- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences

A Successful International Assignment Depends on These Factors
- Boris Groysberg
- Robin Abrahams
Your marriage, your family, and your career will all benefit from advance planning.
The prospect of an international assignment can be equal parts thrilling and alarming: Will it make or break your career? What will it do to your life at home and the people you love? When you’re thinking about relocating, you start viewing questions of work and family — difficult enough under ordinary circumstances — through a kind of high-contrast, maximum-drama filter.
- BG Boris Groysberg is a professor of business administration in the Organizational Behavior unit at Harvard Business School and a faculty affiliate at the school’s Race, Gender & Equity Initiative. He is the coauthor, with Colleen Ammerman, of Glass Half-Broken: Shattering the Barriers That Still Hold Women Back at Work (Harvard Business Review Press, 2021). bgroysberg
- Robin Abrahams is a research associate at Harvard Business School.
Partner Center
Immigration help for your business
- News & Reports
What to Consider When Sending a Foreign Employee Overseas for Work
Nov 1, 2023.

In today’s interconnected world, companies often deploy their employees on overseas assignments. While there are many different factors to consider when sending a U.S. worker abroad, the situation gets more complicated when dealing with foreign national (FN) employees. A company needs to take various steps to ensure FN employees adhere to both U.S. immigration laws and the regulations of their host country.
Assessing the Impact on Visa Status
Before sending an FN employee on a short- or long-term international assignment, it’s a good idea to consult your immigration attorney to evaluate how the overseas work assignment may affect their current visa status, be it positively or negatively.
For example, employees holding H-1B visas are not considered in “H-1B status” while working outside the U.S. This means that the days spent abroad do not count towards the maximum six years allowed in the U.S. under H-1B status. Consequently, a temporary work assignment overseas could extend the duration an employee is permitted to work within the U.S.
Conversely, an employee who has obtained a green card through your company may have specific compliance requirements. Lawful permanent residents (LPR) must spend at least six months of the year within the U.S. to maintain their green card status. Failure to meet this requirement could result in losing the green card. While exceptions exist, it’s a good idea to get guidance from your immigration attorney before proceeding. If an LPR employee needs to travel abroad for an overseas assignment lasting six months or more, you may want to consider applying for a re-entry permit ( Form I-131 ).
Visa Requirements for the Host Country
Although your FN employee is presently employed in the U.S., the visa regulations in the country they are sent to will be contingent on their current citizenship. It’s essential to understand the specific visa requirements for your FN employee’s travel to and employment in the foreign country. You’ll also need to factor in the time frame required for obtaining the necessary visa.
Interested in our biweekly business immigration newsletter?
Enter your email below.
Thank you for your interest in our BIZ newsletter!
We’ll be in touch.
Payroll Considerations for International Assignments
When sending an FN employee on an overseas assignment, keeping them on the U.S. payroll is typically a good idea. Transferring them to a foreign company’s payroll could result in a loss of their employee status with your U.S. company, potentially jeopardizing their current visa status. In such cases, your company might need to initiate a new petition with USCIS before the FN employee can return to their U.S. position with approved visa documents.
Additionally, the U.S. has tax treaties with several foreign nations, enabling reduced tax rates and exemptions. However, if the host country lacks such a treaty, standard tax obligations apply.
Valid Travel Documents
An often overlooked but crucial aspect is verifying that the FN employee’s travel documents are up-to-date. You want to make sure they can re-enter the U.S. on their existing or previously-held visa. Consult with your immigration attorney to confirm the FN employee has a valid U.S. visa stamp in their passport, a passport that remains valid for re-entry, and evidence of ongoing employment with the U.S. company, typically shown by recent pay stubs and, if necessary, a sponsorship letter.
Which Service?
Looks like you were working on a application just now. Applicants typically only require one service at a time.
You unlocked a $50 discount!
Congrats! Because your friend referred you, your application with Boundless is discounted. Start the application with Boundless within the next 14 days, and you'll save $50.

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
Margin Size
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

18.7: The International Assignment
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 12588

\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
Learning Objectives
- Describe how to prepare for an international assignment.
- Discuss the acculturation process as an expatriate.
- Describe effective strategies for living and working abroad.
Suppose you have the opportunity to work or study in a foreign country. You may find the prospect of an international assignment intriguing, challenging, or even frightening; indeed, most professionals employed abroad will tell you they pass through all three stages at some point during the assignment. They may also share their sense of adjustment, even embrace of their host culture, and the challenges of reintegration into their native country.
An international assignment, whether as a student or a career professional, requires work and preparation, and should be given the time and consideration of any major life change. When you lose a loved one, it takes time to come to terms with the loss. When someone you love is diagnosed with a serious illness, the news may take some time to sink in. When a new baby enters your family, a period of adjustment is predictable and prolonged. All these major life changes can stress an individual beyond their capacity to adjust. Similarly, in order to be a successful “expat,” or expatriate, one needs to prepare mentally and physically for the change.
International business assignments are a reflection of increased global trade, and as trade decreases, they may become an expensive luxury. As technology allows for instant face-to-face communication, and group collaboration on documents via cloud computing and storage, the need for physical travel may be reduced. But regardless of whether your assignment involves relocation abroad, supervision of managers in another country at a distance, or supervision by a foreign manager, you will need to learn more about the language, culture, and customs that are not your own. You will need to compare and contrast, and seek experiences that lend insight, in order to communicate more effectively.
An efficient, effective manager in any country is desirable, but one with international experience even more so. You will represent your company and they will represent you, including a considerable financial investment, either by your employer (in the case of a professional assignment) or by whoever is financing your education (in the case of studying abroad). That investment should not be taken lightly. As many as 40 percent of foreign-assigned employees terminate their assignments early (Tu, H. and Sullivan, S., 1994), at a considerable cost to their employers. Of those that remain, almost 50 percent are less than effective (Tu, H. and Sullivan, S., 1994).
Preparation
With this perspective in mind, let’s discuss how to prepare for the international assignment and strategies to make you a more effective professional as a stranger in a strange land. First we’ll dispel a couple of myths associated with an idealized or romantic view of living abroad. Next we’ll examine traits and skills of the successful expatriate. Finally, we’ll examine culture shock and the acculturation process.
Your experience with other cultures may have come firsthand, but for most, a foreign location like Paris is an idea formed from exposure to images via the mass media. Paris may be known for its art, as a place for lovers, or as a great place to buy bread. But if you have only ever known about a place through the lens of a camera, you have only seen the portraits designed and portrayed by others. You will lack the multidimensional view of one who lives and works in Paris, and even if you are aware of its history, its economic development, or its recent changes, these are all academic observations until the moment of experience.
That is not to say that research does not form a solid foundation in preparation for an international assignment, but it does reinforce the distinction between a media-fabricated ideal and real life. Awareness of this difference is an important step as you prepare yourself for life in a foreign culture.
If the decision is yours to make, take your time. If others are involved, and family is a consideration, you should take even more care with this important decision. Residence abroad requires some knowledge of the language, an ability to adapt, and an interest in learning about different cultures. If family members are not a part of the decision, or lack the language skills or interest, the assignment may prove overwhelming and lead to failure. Sixty-four percent of expatriate respondents who terminated their assignment early indicated that family concerns were the primary reason (Contreras, C. D., 2009).
Points to consider include the following:
- How flexible are you?
- Do you need everything spelled out or can you go with the flow?
- Can you adapt to new ways of doing business?
- Are you interested in the host culture and willing to dedicate the time and put forth the effort to learn more about it?
- What has been your experience to date working with people from distinct cultures?
- What are your language skills at present, and are you interested in learning a new language?
- Is your family supportive of the assignment?
- How will it affect your children’s education? Your spouse’s career? Your career?
- Will this assignment benefit your family?
- How long are you willing to commit to the assignment?
- What resources are available to help you prepare, move, and adjust?
- Can you stand being out of the loop, even if you are in daily written and oral communication with the home office?
- What is your relationship with your employer, and can it withstand the anticipated stress and tension that will result as not everything goes according to plan?
- Is the cultural framework of your assignment similar to—or unlike—your own, and how ready are you to adapt to differences in such areas as time horizon, masculinity versus femininity, or direct versus indirect styles of communication?
This list of questions could continue, and feel free to add your own as you explore the idea of an international assignment. An international assignment is not like a domestic move or reassignment. Within the same country, even if there are significantly different local customs in place, similar rules, laws, and ways of doing business are present. In a foreign country, you will lose those familiar traditions and institutions and have to learn many new ways of accomplishing your given tasks. What once took a five-minute phone call may now take a dozen meetings and a month to achieve, and that may cause you some frustration. It may also cause your employer frustration as you try to communicate how things are done locally, and why results are not immediate, as they lack even your limited understanding of your current context. Your relationship with your employer will experience stress, and your ability to communicate your situation will require tact and finesse.
Successful expatriates are adaptable, open to learning new languages, cultures, and skilled at finding common ground for communication. Rather than responding with frustration, they learn the new customs and find the advantage to get the job done. They form relationships and are not afraid to ask for help when it is warranted or required. They feel secure in their place as explorer, and understand that mistakes are a given, even as they are unpredictable. Being a stranger is no easy task, but they welcome the challenge with energy and enthusiasm.
Acculturation Process
Acculturation, or the transition to living abroad, is often described as an emotional rollercoaster. Steven Rhinesmith provides ten steps that show the process of acculturation, including culture shock, that you may experience:
- Initial anxiety
- Initial elation
- Initial culture shock
- Superficial adjustment
- Depression-frustration
- Acceptance of host culture
- Return anxiety
- Return elation
- Reentry shock
- Reintegration
Humans fear the unknown, and even if your tolerance for uncertainty is high, you may experience a degree of anxiety in anticipation of your arrival. At first the “honeymoon” period is observed, with a sense of elation at all the newfound wonders. You may adjust superficially at first, learning where to get familiar foods or new ways to meet your basic needs. As you live in the new culture, divergence will become a trend and you’ll notice many things that frustrate you. You won’t anticipate the need for two hours at a bank for a transaction that once took five minutes, or could be handled over the Internet, and find that businesses close during midday, preventing you from accomplishing your goals. At this stage, you will feel that living in this new culture is simply exhausting. Many expats advise that this is the time to tough it out—if you give in to the temptation to make a visit back home, you will only prolong your difficult adjustment.
Over time, if you persevere, you will come to accept and adjust to your host culture, and learn how to accomplish your goals with less frustration and ease. You may come to appreciate several cultural values or traits and come to embrace some aspects of your host culture. At some point, you will need to return to your first, or home, culture, but that transition will bring a sense of anxiety. People and places change, the familiar is no longer so familiar, and you too have changed. You may once again be elated at your return and the familiar, and experience a sense of comfort in home and family, but culture shock may again be part of your adjustment. You may look at your home culture in a new way and question things that are done in a particular way that you have always considered normal. You may hold onto some of the cultural traits you adopted while living abroad, and begin the process of reintegration.

You may also begin to feel that the “grass is greener” in your host country, and long to return. Expatriates are often noted for “going native,” or adopting the host culture’s way of life, but even the most confirmed expats still gather to hear the familiar sound of their first language, and find community in people like themselves who have blended cultural boundaries on a personal level.
Living and Working Abroad
In order to learn to swim you have to get in the water, and all the research and preparation cannot take the place of direct experience. Your awareness of culture shock may help you adjust, and your preparation by learning some of the language will assist you, but know that living and working abroad take time and effort. Still, there are several guidelines that can serve you well as you start your new life in a strange land:
- Be open and creative . People will eat foods that seem strange or do things in a new way, and your openness and creativity can play a positive role in your adjustment. Staying close to your living quarters or surrounding yourself with similar expats can limit your exposure to and understanding of the local cultures. While the familiar may be comfortable, and the new setting may be uncomfortable, you will learn much more about your host culture and yourself if you make the effort to be open to new experiences. Being open involves getting out of your comfort zone.
- Be self-reliant . Things that were once easy or took little time may now be challenging or consume your whole day. Focus on your ability to resolve issues, learn new ways to get the job done, and be prepared to do new things.
- Keep a balanced perspective . Your host culture isn’t perfect. Humans aren’t perfect, and neither was your home culture. Each location and cultural community has strengths you can learn from if you are open to them.
- Be patient . Take your time, and know a silent period is normal. The textbook language classes only provide a base from which you will learn how people who live in the host country actually communicate. You didn’t learn to walk in a day and won’t learn to successfully navigate this culture overnight either.
- Be a student and a teacher . You are learning as the new member of the community, but as a full member of your culture, you can share your experiences as well.
- Be an explorer . Get out and go beyond your boundaries when you feel safe and secure. Traveling to surrounding villages, or across neighboring borders, can expand your perspective and help you learn.
- Protect yourself . Always keep all your essential documents, money, and medicines close to you, or where you know they will be safe. Trying to source a medicine in a country where you are not fluent in the language, or where the names of remedies are different, can be a challenge. Your passport is essential to your safety and you need to keep it safe. You may also consider vaccination records, birth certificates, or business documents in the same way, keeping them safe and accessible. You may want to consider a “bug-out bag,” with all the essentials you need, including food, water, keys, and small tools, as an essential part of planning in case of emergency.
Key Takeaways
Preparation is key to a successful international assignment. Living and working abroad takes time, effort, and patience.
- Research one organization in a business or industry that relates to your major and has an international presence. Find a job announcement or similar document that discusses the business and its international activities. Share and compare with classmates.
- Conduct a search on expat networks including online forum. Briefly describe your findings and share with classmates.
- What would be the hardest part of an overseas assignment for you and why? What would be the easiest part of an overseas assignment for you and why?
- Find an advertisement for an international assignment. Note the qualifications, and share with classmates.
- Find an article or other first-person account of someone’s experience on an international assignment. Share your results with your classmates.
Contreras, C. D. (2009). Should you accept the international assignment? BNET . Retrieved from findarticles.com/p/articles/mi_qa5350/is_200308/ai_n21334696.
Rhinesmith, S. (1984). Returning home . Ottawa, Canada: Canadian Bureau for International Education.
Tu, H., & Sullivan, S. (1994). Business horizons . Retrieved from findarticles.com/p/articles/mi_m1038/is_nl_v37/ai_14922926.

- Internships
- Career Advice
7 Strategies for a Successful International Work Assignment
Published: Oct 08, 2018

International assignments are exciting for a host of reasons, but having the opportunity to live in another country while finding success in your career at the same time is particularly compelling. Working abroad allows you to gain real-world experience, advance the skills you have, and learn how to thrive in a global environment.
But living and working in a new country with a different culture is a major life change. It’s important to immerse yourself in the experience and remain positive through the ups and downs. Below are 7 tips to make the most of your journey abroad.
1. Keep an Open Mind
Social media and the internet allows us to connect with people from all over the world. Take time to learn about the history of your new home, including any local customs or laws, so you can set more realistic expectations ahead of time.
When you finally touch down in your new destination, keep an open mind. What you think you know about an area or country may end up being turned on its head once you spend more than a few days there.
For Allison Alexander, a participant in Abbott’s Finance Professional Development Program , an international assignment was the ultimate lesson in flexibility. “Going to an international role means you’re stepping into a culture and a set of expectations that are foreign to you,” she explains. “It forces you to be open to the unexpected.”
Unlike traveling for leisure, international assignments allow you to spend months or even years in a location. You can, and should, tap into the global mindset you’ve already developed while leaving room for all the surprises that will come from long-term exposure to a different culture.
2. Set Goals
Maximize the benefits of an international assignment by setting goals for yourself at the beginning. What do you hope to accomplish in the first two weeks? How can you challenge yourself once you’ve settled in? And when you leave, what are the skills you want to take with you? Having clearly defined milestones will help you stay focused on what’s important and define the steps needed to grow your career.
3. Develop Language Skills
You may not become fluent, but practicing the local language can help you build deeper connections within the community and potentially open up new work opportunities in the future. Don’t fret if you stumble through mispronunciations and tenses at first, the more you practice, the more confident you'll become, and the better you'll get.
4. Be Adventurous
When you're abroad, it's great to take advantage of travel. You have a new world at your doorstep! It's also a chance to try activities you've never tried before.
"I've been doing things I thought of all my life but could never muster enough courage to actually do," says Timir Gupta, another member of Abbott's Finance Professional Development Program, who has traveled solo, tried skydiving, and chased the northern lights. "And it's a great conversation starter during an interview," he adds.
5. Apply New Perspectives
Gaining insight into different business practices can help you learn to look at old problems in new ways when you return home. This type of creative problem solving will be an asset no matter what your next assignment is.
"When you finally make your way back to a domestic role, you've now become an expert in two completely different professional structures," says Alexander. "You've seen what works and what doesn't in a global setting, and you can lead the group on new ways of thinking that may lead to more success."
6. Expand Your Network
Get out and build connections, both at your assignment and beyond. "Because of traveling, I have friends all over the world," says Gupta. He now has connections across five continents that he can tap into when looking for a reference or career advice.
Luckily, maintaining the professional network you build abroad is now easier than ever before. Social media, LinkedIn, and apps like WhatsApp can help you stay in contact with your colleagues and mentors.
7. Market Yourself and Build Your Career
When you return home, don't forget to incorporate your experience into your personal branding. You want to make sure prospective employers know how your new skills, perspectives, and connections set you apart. Think: How can I rework my resume and reframe interview answers to showcase what I've learned?
Depending on your experience, you may even refocus your career or choose employers who will use your global mindset. If you want more opportunities to go abroad, many multinational organizations offer international assignments. With offices in more than 150 countries, Abbott has numerous internships and development programs for students in finance, information technology, engineering, manufacturing, environmental health, and quality assurance.
Look for companies expanding in emerging markets, too. This can give you the unique opportunity to get in at the ground level and learn how to evolve a product or service to match the local market.
No matter what you choose or where you go, an international assignment can provide you with the unique opportunity to grow personally and professionally—and hopefully have a little fun along the way too.
This post was sponsored by Abbott .
Enhancing expatriates’ assignments success: the relationships between cultural intelligence, cross-cultural adaptation and performance
- Open access
- Published: 20 July 2020
- Volume 41 , pages 4291–4311, ( 2022 )
Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article

- Ilaria Setti 1 ,
- Valentina Sommovigo ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-9273-5706 1 &
- Piergiorgio Argentero 1
34 Citations
Explore all metrics
Today’s increasingly global marketplace is resulting in more organizations sending employees to work outside their home countries as expatriates. Consequently, identifying factors influencing expatriates’ cross-cultural adjustment at work and performance has become an increasingly important issue for both researchers and firms. Drawing on Kim et al. ( 2008 ), this study examines the critical elements to expatriate success, which are the relationships between cultural intelligence, cross-cultural adjustment at work, and assignment-specific performance. One-hundred and fifty-one expatriates working within the energy sector, who were mainly located in the Middle East completed questionnaires, investigating: cultural intelligence ( Cultural Intelligence Scale ), cross-cultural adjustment ( Expatriate Adjustment Scale ), performance (Expatriate Contextual/Managerial Performance Skills ), cultural distance (Kogut and Singh’ index), length of staying in the host country and international work experience. Findings indicated that the four cultural intelligence components were directly and indirectly (through cross-cultural adjustment at work) associated with performance. The positive relationship between motivational cultural intelligence and cross-cultural adjustment at work was stronger when cultural distance was low, when expatriates were at the beginning of a new international assignment, and when they had lower experience. Organizations can greatly benefit from hiring cross-culturally intelligent expatriates for international assignments, providing their employees with pre-departure training programs aimed at increasing cultural intelligence, and giving them organizational resources and logistical help to support them.
Similar content being viewed by others
Does cultural intelligence matter within cross-cultural teams in hospitality industry? Understanding the role of team dissimilarity climate

Do stays abroad increase intercultural and general competences, affecting employability?

Exploring the Relationship Between International Service Performance and Personal Characteristics in the Latin American Context
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
As globalization of trade encourages multinational corporations (MNCs) to operate in different geographic environments (Sambasivan et al. 2013 ), talent mobility has become one of the key channels through which to develop global organizations’ competitive advantages (Tarique and Schuler 2010 ). This requires the presence of a cross-culturally competent workforce that can manage overseas subsidiaries and liaise with foreign affiliates (Froese and Peltokorpi 2011 ). In this context, expatriates are considered as invaluable assets by MNCs (Wu and Ang 2011 ). Consequently, there have been numerous calls in psychology (e.g., Mol et al. 2005 ) for more research aimed at identifying the psychological factors driving expatriates’ cross-cultural adjustment and performance.
In this context, cultural intelligence (CQ) represents an interesting variable since it is a malleable capability which can be developed through cross-cultural experiences (Chao et al. 2017 ) and specific trainings (Leung et al. 2014 ). CQ is defined as “an individual’s competence to function and manage effectively in culturally diverse settings” (Ang and Van Dyne 2008 , p. 3). CQ is conceptualized as a multidimensional construct which includes four main components: metacognitive CQ (i.e., cultural awareness), cognitive CQ (i.e., cultural knowledge), motivational CQ (i.e., motivation and self-efficacy in functioning in diverse cultural settings), and behavioural CQ (i.e., adoption of appropriate behaviours during cross-cultural interactions). Scholars have called for more research on the CQ dimensions (Ang et al. 2011 ) as the four CQ components have been differently associated with specific intercultural effectiveness outcomes (see Rockstuhl and Van Dyne 2018 for a review).
This study responds to this call by analysing the relationships between specific CQ dimensions, cross-cultural adjustment (CCA; i.e., psychological comfort in a foreign country; Black and Gregersen 1999 ) at work and assignment-specific performance. This latter construct, which refers to the ability to accomplish certain assignment specific tasks (e.g., replacement planning; Caligiuri 1997 ), was chosen in this paper as main dependent variable because successfully executing assignment-specific duties is frequently the main constituent of success, which is evaluated by the home office (Earley and Ang 2003 ). Aside from performance, this study focused on work CCA, namely the extent to which expatriates become psychologically comfortable handling assignment duties and meeting performance expectations (Chen et al. 2010 ; Shaffer et al. 2006 ). Work CCA is one of the three dimensions of CCA, together with general (i.e., general living conditions) and interaction (i.e., interactions with locals) components (Black et al. 1991 ). This paper concentrated on work CCA as it is more predictive of performance than the other CCA dimensions (Chew et al. 2019 ).
The role of overall CQ as a meaningful antecedent of overall CCA (e.g., Chen et al. 2014 ; Rockstuhl and Van Dyne 2018 ) and job performance (e.g., Malek and Budhwar 2013 ; Ramalu et al. 2012 ) has been identified, whereas the literature on the role of the four CQ facets in facilitating work CCA is less consistent (e.g., Ott and Michailova 2018a , 2018b ). The literature on the effect of CQ on performance indicates an intricate association between the variables, the relevance of the specific CQ dimensions, and the role of work CCA in this association (ibidem). Thus, while some researchers found a direct positive CQ-performance association (e.g., Chen et al. 2011 ; Lee et al. 2013 ), there is also evidence that the impact of CQ on performance may be mediated by work CCA (e.g., Jyoti and Kour 2017a , 2017b ; Lee et al. 2013 ).
Additionally, a closer look to the literature on the boundary conditions under which specific CQ dimensions may enhance work CCA and, in turn, assignment-specific performance reveal numerous gaps. To fil this gap, this study aimed to analyse how and when specific CQ facets were more - or less - likely to facilitate assignment-specific performance. To this end, this paper concentrated on cultural distance (CD, i.e., the extent to which the culture of destination differs from expatriates’ home country on various values; Shenkar 2001 ), length of stay in the host country and work international experience. Indeed, although some studies analysed the moderating role of CD in the relationships between various individual features and outcomes in the expatriation area (e.g., Chen et al. 2010 ; Zhang 2013 ), the research on the effect of CD on the association between CQ dimensions and work CCA remains limited. Moreover, even though some studies demonstrated that the length of residence in the local country influenced both CQ (e.g., Li et al. 2013 ) and CCA (e.g., Ramalu et al. 2010 ), no previous research, to the best of our knowledge, has investigated the enhancing effect of length of stay on the association between specific CQ assets and work CCA. Furthermore, though some investigations showed that work experience played a moderating role in the CQ-CCA relationship (e.g., Lee and Sukoco 2010 ; Jyoti and Kour 2017a , 2017b ), no study, to our knowledge, has considered the moderated mediated effect of the four CQ dimensions and work experience - through work CCA - on assignment-specific performance.
Therefore, our research questions are as follows: do the four CQ dimensions directly and indirectly, through work CCA, impact on assignment-specific performance? And what are the effects of CD, length of stay in the host country and previous international experience with regard to this? In answering these questions, this paper drew on Kim et al. ( 2008 ) which presented, for the first time, propositions that delineated the relationships between CQ, CCA and performance analysing them together, so that scholars and practitioners could reach a better understanding of each of these. The authors proposed that overall CQ – conceptualized as the result of its four components – would be directly and indirectly, through each of the three dimensions of CCA, associated with overall performance. Additionally, the authors suggested that the CQ-CCA relationship would be positively moderated by CD, so that such relationship would be stronger when CD would be greater.
The main contribution of the present work is to extend this model by analysing whether specific dimensions of CQ – rather than overall CQ - were related to assignment-specific performance – rather than overall performance. Moreover, this research moves an important step forward in the expatriate literature as it identifies, beyond CD – as proposed by the model - other understudied boundary conditions for CQ effects (i.e., work experience and length of stay in the host country).
In doing so, the study was undertaken on the relatively under-investigated population of expatriates working within the energy sector in the Middle East for several reasons. First, some Middle East countries, such as the United Arab Emirates (UAE), have experienced unprecedented growth over the past years (Bealer and Bhanugopan 2014 ). Second, such nations remain relevant economic hubs in the Middle Eastern region, that attract numerous expatriates from Western countries (ibidem), especially within the energy sector (Finaccord 2018 ). For instance, in 2017 Saudi Arabia hosted the largest number of expatriates, whereas in the UAE expatriates constituted the 87.8% of the total population (ibidem). Nevertheless, only a few studies have concentrated on this population. Third, since most of our research respondents were from Latin America, the subsequent national cultural dissimilarities were likely to result in significant CCA difficulties. Thereby, we contribute to literature surrounding organizational behaviour and psychology as well as international human resource management.
In the next section, we provide theoretical arguments for the reasons why each of the four CQ dimensions might be uniquely posited to contribute to expatriates’ assignment-specific performance and work CCA. We describe each component in more detail, and we give rationale for the mediating role of work CCA. Subsequently, we present conceptual logic for our proposed effects of CD, length of stay in the host country and international work experience in the association between specific CQ components and work CCA. After that, we present the sample investigated and the methodology adopted. Then, we report the results and discuss our findings. Finally, we present theoretical and managerial implications, limitations, and suggestions for future research as well as conclusion.
The Relationship between CQ Dimensions and Expatriates’ Assignment-Specific Performance
The construct of CQ attracted ever-increasing attention since other existing formulations of intelligence, such as emotional intelligence (EQ) or social intelligence (SI), do not provide a comprehensive explanation in culturally diverse situations (Groves and Feyerherm 2011 ). Indeed, both EQ and SI are culture bound, such that although these two forms of intelligence may enable individuals to better understand social situations, this does not turn automatically into successful CCA (Caputo et al. 2018 ). Thus, individuals who have high EQ and SI in one culture may not easily adapt to cross-cultural interactions due to misinterpretations of culture-specific situational cues. Conversely, CQ is culture free and regards a general array of abilities particularly relevant on settings characterized by cultural diversity.
Drawing on Kim et al. ( 2008 ), CQ is related to expatriates’ performance, such that culturally intelligent expatriates may successfully function across cultural settings. We present below conceptual logic for our proposed relationships for each of the CQ dimensions with performance, describing each component in more detail.
Meta-cognitive CQ refers to an individual’s level of conscious cultural awareness of - and control over - cognitions during cross-cultural interactions. Self-awareness and cognitive flexibility can promote expatriates’ performance by facilitating their understanding of culturally appropriate role expectations (Ang et al. 2007 ). Indeed, individuals high in meta-cognitive CQ are better at adjusting their existing knowledge to meet changing environmental demands (ibidem). Thus, they can compensate for cognitive capability when previously acquired knowledge is unreliable, avoiding potential problems. Additionally, in unpredictable situations, their meta-cognitive skills provide them with a means by which supplement the lack of overt cues (Fernandez-Duque et al. 2000 ). This may stimulate the adoption of effective solutions to perform well (Tobias and Everson 2002 ). Meta-cognitive CQ may also facilitate expatriates’ performance by enhancing intercultural creative collaboration (Chua et al. 2012 ), conflict management (Caputo et al. 2018 ), decision-making and task performance (Ang et al. 2007 ) as well as knowledge transfer from headquarters to subsidiaries (Vlajčić et al. 2019 ). Thus, we expected the following:
Hypothesis 1a: meta-cognitive CQ will be positively related to assignment-specific performance.
Cognitive CQ refers to an individual’s general knowledge of norms, practices, and conventions in foreign countries gained from personal experiences and education (Ang et al. 2007 ). Expatriates high in cognitive CQ possess sophisticated mental maps of culture, which allow them to anticipate similarities and differences across cultures (Brislin et al. 2006 ). As a result, they may perform well in foreign workplaces because their in-depth knowledge about diverse cultures enables them to reach a greater understanding of cultural expectations. Additionally, such knowledge leads them to adopt culturally appropriate behaviours by facilitating decision-making, cultural judgment (Ang et al. 2007 ), intercultural negotiation (Groves et al. 2015 ), conflict management (Caputo et al. 2018 ) and knowledge transfer from headquarters to subsidiaries (Vlajčić et al. 2019 ). Thereby, we expected the following:
Hypothesis 1b: cognitive CQ will be positively related to assignment-specific performance.
Motivational CQ refers to individual’s ability to direct attention to understand cultural diversity and maintain energy concentrated on learning about - and operating in - new cultural settings, even when situations are challenging (Ang et al. 2007 ). Expatriates high in motivational CQ are motivated intrinsically and by their efficient beliefs of adaptive capabilities to interact with colleagues from different backgrounds (Templer et al. 2006 ). As a result, they may direct their energy toward learning role expectations, positively coping with problems, and striving to address challenges. Motivational CQ may also facilitate expatriates’ performance by easing intercultural collaboration and negotiation (Chua et al. 2012 ), communication effectiveness (Presbitero and Quita 2017 ), integrative information behaviours (Imai and Gelfand 2010 ), and conflict management (Caputo et al. 2018 ). Therefore, we formulated the following hypothesis:
Hypothesis 1c: motivational CQ will be positively related to assignment-specific performance.
Behavioural CQ reflects the individual’s ability to communicate in a culturally sensitive way and exhibit culturally appropriate (verbal and non-verbal) behaviours when interacting with people from other cultures (Ang et al. 2007 ). This involves having a wide repertoire of overt behavioural responses which fits to a variety of cross-cultural situations, in addition to using culturally appropriate words, body language and conversation style (ibidem). Expatriates high in behavioural CQ can choose appropriate verbal and physical actions when interacting with locals (Ang and Van Dyne 2008 ). This behavioural flexibility may help them to enact culturally appropriate role-related behaviours and meet assignment-specific expectations (ibidem). This may reduce miscommunications and enhance performance (Ng et al. 2012 ; Rose et al. 2010 ). Accordingly, behavioural flexibility was positively related to task performance within intercultural environments (e.g., Chen et al. 2011 ), conflict management (Caputo et al. 2018 ), and intercultural negotiation effectiveness (Groves et al. 2015 ). Then, we hypothesized the following:
Hypothesis 1d: behavioural CQ will be positively related to assignment-specific performance.
The Relationship between CQ Dimensions and Expatriate Adjustment at Work
In line with Kim et al. ( 2008 ), culturally intelligent individuals are better able to adjust to the host country because they are more likely to gain appropriate emotional and informational support through interactions with locals. Then, CQ represents an important factor driving expatriate CCA which may explain individual dissimilarities in adapting to foreign contexts. We provide below theoretical arguments for the reasons why each of the CQ facets might be uniquely positioned to contribute to work CCA.
To date, relatively little research has been conducted to analyse the relationship between meta-cognitive CQ and work CCA, producing mixed results. Indeed, whereas some investigations have found that meta-cognitive CQ exerts a positive influence on work CCA (e.g., Lin et al. 2012 ; Guðmundsdóttir 2015 ), other studies have revealed a nonsignificant effect (e.g., Jyoti and Kour 2015 ; Jyoti et al. 2015 ). Expatriates high in meta-cognitive CQ tend to reflect on cultural dissimilarities before a cross-cultural interaction and develop action plans for how they will interact with locals. This planning prompts cultural learning, problem-solving and interactions with host colleagues, which may reduce uncertainties related to expatriation and, then, facilitate work CCA (Earley and Ang 2003 ; Earley et al. 2006 ). Thus, we proposed the following hypothesis:
Hypothesis 2a: metacognitive CQ will be positively related to work CCA.
Whereas some studies have identified a positive influence of cognitive CQ on work CCA (e.g., Konanahalli et al. 2014 ), other investigations revealed a non-significant association between the two constructs (e.g., Jyoti and Kour 2015 ). Expatriates high in cognitive CQ have a greater understanding of cross-cultural differences (Brislin et al. 2006 ): they are better able to use their cultural knowledge in making decisions and thinking strategically to overcome transition problems. This, in turn, may improve their ability to adjust to the new workplace (Van Dyne et al. 2012 ). Thus, we expected the following:
Hypothesis 2b: cognitive CQ will be positively related to work CCA.
Expatriates high in motivational CQ are more psychologically prepared to adjust to the work demands expected in culturally diverse workplaces (Chen et al. 2010 ). Thus, they have confidence in their capabilities and intrinsic motivation to adjust to new workplaces (Palthe 2004 ) and display newly learn behaviours (Black et al. 1991 ). This may stimulate their involvement in culturally different modes of working and the accomplishment of their assignment objectives (Lin et al. 2012 ). Accordingly, empirical evidence supported that motivational CQ is positively associated with expatriates’ work CCA (Jyoti and Kour 2015 ; Jyoti et al. 2015 ). Thus, we predicted the following:
Hypothesis 2c: motivational CQ will be positively related to work CCA.
Whereas some studies have revealed that behavioural CQ was non-significantly (e.g., Huff et al. 2014 ; Konanahalli et al. 2014 ) or negatively (e.g., Guðmundsdóttir 2015 ; Malek and Budhwar 2013 ) related to work CCA, other investigations have found a positive association between the two constructs (e.g., Ng et al. 2012 ; Ramalu et al. 2011 ). Expatriates with greater behavioural CQ can use culturally appropriate expressions in communication, in addition to flexibly adapting their behaviour to create comfort zones for the other individual(s) involved in cross-cultural encounters (Earley and Peterson 2004 ). The ability to make such adaptations is likely to result in better work CCA because it facilitates communication with host colleagues, reducing the risk of cross-cultural misunderstandings (Ang et al. 2007 ). Therefore, we hypothesized the following:
Hypothesis 2d: behavioural CQ will be positively related to work CCA.
The Relationship between Expatriates’ Work CCA and Assignment-Specific Performance
When expatriates can successfully adjust to the work domain, they are less stressed and, then, have more personal resources to invest in job duties. In this case, they are likely to feel themselves as culturally competent and build closer relationships with local colleagues (Lee and Sukoco 2010 ; Chen et al. 2010 ). As a result, expatriates who are culturally adjusted to their new workplaces are more likely to perform well on their international assignments than those who are unable to adjust well (Lee and Kartika 2014 ; Wu and Ang 2011 ). Therefore, we expected the following:
Hypothesis 3: work CCA will be positively related to assignment-specific performance.
The Mediating Role of Work CCA
Prior research suggested that CCA might mediate the association between CQ and performance (Kim and Slocum 2008 ; Wang and Takeuchi 2007 ). Despite this development, the empirical evidence on the role played by work CCA in mediating the relationship between specific CQ dimensions and assignment-related tasks has been relatively limited in the expatriate literature, requiring further research (e.g., Jyoti and Kour 2015 ; Lee et al. 2014 ). Kim et al. ( 2008 ) proposed that CQ may work through work CCA to affect expatriate performance as the extent to which expatriates are able to successfully adapt to a new work setting may impact on individual work outcomes. They argued that “a smooth transition across work assignments is critical to an expatriate’s success because the work-role that is executed in the host country may be quite unfamiliar, even though the task is the same as it was in their home country, due to different cultural contexts” (ibidem, p. 76). Therefore, expatriates who have greater CQ are more likely to successfully adjust to their new work setting which, in turn, will enable them to reach high levels of performance. Overall, relevant intercultural skills, such as abilities to revise cultural assumptions (meta-cognitive CQ), elaborate sophisticated metal maps about cultures (cognitive CQ), channel one’s own energies toward functioning (motivational CQ) and exhibit appropriate actions (behavioural CQ) in culturally diverse settings, are all factors which are expected to decrease the misunderstandings in role expectations and facilitate interactions with local colleagues (Ramalu et al. 2012 ). As a result, culturally intelligent expatriates, who are better able to cope with stress related to uncertainties (Sambasivan et al. 2017 ), may more easily feel comfortable in any cultural setting they are working in. Then, work CCA holds the potential to be a proximal intercultural effectiveness outcome which may partially mediate the effects of the four CQ dimensions on more distal effectiveness outcomes, such as assignment specific performance. Hence:
Hypothesis 4: work CCA will mediate the relationship between specific dimensions of CQ (Hp4a: meta-cognitive CQ, Hp4b: cognitive CQ, Hp4c: motivational CQ, Hp4d: behavioural CQ) and assignment-specific performance.
The Moderating Role of Cultural Distance
The individual’s capability to successfully adjust abroad is related to the novelty of the foreign culture. A large difference between the country of origin and the destination requires more transitions, which results in more adjustment difficulties than in a country with a similar culture (Bhaskar-Shrinivas et al. 2005 ). Said differently, adjustment is more challenging when the host country is more culturally distant (Wang and Varma 2019 ). In this context, individual differences may become particularly salient. Indeed, prior investigations revealed that CD moderates the relationship between individual characteristics and various outcomes in the expatriation field, such as effectiveness (Chen et al. 2010 ), adjustment (Zhang 2013 ), and intention to work abroad (Remhof et al. 2013 ). Among individual characteristics, CQ seems to be a variable highly likely to interact with CD on work CCA because of its relevance on settings characterized by cultural diversity. In line with Kim et al. ( 2008 ), “as CD increases, it is expected that CQ would become more, rather than less, critical to expatriates’ adjustment and success” (Kim et al. 2008 , p. 78). Accordingly, CD strengthens the CQ-CCA association since the greater cultural challenges inherent in more culturally distant settings demand more cross-cultural competencies. In this context, those with greater CQ may be better equipped to overcome such challenges and, then, better able to adjust and perform well than those with lower CQ. Thus, we expected the following:
Hypothesis 5: CD will strength the relationship between CQ, in all its dimensions (Hp5a: metacognitive CQ, Hp5b: cognitive CQ, Hp5c: motivational CQ, Hp5d: behavioural CQ), and work CCA, such that the positive effect of CQ dimensions through work CCA on assignment-specific performance will be stronger when the home-host CD will be greater.
The Moderating Role of Length of Residence in the Host Country
Previous investigations on CCA have showed that length of residence in the host country influences CCA (e.g., Li et al. 2013 ; Ramalu et al. 2010 ). According to the U-Curve of CCA framework (Black and Mendenhall 1991 ), the first twelve months in a foreign country are characterized by frustration as the newcomer must deal with living in the host country on a daily basis, overcoming the so-called “cultural shock stage”. CQ may become critical to overcome such highly challenging period because culturally intelligent expatriates can more easily use their cultural knowledge and develop action plans to solve transition problems (meta-cognitive and cognitive CQ; Earley et al. 2006 ). In addition, CQ may be salient because it drives expatriates to establish relationships with local colleagues and vicariously learn about appropriate behaviours (motivational CQ; Mendenhall and Oddou 1985 ). This may lead them to make appropriate behavioural adaptations (behavioural CQ). Thereby, expatriates high in CQ are more likely to learn quickly appropriate behaviours, which may decrease the anxiety related to not knowing how to behave in an unfamiliar environment. As a result, the time required to reach the adjustment stage may be shortened. Additionally, the longer the time spent in the host country, the greater the opportunities to build support systems, reach greater cultural knowledge, and become more efficacious in interacting with locals. This suggests that motivational CQ might be more critical in the initial stages of the adjustment process when individuals have to deal with daily challenges. Thus, we expected the following:
Hypothesis 6: the length of residence in the host country will moderate the relationship between CQ, in all its dimensions (Hp6a: metacognitive CQ, Hp6b: cognitive CQ, Hp6c: motivational CQ, Hp6d: behavioural CQ) and work CCA, such that the positive effect of CQ dimensions through work CCA on assignment-specific performance will be stronger when the length of residence will be lower.
The Moderating Role of International Work Experience
Culturally intelligent expatriates having longer experience of working abroad through vicarious learning can more easily make anticipatory adjustments to the new work setting before they ever experience it (Black et al. 1991 ). In this sense, they may benefit from prior international work experience because they can utilize it as an important source of information which facilitates the formation of realistic work expectations and accurate anticipatory work behavioural adaptations (Church 1982 ). Indeed, expatriates with greater CQ will be more likely to acquire more accurate information from their previous experience as, for instance, they will think critically about cultural knowledge and monitor the quality of that knowledge (Ang et al. 2007 ). This may increase attention and retention processes, leading them to make anticipatory adjustments in behaviours, which would turn out to be appropriate in the host workplace. This means that they will learn lessons from their prior experience and form comprehensive cognitive schemata, which will be useful to predict consequences across a variety of future situations (Takeuchi et al. 2005 ). As a result, prior experience will help expatriates with greater CQ to effectively handle future cross-cultural situations (Lee and Sukoco 2010 ; Shannon and Begley 2008 ). This will decrease the uncertainty and, therefore facilitate, the adjustment process (Black et al. 1991 ), leading to a better performance (Jyoti and Kour 2017a , 2017b ). Conversely, expatriates with lower CQ will be less likely to take advantage from their prior experience as the content of the information will be inaccurate and, then, their actual reproduction of the anticipatorily determined behaviours will prove to be inappropriate in the new workplace (Black et al. 1991 ). Furthermore, although some studies showed that prior experience had an enhancing effect on the CQ-CCA relationship (Lee 2010 ; Lee and Sukoco 2010 ; Jyoti and Kour 2017a , 2017b ), the research has not been consistently supportive (Vlajčić et al. 2019 ). Further to this, research analysing whether prior experience might exert an enhancing effect on the association between the four CQ dimensions and specific domains, such as work CCA, is still limited (Kusumoto 2014 ). Thus, we examined whether prior experience would strengthen the CQ- work CCA relationship, expecting the following:
Hypothesis 7: international work experience will moderate the relationship between CQ, in its dimensions (Hp7a: metacognitive, Hp7b: cognitive, Hp7c: motivational, Hp7d: behavioural), and work CCA, such that the culturally intelligent expatriates with greater experience will adapt more easily to the host workplace and, then, perform more effectively than those with lower experience.
As a conceptual framework, Fig. 1 illustrates our proposed model, incorporating our hypothesized relationships.
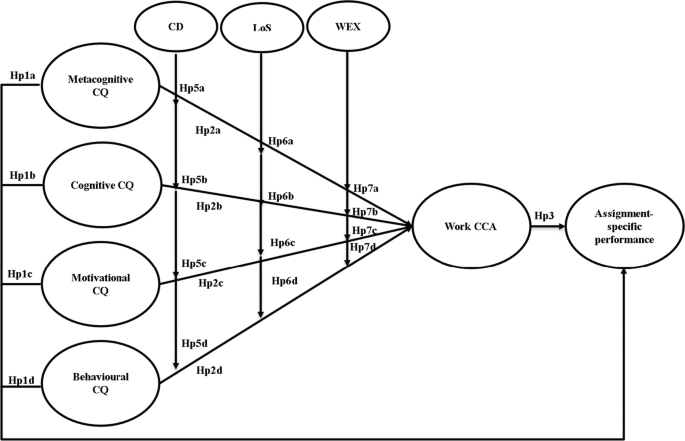
Proposed model regarding the relationships between the four components of cultural intelligence (CQ) and assignment-specific performance as well as the moderating role of cultural distance (CD), length of stay in the host country (LoS) and previous international work experience (WEX) in the association between CQ components and cross-cultural adaptation at work (work CCA)
Participants and Procedure
Our research sample consists of employees who were working in a company in the oil and gas industry with an extensive portfolio of projects around the world. Expatriates’ contacts details were gathered from organizational databases. Questionnaires were administrated in English (see Appendix 1 ), the official working language in the company, through a Web-based solution (i.e., mails and online questionnaires). Once respondents voluntarily agreed to participate, we obtained informed consent from them and ensured them the anonymity and confidentiality of their responses. Data were collected in the period between March and May 2018. In total, we contacted four hundred ninety-four expatriates. Of them, one hundred sixty-eight employees completed the survey (34% response rate). We excluded eight participants working in their home country and nine participants because they did not complete at least the 60 % of the survey. The descriptive statistics of the remaining participants ( N = 151) are reported in Table 1 .
Most of research participants were Latin American expatriates assigned to Middle East countries. The Middle East, especially the Muslim and Arab countries of Sud Arabia, Oman and the UAE, represents a hot spot for international assignments (Raghu and Sartawi 2012 ). For instance, according to the data provided by the World Bank, the UAE’s population in 2020 is 9.89 million of whose the 88.52% is constituted by expatriates and immigrants (GMI 2020 ). Arab countries have practices and habits that contrast with those of the Latin American nations. Since the UAE’s culture is masculine in nature, a Latin American expatriate might have difficulties to adjust to a 100% male environment where there is a dress code for men as well (Konanahalli et al. 2012 ). Additionally, during the holy month of Ramadan the Muslim colleagues observe Ramadan fasting rules, which will require Latin Americans to be respectful of such religious observances (ibidem). According to GLOBE Project’s studies on cultural dimensions (House et al. 2004 ), the Middle East cultural cluster is characterized by high scores on collectivism, average scores on assertiveness, human orientation, institutional collectivism, performance orientation and power distance, while for future-orientation, gender egalitarianism and uncertainty avoidance the scores are low (for a detailed description of each cultural dimension see at the following link: https://globeproject.com/study_2004_2007 ). Although similar for some dimensions, the Middle East cluster differs from the Latin American cluster most significantly on the values of institutional collectivism, performance orientation and gender egalitarianism. These differences might translate in striking contrasts in terms of decision making, negotiation, conflict management, leadership styles and so on (e.g., Caputo et al. 2018 ; Caputo et al. 2019 ). In sum, it is likely that Latin American expatriates working in an Arab country will experience significant national cultural dissimilarities, which might lead them to adjustment difficulties.
CQ was assessed by The Cultural Intelligence Scale (Ang et al. 2007 ) which comprises four sub-scales: meta-cognitive CQ (four items, e.g. “I check the accuracy of my cultural knowledge as I interact with people from different cultures”, α = .81 ) ; cognitive CQ (six items, e.g., “ I know the rules for expressing non-verbal behaviour in other cultures”, α = .83); motivational CQ (five items, e.g., “ I enjoy interacting with people from different cultures”, α = .89 ) ; behavioural CQ (five items, e.g., “ I change my verbal behaviour when a cross-cultural interaction requires it”, α = .84 ) . This robust and reliable scale has been utilized by previous studies (e.g., Gozzoli and Gazzaroli 2018 ), confirming the existence of four specific CQ dimensions. Participants indicated how much they agreed with each statement concerning their cultural abilities on a seven-point Likert-type scale (1 = strongly disagree 7 = strongly agree ), where higher scores indicated higher CQ levels.
Work CCA was measured using three items from the Expatriate Adjustment Scale (Black and Stephens 1989 ). Participants rated their adjustment (e.g., “ How adjusted are you to performance standards and expectations in your job? ”, α = .89) on a seven-point Likert-type scale (1 = very unadjusted 7 = very adjusted ), where greater scores indicated greater work CCA. This measure has been consistently validated by previous studies on expatriates (e.g., Bhaskar-Shrinivas et al. 2005 ) confirming its construct validity among culturally different samples.
Assignment-specific performance was evaluated through five items from the Expatriate Contextual/Managerial Performance Skills (Caligiuri 1997 ). Participants were asked to rate their perceived ability in each of the job performance items (e.g., “ Your effectiveness at transferring information across strategic units (e.g., from the host country to headquarters) ”, α = .73) on a five-point Likert-type scale (1 = poor 5 = outstanding ) , where greater scores indicated greater performance.
CD between expatriates’ home country and host country was computed through the index of Kogut and Singh ( 1988 ) in combination with Hofstede’s ( 2001 ) country-specific scores (i.e., power distance, individualism, masculinity, and uncertainty avoidance), consistent with prior studies (e.g., Ng et al. 2019 ).
Length of residence in the host country was measured in months in line with previous researchers (e.g., Chen et al. 2014 ). Participants indicated the period in the current country of destination in months (i.e., How long have you been working in your current country of residence? ).
International work experience was assessed in years, according to previous studies (e.g., Jyoti and Kour 2017a , b ). Respondents indicated how many years they had been working internationally (i.e., How many years had you spent working abroad before this assignment? ).
Control variables . We controlled for marital status (1 = single, 2 = engaged) and education level (1 = high-school, 2 = degree) because previous studies showed that work-family conflict - that is more likely to occur for married expatriates; Kupka and Cathro 2007 - and education level (e.g., Moon et al. 2012 ) may influence CCA; thereby, potentially affecting performance. Furthermore, we controlled for gender (1 = male, 2 = female) and age since prior investigations (e.g., Li et al. 2016 ; Vlajčić et al. 2019 ) have revealed contrasting results about the impact of age and gender on CQ and CCA. Additionally, we recognized that pre-departure cross-cultural training (i.e., Did you have any cross-cultural training before departure? 1 = yes, 2 = no) might be associated with CCA as some studies showed that expatriates who received cross-cultural pre-departure training were more likely to successfully adjust to the host environment (e.g., Evans 2012 ). Since previous studies found that length of stay in the host country and international work experience could affect both CQ (e.g., Wang et al. 2017 ; Moon et al. 2012 ) and CCA (e.g., Ramalu et al. 2010 ; Lee and Kartika 2014 ), we considered the role of these constructs as control variables. Moreover, we acknowledged that CD might impact on CCA, such that the greater the CD, the greater the adjustment difficulties (e.g., Wang and Varma 2019 ). None of the control variables significantly correlated with - or had any significant impact on - the variables of interest within our models, which is why we decided to exclude them from all subsequent analyses and present models without these controls. This is in line with recommended practices (Aguinis and Vandenberg 2014 ).

Descriptive Analyses
We conducted descriptive statistics and correlations among the study variables using SPSS version 20 (Morgan et al. 2012 ). The four CQ dimensions were significantly and positively correlated with each other and with both work CCA and performance (see Table 2 ). The average inter-item correlations between CQ and outcomes was .24, suggesting that items did contain sufficiently unique variance to not be isomorphic with each other (Piedmont 2014 ).
Confirmatory Factor Analyses and Assessment of Common Method Bias
Firstly, using Mplus Version 7 (Muthén and Muthén 1998-2012 ), a confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) with the maximum likelihood method was carried out to examine the factor structure of the study variables. Results from CFA revealed that the six-factor model (i.e., four CQ dimensions, work CCA, performance) outperformed all the alternative models (χ 2 [335] = 782.70, CFI = .78, TLI = .76, RMSEA = .09, SRMR = .10). However, to obtain a satisfactory fit (χ 2 [330] = 221.59, CFI = .90, TLI = .90, RMSEA = .06, SRMR = .07), it was necessary to take into account the high correlation existing among some items (see Table 3 ). The resulting models were built considering the modification indices which were used in this satisfactory model. Moreover, to control for common method bias, an unmeasured latent method factor was added to the hypothesized CFA model and allowed manifest indicators to load on their respective latent constructs as well as on the method factor (Podsakoff et al. 2012 ). Results indicated that the hypothesized six-factor model yielded a better fit to the data after inclusion of the method factor (Δ χ 2 [302] = 480.28, RMSEA = .06, SRMR = .06, CFI = .91, TLI = .90). The method factor explained only 24% of the variance in the items, which is below the average amount of method variance (25%) reported in self-reported research (Podsakoff et al. 2012 ). Accordingly, common method bias does not appear to have a substantial impact on the present study. Finally, a second order CFA was tested, confirming that CQ loaded into its respective four sub-dimensions (χ 2 [327] = 505.460, CFI = .91, TLI = .90, RMSEA = .06, SRMR = .07).
Hypotheses Testing
Given our relatively small sample size, the Partial Least Squares (PLS) method, which is a variance-based structural equation modelling, was considered as particularly appropriate to simultaneously test whether each of the four CQ dimensions were related to performance directly and indirectly, as mediated by work CCA. Partial least squares structural equation modelling (PLS-SEM) represents a multivariate modelling technique suitable for the analysis of multiple dependent and independent latent constructs (Mathwick et al. 2008 ). This technique computes relationships between all variables simultaneously and does not necessitate multivariate normality (Zhou et al. 2012 ). Since CQ includes four components, a hierarchical component model (HCM) was created to assess the mediation model (Lohmoller 1989 ). This allowed us to reduce the number of associations in the model, making the model more parsimonious and resistant to collinearity problems (Hair et al. 2017 ). PLS-SEM methodology, utilizing a HCM, enables to examine each component of CQ independently through a higher-order construct that, by theoretical classification of HCM modelling, is a full mediator (Hair et al. 2017 ) in the process of direct and indirect associations between each component of CQ and performance. Using PLS-SEM, it is possible to evaluate each dimension separately, in addition to providing a diverse theoretical explanation for each dimension (Ott and Michailova 2018a , 2018b ). The repeated indicator approach was utilized in a reflective-formative type of HCM using SmartPLS v. 3.2.6. (Ringle et al. 2017 ) to further confirm the measurement model which was previously tested. This model comprises six reflective constructs and one second-order construct which contains latent variable scores for the four dimensions of CQ (a similar methodological approach was also taken by Vlajčić et al. 2019 ). All the items showed statistically significant and satisfactory loadings values (> 0.7; de Pablo González et al. 2014 ). The composite reliabilities of all seven constructs were acceptable as values were above 0.80 and below 0.95 (Nunnally and Bernstein 1994 ; see Table 2 ). The convergence validity was acceptable as all the average variance extracted (AVE) values were above the recommended value of 0.5 (Hair et al. 2010 ). Discriminant validity of our constructs was further confirmed as correlations between each pair of latent constructs do not exceed the square root of each construct’s AVE (Fornell and Larcker 1981 ), apart from the second-order formative construct (CQ-HCM) and the latent constructs it includes, as anticipated by Hair et al. ( 2017 ). These results further confirmed the discriminant validity of our constructs of interest.
Subsequently, the structural model was evaluated using a bootstrapping procedure (10,000 sub-samples; Hernández-Perlines et al. 2016 ). Structural coefficients presented in the PLS model (see Table 4 ) indicated that the dimensions of meta-cognitive ( β = .10, t = 4.13, p < .001), cognitive ( β = .12, t = 3.58, p < .001), motivational ( β = .15, t = 4.12, p < .001), and behavioural ( β = .12, t = 3.68, p < .001) CQ were directly and positively associated with performance. Thereby, Hypotheses 1a , 1b , 1c and 1d were confirmed. Additionally, the dimensions of meta-cognitive ( β = .11, t = 3.39, p < .001), cognitive ( β = .13, t = 4.79, p < .001), motivational ( β = .17, t = 4.30, p < .001), and behavioural ( β = .13, t = 4.18, p < .001) CQ were directly and positively related to work CCA. Thereby, Hypotheses 2a , 2b , 2c and 2d were confirmed. Work CCA ( β = .19, t = 1.96, p < .05) was positively related to performance (see Fig. 2 ). Thereby, Hypothesis 3 was supported. Results from mediation models indicated that work CCA partially mediated the associations between meta-cognitive ( β = .02, t = 1.65, p < .05), cognitive ( β = .03, t = 1.83, p < .05), motivational ( β = .03, t = 1.84, p < .05), and behavioural ( β = .02, t = 1.85, p < .05) CQ and assignment specific performance. Therefore, Hypotheses 4a , 4b , 4c and 4d were confirmed. Moreover, our analysis of the structural model also includes the R 2 and Q 2 as indexes of model consistency and predictive relevance. The indicators of consistency were appropriate, even if CQ and its dimensions explained a weak amount of variation in the constructs of interest (R 2 (CCA) = .26; R 2 (performance) = .25). The predictive relevance of the indicators (Q 2 (CCA) = .70; Q 2 (performance) = .35) were in the large effect size range (Neter et al. 1990 ).
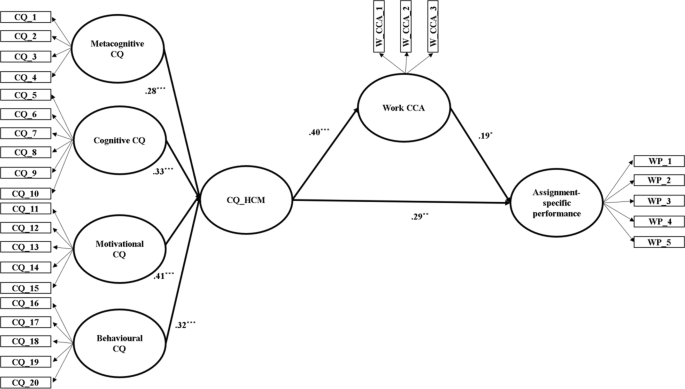
Results from models analysing the mediating effect of work CCA in the relationships between each of CQ dimension and assignment-specific performance
Further, we tested whether the strength of the relationship between CQ and performance through work CCA was conditional on the value of our expected moderators. To this end, we conducted moderated mediation models for each of the CQ dimensions using Mplus Version 7. CD weakened the relationship between motivational CQ and work CCA (β = −.06, p < .05), but no significant interaction terms were revealed for the other CQ dimensions. Then, Hypotheses 5a , 5b and 5d were not supported. The moderated mediation effect of the interaction of motivational CQ and CD through work CCA on performance was significant (see Table 5 ). However, contrary to what expected based on Hypothesis 5c , results indicated that CD weakened the positive relationship between motivational CQ and work CCA, such that the relationship was stronger when CD was low and weaker when CD was high (β = .14, p < .05 for low CD, β = .12, p < .05 for moderate CD, β = .11, p < .05 for high CD).
Length of residence in the host country weakened the positive association between motivational CQ and work CCA (β = −.19, p < .01). The moderated mediation effect of motivational CQ and time of residence in the host country through work CCA on performance was particularly significant for expatriates who had been working in the host country for a shorter time (β = .44, p < .05), but, even if it was still significant, the enhancing effect of length of residence in the host region on the motivational CQ-work CCA relationship decreased with the passage of time (β = .37, p < .05 and β = .31, p < .05; for those working in the foreign country for an average and a longer period of time, respectively; see Table 5 ). Thereby, Hypothesis 6c was supported, whereas Hypotheses 6a , 6b and 6d were rejected.
Experience moderated the relationship between motivational CQ and work CCA (β = −.35, p < .01), but not the associations between the other CQ dimensions. However, contrary to what expected based on Hypothesis 7c , the moderated mediation effect of motivational CQ and experience through work CCA on performance was stronger for expatriates who had lower international work experience (β = .47, p < .05) than for those who had moderate (β = .36, p < .05) or longer (β = .24, p < .05) experience (see Table 5 ). Therefore, Hypotheses 7a , 7b and 7d were rejected and Hypothesis 7c was not confirmed given that the direction was opposed to what expected.
The validity of the hypothesized models was assessed by comparing each of them (i.e., in terms of BIC and AIC comparative indices) with three competing models, as described in detail in Table 6 . The models with motivational CQ were the better-fitting models compared to those which included other CQ dimensions as antecedents.
Several findings emerged from this research which make a meaningful contribution to the existing literature on expatriates (see Fig. 3 for an overview of the confirmed hypotheses).
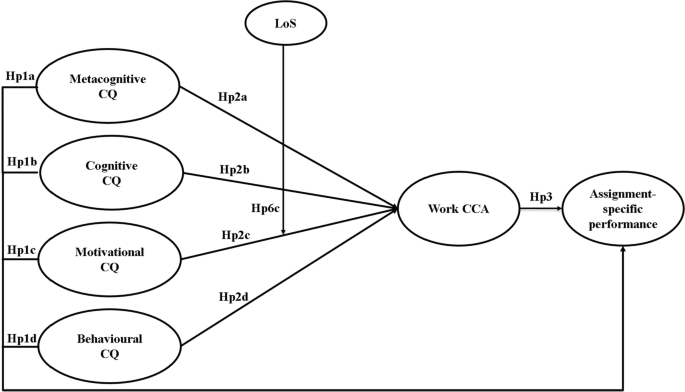
Model representing the hypotheses which were confirmed
First, each of the four CQ components were related to assignment-specific performance, both directly and indirectly, as partially mediated by work CCA. Then, culturally intelligent expatriates are likely to minimize cultural blunders and meet role expectations which, in turn, reduces the likelihood of misunderstandings, increasing performance (Moynihan et al. 2006 ). Moreover, they can successfully adjust to the host workplace, which enables them to channel their energies to improve their performance in assignment-specific tasks (Malek and Budhwar 2013 ; Shaffer et al. 2006 ).
Second, contrary to what expected based on Kim et al. ( 2008 ), CD is more likely to attenuate, rather than amplify, the positive effect of motivational CQ on work CCA in less culturally distant settings, such that the culturally intelligent expatriates are more likely to adjust to the host workplace and, then, perform well when CD is low. A plausible explanation is that when expatriates are confronted with more culturally different workplaces, their motivational CQ might not be sufficient to overcome the challenges posed by more complex assignments due to the greater cultural unfamiliarity (Chen et al. 2010 ; Vlajčić et al. 2018 ; Wang and Varma 2019 ).
Third, the length of residence in the host country weakens the positive relationship between motivational CQ and work CCA, such that motivational CQ is particularly salient when expatriates are in the initial stages of the adjustment process. Said differently, the greater the initial level of motivational CQ, the shorter the time required to adjust to the host country. Therefore, even if motivational CQ facilitates work CCA at any time, expatriates who are at the beginning of their assignment are likely to benefit more from motivational CQ than those who are in the host region from a longer time (Firth et al. 2014 ). Even if they were confronted with failures in their attempts of reproducing the new behaviours, cross-culturally motivated expatriates would be likely to persist at trying to imitate such behaviours longer than those with lower motivational CQ (Bandura 2002 ). This will increase the chances of receiving feedbacks, which will result in displaying appropriate behaviours; thereby, facilitating their adjustment to the new workplace and, then, their performance.
Fourth, motivational CQ is more salient for expatriates who are on their first assignment than for those who have longer experience in international assignments. Even if they have limited experience, the cross-culturally motivated expatriates tend to be more self-confident about their ability to interact with culturally diverse colleagues. They are also more willing to learn about unfamiliar cultures and experiment themselves in imitating culturally appropriate behaviours. Said differently, motivational CQ may counterbalance expatriates’ lack of experience, enabling them to adjust to the host workplace and, then, perform well.
Theoretical Implications
This research has several key contributions to expatriate literature. Firstly, this study extends Kim et al. ( 2008 ) by investigating whether specific CQ dimensions were associated with performance directly and indirectly, as mediated by work CCA. Additionally, by identifying, beyond CD, length of stay in the host country and work experience as boundary conditions for CQ effects, this research helps explain the mixed findings obtained in prior investigations on CQ.
Secondly, this study provides further evidence for the differential role of CQ dimensions (e.g., Rockstuhl and Van Dyne 2018 ) by testing mediating and moderating mechanisms which explain how and when each CQ facet is more - or less - likely to facilitate work CCA and performance.
Thirdly, our findings add to a growing body of literature on expatriate adjustment (e.g., Chew et al. 2019 ; Bhaskar-Shrinivas et al. 2005 ) by confirming the key role of work CCA, which represents a primary factor of interest to MNCs as it is crucial for assignment-specific performance.
Fourthly, this study deepens our understanding of boundary conditions for CQ effects by showing that, of the four CQ factors, only motivational CQ was qualified by CD, length of stay and experience. On the one hand, this suggests that cognitive, metacognitive, and behavioural CQ dimensions had a positive influence on work CCA and, then, assignment-specific performance, regardless of CD, length of stay and experience. In the absence of moderation from such factors, we can confirm that, even if expatriates are on their first assignment, at the beginning of their assignment or assigned to a highly culturally diverse country, a prediction of their success can be based on cognitive, metacognitive and behavioural CQ dimensions. Such dimensions can be particularly useful in promoting performance, since the demanding work setting entails high degrees of culture-related cognitive processing, cultural awareness, and behavioural flexibility to enable for efficient problem solving (Stahl et al. 2009 ). On the other hand, this allows to consider the boundary conditions that provide insights into when motivational CQ has a stronger influence on work CCA and, then, assignment-specific performance. Even motivational CQ is a relevant skill for expatriates at any time of their assignment, expatriates benefited more from motivational CQ when they were working in the host country for a shorter period or when they had lower experience. Motivational CQ plays a peculiar role which differentiates this dimension from the others. Indeed, culturally motivated expatriates are driven to prove themselves in a large quantity of intercultural work situations (Ng et al. 2019 ), despite the challenges experienced at the beginning of a novel assignment. Furthermore, motivational CQ may compensate the lack of work experience by strengthening use of skills and resilience in the face of cultural difficulties (Bandura 2002 ). However, the positive effect of motivational CQ on CCA is necessary yet not sufficient for overcoming the challenges posed by more culturally distant workplaces, as such environments demand less familiar task requirements from expatriates. This makes the effort arouse by motivational CQ less relevant (Chen et al. 2010 ). Overall, this study adds substantially to our understanding of how motivation-related processes may contribute uniquely to expatriate effectiveness.
Practical Implications
The current study has practical implications for MNCs and international human resource management. Firstly, the finding that all CQ dimensions are related to expatriates’ performance suggests that recruiters should select and hire culturally intelligent candidates for international assignments. By evaluating applicants’ CQ and by emphasizing CQ as a critical credential that candidates – especially those with lower international experience - should have, HR representatives can select the most suitable candidates, assigning more cross-culturally motivated expatriates to foreign assignments, if possible, in less culturally distant countries.
Secondly, organizations should provide expatriates with pre-departure training programs aimed at increasing their CQ. For instance, training can offer several scenarios for work so that expatriates may be adequately prepared to comprehend and master different situations (e.g., cultural habits) when facing problems in the host country (Lin et al. 2012 ). Since our findings suggest that motivational CQ is particularly relevant to work CCA, training programs could include a module on motivational CQ (Earley and Peterson 2004 ). For example, training based on dramaturgical exercises, including role plays and simulations about intercultural interactions could be useful tools to build efficacy regarding cross-cultural challenges (ibidem). Furthermore, managers should consider fostering expatriates’ motivation prior to their assignments by emphasizing benefits related to international assignments (e.g., opportunity to develop global career competencies or monetary incentives; Hajro et al. 2017 ) and by stimulating their curiosity about diverse cultures.
Thirdly, considering the mediating role of work CCA in the relationship between CQ and performance, interventions should be implemented to enable expatriates – especially those who are on their first assignment or at the beginning of a new assignment – to receive organizational social support (i.e., from both home and host-country managers and peers) and logistical help (e.g., housing, schooling) to facilitate reaching the adjustment stage (Bhaskar-Shrinivas et al. 2005 ). For instance, companies could consider arranging informal gatherings to help workers build strong bonds with local colleagues and assigning newcomers to experienced mentors (Chen et al. 2010 ). Moreover, MNCs should develop appropriate performance management systems for expatriates and expatriate-host country nationals interaction mechanisms to facilitate work CCA (Wang and Varma 2019 ).
Limitations and Suggestions for Future Research
This research suffers from some limitations which may give venues for future research.
Some concerns regard the cross-sectional design of our study and the exclusive use of self-reported measures. To decrease the risk of common method bias, we followed Podsakoff et al.’ ( 2012 ) recommendations regarding questionnaire design. Additionally, we used the unmeasured method factor technique, showing that common method variance was not a major issue. Future studies should focus on non-same-source outcomes, collect data from multiple sources (e.g., interviews, observations of actual behaviours, performance ratings from supervisors), adopt a longitudinal design and analyse CQ at the team level (Ott and Michailova 2018a , 2018b ).
Since most of research participants were men, and gender has been previously found to affect the levels of performance among expatriates (e.g., Ramalu et al. 2012 ), this might have partially influenced our findings. However, the gender distribution in our sample is highly representative of expatriate workforce in the analysed sector. Future studies should control for other variables (e.g., openness to experience, having family accompanying in the host country).
A further limitation is related to the fact that possible selection bias due to the voluntary participation into the research cannot be ruled out. It is possible that those who experienced successful CCA experiences were more motivated to respond and, as such, are overrepresented.
Since majority of respondents were from Latin America, and cultural orientation has been revealed to impact differing coping styles, such as conflict management and negotiation styles (e.g., Caputo et al. 2018 ; Caputo et al. 2019 ), this might have partially affected our results. Therefore, more research on larger sample sizes is needed to investigate how the effect of CQ on expatriate performance might vary as a function of individual’s cultural values.
As the nature of global work assignment is expanding beyond the traditional expatriation (e.g., frequent international business travel; Shaffer et al. 2012 ), future studies should investigate the relationships between specific CQ dimensions, work CCA and performance by comparing expatriates employed in different international work arrangements and by collecting data also on international skilled migrants (Hajro et al. 2019 ).
Since CQ, EQ and SI are distinct but overlapping constructs which have been found to positively interact with each other (Crowne 2013 ), future investigations should analyse associations at the subcomponent level of CQ, EQ and SI to identify how specific dimensions of each may affect expatriate performance when the three forms of intelligence are examined together.
Future studies should also analyse conditions under which higher motivational CQ levels might undermine expatriate effectiveness (e.g., through complacency; Chen et al. 2010 ), including situations characterized by ambiguous tasks (e.g., Schmidt and DeShon 2010 ).
Finally, it would be especially important to detect further contextual variables (e.g., group climate, performance management practices; Chen et al. 2010 ; Wang and Varma 2019 ) that may facilitate expatriate performance, either directly or through interactions with specific CQ dimensions.
Even though the current cross-sectional study relied only on self-report measures, it was conducted on the relatively under-investigated population of expatriates working within the energy sector in the Middle East and it addressed some gaps in the literature by disentangling the complex relationship between CQ, CCA and performance. To this end, we tested mediating and moderating mechanisms which explain how and when specific CQ facets were more - or less - likely to facilitate assignment-specific performance. Each CQ dimension had a differential role in contributing to assignment-specific performance, directly and through work CCA. Conversely, of the four CQ factors, only motivational CQ was qualified by CD, length of stay and international work experience. Our findings indicated that motivational CQ was particularly salient in overcoming work CCA difficulties for expatriates who were at the beginning of their international assignment and who had lower experience. Moreover, motivational CQ related more positively to expatriate work CCA in less culturally distant countries. We conclude with the hope that our theoretical contributions will stimulate additional multilevel and longitudinal research on factors influencing work CCA and performance to gather further knowledge about cross-cultural management.
Aguinis, H., & Vandenberg, R. J. (2014). An ounce of prevention is worth a pound of cure: Improving research quality before data collection. Annual Review of Organizational Psychology and Organizational Behavior., 1 (1), 569–595. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-orgpsych-031413-091231 .
Article Google Scholar
Ang, S., & Van Dyne, L. (2008). Handbook of cultural intelligence: Theory, measurement, and application . Armonk, NY: M.E. Sharpe, Inc. ISBN: 9780765622624.
Google Scholar
Ang, S., Van Dyne, L., Koh, C., Ng, K. Y., Templer, K. J., Tay, C., & Chandrasekar, N. A. (2007). Cultural intelligence: Its measurement and effects on cultural judgment and decision making, cultural adaptation and task performance. Management and Organization Review, 3 (3), 335–371. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1740-8784.2007.00082.x .
Ang, S., Van Dyne, L., & Tan, I. (2011). Cultural intelligence. In R. J. Sternberg & S. B. Kaufman (Eds.), The Cambridge handbook on intelligence . Cambridge: Cambridge University Press ISBN: 9780521739115.
Bandura, A. (2002). Social cognitive theory in cultural context. Applied Psychology, 51 (2), 269–290.
Bealer, D., & Bhanugopan, R. (2014). Transactional and transformational leadership behaviour of expatriate and national managers in the UAE: A cross-cultural comparative analysis. The International Journal of Human Resource Management, 25 (2), 293–316. https://doi.org/10.1080/09585192.2013.826914 .
Bhaskar-Shrinivas, P., Harrison, D. A., Shaffer, M. A., & Luk, D. M. (2005). Input-based and time-based models of international adjustment: Meta-analytic evidence and theoretical extensions. Academy of Management Journal, 48 (2), 257–281. https://doi.org/10.5465/amj.2005.16928400 .
Black, J. S., & Gregersen, H. B. (1999). The right way to manage expats. Harvard Business Review, 77 (2), 52–53.
Black, J. S., & Mendenhall, M. (1991). The U-curve adjustment hypothesis revisited: A review and theoretical framework. Journal of International Business Studies, 22 (2), 225–247 https://www.jstor.org/stable/155208 .
Black, J. S., & Stephens, G. K. (1989). The influence of the spouse on American expatriate adjustment and intent to stay in Pacific rim overseas assignments. Journal of Management, 15 (4), 529–544. https://doi.org/10.1177/%2F014920638901500403 .
Black, J. S., Mendenhall, M., & Oddou, G. (1991). Toward a comprehensive model of international adjustment: An integration of multiple theoretical perspectives. Academy of Management Review, 16 (2), 291–317. https://doi.org/10.5465/amr.1991.4278938 .
Brislin, R., Worthley, R., & Macnab, B. (2006). Cultural intelligence: Understanding behaviors that serve people’s goals. Group & Organization Management, 31 (1), 40–55. https://doi.org/10.1177/1059601105275262 .
Caligiuri, P. M. (1997). Assessing expatriate success: Beyond just “being there”. In D. M. Saunders & Z. Aycan (Eds.), New approaches to employee management (Vol. 4, pp. 245–260). Greenwich, CT: JAI Press ISBN: 9780762303113.
Caputo, A., Ayoko, O. B., & Amoo, N. (2018). The moderating role of cultural intelligence in the relationship between cultural orientations and conflict management styles. Journal of Business Research, 89 , 10–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2018.03.042 .
Caputo, A., Ayoko, O. B., Amoo, N., & Menke, C. (2019). The relationship between cultural values, cultural intelligence and negotiation styles. Journal of Business Research, 99 , 23–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2019.02.011 .
Chao, M. M., Takeuchi, R., & Farh, J. L. (2017). Enhancing cultural intelligence: The roles of implicit culture beliefs and adjustment. Personnel Psychology, 70 (1), 257–292. https://doi.org/10.1111/peps.12142 .
Chen, G., Kirkman, B. L., Kim, K., & Farh, C. I. C. (2010). When does cross-cultural motivation enhance expatriate effectiveness? A multi-level investigation of the moderating roles of subsidiary support and cultural distance. Academy of Management Journal, 53 (5), 1110–1130. https://doi.org/10.5465/amj.2010.54533217 .
Chen, A. S. Y., Lin, Y. C., & Sawangpattanakul, A. (2011). The relationship between cultural intelligence and performance with the mediating effect of culture shock: A case from Philippine laborers in Taiwan. International Journal of Intercultural Relations, 35 (2), 246–258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijintrel.2010.09.005 .
Chen, A. S. Y., Wu, I. H., & Bian, M. D. (2014). The moderating effects of active and agreeable conflict management styles on cultural intelligence and cross-cultural adjustment. International Journal of Cross Cultural Management, 14 (3), 270–288. https://doi.org/10.1177/1470595814525064 .
Chew, E, Y., Ghurburn, A., Terspstra-Tong, J, L., & Perera, H, K. (2019). Multiple intelligence and expatriate effectiveness: The mediating roles of cross-cultural adjustment. The International Journal of Human Resource Management , 1-33. https://doi.org/10.1080/09585192.2019.1616591 .
Chua, R. Y., Morris, M. W., & Mor, S. (2012). Collaborating across cultures: Cultural metacognition and affect-based trust in creative collaboration. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes, 118 (2), 116–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.obhdp.2012.03.009 .
Church, A. T. (1982). Sojourner adjustment. Psychological Bulletin, 91 (3), 540–572. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-2909.91.3.540 .
Crowne, K. A. (2013). Cultural exposure, emotional intelligence, and cultural intelligence: An exploratory study. International Journal of Cross Cultural Management, 13 (1), 5–22. https://doi.org/10.1177/1470595812452633 .
de Pablo González, J. D. S., Pardo, I. P. G., & Perlines, F. H. (2014). Influence factors of trust building in cooperation agreements. Journal of Business Research, 67 (5), 710–714. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2013.11.032 .
Earley, P. C., & Ang, S. (2003). Cultural intelligence: Individual interactions across cultures . Palo Alto: Stanford University Press ISBN: 9780804743129.
Book Google Scholar
Earley, P. C., & Peterson, R. S. (2004). The elusive cultural chameleon: Cultural intelligence as a new approach to intercultural training for the global manager. Academy of Management Learning & Education, 3 (1), 100–115. https://doi.org/10.5465/amle.2004.12436826 .
Earley, P. C., Ang, S., & Tan, J. (2006). Cultural intelligence: Developing cultural intelligence at work . Palo Alto: Stanford University Press ISBN: 9780804771726.
Evans, E, H. (2012). Expatriate success: Cultural intelligence and personality as predictors for cross-cultural adjustment (doctoral dissertation, the University of Tennessee at Chattanooga).
Fernandez-Duque, D., Baird, J. A., & Posner, M. I. (2000). Executive attention and metacognitive regulation. Consciousness and Cognition, 9 (2), 288–307. https://doi.org/10.1006/ccog.2000.0447 .
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Finaccord (2018). Global expatriates: size, segmentation and forecast for the worldwide market. Available from http://finaccord.com/BlankSite/media/Catalog/Prospectus/report_prospectus _APG_GEP.pdf.
Firth, B. M., Chen, G., Kirkman, B. L., & Kim, K. (2014). Newcomers abroad: Expatriate adaptation during early phases of international assignments. Academy of Management Journal, 57 (1), 280–300. https://doi.org/10.5465/amj.2011.0574 .
Fornell, C., & Larcker, D. F. (1981). Evaluating structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error. Journal of Marketing Research, 18 (1), 39–50.
Froese, F. J., & Peltokorpi, V. (2011). Cultural distance and expatriate job satisfaction. International Journal of Intercultural Relations, 35 (1), 49–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijintrel.2010.10.002 .
GMI (2020). United Arab Emirates population statistics (2020). Available from https://www.globalmediainsight.com/blog/uae-population-statistics/
Gozzoli, C., & Gazzaroli, D. (2018). The cultural intelligence scale: A contribution to the Italian validation. Frontiers in Psychology, 9 , 1183. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2018.01183 .
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Groves, K. S., & Feyerherm, A. E. (2011). Leader cultural intelligence in context: Testing the moderating effects of team cultural diversity on leader and team performance. Group & Organization Management, 36 (5), 535–566. https://doi.org/10.1177/1059601111415664 .
Groves, K. S., Feyerherm, A., & Gu, M. (2015). Examining cultural intelligence and cross-cultural negotiation effectiveness. Journal of Management Education, 39 (2), 209–243. https://doi.org/10.1177/1052562914543273 .
Guðmundsdóttir, S. (2015). Nordic expatriates in the US: The relationship between cultural intelligence and adjustment. International Journal of Intercultural Relations, 47 , 175–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijintrel.2015.05.001 .
Hair, J., Black, W., Babin, B., & Anderson, R. (2010). Multivariate data analysis: A global perspective . Upper Saddle River: Pearson Education.
Hair, J. F., Hult, G. T. M., Ringle, C. M., Sarstedt, M., & Thiele, K. O. (2017). Mirror, mirror on the wall: A comparative evaluation of composite-based structural equation modeling methods. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 45 (5), 616–632.
Hajro, A., Gibson, C. B., & Pudelko, M. (2017). Knowledge exchange processes in multicultural teams: Linking organizational diversity climates to teams’ effectiveness. Academy of Management Journal, 60 (1), 345–372. https://doi.org/10.5465/amj.2014.0442
Hajro, A., Stahl, G. K., Clegg, C. C., & Lazarova, M. B. (2019). Acculturation, coping, and integration success of international skilled migrants: An integrative review and multilevel framework. Human Resource Management Journal, 29 (3), 328–352. https://doi.org/10.1111/1748-8583.12233 .
Hernández-Perlines, F., Moreno-García, J., & Yañez-Araque, B. (2016). The mediating role of competitive strategy in international entrepreneurial orientation. Journal of Business Research, 69 (11), 5383–5389.
Hofstede, G. (2001). Culture’s consequences: Comparing values, behaviors, institutions, and organizations across nations . Thousand Oaks: Sage ISBN: 9780803973244.
House, R. J., Hanges, P. J., Javidan, M., Dorfman, P. W., & Gupta, V. (Eds.). (2004). Culture, leadership, and organizations: The GLOBE study of 62 societies . Thousand Oaks: Sage publications.
Huff, K. C., Song, P., & Gresch, E. B. (2014). Cultural intelligence, personality, and cross-cultural adjustment: A study of expatriates in Japan. International Journal of Intercultural Relations, 38 , 151–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijintrel.2013.08.005 .
Imai, L., & Gelfand, M. J. (2010). The culturally intelligent negotiator: The impact of cultural intelligence on negotiation sequences and outcomes. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes, 112 (2), 83–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.obhdp.2010.02.001 .
Jyoti, J., & Kour, S. (2015). Assessing the cultural intelligence and task performance equation: Mediating role of cultural adjustment. Cross Cultural Management, 22 (2), 236–258. https://doi.org/10.1108/CCM-04-2013-0072 .
Jyoti, J., & Kour, S. (2017a). Factors affecting cultural intelligence and its impact on job performance: Role of cross-cultural adjustment, experience and perceived social support. Personnel Review, 46 (4), 767–791. https://doi.org/10.1108/PR-12-2015-0313 .
Jyoti, J., & Kour, S. (2017b). Cultural intelligence and job performance: An empirical investigation of moderating and mediating variables. International Journal of Cross Cultural Management, 17 (3), 305–326. https://doi.org/10.1177/1470595817718001 .
Jyoti, J., Kour, S., & Bhau, S. (2015). Assessing the impact of cultural intelligence on job performance: Role of cross-cultural adaptability. Journal of IMS Group, 12 (1), 23–33.
Kim, K., & Slocum, J. W. (2008). Individual differences and expatriate assignment effectiveness: The case of US-based Korean expatriates. Journal of World Business, 43 (1), 109–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwb.2007.10.005 .
Kim, K., Kirkman, B. L., & Chen, G. (2008). Cultural intelligence and international assignment effectiveness: A conceptual model and preliminary findings. In S. Ang & L. Van Dyne (Eds.), Handbook of cultural intelligence: Theory, measurement, and applications (pp. 71–90). Armonk: M.E. Sharpe ISBN:9780765622624.
Kogut, B., & Singh, H. (1988). The effect of national culture on the choice of entry mode. Journal of International Business Studies, 19 (3), 411–432. https://doi.org/10.1057/palgrave.jibs.8490394 .
Konanahalli, A., Oyedele, L. O., Coates, R., von Meding, J., & Spillane, J. (2012). International projects and cross-cultural adjustments of British expatriates in Middle East: A qualitative investigation of influencing factors. Construction Economics and Building, 12 (3), 31–54. https://doi.org/10.5130/AJCEB.v12i3.2628 .
Konanahalli, A., Oyedele, L., Spillane, J., Coates, R., Von Meding, J., & Ebohon, J. (2014). Cross-cultural intelligence: Its impact on British expatriate adjustment on international construction projects. International Journal of Managing Projects in Business, 7 (3), 423–448. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJMPB-10-2012-0062 .
Kupka, B., & Cathro, V. (2007). Desperate housewives–social and professional isolation of German expatriated spouses. The International Journal of Human Resource Management, 18 (6), 951–968. https://doi.org/10.1080/09585190701320908 .
Kusumoto, M. (2014). The role of expatriates in cross-subsidiary collaboration. In D. A. Vazquez-Brust, J. Sarkis, & J. J. Cordeiro (Eds.), Collaboration for sustainability and innovation: A role for sustainability driven by the global south? (pp. 43–62). Dordrecht: Springer.
Chapter Google Scholar
Lee, L. Y. (2010). Multiple intelligences and the success of expatriation: The roles of contingency variables. African Journal of Business Management, 4 (17), 3793–3804 Retrieved from http://www.academicjournals.org/AJBM .
Lee, L. Y., & Kartika, N. (2014). The influence of individual, family, and social capital factors on expatriate adjustment and performance: The moderating effect of psychology contract and organizational support. Expert Systems with Applications, 41 (11), 5483–5494. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2014.02.030 .
Lee, L. Y., & Sukoco, B. M. (2010). The effects of cultural intelligence on expatriate performance: The moderating effects of international experience. The International Journal of Human Resource Management, 21 (7), 963–981. https://doi.org/10.1080/09585191003783397 .
Lee, L. Y., Veasna, S., & Wu, W. Y. (2013). The effects of social support and transformational leadership on expatriate adjustment and performance. Career Development International, 18 (4), 377–415. https://doi.org/10.1108/CDI-06-2012-0062 .
Lee, L. Y., Veasna, S., & Sukoco, B. M. (2014). The antecedents of cultural effectiveness of expatriation: Moderating effects of psychological contracts. Asia Pacific Journal of Human Resources, 52 (2), 215–233. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1744-7941.2013.00055.x .
Leung, K., Ang, S., & Tan, M. L. (2014). Intercultural competence. Annual Review of Organizational Psychology and Organizational Behavior, 1 , 489–519. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-orgpsych-031413-091229 .
Li, M., Mobley, W. H., & Kelly, A. (2013). When do global leaders learn best to develop cultural intelligence? An investigation of the moderating role of experiential learning style. Academy of Management Learning & Education, 12 (1), 32–50. https://doi.org/10.5465/amle.2011.0014 .
Li, M., Mobley, W. H., & Kelly, A. (2016). Linking personality to cultural intelligence: An interactive effect of openness and agreeableness. Personality and Individual Differences, 89 , 105–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2015.09.050 .
Lin, Y. C., Chen, A. S. Y., & Song, Y. C. (2012). Does your intelligence help to survive in a foreign jungle? The effects of cultural intelligence and emotional intelligence on cross-cultural adjustment. International Journal of Intercultural Relations, 36 (4), 541–552. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijintrel.2012.03.001 .
Lohmoller, J.-B. (1989). Latent variable path modeling with partial least squares . Heidelberg: Physica.
Malek, M. A., & Budhwar, P. (2013). Cultural intelligence as a predictor of expatriate adjustment and performance in Malaysia. Journal of World Business, 48 (2), 222–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwb.2012.07.006 .
Mathwick, C., Wiertz, C., & De Ruyter, K. (2008). Social capital production in a virtual P3 community. Journal of Consumer Research, 34 (6), 832–849. https://doi.org/10.1086/523291 .
Mendenhall, M., & Oddou, G. (1985). The dimensions of expatriate acculturation: A review. Academy of Management Review, 10 (1), 39–48. https://doi.org/10.5465/amr.1985.4277340 .
Mol, S. T., Born, M. P., Willemsen, M. E., & Van Der Molen, H. T. (2005). Predicting expatriate job performance for selection purposes: A quantitative review. Journal of Cross-Cultural Psychology, 36 (5), 590–620. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022022105278544 .
Moon, H. K., Choi, B. K., & Jung, J. S. (2012). Previous international experience, cross-cultural training, and expatriates’ cross-cultural adjustment: Effects of cultural intelligence and goal orientation. Human Resource Development Quarterly, 23 (3), 285–330. https://doi.org/10.1002/hrdq.21131 .
Morgan, G. A., Leech, N. L., Gloeckner, G. W., & Barrett, K. C. (2012). IBM SPSS for introductory statistics: Use and interpretation . New York, NY: Routledge. https://doi.org/10.4324/9780203127315 .
Moynihan, L. M., Peterson, R. S., & Earley, P. C. (2006). Cultural intelligence and the multinational team experience: Does the experience of working in a multinational team improve cultural intelligence? In Y. R. Chen (Ed.), Research on managing groups and teams: National Culture and groups (pp. 299–323). Greenwich, CT: JAI Press ISBN: 978-0-76231-362-4.
Muthén, L, K., & Muthén, B, O. (1998-2012). Mplus User’s Guide. Seventh Edition. Los Angeles, CA: Muthén & Muthén.
Neter, J., Wasserman, W., & Kutner, M. H. (1990). Applied linear models, regression, analysis of variance and experimental designs . Boston: RD Irwin.
Ng, K. Y., Van Dyne, L., & Ang, S. (2012). Cultural intelligence: A review, reflections, and recommendations for future research. In A. M. Ryan, F. T. L. Leong, & F. L. Oswald (Eds.), Conducting multinational research: Applying organizational psychology in the workplace (pp. 29–58). Washington: American Psychological Association. https://doi.org/10.1037/13743-002 .
Ng, K. Y., Van Dyne, L., & Ang, S. (2019). Speaking out and speaking up in multicultural settings: A two-study examination of cultural intelligence and voice behavior. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes, 151 , 150–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.obhdp.2018.10.005 .
Nunnally, J. C., & Bernstein, I. H. (1994). The assessment of reliability. Psychometric Theory, 3 (1), 248–292.
Ott, D. L., & Michailova, S. (2018a). Cultural intelligence: A review and new research avenues. International Journal of Management Reviews, 20 (1), 99–119. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijmr.12118 .
Ott, D. L., & Michailova, S. (2018b). Cultural intelligence: A review and new research avenues. International Journal of Management Reviews, 20 (1), 99–119.
Palthe, J. (2004). The relative importance of antecedents to cross-cultural adjustment: Implications for managing a global workforce. International Journal of Intercultural Relations, 28 (1), 37–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijintrel.2003.12.004 .
Piedmont, R. L. (2014). Inter-item correlations. In A. C. Michalos (Ed.), Encyclopedia of quality of life and well-being research (pp. 3303–3304). Dordrecht: Springer.
Podsakoff, P. M., MacKenzie, S. B., & Podsakoff, N. P. (2012). Sources of method bias in social science research and recommendations on how to control it. Annual Review of Psychology, 63 , 539–569. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-psych-120710-100452 .
Presbitero, A., & Quita, C. (2017). Expatriate career intentions: Links to career adaptability and cultural intelligence. Journal of Vocational Behavior, 98 , 118–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvb.2016.11.001 .
Raghu, M, R., & Sartawi, M. (2012). ‘GCC demographic shift: intergenerational risk-transfer at play,’ Kuwait Financial Centre “Markaz”. Retrieved from http://www.markaz.com/DesktopModules/CRD/Attachments/DemographicsResearch-MarkazResearch-June%202012.pdf .
Ramalu, S. S., Rose, R. C., Uli, J., & Kumar, N. (2010). Personality and cross-cultural adjustment among expatriate assignees in Malaysia. International Business Research, 3 (4), 96–104. https://doi.org/10.5539/ibr.v3n4p96 .
Ramalu, S. S., Wei, C. C., & Rose, R. C. (2011). The effect of cultural intelligence on cross-cultural adjustment and job performance amongst expatriates in Malaysia. International Journal of Business and Social Science, 2 (9), 59–71 http://ijbssnet.com/journals/Vol._2_No._9_[Special_Issue_-_May_2011]/9.pdf .
Ramalu, S. S., Rose, R. C., Uli, J., & Kumar, N. (2012). Cultural intelligence and expatriate performance in global assignment: The mediating role of adjustment. International Journal of Business and Society, 13 (1), 19–32.
Remhof, S., Gunkel, M., & Schlägel, C. (2013). Working in the “global village”: The influence of cultural intelligence on the intention to work abroad. German Journal of Human Resource Management, 27 (3), 224–250. https://doi.org/10.1177/239700221302700304 .
Ringle, C, M., Wende, S., & Will, A. (2017). SmartPLS v. 3.2.6. Hamburg: SmartPLS. available at www.smartpls.de .
Rockstuhl, T., & Van Dyne, L. (2018). A bi-factor theory of the four-factor model of cultural intelligence: Meta-analysis and theoretical extensions. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes, 148 , 124–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.obhdp.2018.07.005 .
Rose, R. C., Ramalu, S. S., Uli, J., & Kumar, N. (2010). Expatriate performance in international assignments: The role of cultural intelligence as dynamic intercultural competency. International Journal of Business and Management, 5 (8), 76–85. https://doi.org/10.5539/ijbm.v5n8p76 .
Sambasivan, M., Siew-Phaik, L., Mohamed, Z. A., & Leong, Y. C. (2013). Factors influencing strategic alliance outcomes in a manufacturing supply chain: Role of alliance motives, interdependence, asset specificity and relational capital. International Journal of Production Economics, 141 (1), 339–351. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2012.08.016 .
Sambasivan, M., Sadoughi, M., & Esmaeilzadeh, P. (2017). Investigating the factors influencing cultural adjustment and expatriate performance: The case of Malaysia. International Journal of Productivity and Performance Management, 66 (8), 1002–1019. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJPPM-10-2015-0160 .
Schmidt, A. M., & DeShon, R. P. (2010). The moderating effects of performance ambiguity on the relationship between self-efficacy and performance. Journal of Applied Psychology, 95 (3), 572–581. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0018289 .
Shaffer, M. A., Harrison, D. A., Gregerson, H., Black, J. S., & Ferzandi, L. A. (2006). You can take it with you: Individual differences and expatriate effectiveness. Journal of Applied Psychology, 91 (1), 109–125. https://doi.org/10.1037/0021-9010.91.1.109 .
Shaffer, M. A., Kraimer, M. L., Chen, Y., & Bolino, M. C. (2012). Choices, challenges, and career consequences of global work experiences: A review and future agenda. Journal of Management, 38 (4), 1282–1327. https://doi.org/10.1177/0149206312441834 .
Shannon, L. M., & Begley, T. M. (2008). Antecedents of four-factor model of cultural intelligence. In S. Ang & L. Van Dyne (Eds.), Handbook of Cultural Intelligence: Theory, Measurement, and Applications (pp. 41–55). New York, NY: M . E. Sharpe ISBN 9780765622624.
Shenkar, O. (2001). Cultural distance revisited: Towards a more rigorous conceptualization and measurement of cultural differences. Journal of International Business Studies, 32 (3), 519–535. https://doi.org/10.1057/palgrave.jibs.8490982 .
Stahl, G. K., Chua, C. H., Caligiuri, P., Cerdin, J. L., & Taniguchi, M. (2009). Predictors of turnover intentions in learning-driven and demand-driven international assignments: The role of repatriation concerns, satisfaction with company support, and perceived career advancement opportunities. Human Resource Management, 48 (1), 89–109. https://doi.org/10.1002/hrm.20268 .
Takeuchi, R., Tesluk, P. E., Yun, S., & Lepak, D. P. (2005). An integrative view of international experience. Academy of Management Journal, 48 (1), 85–100. https://doi.org/10.5465/amj.2005.15993143 .
Tarique, I., & Schuler, R. S. (2010). Global talent management: Literature review, integrative framework, and suggestions for further research. Journal of World Business, 45 (2), 122–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwb.2009.09.019 .
Templer, K. J., Tay, C., & Chandrasekar, N. A. (2006). Motivational cultural intelligence, realistic job preview, realistic living conditions preview, and cross-cultural adjustment. Group & Organization Management, 31 (1), 154–173 10.1177%2F1059601105275293 .
Tobias, S., & Everson, H. T. (2002). Knowing What You Know and What You Don’t: Further Research on Metacognitive Knowledge Monitoring. College board research report 2002–3 . New York, NY: College Entrance Examination Board.
Van Dyne, L., Ang, S., Ng, K. Y., Rockstuhl, T., Tan, M. L., & Koh, C. (2012). Sub-dimensions of the four factor model of cultural intelligence: Expanding the conceptualization and measurement of cultural intelligence. Social and Personality Psychology Compass, 6 (4), 295–313. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1751-9004.2012.00429.x .
Vlajčić, D., Marzi, G., Caputo, A., & Dabić, M. (2018). The role of geographical distance on the relationship between cultural intelligence and knowledge transfer. Business Process Management Journal, 25 (1), 1–28. https://doi.org/10.1108/BPMJ-05-2017-0129 .
Vlajčić, D., Caputo, A., Marzi, G., & Dabić, M. (2019). Expatriates managers’ cultural intelligence as promoter of knowledge transfer in multinational companies. Journal of Business Research, 94 , 367–377. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2018.01.033 .
Wang, M., & Takeuchi, R. (2007). The role of goal orientation during expatriation: A cross-sectional and longitudinal investigation. Journal of Applied Psychology, 92 (5), 1437–1445. https://doi.org/10.1037/0021-9010.92.5.1437 .
Wang, C. H., & Varma, A. (2019). Cultural distance and expatriate failure rates: The moderating role of expatriate management practices. The International Journal of Human Resource Management, 30 (15), 2211–2230.
Wang, L., Wang, K. T., Heppner, P. P., & Chuang, C. C. (2017). Cross-national cultural competency among Taiwanese international students. Journal of Diversity in Higher Education, 10 (3), 271–287. https://doi.org/10.1037/dhe0000020 .
Wu, P. C., & Ang, S. H. (2011). The impact of expatriate supporting practices and cultural intelligence on cross-cultural adjustment and performance of expatriates in Singapore. The International Journal of Human Resource Management, 22 (13), 2683–2702. https://doi.org/10.1080/09585192.2011.599956 .
Zhang, Y. (2013). Expatriate development for cross-cultural adjustment: Effects of cultural distance and cultural intelligence. Human Resource Development Review, 12 (2), 177–199. https://doi.org/10.1177/1534484312461637 .
Zhou, Z., Zhang, Q., Su, C., & Zhou, N. (2012). How do brand communities generate brand relationships? Intermediate mechanisms. Journal of Business Research, 65 (7), 890–895. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2011.06.034 .
Download references
Open access funding provided by Università degli Studi di Pavia within the CRUI-CARE Agreement.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Brain and Behavioural Sciences, University of Pavia, Unit of Applied Psychology, Piazza Botta 11, 27100, Pavia, Italy
Ilaria Setti, Valentina Sommovigo & Piergiorgio Argentero
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Valentina Sommovigo .
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval.
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee (the research was approved by the social and ethics committee of the private organization where was conducted the study) and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Disclosure Statement
The authors declare that they do not have any conflict of interest with this paper.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix 1: Measurements
Demographic items.
Thank you for participating in this study. Please pay close attention to each question provided and answer each question as honestly as possible by placing a mark in the provided space. Please take care in filling out this form.
1. Gender (Please Check One): [] Male [] Female.
2. Age (in years): ______.
3. Marital status (Please Check One): [] Single [] Married.
4. Education status (Please Check One): [] High school [] Degree.
5. Role (Please Check One):
[] 1. Administrative.
[] 2. Technical.
[] 3. Executive.
[] 4. Other.
6. How many years have you spent working abroad before this assignment: ______.
7. How many months have you been working in your current country of assignment? ______.
8. Did you have any cross-cultural training (any training that prepared you for relocation) before departure? (Please Check One): [] Yes [] No.
9. What is your country of origin? ______.
10. In which country are you currently living? ______
Cultural intelligence
Read each statement and select the response that best describes your capabilities.
Select the answer that BEST describes you AS YOU REALLY ARE .
1: Strongly disagree 2: Disagree 3: Somewhat disagree 4: Neither agree nor disagree 5: Somewhat disagree 6: Agree 7: Strongly Agree.
Cross-cultural adjustment at work
Please indicate how well adjusted (how comfortable) you are with each of the following aspects of living in your current city of residence. Use the following scale:
1: Very unadjusted 2: Unadjusted 3: Somewhat unadjusted 4: Neutral 5: Somewhat adjusted 6: Adjusted 7: Very adjusted.
- Assignment-specific performance
Please rate your level of work performance to the factors listed below using the following scale:
1: Poor 2: Below Average 3: Average 4: Above Average 5: Outstanding.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Setti, I., Sommovigo, V. & Argentero, P. Enhancing expatriates’ assignments success: the relationships between cultural intelligence, cross-cultural adaptation and performance. Curr Psychol 41 , 4291–4311 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-020-00931-w
Download citation
Published : 20 July 2020
Issue Date : July 2022
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-020-00931-w
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Expatriates, cultural intelligence
- Cross-cultural adjustment
- Cultural distance, international work experience
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
14.2 Staffing Internationally
Learning objectives.
- Be able to explain the three staffing strategies for international businesses and the advantages and disadvantages for each.
- Explain the reasons for expatriate failures.
One of the major decisions for HRM when a company decides to operate overseas is how the overseas operation will be staffed. This is the focus of this section.
Types of Staffing Strategy
There are three main staffing strategies a company can implement when entering an overseas market, with each having its advantages and disadvantages. The first strategy is a home-country national strategy . This staffing strategy uses employees from the home country to live and work in the country. These individuals are called expatriates . The second staffing strategy is a host-country national strategy , which means to employ people who were born in the country in which the business is operating. Finally, a third-country national strategy means to employee people from an entirely different country from the home country and host country. Table 14.4 “Advantages and Disadvantages of the Three Staffing Strategies” lists advantages and disadvantages of each type of staffing strategy. Whichever strategy is chosen, communication with the home office and strategic alignment with overseas operations need to occur for a successful venture.
Table 14.4 Advantages and Disadvantages of the Three Staffing Strategies
Human Resource Recall
Compare and contrast a home-country versus a host-country staffing strategy.
Expatriates
According to Simcha Ronen, a researcher on international assignments, there are five categories that determine expatriate success. They include job factors, relational dimensions, motivational state, family situation, and language skills. The likelihood the assignment will be a success depends on the attributes listed in Table 14.5 “Categories of Expatriate Success Predictors with Examples” . As a result, the appropriate selection process and training can prevent some of these failings. Family stress, cultural inflexibility, emotional immaturity, too much responsibility, and longer work hours (which draw the expatriate away from family, who could also be experiencing culture shock) are some of the reasons cited for expatriate failure.
Table 14.5 Categories of Expatriate Success Predictors with Examples
Source: Adapted from Simcha Ronen, Training the International Assignee (San Francisco: Jossey-Bass, 1989), 426–40.
Most expatriates go through four phases of adjustment when they move overseas for an assignment. They include elation/honeymoon , resistance , adaption , and biculturalism . In the elation phase, the employee is excited about the new surroundings and finds the culture exotic and stimulating. In the resistance phase, the employee may start to make frequent comparisons between home and host country and may seek out reminders of home. Frustration may occur because of everyday living, such as language and cultural differences. During the adaptation phase, the employee gains language skills and starts to adjust to life overseas. Sometimes during this phase, expatriates may even tend to reject their own culture. In this phase, the expatriate is embracing life overseas. In the last phase, biculturalism, the expatriate embraces the new culture and begins to appreciate his old life at home equally as much as his new life overseas. Many of the problems associated with expatriate failures, such as family life and cultural stress, have diminished.
Figure 14.2 Phases of Expatriate Adjustment
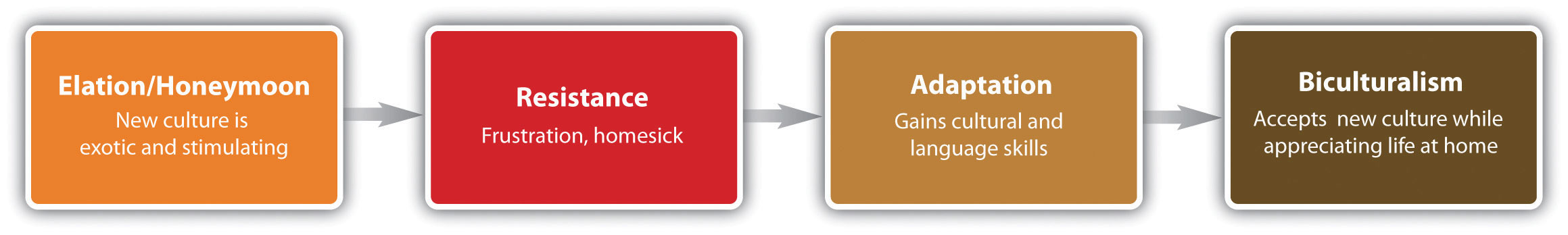
Expat Failures
(click to see video)
A short discussion on why international assignments fail.
Host-Country National
The advantage, as shown in Table 14.4 “Advantages and Disadvantages of the Three Staffing Strategies” , of hiring a host-country national can be an important consideration when designing the staffing strategy. First, it is less costly in both moving expenses and training to hire a local person. Some of the less obvious expenses, however, may be the fact that a host-country national may be more productive from the start, as he or she does not have many of the cultural challenges associated with an overseas assignment. The host-country national already knows the culture and laws, for example. In Russia, 42 percent of respondents in an expatriate survey said that companies operating there are starting to replace expatriates with local specialists. In fact, many of the respondents want the Russian government to limit the number of expatriates working for a company to 10 percent 1 . When globalization first occurred, it was more likely that expatriates would be sent to host countries, but in 2011, many global companies are comfortable that the skills, knowledge, and abilities of managers exist in the countries in which they operate, making the hiring of a host-country national a favorable choice. Also important are the connections the host-country nationals may have. For example, Shiv Argawal, CEO of ABC Consultants in India, says, “An Indian CEO helps influence policy and regulations in the host country, and this is the factor that would make a global company consider hiring local talent as opposed to foreign talent” (Rajagorpal, 2011).
Third-Country Nationals
One of the best examples of third-country nationals is the US military. The US military has more than seventy thousand third-country nationals working for the military in places such as Iraq and Afghanistan. For example, a recruitment firm hired by the US military called Meridian Services Agency recruits hairstylists, construction workers, and electricians from all over the world to fill positions on military bases (Stillman, 2011). Most companies who utilize third-country national labor are not new to multinational businesses. The majority of companies who use third-country national staffing have many operations already overseas. One example is a multinational company based in the United States that also has operations in Spain and transfers a Spanish manager to set up new operations in Argentina. This would be opposed to the company in the United States sending an American (expatriate) manager to Argentina. In this case, the third-country national approach might be the better approach because of the language aspect (both Spain and Argentina speak Spanish), which can create fewer costs in the long run. In fact, many American companies are seeing the value in hiring third-country nationals for overseas assignments. In an International Assignments Survey 2 , 61 percent of United States–based companies surveyed increased the use of third-country nationals by 61 percent, and of that number, 35 percent have increased the use of third-country nationals to 50 percent of their workforce. The main reason why companies use third-country nationals as a staffing strategy is the ability of a candidate to represent the company’s interests and transfer corporate technology and competencies. Sometimes the best person to do this isn’t based in the United States or in the host country.
Key Takeaways
- There are three types of staffing strategies for an international business. First, in the home-country national strategy , people are employed from the home country to live and work in the country. These individuals are called expatriates . One advantage of this type of strategy is easier application of business objectives, although an expatriate may not be culturally versed or well accepted by the host-country employees.
- In a host-country strategy , workers are employed within that country to manage the operations of the business. Visas and language barriers are advantages of this type of hiring strategy.
- A third-country national staffing strategy means someone from a country, different from home or host country, will be employed to work overseas. There can be visa advantages to using this staffing strategy, although a disadvantage might be morale lost by host-country employees.
- Choose a country you would enjoy working in, and visit that country’s embassy page. Discuss the requirements to obtain a work visa in that country.
- How would you personally prepare an expatriate for an international assignment? Perform additional research if necessary and outline a plan.
1 “Russia Starts to Abolish Expat jobs,” Expat Daily , April 27, 2011, accessed August 11, 2011, http://www.expat-daily.com/news/russia-starts-to-abolish-expat-jobs/ .
2 “More Third Country Nationals Being Used,” n.d., SHRM India, accessed August 11, 2011, http://www.shrmindia.org/more-third-country-nationals-being-used .
Rajagorpal, D., and MC Govardhanna Rangan, “Global Firms Prefer Local Executives to Expats to Run Indian Operation,” Economic Times , April 20, 2011, accessed September 15, 2011, http://articles.economictimes.indiatimes.com/2011-04-20/news/29450955_1_global-firms-joint-ventures-investment-banking .
Stillman, S., “The Invisible Army,” New Yorker , June 6, 2011, accessed August 11, 2011, http://www.newyorker.com/reporting/2011/06/06/110606fa_fact_stillman .
Human Resource Management Copyright © 2016 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
- Book a Speaker
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Vivamus convallis sem tellus, vitae egestas felis vestibule ut.
Error message details.
Reuse Permissions
Request permission to republish or redistribute SHRM content and materials.
How to Pay Employees Working Across International Borders
You face some risks if your company hasn't registered to do business in other countries
- Register or make the person an employee of a local affiliate . If you send someone to France and your organization is registered or has a subsidiary there, you can put the person on your payroll or you can “second” them to an affiliate or business partner. But organizations don’t typically incorporate foreign subsidiaries just to payroll one or two employees, so they look for other options.
- Put the employee on the home-country payroll . Say you’re sending an employee from the U.S. to Spain. It would be easy to keep the employee on U.S. payroll, but as soon as Spain becomes the place of employment, Spanish payroll laws likely kick in, making the home-country payroll structure a compliance risk. But home-country payroll can sometimes be legal. If the employee works overseas for a short period of time, like a couple of months, an organization can likely keep the employee on the U.S. payroll “because the place of employment hasn’t shifted,” Dowling said. The host country might tax the employee and require a visa, but personal tax and immigration issues are separate from payroll law compliance. Another way to do this is with a host country workaround . Some countries (not the U.S.) allow workarounds for offshore employers without any in-country presence or place of business, so check with local law. These workarounds generally fall into three categories: Under the f oreign employer exception (available in the U.K. and Thailand), if a company doesn’t do business or have a permanent establishment locally, it can hire and pay local staff without making local withholdings and contributions. The worker bears the burden of tax and social security filings as if self-employed. France, Estonia, Sri Lanka and some other countries offer a payroll law compliance option for the employer , under which foreign employers with no in-country premises can make special “payroll only” registrations with in-country tax and social security agencies so they can issue a legal local payroll. Payroll law option for the worker . Some countries, for example some in Africa, allow an individual employed by a foreign employer not doing business in-country to self-declare as “foreign payrolled” to the local tax agency.
- Make the person a leased or assigned employee . This is a form of secondment or lending. The employee is employed by entity A but doing work on a daily basis for entity B. For example, an organization may need to send an employee to another country to handle customer service and can ask its in-country customer to payroll that person. If there’s no local business partner, temporary agencies like Adecco, Manpower or Kelly often provide leased employment. “You can say we want Steve or Sarah, and Adecco will hire them and put them on the Adecco payroll,” Dowling explained. A floating employee in Argentina could be paid by Adecco, which would second the person’s services to your firm. The former U.S.-based employee typically resigns or his or her employment is suspended during this time, Dowling noted. A variation on leased employment is creating a “ shadow payroll .” Division A of a U.S. company may do something completely different from its sister division B, which alone operates in France. If division A needs to send someone to France, it can ask division B to fill out the paperwork and report wages to French Social Security and the like, and can reimburse division B for doing the payroll. “From the French payrolling point of view, it looks like the employee is being paid by division B, so you’re complying with all the payroll laws,” Dowling explained.
- Pay the worker as a legitimate independent contractor . This is risky and usually not the best route. Say an organization needs a salesperson in England but doesn’t want to register there, so classifies the salesman as an “independent contractor.” If that’s such a great idea, Dowling asks, then why not make all your U.S. salespeople independent contractors, since you’ll save on Social Security, employee benefit contributions and the like? The answer is that you can’t because they’re performing as employees. Dowling said there’s general consensus around the world about legitimate contractor classification. If the person has set work hours and receives benefits and performance evaluations, then he or she is an employee. A salesperson who represents product lines for a variety of companies in addition to yours might be able to be paid as an independent contractor, but if someone’s title is executive vice president and the person is on your organizational chart, that’s not going to fly, Dowling said.
Related Content

A 4-Day Workweek? AI-Fueled Efficiencies Could Make It Happen
The proliferation of artificial intelligence in the workplace, and the ensuing expected increase in productivity and efficiency, could help usher in the four-day workweek, some experts predict.

How One Company Uses Digital Tools to Boost Employee Well-Being
Learn how Marsh McLennan successfully boosts staff well-being with digital tools, improving productivity and work satisfaction for more than 20,000 employees.
Advertisement
Artificial Intelligence in the Workplace
An organization run by AI is not a futuristic concept. Such technology is already a part of many workplaces and will continue to shape the labor market and HR. Here's how employers and employees can successfully manage generative AI and other AI-powered systems.
HR Daily Newsletter
New, trends and analysis, as well as breaking news alerts, to help HR professionals do their jobs better each business day.
Success title
Success caption

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Foreign Service youth, ages 10-18 who are posted overseas, are eligible to enter this contest. Traveling with a Pet to an International Location Outside of the United States. Getting a pet to a foreign country involves understanding country-specific import restrictions, paperwork procedures, and the various offices involved in the process.
The Foreign Service Assignment Notebook (FSAN) offers invaluable information and guidance on various aspects of preparing for an international move. The content is written for all government employees and their family members transitioning to an assignment at a U.S. mission overseas. Organized temporally in 30 chapters, from introduction to the foreign affairs lifestyle, bidding considerations
5 Tips for Managing Successful Overseas Assignments. Sending talented employees overseas can be a promising way to leverage the benefits of a global economy. But expatriate assignments can be ...
About Foreign Service Assignments After you complete orientation and training in Washington, D.C., as a newly hired Foreign Service Officer, you will typically be assigned overseas, although at this time a few officers begin with a domestic assignment. Typically, the first two overseas tours (usually two years each) are designed to develop your talents in different
International assignment management is one of the hardest areas for HR professionals to master—and one of the most costly. The expense of a three-year international assignment can cost millions ...
Expatriates are allowed to participate in U.S.-based retirement plans while working abroad. They can contribute pre-tax dollars to their traditional 401 (k) plans, and employers can offer a match to the employee deferral. Unfortunately, many foreign countries consider the deferral to be taxable income.
4. Obtain All Required Documents - The importance of checking off each and every required piece of documentation - such as passports (including children's passports), work visas, medical prescriptions, international driving permits, and all other obligatory paperwork - before traveling to a foreign country cannot be overstated.
A Successful International Assignment Depends on These Factors. by. Boris Groysberg. and. Robin Abrahams. February 13, 2014. The prospect of an international assignment can be equal parts ...
For purposes of this article, an expatriate is a U.S. citizen or green card holder who is sent by their U.S. employer to work at a branch or other linked organization in a foreign country. Assignment duration may vary anywhere from six months to several years. Employees must obtain a work visa, and—depending upon the host country—may be ...
An international assignment is an overseas task set by a company to an employee. Companies that engage in international assignments are mainly multinational corporations (MNCs). MNCs send employees from the home country to a different country for business operations at overseas offices or subsidiaries. [1] These employees are called expatriates.
Short-Term Assignment. A short-term international assignment usually lasts for a year or less. Employers generally have a specific goal for the employees they send on short-term assignments, such as facilitating training, completing a particular project, or temporarily filling a vacancy. Many short-term assignments are single-status, whereby ...
When sending an FN employee on an overseas assignment, keeping them on the U.S. payroll is typically a good idea. Transferring them to a foreign company's payroll could result in a loss of their employee status with your U.S. company, potentially jeopardizing their current visa status. In such cases, your company might need to initiate a new ...
Foreign assignments work best when employers take steps to make sure that employees understand the language and culture of the country where they'll be working. Cultural sensitivity training is important, and language barriers must be overcome, either through training or by providing a translator.
Provides the employee with a self-assessment tool prior to the international assignment to help set realistic expectations for adjusting to the host country. Provides a mentor in the host country.
Similarly, in order to be a successful "expat," or expatriate, one needs to prepare mentally and physically for the change. International business assignments are a reflection of increased global trade, and as trade decreases, they may become an expensive luxury. As technology allows for instant face-to-face communication, and group ...
Figure 18.7.1 18.7. 1: The international assignment requires adaptability. JT - Euro Note Currency - CC BY-NC-ND 2.0. You may also begin to feel that the "grass is greener" in your host country, and long to return.
Below are 7 tips to make the most of your journey abroad. 1. Keep an Open Mind. Social media and the internet allows us to connect with people from all over the world. Take time to learn about the history of your new home, including any local customs or laws, so you can set more realistic expectations ahead of time.
Secondment. An expatriate remains an employee of the home country employer entity but is assigned to render services to a host country entity, usually the employer's affiliate or business partner ...
Today's increasingly global marketplace is resulting in more organizations sending employees to work outside their home countries as expatriates. Consequently, identifying factors influencing expatriates' cross-cultural adjustment at work and performance has become an increasingly important issue for both researchers and firms. Drawing on Kim et al. (2008), this study examines the critical ...
Host-Country National. The advantage, as shown in Table 14.4 "Advantages and Disadvantages of the Three Staffing Strategies", of hiring a host-country national can be an important consideration when designing the staffing strategy. First, it is less costly in both moving expenses and training to hire a local person.
Nevertheless, some employers may pay 'incentives' such as foreign service or mobility premiums and location-specific hardship premiums to encourage employees to accept certain international assignments, especially assignments to countries with harsh climates, or those that are underdeveloped or potentially dangerous. 5.
Or a company may be trying to hire a worker who lives in a foreign country but would be working entirely on assignments for the U.S. company. Trailing spouses or staff who have personal reasons to ...
Lisette is a Canadian manager working in a foreign country on assignment for her company. Lisette is therefore a(n) _____. expatriate. The situational or environmental characteristics that affect a person's behavior are called _____. context. The ability to operate in different cultures is the definition of _____.