiety, and stress. The study also found that social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO are significant predictors of mental health problems among young adults.
Discussion : The study’s findings suggest that social media use has a negative impact on the mental health of young adults. The study highlights the need for interventions that address the factors contributing to the negative impact of social media, such as social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO.
Conclusion : In conclusion, social media use has a significant impact on the mental health of young adults. The study’s findings underscore the need for interventions that promote healthy social media use and address the negative outcomes associated with social media use. Future research can explore the effectiveness of interventions aimed at reducing the negative impact of social media on mental health. Additionally, longitudinal studies can investigate the long-term effects of social media use on mental health.
Limitations : The study has some limitations, including the use of self-report measures and a cross-sectional design. The use of self-report measures may result in biased responses, and a cross-sectional design limits the ability to establish causality.
Implications: The study’s findings have implications for mental health professionals, educators, and policymakers. Mental health professionals can use the findings to develop interventions that address the negative impact of social media use on mental health. Educators can incorporate social media literacy into their curriculum to promote healthy social media use among young adults. Policymakers can use the findings to develop policies that protect young adults from the negative outcomes associated with social media use.
References :
- Twenge, J. M., & Campbell, W. K. (2019). Associations between screen time and lower psychological well-being among children and adolescents: Evidence from a population-based study. Preventive medicine reports, 15, 100918.
- Primack, B. A., Shensa, A., Escobar-Viera, C. G., Barrett, E. L., Sidani, J. E., Colditz, J. B., … & James, A. E. (2017). Use of multiple social media platforms and symptoms of depression and anxiety: A nationally-representative study among US young adults. Computers in Human Behavior, 69, 1-9.
- Van der Meer, T. G., & Verhoeven, J. W. (2017). Social media and its impact on academic performance of students. Journal of Information Technology Education: Research, 16, 383-398.
Appendix : The survey used in this study is provided below.
Social Media and Mental Health Survey
- How often do you use social media per day?
- Less than 30 minutes
- 30 minutes to 1 hour
- 1 to 2 hours
- 2 to 4 hours
- More than 4 hours
- Which social media platforms do you use?
- Others (Please specify)
- How often do you experience the following on social media?
- Social comparison (comparing yourself to others)
- Cyberbullying
- Fear of Missing Out (FOMO)
- Have you ever experienced any of the following mental health problems in the past month?
- Do you think social media use has a positive or negative impact on your mental health?
- Very positive
- Somewhat positive
- Somewhat negative
- Very negative
- In your opinion, which factors contribute to the negative impact of social media on mental health?
- Social comparison
- In your opinion, what interventions could be effective in reducing the negative impact of social media on mental health?
- Education on healthy social media use
- Counseling for mental health problems caused by social media
- Social media detox programs
- Regulation of social media use
Thank you for your participation!
Applications of Research Paper
Research papers have several applications in various fields, including:
- Advancing knowledge: Research papers contribute to the advancement of knowledge by generating new insights, theories, and findings that can inform future research and practice. They help to answer important questions, clarify existing knowledge, and identify areas that require further investigation.
- Informing policy: Research papers can inform policy decisions by providing evidence-based recommendations for policymakers. They can help to identify gaps in current policies, evaluate the effectiveness of interventions, and inform the development of new policies and regulations.
- Improving practice: Research papers can improve practice by providing evidence-based guidance for professionals in various fields, including medicine, education, business, and psychology. They can inform the development of best practices, guidelines, and standards of care that can improve outcomes for individuals and organizations.
- Educating students : Research papers are often used as teaching tools in universities and colleges to educate students about research methods, data analysis, and academic writing. They help students to develop critical thinking skills, research skills, and communication skills that are essential for success in many careers.
- Fostering collaboration: Research papers can foster collaboration among researchers, practitioners, and policymakers by providing a platform for sharing knowledge and ideas. They can facilitate interdisciplinary collaborations and partnerships that can lead to innovative solutions to complex problems.
When to Write Research Paper
Research papers are typically written when a person has completed a research project or when they have conducted a study and have obtained data or findings that they want to share with the academic or professional community. Research papers are usually written in academic settings, such as universities, but they can also be written in professional settings, such as research organizations, government agencies, or private companies.
Here are some common situations where a person might need to write a research paper:
- For academic purposes: Students in universities and colleges are often required to write research papers as part of their coursework, particularly in the social sciences, natural sciences, and humanities. Writing research papers helps students to develop research skills, critical thinking skills, and academic writing skills.
- For publication: Researchers often write research papers to publish their findings in academic journals or to present their work at academic conferences. Publishing research papers is an important way to disseminate research findings to the academic community and to establish oneself as an expert in a particular field.
- To inform policy or practice : Researchers may write research papers to inform policy decisions or to improve practice in various fields. Research findings can be used to inform the development of policies, guidelines, and best practices that can improve outcomes for individuals and organizations.
- To share new insights or ideas: Researchers may write research papers to share new insights or ideas with the academic or professional community. They may present new theories, propose new research methods, or challenge existing paradigms in their field.
Purpose of Research Paper
The purpose of a research paper is to present the results of a study or investigation in a clear, concise, and structured manner. Research papers are written to communicate new knowledge, ideas, or findings to a specific audience, such as researchers, scholars, practitioners, or policymakers. The primary purposes of a research paper are:
- To contribute to the body of knowledge : Research papers aim to add new knowledge or insights to a particular field or discipline. They do this by reporting the results of empirical studies, reviewing and synthesizing existing literature, proposing new theories, or providing new perspectives on a topic.
- To inform or persuade: Research papers are written to inform or persuade the reader about a particular issue, topic, or phenomenon. They present evidence and arguments to support their claims and seek to persuade the reader of the validity of their findings or recommendations.
- To advance the field: Research papers seek to advance the field or discipline by identifying gaps in knowledge, proposing new research questions or approaches, or challenging existing assumptions or paradigms. They aim to contribute to ongoing debates and discussions within a field and to stimulate further research and inquiry.
- To demonstrate research skills: Research papers demonstrate the author’s research skills, including their ability to design and conduct a study, collect and analyze data, and interpret and communicate findings. They also demonstrate the author’s ability to critically evaluate existing literature, synthesize information from multiple sources, and write in a clear and structured manner.
Characteristics of Research Paper
Research papers have several characteristics that distinguish them from other forms of academic or professional writing. Here are some common characteristics of research papers:
- Evidence-based: Research papers are based on empirical evidence, which is collected through rigorous research methods such as experiments, surveys, observations, or interviews. They rely on objective data and facts to support their claims and conclusions.
- Structured and organized: Research papers have a clear and logical structure, with sections such as introduction, literature review, methods, results, discussion, and conclusion. They are organized in a way that helps the reader to follow the argument and understand the findings.
- Formal and objective: Research papers are written in a formal and objective tone, with an emphasis on clarity, precision, and accuracy. They avoid subjective language or personal opinions and instead rely on objective data and analysis to support their arguments.
- Citations and references: Research papers include citations and references to acknowledge the sources of information and ideas used in the paper. They use a specific citation style, such as APA, MLA, or Chicago, to ensure consistency and accuracy.
- Peer-reviewed: Research papers are often peer-reviewed, which means they are evaluated by other experts in the field before they are published. Peer-review ensures that the research is of high quality, meets ethical standards, and contributes to the advancement of knowledge in the field.
- Objective and unbiased: Research papers strive to be objective and unbiased in their presentation of the findings. They avoid personal biases or preconceptions and instead rely on the data and analysis to draw conclusions.
Advantages of Research Paper
Research papers have many advantages, both for the individual researcher and for the broader academic and professional community. Here are some advantages of research papers:
- Contribution to knowledge: Research papers contribute to the body of knowledge in a particular field or discipline. They add new information, insights, and perspectives to existing literature and help advance the understanding of a particular phenomenon or issue.
- Opportunity for intellectual growth: Research papers provide an opportunity for intellectual growth for the researcher. They require critical thinking, problem-solving, and creativity, which can help develop the researcher’s skills and knowledge.
- Career advancement: Research papers can help advance the researcher’s career by demonstrating their expertise and contributions to the field. They can also lead to new research opportunities, collaborations, and funding.
- Academic recognition: Research papers can lead to academic recognition in the form of awards, grants, or invitations to speak at conferences or events. They can also contribute to the researcher’s reputation and standing in the field.
- Impact on policy and practice: Research papers can have a significant impact on policy and practice. They can inform policy decisions, guide practice, and lead to changes in laws, regulations, or procedures.
- Advancement of society: Research papers can contribute to the advancement of society by addressing important issues, identifying solutions to problems, and promoting social justice and equality.
Limitations of Research Paper
Research papers also have some limitations that should be considered when interpreting their findings or implications. Here are some common limitations of research papers:
- Limited generalizability: Research findings may not be generalizable to other populations, settings, or contexts. Studies often use specific samples or conditions that may not reflect the broader population or real-world situations.
- Potential for bias : Research papers may be biased due to factors such as sample selection, measurement errors, or researcher biases. It is important to evaluate the quality of the research design and methods used to ensure that the findings are valid and reliable.
- Ethical concerns: Research papers may raise ethical concerns, such as the use of vulnerable populations or invasive procedures. Researchers must adhere to ethical guidelines and obtain informed consent from participants to ensure that the research is conducted in a responsible and respectful manner.
- Limitations of methodology: Research papers may be limited by the methodology used to collect and analyze data. For example, certain research methods may not capture the complexity or nuance of a particular phenomenon, or may not be appropriate for certain research questions.
- Publication bias: Research papers may be subject to publication bias, where positive or significant findings are more likely to be published than negative or non-significant findings. This can skew the overall findings of a particular area of research.
- Time and resource constraints: Research papers may be limited by time and resource constraints, which can affect the quality and scope of the research. Researchers may not have access to certain data or resources, or may be unable to conduct long-term studies due to practical limitations.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

How to Cite Research Paper – All Formats and...

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Paper Format – Types, Examples and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples

Organizing Academic Research Papers: 6. The Methodology
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Executive Summary
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tertiary Sources
- What Is Scholarly vs. Popular?
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Annotated Bibliography
- Dealing with Nervousness
- Using Visual Aids
- Grading Someone Else's Paper
- How to Manage Group Projects
- Multiple Book Review Essay
- Reviewing Collected Essays
- About Informed Consent
- Writing Field Notes
- Writing a Policy Memo
- Writing a Research Proposal
- Acknowledgements
The methods section of a research paper provides the information by which a study’s validity is judged. The method section answers two main questions: 1) How was the data collected or generated? 2) How was it analyzed? The writing should be direct and precise and written in the past tense.
Importance of a Good Methodology Section
You must explain how you obtained and analyzed your results for the following reasons:
- Readers need to know how the data was obtained because the method you choose affects the results and, by extension, how you likely interpreted those results.
- Methodology is crucial for any branch of scholarship because an unreliable method produces unreliable results and it misappropriates interpretations of findings .
- In most cases, there are a variety of different methods you can choose to investigate a research problem. Your methodology section of your paper should make clear the reasons why you chose a particular method or procedure .
- The reader wants to know that the data was collected or generated in a way that is consistent with accepted practice in the field of study. For example, if you are using a questionnaire, readers need to know that it offered your respondents a reasonable range of answers to choose from.
- The research method must be appropriate to the objectives of the study . For example, be sure you have a large enough sample size to be able to generalize and make recommendations based upon the findings.
- The methodology should discuss the problems that were anticipated and the steps you took to prevent them from occurring . For any problems that did arise, you must describe the ways in which their impact was minimized or why these problems do not affect the findings in any way that impacts your interpretation of the data.
- Often in social science research, it is useful for other researchers to adapt or replicate your methodology. Therefore, it is important to always provide sufficient information to allow others to use or replicate the study . This information is particularly important when a new method had been developed or an innovative use of an existing method has been utilized.
Bem, Daryl J. Writing the Empirical Journal Article . Psychology Writing Center. University of Washington; Lunenburg, Frederick C. Writing a Successful Thesis or Dissertation: Tips and Strategies for Students in the Social and Behavioral Sciences . Thousand Oaks, CA: Corwin Press, 2008.
Structure and Writing Style
I. Groups of Research Methods
There are two main groups of research methods in the social sciences:
- The empirical-analytical group approaches the study of social sciences in a similar manner that researchers study the natural sciences. This type of research focuses on objective knowledge, research questions that can be answered yes or no, and operational definitions of variables to be measured. The empirical-analytical group employs deductive reasoning that uses existing theory as a foundation for hypotheses that need to be tested. This approach is focused on explanation .
- The interpretative group is focused on understanding phenomenon in a comprehensive, holistic way . This research method allows you to recognize your connection to the subject under study. Because the interpretative group focuses more on subjective knowledge, it requires careful interpretation of variables.
II. Content
An effectively written methodology section should:
- Introduce the overall methodological approach for investigating your research problem . Is your study qualitative or quantitative or a combination of both (mixed method)? Are you going to take a special approach, such as action research, or a more neutral stance?
- Indicate how the approach fits the overall research design . Your methods should have a clear connection with your research problem. In other words, make sure that your methods will actually address the problem. One of the most common deficiencies found in research papers is that the proposed methodology is unsuited to achieving the stated objective of your paper.
- Describe the specific methods of data collection you are going to use , such as, surveys, interviews, questionnaires, observation, archival research. If you are analyzing existing data, such as a data set or archival documents, describe how it was originally created or gathered and by whom.
- Explain how you intend to analyze your results . Will you use statistical analysis? Will you use specific theoretical perspectives to help you analyze a text or explain observed behaviors?
- Provide background and rationale for methodologies that are unfamiliar for your readers . Very often in the social sciences, research problems and the methods for investigating them require more explanation/rationale than widely accepted rules governing the natural and physical sciences. Be clear and concise in your explanation.
- Provide a rationale for subject selection and sampling procedure . For instance, if you propose to conduct interviews, how do you intend to select the sample population? If you are analyzing texts, which texts have you chosen, and why? If you are using statistics, why is this set of statisics being used? If other data sources exist, explain why the data you chose is most appropriate.
- Address potential limitations . Are there any practical limitations that could affect your data collection? How will you attempt to control for potential confounding variables and errors? If your methodology may lead to problems you can anticipate, state this openly and show why pursuing this methodology outweighs the risk of these problems cropping up.
NOTE : Once you have written all of the elements of the methods section, subsequent revisions should focus on how to present those elements as clearly and as logically as possibly. The description of how you prepared to study the research problem, how you gathered the data, and the protocol for analyzing the data should be organized chronologically. For clarity, when a large amount of detail must be presented, information should be presented in sub-sections according to topic.
III. Problems to Avoid
Irrelevant Detail The methodology section of your paper should be thorough but to the point. Don’t provide any background information that doesn’t directly help the reader to understand why a particular method was chosen, how the data was gathered or obtained, and how it was analyzed. Unnecessary Explanation of Basic Procedures Remember that you are not writing a how-to guide about a particular method. You should make the assumption that readers possess a basic understanding of how to investigate the research problem on their own and, therefore, you do not have to go into great detail about specific methodological procedures. The focus should be on how you applied a method , not on the mechanics of doing a method. NOTE: An exception to this rule is if you select an unconventional approach to doing the method; if this is the case, be sure to explain why this approach was chosen and how it enhances the overall research process. Problem Blindness It is almost a given that you will encounter problems when collecting or generating your data. Do not ignore these problems or pretend they did not occur. Often, documenting how you overcame obstacles can form an interesting part of the methodology. It demonstrates to the reader that you can provide a cogent rationale for the decisions you made to minimize the impact of any problems that arose. Literature Review Just as the literature review section of your paper provides an overview of sources you have examined while researching a particular topic, the methodology section should cite any sources that informed your choice and application of a particular method [i.e., the choice of a survey should include any citations to the works you used to help construct the survey].
It’s More than Sources of Information! A description of a research study's method should not be confused with a description of the sources of information. Such a list of sources is useful in itself, especially if it is accompanied by an explanation about the selection and use of the sources. The description of the project's methodology complements a list of sources in that it sets forth the organization and interpretation of information emanating from those sources.
Azevedo, L.F. et al. How to Write a Scientific Paper: Writing the Methods Section. Revista Portuguesa de Pneumologia 17 (2011): 232-238; Butin, Dan W. The Education Dissertation A Guide for Practitioner Scholars . Thousand Oaks, CA: Corwin, 2010; Carter, Susan. Structuring Your Research Thesis . New York: Palgrave Macmillan, 2012; Lunenburg, Frederick C. Writing a Successful Thesis or Dissertation: Tips and Strategies for Students in the Social and Behavioral Sciences . Thousand Oaks, CA: Corwin Press, 2008. Methods Section . The Writer’s Handbook. Writing Center. University of Wisconsin, Madison; Writing the Experimental Report: Methods, Results, and Discussion . The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Methods and Materials . The Structure, Format, Content, and Style of a Journal-Style Scientific Paper. Department of Biology. Bates College.
Writing Tip
Statistical Designs and Tests? Do Not Fear Them!
Don't avoid using a quantitative approach to analyzing your research problem just because you fear the idea of applying statistical designs and tests. A qualitative approach, such as conducting interviews or content analysis of archival texts, can yield exciting new insights about a research problem, but it should not be undertaken simply because you have a disdain for running a simple regression. A well designed quantitative research study can often be accomplished in very clear and direct ways, whereas, a similar study of a qualitative nature usually requires considerable time to analyze large volumes of data and a tremendous burden to create new paths for analysis where previously no path associated with your research problem had existed.
Another Writing Tip
Knowing the Relationship Between Theories and Methods
There can be multiple meaning associated with the term "theories" and the term "methods" in social sciences research. A helpful way to delineate between them is to understand "theories" as representing different ways of characterizing the social world when you research it and "methods" as representing different ways of generating and analyzing data about that social world. Framed in this way, all empirical social sciences research involves theories and methods, whether they are stated explicitly or not. However, while theories and methods are often related, it is important that, as a researcher, you deliberately separate them in order to avoid your theories playing a disproportionate role in shaping what outcomes your chosen methods produce.
Introspectively engage in an ongoing dialectic between theories and methods to help enable you to use the outcomes from your methods to interrogate and develop new theories, or ways of framing conceptually the research problem. This is how scholarship grows and branches out into new intellectual territory.
Reynolds, R. Larry. Ways of Knowing. Alternative Microeconomics. Part 1, Chapter 3. Boise State University; The Theory-Method Relationship . S-Cool Revision. United Kingdom.
- << Previous: What Is Scholarly vs. Popular?
- Next: Qualitative Methods >>
- Last Updated: Jul 18, 2023 11:58 AM
- URL: https://library.sacredheart.edu/c.php?g=29803
- QuickSearch
- Library Catalog
- Databases A-Z
- Publication Finder
- Course Reserves
- Citation Linker
- Digital Commons
- Our Website
Research Support
- Ask a Librarian
- Appointments
- Interlibrary Loan (ILL)
- Research Guides
- Databases by Subject
- Citation Help
Using the Library
- Reserve a Group Study Room
- Renew Books
- Honors Study Rooms
- Off-Campus Access
- Library Policies
- Library Technology
User Information
- Grad Students
- Online Students
- COVID-19 Updates
- Staff Directory
- News & Announcements
- Library Newsletter
My Accounts
- Interlibrary Loan
- Staff Site Login
FIND US ON
International Journal of Science and Research (IJSR) Call for Papers | Fully Refereed | Open Access | Double Blind Peer Reviewed
ISSN: 2319-7064
What is Research Methodology?
Research methodology refers to the overall approach or strategy used by researchers to conduct a scientific investigation or inquiry. It involves a systematic and rigorous process of collecting, analyzing, and interpreting data to answer research questions or test hypotheses.
The methodology of research involves various components, such as Research Design , Data Collection Methods , Sampling Procedures , Data Analysis Techniques , and Ethical Considerations . The choice of methodology depends on the nature of the research problem, research questions, and the available resources.
A well-designed research methodology is essential for producing reliable and valid research results. It helps researchers to avoid bias and errors in their research, to ensure that the research findings are based on sound evidence and to make sure that the research is ethical and respects the rights of participants.
What is Research Design?
Research design refers to the framework or blueprint for conducting a research study. It encompasses the overall strategy, plan, and structure of a study that guides the collection, analysis, and interpretation of data.
A well-designed research study includes a clear statement of the research problem or question, a review of relevant literature, the selection of appropriate research methods, and the determination of data collection and analysis techniques. The research design also includes decisions regarding the sample population, sampling method, and data analysis procedures.
Research design is important because it provides a structure and a systematic approach to conducting research. A well-designed research study can increase the reliability and validity of the results, improve the generalizability of the findings, and enhance the overall quality of the research.
What are the Data Collection Methods?
Data collection methods are the various ways in which researchers gather data or information for their study. Here are some of the most commonly used data collection methods:
- Surveys: Surveys are questionnaires that are administered to a sample of individuals or groups to gather information on their beliefs, attitudes, or behaviors. Surveys can be conducted through various means, such as online, telephone, or face-to-face interviews.
- Interviews: Interviews involve a one-on-one conversation between the researcher and the participant. Interviews can be structured or unstructured, and they may be conducted in person or via phone or video conferencing.
- Focus groups: Focus groups are group interviews conducted with a small group of people who share similar characteristics or experiences. The researcher leads a discussion on a specific topic, and participants share their opinions, attitudes, and experiences.
- Observations: Observations involve the systematic recording of behaviors or events. This method can be done by a researcher directly observing the participants or by using audio or video recordings.
- Experiments: Experiments involve manipulating one or more variables to see how they affect the outcome of the study. This method is often used in scientific research and involves a control group and an experimental group.
- Case studies: Case studies involve the in-depth study of an individual, group, or event. Researchers gather data from a variety of sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents.
- Secondary data analysis: Secondary data analysis involves the use of existing data sources, such as government records, company records, or previously published research. The researcher analyzes the data to answer their research questions.
Each method has its own advantages and limitations and should be chosen based on the research questions, available resources, and ethical considerations.
What are the Sampling Procedures used in Research?
In research, sampling refers to the process of selecting a subset of individuals or units from a larger population for the purpose of conducting research. There are several sampling procedures used in research, including:
- Simple random sampling: In this procedure, every member of the population has an equal chance of being selected. This is done using a random number generator or a table of random numbers.
- Stratified random sampling: This involves dividing the population into subgroups (or strata) and then selecting a sample from each stratum. This is done to ensure that the sample is representative of the population as a whole.
- Cluster sampling: This involves dividing the population into clusters (such as geographic regions) and then selecting a random sample of clusters. Then, all members of the selected clusters are included in the sample.
- Systematic sampling: This involves selecting every nth individual from a list of the population. For example, if you wanted a sample of 100 individuals from a population of 1000, you would select every 10th person from the list.
- Convenience sampling: This involves selecting individuals who are easily accessible or available. This method is often used in situations where it is difficult or impractical to obtain a random sample.
- Purposive sampling: This involves selecting individuals who meet specific criteria or characteristics that are relevant to the research question. This method is often used in qualitative research.
- Snowball sampling: This involves selecting individuals who are known to the researcher or who are referred by other participants. This method is often used in situations where the population is difficult to access or locate.
It's important to note that each sampling method has its own strengths and weaknesses and that the method used will depend on the research question and the characteristics of the population being studied.
What are the Data Analysis Techniques used in Research?
There are many data analysis techniques used in research, and the choice of technique depends on the type of data collected, the research questions, and the hypotheses being tested. Some of the commonly used data analysis techniques are:
- Descriptive statistics: Descriptive statistics include measures of central tendency (mean, median, mode) and measures of variability (standard deviation, range, interquartile range) that are used to summarize and describe the data.
- Inferential statistics: Inferential statistics involve making inferences or drawing conclusions about a population based on a sample of data. Techniques include hypothesis testing, confidence intervals, and regression analysis.
- Qualitative data analysis: Qualitative data analysis involves analyzing data that is non-numeric in nature, such as text or images. Techniques include content analysis, grounded theory, and thematic analysis.
- Data mining: Data mining involves using computational algorithms to analyze large datasets and identify patterns or relationships that may not be immediately apparent. Techniques include association rule mining, clustering, and classification.
- Network analysis: Network analysis involves analyzing the relationships between nodes in a network, such as social networks or communication networks. Techniques include centrality analysis, community detection, and network visualization.
- Machine learning: Machine learning involves using algorithms to automatically learn patterns in data and make predictions or classifications. Techniques include decision trees, neural networks, and support vector machines.
- Text analytics: Text analytics involves analyzing large volumes of text data to identify patterns or relationships. Techniques include sentiment analysis, topic modeling, and named entity recognition.
- Time series analysis: Time series analysis involves analyzing data that is collected over time, such as stock prices or weather data. Techniques include autoregressive integrated moving average (ARIMA) models, exponential smoothing, and spectral analysis.
The choice of data analysis technique(s) depends on the research question(s), the type of data collected, and the goals of the research study.
What Ethical Considerations Should be Taken Care of While Performing a Research?
Performing research entails a significant amount of responsibility, including ethical considerations that should be taken into account throughout the entire research process. The following are some of the key ethical considerations that should be taken care of while performing research:
- Informed Consent: Researchers should obtain informed consent from study participants before conducting any research on them. This includes providing participants with detailed information about the study, including the purpose, procedures, risks, and benefits. Participants must have the right to decline to participate or withdraw from the study at any time.
- Confidentiality: Researchers should protect the confidentiality and privacy of study participants by ensuring that their personal information is kept secure and that their identities are kept anonymous or pseudonymous. Researchers should also inform participants of the limitations of confidentiality, such as legal requirements to report certain findings.
- Avoiding Harm: Researchers must take measures to prevent harm to study participants, including both physical and psychological harm. This may include providing counseling or support services for participants who may experience distress as a result of the research.
- Fairness: Researchers should treat all participants fairly and ensure that they are not discriminated against based on their race, ethnicity, gender, age, religion, or other factors.
- Integrity: Researchers must maintain high standards of research integrity, including being honest and transparent about their methods and findings, avoiding conflicts of interest, and adhering to ethical codes and guidelines.
- Respect: Researchers must respect the autonomy, dignity, and rights of study participants, as well as other stakeholders, such as research sponsors, regulators, and the wider community.
- Responsible Conduct: Researchers should conduct research with a sense of responsibility towards society and the environment. They should consider the potential impact of their research on the community and the environment, and ensure that their research is conducted in a socially responsible and sustainable manner.
In summary, ethical considerations should be an integral part of the research process from its inception through dissemination. By adhering to these ethical principles, researchers can promote the integrity and credibility of their research, protect the welfare of study participants, and contribute to the advancement of knowledge in a responsible and respectful manner.
Managing Editor , International Journal of Science and Research (IJSR)
www.ijsr.net

A new future of work: The race to deploy AI and raise skills in Europe and beyond
At a glance.
Amid tightening labor markets and a slowdown in productivity growth, Europe and the United States face shifts in labor demand, spurred by AI and automation. Our updated modeling of the future of work finds that demand for workers in STEM-related, healthcare, and other high-skill professions would rise, while demand for occupations such as office workers, production workers, and customer service representatives would decline. By 2030, in a midpoint adoption scenario, up to 30 percent of current hours worked could be automated, accelerated by generative AI (gen AI). Efforts to achieve net-zero emissions, an aging workforce, and growth in e-commerce, as well as infrastructure and technology spending and overall economic growth, could also shift employment demand.
By 2030, Europe could require up to 12 million occupational transitions, double the prepandemic pace. In the United States, required transitions could reach almost 12 million, in line with the prepandemic norm. Both regions navigated even higher levels of labor market shifts at the height of the COVID-19 period, suggesting that they can handle this scale of future job transitions. The pace of occupational change is broadly similar among countries in Europe, although the specific mix reflects their economic variations.
Businesses will need a major skills upgrade. Demand for technological and social and emotional skills could rise as demand for physical and manual and higher cognitive skills stabilizes. Surveyed executives in Europe and the United States expressed a need not only for advanced IT and data analytics but also for critical thinking, creativity, and teaching and training—skills they report as currently being in short supply. Companies plan to focus on retraining workers, more than hiring or subcontracting, to meet skill needs.
Workers with lower wages face challenges of redeployment as demand reweights toward occupations with higher wages in both Europe and the United States. Occupations with lower wages are likely to see reductions in demand, and workers will need to acquire new skills to transition to better-paying work. If that doesn’t happen, there is a risk of a more polarized labor market, with more higher-wage jobs than workers and too many workers for existing lower-wage jobs.
Choices made today could revive productivity growth while creating better societal outcomes. Embracing the path of accelerated technology adoption with proactive worker redeployment could help Europe achieve an annual productivity growth rate of up to 3 percent through 2030. However, slow adoption would limit that to 0.3 percent, closer to today’s level of productivity growth in Western Europe. Slow worker redeployment would leave millions unable to participate productively in the future of work.

Demand will change for a range of occupations through 2030, including growth in STEM- and healthcare-related occupations, among others
This report focuses on labor markets in nine major economies in the European Union along with the United Kingdom, in comparison with the United States. Technology, including most recently the rise of gen AI, along with other factors, will spur changes in the pattern of labor demand through 2030. Our study, which uses an updated version of the McKinsey Global Institute future of work model, seeks to quantify the occupational transitions that will be required and the changing nature of demand for different types of jobs and skills.
Our methodology
We used methodology consistent with other McKinsey Global Institute reports on the future of work to model trends of job changes at the level of occupations, activities, and skills. For this report, we focused our analysis on the 2022–30 period.
Our model estimates net changes in employment demand by sector and occupation; we also estimate occupational transitions, or the net number of workers that need to change in each type of occupation, based on which occupations face declining demand by 2030 relative to current employment in 2022. We included ten countries in Europe: nine EU members—the Czech Republic, Denmark, France, Germany, Italy, Netherlands, Poland, Spain, and Sweden—and the United Kingdom. For the United States, we build on estimates published in our 2023 report Generative AI and the future of work in America.
We included multiple drivers in our modeling: automation potential, net-zero transition, e-commerce growth, remote work adoption, increases in income, aging populations, technology investments, and infrastructure investments.
Two scenarios are used to bookend the work-automation model: “late” and “early.” For Europe, we modeled a “faster” scenario and a “slower” one. For the faster scenario, we use the midpoint—the arithmetical average between our late and early scenarios. For the slower scenario, we use a “mid late” trajectory, an arithmetical average between a late adoption scenario and the midpoint scenario. For the United States, we use the midpoint scenario, based on our earlier research.
We also estimate the productivity effects of automation, using GDP per full-time-equivalent (FTE) employee as the measure of productivity. We assumed that workers displaced by automation rejoin the workforce at 2022 productivity levels, net of automation, and in line with the expected 2030 occupational mix.
Amid tightening labor markets and a slowdown in productivity growth, Europe and the United States face shifts in labor demand, spurred not only by AI and automation but also by other trends, including efforts to achieve net-zero emissions, an aging population, infrastructure spending, technology investments, and growth in e-commerce, among others (see sidebar, “Our methodology”).
Our analysis finds that demand for occupations such as health professionals and other STEM-related professionals would grow by 17 to 30 percent between 2022 and 2030, (Exhibit 1).
By contrast, demand for workers in food services, production work, customer services, sales, and office support—all of which declined over the 2012–22 period—would continue to decline until 2030. These jobs involve a high share of repetitive tasks, data collection, and elementary data processing—all activities that automated systems can handle efficiently.
Up to 30 percent of hours worked could be automated by 2030, boosted by gen AI, leading to millions of required occupational transitions
By 2030, our analysis finds that about 27 percent of current hours worked in Europe and 30 percent of hours worked in the United States could be automated, accelerated by gen AI. Our model suggests that roughly 20 percent of hours worked could still be automated even without gen AI, implying a significant acceleration.
These trends will play out in labor markets in the form of workers needing to change occupations. By 2030, under the faster adoption scenario we modeled, Europe could require up to 12.0 million occupational transitions, affecting 6.5 percent of current employment. That is double the prepandemic pace (Exhibit 2). Under a slower scenario we modeled for Europe, the number of occupational transitions needed would amount to 8.5 million, affecting 4.6 percent of current employment. In the United States, required transitions could reach almost 12.0 million, affecting 7.5 percent of current employment. Unlike Europe, this magnitude of transitions is broadly in line with the prepandemic norm.
Both regions navigated even higher levels of labor market shifts at the height of the COVID-19 period. While these were abrupt and painful to many, given the forced nature of the shifts, the experience suggests that both regions have the ability to handle this scale of future job transitions.

Businesses will need a major skills upgrade
The occupational transitions noted above herald substantial shifts in workforce skills in a future in which automation and AI are integrated into the workplace (Exhibit 3). Workers use multiple skills to perform a given task, but for the purposes of our quantification, we identified the predominant skill used.
Demand for technological skills could see substantial growth in Europe and in the United States (increases of 25 percent and 29 percent, respectively, in hours worked by 2030 compared to 2022) under our midpoint scenario of automation adoption (which is the faster scenario for Europe).
Demand for social and emotional skills could rise by 11 percent in Europe and by 14 percent in the United States. Underlying this increase is higher demand for roles requiring interpersonal empathy and leadership skills. These skills are crucial in healthcare and managerial roles in an evolving economy that demands greater adaptability and flexibility.
Conversely, demand for work in which basic cognitive skills predominate is expected to decline by 14 percent. Basic cognitive skills are required primarily in office support or customer service roles, which are highly susceptible to being automated by AI. Among work characterized by these basic cognitive skills experiencing significant drops in demand are basic data processing and literacy, numeracy, and communication.
Demand for work in which higher cognitive skills predominate could also decline slightly, according to our analysis. While creativity is expected to remain highly sought after, with a potential increase of 12 percent by 2030, work activities characterized by other advanced cognitive skills such as advanced literacy and writing, along with quantitative and statistical skills, could decline by 19 percent.
Demand for physical and manual skills, on the other hand, could remain roughly level with the present. These skills remain the largest share of workforce skills, representing about 30 percent of total hours worked in 2022. Growth in demand for these skills between 2022 and 2030 could come from the build-out of infrastructure and higher investment in low-emissions sectors, while declines would be in line with continued automation in production work.
Business executives report skills shortages today and expect them to worsen
A survey we conducted of C-suite executives in five countries shows that companies are already grappling with skills challenges, including a skills mismatch, particularly in technological, higher cognitive, and social and emotional skills: about one-third of the more than 1,100 respondents report a shortfall in these critical areas. At the same time, a notable number of executives say they have enough employees with basic cognitive skills and, to a lesser extent, physical and manual skills.
Within technological skills, companies in our survey reported that their most significant shortages are in advanced IT skills and programming, advanced data analysis, and mathematical skills. Among higher cognitive skills, significant shortfalls are seen in critical thinking and problem structuring and in complex information processing. About 40 percent of the executives surveyed pointed to a shortage of workers with these skills, which are needed for working alongside new technologies (Exhibit 4).

Companies see retraining as key to acquiring needed skills and adapting to the new work landscape
Surveyed executives expect significant changes to their workforce skill levels and worry about not finding the right skills by 2030. More than one in four survey respondents said that failing to capture the needed skills could directly harm financial performance and indirectly impede their efforts to leverage the value from AI.
To acquire the skills they need, companies have three main options: retraining, hiring, and contracting workers. Our survey suggests that executives are looking at all three options, with retraining the most widely reported tactic planned to address the skills mismatch: on average, out of companies that mentioned retraining as one of their tactics to address skills mismatch, executives said they would retrain 32 percent of their workforce. The scale of retraining needs varies in degree. For example, respondents in the automotive industry expect 36 percent of their workforce to be retrained, compared with 28 percent in the financial services industry. Out of those who have mentioned hiring or contracting as their tactics to address the skills mismatch, executives surveyed said they would hire an average of 23 percent of their workforce and contract an average of 18 percent.
Occupational transitions will affect high-, medium-, and low-wage workers differently
All ten European countries we examined for this report may see increasing demand for top-earning occupations. By contrast, workers in the two lowest-wage-bracket occupations could be three to five times more likely to have to change occupations compared to the top wage earners, our analysis finds. The disparity is much higher in the United States, where workers in the two lowest-wage-bracket occupations are up to 14 times more likely to face occupational shifts than the highest earners. In Europe, the middle-wage population could be twice as affected by occupational transitions as the same population in United States, representing 7.3 percent of the working population who might face occupational transitions.
Enhancing human capital at the same time as deploying the technology rapidly could boost annual productivity growth
About quantumblack, ai by mckinsey.
QuantumBlack, McKinsey’s AI arm, helps companies transform using the power of technology, technical expertise, and industry experts. With thousands of practitioners at QuantumBlack (data engineers, data scientists, product managers, designers, and software engineers) and McKinsey (industry and domain experts), we are working to solve the world’s most important AI challenges. QuantumBlack Labs is our center of technology development and client innovation, which has been driving cutting-edge advancements and developments in AI through locations across the globe.
Organizations and policy makers have choices to make; the way they approach AI and automation, along with human capital augmentation, will affect economic and societal outcomes.
We have attempted to quantify at a high level the potential effects of different stances to AI deployment on productivity in Europe. Our analysis considers two dimensions. The first is the adoption rate of AI and automation technologies. We consider the faster scenario and the late scenario for technology adoption. Faster adoption would unlock greater productivity growth potential but also, potentially, more short-term labor disruption than the late scenario.
The second dimension we consider is the level of automated worker time that is redeployed into the economy. This represents the ability to redeploy the time gained by automation and productivity gains (for example, new tasks and job creation). This could vary depending on the success of worker training programs and strategies to match demand and supply in labor markets.
We based our analysis on two potential scenarios: either all displaced workers would be able to fully rejoin the economy at a similar productivity level as in 2022 or only some 80 percent of the automated workers’ time will be redeployed into the economy.
Exhibit 5 illustrates the various outcomes in terms of annual productivity growth rate. The top-right quadrant illustrates the highest economy-wide productivity, with an annual productivity growth rate of up to 3.1 percent. It requires fast adoption of technologies as well as full redeployment of displaced workers. The top-left quadrant also demonstrates technology adoption on a fast trajectory and shows a relatively high productivity growth rate (up to 2.5 percent). However, about 6.0 percent of total hours worked (equivalent to 10.2 million people not working) would not be redeployed in the economy. Finally, the two bottom quadrants depict the failure to adopt AI and automation, leading to limited productivity gains and translating into limited labor market disruptions.

Four priorities for companies
The adoption of automation technologies will be decisive in protecting businesses’ competitive advantage in an automation and AI era. To ensure successful deployment at a company level, business leaders can embrace four priorities.
Understand the potential. Leaders need to understand the potential of these technologies, notably including how AI and gen AI can augment and automate work. This includes estimating both the total capacity that these technologies could free up and their impact on role composition and skills requirements. Understanding this allows business leaders to frame their end-to-end strategy and adoption goals with regard to these technologies.
Plan a strategic workforce shift. Once they understand the potential of automation technologies, leaders need to plan the company’s shift toward readiness for the automation and AI era. This requires sizing the workforce and skill needs, based on strategically identified use cases, to assess the potential future talent gap. From this analysis will flow details about the extent of recruitment of new talent, upskilling, or reskilling of the current workforce that is needed, as well as where to redeploy freed capacity to more value-added tasks.
Prioritize people development. To ensure that the right talent is on hand to sustain the company strategy during all transformation phases, leaders could consider strengthening their capabilities to identify, attract, and recruit future AI and gen AI leaders in a tight market. They will also likely need to accelerate the building of AI and gen AI capabilities in the workforce. Nontechnical talent will also need training to adapt to the changing skills environment. Finally, leaders could deploy an HR strategy and operating model to fit the post–gen AI workforce.
Pursue the executive-education journey on automation technologies. Leaders also need to undertake their own education journey on automation technologies to maximize their contributions to their companies during the coming transformation. This includes empowering senior managers to explore automation technologies implications and subsequently role model to others, as well as bringing all company leaders together to create a dedicated road map to drive business and employee value.
AI and the toolbox of advanced new technologies are evolving at a breathtaking pace. For companies and policy makers, these technologies are highly compelling because they promise a range of benefits, including higher productivity, which could lift growth and prosperity. Yet, as this report has sought to illustrate, making full use of the advantages on offer will also require paying attention to the critical element of human capital. In the best-case scenario, workers’ skills will develop and adapt to new technological challenges. Achieving this goal in our new technological age will be highly challenging—but the benefits will be great.
Eric Hazan is a McKinsey senior partner based in Paris; Anu Madgavkar and Michael Chui are McKinsey Global Institute partners based in New Jersey and San Francisco, respectively; Sven Smit is chair of the McKinsey Global Institute and a McKinsey senior partner based in Amsterdam; Dana Maor is a McKinsey senior partner based in Tel Aviv; Gurneet Singh Dandona is an associate partner and a senior expert based in New York; and Roland Huyghues-Despointes is a consultant based in Paris.
Explore a career with us
Related articles.

Generative AI and the future of work in America

The economic potential of generative AI: The next productivity frontier

What every CEO should know about generative AI
Understanding Naturalistic Observation in Research
This essay is about naturalistic observation, a research method used to observe subjects in their natural environment without interference. It discusses the advantages of this method, such as providing rich, qualitative insights into behavior, and the challenges, including observer bias and lack of control over variables. The essay also touches on ethical considerations and the impact of technological advancements on the effectiveness of naturalistic observation. Examples from various fields like anthropology, ecology, and psychology illustrate the method’s versatility and significance in understanding authentic behaviors in real-world settings.
How it works
Naturalistic observation emerges as a method frequently employed in psychology and the social sciences. This methodology entails the observation of subjects in their native habitat devoid of any manipulation or intrusion by the investigator. The primary objective is to amass data on the behavioral patterns of subjects within authentic settings, proffering insights that may elude capture within a more regimented laboratory milieu. By affording behaviors the latitude to manifest organically, researchers can glean genuine reactions and interchanges, rendering this method invaluable for certain types of inquiries.
An eminent advantage of naturalistic observation lies in its capacity to furnish a nuanced, qualitative comprehension of behavior. For instance, through the observation of juveniles at a recreational area, an investigator can discern not only their play dynamics but also their social dynamics, conflict resolution strategies, and the evolution of their play over time. These observations can subsequently underpin deductions regarding social maturation, aggression, collaboration, and other facets of behavior. Such profundity of insight often eludes attainment through alternative methodologies such as surveys or experiments, wherein the contrived nature of the milieu may exert a sway over the behavior under observation.
Nevertheless, naturalistic observation is not devoid of impediments. One of the principal challenges pertains to the specter of observer partiality. Since the investigator is actively monitoring and documenting behaviors, their own presumptions or convictions may inadvertently color their perceptions and interpretations. To counteract this tendency, researchers frequently deploy strategies such as inter-observer concordance, whereby multiple observers independently record the same occurrence and subsequently compare findings to ascertain congruity. Furthermore, meticulous protocols and training can aid observers in preserving objectivity to the fullest extent feasible.
Another hurdle is the paucity of dominion over extraneous variables. Within a natural setting, myriad factors may influence behavior, ranging from meteorological conditions to the presence of bystanders. This renders the establishment of causal relationships a daunting task. For instance, if an investigator is scrutinizing responses to public art installations, discerning whether reactions stem from the art per se or from ancillary factors such as temporal considerations or pedestrian traffic patterns may prove challenging. Despite these constraints, the concession is often warranted for the genuine, ecological validity that naturalistic observation affords.
Ethical considerations likewise loom large in naturalistic observation. Researchers must strike a delicate equilibrium between the exigencies of unobtrusive observation and the entitlements of the subjects under observation. Frequently, this entails safeguarding the anonymity of subjects and refraining from documenting their conduct without their explicit consent, particularly within private domains. Public settings, wherein individuals lack a reasonable expectation of privacy, typically afford greater latitude for naturalistic observation. Nevertheless, ethical precepts must be rigorously adhered to in order to uphold the dignity and rights of all implicated subjects.
Naturalistic observation has made substantial inroads across various domains of inquiry. In anthropology, it has served as a lens through which to explore cultural customs and social configurations across disparate communities. In ecology, scientists engage in the observation of fauna within their native habitats to fathom behaviors germane to survival, procreation, and social dynamics. In psychology, it has proven instrumental in elucidating human behaviors spanning from the genesis of adolescence to social dynamics and psychological well-being. The method’s malleability renders it adaptable to a panoply of research queries and contexts, endowing it with a versatile utility in the researcher’s repertoire.
Technological strides have further augmented the efficacy of naturalistic observation. Contemporary tools such as video recording apparatuses, mobile devices, and even unmanned aerial vehicles can expedite data collection while minimizing interference. These innovations facilitate more granular and precise observations, which can be reviewed iteratively for analysis. Moreover, analytic software can aid in discerning patterns and drawing inferences from voluminous troves of observational data, thereby engendering a more rigorous and methodical analytical process.
In summation, naturalistic observation emerges as a potent means of dissecting behavior within its native milieu. Despite its impediments, including observer partiality, variable control constraints, and ethical quandaries, it furnishes unparalleled insights into the interplay between subjects and their surroundings. By abstaining from intervention, researchers can procure data that is both authentic and germane to real-world contexts. As technological progress marches onward, the potential for naturalistic observation to enrich our comprehension of intricate behaviors is poised to burgeon, cementing its status as a cornerstone of research methodologies. Recall, this exposition serves as a springboard for contemplation and further exploration. For bespoke guidance and to ensure adherence to scholarly standards, contemplate engaging the services of professionals at EduBirdie.
Cite this page
Understanding Naturalistic Observation in Research. (2024, Jun 01). Retrieved from https://papersowl.com/examples/understanding-naturalistic-observation-in-research/
"Understanding Naturalistic Observation in Research." PapersOwl.com , 1 Jun 2024, https://papersowl.com/examples/understanding-naturalistic-observation-in-research/
PapersOwl.com. (2024). Understanding Naturalistic Observation in Research . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/understanding-naturalistic-observation-in-research/ [Accessed: 1 Jun. 2024]
"Understanding Naturalistic Observation in Research." PapersOwl.com, Jun 01, 2024. Accessed June 1, 2024. https://papersowl.com/examples/understanding-naturalistic-observation-in-research/
"Understanding Naturalistic Observation in Research," PapersOwl.com , 01-Jun-2024. [Online]. Available: https://papersowl.com/examples/understanding-naturalistic-observation-in-research/. [Accessed: 1-Jun-2024]
PapersOwl.com. (2024). Understanding Naturalistic Observation in Research . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/understanding-naturalistic-observation-in-research/ [Accessed: 1-Jun-2024]
Don't let plagiarism ruin your grade
Hire a writer to get a unique paper crafted to your needs.

Our writers will help you fix any mistakes and get an A+!
Please check your inbox.
You can order an original essay written according to your instructions.
Trusted by over 1 million students worldwide
1. Tell Us Your Requirements
2. Pick your perfect writer
3. Get Your Paper and Pay
Hi! I'm Amy, your personal assistant!
Don't know where to start? Give me your paper requirements and I connect you to an academic expert.
short deadlines
100% Plagiarism-Free
Certified writers
This paper is in the following e-collection/theme issue:
Published on 31.5.2024 in Vol 26 (2024)
Evaluation and Comparison of Academic Impact and Disruptive Innovation Level of Medical Journals: Bibliometric Analysis and Disruptive Evaluation
Authors of this article:

Original Paper
- Yuyan Jiang 1 , MPhil ;
- Xue-li Liu 1, 2 , BM ;
- Zixuan Zhang 1 , MPhil ;
- Xinru Yang 1 , MPhil
1 Henan Research Center for Science Journals, Xinxiang Medical University, Xinxiang, China
2 Faculty of Humanities & Social Sciences, Xinxiang Medical University, Xinxiang, China
Corresponding Author:
Xue-li Liu, BM
Faculty of Humanities & Social Sciences
Xinxiang Medical University
Library and Information Building, 2nd Fl.
No. 601, Jinsui Avenue, Hongqi District
Xinxiang, 450003
Phone: 86 1 383 736 0965
Email: [email protected]
Background: As an important platform for researchers to present their academic findings, medical journals have a close relationship between their evaluation orientation and the value orientation of their published research results. However, the differences between the academic impact and level of disruptive innovation of medical journals have not been examined by any study yet.
Objective: This study aims to compare the relationships and differences between the academic impact, disruptive innovation levels, and peer review results of medical journals and published research papers. We also analyzed the similarities and differences in the impact evaluations, disruptive innovations, and peer reviews for different types of medical research papers and the underlying reasons.
Methods: The general and internal medicine Science Citation Index Expanded (SCIE) journals in 2018 were chosen as the study object to explore the differences in the academic impact and level of disruptive innovation of medical journals based on the OpenCitations Index of PubMed open PMID-to-PMID citations (POCI) and H1Connect databases, respectively, and we compared them with the results of peer review.
Results: First, the correlation coefficients of the Journal Disruption Index (JDI) with the Journal Cumulative Citation for 5 years (JCC 5 ), Journal Impact Factor (JIF), and Journal Citation Indicator (JCI) were 0.677, 0.585, and 0.621, respectively. The correlation coefficient of the absolute disruption index (Dz) with the Cumulative Citation for 5 years (CC 5 ) was 0.635. However, the average difference in the disruptive innovation and academic influence rankings of journals reached 20 places (about 17.5%). The average difference in the disruptive innovation and influence rankings of research papers reached about 2700 places (about 17.7%). The differences reflect the essential difference between the two evaluation systems. Second, the top 7 journals selected based on JDI, JCC 5 , JIF, and JCI were the same, and all of them were H-journals. Although 8 (8/15, 53%), 96 (96/150, 64%), and 880 (880/1500, 58.67%) of the top 0.1%, top 1%, and top 10% papers selected based on Dz and CC 5 , respectively, were the same. Third, research papers with the “changes clinical practice” tag showed only moderate innovation (4.96) and impact (241.67) levels but had high levels of peer-reviewed recognition (6.00) and attention (2.83).
Conclusions: The results of the study show that research evaluation based on innovative indicators is detached from the traditional impact evaluation system. The 3 evaluation systems (impact evaluation, disruptive innovation evaluation, and peer review) only have high consistency for authoritative journals and top papers. Neither a single impact indicator nor an innovative indicator can directly reflect the impact of medical research for clinical practice. How to establish an integrated, comprehensive, scientific, and reasonable journal evaluation system to improve the existing evaluation system of medical journals still needs further research.
Introduction
Scientific and technical journals play a crucial role in showcasing research findings, and the value orientation of their published results is closely intertwined with their evaluation orientation. However, since Garfield [ 1 ] put forward the idea that “citation analysis can be used as an evaluation tool for journals” in 1972, the evaluation system of journals based on academic impact has become mainstream. However, relying too much on impact indicators for evaluation may hurt academic research and discipline progress.
On the one hand, some scholars have long pointed out that ranking journals according to their impact factors is noncomprehensive and may lead to misleading conclusions [ 2 , 3 ]. Meanwhile, many academic journals and publishers have engaged in strategic self-citation, leading to an overinflated journal impact factor (JIF) [ 4 ]. Some editorial behaviors to enhance the JIF clearly violate academic norms [ 5 ]. Some scholars are overciting each other’s work to enhance their academic impact [ 6 ]. External contingencies can have a devastating effect on citation indicators [ 7 ]. Scientists themselves also present a mixed attitude toward impact factors [ 8 ].
On the other hand, despite all the benefits of increased academic impact to journals, there is a nonnegligible problem in the evaluation of journals that citation indicators essentially characterize the impact of journals rather than their disruptive innovation [ 9 ]. Relevant studies have confirmed that the level of disruptive innovation of scientific research is getting increasingly lower [ 10 ] and the progress in various disciplines is slowing [ 11 ]. This is often overlooked against the background of impact-only evaluations. Therefore, despite the urgent need for disruptive innovations in science [ 12 ], impact-based journal rankings have made it more difficult to accept novel results [ 13 ], replacing the “taste of science” with the “taste of publication” [ 14 ] in the actual environment.
The evaluation of academic journals is about not only the journals themselves [ 15 ] but also the wide use of the evaluation results in academic review, promotion, and tenure decisions [ 16 ]. Meanwhile, the quality and results of medical research are directly related to human health and life and have a direct impact on human health and well-being. Therefore, the general and internal medicine journals indexed in Science Citation Index Expanded (SCIE) in 2018 were chosen as the study object. The OpenCitations Index of PubMed open PMID-to-PMID citations (POCI) and H1 Connect databases were selected as the sources for citation relationship data and peer review data. We investigated the connections and contrasts between the academic impact, disruptive innovation level, and results of peer review for medical journals and published research papers. We also analyzed the similarities and differences as well as the fundamental causes of the varying evaluation results in terms of impact evaluation, disruptive innovation, and peer review for various types of medical research papers. We aimed to provide a reference for the correct understanding of the innovation level of the results published by journals; the scientific and reasonable evaluation of medical journals; and the construction of a scientific, objective, and fair academic evaluation system.
Research Object
Because there is basically no disruptive innovation in the review literature, this paper only focuses on the general and internal medicine journals indexed in SCIE in 2018 and the research papers involved. In addition, considering the computational efficiency, accuracy, and difficulty of data acquisition, research papers for which citation relationships in the aforementioned journals were not included in POCI and the journals with too few references (less than 10) were excluded. Finally, 114 journals were retained at the journal level, and 15,206 research papers were retained at the paper level.
Data Resource
The data acquired in this study included journal information, literature information, citation relationship data, and peer review data. The data were obtained through the Journal Citation Reports (JCR), Web of Science (WoS), POCI, and H1 Connect databases.
Of these databases, POCI is a Resource Description Framework (RDF) data set containing details of all the citations from publications bearing PMIDs to other PMID-identified publications harvested from the National Institutes of Health Open Citations Collection. POCI covers more than 29 million bibliographic resources and more than 717 million citation links (as of the last update in January 2023). Citations in POCI are not considered simple links but as data entities. This means that it is permissible to assign descriptive attributes to each citation, such as the date of creation of the citation, its time span, and its type [ 17 ].
H1 Connect (formerly Faculty Opinions), the world’s most authoritative peer review database in the biomedical field, incorporates the combined efforts of more than 8000 international authoritative experts from around the globe and is a knowledge discovery tool used to evaluate published research. H1 Connect’s reviewers are authoritative experts in the life sciences and medical fields. They provide commentary, opinions, and validation of key papers in their own field. The quality and rigor of the reviewers mean that researchers can be assured of the quality of the papers they recommend, and H1 Connect brings these recommendations together to recommend high-quality research to a wider audience. H1 Connect’s experts typically evaluate the “high level” of research literature in the field within 2 months of publication, with over 90% of recommendations made within 6 months of publication.
Data Acquisition and Processing
The data acquired for this study consisted of 3 parts. The specific steps for data acquisition and processing were (1) data acquisition and (2) data processing.
Data Acquisition
The steps taken to acquire the data included the following: log in to JCR; select Medicine, General & Internal in the “Browse categories” page; select JCR Year=2018 and Citation Indexes=SCIE in the filters; export the result to XLS format; according to the acquired journal title, select the publication year as 2018 and the literature type as Article to search the WoS core database; and export the full record of the journal literature in XLS format. Finally, we downloaded the related H1 Connect literature data and POCI data according to the list of journals.
Data Processing
To process the data, we undertook the following steps: use Navicat to import the full record of research papers into the local SQLite database, process the downloaded POCI data, extract the PMID numbers of all the focus papers from the full record, retrieve the references and citations of the focus papers as well as the citations of the references of the focus papers in the local database transformed based on the POCI data, and establish the relevant data tables for the subsequent calculations.
Evaluation Indicators
Innovation indicators.
Some researchers have observed, at an early stage, that some technological innovations complete and improve current technologies without replacing them while others outright eliminate technologies that were used in the past. However, for a long time, scholars did not analyze and explain the essence of this phenomenon. It was not until 1986 that Tushman and Anderson [ 18 ] summarized the phenomenon as follows: There are 2 types of major technological shifts that disrupt or enhance the capabilities of existing firms in an industry. However, Christensen [ 19 ], a professor at Harvard Business School in the United States, argued that disruptive innovations are new technologies that replace existing mainstream technologies in unexpected ways. Building on these views, Funk and Owen-Smith [ 20 ] provided deeper and more insightful insights. They argued that the dichotomy between disruptive and augmentative technologies lacks nuance and that the impact of new technologies on the status quo is a matter of degree rather than absolute impact.
In this regard, Govindarajan and Kopalle [ 21 ] also pointed out that disruptive innovation lacks reliable and valid measurement standards. Therefore, Funk and Owen-Smith [ 20 ] created the consolidation-disruption (CD) index, which aims to quantify the degree of technological change brought about by new patents. The index drew the attention of Wu et al [ 22 ], who analogized the basic principle of the CD index to measure disruption by calculating the citation substitution of the focus paper in the citation network and who were the first to apply the evaluation of disruptive innovation to the world of bibliometrics.
As an important carrier of academic results, it is important to evaluate papers quantitatively, rationally, and efficiently in terms of their innovation [ 23 ]. The disruption (D) index has received widespread attention after it was proposed by Wu et al [ 22 ]. A subset of scholars then explored disruptive papers in specific subject areas, including scientometrics [ 24 ], craniofacial surgery [ 25 ], pediatric surgery [ 26 ], synthetic biology [ 27 ], energy security [ 28 ], colorectal surgery [ 29 ], otolaryngology [ 30 ], military trauma [ 31 ], breast cancer [ 32 ], radiology [ 33 ], ophthalmology [ 34 ], plastic surgery [ 35 ], urology [ 36 ], and general surgery [ 37 ], based on the D index. Park et al [ 10 ] also analyzed the annual dynamics of the disruption level of papers and patents across the subject areas.
Another group of scholars conducted in-depth research on the index itself: Bornmann et al [ 38 ] explored the convergent validity of the index and the variants that may enhance the effectiveness of the measure and tested the validity of the D index based on the literature in the field of physics [ 39 ]. Ruan et al [ 40 ] provided an in-depth reflection on the limitations of the application of the D index as a measure of scientific and technological progress. Liu et al [ 41 , 42 ] empirically investigated the stabilization time window of the D index in different subject areas and addressed the mathematical inconsistency of the traditional D index and proposed an absolute disruption index (Dz; as in Equation 2) [ 43 ].
This series of studies has made it possible to evaluate the disruption of research papers based on the D index, which has gradually matured. On this basis, Jiang and Liu [ 44 ] proposed the Journal Disruption Index (JDI) to evaluate the disruptive innovation level of journals (as in Equation 3) and validated the evaluation effect of this indicator based on Chinese SCIE journals [ 45 ].
In Equations 1, 2, and 3, N F refers to the literature that only cites the focus paper (FP), N B refers to the literature that cites both the focus paper and at least one reference (R) of the focus paper, and N R refers to the literature that only cites at least one reference (R) of the focus paper but not the focus paper. n is the number of “Article” type pieces of literature contained in the journal, and Dz i is the Dz of the i th article in the journal.
In this study, Dz and JDI were chosen to evaluate the disruption of the selected studies at the literature and journal levels, respectively. Bornmann and Tekles [ 46 ] argued that 3 years is necessary regardless of the measurement for that discipline. Considering that, in the determination of the stabilization time window of the D index for each discipline conducted by Liu et al [ 42 ], the stabilization time window for clinical medicine is 4 years after publication. Therefore, in the process of calculating Dz in this paper, the citation time window of the focus papers was set to 2018 to 2022 to ensure the validity of the results. In addition, because the JDI value was too small, we multiplied the JDI by 1000 in all subsequent presentations.
Peer Review Indicators
The peer review indicators selected for this study included the peer review score (PScore), weighted peer review stars (PStar_w), and weighted peer review evaluation times (PTime_w). In this case, the weighted indicators refer to the weighting of ratings and number of evaluations by the number of evaluators when an evaluation was completed by more than one reviewer.
The advantage of using peer review indicators is that it can make up for the lag and one-sidedness of relying solely on the citations among the literature to assess the quality of the literature. It also corrects the shortcomings of the traditional JIF to judge the quality of the literature. Compared with a single impact indicator, it is more scientific.
Impact Indicators
The impact indicators selected for this study included the Cumulative Citation for 5 years (CC 5 ), JIF, Journal Citation Indicator (JCI), and Journal Cumulative Citation for 5 years (JCC 5 ). Among these, JIF is the total number of citations for scholarly articles published in the journal in the past 2 years divided by the total number of citable articles. JCI is the average Category Normalized Citation Impact (CNCI) of the citable literature published in the specific journal in the previous 3 years. The JCC 5 is obtained by dividing the sum of the citation frequencies recorded in the POCI repository of the corresponding research papers (focus papers) of the selected journals for the years 2018 to 2022 by the number of research papers published by the journal (as in Equation 4).
In Equation 4, a i C t represents the number of citations of the i th research paper of the journal in year t, and n is the number of research papers published by the journal.
Evaluation and Correlation Analyses of Journals Under Different Evaluation Perspectives
Analysis of differences in academic influence and level of disruptive innovation of journals.
The academic impact and level of disruptive innovation of the selected 114 journals, the results of the correlation analyses of the indicators, and the differences in the rankings are shown in Table 1 , Table 2 , and Figure 1 , respectively. From these, we can see that (1) journals that are at the top of the ranking of impact indicators are usually also ranked at the top in the ranking of disruptive innovation, (2) journals at the bottom of the impact rankings are usually at the bottom of the innovation rankings, and (3) there is little difference in the ranking results of journals under different impact indicators, but there is a big difference in the ranking results of influence and disruptive innovation. Although there are moderate correlations between the JDI of journals and the 3 influence indicators of JIF, JCI, and JCC 5 , the average difference between the disruptive innovation ranking and academic influence ranking of the journals included in the study reached 20 places.
a JCC 5 : Journal Cumulative Citation for 5 years.
b JDI: Journal Disruption Index.
c JIF: Journal Impact Factor.
d JCI: Journal Citation Indicator.
a JDI: Journal Disruption Index.
b JCC 5 : Journal Cumulative Citation for 5 years.
e Not applicable.

Analysis of the Differences Between the Journals’ Impact and Disruption and the Results of Peer Review
In order to better analyze the differences between the academic impact and level of disruptive innovation with peer-reviewed results of journals in the field of general and internal medicine, papers indexed in H1 Connect were referred to as “H-papers,” and the source journals of “H-papers” are referred to as “H-journals.” The evaluation indicators, ranking of H-journals, and the percentage of H-papers are shown in Table 3 and Table 4 . We can see that (1) the top 7 journals in terms of both academic impact and disruptive innovation are all H-journals, (2) the average impact ranking of H-journals is higher than the average innovation ranking, and (3) some journals with low impact and innovation also became H-journals.
a JPScore: journal peer review score.
b JPTime_w: weighted journal peer review evaluation time.
c JFPStar_w: weighted journal peer review star.
b JIF: Journal Impact Factor.
c JCI: Journal Citation Indicator.
Evaluation and Correlation Analyses of Papers Under Different Evaluation Perspectives
Analysis of differences in academic impact and level of disruptive innovation of papers.
Ideally, if an article is accepted by a specific journal, it is because its overall quality is similar to other papers previously published in that journal [ 47 ]. However, journal-level indicators are, at best, only moderately suggestive of the quality of an article [ 48 ], which makes indicators that measure specific articles more popular [ 49 ]. Therefore, in this study, research papers in the field of general and internal medicine were also evaluated in terms of their academic impact and level of disruptive innovation, and the results are shown in Figure 2 . From the results, we can see that research papers that rank high in the impact ranking usually also rank high in the disruptive innovation ranking. There were 8 (8/15, 53%), 96 (96/150, 64%), and 880 (880/1500, 58.67%) of the Top 0.1%, Top 1%, and Top 10% papers, respectively, selected based on the Dz and CC 5 that were the same. Second, the level of disruptive innovation of research papers with the same level of impact varied greatly, and the impact level of research papers with the same level of disruptive innovation also varied greatly. Third, despite the high correlation ( r =0.635, P <.001) between the Dz and CC 5 of the selected research papers, the average difference between their innovation and impact rankings reached about 2700. Fourth, the actual analysis results showed no correlation between the innovation of the selected research paper and the number of references, which indicates that the Dz index is basically unaffected by the difference in the number of references in the actual evaluation process ( r =0.006, P =.43).

Analysis of Differences Between Papers’ Impact and Disruption and the Results of Peer Review
In order to better analyze the differences between the academic impact, level of disruptive innovation, and peer review results of journal research papers in the field of general and internal medicine, the differences between the academic impact and disruptive innovation level and the peer review results of H-papers were analyzed. The specific results are shown in Table 5 and Figure 3 . From the results, we see that there were 8 (8/15, 53%), 65 (65/150, 43.3%), and 187 (187/1500, 12.47%) H-papers among the top 0.1%, top 1%, and top 10% papers, respectively, selected based on Dz. There were 5 (5/15, 33%), 74 (74/150, 49.3%), and 220 (220/1500, 14.67%) H-papers among the top 0.1%, top 1%, and top 10% papers, respectively, selected based on CC 5 . Second, there was a significant positive correlation between the peer review indicators, disruptive innovation indicators, and academic impact indicators of H-papers, reflecting the consistency between the quantitative evaluation and peer review at the overall level. Third, the average impact ranking of H-papers was 865 (top 5.68%), and the average disruptive innovation ranking was 1726 (top 11.35%), which means that the average impact ranking of H-papers was higher than the average disruptive innovation ranking. Fourth, some papers with low academic impact and disruptive innovation level also became H-papers. Fifth, compared with the CC 5 , Dz has a minor correlation advantage with PTime_w and PStar_w.
a CC 5 : Cumulative Citation for 5 years.
b Dz: absolute disruption index.
c PTime_w: weighted peer review evaluation times.
d PStar_w: weighted peer review stars.
e PScore: peer review score.
f Not applicable.

In addition to rating and commenting on the included research papers, different labels are added by the reviewers of articles in H1 Connect according to their different internal characteristics. The relevant definitions are shown in Table 6 (refer to Du et al [ 50 ]). We categorized and counted the 257 H-papers (in this study, if a paper had more than 1 tag, it was counted separately in the calculation of each tag), and the results are shown in Table 7 . From this, we can see that (1) research papers with the tags in the “Novel Drug Target,” “Technical Advance,” and “New Finding” categories had a high academic impact and a high disruptive innovation level; (2) research papers with the “Changes Clinical Practice” tag showed only a moderate academic impact and disruptive innovation level but had high levels of peer-reviewed recognition and attention; (3) experts showed higher recognition and concern for research papers with tags of “Negative/Null Result,” “Controversial,” “Refutation,” and “Interesting Hypothesis,” but their academic impact and disruptive innovation level were lower than others.
c PScore: peer review score.
e PTime_w: weighted peer review evaluation times.
Principal Findings
Evaluation of disruptive innovation is detached from the traditional evaluation system.
From these research results, large differences were seen between the innovation and impact rankings of the journals and research papers included in the study. This is also consistent with the findings of Guo and Zhou [ 51 ]. This phenomenon reflects the essential difference between the 2 different evaluation systems. It also proves that the evaluation of the disruptive innovation of research papers and journals based on Dz and JDI is not consistent with the traditional evaluation system of impact.
The essence of disruptive evaluation is to measure the innovation from the substitution level of knowledge structure. This evaluation method brings new ideas to the field of scientific research evaluation, helps relevant institutions and scholars remove the constraints of the traditional evaluation system, and helps to establish a value orientation of encouraging innovation for scientific research and scientific and technological journals, so as to promote the benign development of the academic ecology.
The 3 Evaluation Systems Only Have High Consensus on the Top Object
Although, given the consistency of scientific evaluation, there will be some uniformity in the level of disruptive innovation, level of academic impact, and peer review results of journals as well as research papers.
However, from the research results presented in this paper, we can see that (1) the top 7 journals in terms of both academic impact and disruptive innovation were all H-journals, (2) more than one-half of the top papers selected based on Dz and CC 5 were the same, (3) the average H-papers were ranked at the top in terms of impact and innovation, and (4) the results of the different evaluation systems only had high consensus on the authoritative journals and top papers in the field.
These findings are also consistent with those of Goman [ 52 ] and Chi et al [ 53 ]. A fundamental reason for this phenomenon is that the purposes of the 3 evaluation systems are inherently different. Therefore, in the actual evaluation process, the 3 kinds of indicators are not interchangeable, and the combination of the 3 evaluation systems may be a feasible solution to establish a comprehensive, scientific, and reasonable journal evaluation system.
A Single Indicator Cannot Accurately Reflect the Impact of Medical Research on Clinical Practice Alone
From the aforementioned findings, we can see that research papers of the “Novel Drug Target,” “ Technical Advance,” and “New Finding” types have high academic impact and high levels of innovation, which is in line with their classification definitions. This is also consistent with the findings of Du et al [ 50 ], Thelwall et al [ 54 ], and Jiang and Liu [ 55 ]. Second, research papers of the “Changes Clinical Practice” type showed only moderate levels of innovation and impact but had high levels of peer-reviewed recognition and attention. This reflects the difficulty of evaluating the impact of a particular academic paper on clinical practice, whether the evaluation system is based on academic impact or level of disruptive innovation. Third, peer-reviewed experts show higher recognition and concern for research papers of the types “Negative/Null Result,” “Controversial,” “Refutation,” and “Interesting Hypothesis,” but the level of impact and disruptive innovation of these papers are lower. This partly reflects the current academic community’s excessive focus on positive results; deliberate avoidance of negative results; and overall lack of support for debatable, falsified, and other types of research.
Several scholars have recently suggested that the evaluation system of medical journals should be redesigned for contemporary clinical impact and utility [ 56 ]. In this regard, Thelwall and Maflahi [ 57 ] advocated that the references of a guideline are an important basis for studying clinical value. However, Traylor and Herrmann-Lingen [ 58 ] found only a weak correlation between the number of citations to individual journals in the guidelines and their respective JIF. Therefore, the JIF is not a suitable tool for assessing the clinical relevance of medical research. The results of this study similarly found that research papers of the “Changes Clinical Practice” type showed only moderate levels of disruptive innovation and academic impact, but such research papers received higher recognition and attention from peer review experts. Therefore, combining quantitative evaluation with peer review may be a feasible way to measure the impact of medical research on clinical practice.
Limitations
However, this study also has the following limitations. First, papers in the medical field have a preference for citing review articles [ 59 ], which has a certain impact on the evaluation of the disruptive innovation of research papers. Second, the scoring mechanism provided to its reviewers by H1 Connect has a low differentiation degree and cannot perfectly distinguish the differences in quality between papers yet. In addition, H1 Connect has too few evaluators. Brezis and Birukou [ 60 ] illustrated that, if the number of reviewers is increased to about 10, the correlation between the results and the quality of the paper will be significantly improved. However, it is difficult to seek so many high-quality experts who are willing to accept open peer review in the high pressure environment of “Publish or Perish” [ 61 ]. Third, since the citation data sources used in this study are all based on PubMed data, this study also suffers from the problem of missing references and citations that are not labeled with a PMID, which affects the accuracy of the evaluation results to a certain extent. In future studies, we will obtain more accurate measurement results by jointly using multiple sources of citation data.
Conclusions
In this study, the general and internal medicine journals indexed in SCIE in 2018 were chosen as the study object. The POCI and H1 Connect databases were selected as sources of citation relationship data and peer review data. We investigated the connections and contrasts between the academic impact, level of disruptive innovation, and results of peer review for medical journals and published research papers. We also analyzed the similarities and differences as well as the fundamental causes of the varying evaluation results in terms of impact evaluation, disruptive innovation, and peer review for various types of medical research papers.
The results of this study show that the evaluation of scientific research based on the innovation index is detached from the traditional impact evaluation system, the 3 evaluation systems only have high consistency for authoritative journals and top papers, and neither the single impact index nor the innovation index can directly reflect the impact of medical research on clinical practice.
In addition, with the increasing importance of replicative science, the accuracy of statistical reports, evidential value of reported data, and replicability of given experimental results [ 62 ] should also be included in the examination of journal quality. How to establish a comprehensive, all-encompassing, scientific, and reasonable journal evaluation system needs to be further investigated.
Acknowledgments
XL was supported by the National Social Science Foundation of China (23BTQ085), Major Project of Basic Research on Philosophy and Social Sciences in Henan Universities (2024-JCZD-23).
Data Availability
All citation data can be obtained from [ 63 ].
Authors' Contributions
XL conceptualized the study, reviewed and edited the manuscript, and supervised the study. YJ was responsible for the methodology, provided the software and other resources, performed the formal analysis, and wrote the original manuscript draft. YJ and XL acquired funding. YJ, XY, and ZZ curated the data. XY and ZZ also contributed to the study investigation.
Conflicts of Interest
None declared.
- Garfield E. Citation analysis as a tool in journal evaluation. Science. Nov 03, 1972;178(4060):471-479. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Hansson S. Impact factor as a misleading tool in evaluation of medical journals. Lancet. Sep 30, 1995;346(8979):906. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Metze K, Borges da Silva FA. Ranking of journals by journal impact factors is not exact and may provoke misleading conclusions. J Clin Pathol. May 11, 2022;75(10):649-650. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Siler K, Larivière V. Who games metrics and rankings? Institutional niches and journal impact factor inflation. Research Policy. Dec 2022;51(10):104608. [ CrossRef ]
- Martin BR. Editors’ JIF-boosting stratagems – Which are appropriate and which not? Research Policy. Feb 2016;45(1):1-7. [ CrossRef ]
- Zaidi SJA, Taqi M. Citation cartels in medical and dental journals. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. Jun 01, 2023;33(6):700-701. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Fassin Y. Research on Covid-19: a disruptive phenomenon for bibliometrics. Scientometrics. May 07, 2021;126(6):5305-5319. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Buela-Casal G, Zych I. What do the scientists think about the impact factor? Scientometrics. Feb 22, 2012;92(2):281-292. [ CrossRef ]
- Thelwall M, Kousha K, Stuart E, Makita M, Abdoli M, Wilson P, et al. In which fields are citations indicators of research quality? Asso for Info Science & Tech. May 04, 2023;74(8):941-953. [ CrossRef ]
- Park M, Leahey E, Funk R. Papers and patents are becoming less disruptive over time. Nature. Jan 2023;613(7942):138-144. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Chu JSG, Evans JA. Slowed canonical progress in large fields of science. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. Oct 12, 2021;118(41):1. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Schattner U, Shatner M. Science desperately needs disruptive innovation. Qeios. Jun 07, 2023:1. [ CrossRef ]
- Liang Z, Mao J, Li G. Bias against scientific novelty: A prepublication perspective. Asso for Info Science & Tech. Nov 19, 2022;74(1):99-114. [ CrossRef ]
- Osterloh M, Frey BS. Ranking games. Eval Rev. Aug 04, 2014;39(1):102-129. [ CrossRef ]
- Kulczycki E, Huang Y, Zuccala AA, Engels TCE, Ferrara A, Guns R, et al. Uses of the Journal Impact Factor in national journal rankings in China and Europe. Asso for Info Science & Tech. Aug 13, 2022;73(12):1741-1754. [ CrossRef ]
- McKiernan E, Schimanski L, Muñoz Nieves C, Matthias L, Niles M, Alperin J. Use of the Journal Impact Factor in academic review, promotion, and tenure evaluations. Elife. Jul 31, 2019;8:8. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Heibi I, Peroni S, Shotton D. Software review: COCI, the OpenCitations Index of Crossref open DOI-to-DOI citations. Scientometrics. Sep 14, 2019;121(2):1213-1228. [ CrossRef ]
- Tushman ML, Anderson P. Technological discontinuities and organizational environments. Administrative Science Quarterly. Sep 1986;31(3):439. [ CrossRef ]
- Christensen CM. The Innovator's Dilemma: When New Technologies Cause Great Firms to Fail (Management of Innovation and Change). Boston, MA. Harvard Business Review Press; 1997.
- Funk RJ, Owen-Smith J. A dynamic network measure of technological change. Management Science. Mar 2017;63(3):791-817. [ CrossRef ]
- Govindarajan V, Kopalle PK. Disruptiveness of innovations: measurement and an assessment of reliability and validity. Strategic Management Journal. Dec 22, 2005;27(2):189-199. [ CrossRef ]
- Wu L, Wang D, Evans JA. Large teams develop and small teams disrupt science and technology. Nature. Feb 13, 2019;566(7744):378-382. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Kostoff RN, Boylan R, Simons GR. Disruptive technology roadmaps. Technological Forecasting and Social Change. Jan 2004;71(1-2):141-159. [ CrossRef ]
- Bornmann L, Devarakonda S, Tekles A, Chacko G. Disruptive papers published in Scientometrics: meaningful results by using an improved variant of the disruption index originally proposed by Wu, Wang, and Evans (2019). Scientometrics. Mar 14, 2020;123(2):1149-1155. [ CrossRef ]
- Horen S, Hansdorfer M, Kronshtal R, Dorafshar A, Becerra A. The most disruptive publications in craniofacial surgery (1954-2014). J Craniofac Surg. Oct 01, 2021;32(7):2426-2430. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Sullivan GA, Skertich NJ, Gulack BC, Becerra AZ, Shah AN. Shifting paradigms: The top 100 most disruptive papers in core pediatric surgery journals. J Pediatr Surg. Aug 2021;56(8):1263-1274. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Meyer C, Nakamura Y, Rasor BJ, Karim AS, Jewett MC, Tan C. Analysis of the innovation trend in cell-free synthetic biology. Life (Basel). Jun 11, 2021;11(6):551. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Jiang Y, Liu X. A bibliometric analysis and disruptive innovation evaluation for the field of energy security. Sustainability. Jan 05, 2023;15(2):969. [ CrossRef ]
- Becerra A, Grimes C, Grunvald M, Underhill J, Bhama A, Govekar H, et al. A new bibliometric index: the top 100 most disruptive and developmental publications in colorectal surgery journals. Dis Colon Rectum. Mar 01, 2022;65(3):429-443. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Sheth AH, Hengartner A, Abdou H, Salehi PP, Becerra AZ, Lerner MZ. Disruption index in otolaryngology: uncovering a bibliometric history of a rapidly evolving field. Laryngoscope. Feb 19, 2024;134(2):629-636. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Dilday J, Gallagher S, Bram R, Williams E, Grigorian A, Matsushima K, et al. Citation versus disruption in the military: Analysis of the top disruptive military trauma research publications. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. May 15, 2023;95(2S):S157-S169. [ CrossRef ]
- Grunvald M, Williams M, Rao R, O’Donoghue C, Becerra A. 100 disruptive publications in breast cancer research. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. Aug 01, 2021;22(8):2385-2389. [ CrossRef ]
- Abu-Omar A, Kennedy P, Yakub M, Robbins J, Yassin A, Verma N, et al. Extra credit for disruption: trend of disruption in radiology academic journals. Clin Radiol. Dec 2022;77(12):893-901. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Patel PA, Javed Ali M. Characterizing innovation in science through the disruption index. Semin Ophthalmol. Aug 18, 2022;37(6):790-791. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Neubauer DC, Blum JD, Labou SG, Heskett KM, Calvo RY, Reid CM, et al. Using the disruptive score to identify publications that changed plastic surgery practice. Ann Plast Surg. 2022;88(4):S385-S390. [ CrossRef ]
- Khusid JA, Gupta M, Sadiq AS, Atallah WM, Becerra AZ. Changing the status quo: the 100 most-disruptive papers in urology? Urology. Jul 2021;153:56-68. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Williams MD, Grunvald MW, Skertich NJ, Hayden DM, O'Donoghue C, Torquati A, et al. Disruption in general surgery: Randomized controlled trials and changing paradigms. Surgery. Dec 2021;170(6):1862-1866. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Bornmann L, Devarakonda S, Tekles A, Chacko G. Are disruption index indicators convergently valid? The comparison of several indicator variants with assessments by peers. Quantitative Science Studies. Aug 2020;1(3):1242-1259. [ CrossRef ]
- Bu Y, Waltman L, Huang Y. A multidimensional framework for characterizing the citation impact of scientific publications. Quantitative Science Studies. 2021;2(1):155-183. [ CrossRef ]
- Ruan X, Lyu D, Gong K, Cheng Y, Li J. Rethinking the disruption index as a measure of scientific and technological advances. Technological Forecasting and Social Change. Nov 2021;172:121071. [ CrossRef ]
- Liu X, Shen Z, Liao Y, Yang L. The research about the improved disruption index and its influencing factors. Library and Information Service. 2020;64(24):84-91. [ CrossRef ]
- Liu X, Shen Z, Liao Y, Zhu M, Yang L. Research on the stable time window of disruption index. Library and Information Service. 2021;65(18):49-57. [ CrossRef ]
- Liu X, Liao Y, Zhu M. A preliminary study on the application of disruption index to scientific research evaluation. Information Studies: Theory & Application. 2021;44(12):34-40. [ CrossRef ]
- Jiang Y, Liu X. A construction and empirical research of the journal disruption index based on open citation data. Scientometrics. May 18, 2023;128(7):3935-3958. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Jiang Y, Wang L, Liu X. Innovative evaluation of Chinese SCIE-indexed scientific journals: An empirical study based on the disruption index. Chinese Journal of Scientific and Technical Periodicals. 2023;34(8):1060-1068. [ CrossRef ]
- Bornmann L, Tekles A. Disruption index depends on length of citation window. EPI. Mar 25, 2019;28(2):1. [ CrossRef ]
- Migheli M, Ramello GB. The unbearable lightness of scientometric indices. Manage Decis Econ. Nov 04, 2021;42(8):1933-1944. [ CrossRef ]
- Thelwall M, Kousha K, Makita M, Abdoli M, Stuart E, Wilson P, et al. In which fields do higher impact journals publish higher quality articles? Scientometrics. May 18, 2023;128(7):3915-3933. [ CrossRef ]
- Iyengar KP, Vaishya R. Article-level metrics: A new approach to quantify reach and impact of published research. J Orthop. Jun 2023;40:83-86. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Du J, Tang X, Wu Y. The effects of research level and article type on the differences between citation metrics and 1000 recommendations. Asso for Info Science & Tech. Jun 2015;67(12):3008-3021. [ CrossRef ]
- Guo L, Zhou Q. Research on characteristics of disruptive papers and their correlation with traditional bibliometric indicators. Journal of Intelligence. 2021;40(1):183-207. [ CrossRef ]
- Gorman DM, Huber C. Ranking of addiction journals in eight widely used impact metrics. J Behav Addict. Jul 13, 2022;11(2):348-360. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Chi P, Ding J, Leng F. Characteristics of the technology impact of breakthrough papers in biology and medicine. Journal of the China Society for Scientific and Technical Information. 2022;41(7):675. [ CrossRef ]
- Thelwall M, Kousha K, Abdoli M. Is medical research informing professional practice more highly cited? Evidence from AHFS DI Essentials in drugs.com. Scientometrics. Feb 21, 2017;112(1):509-527. [ CrossRef ]
- Jiang Y, Liu X. The relationship between absolute disruption index, peer review index and CNCI: a study based on virology papers. Library and Information Service. 2023;67(3):96-105. [ CrossRef ]
- Klein-Fedyshin M, Ketchum A. PubMed's core clinical journals filter: redesigned for contemporary clinical impact and utility. J Med Libr Assoc. Jul 10, 2023;111(3):665-676. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Thelwall M, Maflahi N. Guideline references and academic citations as evidence of the clinical value of health research. Asso for Info Science & Tech. Mar 17, 2015;67(4):960-966. [ CrossRef ]
- Traylor C, Herrmann-Lingen C. Does the journal impact factor reflect the impact of German medical guideline contributions? Scientometrics. Feb 03, 2023;128(3):1951-1962. [ CrossRef ]
- Marks MS, Marsh MC, Schroer TA, Stevens TH. An alarming trend within the biological/biomedical research literature toward the citation of review articles rather than the primary research papers. Traffic. Jan 19, 2013;14(1):1-1. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Brezis ES, Birukou A. Arbitrariness in the peer review process. Scientometrics. Feb 03, 2020;123(1):393-411. [ CrossRef ]
- Jiang Y, Liu X. Open peer review: Mode, technology, problems, and countermeasures. Chinese Journal of Scientific and Technical Periodicals. 2022;33(9):1196-1205. [ CrossRef ]
- Dougherty MR, Horne Z. Citation counts and journal impact factors do not capture some indicators of research quality in the behavioural and brain sciences. R Soc Open Sci. Aug 17, 2022;9(8):220334. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- COCI CSV dataset of all the citation data. Figshare. Feb 07, 2023. URL: https://figshare.com/articles/dataset/Crossref_Open_Citation_Index_CSV_dataset_of_all_the_citation_data/6741422?file=37483791 [accessed 2024-05-24]
Abbreviations
Edited by S Ma; submitted 04.12.23; peer-reviewed by O Beiki, C Oo; comments to author 28.02.24; revised version received 16.04.24; accepted 29.04.24; published 31.05.24.
©Yuyan Jiang, Xue-li Liu, Zixuan Zhang, Xinru Yang. Originally published in the Journal of Medical Internet Research (https://www.jmir.org), 31.05.2024.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work, first published in the Journal of Medical Internet Research, is properly cited. The complete bibliographic information, a link to the original publication on https://www.jmir.org/, as well as this copyright and license information must be included.
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- My Account Login
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Open access
- Published: 27 May 2024
Research on domain ontology construction based on the content features of online rumors
- Jianbo Zhao 1 ,
- Huailiang Liu 1 ,
- Weili Zhang 1 ,
- Tong Sun 1 ,
- Qiuyi Chen 1 ,
- Yuehai Wang 2 ,
- Jiale Cheng 2 ,
- Yan Zhuang 1 ,
- Xiaojin Zhang 1 ,
- Shanzhuang Zhang 1 ,
- Bowei Li 3 &
- Ruiyu Ding 2
Scientific Reports volume 14 , Article number: 12134 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
196 Accesses
1 Altmetric
Metrics details
- Computational neuroscience
- Computer science
- Data acquisition
- Data integration
- Data mining
- Data processing
- Human behaviour
- Information technology
- Literature mining
- Machine learning
- Scientific data
Online rumors are widespread and difficult to identify, which bring serious harm to society and individuals. To effectively detect and govern online rumors, it is necessary to conduct in-depth semantic analysis and understand the content features of rumors. This paper proposes a TFI domain ontology construction method, which aims to achieve semantic parsing and reasoning of the rumor text content. This paper starts from the term layer, the frame layer, and the instance layer, and based on the reuse of the top-level ontology, the extraction of core literature content features, and the discovery of new concepts in the real corpus, obtains the core classes (five parent classes and 88 subclasses) of the rumor domain ontology and defines their concept hierarchy. Object properties and data properties are designed to describe relationships between entities or their features, and the instance layer is created according to the real rumor datasets. OWL language is used to encode the ontology, Protégé is used to visualize it, and SWRL rules and pellet reasoner are used to mine and verify implicit knowledge of the ontology, and judge the category of rumor text. This paper constructs a rumor domain ontology with high consistency and reliability.
Similar content being viewed by others
Testing theory of mind in large language models and humans
Investigating child sexual abuse material availability, searches, and users on the anonymous Tor network for a public health intervention strategy
Explainable chemical artificial intelligence from accurate machine learning of real-space chemical descriptors
Introduction.
Online rumors are false information spread through online media, which have the characteristics of wide content 1 , hard to identify 2 , 3 . Online rumors can mislead the public, disrupt social order, damage personal and collective reputations, and pose a great challenge to the governance of internet information content. Therefore, in order to effectively detect and govern online rumors, it is necessary to conduct an in-depth semantic analysis and understanding of the rumor text content features.
The research on the content features of online rumors focuses on the lexical, syntactic and semantic features of the rumor text, including lexical, syntactic and semantic features 4 , syntactic structure and functional features 5 , source features 5 , 6 , rhetorical methods 7 , narrative structure 6 , 7 , 8 , language style 6 , 9 , 10 , corroborative means 10 , 11 and emotional features 10 , 12 , 13 , 14 , 15 , 16 , 17 , 18 . Most of the existing researches on rumor content features are feature mining under a single domain topic type, and lack of mining the influence relationship between multiple features. Therefore, this paper proposes to build an online rumor domain ontology to realize fine-grained hierarchical modeling of the relationship between rumor content features and credible verification of its effectiveness. Domain ontology is a systematic description of the objective existence in a specific discipline 19 . The construction methods mainly include TOVE method 20 , skeleton method 21 , IDEF-5 method 22 , 23 , methontology method 24 , 25 and seven-step method 26 , 27 , among which seven-step method is the most mature and widely used method at present 28 , which has strong systematicness and applicability 29 , but it does not provide quantitative indicators and methods about the quality and effect of ontology. The construction technology can be divided into the construction technology based on thesaurus conversion, the construction technology based on existing ontology reuse and the semi-automatic and automatic construction technology based on ontology engineering method 30 . The construction technology based on thesaurus conversion and the construction technology based on existing ontology reuse can save construction time and cost, and improve ontology reusability and interoperability, but there are often differences in structure, semantics and scene. Semi-automatic and automatic construction technology based on ontology engineering method The application of artificial intelligence technology can automatically extract ontology elements and structures from data sources with high efficiency and low cost, but the quality and accuracy are difficult to guarantee. Traditional domain ontology construction methods lack effective quality evaluation support, and construction technology lacks effective integration application. Therefore, this paper proposes an improved TFI network rumor domain ontology construction method based on the seven-step method. Starting from the terminology layer, the framework layer and the instance layer, it integrates the top-level ontology and core document content feature reuse technology, the bottom-up semi-automatic construction technology based on N-gram new word discovery algorithm and RoBERTa-Kmeans clustering algorithm, defines the fine-grained features of network rumor content and carries out hierarchical modeling. Using SWRL rules and pellet inference machine, the tacit knowledge of ontology is mined, and the quality of ontology validity and consistency is evaluated and verified.
The structure of this paper is as follows: Sect “ Related work ” introduces the characteristics of rumor content and the related work of domain ontology construction.; Sect “ Research method ” constructs the term layer, the frame layer and the instance layer of the domain ontology; Sect “ Domain ontology construction ” mines and verifies the implicit knowledge of the ontology based on SWRL rules and Pellet reasoner; Sect “ Ontology reasoning and validation ” points out the research limitations and future research directions; Sect “ Discussion ” summarizes the research content and contribution; Sect “ Conclusion ” summarizes the research content and contribution of this paper.
Related Work
Content features of online rumors.
The content features of online rumors refer to the adaptive description of vocabulary, syntax and semantics in rumor texts. Fu et al. 5 have made a linguistic analysis of COVID-19’s online rumors from the perspectives of pragmatics, discourse analysis and syntax, and concluded that the source of information, the specific place and time of the event, the length of the title and statement, and the emotions aroused are the important characteristics to judge the authenticity of the rumors; Zhang et al. 6 summarized the narrative theme, narrative characteristics, topic characteristics, language style and source characteristics of new media rumors; Li et al. 7 found that rumors have authoritative blessing and fear appeal in headline rhetoric, and they use news and digital headlines extensively, and the topic construction mostly uses programmed fixed structure; Yu et al. 8 analyzed and summarized the content distribution, narrative structure, topic scene construction and title characteristics of rumors in detail; Mourao et al. 9 found that the language style of rumors is significantly different from that of real texts, and rumors tend to use simpler, more emotional and more radical discourse strategies; Zhou et al. 10 analyzed the rumor text based on six analysis categories, such as content type, focus object and corroboration means, and found that the epidemic rumors were mostly “infectious” topics, with narrative expression being the most common, strong fear, and preference for exaggerated and polarized discourse style. Huang et al. 11 conducted an empirical study based on WeChat rumors, and found that the “confirmation” means of rumors include data corroboration and specific information, hot events and authoritative release; Butt et al. 12 analyzed the psycholinguistic features of rumors, and extracted four features from the rumor data set: LIWC, readability, senticnet and emotions. Zhou et al. 13 analyzed the semantic features of fake news content in theme and emotion, and found that the distribution of fake news and real news is different in theme features, and the overall mood, negative mood and anger of fake news are higher; Tan et al. 14 divided the content characteristics of rumors into content characteristics with certain emotional tendency and social characteristics that affect credibility; Damstra et al. 15 identified the elements as a consistent indicator of intentionally deceptive news content, including negative emotions causing anger or fear, lengthy sensational headlines, using informal language or swearing, etc. Lai et al. 16 put forward that emotional rumors can make the rumor audience have similar positive and negative emotions through emotional contagion; Yuan et al. 17 found that multimedia evidence form and topic shaping are important means to create rumors, which mostly convey negative emotions of fear and anger, and the provision of information sources is related to the popularity and duration of rumors; Ruan et al. 18 analyzed the content types, emotional types and discourse focus of Weibo’s rumor samples, and found that the proportion of social life rumors was the highest, and the emotional types were mainly hostile and fearful, with the focus on the general public and the personnel of the party, government and military institutions.
The forms and contents of online rumors tend to be diversified and complicated. The existing research on the content features of rumors is mostly aimed at the mining of content characteristics under specific topics, which cannot cover various types of rumor topics, and lacks fine-grained hierarchical modeling of the relationship between features and credible verification of their effectiveness.
Domain ontology construction
Domain ontology is a unified definition, standardized organization and visual representation of the concepts of knowledge in a specific domain 31 , 32 , and it is an important source of information for knowledge-based systems 19 , 33 . Theoretical methods include TOVE method 20 , skeleton method 21 , IDEF-5 method 22 , 23 , methontology method 24 , 25 and seven-step method 26 , 27 . TOVE method transforms informal description into formal ontology, which is suitable for fields that need accurate knowledge, but it is complex and time-consuming, requires high-level domain knowledge and is not easy to expand and maintain. Skeleton method forms an ontology skeleton by defining the concepts and relationships of goals, activities, resources, organizations and environment, which can be adjusted according to needs and is suitable for fields that need multi-perspective and multi-level knowledge, but it lacks formal semantics and reasoning ability. Based on this method, Ran et al. 34 constructed the ontology of idioms and allusions. IDEF5 method uses chart language and detailed description language to construct ontology, formalizes and visualizes objective knowledge, and is suitable for fields that need multi-source data and multi-participation, but it lacks a unified ontology representation language. Based on this method, Li et al. 35 constructed the business process activity ontology of military equipment maintenance support, and Song et al. 36 established the air defense and anti-missile operation process ontology. Methontology is a method close to software engineering. It systematically develops ontologies through the processes of specification, knowledge acquisition, conceptualization, integration, implementation, evaluation and document arrangement, which is suitable for fields that need multi-technology and multi-ontology integration, but it is too complicated and tedious, and requires a lot of resources and time 37 . Based on this method, Yang et al. 38 completed the ontology of emergency plan, Duan et al. 39 established the ontology of high-resolution images of rural residents, and Chen et al. 40 constructed the corpus ontology of Jiangui. Seven-step method is the most mature and widely used method at present 28 . It is systematic and applicable to construct ontology by determining its purpose, scope, terms, structure, attributes, limitations and examples 29 , but it does not provide quantitative indicators and methods about the quality and effect of ontology. Based on this method, Zhu et al. 41 constructed the disease ontology of asthma, Li et al. 42 constructed the ontology of military events, the ontology of weapons and equipment and the ontology model of battlefield environment, and Zhang et al. 43 constructed the ontology of stroke nursing field, and verified the construction results by expert consultation.
Domain ontology construction technology includes thesaurus conversion, existing ontology reuse and semi-automatic and automatic construction technology based on ontology engineering method 30 . The construction technology based on thesaurus transformation takes the existing thesaurus as the knowledge source, and transforms the concepts, terms and relationships in the thesaurus into the entities and relationships of domain ontology through certain rules and methods, which saves the time and cost of ontology construction and improves the quality and reusability of ontology. However, it is necessary to solve the structural and semantic differences between thesaurus and ontology and adjust and optimize them according to the characteristics of different fields and application scenarios. Wu et al. 44 constructed the ontology of the natural gas market according to the thesaurus of the natural gas market and the mapping of subject words to ontology, and Li et al. 45 constructed the ontology of the medical field according to the Chinese medical thesaurus. The construction technology based on existing ontology reuse uses existing ontologies or knowledge resources to generate new domain ontologies through modification, expansion, merger and mapping, which saves time and cost and improves the consistency and interoperability of ontologies, but it also needs to solve semantic differences and conflicts between ontologies. Chen et al. 46 reuse the top-level framework of scientific evidence source information ontology (SEPIO) and traditional Chinese medicine language system (TCMLS) to construct the ontology of clinical trials of traditional Chinese medicine, and Xiao et al. 47 construct the domain ontology of COVID-19 by extracting the existing ontology and the knowledge related to COVID-19 in the diagnosis and treatment guide. Semi-automatic and automatic construction technology based on ontology engineering method semi-automatically or automatically extracts the elements and structures of ontology from data sources by using natural language processing, machine learning and other technologies to realize large-scale, fast and low-cost domain ontology construction 48 , but there are technical difficulties, the quality and accuracy of knowledge extraction can not be well guaranteed, and the quality and consistency of different knowledge sources need to be considered. Suet al. 48 used regular templates and clustering algorithm to construct the ontology of port machinery, Zheng et al. 49 realized the automatic construction of mobile phone ontology through LDA and other models, Dong et al. 50 realized the automatic construction of ontology for human–machine ternary data fusion in manufacturing field, Linli et al. 51 proposed an ontology learning algorithm based on hypergraph, and Zhai et al. 52 learned from it through part-of-speech tagging, dependency syntax analysis and pattern matching.
At present, domain ontology construction methods are not easy to expand, lack of effective quality evaluation support, lack of effective integration and application of construction technology, construction divorced from reality can not guide subsequent practice, subjective ontology verification and so on. Aiming at the problems existing in the research of content characteristics and domain ontology construction of online rumors, this paper proposes an improved TFI network rumor domain ontology construction method based on seven-step method, which combines top-down existing ontology reuse technology with bottom-up semi-automatic construction technology, and establishes rumor domain ontology based on top-level ontology reuse, core document content feature extraction and new concept discovery in the real corpus from the terminology layer, framework layer and instance layer. Using Protégé as a visualization tool, the implicit knowledge mining of ontology is carried out by constructing SWRL rules to verify the semantic parsing ability and consistency of domain ontology.
Research method
This paper proposes a TFI online rumor domain ontology construction method based on the improvement of the seven-step method, which includes the term layer, the frame layer and the instance layer construction.
Term layer construction
Determine the domain and scope: the purpose of constructing the rumor domain ontology is to support the credible detection and governance of online rumors, and the domain and scope of the ontology are determined by answering questions.
Three-dimensional term set construction: investigate the top-level ontology and related core literature, complete the mapping of reusable top-level ontology and rumor content feature concept extraction semi-automatically from top to bottom; establish authoritative real rumor datasets, and complete the domain new concept discovery automatically from bottom to top; based on this, determine the term set of the domain ontology.
Frame layer construction
Define core classes and hierarchical relationships: combine the concepts of the three-dimensional rumor term set, based on the data distribution of the rumor dataset, define the parent class, summarize the subclasses, design hierarchical relationships and explain the content of each class.
Define core properties and facets of properties: in order to achieve deep semantic parsing of rumor text contents, define object properties, data properties and property facets for each category in the ontology.
Instance layer construction
Create instances: analyze the real rumor dataset, extract instance data, and add them to the corresponding concepts in the ontology.
Encode and visualize ontology: use OWL language to encode ontology, and use Protégé to visualize ontology, so that ontology can be understood and operated by computer.
Ontology verification: use SWRL rules and pellet reasoner to mine implicit knowledge of ontology, and verify its semantic parsing ability and consistency.
Ethical statements
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Determine the professional domain and scope of the ontology description
This paper determines the domain and scope of the online rumor domain ontology by answering the following four questions:
(1) What is the domain covered by the ontology?
The “Rumor Domain Ontology” constructed in this paper only considers content features, not user features and propagation features; the data covers six rumor types of politics and military, disease prevention and treatment, social life, science and technology, nutrition and health, and others involved in China’s mainstream internet rumor-refuting websites.
(2) What is the purpose of the ontology?
To perform fine-grained hierarchical modeling of the relationships among the features of multi-domain online rumor contents, realize semantic parsing and credibility reasoning verification of rumor texts, and guide fine-grained rumor detection and governance. It can also be used as a guiding framework and constraint condition for online rumor knowledge graph construction.
(3) What kind of questions should the information in the ontology provide answers for?
To provide answers for questions such as the fine-grained rumor types of rumor instances, the valid features of rumor types, etc.
(4) Who will use the ontology in the future?
Users of online rumor detection and governance, users of online rumor knowledge graphs construction.
Three-dimensional term set construction
Domain concepts reused by top-level ontology.
As a mature and authoritative common ontology, top-level ontology can be shared and reused in a large range, providing reference and support for the construction of domain ontology. The domain ontology of online rumors established in this paper focuses on the content characteristics, mainly including the content theme, events and emotions of rumor texts. By reusing the terminology concepts in the existing top-level ontology, the terminology in the terminology set can be unified and standardized. At the same time, the top-level concept and its subclass structure can guide the framework construction of domain ontology and reduce the difficulty and cost of ontology construction. Reusable top-level ontologies include: SUMO, senticnet and ERE after screening.
SUMO ontology: a public upper-level knowledge ontology containing some general concepts and relations for describing knowledge in different domains. The partial reusable SUMO top-level concepts and subclasses selected in this paper are shown in Table 1 , which provides support for the sub-concept design of text topics in rumor domain ontology.
Senticnet: a knowledge base for concept-based sentiment analysis, which contains semantic, emotional, and polarity information related to natural language concepts. The partial reusable SenticNet top-level concepts and subclasses selected in this paper are shown in Table 2 , which provides support for the sub-concept design of text topics in rumor domain ontology.
Entities, relations, and events (ERE): a knowledge base of events and entity relations. The partial reusable ERE top-level concepts and subclasses selected in this paper are shown in Table 3 , which provides support for the sub-concept design of text elements in the rumor domain ontology.
Extracting domain concepts based on core literature content features
Domain core literature is an important source for extracting feature concepts. This paper uses ‘rumor detection’ as the search term to retrieve 274 WOS papers and 257 CNKI papers from the WOS and CNKI core literature databases. The content features of rumor texts involved in the literature samples are extracted, the repetition content features are eliminated, the core content features are screened, and the canonical naming of synonymous concepts from different literatures yields the domain concepts as shown in Table 4 . Among them, text theme, text element, text style, text feature and text rhetoric are classified as text features; emotional category, emotional appeal and rumor motive are classified as emotional characteristics; source credibility, evidence credibility and testimony method are classified as information credibility characteristics; social context is implicit.
Extracting domain concepts based on new concept discovery
This paper builds a general rumor dataset based on China’s mainstream rumor-refuting websites as data sources, and proposes a domain new concept discovery algorithm to discover domain new words in the dataset, add them to the word segmentation dictionary to improve the accuracy of word segmentation, and cluster them according to rumor type, resulting in a concept subclass dictionary based on the real rumor dataset, which provided realistic basis and data support for the conceptual design of each subclass in domain ontology.
Building a general rumor dataset
The rumor dataset constructed in this paper contains 12,472 texts, with 6236 rumors and 6236 non-rumors; the data sources are China’s mainstream internet rumor-refuting websites: 1032 from the internet rumor exposure platform of China internet joint rumor-refuting platform, 270 from today’s rumor-refuting of China internet joint rumor-refuting platform, 1852 from Tencent news Jiaozhen platform, 1744 from Baidu rumor-refuting platform, 7036 from science rumor-refuting platform, and 538 from Weibo community management center. This paper invited eight researchers to annotate the labels (rumor, non-rumor), categories (politics and military, disease prevention and treatment, social life, science and technology, nutrition and health, others) of the rumor dataset. Because data annotation is artificial and subjective, in order to ensure the effectiveness and consistency of annotation, before inviting researchers to annotate, this paper formulates annotation standards, including the screening method, trigger words and sentence break identification of rumor information and corresponding rumor information, and clearly explains and exemplifies the screening method and trigger words of rumor categories, so as to reduce the understanding differences among researchers; in view of this standard, researchers are trained in labeling to familiarize them with labeling specifications, so as to improve their labeling ability and efficiency. The method of multi-person cross-labeling is adopted when labeling, and each piece of data is independently labeled by at least two researchers. In case of conflicting labeling results, the labeling results are jointly decided by the data annotators to increase the reliability and accuracy of labeling. After labeling, multi-person cross-validation method is used to evaluate the labeling results. Each piece of data is independently verified by at least two researchers who did not participate in labeling, and conflicting labeling results are jointly decided by at least five researchers to ensure the consistency of evaluation results. Examples of the results are shown in Table 5 .
N-gram word granularity rumor text new word discovery algorithm
Existing neologism discovery algorithms are mostly based on the granularity of Chinese characters, and the time complexity of long word discovery is high and the accuracy rate is low. The algorithm’s usefulness is low, and the newly discovered words are mostly already found in general domain dictionaries. To solve these problems, this paper proposes an online rumor new word discovery algorithm based on N-gram word granularity, as shown in Fig. 1 .
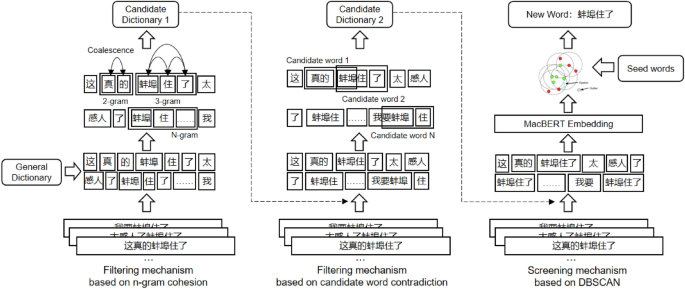
Flowchart of domain new word discovery algorithm.
First, obtain the corpus to be processed \({\varvec{c}}=\{{{\varvec{s}}}_{1},{{\varvec{s}}}_{2},...,{{\varvec{s}}}_{{{\varvec{n}}}_{{\varvec{c}}}}\}\) , and perform the first preprocessing on the corpus to be processed, which includes: sentence segmentation, Chinese word segmentation and punctuation removal for the corpus to be processed. Obtain the first corpus \({{\varvec{c}}}^{{\varvec{p}}}=\{{{\varvec{s}}}_{1}^{{\varvec{p}}},{{\varvec{s}}}_{2}^{{\varvec{p}}},...,{{\varvec{s}}}_{{{\varvec{n}}}_{{\varvec{c}}}}^{{\varvec{p}}}\}\) ; where \({s}_{i}\) represents the \(i\) -th sentence in the corpus to be processed, \({n}_{c}\) represents the number of sentences in the corpus to be processed, and \({s}_{i}^{p}\) is the i-th sentence in the first corpus; perform N-gram operation on each sentence in the first corpus separately, and obtain multiple candidate words \(n=2\sim 5\) ; count the word frequency of each candidate word in the first corpus, and remove the candidate words with word frequency less than the first threshold, and obtain the first class of candidate word set;calculate the cohesion of each candidate word in the first class of candidate word set according to the following formula:
In the formula, \(P(\cdot )\) represents word frequency.Then filter according to the second threshold corresponding to N-gram operation, and obtain the second class of candidate word set; after loading the new words in the second class of candidate word set into LTP dictionary, perform the second preprocessing on the corpus to be processed \({\varvec{c}}=\{{{\varvec{s}}}_{1},{{\varvec{s}}}_{2},...,{{\varvec{s}}}_{{{\varvec{n}}}_{{\varvec{c}}}}\}\) ; and obtain the second corpus \({{\varvec{c}}}^{{\varvec{p}}\boldsymbol{^{\prime}}}=\{{{\varvec{s}}}_{1}^{{\varvec{p}}\boldsymbol{^{\prime}}},{{\varvec{s}}}_{2}^{{\varvec{p}}\boldsymbol{^{\prime}}},...,{{\varvec{s}}}_{{{\varvec{n}}}_{{\varvec{c}}}}^{{\varvec{p}}\boldsymbol{^{\prime}}}\}\) ; where the second preprocessing includes: sentence segmentation, Chinese word segmentation and stop word removal for the corpus to be processed; after obtaining the vector representation of each word in the second corpus, determine the vector representation of each new word in the second class of candidate word set; according to the vector representation of each new word, use K-means algorithm for clustering; according to the clustering results and preset classification rules, classify each new word to the corresponding domain. The examples of new words discovered are shown in Table 6 :
RoBERTa-Kmeans rumor text concepts extraction algorithm
After adding the new words obtained by the new word discovery to the LTP dictionary, the accuracy of LTP word segmentation is improved. The five types of rumor texts established in this paper are segmented by using the new LTP dictionary, and the word vectors are obtained by inputting them into the RoBERTa word embedding layer after removing the stop words. The word vectors are clustered by k-means according to rumor type to obtain the concept subclass dictionary. The main process is as follows:
(1) Word embedding layer
The RoBERTa model uses Transformer-Encode for computation, and each module contains multi-head attention mechanism, residual connection and layer normalization, feed-forward neural network. The word vectors are obtained by representing the rumor texts after accurate word segmentation through one-hot encoding, and the position encoding represents the relative or absolute position of the word in the sequence. The word embedding vectors generated by superimposing the two are used as input X. The multi-head attention mechanism uses multiple independent Attention modules to perform parallel operations on the input information, as shown in formula ( 2 ):
where \(\left\{{\varvec{Q}},{\varvec{K}},{\varvec{V}}\right\}\) is the input matrix, \({{\varvec{d}}}_{{\varvec{k}}}\) is the dimension of the input matrix. After calculation, the hidden vectors obtained after computation are residual concatenated with layer normalization, and then calculated by two fully connected layers of feed-forward neural network for input, as shown in formula ( 3 ):
where \(\left\{{{\varvec{W}}}_{{\varvec{e}}},{{\varvec{W}}}_{0}\boldsymbol{^{\prime}}\right\}\) are the weight matrices of two connected layers, \(\left\{{{\varvec{b}}}_{{\varvec{e}}},{{\varvec{b}}}_{0}\boldsymbol{^{\prime}}\right\}\) are the bias terms of two connected layers.
After calculation, a bidirectional association between word embedding vectors is established, which enables the model to learn the semantic features contained in each word embedding vector in different contexts. Through fine-tuning, the learned knowledge is transferred to the downstream clustering task.
(2) K-means clustering
Randomly select k initial points to obtain k classes, and iterate until the loss function of the clustering result is minimized. The loss function can be defined as the sum of squared errors of each sample point from its cluster center point, as shown in formula ( 4 ).
where \({x}_{i}\) represents the \(i\) sample, \({a}_{i}\) is the cluster that \({x}_{i}\) belongs to, \({u}_{{a}_{i}}\) represents the corresponding center point, \(N\) is the total number of samples.
After RoBERTa-kmeans calculation, the concept subclasses obtained are manually screened, merged repetition items, deleted invalid items, and finally obtained 79 rumor concept subclasses, including 14 politics and military subclasses, 23 disease prevention and treatment subclasses, 15 social life subclasses, 13 science and technology subclasses, and 14 nutrition and health subclasses. Some statistics are shown in Table 7 .
Each concept subclass is obtained by clustering several topic words. For example, the topic words that constitute the subclasses of body part, epidemic prevention and control, chemical drugs, etc. under the disease prevention and treatment topic are shown in Table 8 .
(3) Determining the terminology set
This paper constructs a three-dimensional rumor domain ontology terminology set based on the above three methods, and unifies the naming of the terms. Some of the terms are shown in Table 9 .
Framework layer construction
Define core classes and hierarchy, define parent classes.
This paper aims at fine-grained hierarchical modeling of the relationship between the content characteristics of multi-domain network rumors. Therefore, the top-level parent class needs to include the rumor category and the main content characteristics of a sub-category rumor design. The main content characteristics are the clustering results of domain concepts extracted based on the content characteristics of core documents, that is, rumor text feature, rumor emotional characteristic, rumor credibility and social context. The specific contents of the five top parent classes are as follows:
Rumor type: the specific classification of rumors under different subject categories; Rumor text feature, the common features of rumor texts in terms of theme, style, rhetoric, etc. Rumor emotional characteristic: the emotional elements of rumor texts, the Rumor motive of the publisher, and the emotional changes they hope to trigger in the receiver. Rumor credibility: the authority of the information source, the credibility of the evidence material provided by the publisher, and the effectiveness of the testimony method. Social context: the relevant issues and events in the society when the rumor is published.
Induce subclasses and design hierarchical relationships
In this paper, under the top-level parent class, according to the top-level concepts of top-level ontologies such as SUMO, senticnet and ERE and their subclass structures, and the rumor text features of each category extracted from the real rumor text dataset, we summarize its 88 subclasses and design the hierarchical relationships, as shown in Fig. 2 , which include:
(1) Rumor text feature
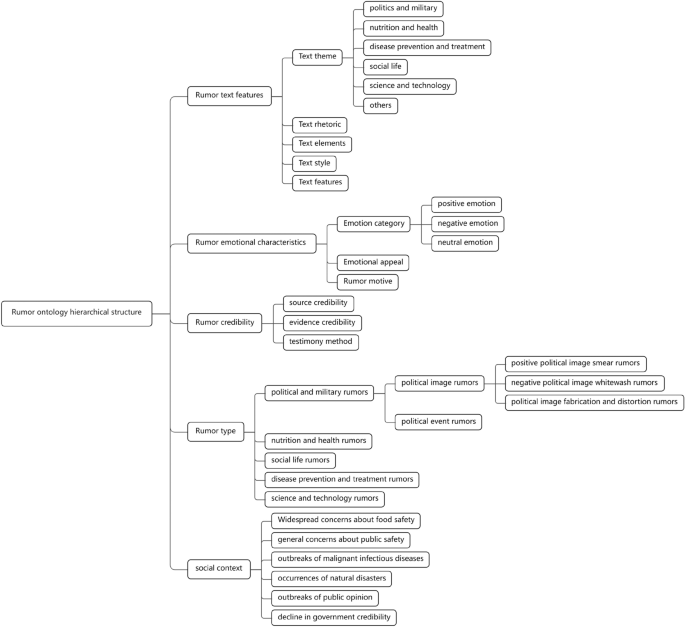
Diagram of the core classes and hierarchy of the rumor domain ontology.
① Text theme 6 , 8 , 13 , 18 , 53 : the theme or topic that the rumor text content involves. Based on the self-built rumor dataset, it is divided into politics and military 54 , involving information such as political figures, political policies, political relations, political activities, military actions, military events, strategic objectives, politics and military reviews, etc.; nutrition and health 55 , involving information such as the relationship between human health and nutrition, the nutritional components and value of food, the plan and advice for healthy eating, health problems and habits, etc.; disease prevention and treatment 10 , involving information such as the definition of disease, vaccine, treatment, prevention, data, etc.; social life 56 , involving information such as social issues, social environment, social values, cultural activities, social media, education system, etc.; science and technology 57 , involving information such as scientific research, scientific discovery, technological innovation, technological application, technological enterprise, etc.; other categories.
② Text element 15 : the structured information of the rumor text contents. It is divided into character, political character, public character, etc.; geographical position, city, region, area, etc.; event, historical event, current event, crisis event, policy event, etc.; action, protection, prevention and control, exercise, fighting, crime, eating, breeding, health preservation, rest, exercise, education, sports, social, cultural, ideological, business, economic, transportation, etc.; material, food, products (food, medicine, health products, cosmetics, etc.) and the materials they contain and their relationship with human health. effect, nutrition, health, harm, natural disaster, man-made disaster, guarantee, prevention, treatment, etc.; institution, government, enterprise, school, hospital, army, police, social group, etc.; nature, weather, astronomy, environment, agriculture, disease, etc.
③ Text style 7 , 10 : the discourse style of the rumor text contents, preferring exaggerated and emotional expression. It is divided into gossip style, creating conflict or entertainment effect; curious style, satisfying people’s curiosity and stimulation; critical style, using receivers’ stereotypes or preconceptions; lyrical style, creating resonance and influencing emotion; didactic style influencing receivers’ thought and behavior from an authoritative perspective; plain style concise objective arousing resonance etc.
④ Text feature 7 , 58 : special language means in the rumor text contents that can increase the transmission and influence of the rumor. It is divided into extensive punctuation reminding or attracting receivers’ attention; many mood words enhancing emotional color and persuasiveness; many emoji conveying attitude; induce forwarding using @ symbol etc. to induce receivers to forward etc.
⑤ Text rhetoric 15 : common rhetorical devices in rumor contents. It is divided into metaphor hyperbole repetition personification etc.
(2) Rumor emotional characteristic
① Emotion category 17 , 59 , 60 : the emotional tendency and intensity expressed in the rumor texts. It is divided into positive emotion happy praise etc.; negative emotion fear 10 anger sadness anxiety 61 dissatisfaction depression etc.; neutral emotion no preference plain objective etc.
② Emotional appeal 16 , 62 , 63 : the online rumor disseminator hopes that the rumor they disseminate can trigger some emotional changes in the receiver. It is divided into “joy” happy pleasant satisfied emotions that prompt receivers to spread or believe some rumors that are conducive to social harmony; “love” love appreciation admiration emotions that prompt receivers to spread or believe some rumors that are conducive to some people or group interests; “anger” angry annoyed dissatisfied emotions that prompt receivers to spread or believe some rumors that are anti-social or intensify conflicts; “fear” fearful afraid nervous emotions that prompt receivers to spread or believe some rumors that have bad effects deliberately exaggerated; “repugnance” disgusted nauseous emotions that prompt receivers to spread or believe some rumors that are detrimental to social harmony; “surprise” surprised shocked amazed emotions that prompt receivers to spread or believe some rumors that deliberately attract traffic exaggerated fabricated etc.
③ Rumor motive 17 , 64 , 65 , 66 : the purpose and need of the rumor publisher to publish rumors and the receiver to forward rumors. Such as profit-driven seeking fame and fortune deceiving receivers; emotional catharsis relieving dissatisfaction emotions by venting; creating panic creating social unrest and riots disrupting social order; entertainment fooling receivers seeking stimulation; information verification digging out the truth of events etc.
(3) Rumor credibility
① source credibility 7 , 17 : the degree of trustworthiness that the information source has. Such as official institutions and authoritative experts and scholars in the field with high credibility; well-known encyclopedias and large-scale civil organizations with medium credibility; small-scale civil organizations and personal hearsay personal experience with low credibility etc.
② evidence credibility 61 : the credibility of the information proof material provided by the publisher. Data support such as scientific basis based on scientific theory or method; related feature with definite research or investigation result in data support; temporal background with clear time place character event and other elements which related to the information content; the common sense of life in line with the facts and scientific common sense that are widely recognized.
③ testimony method 10 , 11 , 17 : the method to support or refute a certain point of view. Such as multimedia material expressing or fabricating content details through pictures videos audio; authority endorsement policy documents research papers etc. of authorized institutions or persons; social identity identity of social relation groups.
(4) Social context
① social issue 67 : some bad phenomena or difficulties in society such as poverty pollution corruption crime government credibility decline 68 etc.
② public attention 63 : events or topics that arouse widespread attention or discussion in the society such as sports events technological innovation food safety religious beliefs Myanmar fraud nuclear wastewater discharge etc.
③ emergency(public sentiment) 69 : some major or urgent events that suddenly occur in society such as earthquake flood public safety malignant infectious disease outbreaks etc.
(5) Rumor type
① Political and military rumor:
Political image rumor: rumors related to images closely connected to politics and military, such as countries, political figures, institutions, symbols, etc. These include positive political image smear rumor, negative political image whitewash rumor, political image fabrication and distortion rumor, etc.
Political event rumor: rumors about military and political events, such as international relations, security cooperation, military strategy, judicial trial, etc. These include positive political event smear rumor, negative political event whitewash rumor, political event fabrication and distortion rumor, etc.
② Nutrition and health rumor:
Food product rumor: rumors related to food, products (food, medicine, health products, cosmetics, etc.), the materials they contain and their association with human health. These include positive effect of food product rumor, negative effect of food product rumor, food product knowledge rumor, etc.
Living habit rumor: rumors related to habitual actions in life and their association with human health. These include positive effect of living habit rumor, negative effect of living habit rumor, living habit knowledge rumor, etc.
③ Disease prevention and treatment rumor:
Disease management rumor: rumors related to disease management and control methods that maintain and promote individual and group health. These include positive prevention and treatment rumor, negative aggravating disease rumor, disease management knowledge rumor, etc.
Disease confirmed transmission rumor: rumors about the confirmation, transmission, and immunity of epidemic diseases at the social level in terms of causes, processes, results, etc. These include local confirmed cases rumor, celebrity confirmed cases rumor, transmission mechanism rumor, etc.
Disease notification and advice rumor: rumors that fabricate or distort the statements of authorized institutions or experts in the field, and provide false policies or suggestions related to diseases. These include institutional notification rumor, expert advice rumor, etc.
④ Social life rumor:
Public figure public opinion rumor: rumors related to public figures’ opinions, actions, private lives, etc. These include positive public figure smear rumor, negative public figure whitewash rumor, public figure life exposure rumor, etc.
Social life event rumor: rumors related to events, actions, and impacts on people's social life. These include positive event sharing rumor, negative event exposure rumor, neutral event knowledge rumor, etc.
Disaster occurrence rumor: rumors related to natural disasters or man-made disasters and their subsequent developments. These include natural disaster occurrence rumor, man-made disaster occurrence rumor, etc.
⑤ Science and technology rumor:
Scientific knowledge rumor: rumors related to natural science or social science theories and knowledge. These include scientific theory rumor, scientific concept rumor, etc.
Science and technology application rumor: rumors related to the research and development and practical application of science and technology and related products. These include scientific and technological product rumor, scientific and technological information rumor, etc.
⑥ Other rumor: rumors that do not contain elements from the above categories.
Definition of core properties and facets of properties
Properties in the ontology are used to describe the relationships between entities or the characteristics of entities. Object properties are relationships that connect two entities, describing the interactions between entities; data properties represent the characteristics of entities, usually in the form of some data type. Based on the self-built rumor dataset, this paper designs object properties, data properties and facets of properties for the parent classes and subclasses of the rumor domain ontology.
Object properties
A partial set of object properties is shown in Table 10 .
Data attributes
The partial data attribute set is shown in Table 11 .
Creating instances
Based on the defined core classes and properties, this paper creates instances according to the real rumor dataset. An example is shown in Table 12 .
This paper selects the online rumor that “Lin Chi-ling was abused by her husband Kuroki Meisa, the tears of betrayal, the shadow of gambling, all shrouded her head. Even if she tried to divorce, she could not get a solution…..” as an example, and draws a structure diagram of the rumor domain ontology instance, as shown in Fig. 3 . This instance shows the seven major text features of the rumor text: text theme, text element, text style, emotion category, emotional appeal, rumor motivation, and rumor credibility, as well as the related subclass instances, laying a foundation for building a multi-source rumor domain knowledge graph.
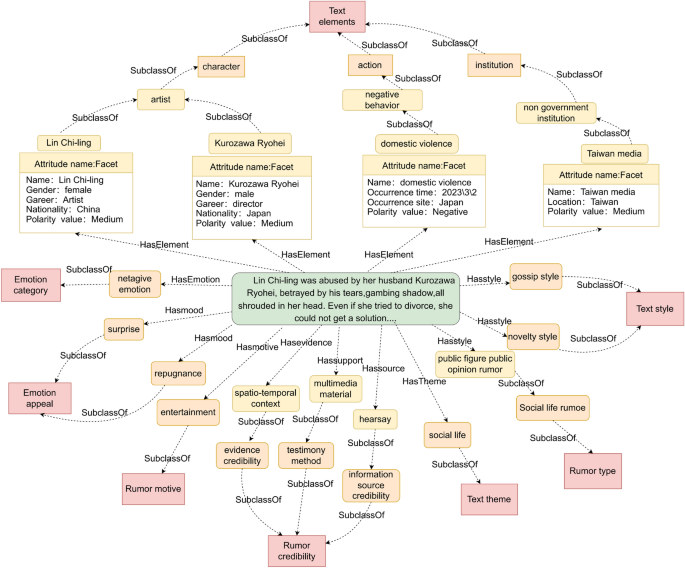
Schematic example of the rumor domain ontology.
Encoding ontology and visualization
Encoding ontology.
This paper uses OWL language to encode the rumor domain ontology, to accurately describe the entities, concepts and their relationships, and to facilitate knowledge reasoning and semantic understanding. Classes in the rumor domain ontology are represented by the class “Class” in OWL and the hierarchical relationship is represented by subclassof. For example, in the creation of the rumor emotional characteristic class and its subclasses, the OWL code is shown in Fig. 4 :

Partial OWL codes of the rumor domain ontology.
The ontology is formalized and stored as a code file using the above OWL language, providing support for reasoning.
Ontology visualization
This paper uses protégé5.5 to visualize the rumor domain ontology, showing the hierarchical structure and relationship of the ontology parent class and its subclasses. Due to space limitations, this paper only shows the ontology parent class “RumorEmotionalFeatures” and its subclasses, as shown in Fig. 5 .
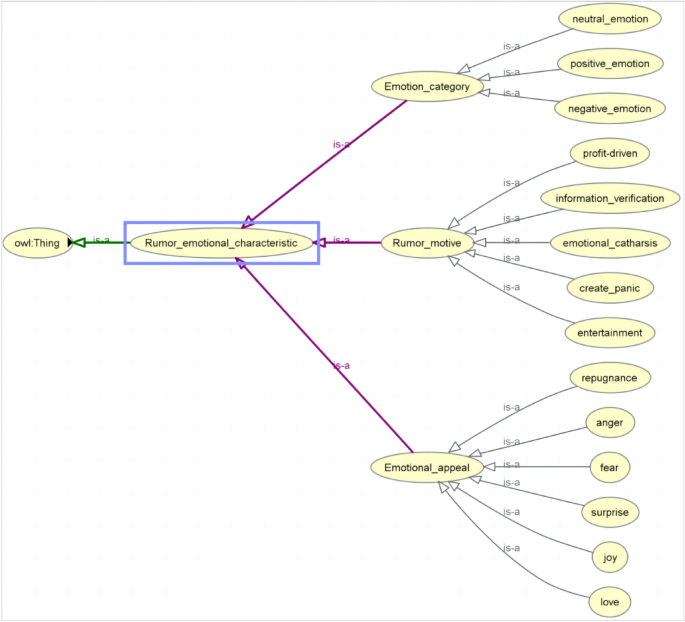
Ontology parent class “RumorEmotionalFeatures” and its subclasses.
Ontology reasoning and validation
Swrl reasoning rule construction.
SWRL reasoning rule is an ontology-based rule language that can be used to define Horn-like rules to enhance the reasoning and expressive ability of the ontology. This paper uses SWRL reasoning rules to deal with the conflict relationships between classes and between classes and instances in the rumor domain ontology, and uses pellet reasoner to deeply mine the implicit semantic relationships between classes and instances, to verify the semantic parsing ability and consistency of the rumor domain ontology.
This paper summarizes the object property features of various types of online rumors based on the self-built rumor dataset, maps the real rumor texts with the rumor domain ontology, constructs typical SWRL reasoning rules for judging 32 typical rumor types, as shown in Table 13 , and imports them into the protégé rule library, as shown in Fig. 6 . In which x, n, e, z, i, t, v, l, etc. are instances of rumor types, text theme, emotion category, effect, institution, event, action, geographical position, etc. in the ontology. HasTheme, HasEmotion, HasElement, HasSource, HasMood and HasSupport are object property relationships. Polarity value is a data property relationship.

Partial SWRL rules for the rumor domain ontology.
Implicit knowledge mining and verification based on pellet reasoner
This paper extracts corresponding instances from the rumor dataset, imports the rumor domain ontology and SWRL rule description into the pellet reasoner in the protégé software, performs implicit knowledge mining of the rumor domain ontology, judges the rumor type of the instance, and verifies the semantic parsing ability and consistency of the ontology.
Positive prevention and treatment of disease rumors are mainly based on the theme of disease prevention and treatment, usually containing products to be sold (including drugs, vaccines, equipment, etc.) and effect of disease names, claiming to have positive effects (such as prevention, cure, relief, etc.) on certain diseases or symptoms, causing positive emotions such as surprise and happiness among patients and their families, thereby achieving the purpose of selling products. The text features and emotional features of this kind of rumors are relatively clear, so this paper takes the rumor text “Hong Kong MDX Medical Group released the ‘DCV Cancer Vaccine’, which can prevent more than 12 kinds of cancers, including prostate cancer, breast cancer and lung cancer.” as an example to verify the semantic parsing ability of the rumor domain ontology. The analysis result of this instance is shown in Fig. 7 . The text theme is cancer prevention in disease prevention and treatment, the text style is plain narrative style, and the text element includes product-DCV cancer vaccine, positive effect-prevention, disease name-prostate cancer, disease name-breast cancer, disease name-lung cancer; the emotion category of this instance is a positive emotion, emotional appeal is joy, love, surprise; The motive for releasing rumors is profit-driven in selling products, the information source is Hong Kong MDX medical group, and pictures and celebrity endorsements are used as testimony method. This paper uses a pellet reasoner to reason on the parsed instance based on SWRL rules, and mines out the specific rumor type of this instance as positive prevention and treatment of disease rumor. This paper also conducted similar instance analysis and reasoning verification for other types of rumor texts, and the results show that the ontology has high consistency and reliability.
Implicit relationship between rumor instance parsing results and pellet reasoner mining.
Comparison and evaluation of ontology performance
In this paper, the constructed ontology is compared with the representative rumor index system in the field. By inviting four experts to make a comprehensive evaluation based on the self-built index system 70 , 71 , 72 , their performance in the indicators of reliability, coverage and operability is evaluated. According to the ranking order given by experts, they are given 1–4 points, and the first place in each indicator item gets four points. The average value given by three experts is taken as the single indicator score of each subject, and the total score of each indicator item is taken as the final score of the subject.
As can be seen from Table 14 , the rumor domain ontology constructed in this paper constructs a term set through three ways: reusing the existing ontology, extracting the content features of core documents and discovering new concepts based on real rumor data sets, and the ontology structure has been verified by SWRL rule reasoning of pellet inference machine, which has high reliability; ontology covers six kinds of Chinese online rumors, including the grammatical, semantic, pragmatic and social characteristics of rumor text characteristics, emotional characteristics, rumor credibility and social background, which has a high coverage; ontology is coded by OWL language specification and displayed visually on protege, which is convenient for further expansion and reuse of scholars and has high operability.
The construction method of TFI domain ontology proposed in this paper includes terminology layer, framework layer and instance layer. Compared with the traditional methods, this paper adopts three-dimensional data set construction method in terminology layer construction, investigates top-level ontology and related core documents, and completes the mapping of reusable top-level ontology from top to bottom and the concept extraction of rumor content features in existing literature research. Based on the mainstream internet rumor websites in China, the authoritative real rumor data set is established, and the new word discovery algorithm of N-gram combined with RoBERTa-Kmeans clustering algorithm is used to automatically discover new concepts in the field from bottom to top; determine the terminology set of domain ontology more comprehensively and efficiently. This paper extracts the clustering results of domain concepts based on the content characteristics of core documents in the selection of parent rumors content characteristics in the framework layer construction, that is, rumors text characteristics, rumors emotional characteristics, rumors credibility characteristics and social background characteristics; based on the emotional characteristics and the entity categories of real rumor data sets, the characteristics of rumor categories are defined. Sub-category rumor content features combine the concept of three-dimensional rumor term set and the concept distribution based on real rumor data set, define the sub-category concept and hierarchical relationship close to the real needs, and realize the fine-grained hierarchical modeling of the relationship between multi-domain network rumor content features. In this paper, OWL language is used to encode the rumor domain ontology in the instance layer construction, and SWRL rule language and Pellet inference machine are used to deal with the conflict and mine tacit knowledge, judge the fine-grained categories of rumor texts, and realize the effective quality evaluation of rumor ontology. This makes the rumor domain ontology constructed in this paper have high consistency and reliability, and can effectively analyze and reason different types of rumor texts, which enriches the knowledge system in this field and provides a solid foundation for subsequent credible rumor detection and governance.
However, the study of the text has the following limitations and deficiencies:
(1) The rumor domain ontology constructed in this paper only considers the content characteristics, but does not consider the user characteristics and communication characteristics. User characteristics and communication characteristics are important factors affecting the emergence and spread of online rumors, and the motivation and influence of rumors can be analyzed. In this paper, these factors are not included in the rumor feature system, which may limit the expressive ability and reasoning ability of the rumor ontology and fail to fully reflect the complexity and multidimensional nature of online rumors.
(2) In this paper, the mainstream Internet rumor-dispelling websites in China are taken as the data source of ontology instantiation. The data covers five rumor categories: political and military, disease prevention, social life, science and technology, and nutrition and health, and the data range is limited. And these data sources are mainly official or authoritative rumor websites, and their data volume and update frequency may not be enough to reflect the diversity and variability of online rumors, and can not fully guarantee the timeliness and comprehensiveness of rumor data.
(3) The SWRL reasoning rules used in this paper are based on manual writing, which may not cover all reasoning scenarios, and the degree of automation needs to be improved. The pellet inference engine used in this paper is an ontology inference engine based on OWL-DL, which may have some computational complexity problems and lack of advanced reasoning ability.
The following aspects can be considered for optimization and improvement in the future:
(1) This paper will introduce user characteristics into the rumor ontology, and analyze the factors that cause and accept rumors, such as social attributes, psychological state, knowledge level, beliefs and attitudes, behavioral intentions and so on. This paper will introduce the characteristics of communication, and analyze the propagation dynamic factors of various types of rumors, such as propagation path, propagation speed, propagation range, propagation period, propagation effect, etc. This paper hopes to introduce these factors into the rumor feature system, increase the breadth and depth of the rumor domain ontology, and provide more credible clues and basis for the detection, intervention and prevention of rumors.
(2) This paper will expand the data sources, collect the original rumor data directly from social media, news media, authoritative rumor dispelling institutions and other channels, and build a rumor data set with comprehensive types, diverse expressions and rich characteristics; regularly grab the latest rumor data from these data sources and update and improve the rumor data set in time; strengthen the expressive ability of rumor ontology instance layer, and provide full data support and verification for the effective application of ontology.
(3) The text will introduce GPT, LLaMA, ChantGLM and other language models, and explore the automatic generation algorithm and technology of ontology inference rules based on rumor ontology and dynamic Prompt, so as to realize more effective and intelligent rumor ontology evaluation and complex reasoning.
This paper proposed a method of constructing TFI network rumor domain ontology. Based on the concept distribution of three-dimensional term set and real rumor data set, the main features of network rumors are defined, including text features, emotional features, credibility features, social background features and category features, and the relationships among these multi-domain features are modeled in a fine-grained hierarchy, including five parent classes and 88 subcategories. At the instance level, 32 types of typical rumor category judgment and reasoning rules are constructed, and the ontology is processed by using SWRL rule language and pellet inference machine for conflict processing and tacit knowledge mining, so that the semantic analysis and reasoning of rumor text content are realized, which proves its effectiveness in dealing with complex, fuzzy and uncertain information in online rumors and provides a new perspective and tool for the interpretable analysis and processing of online rumors.
Data availability
The datasets generated during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Jiang, S. The production scene and content characteristics of scientific rumors. Youth J. https://doi.org/10.15997/j.cnki.qnjz.2020.33.011 (2020).
Article Google Scholar
Jin, X. & Zhao, Y. Analysis of internet rumors from the perspective of co-governance—Practice of rumor governance on wechat platform. News and Writing. 6 , 41–44 (2017).
Bai, S. Research on the causes and countermeasures of internet rumors. Press https://doi.org/10.15897/j.cnki.cn51-1046/g2.2010.04.035 (2010).
Garg, S. & Sharma, D. K. Linguistic features based framework for automatic fake news detection. Comput. Ind. Eng. 172 , 108432 (2022).
Zhao, J., Fu, C. & Kang, X. Content characteristics predict the putative authenticity of COVID-19 rumors. Front. Public Health 10 , 920103 (2022).
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Zhang, Z., Shu, K. & He, L. The theme and characteristics of wechat rumors. News and Writing. 1 , 60–64 (2016).
Li, B. & Yu, G. Research on the discourse space and communication field of internet rumors in the post-truth era—Based on the analysis of 4160 rumors in wechat circle of friends. Journalism Research. 2 , 103–112 (2018).
Yu, G. Text structure and expression characteristics of internet rumors—Analysis of 6000+ rumors based on tencent big data screening and identification. News and Writing. 2 , 53–59 (2018).
Mourão, R. R. & Robertson, C. T. Fake news as discursive integration: An analysis of sites that publish false, misleading, hyperpartisan and sensational information. J. Stud. 20 , 2077–2095 (2019).
Google Scholar
Zhou, G. Analysis on the content characteristics and strategies of epidemic rumors—Based on Sina’s “novel coronavirus epidemic rumors list”. Sci. Popul. https://doi.org/10.19293/j.cnki.1673-8357.2021.05.002 (2021).
Huang, Y. An analysis of the internal logic and methods of rumor “confirmation”—An empirical study based on 60 rumors spread on wechat. J. Party Sch. Tianjin Munic. Comm. CPC 20 , 7 (2018).
Butt, S. et al . What goes on inside rumour and non-rumour tweets and their reactions: A psycholinguistic analyses. Comput. Hum. Behav. 135 , 107345 (2022).
Zhou, L., Tao, J. & Zhang, D. Does fake news in different languages tell the same story? An analysis of multi-level thematic and emotional characteristics of news about COVID-19. Inf. Syst. Front. 25 , 493–512. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10796-022-10329-7 (2023).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Tan, L. et al . Research status of deep learning methods for rumor detection. Multimed. Tools Appl. 82 , 2941–2982 (2023).
Damstra, A. et al. What does fake look like? A review of the literature on intentional deception in the news and on social media. J. Stud. 22 , 1947–1963. https://doi.org/10.1080/1461670X.2021.1979423 (2021).
Lai, S. & Tang, X. Research on the influence of information emotionality on the spread of online rumors. J. Inf. 35 , 116–121 (2016).
ADS Google Scholar
Yuan, H. & Xie, Y. Research on the rumor maker of internet rumors about public events—Based on the content analysis of 118 influential Internet rumors about public events. Journalist https://doi.org/10.16057/j.cnki.31-1171/g2.2015.05.008 (2015).
Ruan, Z. & Yin, L. Types and discourse focus of weibo rumors—Based on the content analysis of 307 weibo rumors. Contemporary Communication. 4 , 77–78+84 (2014).
Zhang, W. & Zhu, Q. Research on the Construction Method of Domain Ontology. Books and Information. 5 , 16–19+40 (2011).
Tham, K.D., Fox, M.S. & Gruninger, M. A cost ontology for enterprise modelling. In Proceedings of 3rd IEEE Workshop on Enabling Technologies: Infrastructure for Collaborative Enterprises. IEEE , 197–210. https://doi.org/10.1109/ENABL.1994.330502 (1994).
Uschold, M. & Gruninger, M. Ontologies: Principles, methods and applications. Knowl. Eng. Rev. 11 , 93–136 (1996).
Menzel, C. P., Mayer, R. J. & Painter, M. K. IDEF5 ontology description capture method: Concepts and formal foundations (Armstrong Laboratory, Air Force Materiel Command, Wright-Patterson Air Force, 1992).
Book Google Scholar
Song, Z., Zhu, F. & ZHANG, D. Research on air and missile defense domain ontology development based on IDEF5 and OWL. Journal of Projectiles, Rockets, Missiles and Guidance. 30 , 176–178 (2010).
Fernández-López, M., Gómez-Pérez, A. & Juristo, N. Methontology: From ontological art towards ontological engineering. AAAI-97 Spring Symposium Series . https://oa.upm.es/5484/ (1997).
Sawsaa, A. & Lu, J. Building information science ontology (OIS) with methontology and protégé. J. Internet Technol. Secur. Trans. 1 , 100–109 (2012).
Yue, L. & Liu, W. Comparative study on the construction methods of domain ontology at home and abroad. Inf. Stud. Theory Appl. 39 , 119–125. https://doi.org/10.16353/j.cnki.1000-7490.2016.08.024 (2016).
Noy, N.F. & McGuinness, D.L. Ontology development 101: A guide to creating your first ontology. Stanford knowledge systems laboratory technical report. KSL-01–05 (2001).
Luo, Y. et al . vim: Research on OWL-based vocabulary ontology construction method for units of measurement. Electronics 12 , 3783 (2023).
Al-Aswadi, F. N., Chan, H. Y. & Gan, K. H. Automatic ontology construction from text: A review from shallow to deep learning trend. Artif. Intell. Rev. 53 , 3901–3928 (2020).
Chen, X. & Mao, T. Ontology construction of documentary heritage—Taking China archives documentary heritage list as an example. Libr. Trib. 43 , 120–131 (2023).
CAS Google Scholar
Zhao, X. & Li, T. Research on the ontology construction of archives oriented to digital humanism—Taking Wanli tea ceremony archives as an example. Inf. Stud. Theory Appl. 45 , 154–161. https://doi.org/10.16353/j.cnki.1000-7490.2022.08.021 (2022).
Huang, X. et al . Construction of special knowledge base of government website pages based on domain ontology—Taking “COVID-19 vaccine science popularization” as an example. Libr. Inf. Serv. 66 , 35–46. https://doi.org/10.13266/j.issn.0252-3116.2022.17.004 (2022).
Jindal, R., Seeja, K. & Jain, S. Construction of domain ontology utilizing formal concept analysis and social media analytics. Int. J. Cogn. Comput. Eng. 1 , 62–69 (2020).
Ran, J. et al . Research on ontology construction of idioms and allusions based on OWL. Comput. Technol. Dev. 20 , 63–66 (2010).
Li, L. et al . Research on business process modeling of army equipment maintenance support based on IDEF5. Technol. Innov. Appl. 11 , 80–82 (2021).
Song, Z. et al . Ontology modeling of air defense and anti-missile operation process based on IDEF5/OWL. J. Missiles Guid. 30 , 176–178 (2010).
Li, A., Xu, Y. & Chi, Y. Summary of ontology construction and application. Inf. Stud. Theory Appl 46 , 189–195. https://doi.org/10.16353/j.cnki.1000-7490.2023.11.024 (2023).
Yang, J., Song, C. & Jin, L. Ontology construction of emergency plan based on methontology method. J. Saf. Environ. 18 , 1427–1431. https://doi.org/10.13637/j.issn.1009-6094.2018.04.033 (2018).
Duan, L. & Li, H. Ontology modeling method of high-resolution image rural residential area supported by OIA technology. Modern Agricultural Science and Technology. 2 , 338–340 (2016).
Chen, Y. & Jiang, H. Construction of fire inspection knowledge map based on GIS geospatial relationship. J. Subtrop. Resour. Environ. 18 , 109–118. https://doi.org/10.19687/j.cnki.1673-7105.2023.03.014 (2023).
Zhu, L. et al. Construction of TCM asthma domain ontology. Chin. J. Exp. Tradit. Med. Formulae 23 , 222–226. https://doi.org/10.13422/j.cnki.syfjx.2017150222 (2017).
Li, H. et al . Domain ontology construction and relational reasoning. J. Inf. Eng. Univ. 24 , 321–327 (2023).
Zhang, Y. et al. Construction of ontology of stroke nursing field based on corpus. Chin. Nurs. Res. 36 , 4186–4190 (2022).
Wu, M. et al. Ontology construction of natural gas market knowledge map. Pet. New Energy 34 , 71–76 (2022).
Li, X. et al . Research on ontology construction based on thesaurus and its semantic relationship. Inf. Sci. 36 , 83–87 (2018).
Article ADS CAS Google Scholar
Chen, Q. et al . Construction of knowledge ontology of clinical trial literature of traditional Chinese medicine. Chin. J. Exp. Tradit. Med. Formulae 29 , 190–197. https://doi.org/10.13422/j.cnki.syfjx.20231115 (2023).
Xiao, Y. et al. Construction and application of novel coronavirus domain ontology. Mil. Med. 46 , 263–268 (2022).
Su, N. et al . Automatic construction method of domain-limited ontology. Lifting the Transport Machinery. 8 , 49–57 (2023).
Zheng, S. et al . Ontology construction method for user-generated content. Inf. Sci. 37 , 43–47. https://doi.org/10.13833/j.issn.1007-7634.2019.11.007 (2019).
Dong, J., Wang, J. & Wang, Z. Ontology automatic construction method for human-machine-object ternary data fusion in manufacturing field. Control Decis. 37 , 1251–1257. https://doi.org/10.13195/j.kzyjc.2020.1298 (2022).
Zhu, L., Hua, G. & Gao, W. Mapping ontology vertices to a line using hypergraph framework. Int. J. Cogn. Comput. Eng. 1 , 1–8 (2020).
Zhai, Y. & Wang, F. Research on the construction method of Chinese domain ontology based on text mining. Inf. Sci. 33 , 3–10. https://doi.org/10.13833/j.cnki.is.2015.06.001 (2015).
Duan, Z. Generation mechanism of internet rumors and countermeasures. Guizhou Soc. Sci. https://doi.org/10.13713/j.cnki.cssci.2016.04.014 (2016).
Du, Z. & Zhi, S. The harm and governance of network political rumors. Academic Journal of Zhongzhou. 4 , 161–165 (2019).
Song, X. et al . Research on influencing factors of health rumor sharing willingness based on MOA theory. J. China Soc. Sci. Tech. Inf. 39 , 511–520 (2020).
Jiang, S. Research on the characteristics, causes and countermeasures of social rumors dissemination in china in recent years. Red Flag Manuscript . 16 , 4 (2011).
Huang, J., Wang, G. & Zhong, S. Research on the propagation law and function mode of sci-tech rumors. Journal of Information. 34 , 156–160 (2015).
Liu, Y. et al . A survey of rumor recognition in social media. Chin. J. Comput. 41 , 1536–1558 (2018).
Wei, D. et al. Public emotions and rumors spread during the covid-19 epidemic in China: Web-based correlation study. J. Med. Internet Res. 22 , e21933 (2020).
Runxi, Z. & Di, Z. A model and simulation of the emotional contagion of netizens in the process of rumor refutation. Sci. Rep. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-50770-4 (2019).
Tang, X. & Lai, S. Research on the forwarding of network health rumors in public health security incidents—Interaction between perceived risk and information credibility. J. Inf. 40 , 101–107 (2021).
Nicolas, P., Dominik, B. & Stefan, F. Emotions in online rumor diffusion. EPJ Data Sci. https://doi.org/10.1140/epjds/s13688-021-00307-5 (2021).
Deng, G. & Tang, G. Research on the spread of network rumors and its social impact. Seeker https://doi.org/10.16059/j.cnki.cn43-1008/c.2005.10.031 (2005).
Ji, Y. Research on the communication motivation of wechat rumors. Youth J. https://doi.org/10.15997/j.cnki.qnjz.2019.17.006 (2019).
Yuan, G. Analysis on the causes and motives of internet rumors in emergencies—Taking social media as an example. Media. 21 , 80–83 (2016).
Zhao, N., Li, Y. & Zhang, J. A review of the research on influencing factors and motivation mechanism of rumor spread. J. Psychol. Sci. 36 , 965–970. https://doi.org/10.16719/j.cnki.1671-6981.2013.04.015 (2013).
Article CAS Google Scholar
Hu, H. On the formation mechanism of social rumors from the perspective of “rumors and salt storm”. J. Henan Univ. 52 , 63–68 (2012).
Yue, Y. et al. Trust in government buffers the negative effect of rumor exposure on people’s emotions. Curr. Psychol. 42 , 23917–23930 (2023).
Wang, C. & Hou, X. Analysis of rumor discourse in major emergencies. J. Commun. 19 , 34–38 (2012).
Xu, L. Research progress of ontology evaluation. J. China Soc. Scie. Tech. Inf. 35 , 772–784 (2016).
Lantow, B. & Sandkuhl, K. An analysis of applicability using quality metrics for ontologies on ontology design patterns. Intell. Syst. Acc. Financ. Manag. 22 , 81–99 (2015).
Pak, J. & Zhou, L. A framework for ontology evaluationIn. Exploring the Grand Challenges for Next Generation E-Business: 8th Workshop on E-Business, WEB 2009, Phoenix, AZ, USA, December 15, 2009, Revised Selected Papers 8. , 10–18. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-17449-0_2 (Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2011).
Download references
Acknowledgements
This study was financially supported by Xi'an Major Scientific and Technological Achievements Transformation and Industrialization Project (20KYPT0003-10).
This work was supported by Xi’an Municipal Bureau of Science and Technology, 20KYPT0003-10.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Economics and Management, Xidian University, 266 Xifeng Road, Xi’an, 710071, China
Jianbo Zhao, Huailiang Liu, Weili Zhang, Tong Sun, Qiuyi Chen, Yan Zhuang, Xiaojin Zhang & Shanzhuang Zhang
School of Artificial Intelligence, Xidian University, 266 Xifeng Road, Xi’an, 710071, China
Yuehai Wang, Jiale Cheng & Ruiyu Ding
School of Telecommunications Engineering, Xidian University, 266 Xifeng Road, Xi’an, 710071, China
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
H.L. formulated the overall research strategy and guided the work. J.Z kept the original data on which the paper was based and verified whether the charts and conclusions accurately reflected the collected data. J.Z. W.Z. and T.S. wrote the main manuscript text. W.Z. Y.W. and Q.C. finished collecting and sorting out the data. J.C. Y.Z. and X.Z. prepared Figs. 1 – 7 , S.Z. B.L. and R.D. prepared Tables 1 – 14 . All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Jianbo Zhao .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Zhao, J., Liu, H., Zhang, W. et al. Research on domain ontology construction based on the content features of online rumors. Sci Rep 14 , 12134 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-62459-4
Download citation
Received : 07 December 2023
Accepted : 16 May 2024
Published : 27 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-62459-4
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Rumor content features
- Domain ontology
- Top-level ontology reuse
- New concept discovery
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines . If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Sign up for the Nature Briefing: AI and Robotics newsletter — what matters in AI and robotics research, free to your inbox weekly.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
What Is a Research Methodology? | Steps & Tips. Published on August 25, 2022 by Shona McCombes and Tegan George. Revised on November 20, 2023. Your research methodology discusses and explains the data collection and analysis methods you used in your research. A key part of your thesis, dissertation, or research paper, the methodology chapter explains what you did and how you did it, allowing ...
The research methodology is an important section of any research paper or thesis, as it describes the methods and procedures that will be used to conduct the research. It should include details about the research design, data collection methods, data analysis techniques, and any ethical considerations.
Definition, Types, and Examples. Research methodology 1,2 is a structured and scientific approach used to collect, analyze, and interpret quantitative or qualitative data to answer research questions or test hypotheses. A research methodology is like a plan for carrying out research and helps keep researchers on track by limiting the scope of ...
What is research methodology? Research methodology simply refers to the practical "how" of a research study. More specifically, it's about how a researcher systematically designs a study to ensure valid and reliable results that address the research aims, objectives and research questions. Specifically, how the researcher went about deciding:
A research methodology encompasses the way in which you intend to carry out your research. This includes how you plan to tackle things like collection methods, statistical analysis, participant observations, and more. You can think of your research methodology as being a formula. One part will be how you plan on putting your research into ...
Revised on 10 October 2022. Your research methodology discusses and explains the data collection and analysis methods you used in your research. A key part of your thesis, dissertation, or research paper, the methodology chapter explains what you did and how you did it, allowing readers to evaluate the reliability and validity of your research.
One of the most common deficiencies found in research papers is that the proposed methodology is not suitable to achieving the stated objective of your paper. Describe the specific methods of data collection you are going to use, such as, surveys, interviews, questionnaires, observation, archival research. If you are analyzing existing data ...
Research methodology is the systematic process of planning, executing, and evaluating scientific investigation. It encompasses the techniques, tools, and procedures used to collect, analyze, and interpret data, ensuring the reliability and validity of research findings.
Research methodology is the process or the way you intend to execute your study. The methodology section of a research paper outlines how you plan to conduct your study. It covers various steps such as collecting data, statistical analysis, observing participants, and other procedures involved in the research process
The methodology section of your paper describes how your research was conducted. This information allows readers to check whether your approach is accurate and dependable. A good methodology can help increase the reader's trust in your findings. First, we will define and differentiate quantitative and qualitative research.
Your Methods Section contextualizes the results of your study, giving editors, reviewers and readers alike the information they need to understand and interpret your work. Your methods are key to establishing the credibility of your study, along with your data and the results themselves. A complete methods section should provide enough detail ...
Research methods are ways of collecting and analysing data. Common methods include surveys, experiments, interviews, and observations. ... In shorter scientific papers, where the aim is to report the findings of a specific study, you might simply describe what you did in a methods section.
The methods section is a fundamental section of any paper since it typically discusses the 'what', 'how', 'which', and 'why' of the study, which is necessary to arrive at the final conclusions. In a research article, the introduction, which serves to set the foundation for comprehending the background and results is usually ...
Learn how to write a strong methodology chapter that allows readers to evaluate the reliability and validity of the research. A good methodology chapter incl...
The methodology in a research paper, thesis paper or dissertation is the section in which you describe the actions you took to investigate and research a problem and your rationale for the specific processes and techniques you use within your research to identify, collect and analyze information that helps you understand the problem. ...
Even though methodological studies can be conducted on qualitative or mixed methods research, this paper focuses on and draws examples exclusively from quantitative research. ... Authors' expertise: The inclusion of authors with expertise in research methodology, biostatistics, and scientific writing is likely to influence the end-product. ...
Definition: Research Paper is a written document that presents the author's original research, analysis, and interpretation of a specific topic or issue. It is typically based on Empirical Evidence, and may involve qualitative or quantitative research methods, or a combination of both. The purpose of a research paper is to contribute new ...
The research method must be appropriate to the objectives of the study. For example, be sure you have a large enough sample size to be able to generalize and make recommendations based upon the findings. ... One of the most common deficiencies found in research papers is that the proposed methodology is unsuited to achieving the stated ...
Research methodology refers to the overall approach or strategy used by researchers to conduct a scientific investigation or inquiry. It involves a systematic and rigorous process of collecting, analyzing, and interpreting data to answer research questions or test hypotheses. The methodology of research involves various components, such as ...
The research methodology is the overall plan that determines the direction of the research and provides the overall philosophical background based upon which, the study is conducted.
This paper is a methodological reflection on a community-based participatory research (CBPR) project that used the photovoice method to unravel the educational experiences of disabled college students in China's higher education institutions.
Amid tightening labor markets and a slowdown in productivity growth, Europe and the United States face shifts in labor demand, spurred not only by AI and automation but also by other trends, including efforts to achieve net-zero emissions, an aging population, infrastructure spending, technology investments, and growth in e-commerce, among others (see sidebar, "Our methodology").
Naturalistic observation emerges as a method frequently employed in psychology and the social sciences. This methodology entails the observation of subjects in their native habitat devoid of any manipulation or intrusion by the investigator. The primary objective is to amass data on the behavioral patterns of subjects within authentic settings ...
Background: As an important platform for researchers to present their academic findings, medical journals have a close relationship between their evaluation orientation and the value orientation of their published research results. However, the differences between the academic impact and level of disruptive innovation of medical journals have not been examined by any study yet.
Mechanical condition monitoring data in real engineering are often severely unbalanced, which can lead to a decrease in the stability and accuracy of intelligent diagnosis methods. In this paper, a fault diagnosis method based on the SMOTE + Tomek Link and dual-channel feature fusion is proposed to improve the performance of the sample imbalance fault diagnosis method, taking the piston pump ...
This paper proposes a TFI online rumor domain ontology construction method based on the improvement of the seven-step method, which includes the term layer, the frame layer and the instance layer ...
Researchers from Cleveland Clinic and IBM recently published findings in the Journal of Chemical Theory and Computation that could lay the groundwork for applying quantum computing methods to protein structure prediction. This publication is the first peer-reviewed quantum computing paper from the Cleveland Clinic-IBM Discovery Accelerator partnership.