The use of triangulation in qualitative research
Affiliations.
- 1 School of Nursing, McMaster University, Hamilton, Ontario.
- 2 School of Nursing and Department of Oncology, McMaster University.
- 3 School of Nursing and the Department of Clinical Epidemiology and Biostatistics, McMaster University.
- 4 School of Nursing, McMaster University.
- 5 Department of Oncology, Faculty of Health Sciences, McMaster University, Canada.
- PMID: 25158659
- DOI: 10.1188/14.ONF.545-547
Triangulation refers to the use of multiple methods or data sources in qualitative research to develop a comprehensive understanding of phenomena (Patton, 1999). Triangulation also has been viewed as a qualitative research strategy to test validity through the convergence of information from different sources. Denzin (1978) and Patton (1999) identified four types of triangulation: (a) method triangulation, (b) investigator triangulation, (c) theory triangulation, and (d) data source triangulation. The current article will present the four types of triangulation followed by a discussion of the use of focus groups (FGs) and in-depth individual (IDI) interviews as an example of data source triangulation in qualitative inquiry.
Keywords: focus groups; in-depth individual interviews; qualitative research; triangulation.
- Data Collection
- Focus Groups
- Group Processes
- Interviews as Topic
- Models, Theoretical
- Qualitative Research*
- Research Design*
- Research Personnel
- Research article
- Open access
- Published: 24 January 2017

Multiple triangulation and collaborative research using qualitative methods to explore decision making in pre-hospital emergency care
- Maxine Johnson ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-0850-234X 1 ,
- Rachel O’Hara 1 ,
- Enid Hirst 2 ,
- Andrew Weyman 3 ,
- Janette Turner 4 ,
- Suzanne Mason 5 ,
- Tom Quinn 6 ,
- Jane Shewan 7 &
- A. Niroshan Siriwardena 8
BMC Medical Research Methodology volume 17 , Article number: 11 ( 2017 ) Cite this article
20k Accesses
34 Citations
11 Altmetric
Metrics details
Paramedics make important and increasingly complex decisions at scene about patient care. Patient safety implications of influences on decision making in the pre-hospital setting were previously under-researched. Cutting edge perspectives advocate exploring the whole system rather than individual influences on patient safety. Ethnography (the study of people and cultures) has been acknowledged as a suitable method for identifying health care issues as they occur within the natural context. In this paper we compare multiple methods used in a multi-site, qualitative study that aimed to identify system influences on decision making.
The study was conducted in three NHS Ambulance Trusts in England and involved researchers from each Trust working alongside academic researchers. Exploratory interviews with key informants e.g. managers ( n = 16) and document review provided contextual information. Between October 2012 and July 2013 researchers observed 34 paramedic shifts and ten paramedics provided additional accounts via audio-recorded ‘digital diaries’ (155 events). Three staff focus groups (total n = 21) and three service user focus groups (total n = 23) explored a range of experiences and perceptions. Data collection and analysis was carried out by academic and ambulance service researchers as well as service users. Workshops were held at each site to elicit feedback on the findings and facilitate prioritisation of issues identified.
The use of a multi-method qualitative approach allowed cross-validation of important issues for ambulance service staff and service users. A key factor in successful implementation of the study was establishing good working relationships with academic and ambulance service teams. Enrolling at least one research lead at each site facilitated the recruitment process as well as study progress. Active involvement with the study allowed ambulance service researchers and service users to gain a better understanding of the research process. Feedback workshops allowed stakeholders to discuss and prioritise findings as well as identify new research areas.
Combining multiple qualitative methods with a collaborative research approach can facilitate exploration of system influences on patient safety in under-researched settings. The paper highlights empirical issues, strengths and limitations for this approach. Feedback workshops were effective for verifying findings and prioritising areas for future intervention and research.
Peer Review reports
Delivery of pre-hospital emergency care takes place in a complex environment where front-line ambulance service (AS) staff are now faced with decision-making over an array of patient care options. For example, rather than simply making a decision to convey patients to an Emergency Department (ED), paramedics can treat patients at scene, refer patients to another service or convey them to a non-emergency service care provider. In the UK, the National Health Service (NHS) comprises a number of ‘Trusts’ that manage hospital, primary, mental health and ambulance service care. There are ten Ambulance Trusts in England, whilst ambulance services in Wales, Scotland and Northern Ireland are each covered by one Trust. Decisions made by paramedics during the course of responding to emergency calls have the potential to impact on patient health outcomes as well as embodying professional risk for individual staff members [ 1 ] and reputational risk to the employing Trust. These decisions are made in the context of organisational constraints, changes in patient demographics and evolving professional roles for paramedics [ 2 ]. Advanced roles and specialist training have developed in an attempt to manage increasing demand from a broad range of patients with non-life threatening conditions where healthcare needs may be more suited to community and/or social care rather than the Emergency Department (ED) [ 3 ]. To fully understand the nature of paramedic decision making in this context and potential threats to patient health outcomes, our research examined macro, meso and micro level systemic influences, in other words, those that are at the organisation, community and person levels [ 4 ]. This paper details and reflects on this research conducted within the complex environment of pre-hospital emergency care. The aim of the paper was to describe the methodological approach employed in this study in order to share lessons on collaboration in multi-method research across multiple sites and investigators.
In line with established approaches to patient safety [ 5 ], we aimed to explore systemic influences on decision making that represent potential threats to patient safety rather than assessing the apparent safety of individual practitioner decisions. We were particularly interested in decisions made in relation to transition points in the patient care pathway, i.e. where a patient is discharged with advice, referred to another service or conveyed to hospital. Details of the study and findings are reported elsewhere [ 6 ].
There are few published multisite studies using multiple qualitative methods and organisations to examine the dynamic and mobile pre-hospital emergency context of ambulance services. Previously published papers provide only brief information about methods used to carry out the research and the lessons learned. This study was conducted in three Ambulance Service Trusts in England, representing a variety of contextual factors in the prehospital emergency care system (e.g. care pathways, staff roles, service configuration). The use of multiple qualitative methods allowed the findings from each method to bring particular insights and understanding, including real-time observation of events and reconstructed accounts of events during interviews and focus groups [ 7 ].
The geographical area covered by each Trust included densely populated urban areas, sparsely populated rural areas, coastline and busy stretches of motorway. The study comprised three phases. Phase 1 aimed to develop a contextual understanding of each site. Phase 2 examined decision making by paramedics across the three Ambulance Trusts using an ethnographic approach to study their actions and accounts in everyday context [ 8 ]. The ethnographic approach uses a range of methods which usually includes observation, to study people and cultures. Ethnography has previously been utilised in healthcare research for assessing collaborative practices, [ 9 ] management cultures [ 10 ] and decision making practices in relation to mental health [ 11 ]. Phase 3 involved feedback workshops at each site.
The multi-disciplinary research team for the study reported here encompassed expertise in social science, emergency care research, risk and patient safety and included representation from healthcare professionals in the Ambulance Service, Emergency Department and primary care, as well as service users. Our aim was to identify systemic influences on paramedic decision making with regard to their potential impact on patient safety. In this paper we describe salient aspects of the research process as well as critically assessing the utility of our approach for addressing the research question.
A primarily qualitative approach was chosen as being best suited to the exploratory nature of the study and to address the research question. In order to maximise credibility, dependability and confirmability of the findings [ 12 ]. We adopted a multiple site, multiple method and multiple investigator design across three phases of the research. The qualitative methods employed in this study included document review, interviews, observation, digital diaries, focus groups and workshops to afford a more thorough and multi-faceted examination of issues than could be gained from any single method. Figure 1 provides a timeline of the multiple methods used to collect data.
Data collection timeline
The study, conducted in three ambulance service Trusts in England, involved the recruitment of clinical and non-clinical based researchers to the study from each Trust to work alongside the academic researchers. Staff and service user participants at each site were recruited through available Ambulance Service and Patient and Public Involvement networks as described for each phase of the study.
Data collection
Phase 1: understanding the context.
The aim of the initial phase of the study was to gain an understanding of the organisational context within each Trust and elicit perceived influences on transition decisions and associated patient safety issues. This involved conducting semi-structured interviews with a small number of key ambulance service staff ( n = 16) who could provide an overview of the organisation and service delivery, including clinical governance leads, directors of operations, medical or clinical leads as well as paramedics with dual operational and managerial or leadership roles. We also collected demographic site information and relevant documentation on policies and procedures. This allowed us to provide context for each Trust in terms of area, population and operational work volumes as well as understanding relevant national and local policies.
Phase 2a: Paramedic decision making in practice
The main phase of the study entailed non–participant field observation of paramedics’ day to day working practices in order to gain insight into potential systemic impacts on conveyance decisions, for example, whether to transport to hospital. At each site Ambulance Service staff were recruited to the study as researchers to assist in recruitment, data collection and analysis. These were either operational paramedics ( n = 2) or Trust research staff ( n = 2). In one Trust, two members of ambulance service staff shared the research role. Thus, a total of four ambulance service staff carried out the research as well as one member of academic staff. A key function of involving ambulance service staff as researchers was to complement the academic researcher data to capture possible ‘insider’ and ‘outsider’ perspectives [ 8 ] on paramedic activity and systemic influences. Employing observers from a range of backgrounds also dilutes tendencies toward ‘going native’ [ 8 ] or conversely, being so overwhelmed by new information that subsequent data is meaningless. The academic researcher had a background in nursing which meant that she was familiar with the medical context though not pre-hospital emergency care.
In order to enhance the robustness of the approach, a familiarisation and pilot observation shift was carried out initially by two of the researchers (one ambulance service and one academic researcher). Subsequent refinement facilitated the development of a data collection template to give focus to the observations and information recorded. Details recorded included date, time, geographical setting and crew roles as well as ‘observational dimensions’ [ 13 ], such as activities at each patient attendance and any other people present, for example, professional emergency services, carers and bystanders.
Following each patient attendance, mini-interviews of variable duration with paramedics were carried out to establish the reasoning behind the decisions made [ 13 ]. These were recorded in written field notes or using an audio-recorder, the choice of method being a product of prevailing practical limitations. For example, it was often challenging to audio-record short sections of conversation that could be interrupted at any time due to work requirements, therefore this method of recording tended to be used for mini-interviews that were carried out during quieter moments.
A total of 36 paramedics (see Table 1 ) were observed between October 2012 and June 2013 over 34 shifts of 8–12 h duration. Observations were conducted over a 9 month period, on different days of the week and times of the day, including night shifts in order to gain insight into variability in work rates, types of care/treatment, types of patient.
In order to supplement data from the observation shifts and to explore decision making events that might not have been observed during the shifts, ‘digital diaries’ (audio-recorders) were used to collect additional data from 10 paramedics (see Table 1 ). Each diary consisted of recordings describing a number of care decisions that were perceived as being challenging, and/or highlighting a potential threat to patient safety. The value of this method of data collection is that it allows participants to voice their experiences and concerns privately, immediately following an event and without intervention from researchers. The digital audio-recorders were distributed and collected by researchers at each site. A total of 13 paramedics initially consented to participate using the digital diary method. Three subsequently dropped out due to ill-health ( n = 1) and feeling self-conscious about speaking into the audio-recorder ( n = 2).
Phase 2b: Paramedic focus groups
We chose focus groups as a complementary method to observations and interviews. Focus groups allow researchers to identify sub-cultures within groups of staff with different roles [ 14 ] which would not necessarily have been evident during observations, given that much paramedic work is carried out as a sole worker or in pairs. Focus groups also added to the interview method of data collection in their generation of dialogue around experiences and perceptions [ 15 ]. Focus groups encourage participants to explore each other’s views, which can lead to a more detailed exploration of ideas than in one-to-one interviews [ 14 ].
We invited paramedics to participate in one focus group at each site in order to explore shared experiences, perspectives and decision criteria. The range of attendance at each focus group was between five and eight participants with a total of 21 staff attending groups across the three Trusts. The use of a topic guide encouraged a broader discussion of issues that had been raised during the Phase 1 interviews [ 14 ]. The focus groups also included a discussion of different aspects of ambulance personnel patient safety culture in their respective organisations using the Manchester Patient Safety Framework (MaPSaF) as a guide [ 16 ]. The MaPSaF tool is designed to help healthcare organisations and teams assess their progress in developing a positive safety culture. It uses critical dimensions of patient safety that relate to areas where attitudes, values and behaviours about patient safety are likely to be reflected in the organisation’s working practices, for example, how patient safety incidents are investigated, staff education, and training in risk management [ 17 ]. The tool provided a framework for discussion following the initial less structured discussion of Phase 1 findings. Engaging with the MaPSaF tool enabled participants to reflect on and discuss perceptions in pairs before exchanging views within the wider group. Focus groups were facilitated by the academic researchers with an ambulance service researcher present. Discussions were audio-recorded.
Phase 2c: Service user focus groups
Focus groups were also conducted with service users recruited through established Patient and Public Involvement (PPI) networks at two of the sites and more widely from community networks at the third site. Contacts within each service user representatives group assisted in the recruitment of participants. Between 7 and 8 service users attended each focus group, giving a total of 23 participants (see Table 2 ). Attendees across the sites comprised 11 females and 12 males across all adult age groups, although 16 (69.5%) were aged over 55 years. They represented a range of perspectives and experiences, including local PPI networks, long-term conditions, mobility issues and communication issues.
Phase 3: Feedback and prioritisation workshops
The final phase of the study entailed delivering stakeholder feedback workshops at each site. Participants from all phases of the study were invited to attend. Additional staff and service user representatives were also invited by each of the Ambulance Service Trusts. A total of 45 ambulance service staff and service users attended the three workshops. In addition to providing feedback on the study findings, the workshops provided an opportunity for further articulation of topics arising from the field work findings. Participants also performed a ranking exercise designed to capture perspectives for future risk reduction and enhanced service delivery intervention. The ranking took the form of individual judgements of the systemic issues identified in Phase 2 using the method of paired comparisons. To simplify what would otherwise be a cognitively challenging task, the method of paired comparisons requires each respondent to compare each priority issue, for example, ‘resources’, was paired with each of the other six issues (‘access to care’, ‘training and development’, ‘communication and feedback’, ‘demand’, ‘risk aversion’ and ‘performance regime’), one pairing at a time, for all permutations of pairings; in each case being asked to indicate which of each pair is deemed the more important [ 18 ].
Data analysis
All audio-recordings, field notes and researcher diaries were fully transcribed. This generated a significant amount of data across researchers, sites and methods. As the data collection was conducted in sequential blocks of time at each site, the initial data analysis followed a thematic approach. Thematic analysis was chosen as it allowed data collected using a range of different qualitative methods to be analysed in a similar way. Data from each case (interview, focus group or observation session) was initially coded to provide a number of categories which were then grouped thematically across cases and compared to ensure that themes incorporated all relevant data. Thematic analysis can be carried out at a superficial level or it can be further developed to include explanatory interpretations and can also be used to develop taxonomies [ 19 ]. Subsequent analysis of the findings across the three sites revealed a high degree of consistency and commonality. In recognition of the high degree of homogeneity it was considered appropriate to pool the data.
Analysis of the Phase 2 data was managed using Atlas ti. TM qualitative data analysis software [ 20 ]. This supported the generation of a taxonomy of transition decisions and systems and structural influences with potential to impact on ambulance crew decision making with implications for patient safety. We began analysing the observation and digital diary data by transferring data from transcriptions into site and shift specific charts that represented each attendance together with the corresponding decision and ambulance crew account of their rationale for the decision. Patterns detected within the data revealed a typology of nine decisions encountered by paramedics representing a continuum of increasing complexity [ 6 , 21 ]. Repeated iterations of coding identified a range of cues that were utilised during decision making as well as potential mitigating and mediating system and structural influences on these decisions. An equivalent approach was adopted for analysis of the paramedic focus group data which was analysed thematically. Analysis of service user focus group data identified areas of concern in relation to potential influences on ambulance service care and patient safety.
All Phase 2 staff data were analysed initially using an inductive approach [ 21 ] which begins close to the data and moves through levels of more abstract analysis to identify patterns and relationships that can be used to explain phenomena. This approach is in contrast to deductive analysis which begins with a supposition that is tested through analysing the data. In our analysis, similarities and differences across the various data collection methods were also explored. Although some differences and contradictions were identified these generally represented local area variations within individual sites rather than between sites. The global picture that emerged was notable consistency across the three sites and between methods. Findings from this inductive analysis were then mapped against Vincent’s Human Factors framework [ 22 ], which resulted in over 20 system influences across the various system levels. We found that the hierarchy of influences on clinical practice within this framework was not ideally suited to extracting more overarching themes from our data, which encompassed different levels of the hierarchy. To take account of this, we continued to analyse the data through repeated iterations until seven overarching issues emerged. The set of issues encompassed overlapping rather than distinct macro, meso and micro level influences [ 6 ]. At regular intervals the emerging themes were shared and discussed with the wider research team to ensure verification of findings and their interpretation.
The analysis of the data from the workshop intervention prioritisation exercise was quantitative, following established practice for the method of paired comparisons. This involved checks of within respondent consistency (Kendall’s K) to determine whether participants could reliably form consistent judgement between the items; and the degree of concordance between respondents (Kendall’s W) [ 23 ]. This analysis showed a high level of internal reliability with 84% of respondents ( N = 44) demonstrating a coefficient (K) of > 0.70. A high level of concordance between ambulance service staff and service user participants (Rho = 0.91) meant that it was acceptable to combine the data for each group [ 23 ]. Transformation of the rankings for the seven issues to standard values (z scores) produced the interval scale along which are plotted the issues presented to participants in respect of their prioritisation. Thus, the scale shows that staff perceived training and development as requiring the highest priority (see Fig. 2 ).
Relative importance of system issues represented on a single continuum
The project received ethical approval for the research involving NHS Ambulance Trust staff from the University of Sheffield Research Ethics Committee (ScHARR 0530/CAO) on the basis that no patient identifying information would be collected during the observations as we were examining paramedic decisions but not patient views at that time. The NRES Committee Yorkshire and the Humber—South Yorkshire (12/YH/0327) provided approval for the research involving service users. All participants were provided with information about the study prior to the consenting process.
Other ethical issues concerned data protection and security which were addressed by maintaining the University code of conduct in respect of storing data only within specified permitted access drives and using encrypted hardware. The safety of observers was optimised by adhering to the codes of practice at each site which, for example, prescribed high visual and safety attire during operational shifts as well as the University policy for lone researchers. The latter was particularly important for this study where researchers were travelling outside of normal office hours to unfamiliar locations. Where appropriate during the observational activity, researchers were identified to patients, carers and other health professionals encountered during observation shifts as observing the paramedics.
Observers needed to ensure that paramedics could practice without any interruption or distraction that could affect patient care. Similarly, we acknowledged that operational demands were paramount and should take precedence throughout the study. For example, on two occasions interviews were cancelled to take account of high seasonal operational demands. Given the relatively small sample at each site and the fact that participating paramedics were known to colleagues and managers; when reporting the findings, care was taken to protect the identities of individuals. Phase 1 interviewees were informed as part of the consenting process that due to the small number of key staff being interviewed at each site, confidentiality or anonymity could not be guaranteed.
The study highlighted two key lessons regarding multi-method, multi-disciplinary collaborative research. Although we found that the use of multiple methods, sources and investigators to obtain data across sites was insightful it added to the complexity of the design, and embodied time penalties. This is considered to have been more than offset by the benefits arising from continual collaboration between academic researchers, the ambulance service Trusts and service user representatives and was a valuable feature of the research process. We now reflect upon these lessons.
Multi - triangulation : the contribution of multiple methods , sources and investigators
Our approach adopted a multiple triangulation approach as described by Denzin [ 24 ] to incorporate multiple methods of data collection, multiple sources of data and multiple investigators with multiple areas of expertise. We present these methods, sources and investigators and the relationship between them in Fig. 3 . The multi-site and multi-method design facilitated the identification and validation of relevant issues. Denzin [ 24 ] states that multiple research methods are desirable because each method reveals a different aspect of reality. This idea has since been developed to include triangulation as a metaphor for strength [ 25 ], trustworthiness [ 12 ], and comprehensiveness [ 26 ]. Guba [ 12 ] argues that trustworthiness through triangulation enhances the credibility, dependability and ‘confirmability’ in qualitative studies.
Applying multi-triangulation to understanding systemic influences on paramedic decision making
Method triangulation
We used a range of qualitative research methods to collect data from each participating site, including document review, interviews, observations, digital diaries and focus groups. Each research method was chosen to access different types of information for comparing findings across methods. For example, an issue that was identified during an interview or focus group could also be examined during observations of practice in the naturalistic work setting. Similarly, issues witnessed during observations or recorded in digital diaries could be explored during discussions. The workshops with Ambulance Service staff and service users provided a further level of verification. The data collection methods that were used and their respective advantages and limitations are presented in Table 3 .
Source triangulation
Obtaining information from a range of sources, across settings and time was an important aspect of the data collection activity. This supported our objective to analyse the data for site specific, role specific and time specific features that might affect decision making. This included identifying practices that varied according to different Ambulance Service Trust protocols or local initiatives. Variation in paramedic responsibilities and roles can occur where those with advanced training undertake more specialist activities. Potential temporal influences include fluctuations in demand for emergency care and access to referral pathways. Observations were conducted across the variety of different paramedic shifts (times and days) to accommodate any potential variation in patient demographics, decision support and decision options.
Investigator triangulation
We included a range of investigator perspectives so that the findings were not based solely on academic researcher interpretations of events and themes. The involvement of ambulance service researchers in data collection and analysis allowed verification of findings from a range of perspectives. Similarly, a service user member of the research team contributed to the thematic analysis of the data from the service user focus groups. Including participation in data collection and interpretation from a range of investigators ensured that a variety of perspectives were taken into account. Involvement of the wider project team which encompassed a range of disciplines and perspectives is described in more detail later in the findings.
A key reported benefit from multiple triangulation is increased confidence in the findings. [ 27 ] The field observations highlighted the potential complexity of the emergency decision making context. Changes in the profile of public demand for ambulance services and structural changes in health care provision have combined to increase the range of care options that paramedics need to consider and in instances where the need for conveyance to an emergency department (ED) is not obvious, they are expected to consider alternative care pathways. These changes have had the effect of increasing the complexity of paramedic decision making, and also brought logistical challenges, for example, due to geographical variability in non-emergency care provision, or encountering resistance to accept patients by some care providers [ 5 ].
Integration of data from multiple methods, sources and investigators
Documents from Phase 1 were reviewed to increase our understanding of the organisational context for the study. We organised Phase 1 interview data using Atlas. ti 7™ [ 20 ] software and to conduct a thematic analysis. Themes from this phase were used as the basis for the discussion guides used during paramedic and service user focus groups. Data from Phase 2 (observations, interviews and digital diaries) was iteratively coded and categorised. Focus group data were then analysed using the constant comparison method [ 6 , 21 ]. Apparent variations in data collected by different researchers were also examined. However it was challenging to make inferences in this respect as the data differed in other ways such as style of reporting and extent of detail included. Working to a broad observation template [ 13 ] helped to maintain a minimal degree of consistency in scope across observations and observers.
Maintaining collaborative working relationships to achieve study objectives .
Developing good working relationships between academic researchers and ambulance service research staff at each site was crucial to achieving the study objectives. During the design and implementation stages of the study we discussed practical and theoretical issues with ambulance service research managers, university academics and patient and public involvement (PPI) representatives. This allowed a broad range of perspectives to be accounted for in the study protocol as well as increasing our understanding of contextual elements and any service user considerations prior to enquiry. Initial meetings and discussions began a phase of ‘prolonged engagement’ within the setting during which researchers could become more familiar with the previously unfamiliar [ 12 ]. This would pave the way for data collection and help to maintain good working relationships throughout the study. The study team included researchers and clinicians in emergency care, from hospital and pre-hospital settings. Ambulance service collaborators were also vital to understanding pertinent contextual issues and negotiating issues relevant to ethics and local governance approvals.
Credibility of the findings was essential [ 12 ], so we regularly discussed interim data and emerging themes within the wider team to clarify our understanding. The study was dependent upon key people from within the three Trusts to facilitate access to study participants. The ambulance service research managers at each site assisted in obtaining relevant organisational documentation and accessing potential interview participants for Phase 1. They also assisted in the recruitment of ambulance service researchers to the study team for Phase 2 activities.
In order to ensure that the study findings would be transferable [ 12 ] rather than context dependent, the study was designed to include the perspectives and experiences of a broad range of ambulance service and service user informants. Paramedics taking part in Phase 2 were recruited from at least two different geographical areas within each Ambulance Service Trust to maximise potential variation in service demands and delivery.
A range of complementary methods were used to communicate details of the study to potential participants, including invitations and information sheets sent via email, and flyers via organisational intranet. Having an ambulance service researcher within each site was important in facilitating study progression during Phase 2 and overcoming one of the major challenges for recruitment and data collection—communicating with paramedics who were ‘out on the road’. Having office based researchers with knowledge of the operational environment and personnel within their organisation was key to the data collection process. They were able to liaise with paramedics and managers in ambulance stations across a number of different ambulance service areas. They were also instrumental in arranging suitable venues for the focus groups and workshops. In one of the sites, liaison with participants to arrange observations was facilitated by the member of staff that arranges placements for trainees.
Collaborating with ambulance service staff
The paramedic role has undergone significant change over the past decade, including professional registration, specialist practice and a growing number of paramedics undertaking higher education courses and becoming involved in research. A benefit of our research collaboration for ambulance service researchers and participants was that they gained a more detailed understanding of the research process through participating in different aspects of the study. Potential challenges for ambulance service researchers included having a previous working relationship with the crews in their paramedic role within the same organisation. There was a concern that crews would behave differently when they were being observed by familiar members of staff. To some extent this was prevented by ambulance service researchers observing crews that worked in a different location to themselves. There was also a concern that researchers with a paramedic background might incur observer bias because they were so familiar with the context. However, the value of their understanding of the nuances of pre-hospital emergency care provided complementary insights to those of the other researchers. For example the explanation for a decision about which hospital to transport a patient to, might not be taken at face value by operational ambulance service researchers because of their prior knowledge about condition-specific pathways. A disadvantage of prior knowledge is that questioning may not occur where the observer makes assumptions about what is being observed or perceives that they know what the response might be. Non-clinical researchers faced the challenge of developing an understanding of the paramedic role, but their questioning should be more in depth because they are less prone to making assumptions.
Ambulance service researchers attended the staff and service user focus groups. Whilst they did not participate in discussions, their expertise was crucial in clarifying some of the issues being addressed, particularly for the service users. Similarly, during feedback workshops, ambulance service researchers were available to comment about their experiences during data collection. A key output of the workshops was that collaborative relationships developed between the academic and ambulance service teams over the duration of the study supported the identification of new ideas for future research. A range of potential avenues for further research were identified. Workshop attendees were asked to rank the seven headline issues that had been identified from our study as topics for future attention as well as identifying areas for future intervention and/or research. In seeking to prioritise issues we were mindful of the difficulty respondents can experience when they attempt to rate multi-faceted constructs and the propensity of rating scales to produce ceiling effects, where the items are all considered ‘important’. The method paired comparisons has the advantages of low cognitive load, formal testing of reproducibility and agreement between respondents, while also translating into an interval scale [ 23 ]. The two highest ranked priorities were training and development, and access to care. Both of these featured strongly in the recommendations for further research. Ongoing collaboration between members of the research team has enabled a number of research recommendations to be explored as part of a mutually agreed research agenda.
Collaborating with service users
PPI was also central to the successful implementation of the study objectives. A local PPI panel focused on supporting emergency care research provided input at key stages from design to completion (e.g. reviewing ethics documentation). A member of this panel (EH) was engaged as a study co-applicant from the outset and actively contributed to the study design, service user recruitment, data collection, data analysis and dissemination stages of the research. Study outputs have included producing a lay leaflet to communicate the findings to the public, which have been distributed via PPI networks and local primary care services.
This study used multiple triangulation of methods, sources and investigators across three sites to explore macro, meso and micro systemic influences on pre-hospital decision making with potential impacts on patient safety. A collaborative approach was adopted between academic and ambulance service teams to develop and implement the study aims and objectives. An important factor in achieving the objectives in this multi-site study was the development of a relationship involving continual collaboration across the distributed network of research team members. This was further supported by enrolling a research lead at each site and using multi-triangulation and feedback throughout to generate and validate the research findings as well as identifying priority areas for service delivery improvement and further research.
Cooper et al. [ 28 ] provide a case for using ethnographic methods in the pre-hospital setting, stating that the approach allows the study of organisation or group culture. This study included observation of paramedics supplemented by mini-interviews where possible around responding to emergency calls to explore system constraints on decision making, including cultural influences. As Cooper et al. [ 28 ] point out, strict adherence to a particular theory can be unhelpful during analysis. Vincent’s Human Factors framework [22] was initially useful in this study for considering different aspects of the system that may influence paramedic decision making. However, the findings from this study did not fit neatly into the hierarchy of influences on clinical practice for this framework, with some issues on the interface between the different levels of the framework. A further iteration of inductive analysis identified overarching factors relevant to potential influences on decision making and patient safety.
Dixon Woods [ 29 ] also highlighted the ability of ethnography, to access information that might be unknown to those being observed, particularly in the area of patient safety. Combining methods in this study allowed researchers to speak to operational staff as well as observe crews whilst carrying out their decision making practices. It was found that during observation shifts practices were not observed to affect patient safety, but there was a potential for system impacts to influence decisions that might not be optimal for patients. In particular the varying degree of access to alternative options to ED across sites was notable.
A key strength of the study was the use of multiple methods to collect data, resulting in different ways of seeing reality [ 24 ], yet similar issues were highlighted in data generated by each method. The collaborative nature of the study strengthened the dissemination of findings from the study as well as opening avenues for collaboration on future research addressing ambulance service priorities.
Limitations of the study include the time taken to negotiate access to participating Trusts. Methods of obtaining access differed at each site, and a more standardised procedure might have improved efficiency in the early stages. It was also challenging to access operational staff ‘on the road’ to recruit to the study. Digital diary entries had to be interpreted without recourse to probing for further information. An additional limitation is the lack of availability of ‘outsider’ observer data at one site due to unforeseen circumstances. However given the challenges, working relationships with the three sites enabled most of the study aims to be met in a timely manner.
The study provided an overview of paramedic decision making, which is considered to be an under researched area, from which a number of issues were raised for further research and future service delivery [ 6 ]. Whilst anecdotally the issues raised may not be surprising to ambulance service staff, publishing this work was an important step in making these issues transparent for policy makers.
Conclusions
Combining multiple qualitative methods with a collaborative research approach can facilitate exploration of system influences on patient safety in under-researched settings. Triangulation of data collection across time, from a range of roles in different settings, using a combination of research methods, carried out by investigators representing clinical, research and service user perspectives allowed different realities to be explored within the same study and enhanced the credibility of findings. A strong collaboration between academics and ambulance services and PPI representatives was crucial to achieving study aims. Feedback workshops were effective in supporting the verification of findings, as well as providing an opportunity to identify priority areas for intervention and research.
Abbreviations
- Ambulance service
Emergency Department
Manchester Patient Safety Framework
National Health Service
National Research Ethics Service
Patient and public involvement
Porter A, Snooks H, Youren A, Gaze S, Whitfield R, Rapport F, et al. ‘Should I stay or should I go?’Deciding whether to go to hospital after a 999 call. J Health Serv Res Policy. 2007;12:32–8.
Article Google Scholar
McCann L, Granter E, Hyde P, Hassard J. Still Blue Collar after all these years? An Ethnography of the Professionalization of Emergency Ambulance Work. J Manage Stud. 2013;50(5):750–76.
NHS England. High quality care for all, now and for future generations: Transforming urgent and emergency care services in England. The evidence base from the urgent and emergency care review. 2013.
Google Scholar
Robert GB, Anderson JE, Burnett SJ, Aase K, Andersson-Gare B, Bal R et al. A longitudinal, multi-level comparative study of quality and safety in European hospitals: the QUASER study protocol. BMC Health Services Res. 2011;11. doi: 10.1186/1472-6963-11-285 .
Vincent C, Moorthy K, Sarker SK, Chang A, Darzi AW. Systems approaches to surgical quality and safety: from concept to measurement. Ann Surg. 2004;239:475.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
O’Hara R, Johnson M, Siriwardena AN, Weyman A, Turner J, Shaw D, et al. A qualitative study of systemic influences on paramedic decision making: care transitions and patient safety. J Health Serv Res Policy. 2015;20:45–53.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Ritchie J. The applications of qualitative methods to social research. In: Ritchie J, Lewis J, editors. Qualitative Research Practice: A Guide for Social Science Students and Researchers. London: Sage; 2003.
Hammersley M, Atkinson P. Ethnography; Principles in practice. London: Routledge; 1995.
Cooper S, O’Carroll J, Jenkin A, Badger B. Collaborative practices in unscheduled emergency care: role and impact of the emergency care practitioner. Quantitative findings. Emerg Med J. 2007;24:630–3.
Wankhade P. Different cultures of management and their relationships with organizational performance: evidence from the UK ambulance service. Public Money Manage. 2012.
Shaban RZ. Accounting for assessments of mental illness in paramedic practice: A new theoretical framework. J Emerg Primary Health Care. 2005;3.
Guba EG. Criteria for assessing the trustworthiness of naturalistic inquiries. Educ Commun Technol. 1981;29:75–91.
Reeves S, Kuper A, Hodges BD. Qualitative research methodologies: ethnography. BMJ. 2008;337:a1020.
Kitzinger J: Focus groups with users and providers of health care. In Qualitative research in health care. Second edition. Edited by Pope C, Mays N. London: BMJ Books; 2000:20–29
Morgan DL. Focus groups as qualitative research, 16 edn. Sage Publications, Inc; 1997.
Kirk S, Parker D, Claridge T, Esmail A, Marshall M. Patient safety culture in primary care: developing a theoretical framework for practical use. Qual Saf Health Care. 2007;16:313–20.
Parker D. Manchester Patient Safety Framework (MaPSaF): Facilitator guidance. 2009. The University of Manchester/NPSA.
David HA. The method of paired comparisons. 12th ed. 1968. DTIC Document.
Pope C, Ziebland S, Mays N: Analysing qualitative data. In Qualitative research in health care. 320 edition. Edited by Pope C., Mays N. Oxford: Bmj; 2006:63–81.
ATLAS.ti 7 [Version 7]. ATLAS.ti Scientific Software Development GmbH: Berlin.
Bradley EH, Curry LA, Devers KJ: Qualitative Data Analysis for Health Services Research: Developing Taxonomy, Themes, and Theory. Health Res Educ Trust. 2007;42(4):1758–71.
Vincent C, Taylor-Adams S, Stanhope N. Framework for analysing risk and safety in clinical medicine. BMJ. 1998;316:1154–7.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Weyman A, Pidgeon NF, Walls J, Horlick-Jones T. Exploring comparative ratings and constituent facets of public trust in risk regulatory bodies and related stakeholder groups. J Risk Res. 2006;9:605–22.
Denzin N. The research act: A theoretical introduction to sociological methods. Chicago: Aldine Pub & Co.; 1970.
Patton MQ. Qualitative Reserach and Evaluation Methods. 3rd ed. Thousand Oaks: Sage Publications; 2002.
Mays N, Pope C: Quality in qualitative research. In Qualitative research in health care . Second edition. Edited by Pope C, Mays N. London: BMJ Books; 2000:89–101.
Thurmond VA. The point of triangulation. J Nurs Scholarsh. 2001;33:253–8.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Cooper S, Endacott R, Chapman Y. Qualitative research: specific designs for qualitative research in emergency care? Emerg Med J. 2009;26:773.
Dixon-Woods M. Why is patient safety so hard? A selective review of ethnographic studies. J Health Serv Res Policy. 2010;15:11–6.
Download references
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the ambulance service staff who participated in and assisted with the study. They also thank Peter Mortimer, Deborah Shaw, Chris Newman, Matthew Storey and the Sheffield Emergency Care Forum patient and public involvement team for their assistance in carrying out this research.
This project is funded by the National Institute for Health Research Health Services and Delivery Research Programme (project number 10/1007/53).
Availability of data and materials
Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Authors’ contributions
MJ carried out the interview and observation data collection, assisted with collecting focus group data collection, carried out data analysis and was a major contributor in writing the manuscript. R O’H conceived of the study, carried out focus group and workshop data collection, data analysis, and edited the manuscript. EH assisted with recruitment of service users and service user focus group data collection, carried out data analysis and edited the manuscript. AW carried out statistical analysis of workshop data and edited the manuscript. JT, SM, TQ, JS and ANS contributed to the design of the study, provided topic expertise throughout the study and edited the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Consent for publication
Consent for publication is not applicable to this article.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
We received ethical approval for the research from the University of Sheffield Research Ethics Committee (ScHARR 0530/CAO) and the NRES Committee Yorkshire and Humber—South Yorkshire (12/YH/0327). All participants provided written informed consent prior to participation.
The views and opinions expressed are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect those of the HS&DR Programme, NIHR, NHS or the Department of Health.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Public Health Section, ScHARR, University of Sheffield, Sheffield, UK
Maxine Johnson & Rachel O’Hara
Sheffield Emergency Care Forum, Sheffield, UK
Department of Psychology, University of Bath, Bath, UK
Andrew Weyman
Emergency & Urgent Care Research, Health Services Research Section, ScHARR, University of Sheffield, Sheffield, UK
Janette Turner
Emergency Medicine, Health Services Research Section, ScHARR, University of Sheffield, Sheffield, UK
Suzanne Mason
Centre for Health and Social Care Research, Kingston and St George’s University, London, UK
Yorkshire Ambulance Service NHS Trust, Wakefield, UK
Jane Shewan
Primary and Prehospital Health Care, Community and Health Research Unit, College of Social Science, University of Lincoln, Brayford Pool, Lincoln, UK
A. Niroshan Siriwardena
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Maxine Johnson .
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ ), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Johnson, M., O’Hara, R., Hirst, E. et al. Multiple triangulation and collaborative research using qualitative methods to explore decision making in pre-hospital emergency care. BMC Med Res Methodol 17 , 11 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12874-017-0290-z
Download citation
Received : 26 July 2016
Accepted : 04 January 2017
Published : 24 January 2017
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12874-017-0290-z
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Multi-method research
- Ethnography
- Qualitative
- Patient safety
- Pre-hospital
BMC Medical Research Methodology
ISSN: 1471-2288
- General enquiries: [email protected]
Criteria for Good Qualitative Research: A Comprehensive Review
- Regular Article
- Open access
- Published: 18 September 2021
- Volume 31 , pages 679–689, ( 2022 )
Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article

- Drishti Yadav ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-2974-0323 1
84k Accesses
28 Citations
72 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
This review aims to synthesize a published set of evaluative criteria for good qualitative research. The aim is to shed light on existing standards for assessing the rigor of qualitative research encompassing a range of epistemological and ontological standpoints. Using a systematic search strategy, published journal articles that deliberate criteria for rigorous research were identified. Then, references of relevant articles were surveyed to find noteworthy, distinct, and well-defined pointers to good qualitative research. This review presents an investigative assessment of the pivotal features in qualitative research that can permit the readers to pass judgment on its quality and to condemn it as good research when objectively and adequately utilized. Overall, this review underlines the crux of qualitative research and accentuates the necessity to evaluate such research by the very tenets of its being. It also offers some prospects and recommendations to improve the quality of qualitative research. Based on the findings of this review, it is concluded that quality criteria are the aftereffect of socio-institutional procedures and existing paradigmatic conducts. Owing to the paradigmatic diversity of qualitative research, a single and specific set of quality criteria is neither feasible nor anticipated. Since qualitative research is not a cohesive discipline, researchers need to educate and familiarize themselves with applicable norms and decisive factors to evaluate qualitative research from within its theoretical and methodological framework of origin.
Similar content being viewed by others

Good Qualitative Research: Opening up the Debate
Beyond qualitative/quantitative structuralism: the positivist qualitative research and the paradigmatic disclaimer.

What is Qualitative in Research
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
“… It is important to regularly dialogue about what makes for good qualitative research” (Tracy, 2010 , p. 837)
To decide what represents good qualitative research is highly debatable. There are numerous methods that are contained within qualitative research and that are established on diverse philosophical perspectives. Bryman et al., ( 2008 , p. 262) suggest that “It is widely assumed that whereas quality criteria for quantitative research are well‐known and widely agreed, this is not the case for qualitative research.” Hence, the question “how to evaluate the quality of qualitative research” has been continuously debated. There are many areas of science and technology wherein these debates on the assessment of qualitative research have taken place. Examples include various areas of psychology: general psychology (Madill et al., 2000 ); counseling psychology (Morrow, 2005 ); and clinical psychology (Barker & Pistrang, 2005 ), and other disciplines of social sciences: social policy (Bryman et al., 2008 ); health research (Sparkes, 2001 ); business and management research (Johnson et al., 2006 ); information systems (Klein & Myers, 1999 ); and environmental studies (Reid & Gough, 2000 ). In the literature, these debates are enthused by the impression that the blanket application of criteria for good qualitative research developed around the positivist paradigm is improper. Such debates are based on the wide range of philosophical backgrounds within which qualitative research is conducted (e.g., Sandberg, 2000 ; Schwandt, 1996 ). The existence of methodological diversity led to the formulation of different sets of criteria applicable to qualitative research.
Among qualitative researchers, the dilemma of governing the measures to assess the quality of research is not a new phenomenon, especially when the virtuous triad of objectivity, reliability, and validity (Spencer et al., 2004 ) are not adequate. Occasionally, the criteria of quantitative research are used to evaluate qualitative research (Cohen & Crabtree, 2008 ; Lather, 2004 ). Indeed, Howe ( 2004 ) claims that the prevailing paradigm in educational research is scientifically based experimental research. Hypotheses and conjectures about the preeminence of quantitative research can weaken the worth and usefulness of qualitative research by neglecting the prominence of harmonizing match for purpose on research paradigm, the epistemological stance of the researcher, and the choice of methodology. Researchers have been reprimanded concerning this in “paradigmatic controversies, contradictions, and emerging confluences” (Lincoln & Guba, 2000 ).
In general, qualitative research tends to come from a very different paradigmatic stance and intrinsically demands distinctive and out-of-the-ordinary criteria for evaluating good research and varieties of research contributions that can be made. This review attempts to present a series of evaluative criteria for qualitative researchers, arguing that their choice of criteria needs to be compatible with the unique nature of the research in question (its methodology, aims, and assumptions). This review aims to assist researchers in identifying some of the indispensable features or markers of high-quality qualitative research. In a nutshell, the purpose of this systematic literature review is to analyze the existing knowledge on high-quality qualitative research and to verify the existence of research studies dealing with the critical assessment of qualitative research based on the concept of diverse paradigmatic stances. Contrary to the existing reviews, this review also suggests some critical directions to follow to improve the quality of qualitative research in different epistemological and ontological perspectives. This review is also intended to provide guidelines for the acceleration of future developments and dialogues among qualitative researchers in the context of assessing the qualitative research.
The rest of this review article is structured in the following fashion: Sect. Methods describes the method followed for performing this review. Section Criteria for Evaluating Qualitative Studies provides a comprehensive description of the criteria for evaluating qualitative studies. This section is followed by a summary of the strategies to improve the quality of qualitative research in Sect. Improving Quality: Strategies . Section How to Assess the Quality of the Research Findings? provides details on how to assess the quality of the research findings. After that, some of the quality checklists (as tools to evaluate quality) are discussed in Sect. Quality Checklists: Tools for Assessing the Quality . At last, the review ends with the concluding remarks presented in Sect. Conclusions, Future Directions and Outlook . Some prospects in qualitative research for enhancing its quality and usefulness in the social and techno-scientific research community are also presented in Sect. Conclusions, Future Directions and Outlook .
For this review, a comprehensive literature search was performed from many databases using generic search terms such as Qualitative Research , Criteria , etc . The following databases were chosen for the literature search based on the high number of results: IEEE Explore, ScienceDirect, PubMed, Google Scholar, and Web of Science. The following keywords (and their combinations using Boolean connectives OR/AND) were adopted for the literature search: qualitative research, criteria, quality, assessment, and validity. The synonyms for these keywords were collected and arranged in a logical structure (see Table 1 ). All publications in journals and conference proceedings later than 1950 till 2021 were considered for the search. Other articles extracted from the references of the papers identified in the electronic search were also included. A large number of publications on qualitative research were retrieved during the initial screening. Hence, to include the searches with the main focus on criteria for good qualitative research, an inclusion criterion was utilized in the search string.
From the selected databases, the search retrieved a total of 765 publications. Then, the duplicate records were removed. After that, based on the title and abstract, the remaining 426 publications were screened for their relevance by using the following inclusion and exclusion criteria (see Table 2 ). Publications focusing on evaluation criteria for good qualitative research were included, whereas those works which delivered theoretical concepts on qualitative research were excluded. Based on the screening and eligibility, 45 research articles were identified that offered explicit criteria for evaluating the quality of qualitative research and were found to be relevant to this review.
Figure 1 illustrates the complete review process in the form of PRISMA flow diagram. PRISMA, i.e., “preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses” is employed in systematic reviews to refine the quality of reporting.
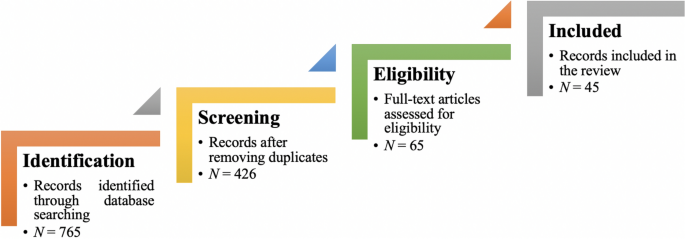
PRISMA flow diagram illustrating the search and inclusion process. N represents the number of records
Criteria for Evaluating Qualitative Studies
Fundamental criteria: general research quality.
Various researchers have put forward criteria for evaluating qualitative research, which have been summarized in Table 3 . Also, the criteria outlined in Table 4 effectively deliver the various approaches to evaluate and assess the quality of qualitative work. The entries in Table 4 are based on Tracy’s “Eight big‐tent criteria for excellent qualitative research” (Tracy, 2010 ). Tracy argues that high-quality qualitative work should formulate criteria focusing on the worthiness, relevance, timeliness, significance, morality, and practicality of the research topic, and the ethical stance of the research itself. Researchers have also suggested a series of questions as guiding principles to assess the quality of a qualitative study (Mays & Pope, 2020 ). Nassaji ( 2020 ) argues that good qualitative research should be robust, well informed, and thoroughly documented.
Qualitative Research: Interpretive Paradigms
All qualitative researchers follow highly abstract principles which bring together beliefs about ontology, epistemology, and methodology. These beliefs govern how the researcher perceives and acts. The net, which encompasses the researcher’s epistemological, ontological, and methodological premises, is referred to as a paradigm, or an interpretive structure, a “Basic set of beliefs that guides action” (Guba, 1990 ). Four major interpretive paradigms structure the qualitative research: positivist and postpositivist, constructivist interpretive, critical (Marxist, emancipatory), and feminist poststructural. The complexity of these four abstract paradigms increases at the level of concrete, specific interpretive communities. Table 5 presents these paradigms and their assumptions, including their criteria for evaluating research, and the typical form that an interpretive or theoretical statement assumes in each paradigm. Moreover, for evaluating qualitative research, quantitative conceptualizations of reliability and validity are proven to be incompatible (Horsburgh, 2003 ). In addition, a series of questions have been put forward in the literature to assist a reviewer (who is proficient in qualitative methods) for meticulous assessment and endorsement of qualitative research (Morse, 2003 ). Hammersley ( 2007 ) also suggests that guiding principles for qualitative research are advantageous, but methodological pluralism should not be simply acknowledged for all qualitative approaches. Seale ( 1999 ) also points out the significance of methodological cognizance in research studies.
Table 5 reflects that criteria for assessing the quality of qualitative research are the aftermath of socio-institutional practices and existing paradigmatic standpoints. Owing to the paradigmatic diversity of qualitative research, a single set of quality criteria is neither possible nor desirable. Hence, the researchers must be reflexive about the criteria they use in the various roles they play within their research community.
Improving Quality: Strategies
Another critical question is “How can the qualitative researchers ensure that the abovementioned quality criteria can be met?” Lincoln and Guba ( 1986 ) delineated several strategies to intensify each criteria of trustworthiness. Other researchers (Merriam & Tisdell, 2016 ; Shenton, 2004 ) also presented such strategies. A brief description of these strategies is shown in Table 6 .
It is worth mentioning that generalizability is also an integral part of qualitative research (Hays & McKibben, 2021 ). In general, the guiding principle pertaining to generalizability speaks about inducing and comprehending knowledge to synthesize interpretive components of an underlying context. Table 7 summarizes the main metasynthesis steps required to ascertain generalizability in qualitative research.
Figure 2 reflects the crucial components of a conceptual framework and their contribution to decisions regarding research design, implementation, and applications of results to future thinking, study, and practice (Johnson et al., 2020 ). The synergy and interrelationship of these components signifies their role to different stances of a qualitative research study.

Essential elements of a conceptual framework
In a nutshell, to assess the rationale of a study, its conceptual framework and research question(s), quality criteria must take account of the following: lucid context for the problem statement in the introduction; well-articulated research problems and questions; precise conceptual framework; distinct research purpose; and clear presentation and investigation of the paradigms. These criteria would expedite the quality of qualitative research.
How to Assess the Quality of the Research Findings?
The inclusion of quotes or similar research data enhances the confirmability in the write-up of the findings. The use of expressions (for instance, “80% of all respondents agreed that” or “only one of the interviewees mentioned that”) may also quantify qualitative findings (Stenfors et al., 2020 ). On the other hand, the persuasive reason for “why this may not help in intensifying the research” has also been provided (Monrouxe & Rees, 2020 ). Further, the Discussion and Conclusion sections of an article also prove robust markers of high-quality qualitative research, as elucidated in Table 8 .
Quality Checklists: Tools for Assessing the Quality
Numerous checklists are available to speed up the assessment of the quality of qualitative research. However, if used uncritically and recklessly concerning the research context, these checklists may be counterproductive. I recommend that such lists and guiding principles may assist in pinpointing the markers of high-quality qualitative research. However, considering enormous variations in the authors’ theoretical and philosophical contexts, I would emphasize that high dependability on such checklists may say little about whether the findings can be applied in your setting. A combination of such checklists might be appropriate for novice researchers. Some of these checklists are listed below:
The most commonly used framework is Consolidated Criteria for Reporting Qualitative Research (COREQ) (Tong et al., 2007 ). This framework is recommended by some journals to be followed by the authors during article submission.
Standards for Reporting Qualitative Research (SRQR) is another checklist that has been created particularly for medical education (O’Brien et al., 2014 ).
Also, Tracy ( 2010 ) and Critical Appraisal Skills Programme (CASP, 2021 ) offer criteria for qualitative research relevant across methods and approaches.
Further, researchers have also outlined different criteria as hallmarks of high-quality qualitative research. For instance, the “Road Trip Checklist” (Epp & Otnes, 2021 ) provides a quick reference to specific questions to address different elements of high-quality qualitative research.
Conclusions, Future Directions, and Outlook
This work presents a broad review of the criteria for good qualitative research. In addition, this article presents an exploratory analysis of the essential elements in qualitative research that can enable the readers of qualitative work to judge it as good research when objectively and adequately utilized. In this review, some of the essential markers that indicate high-quality qualitative research have been highlighted. I scope them narrowly to achieve rigor in qualitative research and note that they do not completely cover the broader considerations necessary for high-quality research. This review points out that a universal and versatile one-size-fits-all guideline for evaluating the quality of qualitative research does not exist. In other words, this review also emphasizes the non-existence of a set of common guidelines among qualitative researchers. In unison, this review reinforces that each qualitative approach should be treated uniquely on account of its own distinctive features for different epistemological and disciplinary positions. Owing to the sensitivity of the worth of qualitative research towards the specific context and the type of paradigmatic stance, researchers should themselves analyze what approaches can be and must be tailored to ensemble the distinct characteristics of the phenomenon under investigation. Although this article does not assert to put forward a magic bullet and to provide a one-stop solution for dealing with dilemmas about how, why, or whether to evaluate the “goodness” of qualitative research, it offers a platform to assist the researchers in improving their qualitative studies. This work provides an assembly of concerns to reflect on, a series of questions to ask, and multiple sets of criteria to look at, when attempting to determine the quality of qualitative research. Overall, this review underlines the crux of qualitative research and accentuates the need to evaluate such research by the very tenets of its being. Bringing together the vital arguments and delineating the requirements that good qualitative research should satisfy, this review strives to equip the researchers as well as reviewers to make well-versed judgment about the worth and significance of the qualitative research under scrutiny. In a nutshell, a comprehensive portrayal of the research process (from the context of research to the research objectives, research questions and design, speculative foundations, and from approaches of collecting data to analyzing the results, to deriving inferences) frequently proliferates the quality of a qualitative research.
Prospects : A Road Ahead for Qualitative Research
Irrefutably, qualitative research is a vivacious and evolving discipline wherein different epistemological and disciplinary positions have their own characteristics and importance. In addition, not surprisingly, owing to the sprouting and varied features of qualitative research, no consensus has been pulled off till date. Researchers have reflected various concerns and proposed several recommendations for editors and reviewers on conducting reviews of critical qualitative research (Levitt et al., 2021 ; McGinley et al., 2021 ). Following are some prospects and a few recommendations put forward towards the maturation of qualitative research and its quality evaluation:
In general, most of the manuscript and grant reviewers are not qualitative experts. Hence, it is more likely that they would prefer to adopt a broad set of criteria. However, researchers and reviewers need to keep in mind that it is inappropriate to utilize the same approaches and conducts among all qualitative research. Therefore, future work needs to focus on educating researchers and reviewers about the criteria to evaluate qualitative research from within the suitable theoretical and methodological context.
There is an urgent need to refurbish and augment critical assessment of some well-known and widely accepted tools (including checklists such as COREQ, SRQR) to interrogate their applicability on different aspects (along with their epistemological ramifications).
Efforts should be made towards creating more space for creativity, experimentation, and a dialogue between the diverse traditions of qualitative research. This would potentially help to avoid the enforcement of one's own set of quality criteria on the work carried out by others.
Moreover, journal reviewers need to be aware of various methodological practices and philosophical debates.
It is pivotal to highlight the expressions and considerations of qualitative researchers and bring them into a more open and transparent dialogue about assessing qualitative research in techno-scientific, academic, sociocultural, and political rooms.
Frequent debates on the use of evaluative criteria are required to solve some potentially resolved issues (including the applicability of a single set of criteria in multi-disciplinary aspects). Such debates would not only benefit the group of qualitative researchers themselves, but primarily assist in augmenting the well-being and vivacity of the entire discipline.
To conclude, I speculate that the criteria, and my perspective, may transfer to other methods, approaches, and contexts. I hope that they spark dialog and debate – about criteria for excellent qualitative research and the underpinnings of the discipline more broadly – and, therefore, help improve the quality of a qualitative study. Further, I anticipate that this review will assist the researchers to contemplate on the quality of their own research, to substantiate research design and help the reviewers to review qualitative research for journals. On a final note, I pinpoint the need to formulate a framework (encompassing the prerequisites of a qualitative study) by the cohesive efforts of qualitative researchers of different disciplines with different theoretic-paradigmatic origins. I believe that tailoring such a framework (of guiding principles) paves the way for qualitative researchers to consolidate the status of qualitative research in the wide-ranging open science debate. Dialogue on this issue across different approaches is crucial for the impending prospects of socio-techno-educational research.
Amin, M. E. K., Nørgaard, L. S., Cavaco, A. M., Witry, M. J., Hillman, L., Cernasev, A., & Desselle, S. P. (2020). Establishing trustworthiness and authenticity in qualitative pharmacy research. Research in Social and Administrative Pharmacy, 16 (10), 1472–1482.
Article Google Scholar
Barker, C., & Pistrang, N. (2005). Quality criteria under methodological pluralism: Implications for conducting and evaluating research. American Journal of Community Psychology, 35 (3–4), 201–212.
Bryman, A., Becker, S., & Sempik, J. (2008). Quality criteria for quantitative, qualitative and mixed methods research: A view from social policy. International Journal of Social Research Methodology, 11 (4), 261–276.
Caelli, K., Ray, L., & Mill, J. (2003). ‘Clear as mud’: Toward greater clarity in generic qualitative research. International Journal of Qualitative Methods, 2 (2), 1–13.
CASP (2021). CASP checklists. Retrieved May 2021 from https://casp-uk.net/casp-tools-checklists/
Cohen, D. J., & Crabtree, B. F. (2008). Evaluative criteria for qualitative research in health care: Controversies and recommendations. The Annals of Family Medicine, 6 (4), 331–339.
Denzin, N. K., & Lincoln, Y. S. (2005). Introduction: The discipline and practice of qualitative research. In N. K. Denzin & Y. S. Lincoln (Eds.), The sage handbook of qualitative research (pp. 1–32). Sage Publications Ltd.
Google Scholar
Elliott, R., Fischer, C. T., & Rennie, D. L. (1999). Evolving guidelines for publication of qualitative research studies in psychology and related fields. British Journal of Clinical Psychology, 38 (3), 215–229.
Epp, A. M., & Otnes, C. C. (2021). High-quality qualitative research: Getting into gear. Journal of Service Research . https://doi.org/10.1177/1094670520961445
Guba, E. G. (1990). The paradigm dialog. In Alternative paradigms conference, mar, 1989, Indiana u, school of education, San Francisco, ca, us . Sage Publications, Inc.
Hammersley, M. (2007). The issue of quality in qualitative research. International Journal of Research and Method in Education, 30 (3), 287–305.
Haven, T. L., Errington, T. M., Gleditsch, K. S., van Grootel, L., Jacobs, A. M., Kern, F. G., & Mokkink, L. B. (2020). Preregistering qualitative research: A Delphi study. International Journal of Qualitative Methods, 19 , 1609406920976417.
Hays, D. G., & McKibben, W. B. (2021). Promoting rigorous research: Generalizability and qualitative research. Journal of Counseling and Development, 99 (2), 178–188.
Horsburgh, D. (2003). Evaluation of qualitative research. Journal of Clinical Nursing, 12 (2), 307–312.
Howe, K. R. (2004). A critique of experimentalism. Qualitative Inquiry, 10 (1), 42–46.
Johnson, J. L., Adkins, D., & Chauvin, S. (2020). A review of the quality indicators of rigor in qualitative research. American Journal of Pharmaceutical Education, 84 (1), 7120.
Johnson, P., Buehring, A., Cassell, C., & Symon, G. (2006). Evaluating qualitative management research: Towards a contingent criteriology. International Journal of Management Reviews, 8 (3), 131–156.
Klein, H. K., & Myers, M. D. (1999). A set of principles for conducting and evaluating interpretive field studies in information systems. MIS Quarterly, 23 (1), 67–93.
Lather, P. (2004). This is your father’s paradigm: Government intrusion and the case of qualitative research in education. Qualitative Inquiry, 10 (1), 15–34.
Levitt, H. M., Morrill, Z., Collins, K. M., & Rizo, J. L. (2021). The methodological integrity of critical qualitative research: Principles to support design and research review. Journal of Counseling Psychology, 68 (3), 357.
Lincoln, Y. S., & Guba, E. G. (1986). But is it rigorous? Trustworthiness and authenticity in naturalistic evaluation. New Directions for Program Evaluation, 1986 (30), 73–84.
Lincoln, Y. S., & Guba, E. G. (2000). Paradigmatic controversies, contradictions and emerging confluences. In N. K. Denzin & Y. S. Lincoln (Eds.), Handbook of qualitative research (2nd ed., pp. 163–188). Sage Publications.
Madill, A., Jordan, A., & Shirley, C. (2000). Objectivity and reliability in qualitative analysis: Realist, contextualist and radical constructionist epistemologies. British Journal of Psychology, 91 (1), 1–20.
Mays, N., & Pope, C. (2020). Quality in qualitative research. Qualitative Research in Health Care . https://doi.org/10.1002/9781119410867.ch15
McGinley, S., Wei, W., Zhang, L., & Zheng, Y. (2021). The state of qualitative research in hospitality: A 5-year review 2014 to 2019. Cornell Hospitality Quarterly, 62 (1), 8–20.
Merriam, S., & Tisdell, E. (2016). Qualitative research: A guide to design and implementation. San Francisco, US.
Meyer, M., & Dykes, J. (2019). Criteria for rigor in visualization design study. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 26 (1), 87–97.
Monrouxe, L. V., & Rees, C. E. (2020). When I say… quantification in qualitative research. Medical Education, 54 (3), 186–187.
Morrow, S. L. (2005). Quality and trustworthiness in qualitative research in counseling psychology. Journal of Counseling Psychology, 52 (2), 250.
Morse, J. M. (2003). A review committee’s guide for evaluating qualitative proposals. Qualitative Health Research, 13 (6), 833–851.
Nassaji, H. (2020). Good qualitative research. Language Teaching Research, 24 (4), 427–431.
O’Brien, B. C., Harris, I. B., Beckman, T. J., Reed, D. A., & Cook, D. A. (2014). Standards for reporting qualitative research: A synthesis of recommendations. Academic Medicine, 89 (9), 1245–1251.
O’Connor, C., & Joffe, H. (2020). Intercoder reliability in qualitative research: Debates and practical guidelines. International Journal of Qualitative Methods, 19 , 1609406919899220.
Reid, A., & Gough, S. (2000). Guidelines for reporting and evaluating qualitative research: What are the alternatives? Environmental Education Research, 6 (1), 59–91.
Rocco, T. S. (2010). Criteria for evaluating qualitative studies. Human Resource Development International . https://doi.org/10.1080/13678868.2010.501959
Sandberg, J. (2000). Understanding human competence at work: An interpretative approach. Academy of Management Journal, 43 (1), 9–25.
Schwandt, T. A. (1996). Farewell to criteriology. Qualitative Inquiry, 2 (1), 58–72.
Seale, C. (1999). Quality in qualitative research. Qualitative Inquiry, 5 (4), 465–478.
Shenton, A. K. (2004). Strategies for ensuring trustworthiness in qualitative research projects. Education for Information, 22 (2), 63–75.
Sparkes, A. C. (2001). Myth 94: Qualitative health researchers will agree about validity. Qualitative Health Research, 11 (4), 538–552.
Spencer, L., Ritchie, J., Lewis, J., & Dillon, L. (2004). Quality in qualitative evaluation: A framework for assessing research evidence.
Stenfors, T., Kajamaa, A., & Bennett, D. (2020). How to assess the quality of qualitative research. The Clinical Teacher, 17 (6), 596–599.
Taylor, E. W., Beck, J., & Ainsworth, E. (2001). Publishing qualitative adult education research: A peer review perspective. Studies in the Education of Adults, 33 (2), 163–179.
Tong, A., Sainsbury, P., & Craig, J. (2007). Consolidated criteria for reporting qualitative research (COREQ): A 32-item checklist for interviews and focus groups. International Journal for Quality in Health Care, 19 (6), 349–357.
Tracy, S. J. (2010). Qualitative quality: Eight “big-tent” criteria for excellent qualitative research. Qualitative Inquiry, 16 (10), 837–851.
Download references
Open access funding provided by TU Wien (TUW).
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Faculty of Informatics, Technische Universität Wien, 1040, Vienna, Austria
Drishti Yadav
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Drishti Yadav .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Yadav, D. Criteria for Good Qualitative Research: A Comprehensive Review. Asia-Pacific Edu Res 31 , 679–689 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40299-021-00619-0
Download citation
Accepted : 28 August 2021
Published : 18 September 2021
Issue Date : December 2022
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s40299-021-00619-0
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Qualitative research
- Evaluative criteria
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Am J Pharm Educ
- v.84(1); 2020 Jan
A Review of the Quality Indicators of Rigor in Qualitative Research
Jessica l. johnson.
a William Carey University School of Pharmacy, Biloxi, Mississippi
Donna Adkins
Sheila chauvin.
b Louisiana State University, School of Medicine, New Orleans, Louisiana
Attributes of rigor and quality and suggested best practices for qualitative research design as they relate to the steps of designing, conducting, and reporting qualitative research in health professions educational scholarship are presented. A research question must be clear and focused and supported by a strong conceptual framework, both of which contribute to the selection of appropriate research methods that enhance trustworthiness and minimize researcher bias inherent in qualitative methodologies. Qualitative data collection and analyses are often modified through an iterative approach to answering the research question. Researcher reflexivity, essentially a researcher’s insight into their own biases and rationale for decision-making as the study progresses, is critical to rigor. This article reviews common standards of rigor, quality scholarship criteria, and best practices for qualitative research from design through dissemination.
INTRODUCTION
Within the past 20 years, qualitative research in health professions education has increased significantly, both in practice and publication. Today, one can pick up most any issue of a wide variety of health professions education journals and find at least one article that includes some type of qualitative research, whether a full study or the inclusion of a qualitative component within a quantitative or mixed methods study. Simultaneously, there have been recurrent calls for enhancing rigor and quality in qualitative research.
As members of the academic community, we share responsibility for ensuring rigor in qualitative research, whether as researchers who design and implement, manuscript reviewers who critique, colleagues who discuss and learn from each other, or scholarly teachers who draw upon results to enhance and innovate education. Therefore, the purpose of this article is to summarize standards of rigor and suggested best practices for designing, conducting, and reporting high-quality qualitative research. To begin, Denzin and Lincoln’s definition of qualitative research, a long-standing cornerstone in the field, provides a useful foundation for summarizing quality standards and best practices:
Qualitative research involves the studied use and collection of a variety of empirical materials – case study; personal experience; introspection; life story; interview; artifacts; cultural texts and productions; observational, historical, interactional, and visual texts – that describe the routine and problematic moments and meanings in individual lives. Accordingly, qualitative researchers deploy a wide range of interconnected interpretative practices, hoping always to get a better understanding of the subject matter at hand. It is understood, however, that each practice makes the world visible in a different way. Hence there is frequently a commitment to using more than one interpretative practice in any study. 1
In recent years, multiple publications have synthesized quality criteria and recommendations for use by researchers and peer reviewers alike, often in the form of checklists. 2-6 Some authors have raised concerns about the use of such checklists and adherence to strict, universal criteria because they do not afford sufficient flexibility to accommodate the diverse approaches and multiple interpretive practices often represented in qualitative studies. 7-11 They argue that a strict focus on using checklists of specific technical criteria may stifle the diversity and multiplicity of practices that are so much a part of achieving quality and rigor within the qualitative paradigm. As an alternative, some of these authors have published best practice guidelines for use by researchers and peer reviewers to achieve and assess methodological rigor and research quality. 12,13
Some journals within the field of health professions education have also established best practice guidance, as opposed to strict criteria or a checklist, for qualitative research. These have been disseminated as guiding questions or evaluation categories. In 2015, Academic Medicine produced an expanded second edition of a researcher/author manual that includes specific criteria with extensive explanations and examples. 14 Still others have disseminated best practice guidelines through a series of methodological articles within journal publications. 2
In this article, attributes of rigor and quality and suggested best practices are presented as they relate to the steps of designing, conducting, and reporting qualitative research in a step-wise approach.
BEST PRACTICES: STEP-WISE APPROACH
Step 1: identifying a research topic.
Identifying and developing a research topic is comprised of two major tasks: formulating a research question, and developing a conceptual framework to support the study. Formulating a research question is often stimulated by real-life observations, experiences, or events in the researcher’s local setting that reflect a perplexing problem begging for systematic inquiry. The research question begins as a problem statement or set of propositions that describe the relationship among certain concepts, behaviors, or experiences. Agee 15 and others 16,17 note that initial questions are usually too broad in focus and too vague regarding the specific context of the study to be answerable and researchable. Creswell reminds us that initial qualitative research questions guide inquiry, but they often change as the author’s understanding of the issue develops throughout the study. 16 Developing and refining a primary research question focused on both the phenomena of interest and the context in which it is situated is essential to research rigor and quality.
Glassick, Huber, and Maeroff identified six criteria applicable to assessing the quality of scholarship. 18,19 Now commonly referred to as the Glassick Criteria ( Table 1 ), these critical attributes outline the essential elements of any scholarly approach and serve as a general research framework for developing research questions and designing studies. The first two criteria, clear purpose and adequate preparation, are directly related to formulating effective research questions and a strong conceptual framework.
Glassick’s Criteria for Assessing the Quality of Scholarship of a Research Study 18

Generating and refining a qualitative research question requires thorough, systematic, and iterative review of the literature, and the use of those results to establish a clear context and foundation for the question and study design. Using an iterative approach, relevant concepts, principles, theories or models, and prior evidence are identified to establish what is known, and more importantly, what is not known. The iterative process contributes to forming a better research question, the criteria for which can be abbreviated by the acronym FINER, ie, f easible, i nteresting, n ovel, e thical, and r elevant, that is answerable and researchable, in terms of research focus, context specificity, and the availability of time, logistics, and resources to carry out the study. Developing a FINER research question is critical to study rigor and quality and should not be rushed, as all other aspects of research design depend on the focus and clarity of the research question(s) guiding the study. 15 Agee provides clear and worthwhile additional guidance for developing qualitative research questions. 15
Reflexivity, the idea that a researcher’s preconceptions and biases can influence decisions and actions throughout qualitative research activities, is a critical aspect of rigor even at the earliest stages of the study. A researcher’s background, beliefs, and experiences may affect any aspect of the research from choosing which specific question to investigate through determining how to present the results. Therefore, even at this early stage, the potential effect of researcher bias and any ethical considerations should be acknowledged and addressed. That is, how will the question’s influence on study design affect participants’ lives, position the researcher in relationship with others, or require specific methods for addressing potential areas of research bias and ethical considerations?
A conceptual framework is then actively constructed to provide a logical and convincing argument for the research. The framework defines and justifies the research question, the methodology selected to answer that question, and the perspectives from which interpretation of results and conclusions will be made. 5,6,20 Developing a well-integrated conceptual framework is essential to establishing a research topic based upon a thorough and integrated review of relevant literature (addressing Glassick criteria #1 and #2: clear purpose and adequate preparation). Key concepts, principles, assumptions, best practices, and theories are identified, defined, and integrated in ways that clearly demonstrate the problem statement and corresponding research question are answerable, researchable, and important to advancing thinking and practice.
Ringsted, Hodges, and Sherpbier describe three essential parts to an effective conceptual framework: theories and/or concepts and principles relevant to the phenomenon of interest; what is known and unknown from prior work, observations, and examples; and the researcher’s observations, ideas, and suppositions regarding the research problem statement and question. 21 Lingard describes four types of unknowns to pursue during literature review: what no one knows; what is not yet well understood; what controversy or conflicting results, understandings, or perspectives exist; and what are unproven assumptions. 22 In qualitative research, these unknowns are critical to achieving a well-developed conceptual framework and a corresponding rigorous study design.
Recent contributions from Ravitch and colleagues present best practices in developing frameworks for conceptual and methodological coherence within a study design, regardless of the research approach. 23,24 Their recommendations and arguments are highly relevant to qualitative research. Figure 1 reflects the primary components of a conceptual framework adapted from Ravitch and Carl 23 and how all components contribute to decisions regarding research design, implementation, and applications of results to future thinking, study, and practice. Notice that each element of the framework interacts with and influences other elements in a dynamic and interactive process from the beginning to the end of a research project. The intersecting bidirectional arrows represent direct relationships between elements as they relate to specific aspects of a qualitative research study.

Adaptation of Ravitch and Carl’s Components of a Conceptual Framework 23
Maxwell also provides useful guidance for developing an effective conceptual framework specific to the qualitative research paradigm. 17 The 2015 second edition of the Review Criteria for Research Manuscripts 14 and work by Ravitch and colleagues 23,24 provide specific guidance for applying the conceptual framework to each stage of the research process to enhance rigor and quality. Quality criteria for assessing a study’s problem statement, conceptual framework, and research question include the following: introduction builds a logical case and provides context for the problem statement; problem statement is clear and well-articulated; conceptual framework is explicit and justified; research purpose and/or question is clearly stated; and constructs being investigated are clearly identified and presented. 14,24,25 As best practice guidelines, these criteria facilitate quality and rigor while providing sufficient flexibility in how each is achieved and demonstrated.
While a conceptual framework is important to rigor in qualitative research, Huberman and Miles caution qualitative researchers about developing and using a framework to the extent that it influences qualitative design deductively because this would violate the very principles of induction that define the qualitative research paradigm. 25 Our profession’s recent emphasis on a holistic admissions process for pharmacy students provides a reasonable example of inductive and deductive reasoning and their respective applications in qualitative and quantitative research studies. Principles of inductive reasoning are applied when a qualitative research study examines a representative group of competent pharmacy professionals to generate a theory about essential cognitive and affective skills for patient-centered care. Deductive reasoning could then be applied to design a hypothesis-driven prospective study that compares the outcomes of two cohorts of students, one group admitted using traditional criteria and one admitted based on a holistic admissions process revised to value the affective skills of applicants. Essentially, the qualitative researcher must carefully generate a conceptual framework that guides the research question and study design without allowing the conceptual framework to become so rigid as to dictate a testable hypothesis, which is the founding principle of deductive reasoning. 26
Step 2: Qualitative Study Design
The development of a strong conceptual framework facilitates selection of appropriate study methods to minimize the bias inherent in qualitative studies and help readers to trust the research and the researcher (see Glassick criteria #3 in Table 1 ). Although researchers can employ great flexibility in the selection of study methods, inclusion of best practice methods for assuring the rigor and trustworthiness of results is critical to study design. Lincoln and Guba outline four criteria for establishing the overall trustworthiness of qualitative research results: credibility, the researcher ensures and imparts to the reader supporting evidence that the results accurately represent what was studied; transferability, the researcher provides detailed contextual information such that readers can determine whether the results are applicable to their or other situations; dependability, the researcher describes the study process in sufficient detail that the work could be repeated; confirmability, the researcher ensures and communicates to the reader that the results are based on and reflective of the information gathered from the participants and not the interpretations or bias of the researcher. 27
Specific best practice methods used in the sampling and data collection processes to increase the rigor and trustworthiness of qualitative research include: clear rationale for sampling design decisions, determination of data saturation, ethics in research design, member checking, prolonged engagement with and persistent observation of study participants, and triangulation of data sources. 28
Qualitative research is focused on making sense of lived, observed phenomenon in a specific context with specifically selected individuals, rather than attempting to generalize from sample to population. Therefore, sampling design in qualitative research is not random but defined purposively to include the most appropriate participants in the most appropriate context for answering the research question. Qualitative researchers recognize that certain participants are more likely to be “rich” with data or insight than others, and therefore, more relevant and useful in achieving the research purpose and answering the question at hand. The conceptual framework contributes directly to determining sample definitions, size, and recruitment of participants. A typical best practice is purposive sampling methods, and when appropriate, convenience sampling may be justified. 29
Purposive sampling reflects intentional selection of research participants to optimize data sources for answering the research question. For example, the research question may be best answered by persons who have particular experience (critical case sampling) or certain expertise (key informant sampling). Similarly, additional participants may be referred for participation by active participants (snowball sampling) or may be selected to represent either similar or opposing viewpoints (confirming or disconfirming samples). Again, the process of developing and using a strong conceptual framework to guide and justify methodological decisions, in this case defining and establishing the study sample, is critical to rigor and quality. 30 Convenience sampling, using the most accessible research participants, is the least rigorous approach to defining a study sample and may result in low accuracy, poor representativeness, low credibility, and lack of transferability of study results.
Qualitative studies typically reflect designs in which data collection and analysis are done concurrently, with results of ongoing analysis informing continuing data collection. Determination of a final sample size is largely based on having sufficient opportunity to collect relevant data until new information is no longer emerging from data collection, new coding is not feasible, and/or no new themes are emerging; that is, reaching data saturation , a common standard of rigor for data collection in qualitative studies . Thus, accurately predicting a sample size during the planning phases of qualitative research can be challenging. 30 Care should be taken that sufficient quantity (think thick description) and quality (think rich description) of data have been collected prior to concluding that data saturation has been achieved. A poor decision regarding sample size is a direct consequence of sampling strategy and quality of data generated, which leaves the researcher unable to fully answer the research question in sufficient depth. 30
Though data saturation is probably the most common terminology used to describe the achievement of sufficient sample size, it does not apply to all study designs. For example, one could argue that in some approaches to qualitative research, data collection could continue infinitely if the event continues infinitely. In education, we often anecdotally observe variations in the personality and structure of a class of students, and as generations of students continue to evolve with time, so too would the data generated from observing each successive class. In such situations, data saturation might never be achieved. Conversely, the number of participants available for inclusion in a sample may be small and some risk of not reaching data saturation may be unavoidable. Thus, the idea of fully achieving data saturation may be unrealistic when applied to some populations or research questions. In other instances, attrition and factors related to time and resources may contribute to not reaching data saturation within the limits of the study. By being transparent in the process and reporting of results when saturation may not have been possible, the resulting data may still contribute to the field and to further inquiry. Replication of the study using other samples and conducting additional types of follow-up studies are other options for better understanding the research phenomenon at hand. 31
In addition to defining the sample and selecting participants, other considerations related to sampling bias may impact the quantity and quality of data generated and therefore the quality of the study result. These include: methods of recruiting, procedures for informed consent, timing of the interviews in relation to experience or emotion, procedures for ensuring participant anonymity/confidentiality, interview setting, and methods of recording/transcribing the data. Any of these factors could potentially change the nature of the relationship between the researcher and the study participants and influence the trustworthiness of data collected or the study result. Thus, ongoing application of previously mentioned researcher reflexivity is critical to the rigor of the study and quality of sampling. 29,30
Common qualitative data collection methods used in health professions education include interview, direct observation methods, and textual/document analysis. Given the unique and often highly sensitive nature of data being collected by the researcher, trustworthiness is an essential component of the researcher-participant relationship. Ethical conduct refers to how moral principles and values are part of the research process. Participants’ perceptions of ethical conduct are fundamental to a relationship likely to generate high quality data. During each step of the research process, care must be taken to protect the confidentiality of participants and shield them from harm relating to issues of respect and dignity. Researchers must be respectful of the participants’ contributions and quotes, and results must be reported truthfully and honestly. 8
Interview methods range from highly structured to increase dependability or completely open-ended to allow for interviewers to clarify a participant’s response for increased credibility and confirmability. Regardless, interview protocols and structure are often modified or refined, based on concurrent data collection and analysis processes to support or refute preliminary interpretations and refine focus and continuing inquiry. Researcher reflexivity, or acknowledgement of researcher bias, is absolutely critical to the credibility and trustworthiness of data collection and analysis in such study designs. 32
Interviews should be recorded and transcribed verbatim prior to coding and analysis. 28 Member checking, a common standard of rigor, is a practice to increase study credibility and confirmability that involves asking a research subject to verify the transcription of an interview. 1,16,28 The research subject is asked to verify the completeness and accuracy of an interview transcript to ensure the transcript truthfully reflects the meaning and intent of the subject’s contribution.
Prolonged engagement involves the researcher gaining familiarity and understanding of the culture and context surrounding the persons or situations being studied. This strategy supports reflexivity, allowing the researcher to determine how they themselves may be a source of bias during the data collection process by altering the nature of how individuals behave or interact with others in the presence of the researcher. Facial expressions, spoken language, body language, style of dress, age, race, gender, social status, culture, and the researcher’s relationship with the participants may potentially influence either participants’ responses or how the researcher interprets those responses. 33 “Fitting in” by demonstrating an appreciation and understanding of the cultural norms of the population being studied potentially allows the researcher to obtain more open and honest responses from participants. However, if the research participants or topic are too familiar or personal, this may also influence data collection or analysis and interpretation of the results. 33 The possible applications of this section to faculty research with student participants in the context of pharmacy education are obvious, and researcher reflexivity is critical to rigor.
Some researchers using observational methods adopt a strategy of direct field observation, while others play partial or full participant roles in the activity being observed. In both observation scenarios, it is impossible to separate the researcher from the environment, and researcher reflexivity is essential. The pros and cons of observation approach, relative to the research question and study purpose, should be evaluated by the researcher, and the justification for the observational strategy selected should be made clear. 34 Regardless of the researcher’s degree of visibility to the study participants, persistent observation of the targeted sample is critical to the confirmability standard and to achieving data saturation. That is, study conclusions must be clearly grounded in persistent phenomena witnessed during the study, rather than on a fluke event. 28
Researchers acknowledge that observational methodologies are limited by the reality that the researcher carries a bias in determining what is observed, what is recorded, how it is recorded, and how it is transcribed for analysis. A study’s conceptual framework is critical to achieving rigor and quality and provides guidance in developing predetermined notions or plans for what to observe, how to record, and how to minimize the influence of potential bias. 34 Researcher notes should be recorded as soon as possible after the observation event to optimize accuracy. The more detailed and complete the notes, the more accurate and useful they can be in data analysis or in auditing processes for enhancing rigor in the interpretation phase of the study. 34
Triangulation is among the common standards of rigor applied within the qualitative research paradigm. Data triangulation is used to identify convergence of data obtained through multiple data sources and methods (eg, observation field notes and interview transcripts) to avoid or minimize error or bias and optimize accuracy in data collection and analysis processes. 33,35,36
Again, researcher practice in reflexivity throughout research processes is integral to rigor in study design and implementation. Researchers must demonstrate attention to appropriate methods and reflective critique, which are represented in both core elements of the conceptual framework ( Figure 1 ) and Glassick criteria ( Table 1 ). In so doing, the researcher will be well-prepared to justify sampling design and data collection decisions to manuscript reviewers and, ultimately, readers.
Step 3: Data Analysis
In many qualitative studies, data collection runs concurrently with data analysis. Specific standards of rigor are commonly used to ensure trustworthiness and integrity within the data analysis process, including use of computer software, peer review, audit trail, triangulation, and negative case analysis.
Management and analyses of qualitative data from written text, observational field notes, and interview transcriptions may be accomplished using manual methods or the assistance of computer software applications for coding and analysis. When managing very large data sets or complex study designs, computer software can be very helpful to assist researchers in coding, sorting, organizing, and weighting data elements. Software applications can facilitate ease in calculating semi-quantitative descriptive statistics, such as counts of specific events, that can be used as evidence that the researcher’s analysis is based on a representative majority of data collected ( inclusivism ) rather than focusing on selected rarities ( anecdotalism ). Using software to code data can also make it easier to identify deviant cases, detect coding errors, and estimate interrater reliability among multiple coders. 37 While such software helps to manage data, the actual analyses and interpretation still reside with the researcher.
Peer review, another common standard of rigor, is a process by which researchers invite an independent third-party researcher to analyze a detailed audit trail maintained by the study author. The audit trail methodically describes the step-by-step processes and decision-making throughout the study. Review of this audit trail occurs prior to manuscript development and enhances study confirmability. 1,16 The peer reviewer offers a critique of the study methods and validation of the conclusions drawn by the author as a thorough check on researcher bias.
Triangulation also plays a role in data analysis, as the term can also be used to describe how multiple sources of data can be used to confirm or refute interpretation, assertions, themes, and study conclusions. If a theme or theory can be arrived at and validated using multiple sources of data, the result of the study has greater credibility and confirmability. 16,33,36 Should any competing or controversial theories emerge during data collection or analysis, it is vital to the credibility and trustworthiness of the study that the author disclose and explore those negative cases. Negative case analysis refers to actively seeking out and scrutinizing data that do not fit or support the researcher’s interpretation of the data. 16
The use of best practices applying to data collection and data analysis facilitates the full examination of data relative to the study purpose and research question and helps to prevent premature closure of the study. Rather than stopping at the initial identification of literal, first-level assertion statements and themes, authors must progress to interpreting how results relate to, revise, or expand the conceptual framework, or offer an improved theory or model for explaining the study phenomenon of interest. Closing the loop on data collection is critical and is achieved when thorough and valid analysis can be linked back to the conceptual framework, as addressed in the next section.
Step 4: Drawing Valid Conclusions
Lingard and Kennedy 38 succinctly state that the purpose of qualitative research is to deepen one’s understanding of specific perspectives, observations, experiences, or events evidenced through the behaviors or products of individuals and groups as they are situated in specific contexts or circumstances. Conclusions generated from study results should enhance the conceptual framework, or contribute to a new theory or model development, and are most often situated within the discussion and conclusion sections of a manuscript.
The discussion section should include interpretation of the results and recommendations for practice. Interpretations should go beyond first-level results or literal description of observed behaviors, patterns, and themes from analysis. The author’s challenge is to provide a complete and thorough examination and explanation of how specific results relate to each other, contribute to answering the research question, and achieve the primary purpose of the research endeavor. The discussion should “close the loop” by integrating study results and analysis with the original conceptual framework. The discussion section should also provide a parsimonious narrative or graphical explanation and interpretation of study results that enhances understanding of the targeted phenomena.
The conclusion section should provide an overall picture or synopsis of the study, including its important and unique contributions to the field from the perspective of both conceptual and practical significance. The conclusion should also include personal and theoretical perspectives and future directions for research. Together, the discussion and conclusion should include responses to the larger questions of the study’s contributions, such as: So what? Why do these results matter? What next?
The strength of conclusions is dependent upon the extent to which standards of rigor and best practices were demonstrated in design, data collection, data analysis, and interpretation, as described in previous sections of this article. 4,12,17,23,24 Quality and rigor expectations for drawing valid conclusions and generating new theories are reflected in the following essential features of rigor and quality, which include: “Close the loop” to clearly link research questions, study design, data collection and analysis, and interpretation of results. Reflect effective integration of the study results with the conceptual framework and explain results in ways that relate, support, elaborate, and/or challenge conclusions of prior scholarship. Descriptions of new or enhanced frameworks or models are clear and effectively grounded in the study results and conclusions. Practical or theoretical implications are effectively discussed, including guidance for future studies. Limitations and issues of reflexivity and ethics are clearly and explicitly described, including references to actions taken to address these areas. 3,4,12,14
Step 5: Reporting Research Results
Key to quality reporting of qualitative research results are clarity, organization, completeness, accuracy, and conciseness in communicating the results to the reader of the research manuscript. O’Brien and others 4 proposed a standardized framework specifically for reporting qualitative studies known as the Standards for Reporting Qualitative Research (SRQR, Table 2 ). This framework provides detailed explanations of what should be reported in each of 21 sections of a qualitative research manuscript. While the SRQR does not explicitly mention a conceptual framework, the descriptions and table footnote clarification for the introduction and problem statement reflect the essential elements and focus of a conceptual framework. Ultimately, readers of published work determine levels of credibility, trustworthiness, and the like. A manuscript reviewer, the first reader of a study report, has the responsibility and privilege of providing critique and guidance to authors regarding achievement of quality criteria, execution and reporting of standards of rigor, and the extent to which meaningful contributions to thinking and practice in the field are presented. 13,39
An Adaptation of the 21 Elements of O’Brien and Colleagues’ Standards for Reporting Qualitative Research (SRQR) 4

Authors must avoid language heavy with connotations or adjectives that insert the researcher’s opinion into the database or manuscript. 14,40 The researcher should be as neutral and objective as possible in interpreting data and in presenting results. Thick and rich descriptions, where robust descriptive language is used to provide sufficient contextual information, enable the reader to determine credibility, transferability, dependability, and confirmability .
The process of demonstrating the credibility of research is rooted in honest and transparent reporting of how biases and other possible confounders were identified and addressed throughout study processes. Such reporting, first described within the study’s conceptual framework, should be revisited in reporting the work. Confounders may include the researcher’s training and previous experiences, personal connections to the background theory, access to the study population, and funding sources. These elements and processes are best represented in Glassick’s criteria for effective presentation and reflective critique ( Table 1 , criteria 5 and 6). Transferability is communicated, in part, through description of sampling factors such as: geographical location of the study, number and characteristics of participants, and the timeframe of data collection and analysis. 40 Such descriptions also contribute to the credibility of the results and readers’ determination of transfer to their and other contexts. To ensure dependability, the research method must be reported in detail such that the reader can determine proper research practices have been followed and that future researchers can repeat the study. 40 The confirmability of the results is influenced by reducing or at a minimum explaining any researcher influence on the result by applying and meeting standards of rigor such as member checking, triangulation, and peer review. 29,33
In qualitative studies, the researcher is often the primary instrument for data collection. Any researcher biases not adequately addressed or errors in judgement can affect the quality of data and subsequent research results. 33 Thus, due to the creative interpretative and contextually bound nature of qualitative studies, the application of standards of rigor and adherence to systematic processes well-documented in an audit trail are essential. The application of rigor and quality criteria extend beyond the researcher and are also important to effective peer review processes within a study and for scholarly dissemination. The goal of rigor in qualitative research can be described as ensuring that the research design, method, and conclusions are explicit, public, replicable, open to critique, and free of bias. 41 Rigor in the research process and results are achieved when each element of study methodology is systematic and transparent through complete, methodical, and accurate reporting. 33 Beginning the study with a well-developed conceptual framework and active use of both researcher reflexivity and rigorous peer review during study implementation can drive both study rigor and quality.
As the number of published qualitative studies in health professions educational research increases, it is important for our community of health care educators to keep in mind the unique aspects of rigor in qualitative studies presented here. Qualitative researchers should select and apply any of the above referenced study methods and research practices, as appropriate to the research question, to achieve rigor and quality. As in any research paradigm, the goal of quality and rigor in qualitative research is to minimize the risk of bias and maximize the accuracy and credibility of research results. Rigor is best achieved through thoughtful and deliberate planning, diligent and ongoing application of researcher reflexivity, and honest communication between the researcher and the audience regarding the study and its results.
Log in using your username and password
- Search More Search for this keyword Advanced search
- Latest content
- Current issue
- Write for Us
- BMJ Journals More You are viewing from: Google Indexer
You are here
- Volume 22, Issue 3
- Triangulation in research, with examples
- Article Text
- Article info
- Citation Tools
- Rapid Responses
- Article metrics
- Helen Noble 1 ,
- Roberta Heale 2
- 1 School of Nursing and Midwifery , Queens University Belfast , Belfast , UK
- 2 School of Nursing , Laurentian University , Sudbury , Ontario , Canada
- Correspondence to Dr Helen Noble, School of Nursing and Midwifery, Queen’s University Belfast, Belfast BT7 1NN, UK; helen.noble{at}qub.ac.uk
https://doi.org/10.1136/ebnurs-2019-103145
Statistics from Altmetric.com
Request permissions.
If you wish to reuse any or all of this article please use the link below which will take you to the Copyright Clearance Center’s RightsLink service. You will be able to get a quick price and instant permission to reuse the content in many different ways.
What is triangulation
Triangulation is a method used to increase the credibility and validity of research findings. 1 Credibility refers to trustworthiness and how believable a study is; validity is concerned with the extent to which a study accurately reflects or evaluates the concept or ideas being investigated. 2 Triangulation, by combining theories, methods or observers in a research study, can help ensure that fundamental biases arising from the use of a single method or a single observer are overcome. Triangulation is also an effort to help explore and explain complex human behaviour using a variety of methods to offer a more balanced explanation to readers. 2 It is a procedure that enables validation of data and can be used in both quantitative and qualitative studies.
Four types of triangulation are proposed by Denzin (p.301): 5 (1) data triangulation, which includes matters such as periods of time, space and people; (2) investigator triangulation, which includes the use of several researchers in a study; (3) theory triangulation, which encourages several theoretical schemes to enable interpretation of a phenomenon and (4) methodological triangulation, which promotes the use of several data collection methods such as interviews and observations.
Examples of studies using triangulation
Below, we offer two examples of triangulation within research studies, providing a context for each study and a description of how triangulation was used and successfully implemented to ensure an in-depth and more unbiased set of findings.
Johnson et al ,s 6 qualitative study aimed to identify system influences on decision making in a pre-hospital setting with paramedics. Several data sets were included and comprised exploratory interviews with ambulance service staff (n=16); document review observations of paramedic shifts (n=34); paramedic accounts (n=10) via audio-recorded ‘digital diaries’; staff focus groups (n=3) and service user focus groups (n=3) to explore a range of experiences and perceptions. The approach followed Denzin’s 5 multiple triangulation approach, which encourages several methods to collect data and multiple investigators with varied expertise.
Phase I of the study focused on understanding the context of the study and included interviews with ambulance service staff and the collection of demographics and local policies. The second phase involved observation of paramedics’ daily work in order to throw light on decisions related to transporting patients. Focus groups with paramedics, followed by focus groups with service users were then completed in order to share personal experiences of the decisions made by the ambulance service in practice. The final phase included workshops to feed back findings.
Data were coded and thematically analysed. The observations of paramedic shifts identified the complexities of the decision-making process related to the context. The observations were supplemented by the interviews and focus groups. Each research method exposed one aspect of reality. 5 This multimethod, multidisciplinary collaborative research was insightful. It permitted cross-validation, and facilitated exploration, of issues that influenced the decision making of paramedics and concerns and experiences of service users.
A study was undertaken to explore the quality of care for patients in a unique model of primary healthcare in Ontario, Canada: the Nurse Practitioner-Led Clinic (NPLC) 7 . The focus was on the care of patients with diabetes and at least one additional chronic condition, with the assumption that this group of patients represents those with the most complex clinical presentations managed in family practice settings. A multiple case study design was chosen for this research because with this approach, analysis of a variety of data arising from several NPLCs allowed for assumptions to be made about the model as a whole. 7 Additionally, both qualitative and quantitative research methods were used in the study. Mixing methods is a form of triangulation in research seen as mitigating the weaknesses found in single methods. 8
The first research method was a chart audit, conducted on randomly selected charts of adult patients in five NPLCs who had diabetes and at least one additional chronic condition. The variables included demographic items as well as clinical data related to the care of patients with diabetes. The data were analysed to determine the completeness of the care of diabetes for the subjects. 9
The second research method was interviews with nurse practitioners (NPs) working at the five NPLCs to determine their perceptions of the quality of care delivered in the NPLC model for patients with diabetes and other chronic conditions. Data from the interviews were analysed using the processes related to an integrative description design. 10 The draft themes arising from the analysis were forwarded to the participants for their feedback and were confirmed through a review of literature. Finally, a detailed document search was undertaken, including but not limited to academic articles, media releases and articles, letters to editor, government policy statements and publications released from the NPLCs. These data were used to confirm and support the findings of the chart review and NP interviews, representing triangulation.
With analysis completed separately for the qualitative and quantitative parts of the study, the final step was analysis of the NPLCs individually and then as a group. An extensive analysis process arising from Stake’s multiple case methodology was implemented. 11 This process included coding and identification of themes for individual NPLCs, then across the NPLC model as a whole. The final product represented triangulation in that each final theme represented analysis of data from at least two data sources, and literature was used to further support these conclusions.
Limitations of triangulation
Triangulation offers richness and clarity to research studies 8 but also has limitations. It adds to the complexity of the research making it more time-consuming. 6 When used as a method for combining research methodologies, triangulation may not be achieved in a uniform or consistent manner. Additionally, researchers may not adequately explain their techniques for blending results. 12 In addition, theremay be times when comparison of the findings of two sources is inconsistent or conflicting. Triangulation does not always adequately mitigate problems in a chosen research methodology. The processes of triangulation are complex and require a skilled analyst. Finally, the value of triangulation may be overestimated in some studies. 13
- Carvalho S ,
- Rothbauer P
- Johnson M ,
- Hirst E , et al
- Wenghofer E ,
- James S , et al
- Wenghofer E , et al
- Thurmond VA
Competing interests None declared.
Provenance and peer review Not commissioned; internally peer reviewed.
Patient consent for publication Not required.
Read the full text or download the PDF:
- Open access
- Published: 16 May 2024

Integrating qualitative research within a clinical trials unit: developing strategies and understanding their implementation in contexts
- Jeremy Segrott ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-6215-0870 1 ,
- Sue Channon 2 ,
- Amy Lloyd 4 ,
- Eleni Glarou 2 , 3 ,
- Josie Henley 5 ,
- Jacqueline Hughes 2 ,
- Nina Jacob 2 ,
- Sarah Milosevic 2 ,
- Yvonne Moriarty 2 ,
- Bethan Pell 6 ,
- Mike Robling 2 ,
- Heather Strange 2 ,
- Julia Townson 2 ,
- Qualitative Research Group &
- Lucy Brookes-Howell 2
Trials volume 25 , Article number: 323 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
239 Accesses
6 Altmetric
Metrics details
Background/aims
The value of using qualitative methods within clinical trials is widely recognised. How qualitative research is integrated within trials units to achieve this is less clear. This paper describes the process through which qualitative research has been integrated within Cardiff University’s Centre for Trials Research (CTR) in Wales, UK. We highlight facilitators of, and challenges to, integration.
We held group discussions on the work of the Qualitative Research Group (QRG) within CTR. The content of these discussions, materials for a presentation in CTR, and documents relating to the development of the QRG were interpreted at a workshop attended by group members. Normalisation Process Theory (NPT) was used to structure analysis. A writing group prepared a document for input from members of CTR, forming the basis of this paper.
Actions to integrate qualitative research comprised: its inclusion in Centre strategies; formation of a QRG with dedicated funding/roles; embedding of qualitative research within operating systems; capacity building/training; monitoring opportunities to include qualitative methods in studies; maximising the quality of qualitative research and developing methodological innovation. Facilitators of these actions included: the influence of the broader methodological landscape within trial/study design and its promotion of the value of qualitative research; and close physical proximity of CTR qualitative staff/students allowing sharing of methodological approaches. Introduction of innovative qualitative methods generated interest among other staff groups. Challenges included: pressure to under-resource qualitative components of research, preference for a statistical stance historically in some research areas and funding structures, and difficulties faced by qualitative researchers carving out individual academic profiles when working across trials/studies.
Conclusions
Given that CTUs are pivotal to the design and conduct of RCTs and related study types across multiple disciplines, integrating qualitative research into trials units is crucial if its contribution is to be fully realised. We have made explicit one trials unit’s experience of embedding qualitative research and present this to open dialogue on ways to operationalise and optimise qualitative research in trials. NPT provides a valuable framework with which to theorise these processes, including the importance of sense-making and legitimisation when introducing new practices within organisations.
Peer Review reports
The value of using qualitative methods within randomised control trials (RCTs) is widely recognised [ 1 , 2 , 3 ]. Qualitative research generates important evidence on factors affecting trial recruitment/retention [ 4 ] and implementation, aiding interpretation of quantitative data [ 5 ]. Though RCTs have traditionally been viewed as sitting within a positivist paradigm, recent methodological innovations have developed new trial designs that draw explicitly on both quantitative and qualitative methods. For instance, in the field of complex public health interventions, realist RCTs seek to understand the mechanisms through which interventions generate hypothesised impacts, and how interactions across different implementation contexts form part of these mechanisms. Proponents of realist RCTs—which integrate experimental and realist paradigms—highlight the importance of using quantitative and qualitative methods to fully realise these aims and to generate an understanding of intervention mechanisms and how context shapes them [ 6 ].
A need for guidance on how to conduct good quality qualitative research is being addressed, particularly in relation to feasibility studies for RCTs [ 7 ] and process evaluations embedded within trials of complex interventions [ 5 ]. There is also guidance on the conduct of qualitative research within trials at different points in the research cycle, including development, conduct and reporting [ 8 , 9 ].
A high proportion of trials are based within or involve clinical trials units (CTUs). In the UK the UKCRC Registered CTU Network describes them as:
… specialist units which have been set up with a specific remit to design, conduct, analyse and publish clinical trials and other well-designed studies. They have the capability to provide specialist expert statistical, epidemiological, and other methodological advice and coordination to undertake successful clinical trials. In addition, most CTUs will have expertise in the coordination of trials involving investigational medicinal products which must be conducted in compliance with the UK Regulations governing the conduct of clinical trials resulting from the EU Directive for Clinical Trials.
Thus, CTUs provide the specialist methodological expertise needed for the conduct of trials, and in the case of trials of investigational medicinal products, their involvement may be mandated to ensure compliance with relevant regulations. As the definition above suggests, CTUs also conduct and support other types of study apart from RCTs, providing a range of methodological and subject-based expertise.
However, despite their central role in the conduct and design of trials, (and other evaluation designs) little has been written about how CTUs have integrated qualitative work within their organisation at a time when such methods are, as stated above, now recognised as an important aspect of RCTs and evaluation studies more generally. This is a significant gap, since integration at the organisational level arguably shapes how qualitative research is integrated within individual studies, and thus it is valuable to understand how CTUs have approached the task. There are different ways of involving qualitative work in trials units, such as partnering with other departments (e.g. social science) or employing qualitative researchers directly. Qualitative research can be imagined and configured in different ways—as a method that generates data to inform future trial and intervention design, as an embedded component within an RCT or other evaluation type, or as a parallel strand of research focusing on lived experiences of illness, for instance. Understanding how trials units have integrated qualitative research is valuable, as it can shed light on which strategies show promise, and in which contexts, and how qualitative research is positioned within the field of trials research, foregrounding the value of qualitative research. However, although much has been written about its use within trials, few accounts exist of how trials units have integrated qualitative research within their systems and structures.
This paper discusses the process of embedding qualitative research within the work of one CTU—Cardiff University’s Centre for Trials Research (CTR). It highlights facilitators of this process and identifies challenges to integration. We use the Normalisation Process Theory (NPT) as a framework to structure our experience and approach. The key gap addressed by this paper is the implementation of strategies to integrate qualitative research (a relatively newly adopted set of practices and processes) within CTU systems and structures. We acknowledge from the outset that there are multiple ways of approaching this task. What follows therefore is not a set of recommendations for a preferred or best way to integrate qualitative research, as this will comprise diverse actions according to specific contexts. Rather, we examine the processes through which integration occurred in our own setting and highlight the potential value of these insights for others engaged in the work of promoting qualitative research within trials units.
Background to the integration of qualitative research within CTR
The CTR was formed in 2015 [ 10 ]. It brought together three existing trials units at Cardiff University: the South East Wales Trials Unit, the Wales Cancer Trials Unit, and the Haematology Clinical Trials Unit. From its inception, the CTR had a stated aim of developing a programme of qualitative research and integrating it within trials and other studies. In the sections below, we map these approaches onto the framework offered by Normalisation Process Theory to understand the processes through which they helped achieve embedding and integration of qualitative research.
CTR’s aims (including those relating to the development of qualitative research) were included within its strategy documents and communicated to others through infrastructure funding applications, annual reports and its website. A Qualitative Research Group (QRG), which had previously existed within the South East Wales Trials Unit, with dedicated funding for methodological specialists and group lead academics, was a key mechanism through which the development of a qualitative portfolio was put into action. Integration of qualitative research within Centre systems and processes occurred through the inclusion of qualitative research in study adoption processes and representation on committees. The CTR’s study portfolio provided a basis to track qualitative methods in new and existing studies, identify opportunities to embed qualitative methods within recently adopted studies (at the funding application stage) and to manage staff resources. Capacity building and training were an important focus of the QRG’s work, including training courses, mentoring, creation of an academic network open to university staff and practitioners working in the field of healthcare, presentations at CTR staff meetings and securing of PhD studentships. Standard operating procedures and methodological guidance on the design and conduct of qualitative research (e.g. templates for developing analysis plans) aimed to create a shared understanding of how to undertake high-quality research, and a means to monitor the implementation of rigorous approaches. As the QRG expanded its expertise it sought to develop innovative approaches, including the use of visual [ 11 ] and ethnographic methods [ 12 ].
Understanding implementation—Normalisation Process Theory (NPT)
Normalisation Process Theory (NPT) provides a model with which to understand the implementation of new sets of practices and their normalisation within organisational settings. The term ‘normalisation’ refers to how new practices become routinised (part of the everyday work of an organisation) through embedding and integration [ 13 , 14 ]. NPT defines implementation as ‘the social organisation of work’ and is concerned with the social processes that take place as new practices are introduced. Embedding involves ‘making practices routine elements of everyday life’ within an organisation. Integration takes the form of ‘sustaining embedded practices in social contexts’, and how these processes lead to the practices becoming (or not becoming) ‘normal and routine’ [ 14 ]. NPT is concerned with the factors which promote or ‘inhibit’ attempts to embed and integrate the operationalisation of new practices [ 13 , 14 , 15 ].
Embedding new practices is therefore achieved through implementation—which takes the form of interactions in specific contexts. Implementation is operationalised through four ‘generative mechanisms’— coherence , cognitive participation , collective action and reflexive monitoring [ 14 ]. Each mechanism is characterised by components comprising immediate and organisational work, with actions of individuals and organisations (or groups of individuals) interdependent. The mechanisms operate partly through forms of investment (i.e. meaning, commitment, effort, and comprehension) [ 14 ].
Coherence refers to how individuals/groups make sense of, and give meaning to, new practices. Sense-making concerns the coherence of a practice—whether it ‘holds together’, and its differentiation from existing activities [ 15 ]. Communal and individual specification involve understanding new practices and their potential benefits for oneself or an organisation. Individuals consider what new practices mean for them in terms of tasks and responsibilities ( internalisation ) [ 14 ].
NPT frames the second mechanism, cognitive participation , as the building of a ‘community of practice’. For a new practice to be initiated, individuals and groups within an organisation must commit to it [ 14 , 15 ]. Cognitive participation occurs through enrolment —how people relate to the new practice; legitimation —the belief that it is right for them to be involved; and activation —defining which actions are necessary to sustain the practice and their involvement [ 14 ]. Making the new practices work may require changes to roles (new responsibilities, altered procedures) and reconfiguring how colleagues work together (changed relationships).
Third, Collective Action refers to ‘the operational work that people do to enact a set of practices’ [ 14 ]. Individuals engage with the new practices ( interactional workability ) reshaping how members of an organisation interact with each other, through creation of new roles and expectations ( relational interaction ) [ 15 ]. Skill set workability concerns how the work of implementing a new set of practices is distributed and the necessary roles and skillsets defined [ 14 ]. Contextual integration draws attention to the incorporation of a practice within social contexts, and the potential for aspects of these contexts, such as systems and procedures, to be modified as a result [ 15 ].
Reflexive monitoring is the final implementation mechanism. Collective and individual appraisal evaluate the value of a set of practices, which depends on the collection of information—formally and informally ( systematisation ). Appraisal may lead to reconfiguration in which procedures of the practice are redefined or reshaped [ 14 , 15 ].
We sought to map the following: (1) the strategies used to embed qualitative research within the Centre, (2) key facilitators, and (3) barriers to their implementation. Through focused group discussions during the monthly meetings of the CTR QRG and in discussion with the CTR senior management team throughout 2019–2020 we identified nine types of documents (22 individual documents in total) produced within the CTR which had relevant information about the integration of qualitative research within its work (Table 1 ). The QRG had an ‘open door’ policy to membership and welcomed all staff/students with an interest in qualitative research. It included researchers who were employed specifically to undertake qualitative research and other staff with a range of study roles, including trial managers, statisticians, and data managers. There was also diversity in terms of career stage, including PhD students, mid-career researchers and members of the Centre’s Executive team. Membership was therefore largely self-selected, and comprised of individuals with a role related to, or an interest in, embedding qualitative research within trials. However, the group brought together diverse methodological perspectives and was not solely comprised of methodological ‘champions’ whose job it was to promote the development of qualitative research within the centre. Thus whilst the group (and by extension, the authors of this paper) had a shared appreciation of the value of qualitative research within a trials centre, they also brought varied methodological perspectives and ways of engaging with it.
All members of the QRG ( n = 26) were invited to take part in a face-to-face, day-long workshop in February 2019 on ‘How to optimise and operationalise qualitative research in trials: reflections on CTR structure’. The workshop was attended by 12 members of staff and PhD students, including members of the QRG and the CTR’s senior management team. Recruitment to the workshop was therefore inclusive, and to some extent opportunistic, but all members of the QRG were able to contribute to discussions during regular monthly group meetings and the drafting of the current paper.
The aim of the workshop was to bring together information from the documents in Table 1 to generate discussion around the key strategies (and their component activities) that had been adopted to integrate qualitative research into CTR, as well as barriers to, and facilitators of, their implementation. The agenda for the workshop involved four key areas: development and history of the CTR model; mapping the current model within CTR; discussing the structure of other CTUs; and exploring the advantages and disadvantages of the CTR model.
During the workshop, we discussed the use of NPT to conceptualise how qualitative research had been embedded within CTR’s systems and practices. The group produced spider diagrams to map strategies and actions on to the four key domains (or ‘generative mechanisms’ of NPT) summarised above, to aid the understanding of how they had functioned, and the utility of NPT as a framework. This is summarised in Table 2 .
Detailed notes were made during the workshop. A core writing group then used these notes and the documents in Table 1 to develop a draft of the current paper. This was circulated to all members of the CTR QRG ( n = 26) and stored within a central repository accessible to them to allow involvement and incorporate the views of those who were not able to attend the workshop. This draft was again presented for comments in the monthly CTR QRG meeting in February 2021 attended by n = 10. The Standards for QUality Improvement Reporting Excellence 2.0 (SQUIRE) guidelines were used to inform the structure and content of the paper (see supplementary material) [ 16 ].
In the following sections, we describe the strategies CTR adopted to integrate qualitative research. These are mapped against NPT’s four generative mechanisms to explore the processes through which the strategies promoted integration, and facilitators of and barriers to their implementation. A summary of the strategies and their functioning in terms of the generative mechanisms is provided in Table 2 .
Coherence—making sense of qualitative research
In CTR, many of the actions taken to build a portfolio of qualitative research were aimed at enabling colleagues, and external actors, to make sense of this set of methodologies. Centre-level strategies and grant applications for infrastructure funding highlighted the value of qualitative research, the added benefits it would bring, and positioned it as a legitimate set of practices alongside existing methods. For example, a 2014 application for renewal of trials unit infrastructure funding stated:
We are currently in the process of undertaking […] restructuring for our qualitative research team and are planning similar for trial management next year. The aim of this restructuring is to establish greater hierarchical management and opportunities for staff development and also provide a structure that can accommodate continuing growth.
Within the CTR, various forms of communication on the development of qualitative research were designed to enable staff and students to make sense of it, and to think through its potential value for them, and ways in which they might engage with it. These included presentations at staff meetings, informal meetings between project teams and the qualitative group lead, and the visibility of qualitative research on the public-facing Centre website and Centre committees and systems. For instance, qualitative methods were included (and framed as a distinct set of practices) within study adoption forms and committee agendas. Information for colleagues described how qualitative methods could be incorporated within funding applications for RCTs and other evaluation studies to generate new insights into questions research teams were already keen to answer, such as influences on intervention implementation fidelity. Where externally based chief investigators approached the Centre to be involved in new grant applications, the existence of the qualitative team and group lead enabled the inclusion of qualitative research to be actively promoted at an early stage, and such opportunities were highlighted in the Centre’s brochure for new collaborators. Monthly qualitative research network meetings—advertised across CTR and to external research collaborators, were also designed to create a shared understanding of qualitative research methods and their utility within trials and other study types (e.g. intervention development, feasibility studies, and observational studies). Training events (discussed in more detail below) also aided sense-making.
Several factors facilitated the promotion of qualitative research as a distinctive and valuable entity. Among these was the influence of the broader methodological landscape within trial design which was promoting the value of qualitative research, such as guidance on the evaluation of complex interventions by the Medical Research Council [ 17 ], and the growing emphasis placed on process evaluations within trials (with qualitative methods important in understanding participant experience and influences on implementation) [ 5 ]. The attention given to lived experience (both through process evaluations and the move to embed public involvement in trials) helped to frame qualitative research within the Centre as something that was appropriate, legitimate, and of value. Recognition by research funders of the value of qualitative research within studies was also helpful in normalising and legitimising its adoption within grant applications.
The inclusion of qualitative methods within influential methodological guidance helped CTR researchers to develop a ‘shared language’ around these methods, and a way that a common understanding of the role of qualitative research could be generated. One barrier to such sense-making work was the varying extent to which staff and teams had existing knowledge or experience of qualitative research. This varied across methodological and subject groups within the Centre and reflected the history of the individual trials units which had merged to form the Centre.
Cognitive participation—legitimising qualitative research
Senior CTR leaders promoted the value and legitimacy of qualitative research. Its inclusion in centre strategies, infrastructure funding applications, and in public-facing materials (e.g. website, investigator brochures), signalled that it was appropriate for individuals to conduct qualitative research within their roles, or to support others in doing so. Legitimisation also took place through informal channels, such as senior leadership support for qualitative research methods in staff meetings and participation in QRG seminars. Continued development of the QRG (with dedicated infrastructure funding) provided a visible identity and equivalence with other methodological groups (e.g. trial managers, statisticians).
Staff were asked to engage with qualitative research in two main ways. First, there was an expansion in the number of staff for whom qualitative research formed part of their formal role and responsibilities. One of the three trials units that merged to form CTR brought with it a qualitative team comprising methodological specialists and a group lead. CTR continued the expansion of this group with the creation of new roles and an enlarged nucleus of researchers for whom qualitative research was the sole focus of their work. In part, this was linked to the successful award of projects that included a large qualitative component, and that were coordinated by CTR (see Table 3 which describes the PUMA study).
Members of the QRG were encouraged to develop their own research ideas and to gain experience as principal investigators, and group seminars were used to explore new ideas and provide peer support. This was communicated through line management, appraisal, and informal peer interaction. Boundaries were not strictly demarcated (i.e. staff located outside the qualitative team were already using qualitative methods), but the new team became a central focus for developing a growing programme of work.
Second, individuals and studies were called upon to engage in new ways with qualitative research, and with the qualitative team. A key goal for the Centre was that groups developing new research ideas should give more consideration in general to the potential value and inclusion of qualitative research within their funding applications. Specifically, they were asked to do this by thinking about qualitative research at an early point in their application’s development (rather than ‘bolting it on’ after other elements had been designed) and to draw upon the expertise and input of the qualitative team. An example was the inclusion of questions on qualitative methods within the Centre’s study adoption form and representation from the qualitative team at the committee which reviewed new adoption requests. Where adoption requests indicated the inclusion of qualitative methods, colleagues were encouraged to liaise with the qualitative team, facilitating the integration of its expertise from an early stage. Qualitative seminars offered an informal and supportive space in which researchers could share initial ideas and refine their methodological approach. The benefits of this included the provision of sufficient time for methodological specialists to be involved in the design of the proposed qualitative component and ensuring adequate costings had been drawn up. At study adoption group meetings, scrutiny of new proposals included consideration of whether new research proposals might be strengthened through the use of qualitative methods where these had not initially been included. Meetings of the QRG—which reviewed the Centre’s portfolio of new studies and gathered intelligence on new ideas—also helped to identify, early on, opportunities to integrate qualitative methods. Communication across teams was useful in identifying new research ideas and embedding qualitative researchers within emerging study development groups.
Actions to promote greater use of qualitative methods in funding applications fed through into a growing number of studies with a qualitative component. This helped to increase the visibility and legitimacy of qualitative methods within the Centre. For example, the PUMA study [ 12 ], which brought together a large multidisciplinary team to develop and evaluate a Paediatric early warning system, drew heavily on qualitative methods, with the qualitative research located within the QRG. The project introduced an extensive network of collaborators and clinical colleagues to qualitative methods and how they could be used during intervention development and the generation of case studies. Further information about the PUMA study is provided in Table 3 .
Increasing the legitimacy of qualitative work across an extensive network of staff, students and collaborators was a complex process. Set within the continuing dominance of quantitative methods with clinical trials, there were variations in the extent to which clinicians and other collaborators embraced the value of qualitative methods. Research funding schemes, which often continued to emphasise the quantitative element of randomised controlled trials, inevitably fed through into the focus of new research proposals. Staff and external collaborators were sometimes uncertain about the added value that qualitative methods would bring to their trials. Across the CTR there were variations in the speed at which qualitative research methods gained legitimacy, partly based on disciplinary traditions and their influences. For instance, population health trials, often located within non-health settings such as schools or community settings, frequently involved collaboration with social scientists who brought with them experience in qualitative methods. Methodological guidance in this field, such as MRC guidance on process evaluations, highlighted the value of qualitative methods and alternatives to the positivist paradigm, such as the value of realist RCTs. In other, more clinical areas, positivist paradigms had greater dominance. Established practices and methodological traditions across different funders also influenced the ease of obtaining funding to include qualitative research within studies. For drugs trials (CTIMPs), the influence of regulatory frameworks on study design, data collection and the allocation of staff resources may have played a role. Over time, teams gained repeated experience of embedding qualitative research (and researchers) within their work and took this learning with them to subsequent studies. For example, the senior clinician quoted within the PUMA case study (Table 3 below) described how they had gained an appreciation of the rigour of qualitative research and an understanding of its language. Through these repeated interactions, embedding of qualitative research within studies started to become the norm rather than the exception.
Collective action—operationalising qualitative research
Collective action concerns the operationalisation of new practices within organisations—the allocation and management of the work, how individuals interact with each other, and the work itself. In CTR the formation of a Qualitative Research Group helped to allocate and organise the work of building a portfolio of studies. Researchers across the Centre were called upon to interact with qualitative research in new ways. Presentations at staff meetings and the inclusion of qualitative research methods in portfolio study adoption forms were examples of this ( interactive workability ). It was operationalised by encouraging study teams to liaise with the qualitative research lead. Development of standard operating procedures, templates for costing qualitative research and methodological guidance (e.g. on analysis plans) also helped encourage researchers to interact with these methods in new ways. For some qualitative researchers who had been trained in the social sciences, working within a trials unit meant that they needed to interact in new and sometimes unfamiliar ways with standard operating procedures, risk assessments, and other trial-based systems. Thus, training needs and capacity-building efforts were multidirectional.
Whereas there had been a tendency for qualitative research to be ‘bolted on’ to proposals for RCTs, the systems described above were designed to embed thinking about the value and design of the qualitative component from the outset. They were also intended to integrate members of the qualitative team with trial teams from an early stage to promote effective integration of qualitative methods within larger trials and build relationships over time.
Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs), formal and informal training, and interaction between the qualitative team and other researchers increased the relational workability of qualitative methods within the Centre—the confidence individuals felt in including these methods within their studies, and their accountability for doing so. For instance, study adoption forms prompted researchers to interact routinely with the qualitative team at an early stage, whilst guidance on costing grants provided clear expectations about the resources needed to deliver a proposed set of qualitative data collection.
Formation of the Qualitative Research Group—comprised of methodological specialists, created new roles and skillsets ( skill set workability ). Research teams were encouraged to draw on these when writing funding applications for projects that included a qualitative component. Capacity-building initiatives were used to increase the number of researchers with the skills needed to undertake qualitative research, and for these individuals to develop their expertise over time. This was achieved through formal training courses, academic seminars, mentoring from experienced colleagues, and informal knowledge exchange. Links with external collaborators and centres engaged in building qualitative research supported these efforts. Within the Centre, the co-location of qualitative researchers with other methodological and trial teams facilitated knowledge exchange and building of collaborative relationships, whilst grouping of the qualitative team within a dedicated office space supported a collective identity and opportunities for informal peer support.
Some aspects of the context in which qualitative research was being developed created challenges to operationalisation. Dependence on project grants to fund qualitative methodologists meant that there was a continuing need to write further grant applications whilst limiting the amount of time available to do so. Similarly, researchers within the team whose role was funded largely by specific research projects could sometimes find it hard to create sufficient time to develop their personal methodological interests. However, the cultivation of a methodologically varied portfolio of work enabled members of the team to build significant expertise in different approaches (e.g. ethnography, discourse analysis) that connected individual studies.
Reflexive monitoring—evaluating the impact of qualitative research
Inclusion of questions/fields relating to qualitative research within the Centre’s study portfolio database was a key way in which information was collected ( systematisation ). It captured numbers of funding applications and funded studies, research design, and income generation. Alongside this database, a qualitative resource planner spreadsheet was used to link individual members of the qualitative team with projects and facilitate resource planning, further reinforcing the core responsibilities and roles of qualitative researchers within CTR. As with all staff in the Centre, members of the qualitative team were placed on ongoing rather than fixed-term contracts, reflecting their core role within CTR. Planning and strategy meetings used the database and resource planner to assess the integration of qualitative research within Centre research, identify opportunities for increasing involvement, and manage staff recruitment and sustainability of researcher posts. Academic meetings and day-to-day interaction fulfilled informal appraisal of the development of the group, and its position within the Centre. Individual appraisal was also important, with members of the qualitative team given opportunities to shape their role, reflect on progress, identify training needs, and further develop their skillset, particularly through line management systems.
These forms of systematisation and appraisal were used to reconfigure the development of qualitative research and its integration within the Centre. For example, group strategies considered how to achieve long-term integration of qualitative research from its initial embedding through further promoting the belief that it formed a core part of the Centre’s business. The visibility and legitimacy of qualitative research were promoted through initiatives such as greater prominence on the Centre’s website. Ongoing review of the qualitative portfolio and discussion at academic meetings enabled the identification of areas where increased capacity would be helpful, both for qualitative staff, and more broadly within the Centre. This prompted the qualitative group to develop an introductory course to qualitative methods open to all Centre staff and PhD students, aimed at increasing understanding and awareness. As the qualitative team built its expertise and experience it also sought to develop new and innovative approaches to conducting qualitative research. This included the use of visual and diary-based methods [ 11 ] and the adoption of ethnography to evaluate system-level clinical interventions [ 12 ]. Restrictions on conventional face-to-face qualitative data collection due to the COVID-19 pandemic prompted rapid adoption of virtual/online methods for interviews, observation, and use of new internet platforms such as Padlet—a form of digital note board.
In this paper, we have described the work undertaken by one CTU to integrate qualitative research within its studies and organisational culture. The parallel efforts of many trials units to achieve these goals arguably come at an opportune time. The traditional designs of RCTs have been challenged and re-imagined by the increasing influence of realist evaluation [ 6 , 18 ] and the widespread acceptance that trials need to understand implementation and intervention theory as well as assess outcomes [ 17 ]. Hence the widespread adoption of embedded mixed methods process evaluations within RCTs. These broad shifts in methodological orthodoxies, the production of high-profile methodological guidance, and the expectations of research funders all create fertile ground for the continued expansion of qualitative methods within trials units. However, whilst much has been written about the importance of developing qualitative research and the possible approaches to integrating qualitative and quantitative methods within studies, much less has been published on how to operationalise this within trials units. Filling this lacuna is important. Our paper highlights how the integration of a new set of practices within an organisation can become embedded as part of its ‘normal’ everyday work whilst also shaping the practices being integrated. In the case of CTR, it could be argued that the integration of qualitative research helped shape how this work was done (e.g. systems to assess progress and innovation).
In our trials unit, the presence of a dedicated research group of methodological specialists was a key action that helped realise the development of a portfolio of qualitative research and was perhaps the most visible evidence of a commitment to do so. However, our experience demonstrates that to fully realise the goal of developing qualitative research, much work focuses on the interaction between this ‘new’ set of methods and the organisation into which it is introduced. Whilst the team of methodological specialists was tasked with, and ‘able’ to do the work, the ‘work’ itself needed to be integrated and embedded within the existing system. Thus, alongside the creation of a team and methodological capacity, promoting the legitimacy of qualitative research was important to communicate to others that it was both a distinctive and different entity, yet similar and equivalent to more established groups and practices (e.g. trial management, statistics, data management). The framing of qualitative research within strategies, the messages given out by senior leaders (formally and informally) and the general visibility of qualitative research within the system all helped to achieve this.
Normalisation Process Theory draws our attention to the concepts of embedding (making a new practice routine, normal within an organisation) and integration —the long-term sustaining of these processes. An important process through which embedding took place in our centre concerned the creation of messages and systems that called upon individuals and research teams to interact with qualitative research. Research teams were encouraged to think about qualitative research and consider its potential value for their studies. Critically, they were asked to do so at specific points, and in particular ways. Early consideration of qualitative methods to maximise and optimise their inclusion within studies was emphasised, with timely input from the qualitative team. Study adoption systems, centre-level processes for managing financial and human resources, creation of a qualitative resource planner, and awareness raising among staff, helped to reinforce this. These processes of embedding and integration were complex and they varied in intensity and speed across different areas of the Centre’s work. In part this depended on existing research traditions, the extent of prior experience of working with qualitative researchers and methods, and the priorities of subject areas and funders. Centre-wide systems, sometimes linked to CTR’s operation as a CTU, also helped to legitimise and embed qualitative research, lending it equivalence with other research activity. For example, like all CTUs, CTR was required to conform with the principles of Good Clinical Practice, necessitating the creation of a quality management system, operationalised through standard operating procedures for all areas of its work. Qualitative research was included, and became embedded, within these systems, with SOPs produced to guide activities such as qualitative analysis.
NPT provides a helpful way of understanding how trials units might integrate qualitative research within their work. It highlights how new practices interact with existing organisational systems and the work needed to promote effective interaction. That is, alongside the creation of a team or programme of qualitative research, much of the work concerns how members of an organisation understand it, engage with it, and create systems to sustain it. Embedding a new set of practices may be just as important as the quality or characteristics of the practices themselves. High-quality qualitative research is of little value if it is not recognised and drawn upon within new studies for instance. NPT also offers a helpful lens with which to understand how integration and embedding occur, and the mechanisms through which they operate. For example, promoting the legitimacy of a new set of practices, or creating systems that embed it, can help sustain these practices by creating an organisational ambition and encouraging (or requiring) individuals to interact with them in certain ways, redefining their roles accordingly. NPT highlights the ways in which integration of new practices involves bi-directional exchanges with the organisation’s existing practices, with each having the potential to re-shape the other as interaction takes place. For instance, in CTR, qualitative researchers needed to integrate and apply their methods within the quality management and other systems of a CTU, such as the formalisation of key processes within standard operating procedures, something less likely to occur outside trials units. Equally, project teams (including those led by externally based chief investigators) increased the integration of qualitative methods within their overall study design, providing opportunities for new insights on intervention theory, implementation and the experiences of practitioners and participants.
We note two aspects of the normalisation processes within CTR that are slightly less well conceptualised by NPT. The first concerns the emphasis within coherence on identifying the distinctiveness of new practices, and how they differ from existing activities. Whilst differentiation was an important aspect of the integration of qualitative research in CTR, such integration could be seen as operating partly through processes of de-differentiation, or at least equivalence. That is, part of the integration of qualitative research was to see it as similar in terms of rigour, coherence, and importance to other forms of research within the Centre. To be viewed as similar, or at least comparable to existing practices, was to be legitimised.
Second, whilst NPT focuses mainly on the interaction between a new set of practices and the organisational context into which it is introduced, our own experience of introducing qualitative research into a trials unit was shaped by broader organisational and methodological contexts. For example, the increasing emphasis placed upon understanding implementation processes and the experiences of research participants in the field of clinical trials (e.g. by funders), created an environment conducive to the development of qualitative research methods within our Centre. Attempts to integrate qualitative research within studies were also cross-organisational, given that many of the studies managed within the CTR drew together multi-institutional teams. This provided important opportunities to integrate qualitative research within a portfolio of studies that extended beyond CTR and build a network of collaborators who increasingly included qualitative methods within their funding proposals. The work of growing and integrating qualitative research within a trials unit is an ongoing one in which ever-shifting macro-level influences can help or hinder, and where the organisations within which we work are never static in terms of barriers and facilitators.
The importance of utilising qualitative methods within RCTs is now widely recognised. Increased emphasis on the evaluation of complex interventions, the influence of realist methods directing greater attention to complexity and the widespread adoption of mixed methods process evaluations are key drivers of this shift. The inclusion of qualitative methods within individual trials is important and previous research has explored approaches to their incorporation and some of the challenges encountered. Our paper highlights that the integration of qualitative methods at the organisational level of the CTU can shape how they are taken up by individual trials. Within CTR, it can be argued that qualitative research achieved high levels of integration, as conceptualised by Normalisation Process Theory. Thus, qualitative research became recognised as a coherent and valuable set of practices, secured legitimisation as an appropriate focus of individual and organisational activity and benefitted from forms of collective action which operationalised these organisational processes. Crucially, the routinisation of qualitative research appeared to be sustained, something which NPT suggests helps define integration (as opposed to initial embedding). However, our analysis suggested that the degree of integration varied by trial area. This variation reflected a complex mix of factors including disciplinary traditions, methodological guidance, existing (un)familiarity with qualitative research, and the influence of regulatory frameworks for certain clinical trials.
NPT provides a valuable framework with which to understand how these processes of embedding and integration occur. Our use of NPT draws attention to the importance of sense-making and legitimisation as important steps in introducing a new set of practices within the work of an organisation. Integration also depends, across each mechanism of NPT, on the building of effective relationships, which allow individuals and teams to work together in new ways. By reflecting on our experiences and the decisions taken within CTR we have made explicit one such process for embedding qualitative research within a trials unit, whilst acknowledging that approaches may differ across trials units. Mindful of this fact, and the focus of the current paper on one trials unit’s experience, we do not propose a set of recommendations for others who are working to achieve similar goals. Rather, we offer three overarching reflections (framed by NPT) which may act as a useful starting point for trials units (and other infrastructures) seeking to promote the adoption of qualitative research.
First, whilst research organisations such as trials units are highly heterogenous, processes of embedding and integration, which we have foregrounded in this paper, are likely to be important across different contexts in sustaining the use of qualitative research. Second, developing a plan for the integration of qualitative research will benefit from mapping out the characteristics of the extant system. For example, it is valuable to know how familiar staff are with qualitative research and any variations across teams within an organisation. Thirdly, NPT frames integration as a process of implementation which operates through key generative mechanisms— coherence , cognitive participation , collective action and reflexive monitoring . These mechanisms can help guide understanding of which actions help achieve embedding and integration. Importantly, they span multiple aspects of how organisations, and the individuals within them, work. The ways in which people make sense of a new set of practices ( coherence ), their commitment towards it ( cognitive participation ), how it is operationalised ( collective action ) and the evaluation of its introduction ( reflexive monitoring ) are all important. Thus, for example, qualitative research, even when well organised and operationalised within an organisation, is unlikely to be sustained if appreciation of its value is limited, or people are not committed to it.
We present our experience of engaging with the processes described above to open dialogue with other trials units on ways to operationalise and optimise qualitative research in trials. Understanding how best to integrate qualitative research within these settings may help to fully realise the significant contribution which it makes the design and conduct of trials.
Availability of data and materials
Some documents cited in this paper are either freely available from the Centre for Trials Research website or can be requested from the author for correspondence.
O’Cathain A, Thomas KJ, Drabble SJ, Rudolph A, Hewison J. What can qualitative research do for randomised controlled trials? A systematic mapping review. BMJ Open. 2013;3(6):e002889.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
O’Cathain A, Thomas KJ, Drabble SJ, Rudolph A, Goode J, Hewison J. Maximising the value of combining qualitative research and randomised controlled trials in health research: the QUAlitative Research in Trials (QUART) study – a mixed methods study. Health Technol Assess. 2014;18(38):1–197.
Clement C, Edwards SL, Rapport F, Russell IT, Hutchings HA. Exploring qualitative methods reported in registered trials and their yields (EQUITY): systematic review. Trials. 2018;19(1):589.
Hennessy M, Hunter A, Healy P, Galvin S, Houghton C. Improving trial recruitment processes: how qualitative methodologies can be used to address the top 10 research priorities identified within the PRioRiTy study. Trials. 2018;19:584.
Moore GF, Audrey S, Barker M, Bond L, Bonell C, Hardeman W, et al. Process evaluation of complex interventions: Medical Research Council guidance. BMJ. 2015;350(mar19 6):h1258.
Bonell C, Fletcher A, Morton M, Lorenc T, Moore L. Realist randomised controlled trials: a new approach to evaluating complex public health interventions. Soc Sci Med. 2012;75(12):2299–306.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
O’Cathain A, Hoddinott P, Lewin S, Thomas KJ, Young B, Adamson J, et al. Maximising the impact of qualitative research in feasibility studies for randomised controlled trials: guidance for researchers. Pilot Feasibility Stud. 2015;1:32.
Cooper C, O’Cathain A, Hind D, Adamson J, Lawton J, Baird W. Conducting qualitative research within Clinical Trials Units: avoiding potential pitfalls. Contemp Clin Trials. 2014;38(2):338–43.
Rapport F, Storey M, Porter A, Snooks H, Jones K, Peconi J, et al. Qualitative research within trials: developing a standard operating procedure for a clinical trials unit. Trials. 2013;14:54.
Cardiff University. Centre for Trials Research. Available from: https://www.cardiff.ac.uk/centre-for-trials-research . Accessed 10 May 2024.
Pell B, Williams D, Phillips R, Sanders J, Edwards A, Choy E, et al. Using visual timelines in telephone interviews: reflections and lessons learned from the star family study. Int J Qual Methods. 2020;19:160940692091367.
Thomas-Jones E, Lloyd A, Roland D, Sefton G, Tume L, Hood K, et al. A prospective, mixed-methods, before and after study to identify the evidence base for the core components of an effective Paediatric Early Warning System and the development of an implementation package containing those core recommendations for use in th. BMC Pediatr. 2018;18:244.
May C, Finch T, Mair F, Ballini L, Dowrick C, Eccles M, et al. Understanding the implementation of complex interventions in health care: the normalization process model. BMC Health Serv Res. 2007;7:148.
May C, Finch T. Implementing, embedding, and integrating practices: an outline of normalization process theory. Sociology. 2009;43(3):535–54.
Article Google Scholar
May CR, Mair F, Finch T, Macfarlane A, Dowrick C, Treweek S, et al. Development of a theory of implementation and integration: normalization process theory. Implement Sci. 2009;4:29.
Ogrinc G, Davies L, Goodman D, Batalden PB, Davidoff F, Stevens D. SQUIRE 2.0 (Standards for QUality Improvement Reporting Excellence): Revised publication guidelines from a detailed consensus process. BMJ Quality and Safety. 2016;25:986-92.
Craig P, Dieppe P, Macintyre S, Michie S, Nazareth I, Petticrew M. Developing and evaluating complex interventions: the new Medical Research Council guidance. BMJ. 2008;337:a1655.
Jamal F, Fletcher A, Shackleton N, Elbourne D, Viner R, Bonell C. The three stages of building and testing mid-level theories in a realist RCT: a theoretical and methodological case-example. Trials. 2015;16(1):466.
Download references
Acknowledgements
Members of the Centre for Trials Research (CTR) Qualitative Research Group were collaborating authors: C Drew (Senior Research Fellow—Senior Trial Manager, Brain Health and Mental Wellbeing Division), D Gillespie (Director, Infection, Inflammation and Immunity Trials, Principal Research Fellow), R Hale (now Research Associate, School of Social Sciences, Cardiff University), J Latchem-Hastings (now Lecturer and Postdoctoral Fellow, School of Healthcare Sciences, Cardiff University), R Milton (Research Associate—Trial Manager), B Pell (now PhD student, DECIPHer Centre, Cardiff University), H Prout (Research Associate—Qualitative), V Shepherd (Senior Research Fellow), K Smallman (Research Associate), H Stanton (Research Associate—Senior Data Manager). Thanks are due to Kerry Hood and Aimee Grant for their involvement in developing processes and systems for qualitative research within CTR.
No specific grant was received to support the writing of this paper.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Centre for Trials Research, DECIPHer Centre, Cardiff University, Neuadd Meirionnydd, Heath Park, Cardiff, CF14 4YS, UK
Jeremy Segrott
Centre for Trials Research, Cardiff University, Neuadd Meirionnydd, Heath Park, Cardiff, CF14 4YS, UK
Sue Channon, Eleni Glarou, Jacqueline Hughes, Nina Jacob, Sarah Milosevic, Yvonne Moriarty, Mike Robling, Heather Strange, Julia Townson & Lucy Brookes-Howell
Division of Population Medicine, School of Medicine, Cardiff University, Neuadd Meirionnydd, Heath Park, Cardiff, CF14 4YS, UK
Eleni Glarou
Wales Centre for Public Policy, Cardiff University, Sbarc I Spark, Maindy Road, Cardiff, CF24 4HQ, UK
School of Social Sciences, Cardiff University, King Edward VII Avenue, Cardiff, CF10 3WA, UK
Josie Henley
DECIPHer Centre, School of Social Sciences, Cardiff University, Sbarc I Spark, Maindy Road, Cardiff, CF24 4HQ, UK
Bethan Pell
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Qualitative Research Group
- , D. Gillespie
- , J. Latchem-Hastings
- , R. Milton
- , V. Shepherd
- , K. Smallman
- & H. Stanton
Contributions
JS contributed to the design of the work and interpretation of data and was responsible for leading the drafting and revision of the paper. SC contributed to the design of the work, the acquisition of data and the drafting and revision of the paper. AL contributed to the design of the work, the acquisition of data and the drafting and revision of the paper. EG contributed to a critical review of the manuscript and provided additional relevant references. JH provided feedback on initial drafts of the paper and contributed to subsequent revisions. JHu provided feedback on initial drafts of the paper and contributed to subsequent revisions. NG provided feedback on initial drafts of the paper and contributed to subsequent revisions. SM was involved in the acquisition and analysis of data and provided a critical review of the manuscript. YM was involved in the acquisition and analysis of data and provided a critical review of the manuscript. MR was involved in the interpretation of data and critical review and revision of the paper. HS contributed to the conception and design of the work, the acquisition and analysis of data, and the revision of the manuscript. JT provided feedback on initial drafts of the paper and contributed to subsequent revisions. LB-H made a substantial contribution to the design and conception of the work, led the acquisition and analysis of data, and contributed to the drafting and revision of the paper.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Jeremy Segrott .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Ethical approval was not sought as no personal or identifiable data was collected.
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
All authors are or were members of staff or students in the Centre for Trials Research. JS is an associate editor of Trials .
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Supplementary material 1., rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Segrott, J., Channon, S., Lloyd, A. et al. Integrating qualitative research within a clinical trials unit: developing strategies and understanding their implementation in contexts. Trials 25 , 323 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13063-024-08124-7
Download citation
Received : 20 October 2023
Accepted : 17 April 2024
Published : 16 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s13063-024-08124-7
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Qualitative research
- Qualitative methods
- Trials units
- Normalisation Process Theory
- Randomised controlled trials
ISSN: 1745-6215
- Submission enquiries: Access here and click Contact Us
- General enquiries: [email protected]
- Open access
- Published: 13 May 2024
Patient medication management, understanding and adherence during the transition from hospital to outpatient care - a qualitative longitudinal study in polymorbid patients with type 2 diabetes
- Léa Solh Dost ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-5767-1305 1 , 2 ,
- Giacomo Gastaldi ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-6327-7451 3 &
- Marie P. Schneider ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-7557-9278 1 , 2
BMC Health Services Research volume 24 , Article number: 620 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
310 Accesses
Metrics details
Continuity of care is under great pressure during the transition from hospital to outpatient care. Medication changes during hospitalization may be poorly communicated and understood, compromising patient safety during the transition from hospital to home. The main aims of this study were to investigate the perspectives of patients with type 2 diabetes and multimorbidities on their medications from hospital discharge to outpatient care, and their healthcare journey through the outpatient healthcare system. In this article, we present the results focusing on patients’ perspectives of their medications from hospital to two months after discharge.
Patients with type 2 diabetes, with at least two comorbidities and who returned home after discharge, were recruited during their hospitalization. A descriptive qualitative longitudinal research approach was adopted, with four in-depth semi-structured interviews per participant over a period of two months after discharge. Interviews were based on semi-structured guides, transcribed verbatim, and a thematic analysis was conducted.
Twenty-one participants were included from October 2020 to July 2021. Seventy-five interviews were conducted. Three main themes were identified: (A) Medication management, (B) Medication understanding, and (C) Medication adherence, during three periods: (1) Hospitalization, (2) Care transition, and (3) Outpatient care. Participants had varying levels of need for medication information and involvement in medication management during hospitalization and in outpatient care. The transition from hospital to autonomous medication management was difficult for most participants, who quickly returned to their routines with some participants experiencing difficulties in medication adherence.
Conclusions
The transition from hospital to outpatient care is a challenging process during which discharged patients are vulnerable and are willing to take steps to better manage, understand, and adhere to their medications. The resulting tension between patients’ difficulties with their medications and lack of standardized healthcare support calls for interprofessional guidelines to better address patients’ needs, increase their safety, and standardize physicians’, pharmacists’, and nurses’ roles and responsibilities.
Peer Review reports
Introduction
Continuity of patient care is characterized as the collaborative engagement between the patient and their physician-led care team in the ongoing management of healthcare, with the mutual objective of delivering high-quality and cost-effective medical care [ 1 ]. Continuity of care is under great pressure during the transition of care from hospital to outpatient care, with a risk of compromising patients’ safety [ 2 , 3 ]. The early post-discharge period is a high-risk and fragile transition: once discharged, one in five patients experience at least one adverse event during the first three weeks following discharge, and more than half of these adverse events are drug-related [ 4 , 5 ]. A retrospective study examining all discharged patients showed that adverse drug events (ADEs) account for up to 20% of 30-day hospital emergency readmissions [ 6 ]. During hospitalization, patients’ medications are generally modified, with an average of nearly four medication changes per patient [ 7 ]. Information regarding medications such as medication changes, the expected effect, side effects, and instructions for use are frequently poorly communicated to patients during hospitalization and at discharge [ 8 , 9 , 10 , 11 ]. Between 20 and 60% of discharged patients lack knowledge of their medications [ 12 , 13 ]. Consideration of patients’ needs and their active engagement in decision-making during hospitalization regarding their medications are often lacking [ 11 , 14 , 15 ]. This can lead to unsafe discharge and contribute to medication adherence difficulties, such as non-implementation of newly prescribed medications [ 16 , 17 ].
Patients with multiple comorbidities and polypharmacy are at higher risk of ADE [ 18 ]. Type 2 diabetes is one of the chronic health conditions most frequently associated with comorbidities and patients with type 2 diabetes often lack care continuum [ 19 , 20 , 21 ]. The prevalence of patients hospitalized with type 2 diabetes can exceed 40% [ 22 ] and these patients are at higher risk for readmission due to their comorbidities and their medications, such as insulin and oral hypoglycemic agents [ 23 , 24 , 25 ].
Interventions and strategies to improve patient care and safety at transition have shown mixed results worldwide in reducing cost, rehospitalization, ADE, and non-adherence [ 26 , 27 , 28 , 29 , 30 , 31 , 32 , 33 , 34 , 35 ]. However, interventions that are patient-centered, with a patient follow-up and led by interprofessional healthcare teams showed promising results [ 34 , 35 , 36 ]. Most of these interventions have not been implemented routinely due to the extensive time to translate research into practice and the lack of hybrid implementation studies [ 37 , 38 , 39 , 40 , 41 ]. In addition, patient-reported outcomes and perspectives have rarely been considered, yet patients’ involvement is essential for seamless and integrated care [ 42 , 43 ]. Interprofessional collaboration in which patients are full members of the interprofessional team, is still in its infancy in outpatient care [ 44 ]. Barriers and facilitators regarding medications at the transition of care have been explored in multiple qualitative studies at one given time in a given setting (e.g., at discharge, one-month post-discharge) [ 8 , 45 , 46 , 47 , 48 ]. However, few studies have adopted a holistic methodology from the hospital to the outpatient setting to explore changes in patients’ perspectives over time [ 49 , 50 , 51 ]. Finally, little is known about whether, how, and when patients return to their daily routine following hospitalization and the impact of hospitalization weeks after discharge.
In Switzerland, continuity of care after hospital discharge is still poorly documented, both in terms of contextual analysis and interventional studies, and is mainly conducted in the hospital setting [ 31 , 35 , 52 , 53 , 54 , 55 , 56 ]. The first step of an implementation science approach is to perform a contextual analysis to set up effective interventions adapted to patients’ needs and aligned to healthcare professionals’ activities in a specific context [ 41 , 57 ]. Therefore, the main aims of this study were to investigate the perspectives of patients with type 2 diabetes and multimorbidities on their medications from hospital discharge to outpatient care, and on their healthcare journey through the outpatient healthcare system. In this article, we present the results focusing on patients’ perspectives of their medications from hospital to two months after discharge.
Study design
This qualitative longitudinal study, conducted from October 2020 to July 2021, used a qualitative descriptive methodology through four consecutive in-depth semi-structured interviews per participant at three, 10-, 30- and 60-days post-discharge, as illustrated in Fig. 1 . Longitudinal qualitative research is characterized by qualitative data collection at different points in time and focuses on temporality, such as time and change [ 58 , 59 ]. Qualitative descriptive studies aim to explore and describe the depth and complexity of human experiences or phenomena [ 60 , 61 , 62 ]. We focused our qualitative study on the 60 first days after discharge as this period is considered highly vulnerable and because studies often use 30- or 60-days readmission as an outcome measure [ 5 , 63 ].
This qualitative study follows the Consolidated Criteria for Reporting Qualitative Research (COREQ). Ethics committee approval was sought and granted by the Cantonal Research Ethics Commission, Geneva (CCER) (2020 − 01779).
Recruitment took place during participants’ hospitalization in the general internal medicine divisions at the Geneva University Hospitals in the canton of Geneva (500 000 inhabitants), Switzerland. Interviews took place at participants’ homes, in a private office at the University of Geneva, by telephone or by secure video call, according to participants’ preference. Informal caregivers could also participate alongside the participants.
Study flowchart
Researcher characteristics
All the researchers were trained in qualitative studies. The diabetologist and researcher (GG) who enrolled the patients in the study was involved directly or indirectly (advice asked to the Geneva University Hospital diabetes team of which he was a part) for most participants’ care during hospitalization. LS (Ph.D. student and community pharmacist) was unknown to participants and presented herself during hospitalization as a “researcher” and not as a healthcare professional to avoid any risk of influencing participants’ answers. This study was not interventional, and the interviewer (LS) invited participants to contact a healthcare professional for any questions related to their medication or medical issues.
Population and sampling strategy
Patients with type 2 diabetes were chosen as an example population to describe polypharmacy patients as these patients usually have several health issues and polypharmacy [ 20 , 22 , 25 ]. Inclusions criteria for the study were: adult patients with type 2 diabetes, with at least two other comorbidities, hospitalized for at least three days in a general internal medicine ward, with a minimum of one medication change during hospital stay, and who self-managed their medications once discharged home. Exclusion criteria were patients not reachable by telephone following discharge, unable to give consent (patients with schizophrenia, dementia, brain damage, or drug/alcohol misuse), and who could not communicate in French. A purposive sampling methodology was applied aiming to include participants with different ages, genders, types, and numbers of health conditions by listing participants’ characteristics in a double-entry table, available in Supplementary Material 1 , until thematic saturation was reached. Thematic saturation was considered achieved when no new code or theme emerged and new data repeated previously coded information [ 64 ]. The participants were identified if they were hospitalized in the ward dedicated to diabetes care or when the diabetes team was contacted for advice. The senior ward physician (GG) screened eligible patients and the interviewer (LS) obtained written consent before hospital discharge.
Data collection and instruments
Sociodemographic (age, gender, educational level, living arrangement) and clinical characteristics (reason for hospitalization, date of admission, health conditions, diabetes diagnosis, medications before and during hospitalization) were collected by interviewing participants before their discharge and by extracting participants’ data from electronic hospital files by GG and LS. Participants’ pharmacies were contacted with the participant’s consent to obtain medication records from the last three months if information regarding medications before hospitalization was missing in the hospital files.
Semi-structured interview guides for each interview (at three, 10-, 30- and 60-days post-discharge) were developed based on different theories and components of health behavior and medication adherence: the World Health Organization’s (WHO) five dimensions for adherence, the Information-Motivation-Behavioral skills model and the Social Cognitive Theory [ 65 , 66 , 67 ]. Each interview explored participants’ itinerary in the healthcare system and their perspectives on their medications. Regarding medications, the following themes were mentioned at each interview: changes in medications, patients’ understanding and implication; information on their medications, self-management of their medications, and patients’ medication adherence. Other aspects were mentioned in specific interviews: patients’ hospitalization and experience on their return home (interview 1), motivation (interviews 2 and 4), and patient’s feedback on the past two months (interview 4). Interview guides translated from French are available in Supplementary Material 2 . The participants completed self-reported and self-administrated questionnaires at different interviews to obtain descriptive information on different factors that may affect medication management and adherence: self-report questionnaires on quality of life (EQ-5D-5 L) [ 68 ], literacy (Schooling-Opinion-Support questionnaire) [ 69 ], medication adherence (Adherence Visual Analogue Scale, A-VAS) [ 70 ] and Belief in Medication Questionnaire (BMQ) [ 71 ] were administered to each participant at the end of selected interviews to address the different factors that may affect medication management and adherence as well as to determine a trend of determinants over time. The BMQ contains two subscores: Specific-Necessity and Specific-Concerns, addressing respectively their perceived needs for their medications, and their concerns about adverse consequences associated with taking their medication [ 72 ].
Data management
Informed consent forms, including consent to obtain health data, were securely stored in a private office at the University of Geneva. The participants’ identification key was protected by a password known only by MS and LS. Confidentiality was guaranteed by pseudonymization of participants’ information and audio-recordings were destroyed once analyzed. Sociodemographic and clinical characteristics, medication changes, and answers to questionnaires were securely collected by electronic case report forms (eCRFs) on RedCap®. Interviews were double audio-recorded and field notes were taken during interviews. Recorded interviews were manually transcribed verbatim in MAXQDA® (2018.2) by research assistants and LS and transcripts were validated for accuracy by LS. A random sample of 20% of questionnaires was checked for accuracy for the transcription from the paper questionnaires to the eCRFs. Recorded sequences with no link to the discussed topics were not transcribed and this was noted in the transcripts.
Data analysis
A descriptive statistical analysis of sociodemographic, clinical characteristics and self-reported questionnaire data was carried out. A thematic analysis of transcripts was performed, as described by Braun and Clarke [ 73 ], by following six steps: raw data was read, text segments related to the study objectives were identified, text segments to create new categories were identified, similar or redundant categories were reduced and a model that integrated all significant categories was created. The analysis was conducted in parallel with patient enrolment to ensure data saturation. To ensure the validity of the coding method, transcripts were double coded independently and discussed by the research team until similar themes were obtained. The research group developed and validated an analysis grid, with which LS coded systematically the transcriptions and met regularly with the research team to discuss questions on data analysis and to ensure the quality of coding. The analysis was carried out in French, and the verbatims of interest cited in the manuscript were translated and validated by a native English-speaking researcher to preserve the meaning.
In this analysis, we used the term “healthcare professionals” when more than one profession could be involved in participants’ medication management. Otherwise, when a specific healthcare professional was involved, we used the designated profession (e.g. physicians, pharmacists).
Patient and public involvement
During the development phase of the study, interview guides and questionnaires were reviewed for clarity and validity and adapted by two patient partners, with multiple health conditions and who experienced previously a hospital discharge. They are part of the HUG Patients Partners + 3P platform for research and patient and public involvement.
Interviews and participants’ descriptions
A total of 75 interviews were conducted with 21 participants. In total, 31 patients were contacted, seven refused to participate (four at the project presentation and three at consent), two did not enter the selection criteria at discharge and one was unreachable after discharge. Among the 21 participants, 15 participated in all interviews, four in three interviews, one in two interviews, and one in one interview, due to scheduling constraints. Details regarding interviews and participants characteristics are presented in Tables 1 and 2 .
The median length of time between hospital discharge and interviews 1,2,3 and 4 was 5 (IQR: 4–7), 14 (13-20), 35 (22-38), and 63 days (61-68), respectively. On average, by comparing medications at hospital admission and discharge, a median of 7 medication changes (IQR: 6–9, range:2;17) occurred per participant during hospitalization and a median of 7 changes (5–12) during the two months following discharge. Details regarding participants’ medications are described in Table 3 .
Patient self-reported adherence over the past week for their three most challenging medications are available in Supplementary Material 3 .
Qualitative analysis
We defined care transition as the period from discharge until the first medical appointment post-discharge, and outpatient care as the period starting after the first medical appointment. Data was organized into three key themes (A. Medication management, B. Medication understanding, and C. Medication adherence) divided into subthemes at three time points (1. Hospitalization, 2. Care transition and 3. Outpatient care). Figure 2 summarizes and illustrates the themes and subthemes with their influencing factors as bullet points.
Participants’ medication management, understanding and adherence during hospitalization, care transition and outpatient care
A. Medication management
A.1 medication management during hospitalization: medication management by hospital staff.
Medications during hospitalization were mainly managed by hospital healthcare professionals (i.e. nurses and physicians) with varying degrees of patient involvement: “At the hospital, they prepared the medications for me. […] I didn’t even know what the packages looked like.” Participant 22; interview 1 (P22.1) Some participants reported having therapeutic education sessions with specialized nurses and physicians, such as the explanation and demonstration of insulin injection and glucose monitoring. A patient reported that he was given the choice of several treatments and was involved in shared decision-making. Other participants had an active role in managing and optimizing dosages, such as rapid insulin, due to prior knowledge and use of medications before hospitalization.
A.2 Medication management at transition: obtaining the medication and initiating self-management
Once discharged, some participants had difficulties obtaining their medications at the pharmacy because some medications were not stored and had to be ordered, delaying medication initiation. To counter this problem upstream, a few participants were provided a 24-to-48-hour supply of medications at discharge. It was sometimes requested by the patient or suggested by the healthcare professionals but was not systematic. The transition from medication management by hospital staff to self-management was exhausting for most participants who were faced with a large amount of new information and changes in their medications: “ When I was in the hospital, I didn’t even realize all the changes. When I came back home, I took away the old medication packages and got out the new ones. And then I thought : « my God, all this…I didn’t know I had all these changes » ” P2.1 Written documentation, such as the discharge prescription or dosage labels on medication packages, was helpful in managing their medication at home. Most participants used weekly pill organizers to manage their medications, which were either already used before hospitalization or were introduced post-discharge. The help of a family caregiver in managing and obtaining medications was reported as a facilitator.
A.3 Medication management in outpatient care: daily self-management and medication burden
A couple of days or weeks after discharge, most participants had acquired a routine so that medication management was less demanding, but the medication burden varied depending on the participants. For some, medication management became a simple action well implemented in their routine (“It has become automatic” , P23.4), while for others, the number of medications and the fact that the medications reminded them of the disease was a heavy burden to bear on a daily basis (“ During the first few days after getting out of the hospital, I thought I was going to do everything right. In the end, well [laughs] it’s complicated. I ended up not always taking the medication, not monitoring the blood sugar” P12.2) To support medication self-management, some participants had written documentation such as treatment plans, medication lists, and pictures of their medication packages on their phones. Some participants had difficulties obtaining medications weeks after discharge as discharge prescriptions were not renewable and participants did not see their physician in time. Others had to visit multiple physicians to have their prescriptions updated. A few participants were faced with prescription or dispensing errors, such as prescribing or dispensing the wrong dosage, which affected medication management and decreased trust in healthcare professionals. In most cases, according to participants, the pharmacy staff worked in an interprofessional collaboration with physicians to provide new and updated prescriptions.
B. Medication understanding
B.1 medication understanding during hospitalization: new information and instructions.
The amount of information received during hospitalization varied considerably among participants with some reporting having received too much, while others saying they received too little information regarding medication changes, the reason for changes, or for introducing new medications: “They told me I had to take this medication all my life, but they didn’t tell me what the effects were or why I was taking it.” P5.3
Hospitalization was seen by some participants as a vulnerable and tiring period during which they were less receptive to information. Information and explanations were generally given verbally, making it complicated for most participants to recall it. Some participants reported that hospital staff was attentive to their needs for information and used communication techniques such as teach-back (a way of checking understanding by asking participants to say in their own words what they need to know or do about their health or medications). Some participants were willing to be proactive in the understanding of their medications while others were more passive, had no specific needs for information, and did not see how they could be engaged more.
B.2 Medication understanding at transition: facing medication changes
At hospital discharge, the most challenging difficulty for participants was to understand the changes made regarding their medications. For newly diagnosed participants, the addition of new medications was more difficult to understand, whereas, for experienced participants, changes in known medications such as dosage modification, changes within a therapeutic class, and generic substitutions were the most difficult to understand. Not having been informed about changes caused confusion and misunderstanding. Therefore, medication reconciliation done by the patient was time-consuming, especially for participants with multiple medications: “ They didn’t tell me at all that they had changed my treatment completely. They just told me : « We’ve changed a few things. But it was the whole treatment ». ” P2.3 Written information, such as the discharge prescription, the discharge report (brief letter summarizing information about the hospitalization, given to the patient at discharge), or the label on the medication box (written by the pharmacist with instructions on dosage) helped them find or recall information about their medications and diagnoses. However, technical terms were used in hospital documentations and were not always understandable. For example, this participant said: “ On the prescription of valsartan, they wrote: ‘resume in the morning once profile…’[once hypertension profile allows]… I don’t know what that means.” P8.1 In addition, some documents were incomplete, as mentioned by a patient who did not have the insulin dosage mentioned on the hospital prescription. Some participants sought help from healthcare professionals, such as pharmacists, hospital physicians, or general practitioners a few days after discharge to review medications, answer questions, or obtain additional information.
B.3 Medication understanding in the outpatient care: concerns and knowledge
Weeks after discharge, most participants had concerns about the long-term use of their medications, their usefulness, and the possible risk of interactions or side effects. Some participants also reported having some lack of knowledge regarding indications, names, or how the medication worked: “I don’t even know what Brilique® [ticagrelor, antiplatelet agent] is for. It’s for blood pressure, isn’t it?. I don’t know.” P11.4 According to participants, the main reasons for the lack of understanding were the lack of information at the time of prescribing and the large number of medications, making it difficult to search for information and remember it. Participants sought information from different healthcare professionals or by themselves, on package inserts, through the internet, or from family and friends. Others reported having had all the information needed or were not interested in having more information. In addition, participants with low medication literacy, such as non-native speakers or elderly people, struggled more with medication understanding and sought help from family caregivers or healthcare professionals, even weeks after discharge: “ I don’t understand French very well […] [The doctor] explained it very quickly…[…] I didn’t understand everything he was saying” P16.2
C. Medication adherence
C.2 medication adherence at transition: adopting new behaviors.
Medication adherence was not mentioned as a concern during hospitalization and a few participants reported difficulties in medication initiation once back home: “I have an injection of Lantus® [insulin] in the morning, but obviously, the first day [after discharge], I forgot to do it because I was not used to it.” P23.1 Participants had to quickly adopt new behaviors in the first few days after discharge, especially for participants with few medications pre-hospitalization. The use of weekly pill organizers, alarms and specific storage space were reported as facilitators to support adherence. One patient did not initiate one of his medications because he did not understand the medication indication, and another patient took her old medications because she was used to them. Moreover, most participants experienced their hospitalization as a turning point, a time when they focused on their health, thought about the importance of their medications, and discussed any new lifestyle or dietary measures that might be implemented.
C.3 Medication adherence in outpatient care: ongoing medication adherence
More medication adherence difficulties appeared a few weeks after hospital discharge when most participants reported nonadherence behaviors, such as difficulties implementing the dosage regimen, or intentionally discontinuing the medication and modifying the medication regimen on their initiative. Determinants positively influencing medication adherence were the establishment of a routine; organizing medications in weekly pill-organizers; organizing pocket doses (medications for a short period that participants take with them when away from home); seeking support from family caregivers; using alarm clocks; and using specific storage places. Reasons for nonadherence were changes in daily routine; intake times that were not convenient for the patient; the large number of medications; and poor knowledge of the medication or side effects. Healthcare professionals’ assistance for medication management, such as the help of home nurses or pharmacists for the preparation of weekly pill-organizers, was requested by participants or offered by healthcare professionals to support medication adherence: “ I needed [a home nurse] to put my pills in the pillbox. […] I felt really weak […] and I was making mistakes. So, I’m very happy [the doctor] offered me [home care]. […] I have so many medications.” P22.3 Some participants who experienced prehospitalization non-adherence were more aware of their non-adherence and implemented strategies, such as modifying the timing of intake: “I said to my doctor : « I forget one time out of two […], can I take them in the morning? » We looked it up and yes, I can take it in the morning.” P11.2 In contrast, some participants were still struggling with adherence difficulties that they had before hospitalization. Motivations for taking medications two months after discharge were to improve health, avoid complications, reduce symptoms, reduce the number of medications in the future or out of obligation: “ I force myself to take them because I want to get to the end of my diabetes, I want to reduce the number of pills as much as possible.” P14.2 After a few weeks post-hospitalization, for some participants, health and illness were no longer the priority because of other life imperatives (e.g., family or financial situation).
This longitudinal study provided a multi-faceted representation of how patients manage, understand, and adhere to their medications from hospital discharge to two months after discharge. Our findings highlighted the varying degree of participants’ involvement in managing their medications during their hospitalization, the individualized needs for information during and after hospitalization, the complicated transition from hospital to autonomous medication management, the adaptation of daily routines around medication once back home, and the adherence difficulties that surfaced in the outpatient care, with nonadherence prior to hospitalization being an indicator of the behavior after discharge. Finally, our results confirmed the lack of continuity in care and showed the lack of patient care standardization experienced by the participants during the transition from hospital to outpatient care.
This in-depth analysis of patients’ experiences reinforces common challenges identified in the existing literature such as the lack of personalized information [ 9 , 10 , 11 ], loss of autonomy during hospitalization [ 14 , 74 , 75 ], difficulties in obtaining medication at discharge [ 11 , 45 , 76 ] and challenges in understanding treatment modifications and generics substitution [ 11 , 32 , 77 , 78 ]. Some of these studies were conducted during patients’ hospitalization [ 10 , 75 , 79 ] or up to 12 months after discharge [ 80 , 81 ], but most studies focused on the few days following hospital discharge [ 9 , 11 , 14 , 82 ]. Qualitative studies on medications at transition often focused on a specific topic, such as medication information, or a specific moment in time, and often included healthcare professionals, which muted patients’ voices [ 9 , 10 , 11 , 47 , 49 ]. Our qualitative longitudinal methodology was interested in capturing the temporal dynamics, in-depth narratives, and contextual nuances of patients’ medication experiences during transitions of care [ 59 , 83 ]. This approach provided a comprehensive understanding of how patients’ perspectives and behaviors evolved over time, offering insights into the complex interactions of medication management, understanding and adherence, and turning points within their medication journeys. A qualitative longitudinal design was used by Fylan et al. to underline patients’ resilience in medication management during and after discharge, by Brandberg et al. to show the dynamic process of self-management during the 4 weeks post-discharge and by Lawton et al. to examine how patients with type 2 diabetes perceived their care after discharge over a period of four years [ 49 , 50 , 51 ]. Our study focused on the first two months following hospitalization and future studies should focus on following discharged and at-risk patients over a longer period, as “transitions of care do not comprise linear trajectories of patients’ movements, with a starting and finishing point. Instead, they are endless loops of movements” [ 47 ].
Our results provide a particularly thorough description of how participants move from a state of total dependency during hospitalization regarding their medication management to a sudden and complete autonomy after hospital discharge impacting medication management, understanding, and adherence in the first days after discharge for some participants. Several qualitative studies have described the lack of shared decision-making and the loss of patient autonomy during hospitalization, which had an impact on self-management and created conflicts with healthcare professionals [ 75 , 81 , 84 ]. Our study also highlights nuanced patient experiences, including varying levels of patient needs, involvement, and proactivity during hospitalization and outpatient care, and our results contribute to capturing different perspectives that contrast with some literature that often portrays patients as more passive recipients of care [ 14 , 15 , 74 , 75 ]. Shared decision-making and proactive medication are key elements as they contribute to a smoother transition and better outcomes for patients post-discharge [ 85 , 86 , 87 ].
Consistent with the literature, the study identifies some challenges in medication initiation post-discharge [ 16 , 17 , 88 ] but our results also describe how daily routine rapidly takes over, either solidifying adherence behavior or generating barriers to medication adherence. Participants’ nonadherence prior to hospitalization was a factor influencing participants’ adherence post-hospitalization and this association should be further investigated, as literature showed that hospitalized patients have high scores of non-adherence [ 89 ]. Mortel et al. showed that more than 20% of discharged patients stopped their medications earlier than agreed with the physician and 25% adapted their medication intake [ 90 ]. Furthermore, patients who self-managed their medications had a lower perception of the necessity of their medication than patients who received help, which could negatively impact medication adherence [ 91 ]. Although participants in our study had high BMQ scores for necessity and lower scores for concerns, some participants expressed doubts about the need for their medications and a lack of motivation a few weeks after discharge. Targeted pharmacy interventions for newly prescribed medications have been shown to improve medication adherence, and hospital discharge is an opportune moment to implement this service [ 92 , 93 ].
Many medication changes were made during the transition of care (a median number of 7 changes during hospitalization and 7 changes during the two months after discharge), especially medication additions during hospitalization and interruptions after hospitalization. While medication changes during hospitalization are well described, the many changes following discharge are less discussed [ 7 , 94 ]. A Danish study showed that approximately 65% of changes made during hospitalization were accepted by primary healthcare professionals but only 43% of new medications initiated during hospitalization were continued after discharge [ 95 ]. The numerous changes after discharge may be caused by unnecessary intensification of medications during hospitalization, delayed discharge letters, lack of standardized procedures, miscommunication, patient self-management difficulties, or in response to an acute situation [ 96 , 97 , 98 ]. During the transition of care, in our study, both new and experienced participants were faced with difficulties in managing and understanding medication changes, either for newly prescribed medication or changes in previous medications. Such difficulties corroborate the findings of the literature [ 9 , 10 , 47 ] and our results showed that the lack of understanding during hospitalization led to participants having questions about their medications, even weeks after discharge. Particular attention should be given to patients’ understanding of medication changes jointly by physicians, nurses and pharmacists during the transition of care and in the months that follow as medications are likely to undergo as many changes as during hospitalization.
Implication for practice and future research
The patients’ perspectives in this study showed, at a system level, that there was a lack of standardization in healthcare professional practices regarding medication dispensing and follow-up. For now, in Switzerland, there are no official guidelines on medication prescription and dispensation during the transition of care although some international guidelines have been developed for outpatient healthcare professionals [ 3 , 99 , 100 , 101 , 102 ]. Here are some suggestions for improvement arising from our results. Patients should be included as partners and healthcare professionals should systematically assess (i) previous medication adherence, (ii) patients’ desired level of involvement and (iii) their needs for information during hospitalization. Hospital discharge processes should be routinely implemented to standardize hospital discharge preparation, medication prescribing, and dispensing. Discharge from the hospital should be planned with community pharmacies to ensure that all medications are available and, if necessary, doses of medications should be supplied by the hospital to bridge the gap. A partnership with outpatient healthcare professionals, such as general practitioners, community pharmacists, and homecare nurses, should be set up for effective asynchronous interprofessional collaboration to consolidate patients’ medication management, knowledge, and adherence, as well as to monitor signs of deterioration or adverse drug events.
Future research should consolidate our first attempt to develop a framework to better characterize medication at the transition of care, using Fig. 2 as a starting point. Contextualized interventions, co-designed by health professionals, patients and stakeholders, should be tested in a hybrid implementation study to test the implementation and effectiveness of the intervention for the health system [ 103 ].
Limitations
This study has some limitations. First, the transcripts were validated for accuracy by the interviewer but not by a third party, which could have increased the robustness of the transcription. Nevertheless, the interviewer followed all methodological recommendations for transcription. Second, patient inclusion took place during the COVID-19 pandemic, which may have had an impact on patient care and the availability of healthcare professionals. Third, we cannot guarantee the accuracy of some participants’ medication history before hospitalization, even though we contacted the participants’ main pharmacy, as participants could have gone to different pharmacies to obtain their medications. Fourth, our findings may not be generalizable to other populations and other healthcare systems because some issues may be specific to multimorbid patients with type 2 diabetes or to the Swiss healthcare setting. Nevertheless, issues encountered by our participants regarding their medications correlate with findings in the literature. Fifth, only 15 out of 21 participants took part in all the interviews, but most participants took part in at least three interviews and data saturation was reached. Lastly, by its qualitative and longitudinal design, it is possible that the discussion during interviews and participants’ reflections between interviews influenced participants’ management, knowledge, and adherence, even though this study was observational, and no advice or recommendations were given by the interviewer during interviews.
Discharged patients are willing to take steps to better manage, understand, and adhere to their medications, yet they are also faced with difficulties in the hospital and outpatient care. Furthermore, extensive changes in medications not only occur during hospitalization but also during the two months following hospital discharge, for which healthcare professionals should give particular attention. The different degrees of patients’ involvement, needs and resources should be carefully considered to enable them to better manage, understand and adhere to their medications. At a system level, patients’ experiences revealed a lack of standardization of medication practices during the transition of care. The healthcare system should provide the ecosystem needed for healthcare professionals responsible for or involved in the management of patients’ medications during the hospital stay, discharge, and outpatient care to standardize their practices while considering the patient as an active partner.
Data availability
The anonymized quantitative survey datasets and the qualitative codes are available in French from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
adverse drug events
Adherence Visual Analogue Scale
Belief in Medication Questionnaire
Consolidated Criteria for Reporting Qualitative Research
case report form
standard deviation
World Health Organization
American Academy of Family Physician. Continuity of Care, Definition of 2020. Accessed 10 July 2022 https://www.aafp.org/about/policies/all/continuity-of-care-definition.html
Kripalani S, LeFevre F, Phillips CO, Williams MV, Basaviah P, Baker DW. Deficits in communication and information transfer between hospital-based and primary care physicians: implications for patient safety and continuity of care. JAMA. 2007;297(8):831–41.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
World Health Organization (WHO). Medication Safety in Transitions of Care. 2019.
Forster AJ, Murff HJ, Peterson JF, Gandhi TK, Bates DW. The incidence and severity of adverse events affecting patients after discharge from the hospital. Ann Intern Med. 2003;138(3):161–7.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Krumholz HM. Post-hospital syndrome–an acquired, transient condition of generalized risk. N Engl J Med. 2013;368(2):100–2.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Banholzer S, Dunkelmann L, Haschke M, Derungs A, Exadaktylos A, Krähenbühl S, et al. Retrospective analysis of adverse drug reactions leading to short-term emergency hospital readmission. Swiss Med Wkly. 2021;151:w20400.
Blozik E, Signorell A, Reich O. How does hospitalization affect continuity of drug therapy: an exploratory study. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2016;12:1277–83.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Allen J, Hutchinson AM, Brown R, Livingston PM. User experience and care for older people transitioning from hospital to home: patients’ and carers’ perspectives. Health Expect. 2018;21(2):518–27.
Daliri S, Bekker CL, Buurman BM, Scholte Op Reimer WJM, van den Bemt BJF, Karapinar-Çarkit F. Barriers and facilitators with medication use during the transition from hospital to home: a qualitative study among patients. BMC Health Serv Res. 2019;19(1):204.
Bekker CL, Mohsenian Naghani S, Natsch S, Wartenberg NS, van den Bemt BJF. Information needs and patient perceptions of the quality of medication information available in hospitals: a mixed method study. Int J Clin Pharm. 2020;42(6):1396–404.
Foulon V, Wuyts J, Desplenter F, Spinewine A, Lacour V, Paulus D, et al. Problems in continuity of medication management upon transition between primary and secondary care: patients’ and professionals’ experiences. Acta Clin Belgica: Int J Clin Lab Med. 2019;74(4):263–71.
Article Google Scholar
Micheli P, Kossovsky MP, Gerstel E, Louis-Simonet M, Sigaud P, Perneger TV, et al. Patients’ knowledge of drug treatments after hospitalisation: the key role of information. Swiss Med Wkly. 2007;137(43–44):614–20.
PubMed Google Scholar
Ziaeian B, Araujo KL, Van Ness PH, Horwitz LI. Medication reconciliation accuracy and patient understanding of intended medication changes on hospital discharge. J Gen Intern Med. 2012;27(11):1513–20.
Allen J, Hutchinson AM, Brown R, Livingston PM. User experience and care integration in Transitional Care for older people from hospital to home: a Meta-synthesis. Qual Health Res. 2016;27(1):24–36.
Mackridge AJ, Rodgers R, Lee D, Morecroft CW, Krska J. Cross-sectional survey of patients’ need for information and support with medicines after discharge from hospital. Int J Pharm Pract. 2018;26(5):433–41.
Mulhem E, Lick D, Varughese J, Barton E, Ripley T, Haveman J. Adherence to medications after hospital discharge in the elderly. Int J Family Med. 2013;2013:901845.
Fallis BA, Dhalla IA, Klemensberg J, Bell CM. Primary medication non-adherence after discharge from a general internal medicine service. PLoS ONE. 2013;8(5):e61735.
Zhou L, Rupa AP. Categorization and association analysis of risk factors for adverse drug events. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2018;74(4):389–404.
Moreau-Gruet F. La multimorbidité chez les personnes de 50 ans et plus. Résultats basés sur l’enqête SHARE (Survey of Health, Ageing and Retirement in Europe. Obsan Bulletin 4/2013. 2013(Neuchâtel: OBservatoire suisse de la santé).
Iglay K, Hannachi H, Joseph Howie P, Xu J, Li X, Engel SS, et al. Prevalence and co-prevalence of comorbidities among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Curr Med Res Opin. 2016;32(7):1243–52.
Sibounheuang P, Olson PS, Kittiboonyakun P. Patients’ and healthcare providers’ perspectives on diabetes management: a systematic review of qualitative studies. Res Social Adm Pharm. 2020;16(7):854–74.
Müller-Wieland D, Merkel M, Hamann A, Siegel E, Ottillinger B, Woker R, et al. Survey to estimate the prevalence of type 2 diabetes mellitus in hospital patients in Germany by systematic HbA1c measurement upon admission. Int J Clin Pract. 2018;72(12):e13273.
Blanc AL, Fumeaux T, Stirnemann J, Dupuis Lozeron E, Ourhamoune A, Desmeules J, et al. Development of a predictive score for potentially avoidable hospital readmissions for general internal medicine patients. PLoS ONE. 2019;14(7):e0219348.
Hansen LO, Greenwald JL, Budnitz T, Howell E, Halasyamani L, Maynard G, et al. Project BOOST: effectiveness of a multihospital effort to reduce rehospitalization. J Hosp Med. 2013;8(8):421–7.
Khalid JM, Raluy-Callado M, Curtis BH, Boye KS, Maguire A, Reaney M. Rates and risk of hospitalisation among patients with type 2 diabetes: retrospective cohort study using the UK General Practice Research Database linked to English Hospital Episode statistics. Int J Clin Pract. 2014;68(1):40–8.
Lussier ME, Evans HJ, Wright EA, Gionfriddo MR. The impact of community pharmacist involvement on transitions of care: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Pharm Assoc. 2020;60(1):153–.
van der Heijden A, de Bruijne MC, Nijpels G, Hugtenburg JG. Cost-effectiveness of a clinical medication review in vulnerable older patients at hospital discharge, a randomized controlled trial. Int J Clin Pharm. 2019;41(4):963–71.
Bingham J, Campbell P, Schussel K, Taylor AM, Boesen K, Harrington A, et al. The Discharge Companion Program: an interprofessional collaboration in Transitional Care Model Delivery. Pharm (Basel). 2019;7(2):68.
Google Scholar
Farris KB, Carter BL, Xu Y, Dawson JD, Shelsky C, Weetman DB, et al. Effect of a care transition intervention by pharmacists: an RCT. BMC Health Serv Res. 2014;14:406.
Meslot C, Gauchet A, Hagger MS, Chatzisarantis N, Lehmann A, Allenet B. A Randomised Controlled Trial to test the effectiveness of planning strategies to improve Medication Adherence in patients with Cardiovascular Disease. Appl Psychol Health Well Being. 2017;9(1):106–29.
Garnier A, Rouiller N, Gachoud D, Nachar C, Voirol P, Griesser AC, et al. Effectiveness of a transition plan at discharge of patients hospitalized with heart failure: a before-and-after study. ESC Heart Fail. 2018;5(4):657–67.
Daliri S, Bekker CL, Buurman BM, Scholte Op Reimer WJM, van den Bemt BJF, Karapinar-Çarkit F. Medication management during transitions from hospital to home: a focus group study with hospital and primary healthcare providers in the Netherlands. Int J Clin Pharm. 2020.
Hansen LO, Young RS, Hinami K, Leung A, Williams MV. Interventions to reduce 30-day rehospitalization: a systematic review. Ann Intern Med. 2011;155(8):520–8.
Leppin AL, Gionfriddo MR, Kessler M, Brito JP, Mair FS, Gallacher K, et al. Preventing 30-day hospital readmissions: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized trials. JAMA Intern Med. 2014;174(7):1095–107.
Donzé J, John G, Genné D, Mancinetti M, Gouveia A, Méan M et al. Effects of a Multimodal Transitional Care Intervention in patients at high risk of readmission: the TARGET-READ Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Intern Med. 2023.
Rodrigues CR, Harrington AR, Murdock N, Holmes JT, Borzadek EZ, Calabro K, et al. Effect of pharmacy-supported transition-of-care interventions on 30-Day readmissions: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. Ann Pharmacother. 2017;51(10):866–89.
Lam MYY, Dodds LJ, Corlett SA. Engaging patients to access the community pharmacy medicine review service after discharge from hospital: a cross-sectional study in England. Int J Clin Pharm. 2019;41(4):1110–7.
Hossain LN, Fernandez-Llimos F, Luckett T, Moullin JC, Durks D, Franco-Trigo L, et al. Qualitative meta-synthesis of barriers and facilitators that influence the implementation of community pharmacy services: perspectives of patients, nurses and general medical practitioners. BMJ Open. 2017;7(9):e015471.
En-Nasery-de Heer S, Uitvlugt EB, Bet PM, van den Bemt BJF, Alai A, van den Bemt P et al. Implementation of a pharmacist-led transitional pharmaceutical care programme: process evaluation of medication actions to reduce hospital admissions through a collaboration between Community and Hospital pharmacists (MARCH). J Clin Pharm Ther. 2022.
Morris ZS, Wooding S, Grant J. The answer is 17 years, what is the question: understanding time lags in translational research. J R Soc Med. 2011;104(12):510–20.
De Geest S, Zúñiga F, Brunkert T, Deschodt M, Zullig LL, Wyss K, et al. Powering Swiss health care for the future: implementation science to bridge the valley of death. Swiss Med Wkly. 2020;150:w20323.
Noonan VK, Lyddiatt A, Ware P, Jaglal SB, Riopelle RJ, Bingham CO 3, et al. Montreal Accord on patient-reported outcomes (PROs) use series - paper 3: patient-reported outcomes can facilitate shared decision-making and guide self-management. J Clin Epidemiol. 2017;89:125–35.
Hesselink G, Schoonhoven L, Barach P, Spijker A, Gademan P, Kalkman C, et al. Improving patient handovers from hospital to primary care: a systematic review. Ann Intern Med. 2012;157(6):417–28.
(OFSP) Interprofessionnalité dans le domaine de la santé Soins ambulatoire. Accessed 4 January 2024. https://www.bag.admin.ch/bag/fr/home/strategie-und-politik/nationale-gesundheitspolitik/foerderprogramme-der-fachkraefteinitiative-plus/foerderprogramme-interprofessionalitaet.html
Mitchell SE, Laurens V, Weigel GM, Hirschman KB, Scott AM, Nguyen HQ, et al. Care transitions from patient and caregiver perspectives. Ann Fam Med. 2018;16(3):225–31.
Davoody N, Koch S, Krakau I, Hägglund M. Post-discharge stroke patients’ information needs as input to proposing patient-centred eHealth services. BMC Med Inf Decis Mak. 2016;16:66.
Ozavci G, Bucknall T, Woodward-Kron R, Hughes C, Jorm C, Joseph K, et al. A systematic review of older patients’ experiences and perceptions of communication about managing medication across transitions of care. Res Social Adm Pharm. 2021;17(2):273–91.
Fylan B, Armitage G, Naylor D, Blenkinsopp A. A qualitative study of patient involvement in medicines management after hospital discharge: an under-recognised source of systems resilience. BMJ Qual Saf. 2018;27(7):539–46.
Fylan B, Marques I, Ismail H, Breen L, Gardner P, Armitage G, et al. Gaps, traps, bridges and props: a mixed-methods study of resilience in the medicines management system for patients with heart failure at hospital discharge. BMJ Open. 2019;9(2):e023440.
Brandberg C, Ekstedt M, Flink M. Self-management challenges following hospital discharge for patients with multimorbidity: a longitudinal qualitative study of a motivational interviewing intervention. BMJ Open. 2021;11(7):e046896.
Lawton J, Rankin D, Peel E, Douglas M. Patients’ perceptions and experiences of transitions in diabetes care: a longitudinal qualitative study. Health Expect. 2009;12(2):138–48.
Mabire C, Bachnick S, Ausserhofer D, Simon M. Patient readiness for hospital discharge and its relationship to discharge preparation and structural factors: a cross-sectional study. Int J Nurs Stud. 2019;90:13–20.
Meyers DC, Durlak JA, Wandersman A. The quality implementation framework: a synthesis of critical steps in the implementation process. Am J Community Psychol. 2012;50(3–4):462–80.
Meyer-Massetti C, Hofstetter V, Hedinger-Grogg B, Meier CR, Guglielmo BJ. Medication-related problems during transfer from hospital to home care: baseline data from Switzerland. Int J Clin Pharm. 2018;40(6):1614–20.
Neeman M, Dobrinas M, Maurer S, Tagan D, Sautebin A, Blanc AL, et al. Transition of care: a set of pharmaceutical interventions improves hospital discharge prescriptions from an internal medicine ward. Eur J Intern Med. 2017;38:30–7.
Geese F, Schmitt KU. Interprofessional Collaboration in Complex Patient Care Transition: a qualitative multi-perspective analysis. Healthc (Basel). 2023;11(3).
Craig P, Dieppe P, Macintyre S, Michie S, Nazareth I, Petticrew M. Developing and evaluating complex interventions: the new Medical Research Council guidance. Int J Nurs Stud. 2013;50(5):587–92.
Thomson R, Plumridge L, Holland J, Editorial. Int J Soc Res Methodol. 2003;6(3):185–7.
Audulv Å, Hall EOC, Kneck Å, Westergren T, Fegran L, Pedersen MK, et al. Qualitative longitudinal research in health research: a method study. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2022;22(1):255.
Kim H, Sefcik JS, Bradway C. Characteristics of qualitative descriptive studies: a systematic review. Res Nurs Health. 2017;40(1):23–42.
Sandelowski M. Whatever happened to qualitative description? Res Nurs Health. 2000;23(4):334–40.
Bradshaw C, Atkinson S, Doody O. Employing a qualitative description Approach in Health Care Research. Glob Qual Nurs Res. 2017;4:2333393617742282.
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Bellone JM, Barner JC, Lopez DA. Postdischarge interventions by pharmacists and impact on hospital readmission rates. J Am Pharm Assoc (2003). 2012;52(3):358–62.
Hennink MM, Kaiser BN, Marconi VC. Code saturation versus meaning saturation: how many interviews are Enough? Qual Health Res. 2016;27(4):591–608.
World Health Organization. Adherence to long-term therapies: evidence for action. 2003.
Fisher JD, Fisher WA, Amico KR, Harman JJ. An information-motivation-behavioral skills model of adherence to antiretroviral therapy. Health Psychol. 2006;25(4):462–73.
Bandura A. Health promotion from the perspective of social cognitive theory. Psychol Health. 1998;13(4):623–49.
ShiftEUROQOL Research FOndation EQ 5D Instruments. Accessed 30 July 2022 https://euroqol.org/eq-5d-instruments/sample-demo/
Jeppesen KM, Coyle JD, Miser WF. Screening questions to predict limited health literacy: a cross-sectional study of patients with diabetes mellitus. Ann Fam Med. 2009;7(1):24–31.
Giordano TP, Guzman D, Clark R, Charlebois ED, Bangsberg DR. Measuring adherence to antiretroviral therapy in a diverse population using a visual analogue scale. HIV Clin Trials. 2004;5(2):74–9.
Horne R, Weinman J, Hankins M. The beliefs about medicines questionnaire: the development and evaluation of a new method for assessing the cognitive representation of medication. Psychol Health. 1999;14(1):1–24.
Horne R, Chapman SC, Parham R, Freemantle N, Forbes A, Cooper V. Understanding patients’ adherence-related beliefs about medicines prescribed for long-term conditions: a meta-analytic review of the necessity-concerns Framework. PLoS ONE. 2013;8(12):e80633.
Braun V, Clarke V. Using thematic analysis in psychology. Qualitative Res Psychol. 2006;3(2):77–101.
Waibel S, Henao D, Aller M-B, Vargas I, Vázquez M-L. What do we know about patients’ perceptions of continuity of care? A meta-synthesis of qualitative studies. Int J Qual Health Care. 2011;24(1):39–48.
Rognan SE, Jørgensen MJ, Mathiesen L, Druedahl LC, Lie HB, Bengtsson K, et al. The way you talk, do I have a choice?’ Patient narratives of medication decision-making during hospitalization. Int J Qualitative Stud Health Well-being. 2023;18(1):2250084.
Michel B, Hemery M, Rybarczyk-Vigouret MC, Wehrle P, Beck M. Drug-dispensing problems community pharmacists face when patients are discharged from hospitals: a study about 537 prescriptions in Alsace. Int J Qual Health Care. 2016;28(6):779–84.
Bruhwiler LD, Hersberger KE, Lutters M. Hospital discharge: what are the problems, information needs and objectives of community pharmacists? A mixed method approach. Pharm Pract (Granada). 2017;15(3):1046.
Knight DA, Thompson D, Mathie E, Dickinson A. Seamless care? Just a list would have helped!’ Older people and their carer’s experiences of support with medication on discharge home from hospital. Health Expect. 2013;16(3):277–91.
Gualandi R, Masella C, Viglione D, Tartaglini D. Exploring the hospital patient journey: what does the patient experience? PLoS ONE. 2019;14(12):e0224899.
Norberg H, Håkansson Lindqvist M, Gustafsson M. Older individuals’ experiences of Medication Management and Care after Discharge from Hospital: an interview study. Patient Prefer Adherence. 2023;17:781–92.
Jones KC, Austad K, Silver S, Cordova-Ramos EG, Fantasia KL, Perez DC, et al. Patient perspectives of the hospital discharge process: a qualitative study. J Patient Exp. 2023;10:23743735231171564.
Hesselink G, Flink M, Olsson M, Barach P, Dudzik-Urbaniak E, Orrego C, et al. Are patients discharged with care? A qualitative study of perceptions and experiences of patients, family members and care providers. BMJ Qual Saf. 2012;21(Suppl 1):i39–49.
Murray SA, Kendall M, Carduff E, Worth A, Harris FM, Lloyd A, et al. Use of serial qualitative interviews to understand patients’ evolving experiences and needs. BMJ. 2009;339:b3702.
Berger ZD, Boss EF, Beach MC. Communication behaviors and patient autonomy in hospital care: a qualitative study. Patient Educ Couns. 2017;100(8):1473–81.
Davis RE, Jacklin R, Sevdalis N, Vincent CA. Patient involvement in patient safety: what factors influence patient participation and engagement? Health Expect. 2007;10(3):259–67.
Greene J, Hibbard JH. Why does patient activation matter? An examination of the relationships between patient activation and health-related outcomes. J Gen Intern Med. 2012;27(5):520–6.
Mitchell SE, Gardiner PM, Sadikova E, Martin JM, Jack BW, Hibbard JH, et al. Patient activation and 30-day post-discharge hospital utilization. J Gen Intern Med. 2014;29(2):349–55.
Weir DL, Motulsky A, Abrahamowicz M, Lee TC, Morgan S, Buckeridge DL, et al. Failure to follow medication changes made at hospital discharge is associated with adverse events in 30 days. Health Serv Res. 2020;55(4):512–23.
Kripalani S, Goggins K, Nwosu S, Schildcrout J, Mixon AS, McNaughton C, et al. Medication nonadherence before hospitalization for Acute Cardiac events. J Health Commun. 2015;20(Suppl 2):34–42.
Mortelmans L, De Baetselier E, Goossens E, Dilles T. What happens after Hospital Discharge? Deficiencies in Medication Management encountered by geriatric patients with polypharmacy. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18(13).
Mortelmans L, Goossens E, Dilles T. Beliefs about medication after hospital discharge in geriatric patients with polypharmacy. Geriatr Nurs. 2022;43:280–7.
Bandiera C, Ribaut J, Dima AL, Allemann SS, Molesworth K, Kalumiya K et al. Swiss Priority setting on implementing Medication Adherence interventions as Part of the European ENABLE COST action. Int J Public Health. 2022;67.
Elliott R, Boyd M, Nde S. at e. Supporting adherence for people starting a new medication for a long-term condition through community pharmacies: a pragmaticrandomised controlled trial of the New Medicine Service. 2015.
Grimmsmann T, Schwabe U, Himmel W. The influence of hospitalisation on drug prescription in primary care–a large-scale follow-up study. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2007;63(8):783–90.
Larsen MD, Rosholm JU, Hallas J. The influence of comprehensive geriatric assessment on drug therapy in elderly patients. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2014;70(2):233–9.
Viktil KK, Blix HS, Eek AK, Davies MN, Moger TA, Reikvam A. How are drug regimen changes during hospitalisation handled after discharge: a cohort study. BMJ Open. 2012;2(6):e001461.
Strehlau AG, Larsen MD, Søndergaard J, Almarsdóttir AB, Rosholm J-U. General practitioners’ continuation and acceptance of medication changes at sectorial transitions of geriatric patients - a qualitative interview study. BMC Fam Pract. 2018;19(1):168.
Anderson TS, Lee S, Jing B, Fung K, Ngo S, Silvestrini M, et al. Prevalence of diabetes medication intensifications in older adults discharged from US Veterans Health Administration Hospitals. JAMA Netw Open. 2020;3(3):e201511.
Royal Pharmaceutical Society. Keeping patients safewhen they transfer between care providers– getting the medicines right June 2012. Accessed 27 October 2023 https://www.rpharms.com/Portals/0/RPS%20document%20library/Open%20access/Publications/Keeping%20patients%20safe%20transfer%20of%20care%20report.pdf
International Pharmaceutical Federation (FIP). Medicines reconciliation: A toolkit for pharmacists. Accessed 23 September 2023 https://www.fip.org/file/4949
Californian Pharmacist Assiociation Transitions of Care Resource Guide. https://cdn.ymaws.com/www.cshp.org/resource/resmgr/Files/Practice-Policy/For_Pharmacists/transitions_of_care_final_10.pdf
Royal Collegue of Physicians. Medication safety at hospital discharge: Improvement guide and resource. Accessed 18 September 2023 https://www.rcplondon.ac.uk/file/33421/download
Douglas N, Campbell W, Hinckley J. Implementation science: buzzword or game changer. J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2015;58.
Download references
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank all the patients who took part in this study. We would also like to thank the Geneva University Hospitals Patients Partners + 3P platform as well as Mrs. Tourane Corbière and Mr. Joël Mermoud, patient partners, who reviewed interview guides for clarity and significance. We would like to thank Samuel Fabbi, Vitcoryavarman Koh, and Pierre Repiton for the transcriptions of the audio recordings.
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Open access funding provided by University of Geneva
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, University of Geneva, Geneva, Switzerland
Léa Solh Dost & Marie P. Schneider
Institute of Pharmaceutical Sciences of Western Switzerland, University of Geneva, Geneva, Switzerland
Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes, Hypertension and Nutrition, Department of Medicine, Geneva University Hospitals, Geneva, Switzerland
Giacomo Gastaldi
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
LS, GG, and MS conceptualized and designed the study. LS and GG screened and recruited participants. LS conducted the interviews. LS, GG, and MS performed data analysis and interpretation. LS drafted the manuscript and LS and MS worked on the different versions. MS and GG approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Correspondence to Léa Solh Dost or Marie P. Schneider .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Ethics approval was sought and granted by the Cantonal Research Ethics Commission, Geneva (CCER) (2020 − 01779), and informed consent to participate was obtained from all participants.
Consent for publication
Informed consent for publication was obtained from all participants.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Material 1
Supplementary material 2, supplementary material 3, rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Solh Dost, L., Gastaldi, G. & Schneider, M. Patient medication management, understanding and adherence during the transition from hospital to outpatient care - a qualitative longitudinal study in polymorbid patients with type 2 diabetes. BMC Health Serv Res 24 , 620 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-024-10784-9
Download citation
Received : 28 June 2023
Accepted : 26 February 2024
Published : 13 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-024-10784-9
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Continuity of care
- Transition of care
- Patient discharge
- Medication management
- Medication adherence
- Qualitative research
- Longitudinal studies
- Patient-centered care
- Interprofessional collaboration
- Type 2 diabetes
BMC Health Services Research
ISSN: 1472-6963
- General enquiries: [email protected]
- Search Menu
- Sign in through your institution
- Supplements
- Advance articles
- Editor's Choice
- Special Issues
- Author Guidelines
- Submission Site
- Why Publish With Us?
- Open Access
- About Nicotine & Tobacco Research
- About Society for Nicotine & Tobacco Research
- Editorial Board
- Advertising and Corporate Services
- Journals Career Network
- Self-Archiving Policy
- Dispatch Dates
- Journals on Oxford Academic
- Books on Oxford Academic
Article Contents
‘it’s the wild west out there’: a qualitative study of the views and preparedness of health professionals in helping young adult e-cigarette users to quit.
- Article contents
- Figures & tables
- Supplementary Data
Nicola Rahman, Bernadette Sebar, Ernesta Sofija, ‘It’s the wild west out there’: A qualitative study of the views and preparedness of health professionals in helping young adult e-cigarette users to quit, Nicotine & Tobacco Research , 2024;, ntae117, https://doi.org/10.1093/ntr/ntae117
- Permissions Icon Permissions
Young adults are attempting to quit vaping, with many accessing smoking cessation programs with a lack of reported efficacy, highlighting the need for targeted vaping cessation support. Young people report seeing health professionals as potential sources of support in the quitting process. Additionally, the current changing regulatory landscape around vaping in Australia potentially increases numbers of those seeking health professional help for cessation. However, limited research exists on health professionals’ views and preparedness to assist young adults with their vaping cessation; thus, this exploratory study aimed to gain insights into their readiness to support young adults in quitting vaping.
Data were gathered via eight co-design workshops (two groups each of two hours duration and six semi-structured interviews of 1 hour duration), facilitated online with 12 health professionals. Data underwent thematic analysis.
Health professionals expressed a need for more information in supporting young adults to quit vaping, with them presently relying on informal pathways of support and information for their practice. Participants reported a lack of evidence-based guidelines and a reluctance to prescribe nicotine vapes, expressing conflict with the changing regulatory landscape in Australia.
Our findings identify a significant gap in health professional preparedness in supporting vaping cessation. Health professionals are working within a rapidly evolving regulatory environment and are feeling unprepared to address the widely spread issue of vaping, especially among young people. We demonstrate the critical need for guidelines and training of health professionals to enable them to better support young people in quitting vaping.
This qualitative study offers unique insights into the views and readiness of Australian health professionals to support young people to quit vaping, specifically in the context of recent regulatory reforms. The results highlight the need for evidence-based guidance and training for health professionals to inform their vaping cessation support practice.
Supplementary data
Email alerts, citing articles via.
- About Nicotine & Tobacco Research
- Recommend to your Library
Affiliations
- Online ISSN 1469-994X
- Copyright © 2024 Society for Research on Nicotine and Tobacco
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Institutional account management
- Rights and permissions
- Get help with access
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
In qualitative research, early conceptualizations of triangulation highlighted how multiple methods can reveal shared perspectives and realities, without making epistemological claims regarding the "truth" of the findings (Denzin, 1978; Lincoln & Guba, 1985).
For Cowman, triangulation is defined as the combination of multiple methods in studying the same object or event to better address the phenomenon researched. In turn, Morse defines as the use of at least two methods, usually qualitative and quantitative, to guide the same research problem. When a singular research method is inadequate ...
Abstract. Triangulation refers to the use of multiple methods or data sources in qualitative research to develop a comprehensive understanding of phenomena (Patton, 1999). Triangulation also has been viewed as a qualitative research strategy to test validity through the convergence of information from different sources.
qualitative research, but one should weigh the advantages and disadvantages before application in Extension work. If researchers decide that triangulation is desired, there are several types of triangulation that can be used: data, investigator, theory, methodological, and environmental. Triangulation can be used to deepen the researchers'
Denzin's Paradigm Shift: Triangulation in Qualitative Research. Triangulation is an important concept regarding data analysis for an empirical study. To be sure, multiple external analysis methods concerning the same events and the validity of the process can be enhanced by triangulation (G. Fusch, 2001; P. Fusch & Fusch, 2015; P. Fusch ...
Abstract. Triangulation refers to the use of multiple methods or data sources in qualitative research to develop a comprehensive understanding of phenomena (Patton, 1999). Triangulation also has ...
The idea behind MPI research is captured by the triangulation metaphor. Accounts of related individuals are triangulated, for example, as family members, close friends, doctor and patient, and teacher and student. ... Google Scholar. Bergman, M. M. (2008). ... Crafting qualitative research articles on marriages and families. Journal of Marriage ...
What is triangulation. Triangulation is a method used to increase the cred-ibility and validity of research findings.1 Credibility refers to trustworthiness and how believable a study is; validity is concerned with the extent to which a study accurately reflects or evaluates the concept or ideas being investigated.2 Triangulation, by combining ...
Abstract. This paper aims to provide an overview of the use and assessment of qualitative research methods in the health sciences. Qualitative research can be defined as the study of the nature of phenomena and is especially appropriate for answering questions of why something is (not) observed, assessing complex multi-component interventions ...
Research strives to understand truths about particular phenomena, whether it be the pathophysiology of a disease process or how nursing care affects the outcomes of patients. Our knowledge is always evolving over time. To ensure that the information we derive from research data accurately reflects the truth about phenomena under investigation, different research methods are used. Triangulation ...
This special issue of the Journal of Mixed Methods Research (JMMR) analyzes and explores the variety of ways triangulation is used in mixed methods research and the range of issues and controversies surrounding triangulation praxis.To date, there are few scholarly in-depth discussions of its deployment in mixed methods research. The choice of triangulation as the topic for this first special ...
Triangulation is often used to describe research. where two or more methods are used, known as mixed. methods. Combining both quantitative and qualitative. methods to answer a speci fic research ...
The current article will present the four types of triangulation followed by a discussion of the use of focus groups (FGs) and indepth individual (IDI) interviews as an example of data source triangulation in qualitative inquiry. Types of Triangulation. The first type of triangulation is method triangulation. Method triangulation involves the ...
Triangulation involves the use of various data sources or different data collection methods to confirm or verify findings or interpretations in the study (Bans-Akutey & Tiimub, 2021). In analyzing ...
While many books and articles guide various qualitative research methods and analyses, there is currently no concise resource that explains and differentiates among the most common qualitative approaches. We believe novice qualitative researchers, students planning the design of a qualitative study or taking an introductory qualitative research course, and faculty teaching such courses can ...
A primarily qualitative approach was chosen as being best suited to the exploratory nature of the study and to address the research question. In order to maximise credibility, dependability and confirmability of the findings [].We adopted a multiple site, multiple method and multiple investigator design across three phases of the research.
Methodological triangulation is the most common type of triangulation.2 Studies that use triangulation may include two or more sets of data collection using the same methodology, such as from qualitative data sources. Alternatively, the study may use two different data collection methods as with qualitative and quantitative.4 "This can allow the limitations from each method to be transcended ...
This review aims to synthesize a published set of evaluative criteria for good qualitative research. The aim is to shed light on existing standards for assessing the rigor of qualitative research encompassing a range of epistemological and ontological standpoints. Using a systematic search strategy, published journal articles that deliberate criteria for rigorous research were identified. Then ...
Researcher reflexivity, essentially a researcher's insight into their own biases and rationale for decision-making as the study progresses, is critical to rigor. This article reviews common standards of rigor, quality scholarship criteria, and best practices for qualitative research from design through dissemination.
Triangulation is a method used to increase the credibility and validity of research findings.1 Credibility refers to trustworthiness and how believable a study is; validity is concerned with the extent to which a study accurately reflects or evaluates the concept or ideas being investigated.2 Triangulation, by combining theories, methods or observers in a research study, can help ensure that ...
Examples: Triangulation in different types of research. Qualitative research: You conduct in-depth interviews with different groups of stakeholders, such as parents, teachers, and children. Quantitative research: You run an eye-tracking experiment and involve three researchers in analyzing the data. Mixed methods research: You conduct a ...
This article analyzes more than 120 peer-reviewed articles that reported the findings of elite interview research to understand the researchers' use of triangulation. This analysis found that triangulation was common in studies that involved elite interviews, particularly by combining interviews with document review.
Dear Editor, The global community of medical and nursing researchers has increasingly embraced qualitative research approaches. This surge is seen in their autonomous utilization or incorporation as essential elements within mixed-method research attempts [1].The growing trend is driven by the recognized additional benefits that qualitative approaches provide to the investigation process [2], [3].
The value of using qualitative methods within clinical trials is widely recognised. How qualitative research is integrated within trials units to achieve this is less clear. This paper describes the process through which qualitative research has been integrated within Cardiff University's Centre for Trials Research (CTR) in Wales, UK. We highlight facilitators of, and challenges to, integration.
Study design. This qualitative longitudinal study, conducted from October 2020 to July 2021, used a qualitative descriptive methodology through four consecutive in-depth semi-structured interviews per participant at three, 10-, 30- and 60-days post-discharge, as illustrated in Fig. 1.Longitudinal qualitative research is characterized by qualitative data collection at different points in time ...
The research design and consent procedures for this study were reviewed and approved by Sheffield Hallam University Research Ethics Committee (Reference number: ER42513594). Written and verbal informed consent was received from all participants before the online interviews. Final transcripts were approved by the participants before use in the ...
Sessional Academic, School of Medicine and Dentistry (Public Health), Griffith University , Gold Coast, QLD Correspondence: Nicola Rahman, School of Medicine and Dentistry (Public Health), Gold Coast Campus, Griffith University, 1 Parklands Drive, Southport, QLD 4215, G01_3.30, Email: [email protected] , T +61 7 55527708
Availability of grants, funding, and other incentives and demand for qualitative research in healthcare were described as opportunities for qualitative research practice. Despite the available opportunities, study participants uncovered different challenges that encountered by health academic staffs in conducting qualitative research.