

Financial Plan Assumptions

Written by True Tamplin, BSc, CEPF®
Reviewed by subject matter experts.
Updated on July 11, 2023
Get Any Financial Question Answered
Table of contents, what are financial plan assumptions.
Financial plan assumptions are the key variables, estimates, and predictions used to develop a company's financial projections and strategy. They serve as the foundation for forecasting revenues , costs, investments, and taxes , among other elements.
Assumptions are critical in financial planning because they help businesses set realistic goals, allocate resources efficiently, and identify potential risks and opportunities. They also enable management to make informed decisions based on the best available data and industry insights.
Financial plan assumptions aim to create a comprehensive picture of a company's future financial performance by incorporating a range of factors.
These assumptions are designed to be flexible and adaptable, allowing for adjustments as new information becomes available or market conditions change.
Key Financial Plan Assumptions
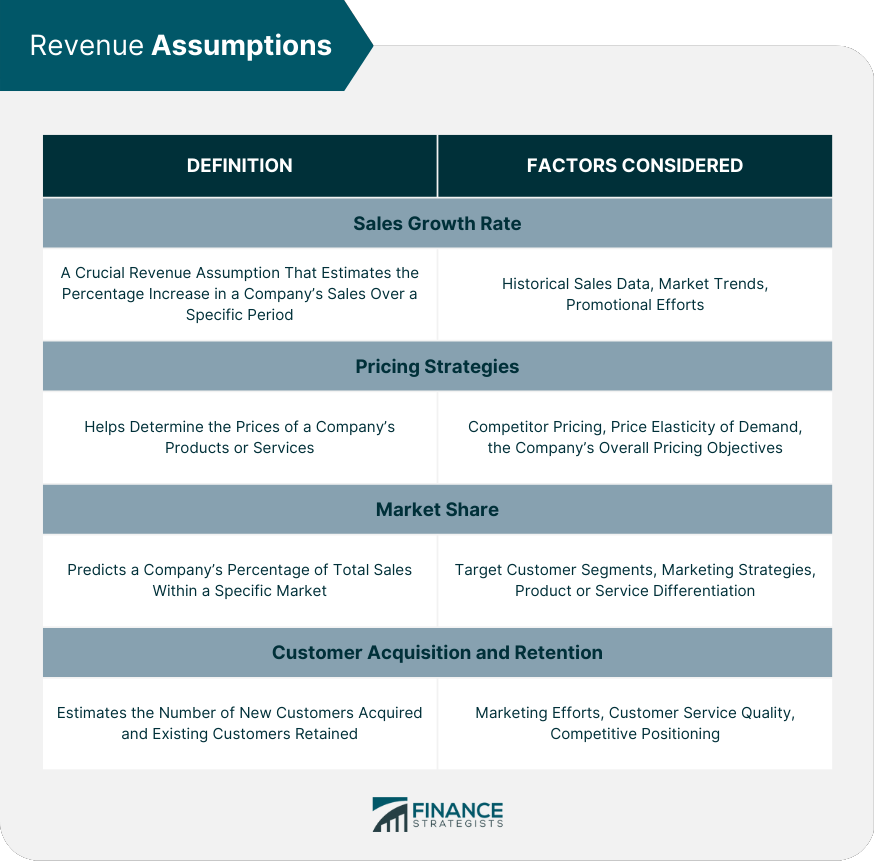
Revenue assumptions, sales growth rate.
The sales growth rate is a crucial revenue assumption that estimates the percentage increase in a company's sales over a specific period. This rate takes into account factors such as historical sales data, market trends, and promotional efforts.
Pricing Strategies
Pricing strategies help determine the prices of a company's products or services. Assumptions related to pricing may include competitor pricing, price elasticity of demand, and the company's overall pricing objectives.
Market Share
Market share assumptions predict a company's percentage of total sales within a specific market. Estimations consider factors such as target customer segments, marketing strategies, and product or service differentiation.
Customer Acquisition and Retention
Customer acquisition and retention assumptions estimate the number of new customers acquired and existing customers retained. These assumptions depend on factors such as marketing efforts, customer service quality, and competitive positioning.
Cost Assumptions
Fixed and variable costs.
Fixed and variable costs are essential components of a company's financial plan . Fixed costs include expenses that remain constant, regardless of production levels or sales, such as rent and salaries. Variable costs vary with production or sales, including raw materials and shipping costs.
Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
COGS is the total cost of producing goods or services sold by a company. Key assumptions for COGS may include production costs , labor costs, and manufacturing overheads.
Operating Expenses
Operating expenses are the costs associated with running a business, excluding COGS. Assumptions for operating expenses may include marketing costs, administrative expenses, and research and development expenditures .
Inflation Rate
The inflation rate assumption estimates the increase in the general price level over time. This assumption affects various cost projections, such as wages, raw materials, and utilities.
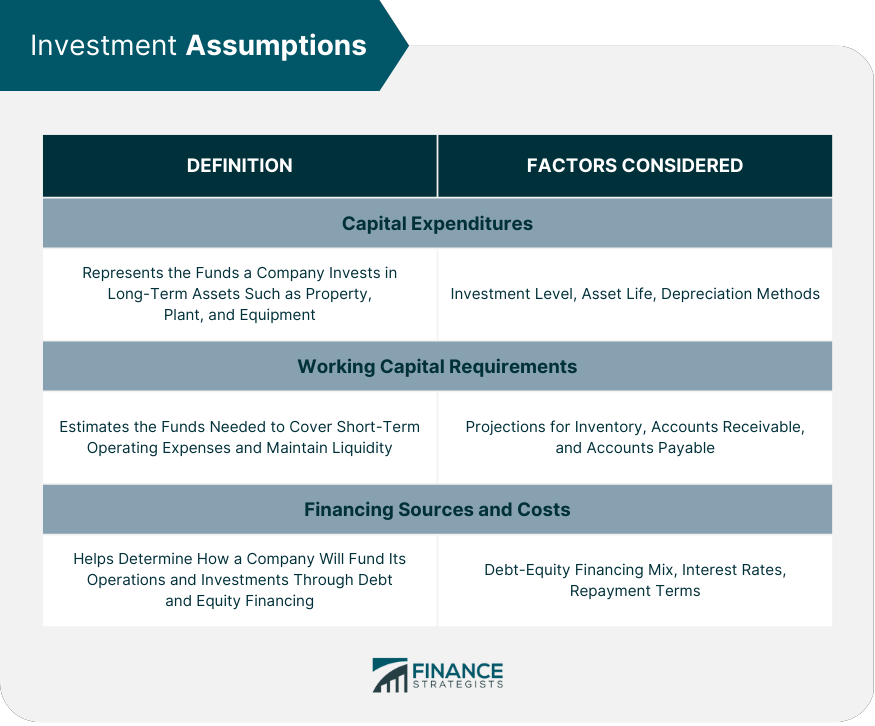
Investment Assumptions
Capital expenditures.
Capital expenditures represent the funds a company invests in long-term assets, such as property, plant, and equipment. Assumptions for capital expenditures may include the anticipated level of investment , the useful life of assets , and depreciation methods.
Working Capital Requirements
Working capital assumptions estimate the funds needed to cover short-term operating expenses and maintain sufficient liquidity . These assumptions may include projections for inventory levels, accounts receivable , and accounts payable .
Financing Sources and Costs
Financing assumptions help determine how a company will fund its operations and investments. These assumptions include the mix of debt and equity financing, interest rates , and repayment terms.
Tax Assumptions
Corporate tax rates.
Corporate tax rate assumptions estimate the percentage of a company's profits subject to taxation. These assumptions take into account federal, state, and local tax rates, as well as any changes to tax laws.
Tax Credits and Incentives
Tax credits and incentives are reductions in tax liability offered by governments to encourage specific business activities. Assumptions related to tax credits may include eligibility criteria, application deadlines, and the expected amount of tax savings.
Tax Planning Strategies
Tax planning strategies are methods used by companies to minimize their tax liabilities. Assumptions related to tax planning may include the use of tax-efficient structures, deductions, and loss carryforwards.
Economic and Industry Assumptions
Macroeconomic factors.
Gross domestic product (GDP) growth rate assumptions estimate the overall economic growth of a country or region. These assumptions impact a company's revenue projections, as they help gauge the general health of the economy and consumer spending.
Interest Rates
Interest rate assumptions estimate the cost of borrowing or lending money. These rates affect a company's financing costs, investment decisions, and overall financial performance.
Unemployment Rates
Unemployment rate assumptions predict the percentage of the labor force without jobs. High unemployment rates can impact consumer spending and may indicate a sluggish economy, affecting a company's sales projections.

Industry Trends and Competition
Market size and growth.
Market size and growth assumptions help estimate the overall potential of an industry and the opportunities it presents for a company. Factors considered may include historical data, demographic trends, and technological advancements.
Technological Advancements
Technological advancements can disrupt industries and create new markets. Assumptions related to technology may include the adoption of new technologies, the impact of innovations on the market, and the potential for competitive advantage.
Regulatory Changes
Regulatory changes can significantly impact a company's operations and financial performance. Assumptions related to regulation may include potential changes in laws, compliance requirements, and the effects on the industry landscape.
Competitive Landscape
Competitive landscape assumptions evaluate a company's position within its industry and the level of competition it faces. These assumptions may consider factors such as market share, competitor strategies, and barriers to entry.
Sensitivity Analysis and Scenario Planning
Identifying key variables and uncertainties.
Sensitivity analysis and scenario planning involve identifying key variables and uncertainties in a company's financial plan. These variables may include economic factors, industry trends, or company-specific factors.
Developing Scenarios and Assumptions
Scenario planning involves creating alternative future scenarios based on varying assumptions. Companies develop multiple scenarios to explore the potential impact of different events, trends, and risks on their financial performance.
Analyzing the Impact on Financial Performance
Companies analyze the impact of different scenarios on their financial performance to identify potential risks and opportunities. This analysis helps management make informed decisions and adapt their strategies as needed.
Risk Mitigation and Contingency Planning
Based on the results of sensitivity analysis and scenario planning, companies develop risk mitigation and contingency plans. These plans help companies prepare for potential challenges and capitalize on emerging opportunities.
Regular Review and Update of Assumptions
Importance of ongoing monitoring.
Regularly reviewing and updating financial plan assumptions is essential to ensure their continued relevance and accuracy. Ongoing monitoring helps companies stay informed of market changes and adapt their strategies accordingly.
Frequency of Assumption Updates
The frequency of assumption updates depends on the nature of the company and its industry. Companies operating in rapidly changing environments may need to update their assumptions more frequently than those in more stable industries.
Incorporating New Information and Data
As new information and data become available, companies should incorporate them into their financial plan assumptions. This ensures that the assumptions remain relevant and provide an accurate basis for decision-making.
Adjusting Financial Plans as Needed
Based on updated assumptions, companies may need to adjust their financial plans to reflect changes in market conditions, industry trends, or company-specific factors. Regular adjustments help maintain the accuracy and relevance of financial projections.
Financial plan assumptions play a crucial role in the development of a company's financial strategy and projections. By incorporating a wide range of factors and estimates, assumptions help create a comprehensive picture of a company's future financial performance.
Regularly reviewing and updating financial plan assumptions is essential for ensuring their continued relevance and accuracy. As new information becomes available or market conditions change, companies must adapt their assumptions and adjust their financial plans accordingly.
Sensitivity analysis and scenario planning are valuable tools for managing risks and identifying potential opportunities.
By analyzing the impact of different scenarios on a company's financial performance, management can make informed decisions and develop risk mitigation and contingency plans.
In conclusion, financial plan assumptions are critical components of a company's financial planning process.
By incorporating a wide range of factors and regularly reviewing and updating these assumptions, companies can create accurate financial projections, identify potential risks and opportunities, and make informed decisions that drive their long-term success.
Financial Plan Assumptions FAQs
What are financial plan assumptions, and why are they important.
Financial plan assumptions are the underlying estimates and predictions that a financial plan is based upon. They are essential because they provide the framework for determining how much money you need to save, how much you can expect to earn on your investments, and how long your money will last in retirement.
How do I choose the right financial plan assumptions for my personal financial plan?
The right financial plan assumptions will depend on your personal circumstances, financial goals, and risk tolerance. You should consider your current income, expenses, debts, and assets when selecting your assumptions. Additionally, you should consider factors such as inflation, investment returns, and life expectancy.
What are some common financial plan assumptions used by financial planners?
Common financial plan assumptions used by financial planners include assumptions about inflation rates, investment returns, life expectancy, and tax rates. Other assumptions may include future expenses such as college tuition or medical costs, changes in income or employment, and changes in interest rates.
How often should I review and update my financial plan assumptions?
You should review and update your financial plan assumptions regularly, at least annually, and whenever there are significant changes in your life circumstances, such as a new job, a significant change in income or expenses, or a change in your investment portfolio.
What are the potential risks of relying on incorrect financial plan assumptions?
Relying on incorrect financial plan assumptions can lead to a variety of risks, including not saving enough for retirement, running out of money in retirement, or being unable to meet other financial goals. Additionally, incorrect assumptions can lead to poor investment decisions, resulting in lower investment returns and higher taxes. It is essential to ensure that your financial plan assumptions are as accurate as possible to help you achieve your financial goals.
About the Author
True Tamplin, BSc, CEPF®
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide , a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University , where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon , Nasdaq and Forbes .
Related Topics
- Affordable Care Act's (ACA) Medicaid
- Aggressive Investing
- Behavioral Finance
- Brick and Mortar
- Cash Flow From Operating Activities
- Cash Flow Management
- Debt Reduction Strategies
- Depreciation Recapture
- Divorce Financial Planning
- Education Planning
- Envelope Budgeting
- Farmland Investments
- Financial Planning for Allied Health Professionals
- Financial Planning for Military Families
- Global Macro Hedge Fund
- Inventory Turnover Rate (ITR)
- Lieutenant Colonel Pension Plans
- Medicaid Asset Protection Trust
- Medical Lines of Credit
- Military Spouse Financial Planning
- Multi-Family Line of Credit
- Pension Pillar
- Pension Scheme
- Post-Divorce Debt Management
- Succession Planning
- Trustee Succession
- Types of Fixed Income Investments
Ask a Financial Professional Any Question
Meet top certified financial advisors near you, find advisor near you, our recommended advisors.

Taylor Kovar, CFP®
WHY WE RECOMMEND:
Fee-Only Financial Advisor Show explanation
Certified financial planner™, 3x investopedia top 100 advisor, author of the 5 money personalities & keynote speaker.
IDEAL CLIENTS:
Business Owners, Executives & Medical Professionals
Strategic Planning, Alternative Investments, Stock Options & Wealth Preservation

Claudia Valladares
Bilingual in english / spanish, founder of wisedollarmom.com, quoted in gobanking rates, yahoo finance & forbes.
Retirees, Immigrants & Sudden Wealth / Inheritance
Retirement Planning, Personal finance, Goals-based Planning & Community Impact
We use cookies to ensure that we give you the best experience on our website. If you continue to use this site we will assume that you are happy with it.
Fact Checked
At Finance Strategists, we partner with financial experts to ensure the accuracy of our financial content.
Our team of reviewers are established professionals with decades of experience in areas of personal finance and hold many advanced degrees and certifications.
They regularly contribute to top tier financial publications, such as The Wall Street Journal, U.S. News & World Report, Reuters, Morning Star, Yahoo Finance, Bloomberg, Marketwatch, Investopedia, TheStreet.com, Motley Fool, CNBC, and many others.
This team of experts helps Finance Strategists maintain the highest level of accuracy and professionalism possible.
Why You Can Trust Finance Strategists
Finance Strategists is a leading financial education organization that connects people with financial professionals, priding itself on providing accurate and reliable financial information to millions of readers each year.
We follow strict ethical journalism practices, which includes presenting unbiased information and citing reliable, attributed resources.
Our goal is to deliver the most understandable and comprehensive explanations of financial topics using simple writing complemented by helpful graphics and animation videos.
Our writing and editorial staff are a team of experts holding advanced financial designations and have written for most major financial media publications. Our work has been directly cited by organizations including Entrepreneur, Business Insider, Investopedia, Forbes, CNBC, and many others.
Our mission is to empower readers with the most factual and reliable financial information possible to help them make informed decisions for their individual needs.
How It Works
Step 1 of 3, ask any financial question.
Ask a question about your financial situation providing as much detail as possible. Your information is kept secure and not shared unless you specify.

Step 2 of 3
Our team will connect you with a vetted, trusted professional.
Someone on our team will connect you with a financial professional in our network holding the correct designation and expertise.

Step 3 of 3
Get your questions answered and book a free call if necessary.
A financial professional will offer guidance based on the information provided and offer a no-obligation call to better understand your situation.

Where Should We Send Your Answer?

Just a Few More Details
We need just a bit more info from you to direct your question to the right person.
Tell Us More About Yourself
Is there any other context you can provide.
Pro tip: Professionals are more likely to answer questions when background and context is given. The more details you provide, the faster and more thorough reply you'll receive.
What is your age?
Are you married, do you own your home.
- Owned outright
- Owned with a mortgage
Do you have any children under 18?
- Yes, 3 or more
What is the approximate value of your cash savings and other investments?
- $50k - $250k
- $250k - $1m
Pro tip: A portfolio often becomes more complicated when it has more investable assets. Please answer this question to help us connect you with the right professional.
Would you prefer to work with a financial professional remotely or in-person?
- I would prefer remote (video call, etc.)
- I would prefer in-person
- I don't mind, either are fine
What's your zip code?
- I'm not in the U.S.
Submit to get your question answered.
A financial professional will be in touch to help you shortly.

Part 1: Tell Us More About Yourself
Do you own a business, which activity is most important to you during retirement.
- Giving back / charity
- Spending time with family and friends
- Pursuing hobbies
Part 2: Your Current Nest Egg
Part 3: confidence going into retirement, how comfortable are you with investing.
- Very comfortable
- Somewhat comfortable
- Not comfortable at all
How confident are you in your long term financial plan?
- Very confident
- Somewhat confident
- Not confident / I don't have a plan
What is your risk tolerance?
How much are you saving for retirement each month.
- None currently
- Minimal: $50 - $200
- Steady Saver: $200 - $500
- Serious Planner: $500 - $1,000
- Aggressive Saver: $1,000+
How much will you need each month during retirement?
- Bare Necessities: $1,500 - $2,500
- Moderate Comfort: $2,500 - $3,500
- Comfortable Lifestyle: $3,500 - $5,500
- Affluent Living: $5,500 - $8,000
- Luxury Lifestyle: $8,000+
Part 4: Getting Your Retirement Ready
What is your current financial priority.
- Getting out of debt
- Growing my wealth
- Protecting my wealth
Do you already work with a financial advisor?
Which of these is most important for your financial advisor to have.
- Tax planning expertise
- Investment management expertise
- Estate planning expertise
- None of the above
Where should we send your answer?
Submit to get your retirement-readiness report., get in touch with, great the financial professional will get back to you soon., where should we send the downloadable file, great hit “submit” and an advisor will send you the guide shortly., create a free account and ask any financial question, learn at your own pace with our free courses.
Take self-paced courses to master the fundamentals of finance and connect with like-minded individuals.
Get Started
Hey, did we answer your financial question.
We want to make sure that all of our readers get their questions answered.
Great, Want to Test Your Knowledge of This Lesson?
Create an Account to Test Your Knowledge of This Topic and Thousands of Others.
Get Your Question Answered by a Financial Professional
Create a free account and submit your question. We'll make sure a financial professional gets back to you shortly.
To Ensure One Vote Per Person, Please Include the Following Info
Great thank you for voting..
- AI ASSISTANTS
Upmetrics AI Your go-to AI-powered business assistant
AI Writing Assist Write, translate, and refine your text with AI
AI Financial Assist Automated forecasts and AI recommendations
- TOP FEATURES
AI Business Plan Generator Create business plans faster with AI
Financial Forecasting Make accurate financial forecasts faster
Strategic Planning Develop actionable strategic plans on-the-go
AI Pitch Deck Generator Use AI to generate your investor deck
See how it works →
AI-powered business planning software
Very useful business plan software connected to AI. Saved a lot of time, money and energy. Their team is highly skilled and always here to help.
- Julien López
- BY USE CASE
Starting & Launching a Business Plan your business for launch and success
Validate Your Business Idea Discover the potential of your business idea
Secure Funding, Loans, Grants Create plans that get you funded
Business Consultant & Advisors Plan with your team members and clients
Business Schools & Educators Simplify business plan education for students
Students & Learners Your e-tutor for business planning
- Sample Plans
- WHY UPMETRICS?
Reviews See why customers love Upmetrics
Customer Success Stories Read our customer success stories
Blogs Latest business planning tips and strategies
Strategic Planning Templates Ready-to-use strategic plan templates
Business Plan Course A step-by-step business planning course
Ebooks & Guides A free resource hub on business planning
Business Tools Free business tools to help you grow
- 400+ Sample Business Plans
How to Prepare a Financial Plan for Startup Business (w/ example)

Free Financial Statements Template
Ajay Jagtap
- December 7, 2023
13 Min Read

If someone were to ask you about your business financials, could you give them a detailed answer?
Let’s say they ask—how do you allocate your operating expenses? What is your cash flow situation like? What is your exit strategy? And a series of similar other questions.
Instead of mumbling what to answer or shooting in the dark, as a founder, you must prepare yourself to answer this line of questioning—and creating a financial plan for your startup is the best way to do it.
A business plan’s financial plan section is no easy task—we get that.
But, you know what—this in-depth guide and financial plan example can make forecasting as simple as counting on your fingertips.
Ready to get started? Let’s begin by discussing startup financial planning.
What is Startup Financial Planning?
Startup financial planning, in simple terms, is a process of planning the financial aspects of a new business. It’s an integral part of a business plan and comprises its three major components: balance sheet, income statement, and cash-flow statement.
Apart from these statements, your financial section may also include revenue and sales forecasts, assets & liabilities, break-even analysis , and more. Your first financial plan may not be very detailed, but you can tweak and update it as your company grows.
Key Takeaways
- Realistic assumptions, thorough research, and a clear understanding of the market are the key to reliable financial projections.
- Cash flow projection, balance sheet, and income statement are three major components of a financial plan.
- Preparing a financial plan is easier and faster when you use a financial planning tool.
- Exploring “what-if” scenarios is an ideal method to understand the potential risks and opportunities involved in the business operations.
Why is Financial Planning Important to Your Startup?
Poor financial planning is one of the biggest reasons why most startups fail. In fact, a recent CNBC study reported that running out of cash was the reason behind 44% of startup failures in 2022.
A well-prepared financial plan provides a clear financial direction for your business, helps you set realistic financial objectives, create accurate forecasts, and shows your business is committed to its financial objectives.
It’s a key element of your business plan for winning potential investors. In fact, YC considered recent financial statements and projections to be critical elements of their Series A due diligence checklist .
Your financial plan demonstrates how your business manages expenses and generates revenue and helps them understand where your business stands today and in 5 years.
Makes sense why financial planning is important to your startup, doesn’t it? Let’s cut to the chase and discuss the key components of a startup’s financial plan.
Say goodbye to old-school excel sheets & templates
Make accurate financial plan faster with AI
Plans starting from $7/month

Key Components of a Startup Financial Plan
Whether creating a financial plan from scratch for a business venture or just modifying it for an existing one, here are the key components to consider including in your startup’s financial planning process.
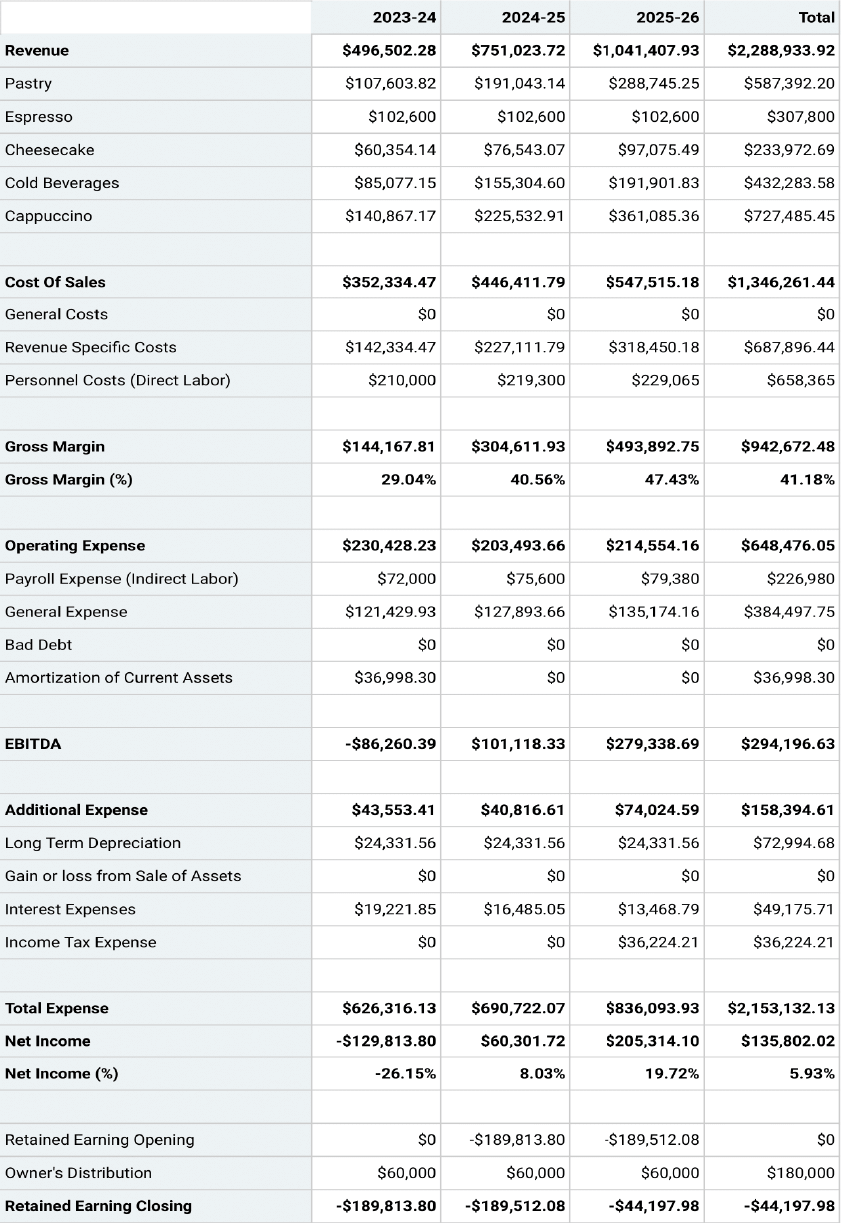
Income Statement
An Income statement , also known as a profit-and-loss statement(P&L), shows your company’s income and expenditures. It also demonstrates how your business experienced any profit or loss over a given time.
Consider it as a snapshot of your business that shows the feasibility of your business idea. An income statement can be generated considering three scenarios: worst, expected, and best.
Your income or P&L statement must list the following:
- Cost of goods or cost of sale
- Gross margin
- Operating expenses
- Revenue streams
- EBITDA (Earnings before interest, tax, depreciation , & amortization )
Established businesses can prepare annual income statements, whereas new businesses and startups should consider preparing monthly statements.
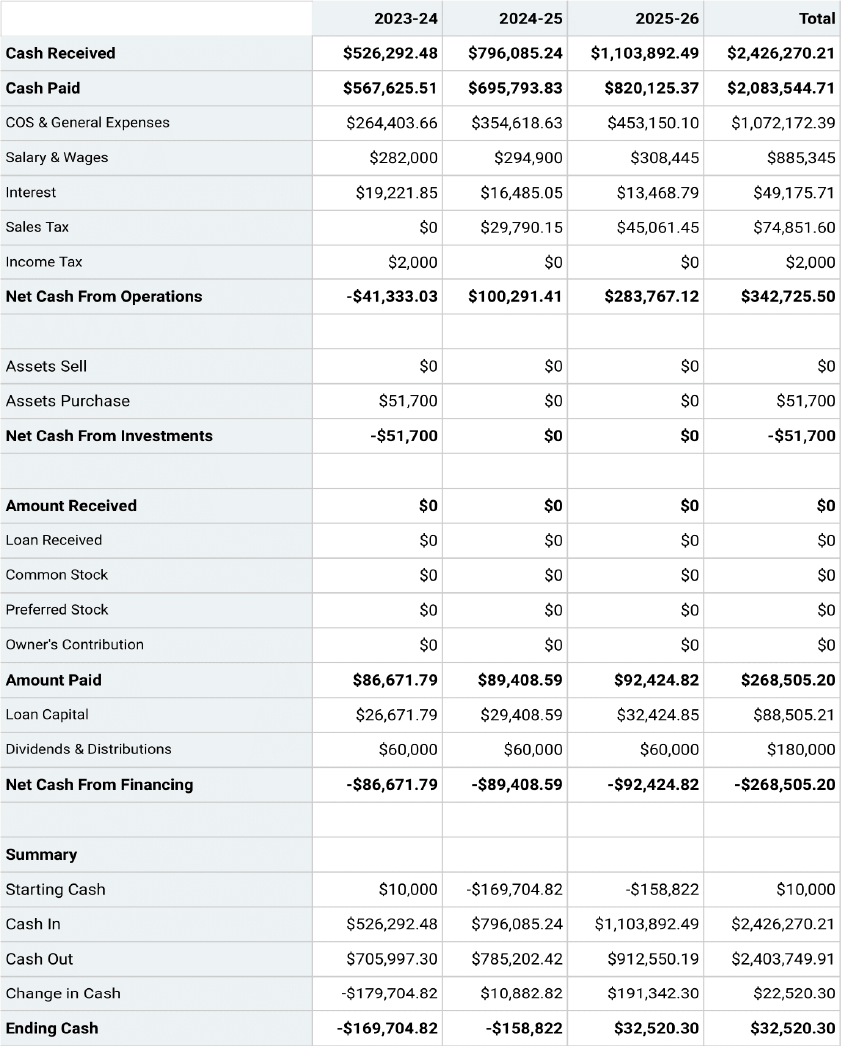
Cash flow Statement
A cash flow statement is one of the most critical financial statements for startups that summarize your business’s cash in-and-out flows over a given time.
This section provides details on the cash position of your business and its ability to meet monetary commitments on a timely basis.
Your cash flow projection consists of the following three components:
✅ Cash revenue projection: Here, you must enter each month’s estimated or expected sales figures.
✅ Cash disbursements: List expenditures that you expect to pay in cash for each month over one year.
✅ Cash flow reconciliation: Cash flow reconciliation is a process used to ensure the accuracy of cash flow projections. The adjusted amount is the cash flow balance carried over to the next month.
Furthermore, a company’s cash flow projections can be crucial while assessing liquidity, its ability to generate positive cash flows and pay off debts, and invest in growth initiatives.
Balance Sheet
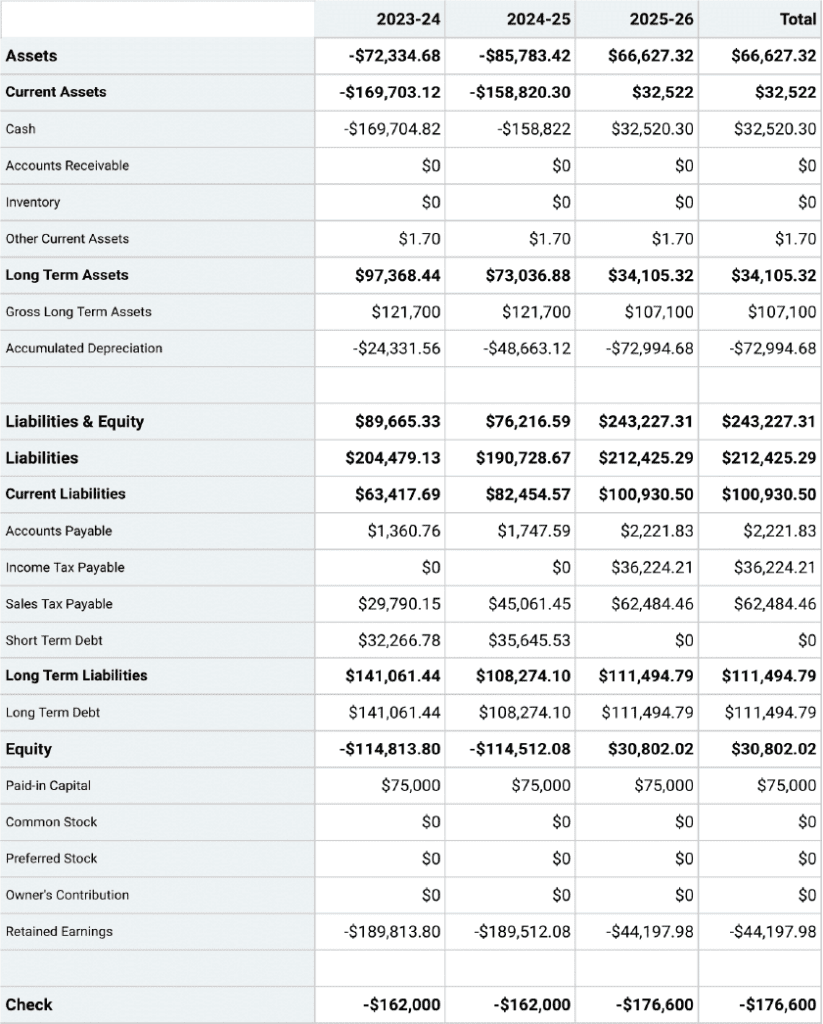
Your balance sheet is a financial statement that reports your company’s assets, liabilities, and shareholder equity at a given time.
Consider it as a snapshot of what your business owns and owes, as well as the amount invested by the shareholders.
This statement consists of three parts: assets , liabilities, and the balance calculated by the difference between the first two. The final numbers on this sheet reflect the business owner’s equity or value.
Balance sheets follow the following accounting equation with assets on one side and liabilities plus Owner’s equity on the other:
Here is what’s the core purpose of having a balance-sheet:
- Indicates the capital need of the business
- It helps to identify the allocation of resources
- It calculates the requirement of seed money you put up, and
- How much finance is required?
Since it helps investors understand the condition of your business on a given date, it’s a financial statement you can’t miss out on.
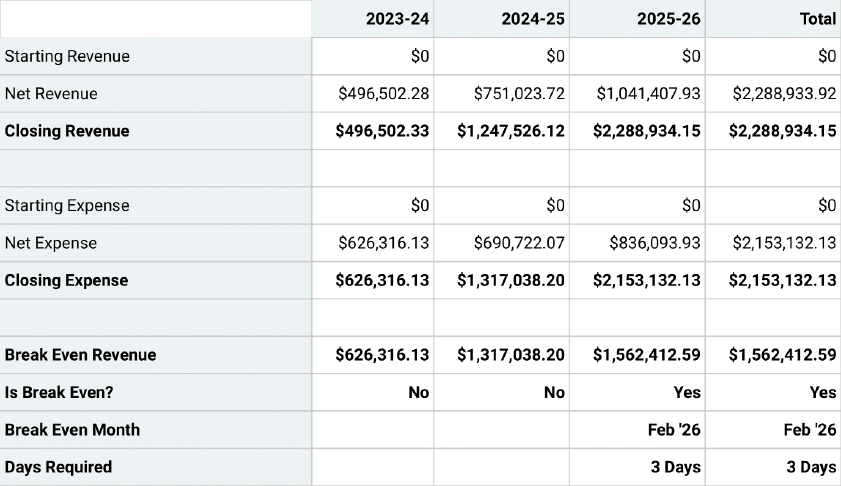
Break-even Analysis
Break-even analysis is a startup or small business accounting practice used to determine when a company, product, or service will become profitable.
For instance, a break-even analysis could help you understand how many candles you need to sell to cover your warehousing and manufacturing costs and start making profits.
Remember, anything you sell beyond the break-even point will result in profit.
You must be aware of your fixed and variable costs to accurately determine your startup’s break-even point.
- Fixed costs: fixed expenses that stay the same no matter what.
- Variable costs: expenses that fluctuate over time depending on production or sales.
A break-even point helps you smartly price your goods or services, cover fixed costs, catch missing expenses, and set sales targets while helping investors gain confidence in your business. No brainer—why it’s a key component of your startup’s financial plan.
Having covered all the key elements of a financial plan, let’s discuss how you can create a financial plan for your startup.
How to Create a Financial Section of a Startup Business Plan?
1. determine your financial needs.
You can’t start financial planning without understanding your financial requirements, can you? Get your notepad or simply open a notion doc; it’s time for some critical thinking.
Start by assessing your current situation by—calculating your income, expenses , assets, and liabilities, what the startup costs are, how much you have against them, and how much financing you need.
Assessing your current financial situation and health will help determine how much capital you need for your startup and help plan fundraising activities and outreach.
Furthermore, determining financial needs helps prioritize operational activities and expenses, effectively allocate resources, and increase the viability and sustainability of a business in the long run.
Having learned to determine financial needs, let’s head straight to setting financial goals.
2. Define Your Financial Goals
Setting realistic financial goals is fundamental in preparing an effective financial plan. So, it would help to outline your long-term strategies and goals at the beginning of your financial planning process.
Let’s understand it this way—if you are a SaaS startup pursuing VC financing rounds, you may ask investors about what matters to them the most and prepare your financial plan accordingly.
However, a coffee shop owner seeking a business loan may need to create a plan that appeals to banks, not investors. At the same time, an internal financial plan designed to offer financial direction and resource allocation may not be the same as previous examples, seeing its different use case.
Feeling overwhelmed? Just define your financial goals—you’ll be fine.
You can start by identifying your business KPIs (key performance indicators); it would be an ideal starting point.
3. Choose the Right Financial Planning Tool
Let’s face it—preparing a financial plan using Excel is no joke. One would only use this method if they had all the time in the world.
Having the right financial planning software will simplify and speed up the process and guide you through creating accurate financial forecasts.
Many financial planning software and tools claim to be the ideal solution, but it’s you who will identify and choose a tool that is best for your financial planning needs.

Create a Financial Plan with Upmetrics in no time
Enter your Financial Assumptions, and we’ll calculate your monthly/quarterly and yearly financial projections.
Start Forecasting
4. Make Assumptions Before Projecting Financials
Once you have a financial planning tool, you can move forward to the next step— making financial assumptions for your plan based on your company’s current performance and past financial records.
You’re just making predictions about your company’s financial future, so there’s no need to overthink or complicate the process.
You can gather your business’ historical financial data, market trends, and other relevant documents to help create a base for accurate financial projections.
After you have developed rough assumptions and a good understanding of your business finances, you can move forward to the next step—projecting financials.
5. Prepare Realistic Financial Projections
It’s a no-brainer—financial forecasting is the most critical yet challenging aspect of financial planning. However, it’s effortless if you’re using a financial planning software.
Upmetrics’ forecasting feature can help you project financials for up to 7 years. However, new startups usually consider planning for the next five years. Although it can be contradictory considering your financial goals and investor specifications.
Following are the two key aspects of your financial projections:
Revenue Projections
In simple terms, revenue projections help investors determine how much revenue your business plans to generate in years to come.
It generally involves conducting market research, determining pricing strategy , and cash flow analysis—which we’ve already discussed in the previous steps.
The following are the key components of an accurate revenue projection report:
- Market analysis
- Sales forecast
- Pricing strategy
- Growth assumptions
- Seasonal variations
This is a critical section for pre-revenue startups, so ensure your projections accurately align with your startup’s financial model and revenue goals.
Expense Projections
Both revenue and expense projections are correlated to each other. As revenue forecasts projected revenue assumptions, expense projections will estimate expenses associated with operating your business.
Accurately estimating your expenses will help in effective cash flow analysis and proper resource allocation.
These are the most common costs to consider while projecting expenses:
- Fixed costs
- Variable costs
- Employee costs or payroll expenses
- Operational expenses
- Marketing and advertising expenses
- Emergency fund
Remember, realistic assumptions, thorough research, and a clear understanding of your market are the key to reliable financial projections.
6. Consider “What if” Scenarios
After you project your financials, it’s time to test your assumptions with what-if analysis, also known as sensitivity analysis.
Using what-if analysis with different scenarios while projecting your financials will increase transparency and help investors better understand your startup’s future with its best, expected, and worst-case scenarios.
Exploring “what-if” scenarios is the best way to better understand the potential risks and opportunities involved in business operations. This proactive exercise will help you make strategic decisions and necessary adjustments to your financial plan.
7. Build a Visual Report
If you’ve closely followed the steps leading to this, you know how to research for financial projections, create a financial plan, and test assumptions using “what-if” scenarios.
Now, we’ll prepare visual reports to present your numbers in a visually appealing and easily digestible format.
Don’t worry—it’s no extra effort. You’ve already made a visual report while creating your financial plan and forecasting financials.
Check the dashboard to see the visual presentation of your projections and reports, and use the necessary financial data, diagrams, and graphs in the final draft of your financial plan.
Here’s what Upmetrics’ dashboard looks like:
8. Monitor and Adjust Your Financial Plan
Even though it’s not a primary step in creating a good financial plan, it’s quite essential to regularly monitor and adjust your financial plan to ensure the assumptions you made are still relevant, and you are heading in the right direction.
There are multiple ways to monitor your financial plan.
For instance, you can compare your assumptions with actual results to ensure accurate projections based on metrics like new customers acquired and acquisition costs, net profit, and gross margin.
Consider making necessary adjustments if your assumptions are not resonating with actual numbers.
Also, keep an eye on whether the changes you’ve identified are having the desired effect by monitoring their implementation.
And that was the last step in our financial planning guide. However, it’s not the end. Have a look at this financial plan example.
Startup Financial Plan Example
Having learned about financial planning, let’s quickly discuss a coffee shop startup financial plan example prepared using Upmetrics.
Important Assumptions
- The sales forecast is conservative and assumes a 5% increase in Year 2 and a 10% in Year 3.
- The analysis accounts for economic seasonality – wherein some months revenues peak (such as holidays ) and wanes in slower months.
- The analysis assumes the owner will not withdraw any salary till the 3rd year; at any time it is assumed that the owner’s withdrawal is available at his discretion.
- Sales are cash basis – nonaccrual accounting
- Moderate ramp- up in staff over the 5 years forecast
- Barista salary in the forecast is $36,000 in 2023.
- In general, most cafes have an 85% gross profit margin
- In general, most cafes have a 3% net profit margin
Projected Balance Sheet
Projected Cash-Flow Statement
Projected Profit & Loss Statement
Break Even Analysis
Start Preparing Your Financial Plan
We covered everything about financial planning in this guide, didn’t we? Although it doesn’t fulfill our objective to the fullest—we want you to finish your financial plan.
Sounds like a tough job? We have an easy way out for you—Upmetrics’ financial forecasting feature. Simply enter your financial assumptions, and let it do the rest.
So what are you waiting for? Try Upmetrics and create your financial plan in a snap.
Build your Business Plan Faster
with step-by-step Guidance & AI Assistance.

Frequently Asked Questions
How often should i update my financial projections.
Well, there is no particular rule about it. However, reviewing and updating your financial plan once a year is considered an ideal practice as it ensures that the financial aspirations you started and the projections you made are still relevant.
How do I estimate startup costs accurately?
You can estimate your startup costs by identifying and factoring various one-time, recurring, and hidden expenses. However, using a financial forecasting tool like Upmetrics will ensure accurate costs while speeding up the process.
What financial ratios should startups pay attention to?
Here’s a list of financial ratios every startup owner should keep an eye on:
- Net profit margin
- Current ratio
- Quick ratio
- Working capital
- Return on equity
- Debt-to-equity ratio
- Return on assets
- Debt-to-asset ratio
What are the 3 different scenarios in scenario analysis?
As discussed earlier, Scenario analysis is the process of ascertaining and analyzing possible events that can occur in the future. Startups or businesses often consider analyzing these three scenarios:
- base-case (expected) scenario
- Worst-case scenario
- best case scenario.
About the Author

Ajay is a SaaS writer and personal finance blogger who has been active in the space for over three years, writing about startups, business planning, budgeting, credit cards, and other topics related to personal finance. If not writing, he’s probably having a power nap. Read more
Reach Your Goals with Accurate Planning
No Risk – Cancel at Any Time – 15 Day Money Back Guarantee
Popular Templates

How to Write a Small Business Financial Plan

Noah Parsons
4 min. read
Updated April 22, 2024
Creating a financial plan is often the most intimidating part of writing a business plan.
It’s also one of the most vital. Businesses with well-structured and accurate financial statements are more prepared to pitch to investors, receive funding, and achieve long-term success.
Thankfully, you don’t need an accounting degree to successfully create your budget and forecasts.
Here is everything you need to include in your financial plan, along with optional performance metrics, funding specifics, mistakes to avoid , and free templates.
- Key components of a financial plan
A sound financial plan is made up of six key components that help you easily track and forecast your business financials. They include your:
Sales forecast
What do you expect to sell in a given period? Segment and organize your sales projections with a personalized sales forecast based on your business type.
Subscription sales forecast
While not too different from traditional sales forecasts—there are a few specific terms and calculations you’ll need to know when forecasting sales for a subscription-based business.
Expense budget
Create, review, and revise your expense budget to keep your business on track and more easily predict future expenses.
How to forecast personnel costs
How much do your current, and future, employees’ pay, taxes, and benefits cost your business? Find out by forecasting your personnel costs.
Profit and loss forecast
Track how you make money and how much you spend by listing all of your revenue streams and expenses in your profit and loss statement.
Cash flow forecast
Manage and create projections for the inflow and outflow of cash by building a cash flow statement and forecast.
Balance sheet
Need a snapshot of your business’s financial position? Keep an eye on your assets, liabilities, and equity within the balance sheet.
What to include if you plan to pursue funding
Do you plan to pursue any form of funding or financing? If the answer is yes, then there are a few additional pieces of information that you’ll need to include as part of your financial plan.
Highlight any risks and assumptions
Every entrepreneur takes risks with the biggest being assumptions and guesses about the future. Just be sure to track and address these unknowns in your plan early on.
Plan your exit strategy
Investors will want to know your long-term plans as a business owner. While you don’t need to have all the details, it’s worth taking the time to think through how you eventually plan to leave your business.
- Financial ratios and metrics
With your financial statements and forecasts in place, you have all the numbers needed to calculate insightful financial ratios.
While including these metrics in your plan is entirely optional, having them easily accessible can be valuable for tracking your performance and overall financial situation.
Key financial terms you should know
It’s not hard. Anybody who can run a business can understand these key financial terms. And every business owner and entrepreneur should know them.
Common business ratios
Unsure of which business ratios you should be using? Check out this list of key financial ratios that bankers, financial analysts, and investors will want to see.
Break-even analysis
Do you want to know when you’ll become profitable? Find out how much you need to sell to offset your production costs by conducting a break-even analysis.
How to calculate ROI
How much could a business decision be worth? Evaluate the efficiency or profitability by calculating the potential return on investment (ROI).
- How to improve your financial plan
Your financial statements are the core part of your business plan that you’ll revisit most often. Instead of worrying about getting it perfect the first time, check out the following resources to learn how to improve your projections over time.
Common mistakes with business forecasts
I was glad to be asked about common mistakes with startup financial projections. I read about 100 business plans per year, and I have this list of mistakes.
How to improve your financial projections
Learn how to improve your business financial projections by following these five basic guidelines.
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
- Financial plan templates and tools
Download and use these free financial templates and calculators to easily create your own financial plan.

Sales forecast template
Download a free detailed sales forecast spreadsheet, with built-in formulas, to easily estimate your first full year of monthly sales.
Download Template

Accurate and easy financial forecasting
Get a full financial picture of your business with LivePlan's simple financial management tools.
Get Started
Noah is the COO at Palo Alto Software, makers of the online business plan app LivePlan. He started his career at Yahoo! and then helped start the user review site Epinions.com. From there he started a software distribution business in the UK before coming to Palo Alto Software to run the marketing and product teams.

Table of Contents
- What to include for funding
Related Articles

24 Min. Read
The 10 AI Prompts You Need to Write a Business Plan

6 Min. Read
How to Write Your Business Plan Cover Page + Template

10 Min. Read
How to Set and Use Milestones in Your Business Plan

How to Write a Competitive Analysis for Your Business Plan
The Bplans Newsletter
The Bplans Weekly
Subscribe now for weekly advice and free downloadable resources to help start and grow your business.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
What Are the Financial Assumptions on a Business Plan?
- Small Business
- Business Planning & Strategy
- Financial Business Plans
- ')" data-event="social share" data-info="Pinterest" aria-label="Share on Pinterest">
- ')" data-event="social share" data-info="Reddit" aria-label="Share on Reddit">
- ')" data-event="social share" data-info="Flipboard" aria-label="Share on Flipboard">
How to Obtain Short-Term Financing for a Business
Keys to a successful business pitch, how to write the perfect business plan.
- How to Start a Candy Store Business
- How to Write a One-Year Profit Projection Letter
Business plans are required for all small businesses seeking loans or investors. Financial assumptions and projections are critical components of all business plans. Three universal financial presentations are expected in all business plans.
You must include a projected income statement, balance sheet and cash flow statement for the coming three to five years. Along with the numbers, include a narrative that explains your assumptions and how the line items were computed.
Financial assumptions and projections are critical components of all business plans. They include income and expense assumptions, as well as the inventory and accounts receivable in the balance sheet. Assumptions for balance sheet presentations should be conservative and based on reasonable expectations of asset acquisitions in the coming five years. These will help to construct the assumptions in the cash flow statement.
Construct an Income Statement
Construct your income statement on a month-to-month basis for the first one to two years. You can then switch to quarterly projections for years three through five. One key item dominates this presentation. Base your income and expense assumptions on factual, verifiable information.
For example, if your product competitively sells for $25 to $40, refrain from using a $60 selling price to craft your sales projections. Also, base your sales volume assumptions on realistic statistics, easily verified by a quick market analysis.
Balance Sheet Presentations
Assumptions for balance sheet presentations should be conservative and based on reasonable expectations of asset acquisitions in the coming five years. Of particular concern to lenders and investors are inventory and accounts receivable. Both are functions of sales. Therefore, carefully match your inventory assumptions with your gross income projections.
Unless accounts receivable are typically large in your industry, do not project high balances. Because cash is usually in short supply for small businesses, tying up this precious resource in excessive inventory or accounts receivable can be damaging.
Cash Flow Statement
If you have a new small business or a modest company needing financing or investment, the projected cash flow Statement may be the most important financial assumption you make. While both lenders and investors want your small business to generate solid net income and have a strong balance sheet, cash flow is more important. It is from cash flow that you can repay loans or distribute cash to investors from profits.
Warning when Making Assumptions
Making financial projections based on solid assumptions is wonderful. But you must explain the derivation and calculations to give business plan readers confidence in your data. Don't commit newer entrepreneur mistakes. Many spend hours pouring over data and create reasonable financial projections.
However, newbies often forget or feel inadequate to explain their assumptions in text format. Assuming that loan officers are experts in reading business plans is smart. However, assuming they are experts in your industry is a mistake. Write as detailed a narrative as possible for your financial assumptions, with references that your loan officer can verify.
Diligent Research and Expert Insight
Making valid financial assumptions, and explaining them clearly, can make the difference in receiving the funds you need or suffering rejection by lenders or investors. Often, the primary reason for approval or rejection relates to your display of expertise in your industry. Perform your industry and competition research diligently and with a total focus on becoming an expert. You must then make financial assumptions based on this expertise – and communicate this clearly in your business plan. Your financial assumptions will be challenged. Have knowledgeable answers ready for these challenges.
- Growthink: How to Develop Reasonable Financial Assumptions
- Inc.: How to Write the Financial Section of a Business Plan
- Rodgers Associates: Three Key Assumptions To Make in Financial Planning
- PlanWare: Software to Make Good Financial Projections
Related Articles
How to present business plans to donors, differences between forecasting & budgeting, why is it important for entrepreneurs to develop financial plans for their companies, how to sell business ideas, how to write your business proposal, business objectives in designing reports, what factors make the difference between a good business plan & an excellent one, how to design a corporate financial plan, what are the key assumptions of a business plan, most popular.
- 1 How to Present Business Plans to Donors
- 2 Differences Between Forecasting & Budgeting
- 3 Why Is It Important for Entrepreneurs to Develop Financial Plans for Their Companies?
- 4 How to Sell Business Ideas
How Financial Assumptions Can Make Or Break Your Business Plan

May 9, 2022
Adam Hoeksema
A business plan is only as good as its financial assumptions. These are the key input data that your financial projections will extrapolate from and will form a picture of the future of your company. With a robust method of researching for these assumptions, and then the corresponding analysis of the available data, you’re left with more accurate assumptions, leading to a more realistic picture of your financial future.
Conversely, with weak assumptions from lack of sufficient research or bad analysis, you can get a dramatically different output that doesn’t remotely reflect reality. When looking for outside investment, these are the skills a savvy investor is going to value in an entrepreneur. So how best to improve your assumptions? Keep reading for the answer.
Financial Assumptions
Any entrepreneur, startup founder, or young company is going to need to form detailed financial reports, including forecasts and projections of the financial situation to come. These documents rely entirely on input data to extrapolate from, and these data are based on historical records and key assumptions .
The accuracy of these financial assumptions determines the accuracy of the output of these projections, and since the divergence from reality increases over time, it’s important for them to be as accurate as possible to precisely depict a realistic situation in the future.
The importance of these assumptions comes into play significantly when trying to attract capital from outside. These investors or lenders will be looking closely at your assumptions as a metric of your credibility; strong assumptions show you’ve done your due diligence and you know what you’re talking about. Weak ones will greatly harm your chances of success.
Here we’re going to go over the basics of financial assumptions, what they’re for, and common mistakes people make with them.
The Role of Financial Assumptions in Forecasting
In business planning, forecasting is a crucial step in visualizing how a company will perform in the future. Companies forecast future outcomes based on past and current data, using assumptions.
Forecasted elements of a financial plan include revenue, margin, and expenses, among others. When done accurately, these forecasts allow businesses to:
- Predict future expenses
- Make budgets
- Make informed decisions about the direction of the company
- Plan growth and financing options
However, accuracy requires more than just historical data; it’s important to input the rate of change over time correctly, and this is where assumptions come in.
Essentially, assumptions are educated guesses about the nature of your business and its market, and how these will affect future outcomes in your forecasts. As projections reach further into the future, the need for accuracy of the input assumptions increases. Small mistakes become significantly larger over time, and this skews projections to the point of making them worthless.
For investors to take notice, you’ll need accurate and well-thought-out assumptions that aren’t plucked from thin air. We’ll go into more detail about how to find these assumptions shortly, but first, let’s consider why accuracy is so important.
The Importance of Accuracy in Financial Assumptions
The financial statements of a business plan are an indication of the company’s profitability. They are the strongest display of the worthiness of investment that your company has, therefore, they’re going to need to be founded on accurate assumptions.
Even with relatively accurate initial figures, long-term projections can still be way off the mark. Essentially, any forecast is a calculation with decreasing accuracy over time, which is why they usually don’t project out past time frames of longer than around five years. Take the following example:
Let’s say you’ve done the research into the market, into the reducing costs of production over time, the rapid expected growth of your company, and the increase in value you’re going to make to your product or service over the next few years. What comes out is an assumed increase in revenue projected into the future.
If you assume your total revenue will increase by 20% over 5 years with a starting revenue of $20,000, the first-year outcome will be $24,000, an increase of four thousand dollars. The fifth-year outcome will be $49,767; an increase of almost thirty thousand dollars.
If your initial assumption is off by only 5% in either direction, the first year will show a difference from the above forecast of $1000 , either returning $23,000 or $25,000 at the low and high ends, respectively.
This isn’t a huge amount of money at this stage, so a misjudgment of 5% seems reasonable. However, if we extend this effect to the fifth year, an error of 5% brings a difference of either $9,500 or $11,268 to what you had projected, depending on whether your assumption was low or high.
If you’re smart or lucky enough to have made a conservative assumption, you’re now $11k better off. On the other hand, if you were too hasty and overestimated in your assumption, you may now owe somebody over $9k.
So, the effect of an assumption is greater with distance from the starting point. This means that when you’re designing a business plan to show to potential investors, they’re going to be very critical of your assumptions in order to assess the chances of their ROI in your company.
Regardless of whether you assumed low or high, if there’s a discrepancy that becomes obvious to investors, it will make them question the rest of your estimates and how accurate you will be in future calculations.
Therefore, accurate assumptions are critically Important to not only the precise understanding of the state of your company in the future but any chances of investors taking you seriously. Without good assumptions there is no forecast. Without a forecast, there’s not going to be any investment.
If your business is going to be relying on VC or other investors helping out, you’re going to find yourself out of luck. So, with that in mind, let’s take a look at some of the classic assumptions you’ll need to make when designing your forecasts and projections.
Key Financial Assumptions Examples
Building a business plan relies on numerous assumptions. These are the where, when, and how’s of your company, and will create projections in order for you to know where to direct your energy. The most important assumptions are called key assumptions, and without these, it’s going to be impossible to make informed decisions on the direction of your company.
Changes in assumptions can dramatically alter the outcomes of your forecasts. If you assume, for example, that your product or service is going to have a decreasing churn rate - or loss of customers - over the coming years of service improvement, you have to know what that rate is going to decrease by each year for your forecast to be of any use.
It’s worth thinking about these assumptions in terms of how you will persuade investors to commit. Here is a list of some of the areas in which key assumptions are needed for financial planning, for use as financial assumptions examples:
- Market – There’s no business without a market. This assumption isn’t so much a financial one as a general business one, but it has strong financial implications.
By the time you come to financial planning for your startup, you should know who your ideal customer is and how you’re addressing their pain points.
You should also know how much they’re willing to spend on your product or service, which will come in handy for your income statement and cash flow projections.
- Cost of production - Production cost changes over time. Even if it’s simply an increase in outgoings to match an increase in demand, this needs to be assumed. Usually, production costs can be reduced as economies of scale come into play, but regardless, it’s easy to overlook some data here.
Calculating production costs involves covering rent for manufacturing spaces, materials, utilities such as power and water, and essentially every little thing that goes into the manufacture of your product or provision of your service. Obviously, these will be more or less complicated depending on the type of business you’re running.
This step is crucial for the following revenue and costs to be accurate.
- Cost of Sales – This one is closely related to the cost of production and there may be some overlap in these costs such as labor, so separate them as you wish, however, make sure to calculate the cost of distribution; shipping, handling, marketing, etc. it’s possible to combine these assumptions under production and sales for convenience.
- Cost of Administration – This is a monthly expenditure covering all the outgoings related to your workforce and company maintenance. Payroll needs to be financially covered by any income or capital funding you’re expecting and this includes any bonuses you’re expecting to put out. One key assumption regarding bonuses will be in their timing, should you choose to pay them, and this needs to be factored into projections for costs.
- Pricing – This assumption should be made with detailed research backing it up. Since pricing alone can make or break your company, investors are going to want to see how you came up with your figures here. The costs of sales and production are going to determine your range of pricing options.
To accurately calculate prices, you’re going to need to understand how much value your product or service has to your customers, which is where the key assumptions from the Market section above come in. Pricing needs to match the value of what you’re offering, so this is the opposing force to the production and distribution costs, since it will always be pulling your price down towards its value, while costs of production and distribution will be pushing it up.
- Sales Forecast – For every different service or product that you’re offering, a sales forecast needs to be calculated. For an accurate sales forecast, you’re going to need to know the desired sales funnel in detail and how long the conversion process will take. These assumptions need to be backed up by your market research.
Further, you’re going to have to make assumptions on when your sales will complete; this means how long banking processes will take, etc. These assumptions will be critical to accurately forecast your profits in your financial plan.
- Cash Flow – This section will involve numerous key assumptions. Capital will hopefully be flowing into the company from numerous streams, and these need to be calculated well in order to project financial coverage of the aforementioned costs.
Timings of loan payments, loan repayments, cash equity, and others need to be reliably assumed to make sound predictions in these cases. Interest adjustments or early repayment fees are also things to take into consideration, and if you will be offering customer credit, this will create more complexities to look into in terms of when you’ll see that capital again.
These are some of the major areas in which financial assumptions are necessary, and their need for accuracy is obvious. An accurate assumption comes down to reliable and robust research and analysis practices, and for these, it’s important to follow the best practices of business planning, and consider expert help where needed.
Of course, the specifics of these areas and their significance to your company will depend entirely on the type of service, product, business, or market you’re involved with. As such, there’s no standard template, but there are some key practices worth following.
Find Your Industry Specific Projections Template to Help Create Assumptions:
Why There are no one-size-fits-all Financial Assumptions
Startup founders and entrepreneurs need to provide convincing projections of the financial state of the company over the following years to reassure investors that their capital will be returned. They do this by creating robust assessments of their current state and the state of company and market metrics as accurately as possible and factoring them into projection calculations as assumptions.
The best way to begin building your financial assumptions is to consider them from the perspective of an investor. If you’re looking to put down a significant investment in a project you’re going to want to guarantee your ROI, and to do that, you need to be persuaded of the project’s profitability.
Every company is different, and every market has its own needs and challenges. This is why there’s no strict financial assumptions template to follow, but by following these four basic principles, you’ll be closer to developing more accurate assumptions.
At the planning stage of a company, the historical financial data simply won’t exist. This reduces the power of the financial assumptions, and even further necessitates their precision. The trouble is, this is a lengthy process. AQPC showed that even financial analysts spend almost half their time collecting and validating data, and they’re experts at it.
This means you have to expect a grind. If you’re going it alone with this process, make sure to get a handle on your research methods, and which areas to focus on and in the right order. This is a topic for its very own article, but the point is, expect to dedicate and schedule a lot of time for this part of the process.
So we know the research is important, but how do you go about it? For costs of manufacturing, meeting with suppliers is essential to get written quotes for supplies covering any wholesale discounts that might be available. Then, for marketing and distribution, studying your market in depth is crucial to making accurate assumptions about the value of what you’re offering and how much it’ll cost to get it out there.
Find out exactly where and how to look, and gather the necessary data on all the elements your company needs to be able to predict. From this, you will work on the analysis.
Outsourcing
There are definitely ways to go this alone, especially if this relates to a field you’re familiar with, but the option to use outside help shouldn’t be overlooked. ProjectionHub offers a range of services that can help with the financial planning process. From basic projection templates to detailed, expert guidance and tailored forecasting spreadsheets specifically designed for your business, there are a lot of useful options that can help speed up the process and improve your accuracy.
Demonstration
Finally, show your workings! If you’ve spent the due time and energy collecting and analyzing the data, it’s not going to matter if you can’t demonstrate how you came to the conclusions you did. Putting in the work is how you get accurate assumptions, but describing your process is how you persuade others to trust them.
Financial forecasts are the backbone of a business plan for investors. They’re a demonstration that you’ve done your homework and you know what you’re doing, and with bold claims, there comes the need for strong evidence.
Making assumptions is the key to any projection. Assumptions about change over time, consistency over time, and any other incomings and outgoings that you anticipate as part of the process. The accuracy of these assumptions is what makes or breaks a business plan, as they hold the key to future, long-term investment as well as countless other business choices made by decision-makers.
If this seems like a daunting task, don’t’ worry. There are countless opportunities to take advantage of expert help with services like ours at ProjectionHub , which provides templates and expert advice to get you started.
Accurate assumptions should not be underestimated. Putting in the work at this stage of your financial projections will pay dividends and command great respect from investors.
About the Author
Adam is the Co-founder of ProjectionHub which helps entrepreneurs create financial projections for potential investors, lenders and internal business planning. Since 2012, over 40,000 entrepreneurs from around the world have used ProjectionHub to help create financial projections.
Other Stories to Check out
How to know if your financial projections are realistic.
It is important for financial projections for a small business or startup to be realistic or else an investor or lender may not take them seriously. More importantly, the founder may make a financial mistake without a reliable plan.
How to Finance a Small Business Acquisition
In this article we are going to walk through how to finance a small business acquisition and answer some key questions related to financing options.
How to Acquire a Business in 11 Steps
Many people don't realize that acquiring a business can be a great way to become a business owner if they prefer not to start one from scratch. But the acquisition process can be a little intimidating so here is a guide helping you through it!
Have some questions? Let us know and we'll be in touch.
- Business Planning

Business Plan Financial Projections
Written by Dave Lavinsky

Financial projections are forecasted analyses of your business’ future that include income statements, balance sheets and cash flow statements. We have found them to be an crucial part of your business plan for the following reasons:
- They can help prove or disprove the viability of your business idea. For example, if your initial projections show your company will never make a sizable profit, your venture might not be feasible. Or, in such a case, you might figure out ways to raise prices, enter new markets, or streamline operations to make it profitable.
- Financial projections give investors and lenders an idea of how well your business is likely to do in the future. They can give lenders the confidence that you’ll be able to comfortably repay their loan with interest. And for equity investors, your projections can give them faith that you’ll earn them a solid return on investment. In both cases, your projections can help you secure the funding you need to launch or grow your business.
- Financial projections help you track your progress over time and ensure your business is on track to meet its goals. For example, if your financial projections show you should generate $500,000 in sales during the year, but you are not on track to accomplish that, you’ll know you need to take corrective action to achieve your goal.
Below you’ll learn more about the key components of financial projections and how to complete and include them in your business plan.
What Are Business Plan Financial Projections?
Financial projections are an estimate of your company’s future financial performance through financial forecasting. They are typically used by businesses to secure funding, but can also be useful for internal decision-making and planning purposes. There are three main financial statements that you will need to include in your business plan financial projections:
1. Income Statement Projection
The income statement projection is a forecast of your company’s future revenues and expenses. It should include line items for each type of income and expense, as well as a total at the end.
There are a few key items you will need to include in your projection:
- Revenue: Your revenue projection should break down your expected sales by product or service, as well as by month. It is important to be realistic in your projections, so make sure to account for any seasonal variations in your business.
- Expenses: Your expense projection should include a breakdown of your expected costs by category, such as marketing, salaries, and rent. Again, it is important to be realistic in your estimates.
- Net Income: The net income projection is the difference between your revenue and expenses. This number tells you how much profit your company is expected to make.
Sample Income Statement
2. cash flow statement & projection.
The cash flow statement and projection are a forecast of your company’s future cash inflows and outflows. It is important to include a cash flow projection in your business plan, as it will give investors and lenders an idea of your company’s ability to generate cash.
There are a few key items you will need to include in your cash flow projection:
- The cash flow statement shows a breakdown of your expected cash inflows and outflows by month. It is important to be realistic in your projections, so make sure to account for any seasonal variations in your business.
- Cash inflows should include items such as sales revenue, interest income, and capital gains. Cash outflows should include items such as salaries, rent, and marketing expenses.
- It is important to track your company’s cash flow over time to ensure that it is healthy. A healthy cash flow is necessary for a successful business.
Sample Cash Flow Statements
3. balance sheet projection.
The balance sheet projection is a forecast of your company’s future financial position. It should include line items for each type of asset and liability, as well as a total at the end.
A projection should include a breakdown of your company’s assets and liabilities by category. It is important to be realistic in your projections, so make sure to account for any seasonal variations in your business.
It is important to track your company’s financial position over time to ensure that it is healthy. A healthy balance is necessary for a successful business.
Sample Balance Sheet
How to create financial projections.
Creating financial projections for your business plan can be a daunting task, but it’s important to put together accurate and realistic financial projections in order to give your business the best chance for success.
Cost Assumptions
When you create financial projections, it is important to be realistic about the costs your business will incur, using historical financial data can help with this. You will need to make assumptions about the cost of goods sold, operational costs, and capital expenditures.
It is important to track your company’s expenses over time to ensure that it is staying within its budget. A healthy bottom line is necessary for a successful business.
Capital Expenditures, Funding, Tax, and Balance Sheet Items
You will also need to make assumptions about capital expenditures, funding, tax, and balance sheet items. These assumptions will help you to create a realistic financial picture of your business.
Capital Expenditures
When projecting your company’s capital expenditures, you will need to make a number of assumptions about the type of equipment or property your business will purchase. You will also need to estimate the cost of the purchase.
When projecting your company’s funding needs, you will need to make a number of assumptions about where the money will come from. This might include assumptions about bank loans, venture capital, or angel investors.
When projecting your company’s tax liability, you will need to make a number of assumptions about the tax rates that will apply to your business. You will also need to estimate the amount of taxes your company will owe.
Balance Sheet Items
When projecting your company’s balance, you will need to make a number of assumptions about the type and amount of debt your business will have. You will also need to estimate the value of your company’s assets and liabilities.
Financial Projection Scenarios
Write two financial scenarios when creating your financial projections, a best-case scenario, and a worst-case scenario. Use your list of assumptions to come up with realistic numbers for each scenario.
Presuming that you have already generated a list of assumptions, the creation of best and worst-case scenarios should be relatively simple. For each assumption, generate a high and low estimate. For example, if you are assuming that your company will have $100,000 in revenue, your high estimate might be $120,000 and your low estimate might be $80,000.
Once you have generated high and low estimates for all of your assumptions, you can create two scenarios: a best case scenario and a worst-case scenario. Simply plug the high estimates into your financial projections for the best-case scenario and the low estimates into your financial projections for the worst-case scenario.
Conduct a Ratio Analysis
A ratio analysis is a useful tool that can be used to evaluate a company’s financial health. Ratios can be used to compare a company’s performance to its industry average or to its own historical performance.
There are a number of different ratios that can be used in ratio analysis. Some of the more popular ones include the following:
- Gross margin ratio
- Operating margin ratio
- Return on assets (ROA)
- Return on equity (ROE)
To conduct a ratio analysis, you will need financial statements for your company and for its competitors. You will also need industry average ratios. These can be found in industry reports or on financial websites.
Once you have the necessary information, you can calculate the ratios for your company and compare them to the industry averages or to your own historical performance. If your company’s ratios are significantly different from the industry averages, it might be indicative of a problem.
Be Realistic
When creating your financial projections, it is important to be realistic. Your projections should be based on your list of assumptions and should reflect your best estimate of what your company’s future financial performance will be. This includes projected operating income, a projected income statement, and a profit and loss statement.
Your goal should be to create a realistic set of financial projections that can be used to guide your company’s future decision-making.
Sales Forecast
One of the most important aspects of your financial projections is your sales forecast. Your sales forecast should be based on your list of assumptions and should reflect your best estimate of what your company’s future sales will be.
Your sales forecast should be realistic and achievable. Do not try to “game” the system by creating an overly optimistic or pessimistic forecast. Your goal should be to create a realistic sales forecast that can be used to guide your company’s future decision-making.
Creating a sales forecast is not an exact science, but there are a number of methods that can be used to generate realistic estimates. Some common methods include market analysis, competitor analysis, and customer surveys.
Create Multi-Year Financial Projections
When creating financial projections, it is important to generate projections for multiple years. This will give you a better sense of how your company’s financial performance is likely to change over time.
It is also important to remember that your financial projections are just that: projections. They are based on a number of assumptions and are not guaranteed to be accurate. As such, you should review and update your projections on a regular basis to ensure that they remain relevant.
Creating financial projections is an important part of any business plan. However, it’s important to remember that these projections are just estimates. They are not guarantees of future success.
Business Plan Financial Projections FAQs
What is a business plan financial projection.
A business plan financial projection is a forecast of your company's future financial performance. It should include line items for each type of asset and liability, as well as a total at the end.
What are annual income statements?
The Annual income statement is a financial document and a financial model that summarize a company's revenues and expenses over the course of a fiscal year. They provide a snapshot of a company's financial health and performance and can be used to track trends and make comparisons with other businesses.
What are the necessary financial statements?
The necessary financial statements for a business plan are an income statement, cash flow statement, and balance sheet.
How do I create financial projections?
You can create financial projections by making a list of assumptions, creating two scenarios (best case and worst case), conducting a ratio analysis, and being realistic.
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- Building Your Business
- Becoming an Owner
- Business Plans
How to Write a Financial Analysis
Know what to include in important section of business plan
Alyssa Gregory is an entrepreneur, writer, and marketer with 20 years of experience in the business world. She is the founder of the Small Business Bonfire, a community for entrepreneurs, and has authored more than 2,500 articles for The Balance and other popular small business websites.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/alyssa-headshot-2018-5b73ee0046e0fb002531cb50.png)
Financial Analysis of a Business Plan
Assumptions, know the ground rules, use visuals, check your math.
The financial analysis section of a business plan should contain the data for financing your business for the present, what will be needed for future growth, and an estimation of your operating expenses.
The financial analysis section of your business plan may be the most challenging for you to complete on your own, but it also could be the deal-maker or deal-breaker when you are searching for funding.
Because of the structured, in-depth financial data required for this section, you should consult your accountant or other trusted and qualified financial professional before writing this section .
The financial analysis section should be based on estimates for new businesses or recent data for established businesses. It should include these elements:
- Balance sheet : Your assumed and anticipated business financials, including assets , liabilities, and equity.
- Cash-flow analysis : An overview of the cash you anticipate will be coming into your business based on sales forecasts, minus the anticipated cash expenses of running the business.
- Profit-and-loss analysis : Your income statement that subtracts the costs of the business from the earnings over a specific period of time, typically a quarter or a year.
- Break-even analysis : Demonstrates the point when the cost of doing business is fully covered by sales.
- Personnel-expense forecast : The expenses of your team, as outlined in a management summary section .
Completing a financial analysis section for a business that hasn't been started yet requires some assumptions. However, these aren't guesses. What you expect from the business needs to be based on detailed research and data.
Go back to the other sections of your business plan and write down any financial assumptions you made while drafting those sections. You then can use those assumptions in your financial analysis section. The most important factor is ensuring that the data in the financial analysis section is consistent with the assumptions made in other sections of your business plan.
There may be no section of your business plan where you need help as much as you do with your financial analysis section. The assumptions, forecasting, and specific numbers can be complicated and generally difficult to wrap your head around, especially if you don’t have a financial background. This financial information, though, is exactly the data your audience will be looking for.
You can avoid the stress and uncertainty by getting help from a qualified financial professional early in the process.
When it comes to the financial analysis of your business plan, have a basic idea of what each element should include, where the data comes from, and what the numbers mean. This stands even if you have help developing the financial analysis section because you will be the one left to explain and expand on the financial data in face-to-face situations.
GAAP (generally accepted accounting principles ), a collection of rules, procedures, and conventions that define accepted accounting practices should be followed throughout this section.
Use graphs and charts in the financial analysis section to illustrate the financial data , just as you should in other sections of your business plan that include extensive data, numbers, statistics, and trends. Put the most important visuals in the financial analysis, with the supporting graphics included in the Appendix.
A quick way to lose the attention of a potential investor is by having flawed calculations or numbers that are not backed up. Double and triple check all of your calculations and figures, and have a third-party do the same to ensure everything adds up.
You also should avoid including any figures that are not explained, backed up and otherwise researched extensively, especially when it comes to assumptions you've made. Use data from current and past markets and financial situations to substantiate your numbers.
Free Financial Templates for a Business Plan
By Andy Marker | July 29, 2020
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Link copied
In this article, we’ve rounded up expert-tested financial templates for your business plan, all of which are free to download in Excel, Google Sheets, and PDF formats.
Included on this page, you’ll find the essential financial statement templates, including income statement templates , cash flow statement templates , and balance sheet templates . Plus, we cover the key elements of the financial section of a business plan .
Financial Plan Templates
Download and prepare these financial plan templates to include in your business plan. Use historical data and future projections to produce an overview of the financial health of your organization to support your business plan and gain buy-in from stakeholders
Business Financial Plan Template
Use this financial plan template to organize and prepare the financial section of your business plan. This customizable template has room to provide a financial overview, any important assumptions, key financial indicators and ratios, a break-even analysis, and pro forma financial statements to share key financial data with potential investors.
Download Financial Plan Template
Word | PDF | Smartsheet
Financial Plan Projections Template for Startups
This financial plan projections template comes as a set of pro forma templates designed to help startups. The template set includes a 12-month profit and loss statement, a balance sheet, and a cash flow statement for you to detail the current and projected financial position of a business.
Download Startup Financial Projections Template
Excel | Smartsheet
Income Statement Templates for Business Plan
Also called profit and loss statements , these income statement templates will empower you to make critical business decisions by providing insight into your company, as well as illustrating the projected profitability associated with business activities. The numbers prepared in your income statement directly influence the cash flow and balance sheet forecasts.
Pro Forma Income Statement/Profit and Loss Sample
Use this pro forma income statement template to project income and expenses over a three-year time period. Pro forma income statements consider historical or market analysis data to calculate the estimated sales, cost of sales, profits, and more.
Download Pro Forma Income Statement Sample - Excel
Small Business Profit and Loss Statement
Small businesses can use this simple profit and loss statement template to project income and expenses for a specific time period. Enter expected income, cost of goods sold, and business expenses, and the built-in formulas will automatically calculate the net income.
Download Small Business Profit and Loss Template - Excel
3-Year Income Statement Template
Use this income statement template to calculate and assess the profit and loss generated by your business over three years. This template provides room to enter revenue and expenses associated with operating your business and allows you to track performance over time.
Download 3-Year Income Statement Template
For additional resources, including how to use profit and loss statements, visit “ Download Free Profit and Loss Templates .”
Cash Flow Statement Templates for Business Plan
Use these free cash flow statement templates to convey how efficiently your company manages the inflow and outflow of money. Use a cash flow statement to analyze the availability of liquid assets and your company’s ability to grow and sustain itself long term.
Simple Cash Flow Template

Use this basic cash flow template to compare your business cash flows against different time periods. Enter the beginning balance of cash on hand, and then detail itemized cash receipts, payments, costs of goods sold, and expenses. Once you enter those values, the built-in formulas will calculate total cash payments, net cash change, and the month ending cash position.
Download Simple Cash Flow Template
12-Month Cash Flow Forecast Template
Use this cash flow forecast template, also called a pro forma cash flow template, to track and compare expected and actual cash flow outcomes on a monthly and yearly basis. Enter the cash on hand at the beginning of each month, and then add the cash receipts (from customers, issuance of stock, and other operations). Finally, add the cash paid out (purchases made, wage expenses, and other cash outflow). Once you enter those values, the built-in formulas will calculate your cash position for each month with.
Download 12-Month Cash Flow Forecast
3-Year Cash Flow Statement Template Set
Use this cash flow statement template set to analyze the amount of cash your company has compared to its expenses and liabilities. This template set contains a tab to create a monthly cash flow statement, a yearly cash flow statement, and a three-year cash flow statement to track cash flow for the operating, investing, and financing activities of your business.
Download 3-Year Cash Flow Statement Template
For additional information on managing your cash flow, including how to create a cash flow forecast, visit “ Free Cash Flow Statement Templates .”
Balance Sheet Templates for a Business Plan
Use these free balance sheet templates to convey the financial position of your business during a specific time period to potential investors and stakeholders.
Small Business Pro Forma Balance Sheet
Small businesses can use this pro forma balance sheet template to project account balances for assets, liabilities, and equity for a designated period. Established businesses can use this template (and its built-in formulas) to calculate key financial ratios, including working capital.
Download Pro Forma Balance Sheet Template
Monthly and Quarterly Balance Sheet Template
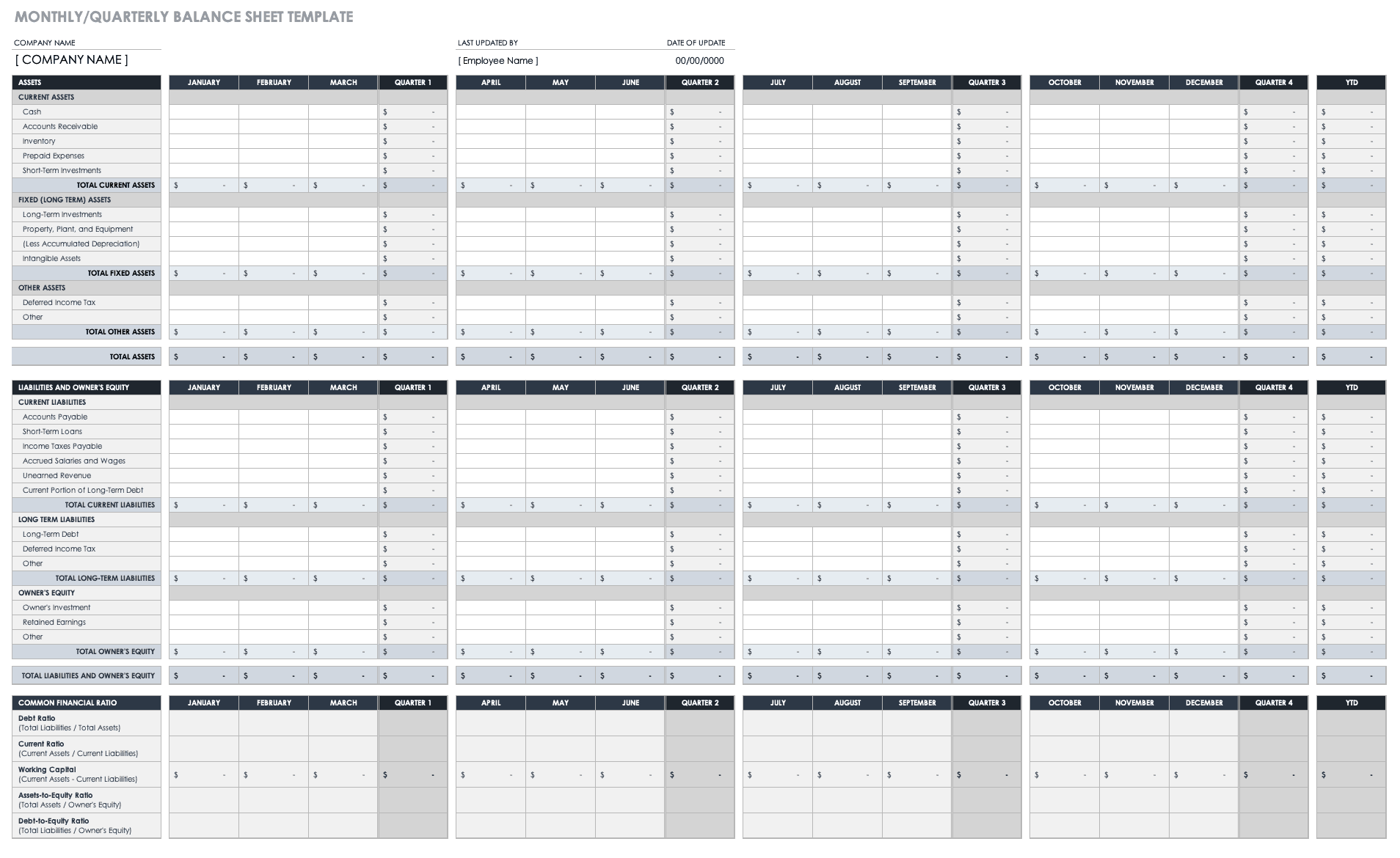
Use this balance sheet template to evaluate your company’s financial health on a monthly, quarterly, and annual basis. You can also use this template to project your financial position for a specified time in the future. Once you complete the balance sheet, you can compare and analyze your assets, liabilities, and equity on a quarter-over-quarter or year-over-year basis.
Download Monthly/Quarterly Balance Sheet Template - Excel
Yearly Balance Sheet Template
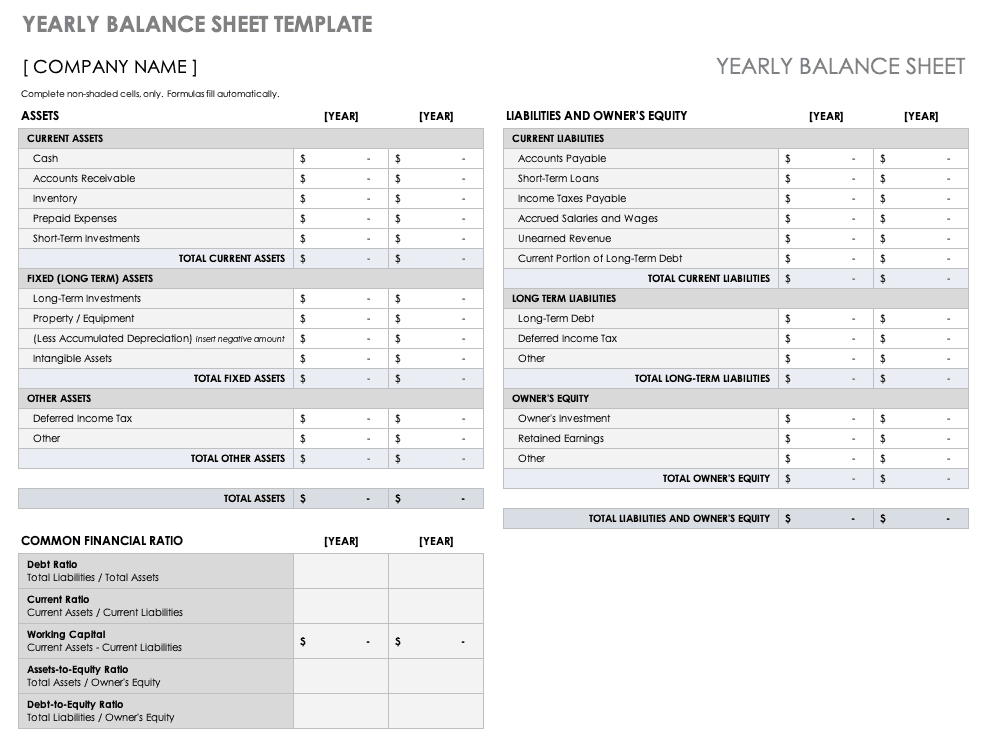
Use this balance sheet template to compare your company’s short and long-term assets, liabilities, and equity year-over-year. This template also provides calculations for common financial ratios with built-in formulas, so you can use it to evaluate account balances annually.
Download Yearly Balance Sheet Template - Excel
For more downloadable resources for a wide range of organizations, visit “ Free Balance Sheet Templates .”
Sales Forecast Templates for Business Plan
Sales projections are a fundamental part of a business plan, and should support all other components of your plan, including your market analysis, product offerings, and marketing plan . Use these sales forecast templates to estimate future sales, and ensure the numbers align with the sales numbers provided in your income statement.
Basic Sales Forecast Sample Template
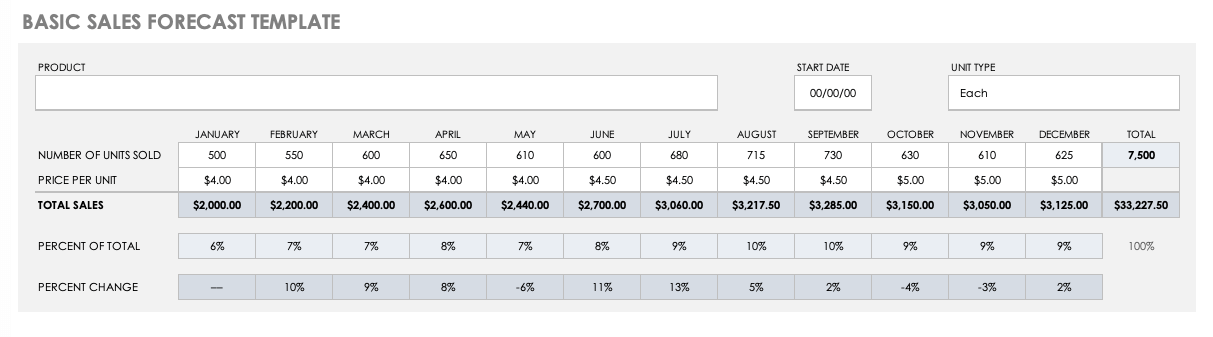
Use this basic forecast template to project the sales of a specific product. Gather historical and industry sales data to generate monthly and yearly estimates of the number of units sold and the price per unit. Then, the pre-built formulas will calculate percentages automatically. You’ll also find details about which months provide the highest sales percentage, and the percentage change in sales month-over-month.
Download Basic Sales Forecast Sample Template
12-Month Sales Forecast Template for Multiple Products
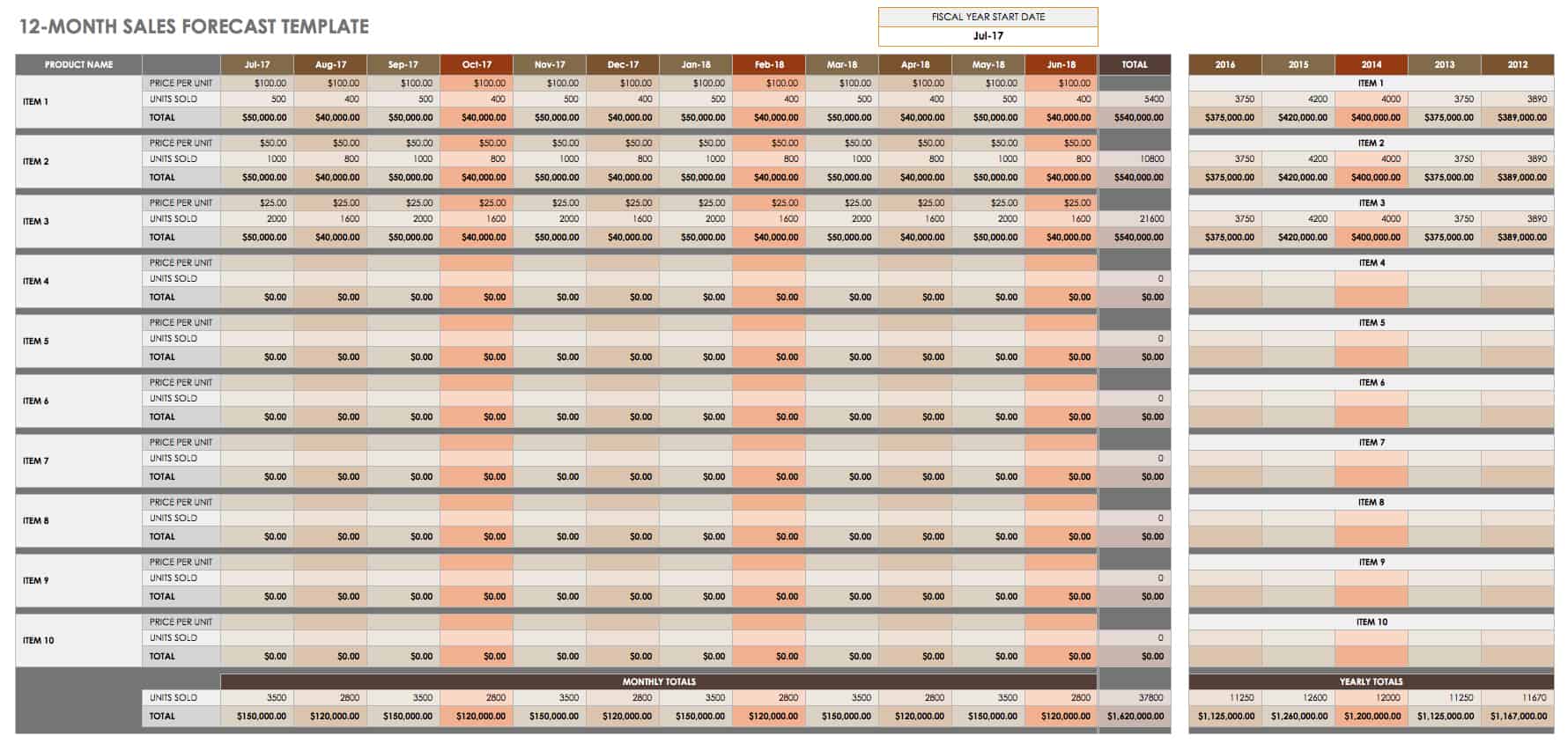
Use this sales forecast template to project the future sales of a business across multiple products or services over the course of a year. Enter your estimated monthly sales, and the built-in formulas will calculate annual totals. There is also space to record and track year-over-year sales, so you can pinpoint sales trends.
Download 12-Month Sales Forecasting Template for Multiple Products
3-Year Sales Forecast Template for Multiple Products
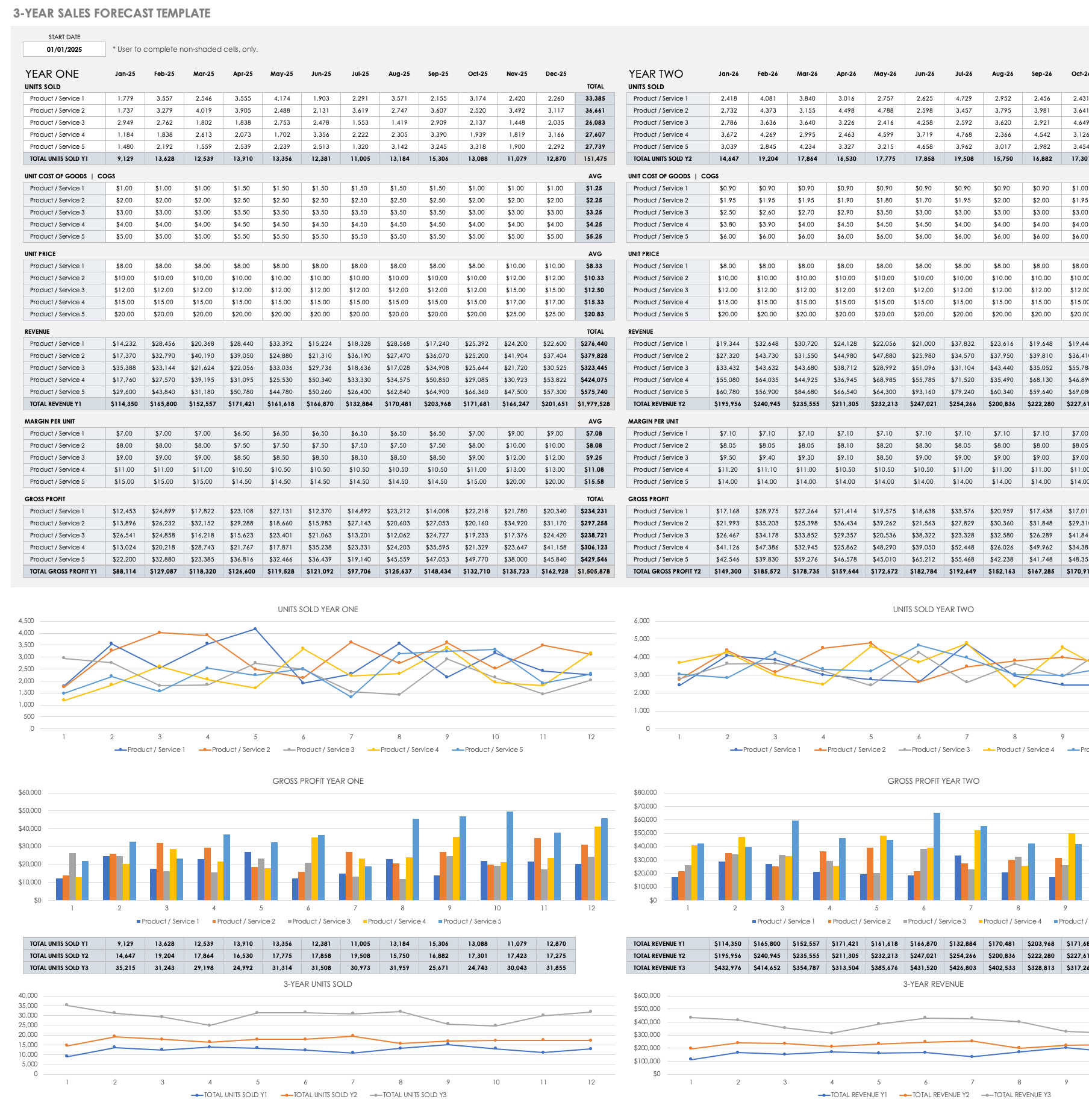
Use this sales forecast template to estimate the monthly and yearly sales for multiple products over a three-year period. Enter the monthly units sold, unit costs, and unit price. Once you enter those values, built-in formulas will automatically calculate revenue, margin per unit, and gross profit. This template also provides bar charts and line graphs to visually display sales and gross profit year over year.
Download 3-Year Sales Forecast Template - Excel
For a wider selection of resources to project your sales, visit “ Free Sales Forecasting Templates .”
Break-Even Analysis Template for Business Plan
A break-even analysis will help you ascertain the point at which a business, product, or service will become profitable. This analysis uses a calculation to pinpoint the number of service or unit sales you need to make to cover costs and make a profit.
Break-Even Analysis Template
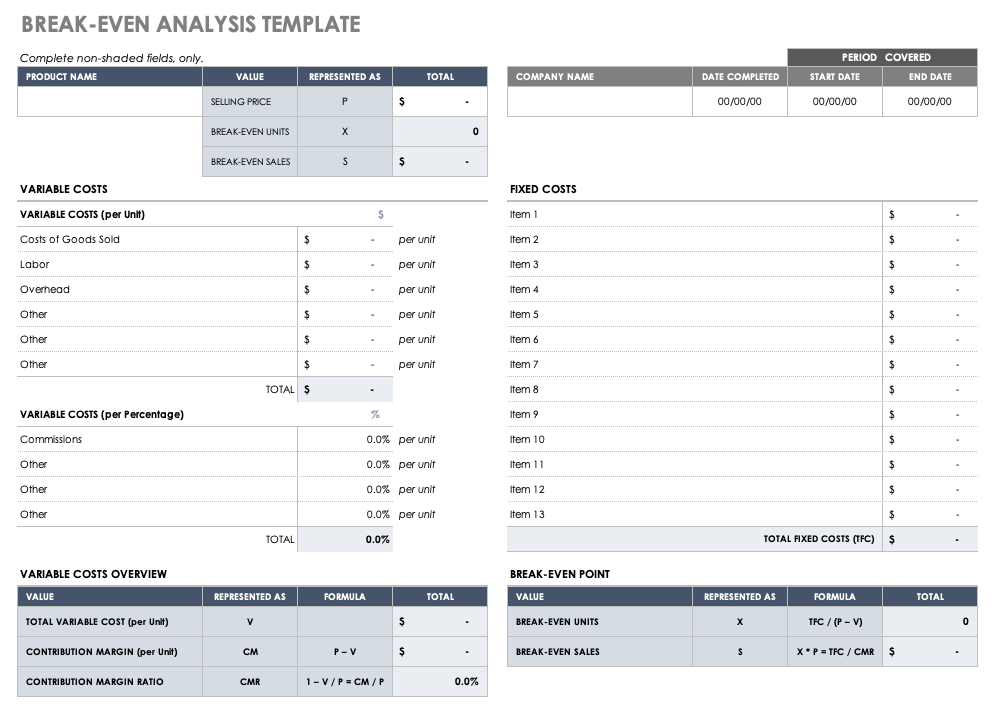
Use this break-even analysis template to calculate the number of sales needed to become profitable. Enter the product's selling price at the top of the template, and then add the fixed and variable costs. Once you enter those values, the built-in formulas will calculate the total variable cost, the contribution margin, and break-even units and sales values.
Download Break-Even Analysis Template
For additional resources, visit, “ Free Financial Planning Templates .”
Business Budget Templates for Business Plan
These business budget templates will help you track costs (e.g., fixed and variable) and expenses (e.g., one-time and recurring) associated with starting and running a business. Having a detailed budget enables you to make sound strategic decisions, and should align with the expense values listed on your income statement.
Startup Budget Template
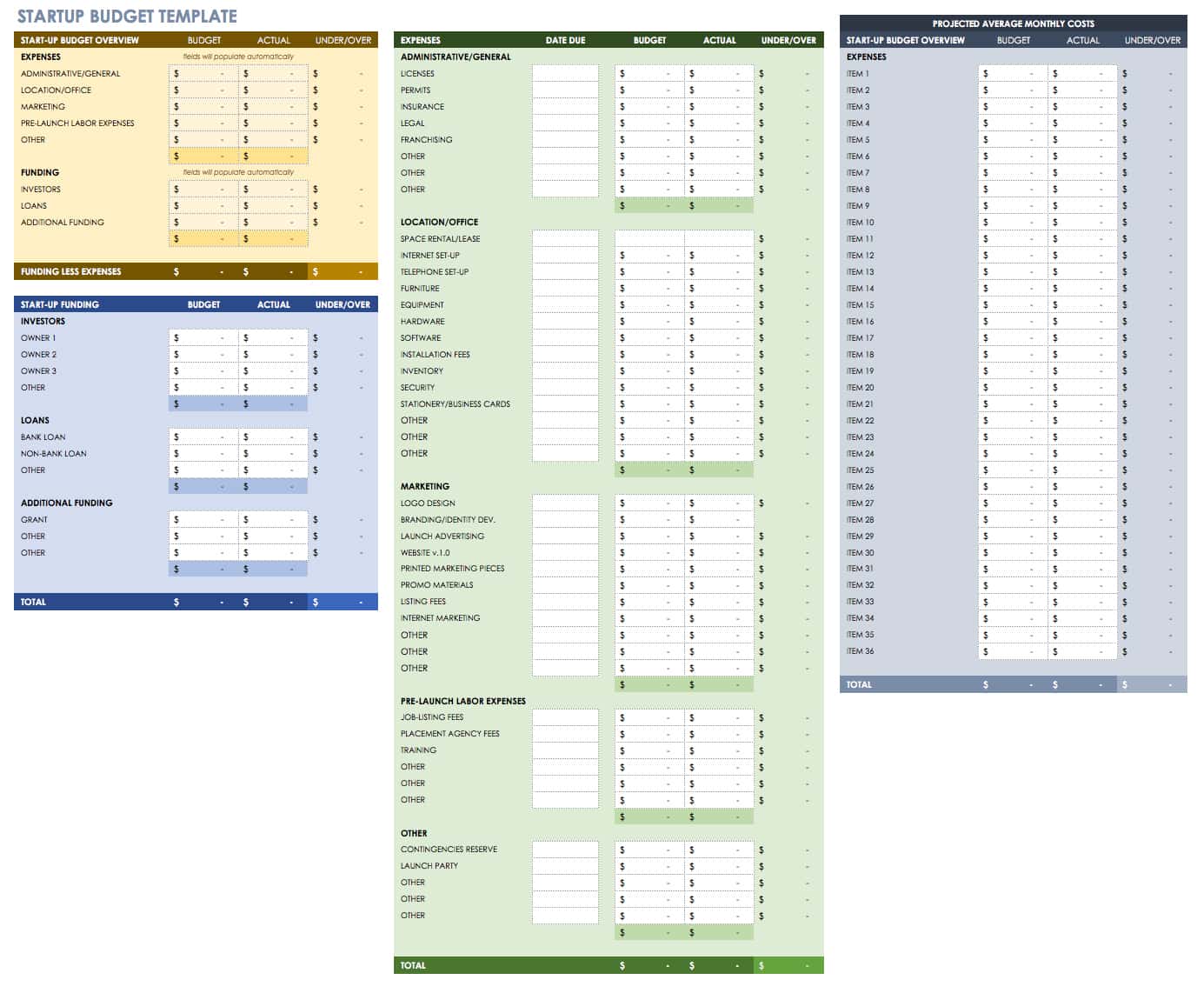
Use this startup budget template to track estimated and actual costs and expenses for various business categories, including administrative, marketing, labor, and other office costs. There is also room to provide funding estimates from investors, banks, and other sources to get a detailed view of the resources you need to start and operate your business.
Download Startup Budget Template
Small Business Budget Template
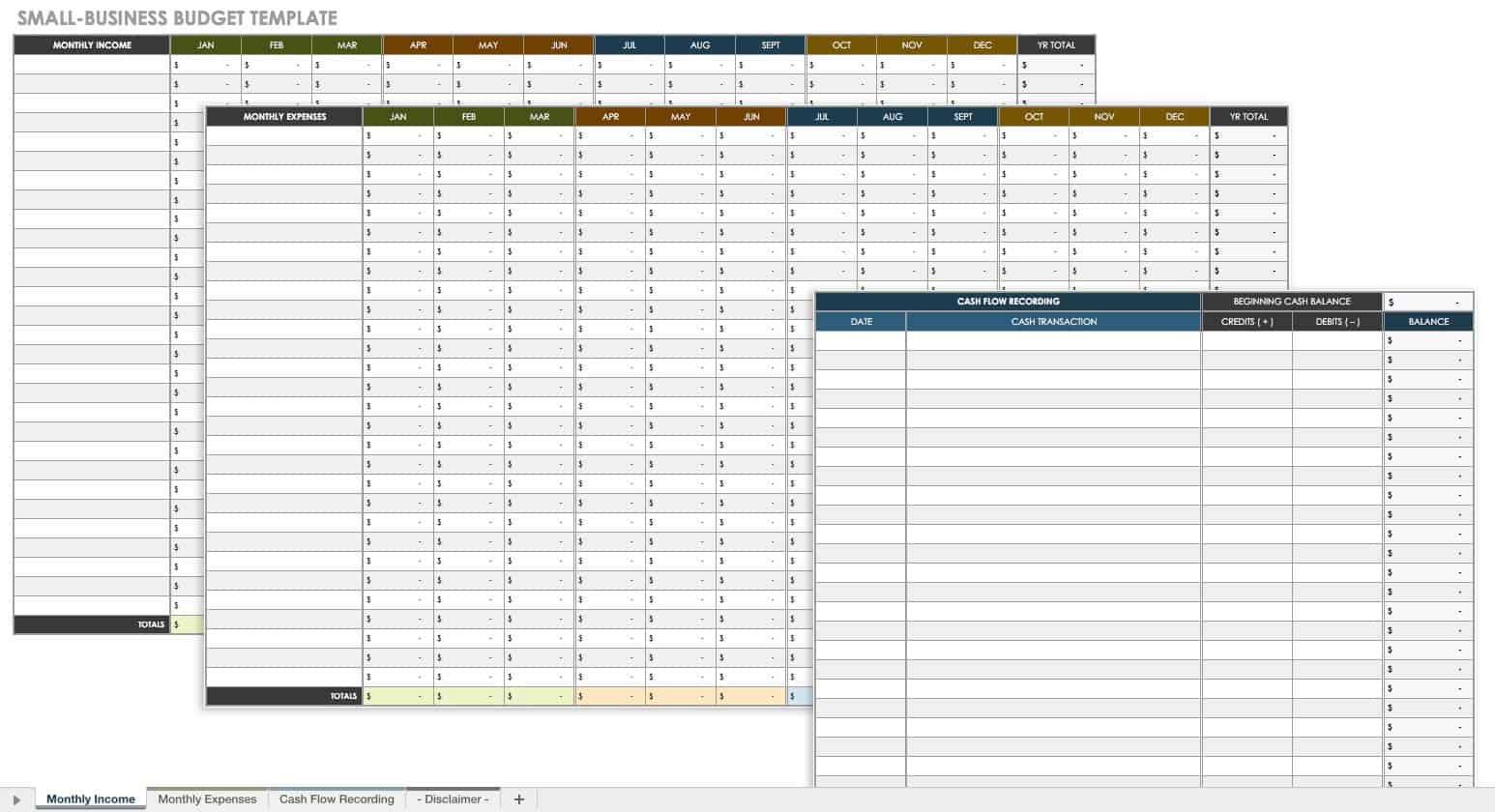
This business budget template is ideal for small businesses that want to record estimated revenue and expenditures on a monthly and yearly basis. This customizable template comes with a tab to list income, expenses, and a cash flow recording to track cash transactions and balances.
Download Small Business Budget Template
Professional Business Budget Template

Established organizations will appreciate this customizable business budget template, which contains a separate tab to track projected business expenses, actual business expenses, variances, and an expense analysis. Once you enter projected and actual expenses, the built-in formulas will automatically calculate expense variances and populate the included visual charts.
Download Professional Business Budget Template
For additional resources to plan and track your business costs and expenses, visit “ Free Business Budget Templates for Any Company .”
Other Financial Templates for Business Plan
In this section, you’ll find additional financial templates that you may want to include as part of your larger business plan.
Startup Funding Requirements Template
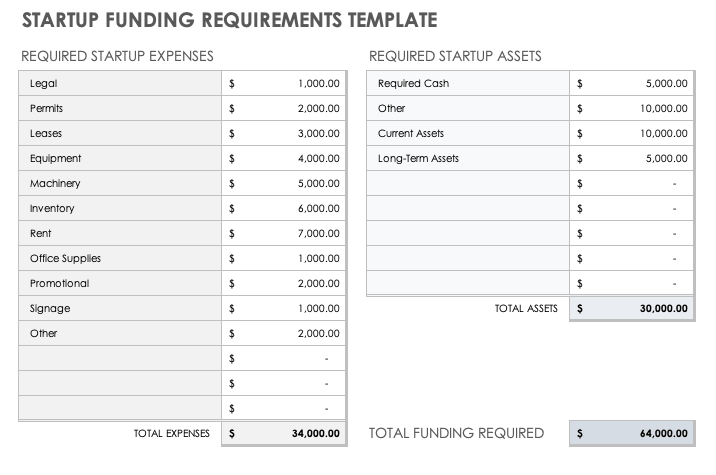
This simple startup funding requirements template is useful for startups and small businesses that require funding to get business off the ground. The numbers generated in this template should align with those in your financial projections, and should detail the allocation of acquired capital to various startup expenses.
Download Startup Funding Requirements Template - Excel
Personnel Plan Template
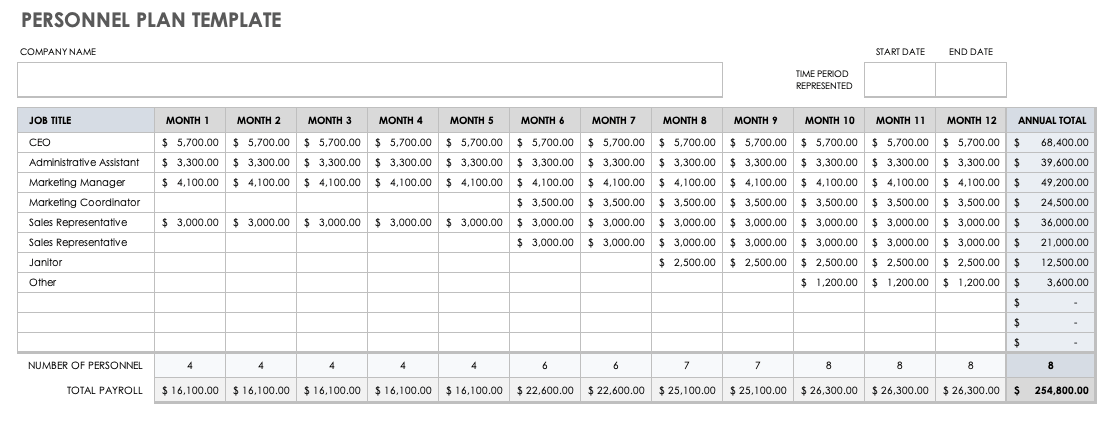
Use this customizable personnel plan template to map out the current and future staff needed to get — and keep — the business running. This information belongs in the personnel section of a business plan, and details the job title, amount of pay, and hiring timeline for each position. This template calculates the monthly and yearly expenses associated with each role using built-in formulas. Additionally, you can add an organizational chart to provide a visual overview of the company’s structure.
Download Personnel Plan Template - Excel
Elements of the Financial Section of a Business Plan
Whether your organization is a startup, a small business, or an enterprise, the financial plan is the cornerstone of any business plan. The financial section should demonstrate the feasibility and profitability of your idea and should support all other aspects of the business plan.
Below, you’ll find a quick overview of the components of a solid financial plan.
- Financial Overview: This section provides a brief summary of the financial section, and includes key takeaways of the financial statements. If you prefer, you can also add a brief description of each statement in the respective statement’s section.
- Key Assumptions: This component details the basis for your financial projections, including tax and interest rates, economic climate, and other critical, underlying factors.
- Break-Even Analysis: This calculation helps establish the selling price of a product or service, and determines when a product or service should become profitable.
- Pro Forma Income Statement: Also known as a profit and loss statement, this section details the sales, cost of sales, profitability, and other vital financial information to stakeholders.
- Pro Forma Cash Flow Statement: This area outlines the projected cash inflows and outflows the business expects to generate from operating, financing, and investing activities during a specific timeframe.
- Pro Forma Balance Sheet: This document conveys how your business plans to manage assets, including receivables and inventory.
- Key Financial Indicators and Ratios: In this section, highlight key financial indicators and ratios extracted from financial statements that bankers, analysts, and investors can use to evaluate the financial health and position of your business.
Need help putting together the rest of your business plan? Check out our free simple business plan templates to get started. You can learn how to write a successful simple business plan here .
Visit this free non-profit business plan template roundup or download a fill-in-the-blank business plan template to make things easy. If you are looking for a business plan template by file type, visit our pages dedicated specifically to Microsoft Excel , Microsoft Word , and Adobe PDF business plan templates. Read our articles offering startup business plan templates or free 30-60-90-day business plan templates to find more tailored options.
Discover a Better Way to Manage Business Plan Financials and Finance Operations
Empower your people to go above and beyond with a flexible platform designed to match the needs of your team — and adapt as those needs change.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.
Discover why over 90% of Fortune 100 companies trust Smartsheet to get work done.
Plan Projections
ideas to numbers .. simple financial projections
Home > Business Plan > Business Plan Assumptions

Business Plan Assumptions
Financial projections business plan assumptions.
All financial projections are based on business plan assumptions. Listed below is a selection of the most important assumptions which need to be considered and decided upon when using the Financial Projections Template to produce the financials section of your business plan.
Business Plan Assumptions List
Inflation rates and foreign exchange rates, sales and marketing, cash collection, distribution, research and development, fixed assets, gross margin, operating expenses, depreciation.
You need to prepare a business plan assumptions sheet as part of your plan, however, the important point to remember is that the assumptions should be kept simple and to a minimum, to avoid over complicating the financial projection. Remember this is planning not accounting. The calculation of key assumptions is further discussed in our financial projection assumptions post.
About the Author
Chartered accountant Michael Brown is the founder and CEO of Plan Projections. He has worked as an accountant and consultant for more than 25 years and has built financial models for all types of industries. He has been the CFO or controller of both small and medium sized companies and has run small businesses of his own. He has been a manager and an auditor with Deloitte, a big 4 accountancy firm, and holds a degree from Loughborough University.
You May Also Like

Simple Business Plan Template for Startups, Small Businesses & Entrepreneurs
Financial plan, what is a financial plan.
A business’ financial plan is the part of your business plan that details how your company will achieve its financial goals. It includes information on your company’s projected income, expenses, and cash flow in the form of a 5-Year Income Statement, Balance Sheet and Cash Flow Statement. The plan should also detail how much funding your company needs and the key uses of these funds.
The financial plan is an important part of the business plan, as it provides a framework for making financial decisions. It can be used to track progress and make adjustments as needed.
Why Your Financial Plan is Important
The financial section of your business plan details the financial implications of running your company. It is important for the following two reasons:
Making Informed Decisions
A financial plan provides a framework for making decisions about how to use your money. It can help you determine whether or not you can afford to make a major purchase, such as a new piece of equipment.
It can also help you decide how much money to reinvest in your business, and how much to save for paying taxes.
A financial plan is like a roadmap for your business. It can help you track your progress and make adjustments as needed. The plan can also help you identify potential problems before they arise.
For example, if your sales are below your projections, you may need to adjust your budget accordingly.
Your financial plan helps you understand how much outside funding is required, when your levels of cash might fall low, and what sales and other goals you need to hit to become financially viable.
Securing Funding
This section of your plan is absolutely critical if you are trying to secure funding. Your financial plan should include information on your revenue, expenses, and cash flow.
This information will help potential investors or lenders understand your business’s financial situation and decide whether or not to provide funding.
Include a detailed description of how you plan to use the funds you are requesting. For example, what are the key uses of the funds (e.g., purchasing equipment, paying staff, etc.) and what are the future timings of these financial outlays.
The financial information in your business plan should be realistic and accurate. Do not overstate your projected revenues or underestimate your expenses. This can lead to problems down the road.
Potential investors and lenders will be very interested in your future projections since it indicates whether you will be able to repay your loans and/or provide a nice return on investment (ROI) upon exit.
Financial Plan Template: 4 Components to Include in Your Financial Plan
The financial section of a business plan should have the following four sub-sections:
Revenue Model
Here you will detail how your company generates revenues. Oftentimes this is very straightforward, for instance, if you sell products. Other times, your answer might be more complex, such as if you’re selling subscriptions (particularly at different price/service levels) or if you are selling multiple products and services.
Financial Overview & Highlights
In developing your financial plan, you need to create full financial forecasts including the following financial statements.
5-Year Income Statement / Profit and Loss Statement
An income statement, also known as a profit and loss statement (P&L), shows how much revenue your business has generated over a specific period of time, and how much of that revenue has turned into profits. The statement includes your company’s revenues and expenses for a given time period, such as a month, quarter, or year. It can also show your company’s net income, which is the amount of money your company has made after all expenses have been paid.
5-Year Balance Sheet
A balance sheet shows a company’s financial position at a specific point in time. The balance sheet lists a company’s assets (what it owns), its liabilities (what it owes), and its equity (the difference between its assets and its liabilities).
The balance sheet is important because it shows a company’s financial health at a specific point in time. A strong balance sheet indicates that a company has the resources it needs to grow and expand. A weak balance sheet, on the other hand, may indicate that a company is struggling to pay its bills and may be at risk of bankruptcy.
5-Year Cash Flow Statement
A cash flow statement shows how much cash a company has on hand, as well as how much cash it is generating (or losing) over a specific period of time. The statement includes both operating and non-operating activities, such as revenue from sales, expenses, investing activities, and financing activities.
While your full financial projections will go in your Appendix, highlights of your financial projections will go in the Financial Plan section.
These highlights include your Total Revenue, Direct Expenses, Gross Profit, Other Expenses, EBITDA (Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation and Amortization), and Net Income projections. Also include key assumptions used in creating these future projections such as revenue and cost growth rates.
Funding Requirements/Use of Funds
In this section, you will detail how much outside funding you require, if any, and the core uses of these funds.
For example, detail how much of the funding you need for:
- Product Development
- Product Manufacturing
- Rent or Office/Building Build-Out
Exit Strategy
If you are seeking equity capital, you need to explain your “exit strategy” here or how investors will “cash out” from their investment.
To add credibility to your exit strategy, conduct market research. Specifically, find other companies in your market who have exited in the past few years. Mention how they exited and the amounts of the exit (e.g., XYZ Corp. bought ABC Corp. for $Y).
Business Plan Financial Plan FAQs
What is a financial plan template.
A financial plan template is a pre-formatted spreadsheet that you can use to create your own financial plan. The financial plan template includes formulas that will automatically calculate your revenue, expenses, and cash flow projections.
How Can I Download a Financial Plan Template?
Download Growthink’s Ultimate Business Plan Template which includes a complete financial plan template and more to help you write a solid business plan in hours.
How Do You Make Realistic Assumptions in Your Business Plan?
When forecasting your company’s future, you need to make realistic assumptions. Conduct market research and speak with industry experts to get a better idea of the key trends affecting your business and realistic growth rates.
You should also use historical data to help inform your projections. For example, if you are launching a new product, use past sales data to estimate how many units you might sell in Year 1, Year 2, etc.
Learn more about how to make the appropriate financial assumptions for your business plan.
How Do You Make the Proper Financial Projections for Your Business Plan?
Your business plan’s financial projections should be based on your business model and your market research. The goal is to make as realistic and achievable projections as possible.
To create a good financial projection, you need to understand your revenue model and your target market. Once you have this information, you can develop assumptions around revenue growth, cost of goods sold, margins, expenses, and other key metrics.
Once you have your assumptions set, you can plug them into a financial model to generate your projections.
Learn more about how to make the proper financial projections for your business plan.
What Financials Should Be Included in a Business Plan?
There are a few key financials that should be included in a traditional business plan format. These include the Income Statement, Balance Sheet, and Cash Flow Statement.
Income Statements, also called Profit and Loss Statements, will show your company’s expected income and expense projections over a specific period of time (usually 1 year, 3 years, or 5 years). Balance Sheets will show your company’s assets, liabilities, and equity at a specific point in time. Cash Flow Statements will show how much cash your company has generated and used over a specific period of time.
Growthink's Ultimate Business Plan Template includes a complete financial plan template to easily create these financial statements and more so you can write a great business plan in hours.
BUSINESS PLAN TEMPLATE OUTLINE
- Business Plan Template Home
- 1. Executive Summary
- 2. Company Overview
- 3. Industry Analysis
- 4. Customer Analysis
- 5. Competitive Analysis
- 6. Marketing Plan
- 7. Operations Plan
- 8. Management Team
- 9. Financial Plan
- 10. Appendix
- Business Plan Summary
Other Helpful Business Planning Articles & Templates
- Link to Follow us on Twitter
- Link to Like us on Facebook
- Link to Connect with us on LinkedIn
Ivey Business Journal
Strategic assumptions: the essential (and missing) element of your strategic plan.
- Share on LinkedIn
- Share on googlePlus
- Share on facebook
- Share on twitter
- Share by email
Stakeholders often approve a strategic plan without scrutinizing the strategic assumptions, the very foundation on which the plan has been built (Sound familiar? As in, “…the value of this derivative, which we call a Collaterized Debt Obligation, is built on the value of the underlying securities.” (which we have looked at…but uh..not very closely). This author sees an inherent danger in such a practice and states that stakeholders need to start scrutinizing the strategic assumptions that underlie the very plan they are being asked to approve.
In the field of strategy, the admission that assumptions are being made in the preparation of strategic plans needs to be acknowledged. Moreover, transparency and discussion surrounding these assumptions need to be viewed as key elements and the responsibility of the strategy creators.
In doing so, the practitioners themselves – be they CEOs, consultants, Chief Strategy Officers, or employees in the Strategy Management Office – will be forced to elevate both their own performance standards and the rigor of the strategy process to a level comparable to that exercised in the fields of science, economics and finance, where the publication and debate of assumptions are the norm. This will pave the way for strategy creators to gain greater credibility and build a stronger voice on executive teams. Finally, it will provide them with the opportunity to increase their contributions in determining direction and forecasting the future performance of the organization.
The reality is that strategic assumptions form an identical, underlying foundation for the strategic plan. They underpin everything contained therein – and hence reflect the vision, strategic map, performance targets and project portfolio which subsequently follow. The problem is that in the field of strategic planning, the assumptions that have been made are almost never clearly documented or highlighted. As a consequence, they are rarely scrutinized or challenged as they should be.
Too often, shareholders, employees and other major stakeholders unnecessarily invest time, money and energy in supporting an organization’s vision and strategic plan, not recognizing that the vision and plan were doomed to fail from the day they were conceived.
This article posits that the identification and in-depth analysis of an organization’s strategic assumptions need to become an integral part of the strategic planning process, and that the presentation of these underlying strategic assumptions should become an implied and required part of any written strategic plan.
The rationale for preparing a set of strategic assumptions
Financial analysts examining a set of projections insist on seeing a complete and detailed set of financial assumptions. These assumptions represent the raw material — the opinions, beliefs and more often, the hopes, of the management team — on which the projections are based. They usually receive very close scrutiny, especially since financial projections are only as valid as the assumptions upon which they are based. If the assumptions are deemed unrealistic or otherwise questionable, so are the projections. Analysts also understand that while financial projections can be manipulated, clearly presented financial assumptions cannot.
It is not just in the realm of finance that stakeholders demand to see assumptions. In almost all other fields, be they marketing and sales, or even engineering, science and economics, the assumptions used for future predictions are the first element to be examined and rigorously challenged.
Generally, this is not due to management duplicity – although in certain cases that cannot be ruled out. After all, it is easier to defend a set of financial projections when the financial assumptions are not attached; that is the reason financial analysts insist on receiving them. Likewise, it is easier to defend a strategy, business model, value proposition, value chain network, etc. when interlocutors are not aware of the underlying assumptions.
A major reason for the absence of a set of strategic assumptions is that often senior management does not recognize that assumptions are, indeed, being made. They genuinely believe that future markets, competition, customer needs, etc. will evolve exactly as they are expected to. The resulting “group think” – valid and well-founded or not – is therefore not viewed as a set of assumptions at all. It is viewed as fact, the most dangerous assumption of all!
Given today’s shift towards greater transparency, tighter governance, greater accountability for board members, and most importantly, the high levels of uncertainty about tomorrow, next quarter or next year, the business community requires a new paradigm for preparing and certifying a plan as “strategic.” Quite clearly, the moment has come to recognize that the content of any organization’s strategic plan is incomplete unless a complete set of strategic assumptions are included.
Preparing a set of strategic assumptions
The contents of an organization’s business plan often reflect the difficult choices made by management during the strategic planning process. The identification and discussion of the key issues are not intended to generate right or wrong “answers;” rather, they represent choices and shared points-of-view about what the team believes will happen. Together, they form a set of approximately 12-15 strategic assumptions upon which management intends to build its strategic plan and business.
Because all markets and organizations are unique, there is no universal set of strategic questions that must be posed when assembling a business plan. Indeed, a major challenge in strategic planning is the identification of the major questions an organization needs to address. Likewise, there is no universal set of strategic assumptions that must absolutely be generated and covered in every organization’s strategic plan. There are, however, generic areas where strategic assumptions generally must be made and which stakeholders should realistically expect management to disclose:
The category “Background of Shared Obviousness” makes explicit the existing, but often hidden strategic assumptions (or shared beliefs) that emerge from conversations and discussions that take place during the strategic planning process.
Shared beliefs about who the company is and beliefs on how it must operate in order to be successful are often seen as “obvious” by the participants and are rarely challenged, unless captured in real-time – often by a consultant, facilitator, or other outsider present –during the strategic planning sessions. Simple examples include:
These types of assumptions are very powerful and can be the sources of best practices, historical wisdom, norms of positive organizational culture or, alternatively, barriers to change. They can epitomize strategic and organizational rigidity, and guarantee that mistakes of the past are likely to be repeated. As with all strategic assumptions, this category of assumptions is not, by definition, positive or negative. It is, however, crucial that they be identified and recognized as being merely assumptions, not fact. They should also be made explicit, challenged, and only retained if they remain valid in the context of the future of the market and not as remnants of the past.
An example: The importance of a single strategic assumption
Let’s consider a simple example and examine the role of just one key strategic assumption: the strategic assumption about the future structure of an industry.
Imagine that we are considering investing in a relatively small steel company, “X”. There are major differences in the strategic assumptions X’s management team might make about the future development of the global steel industry. Will the business plan for the company be built upon the strategic assumption that:
- The steel market will be dominated by a few global players, with all other contenders seeking to partner or avoid direct competition?
- There will be regional consolidation, with key (different) players dominating markets in Asia, Europe and the Americas?
- The high-margin steel businesses of the future will lie in specialty steel that serves one or several specific industries (i.e. automotive, aerospace, medical, etc.), thereby allowing for “niche” players?
- There is no future in the steel industry for small players; the company needs to reposition itself as a supplier of “materials” (i.e. a supplier of composites, plastics, rubber as well steel) as opposed to being a supplier of steel products exclusively?
- All trading of commodity steel products will soon be done through one global web site?
The contents of the strategic plan – and the future success of the company – will largely depend upon which of these, and perhaps a dozen other, strategic assumptions are made.
Lakshmi Mittal, President of Arcelor Mittal Steel, made his own personal strategic assumption about the future structure of the steel industry very clear in the following quote:
“I strongly believe that in the steel industry, scale is a crucial ingredient in the pursuit of value. Arcelor Mittal will be three times the size of its nearest competitor. The steel industry consolidation is under way and I have repeatedly said that by 2015, I expect each of the two to three largest global players to produce 150 million to 200 million tons of steel a year. This compares to 116 million tons produced by Arcelor and Mittal today.” Wall Street Journal, August 3, 2006
In this quote, Mr. Mittal clearly communicates one of his strategic assumptions about the future of the steel industry. The company’s corporate strategy, M&A activities, global distribution and marketing strategies, are all built upon this fundamental strategic assumption.
As potential investors in steel company “X”, we need to know whether and why its CEO agrees or disagrees with Mittal’s strategic assumption. We also need to know which other strategic assumptions that he is making. If he provides us with a complete list, we should be able to do a very accurate and thorough initial screening of the company’s request for funds – before we invest more of our time and energy examining the contents of the business plan.
Other examples of powerful strategic assumptions
- In 2002, when one Canadian dollar was worth approximately US $0.65, a shared strategic assumption of almost all Canadian manufacturers was that parity between the Canadian/US dollar was simply unthinkable. In 2008, how have their beliefs changed? What is their strategic assumption of exchange rates for 2013? It is a crucial assumption that will form the foundation of their production strategy for the next five years.
- An Asian hydro-electricity corporation built many facilities based upon two strategic assumptions: that there would always be glacial melt waters, and that there would be a predictable monsoon season each year. These strategic assumptions are no longer valid.
- One of Jack Welch’s major strategic assumptions while at GE was that the company could not compete in commodity markets. Therefore, during his entire tenure, he moved GE in the direction of product differentiation and value-added services. This “Background of Shared Obviousness” strategic assumption drove GE’s strategic direction for many years.
- What is a wine merchant’s strategic assumption around packaging? Will bottles prevail? Will the green movement see Tetrapak packaging make significant penetration in the market? Investment in manufacturing lines will rely on this assumption. Based on these assumptions, will the company perceive itself as a “packager of liquids” or as an “exclusive wine packager”?
- What are the strategic assumptions envisioned by a university? Is it a research-based university? Does it serve the global market or is it focused on local population needs? Does it see e-learning as the way of the future or does it believe that students will always choose to “come to class”? The types of professors recruited, courses offered and delivery mechanisms all depend on the answers to these questions.
- Does the mayor of a town located close to a major urban centre see itself as a bedroom-community or as a fast–growing potential rival which should attempt to attract new industry to locate within its boundaries?
- Is the strategic assumption of a country based upon the assumption that economic growth (GNP) is paramount or does it subscribe to the theory of Gross National Happiness (GNH)?
Examples of the strategic assumptions adopted by the individuals, teams, organizations and nations in the above cases will determine their future plans and all the actions, projects, programs that will follow. We, as stakeholders in any of them, should be able to identify the strategic assumptions that have been made without having to try to read between the lines of a strategic plan. They should be clearly and proudly highlighted for all to see, for Strategic Assumptions show how we view the world, how we view ourselves, and who we really are.
Publicizing strategic Assumptions: The tipping point
It is unlikely that all CEOs will voluntarily choose to publish their strategic assumptions for evaluation overnight. Divulgence will only occur when important stakeholders demand to see them included as outcomes of the strategic-planning process and included as a separate item in the contents page of the plan.
There are several benefits which result from demanding to see the set of strategic assumptions included in a strategic plan:
- Inclusion facilitates the analysis of any organization’s business plan by a financial institution, venture capitalist or angel investor. The risk of making a bad investment will be reduced if the investors understand and share the strategic assumptions of the organization’s management team.
- Differences in points-of-view about strategic assumptions are the source of many of the conflicts that arise between investors and company management – and within a management team itself. Strategic assumptions represent the shared values, beliefs and vision of the management team. Demanding that they be included in a strategic plan will force management teams to hold the difficult internal conversations required and that allow them to uncover, challenge, and capture their shared assumptions.
- Knowing they need to exit a strategic planning process with a complete, shared set of strategic assumptions forces a management team to use a much more rigorous strategic planning process.
- Face-to-face, it is very difficult for most people to defend strategic assumptions which are ungrounded or that they do not believe or share.
- Developing and debating strategic assumptions with groups of employees is an excellent way to gain buy-in and commitment to the organization. Having to declare and justify the assumptions upon which a plan is built means that it is difficult for a CEO to impose his or her views. With increased levels of employee buy-in, there is a greater probability that the strategic plan will actually be implemented.
- By presenting strategic assumptions for rigorous debate and analysis, the probability is minimized that investors, employees, management and any other stakeholders will waste time, money and energy on trying to implement plans that have little chance of generating the promised results.
Strategic assumptions have been missing from the strategic planning lexicon for too long. It is time to put them in their rightful place.

© Copyright 2022 Ivey Business School Foundation. All rights reserved. Privacy Policy .

Business Assumptions: Understanding Key Predictions in Entrepreneurship
✅ All InspiredEconomist articles and guides have been fact-checked and reviewed for accuracy. Please refer to our editorial policy for additional information.
Business Assumptions Definition
Business assumptions refer to the expected financial and operational projections a business makes about future market conditions, business environment, and internal company dynamics that influence business decisions and strategy. They are yet-to-be-proven elements considered true for the purposes of planning and budgeting.
Types of Business Assumptions
Some key types of business assumptions that can play a significant role in shaping an entrepreneur’s business model and strategy include revenue assumptions, market size assumptions, and operational expense assumptions.
Revenue Assumptions
Revenue assumptions guide a company’s sales expectations, based on factors like pricing strategies and the volume of products or services they expect to sell. For instance, an ecommerce business may anticipate selling 1,000 units of a product every month, priced at $50 each. This results in a monthly revenue assumption of $50,000. It’s crucial to note that revenue assumptions should be realistic, grounded in market research and business analytics.
Market Size Assumptions
Market size is a critical factor in business forecasting. Market size assumptions can help a company estimate the total demand for their product or service within the target market. For companies launching a new product or venture, this might involve assuming the population size and demographic that will use their product. Similarly, for companies expanding into a new region, market size assumptions would include the potential customer base in that area. Misjudging the market size can lead to either overestimating or underestimating the potential for sales, both of which can negatively affect business planning and financial projections.
Operational Expense Assumptions
Operational expense assumptions encompass the anticipated costs required to maintain business operations, including rent, utilities, wages and salaries, maintenance, and technological infrastructure costs. These assumptions are crucial to controlling costs, planning for growth, and ensuring profitability. For example, a startup in the tech industry may anticipate needing large sums of capital for software development, tech hardware, and skilled personnel. On the other hand, a small retail business would focus more on rent and product costs. Understanding these operational costs will contribute to more accurate financial planning and prevent budget overruns.
The Role of Business Assumptions in Financial Planning
Business assumptions play a pivotal role in the entire financial planning process. They form the backbone of the strategic decision-making process and significantly impact budgeting, forecasting, and strategic planning initiatives of any business.
Budgeting refers to a financial plan that quantifies the expectations of revenues that a business wants to achieve for a future period. It uses business assumptions as a foundation to estimate both income and expenditure for a certain period. For example, a business might assume a specific rate of growth in sales based on factors like past trends, marketing strategies in place, and market research data. These assumptions, in turn, dictate how much can be spent on different business activities within the set budget.
Forecasting
Forecasting, on the other hand, is an estimation or prediction of future developments in business such as sales, expenditures, and profits. Given its predictive nature, forecasting heavily relies on business assumptions. Forecasting might involve assumptions on variables like future demand for the company’s products or services, price changes, cost inflation, or possible changes in the economy or industry. These assumptions help gauge what future performance might look like and guide decision making on matters such as investment in new projects.
Strategic Planning
Strategic planning is a process of setting long-term goals for the business and determining the best approach to achieve these goals. Business assumptions are used in this stage to consider various scenarios and their potential outcomes. For instance, a business might assume a particular market growth rate based on trends, competitor analysis, and industry insights. Depending on these assumptions, strategies are then formulated to achieve set objectives, such as entering a new market, launching a new product, or improving market share.
In conclusion, the role of business assumptions in financial planning cannot be overstated. They provide a well-defined path for budgeting, forecasting, and strategic planning, enabling businesses to make informed financial decisions and strategic choices. They act as a bridge between the present state of a company and its future vision, helping in efficient capital allocation and risk management.
The Impact of Business Assumptions on Risk Assessment
Business assumptions and risk assessment.
When conducting risk assessment exercises, the influence of business assumptions can be substantial. Assumptions help to create a framework for anticipating potential scenarios, providing a sort of guide or roadmap for decision-making. However, these guiding assumptions can color the ways in which risks are perceived and managed.
Consider a company planning a new product launch. It may hold certain assumptions about customer demand, manufacturing capabilities, and market trends. These assumptions will shape how the company perceives potential risks associated with the launch. It might focus on tackling risks that align with its assumptions while neglecting those that don’t.
The Pitfall of Over-Optimism
An overly optimistic business assumption could lead to underestimation of potential risks. If a company anticipates high demand for its new product, it may neglect to adequately consider the risks of low customer demand, poor product reception, or the presence of competent competitors. This, in turn, may result in an insufficient contingency plan, increasing the company’s vulnerability to unforeseen circumstances.
Similarly, a business that assumes a seamless manufacturing process may fail to take into account possible challenges or disruptions. It may not adequately prepare for supply chain disruption, equipment failure, or manpower shortage, all of which increase operational risk.
The Danger of Over-Pessimism
On the other hand, overly pessimistic business assumptions may lead to an over-focus on avoiding negative outcomes. This could stifle innovation and aggressive strategic moves, limiting the business’s ability to seize growth opportunities.
A company expecting extremely low demand for its new product might overestimate the potential risks, devote excessive resources to contingency planning, and divert capital from investments in growth-driving activities such as research and development or marketing. This overly conservative approach could lead to missed opportunities and prevent the business from achieving its full potential.
In conclusion, striking a balance between optimism and pessimism in business assumptions is key in risk assessment. A well-considered, realistic assumption can help businesses navigate potential obstacles while still keeping sight of growth opportunities.
Criticality of Validating Business Assumptions
Ensuring the validity of business assumptions is a critical step in strategic planning and decision making. Assumptions, by definition, are subject to scrutiny and must be verified to establish their accuracy. The consequences of unverified or inaccurately-based assumptions can have far-reaching impacts, potentially jeopardizing a business’s competitiveness and overall success.
Methods for Validating Business Assumptions
There are various approaches to validating business assumptions. The choice of method often depends on the nature of the assumption and the context in which it is being applied.
Market Research
One of the most common methods is market research. This may involve surveys, focus groups, interviews, or analysis of secondary data like existing research reports and public market data. For instance, if the business assumption is about customer preferences or behavior, conducting a survey or organizing focus groups may provide insights to either validate or question the assumption.
Furthermore, market research is particularly useful in analyzing external business environment factors. It provides data on market trends, demographics, consumer preferences, and competitor analysis that can help in forming accurate assumptions.
Example of Markdown for Market Research
Hypothesis Testing
Another approach is through hypothesis testing. Essentially, this consists of establishing a null hypothesis that opposes the business assumption. Subsequently, relevant data is collected and analyzed to either accept or reject the null hypothesis.
For example, if a business assumes that a new product will increase sales by 10%, the null hypothesis would state that the new product will not lead to any change in sales. Following this, the company can monitor sales to confirm or disprove their assumption.
Example of Markdown for Hypothesis Testing
These methods, coupled with a persistent and critical approach to the validation process, can prevent the costly implications of inaccurate assumptions, enhancing the decision-making process. It’s vital to remember that business conditions are continually changing, necessitating regular reviews and validations of our business assumptions.
Business Assumptions in Startup Ecosystems
Startups operate in volatile environments with varying degrees of uncertainty, and business assumptions form the structural framework on which their financial modeling and investment pitches are built. Financial models for startups are primarily created to forecast potential revenues and expenditures, identify integral key drivers for growth, calculate the necessity and timing for external funding, and, in the process, model possible financial performance based on a set of assumptions.
Let’s first look at Financial Modeling . In this context, important assumptions usually revolve around the total addressable market size, product pricing, estimated customer acquisition costs, churn rates, revenue growth, and cost structure. It also includes assumptions concerning the competitive landscape and how the startup’s offering would fare against it. These assumptions are quite critical to forecasting the startup’s revenues, costs, cash flow and hence, its profitability and financial viability in the long run.
Parallelly, Investor presentations and Pitches rely heavily on the credibility of these business assumptions. Investors scrutinize these assumptions for their validity, robustness, and flexibility under changing circumstances. The quality and realistic nature of business assumptions act as a mirror, reflecting the strategic acumen and forward-thinking capability of the entrepreneurial team. However, it’s important for founders to balance ambition with pragmatism. While it’s essential to show potential for high growth and attractive returns, over-ambitious or unrealistic assumptions might raise skepticism among investors and might hinder their chances of securing investment.
The implication of business assumptions for early-stage entrepreneurs are far reaching. Not only do they guide the strategic decisions but also help in foreseeing challenges and planning for contingencies. It’s quite common for initial business assumptions to be off-target since they are based on limited information and insights. Over time though, with increasing market knowledge and operational experiences, these assumptions should evolve to become more accurate and reliable. Consequently, it’s critical for startups to regularly re-visit and update their business assumptions, aligning them with their real-time learnings and changing market dynamics.
Furthermore, it’s crucial for entrepreneurs to clearly communicate the basis of these business assumptions to their team and investors. This transparency fosters trust, promotes collective understanding and provides the foundation for strategic alignment across the organization. It also demonstrates to potential investors the team’s ability to critically analyze their business environment, thereby strengthening their confidence in the entrepreneurial team and hence, the startup.
At the end, it’s important to remember, business assumptions are just assumptions. They serve as a guide rather than the absolute truth. Thus, while they can drastically improve the chances of startup success, they should be utilized with caution, flexibility, and a good degree of open-minded skepticism.
Link Between Business Assumptions and Sustainable Business Models
Understanding the link between business assumptions and sustainable business models is crucial for business longevity.
The Role of Business Assumptions in Creating Sustainable Business Models
In creating a sustainable business model, it is critical for businesses to establish accurate business assumptions. This is because the underlying assumptions will carve the path for the business’s approach to maintain economic, social, and environmental value over the long term.
For instance, assumptions about customer preferences can influence the business’s strategy in offering eco-friendly products. If the business assumes that the customer base values environmental stewardship, it might adopt a model based on the offer of sustainable goods. This impacts resource utilization, easing pressure on finite resources by supporting more ethical supply chains.
Business Assumptions Impact on Long-term Viability
Moreover, business assumptions regarding costs, revenues, and market dynamics can greatly influence long-term viability. If a firm assumes steady growth and stable market conditions, it is likely to focus on expanding operations and increasing revenues. However, these assumptions might not hold in times of economic downturns. So businesses need to constantly rethink and reevaluate their assumptions, adapting their strategies to reflect the realities of their operating environment.
The Influence on Corporate Social Responsibility
Business assumptions also play a considerable role in shaping a business’s Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) initiatives. If a firm assumes that their stakeholders value CSR, the business model might incorporate CSR initiatives to drive sustainability. This impacts not only environmental sustainability but also social sustainability. By making such strategic decisions, businesses can enhance their reputation, drive customer loyalty and ultimately secure their market position.
In summary, the assumptions a business operates under may significantly affect the formulation and success of their sustainable business models. Regular review and adjustment of these assumptions allow for a more accurate, resonate, and ultimately successful approach to sustainability.
Guidelines for Making Reasonable Business Assumptions
When crafting business assumptions, the ultimate goal is making them as reasonable and realistic as possible. A well-reasoned assumption lies at the heart of any prudent business decision. Here are effective guidelines to follow:
Adopt a Conservative Approach
It is wise to err on the side of caution. Over-optimistic assumptions can spiral into unattainable goals and failed operational plans. Therefore, a conservative approach is often best. For instance, overestimate your costs and underestimate your revenues. This stance creates a buffer for unpredictable market events and uncontrollable factors that might increase your costs or decrease revenues.
Consider Current Market Trends
To make the most realistic assumptions, current market trends must be considered. This means regularly monitoring and familiarly understanding your industry trends while keeping an eye on the broader economic landscape. Your assumptions should align with these trends. For instance, if the trend shows a decline in the market segment that corresponds to your product, it would be unrealistic to assume robust growth in your sales.
Regular Review and Update of Assumptions
Business assumptions should never be stagnant. As you gather more data, and as the business climate evolves, your assumptions should, too. Regular reviews and updates of your assumptions can help significantly in keeping your business strategy relevant and realistic. It also allows you to assess view your business situation from different angles and make swift pivots when necessary.
Sound Underlying Logic
Every business assumption you make should have a sound underlying logic. It shouldn’t merely be a number picked out of thin air. When setting assumptions, make sure to document the reasoning behind each one. This approach allows for healthy discussion and challenge of the figures and underlying methodologies.
Adopting these guidelines helps create business assumptions that reflect reality and are defensible, increasing the likelihood of creating a viable and successful business strategy.
Share this article with a friend:
About the author.
Inspired Economist
Related posts.

Accounting Close Explained: A Comprehensive Guide to the Process

Accounts Payable Essentials: From Invoice Processing to Payment

Operating Profit Margin: Understanding Corporate Earnings Power

Capital Rationing: How Companies Manage Limited Resources

Licensing Revenue Model: An In-Depth Look at Profit Generation

Operating Income: Understanding its Significance in Business Finance

Cash Flow Statement: Breaking Down Its Importance and Analysis in Finance

Human Capital Management: Understanding the Value of Your Workforce
Leave a comment cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Start typing and press enter to search
What Are Key Assumptions of a Business Plan?
A business plan is a document that outlines the strategy and goals of a business.
It serves as a roadmap for the company, helping it stay on track and achieve its objectives.
A key aspect of any business plan is the assumptions it is built on. These assumptions are the underlying beliefs and assumptions that the business plan is based on and that help shape the way the company operates and makes decisions.
In this blog post, we will take a closer look at what key assumptions are and why they are important for the success of a business.
What are key assumptions?
Key assumptions are the underlying beliefs and assumptions that shape the way a business operates and makes decisions.
They can be related to various aspects of the business, including its target market, competitive landscape, revenue streams, and financial projections. These assumptions serve as the foundation of a business plan, and they help the company make informed decisions about its strategy and goals.
It is important for a business to carefully consider its key assumptions, as they can have a significant impact on the overall success of the company.
If the assumptions are not well thought out or are overly optimistic, the business plan may be based on false premises, leading to poor decision-making and ultimately, failure.
On the other hand, if the assumptions are well-founded and realistic, they can help the business navigate challenges and make informed decisions that lead to long-term success.
Why are key assumptions important in a business plan?
Key assumptions are a crucial part of a business plan because they help the company make informed decisions about its strategy and goals.
By clearly outlining the underlying beliefs and assumptions on which the business plan is based, a company can better understand the potential risks and opportunities it may face, and make decisions accordingly.
For example, if a company assumes that its target market is a specific demographic with certain buying habits, it can tailor its marketing efforts and product offerings to meet the needs and preferences of that market.
If this assumption is incorrect, the company may struggle to reach its target market and may not be successful in selling its products or services.
In addition to informing decision-making , key assumptions can also help a company set realistic goals and financial projections.
By basing these projections on well-informed assumptions, a company can better understand the resources and investments it will need to achieve its goals and can allocate these resources accordingly.
In summary, key assumptions are a vital component of a business plan, as they help shape the direction and strategy of the company and inform decision-making and goal-setting.
It is important for a business to carefully consider and review its key assumptions to ensure that they are well-informed and realistic, to increase the chances of success.
Examples of key assumptions in a business plan
There are many different types of key assumptions that can be included in a business plan.
Here are some examples.
Target market assumptions
These assumptions relate to the characteristics and behavior of the customers that a company is targeting. For example, a business may assume that its target market is primarily young, tech-savvy individuals who are interested in sustainable products. This assumption would inform the company’s marketing efforts and product development.
Competitive landscape assumptions
These assumptions relate to the competition that a company may face in its industry. For example, a business may assume that there are several well-established competitors in its market and that it will need to differentiate itself to succeed. This assumption could influence the company’s pricing strategy and marketing efforts.
Revenue stream assumptions
These assumptions relate to the sources of income that a company expects to generate. For example, a business may assume that it will generate revenue from sales of its products, as well as from services it provides to customers. This assumption could inform the company’s pricing strategy and sales efforts.
Financial projections
These assumptions relate to the company’s financial performance and projections for the future. For example, a business may assume that it will achieve a certain level of sales and profit margins in the coming year, based on its target market, competitive landscape, and revenue streams. These assumptions would inform the company’s budget and resource allocation.
Considerations for making key assumptions in a business plan
When making key assumptions for a business plan, a company needs to consider several factors to ensure that the assumptions are well-informed and realistic.
Here are some key considerations.
A company needs to gather as much information as possible about its target market, competitive landscape, and other relevant factors. This can involve conducting market research, analyzing industry trends, and consulting with experts. By basing its assumptions on solid research, a company can increase the chances that they are accurate and well-informed.
Conservatism
While it is important for a business to be ambitious and strive for success, it is also important to be realistic and avoid making overly optimistic assumptions. By being conservative in its assumptions, a company can better manage its expectations and be better prepared to handle challenges and setbacks.
Flexibility
It is also important for a business to be flexible and open to adjusting its assumptions as needed. As the business grows and evolves, it may become clear that certain assumptions are no longer valid or accurate. By being open to revising its assumptions, a company can better adapt to changing circumstances and remain agile.
Tips for reviewing and updating key assumptions in a business plan
Once a business has established its key assumptions, it is important to regularly review and update them to ensure that they are still relevant and accurate.
Here are some tips for reviewing and updating key assumptions.
Regularly review and assess the accuracy of your assumptions
It is important to regularly review and assess the accuracy of your assumptions, especially as your business grows and changes. This can involve analyzing market trends, reviewing financial performance, and soliciting feedback from customers and employees.
By regularly reviewing your assumptions, you can ensure that they remain relevant and accurate.
Be open to revising your assumptions
As mentioned earlier, a business needs to be flexible and open to revising its assumptions as needed. If you discover that certain assumptions are no longer accurate or relevant, be willing to adjust them accordingly.
Communicate updates to your team
If you make changes to your key assumptions, it is important to communicate these updates to your team. This can help ensure that everyone is on the same page and working towards the same goals.
Use your updated assumptions to inform your decision-making
Once you have updated your key assumptions, be sure to use them to inform your decision-making and strategy moving forward. This can help ensure that your business is well-positioned to achieve its goals and succeed in the long term.
In conclusion, key assumptions are an important part of any business plan.
They are the underlying beliefs and assumptions that shape the way a business operates and makes decisions, and they inform the company’s strategy and goals.
By carefully considering and reviewing its key assumptions, a company can increase its chances of success by making informed decisions and setting realistic goals.
Some key considerations for making and reviewing key assumptions include researching, being conservative, and being flexible.
By following these tips, a business can ensure that its key assumptions are well-informed, relevant, and accurate, which can help it navigate challenges and achieve long-term success.
What’s your entrepreneurial potential? Find out with our self-assessment!
Disclaimers
All the information on this website - https://melbado.com/ - is published in good faith and for general information purpose only. Melbado does not make any warranties about the completeness, reliability and accuracy of this information. Any action you take upon the information you find on this website (Melbado), is strictly at your own risk. Melbado will not be liable for any losses and/or damages in connection with the use of our website.
From our website, you can visit other websites by following hyperlinks to such external sites. While we strive to provide only quality links to useful and ethical websites, we have no control over the content and nature of these sites. These links to other websites do not imply a recommendation for all the content found on these sites. Site owners and content may change without notice and may occur before we have the opportunity to remove a link which may have gone 'bad'.
Please be also aware that when you leave our website, other sites may have different privacy policies and terms which are beyond our control. Please be sure to check the Privacy Policies of these sites as well as their "Terms of Service" before engaging in any business or uploading any information.
By using our website, you hereby consent to our disclaimer and agree to its terms.
More From Forbes
How To Avoid Common Financial Pitfalls In Your Small Business
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
Good money management is crucial for the success and sustainability of any small business. Effective financial management ensures that you can meet your operational expenses, invest in growth opportunities, and weather any unforeseen challenges that may arise. It provides a clear picture of your financial health, helping you make informed decisions and avoid debt traps.
By maintaining a healthy cash flow and a solid financial cushion, you can focus on delivering quality products or services to your customers, fostering innovation, and building a robust, resilient business. Ultimately, good money management is the foundation upon which you can achieve your long-term business goals and secure financial stability.
Here are some common pitfalls to avoid in your small business:
1. poor cash flow management.
Cash flow is the lifeblood of any business. Without a steady flow of cash, even profitable businesses can face trouble. Effective cash flow management ensures that you have enough liquidity to cover your daily operational expenses, pay your employees, and invest in growth opportunities. It also provides a buffer against unexpected financial challenges, such as sudden drops in revenue or unforeseen expenses.
By closely monitoring and managing your cash flow , you can maintain financial stability, avoid the pitfalls of debt, and position your business for long-term success. In essence, strong cash flow management is essential for the health and sustainability of your business.
Best Buy Memorial Day Sale: 70 Deals On TVs, Tablets And Appliances
The best beers in canada according to the canadian brewing awards, nyt strands 84 hints spangram and answers for sunday may 26th, 2. lack of budgeting and financial planning.
Failing to create a realistic budget can lead to overspending and financial shortfalls. Without a well-defined budget, it becomes challenging to track expenses and ensure that you are not exceeding your financial limits. This lack of oversight can result in unnecessary expenditures, ultimately straining your cash flow and leaving you unprepared for unexpected costs.
Without a clear budget, you may miss opportunities to allocate resources effectively, hindering your business's growth and stability. By creating and adhering to a realistic budget, you can maintain control over your finances, make informed spending decisions, and ensure that your business remains on a path to financial health and success.
3. Ignoring Expenses
Small expenses can add up and significantly impact your bottom line if not tracked. These seemingly minor costs, such as office supplies, subscriptions, and incidental purchases, can accumulate over time and erode your profits. Without diligent tracking, it's easy to overlook these expenses, leading to budget overruns and financial strain.
Consistently monitoring and managing all expenditures, no matter how small, is essential to maintaining a clear picture of your financial health. Implementing a robust expense tracking system helps identify areas where you can cut costs, optimize spending, and ultimately improve your business's profitability. Attention to detail in expense management ensures that every dollar is accounted for and contributes to your financial stability and growth.
4. Inadequate Pricing Strategy
Setting prices too low can hurt your profitability, while setting them too high can drive customers away. When prices are too low, your business may struggle to cover costs, leading to reduced margins and potentially unsustainable operations. This underpricing can also create a perception of low value, diminishing your brand's reputation.
Conversely, setting prices too high can alienate potential customers, making your products or services less competitive in the market. It is crucial to strike a balance by understanding your costs, analyzing competitor pricing, and assessing the value you provide to customers. A well-researched pricing strategy ensures you remain profitable while attracting and retaining customers, thereby supporting the long-term success and growth of your business.
5. Not Having a Financial Cushion
Unexpected expenses can arise, and without a financial cushion, your business may struggle to stay afloat. These unforeseen costs can come in many forms, such as emergency repairs, sudden market shifts, or unexpected legal fees.
Without a reserve fund , these expenses can quickly deplete your operating capital, disrupting daily operations and putting your business at risk of insolvency. Maintaining a financial cushion allows you to absorb these shocks, ensuring that your business remains resilient and capable of handling adverse situations.
By setting aside a portion of your profits into an emergency fund, you create a safety net that provides stability and peace of mind, allowing you to navigate challenges without compromising your business's long-term viability.
The bottom line is that avoiding financial pitfalls requires diligence, planning, and constant monitoring of your business’s financial health. By implementing these strategies, you can steer your small business towards financial stability and long-term success. Remember, the goal is not just to avoid failure, but to build a resilient business capable of thriving in any economic environment.
Melissa Houston, CPA is the author of Cash Confident: An Entrepreneur’s Guide to Creating a Profitable Business and the founder of She Means Profit , a bookkeeping and financial consultancy firm. As a Business Strategist for small business owners, Melissa helps women making mid-career shifts, to launch their dream businesses, and I also guide established business owners to grow their businesses to more profitably.
The opinions expressed in this article are not intended to replace any professional or expert accounting and/or tax advice whatsoever.

- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions
Join The Conversation
One Community. Many Voices. Create a free account to share your thoughts.
Forbes Community Guidelines
Our community is about connecting people through open and thoughtful conversations. We want our readers to share their views and exchange ideas and facts in a safe space.
In order to do so, please follow the posting rules in our site's Terms of Service. We've summarized some of those key rules below. Simply put, keep it civil.
Your post will be rejected if we notice that it seems to contain:
- False or intentionally out-of-context or misleading information
- Insults, profanity, incoherent, obscene or inflammatory language or threats of any kind
- Attacks on the identity of other commenters or the article's author
- Content that otherwise violates our site's terms.
User accounts will be blocked if we notice or believe that users are engaged in:
- Continuous attempts to re-post comments that have been previously moderated/rejected
- Racist, sexist, homophobic or other discriminatory comments
- Attempts or tactics that put the site security at risk
- Actions that otherwise violate our site's terms.
So, how can you be a power user?
- Stay on topic and share your insights
- Feel free to be clear and thoughtful to get your point across
- ‘Like’ or ‘Dislike’ to show your point of view.
- Protect your community.
- Use the report tool to alert us when someone breaks the rules.
Thanks for reading our community guidelines. Please read the full list of posting rules found in our site's Terms of Service.

COMMENTS
Financial assumptions are the guidelines you give your business plan to follow. They can range from financial forecasts about costs, revenue, return on investment, and operating and startup expenses. Basically, financial assumptions serve as a forecast of what your business will do in the future.
Financial plan assumptions are the key variables, estimates, and predictions used to develop a company's financial projections and strategy. They serve as the foundation for forecasting revenues, costs, investments, and taxes, among other elements. Assumptions are critical in financial planning because they help businesses set realistic goals ...
3. Assess Current Performance. Now it's time to analyze your current and historical financial performance for each of your assumptions. For instance, if you want to make an assumption for monthly revenue growth, look at your performance year-to-date (YTD) to give you a baseline before you start making future assumptions.
Financial assumptions are an integral part of any business plan. They provide a foundation for the financial projections and help investors and stakeholders understand the underlying assumptions behind the numbers. Financial assumptions can cover a wide range of topics, including revenue growth, cost of goods sold, expenses, and capital ...
7. Build a Visual Report. If you've closely followed the steps leading to this, you know how to research for financial projections, create a financial plan, and test assumptions using "what-if" scenarios. Now, we'll prepare visual reports to present your numbers in a visually appealing and easily digestible format.
Use the numbers that you put in your sales forecast, expense projections, and cash flow statement. "Sales, lest cost of sales, is gross margin," Berry says. "Gross margin, less expenses, interest ...
Here is everything you need to include in your financial plan, along with optional performance metrics, funding specifics, mistakes to avoid, and free templates. Key components of a financial plan. A sound financial plan is made up of six key components that help you easily track and forecast your business financials. They include your:
Financial assumptions and projections are critical components of all business plans. Three universal financial presentations are expected in all business plans. You must include a projected income ...
Note: Every common assumption you find above are designed to help you prepare better financial projections for your business plan. Take what you like, ignore what you do not.
The Role of Financial Assumptions in Forecasting. In business planning, forecasting is a crucial step in visualizing how a company will perform in the future. Companies forecast future outcomes based on past and current data, using assumptions. Forecasted elements of a financial plan include revenue, margin, and expenses, among others.
There are three main financial statements that you will need to include in your business plan financial projections: 1. Income Statement Projection. The income statement projection is a forecast of your company's future revenues and expenses. It should include line items for each type of income and expense, as well as a total at the end.
The cost assumptions based on customer acquisition are some of the most important financial assumptions we'll make in our business plan and typically represents one of the largest startup expenses. Note that in these examples we use "visitor" to mean anyone coming to buy from us, whether it's to our website or to our storefront.
Your financial plan is the main component of your business plan. Mike Figiluolo explains that the first step in building that financial plan is documenting your assumption.
The financial analysis section should be based on estimates for new businesses or recent data for established businesses. It should include these elements: Balance sheet: Your assumed and anticipated business financials, including assets, liabilities, and equity. Cash-flow analysis: An overview of the cash you anticipate will be coming into ...
Use this financial plan template to organize and prepare the financial section of your business plan. This customizable template has room to provide a financial overview, any important assumptions, key financial indicators and ratios, a break-even analysis, and pro forma financial statements to share key financial data with potential investors.
Funding. You need to prepare a business plan assumptions sheet as part of your plan, however, the important point to remember is that the assumptions should be kept simple and to a minimum, to avoid over complicating the financial projection. Remember this is planning not accounting. The calculation of key assumptions is further discussed in ...
Collect relevant historical financial data and market analysis. Forecast expenses. Forecast sales. Build financial projections. The following five steps can help you break down the process of developing financial projections for your company: 1. Identify the purpose and timeframe for your projections.
A business' financial plan is the part of your business plan that details how your company will achieve its financial goals. It includes information on your company's projected income, expenses, and cash flow in the form of a 5-Year Income Statement, Balance Sheet and Cash Flow Statement. The plan should also detail how much funding your ...
Inclusion facilitates the analysis of any organization's business plan by a financial institution, venture capitalist or angel investor. The risk of making a bad investment will be reduced if the investors understand and share the strategic assumptions of the organization's management team.
Startup financial projections are built around making a series of educated guesses about how things might go. Public companies make sales projections, issue projected income statements, and create revenue forecasts all the time. The difference is they are going off of lots of history. As startup founders, we make assumptions about how much ...
The key assumptions subsection is the second subsection of the financial plan section. It follows the sources and uses, and precedes your sales forecast. The goal of this subsection is to give readers on overview of how you built your forecast. So that they can understand both the methodology and the key drivers used to model your revenues ...
Financial Assumptions The Handbook of Business Planning Powered by BizPlanBuilder ® 96 Human history becomes more and more a race between education and catastrophe. ~ H.G. Wells Historical Financials If you have financial information from the recent past (last 1-3 years) enter it on this page. As you can see, there are not many numbers to enter.
Business Assumptions Definition. Business assumptions refer to the expected financial and operational projections a business makes about future market conditions, business environment, and internal company dynamics that influence business decisions and strategy. They are yet-to-be-proven elements considered true for the purposes of planning and ...
Key assumptions are the underlying beliefs and assumptions that shape the way a business operates and makes decisions. They can be related to various aspects of the business, including its target market, competitive landscape, revenue streams, and financial projections. These assumptions serve as the foundation of a business plan, and they help ...
Here are some common pitfalls to avoid in your small business: 1. Poor Cash Flow Management. Cash flow is the lifeblood of any business. Without a steady flow of cash, even profitable businesses ...
Devin Harris ENP-7320-MB900 Final Project: (Part 4) Managing/Operating the Business and Critical Risk Assumptions April 12, 2024 Sports Marketing Agency *All based on a three-year financial plan* Management Team Describe the functions that will need to be filled in your venture Graphic & Web Designs, Event Planning and Management, Negotiating Contracts & Sponsorships, Facilitating Success for ...