Research Hypothesis In Psychology: Types, & Examples
Saul Mcleod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul Mcleod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
On This Page:
A research hypothesis, in its plural form “hypotheses,” is a specific, testable prediction about the anticipated results of a study, established at its outset. It is a key component of the scientific method .
Hypotheses connect theory to data and guide the research process towards expanding scientific understanding

Some key points about hypotheses:
- A hypothesis expresses an expected pattern or relationship. It connects the variables under investigation.
- It is stated in clear, precise terms before any data collection or analysis occurs. This makes the hypothesis testable.
- A hypothesis must be falsifiable. It should be possible, even if unlikely in practice, to collect data that disconfirms rather than supports the hypothesis.
- Hypotheses guide research. Scientists design studies to explicitly evaluate hypotheses about how nature works.
- For a hypothesis to be valid, it must be testable against empirical evidence. The evidence can then confirm or disprove the testable predictions.
- Hypotheses are informed by background knowledge and observation, but go beyond what is already known to propose an explanation of how or why something occurs.
Predictions typically arise from a thorough knowledge of the research literature, curiosity about real-world problems or implications, and integrating this to advance theory. They build on existing literature while providing new insight.
Types of Research Hypotheses
Alternative hypothesis.
The research hypothesis is often called the alternative or experimental hypothesis in experimental research.
It typically suggests a potential relationship between two key variables: the independent variable, which the researcher manipulates, and the dependent variable, which is measured based on those changes.
The alternative hypothesis states a relationship exists between the two variables being studied (one variable affects the other).
A hypothesis is a testable statement or prediction about the relationship between two or more variables. It is a key component of the scientific method. Some key points about hypotheses:
- Important hypotheses lead to predictions that can be tested empirically. The evidence can then confirm or disprove the testable predictions.
In summary, a hypothesis is a precise, testable statement of what researchers expect to happen in a study and why. Hypotheses connect theory to data and guide the research process towards expanding scientific understanding.
An experimental hypothesis predicts what change(s) will occur in the dependent variable when the independent variable is manipulated.
It states that the results are not due to chance and are significant in supporting the theory being investigated.
The alternative hypothesis can be directional, indicating a specific direction of the effect, or non-directional, suggesting a difference without specifying its nature. It’s what researchers aim to support or demonstrate through their study.
Null Hypothesis
The null hypothesis states no relationship exists between the two variables being studied (one variable does not affect the other). There will be no changes in the dependent variable due to manipulating the independent variable.
It states results are due to chance and are not significant in supporting the idea being investigated.
The null hypothesis, positing no effect or relationship, is a foundational contrast to the research hypothesis in scientific inquiry. It establishes a baseline for statistical testing, promoting objectivity by initiating research from a neutral stance.
Many statistical methods are tailored to test the null hypothesis, determining the likelihood of observed results if no true effect exists.
This dual-hypothesis approach provides clarity, ensuring that research intentions are explicit, and fosters consistency across scientific studies, enhancing the standardization and interpretability of research outcomes.
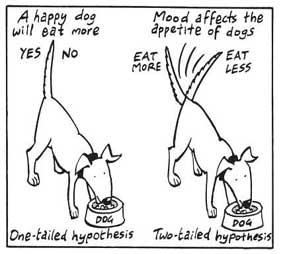
Nondirectional Hypothesis
A non-directional hypothesis, also known as a two-tailed hypothesis, predicts that there is a difference or relationship between two variables but does not specify the direction of this relationship.
It merely indicates that a change or effect will occur without predicting which group will have higher or lower values.
For example, “There is a difference in performance between Group A and Group B” is a non-directional hypothesis.
Directional Hypothesis
A directional (one-tailed) hypothesis predicts the nature of the effect of the independent variable on the dependent variable. It predicts in which direction the change will take place. (i.e., greater, smaller, less, more)
It specifies whether one variable is greater, lesser, or different from another, rather than just indicating that there’s a difference without specifying its nature.
For example, “Exercise increases weight loss” is a directional hypothesis.
Falsifiability
The Falsification Principle, proposed by Karl Popper , is a way of demarcating science from non-science. It suggests that for a theory or hypothesis to be considered scientific, it must be testable and irrefutable.
Falsifiability emphasizes that scientific claims shouldn’t just be confirmable but should also have the potential to be proven wrong.
It means that there should exist some potential evidence or experiment that could prove the proposition false.
However many confirming instances exist for a theory, it only takes one counter observation to falsify it. For example, the hypothesis that “all swans are white,” can be falsified by observing a black swan.
For Popper, science should attempt to disprove a theory rather than attempt to continually provide evidence to support a research hypothesis.
Can a Hypothesis be Proven?
Hypotheses make probabilistic predictions. They state the expected outcome if a particular relationship exists. However, a study result supporting a hypothesis does not definitively prove it is true.
All studies have limitations. There may be unknown confounding factors or issues that limit the certainty of conclusions. Additional studies may yield different results.
In science, hypotheses can realistically only be supported with some degree of confidence, not proven. The process of science is to incrementally accumulate evidence for and against hypothesized relationships in an ongoing pursuit of better models and explanations that best fit the empirical data. But hypotheses remain open to revision and rejection if that is where the evidence leads.
- Disproving a hypothesis is definitive. Solid disconfirmatory evidence will falsify a hypothesis and require altering or discarding it based on the evidence.
- However, confirming evidence is always open to revision. Other explanations may account for the same results, and additional or contradictory evidence may emerge over time.
We can never 100% prove the alternative hypothesis. Instead, we see if we can disprove, or reject the null hypothesis.
If we reject the null hypothesis, this doesn’t mean that our alternative hypothesis is correct but does support the alternative/experimental hypothesis.
Upon analysis of the results, an alternative hypothesis can be rejected or supported, but it can never be proven to be correct. We must avoid any reference to results proving a theory as this implies 100% certainty, and there is always a chance that evidence may exist which could refute a theory.
How to Write a Hypothesis
- Identify variables . The researcher manipulates the independent variable and the dependent variable is the measured outcome.
- Operationalized the variables being investigated . Operationalization of a hypothesis refers to the process of making the variables physically measurable or testable, e.g. if you are about to study aggression, you might count the number of punches given by participants.
- Decide on a direction for your prediction . If there is evidence in the literature to support a specific effect of the independent variable on the dependent variable, write a directional (one-tailed) hypothesis. If there are limited or ambiguous findings in the literature regarding the effect of the independent variable on the dependent variable, write a non-directional (two-tailed) hypothesis.
- Make it Testable : Ensure your hypothesis can be tested through experimentation or observation. It should be possible to prove it false (principle of falsifiability).
- Clear & concise language . A strong hypothesis is concise (typically one to two sentences long), and formulated using clear and straightforward language, ensuring it’s easily understood and testable.
Consider a hypothesis many teachers might subscribe to: students work better on Monday morning than on Friday afternoon (IV=Day, DV= Standard of work).
Now, if we decide to study this by giving the same group of students a lesson on a Monday morning and a Friday afternoon and then measuring their immediate recall of the material covered in each session, we would end up with the following:
- The alternative hypothesis states that students will recall significantly more information on a Monday morning than on a Friday afternoon.
- The null hypothesis states that there will be no significant difference in the amount recalled on a Monday morning compared to a Friday afternoon. Any difference will be due to chance or confounding factors.
More Examples
- Memory : Participants exposed to classical music during study sessions will recall more items from a list than those who studied in silence.
- Social Psychology : Individuals who frequently engage in social media use will report higher levels of perceived social isolation compared to those who use it infrequently.
- Developmental Psychology : Children who engage in regular imaginative play have better problem-solving skills than those who don’t.
- Clinical Psychology : Cognitive-behavioral therapy will be more effective in reducing symptoms of anxiety over a 6-month period compared to traditional talk therapy.
- Cognitive Psychology : Individuals who multitask between various electronic devices will have shorter attention spans on focused tasks than those who single-task.
- Health Psychology : Patients who practice mindfulness meditation will experience lower levels of chronic pain compared to those who don’t meditate.
- Organizational Psychology : Employees in open-plan offices will report higher levels of stress than those in private offices.
- Behavioral Psychology : Rats rewarded with food after pressing a lever will press it more frequently than rats who receive no reward.
Related Articles

Research Methodology
Qualitative Data Coding

What Is a Focus Group?

Cross-Cultural Research Methodology In Psychology

What Is Internal Validity In Research?

Research Methodology , Statistics
What Is Face Validity In Research? Importance & How To Measure

Criterion Validity: Definition & Examples
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.
Biology library
Course: biology library > unit 1, the scientific method.
- Controlled experiments
- The scientific method and experimental design
Introduction
- Make an observation.
- Ask a question.
- Form a hypothesis , or testable explanation.
- Make a prediction based on the hypothesis.
- Test the prediction.
- Iterate: use the results to make new hypotheses or predictions.
Scientific method example: Failure to toast
1. make an observation., 2. ask a question., 3. propose a hypothesis., 4. make predictions., 5. test the predictions..
- If the toaster does toast, then the hypothesis is supported—likely correct.
- If the toaster doesn't toast, then the hypothesis is not supported—likely wrong.
Logical possibility
Practical possibility, building a body of evidence, 6. iterate..
- If the hypothesis was supported, we might do additional tests to confirm it, or revise it to be more specific. For instance, we might investigate why the outlet is broken.
- If the hypothesis was not supported, we would come up with a new hypothesis. For instance, the next hypothesis might be that there's a broken wire in the toaster.
Want to join the conversation?
- Upvote Button navigates to signup page
- Downvote Button navigates to signup page
- Flag Button navigates to signup page


- Teesside University Student & Library Services
- Learning Hub Group
Quantitative data collection and analysis
- Testing hypotheses
- Quantitative data collection
- Averages and percentiles
- Measures of Spread or Dispersion
- Samples and population
- Statistical tests - parametric
- Statistical tests - non-parametric
- Probability
- Reliability and Validity
- Analysing relationships
- Useful Books
Testing Hypotheses
- What is a hypothesis?
- Significance testing
- One-tailed or two-tailed?
- Degrees of freedom
A hypothesis is a statement that we are trying to prove or disprove. It is used to express the relationship between variables and whether this relationship is significant. It is specific and offers a prediction on the results of your research question.
Your research question will lead you to developing a hypothesis, this is why your research question needs to be specific and clear.
The hypothesis will then guide you to the most appropriate techniques you should use to answer the question. They reflect the literature and theories on which you basing them. They need to be testable (i.e. measurable and practical).
Null hypothesis (H 0 ) is the proposition that there will not be a relationship between the variables you are looking at. i.e. any differences are due to chance). They always refer to the population. (Usually we don't believe this to be true.)
e.g. There is no difference in instances of illegal drug use by teenagers who are members of a gang and those who are not..
Alternative hypothesis (H A ) or ( H 1 ): this is sometimes called the research hypothesis or experimental hypothesis. It is the proposition that there will be a relationship. It is a statement of inequality between the variables you are interested in. They always refer to the sample. It is usually a declaration rather than a question and is clear, to the point and specific.
e.g. The instances of illegal drug use of teenagers who are members of a gang is different than the instances of illegal drug use of teenagers who are not gang members.
A non-directional research hypothesis - reflects an expected difference between groups but does not specify the direction of this difference (see two-tailed test).
A directional research hypothesis - reflects an expected difference between groups but does specify the direction of this difference. (see one-tailed test)
e.g. The instances of illegal drug use by teenagers who are members of a gang will be higher t han the instances of illegal drug use of teenagers who are not gang members.
Then the process of testing is to ascertain which hypothesis to believe.
It is usually easier to prove something as untrue rather than true, so looking at the null hypothesis is the usual starting point.
The process of examining the null hypothesis in light of evidence from the sample is called significance testing . It is a way of establishing a range of values in which we can establish whether the null hypothesis is true or false.
The debate over hypothesis testing
There has been discussion over whether the scientific method employed in traditional hypothesis testing is appropriate.
See below for some articles that discuss this:
- Gill, J. (1999) 'The insignificance of null hypothesis testing', Politics Research Quarterly , 52(3), pp. 647-674 .
- Wainer, H. and Robinson, D.H. (2003) 'Shaping up the practice of null hypothesis significance testing', Educational Researcher, 32(7), pp.22-30 .
- Ferguson, C.J. and Heener, M. (2012) ' A vast graveyard of undead theories: publication bias and psychological science's aversion to the null' , Perspectives on Psychological Science, 7(6), pp.555-561 .
Taken from: Salkind, N.J. (2017) Statistics for people who (think they) hate statistics. 6th edn. London: SAGE pp. 144-145.
- Null hypothesis - a simple introduction (SPSS)
A significance level defines the level when your sample evidence contradicts your null hypothesis so that your can then reject it. It is the probability of rejecting the null hypothesis when it is really true.
e.g. a significance level of 0.05 indicates that there is a 5% (or 1 in 20) risk of deciding that there is an effect when in fact there is none.
The lower the significance level that you set, then the evidence from the sample has to be stronger to be able to reject the null hypothesis.
N.B. - it is important that you set the significance level before you carry out your study and analysis.
Using Confidence Intervals
I t is possible to test the significance of your null hypothesis using Confidence Interval (see under samples and populations tab).
- if the range lies outside our predicted null hypothesis value we can reject it and accept the alternative hypothesis
The test statistic
This is another commonly used statistic
- Write down your null and alternative hypothesis
- Find the sample statistic (e.g.the mean of your sample)
- Calculate the test statistic Z score (see under Measures of spread or dispersion and Statistical tests - parametric). In this case the sample mean is compared to the population mean (assumed from the null hypothesis) and the standard error (see under Samples and population) is used rather than the standard deviation.
- Compare the test statistic with the critical values (e.g. plus or minus 1.96 for 5% significance)
- Draw a conclusion about the hypotheses - does the calculated z value lies in this critical range i.e. above 1.96 or below -1.96? If it does we can reject the null hypothesis. This would indicate that the results are significant (or an effect has been detected) - which means that if there were no difference in the population then getting a result that you have observed would be highly unlikely therefore you can reject the null hypothesis.

Type I error - this is the chance of wrongly rejecting the null hypothesis even though it is actually true, e.g. by using a 5% p level you would expect the null hypothesis to be rejected about 5% of the time when the null hypothesis is true. You could set a more stringent p level such as 1% (or 1 in 100) to be more certain of not seeing a Type I error. This, however, makes more likely another type of error (Type II) occurring.
Type II error - this is where there is an effect, but the p value you obtain is non-significant hence you don’t detect this effect.
- Statistical significance - what does it really mean?
- Statistical tables
One-tailed tests - where we know in which direction (e.g. larger or smaller) the difference between sample and population will be. It is a directional hypothesis.
Two-tailed tests - where we are looking at whether there is a difference between sample and population. This difference could be larger or smaller. This is a non-directional hypothesis.
If the difference is in the direction you have predicted (i.e. a one-tailed test) it is easier to get a significant result. Though there are arguments against using a one-tailed test (Wright and London, 2009, p. 98-99)*
*Wright, D. B. & London, K. (2009) First (and second) steps in statistics . 2nd edn. London: SAGE.
N.B. - think of the ‘tails’ as the regions at the far-end of a normal distribution. For a two-tailed test with significance level of 0.05% then 0.025% of the values would be at one end of the distribution and the other 0.025% would be at the other end of the distribution. It is the values in these ‘critical’ extreme regions where we can think about rejecting the null hypothesis and claim that there has been an effect.
Degrees of freedom ( df) is a rather difficult mathematical concept, but is needed to calculate the signifcance of certain statistical tests, such as the t-test, ANOVA and Chi-squared test.
It is broadly defined as the number of "observations" (pieces of information) in the data that are free to vary when estimating statistical parameters. (Taken from Minitab Blog ).
The higher the degrees of freedom are the more powerful and precise your estimates of the parameter (population) will be.
Typically, for a 1-sample t-test it is considered as the number of values in your sample minus 1.
For chi-squared tests with a table of rows and columns the rule is:
(Number of rows minus 1) times (number of columns minus 1)
Any accessible example to illustrate the principle of degrees of freedom using chocolates.
- You have seven chocolates in a box, each being a different type, e.g. truffle, coffee cream, caramel cluster, fudge, strawberry dream, hazelnut whirl, toffee.
- You are being good and intend to eat only one chocolate each day of the week.
- On the first day, you can choose to eat any one of the 7 chocolate types - you have a choice from all 7.
- On the second day, you can choose from the 6 remaining chocolates, on day 3 you can choose from 5 chocolates, and so on.
- On the sixth day you have a choice of the remaining 2 chocolates you haven't ate that week.
- However on the seventh day - you haven't really got any choice of chocolate - it has got to be the one you have left in your box.
- You had 7-1 = 6 days of “chocolate” freedom—in which the chocolate you ate could vary!
- << Previous: Samples and population
- Next: Statistical tests - parametric >>
- Last Updated: Jan 9, 2024 11:01 AM
- URL: https://libguides.tees.ac.uk/quantitative
What Is A Research (Scientific) Hypothesis? A plain-language explainer + examples
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Reviewed By: Dr Eunice Rautenbach | June 2020
If you’re new to the world of research, or it’s your first time writing a dissertation or thesis, you’re probably noticing that the words “research hypothesis” and “scientific hypothesis” are used quite a bit, and you’re wondering what they mean in a research context .
“Hypothesis” is one of those words that people use loosely, thinking they understand what it means. However, it has a very specific meaning within academic research. So, it’s important to understand the exact meaning before you start hypothesizing.
Research Hypothesis 101
- What is a hypothesis ?
- What is a research hypothesis (scientific hypothesis)?
- Requirements for a research hypothesis
- Definition of a research hypothesis
- The null hypothesis
What is a hypothesis?
Let’s start with the general definition of a hypothesis (not a research hypothesis or scientific hypothesis), according to the Cambridge Dictionary:
Hypothesis: an idea or explanation for something that is based on known facts but has not yet been proved.
In other words, it’s a statement that provides an explanation for why or how something works, based on facts (or some reasonable assumptions), but that has not yet been specifically tested . For example, a hypothesis might look something like this:
Hypothesis: sleep impacts academic performance.
This statement predicts that academic performance will be influenced by the amount and/or quality of sleep a student engages in – sounds reasonable, right? It’s based on reasonable assumptions , underpinned by what we currently know about sleep and health (from the existing literature). So, loosely speaking, we could call it a hypothesis, at least by the dictionary definition.
But that’s not good enough…
Unfortunately, that’s not quite sophisticated enough to describe a research hypothesis (also sometimes called a scientific hypothesis), and it wouldn’t be acceptable in a dissertation, thesis or research paper . In the world of academic research, a statement needs a few more criteria to constitute a true research hypothesis .
What is a research hypothesis?
A research hypothesis (also called a scientific hypothesis) is a statement about the expected outcome of a study (for example, a dissertation or thesis). To constitute a quality hypothesis, the statement needs to have three attributes – specificity , clarity and testability .
Let’s take a look at these more closely.
Need a helping hand?
Hypothesis Essential #1: Specificity & Clarity
A good research hypothesis needs to be extremely clear and articulate about both what’ s being assessed (who or what variables are involved ) and the expected outcome (for example, a difference between groups, a relationship between variables, etc.).
Let’s stick with our sleepy students example and look at how this statement could be more specific and clear.
Hypothesis: Students who sleep at least 8 hours per night will, on average, achieve higher grades in standardised tests than students who sleep less than 8 hours a night.
As you can see, the statement is very specific as it identifies the variables involved (sleep hours and test grades), the parties involved (two groups of students), as well as the predicted relationship type (a positive relationship). There’s no ambiguity or uncertainty about who or what is involved in the statement, and the expected outcome is clear.
Contrast that to the original hypothesis we looked at – “Sleep impacts academic performance” – and you can see the difference. “Sleep” and “academic performance” are both comparatively vague , and there’s no indication of what the expected relationship direction is (more sleep or less sleep). As you can see, specificity and clarity are key.

Hypothesis Essential #2: Testability (Provability)
A statement must be testable to qualify as a research hypothesis. In other words, there needs to be a way to prove (or disprove) the statement. If it’s not testable, it’s not a hypothesis – simple as that.
For example, consider the hypothesis we mentioned earlier:
Hypothesis: Students who sleep at least 8 hours per night will, on average, achieve higher grades in standardised tests than students who sleep less than 8 hours a night.
We could test this statement by undertaking a quantitative study involving two groups of students, one that gets 8 or more hours of sleep per night for a fixed period, and one that gets less. We could then compare the standardised test results for both groups to see if there’s a statistically significant difference.
Again, if you compare this to the original hypothesis we looked at – “Sleep impacts academic performance” – you can see that it would be quite difficult to test that statement, primarily because it isn’t specific enough. How much sleep? By who? What type of academic performance?
So, remember the mantra – if you can’t test it, it’s not a hypothesis 🙂

Defining A Research Hypothesis
You’re still with us? Great! Let’s recap and pin down a clear definition of a hypothesis.
A research hypothesis (or scientific hypothesis) is a statement about an expected relationship between variables, or explanation of an occurrence, that is clear, specific and testable.
So, when you write up hypotheses for your dissertation or thesis, make sure that they meet all these criteria. If you do, you’ll not only have rock-solid hypotheses but you’ll also ensure a clear focus for your entire research project.
What about the null hypothesis?
You may have also heard the terms null hypothesis , alternative hypothesis, or H-zero thrown around. At a simple level, the null hypothesis is the counter-proposal to the original hypothesis.
For example, if the hypothesis predicts that there is a relationship between two variables (for example, sleep and academic performance), the null hypothesis would predict that there is no relationship between those variables.
At a more technical level, the null hypothesis proposes that no statistical significance exists in a set of given observations and that any differences are due to chance alone.
And there you have it – hypotheses in a nutshell.
If you have any questions, be sure to leave a comment below and we’ll do our best to help you. If you need hands-on help developing and testing your hypotheses, consider our private coaching service , where we hold your hand through the research journey.

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
You Might Also Like:

16 Comments
Very useful information. I benefit more from getting more information in this regard.
Very great insight,educative and informative. Please give meet deep critics on many research data of public international Law like human rights, environment, natural resources, law of the sea etc
In a book I read a distinction is made between null, research, and alternative hypothesis. As far as I understand, alternative and research hypotheses are the same. Can you please elaborate? Best Afshin
This is a self explanatory, easy going site. I will recommend this to my friends and colleagues.
Very good definition. How can I cite your definition in my thesis? Thank you. Is nul hypothesis compulsory in a research?
It’s a counter-proposal to be proven as a rejection
Please what is the difference between alternate hypothesis and research hypothesis?
It is a very good explanation. However, it limits hypotheses to statistically tasteable ideas. What about for qualitative researches or other researches that involve quantitative data that don’t need statistical tests?
In qualitative research, one typically uses propositions, not hypotheses.
could you please elaborate it more
I’ve benefited greatly from these notes, thank you.
This is very helpful
well articulated ideas are presented here, thank you for being reliable sources of information
Excellent. Thanks for being clear and sound about the research methodology and hypothesis (quantitative research)
I have only a simple question regarding the null hypothesis. – Is the null hypothesis (Ho) known as the reversible hypothesis of the alternative hypothesis (H1? – How to test it in academic research?
this is very important note help me much more
Trackbacks/Pingbacks
- What Is Research Methodology? Simple Definition (With Examples) - Grad Coach - […] Contrasted to this, a quantitative methodology is typically used when the research aims and objectives are confirmatory in nature. For example,…
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support

How to Write a Great Hypothesis
Hypothesis Definition, Format, Examples, and Tips
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Amy Morin, LCSW, is a psychotherapist and international bestselling author. Her books, including "13 Things Mentally Strong People Don't Do," have been translated into more than 40 languages. Her TEDx talk, "The Secret of Becoming Mentally Strong," is one of the most viewed talks of all time.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/VW-MIND-Amy-2b338105f1ee493f94d7e333e410fa76.jpg)
Verywell / Alex Dos Diaz
- The Scientific Method
Hypothesis Format
Falsifiability of a hypothesis.
- Operationalization
Hypothesis Types
Hypotheses examples.
- Collecting Data
A hypothesis is a tentative statement about the relationship between two or more variables. It is a specific, testable prediction about what you expect to happen in a study. It is a preliminary answer to your question that helps guide the research process.
Consider a study designed to examine the relationship between sleep deprivation and test performance. The hypothesis might be: "This study is designed to assess the hypothesis that sleep-deprived people will perform worse on a test than individuals who are not sleep-deprived."
At a Glance
A hypothesis is crucial to scientific research because it offers a clear direction for what the researchers are looking to find. This allows them to design experiments to test their predictions and add to our scientific knowledge about the world. This article explores how a hypothesis is used in psychology research, how to write a good hypothesis, and the different types of hypotheses you might use.
The Hypothesis in the Scientific Method
In the scientific method , whether it involves research in psychology, biology, or some other area, a hypothesis represents what the researchers think will happen in an experiment. The scientific method involves the following steps:
- Forming a question
- Performing background research
- Creating a hypothesis
- Designing an experiment
- Collecting data
- Analyzing the results
- Drawing conclusions
- Communicating the results
The hypothesis is a prediction, but it involves more than a guess. Most of the time, the hypothesis begins with a question which is then explored through background research. At this point, researchers then begin to develop a testable hypothesis.
Unless you are creating an exploratory study, your hypothesis should always explain what you expect to happen.
In a study exploring the effects of a particular drug, the hypothesis might be that researchers expect the drug to have some type of effect on the symptoms of a specific illness. In psychology, the hypothesis might focus on how a certain aspect of the environment might influence a particular behavior.
Remember, a hypothesis does not have to be correct. While the hypothesis predicts what the researchers expect to see, the goal of the research is to determine whether this guess is right or wrong. When conducting an experiment, researchers might explore numerous factors to determine which ones might contribute to the ultimate outcome.
In many cases, researchers may find that the results of an experiment do not support the original hypothesis. When writing up these results, the researchers might suggest other options that should be explored in future studies.
In many cases, researchers might draw a hypothesis from a specific theory or build on previous research. For example, prior research has shown that stress can impact the immune system. So a researcher might hypothesize: "People with high-stress levels will be more likely to contract a common cold after being exposed to the virus than people who have low-stress levels."
In other instances, researchers might look at commonly held beliefs or folk wisdom. "Birds of a feather flock together" is one example of folk adage that a psychologist might try to investigate. The researcher might pose a specific hypothesis that "People tend to select romantic partners who are similar to them in interests and educational level."
Elements of a Good Hypothesis
So how do you write a good hypothesis? When trying to come up with a hypothesis for your research or experiments, ask yourself the following questions:
- Is your hypothesis based on your research on a topic?
- Can your hypothesis be tested?
- Does your hypothesis include independent and dependent variables?
Before you come up with a specific hypothesis, spend some time doing background research. Once you have completed a literature review, start thinking about potential questions you still have. Pay attention to the discussion section in the journal articles you read . Many authors will suggest questions that still need to be explored.
How to Formulate a Good Hypothesis
To form a hypothesis, you should take these steps:
- Collect as many observations about a topic or problem as you can.
- Evaluate these observations and look for possible causes of the problem.
- Create a list of possible explanations that you might want to explore.
- After you have developed some possible hypotheses, think of ways that you could confirm or disprove each hypothesis through experimentation. This is known as falsifiability.
In the scientific method , falsifiability is an important part of any valid hypothesis. In order to test a claim scientifically, it must be possible that the claim could be proven false.
Students sometimes confuse the idea of falsifiability with the idea that it means that something is false, which is not the case. What falsifiability means is that if something was false, then it is possible to demonstrate that it is false.
One of the hallmarks of pseudoscience is that it makes claims that cannot be refuted or proven false.
The Importance of Operational Definitions
A variable is a factor or element that can be changed and manipulated in ways that are observable and measurable. However, the researcher must also define how the variable will be manipulated and measured in the study.
Operational definitions are specific definitions for all relevant factors in a study. This process helps make vague or ambiguous concepts detailed and measurable.
For example, a researcher might operationally define the variable " test anxiety " as the results of a self-report measure of anxiety experienced during an exam. A "study habits" variable might be defined by the amount of studying that actually occurs as measured by time.
These precise descriptions are important because many things can be measured in various ways. Clearly defining these variables and how they are measured helps ensure that other researchers can replicate your results.
Replicability
One of the basic principles of any type of scientific research is that the results must be replicable.
Replication means repeating an experiment in the same way to produce the same results. By clearly detailing the specifics of how the variables were measured and manipulated, other researchers can better understand the results and repeat the study if needed.
Some variables are more difficult than others to define. For example, how would you operationally define a variable such as aggression ? For obvious ethical reasons, researchers cannot create a situation in which a person behaves aggressively toward others.
To measure this variable, the researcher must devise a measurement that assesses aggressive behavior without harming others. The researcher might utilize a simulated task to measure aggressiveness in this situation.
Hypothesis Checklist
- Does your hypothesis focus on something that you can actually test?
- Does your hypothesis include both an independent and dependent variable?
- Can you manipulate the variables?
- Can your hypothesis be tested without violating ethical standards?
The hypothesis you use will depend on what you are investigating and hoping to find. Some of the main types of hypotheses that you might use include:
- Simple hypothesis : This type of hypothesis suggests there is a relationship between one independent variable and one dependent variable.
- Complex hypothesis : This type suggests a relationship between three or more variables, such as two independent and dependent variables.
- Null hypothesis : This hypothesis suggests no relationship exists between two or more variables.
- Alternative hypothesis : This hypothesis states the opposite of the null hypothesis.
- Statistical hypothesis : This hypothesis uses statistical analysis to evaluate a representative population sample and then generalizes the findings to the larger group.
- Logical hypothesis : This hypothesis assumes a relationship between variables without collecting data or evidence.
A hypothesis often follows a basic format of "If {this happens} then {this will happen}." One way to structure your hypothesis is to describe what will happen to the dependent variable if you change the independent variable .
The basic format might be: "If {these changes are made to a certain independent variable}, then we will observe {a change in a specific dependent variable}."
A few examples of simple hypotheses:
- "Students who eat breakfast will perform better on a math exam than students who do not eat breakfast."
- "Students who experience test anxiety before an English exam will get lower scores than students who do not experience test anxiety."
- "Motorists who talk on the phone while driving will be more likely to make errors on a driving course than those who do not talk on the phone."
- "Children who receive a new reading intervention will have higher reading scores than students who do not receive the intervention."
Examples of a complex hypothesis include:
- "People with high-sugar diets and sedentary activity levels are more likely to develop depression."
- "Younger people who are regularly exposed to green, outdoor areas have better subjective well-being than older adults who have limited exposure to green spaces."
Examples of a null hypothesis include:
- "There is no difference in anxiety levels between people who take St. John's wort supplements and those who do not."
- "There is no difference in scores on a memory recall task between children and adults."
- "There is no difference in aggression levels between children who play first-person shooter games and those who do not."
Examples of an alternative hypothesis:
- "People who take St. John's wort supplements will have less anxiety than those who do not."
- "Adults will perform better on a memory task than children."
- "Children who play first-person shooter games will show higher levels of aggression than children who do not."
Collecting Data on Your Hypothesis
Once a researcher has formed a testable hypothesis, the next step is to select a research design and start collecting data. The research method depends largely on exactly what they are studying. There are two basic types of research methods: descriptive research and experimental research.
Descriptive Research Methods
Descriptive research such as case studies , naturalistic observations , and surveys are often used when conducting an experiment is difficult or impossible. These methods are best used to describe different aspects of a behavior or psychological phenomenon.
Once a researcher has collected data using descriptive methods, a correlational study can examine how the variables are related. This research method might be used to investigate a hypothesis that is difficult to test experimentally.
Experimental Research Methods
Experimental methods are used to demonstrate causal relationships between variables. In an experiment, the researcher systematically manipulates a variable of interest (known as the independent variable) and measures the effect on another variable (known as the dependent variable).
Unlike correlational studies, which can only be used to determine if there is a relationship between two variables, experimental methods can be used to determine the actual nature of the relationship—whether changes in one variable actually cause another to change.
The hypothesis is a critical part of any scientific exploration. It represents what researchers expect to find in a study or experiment. In situations where the hypothesis is unsupported by the research, the research still has value. Such research helps us better understand how different aspects of the natural world relate to one another. It also helps us develop new hypotheses that can then be tested in the future.
Thompson WH, Skau S. On the scope of scientific hypotheses . R Soc Open Sci . 2023;10(8):230607. doi:10.1098/rsos.230607
Taran S, Adhikari NKJ, Fan E. Falsifiability in medicine: what clinicians can learn from Karl Popper [published correction appears in Intensive Care Med. 2021 Jun 17;:]. Intensive Care Med . 2021;47(9):1054-1056. doi:10.1007/s00134-021-06432-z
Eyler AA. Research Methods for Public Health . 1st ed. Springer Publishing Company; 2020. doi:10.1891/9780826182067.0004
Nosek BA, Errington TM. What is replication ? PLoS Biol . 2020;18(3):e3000691. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.3000691
Aggarwal R, Ranganathan P. Study designs: Part 2 - Descriptive studies . Perspect Clin Res . 2019;10(1):34-36. doi:10.4103/picr.PICR_154_18
Nevid J. Psychology: Concepts and Applications. Wadworth, 2013.
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
What Is a Testable Hypothesis?
- Scientific Method
- Chemical Laws
- Periodic Table
- Projects & Experiments
- Biochemistry
- Physical Chemistry
- Medical Chemistry
- Chemistry In Everyday Life
- Famous Chemists
- Activities for Kids
- Abbreviations & Acronyms
- Weather & Climate
- Ph.D., Biomedical Sciences, University of Tennessee at Knoxville
- B.A., Physics and Mathematics, Hastings College
A hypothesis is a tentative answer to a scientific question. A testable hypothesis is a hypothesis that can be proved or disproved as a result of testing, data collection, or experience. Only testable hypotheses can be used to conceive and perform an experiment using the scientific method .
Requirements for a Testable Hypothesis
In order to be considered testable, two criteria must be met:
- It must be possible to prove that the hypothesis is true.
- It must be possible to prove that the hypothesis is false.
- It must be possible to reproduce the results of the hypothesis.
Examples of a Testable Hypothesis
All the following hypotheses are testable. It's important, however, to note that while it's possible to say that the hypothesis is correct, much more research would be required to answer the question " why is this hypothesis correct?"
- Students who attend class have higher grades than students who skip class. This is testable because it is possible to compare the grades of students who do and do not skip class and then analyze the resulting data. Another person could conduct the same research and come up with the same results.
- People exposed to high levels of ultraviolet light have a higher incidence of cancer than the norm. This is testable because it is possible to find a group of people who have been exposed to high levels of ultraviolet light and compare their cancer rates to the average.
- If you put people in a dark room, then they will be unable to tell when an infrared light turns on. This hypothesis is testable because it is possible to put a group of people into a dark room, turn on an infrared light, and ask the people in the room whether or not an infrared light has been turned on.
Examples of a Hypothesis Not Written in a Testable Form
- It doesn't matter whether or not you skip class. This hypothesis can't be tested because it doesn't make any actual claim regarding the outcome of skipping class. "It doesn't matter" doesn't have any specific meaning, so it can't be tested.
- Ultraviolet light could cause cancer. The word "could" makes a hypothesis extremely difficult to test because it is very vague. There "could," for example, be UFOs watching us at every moment, even though it's impossible to prove that they are there!
- Goldfish make better pets than guinea pigs. This is not a hypothesis; it's a matter of opinion. There is no agreed-upon definition of what a "better" pet is, so while it is possible to argue the point, there is no way to prove it.
How to Propose a Testable Hypothesis
Now that you know what a testable hypothesis is, here are tips for proposing one.
- Try to write the hypothesis as an if-then statement. If you take an action, then a certain outcome is expected.
- Identify the independent and dependent variable in the hypothesis. The independent variable is what you are controlling or changing. You measure the effect this has on the dependent variable.
- Write the hypothesis in such a way that you can prove or disprove it. For example, a person has skin cancer, you can't prove they got it from being out in the sun. However, you can demonstrate a relationship between exposure to ultraviolet light and increased risk of skin cancer.
- Make sure you are proposing a hypothesis you can test with reproducible results. If your face breaks out, you can't prove the breakout was caused by the french fries you had for dinner last night. However, you can measure whether or not eating french fries is associated with breaking out. It's a matter of gathering enough data to be able to reproduce results and draw a conclusion.
- Null Hypothesis Examples
- Examples of Independent and Dependent Variables
- What Is the Visible Light Spectrum?
- What Glows Under Black Light?
- Difference Between Independent and Dependent Variables
- What Are Examples of a Hypothesis?
- What Is a Black Light?
- What Is a Hypothesis? (Science)
- What Are the Elements of a Good Hypothesis?
- How To Design a Science Fair Experiment
- Understanding Simple vs Controlled Experiments
- Scientific Method Vocabulary Terms
- Hypothesis, Model, Theory, and Law
- Theory Definition in Science
- Null Hypothesis Definition and Examples
- What 'Fail to Reject' Means in a Hypothesis Test
- More from M-W
- To save this word, you'll need to log in. Log In
Definition of disprove
transitive verb
Examples of disprove in a Sentence
These examples are programmatically compiled from various online sources to illustrate current usage of the word 'disprove.' Any opinions expressed in the examples do not represent those of Merriam-Webster or its editors. Send us feedback about these examples.
Word History
Middle English, from Anglo-French desprover , from des- dis- + prover to prove
14th century, in the meaning defined above
Dictionary Entries Near disprove
disprovable
disprovided
Cite this Entry
“Disprove.” Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary , Merriam-Webster, https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/disprove. Accessed 4 Jun. 2024.
Kids Definition
Kids definition of disprove, more from merriam-webster on disprove.
Nglish: Translation of disprove for Spanish Speakers
Britannica English: Translation of disprove for Arabic Speakers
Subscribe to America's largest dictionary and get thousands more definitions and advanced search—ad free!

Can you solve 4 words at once?
Word of the day.
See Definitions and Examples »
Get Word of the Day daily email!
Popular in Grammar & Usage
More commonly misspelled words, commonly misspelled words, how to use em dashes (—), en dashes (–) , and hyphens (-), absent letters that are heard anyway, how to use accents and diacritical marks, popular in wordplay, the words of the week - may 31, pilfer: how to play and win, 9 superb owl words, 10 words for lesser-known games and sports, etymologies for every day of the week, games & quizzes.

COVID Select Subcommittee Releases Dr. Fauci’s Transcript, Highlights Key Takeaways in New Memo
WASHINGTON — Today, Select Subcommittee on the Coronavirus Pandemic Chairman Brad Wenstrup (R-Ohio) released the transcript from Dr. Anthony Fauci’s transcribed interview. Dr. Fauci served as the Director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) and was the face of America’s public health response during the COVID-19 pandemic. His closed door, 14-hour, two-day testimony in January 2024 has served as a critical component of the Select Subcommittee’s investigations into the origins of COVID-19, pandemic-era domestic policy failures, and improvements to the United States’ public health system. In conjunction with the transcript, the Select Subcommittee also released a new staff memo that highlights the key takeaways from Dr. Fauci’s transcribed interview. The memo can be found here .
The Select Subcommittee also released four additional transcripts from senior public health officials. These transcripts, as well as Dr. Fauci’s transcript, can be found below:
- Dr. Anthony Fauci Part 1
- Dr. Anthony Fauci Part 2
- Dr. Hugh Auchincloss
- Dr. Cliff Lane
- Greg Folkers
- Gray Handley
Below are important exchanges from Dr. Fauci’s transcribed interview:
SOCIAL DISTANCING : The “6 feet apart” social distancing recommendation forced on Americans by federal health officials was arbitrary and not based on science. Dr. Fauci testified that this guidance — which shut down schools and small businesses nationwide — “sort of just appeared” and was not based on any scientific studies.
Majority Counsel: “ Do you recall when discussions regarding, kind of, the at least a 6 foot threshold began? ”
Dr. Fauci: “The 6 foot in the school?”
Majority Counsel: “Six foot overall. I mean, 6-foot was applied at businesse s—”
Dr. Fauci: “Yeah.”
Majority Counsel: “ —it was applied in schools, it was applied here. At least how the messaging was applied was that 6-foot distancing was the distance that needed to be— “
Dr. Fauci: “ You know, I don’t recall. It sort of just appeared. I don’t recall, like, a discussion of whether it should be 5 or 6 or whatever. It was just that 6 foot is— ”
Majority Counsel: “ Did you see any studies that supported 6 feet? ”
Dr. Fauci: “ I was not aware of studies that in fact, that would be a very difficult study to do. ”
MASKING : Dr. Fauci testified that he did not recall any supporting evidence for masking children. Concerningly, mask-wearing has been associated with learning loss and severe speech development issues in America’s children.
Majority Counsel: “ Do you recall reviewing any studies or data supporting masking for children? ”
Dr. Fauci: “ You know, I might have, Mitch, but I don’t recall specifically that I did. I might have. ”
Majority Counsel: “ Since the — there’s been a lot of studies that have come out since the pandemic started, but specifically on this there have been significant on kind of like the learning loss and speech and development issues that have been associated with particularly young children wearing masks while they’re growing up. They can’t see their teacher talk and can’t learn how to form words. Have you followed any of those studies? ”
Dr. Fauci: “ No. But I believe that there are a lot of conflicting studies too, that there are those that say, yes, there is an impact, and there are those that say there’s not. I still think that’s up in the air. ”
TRAVEL RESTRICTIONS : Dr. Fauci unequivocally agreed with EVERY travel restriction issued by the Trump Administration at the height of the COVID-19 pandemic. This testimony runs counter to the public narrative that the Trump Administration’s travel restrictions were xenophobic. During his transcribed interview, the Biden Administration’s counsel curiously prohibited Dr. Fauci from answering questions on whether he recommended the travel restrictions.
Majority Counsel: “ Did you agree with President Trump’s decision to restrict travel from China? ”
Dr. Fauci: “ I did , and I said there were caveats to restrictions. I agreed with it, but I said we have to be careful because sometimes when you do restrictions they have negative consequences in that you don’t have open access to help or even information. But fundamentally, I agreed at that time, since we had almost no infections that we knew of in our country, that at least a temporary restriction would be important. ”
Majority Counsel: “ Did you also agree with the EU travel restriction? ”
Dr. Fauci: “ I agreed with the suggestion that that be done, yes. ”
Majority Counsel: “ Did you agree with the U.K. travel restriction? ”
Dr. Fauci: “ Yes, I did. ”
Majority Counsel: “ Did you recommend instituting travel restrictions in response to the pandemic? ”
Biden Administration Official: “ I’m going to step in here .”
VACCINE MANDATES: Dr. Fauci admitted that vaccine mandates during the COVID-19 pandemic could increase vaccine hesitancy in the future. He also claimed that these mandates were not sufficiently studied ahead of the pandemic. Previously, Dr. Fauci advocated “that when you make it difficult for people in their lives, they lose their ideological bullshit, and they get vaccinated.”
Majority Counsel: “ Do you think mandating vaccines can result in some hesitancy? ”
Dr. Fauci: “ I think one of the things that we really need to do after the fact, now, to — you know, after-the-game, after-the-event evaluation of things that need to be done, we really need to take a look at the psyche of the country, have maybe some social-type studies to figure out, does the mandating of vaccines in the way the country’s mental framework is right now, does that actually cause more people to not want to get vaccinated, or not? I don’t know. But I think that’s something we need to know. ”
LAB LEAK THEORY : Dr. Fauci acknowledged that the lab leak hypothesis is not a conspiracy theory. This comes nearly four years after prompting the publication of the now infamous “Proximal Origin” paper that attempted to vilify and disprove the lab leak hypothesis.
Majority Counsel: “ Just you sitting here today, do you think the possibility or the hypothesis that the coronavirus emerged from a laboratory accident is a conspiracy theory? ”
Dr. Fauci: “ Well, it’s a possibility. I think people have made conspiracy aspects from it. And I think you have to separate the two when you keep an open mind, that it could be a lab leak or it could be a natural occurrence. I’ve mentioned in this committee that I believe the evidence that I’ve seen weighs my opinion towards one, which is a natural occurrence, but I still leave an open mind. So I think that in and of itself isn’t inherently a conspiracy theory, but some people spin off things from that that are kind of crazy .”
GAIN-OF-FUNCTION RESEARCH : Dr. Fauci repeatedly played semantics with the definition of “gain-of-function” research in an effort to avoid conceding that the NIH’s funded this dangerous research in China . As the head of NIAID and the face of America’s response to the pandemic, Dr. Fauci certainly understood the common definition of “gain-of-function.” Yet, he repeatedly refused — both behind closed doors and to Sen. Rand Paul during a 2021 hearing — to clarify a general understanding of the term and instead only referred to his own “operative definition.
Dr. Fauci: “ So, when I, to repeat, when I’m asked is something gain of function, I’m referring to the operative definition of gain of function according to the framework of the 3PCO…That’s my definition. That is the regulatory operational definition. And as we were talking about before, other people use the word “gain of function” this, “gain of function” that, and everybody’s got their own interpretation of it. But when you’re deciding whether a grant should be funded, this is the operational definition. And when I was asked anywhere by the Congress, by the Senate, by Senator Paul this is what I was referring to .”
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST : Dr. Fauci claimed that his staff had no conflicts of interest regarding the origins of COVID-19, yet his Senior Advisor — Dr. David Morens — was “best-friends” with disgraced and soon-to-be debarred EcoHealth Alliance President Dr. Peter Daszak . Considering Dr. Morens worked under Dr. Fauci’s leadership for more than 20 years, it seems highly unlikely that Dr. Fauci was genuinely unaware of this relationship.
Majority Counsel: “ I was wondering if you had thoughts on whether Dr. Daszak should have filed competing interest statements when he was weighing in on these issues, whether through the National Academies or other venues. ”
Dr. Fauci: “ You know, I hesitate to speculate about what someone else should do. The only people that I am involved with is my own staff, who we’ve mentioned many times in this discussion, who don’t have a conflict of interest. ”
GRANT APPROVAL : Dr. Fauci testified that he signed off on every foreign and domestic NIAID grant without reviewing the proposals. He was also unable to confirm if NIAID has ANY mechanisms to conduct oversight of the foreign laboratories they fund . NIAID’s flawed grant process — which relies heavily on trusting its grantees without verifying — leaves opportunities for adversaries to exploit.
Majority Counsel: “ Who gives the final approval? ”
Dr. Fauci: “ You know, technically, I sign off on each council, but I don’t see the grants and what they are. I never look at what grants are there. It’s just somebody at the end of the council where they’re all finished and they go, ‘Here,’ and you sign it .”
Majority Counsel: “ Okay. So to your knowledge, NIAID wouldn’t kind of independently verify the biosafety of a foreign lab? ”
Dr. Fauci: “ Again, I’d have to say I’m not sure. To my knowledge, I wouldn’t be able to make a statement that I would be confident it would be. ”
Majority Counsel: “ Do you know if NIAID grants go through any type of national security review as part of the process? ”
Dr. Fauci: “ National security review? ”
Majority Counsel: “ So, like, through the National Security Council or— “
Dr. Fauci: “ No. ”
Majority Counsel: “ —or anyone in the [intelligence community]— “
Dr. Fauci: “ Not to my knowledge .”
Majority Counsel: “ I guess what we’re trying to learn going forward is, obviously, U.S. labs are vetted, certified, and there’s a standard of how U.S. labs operate. Are foreign labs held to the same standard as U.S. labs when they receive U.S. money, or are they the standards of the country in which they operate? ”
Dr. Fauci: “ I am not certain. I have heard again, I think it was subsequent to of course, that was never brought up. ”
Majority Counsel: “ Uh huh. ”
Dr. Fauci: “ When I was the director, no one ever asked me, you know, who determines, you know, what the standards of a foreign lab are. But so the answer to your question is I don’t know, okay? ”
FEIGNED IGNORANCE : Dr. Fauci claimed he “did not recall” numerous issues and events surrounding the pandemic more than 100 times . Specifically, Dr. Fauci testified that despite the fact EcoHealth Alliance was conducting risky gain-of-function research in China, he did not know any details about the grant, nor did he maintain a relationship with its President, Dr. Peter Daszak.
Majority Counsel: “ Do you recall when you first found out that the year 5 progress report was missing from the EcoHealth grant? ”
Dr. Fauci: “ I don’t recall precisely. It was somewhere on a briefing that the staff gave to me. I don’t know exactly when that was. It could have been later. I don’t know. ”
Majority Counsel: “ Okay. Do you think, just to the best of your recollection, whether it was before you were aware that the year 5 progress report was late before May 2021 or it would have been after? ”
Dr. Fauci: “ I don’t recall. ”
How does 'not' affect what we understand? Scientists find negation mitigates our interpretation of phrases
New study shows how the brain builds new meanings through word combinations.
When we're told "This coffee is hot" upon being served a familiar caffeinated beverage at our local diner or cafe, the message is clear. But what about when we're told "This coffee is not hot"? Does that mean we think it's cold ? Or room temperature? Or just warm?
A team of scientists has now identified how our brains work to process phrases that include negation (i.e., "not"), revealing that it mitigates rather than inverts meaning -- in other words, in our minds, negation merely reduces the temperature of our coffee and does not make it "cold."
"We now have a firmer sense of how negation operates as we try to make sense of the phrases we process," explains Arianna Zuanazzi, a postdoctoral fellow in New York University's Department of Psychology at the time of the study and the lead author of the paper, which appears in the journal PLOS Biology . "In identifying that negation serves as a mitigator of adjectives -- 'bad' or 'good,' 'sad' or 'happy,' and 'cold' or 'hot' -- we also have a better understanding of how the brain functions to interpret subtle changes in meaning."
In an array of communications, ranging from advertising to legal filings, negation is often used intentionally to mask a clear understanding of a phrase. In addition, large language models in AI tools have difficulty interpreting passages containing negation. The researchers say that their results show how humans process such phrases while also potentially pointing to ways to understand and improve AI functionality.
While the ability of human language to generate novel or complex meanings through the combination of words has long been known, how this process occurs is not well understood.
To address this, Zuanazzi and her colleagues conducted a series of experiments to measure how participants interpreted phrases and also monitored participants' brain activity during these tasks -- in order to precisely gauge related neurological function.
In the experiments, participants read -- on a computer monitor -- adjective phrases with and without negation (e.g., "really not good" and "really really good") and rated their meaning on a scale from 1 ("really really bad") to 10 ("really really good") using a mouse cursor. This scale was designed, in part, to determine if participants interpreted phrases with negation as the opposite of those without negation -- in other words, did they interpret "really not good" as "bad" -- or, instead, as something more measured?
Here, the researchers found that participants took longer to interpret phrases with negation than they did phrases without negation -- indicating, not surprisingly given the greater complexity, that negation slows down our processing of meaning. In addition, drawing from how the participants moved their cursors, negated phrases were first interpreted as affirmative (i.e., "not hot" was initially interpreted as closer to "hot" than to "cold"), but later shifted to a mitigated meaning, suggesting that, for instance, "not hot" is not interpreted as either "hot" or "cold," but, rather, as something between "hot" and "cold."
The scientists also used magnetoencephalography (MEG) to measure the magnetic fields generated by the electrical activity of participants' brains while they were performing these phrase-interpretation tasks. As with the behavioral experiments, neural representations of polar adjectives such as "cold" and "hot" were made more similar by negation, suggesting that the meaning of "not hot" is interpreted as "less hot" and the meaning of "not cold" as "less cold," becoming less distinguishable. In sum, neural data matched what was observed for the mouse movements in the behavioral experiments: negation does not invert the meaning of "hot" to "cold," but rather weakens or mitigates its representation along the semantic continuum between "cold" and "hot."
"This research spotlights the complexity that goes into language comprehension, showing that this cognitive process goes above and beyond the sum of the processing of individual word meanings," observes Zuanazzi, now at the Child Mind Institute.
The paper's other authors were: Pablo Ripollés, an assistant professor in NYU's Department of Psychology and associate director of Music and Audio Research Laboratory at NYU's Steinhardt School of Culture, Education, and Human Development; Jean-Rémi King, a researcher at France's École Normale Supérieure; Wy Ming Lin, a doctoral student at the University of Tübingen; Laura Gwilliams, an NYU doctoral student at the time of the study; and David Poeppel, a professor in NYU's Department of Psychology and managing director of the Ernst Strüngmann Institute for Neuroscience in Frankfurt, Germany.
The research was supported by a grant from the National Science Foundation (2043717).
- Language Acquisition
- Intelligence
- Brain-Computer Interfaces
- Social Psychology
- Child Development
- Psychoactive drug
- Circadian rhythm
- Intellectual giftedness
Story Source:
Materials provided by New York University . Original written by James Devitt. Note: Content may be edited for style and length.
Journal Reference :
- Arianna Zuanazzi, Pablo Ripollés, Wy Ming Lin, Laura Gwilliams, Jean-Rémi King, David Poeppel. Negation mitigates rather than inverts the neural representations of adjectives . PLOS Biology , 2024; 22 (5): e3002622 DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3002622
Cite This Page :
Explore More
- How Quantum Field Theories Decay and Fission
- River Nile's Evolution During Ancient Egypt
- Giraffes: Need to Feed Drove Long Neck
- More Effective Multipurpose Robots
- CO2 Conversion at a Much Larger Scale
- The Embryo Assembles Itself
- Thawing Permafrost: Not A Tipping Point
- Climate Change Was No Problem for Sharks
- Fungus Breaks Down Ocean Plastic
- Kinship and Ancestry of the Celts
Trending Topics
Strange & offbeat.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Rejecting the null hypothesis means that a relationship does exist between a set of variables and the effect is statistically significant (p > 0.05). ... The primary purpose of the null hypothesis is to disprove an assumption. Whether rejected or accepted, the null hypothesis can help further progress a theory in many scientific cases. ...
Examples. A research hypothesis, in its plural form "hypotheses," is a specific, testable prediction about the anticipated results of a study, established at its outset. It is a key component of the scientific method. Hypotheses connect theory to data and guide the research process towards expanding scientific understanding.
A hypothesis is considered scientific only if there is the possibility to disprove the hypothesis. The proof lies in being able to disprove. A hypothesis or model is called falsifiable if it is possible to conceive of an experimental observation that disproves the idea in question. That is, one of the possible outcomes of the designed ...
How a hypothesis is formed. Technically speaking, a hypothesis is only a hypothesis if it can be tested. Otherwise, it's just an idea to discuss at the water cooler. Researchers are always prepared for the possibility that those tests could disprove their hypotheses — that's part of the reason they do the studies.
The scientific method. At the core of biology and other sciences lies a problem-solving approach called the scientific method. The scientific method has five basic steps, plus one feedback step: Make an observation. Ask a question. Form a hypothesis, or testable explanation. Make a prediction based on the hypothesis.
• By comparing the null hypothesis to an alternative hypothesis, scientists can either reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis. • The null hypothesis cannot be positively proven. Rather, all that scientists can determine from a test of significance is that the evidence collected does or does not disprove the null hypothesis.
Misconception: Science can only disprove ideas. Correction: ... Hypothesis 2: The coral that makes up Eniwetok might have grown in a ring atop an underwater mountain already near the surface. The key to this hypothesis is the idea that underwater mountains don't sink; instead the remains of dead sea animals (shells, etc.) accumulate on ...
A hypothesis is a statement that we are trying to prove or disprove. It is used to express the relationship between variables and whether this relationship is significant. It is specific and offers a prediction on the results of your research question. Your research question will lead you to developing a hypothesis, this is why your research ...
A research hypothesis (also called a scientific hypothesis) is a statement about the expected outcome of a study (for example, a dissertation or thesis). To constitute a quality hypothesis, the statement needs to have three attributes - specificity, clarity and testability. Let's take a look at these more closely.
hypothesis. science. scientific hypothesis, an idea that proposes a tentative explanation about a phenomenon or a narrow set of phenomena observed in the natural world. The two primary features of a scientific hypothesis are falsifiability and testability, which are reflected in an "If…then" statement summarizing the idea and in the ...
Step 5: Present your findings. The results of hypothesis testing will be presented in the results and discussion sections of your research paper, dissertation or thesis.. In the results section you should give a brief summary of the data and a summary of the results of your statistical test (for example, the estimated difference between group means and associated p-value).
A hypothesis (plural hypotheses) is a proposed explanation for an observation. The definition depends on the subject. In science, a hypothesis is part of the scientific method. It is a prediction or explanation that is tested by an experiment. Observations and experiments may disprove a scientific hypothesis, but can never entirely prove one.
The null hypothesis in statistics states that there is no difference between groups or no relationship between variables. It is one of two mutually exclusive hypotheses about a population in a hypothesis test. When your sample contains sufficient evidence, you can reject the null and conclude that the effect is statistically significant.
Misconceptions. Testing ideas with evidence from the natural world is at the core of science. Scientific testing involves figuring out what we would expect to observe if an idea were correct and comparing that expectation to what we actually observe. Scientific arguments are built from an idea and the evidence relevant to that idea. Scientific ...
A hypothesis is a tentative statement about the relationship between two or more variables. It is a specific, testable prediction about what you expect to happen in a study. It is a preliminary answer to your question that helps guide the research process. Consider a study designed to examine the relationship between sleep deprivation and test ...
When your p-value is less than or equal to your significance level, you reject the null hypothesis. The data favors the alternative hypothesis. Congratulations! Your results are statistically significant. When your p-value is greater than your significance level, you fail to reject the null hypothesis. Your results are not significant.
When the research question asks "Does the independent variable affect the dependent variable?": The null hypothesis ( H0) answers "No, there's no effect in the population.". The alternative hypothesis ( Ha) answers "Yes, there is an effect in the population.". The null and alternative are always claims about the population.
A hypothesis is a tentative answer to a scientific question. A testable hypothesis is a hypothesis that can be proved or disproved as a result of testing, data collection, or experience. Only testable hypotheses can be used to conceive and perform an experiment using the scientific method .
Now that you know what facts you need to gather because your architecture told you so, those facts are either going to prove or disprove your hypotheses. If your hypotheses are proven, you'll move ...
The hypothesis of Andreas Cellarius, showing the planetary motions in eccentric and epicyclical orbits.. A hypothesis (pl.: hypotheses) is a proposed explanation for a phenomenon.For a hypothesis to be a scientific hypothesis, the scientific method requires that one can test it. Scientists generally base scientific hypotheses on previous observations that cannot satisfactorily be explained ...
hypothesis: [noun] an assumption or concession made for the sake of argument. an interpretation of a practical situation or condition taken as the ground for action.
The meaning of DISPROVE is to prove to be false or wrong : refute. How to use disprove in a sentence.
The scientific method is an empirical method for acquiring knowledge that has characterized the development of science since at least the 17th century. The scientific method involves careful observation coupled with rigorous scepticism, because cognitive assumptions can distort the interpretation of the observation.Scientific inquiry includes creating a hypothesis through inductive reasoning ...
To test a hypothesis and to contribute to and/or generate new knowledge that can be generalized. Starting Point . To improve performance To answer a question or test a hypothesis . Benefits . Knowledge sought directly benefits a process/ program/ system, and may or may not directly benefit individuals (e.g. patients, families, or staff)
I mean, 6-foot was applied at businesses ... Dr. Fauci acknowledged that the lab leak hypothesis is not a conspiracy theory. This comes nearly four years after prompting the publication of the now infamous "Proximal Origin" paper that attempted to vilify and disprove the lab leak hypothesis.
How does 'not' affect what we understand? Scientists find negation mitigates our interpretation of phrases New study shows how the brain builds new meanings through word combinations